Funded articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse articles > Funded articles
Research Papers
- Development of a predictive model for exclusive breastfeeding at 3 months using machine learning : a secondary analysis of a cross-sectional survey
- Hyun Kyoung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):519-527. Published online October 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25086
- Funded: Kongju National University, National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science and ICT
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
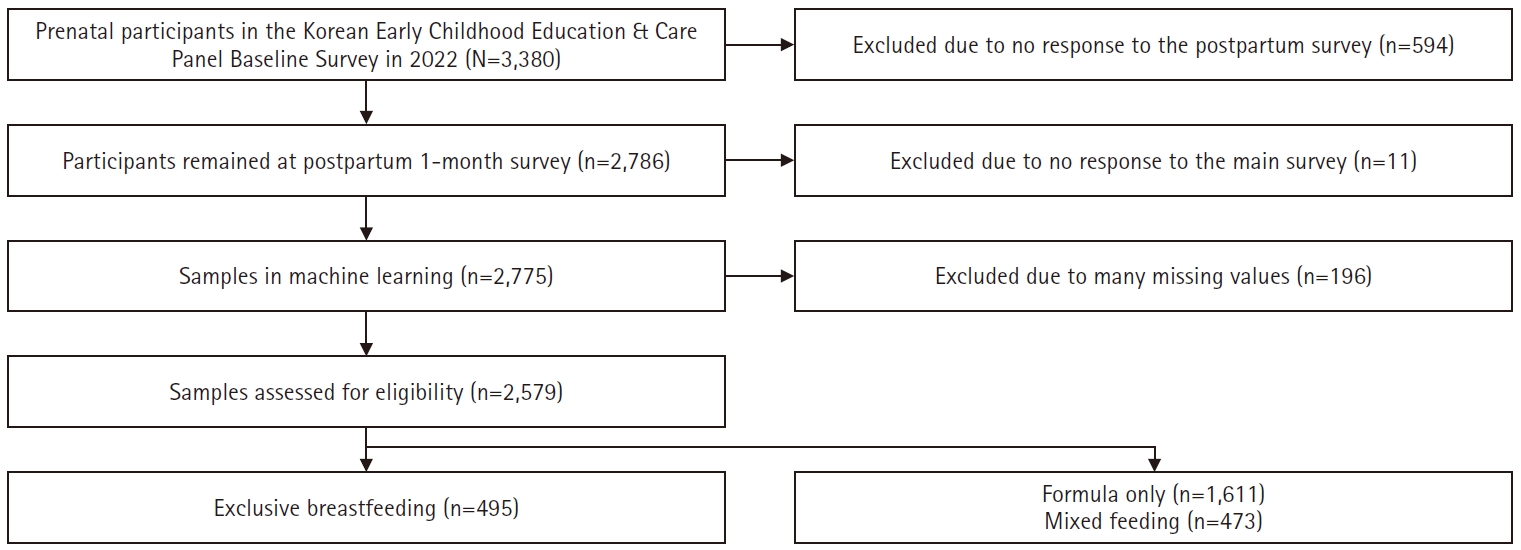
This study aimed to develop a machine learning model to predict exclusive breastfeeding during the first 3 months after birth and to explore factors affecting breastfeeding outcomes.
Methods
Data from 2,579 participants in the Korean Early Childhood Education & Care Panel between March 1 and June 3, 2025 were analyzed using Python version 3.12.8 and Colab. The dataset was split into training and testing sets at an 80:20 ratio, and five classifiers (random forest, logistic regression, decision tree, AdaBoost, and XGBoost) were trained and evaluated using multiple performance metrics and feature importance analysis.
Results
The confusion matrix of the random forest classifier model demonstrated strong performance, with a precision of 86.6%, accuracy of 84.8%, recall of 96.8%, F1-score of 91.9%, and an area under the curve of 86.0%. Twenty-one features were analyzed, from which feeding plan, breastfeeding at 1 month, marriage period, maternal prenatal weight, self-respect, alcohol consumption, grit, value placed on children, maternal age, and depression emerged as important predictors of exclusive breastfeeding in the first 3 months.
Discussion
A robust model was developed to predict exclusive breastfeeding that identified feeding planning and breastfeeding at 1 month as the most influential predictors. The model could be implemented in clinical and community settings to guide tailored breastfeeding support strategies, coupled with the integration of maternal self-respect, grit, and the value placed on children in counseling programs to promote exclusive breastfeeding.
- 1,459 View
- 130 Download

- Development of a machine learning-based prediction model for early hospital readmission after kidney transplantation: a retrospective study
- Hye Jin Chong, Ji-hyun Yeom
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):528-542. Published online November 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25030
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science and ICT
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and validate a machine learning-based prediction model for early hospital readmission (EHR) post-kidney transplantation.
Methods
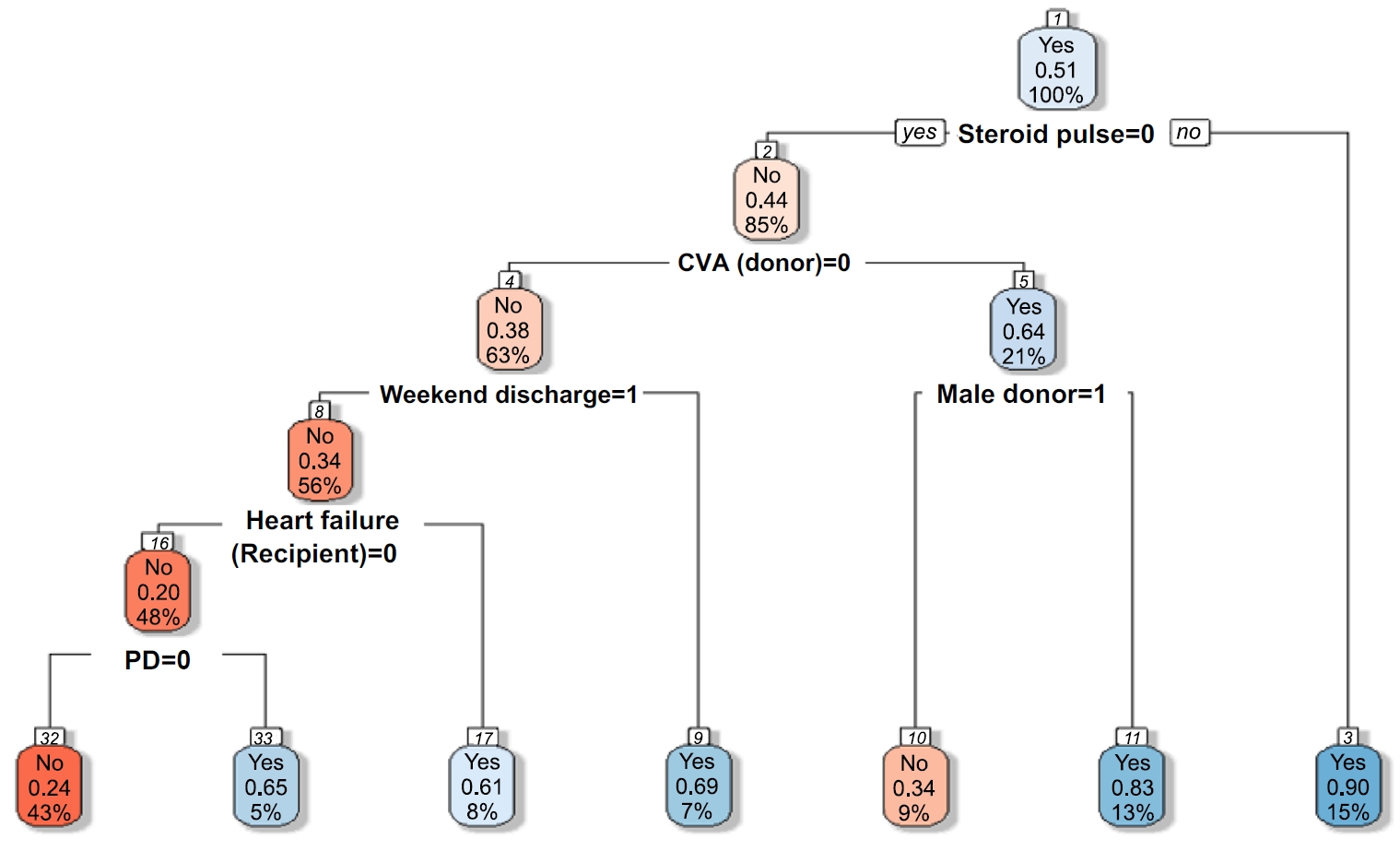
The study was conducted at the organ transplantation center of a university hospital, utilizing data from 470 kidney transplant recipients. We built and trained four machine learning models and tested them to identify the strongest EHR predictors. Predictive performance was evaluated using confusion matrices and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC AUC).
Results
Among the 470 kidney transplant recipients with a mean age of 46.1 ± 12.02 years, 322 (68.5%) were males, and 74 (15.7%) were readmitted within 30 days after kidney transplantation. In total, 241 (51.2%) recipients were found to have experienced EHR after applying the random over-sampling examples method. The random forest model achieved the best performance, with an ROC AUC of .87 (validation set) and .82 (test set). The 15 most important features were steroid pulse therapy (recipient), cerebrovascular accident (recipient), heart failure (recipient), male sex (donor), cardiovascular disease (recipient), weekend discharge (recipient), peritoneal dialysis (recipient) cerebrovascular accident as the cause of brain death (donor), current smoker (recipient), cardiac arrest (donor), previous kidney transplantation (recipient), age (donor), hypertension (donor), male sex (recipient), and dialysis duration (recipient).
Conclusion
Our framework demonstrated strong predictive interpretability. It can support appropriate and effective clinical decision-making by assisting transplant professionals in stratifying recipients based on their risk of EHR. prioritizing post-discharge care and follow-up for high-risk individuals, and allocating targeted interventions such as closer monitoring or education.
- 907 View
- 113 Download

- Strategies for expanding the role of advanced practice providers in the Korean nursing workforce: a mixed-methods approach
- Jeong Hye Kim, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Suyoung Choi, Mimi Lee, Su Jung Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):568-583. Published online November 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25106
- Funded: Seoul Nurses Association
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to propose strategies for strengthening the nursing workforce by expanding their roles as advanced practice providers (APPs).
Methods
A mixed-methods approach was employed, consisting of five focus group interviews (FGIs) with 30 healthcare professionals (including 10 physicians) and a two-round Delphi survey with 49 experts. The FGIs explored practical insights from clinical settings, while the Delphi process validated and prioritized strategic recommendations through expert consensus.
Results
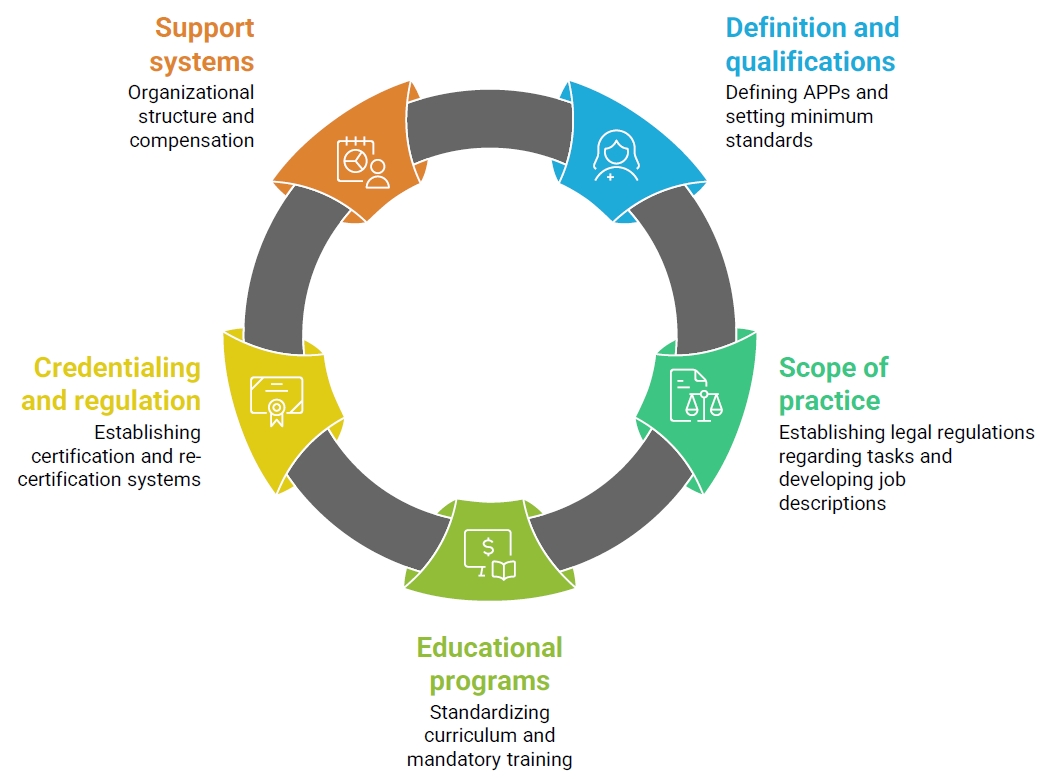
Four major themes emerged from the FGI analysis: (1) utilization of diverse APPs to ensure quality care, (2) expanding the scope of practice of APPs, (3) requirements to ensure the quality of APPs, and (4) strategies for sustainable management of the APP workforce. Building on these findings, the Delphi survey identified five strategic domains: “definition and qualifications,” “scope of practice,” “educational programs,” “credentialing and regulation,” and “support systems.” Key areas of consensus included the need for mandatory clinical experience and specialty training, legal clarification of role boundaries, standardized curricula with certification mechanisms, and institution-led support systems such as task-specific job descriptions and recredentialing processes.
Conclusion
To effectively strengthen APP roles, it is essential to build on the existing advanced practice nurse (APN) framework, which already includes structured curricula and national certification. Furthermore, integrative strategies should be developed to incorporate experienced clinical nurses without APN licenses into the APN system.
- 1,413 View
- 120 Download

Review Paper
- Risk factors for the readmission of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hyerim Ji, Sun-Kyung Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):634-650. Published online November 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25072
- Funded: Pusan National University
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify risk factors associated with the readmission of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
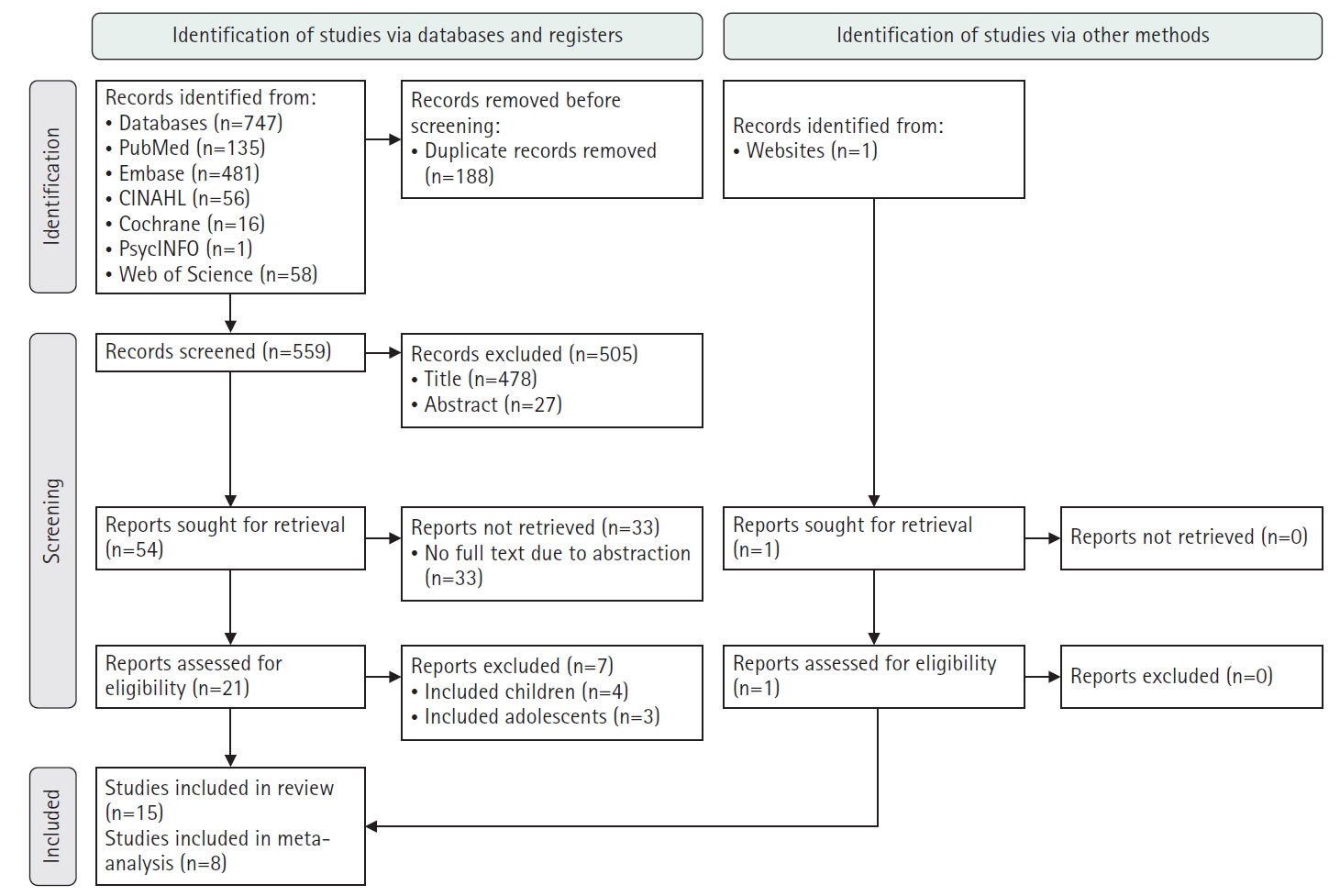
A systematic literature review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines. Relevant studies were retrieved from international databases (PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Web of Science) and Korean databases (RISS, KoreaMed, KMbase, KISS, and DBpia). Study quality was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Meta-analysis was performed using a random-effects model with the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman adjustment to account for the limited number of studies and heterogeneity.
Results
Fifteen studies were included in the review, and eight were eligible for meta-analysis. From the systematic review, 21 risk factors for DKA readmission were identified and categorized into five domains: demographic, socioeconomic, diabetes-related, comorbidity, and health-behavioral factors. In the meta-analysis, significant risk factors included low income, psychiatric disorders, and discharge against medical advice.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that DKA readmissions result from the complex interplay of multiple clinical and social factors. By identifying these risk factors and suggesting risk-stratification criteria, the findings may support the development of tailored interventions, such as self-management education, integrated mental health care, structured discharge planning, and coordinated post-discharge follow-up.
- 1,010 View
- 145 Download

Research Papers
- A qualitative exploration of acute stroke patients’ experiences with aphasia in Korea
- Jiyeon Kang, Hyunyoung Heo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):621-633. Published online November 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25132
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science and ICT
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to explore the lived experiences of patients with acute stroke-related aphasia within the Korean healthcare context.
Methods
A qualitative research design using inductive content analysis was employed, following the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research guidelines. Fourteen adults with acute stroke-related aphasia participated in one-on-one, in-depth interviews conducted between January and May 2025. Participants were recruited through purposive sampling until theoretical saturation was reached. Data were analyzed using an inductive qualitative content analysis approach.
Results
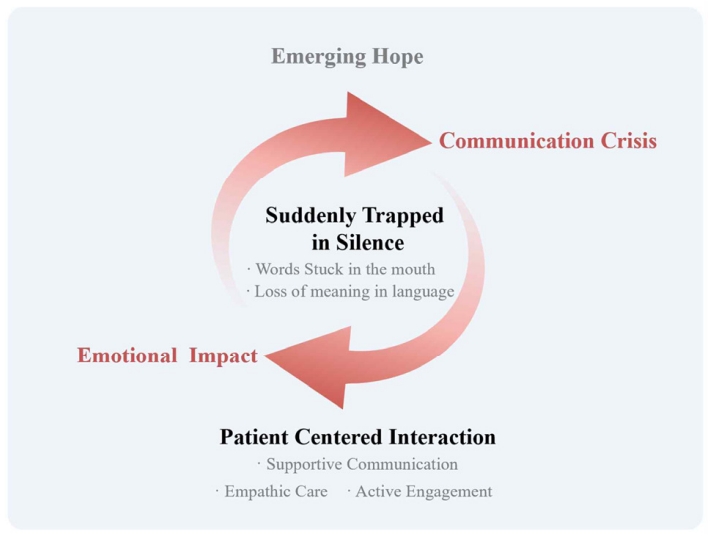
Five main categories emerged: “suddenly trapped in silence” described the abrupt loss of language, including the inability to articulate intended words and understand others; “emotional impact” captured psychological shock and feelings of loss; “communication crisis” encompassed expressive difficulties, exclusion from decision-making, and social withdrawal; “patient-centered interaction” highlighted supportive communication, empathic care, and active engagement by others; and “emerging hope” reflected signs of recovery, self-directed efforts, and anticipation of improvement. These categories converged into the overarching theme, “communication beyond language,” illustrating how patients sought meaningful interaction despite linguistic limitations.
Conclusion
Acute aphasia extends beyond a language disorder to encompass profound emotional and social experiences. Although communication barriers exist, meaningful interaction remains possible through empathetic, person-centered approaches. Healthcare professionals should recognize that patients with aphasia retain cognitive competence despite expressive limitations. These findings underscore the need to integrate emotional sensitivity into clinical care and to develop training programs that enhance person-centered communication skills in stroke rehabilitation settings.
- 1,002 View
- 94 Download

- Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
- Haesun Lee, Hye Jin Nam, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):454-467. Published online August 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25018
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Education
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
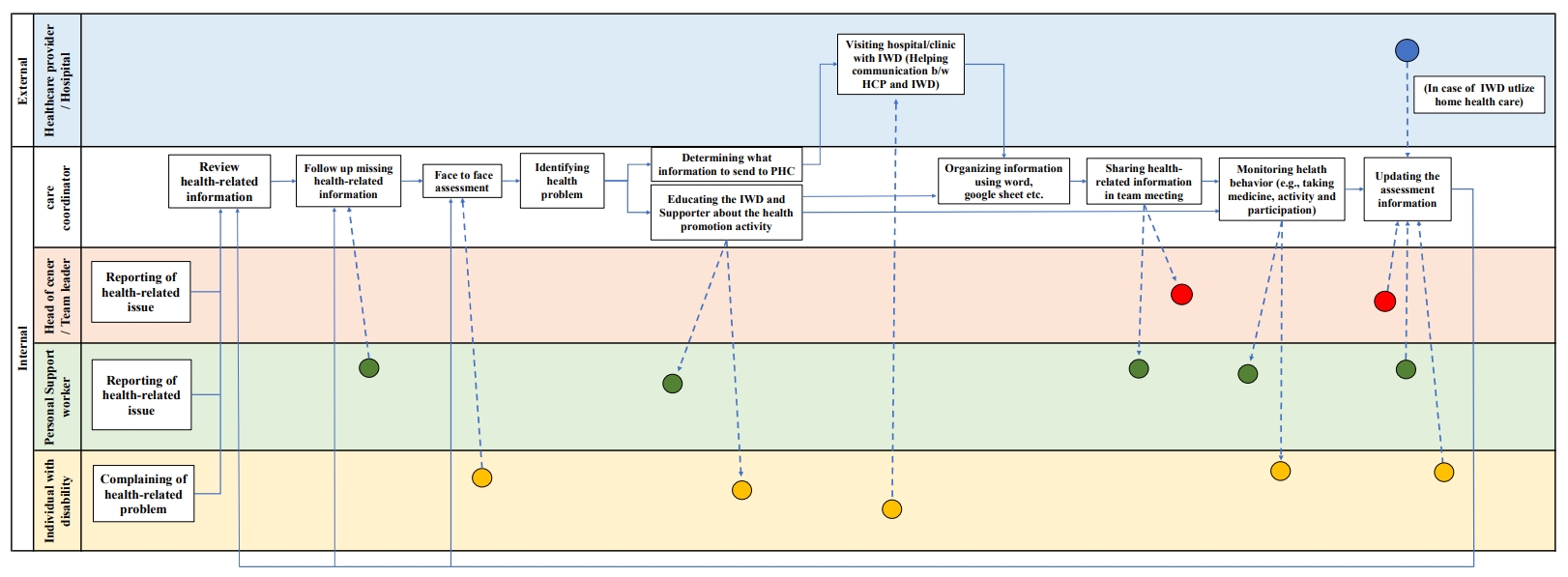
This study conducted a work-system analysis using the Systems Engineering Initiative for Patient Safety (SEIPS) framework to assess the flow of health-related information, and the current status of health management tasks for individuals with disabilities (IWD) in supportive housing.
Methods
This qualitative study utilized focus groups. Participants included a head of supportive housing, a team leader, a care coordinator and three personal support workers for IWD. Semi-structured interviews were guided by the SEIPS framework to explore the components of persons, tasks, tools and technology, organization, and environments.
Results
This study identified five key themes within the five SEIPS components: (1) disparities in role identity and health literacy among staff, (2) challenges in health care support reflecting a person-centered approach, (3) barriers in health-related information exchange and communication tools, (4) needs for organizational strategies or information communication, and (5) needs for integrating health-related information across external healthcare institutions. Additionally, 10 sub-themes were identified.
Conclusions
These findings provide a comprehensive system-wide perspective and offer insights into the systematic approaches needed to improve healthcare processes and structures within disability supportive housing. Specifically, healthcare providers and effective tools for integrating health-related information are identified as critical components.
- 1,324 View
- 80 Download

- Effects of social support on organizational commitment among experienced nurses experiencing department rotation: the mediating effect of organizational socialization
- Young Jun Jang, Jeong A Jeong, Yu Seung Ban, Seon Hwa Park, Eun Jee Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):364-376. Published online August 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25042
- Funded: Jeonbuk National University Hospital
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study explored the mediating role of organizational socialization in the relationship between social support and organizational commitment among nurses in hospitals who had experienced department rotation.
Methods
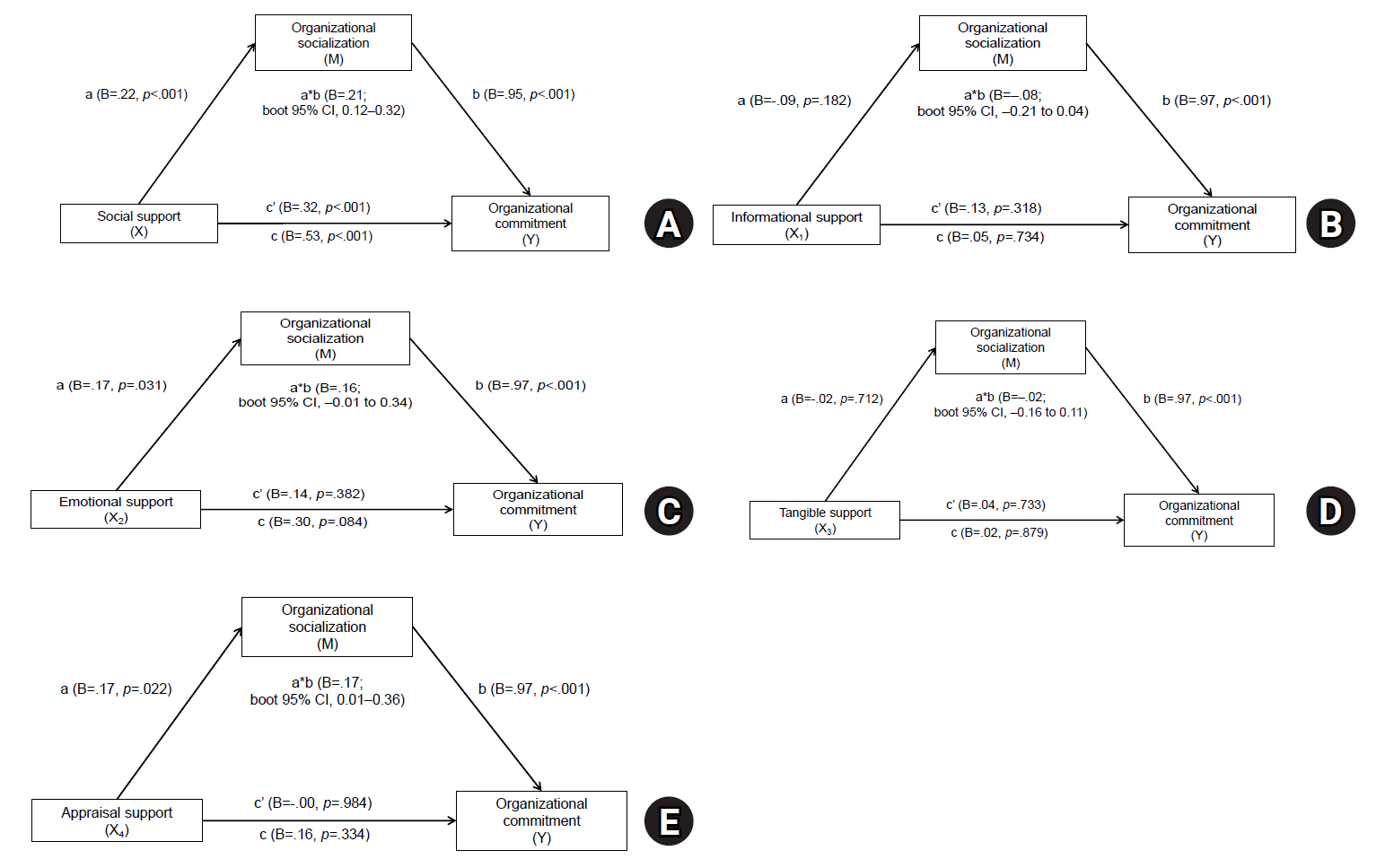
A descriptive survey design was used with 202 nurses from a tertiary hospital who had experienced department rotation within the past 12 months. Data were collected via an online questionnaire from August 1 to August 30, 2024. Analyses included frequency analysis, descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation, and multiple regression. The mediating effect was tested using IBM SPSS WIN ver. 23.0 and the PROCESS macro (model 4) with 10,000 bootstrap resamples.
Results
Organizational socialization partially mediated the relationship between social support and organizational commitment (B=.21; bootstrapped 95% confidence interval, 0.12–0.32).
Conclusion
The findings suggest that both social support and organizational socialization play essential roles in improving nurses’ organizational commitment following department rotation. Thus, practical programs, such as mentoring systems, should be implemented that both enhance social support and actively promote organizational socialization. These efforts have the potential to help nurses adjust more effectively to new units and ultimately improve retention and performance within healthcare organizations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Nurses’ Dispatch Work Characteristics on Job Embeddedness, Organizational Commitment, and Turnover Intention
Eejee Jung, Gunjeong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 560. CrossRef - Nurses' Experience Working with Substitute Nurses
Hye Mi Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 208. CrossRef
- The Effects of Nurses’ Dispatch Work Characteristics on Job Embeddedness, Organizational Commitment, and Turnover Intention
- 1,956 View
- 228 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Comparison of educational needs and priorities for work-related laws between hospital and community-based nurses
- Jeonghyun Kim, Min Kyoung Han, Minjae Lee, Sujin Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):400-412. Published online August 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25049
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science and ICT
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the practical utilization of work-related laws in nursing practice and to prioritize educational needs to provide foundational data for improving nurses’ legal competencies.
Methods
A descriptive survey was employed using an online self-reported questionnaire. Participants included 275 nurses with over 3 years of clinical experience, categorized into hospital and community-based. Convenience sampling was used, and data were collected between January 9 and February 3, 2025. Descriptive statistics and the paired t-test were conducted using IBM SPSS 26.0. Educational needs were analyzed using the Borich Needs Assessment and the Locus for Focus model.
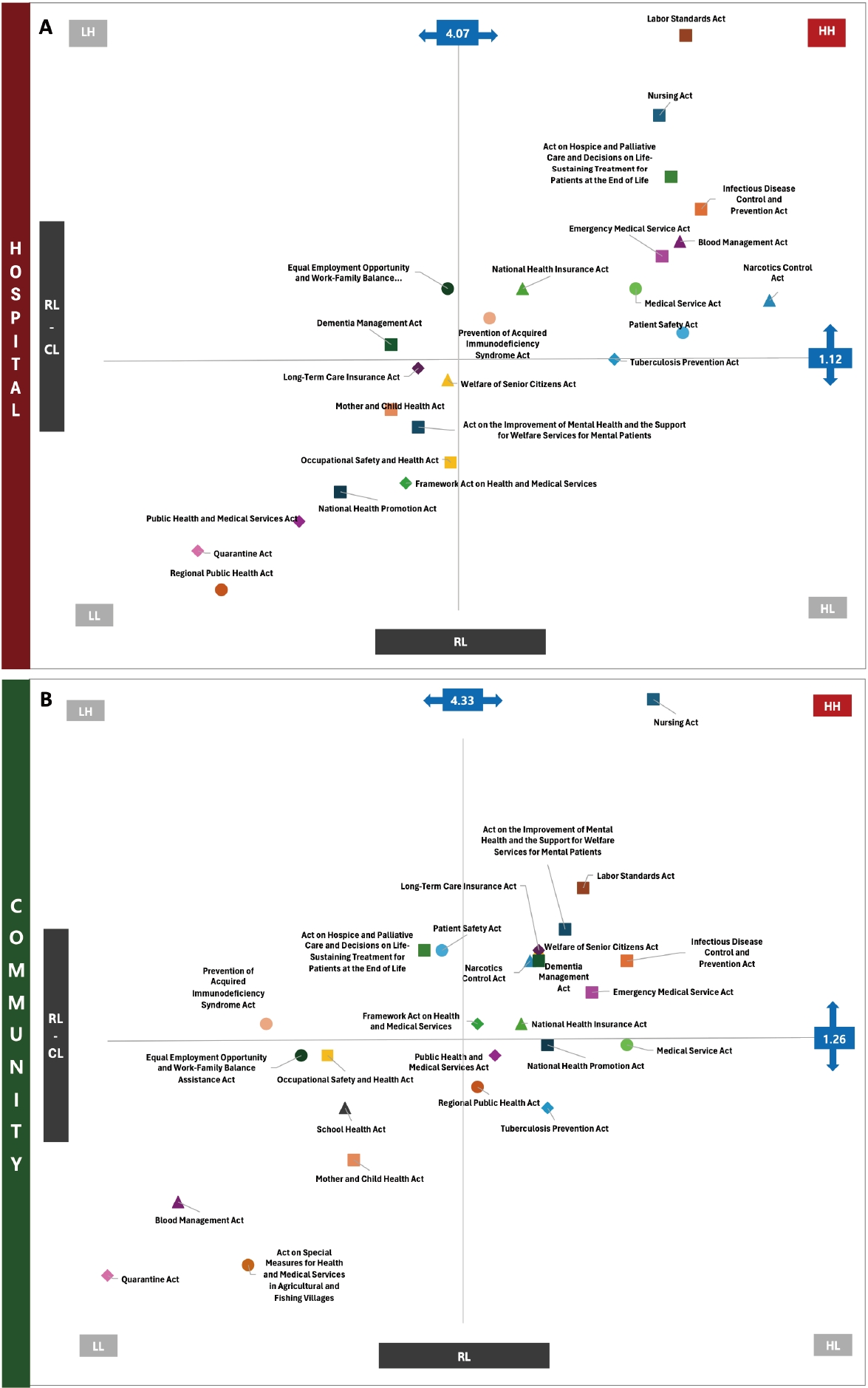
Results
Among participants, 75.6% had received education on work-related laws, and 79.3% of those participants received related education during their undergraduate studies. However, 32.4% of nurses reported experiencing practice related difficulties due to insufficient legal knowledge, particularly related to unclear legal responsibilities and ambiguity in the scope of practice. High educational needs were identified for the Nursing Act and the Labor Standards Act across all workplaces. Hospital nurses emphasized the Hospice and Palliative Care Act and Emergency Medical Services Act, while community-based nurses prioritized the Mental Health Welfare Act, Elderly Welfare Act, and Dementia Management Act.
Conclusion
Nurses’ legal education needs are related to practical applications and their capability to respond appropriately to legal requirements, and these needs vary depending on their work environment and social changes. These findings underscore the necessity of restructuring legal education curricula to improve practical relevance and support nurses’ rights, providing a basis for developing workplace-specific legal education programs.
- 1,915 View
- 139 Download

- Development of a scale to measure fear of falling in older adults: a psychometric validation study
- Dayeon Lee, Sunghee H Tak
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):413-424. Published online August 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25036
- Funded: Korean Gerontological Nursing Society, Center for Human-Caring Nurse Leaders for the Future, National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science and ICT
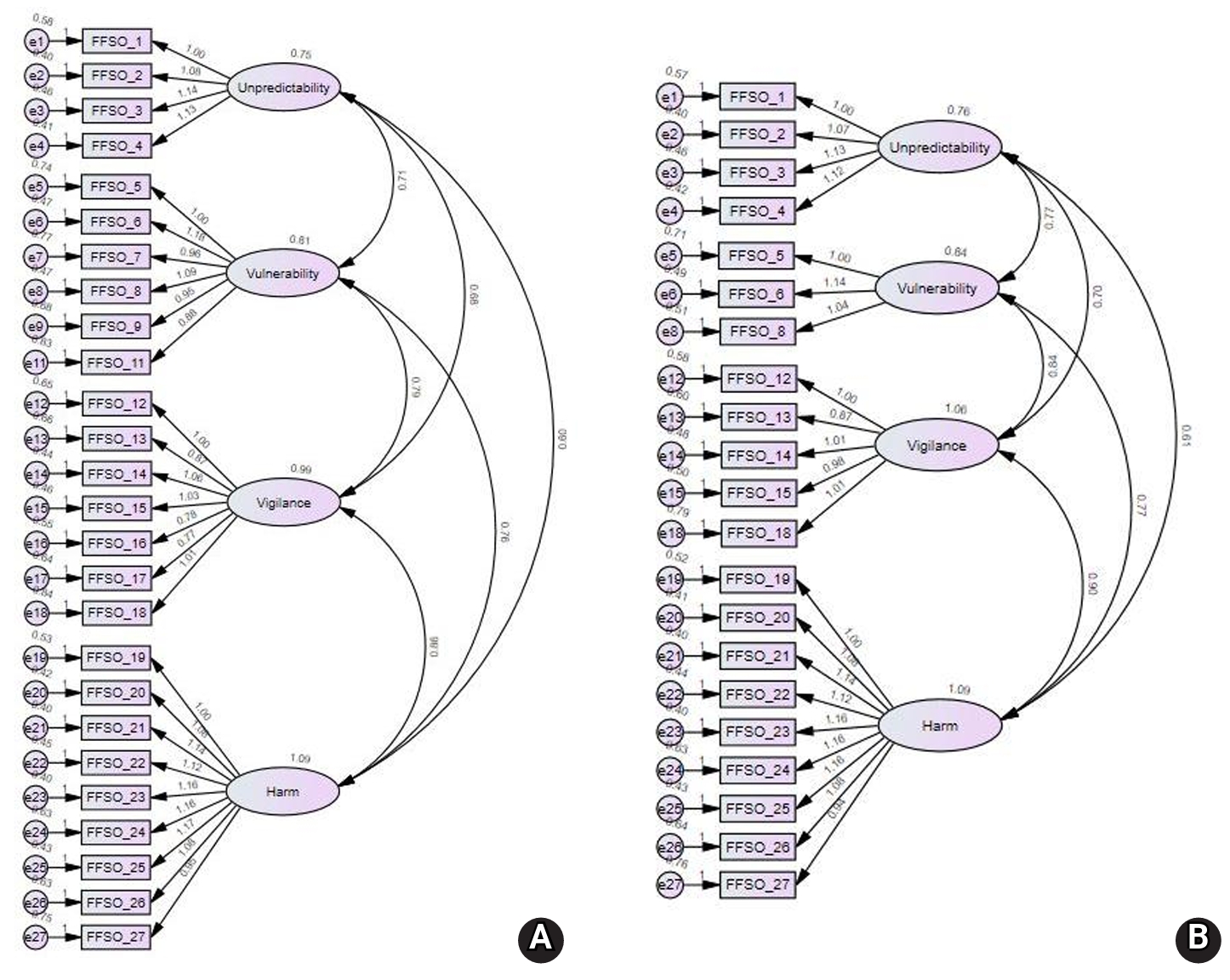
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure fear of falling in older adults and to validate its reliability and validity.
Methods
In total, 31 initial items were developed by referring to expressions from previous studies and items from existing instruments. After verifying content validity through expert evaluation, the remaining 27 items were used to construct a survey. Data from 252 participants recruited at three senior welfare centers in the metropolitan area were analyzed to examine item analysis, construct validity, convergent validity, discriminant validity, and reliability. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was conducted to test construct validity. The correlation with the Korean version of the Falls Efficacy Scale-International (KFES-I) was used to assess convergent validity. Cronbach’s alpha was calculated to determine reliability.
Results
The final instrument consisted of 21 items. CFA confirmed acceptable model fit. Convergent validity was also acceptable and discriminant validity was partially supported. Correlations with the KFES-I ranged from .54 to .63. The Cronbach’s alpha coefficients for the total score and all factors ranged from .84 to .97.
Conclusion
The Fear of Falling Scale for Older Adults developed in this study is a validated tool capable of measuring various dimensions of fear of falling. It provides a foundation for accurately assessing fear of falling in older adults and addressing its specific aspects.
- 1,257 View
- 154 Download

- Prenatal psychosocial factors and postpartum post-traumatic stress disorder in low-risk postnatal women: a longitudinal study
- Jung Hee Yeo, So Yeon Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):353-363. Published online August 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25027
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Education, Dong-A University
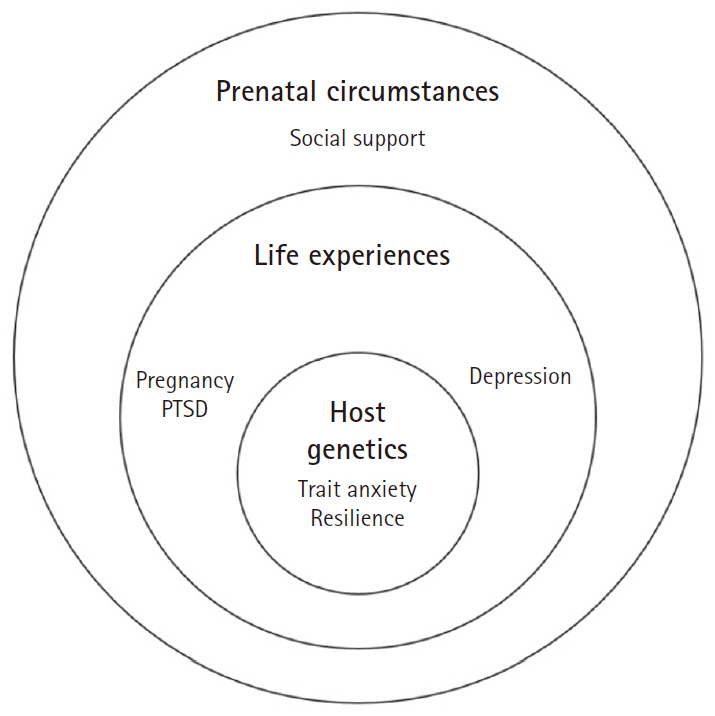
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify prenatal psychosocial factors influencing the development of postpartum post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in both short-term (4–6 weeks postpartum) and long-term (4–6 and 14–18 weeks postpartum) assessments using the wheel model.
Methods
This study employed a longitudinal design with 359 women in their third trimester who received care at two maternity hospitals in City B. Surveys were used to measure depression, anxiety, resilience, and pregnancy-related PTSD during the third trimester (n=318). Postpartum PTSD was assessed at 4–6 weeks (n=198) and at 14–18 weeks postpartum (n=156). Data were analyzed using the t-test, chi-square test, and logistic regression.
Results
The prevalence of short-term postpartum PTSD was 32.7%, and that of long-term PTSD was 19.9%. The risk of short-term PTSD increased with higher pregnancy-related PTSD symptoms (odds ratio [OR], 1.04; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02–1.07), higher prenatal resilience (OR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.00–1.18), and lower social support (OR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.87–0.99). Similarly, the risk of long-term PTSD increased with higher pregnancy-related PTSD (OR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.04–1.13), higher prenatal resilience (OR, 1.19; 95% CI, 1.06–1.34), and low educational attainment (OR, 6.75; 95% CI, 1.03–44.30).
Conclusion
The high prevalence of short- and long-term postpartum PTSD highlights the need for systematic screening and interventions for prenatal factors, including pregnancy-related PTSD, social support, resilience, and education level. Therefore, it is necessary to alleviate pregnancy-related PTSD and strengthen social support during prenatal care to prevent postpartum PTSD. Furthermore, women with high resilience should also be targeted in these interventions, because they can also develop postpartum PTSD.
- 1,347 View
- 138 Download

- Triglyceride-glucose parameters as predictors of diabetes mellitus incidence in Korean adults: a secondary analysis of a Prospective Cohort Study
- Yu Jin Park, Miseon Shin, Hyun Seon Jeon, Eun Hee Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):205-221. Published online April 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24108
- Funded: National Biobank of Korea, Agency for Disease Control and Prevention
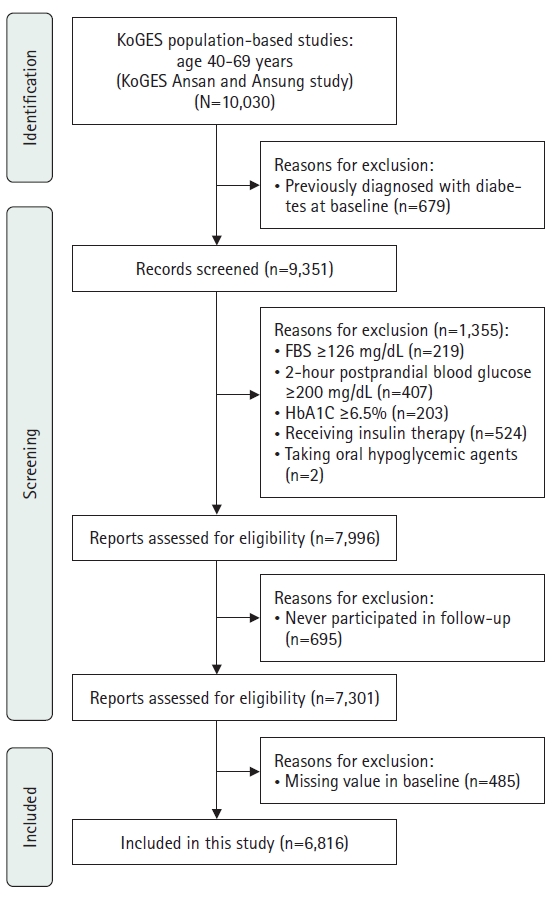
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the association between triglyceride-glucose (TyG)–related parameters and the incidence of diabetes mellitus in Korean adults. Data were obtained from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES).
Methods
This secondary analysis examined data from 6,816 adults aged 40–69 years who participated in the KoGES from 2001 to 2020. TyG–related parameters, including the TyG index, TyG–body mass index (TyG–BMI), TyG–waist circumference (TyG–WC), and TyG–waist-to-height ratio (TyG–WHtR), were assessed. Cox proportional hazards models were employed to determine the association between these parameters and the incidence of diabetes mellitus, with adjustments made for demographic, lifestyle, and health-related characteristics.
Results
Higher levels of all TyG–related parameters were significantly associated with an increased risk of developing diabetes mellitus. Specifically, participants in the highest quartile of the TyG index, TyG–BMI, TyG–WC, and TyG–WHtR exhibited significantly higher hazard ratios for diabetes mellitus incidence compared with those in the lowest quartile (p<.001 for all). Notably, the TyG index demonstrated a stronger predictive value for diabetes mellitus than traditional measures such as the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance.
Conclusion
TyG–related parameters are robust predictors of diabetes mellitus incidence in Korean adults. These findings support the incorporation of TyG–related measures into clinical settings for the early identification and intervention of high-risk populations. Utilizing these parameters for early diagnosis and preventive strategies may significantly enhance diabetes mellitus management.
- 2,315 View
- 148 Download

- Impact of smoking on diabetes complications: a secondary analysis of the Korean National Health Insurance Service-health screening cohort (2002–2019)
- Seonmi Yeom, Youngran Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):222-235. Published online April 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24109
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science and ICT
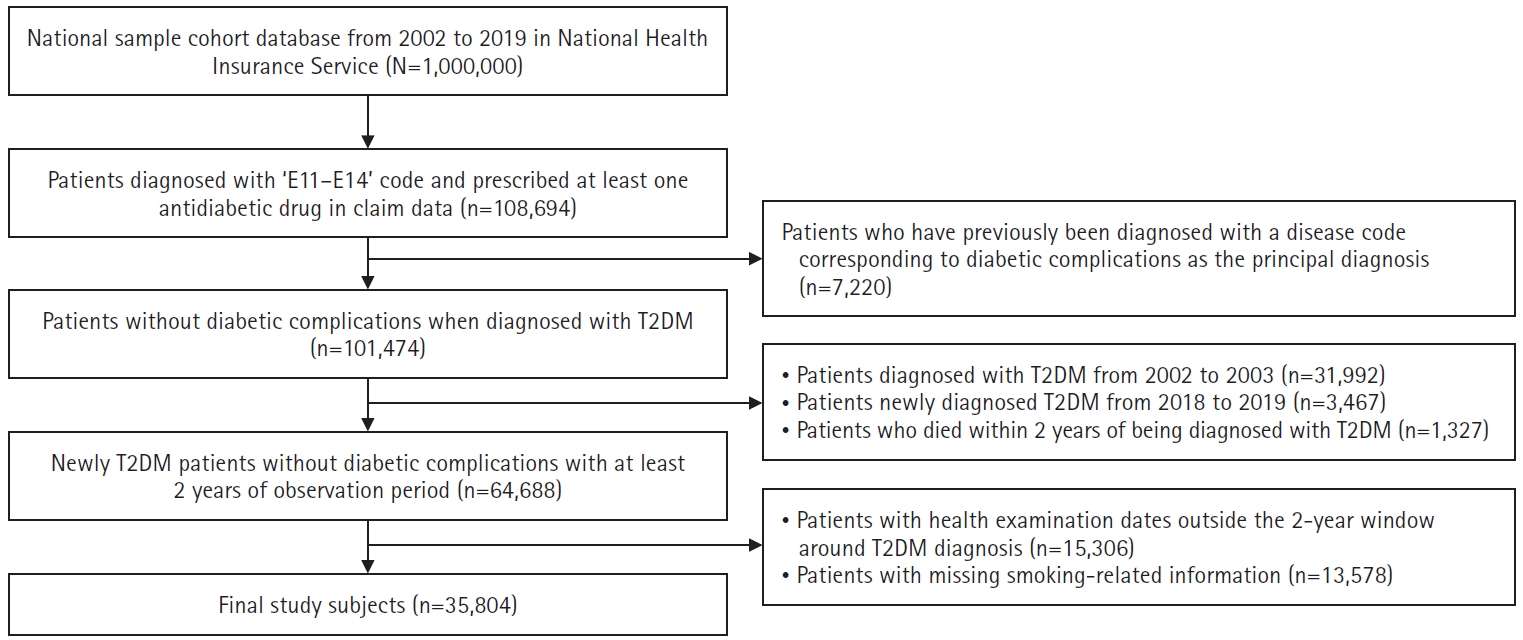
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the effects of smoking on the incidence of macrovascular and microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods
We analyzed 35,804 patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes between 2004 and 2017 using the Korean National Health Insurance Service–National Health Screening Cohort (2002–2019). Smoking status was categorized into never, former, and current smoking, with further classification based on duration of smoking and daily smoking amount. We conducted survival analysis using a Cox proportional hazards model.
Results
Both former and current smokers had significantly elevated risks of macrovascular complications compared to non-smokers, with hazard ratios (HRs) of 1.60 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.49–1.66) and 1.10 (95% CI, 1.08–1.17), respectively. Long-term smokers (over 30 years) had significantly higher risks of both macrovascular (HR, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.29–1.42) and microvascular complications (HR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.30–1.42). Heavy smokers (over 2 packs/day) more frequently developed macrovascular (HR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.30–1.64) and microvascular (HR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.60–1.98) complications than never smokers. Notably, former smokers had increased risks of developing neuropathy (HR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.31–1.49), nephropathy (HR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.16–1.39), and retinopathy (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.39–1.60).
Conclusion
Patients with type 2 diabetes and a history of smoking are at higher risk of developing macrovascular and microvascular complications. Smoking cessation, along with reducing smoking duration and amount, is crucial for lowering these risks.
- 1,980 View
- 112 Download

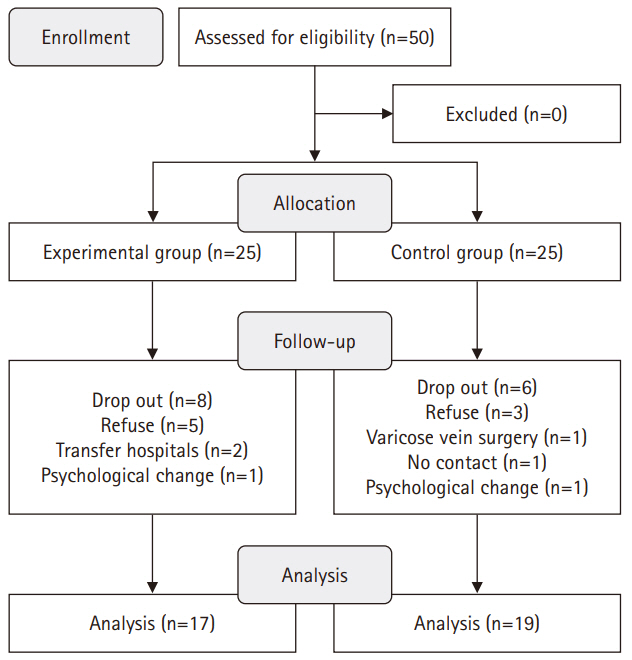
- The effects of a lifestyle intervention for men in infertile couples in South Korea: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Yun Mi Kim, Ju-Hee Nho
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):191-204. Published online April 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24104
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of an interaction model of client health behavior (IMCHB)-based lifestyle intervention on health-promoting behaviors, infertility stress, fertility-related quality of life, and semen quality in men in infertile couples.
Methods
This study used a quasi-experimental, non-equivalent control group, pretest-posttest design, with participants divided into an experimental group (n=17) and a control group (n=19). The 16-session, 8-week intervention included components such as reproductive health education, physical activity, nutritional management, and stress management. Data collection occurred between July 1, 2021 and September 27, 2022. The outcomes measured included health-promoting behaviors, infertility stress, fertility-related quality of life, and sperm quality (volume, total motility, immobility, concentration, and normal morphology).
Results
The experimental group showed significant improvements in health-promoting behaviors (z=–2.27, p=.023) and reductions in infertility stress (t=–2.40, p=.022) compared to the control group. Total sperm motility (F=4.39, p=.045) and normal morphology (z=2.86, p=.017) were also significantly higher in the experimental group than in the control group.
Conclusion
The IMCHB-based lifestyle intervention significantly increased health-promoting behaviors, reduced infertility stress, and improved key sperm parameters, indicating its effectiveness in supporting the reproductive health of men in infertile couples. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychological Stress and Male Infertility: Oxidative Stress as the Common Downstream Pathway
Aris Kaltsas, Stamatis Papaharitou, Fotios Dimitriadis, Michael Chrisofos, Nikolaos Sofikitis
Biomedicines.2026; 14(2): 259. CrossRef
- Psychological Stress and Male Infertility: Oxidative Stress as the Common Downstream Pathway
- 3,462 View
- 130 Download
- 1 Crossref

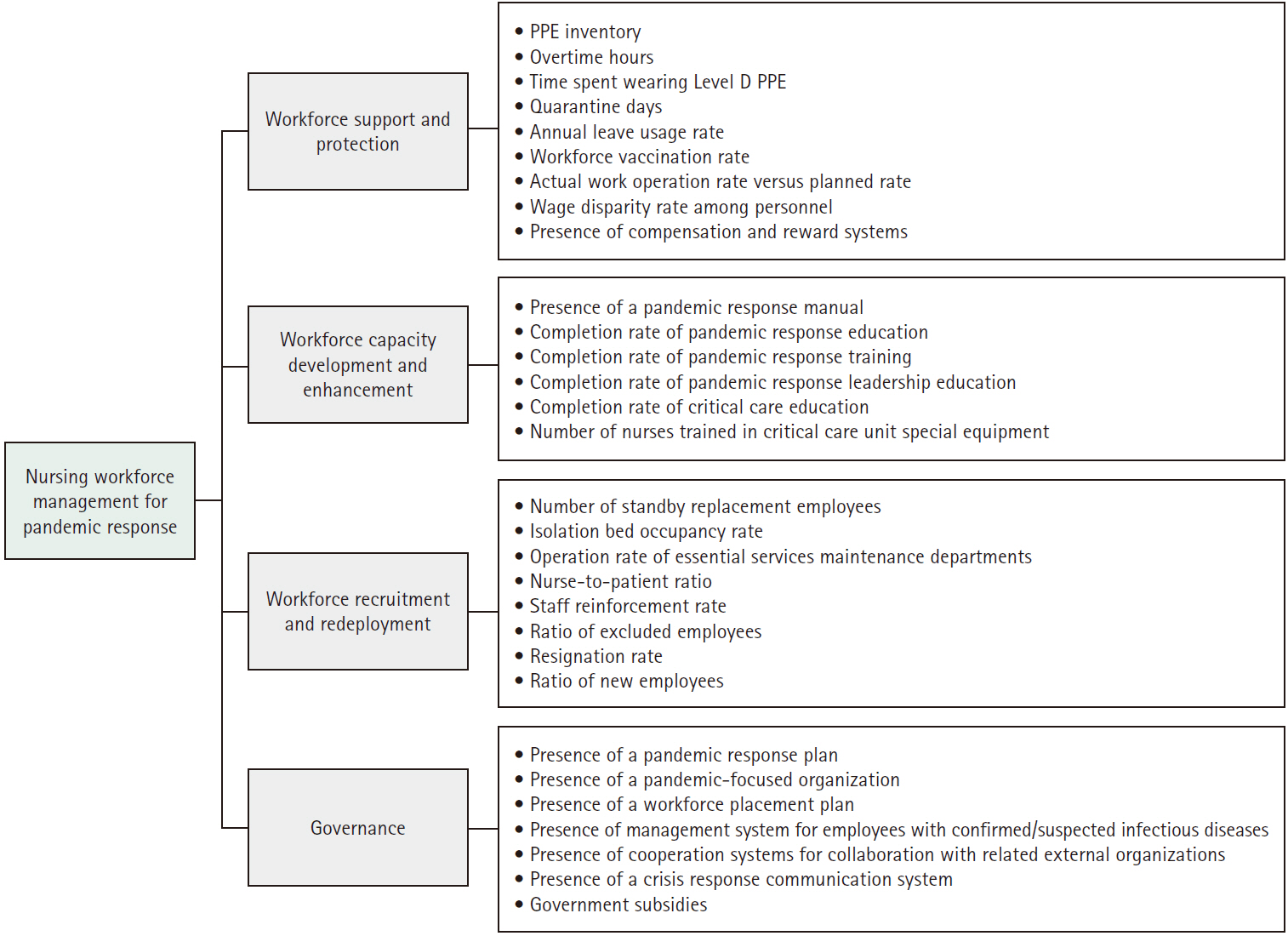
- Analysis of the relative importance of key factors in nursing workforce management for pandemic response in general hospitals and long-term care hospitals
- Jeong Eun Cha, Eun Kyoung Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):236-248. Published online May 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24112
- Funded: Government-wide R&D Fund for Infectious Disease Research
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the key factors in nursing workforce management for pandemic response in general hospitals and long-term care hospitals and to analyze the relative importance of these factors.
Methods
A validity test was conducted with experts to select four categories and 30 key factors related to nursing workforce management for pandemic response. Surveys were collected from 25 nursing managers in general hospitals and 21 nursing managers in long-term care hospitals, and the relative importance of the key factors was analyzed using the analytic hierarchy process method.
Results
Differences were found between the two groups in the relative importance of nursing workforce management for pandemic response. Specifically, the highest-ranking category was “workforce recruitment and redeployment” for general hospitals, but “workforce support and protection” for long-term care hospitals. The most important factor regarding nursing workforce management was the “nurse-to-patient ratio” for both general and long-term care hospitals.
Conclusion
General and long-term care hospitals need to establish nursing workforce management strategies to effectively respond to pandemics with appropriate consideration of the relative importance and prioritization of key factors based on hospital characteristics.
- 1,823 View
- 72 Download

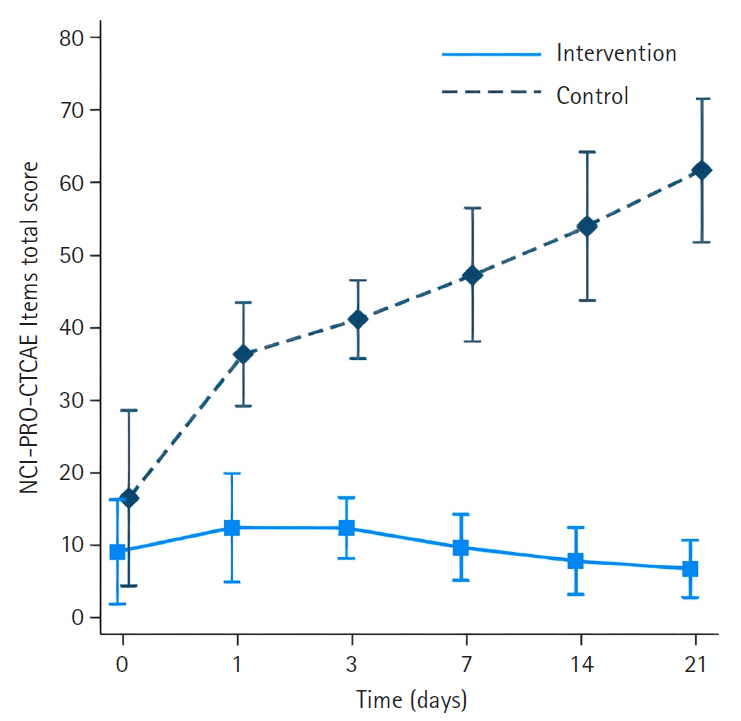
- Effectiveness of a mobile application for tracking symptoms and enhancing symptom management among breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy in Bangkok, Thailand: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Duangrat Kaveenuntachai, Supawan Jaiboon, Bualuang Sumdaengrit, Chureeporn Silaguntsuti, Arveewan Vittayatigonnasak, Pornchan Sailamai
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):178-190. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25011
- Funded: Navamindradhiraj University Research Fund
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study evaluated the effectiveness of a mobile application in tracking symptoms and improving symptom management and quality of life (QoL) among breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in Thailand.
Methods
A non-randomized controlled trial was used, with 25 participants in the intervention group and 25 in the control group. Research instruments included a demographic data form, the NCI-PRO-CTCAE Items-Thai-Thailand version 1.0, and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Core Questionnaire and Breast Cancer-Specific Module.
Results
The intervention group had significantly less severe side effects than the control group, with mean differences of –23.33 (95% confidence interval [CI], –27.82 to –18.83) on day 1, –28.18 (95% CI, –33.22 to –23.14) on day 3, –34.63 (95% CI, –40.18 to –29.08) on day 7, –42.56 (95% CI, –48.72 to –36.40) on day 14, and –51.31 (95% CI, –58.13 to –44.48) on day 21 (p<.001 for all). On day 21, participants in the intervention group reported significantly higher scores in the Global Health QoL and Functional Scales compared to the control group (p<.001). Additionally, intervention group participants reported lower scores on the Symptom Scales and higher scores on the Functional Scales than those in the control group (p<.001).
Conclusion
The ChemoPro application helped manage chemotherapy-related symptoms and was associated with improved symptom monitoring and QoL. Nonetheless, the study was limited by a small sample size and restriction to Android users. Future research with larger and more diverse populations is recommended before broader implementation in clinical practice.
- 4,053 View
- 207 Download

- Core domains for pre-registered nurses based on program outcomes and licensing competencies
- Soyoung Yu, Hye Young Kim, Jeung-Im Kim, JuHee Lee, Ju-Eun Song, Hyang Yuol Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):249-268. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25017
- Funded: Korean Society of Nursing Science, Soonchunhyang University
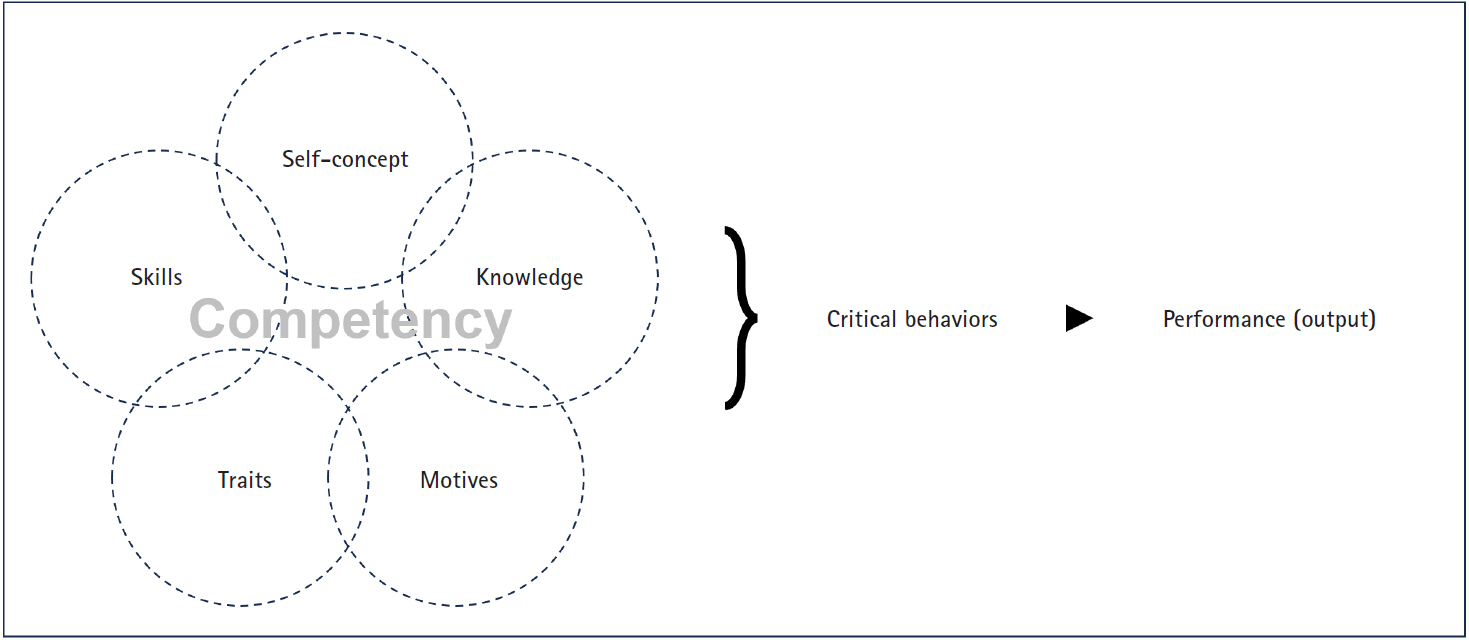
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify core domains for pre-registered nurses by comparing licensing competencies with program outcomes (POs) in undergraduate nursing education. This was accomplished in preparation for the transition of the Korean Nurse Licensing Examination (KNLE) from a tradition seven-subject format to a newly integrated, competency-based single-subject format that reflects current trends in nursing assessment.
Methods
A literature review and survey were conducted. From 828 studies retrieved via PubMed, CINAHL, and Google Scholar using keywords such as “newly graduated registered nurses” and “competency OR competence,” 18 were selected according to pre-established inclusion and exclusion criteria. Documents from national and international nursing organizations were included to extract relevant licensing competencies. We also reviewed POs from all undergraduate nursing schools in South Korea to align educational outcomes with the identified core domains.
Results
The core domains identified were clinical performance and decision-making, professional attitudes and ethics, communication and interpersonal skills, leadership and teamwork, quality improvement and safety, health promotion and prevention, and information technology and digital health. These domains showed strong alignment with POs under the fourth-cycle accreditation standards.
Conclusion
It concludes the seven core domains will be appropriate for evaluating pre-registered nurses in the integrated KNLE. Based on the seven identified core domains, expert consensus should be sought in the next phase to support the development of integrated, competency-based test items grounded in these domains.
- 3,874 View
- 150 Download

Review Paper
- A review of domestic and international contexts for establishing a communication platform for early-career nurse scientists
- Jeung-Im Kim, Jin-Hee Park, Hye Young Kim, Mi Yu, Sun Joo Jang, Yeonsoo Jang, Sangeun Jun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):317-325. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25041
- Funded: Korean Society of Nursing Science, Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies, Soonchunhyang University
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
As nursing continues to advance through digital health, clinical specialization, and interdisciplinary research, early-career nurse scientists are central to advancing innovation. However, Korea lacks a structured platform to support their research, collaboration, and career development. This review aimed to identify the needs of early-career nurse scientists and examine international best practices to guide the creation of an effective communication platform.
Methods
This study involved a secondary analysis of the final report from the project “Establishment of a communication platform for young nursing scientists,” carried out by the Korean Society of Nursing Science. The report comprises data from focus group interviews with domestic graduate students and early-career researchers, a literature review of international communication and support systems, and a global policy analysis related to young nursing scientists. Based on this report, the present review synthesizes key findings and draws implications for the development of a communication platform in Korea.
Results
International examples, such as grant writing programs, mentoring initiatives, and digital collaboration hubs, showed positive outcomes in strengthening research capacity and promoting the professional growth of nurse scientists. Based on these findings, key considerations for platform development include: (1) establishing clear leadership and a participatory governance model; (2) providing demand-driven content such as research guides, mentoring, and mental health resources; (3) implementing mechanisms to ensure sustainability, content quality, and user data protection; and (4) designing an integrated platform that fosters synergy across research, policy development, education, and global networking.
Conclusion
A digital platform for early-career nurse scientists should function not merely as an information portal, but also as dynamic infrastructure for collaboration, mentorship, and growth. It is recommended that the Korean Society of Nursing Science spearhead this initiative, with governmental support, to enhance the research capacity and expand the global engagement of Korean nursing scientists.
- 2,285 View
- 77 Download

Research Papers
- Serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression on the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety in high-risk pregnant couples of South Korea
- Mihyeon Park, Sukhee Ahn
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):19-33. Published online February 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24070
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study examined the direct effects of fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression on anxiety in pregnant women with high-risk pregnancy-related conditions and their husbands. Furthermore, it aimed to explore the serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression in the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety.
Methods
A survey-based study was conducted among pregnant women diagnosed with high-risk pregnancy conditions at 24–32 weeks and their husbands, recruited from a pregnant women’s online community between January 20, 2021 and July 20, 2022. Data were collected from 294 individuals (147 couples) using self-report questionnaires. Correlations between variables were analyzed using the IBM SPSS software ver. 26.0 (IBM Corp.), and the mediation effects were assessed using the PROCESS macro, model 6.
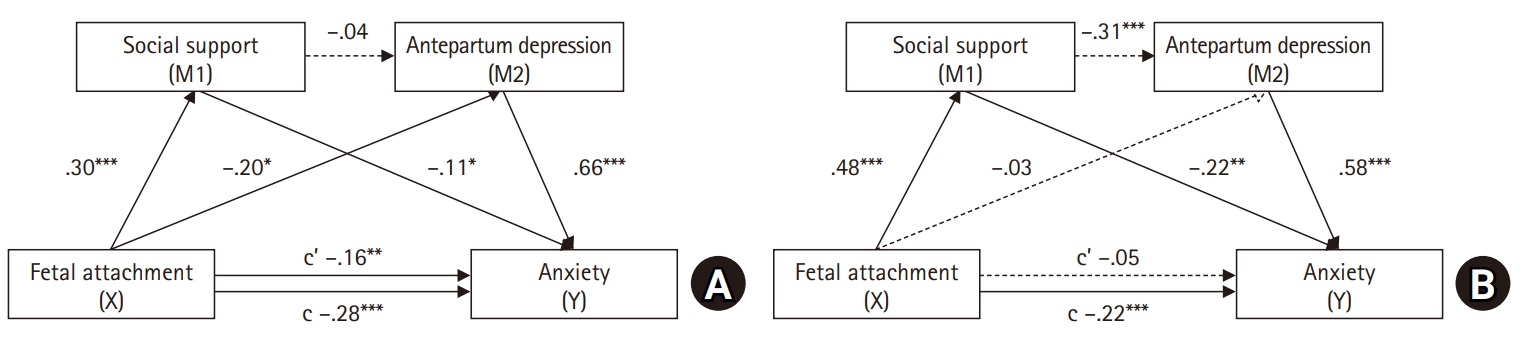
Results
In the maternal model, maternal-fetal attachment directly affected anxiety (p=.005), with antepartum depression partially mediating this relationship (95% confidence interval [CI], –0.26 to –0.01). In the paternal model, paternal-fetal attachment had no direct effect on anxiety (p=.458). However, social support and antepartum depression fully mediated the relationship between paternal-fetal attachment and anxiety (95% CI, –0.14 to –0.03).
Conclusion
The findings indicate that social support in the relationship between fetal attachment and depression in high-risk pregnant women and their partners can have direct or indirect effects on the negative emotions of high-risk pregnant couples. It is necessary to assess the level of anxiety in couples experiencing high-risk pregnancies and provide comprehensive nursing interventions that address fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression in order to reduce anxiety.
- 2,530 View
- 243 Download

- Factors influencing smartphone overdependence in university students: an ecological model: a descriptive study
- Jeong Soon Yu, Myung Soon Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):64-80. Published online February 20, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24092
- Funded: Hallym University Research Fund
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
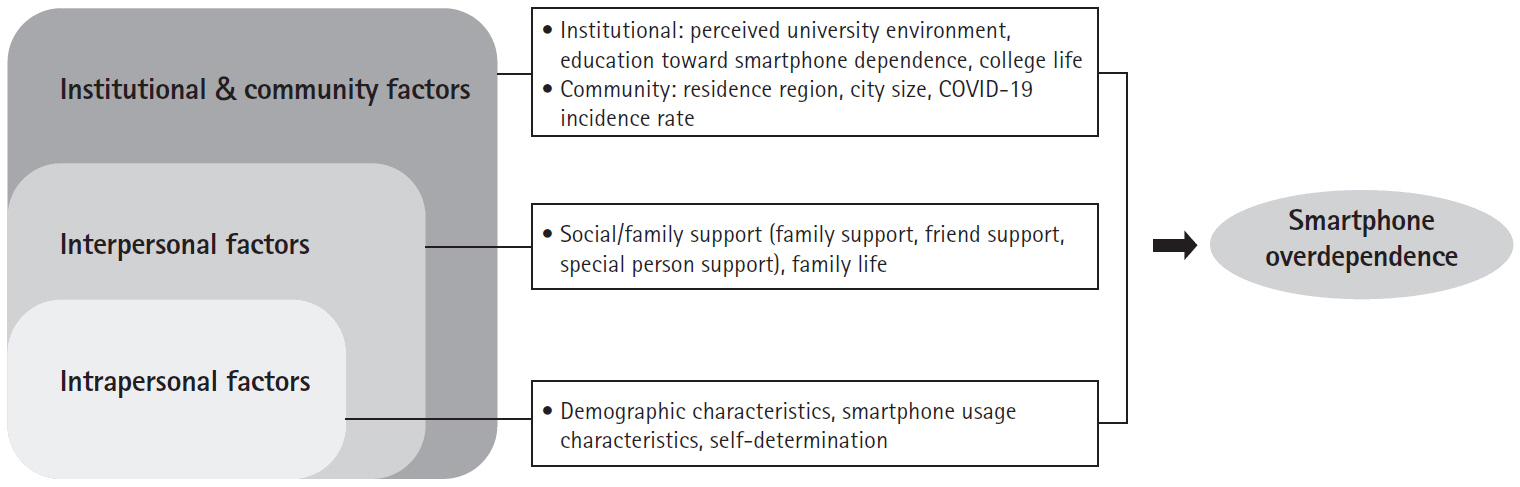
ePub - Purpose
This study investigated the factors influencing smartphone overdependence in university students using an ecological model and descriptive research.
Methods
Data were collected from 482 students at 13 universities in the six regions in South Korea from October 20, 2020, to March 25, 2021. Data analysis involved descriptive statistics, the chi-square test, the independent samples t-test, analysis of variance, and hierarchical multiple regression.
Results
The significant ecological factors influencing smartphone overdependence included self-awareness of smartphone overdependence (β=.33, p<.001), autonomy (β=–.25, p<.001), average daily smartphone usage time (β=.18, p<.001), gender (β=.15, p=.001), college year (β=.15, p=.020), forming relationships with others as a motivation for smartphone use (β=–.15, p=.008), friend support (β=.14, p=.006), and age (β=–.12, p=.047). The model explained 34.9% of the variance.
Conclusion
The study emphasized the role of personal and interpersonal factors, in smartphone overdependence among university students. Tailored intervention strategies are necessary to address smartphone overdependence, considering the unique characteristics of students’ environments. A significant aspect of this study is that it provides an explanation of the multidimensional factors contributing to smartphone overdependence among university students, including intrapersonal, interpersonal, and environmental influences.
- 3,586 View
- 193 Download

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


