Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 55(3); 2025 > Article
-
Research Paper
장애인지원주택 내 장애인 건강관리 지원업무 시스템 분석: SEIPS framework 기반 포커스 그룹 연구 -
이혜선1
 , 남혜진1
, 남혜진1 , 김보혜1,2
, 김보혜1,2 , 윤주영1,2,3
, 윤주영1,2,3
- Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
-
Haesun Lee1
 , Hye Jin Nam1
, Hye Jin Nam1 , Bohye Kim1,2
, Bohye Kim1,2 , Ju Young Yoon1,2,3
, Ju Young Yoon1,2,3
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2025;55(3):454-467.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25018
Published online: August 4, 2025
1서울대학교 간호대학
2서울대학교 간호대학 BK21 미래간호인재 양성사업단
3서울대학교 간호과학연구소
1College of Nursing, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
2Center for Human-Caring Nurse Leaders for the Future by Brain Korea 21 (BK 21) Four Project, College of Nursing, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
3Research Institute of Nursing Science, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding author: Ju Young Yoon College of Nursing, Seoul National University, 103 Daehak-ro, Jongno-gu, Seoul 03080, Korea E-mail: yoon26@snu.ac.kr
© 2025 Korean Society of Nursing Science
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NoDerivs License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0) If the original work is properly cited and retained without any modification or reproduction, it can be used and re-distributed in any format and medium.
- 1,445 Views
- 89 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study conducted a work-system analysis using the Systems Engineering Initiative for Patient Safety (SEIPS) framework to assess the flow of health-related information, and the current status of health management tasks for individuals with disabilities (IWD) in supportive housing.
-
Methods
- This qualitative study utilized focus groups. Participants included a head of supportive housing, a team leader, a care coordinator and three personal support workers for IWD. Semi-structured interviews were guided by the SEIPS framework to explore the components of persons, tasks, tools and technology, organization, and environments.
-
Results
- This study identified five key themes within the five SEIPS components: (1) disparities in role identity and health literacy among staff, (2) challenges in health care support reflecting a person-centered approach, (3) barriers in health-related information exchange and communication tools, (4) needs for organizational strategies or information communication, and (5) needs for integrating health-related information across external healthcare institutions. Additionally, 10 sub-themes were identified.
-
Conclusion
- These findings provide a comprehensive system-wide perspective and offer insights into the systematic approaches needed to improve healthcare processes and structures within disability supportive housing. Specifically, healthcare providers and effective tools for integrating health-related information are identified as critical components.
서론
방법
1) 질문개발
2) FGI를 통한 자료수집
결과
1) 인적 요인: 인력 간 역할정체성 및 건강정보이해능력의 차이
(1) 건강관리 지원 권한과 역할에 대한 인력 간 인식 차이
(2) 장애인활동지원사의 낮은 건강정보이해능력
2) 업무요인: 장애당사자의 자기결정권이 반영된 건강관리 지원의 어려움
(1) 장애유형별 맞춤형 건강관리 지원 접근의 어려움
(2) 건강신념 차이에서 비롯된 건강관리 지원의 어려움
3) 기술과 도구요인: 건강 관련 정보 공유 및 의사소통 지원도구의 부재
(1) 유의미한 건강 관련 정보 공유의 부족
(2) 정보 공유를 위한 의사소통 지원도구의 필요성
4) 조직적 요인: 상호신뢰 기반 의사소통체계 확립의 필요성
(1) 정확한 정보 공유를 위한 구성원 간 상호신뢰 구축의 필요성
(2) 건강 관련 정보 및 축적을 위한 체계 마련
5) 환경적 요인: 외부 보건의료 기관과 건강 관련 정보 통합의 필요성
(1) 외부 의료기관과의 유기적 소통창구의 필요성
(2) 건강 관련 정보 통합관리 필요성
고찰
결론
-
Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
Acknowledgements
None.
-
Funding
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (No. 2022R1I1A207290712).
-
Data Sharing Statement
Please contact the corresponding author for data availability.
-
Supplementary Data
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25018.
Supplementary Table 1.
-
Author Contributions
Conceptualization or/and Methodology: JYY, HL, HJN, BK. Data curation or/and Analysis: JYY, HL. Funding acquisition: JYY. Investigation: JYY, HL. Project administration or/and Supervision: JYY. Resources or/and Software: JYY. Validation: JYY. Visualization: JYY, HL, HJN, BK. Writing: original draft or/and Review & Editing: JYY, HL, HJN. Final approval of the manuscript: all authors.
Article Information
| Position | Role |
|---|---|
| Head of center | • Human resource management |
| • Supervising coordinators’ worka) | |
| Team leader | • Conflict management |
| • Right advocacy activities | |
| • Legal issue resolution coordination | |
| Health coordinator | • Conducting intake of health-related information from other staff members and IWD |
| • Reviewing health-related information | |
| • Carrying out follow-up for missing health-related information | |
| • Performing face-to-face assessments | |
| • Identifying health problems | |
| • Determining what information to send to the primary health center (e.g., clinics, etc.) | |
| • Visiting hospital/clinic with IWD | |
| • Helping communicating between health provider and IWD | |
| • Organizing and integrating information | |
| • Sharing health-related information in team meeting | |
| • Monitoring health behavior (e.g., medication, activities, etc.) | |
| • Updating the assessment information | |
| • Educating the IWD and support staff about the health promotion activity | |
| • Providing feedback on personal support workers’ strategies to promote health management in daily living | |
| • Communicating with external healthcare providers in the context of disciplinary actions | |
| Personal support worker | • Helping with bathing, dressing, grooming, and toileting |
| • Assisting with mobility and transfer | |
| • Accompanying individuals to medical appointments, workplace, and community events, etc. | |
| • Supporting proper nutrition through meal preparation | |
| • Reporting changes in IWDs’ health status | |
| • Assisting with medication management | |
| • Assisting with rehabilitation exercises or therapies as directed by healthcare providers |
- 1. Lee S, Lee B, Kim H. Major issues and tasks of the deinstitutionalization for the people with disabilities: a focus on Seoul. Health Welf. 2019;21(4):69-86. https://doi.org/10.23948/kshw.2019.12.21.4.69Article
- 2. Kim JY, Kang MW, Seo WY, Lee JW. Chronic diseases, health behaviors, and mortality in persons with disabilities: an analysis of the National Health Insurance Service-Health Screening (NHIS-HEALS) database. Health Soc Welf Rev. 2020;40(2):121-150. https://doi.org/10.15709/hswr.2020.40.2.121Article
- 3. Seo H, Min S, Kim J, Lee S. A study on ways to build a support housing system for de-institutionalized people with disabilities. Korea’s Disabled People’s Development Institute; 2021. Report No.: 21-15.
- 4. Seoul Welfare Foundation (SWF). Operational manual for Seoul support housing for people with disabilities [Internet]. SWF; c2021 [cited Feb 5]. Available from: https://www.welfare.seoul.kr/idl/contents/idlcomm1-4.do?&schM=view&page=1&viewCount=10&id=19945&schBdcode=&schGroupCode=
- 5. Nam HJ, Lee H, Park HN, Lee S, Kim B, Yoon JY. Support needs for health promotion of community-dwelling people with disabilities: perspectives of operators managing disability supportive housing. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2024;54(2):211-223. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23143ArticlePubMed
- 6. Rimmer JH, Rowland JL. Health promotion for people with disabilities: implications for empowering the person and promoting disability-friendly environments. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2008;2(5):409-420. https://doi.org/10.1177/1559827608317397Article
- 7. Lee Y. The study on the factors of life satisfaction among disabled elderly focused on comparison between aging with disability and disability with aging. Korean J Gerontol Soc Welf. 2013;(62):35-58. https://doi.org/10.21194/kjgsw..62.201312.35Article
- 8. Holden RJ, Carayon P, Gurses AP, Hoonakker P, Hundt AS, Ozok AA, et al. SEIPS 2.0: a human factors framework for studying and improving the work of healthcare professionals and patients. Ergonomics. 2013;56(11):1669-1686. https://doi.org/10.1080/00140139.2013.838643ArticlePubMed
- 9. Wiegmann DA, Eggman AA, Elbardissi AW, Parker SH, Sundt TM 3rd. Improving cardiac surgical care: a work systems approach. Appl Ergon. 2010;41(5):701-712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apergo.2009.12.008ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Carayon P, Schoofs Hundt A, Karsh BT, Gurses AP, Alvarado CJ, Smith M, et al. Work system design for patient safety: the SEIPS model. Qual Saf Health Care. 2006;15(Suppl 1):i50-i58. https://doi.org/10.1136/qshc.2005.015842ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Strauven G, Vanhaecht K, Anrys P, De Lepeleire J, Spinewine A, Foulon V. Development of a process-oriented quality improvement strategy for the medicines pathway in nursing homes using the SEIPS model. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2020;16(3):360-376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sapharm.2019.06.003ArticlePubMed
- 12. Barbieri DF, Srinivasan D, Ulrich J, Ranganathan S, Chang C, Gerac JA, et al. Systems-based framework for clinical decision-support system integration for patient sepsis management: a theoretical application of the SEIPS model. Hum Factors Healthc. 2025;7:100098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hfh.2025.100098Article
- 13. Hwang JI, Kim SW, Park HA. Relationships between nurses' work system, safety-related performance, and outcomes: a structural equation model. J Patient Saf. 2021;17(8):e1638-e1645. https://doi.org/10.1097/PTS.0000000000000866ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Doody O, Slevin E, Taggart L. Focus group interviews in nursing research: part 1. Br J Nurs. 2013;22(1):16-19. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.2013.22.1.16ArticlePubMed
- 15. Dilshad RM, Latif MI. Focus group interview as a tool for qualitative research: an analysis. Pak J Soc Sci. 2013;33(1):191-198.
- 16. Holden RJ, Carayon P. SEIPS 101 and seven simple SEIPS tools. BMJ Qual Saf. 2021;30(11):901-910. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs-2020-012538ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Krueger RA, Casey MA. Focus groups: a practical guide for applied research. 5th ed. Sage Publications; 2014. 280 p.
- 18. Elo S, Kyngäs H. The qualitative content analysis process. J Adv Nurs. 2008;62(1):107-115. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2007.04569.xArticlePubMed
- 19. Lincoln YS, Guba EG. Naturalistic inquiry. Sage Publications; 1985. 146 p.
- 20. Korea Disabled people’s Developmental Institute. A study on strategies to enhance the professionalism of personal assistants for persons with disabilities. Korea Disabled people’s Developmental Institute; 2023. Report No.: 23-14.
- 21. Yuen EY, Knight T, Ricciardelli LA, Burney S. Health literacy of caregivers of adult care recipients: a systematic scoping review. Health Soc Care Community. 2018;26(2):e191-e206. https://doi.org/10.1111/hsc.12368ArticlePubMed
- 22. Nutt M, Hungerford C. Nurse care coordinators: definitions and scope of practice. Contemp Nurse. 2010;36(1-2):71-81. https://doi.org/10.5172/conu.2010.36.1-2.071ArticlePubMed
- 23. Schultz EM, McDonald KM. What is care coordination? Int J Care Coord. 2014;17(1-2):5-24. https://doi.org/10.1177/2053435414540615Article
- 24. McDonald KM, Sundaram V, Bravata DM, Lewis R, Lin N, Kraft SA, et al. Closing the quality gap: a critical analysis of quality improvement strategies (Vol. 7: care coordination). Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2007. Report No.: 04(07)-0051-7.
- 25. Yang J, Sun A, Choi M, Sohn M. Community care health human resources management alternatives: cases from Korea, Japan, and the United Kingdom. Health Welf. 2023;25(4):95-139. https://doi.org/10.23948/kshw.2023.12.25.4.95Article
- 26. Ruiz S, Giuriceo K, Caldwell J, Snyder LP, Putnam M. Care coordination models improve quality of care for adults aging with intellectual and developmental disabilities. J Disabil Policy Stud. 2020;30(4):191-201. https://doi.org/10.1177/1044207319835195Article
- 27. Williamson HJ, Perkins EA, Levin BL, Baldwin JA, Lulinski A, Armstrong MI, et al. Implementation of Medicaid managed long-term services and supports for adults with intellectual and/or developmental disabilities in Kansas. Intellect Dev Disabil. 2017;55(2):84-96. https://doi.org/10.1352/1934-9556-55.2.84ArticlePubMed
- 28. Conway A, O'Donnell C, Yates P. The effectiveness of the nurse care coordinator role on patient-reported and health service outcomes: a systematic review. Eval Health Prof. 2019;42(3):263-296. https://doi.org/10.1177/0163278717734610ArticlePubMed
- 29. Bickenbach J. The world report on disability. Disabil Soc. 2011;26(5):655-658. https://doi.org/10.1080/09687599.2011.589198Article
- 30. Judd MJ, Dorozenko KP, Breen LJ. Workplace stress, burnout and coping: a qualitative study of the experiences of Australian disability support workers. Health Soc Care Community. 2017;25(3):1109-1117. https://doi.org/10.1111/hsc.12409ArticlePubMed
- 31. Windley D, Chapman M. Support workers within learning/intellectual disability services perception of their role, training and support needs. Br J Learn Disabil. 2010;38(4):310-318. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3156.2010.00610.xArticle
- 32. Ministry of Health & Welfare. Overview of the personal supportive worker service for persons with disabilities [Internet]. Ministry of Health & Welfare; c2024 [cited 2025 May 2]. Available from: https://www.mohw.go.kr/synap/doc.html?fn=202405171619348781.pdf&rs=/upload/result/202505/
- 33. Reinhard SC, Given B, Petlick NH, Bemis A. Supporting family caregivers in providing care. In: Hughes RG, editor. Patient safety and quality: an evidence-based handbook for nurses. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2008. p. 341-404.
- 34. Glanze K, Rimer BK, Viswanath K. Health behavior: theory, research, and practice. 5th ed. Wiley; 2024. 512 p.
- 35. Ravesloot C, Ruggiero C, Ipsen C, Traci M, Seekins T, Boehm T, et al. Disability and health behavior change. Disabil Health J. 2011;4(1):19-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dhjo.2010.05.006ArticlePubMed
- 36. Taberna M, Gil Moncayo F, Jané-Salas E, Antonio M, Arribas L, Vilajosana E, et al. The multidisciplinary team (MDT) approach and quality of care. Front Oncol. 2020;10:85. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.00085ArticlePubMedPMC
- 37. Uitdewilligen S, Waller MJ. Information sharing and decision‐making in multidisciplinary crisis management teams. J Organ Behav. 2018;39(6):731-748. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.2301Article
- 38. World Health Organization (WHO). National ehealth strategy toolkit [Internet]. WHO; 2012 [cited 2025 Jan 30]. Available from: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/75211/9789241548465_eng.pdf?sequence=1
- 39. World Health Organization (WHO). Framework for action on inter-professional education and collaborative practice [Internet]. WHO; 2010 [cited 2025 Jan 30]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/framework-for-action-on-interprofessional-education-collaborative-practice
- 40. Kitsios F, Stefanakakis S, Kamariotou M, Dermentzoglou L. Digital service platform and innovation in healthcare: measuring users’ satisfaction and implications. Electronics. 2023;12(3):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030662Article
- 41. Lee J, Park S, Cho MH, Kang JW, Kim M, Choi S, et al. Development of a web-based care networking system to support visiting healthcare professionals in the community. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023;23(1):1427. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-023-10434-6ArticlePubMedPMC
- 42. Fairhall N, Sherrington C, Kurrle SE, Lord SR, Lockwood K, Howard K, et al. Economic evaluation of a multifactorial, interdisciplinary intervention versus usual care to reduce frailty in frail older people. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2015;16(1):41-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2014.07.006ArticlePubMed
- 43. Edmondson AC, Lei Z. Psychological safety: the history, renaissance, and future of an interpersonal construct. Annu Rev Organ Psychol Organ Behav. 2014;1(1):23-43. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-031413-091305Article
- 44. Siemsen E, Roth AV, Balasubramanian S, Anand G. The influence of psychological safety and confidence in knowledge on employee knowledge sharing. Manuf Serv Oper Manag. 2009;11(3):429-447. https://doi.org/10.1287/msom.1080.0233Article
- 45. Ridings CM, Gefen D, Arinze B. Some antecedents and effects of trust in virtual communities. J Strateg Inf Syst. 2002;11(3-4):271-295. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0963-8687(02)00021-5Article
- 46. O'donovan R, Mcauliffe E. A systematic review of factors that enable psychological safety in healthcare teams. Int J Qual Health Care. 2020;32(4):240-250. https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzaa025ArticlePubMed
- 47. Dusenberry L, Robinson J. Building psychological safety through training interventions: manage the team, not just the project. IEEE Trans Prof Commun. 2020;63(3):207-226. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPC.2020.3014483Article
- 48. O'Donovan R, McAuliffe E. A systematic review exploring the content and outcomes of interventions to improve psychological safety, speaking up and voice behaviour. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20(1):101. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-4931-2ArticlePubMedPMC
- 49. Korea Disabled people’s Developmental Institute. 2024 Disability statistics yearbook. Korea Disabled people’s Developmental Institute; 2024. Report No.: 24-05.
References
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

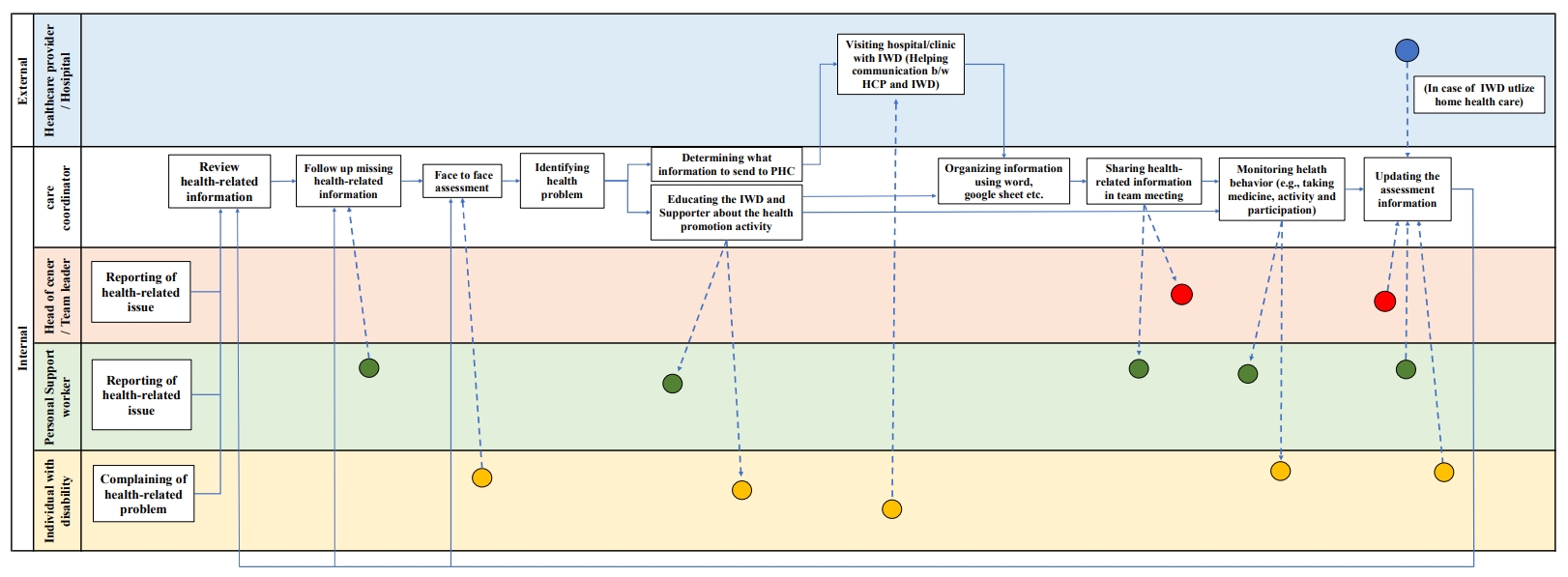
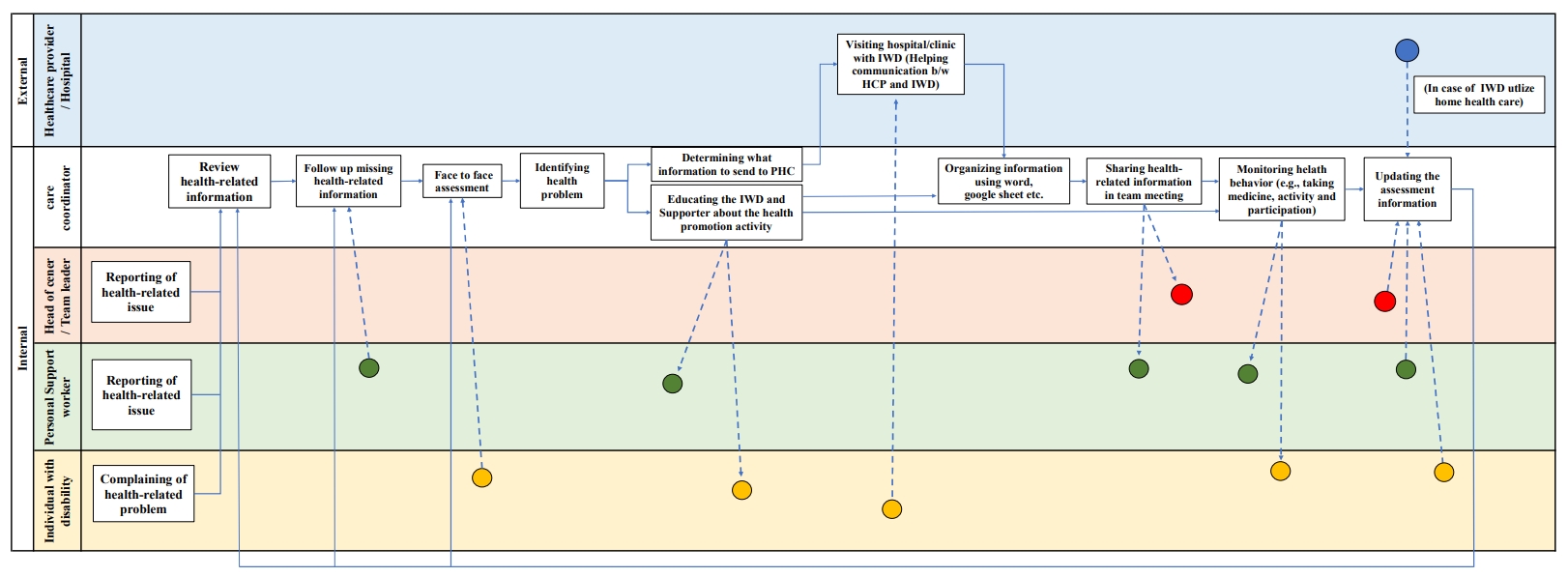
Fig. 1.
| Participant no. (focus group) | Gender | Age (yr) | Occupation | Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (1) | F | 40 | Social worker | Head of supportive housing |
| B (1) | M | 54 | Social worker | Team leader |
| C (1) | F | 38 | Occupational therapist | Care-coordinator |
| D (2) | F | 69 | Personal support worker | Personal support workers |
| E (2) | F | 55 | Personal support worker | Personal support workers |
| F (2) | M | 57 | Personal support worker | Personal support workers |
| Position | Role |
|---|---|
| Head of center | • Human resource management |
| • Supervising coordinators’ work |
|
| Team leader | • Conflict management |
| • Right advocacy activities | |
| • Legal issue resolution coordination | |
| Health coordinator | • Conducting intake of health-related information from other staff members and IWD |
| • Reviewing health-related information | |
| • Carrying out follow-up for missing health-related information | |
| • Performing face-to-face assessments | |
| • Identifying health problems | |
| • Determining what information to send to the primary health center (e.g., clinics, etc.) | |
| • Visiting hospital/clinic with IWD | |
| • Helping communicating between health provider and IWD | |
| • Organizing and integrating information | |
| • Sharing health-related information in team meeting | |
| • Monitoring health behavior (e.g., medication, activities, etc.) | |
| • Updating the assessment information | |
| • Educating the IWD and support staff about the health promotion activity | |
| • Providing feedback on personal support workers’ strategies to promote health management in daily living | |
| • Communicating with external healthcare providers in the context of disciplinary actions | |
| Personal support worker | • Helping with bathing, dressing, grooming, and toileting |
| • Assisting with mobility and transfer | |
| • Accompanying individuals to medical appointments, workplace, and community events, etc. | |
| • Supporting proper nutrition through meal preparation | |
| • Reporting changes in IWDs’ health status | |
| • Assisting with medication management | |
| • Assisting with rehabilitation exercises or therapies as directed by healthcare providers |
| Components | Themes | Sub-themes | Contents |
|---|---|---|---|
| Person(s) | Disparities in role identity and health literacy across staff | Differences in perceptions of authority and responsibility for health management support among staff | Health coordinators apply specialized knowledge from their health and medical studies to support the health management of individuals with disabilities, while personal support workers rely on informal sources like caregiving experience, online research, and advice from acquaintances. |
| Limited health literacy among personal support workers | Personal support workers relied primarily on their own experiences when identifying health-related issues of individuals with disabilities, and their interpretation of health information was often inconsistent. | ||
| Tasks | Challenges in health care support reflecting a person-centered approach | Challenges in health care tasks considering the characteristics of different types of disabilities | High level of job demands in caring for individuals with disabilities, considering their disability-related characteristics |
| Challenges in health care tasks arising from differences in health beliefs | When individuals with disabilities have low health beliefs or lack awareness of the need for health management, it creates conflicts between the support staff's role and the autonomy of the individuals | ||
| Tools and technology | Barriers in health-related information exchange and communication tools | Lack of meaningful health-related information exchange | Need to implement a checklist or platform that enables personal support workers to assess the health status of individuals with disabilities |
| Needs for communication support tools for information sharing | Introducing a platform to facilitate real-time monitoring and sharing of information among support staff | ||
| Organization | Needs for organizational strategies or information communication | Needs for establishing mutual trust among staff for exchanging accurate information | Establishing a psychologically safe working environment to enhance information sharing without fear. |
| Needs for establishing a system for the sharing and accumulation of health-related information | Improving organizational systems for communicating and collecting information and approaches used in supporting the health of persons with disabilities. | ||
| External environment | Needs for integrating health-related information across external healthcare institutions | Need for an integrated communication channel with external healthcare institutions | Requirement for an information exchange system among support staff and primary care organizations to facilitate extensive communication with external healthcare institutions |
| Needs for platform to integrate health-related information from various external sources | Design and deployment of a platform to create a comprehensive health record system that consolidates health-related data across healthcare providers, facilitating seamless access and enhancing care coordination. |
F, female; M, male.
IWD, individual with disability. In supportive housing, coordinators are employed to support the health, financial management, and housing management of IWD.
SEIPS, Systems Engineering Initiative for Patient Safety.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

