Most cited articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse articles > Most cited articles
Most-cited are based on citations from 2024 ~ 2026.
- Legal and Practical Solutions for the Expanding the Roles of Medical Support Staff Nurses
- Su Jung Choi, Min Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):300-310. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24075
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Medical support staff nurses have traditionally performed various supportive tasks for physicians, often extending beyond standard nursing roles. Despite these long-standing practices, there is a notable lack of official recognition and legal protection for these expanded responsibilities, leading to increasing legal concerns. Therefore, there is a need for proposing a rational solution to address these issues.
Methods
The number of medical support staff nurses is rising, particularly as they fill gaps left by the 2024 resident physician strike. The study focuses on identifying potential challenges arising from this shift and developing strategic improvements to address these challenges effectively.
Results
This study proposed legally expanding the scope of nursing duties and creating a robust system for training and certifying nurses to handle these responsibilities effectively, by integrating these roles within the advanced practice nurse (APN) framework.
Conclusion
Integrating these roles within the framework of APN can offer a sustainable and legally sound solution to the ongoing healthcare crisis, ensuring patient safety and safeguarding healthcare workers’ legal rights. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of role conflict and job stress on turnover intention among Korean physician assistant nurses: A cross-sectional study
Jin-Won Lee, Eun-Hi Choi, Ji-Sun Back
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Legislation of Medical Support Tasks in the Nursing Act as a Foundation for Nursing Professionalism and Role Expansion
Su Jung Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(2): 69. CrossRef - Role Transformation and Adaptation of Physician Assistants during the 2024 Medical Workforce Shortage: A Phenomenological Study
Tae Yeong Yang, Nahyun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 259. CrossRef - Effects of Role Conflict, Work Environment, and Meaning of Work on Job Embeddedness among Physician Assistants
Kwang Hoon Seo, Tae Yeong Yang, Nam Gyu Park, Jung Eun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 249. CrossRef - Media discourse on physician assistant nurses in South Korea: a text network and topic modeling approach
Young Gyu Kwon, Daun Jeong, Song Hee Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Chan Woong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(3): 388. CrossRef - Comparison of educational needs and priorities for work-related laws between hospital and community-based nurses
Jeonghyun Kim, Min Kyoung Han, Minjae Lee, Sujin Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(3): 400. CrossRef - Predictors of end-of-life care among emergency nurses: A cross-sectional study in Korea
Ji Seon Lee, Sook Jung Kang
Australasian Emergency Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Clinical Practice Nurses' Self-Leadership, Role Conflict, and Practice Environment on Patient Safety Competency
Jeong Hwa Heo, Ji Hyun Sung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 458. CrossRef - Strategies for expanding the role of advanced practice providers in the Korean nursing workforce: a mixed-methods approach
Jeong Hye Kim, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Suyoung Choi, Mimi Lee, Su Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(4): 568. CrossRef - Development and Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of the Novice Nursing Practitioner Role Transition Scale
Eun Sook Kim, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Su Jung Choi, Onam Ok, Genehee Lee, Ahyeong Song
Asian Nursing Research.2025; 19(5): 462. CrossRef - Nurses' Patient Care Experiences in a Changing Healthcare Environment Following One Year of Healthcare Policy Conflict - A Focus Group Interview
Eun Hee Kang, Yunhyung Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 280. CrossRef
- Impact of role conflict and job stress on turnover intention among Korean physician assistant nurses: A cross-sectional study
- 5,392 View
- 306 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- Sleep Deprivation and Fatigue among Nurses Working Consecutive Night Shifts: A Prospective Observational Study
- Ari Min, Jisu Seo, Minkyung Kang, Hye Chong Hong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):139-150. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23164
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify changes in sleep patterns and fatigue levels during consecutive night shifts among shift nurses and to determine the association between sleep parameters and increased fatigue levels during work.
Methods
This prospective observational study employing ecological momentary assessments was conducted using data collected from 98 shift nurses working in Korean hospitals between June 2019 and February 2021. The sleep patterns were recorded using actigraphy. The participants reported their fatigue levels at the beginning and end of each night shift in real time via a mobile link. Linear mixed models were used for the analysis.
Results
Nurses spent significantly less time in bed and had shorter sleep durations during consecutive night shifts than on off-duty days, whereas their wake times after sleep onset were much longer on off-duty days than on on-duty days. Fatigue levels were higher on the second and third night-shift days than on the first night-shift days. A shorter time spent in bed and asleep was associated with a greater increase in fatigue levels at the end of the shift than at the beginning.
Conclusion
Nurses experience significant sleep deprivation during consecutive night shifts compared with off-duty days, and this sleep shortage is associated with a considerable increase in fatigue levels at the end of shifts. Nurse managers and administrators must ensure sufficient intershift recovery time during consecutive night shifts to increase the time spent in bed and sleeping. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of digital cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia in nurses with shift work sleep disorder: Results of a randomized controlled trial
Hanna A. Brückner, Johanna Ell, Lina Kalon, Jana Strahler, Antje Ducki, Dieter Riemann, Claudia Buntrock, Kai Spiegelhalder, Dirk Lehr
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2025; 169: 105112. CrossRef - Fatigue and coping strategies among Chinese night-shift nurses: a cross-sectional study
Bin He, Yanle Zhang, Shengjun Qian, Qun Ye, Ying Ren, Zhan Wang
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigating the associations between weekend catch-up sleep and insulin resistance: NHANES cross-sectional study
Xianling Liu, Aihui Chu, Xiahao Ding
BMC Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Text Network Analysis of Nurse Managers’ Feedback Journals
Naru Kang, Shinhye Ahn, Hye Won Jeong
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sleep Quality in Shift-Working Nurses: Subjective and Objective Evaluation
Željka Dujmić, Štefica Mikšić, Ivana Barać, Josip Samardžić, Lea Maršić, Petar Samardžić, Zvjezdana Gvozdanović, Ivana Jelinčić, Blaženka Kljajić Bukvić, Marija Barišić, Davorka Čavar-Lovrić, Ružica Mrkonjić, Ivica Mihaljević, Nikolina Farčić
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2025; 23(1): 64. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of digital cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia in nurses with shift work sleep disorder: Results of a randomized controlled trial
- 12,302 View
- 421 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Temporal Exploration of New Nurses’ Field Adaptation Using Text Network Analysis
- Shin Hye Ahn, Hye Won Jeong, Seong Gyeong Yang, Ue Seok Jung, Myoung Lee Choi, Heui Seon Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):358-371. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24034
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to analyze the experiences of new nurses during their first year of hospital employment to gather data for the development of an evidence-based new nurse residency program focused on adaptability. Methods: This study was conducted at a tertiary hospital in Korea between March and August 2021 with 80 new nurses who wrote in critical reflective journals during their first year of work. NetMiner 4.5.0 was used to conduct a text network analysis of the critical reflective journals to uncover core keywords and topics across three periods. Results: In the journals, over time, degree centrality emerged as “study” and “patient understanding” for 1 to 3 months, “insufficient” and “stress” for 4 to 6 months, and “handover” and “preparation” for 7 to 12 months. Major sub-themes at 1 to 3 months were: “rounds,” “intravenous-cannulation,” “medical device,” and “patient understanding”; at 4 to 6 months they were “admission,” “discharge,” “oxygen therapy,” and “disease”; and at 7 to 12 months they were “burden,” “independence,” and “solution.” Conclusion: These results provide valuable insights into the challenges and experiences encountered by new nurses during different stages of their field adaptation process. This information may highlight the best nurse leadership methods for improving institutional education and supporting new nurses’ transitions to the hospital work environment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Text Network Analysis of Nurse Managers’ Feedback Journals
Naru Kang, Shinhye Ahn, Hye Won Jeong
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and evaluation of a stepwise clinical competency development program for new nurses: A single-group repeated-measures quasi-experimental study
Shinhye Ahn, Hye Won Jeong, Joyce Jebet Cheptum
PLOS One.2026; 21(2): e0342464. CrossRef - Analysis of clinical nurse educators’ mentoring feedback on new nurse journals at a tertiary hospital in South Korea: utilizing text network analysis
Shinhye Ahn, Hye Won Jeong
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Kirkpatrick Model Evaluation of the Development and Assessment of an Integrated, Adaptation Support Program for New Nurses Led by Clinical Nurse Educators: Using a Single, Group Repeated‐Measures Design
Hye Won Jeong
Nursing & Health Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- A Text Network Analysis of Nurse Managers’ Feedback Journals
- 3,722 View
- 93 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Moderating Effect of General Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Pregnancy Stress, Daily Hassles Stress, and Preterm Birth Risk in Women Experiencing Preterm Labor: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Hyun-Jeong Cho, Jeung-Im Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):329-339. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated the moderating role of general self-efficacy (GSE) on how stress caused by pregnancy and daily hassle affect the risk of preterm birth (PTB) in women experiencing preterm labor.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 196 pregnant women experiencing preterm labor before 37 weeks of gestation. We used IBM SPSS Statistics 27 and employed Hayes process macro version 4 (model 1) and hierarchical regression to analyze the moderating effect of GSE on the relationship between pregnancy stress, daily hassle stress, and PTB risk.
Results
Stress caused by pregnancy and daily hassle was positively correlated to PTB risk (r = .54, p < .001; r = .25, p < .001, respectively). While GSE did not significantly correlate with pregnancy stress, it negatively correlated with daily hassle stress (r = - .19, p = .009). GSE significantly moderated the relationship between combined stressors and PTB risk. As GSE levels increased, escalation in PTB risk in response to increasing stress levels was a more pronounced, highlighting a complex interaction between higher GSE levels and response to escalating stress levels. This model accounted for 39.5% of the variance in the PTB risk.
Conclusion
Higher GSE may amplify the impact of stress on PTB risk, rather than mitigate it, which suggests a more nuanced role of GSE in the stress response of pregnant women at risk of preterm labor. GSE should be considered in care strategies, and managing its impact on stress perception and responses in pregnant women is crucial. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Digital Interventions for Stress Management in Pregnant Women: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jeung-Im Kim, Joo Yun Lee, So-Hee Park
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2026; 14: e66267. CrossRef - Pregnancy stress in women at high risk of preeclampsia with their anxiety, depression, self-management capacity: a cross-sectional study
Xing Cong, Jinmei Wang, Liu Yang, Lingling Cui, Yurong Hua, Ping Gong
Frontiers in Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Anxiety, Coping, and Self-Efficacy as a Psychological Adjustment in Mothers Who Have Experienced a Preterm Birth
Agata Białas, Karolina Kamecka, Paweł Rasmus, Dariusz Timler, Remigiusz Kozłowski, Anna Lipert
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(12): 4174. CrossRef - Associations Among Pregnancy Stress, Childbirth Confidence, and COVID-19 Infection Experience in Pregnant Women in the Early Third Trimester (28–32 Weeks)
Yun-Sun Yang, Jeung-Im Kim
Journal of Korean Maternal and Child Health.2025; 29(3): 147. CrossRef
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Digital Interventions for Stress Management in Pregnant Women: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 2,023 View
- 80 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Development of the Hospital Nurses’ Silence Behavior Scale
- Soojin Chung, Jee-In Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):279-295. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23138
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure hospital nurses’ silence behavior and examine its validity and reliability.
Methods
A total of 52 preliminary items on hospital nurses’ silence behavior were selected using a content validity test by seven experts on 53 candidate items derived from a literature review and in-depth interviews with 14 nurses. A total of 405 hospital nurses participated in a psychometric testing. Data analysis comprised item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses, and convergent and discriminant validity tests. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used for assessing concurrent validity, and Cronbach’s alpha was used for the reliability test.
Results
The final scale consisted of nine factors with 31 items, exhibiting acceptable model fit indices, convergent validity, and discriminant validity. The score of the entire scale was positively correlated with the ‘Organizational Silence Scale (OSS)-the issues on which nurses remain silent’ (r = .60, p < .001) and ‘OSS-the reasons why nurses remain silent’ (r = .68, p < .001). Cronbach’s α of the scale was .92, and α of each subscale ranged from .71 to .90.
Conclusion
The Hospital Nurses’ Silence Behavior Scale is a useful tool for assessing multifaceted silence behavior among nurses. It can provide basic data for developing better communication strategies among nurses and other hospital staff. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating Effect of Emotional Labour on the Role Pressure and Silence Behaviour of Nurses
Lianci He, Jianhua Liu, Rong Sun, Yuan Deng, Ling Tang, Shaochuan Chen
Evaluation & the Health Professions.2026; 49(1): 3. CrossRef - Mediating effect of grit on the influence of nurses’ silence behavior on medication safety competence: a cross-sectional study
Haengsuk Kim, Wanju Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(1): 81. CrossRef - Influence of Clinical Nurses’ Organizational Silence on Organizational Citizenship Behavior: Mediating Effect of Organizational Commitment Moderated by Organizational Justice
Shin Ae Hwang, Haeyoung Min
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 416. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation and translation of the Persian version of the Organizational Silence Behavior Scale (OSBS-P) for clinical nurses
Alireza Mirzaei, Mobina Jamshidinia, Mehrzad Aghabarari, Pouya Dolat Abadi, Reza Nemati-Vakilabad, Ehsan Namaziandost
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(12): e0314155. CrossRef
- Mediating Effect of Emotional Labour on the Role Pressure and Silence Behaviour of Nurses
- 4,967 View
- 289 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Factors Influencing the Intention for Continual Fertility Treatments by the Women Undergoing Assisted Reproductive Technology Procedures: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Miok Kim, Minkyung Kim, Minkyung Ban
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):59-72. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23095
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This cross-sectional study aimed to identify factors influencing the intention for continual fertility treatments among women undergoing assisted reproductive technology (ART).
Methods
A total of 197 women were recruited through convenience sample from fertility hospitals in Gyeonggi-do and Busan, South Korea. Data were collected using a self-report questionnaire incorporating measures of uncertainty; Depression Anxiety Stress Scales; Fatigue Severity Scale; Coping Scale for Infertility-Women; spousal support; treatment environment; and intention for continual fertility treatment. Descriptive statistics, chi-square tests, t-tests, and logistic regression analysis were conducted using IBM SPSS 26.0.
Results
As many as 70.6% of the participants expressed an intention for continual fertility treatments. Logistic regression analysis revealed that factors such as uncertainty (odds ratio [OR] = 0.44, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.20~0.95), active coping (OR = 4.04, 95% CI 1.11~14.71), treatment environment (OR = 2.77, 95% CI 1.26~6.07), and the duration of marriage (OR = 2.61, 95% CI 1.24~5.49) were significantly related with this intention.
Conclusion
These findings underscore the significance of uncertainty management, having proactive coping strategies, having supportive treatment environments, and considering the duration of marriage concerning women’s intention for continual fertility treatment in the context of ART. The implications of these results extend to the development of nursing intervention programs aimed at providing crucial support for women undergoing ART and seeking to continue their infertility treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Uncertainty on Depression in Women Undergoing Assisted Reproductive Technology: The Mediating Role of Perceived Stigma and the Moderated Mediation by Spousal Support
Miok Kim
Nursing & Health Sciences.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness and Safety of Korean Medicine in Treating Female Infertility: A Prospective Multicenter Observational Study
Hyo-Jeong Jung, Dong-Il Kim, Su-Ji Choi, Jang-Kyung Park, Jin-Moo Lee
International Journal of Women's Health.2025; Volume 17: 1771. CrossRef - The experiences of infertile women discontinuing in vitro fertilization treatment: a grounded theory approach
Eunmi Park, Yeoungsuk Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(3): 440. CrossRef - Psychiatric Considerations of Infertility
Yoon Jung Hwang, Junhee Lee, Jihyun Hwang, Hyeonhee Sim, Namwoo Kim, Tae-Suk Kim
Psychiatry Investigation.2024; 21(11): 1175. CrossRef
- Effects of Uncertainty on Depression in Women Undergoing Assisted Reproductive Technology: The Mediating Role of Perceived Stigma and the Moderated Mediation by Spousal Support
- 2,499 View
- 121 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

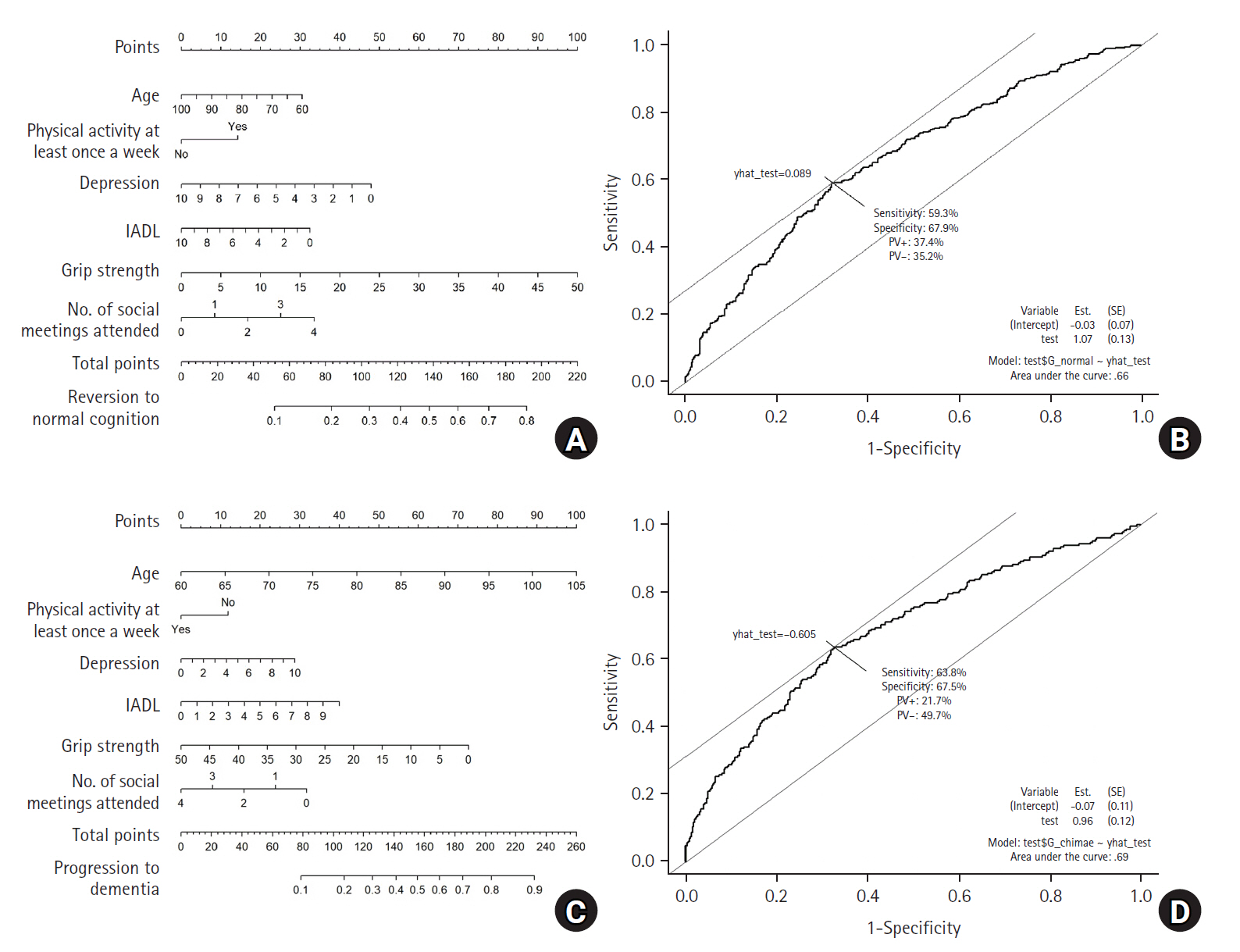
- Nomogram for predicting changes in cognitive function in community dwelling older adults with mild cognitive impairment based on Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing Panel Data: a retrospective study
- Hyuk Joon Kim, Hye Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):50-63. Published online February 7, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24059
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify factors associated with normal cognitive reversion and progression to dementia in older adults with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) residing in the community and to develop a nomogram.
Methods
This longitudinal study used secondary data from the Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing Panel Data (2006–2018). The study included 1,262 participants aged 60 or older, with initial Mini-Mental State Examination scores ranging from 18 to 23. Data were analyzed using the Rao-Scott chi-square test, panel binary logistic regression, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve in Stata ver. 17.0 (Stata Corp.).
Results
The rate of reversion from MCI to normal cognition was 37.0% after 2 years and 32.9% after 12 years. The rate of progression to dementia was 18.0% after 2 years and 30.2% after 12 years. In the nomogram for reversion to normal cognition, the most significant influences were grip strength, depression, number of meetings, age, and regular exercise, with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of .66. In contrast, in the nomogram for progression to dementia, the most significant influences were age, grip strength, instrumental activities of daily living, number of social meetings attended, depression, and regular exercise, with an AUC of .69.
Conclusion
These nomograms can serve as an effective intervention tool for preventing dementia in the field of community health care since they can serve as a visual technique for presenting information on risk to individuals with MCI. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Longitudinal Relationship Between Physical Functions and Cognitive Functions Among Middle-Aged and Older Adults in Primary Care
Nan Hu, Wupeng Yin, Rabeya Illyas Noon, Noof Alabdullatif
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2025; 22(6): 908. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Nomogram Predicting Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults
Sook Kyoung Park, Hyuk Joo Kim, Young-Me Lee, Hye Young Kim
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Emotional Labor on Burnout in Nurses: Focusing on the Moderating Effects of Social Intelligence and Emotional Intelligence
Kyung Ran Lee, Jeoung Mi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(1): 22. CrossRef
- The Longitudinal Relationship Between Physical Functions and Cognitive Functions Among Middle-Aged and Older Adults in Primary Care
- 3,612 View
- 216 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Experiences of Patients and Their Families Receiving Medical Services Provided by Advanced Practice Nurses at Tertiary General Hospitals
- Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Su Jung Choi, Ji Eun Han, Eun Kyung Kwon, Jeong Hee Park, Jeong Hye Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):594-606. Published online November 4, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24069
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study aimed to understand and describe the experiences of patients and their families who have received medical services from advanced practice nurses in tertiary general hospitals in Korea.
Methods Data were collected through four focus group interviews with 20 patients and their families who had received medical services from advanced practice nurses for more than six months at four tertiary hospitals from November 29 to December 28, 2023. Verbatim transcripts were analyzed using qualitative content analysis.
Results The four themes extracted from the experiences of patients and their families were as follows: unfamiliar medical personnel encountered during the treatment process, healthcare professionals who exhibited excellence, companions to light my way through the tunnel of illness, and an advanced practice nurse system that must be activated urgently.
Conclusion The study’s findings indicate that patients and their families view the care provided by advanced practice nurses as excellent, reliable, and holistic. Research suggests that advanced practice nurses are valuable healthcare professionals in team-based care. The findings suggest that hospitals should utilize an advanced practice nurse system to improve patient outcomes and ensure the quality of care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Legislation of Medical Support Tasks in the Nursing Act as a Foundation for Nursing Professionalism and Role Expansion
Su Jung Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(2): 69. CrossRef - Strategies for expanding the role of advanced practice providers in the Korean nursing workforce: a mixed-methods approach
Jeong Hye Kim, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Suyoung Choi, Mimi Lee, Su Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(4): 568. CrossRef - Nurses' Patient Care Experiences in a Changing Healthcare Environment Following One Year of Healthcare Policy Conflict - A Focus Group Interview
Eun Hee Kang, Yunhyung Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 280. CrossRef
- Legislation of Medical Support Tasks in the Nursing Act as a Foundation for Nursing Professionalism and Role Expansion
- 4,580 View
- 270 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

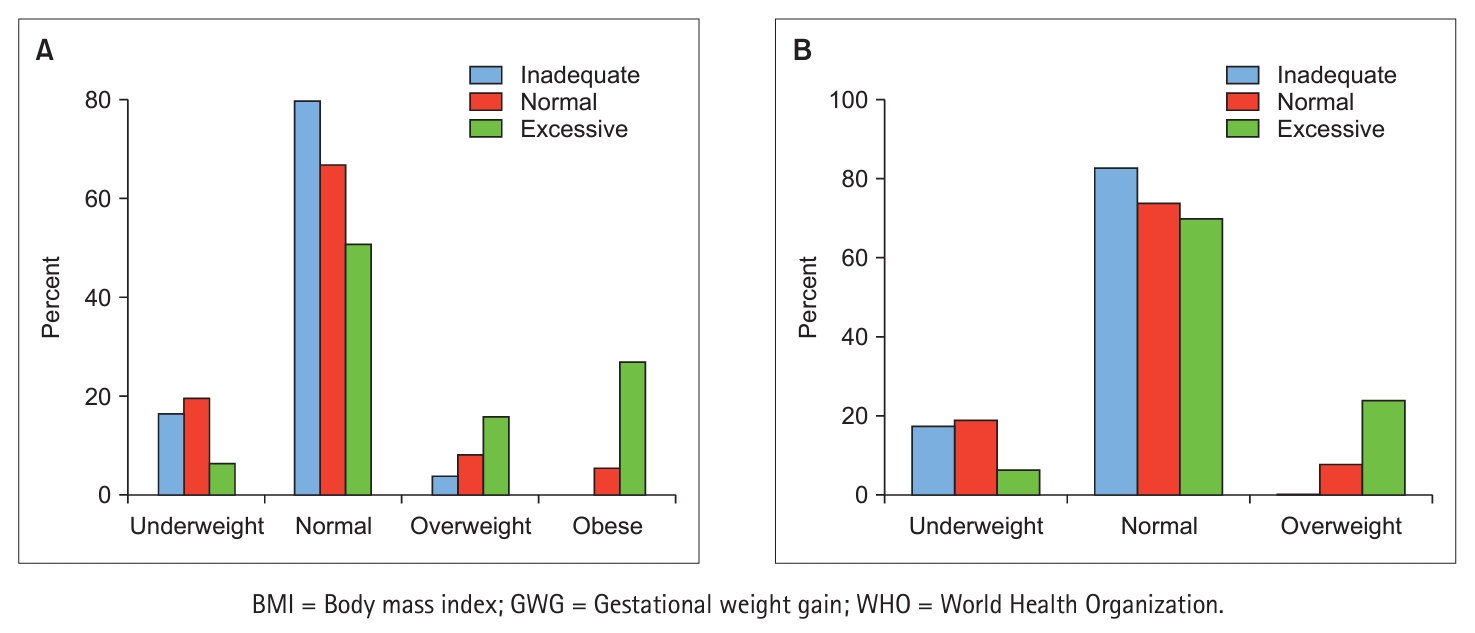
- Perceptual Factors Associated with Gestational Weight Gain: A Cross-Sectional Survey
- Sehee Kim, Sukhee Ahn
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):495-508. Published online November 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose Recent years have seen an increase in the number of pregnant women whose weight gain during pregnancy exceeds the recommended range. This study was intended to determine the relationships among demographic attributes, key perceptual factors, and gestational weight gain (GWG).
Methods This cross-sectional study was conducted between April and July 2022. First-time pregnant women beyond 36 weeks of gestation who were recruited via social media completed an online survey. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA, chi-square test, and logistic regression, all performed using SPSS software.
Results Of the 369 participants, 63 (17.1%) exceeded the recommended GWG guidelines, while 148 (40.1%) fell within the recommended range, and the remaining 158 (42.8%) had inadequate GWG. Being overweight or obese before pregnancy significantly increased the risk of excessive GWG (
p < .001). This risk was also significantly greater for women with low internal weight locus of control (OR = 0.58, 95% CI 0.41~0.82), high external weight locus of control (OR = 1.75, 95% CI 1.31~2.34), and negative body image (OR = 0.62, 95% CI 0.51~0.75).Conclusion The growing trend of excessive GWG among pregnant women is influenced by a combination of prepregnancy body mass index (BMI) and perceptual factors, including weight locus of control and body image. These findings underscore the need to implement weight management intervention strategies before pregnancy, taking into consideration BMI, and to enhance positive body image and internal locus of control.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond the mirror: Exploring the impact of maternal body image attitudes on gestational weight gain and maternal and neonatal outcomes, a systematic review
Malshani Lakshika Pathirathna, Megumi Haruna, Hapugahapitiya Mohottalalage Renu Kalhari Geethani Nandasena, Atapattu Mudiyanselage Muditha Piumali, Ganegoda Widanage Umanda Dilrukshi Ganegoda
International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated With Gestational Weight Gain Among Nurses in Korea
Sook Jung Kang, Woon Young Hwang, Hyunju Dan, Sue Kim, Kwang-Pil Ko
Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, & Neonatal Nursing.2025; 54(5): 543. CrossRef - Attitudes toward body weight and shape during pregnancy among Japanese women who were underweight before pregnancy: A qualitative study
Chisato KOROGI, Mie SHIRAISHI, Kaori MATSUDA, Natsuki HORI, Hanna HORIGUCHI
Journal of Japan Academy of Midwifery.2025; 39(3): 456. CrossRef
- Beyond the mirror: Exploring the impact of maternal body image attitudes on gestational weight gain and maternal and neonatal outcomes, a systematic review
- 2,872 View
- 109 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Challenges for the Activation of Advanced Practice Nursing in Korea
- Young Hee Yi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):297-299. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24074
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Role Conflict, Work Environment, and Meaning of Work on Job Embeddedness among Physician Assistants
Kwang Hoon Seo, Tae Yeong Yang, Nam Gyu Park, Jung Eun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 249. CrossRef - Role Transformation and Adaptation of Physician Assistants during the 2024 Medical Workforce Shortage: A Phenomenological Study
Tae Yeong Yang, Nahyun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 259. CrossRef - Core Competencies and Associated Determinants for Infection Control Nurses by Career Stage Following COVID-19
Sun Jung, Jeong Sil Choi
Korean Journal of Healthcare-Associated Infection Control and Prevention.2025; 30(1): 50. CrossRef
- Effects of Role Conflict, Work Environment, and Meaning of Work on Job Embeddedness among Physician Assistants
- 4,721 View
- 435 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Support Needs for Health Promotion of Community-Dwelling People with Disabilities: Perspectives of Operators Managing Disability Supportive Housing
- Hye Jin Nam, Haesun Lee, Han Nah Park, Sujin Lee, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):211-223. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Recent studies have focused on policies aimed at supporting the independence of individuals with disabilities in communities. As part of this initiative, supportive housing, integrated care, and residential spaces offer tailored services based on individual needs and autonomy. The attitudes and knowledge of the administrators supporting supportive housing residents regarding health management can influence the well-being of individuals with disabilities. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the challenges faced by supporting housing workers in enhancing the self-management skills of individuals with disabilities.
Methods
In this qualitative study, focus group interviews were conducted in August 2023 with nine administrators working to support housing in Seoul. Qualitative content analysis was used to analyze the interview data.
Results
The needs and challenges in enhancing the self-management skills of individuals with disabilities were as follows: (1) the complexity of health management challenges, (2) bidirectional strategies for strengthening health management capabilities, and (3) support for systematic health management. Additionally, eight subthemes were derived.
Conclusion
By investigating the difficulties experienced and identifying the necessary support requirements for supportive housing workers, this study seeks to uncover insights and identifies areas for improvement and strategies for health management. This study acknowledges the educational and institutional support necessary to improve the health and quality of life of individuals with disabilities residing in supportive housing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
Haesun Lee, Hye Jin Nam, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(3): 454. CrossRef - Intention to use a health information platform in supportive housing for people with disabilities: An application of the UTAUT model
Bohye Kim, Hye Jin Nam, Haesun Lee, Hannah Park, Ju Young Yoon, Nicola Diviani
PLOS One.2025; 20(10): e0332072. CrossRef - A preliminary study on the development of a chronic disease self-management curriculum for disability support workers: educational needs analysis
Han Nah PARK, Hye Jin NAM, Haesun LEE MSN, Sujin LEE, Bohye KIM, Ju Young YOON
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
- 2,313 View
- 101 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Influence of Illness Uncertainty on Health Behavior in Individuals with Coronary Artery Disease: A Path Analysis
- Hyesun Jeong, Yesul Lee, Jin Sup Park, Yoonju Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):162-177. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the influence of uncertainty-related factors on the health behavior of individuals with coronary artery disease (CAD) based on Mishel’s uncertainty in illness theory (UIT).
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional study and path analysis to investigate uncertainty and factors related to health behavior. The study participants were 228 CAD patients who visited the outpatient cardiology department between September 2020 and June 2021. We used SPSS 25.0 and AMOS 25.0 software to analyze the data.
Results
The final model demonstrated a good fit with the data. Eleven of the twelve paths were significant. Uncertainty positively affected danger and negatively affected self-efficacy and opportunity. Danger had a positive effect on perceived risk. Opportunity positively affected social support, self-efficacy, perceived benefit and intention, whereas it negatively affected perceived risk. Social support, self-efficacy, perceived benefit and intention had a positive effect on health behavior. We found that perceived benefit and intention had the most significant direct effects, whereas self-efficacy indirectly affected the relationship between uncertainty and health behavior.
Conclusion
The path model is suitable for predicting the health behavior of CAD patients who experience uncertainty. When patients experience uncertainty, interventions to increase their self-efficacy are required first. Additionally, we need to develop programs that quickly shift to appraisal uncertainty as an opportunity, increase perceived benefits of health behavior, and improve intentions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health uncertainty: Scale development and its effect on health behaviors
Rui Ren, Su Tao, Yuhua Ouyang, Wenchong Du
Journal of Health Psychology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Self-Care, Resilience, and Uncertainty in Patients After Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
Eun-Hye Park, JiYeon Choi, Phill Ja Kim, Jiyeon Lee
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Coping Profiles and Cardiac Health Behavior among Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: A Latent Profile Analysis
Yesul Lee, Yoonju Lee, Jeong Cheon Choe, Hyesun Jeong, Sunyoung Jung
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(3): 228. CrossRef
- Health uncertainty: Scale development and its effect on health behaviors
- 3,702 View
- 177 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Impact of Anthropometric Indices of Obesity on the Risk of Incident Hypertension in Adults with Prehypertension: A Secondary Analysis of a Cohort Study
- Se Young Jang, Jihun Kim, Seonhwa Kim, Eun Sun Lee, Eun Jeong Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):18-31. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23067
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the impact of anthropometric indices of obesity (body mass index [BMI], waist circumference, waist hip ratio, and body fat percentage) on the incidence of hypertension in adults with prehypertension.
Methods
A longitudinal study design using secondary data form the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study was employed. The study included 1,838 adults with prehypertension tracked every two years from 2001 to 2018. Statistical analyses, including frequency assessments, number of cases per 1,000 person-years, log-rank tests, Kaplan-Meier curves, and Cox’s proportional hazards regression, were conducted using SPSS version 25.
Results
Over the observation period (15,783.6 person-years), 1,136 individuals developed hypertension. The incidence of hypertension was significantly higher in the obesity groups defined by BMI (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.33), waist circumference (HR = 1.34), waist hip ratio (HR = 1.29), and body fat percentage (HR = 1.31) compared to the non-obese group. These findings indicate an increased risk of hypertension associated with obesity as measured by these indices.
Conclusion
The study underscores the importance of avoiding obesity to prevent hypertension in individuals with prehypertension. Specifically, BMI, waist circumference, waist hip circumference, and body fat percentage were identified as significant risk factors for hypertension. The results suggest the need for individualized weight control interventions, emphasizing the role of health professionals in addressing the heightened hypertension risk in this population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigating the Gut Microbiota Profile in Prehypertensive Individuals Exhibiting Phlegm-Dampness Constitution
Ning Yu, Yaotang Yang, Guangyun Wang, Yanhong Wang, Mei Feng, Peilin Yang, Shuang Liu, Rui-rui Wang, Lei Zhang
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Relationship Between Inflammatory Biomarkers and Anthropometric Measures of Obesity in Healthy Adults: A Case Control Study
Dekra El-Aghbary, Rashad Thabet, Mohammed Almorish, Khaled AlSayaghi, Ahmed Elkhalifa
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2025; Volume 18: 3403. CrossRef - Association between body roundness index and psoriasis among US adults: a nationwide population-based study
Genlong Bai, Yuting Peng, Qian Liu, Xinyi Shao, Yuan Zhan, Aijun Chen, Jingbo Zhang
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Investigating the Gut Microbiota Profile in Prehypertensive Individuals Exhibiting Phlegm-Dampness Constitution
- 2,582 View
- 114 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

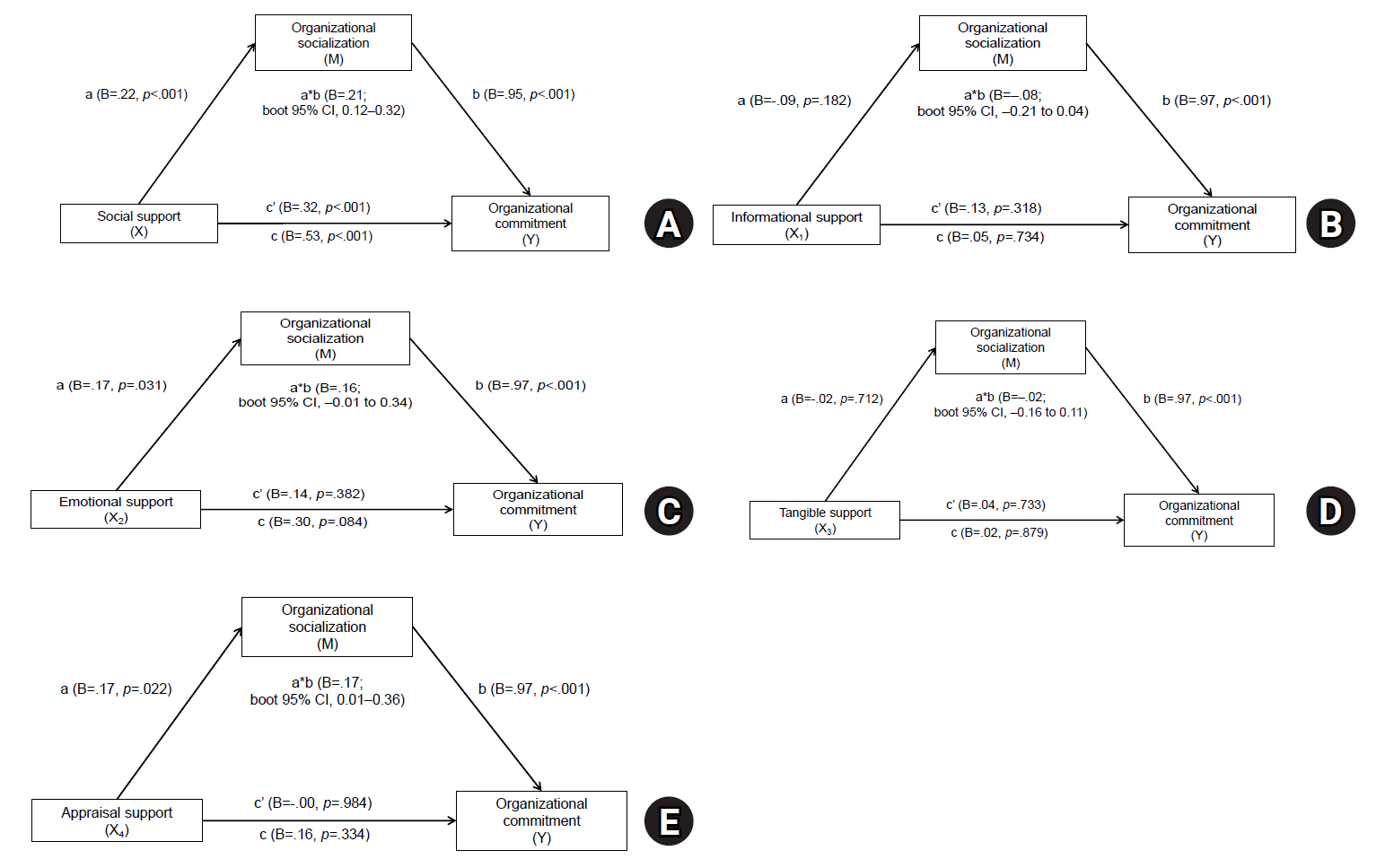
- Effects of social support on organizational commitment among experienced nurses experiencing department rotation: the mediating effect of organizational socialization
- Young Jun Jang, Jeong A Jeong, Yu Seung Ban, Seon Hwa Park, Eun Jee Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):364-376. Published online August 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25042
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study explored the mediating role of organizational socialization in the relationship between social support and organizational commitment among nurses in hospitals who had experienced department rotation.
Methods
A descriptive survey design was used with 202 nurses from a tertiary hospital who had experienced department rotation within the past 12 months. Data were collected via an online questionnaire from August 1 to August 30, 2024. Analyses included frequency analysis, descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation, and multiple regression. The mediating effect was tested using IBM SPSS WIN ver. 23.0 and the PROCESS macro (model 4) with 10,000 bootstrap resamples.
Results
Organizational socialization partially mediated the relationship between social support and organizational commitment (B=.21; bootstrapped 95% confidence interval, 0.12–0.32).
Conclusion
The findings suggest that both social support and organizational socialization play essential roles in improving nurses’ organizational commitment following department rotation. Thus, practical programs, such as mentoring systems, should be implemented that both enhance social support and actively promote organizational socialization. These efforts have the potential to help nurses adjust more effectively to new units and ultimately improve retention and performance within healthcare organizations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Nurses’ Dispatch Work Characteristics on Job Embeddedness, Organizational Commitment, and Turnover Intention
Eejee Jung, Gunjeong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 560. CrossRef - Nurses' Experience Working with Substitute Nurses
Hye Mi Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 208. CrossRef
- The Effects of Nurses’ Dispatch Work Characteristics on Job Embeddedness, Organizational Commitment, and Turnover Intention
- 2,183 View
- 241 Download
- 2 Crossref

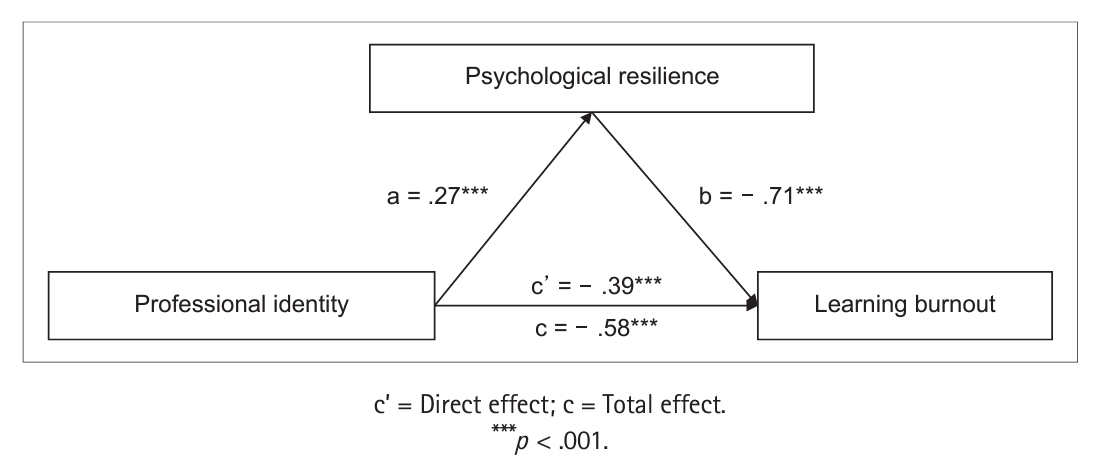
- The Mediating Role of Psychological Resilience in Chinese Nursing Students’ Professional Identity and Learning Burnout
- Liu Zhang, Qin Zhang, ShuWen Li, YuHong Li, GuoCui Wu, Ying Chen, YunNa Zhou
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):509-518. Published online November 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24044
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study investigated whether professional identity predicts learning burnout among Chinese nursing students, and whether resilience moderates this relationship.
Methods This cross-sectional study recruited 635 students from a nursing college at a medical university in Hefei, China. Data were collected using the professional identity questionnaire, learning burnout scale for college students, and 10-item Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale. Pearson’s correlation analysis was used to investigate the relationships between variables. The mediation effect was evaluated using linear regression and the bootstrap method in SPSS.
Results Nursing students exhibited intermediate learning burnout levels (score: 54.95 ± 10.42). Professional identity was positively correlated with psychological resilience (r = .42,
p < . 001), whereas learning burnout was negatively correlated with professional identity (r = - .54,p < . 001) and psychological resilience (r = - .57,p < . 001). Psychological resilience mediated the relationship between professional identity and learning burntout to the tune of 32.8%.Conclusion Psychological resilience mediates the relationship between professional identity and learning burnout. Thus, nursing educators can mitigate student burnout by developing their students' professional identities and psychological resilience.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of creative anxiety on professional identity among master’s nursing students: a chain mediation effect of psychological resilience and achievement motivation
Yao Ding, Xiaolan Guo, Ruifeng Wang, Lu Xu, Shajie Hou, Fengjiao Chang
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sense of Coherence and Perceived Academic Stress Among Nursing Students: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study
David Ballester-Ferrando, Esther Cáceres-Malagelada, Carolina Rascón-Hernán, Teresa Botigué, Ana Lavedán, Olga Masot, Dolors Burjalés, Luis González-Osorio, Ximena Osorio-Spuler, Eva Serrat-Graboleda, Concepció Fuentes-Pumarola
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(8): 288. CrossRef
- The impact of creative anxiety on professional identity among master’s nursing students: a chain mediation effect of psychological resilience and achievement motivation
- 4,538 View
- 186 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

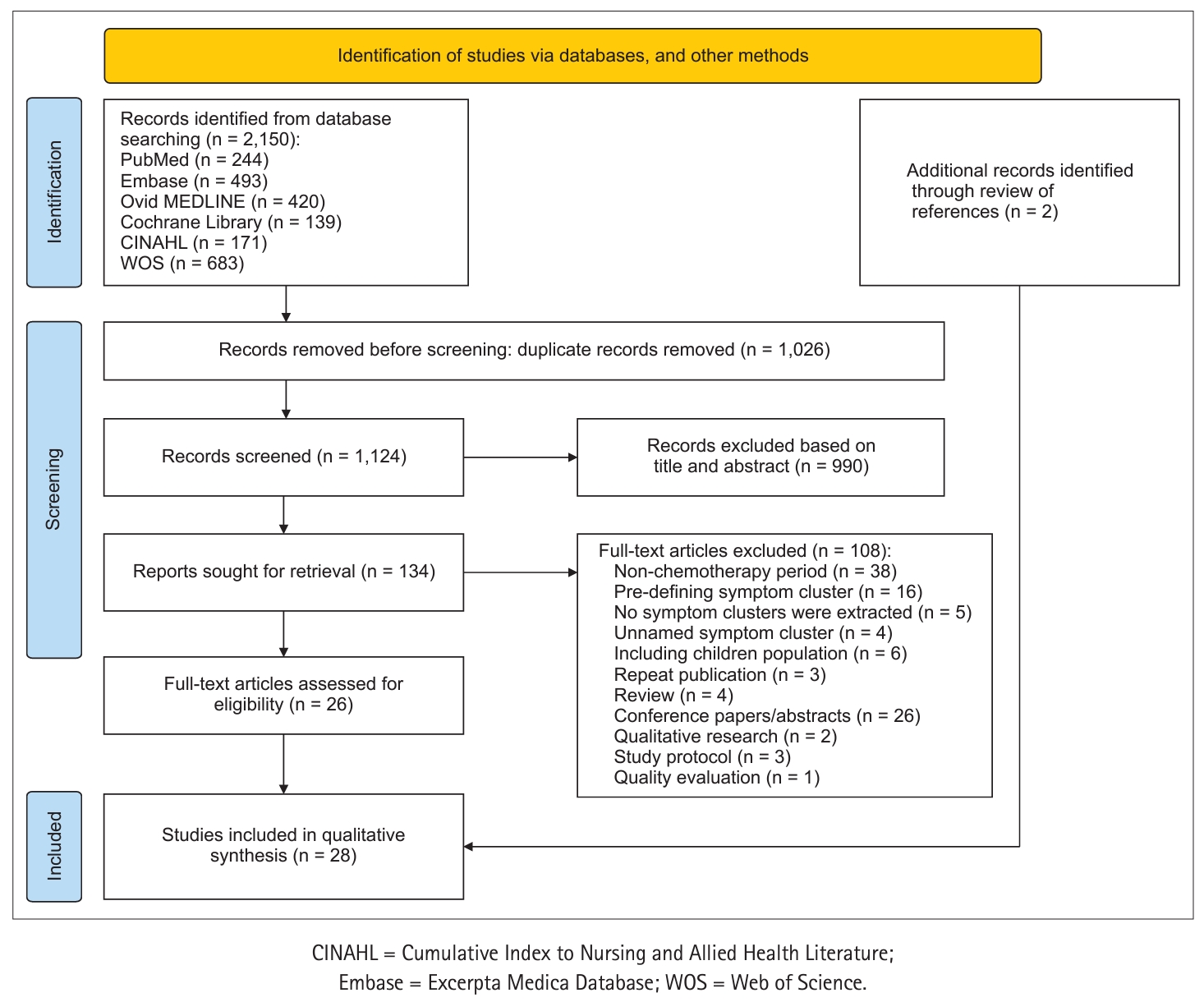
- Exploring Symptom Cluster Patterns in Adult Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review
- Pan Yang, Hui-juan Mei, Hao-yu Zhao, Rong-rong Wu, Yong-qin Ge, Yin Lu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):478-494. Published online November 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24041
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material ePub
ePub Purpose This systematic review aimed to scrutinize the progression of symptom cluster research in adult cancer patients who received primary or adjuvant chemotherapy between 2001 and 2023, providing a comprehensive understanding of clinical practice and future research.
Methods PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, Excerpta Medica Database, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases were searched for theme words and free words related to symptom clusters, cancer, and chemotherapy. Eligible studies were published between January 1, 2001, and May 30, 2023; adults who were diagnosed with cancer and received primary or adjuvant chemotherapy were evaluated.
Results Twenty-eight studies were included in this review. The Memorial Symptom Assessment Scale emerged as the predominant instrument and exploratory factor analysis was the most frequently employed statistical method to identify symptom clusters. Psychological, gastrointestinal, and physical image symptom clusters were the most commonly delineated. Furthermore, the temporal stability of the symptom clusters showed varying dynamics, with psychological symptom clusters displaying relative consistency over time.
Conclusion Interventions are needed for the most common and stable symptoms in patients with cancer undergoing chemotherapy. Future endeavors may necessitate more longitudinal studies to delve deeper into the temporal stability and dynamic variations of symptom clusters. Such investigations hold promise for advancing symptom cluster research, elucidating the underlying mechanisms, and fostering the development of targeted interventions, thereby enriching the symptom management paradigm in oncological care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Network analysis used to investigate the symptoms of cancer patients during chemotherapy: a scoping review
Xiaodan Shao, Na Wang, Ke Tang, Kunning Wang, Zhangyan Tan, Jiangxiu Xie, Zhiwei Shen, Yuting Jiang, Yan Zhang
Discover Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Symptom cluster in patients with resected pancreatic cancer during adjuvant chemotherapy: A cross-sectional study
Yun Wang, Ningning Xia, Yuan Song, Neng Shi, Kuei-Ching Pan
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100810. CrossRef
- Network analysis used to investigate the symptoms of cancer patients during chemotherapy: a scoping review
- 2,832 View
- 152 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- The Effects of a Self-Efficacy Theory-Based Exercise Program for Patients Undergoing with Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Kyung-Hye Park, Hee-Young Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):547-562. Published online October 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24027
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material ePub
ePub Purpose This study was performed to develop a self-efficacy theory-based exercise program for total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and to test the program’s efficacy in ameliorating knee pain and restoring function as measured by lower extremity muscle strength, 3 meter walking time, Korean Western Ontario McMaster Index (WOMAC), exercise self-efficacy, and length of hospital stay for TKA patients.
Methods This quasi-experimental study incorporating a non-equivalent control group and pretest-posttest non-synchronized design non-synchronous design was applied to assess self-efficacy reinforcement strategies based on self-efficacy theory. The exercise program consisted of the following steps: TKA, education to prevent postoperative complications, and muscle strength exercises. Respective exercise and control groups included 29 and 27 participants. The experimental group received eight sessions of the program from three weeks before TKA to four weeks after TKA. Collected data were analyzed using the chi-square test, Mann–Whitney U test, and ranked ANCOVA and t-tests using IBM SPSS Statistics 23.
Results Experimental group showed significant improvement in lower extremity muscle strength (F = 8.63,
p = .005), 3 meter walking time (z = - 5.02,p < .001), WOMAC index (z = - 2.22,p = .027), self-efficacy for exercise (z = - 3.29,p = .001), and length of hospital stay (t = - 2.11,p = .040) compared to the control group. No significant differences in knee pain and range of motion were observed.Conclusion These findings indicate that a self-efficacy theory-based exercise program can be an effective exercise strategy that patients undergoing TKA can easily follow at home without assistance. It is thus recommended as an exercise intervention for TKA patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Self-efficacy and implementation intentions in home rehabilitation of stroke patients: the parallel mediating role of recurrence risk perception and outcome expectations
Xiaowen Jiang, Qiuxue Sun, Rong Tang, Shuxian Liu, Xi Chen, Yumei Lv
Frontiers in Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Decision-Making and Rehabilitation Among Older Women Who Underwent Total Knee Replacement: A Qualitative Study in Taiwan
Ching Han Huang, Yun Yee Chen, Shu Wen Chen, Chen Ti Wang, Mei Hsiang Lin
Patient Preference and Adherence.2025; Volume 19: 3931. CrossRef
- Self-efficacy and implementation intentions in home rehabilitation of stroke patients: the parallel mediating role of recurrence risk perception and outcome expectations
- 3,332 View
- 284 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- An Exploratory Study on Non-Contact Nursing Experiences of Clinical Nurses during the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Hye Min Byun, Eun Kyoung Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):446-458. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24045
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to understand the non-contact nursing experiences of clinical nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
A qualitative research design applying thematic analysis was used. The participants were purposive sampled from three institutes: a tertiary hospital, a general hospital, and a residential treatment center in Seoul. Data were collected between December 2021 and January 2022 through individual in-depth interviews with 12 clinical nurses. The data were analyzed using Braun and Clarke’s method to identify the meaning of the participants’ experiences.
Results
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the fields where the participants performed non-contact nursing included intensive care units and isolation wards of hospitals, a residential treatment center, and home cares. Their tasks in non-contact nursing commonly involved remote monitoring using digital devices or equipment, consultation and education. From their experiences performing tasks in these fields, the four theme clusters and nine themes were derived. The four theme clusters are as follows: (1) Confusion of nursing role; (2) Conflict due to insufficient support system; (3) Concern about the quality of nursing; (4) Reflection on the establishment of nursing professionalism.
Conclusion
This study highlights the necessity for institutionalizing professional nursing areas, nursing education, and practical support by clarifying the purpose and goals of non-contact nursing and developing nursing knowledge through frameworks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Da-Jung Kim
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2025; 21(5): 234. CrossRef - Telecare legislation priorities: A Delphi study grounded in ethical challenges
Seongyu Han, Eun Kyoung Yun
Nursing Ethics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- 1,885 View
- 87 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of a Pre-Conception Care Program in Women with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Mixed-Methods Study Including a Randomized Controlled Trial
- Young Jin Lee, Hae Won Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Suk-Kyun Yang, Ji-Yeon Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):386-402. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to conduct a pre-conception care program for women of childbearing age with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in Korea and verify its effects on self-efficacy for IBD management, IBD-related pregnancy knowledge, and IBD-related pregnancy anxiety. It also aimed to explore the changes in participants through the program.
Methods
A convergent mixed-methods study design was adopted. In the quantitative phase, 35 women (17 and 18 in the intervention and control group, respectively) participated. The intervention group attended a program that included small-group sessions and individual tele-coaching. To confirm the effects, data were collected before and one and four weeks after the intervention. In the qualitative stage, focus group interviews and tele-coaching were conducted with the intervention group.
Results
After the program ended, significant differences were observed over time between the intervention and control groups for self-efficacy for IBD management (Wald χ2 = 4.41, p = .036), IBD-related pregnancy knowledge (Wald χ2 = 13.80, p < .001) and IBD-related pregnancy anxiety (Wald χ2 = 8.61, p = .003). Qualitative data analysis revealed the following themes: (1) improving confidence in IBD management and awareness for planned pregnancy; (2) improving IBD awareness related to pregnancy and childbirth; and (3) relieving anxiety about and actively facing pregnancy.
Conclusion
This study is meaningful in that, to the best of our knowledge, it is the first to develop a pre-conception care program for women diagnosed with IBD and confirm its effectiveness. Furthermore, this program is expected to be suitable for patient counseling and education in clinical practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The experiences of fertility concerns in women with inflammatory bowel disease of childbearing age: a descriptive qualitative study
Lewei Tu, Qiaoyu Wu, Mengxiao Jiang, Meihao Wei, Ying Wang, Ying Xiao
BMC Gastroenterology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Health Literacy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review of Health Outcomes, Predictors and Barriers
Caterina Mercuri, Rita Nocerino, Vincenzo Bosco, Teresa Rea, Vincenza Giordano, Michele Virgolesi, Patrizia Doldo, Silvio Simeone
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(23): 8577. CrossRef
- The experiences of fertility concerns in women with inflammatory bowel disease of childbearing age: a descriptive qualitative study
- 2,490 View
- 97 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- The Influence of Diversity Management of Nursing Organization on Organizational Commitment: Double Mediating Effect of Diversity Sensitivity Orientation and Positive Nursing Organizational Culture
- Hwi Gon Jeon, Keum Seong Jang, Eun A Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):403-417. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aim of this study was to identify the double mediating effect of effect of diversity sensitivity orientation and positive nursing organizational culture between diversity management and organizational commitment.
Methods
Participants were 245 nurses working in six tertiary hospitals located in 3 different regions. Data collection was conducted from February 13, 2023 to March 6, 2023 through online self-reported questionnaire. The data were analyzed by IBM SPSS Statistics 27 and SPSS PROCESS Macro 4.2 program.
Results
The direct effect of diversity management on organizational commitment was significant (β = .21, p < .001). The indirect effect of diversity management on organization commitment was .34 (95% confidence interval [CI] = .23~.47). The double mediating effect of diversity sensitivity orientation and positive nursing organizational culture in the relationship between diversity management and organizational commitment was .02 (95% CI = .00~.05).
Conclusion
Diversity sensitivity orientation and positive nursing organizational culture show double mediating effect on the relationship between diversity management and organizational commitment. Education program and human resource management strategy for enhancing diversity management, diversity sensitivity orientation and positive nursing organizational culture should be provided to improve organizational commitment, and which are needed active support of the association and nursing organization. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Resilience, Emotional Exhaustion, and Communication Competency on Organizational Commitment Among Nurses in a Tertiary Hospital Setting in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
Ho Young Kim, Hee Jeong Kim, Eun Ja Yeun
Sage Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Organizational commitment of nursing staff: Definition of the concept and specifics of measurement (review of foreign publications)
K. V. Kuzmin, L. E. Petrova, V. S. Kharchenko
Kuban Scientific Medical Bulletin.2025; 32(5): 96. CrossRef
- Impact of Resilience, Emotional Exhaustion, and Communication Competency on Organizational Commitment Among Nurses in a Tertiary Hospital Setting in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 2,099 View
- 162 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Development and Effectiveness Evaluation of Comprehensive Mobile-Based, Breastfeeding Promotion Program for Mothers with Gestational Diabetes
- Eunju Kwak, Seungmi Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):224-236. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23098
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of a mobile-based breastfeeding promotion program (M-BFGDM) that helps mothers with gestational diabetes.
Methods
Forty-seven mothers participated in the study, of whom 22 were in the experimental group and 25 in the control group. To verify the effects, a lag design before and after the non-equivalence control group was used. The data collection for the experimental group was done before and after the intervention.
Results
In the results, breastfeeding knowledge showed a significant difference in the interaction between measurement period and group (χ2 = 8.14, p = .017), whereas breastfeeding intention did not show a significant difference in the interaction (χ2 = 4.73, p = .094). There was no difference in self-efficacy interaction (F = 0.13, p = .856). The breastfeeding method showed no difference in interaction (F = 0.04, p = .952), whereas cross-analysis showed a significant difference in breastfeeding practice rate between the experimental group and the control group at 1 month postpartum (χ2 = 7.59, p = .006).
Conclusion
A mobile-based breastfeeding promotion program was developed and applied for gestational diabetic mothers, resulting in an increase in breastfeeding knowledge and an improvement in breastfeeding practice rate one month after childbirth. In addition, M-BFGDM managed to create a breastfeeding practice environment with fewer time and place restrictions. A program study that complements motivation is needed to improve breastfeeding in pregnant diabetic mothers in the future. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by
- 3,065 View
- 183 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling of Health Promotion Behavior on Migrant Workers: A Multi-Group Analysis Based on the Period of Residence
- Hanna Jeong, Youngsuk Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):73-92. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study developed and tested a hypothetical model of health promotion behavior on migrant workers based on the Health Promotion Model and the Health Literacy Skills Framework.
Methods
Data were collected from 298 migrant workers in 9 regions across the country from December 2020 to March 2021. The exogenous variables were e-health literacy, occupational stress, acculturation, and social support. The endogenous variables were perceived benefits of action, self-efficacy, and health promotion behavior. Data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 25.0, AMOS 20.0, and R-4.0.3 program.
Results
The model fit was appropriate. Social support had the most significant direct impact on the health promotion behavior of migrant workers. Perceived benefits of action and self-efficacy played a mediating role in the relationship among e-health literacy, social support, and health promotion behavior. Based on multi-group analysis, the migrant worker group with less than 5 years of residency had a more statistically significant effect on the relationship between perceived benefits of action and health promotion behavior than those with over 5 years.
Conclusion
Providing social support as a critical administrative strategy to enhance the health promotion behavior of migrant workers is necessary. Furthermore, when developing an intervention program utilizing the internal mechanism between social support and health promotion behavior, a self-efficacy-enhancing strategy is considered to be more effective. Additionally, educating migrant workers with short-term residence of less than 5 years about the benefits of health behaviors is essential. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing cardiovascular health behaviors among Korean-Chinese migrant workers with metabolic syndrome using mixed methods
Yu Zhu Zhang, Seon Young Hwang
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated With Physical Activity in Home‐Based Rehabilitation Patients With Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Prospective Longitudinal Study
Heng‐Ying Fang, Ying‐Hua Pan, Yi‐Heng Zhang, Yu‐Hua Deng, Xiao‐Wen Li, Lei Huang, Hui‐Ting Gu, Yue Ding, Xin‐Xin Hu, Mu Liu, Rui‐Chong Wang, MeiFen Zhang
Musculoskeletal Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Factors influencing cardiovascular health behaviors among Korean-Chinese migrant workers with metabolic syndrome using mixed methods
- 2,838 View
- 104 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Eun Jin Kim, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):44-58. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23090
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to apply a health partnership program using commercially available mobile health apps to improve cardiovascular risk factors in male employees and verify its effectiveness.
Methods
Using a randomized control group pretest-posttest design, male employees with cardiovascular risk factors from five small and medium-sized workplaces were randomly assigned to an experimental group (n = 32) and a control group (n = 31). The experimental group was encouraged to use three mobile health apps for 12 weeks to acquire the necessary cardiovascular disease-related information and practice strengthening training, walking, and diet management appropriate to their level. They also received feedback on their weekly activities and motivational text messages from health partners. Hypotheses were tested using the SPSS WIN 22.0.
Results
The experimental group showed a significant difference compared to the control group in terms of their perception of mobile health app (p < .05), self-efficacy for exercise and diet, self-management partnership, and cardiovascular disease prevention health behavior (p < .001). In particular, there were significant decreases in the body mass index, ratio, serum fasting blood sugar, total cholesterol, and triglyceride in the experimental group (p < .001); however, there was no significant difference in high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol.
Conclusion
Intervention using mobile apps based on partnership with health managers is effective in improving the objective cardiovascular risk index in male employees; therefore, such intervention should be continuously used as a useful lifestyle modification strategy in the workplace. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adherence to a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle: Testing of the Information–Motivation–Behavioral Skills Model
Yura Shin, Jina Choo, Songwhi Noh
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2026; 41(2): 125. CrossRef - A Prospective Study of Relation between Academic & Exercise Stress, Quality of Life and Mibyeong in the College Students Majoring Physical Education
Yeonju Woo, Soojin Lee
Journal of Physiology & Pathology in Korean Medicine.2025; 39(1): 36. CrossRef
- Adherence to a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle: Testing of the Information–Motivation–Behavioral Skills Model
- 3,776 View
- 216 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

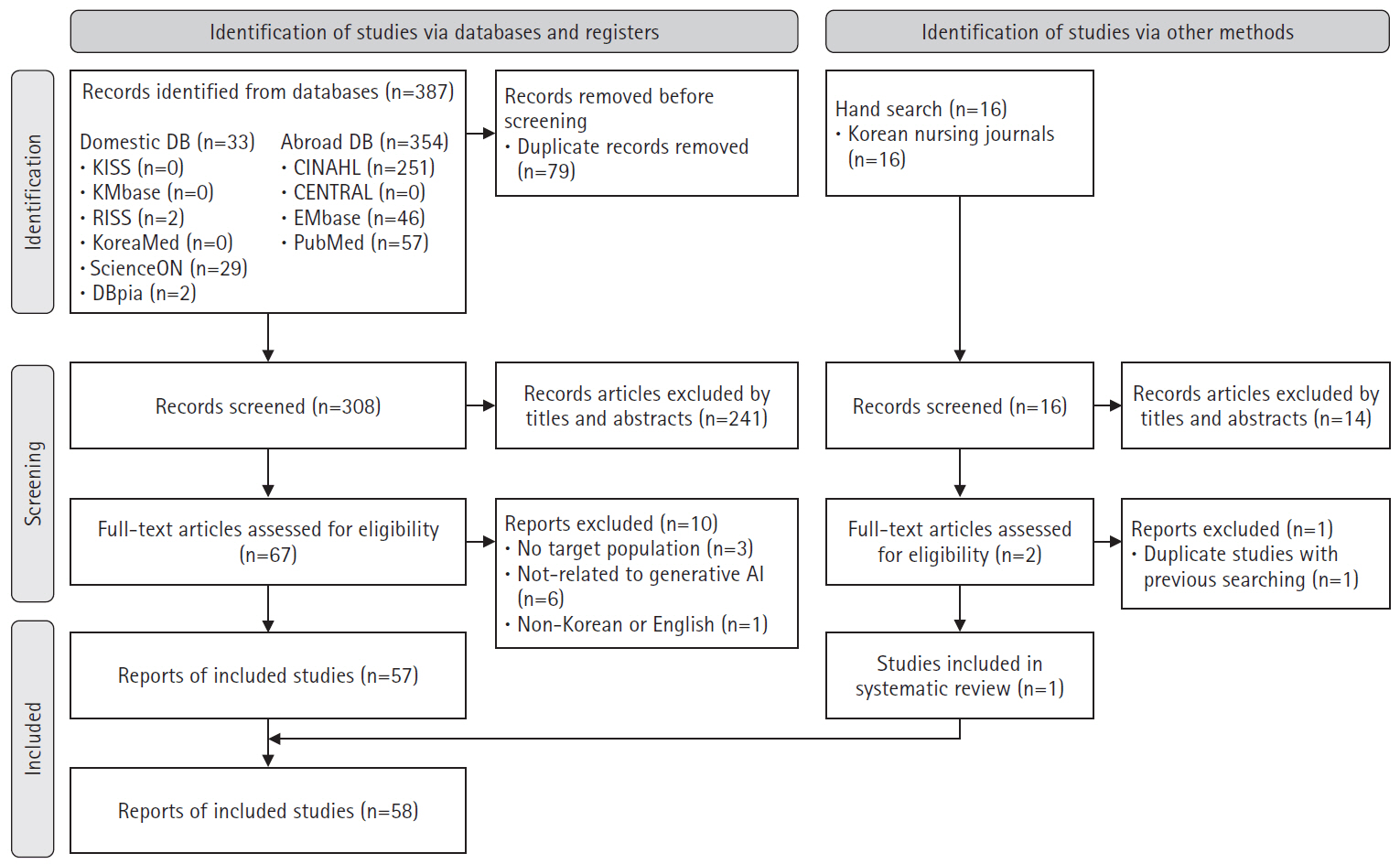
- Research trends in generative artificial intelligence in nursing: a scoping review
- Myung Jin Choi, Myoung Hee Seo, Jihun Kim, Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):468-487. Published online August 5, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) has yet to be comprehensively analyzed in the nursing literature. This study aimed to identify research trends in generative AI within the nursing field through a scoping review and propose strategies for its effective utilization in nursing.
Methods
A scoping review was conducted following Arksey and O’Malley’s six-stage framework. The inclusion criteria included: (1) studies conducted in nursing; (2) research related to generative AI; and (3) original research articles, theses, communications, editorials, letters, or commentaries published in academic journals. Database used PubMed, Embase, CENTRAL, CINAHL, KMbase, KoreaMed, KISS, ScienceON, RISS, DBpia, and 27 nursing-specific journals.
Results
In total, 403 studies were initially identified, and 58 were included in the final analysis. In the care domain, strengths included rapid information retrieval and improved nurse-patient communication, while limitations included the irreplaceable human element and low reliability. The administration domain had no relevant studies. In the research domain, generative AI exhibited strengths such as enhanced efficiency in the paper writing process and improved dissemination speed, but its weaknesses included lack of ethical and legal accountability and a risk of inaccurate or biased information. In the education domain, generative AI was effective in saving time in educational design and implementation, as well as supporting content creation, but challenges included algorithmic bias and risks of plagiarism.
Conclusion
This study identified potential benefits and limitations of generative AI across nursing domains. For effective application, it is essential to develop comprehensive guidelines and policies, provide user education and support, and create opportunities for nurses, educators, and students to learn about strengths and risks of generative AI. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nursing Students' Perspectives on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Psychiatric Nursing Education: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
Sukyung Son, Eunyoung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(Special Is): 9. CrossRef
- Nursing Students' Perspectives on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Psychiatric Nursing Education: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
- 7,325 View
- 552 Download
- 1 Crossref

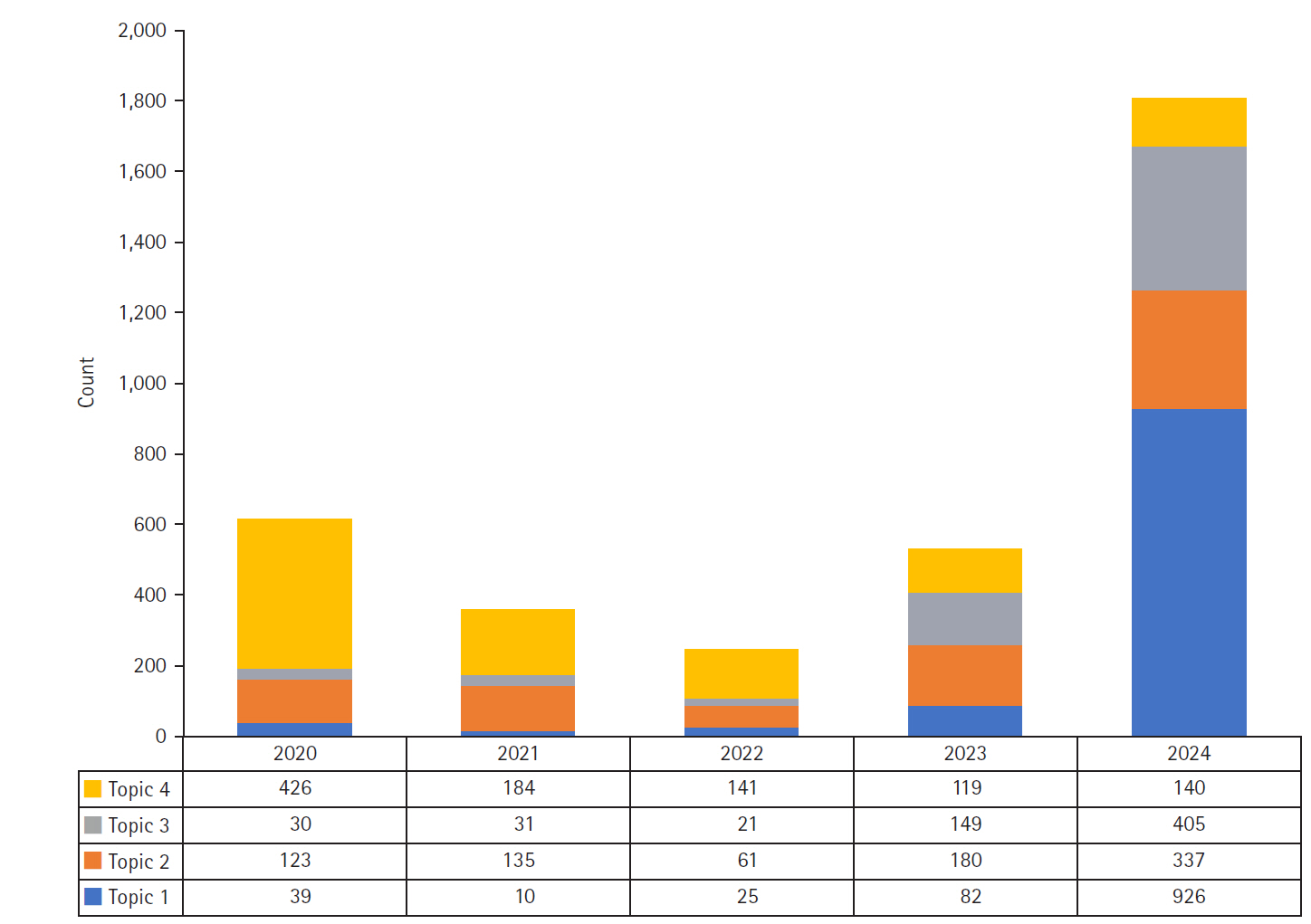
- Media discourse on physician assistant nurses in South Korea: a text network and topic modeling approach
- Young Gyu Kwon, Daun Jeong, Song Hee Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Chan Woong Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):388-399. Published online July 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25038
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study quantitatively examined the portrayal of physician assistant (PA) nurses in Korean media by integrating text network analysis with latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) topic modeling.
Methods
A total of 3,564 news articles published by nine major Korean media outlets between 2020 and 2024 were analyzed. Content analysis was conducted using term frequency-inverse document frequency calculations, network centrality analysis, and LDA topic modeling to extract key terms, map discourse structures, and identify latent topics.
Results
The analysis identified four primary topics in Korean media discourse: “healthcare workforce expansion policies” (30.4%), “hospital clinical practice and operational management” (23.5%), “institutionalization of the PA nursing role” (17.8%), and “COVID-19 response and public health crisis management” (28.3%). High-centrality keywords included “hospital,” “medical,” “patient,” “physician,” “government,” and “nurse,” indicating that the discourse primarily focused on clinical settings. Topic modeling revealed a major shift from pandemic-centered coverage in 2020 to a focus on healthcare workforce policy and PA nurse institutionalization in 2024, coinciding with the passage of the Nursing Act.
Conclusion
This study provides empirical evidence suggesting that the portrayal of PA nurses in Korean media discourse evolved from a peripheral regulatory issue to a central healthcare delivery solution, particularly in the contexts of workforce management, clinical practice, and crisis response. Our findings suggest that PA nurse institutionalization received broader attention when positioned as part of systemic healthcare improvements addressing concrete clinical needs. These results offer valuable insights for policymakers and administrators in framing and implementing workforce policy reforms. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of role conflict and job stress on turnover intention among Korean physician assistant nurses: A cross-sectional study
Jin-Won Lee, Eun-Hi Choi, Ji-Sun Back
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Impact of role conflict and job stress on turnover intention among Korean physician assistant nurses: A cross-sectional study
- 3,525 View
- 123 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Core domains for pre-registered nurses based on program outcomes and licensing competencies
- Soyoung Yu, Hye Young Kim, Jeung-Im Kim, JuHee Lee, Ju-Eun Song, Hyang Yuol Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):249-268. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify core domains for pre-registered nurses by comparing licensing competencies with program outcomes (POs) in undergraduate nursing education. This was accomplished in preparation for the transition of the Korean Nurse Licensing Examination (KNLE) from a tradition seven-subject format to a newly integrated, competency-based single-subject format that reflects current trends in nursing assessment.
Methods
A literature review and survey were conducted. From 828 studies retrieved via PubMed, CINAHL, and Google Scholar using keywords such as “newly graduated registered nurses” and “competency OR competence,” 18 were selected according to pre-established inclusion and exclusion criteria. Documents from national and international nursing organizations were included to extract relevant licensing competencies. We also reviewed POs from all undergraduate nursing schools in South Korea to align educational outcomes with the identified core domains.
Results
The core domains identified were clinical performance and decision-making, professional attitudes and ethics, communication and interpersonal skills, leadership and teamwork, quality improvement and safety, health promotion and prevention, and information technology and digital health. These domains showed strong alignment with POs under the fourth-cycle accreditation standards.
Conclusion
It concludes the seven core domains will be appropriate for evaluating pre-registered nurses in the integrated KNLE. Based on the seven identified core domains, expert consensus should be sought in the next phase to support the development of integrated, competency-based test items grounded in these domains. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Transforming nursing education to enhance integrated nursing competency: a Delphi-based methodological study on symptom-based clinical reasoning
Jeung-Im Kim, Soyoung Yu, Jin-Hee Park, Ju-Eun Song, Eunjung Ryu, JuHee Lee, YeoJin Im
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2026; 56(1): 39. CrossRef
- Transforming nursing education to enhance integrated nursing competency: a Delphi-based methodological study on symptom-based clinical reasoning
- 4,238 View
- 161 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effectiveness of a mobile application for tracking symptoms and enhancing symptom management among breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy in Bangkok, Thailand: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Duangrat Kaveenuntachai, Supawan Jaiboon, Bualuang Sumdaengrit, Chureeporn Silaguntsuti, Arveewan Vittayatigonnasak, Pornchan Sailamai
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):178-190. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25011
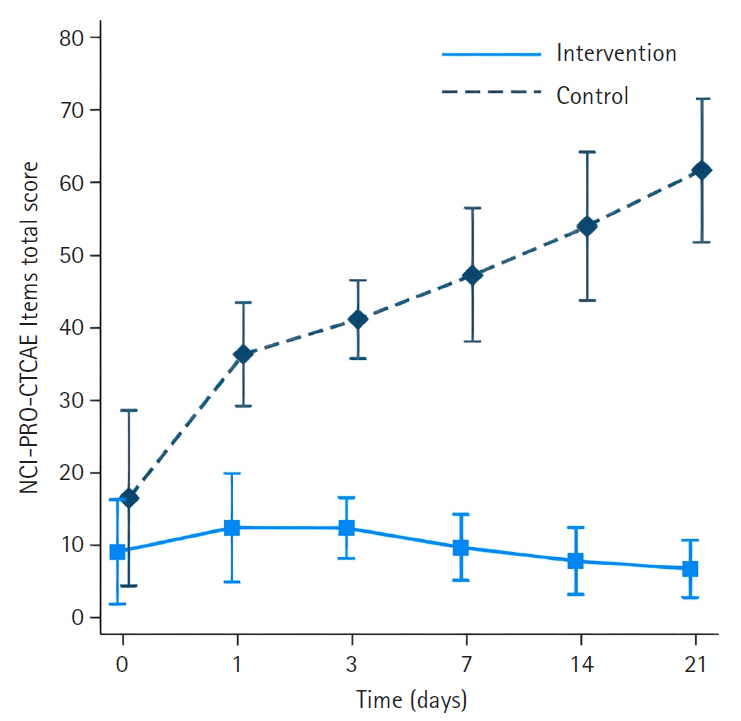
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study evaluated the effectiveness of a mobile application in tracking symptoms and improving symptom management and quality of life (QoL) among breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in Thailand.
Methods
A non-randomized controlled trial was used, with 25 participants in the intervention group and 25 in the control group. Research instruments included a demographic data form, the NCI-PRO-CTCAE Items-Thai-Thailand version 1.0, and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Core Questionnaire and Breast Cancer-Specific Module.
Results
The intervention group had significantly less severe side effects than the control group, with mean differences of –23.33 (95% confidence interval [CI], –27.82 to –18.83) on day 1, –28.18 (95% CI, –33.22 to –23.14) on day 3, –34.63 (95% CI, –40.18 to –29.08) on day 7, –42.56 (95% CI, –48.72 to –36.40) on day 14, and –51.31 (95% CI, –58.13 to –44.48) on day 21 (p<.001 for all). On day 21, participants in the intervention group reported significantly higher scores in the Global Health QoL and Functional Scales compared to the control group (p<.001). Additionally, intervention group participants reported lower scores on the Symptom Scales and higher scores on the Functional Scales than those in the control group (p<.001).
Conclusion
The ChemoPro application helped manage chemotherapy-related symptoms and was associated with improved symptom monitoring and QoL. Nonetheless, the study was limited by a small sample size and restriction to Android users. Future research with larger and more diverse populations is recommended before broader implementation in clinical practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of a digital health intervention on the supportive care needs and quality of life in Mexican patients with breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial
Saúl Eduardo Contreras-Sánchez, Svetlana V. Doubova, Rocío Grajales-Álvarez, Ricardo Villalobos-Valencia, Abdel Karim Dip-Borunda, José Gustavo Nuñez-Cerrillo, Alma Diana Huerta-López, Álvaro José Montiel-Jarquín, Arturo García-Galicia, Enrique Isay Talam
BMC Cancer.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effectiveness of a digital health intervention on the supportive care needs and quality of life in Mexican patients with breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial
- 4,401 View
- 219 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Development and evaluation of a question-answering chatbot to provide information for patients with coronary artery disease after percutaneous coronary intervention
- Geunhee Lee, Yun Hee Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):153-164. Published online May 13, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24128
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a question-answering chatbot that provides accurate and consistent answers to questions that may arise during the recovery process of patients with coronary artery disease after percutaneous coronary intervention, and to evaluate the chatbot.
Methods
The chatbot was developed through the stages of analysis, design, implementation, and evaluation. It was evaluated by five experts, and the user experience was evaluated by 27 patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention. Furthermore, chatbot utilization was analyzed based on user experience logs.
Results
The chatbot was constructed as a question-answering database that included three categories: coronary artery disease, percutaneous coronary intervention, and post-intervention management. The question-answering chatbot, referred to as the “Cardiovascular Strong” channel, has been launched and implemented. An expert evaluation of the chatbot revealed no usability issues or necessary modifications. The overall result of the user experience evaluation was 4.26 points. Based on the user experience log, the question-answer accuracy was 84.6%, and medications during post-intervention management were the most frequently searched topic, accounting for 110 cases (20.8%) out of a total of 528.
Conclusion
The chatbot that was developed to provide information via real-time answers to questions after the intervention can be easily accessed in clinical settings with no time or space constraints. It also will contribute to providing accurate disease-related information via the familiar KakaoTalk platform. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Generative AI at the Bedside: An Integrative Review of Applications and Implications in Clinical Nursing Practice
Adrianna L. Watson, Carmel Bond, Helen Aveyard, Graeme D. Smith, Debra Jackson
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Generative AI at the Bedside: An Integrative Review of Applications and Implications in Clinical Nursing Practice
- 2,484 View
- 264 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- The effects of a lifestyle intervention for men in infertile couples in South Korea: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Yun Mi Kim, Ju-Hee Nho
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):191-204. Published online April 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of an interaction model of client health behavior (IMCHB)-based lifestyle intervention on health-promoting behaviors, infertility stress, fertility-related quality of life, and semen quality in men in infertile couples.
Methods
This study used a quasi-experimental, non-equivalent control group, pretest-posttest design, with participants divided into an experimental group (n=17) and a control group (n=19). The 16-session, 8-week intervention included components such as reproductive health education, physical activity, nutritional management, and stress management. Data collection occurred between July 1, 2021 and September 27, 2022. The outcomes measured included health-promoting behaviors, infertility stress, fertility-related quality of life, and sperm quality (volume, total motility, immobility, concentration, and normal morphology).
Results
The experimental group showed significant improvements in health-promoting behaviors (z=–2.27, p=.023) and reductions in infertility stress (t=–2.40, p=.022) compared to the control group. Total sperm motility (F=4.39, p=.045) and normal morphology (z=2.86, p=.017) were also significantly higher in the experimental group than in the control group.
Conclusion
The IMCHB-based lifestyle intervention significantly increased health-promoting behaviors, reduced infertility stress, and improved key sperm parameters, indicating its effectiveness in supporting the reproductive health of men in infertile couples. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychological Stress and Male Infertility: Oxidative Stress as the Common Downstream Pathway
Aris Kaltsas, Stamatis Papaharitou, Fotios Dimitriadis, Michael Chrisofos, Nikolaos Sofikitis
Biomedicines.2026; 14(2): 259. CrossRef
- Psychological Stress and Male Infertility: Oxidative Stress as the Common Downstream Pathway
- 3,829 View
- 141 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of a nursing leadership program on self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, problem-solving abilities, and nursing professionalism among nursing students in South Korea: a quasi-experimental study
- Sunmi Kim, Young Ju Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):137-151. Published online February 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24110
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study investigated the effects of a nursing leadership program on self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, problem-solving abilities, and nursing professionalism among nursing students in South Korea.
Methods
A quasi-experimental study was conducted. The Practice-Driven Nursing Leadership Program for Students (PDNLP-S) was developed based on the ADDIE model (analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation). This quasi-experimental study design included 60 nursing students. The experimental group (n=30) participated in the PDNLP-S for 120-minute sessions over 5 weeks, while the control group (n=30) received usual lectures. The PDNLP-S included lectures, discussions, and individual and group activities to cultivate core nursing leadership competencies such as individual growth, collaboration, nursing excellence, creative problem-solving, and influence. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, the Mann-Whitney U-test, and the independent t-test with IBM SPSS Windows ver. 26.0.
Results
The experimental group demonstrated significant improvements in self-leadership (t=3.28, p=.001), interpersonal relationships (t=3.07, p=.002), clinical performance (U=268.50, p=.004), and problem-solving abilities (t=2.20, p=.017) compared to the control group. No significant difference was observed in nursing professionalism (t=0.50, p=.311).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that the PDNLP-S improved nursing students’ self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, and problem-solving abilities. The PDNLP-S can play a significant role in cultivating future nurse leaders by enhancing these nursing leadership competencies among nursing students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Self-Determination Theory in Return to Work Interventions: A Scoping Review
Kexin Chen, Ling Yang, Jiajia Tu
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2025; Volume 18: 7539. CrossRef
- Self-Determination Theory in Return to Work Interventions: A Scoping Review
- 7,567 View
- 322 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy Scale for Nurses
- Youngrye Park, Sunah Park, Hee Ran Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):633-644. Published online November 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24094
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study aimed to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the occupational coping self-efficacy for nurses (K-OCSE-N) scale.
Methods The English version of the OCSE-N scale was translated into Korean using a translation and back-translation process. Data were gathered from 213 nurses employed in a general hospital in South Korea. The content validity was assessed using the content validity index. The construct validity was verified through exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses. Criterion validity was assessed using Pearson’s correlation coefficients with the job stress coping and general self-efficacy scales. Reliability was examined using item-total score correlation and Cronbach’s α coefficient for internal consistency.
Results The exploratory factor analysis identified two factors that explained 61.8% of the cumulative variance: occupational burden and relational difficulty. In confirmatory factor analysis, the model exhibited adequate fit (
χ 2/df = 2.07, GFI = .95, SRMR = .04, RMSEA = .07, CFI = .97, and TLI = .95), with both convergent and discriminant validity deemed acceptable. The criterion validity presented a positive correlation of the K-OCSE-N with both job stress coping (r = .72,p < .001) and general self-efficacy (r = .72,p < .001). The internal consistency of the scale using Cronbach’s α for the total items was .89.Conclusion The K-OCSE-N scale is a valid and reliable tool for measuring nurses’ occupational coping self-efficacy. This study suggests that various intervention studies can use the scale to assess and strengthen nurses’ occupational coping self-efficacy in nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Patient Safety and Quality Improvement in Nursing Practice: Associations Among Workload, Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy and Medical Device-Related Pressure Injury Prevention
Hyun Suk Gwag, Jin Ah Kim
Healthcare.2026; 14(2): 270. CrossRef
- Patient Safety and Quality Improvement in Nursing Practice: Associations Among Workload, Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy and Medical Device-Related Pressure Injury Prevention
- 7,347 View
- 414 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Experiences of Unmarried Women Undergoing Planned Oocyte Cryopreservation
- Miok Kim, Kim Mingyoung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):577-593. Published online November 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24064
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose The present study investigated the experiences of unmarried women undergoing planned oocyte cryopreservation (OC).
Methods Data were collected from August 2022 to February 2023 through individual in-depth interviews with thirteen unmarried women undergoing planned OC. Data were analyzed using Colazzi’s phenomenological method.
Results The findings revealed four distinct clusters. The first cluster, “Safeguards against Future Uncertainty,” examined experiences associated with uncertainties in several aspects of reproductive health threats and decision-making regarding planned OC. The second cluster, “Indescribable Pain and Chaos,” explored the psychological and physical pain, complications, concerns about repeat procedures, and uncertainties about the use of frozen oocytes experienced during the planned OC process and afterward. The third cluster, “Motivation to Rebuild Resilience,” explored participants’ resilience in overcoming difficulties and shocks during the planned OC process and regaining their inner strength through the support of family and friends. The fourth cluster, “Finally Freeing the Mind,” focused on the sense of liberation from the pressure of marriage and childbirth, which enabled participants to engage in their present self and concentrate on self-stability and growth in preparation for the future.
Conclusion The present study enhances our understanding of the emotional difficulties and distress experienced by women considering OC, thereby assisting in improving approaches for psychological support and clinical management. Furthermore, providing insights into these first-hand experiences to women considering planned OC, healthcare professionals, and policymakers could help establish systems to support the decision-making process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Experiences of Female Cancer Patients Undergoing Fertility Preservation: A Qualitative Study
Menekşe Nazlı Aker, Neslihan Yılmaz Sezer, Melek Hava Köprülü, Gülşah Kaya, Batuhan Özmen, Wenjun Mao
European Journal of Cancer Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Experiences of Female Cancer Patients Undergoing Fertility Preservation: A Qualitative Study
- 3,273 View
- 125 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of the Spinning Babies Program on Birth Outcomes and Satisfaction during Labor: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
- Mi-Yeon Jeong, Hyang Mi Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):607-619. Published online November 20, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24097
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study evaluated the effects of the Spinning Babies program applied during labor on birth outcomes and satisfaction among pregnant women.
Methods This non-equivalent control group, non-synchronized post-test only design study included 42 participants (22 in the experimental group and 20 in the control group). The Spinning Babies program was conducted four times in the experimental group during the first and second stages of delivery for 50 min per session. The program comprised performing pelvic circles on a birth ball, followed by wide squatting and adopting of open knee-chest and side-lying positions.
Results Compared with those in the control group, pregnant women in the experimental group had a significantly shorter labor time (t = - 6.64,
p < .001), a higher success rate for normal vaginal delivery (χ 2 = 4.86,p = .043), improved Apgar scores of newborns (z 2 = - 2.18,p = .029), differences in neonatal oxygen therapy use (χ 2 = 4.86,p = .043), and improved birth satisfaction (t = 11.99,p < .001).Conclusion The Spinning Babies program improves the birth environment by increasing the normal vaginal delivery success rate, as well as pregnant women’s birth satisfaction, and promotes neonatal health.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Da-Jung Kim
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2025; 21(5): 234. CrossRef
- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- 5,839 View
- 358 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Clinical Nurses’ Perception of Structural and Content Career Plateau
- Ji Hye Kim, Ji Yun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):534-546. Published online October 23, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study was intended to provide basic data for reducing the career plateaus of clinical nurses.
Methods The participants were 288 clinical nurses who worked at five hospitals, general hospitals, and tertiary hospitals in Seoul, Gyeonggi, and Chungcheong provinces and had more than one year of clinical experience. The research data were collected from December 26, 2022, to April 7, 2023, using structured questionnaires and analyzed using SPSS software. The study conducted mean, standard deviation, percentage, t-test, ANOVA, Pearson‘s correlation coefficient, and hierarchical regression analysis.
Results Perceived organizational support was identified as the factor influencing structural career plateaus. Factors influencing content career plateaus included growth needs, skill variety, organizational justice, and perceived organizational support.
Conclusion The above research results suggest that to increase the motivation of clinical nurses and reduce career plateaus, it is necessary to improve awareness and systems of human resource management at the organizational level.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nursing managers’ perceptions of clinical nurses’ self-management in professional title promotion: a qualitative user persona study
Xiang Gao, Xuemei Wang
BMC Nursing.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Nursing managers’ perceptions of clinical nurses’ self-management in professional title promotion: a qualitative user persona study
- 2,501 View
- 175 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Development and Effectiveness of Progressive Simulation Education Program on Medication Safety for Nursing Students
- Se-Young Jung, Eun-Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):563-576. Published online October 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24054
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study aimed to develop and verify a progressive simulation education program aimed at enhancing nursing students’ medication safety competency.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was adopted. The participants were 40 third-year nursing students with no prior simulation education experience, comprising 20 each in the experimental and control groups. The experimental treatment utilized a hybrid simulation approach incorporating both full-body mannequins and standardized patients and was, conducted over three sessions with durations of 65, 80, and 95 minutes for the first, second, and third sessions, respectively, for a total of 240 minutes. The program was constructed based on Jeffries’ simulation model.
Results The levels of medication safety competencies, communication self-efficacy, learning self-efficacy, and problem-solving abilities of the experimental group were significantly higher than that of the control group.
Conclusion Our results confirm that the program effectively improves nursing students’ medication safety competence, communication self-efficacy, learning self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability. Therefore, this program can serve as a basis for developing educational strategies related to medication safety for nursing education institutions. Furthermore, the program is anticipated to have a positive impact on novice nurses’ education and practice in clinical settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Safety-centered simulation education using the 360-degree video room of errors: A mixed-methods study
Jiyoung Kim, Yeji Kim, Hyunji Park, Jiyeong Won, Jiwon Yun, Yuran Lee
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2026; 111: 101899. CrossRef
- Safety-centered simulation education using the 360-degree video room of errors: A mixed-methods study
- 4,964 View
- 425 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- How Do We Approach Quality Care for Patients from Middle Eastern Countries? A Phenomenological Study of Korean Nurses’ Experiences
- Dael Jang, Seonhwa Choi, Gahui Hwang, Sanghee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):372-385. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24036
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Although more people from Middle Eastern countries are visiting South Korea for medical treatment, Korean nurses lack experience in treating them. Understanding and describing Korean nurses’ experiences can help them provide quality care to these patients by enhancing their competency in culturally appropriate care. This study described the experiences of nurses who provide care to Middle Eastern patients in clinical settings in South Korea.
Methods
We conducted a phenomenological study to describe nurses’ experience of caring for patients from Middle Eastern countries. Ten nurses with prior experience in caring for these patients were recruited from a university-affiliated tertiary hospital. Semi-structured face-to-face interviews were conducted between May 1 and June 4, 2020. The transcribed data were analyzed using Giorgi’s phenomenological method to identify the primary and minor categories representing nurses’ experiences.
Results
Four major categories (new experiences in caring for culturally diverse patients, challenges in caring for patients in a culturally appropriate manner, nursing journey of mutual agreement with culturally diverse patients, and being and becoming more culturally competent) and 11 subcategories were identified.
Conclusion
Nurses experience various challenges when caring for Middle Eastern patients with diverse language and cultural needs. However, nurses strive to provide high-quality care using various approaches and experience positive emotions through this process. To provide quality care to these patients, hospital environments and educational programs must be developed that center on field nurses and students and support them in delivering quality care while utilizing their cultural capabilities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The roles of nurses employed as medical tourism facilitators in Taiwan: A qualitative study
Eimi Nakada, Keiko Sugimoto, Rieko K. Fukuzawa, Thomas Mayers, Yi-Chuan Chen, Judith S. C. Shiao
International Journal of Healthcare Management.2026; : 1. CrossRef
- The roles of nurses employed as medical tourism facilitators in Taiwan: A qualitative study
- 2,704 View
- 71 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effectiveness of the Eye Care Protocol in the Intensive Care Unit Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Kyu Won Lim, Shin Young Ha, In Soon Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):432-445. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated the effects of an eye care protocol (ECP) on patients in the intensive care unit (ICU).
Methods
This study utilized a randomized controlled design. Participants were patients who met the inclusion criteria and were admitted to the ICU (36 in the experimental group and 38 in the control group). The experimental group received an ECP, while the control group received standard eye care, starting the day after admission, for a duration of 10 days. The ECP classifies the degree of eyelid obstruction into three stages based on the degree of exposure to the lower eyelid conjunctiva and cornea. The protocol included cleansing with normal saline gauze, administering eye drops, applying silicone and polyurethane films, and recommending consultation with an ophthalmologist if necessary. The effectiveness of ECP was assessed by analyzing tear volume, hyperemia, chemosis, and eye discharge. Data analysis was conducted using SPSS 27.0, employing the Mann-Whitney U-test and generalized estimating equations.
Results
On day 5, the experimental group demonstrated a significant increase in tear volume in both eyes compared with the control group. However, no statistically significant differences were observed in the incidence of hyperemia, chemosis, and eye discharge on days 5 and 10 of the intervention.
Conclusion
The application of the ECP in this study increased tear volume in ICU patients, thereby reducing discomfort caused by dry eyes. It has the potential to prevent complications such as damage to the surface of the eyeball resulting from decreased tear volume. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Da-Jung Kim
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2025; 21(5): 234. CrossRef
- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- 1,487 View
- 204 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Development of the Hybrid Clinical Practicum Environment Scale for Nursing Students
- Seoyoung Yoon, Hye-Ah Yeom
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):340-357. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24016
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a Hybrid Clinical Practicum Environment Scale for Nursing Students (HCPES-NS) and verify its validity and reliability.
Methods
The HCPES-NS was constructed following the DeVellis guidelines. The initial items were written based on a literature review and individual in-depth interviews. Content validity was verified through an expert panel review. To confirm the validity and reliability of the scale, a survey was conducted with 449 nursing students enrolled in 12 nursing colleges. Data were analyzed using item analysis, exploratory factor analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, concurrent validity, and reliability tests.
Results
Factor analysis showed that the HCPES-NS consists of 15 items on five subdomains: clinical site atmosphere, interpersonal relationship, alternative online practicum contents, provision of learning information, and clinical performance facilitation. A higher score indicated a more positive perception of the clinical practicum environment. The concurrent validity of the HCPES-NS was confirmed by its positive correlation with the Clinical Learning Environment Scale (r = .77). The Cronbach’s α reliability of the HCPES-NS was .84.
Conclusion
The HCPES-NS is both valid and reliable. This scale reflects the clinical practicum environment and includes an online practicum factor. It may be used effectively by faculty members and educators to evaluate nursing students’ perceptions of clinical practicum environments. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Environmental and Individual Factors Associated with Clinical Practice Stress in Korean Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
Ui Rim Song
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(4): 355. CrossRef
- Environmental and Individual Factors Associated with Clinical Practice Stress in Korean Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
- 3,091 View
- 103 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Oncofertility in Gynecological Cancer Patients: Application of Mixed Methods Study
- Minji Kim, Juyoung Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):418-431. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify factors influencing oncofertility and to explore the oncofertility experiences of patients with gynecological cancer using quantitative and qualitative methods, respectively. Methods: An explanatory sequential mixed-methods study was conducted. The quantitative study involved 222 patients with gynecological cancer recruited from online cafes and hospitals. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics 28. For qualitative research, eight patients with gynecological cancer were interviewed. Data were analyzed using theme analysis method. Results: Oncofertility performance was quantitatively assessed in 40 patients (18.0%). Factors that significantly affected oncofertility were fertility preservation awareness (odds ratio [OR] = 14.97, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 4.22~53.08), number of children planned before cancer diagnosis (OR = 6.08, 95% CI: 1.89~19.62; OR = 5.04, 95% CI: 1.56~16.29), monthly income (OR = 3.29, 95% CI: 1.23~8.86), social support (OR = 1.08, 95% CI: 1.01~1.17), and anxiety (OR = 0.79, 95% CI: 0.66~0.95). Qualitative results showed three theme clusters and eight themes: (1) themes for determinant factors affecting oncofertility selection: ‘desire to have children’ and ‘special meaning of the uterus and ovaries;’ (2) themes for obstructive factors affecting oncofertility selection: ‘fertility preservation fall behind priorities,’ ‘confusion caused by inaccurate information,’ and ‘my choice was not supported;’ (3) themes for support factors affecting oncofertility selection: ‘provide accurate and reasonable information about oncofertility,’ ‘addressing the healthcare gap,’ and ‘need financial support for oncofertility.’ Conclusion: Financial support, sufficient information, social support, and anxiety-relief interventions are required for oncofertility in patients with gynecological cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Digital health interventions for oncofertility in female patients: a systematic review
Juyoung Ha, Minji Kim, Hyojin Park
Women's Health Nursing.2025; 31(2): 119. CrossRef
- Digital health interventions for oncofertility in female patients: a systematic review
- 2,240 View
- 123 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Factors Related to Emotional Leadership in Nurses Manager: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Se Young Jang, Chan Mi Park, Eun Hee Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):119-138. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24026
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify research trends related to emotional leadership among nurse managers by conducting a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. This study sought to derive insights that could contribute to improving emotional leadership in nursing practice.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) and Meta-Analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines. Databases including PubMed, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, Scopus, Web of Science, Research Information Sharing Service, Koreanstudies Information Service System, Korean Medical Database, KoreaMed, ScienceON, and DBpia were searched to obtain papers published in English and Korean. Literature searches and screenings were conducted for the period December 1, 2023 to December 17, 2023. The effect size correlation (ESr) was calculated for each variable and the meta-analysis was performed using the statistical software SPSS 29.0, R 4.3.1.
Results
Twenty-five (four personal, six job, and fifteen organizational) relevant variables were identified through the systematic review. The results of the meta-analysis showed that the total overall effect size was ESr = .33. Job satisfaction (ESr = .40) and leader-member exchange (ESr = .75) had the largest effect size among the job and organizational-related factors.
Conclusion
Emotional leadership helps promote positive changes within organizations, improves organizational effectiveness, and increases member engagement and satisfaction. Therefore, it is considered an important strategic factor in improving organizational performance. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Emotional leadership in health care: A dire need illuminated by pivotal resource cuts
Jacqueline Hoare
South African Journal of Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Emotional leadership in health care: A dire need illuminated by pivotal resource cuts
- 3,834 View
- 195 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Structural Topic Modeling Analysis of Patient Safety Interest among Health Consumers in Social Media
- Nari Kim, Nam-Ju Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):266-278. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate healthcare consumers’ interest in patient safety on social media using structural topic modeling (STM) and to identify changes in interest over time.
Methods
Analyzing 105,727 posts from Naver news comments, blogs, internet cafés, and Twitter between 2010 and 2022, this study deployed a Python script for data collection and preprocessing. STM analysis was conducted using R, with the documents’ publication years serving as metadata to trace the evolution of discussions on patient safety.
Results
The analysis identified a total of 13 distinct topics, organized into three primary communities: (1) “Demand for systemic improvement of medical accidents,” underscoring the need for legal and regulatory reform to enhance accountability; (2) “Efforts of the government and organizations for safety management,” highlighting proactive risk mitigation strategies; and (3) “Medical accidents exposed in the media,” reflecting widespread concerns over medical negligence and its repercussions. These findings indicate pervasive concerns regarding medical accountability and transparency among healthcare consumers.
Conclusion
The findings emphasize the importance of transparent healthcare policies and practices that openly address patient safety incidents. There is clear advocacy for policy reforms aimed at increasing the accountability and transparency of healthcare providers. Moreover, this study highlights the significance of educational and engagement initiatives involving healthcare consumers in fostering a culture of patient safety. Integrating consumer perspectives into patient safety strategies is crucial for developing a robust safety culture in healthcare. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- From Posts to Protection: Understanding User-Generated Safety Content on Reddit
Mashael Yousef Almoqbel
International Journal of Computational and Experimental Science and Engineering.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- From Posts to Protection: Understanding User-Generated Safety Content on Reddit
- 2,241 View
- 71 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Sexual Experiences in Adolescents Using a Random Forest Model: Secondary Data Analysis of the 2019~2021 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey Data
- Yoonseok Yang, Ju Won Kwon, Youngran Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):193-210. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23134
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The objective of this study was to develop a predictive model for the sexual experiences of adolescents using the random forest method and to identify the “variable importance.” Methods: The study utilized data from the 2019 to 2021 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey, which included 86,595 man and 80,504 woman participants. The number of independent variables stood at 44. SPSS was used to conduct Rao-Scott χ2 tests and complex sample t-tests. Modeling was performed using the random forest algorithm in Python. Performance evaluation of each model included assessments of precision, recall, F1-score, receiver operating characteristics curve, and area under the curve calculations derived from the confusion matrix.
Results
The prevalence of sexual experiences initially decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic, but later increased. “Variable importance” for predicting sexual experiences, ranked in the top six, included week and weekday sedentary time and internet usage time, followed by ease of cigarette purchase, age at first alcohol consumption, smoking initiation, breakfast consumption, and difficulty purchasing alcohol.
Conclusion
Education and support programs for promoting adolescent sexual health, based on the top-ranking important variables, should be integrated with health behavior intervention programs addressing internet usage, smoking, and alcohol consumption. We recommend active utilization of the random forest analysis method to develop high-performance predictive models for effective disease prevention, treatment, and nursing care. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gender differences in the associations among adolescent problem behaviors: a secondary data analysis of the 2023 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Jaeyoung Lee, So Yeon Park
Child Health Nursing Research.2025; 31(3): 155. CrossRef
- Gender differences in the associations among adolescent problem behaviors: a secondary data analysis of the 2023 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
- 4,178 View
- 71 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of an App-Based Self-Management Program for Exercise Practice of Breast Cancer Survivors: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
- Suyoun Maeng, Jungok Yu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):250-265. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23119
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop an app-based self-management program based on the transtheoretical model (TTM) for breast cancer survivors’ exercise practice, as well as to investigate the program’s effects on the stage of change for exercise, exercise self-efficacy, exercise decisional balance, exercise amount, and body composition.
Methods
This non-randomized controlled study included 52 participants (26 in each of the experimental and control groups, respectively). An app-based self-management program based on the TTM was conducted with the experimental group for a 12-week period. The program comprised three components: individual coaching for each stage of change for exercise based on TTM, amount of exercise and body composition monitoring, and online self-help meetings.
Results
Compared with the control group, the experimental group had significantly higher stages of change for exercise (p < .001), exercise self-efficacy (p < .001), exercise decisional balance (p = .002), exercise amount (p < .001), and body composition (body weight [p = .006], body mass index [p = .005], and body fat percentage [p = .010]) immediately and four weeks after the intervention.
Conclusion
An appbased self-management program based on the TTM improves exercise behaviors in breast cancer survivors and provides physical benefits. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a mobile health coaching intervention on symptom experience, self-management, and quality of life in breast cancer survivors: A quasi-experimental study
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Yong Sik Jung, Min Hee Hur, Ji Young Kim, Su Jin Jung
Medicine.2025; 104(12): e41894. CrossRef
- Effects of a mobile health coaching intervention on symptom experience, self-management, and quality of life in breast cancer survivors: A quasi-experimental study
- 4,332 View
- 222 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Analysis of the Adequacy of Nurse Staffing Level through the Estimation of Nursing Activity Hours and Implementation of Focus Group Interviews in a Tertiary Hospital: Using a Mixed-Method Design
- Hyun-Joo Kim, Sun-Hee Lee, Jai-Jung Lee, Sun-Suk Seong, Hee Yang, Hyang-Yuol Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):237-249. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22142
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the adequacy of current nurse staffing levels by identifying nursing activities and workload.
Methods
The study used a mixed-method design. A nursing activity survey was conducted using the work sampling method over 2 working days with 119 general ward nurses. A focus group interview was conducted with 12 nurses. Quantitative and qualitative data were analyzed using SPSS 20.0 and content analysis, respectively.
Results
The most amount of time was spent on medication (in direct nursing) and electronic medical record documentation (in indirect nursing). The appropriate nurse-to-patient ratio is 1:7.7 for the day shift, 1:9.0 for the evening shift, and 1:11.9 for the night shift. However, the current nurse-to-patient ratio is 1:9.4, 1:11.0, and 1:13.8 for the day, evening, and night shifts, respectively. Therefore, the current nurse staffing level is insufficient for the workload. In the focus group interview, the main reasons cited for being unable to complete tasks within working hours were communication and coordination, and the nursing electronic medical record. The essential nursing activities of basic nursing and emotional support were overlooked owing to a heavy workload. Therefore, an adequate nurse staffing level should be higher than the measured quantitative workload.
Conclusion
These results suggest the general wards of tertiary hospitals should evaluate the adequacy of their current nurse staffing and allocate sufficient nurses to improve patient safety and nursing care quality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nurses' Experience Working with Substitute Nurses
Hye Mi Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 208. CrossRef
- Nurses' Experience Working with Substitute Nurses
- 3,130 View
- 270 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Lived Experience of Kidney Transplant Recipients with Kidney Graft Failure
- Younghui Hwang, Kyoungok Min, Haeng-Mi Son
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):93-105. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The study aimed to understand the semantic structure and nature of the disease experience of kidney transplant recipients with kidney graft failure by applying phenomenological research methods.
Methods
Data were collected between February and September 2021 through individual in-depth interviews with 12 kidney transplant recipients with kidney graft failure. Colaizzi’s phenomenological analysis was used to analyze the meaning of the participants’ illness experiences.
Results
5 theme clusters and 15 themes were derived. The five theme clusters are as follows: (1) First transplant giving me a second life; (2) Body and mind becoming sick again; (3) Waiting for a re-transplant with hope and worry; (4) Life supported by gratefulness; (5) Having control over my own life.
Conclusion
This study shows that kidney transplant recipients with kidney graft failure experience physical and psychological difficulties during the long disease period and require help from many people, including family members, friends, colleagues, and health care providers, to overcome their difficulties. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perceived Threat of the Risk for Graft Rejection and Its Related Factors in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Cross- Sectional Study
Seolhwa Baek, Sung Reul Kim, Kyounghae Kim, Yusun Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2026; 38(1): 81. CrossRef
- Perceived Threat of the Risk for Graft Rejection and Its Related Factors in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Cross- Sectional Study
- 1,462 View
- 57 Download
- 1 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


