Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Usefulness of Charlson comorbidity index-adjusted mortality prediction tools and factors influencing mortality in intensive care unit patients: a retrospective medical record review–based study
- Jai Jung Lee, Dong Yeon Kim, Min Ji Lee, Ji Young Kim
- Received July 10, 2025 Accepted December 1, 2025 Published online February 11, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25094 [Epub ahead of print]
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to estimate the mortality rate in adult intensive care units (ICUs) using the Charlson comorbidity index (CCI)-adjusted Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II and Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS) III models, and to identify factors influencing mortality.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study included adult patients admitted to the ICU at a tertiary hospital between June 1 and August 31, 2022. Among the 1,098 screened patients, those younger than 18 years, those discharged within 48 hours, and those with missing medical records were excluded. In total, 482 patients were analyzed using the chi-square test, independent t-test, and multivariate logistic regression. Model performance was evaluated using the c-statistic and the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test.
Results
The predictive accuracy of the mortality models was shown by c-statistic values of 0.817 for APACHE II, 0.857 for SAPS III, 0.697 for CCI, and 0.834 for CCI-adjusted APACHE II (0.834). Mechanical ventilation, cardiopulmonary cerebral resuscitation, continuous renal replacement therapy, and the presence of leukemia or lymphoma were significant predictors of mortality in adult ICU patients. Among the evaluated models, SAPS III and CCI-adjusted APACHE II demonstrated the highest predictive power.
Conclusion
The findings indicate that incorporating comorbidity indices such as the CCI with acute physiological parameters improves the accuracy of mortality prediction in ICU patients. Understanding mortality prediction models is essential for nurses to provide individualized, evidence-based, and high-quality care in adult ICUs.
- 77 View
- 0 Download

- Development of an end-of-life care competency scale for nurses in long-term care hospitals: a psychometric validation study
- Sookyeon Son, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):598-612. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure end-of-life care (EOLC) competency among nurses working in long-term care hospitals and to evaluate its validity and reliability.
Methods
Preliminary items were developed based on attributes and indicators identified through a conceptual analysis of EOLC competency. The initial version of the scale was refined through expert content validity assessment, item revision, and a pilot test. The main survey was conducted among 460 nurses in long-term care hospitals, and 409 valid responses were analyzed after excluding 51 incomplete or invalid cases. Data were analyzed using software-assisted item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses, and assessments of convergent, discriminant, and criterion-related validity, as well as reliability testing.
Results
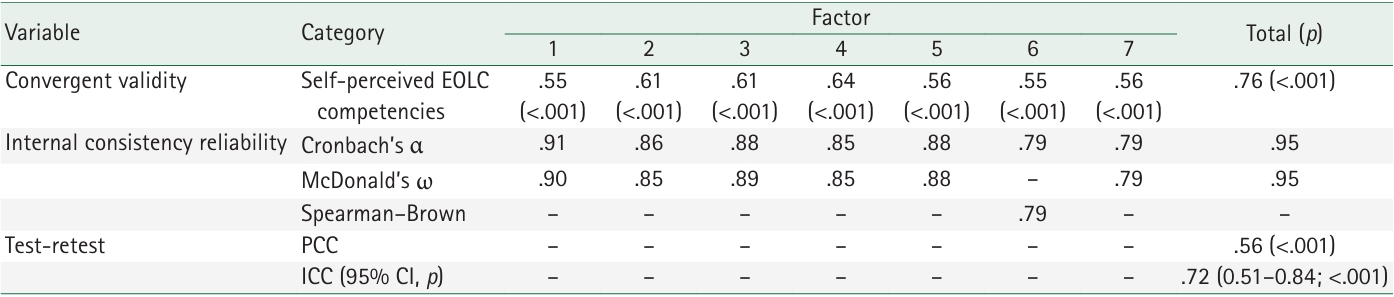
The initial 55 items were reduced to a final set of 30 items across seven dimensions. Model fit indices indicated good construct validity (χ²/degrees of freedom=1.91, standardized root mean square residual=.06, root mean square error of approximation=.07, Tucker-Lewis index=.90, comparative fit index=.91), with a total explained variance of 70.2%. The scale demonstrated strong criterion-related validity (r=.76, p<.001), high internal consistency (Cronbach’s α=.95; McDonald’s ω=.95), acceptable test–retest reliability (r=.56, p<.001), and an intraclass correlation coefficient of .72 (95% confidence interval, .51–.84; p<.001).
Conclusion
The developed scale is a valid and reliable instrument for assessing EOLC competency among nurses in long-term care hospitals. It can be effectively utilized for educational assessment, training evaluation, and the measurement of program effectiveness in end-of-life care.
- 872 View
- 102 Download

- A qualitative exploration of acute stroke patients’ experiences with aphasia in Korea
- Jiyeon Kang, Hyunyoung Heo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):621-633. Published online November 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to explore the lived experiences of patients with acute stroke-related aphasia within the Korean healthcare context.
Methods
A qualitative research design using inductive content analysis was employed, following the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research guidelines. Fourteen adults with acute stroke-related aphasia participated in one-on-one, in-depth interviews conducted between January and May 2025. Participants were recruited through purposive sampling until theoretical saturation was reached. Data were analyzed using an inductive qualitative content analysis approach.
Results
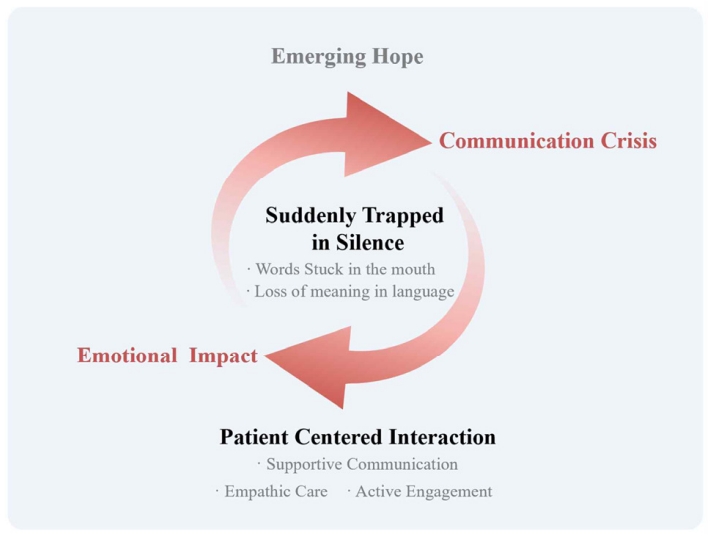
Five main categories emerged: “suddenly trapped in silence” described the abrupt loss of language, including the inability to articulate intended words and understand others; “emotional impact” captured psychological shock and feelings of loss; “communication crisis” encompassed expressive difficulties, exclusion from decision-making, and social withdrawal; “patient-centered interaction” highlighted supportive communication, empathic care, and active engagement by others; and “emerging hope” reflected signs of recovery, self-directed efforts, and anticipation of improvement. These categories converged into the overarching theme, “communication beyond language,” illustrating how patients sought meaningful interaction despite linguistic limitations.
Conclusion
Acute aphasia extends beyond a language disorder to encompass profound emotional and social experiences. Although communication barriers exist, meaningful interaction remains possible through empathetic, person-centered approaches. Healthcare professionals should recognize that patients with aphasia retain cognitive competence despite expressive limitations. These findings underscore the need to integrate emotional sensitivity into clinical care and to develop training programs that enhance person-centered communication skills in stroke rehabilitation settings.
- 1,117 View
- 108 Download

- Multidimensional factors influencing the completion of advance directives among community-dwelling older Koreans
- Hee-Ju Ji, Soong-Nang Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):543-556. Published online November 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25098
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the multidimensional factors associated with the completion of advance directives (ADs) among community-dwelling older Koreans, guided by conceptual frameworks developed in Asian contexts.
Methods
Data from the 2023 National Survey of Older Koreans (sixth wave) were analyzed for 9,951 community-dwelling older Koreans aged 65 years or older. Complex sample cross-tabulation and binary logistic regression analyses were conducted.
Results
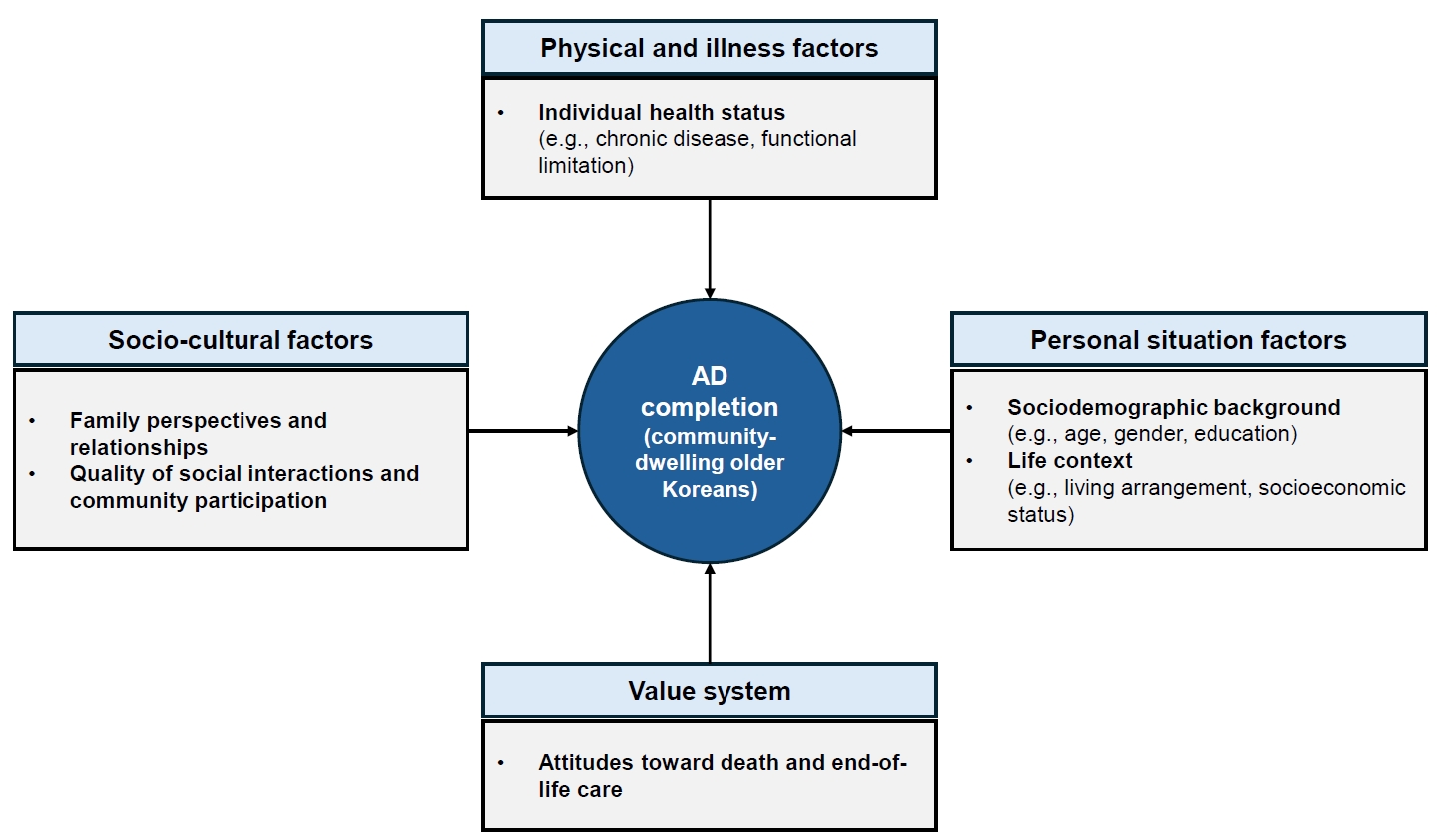
In total, 11.1% of community-dwelling older Koreans had completed an AD. Significant factors associated with AD completion were identified across four domains—personal situation: age, educational level, religion, and housing preference in the event of poor health; socio-cultural: presence of children, participation in social activities and satisfaction with social relationships; physical and illness: the number of chronic diseases; and value system: awareness of hospice and palliative services, participation in death preparedness education, and documentation of organ donation.
Conclusion
Among older Koreans, AD completion represents more than a documentation process; it reflects a complex decision-making process shaped by their values and life circumstances, underscoring the need for supportive interventions. As the highest AD completion rates are found among older adults, related policies should be aligned with older adult-centered policy frameworks.
- 1,428 View
- 136 Download

- Effects of presenteeism on turnover intention in clinical nurses through the serial mediating roles of missed nursing care and job satisfaction: a cross-sectional predictive correlational study
- Hyeonseon Cheon, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyung Kim, Hyoung Eun Chang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):584-597. Published online November 10, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25015
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the two-mediator serial mediation effect of missed nursing care and job satisfaction on the relationship between presenteeism and turnover intention in clinical nurses.
Methods
A cross-sectional predictive correlational study was conducted, and the participants were 208 clinical nurses working in advanced general hospitals in South Korea. Data were collected from October 6 to November 7, 2023 using self-reported questionnaires, including general characteristics, presenteeism, missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS/WIN ver. 29.0 and PROCESS macro ver. 4.2.
Results
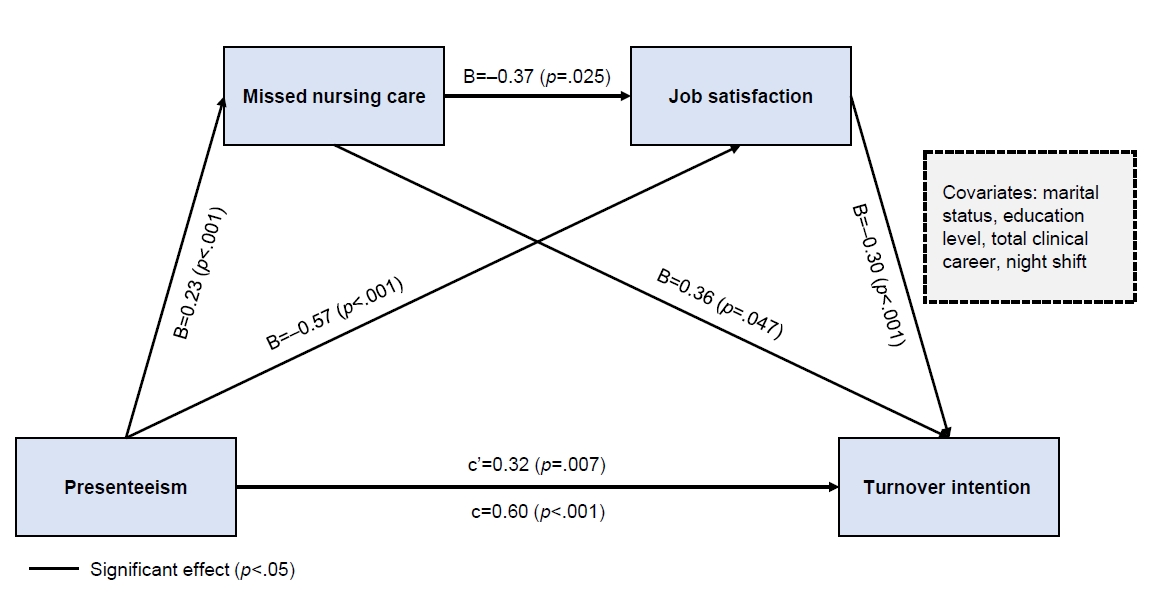
Missed nursing care and job satisfaction exhibited a double mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. In addition, missed nursing care showed a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Job satisfaction had a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Presenteeism had a direct effect on missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Missed nursing care exerted a direct effect on job satisfaction and turnover intention among clinical nurses. Job satisfaction had a direct effect on turnover intention.
Conclusion
To reduce nurses’ turnover intention, it is essential to develop and implement programs focused on preventing presenteeism. Additionally, organizational initiatives should prioritize active support for nurses’ health management, alleviating the shortage of nursing staff, augmenting job satisfaction, and improving the overall working environment.
- 1,438 View
- 192 Download

- Prenatal psychosocial factors and postpartum post-traumatic stress disorder in low-risk postnatal women: a longitudinal study
- Jung Hee Yeo, So Yeon Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):353-363. Published online August 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25027
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
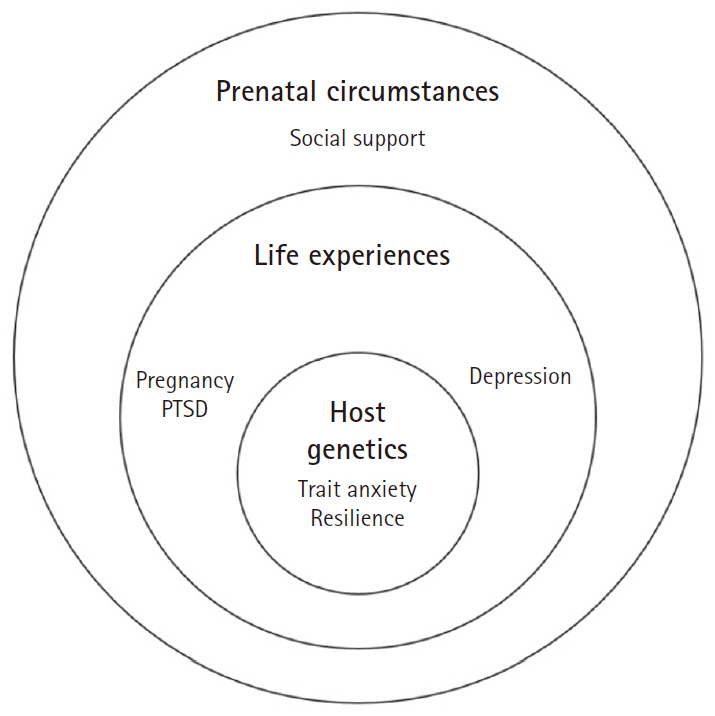
This study aimed to identify prenatal psychosocial factors influencing the development of postpartum post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in both short-term (4–6 weeks postpartum) and long-term (4–6 and 14–18 weeks postpartum) assessments using the wheel model.
Methods
This study employed a longitudinal design with 359 women in their third trimester who received care at two maternity hospitals in City B. Surveys were used to measure depression, anxiety, resilience, and pregnancy-related PTSD during the third trimester (n=318). Postpartum PTSD was assessed at 4–6 weeks (n=198) and at 14–18 weeks postpartum (n=156). Data were analyzed using the t-test, chi-square test, and logistic regression.
Results
The prevalence of short-term postpartum PTSD was 32.7%, and that of long-term PTSD was 19.9%. The risk of short-term PTSD increased with higher pregnancy-related PTSD symptoms (odds ratio [OR], 1.04; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02–1.07), higher prenatal resilience (OR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.00–1.18), and lower social support (OR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.87–0.99). Similarly, the risk of long-term PTSD increased with higher pregnancy-related PTSD (OR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.04–1.13), higher prenatal resilience (OR, 1.19; 95% CI, 1.06–1.34), and low educational attainment (OR, 6.75; 95% CI, 1.03–44.30).
Conclusion
The high prevalence of short- and long-term postpartum PTSD highlights the need for systematic screening and interventions for prenatal factors, including pregnancy-related PTSD, social support, resilience, and education level. Therefore, it is necessary to alleviate pregnancy-related PTSD and strengthen social support during prenatal care to prevent postpartum PTSD. Furthermore, women with high resilience should also be targeted in these interventions, because they can also develop postpartum PTSD.
- 1,393 View
- 143 Download

- Impact of an integrated disease-specific nursing care model on parental anxiety and depression in severe hypospadias patients in China: a randomized controlled trial
- Ruijuan Wu, Lucai Jia, Biyu Ding, Ying Li, Yaqing Cao, Zhaojun Shi, Yanfang Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):327-341. Published online August 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24147
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to explore the effects of an integrated disease-specific nursing care model on alleviating perioperative and post-surgical anxiety and depression in parents of children with severe hypospadias.
Methods
Parents of children with severe hypospadias were recruited and randomly allocated into a control group (n=87), which received standard nursing care, and an intervention group (n=93), which was given an integrated disease-specific nursing intervention in addition to standard care. Parental anxiety and depression were measured using the Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS) and Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS) at admission, discharge, and 6-month follow-up post-surgery.
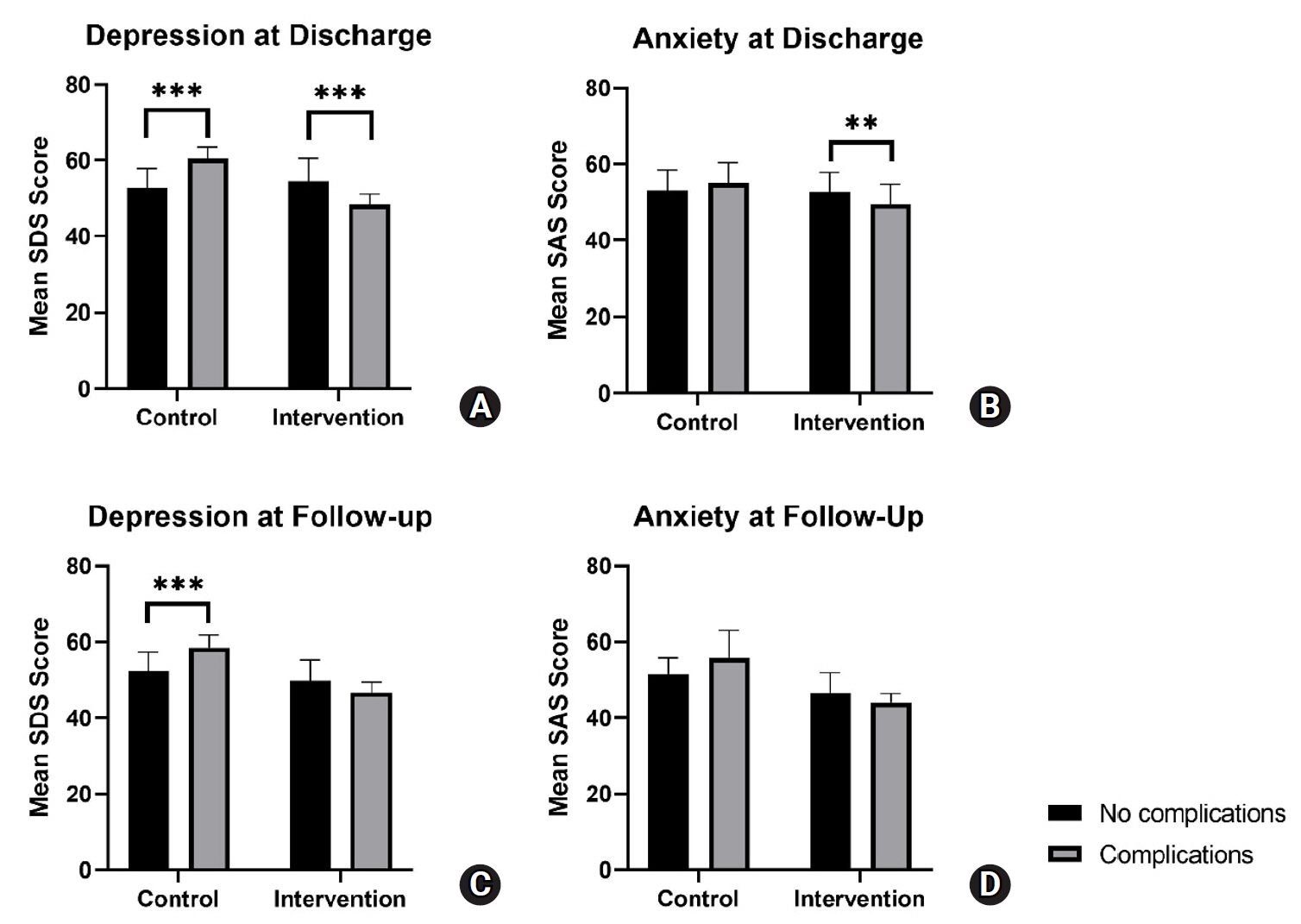
Results
A linear mixed-effects model showed that SAS and SDS scores in the intervention group decreased to a significantly greater extent over time, from admission to follow-up, compared to the control group. Post-hoc analysis showed a trend for increased parental anxiety and depression among patients with complications at discharge and follow-up for the control group. Meanwhile, the intervention group exhibited a trend for decreased parental anxiety and depression among patients with complications at discharge and follow-up.
Conclusion
The integrated disease-specific nursing model significantly alleviated parental anxiety and depression over time compared to standard care, highlighting its effectiveness in supporting families of children with severe hypospadias. Notably, the intervention appeared to mitigate the negative emotional impact of postoperative and follow-up complications, suggesting its potential as a targeted approach to improve both emotional well-being and overall care outcomes.
- 2,399 View
- 160 Download

- Factors Affecting the Intention to Use Smartmonitor-Based Mobile Health in Middle-Aged in Patients Applying the Technology Acceptance Model II
- Ol Eum Joo, Yi Kyung Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):620-632. Published online November 13, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24091
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study aimed to identify factors that influence the intention to use smart monitor-based mobile health (SBM) technology among middle-aged inpatients, based on the technology acceptance model II (TAM II).
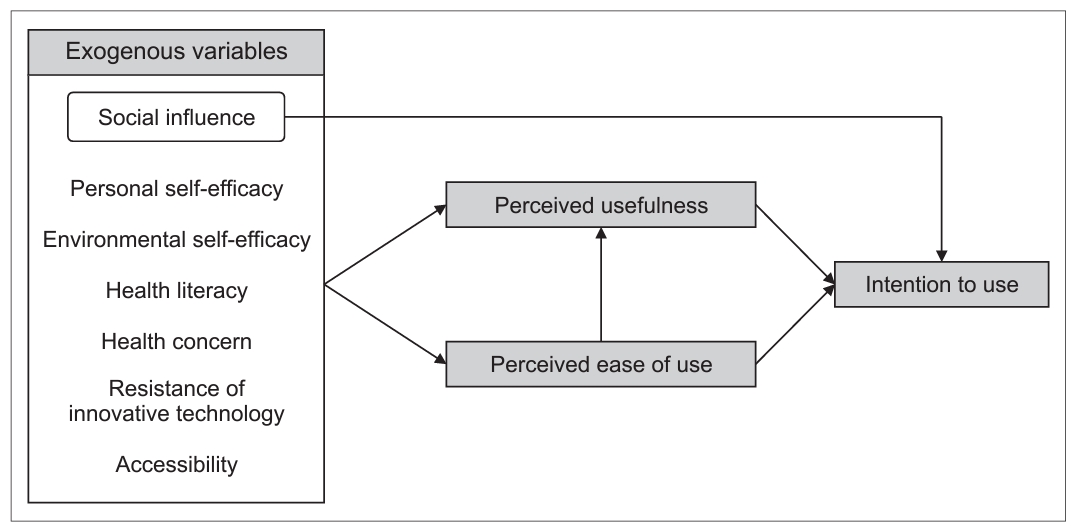
Methods A total of 222 participants were surveyed. Data were analyzed using SPSS Statistics 23.0 and IBM SPSS Amos 23. Seven exogenous variables–social influence (SI), personal self-efficacy, (PSE), environmental self-efficacy (ESE), health literacy, health concerns, resistance to innovative technology (RIT), accessibility (AC)– and three endogenous variables–perceived ease of use (PEOU), perceived usability (PU), and intention to use (ITU)–were investigated.
Results The hypothesized path model demonstrated a good fit for the data. SI (β = .13,
p = .042), PU (β = .46,p < .001), and PEOU (β = .16,p = .008) had significant direct effects on the ITU, which explained 39.5% of the variance. Additionally, SI (β = .27,p < .001), ESE (β = .16,p = .010), RIT (β = - .12,p = .026), AC (β = .28,p < .001), and PEOU (β = .20,p = .001) indirectly affected ITU through PU, which explained 50.7% of the variance. Furthermore, PSE (β = .38,p < .001) indirectly influenced ITU via PEOU, which explained 38.4% of the variance.Conclusion This study demonstrates that the TAM II can be used to effectively predict ITU in SBMs among middle-aged inpatients. To expand the intention to use SBMs, it is necessary to develop SBMs that include content and programs that promote PU, SI, and PEOU.
- 1,705 View
- 80 Download

- Perceptual Factors Associated with Gestational Weight Gain: A Cross-Sectional Survey
- Sehee Kim, Sukhee Ahn
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):495-508. Published online November 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose Recent years have seen an increase in the number of pregnant women whose weight gain during pregnancy exceeds the recommended range. This study was intended to determine the relationships among demographic attributes, key perceptual factors, and gestational weight gain (GWG).
Methods This cross-sectional study was conducted between April and July 2022. First-time pregnant women beyond 36 weeks of gestation who were recruited via social media completed an online survey. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA, chi-square test, and logistic regression, all performed using SPSS software.
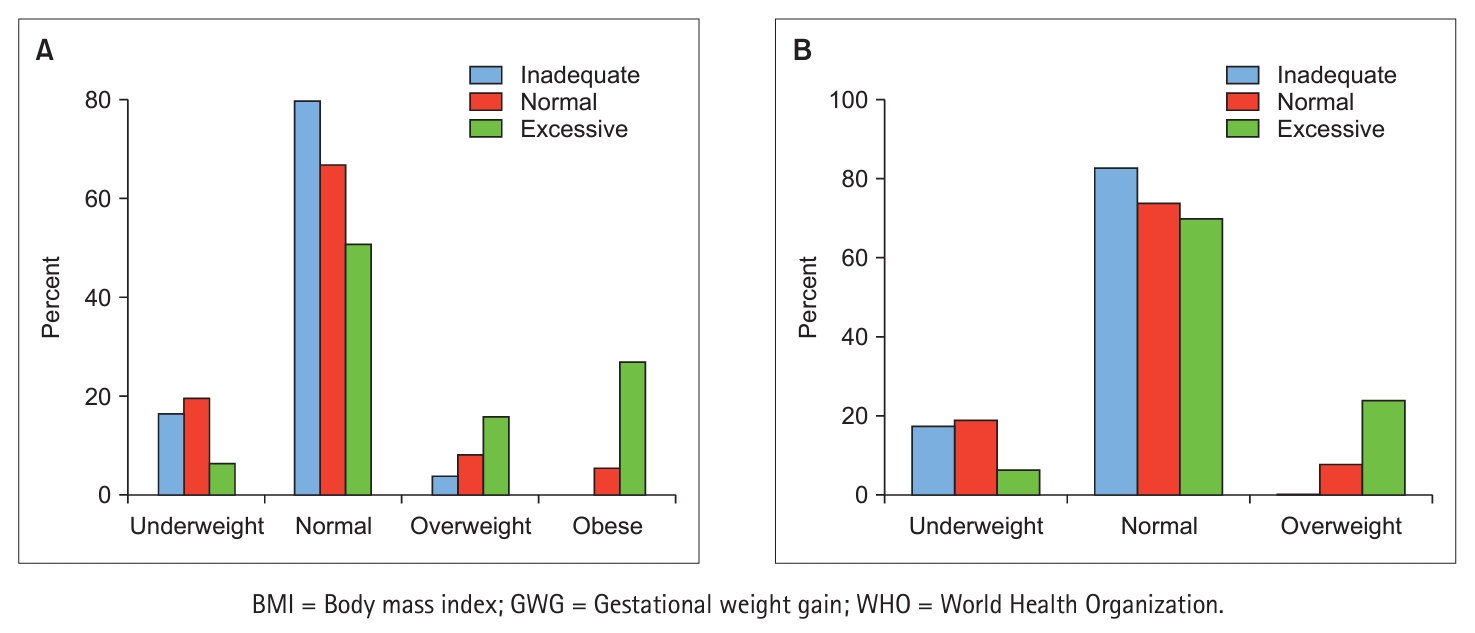
Results Of the 369 participants, 63 (17.1%) exceeded the recommended GWG guidelines, while 148 (40.1%) fell within the recommended range, and the remaining 158 (42.8%) had inadequate GWG. Being overweight or obese before pregnancy significantly increased the risk of excessive GWG (
p < .001). This risk was also significantly greater for women with low internal weight locus of control (OR = 0.58, 95% CI 0.41~0.82), high external weight locus of control (OR = 1.75, 95% CI 1.31~2.34), and negative body image (OR = 0.62, 95% CI 0.51~0.75).Conclusion The growing trend of excessive GWG among pregnant women is influenced by a combination of prepregnancy body mass index (BMI) and perceptual factors, including weight locus of control and body image. These findings underscore the need to implement weight management intervention strategies before pregnancy, taking into consideration BMI, and to enhance positive body image and internal locus of control.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated With Gestational Weight Gain Among Nurses in Korea
Sook Jung Kang, Woon Young Hwang, Hyunju Dan, Sue Kim, Kwang-Pil Ko
Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, & Neonatal Nursing.2025; 54(5): 543. CrossRef - Attitudes toward body weight and shape during pregnancy among Japanese women who were underweight before pregnancy: A qualitative study
Chisato KOROGI, Mie SHIRAISHI, Kaori MATSUDA, Natsuki HORI, Hanna HORIGUCHI
Journal of Japan Academy of Midwifery.2025; 39(3): 456. CrossRef
- Factors Associated With Gestational Weight Gain Among Nurses in Korea
- 2,734 View
- 107 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Clinical Nurses’ Perception of Structural and Content Career Plateau
- Ji Hye Kim, Ji Yun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):534-546. Published online October 23, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24002
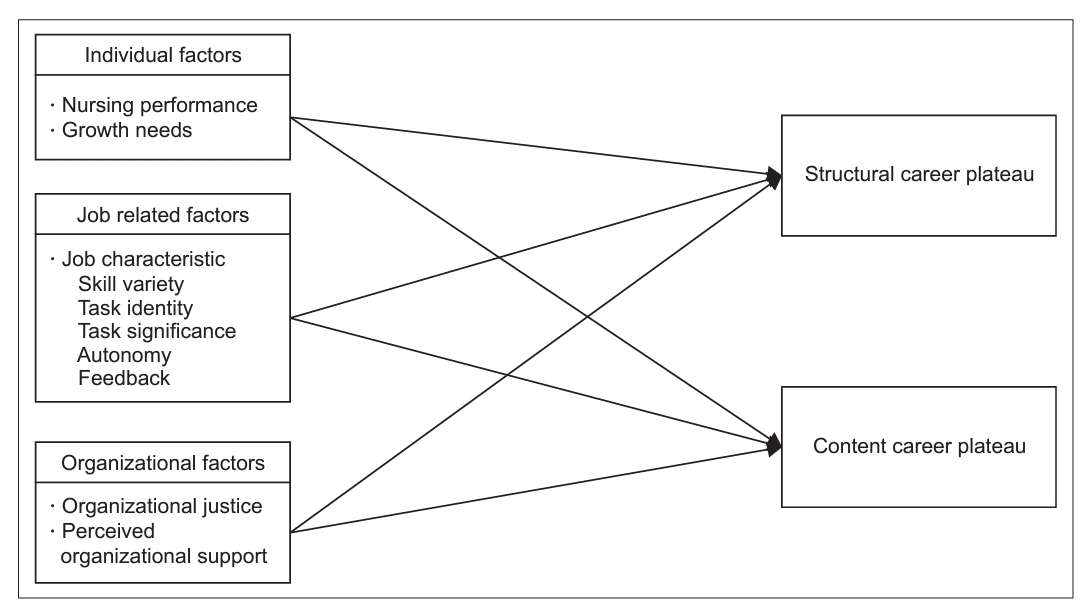
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study was intended to provide basic data for reducing the career plateaus of clinical nurses.
Methods The participants were 288 clinical nurses who worked at five hospitals, general hospitals, and tertiary hospitals in Seoul, Gyeonggi, and Chungcheong provinces and had more than one year of clinical experience. The research data were collected from December 26, 2022, to April 7, 2023, using structured questionnaires and analyzed using SPSS software. The study conducted mean, standard deviation, percentage, t-test, ANOVA, Pearson‘s correlation coefficient, and hierarchical regression analysis.
Results Perceived organizational support was identified as the factor influencing structural career plateaus. Factors influencing content career plateaus included growth needs, skill variety, organizational justice, and perceived organizational support.
Conclusion The above research results suggest that to increase the motivation of clinical nurses and reduce career plateaus, it is necessary to improve awareness and systems of human resource management at the organizational level.
- 2,375 View
- 167 Download

- The Effects of a Self-Efficacy Theory-Based Exercise Program for Patients Undergoing with Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Kyung-Hye Park, Hee-Young Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):547-562. Published online October 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24027
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material ePub
ePub Purpose This study was performed to develop a self-efficacy theory-based exercise program for total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and to test the program’s efficacy in ameliorating knee pain and restoring function as measured by lower extremity muscle strength, 3 meter walking time, Korean Western Ontario McMaster Index (WOMAC), exercise self-efficacy, and length of hospital stay for TKA patients.
Methods This quasi-experimental study incorporating a non-equivalent control group and pretest-posttest non-synchronized design non-synchronous design was applied to assess self-efficacy reinforcement strategies based on self-efficacy theory. The exercise program consisted of the following steps: TKA, education to prevent postoperative complications, and muscle strength exercises. Respective exercise and control groups included 29 and 27 participants. The experimental group received eight sessions of the program from three weeks before TKA to four weeks after TKA. Collected data were analyzed using the chi-square test, Mann–Whitney U test, and ranked ANCOVA and t-tests using IBM SPSS Statistics 23.
Results Experimental group showed significant improvement in lower extremity muscle strength (F = 8.63,
p = .005), 3 meter walking time (z = - 5.02,p < .001), WOMAC index (z = - 2.22,p = .027), self-efficacy for exercise (z = - 3.29,p = .001), and length of hospital stay (t = - 2.11,p = .040) compared to the control group. No significant differences in knee pain and range of motion were observed.Conclusion These findings indicate that a self-efficacy theory-based exercise program can be an effective exercise strategy that patients undergoing TKA can easily follow at home without assistance. It is thus recommended as an exercise intervention for TKA patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Self-efficacy and implementation intentions in home rehabilitation of stroke patients: the parallel mediating role of recurrence risk perception and outcome expectations
Xiaowen Jiang, Qiuxue Sun, Rong Tang, Shuxian Liu, Xi Chen, Yumei Lv
Frontiers in Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Decision-Making and Rehabilitation Among Older Women Who Underwent Total Knee Replacement: A Qualitative Study in Taiwan
Ching Han Huang, Yun Yee Chen, Shu Wen Chen, Chen Ti Wang, Mei Hsiang Lin
Patient Preference and Adherence.2025; Volume 19: 3931. CrossRef
- Self-efficacy and implementation intentions in home rehabilitation of stroke patients: the parallel mediating role of recurrence risk perception and outcome expectations
- 3,123 View
- 269 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- An Exploratory Study on Non-Contact Nursing Experiences of Clinical Nurses during the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Hye Min Byun, Eun Kyoung Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):446-458. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24045
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to understand the non-contact nursing experiences of clinical nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
A qualitative research design applying thematic analysis was used. The participants were purposive sampled from three institutes: a tertiary hospital, a general hospital, and a residential treatment center in Seoul. Data were collected between December 2021 and January 2022 through individual in-depth interviews with 12 clinical nurses. The data were analyzed using Braun and Clarke’s method to identify the meaning of the participants’ experiences.
Results
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the fields where the participants performed non-contact nursing included intensive care units and isolation wards of hospitals, a residential treatment center, and home cares. Their tasks in non-contact nursing commonly involved remote monitoring using digital devices or equipment, consultation and education. From their experiences performing tasks in these fields, the four theme clusters and nine themes were derived. The four theme clusters are as follows: (1) Confusion of nursing role; (2) Conflict due to insufficient support system; (3) Concern about the quality of nursing; (4) Reflection on the establishment of nursing professionalism.
Conclusion
This study highlights the necessity for institutionalizing professional nursing areas, nursing education, and practical support by clarifying the purpose and goals of non-contact nursing and developing nursing knowledge through frameworks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Da-Jung Kim
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2025; 21(5): 234. CrossRef - Telecare legislation priorities: A Delphi study grounded in ethical challenges
Seongyu Han, Eun Kyoung Yun
Nursing Ethics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- 1,783 View
- 87 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effectiveness of the Eye Care Protocol in the Intensive Care Unit Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Kyu Won Lim, Shin Young Ha, In Soon Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):432-445. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated the effects of an eye care protocol (ECP) on patients in the intensive care unit (ICU).
Methods
This study utilized a randomized controlled design. Participants were patients who met the inclusion criteria and were admitted to the ICU (36 in the experimental group and 38 in the control group). The experimental group received an ECP, while the control group received standard eye care, starting the day after admission, for a duration of 10 days. The ECP classifies the degree of eyelid obstruction into three stages based on the degree of exposure to the lower eyelid conjunctiva and cornea. The protocol included cleansing with normal saline gauze, administering eye drops, applying silicone and polyurethane films, and recommending consultation with an ophthalmologist if necessary. The effectiveness of ECP was assessed by analyzing tear volume, hyperemia, chemosis, and eye discharge. Data analysis was conducted using SPSS 27.0, employing the Mann-Whitney U-test and generalized estimating equations.
Results
On day 5, the experimental group demonstrated a significant increase in tear volume in both eyes compared with the control group. However, no statistically significant differences were observed in the incidence of hyperemia, chemosis, and eye discharge on days 5 and 10 of the intervention.
Conclusion
The application of the ECP in this study increased tear volume in ICU patients, thereby reducing discomfort caused by dry eyes. It has the potential to prevent complications such as damage to the surface of the eyeball resulting from decreased tear volume. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Da-Jung Kim
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2025; 21(5): 234. CrossRef
- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- 1,335 View
- 194 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of a Pre-Conception Care Program in Women with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Mixed-Methods Study Including a Randomized Controlled Trial
- Young Jin Lee, Hae Won Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Suk-Kyun Yang, Ji-Yeon Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):386-402. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to conduct a pre-conception care program for women of childbearing age with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in Korea and verify its effects on self-efficacy for IBD management, IBD-related pregnancy knowledge, and IBD-related pregnancy anxiety. It also aimed to explore the changes in participants through the program.
Methods
A convergent mixed-methods study design was adopted. In the quantitative phase, 35 women (17 and 18 in the intervention and control group, respectively) participated. The intervention group attended a program that included small-group sessions and individual tele-coaching. To confirm the effects, data were collected before and one and four weeks after the intervention. In the qualitative stage, focus group interviews and tele-coaching were conducted with the intervention group.
Results
After the program ended, significant differences were observed over time between the intervention and control groups for self-efficacy for IBD management (Wald χ2 = 4.41, p = .036), IBD-related pregnancy knowledge (Wald χ2 = 13.80, p < .001) and IBD-related pregnancy anxiety (Wald χ2 = 8.61, p = .003). Qualitative data analysis revealed the following themes: (1) improving confidence in IBD management and awareness for planned pregnancy; (2) improving IBD awareness related to pregnancy and childbirth; and (3) relieving anxiety about and actively facing pregnancy.
Conclusion
This study is meaningful in that, to the best of our knowledge, it is the first to develop a pre-conception care program for women diagnosed with IBD and confirm its effectiveness. Furthermore, this program is expected to be suitable for patient counseling and education in clinical practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The experiences of fertility concerns in women with inflammatory bowel disease of childbearing age: a descriptive qualitative study
Lewei Tu, Qiaoyu Wu, Mengxiao Jiang, Meihao Wei, Ying Wang, Ying Xiao
BMC Gastroenterology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Health Literacy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review of Health Outcomes, Predictors and Barriers
Caterina Mercuri, Rita Nocerino, Vincenzo Bosco, Teresa Rea, Vincenza Giordano, Michele Virgolesi, Patrizia Doldo, Silvio Simeone
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(23): 8577. CrossRef
- The experiences of fertility concerns in women with inflammatory bowel disease of childbearing age: a descriptive qualitative study
- 2,370 View
- 92 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Support Needs for Health Promotion of Community-Dwelling People with Disabilities: Perspectives of Operators Managing Disability Supportive Housing
- Hye Jin Nam, Haesun Lee, Han Nah Park, Sujin Lee, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):211-223. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Recent studies have focused on policies aimed at supporting the independence of individuals with disabilities in communities. As part of this initiative, supportive housing, integrated care, and residential spaces offer tailored services based on individual needs and autonomy. The attitudes and knowledge of the administrators supporting supportive housing residents regarding health management can influence the well-being of individuals with disabilities. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the challenges faced by supporting housing workers in enhancing the self-management skills of individuals with disabilities.
Methods
In this qualitative study, focus group interviews were conducted in August 2023 with nine administrators working to support housing in Seoul. Qualitative content analysis was used to analyze the interview data.
Results
The needs and challenges in enhancing the self-management skills of individuals with disabilities were as follows: (1) the complexity of health management challenges, (2) bidirectional strategies for strengthening health management capabilities, and (3) support for systematic health management. Additionally, eight subthemes were derived.
Conclusion
By investigating the difficulties experienced and identifying the necessary support requirements for supportive housing workers, this study seeks to uncover insights and identifies areas for improvement and strategies for health management. This study acknowledges the educational and institutional support necessary to improve the health and quality of life of individuals with disabilities residing in supportive housing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
Haesun Lee, Hye Jin Nam, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(3): 454. CrossRef - Intention to use a health information platform in supportive housing for people with disabilities: An application of the UTAUT model
Bohye Kim, Hye Jin Nam, Haesun Lee, Hannah Park, Ju Young Yoon, Nicola Diviani
PLOS One.2025; 20(10): e0332072. CrossRef - A preliminary study on the development of a chronic disease self-management curriculum for disability support workers: educational needs analysis
Han Nah PARK, Hye Jin NAM, Haesun LEE MSN, Sujin LEE, Bohye KIM, Ju Young YOON
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
- 2,217 View
- 96 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Analysis of the Adequacy of Nurse Staffing Level through the Estimation of Nursing Activity Hours and Implementation of Focus Group Interviews in a Tertiary Hospital: Using a Mixed-Method Design
- Hyun-Joo Kim, Sun-Hee Lee, Jai-Jung Lee, Sun-Suk Seong, Hee Yang, Hyang-Yuol Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):237-249. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22142
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the adequacy of current nurse staffing levels by identifying nursing activities and workload.
Methods
The study used a mixed-method design. A nursing activity survey was conducted using the work sampling method over 2 working days with 119 general ward nurses. A focus group interview was conducted with 12 nurses. Quantitative and qualitative data were analyzed using SPSS 20.0 and content analysis, respectively.
Results
The most amount of time was spent on medication (in direct nursing) and electronic medical record documentation (in indirect nursing). The appropriate nurse-to-patient ratio is 1:7.7 for the day shift, 1:9.0 for the evening shift, and 1:11.9 for the night shift. However, the current nurse-to-patient ratio is 1:9.4, 1:11.0, and 1:13.8 for the day, evening, and night shifts, respectively. Therefore, the current nurse staffing level is insufficient for the workload. In the focus group interview, the main reasons cited for being unable to complete tasks within working hours were communication and coordination, and the nursing electronic medical record. The essential nursing activities of basic nursing and emotional support were overlooked owing to a heavy workload. Therefore, an adequate nurse staffing level should be higher than the measured quantitative workload.
Conclusion
These results suggest the general wards of tertiary hospitals should evaluate the adequacy of their current nurse staffing and allocate sufficient nurses to improve patient safety and nursing care quality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nurses' Experience Working with Substitute Nurses
Hye Mi Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 208. CrossRef
- Nurses' Experience Working with Substitute Nurses
- 2,995 View
- 255 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Association between Resilience, Professional Quality of Life, and Caring Behavior in Oncology Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Misun Jeon, Sue Kim, Sanghee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):597-609. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23058
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The degree of caring behavior of oncology nurses is a crucial factor in the care provided to patients with cancer. In this study, we aimed to investigate factors related to oncology nurses’ caring behavior, including their resilience and professional quality of life.
Methods
A cross-sectional descriptive study was conducted with 107 oncology nurses at an urban tertiary hospital from May 18 to 24, 2015. We used a self-report questionnaire to measure resilience, professional quality of life, and degree of caring behavior. Data analysis included descriptive statistics, correlations, and multiple regression analysis using SPSS/WIN 20.0.
Results
Oncology nurses presented with low levels of resilience and caring behavior, and high levels of compassion satisfaction, burnout, and secondary traumatic stress. There was a statistically significant relationship between the degree of caring behavior, resilience (r = .43, p < .001), compassion satisfaction (r = .51, p < .001), and burnout (r = - .42, p < .001), as well as between secondary traumatic stress and burnout (r = .34, p < .001). Factors associated with oncology nurses’ degree of caring behavior were compassion satisfaction (t = 6.00, p < .001) and educational level (t = 3.45, p = .001).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that oncology nurses’ degree of caring behavior is related to their professional quality of life and education. These findings suggest that enhancing oncology nurses’ healthy coping strategies at both the individual and organizational levels can further develop holistic nursing care. Additionally, it is necessary to examine the factors affecting nurses’ compassion satisfaction and to try to promote this aspect. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Mediating Role of Resilience Between Empathy and Professional Competence Among Emergency Nurses in the West Bank, Palestine: Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling
Anas Shehadeh, Ahmad Shuhaiber, Malakeh Z. Malak, Ahmad Ayed, Hisham Zahran
International Nursing Review.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Burnout among health professionals working in oncology: current evidence and challenges for future research
Javier Martinez-Calderon, Cristina García-Muñoz
Current Opinion in Oncology.2025; 37(4): 302. CrossRef - Personal and work-related factors associated with nurse resilience: An updated systematic review using meta-analysis and narrative synthesis
Fiona Yu, Deborah Raphael, Lisa Mackay, Melody Smith, Ritin Fernandez
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2025; 166: 105054. CrossRef - Impact of an oncology training program on nursing personnel knowledge: A pilot study
Sara Gabriela Yeverino-Castro, Francisco Zamora-Rosales, Rodrigo Álvarez-Calderon , Oswaldo Enrique Sánchez-Dávila , Erika Evangelina Coronado-Cerda , Sonia Esquivel Ochotorena
Revista de Estudios e Investigación en Psicología y Educación.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Compassion fatigue, psychological resilience, moral sensitivity, and humanistic caring ability in clinical nurses: a structural equation model
Shuqi Zhai, Qinqin Liu, Congcong Dai, Yifan Lu, Huanhuan Zhang, Jie Liu, Chaoran Chen
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Impact of Resilience on Professional Quality of Life Among Oncology Nurses
Asma Al Yahyaei, Wafa Al Jabri, Nabiha Al Hasni, Zainab Al Kindi, Sulaiman Al Sabei, Omar Al Omari, Joshua Muliira, Foroozan Atashzadeh-Shoorideh
Nursing Forum.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of the Quranic Teachings on the Resilience and Caring Behaviors of Nursing Students Amid Crises Such as the COVID-19 Pandemic
Maryam Shaygan, Fatemeh Vizeshfar, Azadeh Amiri, Marzieh Kargar Jahromi
International Perspectives in Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Professional Quality of Life in Nursing: The Role of Psychological Resources—A Cross-Sectional Study
Lovorka Brajković, Dora Korać, Vanja Kopilaš
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(12): 434. CrossRef - Connectedness to Nature and Professional Quality of Life Among Nurses in South Korea in the Context of COVID-19
Hyeon Sik Chu, Young Ran Tak, Hanyi Lee
HERD: Health Environments Research & Design Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study on Moral Distress, Compassion Fatigue, Compassion Satisfaction, and Their Predictors among Nurses Caring for Patients with Cancer
Soomin Hong, Yesol Kim, Mi Sook Jung, Yoonjung Lee, Hyunju Hong, Mijin Jeon, Mee-Young Cho, Jiyeon Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(4): 217. CrossRef - Mindful self-care among oncology nurses in China: a latent profile analysis
Yan Shi, Peng Wang, Lamei Liu, Mengmeng Li
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The mediating role of compassion fatigue between perceived organization support and caring behavior among outpatient nurses in China: a cross-sectional study
Xingxing Liu, Fang He, Tian Tian, Jun Zhang, Yuanjiao Ji, Yuexia Zhong
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Critical Role of Nursing in Identifying and Managing Care Fatigue Among Hospitalized Patients
Haya Semah D Alreshidi, Alanazi, Maryam Munadi, May Farhan Salem Alanazi, Hamidah Matrouk Alruwaili, Alruwaili, Rehab Mulhi A, Awatif Rakyan Murayr Alruwaili, Huda Alshawi J Alruwaili, Adhwaa Alohaylim Aldaghmani, Almatrafi, Rawan Wadi S, Hana M
International Journal of Computational and Experimental Science and Engineering.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Mediating Role of Resilience Between Empathy and Professional Competence Among Emergency Nurses in the West Bank, Palestine: Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling
- 4,694 View
- 198 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

- Perspectives of Frontline Nurses Working in South Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Combined Method of Text Network Analysis and Summative Content Analysis
- SangA Lee, Tae Wha Lee, Seung Eun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):584-596. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23048
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to explore the perspectives of frontline nurses working during the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
Methods
An online qualitative study was conducted using a pragmatic approach. The data were collected in August 2021. Registered Korean nurses who provided direct nursing care to patients with confirmed COVID-19 were eligible for this study. An online survey was used to gather free-text data, which were then analyzed using machine-based network analysis and summative content analysis.
Results
The analysis examined the responses of 126 participants and led to the identification of six prominent themes. These themes were further classified into three distinct levels: personal, task, and organizational. The identified themes are as follows: “collapse of personal life,” “being overwhelmed by the numerous roles required,” “personal protective equipment was sufficiently provided, but that is not enough,” “changes in interprofessional collaboration,” “inappropriate workforce management,” and “diverted allocation of healthcare services and resources.” Conclusion: Our findings highlight areas for improvement in resources, systems, and policies to enhance preparedness for future pandemics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Skill mix changes in healthcare professions during the COVID-19 pandemic: a scoping review
Natalia Petka-Nosal, Iwona A Bielska, Katarzyna Badora-Musiał, Katarzyna Nowak-Zając, Alicja Domagała, Małgorzata Gałązka-Sobotka, Iwona Kowalska-Bobko
BMJ Open.2025; 15(10): e100024. CrossRef
- Skill mix changes in healthcare professions during the COVID-19 pandemic: a scoping review
- 2,759 View
- 35 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Development of Nursing Clinical Judgment Scale
- Shi Nae Kwon, Hyojung Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):652-665. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23042
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a nursing clinical judgment scale (NCJS) and verify its validity and reliability in assessing the clinical judgment of nurses.
Methods
A preliminary instrument of the NCJS comprising 38 items was first developed from attributes and indicators derived from a literature review and an in-depth/focus interview with 12 clinical nurses. The preliminary tool was finalized after 7 experts conducted a content validity test based on a data from a preliminary survey of 30 hospital nurses in Korea. Data were collected from 443 ward, intensive care unit, emergency room nurses who voluntarily participated in the survey through offline and online for the verification of the construct validity and reliability of the scale.
Results
The final scale comprised 23 items scored on a 5-point Likert scale. Six factors – integrated data analysis, evaluation and reflection on interventions, evidence on interventions, collaboration among health professionals, patient-centered nursing, and collaboration among nurse colleagues – accounted for 64.9% of the total variance. Confirmatory factor analysis supported the fit of the measurement model, comprising six factors (root mean square error of approximation = .07, standardized root mean square residual = .04, comparative fit index = .90). Cronbach’s α for all the items was .92.
Conclusion
The NCJS is a valid and reliable tool that fully reflects the characteristics of clinical practice, and it can be used effectively to evaluate the clinical judgment of Korean nurses. Future research should reflect the variables influencing clinical judgment and develop an action plan to improve it. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How the nursing work environment moderates the relationship between clinical judgment and person-centered care among intensive care unit nurses
Mi Hwa Seo, Eun A. Kim, Hae Ran Kim, Mohammad Jamil Rababa
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(1): e0316654. CrossRef - Effects of Critical Thinking Disposition, Clinical Judgement, and Nurse–Physician Collaboration on Triage Competency Among Triage Nurses
Ji-Won Song, Hyung-Ran Park
Healthcare.2025; 13(4): 405. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a virtual reality nursing simulation for pediatric pneumonia care: a Korean pilot study using a single-group pre-post test design
Eun Joo Kim, Seong Kwang Kim, Sung Sook Song
Child Health Nursing Research.2025; 31(4): 198. CrossRef - The Influence of Clinical Nurses' Clinical Judgment, Nursing Work Environment and Ethical Nursing Competence on Patient Safety Nursing Activities
Eunseo Hong, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2025; 39(3): 368. CrossRef
- How the nursing work environment moderates the relationship between clinical judgment and person-centered care among intensive care unit nurses
- 4,753 View
- 284 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Experiences of Transitional Care for Medicaid Case Managers
- Yunhee Hwang, Gaeon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(5):556-569. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23031
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This phenomenological study tried to understand the essence of the transitional care experience of medicaid case managers and its structural meaning. In addition, it was attempted to establish a system of transitional care and seek support measures for medicaid case managers.
Methods
The participants of this study were 7 medicaid case managers who had spent more than 1 year and 6 months in medicaid pilot project. Data were collected with individual in-depth interviews from June to December 2021. The data were analyzed by Giorgi's phenomenological analysis method.
Results
The seven constituents derived from the results of this study were 'struggle to establish a living environment', 'dedication to supporting independent living', 'anxiety about safety', 'pressure on care responsibilities', ‘distress in building the pilot project’, 'pride in role', and 'expectation for improvement'.
Conclusion
The study results provide a comprehensive understanding of the transition care reality for medicaid case managers. They also shed light on managers’ perceptions and attitudes. These findings can serve as fundamental information for establishing support measures for medicaid case managers and transitional care systems.
- 1,752 View
- 29 Download

- Analysis of ROX Index, ROX-HR Index, and SpO 2 /FIO 2 Ratio in Patients Who Received HighFlow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy in Pediatric Intensive Care Unit
- Sun Hee Choi, Dong Yeon Kim, Byung Yun Song, Yang Sook Yoo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):468-479. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22152
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the use of the respiratory rate oxygenation (ROX) index, ROX-heart rate (ROX-HR) index, and saturation of percutaneous oxygen/fraction of inspired oxygen ratio (SF ratio) to predict weaning from high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) in patients with respiratory distress in a pediatric intensive care unit.
Methods
A total of 107 children admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit were enrolled in the study between January 1, 2017, and December 31, 2021. Data on clinical and personal information, ROX index, ROX-HR index, and SF ratio were collected from nursing records. The data were analyzed using an independent t-test, χ2 test, Mann–Whitney U test, and area under the curve (AUC).
Results
Seventy-five (70.1%) patients were successfully weaned from HFNC, while 32 (29.9%) failed. Considering specificity and sensitivity, the optimal cut off points for predicting treatment success and failure of HFNC oxygen therapy were 6.88 and 10.16 (ROX index), 5.23 and 8.61 (ROX-HR index), and 198.75 and 353.15 (SF ratio), respectively. The measurement of time showed that the most significant AUC was 1 hour before HFNC interruption.
Conclusion
The ROX index, ROX-HR index, and SF ratio appear to be promising tools for the early prediction of treatment success or failure in patients initiated on HFNC for acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. Nurses caring for critically ill pediatric patients should closely observe and periodically check their breathing patterns. It is important to continuously monitor three indexes to ensure that ventilation assistance therapy is started at the right time. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Non-invasive SpO2/FiO2 ratio (SFR) as surrogate for PaO2/FiO2 ratio (PFR): A scoping review
Madhura Reddy, Malavika Kulkarni, Sushma Thimmaiah Kanakalakshmi, Laxmi Shenoy, Rama Rani KrishnaBhat
The Journal of Critical Care Medicine.2025; 11(3): 221. CrossRef - Can the ROX index predict high‐flow nasal cannula failure in children under 2 with lower respiratory tract infection?
Pablo Vasquez‐Hoyos, Alvaro L. Jacome‐Orozco, Andrea P. Rodriguez‐Mayorga, Leidy E. Sepulveda‐Forero, Diana P. Escobar‐Serna, Juan S. Barajas, Evelyn Obando‐Belalcazar, Claudia M. Salinas‐Jaimes, Juan J. Peralta‐Palmezano, Alexandra Jimenez‐Chavez, Rafael
Pediatric Pulmonology.2024; 59(5): 1246. CrossRef - Impact of Surgical Mask Placement Over High-Flow Nasal Cannula on Oxygenation Parameters in COVID-19 Patients Experiencing Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure
Aadila Coatwala, Mayank Dhir, Sagar Sinha, Dattatray Bhusare
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Non-invasive SpO2/FiO2 ratio (SFR) as surrogate for PaO2/FiO2 ratio (PFR): A scoping review
- 5,650 View
- 163 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of Self-Efficacy for HIV Disease Management Skills
- Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Mi-So Shim, Seoyoung Baek, Namhee Kim, Min Kyung Park, Youngjin Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(3):295-308. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23016
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study evaluated the validity and reliability of Shively and colleagues’ self-efficacy for HIV disease management skills (HIVSE) among Korean participants.
Methods
The original HIV-SE questionnaire, comprising 34 items, was translated into Korean using a translation and back-translation process. To enhance clarity and eliminate redundancy, the author and expert committee engaged in multiple discussions and integrated two items with similar meanings into a single item. Further, four HIV nurse experts tested content validity. Survey data were collected from 227 individuals diagnosed with HIV from five Korean hospitals. Construct validity was verified through confirmatory factor analysis. Criterion validity was evaluated using Pearson’s correlation coefficients with the new general self-efficacy scale. Internal consistency reliability and test-retest were examined for reliability.
Results
The Korean version of HIV-SE (K-HIV-SE) comprises 33 items across six domains: “managing depression/mood,” “managing medications,” “managing symptoms,” “communicating with a healthcare provider,” “getting support/help,” and “managing fatigue.” The fitness of the modified model was acceptable (minimum value of the discrepancy function/degree of freedom = 2.49, root mean square error of approximation = .08, goodnessof-fit index = .76, adjusted goodness-of-fit index = .71, Tucker-Lewis index = .84, and comparative fit index = .86). The internal consistency reliability (Cronbach’s α = .91) and test-retest reliability (intraclass correlation coefficient = .73) were good. The criterion validity of the K-HIV-SE was .59 (p < .001).
Conclusion
This study suggests that the K-HIV-SE is useful for efficiently assessing self-efficacy for HIV disease management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Providing 2 Types of mHealth Interventions to Support Self-Management Among People Living With HIV: Randomized Clinical Trial
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Seoyoung Baek, Sooyoung Kwon, Ji Min Kim, Jun Yong Choi, Jae-Phil Choi
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2025; 13: e60905. CrossRef - Factors associated with health-related quality of life among people living with HIV in South Korea: Tobit regression analysis
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, SangA Lee, Mi-So Shim, Youngjin Lee, Seoyoung Baek, Claus Kadelka
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(5): e0303568. CrossRef - Three cycles of mobile app design to improve HIV self-management: A development and evaluation study
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Seoyoung Baek, Mi-So Shim, SangA Lee, Ji Min Kim, Jong Yae Yoon, Jin Kim, JunYong Choi, Jae-Phil Choi
DIGITAL HEALTH.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Providing 2 Types of mHealth Interventions to Support Self-Management Among People Living With HIV: Randomized Clinical Trial
- 2,875 View
- 64 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of Evidence-Based Nursing Protocol for Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation to Critically Ill Patients
- Soomi Kim, Chul-Gyu Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(3):275-294. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22109
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop an evidence-based extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) nursing protocol for critically ill patients receiving ECMO treatment by using an adaptation process, and to verify the effects of the protocol.
Methods
The protocol was developed according to the adaptation guidelines. A non-randomized controlled trial was conducted to test the protocol’s effects. Data were collected between April 2019 and March 2021. The differences in physiological indicators and complication rates between the two groups were investigated using a chart review to evaluate patient outcomes. The nurses’ outcome variables were evaluated using a questionnaire.
Results
First, after reviewing 11 guidelines by appraisal of the guidelines for research and evaluation collaboration II, 5 guidelines with a standardization grade of over 50 points were selected. An ECMO nursing protocol was developed based on these guidelines. Second, there were no statistically significant differences in physiological indicators between the two groups of patients. However, the experimental group showed a statistically significant decrease in the infection rate (p = .026) and pressure injury rates (p = .041). The levels of satisfaction with ECMO nursing care, and empowerment and performance of the nurses who used the ECMO nursing protocol were higher than those of nurses who did not (p < .001).
Conclusion
This protocol may help prevent infections and pressure injuries in patients, and improve nurses’ satisfaction and empowerment. The nursing protocol developed for critically ill patients receiving ECMO treatment can be utilized in evidence-based nursing practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Advances in Evidence-Based Nursing for Clinical Practice Standards and Technological Optimization in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine
晓婷 汤
Asian Case Reports in Emergency Medicine.2025; 13(03): 300. CrossRef - Factors associated with nursing workload in patients undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: a retrospective cohort study
André Lucas da Silva Guideli, Luana Letícia Ribeiro de Luna, Larissa Fernandes Araújo da Silva, Marcele Liliane Pesavento, Lilia de Souza Nogueira, Filipe Utuari de Andrade Coelho
einstein (São Paulo).2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of ECMO training program for ICU nurses knowledge gain and self-efficacy outcomes assessment: quasi-experimental evaluation
Hafize Savaş, Sevil Güler, Sinan Sabit Kocabeyoğlu
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A comprehensive evidence-based intervention programme significantly reduces intensive care unit-acquired weakness and improves functional recovery: a retrospective analysis
Hongrui Zhu, Yueming Zhang, Yan Zhou, Hongxia Yan
Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine.2025; 57: jrm43563. CrossRef
- Research Advances in Evidence-Based Nursing for Clinical Practice Standards and Technological Optimization in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine
- 9,018 View
- 386 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Pathway Analysis on the Effects of Nursing Informatics Competency, Nursing Care Left Undone, and Nurse Reported Quality of Care on Nursing Productivity among Clinical Nurses
- Mi Yu, Se Young Kim, Ji Min Ryu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):236-248. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22110
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Nursing informatics competency is used to manage and improve the delivery of safe, high-quality, and efficient healthcare services in accordance with best practices and professional and regulatory standards. This study examined the relationship between nursing informatics competency (NIC), nursing care left undone, and nurse reported quality of care (NQoC) and nursing productivity. A path model for their effects on nursing productivity among clinical nurses was also established.
Methods
Data were collected using structured questionnaires answered by 192 nurses working in a tertiary hospital located in J city, Korea, and analyzed using SPSS/WIN 23.0 and AMOS 21.0 program.
Results
The fit indices of the alternative path model satisfied recommended levels χ2 = .11 (p= .741), normed χ2 (χ2/df) = .11, SRMR = .01, RMSEA = .00, GFI = 1.00, NFI = 1.00, AIC = 18.11. Among the variables, NIC (β = .44, p < .001), NQoC (β = .35, p < .001) had a direct effect on nursing productivity. Due to the mediating effect of NQoC on the relationship between NIC and nursing productivity, the effect size was .14 (95% CI .08~.24). Meanwhile, nursing care left undone through NQoC in the relationship between NIC and nursing productivity, has a significant mediation effect (estimate .01, 95% CI .00~.03). The explanatory power of variables was 44.0%.
Conclusion
Education and training for enhancing NIC should be provided to improve nursing productivity, quality of care and to reduce missed nursing care. Furthermore, monitoring the quality of nursing care and using it as a productivity index is essential. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Information Literacy Competencies and Associated Variables among Korean Nursing Students
Shin Hyang Kim, Jong Mi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 358. CrossRef - The impact of nursing informatics competency, social influence, and medical information culture on nurses’ intention to use new medical technology in general hospitals
Jeong Ho Ji, Kyungja Kang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(4): 484. CrossRef - Effects of digital literacy and nursing informatics competency as job resources on nurses’ burnout and work engagement: a cross-sectional study
Jeehae Chung, Hyesil Jung, Sang Mi Park, Kyeongmin Lee
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Care Left Undone by Cancer Ward Nurses
Chung Hee Woo, Yeon Joo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 594. CrossRef
- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Information Literacy Competencies and Associated Variables among Korean Nursing Students
- 2,883 View
- 124 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Conceptual Analysis of Career Anchors of Nurses
- Jae Woo Oh, Mi Ran Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):28-38. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22091
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to provide a theoretical basis for career anchors of nurses by defining and organizing its concept.
Methods
Using the Walker and Avant concept analysis, a total of 29 articles were analyzed through a literature search in this study.
Results
The career anchors of nurses are individual career choice motives, a self-concept where in competency and values are harmonized, which act as a desire for growth and development in nursing, and are actions that maintain careers. Additionally, they indicate the direction for achieving individual career goals and act as a core value expected of nurses by nursing organizations, indicating continuous and integrated professional growth and development of the nursing profession.
Conclusion
The career anchors of nurses identified in the results contribute to securing patient safety, providing quality care through policies, institutionalizing bases for career development, preventing nurse turnover, and retaining skilled nurses. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Developing a tailored retention model for healthcare professionals: A mixed-methods study in South African pathology laboratories
Shiksha Gallow, Ravinder Rena, Manjeet Kharub
International Journal of Healthcare Management.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Effects of Career Anchors on Nursing Students’ Professional Self-concept and Work Values
Jae Woo Oh, Ji Ah Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(4): 435. CrossRef
- Developing a tailored retention model for healthcare professionals: A mixed-methods study in South African pathology laboratories
- 2,162 View
- 86 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of Self-Care Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Inventory (SC-COPD) and Self-Care Self-Efficacy Scale (SCES-COPD)
- Ja Yun Choi, So Young Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(5):522-534. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22062
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the Self-Care in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Inventory (SC-COPDI) and the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Self-Care Self-Efficacy Scale (SCES-COPD). The SC-COPDI consists of the Self-Care Maintenance Scale (SCMES), Self-Care Monitoring Scale (SCMOS), and Self-Care Management Scale (SCMAS).
Methods
The original tool was translated using a back-translation process. Participants were 241 patients with COPD at the Chonnam National University Hospital in Korea. The construct validity was verified through confirmatory factor analysis, and reliability was verified using Cronbach’s α.
Results
The SCMES consisted of 10 items of three factors―one of four factors was deleted from the original tool. In the SC-MOS, there were six items of two factors after two items were deleted from the original tool. The SCMAS consisted of the original 10 items of three factors. The SCES-COPD consisted of six items of two factors, with one item removed from the original tool. The model fit indices of all tools were good, and the construct validity was confirmed. Cronbach’s α of SCMES was .72, SCMOS was .90, SCMAS was .81, and SCES-COPD was .85.
Conclusion
The Korean version of SC-COPDI and SCES-COPD are valid and reliable instruments for measuring selfcare in people with COPD. These instruments can be used in self-care studies of COPD patients in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Ruminative Thinking on Breathlessness Catastrophizing With Elderly COPD Patients: The Mediating Role of Self‐Efficacy
Yuye Zhang, Qiufang Li, Xiaokai Wang, Tianci Xiao, Chenmeng Wei, Na Song, Lamei Liu
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025; 34(11): 4854. CrossRef - The influence of depression, social support, and uncertainty on self-management compliance in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases: A descriptive survey study
Han-na Jang, Jeong-soo Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(3): 318. CrossRef - Enhancing deep learning models for predicting smoking Status using clinical data in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Sehyun Cho, Hyeonseok Jin, Kyungbaek Kim, Sola Cho, Ja Yun Choi
DIGITAL HEALTH.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influences of Illness Uncertainty, Health Literacy, and Self-Care on Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Min Jin Chu, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 530. CrossRef - E-health literacy and attitudes toward internet health information in relation to self-care adherence among Korean patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a cross-sectional study
Na Yeong Park, Insook Lee
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric testing of the cross-culturally adapted Thai version of the Self-Care Self-Efficacy Scale version 3.0 in individuals with chronic illnesses
Chennet Phonphet, Jom Suwanno, Chonchanok Bunsuk, Wanna Kumanjan, Ladda Thiamwong
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2024; 11(4): 473. CrossRef
- Impact of Ruminative Thinking on Breathlessness Catastrophizing With Elderly COPD Patients: The Mediating Role of Self‐Efficacy
- 2,593 View
- 72 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- An Analysis of Tasks of Nurses Caring for Patients with COVID-19 in a Nationally-Designated Inpatient Treatment Unit
- Minho Jung, Moon-Sook Kim, Joo-Yeon Lee, Kyung Yi Lee, Yeon-Hwan Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):391-406. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22056
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to provide foundational knowledge on nursing tasks performed on patients with COVID-19 in a nationally-designated inpatient treatment unit.
Methods
This study employs both quantitative and qualitative approaches. The quantitative method investigated the content and frequency of nursing tasks for 460 patients (age ≥ 18y, 57.4% men) from January 20, 2020, to September 30, 2021, by analyzing hospital information system records. Qualitative data were collected via focus group interviews. The study involved interviews with three focus groups comprising 18 nurses overall to assess their experiences and perspectives on nursing care during the pandemic from February 3, 2022, to February 15, 2022. The data were examined with thematic analysis.
Results
Overall, 49 different areas of nursing tasks (n = 130,687) were identified based on the Korean Patient Classification System for nurses during the study period. Among the performed tasks, monitoring of oxygen saturation and measuring of vital signs were considered high-priority. From the focus group interview, three main themes and eleven sub-themes were generated. The three main themes are “Experiencing eventfulness in isolated settings,” “All-around player,” and “Reflections for solutions.” Conclusion: During the COVID-19 pandemic, it is imperative to ensure adequate staffing levels, compensation, and educational support for nurses. The study further propose improving guidelines for emerging infectious diseases and patient classification systems to improve the overall quality of patient care. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring Nursing Care for Patients With COVID-19 Using International Classification for Nursing Practice–Based Nursing Records
Sumi Sung, Hyesil Jung, Youlim Kim
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2024; 42(2): 127. CrossRef - Burnout among Nurses in COVID-19 Designated Units Compared with Those in General Units Caring for Both COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Patients
Kyung Ah Woo, Eun Kyoung Yun, JiSun Choi, Hye Min Byun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 374. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of the Functional Ingredients and Physiological Activities of Taraxacum coreanum Nakai
In-Seo Yoo, Ae-Jung Kim
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2023; 21(4): 719. CrossRef
- Exploring Nursing Care for Patients With COVID-19 Using International Classification for Nursing Practice–Based Nursing Records
- 2,012 View
- 20 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- The Caring Experience of Family Caregivers for Patients of Living Donor Liver Transplantation from the Family Members
- Miseon Bang, Suhye Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):435-450. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22043
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of the study was to understand the care experiences of the family of living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) patients where the donation had occurred within the family.
Methods
Participants were eight family caregivers who cared for recipients and donors of LDLT. Data were collected through individual in-depth interviews from November, 2020 to April, 2021. Data analysis was performed through a cyclical process of data collection and analysis by applying Giorgi’s phenomenological research method.
Results
The five main components extracted from the experiences of the family caregivers were: "A double-edged choice to save the family", "The harsh daily life of liver transplantation care", "The yoke of double care on both shoulders", "The power to withstand the adversity of caring", and "The recovery and growth of life pursued by trusting each other".
Conclusion
The participants tried to do their best in their daily lives, while providing reassurance and care to the LDLT patients in the family; however, they expressed some worry and hardship while doing so. The results of this study provide a deeper understanding of the caring experience of the family caregivers, which may contribute to the development of nursing interventions that will aid these caregivers in providing care to their LDLT family members. Furthermore, the development and application of an integrated management program for LDLT patients in the family is required. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Challenges and support needs among family caregivers involved in solid organ transplant care process: a scoping review protocol
Shi He, Ningbin Huang, Meiqi Lai, Wenwen Li, Siting Chen, Guolong Zhang, Danxia Huang, Guilin Peng, Ying Huang, Liang Ruan
BMJ Open.2025; 15(3): e086771. CrossRef
- Challenges and support needs among family caregivers involved in solid organ transplant care process: a scoping review protocol
- 2,149 View
- 44 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Development and Effects of a Person-Centered Fall Prevention Program for Older Adults with Dementia in Long-Term Care Hospitals: For Older Adults with Dementia and Caregivers in LongTerm Care Hospitals
- Jeong Ok Lim, Mee Ock Gu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):341-358. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21230
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the effects of a person-centered fall prevention program for older adults with dementia in long-term care hospitals.
Methods
A nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The study sample included 42 older adults with dementia (experimental group: 21, control group: 21) and 42 caregivers (experimental group: 21, control group: 21). The program comprised 48 sessions held over 12 weeks and included exercise intervention with resistance and balance, dance walking (45~60 min, three times/week), cognitive and emotional intervention (35~50 min, once per week), and person-centered fall prevention education (10 min, once per week). The program for caregivers consisted of six educational sessions (i.e., fall prevention competency enhancement and person-centered care strategy education, 80 min, once per week) for six weeks. Data were collected before participation and 12 weeks after program completion from February 18 to May 12, 2019. Data analysis was conducted using the chi-square test, t-test, and Mann―Whitney U test with SPSS/WIN 21.0.
Results
The experimental group of older adults with dementia showed significant improvement in physical and cognitive functions, and a decrease in depression, and behavioral and psychological symptoms, when compared with the control group. caregivers in the experimental group exhibited significant improvement in fall-related knowledge and person-centered care of older adults with dementia compared to the control group.
Conclusion
The study findings indicate that this program was effective as a nursing intervention for fall prevention among older adults with dementia in long-term care hospitals. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influencing factors of depressive and anxiety symptoms among caregivers of Alzheimer's disease patients: A cross-sectional study
Chengfei Duan, Mo Zhu, Xia Li, Ling Yue
Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.2026; 109(3): 1264. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Fall Incidents at Long-term Care Hospitals: Using Data from the Korea Patient Safety Reporting and Learning System
Soojin Chung, Jeongim Lee
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2025; 50(1): 96. CrossRef - Current Trends of Exercise Programs for Improving Cognitive Function in Older Adults
Jae-Hyun Lee, Wooyeon Jo, Jaeho Jin, Yaxiong Zheng, Soyoon Lee, Se-Yeon Jang, Minseo Kim, Young-Jin Moon, Hye Gwang Jeong, Sang Ki Lee
Exercise Science.2024; 33(3): 254. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Dementia Care Competence among Care Staff: A Mixed-Methods Systematic Review Protocol
Jinfeng Zhu, Jing Wang, Bo Zhang, Xi Zhang, Hui Wu
Healthcare.2024; 12(11): 1155. CrossRef - Falls in Patients of Medical Institutions in South Korea: A Literature Review
Jongwon Choi, Woochol Joseph Choi
Physical Therapy Korea.2023; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - A Study on Emotions to Improve the Quality of Life of South Korean Senior Patients Residing in Convalescent Hospitals
Aeju Kim, Yucheon Kim, Jongtae Rhee, Songyi Lee, Youngil Jeong, Jeongeun Lee, Youngeun Yoo, Haechan Kim, Hyeonji So, Junhyeong Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(21): 14480. CrossRef
- Influencing factors of depressive and anxiety symptoms among caregivers of Alzheimer's disease patients: A cross-sectional study
- 2,797 View
- 177 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Delirium Experience of the Intensive Care Unit Patients
- Jaeyeon Jung, Sujin Jang, Seonmi Jo, Sunhee Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):134-143. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21240
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The study aimed to understand the delirium experience of intensive care unit (ICU) patients.
Methods
We performed a qualitative study using Colaizzi’s phenomenological method. Eleven patients, who experienced delirium according to the Confusion Assessment Method for ICU, participated after transferring to general wards from the ICU. Individual in-depth semi-structured interviews ranging from 30 minutes to 2 hours in length were conducted between November 2018 and August 2019.
Results
Nine themes and four theme clusters emerged. The four theme clusters were: 1) “Overwhelmed by fear,” which describes the experience of a patient close to death and the feeling of difficulty in understanding disorganized thinking; 2) “Anxious about not understanding the situation,” which means that patients’ sense of time and space were disordered in the ICU; 3) “Being deserted,” which indicates the feeling of being separated from others and yourself; and 4) “Resistance to protect my dignity,” which indicates that the dignity and autonomy of an individual in the patient’s position at the ICU, are ignored.
Conclusion
Nursing interventions are needed that would enable patients to maintain orientation and self-esteem in the ICU. In addition, healthcare providers need to provide information about the unfamiliar environment in the ICU in advance. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Patients' and family members' dyadic experience of post‐operative delirium in the intensive care unit: A qualitative study
Jing Dong, Weijing Sui, Yiyu Zhuang
Nursing in Critical Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Person-centered Care, Intensive Care Experience, and Post-intensive Care Syndrome in Critical Care Survivors: A Multi-center Prospective Cohort Study
Jiyeon Kang, Seonyoung Yun
Asian Nursing Research.2025; 19(3): 274. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Intensive Care Unit Nurses’ Competency in Delirium Care in A Tertiary General Hospital
Mi Ran Lim, Gyoo Yeong Cho
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(3): 37. CrossRef - Exploring patients’ and families’ preferences for auditory stimulation in ICU delirium prevention: A qualitative study
Yajun Ma, Nianqi Cui, Zhiting Guo, Yuping Zhang, Jingfen Jin
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2024; 82: 103629. CrossRef - The Influence of Ethical Nursing Competence and Positive Nursing Organizational Culture on Person-Centered Care in Intensive Care Unit Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Jae Eun Lee, Hye-Young Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(3): 304. CrossRef - A Study on Nurses' Communication Experiences with Intubation Patients
Ye Rim Kim, Hye Ree Park, Mee Kyung Shin
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2023; 26(1): 28. CrossRef - Intensive Care Experience of Critical Care Patients and Its Related Factors : A Secondary Analysis Study
Jiyeon Kang, Hyojeong Woo
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2023; 16(3): 11. CrossRef - Item analysis of the Korean version of the Intensive Care Experience Questionnaire: Using the Rasch Model based on Item Response Theory
Jiyeon Kang, Minhui Kim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2022; 15(3): 37. CrossRef
- Patients' and family members' dyadic experience of post‐operative delirium in the intensive care unit: A qualitative study
- 2,709 View
- 170 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Job Analysis of Nurse Care Coordinators for Chronic Illness Management in Primary Care Settings: Using Developing a Curriculum Process
- Ju-Hee Hwang, Yong-Jun Choi, Mi-Sook Kim, Seng-Eun Yi, Yong-Soon Park, Ji-Hyang Kim, Ju-Young Yoon, Dong-Soo Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):758-768. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21065
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to conduct a job analysis of nurse carecoordinators and to identify the frequency, importance and difficulty of each task of their job.
Methods
A committee for developing a curriculum (DACUM) was formed and members of the committee defined nurse care coordinators’ jobs and enumerated the duties, tasks and task elements by applying the DACUM technique. Then nurse care coordinators enrolled in the pilot project evaluated the frequency, importance and difficulty of each task.
Results
From the job descriptions of nurse care coordinators, we identified 12 duties and 42 tasks. Each task comprised 1~5 task elements. Among tasks, ‘assess the patient’s general health status’ was carried out most frequently. Nurse care coordinators perceived that ‘check vital signs’ and ‘strengthen patient competence to promote health behaviors’ were more important than all other tasks. The most difficult task was ‘develop professionalism as a nurse care coordinator’.
Conclusion
The nurse care coordinators' roles developed in this study will serve as the key guidelines for human resource management of care coordinators. Further, job specifications for nurse care coordinators need to be developed, which is necessary for designing education and training programs. We also need to integrate primary health care as an essential component in nursing education. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Job Analysis of Nurses Working at Dementia Care Centers Using DACUM
Yong-Sun Shin, Jong-Eun Lee
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2025; 36: 21. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Care Coordination for Chronic Disease Patients with a Usual Source of Care
Hyunsang Kwon, Ju Young Yoon
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2025; 36: 339. CrossRef - Job analysis of vaccination health workers at public health centers and sub‐centers
No‐Yai Park, Chung‐Min Cho, Eun‐Hyun Lee, Jeong‐Mo Park, Young‐Ran Lee, Jeong‐Ik Hong, Geun‐Yong Kwon
Public Health Nursing.2024; 41(4): 723. CrossRef - Development and Analysis of the Job Description for Dementia Care Center Nurses in Korea Using Developing a Curriculum (DACUM)
Hana Ko, SuJung Jung
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2023; 49(10): 29. CrossRef - Analysis of flow rate and pressure in syringe-based wound irrigation using Bernoulli's equation
Hanna Lee, Ye-kyung Lee, Ji-Yun Park, Jeong-won Han
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Preliminary Study for the Curriculum Development of Community Care Coordinators: Educational Needs Analysis
Han Nah Park, Ju Young Yoon, Soong-Nang Jang, Hye Jin Nam
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(2): 153. CrossRef
- Job Analysis of Nurses Working at Dementia Care Centers Using DACUM
- 2,321 View
- 54 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Nurses’ Experience with Caring for COVID-19 Patients in a Negative Pressure Room Amid the Pandemic Situation
- Eun-Young Noh, Young Jun Chai, Hyun Jeong Kim, Eunjin Kim, Yeon-Hwan Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):585-596. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21148
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to explore nurses’ experience with caring for COVID-19 patients in a negative pressure room amid the spread of the pandemic.
Methods
This study was a qualitative research, and focus group interviews were used to collect data. Three focus groups comprising 19 nurses were interviewed from February 17 to 25, 2021. All interviews were recorded and transcribed verbatim with the consent of the participants. The verbatim transcripts were scrutinized using thematic analysis.
Results
Two main themes emerged from the analysis: ‘Struggling in an isolated space’ and ’Limitations of nursing infrastructure and system’. The nurses caring for COVID-19 patients experienced anxiety and fear about the infection, physical exhaustion, emotional burnout, and a sense of duty as a nurse. They also acknowledged the lack of guidelines, increased task and burden, limitations of nursing care, and the demand for improving the limitations of the nursing system.
Conclusion
The results of this study demonstrate that nurses caring for COVID-19 patients encounter physical and emotional problems within the limited healthcare system. The study suggests that comprehensive interventions are needed for nurses. Furthermore, detailed guidelines, strengthening of nursing personnel, and improvements to the nursing system are vital to effectively cope with the pandemic. The government and medical institutions should be aware of the needs of nurses and what they are going through, and make efforts to improve the quality of life of healthcare workers and create a safe healthcare environment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing Posttraumatic Growth among Nurses in COVID-19 Isolation Wards in Tertiary Hospitals
Ye Seul Im, Hyun Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(2): 233. CrossRef - Experiences of Person‐Centred Care Among Nurses in COVID‐19 Wards: A Qualitative Study
Myoungsuk Kim, Yongmi Lee, Hyun‐Ju Kang
Nursing Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on Non-Contact Nursing Experiences of Clinical Nurses during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Hye Min Byun, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 446. CrossRef - Nurses’ intention to care of COVID-19 patients in hospitals dedicated to infectious disease in South Korea: application of the theory of planned behavior and verification of the moderating effect of ethical nursing competence
Mira Mo, Seongmi Moon, Eun Kyeung Song
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurses' perceptions of medical service robots in negative‐pressure isolated wards and in general wards: A cross‐sectional survey
Jung Hwan Lee, In Ho Han, Jong Hwan Park, Kye‐Hyung Kim, Jaehyun Hwang, Dong Hwan Kim, Jae Il Lee, Kyoung Hyup Nam
Nursing Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Korean Hospital Nurses’ Experiences with COVID-19: A Meta-Synthesis of Qualitative Findings
Suk-Jung Han, Hee-Jung Hong, Bok-Soon Shin
Healthcare.2024; 12(9): 903. CrossRef - Improving Emerging Infectious Disease Control Based on the Experiences of South Korean Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Qualitative Systematic Review
Ha-Young Park, In-Sun Yeom
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Need for Information and Communication Technology during COVID-19: An Exploratory Study Using Nurses’ Activity Diaries
Hyeongsuk Lee, Dongmin Lee, Seungmin Lee
Healthcare Informatics Research.2023; 29(3): 256. CrossRef - Factors Influencing SARS-CoV-2 Infection Control Practices of Nurses Caring for COVID-19 Patients in South Korea: Based on Health Belief Model
Dain Jeong, Young Eun
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(4): 3223. CrossRef - Perspectives of Frontline Nurses Working in South Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Combined Method of Text Network Analysis and Summative Content Analysis
SangA Lee, Tae Wha Lee, Seung Eun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 584. CrossRef - Experiences of Psychiatric Nurses Working in a Closed Psychiatric Unit during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Ji Young Kim, Hyun Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(4): 374. CrossRef - Experiences of Caring for Cohort-Isolated Patients among Nurses in Locked Psychiatric Units
Hyeran An, Kyungmi Kim, Jongeun Lee, Sunhwa Won
Healthcare.2023; 11(19): 2650. CrossRef - Effect of Anxiety and Calling on Professional Quality of Life in COVID-19 Dedicated Nurses in Korea
Minjung Moon, Kyoungsan Seo
Healthcare.2022; 10(9): 1797. CrossRef - Critical role of information and communication technology in nursing during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A qualitative study
Hye Jin Yoo, Hyeongsuk Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(8): 3677. CrossRef - Correlation between COVID-19 and Nurses’ Job Stress and Burnout
Seyoung Yun, Song Vogue Ahn
Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service Research.2022; 2(2): 202. CrossRef - Experience of Nurses in Charge of COVID-19 Screening at General Hospitals in Korea
Boo Young Ha, Yun-Sook Bae, Han Sol Ryu, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 66. CrossRef - Frontline nurses' burnout and its associated factors during the COVID-19 pandemic in South Korea
Eun-Young Noh, Yeon-Hwan Park, Young Jun Chai, Hyun Jeong Kim, Eunjin Kim
Applied Nursing Research.2022; 67: 151622. CrossRef - Emergency nurses' attitudes, perceptions about personal protective equipment and willingness to care for COVID‐19 patients: A descriptive, cross‐sectional study
Ha‐Ra Jang, Ji‐Soo Kim
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2514. CrossRef - Clinical Field and Alternative Clinical Practice Experience in a Pandemic Situation of Nursing Students Who Have Experienced Clinical Practice before COVID-19
Hyeran An, Sunnam Park, Jongeun Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(20): 13372. CrossRef - Fourth Industrial Revolution and Nursing Research
Young Whee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 1. CrossRef - Nurses’ Experience in COVID-19 Patient Care
Soojin Chung, Mihyeon Seong, Ju-young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(2): 142. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing Posttraumatic Growth among Nurses in COVID-19 Isolation Wards in Tertiary Hospitals
- 1,914 View
- 26 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref

- Untact Visit Service Development Based on an Application Reflecting the Circumstances during COVID-19: Focusing on Utilization in the Pediatric Intensive Care Units
- Dahae Woo, Hanui Yu, Hyo Jin Kim, Minyoung Choi, Dong Hee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):573-584. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop an untact visit service based on an application that can be utilized in the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) during COVID-19.
Methods
This study adopted the double diamond process of service design comprising the discovery, defining, and development stages.
Results
We developed an untact visit service based on an application that considered the child’s status, schedule, photo, and video messages, and so on. Moreover, we derived a service flow regarding the required roles and the type of flow shown between each stakeholder.
Conclusion
Considering the ongoing pandemic, the untact visit service is designed to increase rapport and participation of parents, share the child’s information in real-time, and provide one-stop service without increasing healthcare providers’ work. It will be a useful visit service that can be applied and evaluated in various hospital settings and the PICU. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors affecting pediatric nurses’ development of partnerships with parents of hospitalized children: An evaluation based on the stress-coping adaptation model
In Young Cho, So Hyoung Hong, Ji Yeong Yun
Journal of Child Health Care.2025; 29(1): 53. CrossRef - Correlation between oral health knowledge, demand for remote education tools, and self-efficacy among parents of children and adolescents
Min-Ji Park, Herry Novrinda, Jae-Young Lee
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2025; 25(1): 69. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Family-centered Care Application for Intensive Care Unit Families Based on the Facilitated Sensemaking Model : Focusing on Family Satisfaction, Family Stress, and Self-Efficacy
Yun Ha Oak, Eun Ha Kim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2025; 18(2): 1. CrossRef - Experiences of Family Members With Visitation Prohibition for Critically Ill Patients
Sunjung Kim, Sunghee H. Tak
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2024; 46(11): 854. CrossRef - Factors influencing neonatal intensive care unit nurses' parent partnership development
Eun Kyoung Kim, In Young Cho, Ji Yeong Yun, Bobae Park
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2023; 68: e27. CrossRef - National Petition Analysis Related to Nursing: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
HyunJung Ko, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee, Hee Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 635. CrossRef - Relationship between parental stress and post‐traumatic stress disorder: The moderating effect of visitation restrictions in paediatric intensive care units during COVID‐19
Young Il Cho, Hyo Jin Kim, Dong Hee Kim
Nursing in Critical Care.2023; 28(5): 808. CrossRef - Need for Information and Communication Technology during COVID-19: An Exploratory Study Using Nurses’ Activity Diaries
Hyeongsuk Lee, Dongmin Lee, Seungmin Lee
Healthcare Informatics Research.2023; 29(3): 256. CrossRef - Effects of a Noncontact Visit Program in the NICU for the Prevention of COVID-19
Hye Young Ahn, Hee Jee Jo, Hyun Jeong Ko
Healthcare.2023; 11(15): 2152. CrossRef - The Development of Automated Personalized Self-Care (APSC) Program for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Gaeun Park, Haejung Lee, Ah Reum Khang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(5): 535. CrossRef
- Factors affecting pediatric nurses’ development of partnerships with parents of hospitalized children: An evaluation based on the stress-coping adaptation model
- 1,604 View
- 28 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Person-Centered Practice Inventory–Staff for Nurses
- Sohyun Kim, Sunghee H Tak
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):363-379. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21027
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of Person-Centered Practice Inventory– Staff (PCPI-S) for nurses.
Methods
The English PCPI-S was translated into Korean with forward and backward translation. Data were collected from 338 nurses at one general hospital in Korea. Construct validity was evaluated with confirmatory factor analysis, convergent validity, and discriminant validity. Known-group validity was also evaluated. Cronbach’s α was used to assess the reliability.
Results
The PCPI-S Korean version consisted of 51 items in three areas: prerequisites, the care environment, and person-centered process. The comparative fit index (CFI) and values of person-centered care process were improved after engagement and having sympathetic presence items were combined as one component. The construct validity of PCPI-S Korean version was verified using four-factor structures (.05 < RMSEA < .10, AGFI > .70, CFI > .70, and AIC). The convergent validity and discriminant validity of the entire PCPI-S question were verified using a two-factor structures (AVE > .50, construct reliability > .70). There was an acceptable known-group validity with a significant correlation between the PCPI-S level and the degree of person-centered care awareness and education. Internal consistency was reliable with Cronbach’s α .95.
Conclusion
The Korean version of PCPI-S is valid and reliable. It can be used as a standardized Korean version of person-centered care measurement tool. Abbreviation: RMSEA = root mean square error of approximation; AGFI = adjusted goodness of fit index; AIC = Akaike information criterion; AVE = average variance extracted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The moderating effects of nurses’ characteristics on the perceptions and practices of family-centered care for chronically ill children and their families in Saudi Arabia
Nada Alqarawi, Eman Alhalal, Ibrahim Alasqah
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric validation and cultural adaptation of the family-centered care Questionnaire-Revised for use among nurses in Saudi Arabia
Nada Alqarawi, Ibrahim Alasqah
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adaptación transcultural y validación del Person-centred Practice Inventory-Staff para la cultura brasileña
Juliana Andrioli Nucci, Edinêis de Brito Guirardello, Ariane Polidoro Dini
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Person-centered Practice Inventory-Staff for Brazilian culture
Juliana Andrioli Nucci, Edinêis de Brito Guirardello, Ariane Polidoro Dini
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adaptação transcultural e validação do Person-centred Practice Inventory-Staff para a cultura brasileira
Juliana Andrioli Nucci, Edinêis de Brito Guirardello, Ariane Polidoro Dini
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Self-Compassion, Burden of BPSD, Communication Behavior, and Nursing Work Environment on Person-Centered Care for Patients with Dementia Among Long-Term Care Hospital Nurses
Yong Min Kim, Mi Heui Jang, Min Jung Sun
Healthcare.2025; 14(1): 15. CrossRef - Impact of Moral Distress, Person-Centred Care, and Nursing Professional Pride on Turnover Intention Among Intensive Care Unit Nurses in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
WonSuk Choi, Younjae Oh
Healthcare.2025; 14(1): 22. CrossRef - Influence of Nursing Professionalism, Nursing Work Environment, and Compassion Competence on Person-Centered Care of Nurses in Comprehensive Nursing Care
Yeon-Jin Lee, Eun-Mi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 572. CrossRef - Person-Centred Care: A Support Strategy for Managing Non-Communicable Diseases
Mateja Lorber, Nataša Mlinar Reljić, Barbara Kegl, Zvonka Fekonja, Gregor Štiglic, Adam Davey, Sergej Kmetec
Healthcare.2024; 12(5): 526. CrossRef - Nurses' practices of children and family-centered care for chronically ill children: A cross-sectional study
Nada Alqarawi, Eman Alhalal
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2024; 77: 172. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Person-Centered Care Among Psychiatric Nurses in Hospitals
Ji Su Lee, Mi Heui Jang, Min Jung Sun
Healthcare.2024; 12(22): 2269. CrossRef - Translation, Cultural Adaptation, and Validation of the Spanish Version of the Person-Centred Practice Inventory-Staff (PCPI-S)
Ana Carvajal-Valcárcel, Edgar Benitez, Marta Lizarbe-Chocarro, María José Galán-Espinilla, Mónica Vázquez-Calatayud, Begoña Errasti-Ibarrondo, Ana Choperena, Brendan McCormack, Vaibhav Tyagi, Virginia La Rosa-Salas
Healthcare.2024; 12(23): 2485. CrossRef - Validation of the Korean Version of Patient-Centered Care Tool: For Outpatients
Yeo Ju Kim, Gunjeong Lee, Sunyeob Choi
Patient Preference and Adherence.2023; Volume 17: 1525. CrossRef - The influence of Critical Reflection Competency, Nursing Work Environment and Job Crafting on Person-Centered Care in Tertiary Hospital Nurses: A Cross-sectional Study
Jinseon Hwang, Sujin Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(3): 245. CrossRef - Translation and transcultural adaptation of the Person-Centred Practice Inventory Staff (PCPI-S) for health professionals in Spain
Begoña Errasti-Ibarrondo, Virginia La Rosa-Salas, Marta Lizarbe-Chocarro, Yvonne Gavela-Ramos, Ana Choperena, Leire Arbea Moreno, Mónica Vázquez-Calatayud, María José Galán-Espinilla, Brendan McCormack, Ana Carvajal-Valcárcel
Anales del Sistema Sanitario de Navarra.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with Person-Centered Care among Hospice Nurses
Sinyoung Kwon, Kyoung Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2022; 25(2): 66. CrossRef - Moral sensitivity and person‐centred care among mental health nurses in South Korea: A cross‐sectional study
Sun Joo Jang, Eun Hye Kim, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2227. CrossRef - Translation and transcultural adaptation of the theoretical Person-Centred Practice Framework to the Spanish context
Ana Choperena, Yvonne Gavela-Ramos, Marta Lizarbe-Chocarro, María José Galán-Espinilla, Begoña Errasti-Ibarrondo, Virginia La Rosa-Salas, Mónica Vázquez-Calatayud, Brendan McCormack, Ana Carvajal-Valcárcel
Anales del Sistema Sanitario de Navarra.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The moderating effects of nurses’ characteristics on the perceptions and practices of family-centered care for chronically ill children and their families in Saudi Arabia
- 3,084 View
- 121 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref

- Influence of Self-care on Burnout in Primary Family Caregiver of Person with Dementia
- Jeong Hwa Kwon, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(2):217-231. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20274
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the influence of self-care on burnout experienced by primary family caregivers of persons with dementia.
Methods
The subjects of the study were 156 primary family caregivers of persons with dementia at home in Korea. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, independent t-test, one-way ANOVA, Pearson correlation coefficient, and hierarchical multiple regression using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 24.0 for Windows.
Results
The mean scores for self-care and burnout were 42.35 and 61.60, respectively. Self-care, subjective health status, living with a person with dementia, and behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia were significant factors affecting burnout in family caregivers. Self-care was identified as the strongest factor affecting burnout, explaining 13.9% of burnout with controlling factors in caregivers and care receivers.
Conclusion
To prevent burnout in primary family caregivers of persons with dementia, self-care of family caregivers should be emphasized. In nursing education, family caregivers should be recognized and approached as nursing clients who are responsible for taking care of their health. In nursing practice and research, digital self-care or self-care improvement intervention programs should be designed to help family caregivers, and further studies on self-care centered on health of family caregivers should be conducted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a Tool to Measure Slow Nursing for Older Adults in Long-term Care Hospitals: A Methodological Study
Hyeon Mi Woo
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(3): 212. CrossRef - Factors influencing the care burden among family caregivers using dementia care centers for older adults with dementia in Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive study
Ja Eun Kim, Soo Jin Lee
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2024; 26(4): 382. CrossRef - Effects of stress on burnout among infection control nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic: the mediating effects of social support and self-efficacy
Su-jin Lee, Ju-Young Park, Seo-Hyeon Kim
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Survey on Tele-Rehabilitation Therapy Awareness Among Primary Caregivers of Dementia Patients
Ae-Lyeong Kwon, Hye-Jin Jang, Ki-Jeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Physical Therapy.2024; 36(6): 190. CrossRef - Time usage analysis according to occupational area and satisfaction level in family caregivers of dementia patients
Woo-Hyuk Jang, Jong-Sik Jang, Jong-Hwi Park
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15178. CrossRef - Self-Care Experiences of Family Members of Mentally Ill Patients
Won Hee Jun, Eun Ju Cho, Eun Joung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2022; 31(4): 458. CrossRef
- Development of a Tool to Measure Slow Nursing for Older Adults in Long-term Care Hospitals: A Methodological Study
- 3,966 View
- 152 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of Direct Breastfeeding Program for Premature Infants in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Ji Hyun Kang, Hyunmi Son, Shin Yun Byun, Gyumin Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):119-132. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20240
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the effects of a direct breastfeeding program for premature infants in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs).
Methods
This quasi-experimental study was conducted during August 2016 to April 2017. Sixty mothers of premature infants were assigned to the experimental (n = 31) or control groups (n = 29). The program was comprised of breastfeeding education and direct breastfeeding support. The experimental and control groups were provided with education and counseling on breastfeeding at the time of admission and discharge. In the experimental group, the mothers initiated oral feeding with direct breastfeeding and engaged in breastfeeding at least seven times during the NICU stay. The collected data were analyzed by the χ2 -test and repeated measures ANOVA using an SPSS program.
Results
The experimental group showed a higher direct breastfeeding practice rate (χ2 = 19.29, p < .001), breastfeeding continuation rate (χ2 = 3.76, p < .001), and self-efficacy (F = 25.37, p < .001) than the control group except for maternal attachment.
Conclusion
The direct breastfeeding program in the NICU has significant effects on the practice and continuation rate of breastfeeding and breastfeeding self-efficacy. Therefore, this program can be applied in the NICU settings where direct breastfeeding is limited. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploration of Family-Centered Care in NICUs: A Grounded Theory Methodology
Young Ah Park, YeoJin Im
Qualitative Health Research.2025; 35(10-11): 1231. CrossRef - Fresh Parent’s Own Milk for Preterm Infants: Barriers and Future Opportunities
Carrie-Ellen Briere, Jessica Gomez
Nutrients.2024; 16(3): 362. CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness Evaluation of Comprehensive Mobile-Based, Breastfeeding Promotion Program for Mothers with Gestational Diabetes
Eunju Kwak, Seungmi Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(2): 224. CrossRef
- Exploration of Family-Centered Care in NICUs: A Grounded Theory Methodology
- 3,118 View
- 162 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Family’s Perception of Proxy Decision Making to Authorize Do Not Resuscitate Order of Elderly Patients in Long Term Care Facility: A Q-Methodological Study
- Hyeon Jin Cho, Jiyeon Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):15-26. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20188
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to distinguish and describe the types of perceptions of do not resuscitate (DNR) proxy decisions among families of elderly patients in a long-term care facility.
Methods
This exploratory study applied Q-methodology, which focuses on individual subjectivity. Thirty-four Q-statements were selected from 130 Q-populations formed based on the results of in-depth interviews and literature reviews. The P-samples were 34 families of elderly patients in a long-term care hospital in Busan, Korea. They categorized the Q-statements using a 9-point scale. Using the PC-QUANL program, factor analysis was performed with the P-samples along an axis.
Results
The families’ perceptions of the DNR proxy decision were categorized into three types. Type I, rational acceptance, valued consensus among family members based on comprehensive support from medical staff. Type II, psychological burden, involved hesitance in making a DNR proxy decision because of negative emotions and psychological conflict. Type III, discreet decisions, valued the patients’ right to self-determination and desire for a legitimate proxy decision. Type I included 18 participants, which was the most common type, and types II and III each included eight participants.
Conclusion
Families’ perceptions of DNR proxy decisions vary, requiring tailored care and intervention. We suggest developing and providing interventions that may psychologically support families. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Subjectivity study on health conservation of elderly hemodialysis patients
Eunji Yim, Mijin Yun, Sohyune Sok
BMC Geriatrics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Types of Empathy Among Certified Caregivers of Older Adults with Dementia
So-Hyeong Sim, Geun Myun Kim, Eun Joo Kim, Soo Jung Chang
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2023; Volume 16: 2715. CrossRef
- Subjectivity study on health conservation of elderly hemodialysis patients
- 1,466 View
- 32 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Cut-Off Values of the Post-Intensive Care Syndrome Questionnaire for the Screening of Unplanned Hospital Readmission within One Year
- Jiyeon Kang, Yeon Jin Jeong, Jiwon Hong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(6):787-798. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20233
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to assign weights for subscales and items of the Post-Intensive Care Syndrome questionnaire and suggest optimal cut-off values for screening unplanned hospital readmissions of critical care survivors.
Methods
Seventeen experts participated in an analytic hierarchy process for weight assignment. Participants for cut-off analysis were 240 survivors who had been admitted to intensive care units for more than 48 hours in three cities in Korea. We assessed participants using the 18-item Post-Intensive Care Syndrome questionnaire, generated receiver operating characteristic curves, and analysed cut-off values for unplanned readmission based on sensitivity, specificity, and positive likelihood ratios.
Results
Cognitive, physical, and mental subscale weights were 1.13, 0.95, and 0.92, respectively. Incidence of unplanned readmission was 25.4%. Optimal cut-off values were 23.00 for raw scores and 23.73 for weighted scores (total score 54.00), with an area of under the curve (AUC) of .933 and .929, respectively. There was no significant difference in accuracy for original and weighted scores.
Conclusion
The optimal cut-off value accuracy is excellent for screening of unplanned readmissions. We recommend that nurses use the Post-Intensive Care Syndrome Questionnaire to screen for readmission risk or evaluating relevant interventions for critical care survivors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cutoff Values for Screening Post-Intensive Care Syndrome Using the Post-Intensive Care Syndrome Questionnaire
Jiwon Hong, Jiyeon Kang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(11): 3897. CrossRef - Translation and validation of the Chinese version of the post-intensive care syndrome questionnaire
Caidie Yang, Hongmei Wu, Chunmei Luo
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Post‐Intensive Care Syndrome in Family: A Concept Analysis
Jiaqi Wen, Zhenjing Hu, Ziwei Li, Yu Liu, Liting Zhang, Chenchen Zhong
Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Post intensive care syndrome: A review of clinical symptoms, evaluation, intervention
Xiaofang He, Yuwei Song, Yuchun Cao, Liying Miao, Bin Zhu
Heliyon.2024; 10(10): e31278. CrossRef - Screening tools for post–intensive care syndrome and post-traumatic symptoms in intensive care unit survivors: A scoping review
Usha Pant, Krooti Vyas, Shaista Meghani, Tanya Park, Colleen M. Norris, Elizabeth Papathanassoglou
Australian Critical Care.2023; 36(5): 863. CrossRef
- Cutoff Values for Screening Post-Intensive Care Syndrome Using the Post-Intensive Care Syndrome Questionnaire
- 2,688 View
- 64 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Disease Prevention Knowledge, Anxiety, and Professional Identity during COVID-19 Pandemic in Nursing Students in Zhengzhou, China
- Yuyan Sun, Dongyang Wang, Ziting Han, Jie Gao, Shanshan Zhu, Huimin Zhang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(4):533-540. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate nursing students’ understanding of the prevention of COVID-19, as well as their anxiety towards the disease and their perception of their professional identity in the wake of the pandemic, in Zhengzhou, China.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was designed to investigate 474 nursing students by cluster sampling using a stratified questionnaire from February 15 to March 31, 2020. Multiple linear regression was used to identify the factors affecting professional identity. Binary and multiple logistic regression were used to identify the factors affecting anxiety.
Results
Responders with a high level of understanding of COVID-19 and frequent use of behavioral strategies for its prevention comprised 93.2% and 30.0% of the cohort, respectively. Professional identity was significantly associated with gender and anxiety (p < .050). The prevalence of anxiety among nursing students was 12.4%. Male (odds ratio [OR] = 2.39; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.26~4.52), sophomores (OR = 5.30; 95% CI = 1.61~7.45), and infrequent use of prevention measures (OR = 3.49; 95% CI = 1.16~5.19) had a significant effect on anxiety.
Conclusion
Anxiety during the COVID-19 epidemic gives an adverse effect on the professional identity of nursing in students. Nursing education institutions need to provide psychological counseling services for nursing students, in addition to improving their teaching of COVID-19 prevention strategies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Global prevalence of different levels of anxiety and stress symptoms in healthcare students: A meta-analysis and meta-regression
Ying Xuan Loh, Ying Lau, Wen Wei Ang, Shean Ern Shannen Lee, Siew Tiang Lau
Annals of General Psychiatry.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Anatomical dissection influences emotions of podiatry students
Alicia Mohedano‐Moriano, Carmen Romo‐Barrientos, Alicia Flores‐Cuadrado, Isabel Ubeda‐Bañon, Jaime Gonzalez‐Gonzalez, Maria Teresa Gil Ruiz, Daniel Saiz‐Sanchez, Veronica Astillero‐Lopez, Felix Marcos‐Tejedor, Alino Martinez‐Marcos, Antonio Viñuela, Juan
Journal of Foot and Ankle Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Hand Hygiene Practices and Educational Interventions Among Indonesian Nursing Students: An Analysis Using ATP Wipe Tests and Hand Hygiene Checkers
Mayumi Sato, Syahrul, Tantut Susanto, Fithria, Naoki Hokama, Ruka Saito, Andi Muhammad Fiqri Muslih Djaya, Hiroshi Sugimoto
Journal of Rural Community Nursing Practice.2025; 3(1): 60. CrossRef - The transformation of ambivalent professional identity of nursing students following clinical placement in China: A qualitative study from the perspectives of the “post-00s” generation
Jingyi Chen, Xiao Zhang, Yidan Yang, Rong Hu
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 86: 104387. CrossRef - Resilience, perceived control, and intention to receive additional vaccines for COVID‐19 among healthcare university students: Mediating role of knowledge of vaccine and infection‐preventive behaviors
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Erika Ota, Tomomi Oki, Kazuko Naruse
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The influences of nursing students’ prevention and control practice behaviours on emerging and re-emerging respiratory viral illnesses: An integrative review and narrative synthesis
Gift A. Mutsonziwa, Paul Glew, Rona Pillay
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 88: 104564. CrossRef - Ser enfermeiro na perspectiva de estudantes de enfermagem do nordeste brasileiro no contexto pandemico
Thais Araujo da Silva, Ruth Silva dos Santos, Nayhara Rayanna Gomes da Silva, Ryanne Carolynne Marques Gomes Mendes
Journal of Nursing and Health.2025; 15(2): e1528145. CrossRef - Kayseri İlinde Öğrenim Gören Paramedik Öğrencilerinin Mesleki Kaygı Düzeyinin Belirlenmesi
Emre Bulbul, Etem Hızaler, Mehmet Doğan
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2025; 6(1): 8. CrossRef - Nursing Students’ Perceptions of Factors Influencing Nursing Intentions toward COVID-19 Patients
Nari Lee, Hae Ran Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 285. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of the training on “Home care of COVID-19 positive/suspicious patients” given to nursing students: A quasi-experimental study
Hande Sabandüzen, Öznur Kavaklı
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of alexithymia, anxiety, social pressure, and academic burnout on depression in Chinese university students: an analysis based on SEM
Mingyang Sun, Ming Piao, Zhaona Jia
BMC Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between anxiety and academic identity and the motivation to study nursing and midwifery in the covid-19 pandemic: A structural model
Ashraf Khoramirad, Sarallah Shojaei, Heydar Ghaderi, Zahra Abedini
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Holistic Approach to Nursing Students’ Changing Life and Anxiety in the Pandemic: A Descriptive Cross Sectional Study Utilizing Positive Psychotherapy
Ayşe Kuzu Durmaz, Ferhan Açıkgöz, Çiğdem Şen Tepe
Journal of Higher Education and Science.2024; 14(2): 349. CrossRef - The Mediating Role of Psychological Resilience in Chinese Nursing Students’ Professional Identity and Learning Burnout
Liu Zhang, Qin Zhang, ShuWen Li, YuHong Li, GuoCui Wu, Ying Chen, YunNa Zhou
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(4): 509. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Nurses’ Perceptions of Spirituality and Spiritual Care and Their Attitudes Towards the Nursing Profession
İbrahim Nas, Gülay İpekçoban
Gümüşhane Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2024; 13(2): 542. CrossRef - Anxiety in Nursing Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Aroa García-Rivas, María Begoña Martos-Cabrera, María José Membrive Jiménez, Raimundo Aguayo-Estremera, Nora Suleiman Martos, Luis Albendín-García, José L. Gómez-Urquiza
Healthcare.2024; 12(16): 1575. CrossRef - Work environment as perceived by nursing interns and its relation to their professional identity
Habiba A.A. Gadallah, Sahar H.A. El Banan, Faten S.A. Ahmed
Egyptian Nursing Journal.2024; 21(2): 129. CrossRef - Assesment of Occupational Anxiety of Emergency Aid and Disaster Management Students
Cüneyt Çalışkan, Kerem Kınık
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2024; 5(1): 51. CrossRef - COVID-19 Perceptions, Avoidance and Vaccine Attitudes of Nursing Students: Case of Türkiye
Gülşen ULAŞ KARAAHMETOĞLU, Zeynep ARABACI
Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Fakültesi Elektronik Dergisi.2024; : 111. CrossRef - COVID-19 Pandemi Süreci Uzaktan Eğitim Döneminde Hemşirelik Öğrencilerinde Anksiyete ve Klinik Performans Öz-Yeterlilik Algısı İlişkisi
Yeliz AKKUŞ, Nihal BOSTANCI DAŞTAN
Sağlık Bilimlerinde Değer.2024; 14(1): 106. CrossRef - Comparing factors related to perceived control and preventive behaviors from COVID‐19 between Japanese and American nursing students: A cross‐sectional study
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Kosuke Niitsu, Kazuko Naruse, Tomomi Oki, Erika Ota, Mabel C. Ezeonwu
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sağlık Hizmetleri Meslek Yüksekokulu Öğrencilerinin Mesleğe Yönelik Kaygı Düzeylerinin Belirlenmesi
Dilan AKTEPE COŞAR, Nuray BİNGÖL, Hatice DEMİRAĞ
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2023; 4(2): 66. CrossRef - Satisfied with teaching? Psychometric properties of the Teaching Satisfaction Scale
Tyrone B. Pretorius, Anita Padmanabhanunni, Kyle M. Jackson, Brendon D. Faroa
African Journal of Psychological Assessment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Risk Factors for Anxiety Symptoms among Student Nurses in Gauteng Province of South Africa
Maleke Manana, Sam Thembelihle Ntuli, Kebogile Mokwena, Kgomotso Maaga
Behavioral Sciences.2023; 13(8): 630. CrossRef - Factors related to mental health effect among nursing students in Japan and the United States during the coronavirus pandemic: A cross‐sectional study
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Kosuke Niitsu, Kazuko Naruse, Tomomi Oki, Erika Ota, Mabel C. Ezeonwu
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(1): 186. CrossRef - Effects of a Nursing Simulation Learning Module on Clinical Reasoning Competence, Clinical Competence, Performance Confidence, and Anxiety in COVID-19 Patient-Care for Nursing Students
Ye-Eun Kim, Hee-Young Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(1): 87. CrossRef - Research Progress of Chinese Nursing Students’ Professional Identity during COVID-19
毓 徐
Nursing Science.2023; 12(01): 7. CrossRef - Prevalence and levels of burnout in nursing students: A systematic review with meta-analysis
José L. Gómez-Urquiza, Almudena Velando-Soriano, María José Membrive-Jiménez, Lucia Ramírez-Baena, Raimundo Aguayo-Estremera, Elena Ortega-Campos, Guillermo A. Cañadas-De la Fuente
Nurse Education in Practice.2023; 72: 103753. CrossRef - Psychological impacts of transition to distance learning due to COVID‐19 on nursing students
Ahmad Rayan
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(3): 767. CrossRef - COMPARISON OF TWO DIFFERENT TECHNIQUES FOR TEACHING LEARNING SKILLS: EVALUATION IN THE PERIOD OF PANDEMIC
Sevim ÇELİK, Elif KARAHAN, Sibel ALTINTAŞ, Özge UÇAR
International Journal of Health Services Research and Policy.2023; 8(2): 114. CrossRef - How has the COVID-19 pandemic influenced nursing students' academic experience and career choices? A qualitative descriptive analysis
Masamitsu Kobayashi, Yuji Koga, Jun Kako, Takahiro Kakeda, Hana Kiyohara, Yasutaka Kimura, Michiko Ishida, Michihiro Tsubaki, Yoko Nishida, Kimie Harada, Yuki Wakiguchi, Yoji Endo, Yoshiyasu Ito, Shinsuke Sasaki, Kohei Kajiwara, Seiji Hamanishi, Makoto Ya
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2023; 18(1): 30. CrossRef - Perceived social support and professional identity in nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic era: the mediating effects of self-efficacy and the moderating role of anxiety
Zhi-Hui Zhao, Jin-Yi Guo, Jie Zhou, Jia Qiao, Shu-Wen Yue, Yan-Qiong Ouyang, Sharon R. Redding, Rong Wang, Zhong-Xiang Cai
BMC Medical Education.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Anxiety, depression, and stress prevalence among college students during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Chunyi Wang, Wen Wen, Haifu Zhang, Jie Ni, Jingjie Jiang, Yongran Cheng, Mengyun Zhou, Lan Ye, Zhanhui Feng, Zhongjun Ge, Hong Luo, Mingwei Wang, Xingwei Zhang, Wenmin Liu
Journal of American College Health.2023; 71(7): 2123. CrossRef - Factors associated with mental health among undergraduate nursing students early in the COVID-19 pandemic: an integrative review
Keiko Sugimoto, Rieko K. Fukuzawa, Ganchimeg Togoobaatar, Chang G. Park, Susan C. Vonderheid
International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - PANDEMİ SÜRECİNDE KLİNİK UYGULAMA YAPAMAYAN İLK VE ACİL YARDIM ÖĞRENCİLERİNİN MESLEKİ YAŞAM İLE İLGİLİ KAYGI DÜZEYLERİNİN VE İLİŞKİLİ FAKTÖRLERİN BELİRLENMESİ
Elif KILIÇ GÜNER, Özge AKBABA, Elanur YILMAZ KARABULUTLU, Havva ÖZTÜRK
Hastane Öncesi Dergisi.2023; 7(3): 331. CrossRef - Hemşirelik Öğrencilerinin Mesleğe Yönelik Tutumu ile COVID-19 Enfeksiyonu Korkusu Arasındaki İlişki
Süreyya Bulut, Nihal Taşkıran
Hacettepe Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Fakültesi Dergisi.2023; 10(3): 207. CrossRef - Investigation of the Stress Level and Coping Behaviors of Nursing Students, and Their Thoughts on Professional Life in COVİD-19 Pandemic
Belkız KIZILTAN, Nurgül KAPLAN, Seda UZUNALİ
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2023; 4(1): 26. CrossRef - The development and effects of a COVID-19 nursing education program for nursing students
Hyewon Choi, Hyunju Kang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 368. CrossRef - Hemşirelik Son Sınıf Öğrencilerinin Mezuniyet Sonrası Covid-19 Kliniklerinde Çalışmaya İlişkin Görüşleri: Nitel Bir Çalışma
Ilknur TURA, Sevilay ERDEN
Hemşirelik Bilimi Dergisi.2022; 5(3): 149. CrossRef - The multidimensionality of anxiety among nursing students during COVID‐19 pandemic: A cross‐sectional study
Rizal Angelo N. Grande, Daniel Joseph E. Berdida, Rolan Rodolfo Jr C. Paulino, Eric A. Anies, Reinhard Roland T. Ebol, Roger R. Molina
Nursing Forum.2022; 57(2): 267. CrossRef - Identity Matters: Validation of the Professional Identification Scale in a Sample of Teachers in South Africa During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Tyrone B. Pretorius, Anita Padmanabhanunni, Serena Ann Isaacs
Trends in Psychology.2022; 32(4): 1426. CrossRef - The study of psychological traits among Chinese college students during the COVID-19 campus lockdown
Haibo Xu, Zhen Wang, Lixin Peng, Yanyan Mi, Ping Zeng, Xin Liu
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Perceived professional identity and related factors in Iranian nursing students: a cross-sectional study
Tahereh Gilvari, Hassan Babamohamadi, Fatemeh Paknazar
BMC Nursing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Nursing students’ experiences of mental wellness during the COVID-19 pandemic: A phenomenological study
Dana Laczko, Alex Hodson, Melissa Dykhuizen, Kelsey Knipple, Kassandra Norman, Paula Hand-Cortes
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2022; 17(4): 392. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Infection Control Performance of School Health Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic in South Korea
Mi-Ra Yim, Boyoung Kim
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2022; Volume 15: 805. CrossRef - The Beneficial Effects of Professional Identity: The Mediating Role of Teaching Identification in the Relationship between Role Stress and Psychological Distress during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Tyrone Brian Pretorius, Anita Padmanabhanunni
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(18): 11339. CrossRef - Being a Nursing Student In a Pandemic: Fear of COVID-19 and Clinical Practice
Pınar TUNÇ TUNA, Halil İbrahim TUNA, Birsel MOLU, Alev YILDIRIM KESKİN
Genel Tıp Dergisi.2022; 32(5): 506. CrossRef - Mental Health Among Medical Students During COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Qingwen Jia, Yi Qu, Huiyuan Sun, Huisheng Huo, Hongxia Yin, Dianping You
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge and attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccination among student nurses from Saudi Arabia
Romeo Mostoles Jr, Richard Maestrado, Joyce Buta, Salman Alsaqri, Evalynn Rondilla, Hamdan Mohammad Albaqawi
Jurnal Ners.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of anxiety symptoms among Chinese university students amid the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Xiaohang Wang, Quzhi Liu
Heliyon.2022; 8(8): e10117. CrossRef - Has the COVID-19 pandemic affected nursing students’ career self-efficacy and professional calling? The mediating impact of professional identity
Li Yang, Mengfan Xu, Jinke Kuang, Kexin Zhou, Xuemei Zhu, Lingna Kong, Li QI, Heng Liu
BMC Medical Education.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research on Health Education Strategies for Improving Student Knowledge on Infectious Disease Prevention
Shailly Gupta , Manashree Mane , Debashree Priyadarshini , Ajab Singh Choudhary
Health Leadership and Quality of Life.2022; 1: 126. CrossRef - Relationship between nursing students’ attitudes toward nursing profession and online learning satisfaction during COVID-19 lockdown
Maša Černelič-Bizjak, Petra Dolenc, Ali B. Mahmoud
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(11): e0277198. CrossRef - Anxiety and fear of COVID‐19 among nursing students during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A descriptive correlation study
Nilgun Kuru Alici, Ebru Ozturk Copur
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2022; 58(1): 141. CrossRef - Professional Identity of 0.24 Million Medical Students in China Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Three Waves of National Cross-Sectional Studies
Chen Yu, Qiao Liu, Weimin Wang, Ana Xie, Jue Liu
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Attitudes of Nursing Students towards Vaccination and Other Preventive Measures for Limitation of COVID-19 Pandemic: Cross-Sectional Study in Three European Countries
Nevenka Kregar Velikonja, Beata Dobrowolska, Sanja Stanisavljević, Karmen Erjavec, Vislava Globevnik Velikonja, Ivan Verdenik
Healthcare.2021; 9(7): 781. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Preventive Practice of International Students in South Korea against COVID-19 during the Pandemic
Gun Ja Jang, Ginam Jang, Sangjin Ko
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(5): 2259. CrossRef - Perceived Control, Preventative Health Behaviors, and the Mental Health of Nursing Students During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Kazuko Naruse, Tomomi Oki, Kosuke Niitsu, Mabel C. Ezeonwu
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Individual and Joint Effects of Cumulative Confirmed Cases and Attention Level of COVID-19 on Medical Students' Professional Identity: A National Cross-Sectional Study in China
Qiao Liu, Chen Yu, Ana Xie, Weimin Wang, Jue Liu
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of mental health problems and sleep disturbances in nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mulyadi Mulyadi, Santo Imanuel Tonapa, Suwandi Luneto, Wei-Ting Lin, Bih-O Lee
Nurse Education in Practice.2021; 57: 103228. CrossRef - Transition in learning during COVID‐19: Student nurse anxiety, stress, and resource support
Anita Fitzgerald, Sharon Konrad
Nursing Forum.2021; 56(2): 298. CrossRef - Nursing Students in Crisis Mode
Bella Savitsky, Yifat Findling, Anat Ereli, Tova Hendel
Nurse Educator.2021; 46(3): E33. CrossRef - Impact of Anxiety on Readiness for COVID-19 Vaccination among Polish Nursing Undergraduate Students: Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study
Joanna Gotlib, Mariusz Jaworski, Dominik Wawrzuta, Tomasz Sobierajski, Mariusz Panczyk
Vaccines.2021; 9(12): 1385. CrossRef
- Global prevalence of different levels of anxiety and stress symptoms in healthcare students: A meta-analysis and meta-regression
- 2,458 View
- 18 Download
- 48 Web of Science
- 63 Crossref

- Continuity of Care in Chronic Diseases: A Concept Analysis by Literature Review
- Jingjing Hu, Yuexia Wang, Xiaoxi Li
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(4):513-522. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20079
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to utilize concept analysis to obtain a better understanding of the concept of “continuity of care” in chronic diseases.
Methods
The concept of continuity of care was analyzed using the Walker and Avant method. Covering literature in English from 1930 to 2018, the data sources included CINAHL Complete, Academic Search Complete, MEDLINE, PsyARTICLES, Health Source: Nursing/ Academic Edition, Google Scholar, Science Direct, and the Cochrane Library.
Results
A comprehensive definition of concept of continuity of care was developed based on a systematic search and synthesis. The key defining attributes were identified as (a) care over time, (b) the relationship between an individual patient and a care team, (c) information transfer, (d) coordination, and (e) meeting changing needs. The antecedents of continuity of care were having a chronic disease, inexperienced with disease management, a poorly coordinated healthcare system, and medical care limitations. The consequences of continuity of care were decreasing hospital admissions, reducing costs, reducing emergency room visits, improving the quality of life, improving patient satisfaction, and delivering good healthcare.
Conclusion
The thorough concept analysis provides insight into the nature of “continuity of care” in chronic diseases and also helps ground the concept in healthcare. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Patient-Centered Care in Family Medicine: Strategies for Continuity and Comprehensive Care for Older Adults – A Mixed-Methods Study
Abdulaziz Alodhialah, Ashwaq Almutairi, Mohammed Almutairi
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2025; Volume 20: 985. CrossRef - Roy adaptation model-based nursing combined with transitional care for enhancing mental health and quality of life after cancer surgery: results from a randomized controlled study
Lijie Yuan, Ying Fu
Perioperative Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Patient perceptions of relational continuity in England: insights from two cross-sectional surveys
Bolanle Odebiyi, Jonathan Gibson, Mhorag Goff, Ali MK Hindi, Jonathan Hammond, Katherine Checkland, Matt Sutton, Sally Jacobs
BJGP Open.2025; : BJGPO.2024.0267. CrossRef - Primary Care Utilization and Prehospital Emergency Demand Among Patients with Multimorbidity in Spain
Enrique Coca-Boronat, José Miguel Morales-Asencio, Daniel Coca-Gallen, Laura Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, Inmaculada Lupiáñez-Pérez, Cristina Guerra-Marmolejo, José Sáenz-Gómez, Bibiana Pérez-Ardanaz
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(11): 377. CrossRef - Evaluation of a telemedicine pilot project for hypertension in Korea: a nationwide real-world data study
Jeong-Yeon Kim, Yeryeon Jung, Seongwoo Seo, Youseok Kim, Min Jung Ko, Hun-Sung Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2025; 47: e2025048. CrossRef - The meaning of continuity of care from the perspective of older people with complex care needs–A scoping review
Ingrid Djukanovic, Amanda Hellström, Anna Wolke, Kristina Schildmeijer
Geriatric Nursing.2024; 55: 354. CrossRef - Care needs of chronically ill patients with intellectual disabilities in Dutch general practice: patients’ and providers’ perspectives
Milou van den Bemd, Monique Koks-Leensen, Maarten Cuypers, Geraline L. Leusink, Bianca Schalk, Erik W. M. A. Bischoff
BMC Health Services Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - KRONİK HASTALIĞI OLAN YETİŞKİN BİREYLERİN 6 ŞUBAT 2023 KAHRAMANMARAŞ MERKEZLİ DEPREMLER SONRASI HASTALIK YÖNETİMİNE İLİŞKİN DENEYİMLERİ: NİTEL BİR ARAŞTIRMA
Uğur Doğan, Murat Tamer
Kocatepe Tıp Dergisi.2024; 25(4): 429. CrossRef - Measuring patients' experiences of continuity of care in a primary care context—Development and evaluation of a patient‐reported experience measure
Linda Ljungholm, Kristofer Årestedt, Cecilia Fagerström, Ingrid Djukanovic, Mirjam Ekstedt
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2024; 80(1): 387. CrossRef - Assessing multidisciplinary follow-up pattern efficiency and cost in follow-up care for patients in cervical spondylosis surgery: a non-randomized controlled study
Zhongmin Fu, Yan Xie, Peifang Li, Menghui Gao, Jiali Chen, Ning Ning
Frontiers in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lessons Learned From a Retrospective Analysis of Medicolegal Risks for Physicians Treated Adolescents and Young Adults With Medical Complexity
Rana Aslanova, Laura Payant, Richard Liu, Karen Pacheco, Jacqueline H. Fortier, Gary E. Garber
Journal of Adolescent Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Implementation and evaluation of a complex intervention to improve information availability at the interface between inpatient and outpatient care in older patients with multimorbidity and polypharmacy (HYPERION-TransCare) — study protocol for a pilot and
Astrid-Alexandra Klein, Jenny Petermann, Franziska Brosse, Steve Piller, Martin Kramer, Maria Hanf, Truc Sophia Dinh, Sylvia Schulz-Rothe, Jennifer Engler, Karola Mergenthal, Hanna M. Seidling, Sophia Klasing, Nina Timmesfeld, Marjan van den Akker, Karen
Pilot and Feasibility Studies.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Young adults with eating disorders perspectives on educational resources to support the transition into adult medicine: a thematic analysis
Jennifer Mooney, Anna Dominic, Alyona Lewis, Roger Chafe
Journal of Eating Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of medical care linkage-continuous management mode in patients with posterior circulation cerebral infarction undergoing endovascular interventional therapy
Fen-Xia Zhu, Qian Ye
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(29): 10478. CrossRef - Effect of continuous nursing on angina attack and quality of life in patients with coronary artery disease
Xiaohuan Zhou, Yamin Yuan, Zhanglin Wang, Ke Zhang, Weiwei Fan, Yawei Zhang, Pu Ma
Medicine.2021; 100(5): e24536. CrossRef - Sårbar sammenheng i helse- og omsorgstjenesten til eldre pasienter
Maren Kristine Raknes Sogstad, Astrid Bergland
Tidsskrift for omsorgsforskning.2021; 7(2): 9. CrossRef - CONTINUIDADE DE CUIDADOS DE REABILITAÇÃO ENTRE CONTEXTOS DE SAÚDE: ESTUDO DE CASO
Rui Pedro Silva, Elisabeth Sousa
Revista Portuguesa de Enfermagem de Reabilitação.2020; 3(Sup 1): 70. CrossRef
- Patient-Centered Care in Family Medicine: Strategies for Continuity and Comprehensive Care for Older Adults – A Mixed-Methods Study
- 4,429 View
- 169 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref

- Development of Caring as a Human Science: 50 Years of History of the Korean Society of Nursing Science
- Jeung-Im Kim, Eunyoung E. Suh, Ju-Eun Song, YeoJin Im, Jin-Hee Park, Soyoung Yu, Sun Joo Jang, Da-Hee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):313-332. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20142
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This year 2020 marks the 50th anniversary of the founding of the Korean Society of Nursing Science (KSNS). This study wasaimed to explore development of caring and describe the 50 years of history of KSNS within the sociocultural context of Korea regardingacademic footsteps, meanings, and implications for the future.
Methods
This study used a historical research methodology using a literaturereview and bibliometric analysis. Relevant literature was reviewed and the published abstracts in the Journal of Korean Academy ofNursing (JKAN) were analyzed using VOSviewer.
Results
Birth control and family planning in the 1970s was the main research topic. In the1980s, the development of nursing concepts, theories, and philosophies was the mission of KSNS to extend the disciplinary boundary. In the1990s, the progress of KSNS to become one of the woman-dominant healthcare professionals was the mission in the given period. Expandingthe frontiers of KSNS to the extent of global standards was the undertaking of the nursing scholars in the 2000s. Lastly, in the 2010s,the quality and quantity improvement of KSNS and JKAN is expected to make our future even prosperous. The map visualization of the 50years of research accumulation showed the comparable opposition of quantitative vs. qualitative research methodologies, equation modeling,and instrument development.
Conclusion
These clusters of research demonstrates the efforts to make nursing evidence by Koreannursing scholars for the last five decades. The growth in the slope of KSNS and outcomes of JKAN are to carry on to an unimaginable extentin the future. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ten-year trends in research designs and keywords: a bibliometric comparison of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and leading international nursing journals
Jin-Hee Park, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Gaeun Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(4): 557. CrossRef - Editorials in February Issue of Asian Nursing Research
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(1): 1. CrossRef - PERCURSO METODOLÓGICO PARA CONSTRUÇÃO DE DEFINIÇÕES OPERACIONAIS DE DIAGNÓSTICOS DE ENFERMAGEM
Thaís Rodrigues de Albuquerque, Francisco Henryque Soares Morais, Glauberto da Silva Quirino, Marcos Antônio Gomes Brandão, Cândida Caniçali Primo, Rachel de Sá Barreto Luna Callou Cruz
Enfermagem em Foco.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lived experiences of work-life balance among doctoral nursing students: a qualitative descriptive study
Ji Yeon Lee, Yong Sook Yang, Gi Wook Ryu, Kyoungjin Lee
International Journal of Qualitative Studies on Health and Well-being.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Telephone Counseling of Patients in Chemotherapy Using Text Mining Technique
Seoyeon Kim, Jihyun Jung, Heiyoung Kang, Jeehye Bae, Kayoung Sim, Miyoung Yoo, Eunyoung, E. Suh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 46. CrossRef - Fourth Industrial Revolution and Nursing Research
Young Whee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Topics and Trends in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing to Improve Its International Influence
Soyoung Yu, Jeung-Im Kim, Jin-Hee Park, Sun Joo Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh, Ju-Eun Song, YeoJin Im
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(4): 501. CrossRef - Commemorating the 50th Anniversary of Korean Society of Nursing Science and Contemplating Direction to Move Forward
Kyung-Sook Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 641. CrossRef
- Ten-year trends in research designs and keywords: a bibliometric comparison of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and leading international nursing journals
- 2,733 View
- 33 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Development and Validation of the Self-Care for Aspiration Pneumonia Prevention Scale in the Community Dwelling Elderly with Risk of Dysphasia
- Eun Young Yang, Shin-Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):474-486. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20041
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop and validate a Korean version of the Self-Care for Aspiration Pneumonia Prevention(SCAPP-K) scale in older adults at risk of dysphasia.
Methods
The Hertz and Baas model of scale development and validation was used. Inthe development stage, items were generated via literature review and interviews with medical experts, older adults, and caregivers. Tenexperts assessed the items for content validity. Subsequently, 12 older adults participated in a pilot test to determine the comprehensibilityand appropriateness of the SCAPP-K scale. The validation stage involved a cross-sectional survey with 203 older adults for exploratoryfactor analysis (EFA) and 200 older adults for confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) and to determine convergent and discriminant validity. Totest the validity and reliability of the scale, EFA using principal component analysis with varimax rotation and CFA were conducted, andconvergent and discriminant validity as well as internal consistency reliability were determined.
Results
As a result of EFA, three self-carefactors (knowledge, resources, behaviors) with 21 items were validated. The CFA and convergent and discriminant validity indicated theapplicability of the three-factor self-care scale. The reliability of the SCAPP-K scale was acceptable, with Cronbach’s a=.87~.91.
Conclusion
The SCAPP-K scale has acceptable validity and reliability and can contribute to clinical practice, research, and education to improveself-care for the prevention of aspiration pneumonia in older adults at risk of dysphasia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cause-specific mortality in Korea during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic
Jinwook Bahk, Kyunghee Jung-Choi
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022110. CrossRef - Translation of the Chinese version of the Self‐Care for Aspiration Pneumonia Prevention Scale and its validation among Chinese community dwelling elderly with risk of dysphasia
Zhen Yang, Fengmin Chen, Yibo Zhang, Sien Pan, Yingying Lu, Huijun Zhang
Nursing Open.2022; 9(3): 1902. CrossRef - Development and validation of a self-care scale for older adults undergoing hip fracture surgery: the HFS-SC
Eun-Jeong Jeon, Kyeong-Yae Sohng, Hye-Ah Yeom
BMC Nursing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on the characterization, biocompatibility and efficacy of sponge brush products for oral care
Song-Yi Yang, Ji-Won Choi, Sang-Hwan Oh
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2021; 48(1): 27. CrossRef
- Cause-specific mortality in Korea during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic
- 2,166 View
- 73 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Factors Relating to the Quality of Care for Nursing Home Residents in Korea: Using the Delphi Method
- Juh Hyun Shin, Eun Mee Kim, Ji Yeon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):783-794. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.783
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study identified factors related to the quality of care in nursing homes, and elicited consensus opinions from experts on nursing homes.
Methods A Delphi questionnaire was developed based on a review of the literature using the keywords “nursing homes,” “workforce,” and “quality of care.” A total of two Delphi surveys were conducted with 14 experts. The important and urgent factors related to the quality of care for nursing home residents emerged.
Results A consensus was achieved on the important and urgent factors relating to the quality of care. The related factors were grouped into four sections: Organizational Characteristics, Staffing Characteristics, the Long-Term Care Market and Legal and Policy Issues, and Nursing Processes. In total, 23 items were important factors and 26 items were urgent factors relating to the quality of care. In addition, the unanimous advocacy by the experts for increased hours per resident day for registered nurses (RNs, 41 minutes 59 seconds) was much higher than the current hours per resident day of RNs in Korea.
Conclusion To provide optimal care for residents in nursing homes in Korea, the mandatory and essential placement of RNs with professional knowledge and skills is paramount.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of special nursing units in nursing homes on healthcare utilization and cost: A case-control study using propensity score matching
Eunhee Cho, Eun-Young Kim, Kyung Hee Lee, Hye-Ryoung Kim, Seonhwa Choi, Yea Seul Yoon, EunKyo Kim, Seok-Jae Heo, Se Young Jung, Jiyoon Jang
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2023; 147: 104587. CrossRef - Effects of registered nurse staffing levels, work environment, and education levels on adverse events in nursing homes
Seonhwa Choi, Eunhee Cho, Eunkyo Kim, Kyongeun Lee, Soo Jung Chang
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cost of Care and Pattern of Medical Care Use in the Last Year of Life among Long-Term Care Insurance Beneficiaries in South Korea: Using National Claims Data
Sunjoo Boo, Jungah Lee, Hyunjin Oh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(23): 9078. CrossRef - Impact of Nurse Staffing, Skill Mix and Stability on Resident Health Outcomes in Korean Nursing Homes
Juh Hyun Shin, Gui Yun Choi, Jiyeon Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2020; 22(4): 291. CrossRef - The Effects of Long-term Care Hospitals' Nurse Staffing Level on Patient Outcomes: Differences according to Region
Kyung Jin Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 354. CrossRef
- The effects of special nursing units in nursing homes on healthcare utilization and cost: A case-control study using propensity score matching
- 1,933 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Path Analysis for Delirium on Patient Prognosis in Intensive Care Units
- Sunhee Lee, Sun-Mi Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):724-735. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.724
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to investigate relationship between delirium, risk factors on delirium, and patient prognosis based on Donabedian's structure-process-outcome model.
Methods This study utilized a path analysis design. We extracted data from the electronic medical records containing delirium screening data. Each five hundred data in a delirium and a non-delirium group were randomly selected from electronic medical records of medical and surgical intensive care patients. Data were analyzed using SPSS 20 and AMOS 24.
Results In the final model, admission via emergency department (B=.06,
p =.019), age over 65 years (B=.11,p =.001), unconsciousness (B=.18,p =.001), dependent activities (B=.12,p =.001), abnormal vital signs (B=.12,p =.001), pressure ulcer risk (B=.12,p =.001), enteral nutrition (B=.12,p =.001), and use of restraint (B=.30,p =.001) directly affecting delirium accounted for 56.0% of delirium cases. Delirium had a direct effect on hospital mortality (B=.06,p =.038), hospital length of stay (B=5.06,p =.010), and discharge to another facility (not home) (B=.12,p =.001), also risk factors on delirium indirectly affected patient prognosis through delirium.Conclusion The use of interventions to reduce delirium may improve patient prognosis. To improve the dependency activities and risk of pressure ulcers that directly affect delirium, early ambulation is encouraged, and treatment and nursing interventions to remove the ventilator and drainage tube quickly must be provided to minimize the application of restraint. Further, delirium can be prevented and patient prognosis improved through continuous intervention to stimulate cognitive awareness and monitoring of the onset of delirium. This study also discussed the effects of delirium intervention on the prognosis of patients with delirium and future research in this area.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Does ICU admission dysphagia independently contribute to delirium risk in ischemic stroke patients? Results from a cohort study
Hongtao Cheng, Simeng Song, Yonglan Tang, Shiqi Yuan, Xiaxuan Huang, Yitong Ling, Zichen Wang, Xiaoying Tian, Jun Lyu
BMC Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Preoperative Anxiety and Its Postoperative Associated Factors in Patients Receiving Post Anesthetic Recovery Care at Surgical Intensive Care Unit
Yul Ha Lee, Hye-Ja Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(3): 267. CrossRef - Delirium Experience of the Intensive Care Unit Patients
Jaeyeon Jung, Sujin Jang, Seonmi Jo, Sunhee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(2): 134. CrossRef - The training needs of Korean intensive care unit nurses regarding delirium
Young Sook Roh
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2021; 62: 102954. CrossRef - Effect on Quality of Care of a Delirium Prevention Campaign for Surgical Intensive Care Nurses
Heejeong Kim, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of Nursing Care Quality.2021; 36(4): 361. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis on the Effect of Delirium Prevention Intervention in Korean Intensive Care Units
Jiyeon Kang, Min Jeong Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2021; 14(3): 141. CrossRef
- Does ICU admission dysphagia independently contribute to delirium risk in ischemic stroke patients? Results from a cohort study
- 2,447 View
- 52 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Development and Application of Cost Management Program for Visiting Nursing Centers Using Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing
- Juhang Kim, Ji Young Lim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(5):586-600. Published online October 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.5.586
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to develop a web-based cost management program for visiting nursing centers (CMP-VNC), using time-driven activity-based costing (TD-ABC), and to analyze effects of the program.
Methods The CMP-VNC was developed using the combined prototyping approach and system developing life cycle method following four stages: need analysis with comprehensive literature reviews and focus group interviews, design and development of program algorithm, evaluation of the developed program validity using experts and users group, and application and effects analysis. The non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used to analyze the effects of the program. The program demonstration was conducted for four weeks with 60 visiting nurses in 35 visiting centers.
Results The web-based program was developed. It has five interfaces with basic and special functions using TD-ABC, namely, input, visiting nursing activity, visiting nursing activity cost, cost efficiency, and cost calculation report. The experimental group showed significantly higher cost perception and cost confidence than control group.
Conclusion We found that the CMP-VNC can be an effective tool to increase visiting nurses’ competency of costing and enhance efficiencies of visiting nursing centers.
- 1,711 View
- 13 Download

- Development and Effect of a Fall Prevention Program Based on the King's Goal Attainment Theory for Fall High-Risk Elderly Patients in Long-Term Care Hospital
- Bom Mi Park, Ho Sihn Ryu, Kyeung Eun Kwon, Chun Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):203-214. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.203
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study to develop a fringed fall prevention program based on King's goal attainment theory and education. This study is applied to the personal, interpersonal, and social systems of fall high-risk patients to test its effects.
Methods This study was a nonequivalent control group pre- and post-test design. There were 52 fall high-risk patients in the experimental group and 45 in the control group. The experimental group received six sessions, with the group sessions lasting 60 minutes and the individual sessions lasting 20~30 minutes. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, an χ2-test, a paired sample t-test, and a Wilcoxon signed-ranks test utilizing IBM SPSS software.
Results For the 3-month intervention period, the fall prevention program was found to be particularly effective for patients in the experimental group (from 3.38 to 1.69 per 1000 patient days;
p =.044), as opposed to the control group (from 1.94 to 1.49 per 1000 patient days;p =.300). For the 6-month follow up period, the fall prevention program was again found to be effective for patients in the experimental group (from 3.26 to 0.76 per 1000 patient days;p =.049) compared to the control group (from 1.98 to 1.01 per 1000 patient days;p =.368).Conclusion These results indicate that the fringed fall prevention program is very effective in reducing falls, not only during the intervention period, but also after the intervention period has ended. We can therefore recommend this program for use concerning fall high-risk patients in long-term care hospitals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent advances in the identification of related factors and preventive strategies of hip fracture
Yaohui Yu, Yudan Wang, Xiaoli Hou, Faming Tian
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Falls in Patients of Medical Institutions in South Korea: A Literature Review
Jongwon Choi, Woochol Joseph Choi
Physical Therapy Korea.2023; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of a Fall Prevention Program Based on Goal Attainment Theory for Homebound Older Adults With Osteoarthritis of the Lower Extremities
Chunhee Lee, Heeok Park
Orthopaedic Nursing.2022; 41(6): 414. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Led Intervention Programs Based on Goal Attainment Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 699. CrossRef - EFFECTIVENESS OF EDUCATIONAL INTERVENTIONS FOR FALL PREVENTION: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Maria Aline Moreira Ximenes, Maria Girlane Sousa Albuquerque Brandão, Thiago Moura de Araújo, Nelson Miguel Galindo Neto, Lívia Moreira Barros, Joselany Áfio Caetano
Texto & Contexto - Enfermagem.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Application Value of Rehabilitation Nursing in Patients with Stroke Based on the Theory of Interactive Standard: A Randomized Controlled Study
Ningning Li, Jun Wang, Mei Zheng, Qunying Ge, Mozaniel Oliveira
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - A prospective cohort study of the risk factors for new falls and fragility fractures in self-caring elderly patients aged 80 years and over
Jian Zhou, Bo Liu, Ming-Zhao Qin, Jin-Ping Liu
BMC Geriatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Fall Prevention Program Based on King’s Theory of Goal Attainment in Long-Term Care Hospitals: An Experimental Study
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 715. CrossRef - Development of Fall Inducement System based on Pedestrian Biological Data for Fall Reproduction
Jong-il Lee, Jong-Boo Han, Jae Wan Koo, Seokjae Lee, Dong-Seop Sohn, Kap-Ho Seo
Journal of Korea Robotics Society.2020; 15(3): 286. CrossRef
- Recent advances in the identification of related factors and preventive strategies of hip fracture
- 3,038 View
- 106 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- A Predictive Model on Patient-Centered Care of Hospital Nurses in Korea
- Hyun Jeong, Myonghwa Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):191-202. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Patient-centered care is a widely utilized concept in nursing and health care. However, the key components of patient-centered nursing have not yet been reported. Moreover, previous studies on patient-centered care have mostly focused on components of nursing rather than organizational factors. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of influential factors of patient-centered care is required.
Methods The purpose of this study was to develop a theoretical model based on person-centered care theory, and the relevant literature and to test the developed model with covariance structure analysis in order to determine the causal paths among the variables.
Results The model fit indices for the hypothetical model were suitable for the recommended level (goodness of fit index=.87, standardized root mean residual=.01, root mean square error of approximation=.06, Tucker-Lewis index=.90, comparative fit index=.92, parsimonious normed fit index=.75). In this study, five of the six paths established in the initial hypothetical model were supported. The variables of teamwork, self-leadership, and empathy accounted for 56.4% of hospital nurses' patient-centered care. Among these, empathy was the strongest predictor of patient-centered care.
Conclusion These results suggest that it is necessary to use strategies to improve self-leadership and empathy. In addition to enhancing the personal factors of nurses, nursing organizations should strive for effective multidisciplinary cooperation with active support for patient-centered care and openness to change.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Clinical Nursing Competency and Nursing Working Environment of Psychiatric Nurses on Person-Centered Care
Pan Heui Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(3): 229. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Person-Centered Care Among Psychiatric Nurses in Hospitals
Ji Su Lee, Mi Heui Jang, Min Jung Sun
Healthcare.2024; 12(22): 2269. CrossRef - Factors Associated With Changes in Patient-Centered Care in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Seongkum Heo, Brandy Haley, Patricia Wright, Claudia P. Barone, Michael Anders, Tara Bertulfo, Patricia Troyan
Nursing Education Perspectives.2023; 44(2): 82. CrossRef - Factors associated with the person-centered care competence of nursing students
Ju Young Park, Chung Hee Woo
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(1): 48. CrossRef - Listening to patients' voices: Applying the design‐thinking method for teaching person‐centered care to nursing students
Myonghwa Park, Thi‐Thanh‐Tinh Giap, Insook Jang, Miri Jeong, Jahyeon Kim
Nursing Forum.2022; 57(1): 9. CrossRef - Factors influencing mental health nurses in providing person-centered care
Suyoun Ahn, Yeojin Yi
Nursing Ethics.2022; 29(6): 1491. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Schwartz Center Compassionate Care Scale*
Seong Eun KIM, Jeong Suk KIM
Korean Journal of Medical Ethics.2022; 25(2): 137. CrossRef - A Meta-Synthesis Study of Person-Centered Care Experience from the Perspective of Nursing Home Residents
Eun-Young Kim, Sung-Ok Chang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(14): 8576. CrossRef - Effects of health literacy competencies on patient-centered care among nurses
Yaki Yang
BMC Health Services Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Person-Centered Care Experience of Nursing Home Workers: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis Study
Eun Young Kim, Sung Ok Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(1): 33. CrossRef - Nurse Spiritual Care Therapeutics Scale
Kyung-Ah Kang, Elizabeth Johnston Taylor, Jiyoung Chun
Journal of Hospice & Palliative Nursing.2022; 24(6): E250. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Person-Centered Care among Hospice Nurses
Sinyoung Kwon, Kyoung Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2022; 25(2): 66. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Person-Centered Fall Prevention Program for Older Adults with Dementia in Long-Term Care Hospitals: For Older Adults with Dementia and Caregivers in Long-Term Care Hospitals
Jeong Ok Lim, Mee Ock Gu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 341. CrossRef - Role of self‐efficacy in nursing organizational climate: A way to develop nurses' humanistic practice ability
Mengru Bu, Haiqi Ma, Huimin Zhai, Yue Ma, Ningjun Xu
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2107. CrossRef - Effects of Compassionate Competence, Communication Skills, and Nursing Work Environment on Person-centered Care in General Hospital Nurses who Care for Cancer Patients
Mi Jin Han, Seonho Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2022; 25(1): 11. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Performance of Person-centered Care Among Nurses in Designated COVID-19 Hospitals
Hyun-Joung Yun, Jaehee Jeon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(4): 413. CrossRef - Hospital Culture and Healthcare Workers' Provision of Patient-Centered Care: A Moderated Mediation Analysis
Xianhong Huang, Yuan Gao, Hanlin Chen, Hao Zhang, Xiaoting Zhang
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influencing Factors on Performance of Person-Centered Care among Intensive Care Unit Nurses: An Ecological Perspective
Yein Lee, Yunhee Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(5): 522. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Person-Centered Care among Care Workers at Long-term Care Facilities
Geun-Young Kim, Hye-Young Jang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(1): 13. CrossRef - A predictive model of the perceptions of patient-centered care among nurses in long-term care hospitals: A cross-sectional study
Myonghwa Park, Hyun Jeong, Thi-Thanh-Tinh Giap
Geriatric Nursing.2021; 42(3): 687. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Person-Centered Practice Inventory-Staff for Nurses
Sohyun Kim, Sunghee H Tak
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(3): 363. CrossRef - Hospital Nurses’ Experience of Patient-Centered Nursing
Soojin Chung, Jee-In Hwang
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2021; 27(1): 26. CrossRef - Inducing a sense of worthiness in patients: the basis of patient-centered palliative care for cancer patients in Iran
Mir Hossein Aghaei, Zohreh Vanaki, Eesa Mohammadi
BMC Palliative Care.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of the Nursing Practice Environment and Self-leadership on Person-centered Care Provided by Oncology Nurses
Sun-Ui Shin, Hyun-E Yeom
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2021; 24(3): 174. CrossRef - The influence of health literacy competencies on patient-centered care among clinical nurses
Minyeon Kim, Jieun Cha
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(2): 132. CrossRef - “Walking in the patient’s shoes”: An innovative training method using storytelling to promote knowledge transfer of patient-centered care in hospital: A quasi-experimental study
Myonghwa Park, Insook Jang, Thi-Thanh-Tinh Giap
Nurse Education in Practice.2021; 56: 103199. CrossRef - Factors affecting to the Person-Centered Care among Critical Care Nurses
Seunghye Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2020; 13(2): 36. CrossRef - A Concept Analysis on Patient-Centered Care in Hospitalized Older Adults with Multimorbidity
Youn-Jung Son, Heun-Keung Yoon
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(2): 61. CrossRef - The Relationship between Person-Centered Nursing and Family Satisfaction in ICUs
Jiyeon Kang, Eun-Ja Shin
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(3): 1. CrossRef - The Influence of Lateral Violence on Burnout and Empathy with Patients among Nurses: The Moderating Effect of Communication
Soohyun Nam, Boyoung Hwang
Stress.2019; 27(3): 224. CrossRef
- Influence of Clinical Nursing Competency and Nursing Working Environment of Psychiatric Nurses on Person-Centered Care
- 5,002 View
- 185 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 30 Crossref

- Public Reporting on the Quality Ratings of Nursing Homes in the Republic of Korea
- Hyang Yuol Lee, Juh Hyun Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):161-170. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.161
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Quality ratings could provide vital information to help people in choosing a nursing home.
Purpose This study investigated factors aligned with quality ratings of nursing homes.
Methods We employed a cross-sectional descriptive design to assess publicly available data on 1,354 nursing homes with 30 or more beds in the Republic of Korea. After excluding 289 nursing homes with no reported quality-evaluation ratings, we analyzed the 2015 data of 1,065 nursing homes. To prevent multicollinearity among independent variables, we carefully selected the final set of variables based on clinical and theoretical meaningfulness to direct nursing care. Quality, the ordinal outcome, was scored from 1 to 5 with a higher score indicating higher quality of the organization. We constructed a multivariate ordered logistic regression model.
Results Higher quality ratings of nursing homes was significantly related to the number of unoccupied beds (OR=0.99,
p =.024), registered nurses (RNs) (OR=1.30,p =.003), qualified care workers (OR=1.03,p =.011), cognitive-improvement programs (OR=1.05,p =.024), and other programs for residents' activities (OR=1.09,p <.001).Conclusion The number of RNs had the strongest influence on the publicly reported quality rating, while the rating of qualified care workers demonstrated little effect and that of nursing assistants had no effect. The number of RNs could be used as a crucial indicator for high-quality homes; more resident-engaging programs also demonstrated better quality of nursing home care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Performance indicators on long-term care for older people in 43 high- and middle-income countries: literature review, web search and expert consultation
Mircha Poldrugovac, Joost D. Wammes, Véronique L. L. C. Bos, Erica Barbazza, Damir Ivanković, Hanneke Merten, Janet L. MacNeil Vroomen, Niek S. Klazinga, Dionne S. Kringos
BMC Health Services Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency and equity of elderly care service resource allocation in China, 2014–2022
Min Bao, Rongji Ma, Jianqian Chao
Health Policy and Technology.2025; 14(3): 101016. CrossRef - Institutional and individual factors influencing urinary tract infections and pressure injuries in Korean nursing home residents: A multilevel analysis of National Health Insurance Service Data
Hee Seung Lee, Jung Suk Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(4): 349. CrossRef - Nurse staffing and adverse events in residential aged care: Retrospective multi-site analysis
Dorika Nhongo, Annie Holt, Tracy Flenady, Amanda Rebar, Kasia Bail
Collegian.2023; 30(2): 343. CrossRef - Nursing Management-Associated Factors Associated with Urinary Tract Infection in Residents from Nursing Home Based on LTCfocus Database
Wei Wang, Hui Wang
Urologia Internationalis.2022; 106(7): 744. CrossRef - Effects of registered nurse staffing levels, work environment, and education levels on adverse events in nursing homes
Seonhwa Choi, Eunhee Cho, Eunkyo Kim, Kyongeun Lee, Soo Jung Chang
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Increasing Registered Nurse Hours Per Resident Day for Improved Nursing Home Residents’ Outcomes Using a Longitudinal Study
Juh Hyun Shin, Rosemary Anne Renaut, Mark Reiser, Ji Yeon Lee, Ty Yi Tang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(2): 402. CrossRef
- Performance indicators on long-term care for older people in 43 high- and middle-income countries: literature review, web search and expert consultation
- 2,294 View
- 11 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of a Reinforcement Program for Postpartum Care Behavioral Skills of Couples with Their First Baby
- Meera Park, Kyung Min Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):137-148. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.137
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to investigate the effects of a reinforcement program for behavioral skills in postpartum care for couples with their first baby.
Methods The study used a non-equivalent control group and pretest-posttest design. It was conducted from January 14 to April 10, 2016 at a postpartum care center in D city. It analyzed 43 couples (22 in the experimental group and 21 in the control group.) For data analysis, descriptive statistics, test of homogeneity in pretest, independent t-tests, and repeated measures ANOVA were used.
Results For maternal fulfillment of postpartum care and postpartum fatigue, there was no significant difference in the interaction between group and time. In terms of parent-newborns attachment, the interaction between group and time showed a significant difference for mothers (F=13.63,
p =.001) and fathers (F=6.51,p =.001). In marital intimacy, the interaction between group and time showed a significant difference for mothers (F=14.40,p <.001) and fathers (F=9.46,p =.004). In parenting stress, the interaction between group and time showed a significant difference for mothers (F=31.8,p <.001) and fathers (F=11.69,p =.001). A significant difference was found for the mothers' postpartum sleeping hours (F=0.14p =.004).Conclusion This program for behavioral skills in postpartum care, which is based on the information-motivation-behavioral skills model, improves postpartum care, parent-newborn attachment, marital intimacy, parenting stress, and maternal postpartum sleeping, by reinforcing behavioral skills required for postpartum care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of postpartum fatigue, parenting stress, and family support on postpartum depression in Chinese first-time mothers: a cross-sectional study
Feiyan Yi, Sukhee Ahn
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(3): 226. CrossRef - Maternal Health Effects of Internet-Based Education Interventions during the Postpartum Period: A Systematic Review
Jung Mi Chae, Hyun Kyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(1): 116. CrossRef - A Structural Model for Breastfeeding Behavior of First-Time Mothers
Seol Hui Park, Seang Ryu
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2021; 25(3): 184. CrossRef
- Effects of postpartum fatigue, parenting stress, and family support on postpartum depression in Chinese first-time mothers: a cross-sectional study
- 1,501 View
- 15 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Influencing Factors and Consequences of Near Miss Experience in Nurses’ Medication Error
- Jin Hee Park, Eun Nam Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(5):631-642. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.5.631
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to predict the influencing factors and the consequences of near miss in nurses’ medication error based upon Salazar & Primomo's ecological system theory.
Methods A convenience sample of 198 nurses was recruited for the cross-sectional survey design. Data were collected from July to September 2016. Using the collected data, the developed model was verified by structural equation modeling analysis using SPSS and AMOS program.
Results For the fitness of the hypothetical model, the results showed that χ 2 (χ 2=258.50,
p <.001) was not fit, but standardized χ 2 (χ 2/df=2.35) was a good fit for this model. Additionally, absolute fit index RMR=.06, RMSEA=.08, GFI=.86, AGFI=.81 reached the recommended level, but the Incremental fit index TLI=.82, CFI=.85 was not enough to reach to the recommended level. With the path diagram of the hypothetical model, caution (β=-.29p <.001), patient safety culture (β=-.20,p =.041), and work load (β=.18,p =.037) had a significant effect on the near miss experiences in nurses’ medication error, while fatigue (β=-.06,p =.575) did not affect it. Moreover, the near miss experience had a significant effect on work productivity (β=-.25,p =.001).Conclusion These results have shown that to decrease the near miss experience by nurses and increase their work productivity in hospital environments would require both personal and organizational effort.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Patient Safety and Quality Improvement in Nursing Practice: Associations Among Workload, Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy and Medical Device-Related Pressure Injury Prevention
Hyun Suk Gwag, Jin Ah Kim
Healthcare.2026; 14(2): 270. CrossRef - The effects of aroma inhalation on the quality of sleep, professional quality of life, and near-misses in medication errors among emergency room nurses on night duty in Korea: a randomized controlled trial
Jungha Son, Chul-Gyu Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(1): 25. CrossRef - Effects of Clinical Nurses’ Communication Ability, Critical Reflection Competency, and Nursing Professional Self-efficacy
on Medication Safety Competency
Seongyoun Jang, Sujin Shin
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2025; 13(1): 43. CrossRef - The effect of a clinical decision-making program for preventing high-alert medication errors among intensive care unit nurses in South Korea: a quasi-experimental study with a nonequivalent control group design
Se Yeong Park, SoMi Park, Ga Young Kim, Seung Ah Hong, Hyang Ok Choi, Sunyoung Moon
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(3): 366. CrossRef - A comparative study of back pain, task-load and presenteeism in nursing homes
Hye Young Shim, Jin H. Park, Sook Hee Jeong
Disability and Rehabilitation: Assistive Technology.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Nursing near miss: a concept analysis
Dan Zhou, Sisi Guo, Qin Tan, Xuerong Lin
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurses' Medication Errors in General Hospitals: Analysis of Patient Safety Reports and Nurse Experiences Using Mixed Methods
Hyo Hoon Ku, Jooyoung Cheon
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 251. CrossRef - The Association of Job Stress, Quality of Sleep, and the Experience of Near-Miss Errors among Nurses in General Hospitals
Seong-Kyeong Kwak, Jin-Soo Ahn, Yeon-Ha Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(6): 699. CrossRef - Association between Nurses’ Perceptions of Patient Safety Culture, Willingness to Report Near Misses, Critical Thinking Disposition, and Nursing Care Activities for Patient Safety
Da Eun Lee, Bo Gyeong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 283. CrossRef - The associations of psychological burnout and time factors on medication errors in rotating shift nurses in Korea: A cross sectional descriptive study
Cheongin Im, Suyoung Song, Kyoungja Kim
Nursing Open.2023; 10(8): 5550. CrossRef - Clinical nurses’ recovery experiences after adverse events in South Korea: A qualitative study
Hyoung Eun Chang, Haena Jang, Yong Ik Bak
Collegian.2022; 29(4): 456. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Nursing Work Interruption Scale
Eun-Jeong Yu, Eun-Nam Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(20): 13487. CrossRef - Relationship between Clinical Nurses' Job Stress and Medication Safety Performance: Mediating Effect of Fatigue
Se Yeong Park, Hea Kung Hur
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 283. CrossRef - A Study on Factors Affecting Near Misses by Nurses in Small-Medium Sized Hospitals
San-Na Lee, Seon-Ha Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(2): 75. CrossRef - Impact of Hospital Nurses’ Perception on Clinical Alarms and Patient Safety Culture on Alarm Management Practice
Soo-Joung Lee, Yun-Mi Lee, Eun Ji Seo, Youn-Jung Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4018. CrossRef - Factors causing medication errors in an electronic reporting system
Seonhee Yoon, Kyeongyae Sohng
Nursing Open.2021; 8(6): 3251. CrossRef
- Patient Safety and Quality Improvement in Nursing Practice: Associations Among Workload, Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy and Medical Device-Related Pressure Injury Prevention
- 2,421 View
- 144 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


