Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Multidimensional factors influencing the completion of advance directives among community-dwelling older Koreans
- Hee-Ju Ji, Soong-Nang Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):543-556. Published online November 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25098
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the multidimensional factors associated with the completion of advance directives (ADs) among community-dwelling older Koreans, guided by conceptual frameworks developed in Asian contexts.
Methods
Data from the 2023 National Survey of Older Koreans (sixth wave) were analyzed for 9,951 community-dwelling older Koreans aged 65 years or older. Complex sample cross-tabulation and binary logistic regression analyses were conducted.
Results
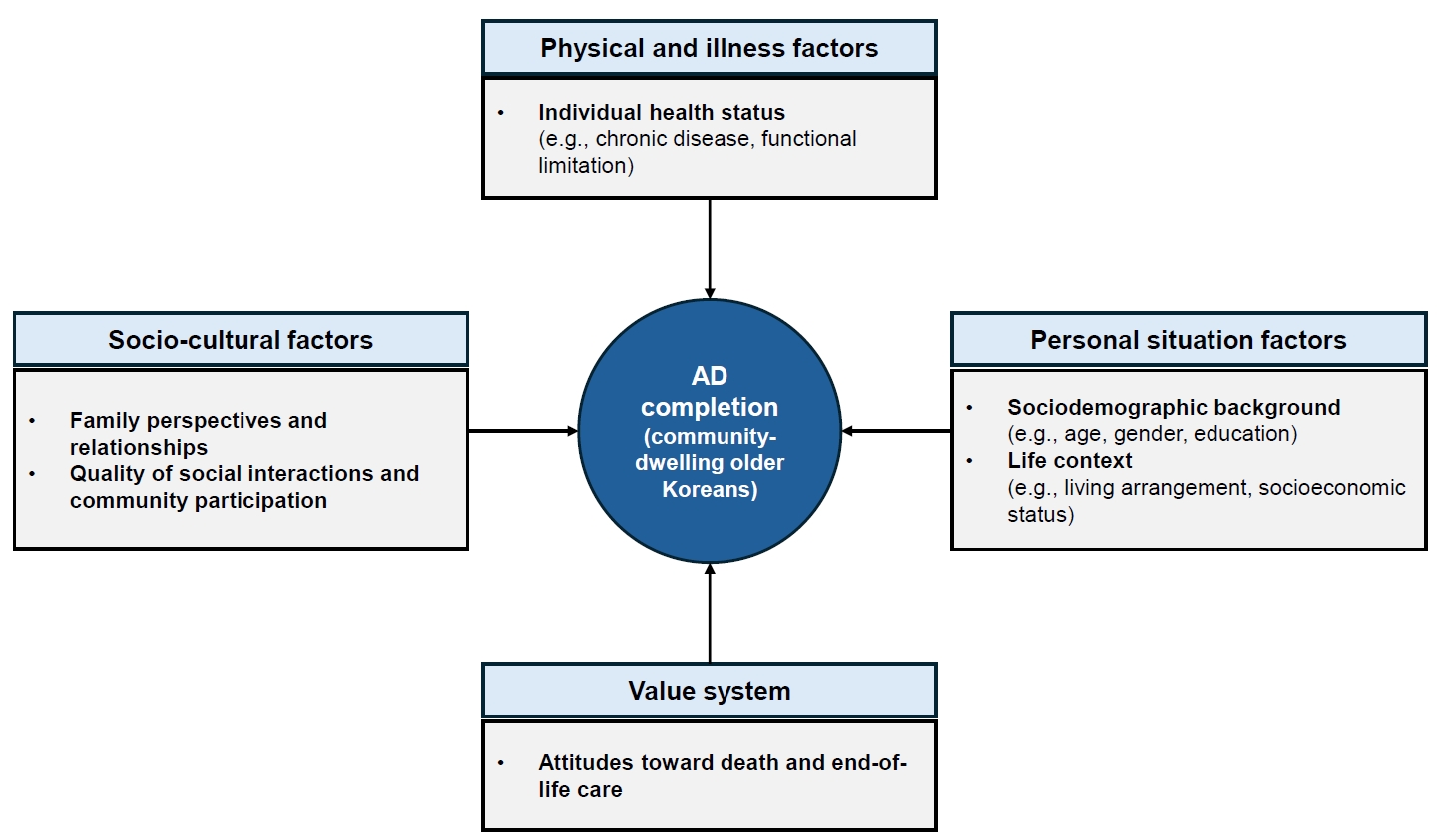
In total, 11.1% of community-dwelling older Koreans had completed an AD. Significant factors associated with AD completion were identified across four domains—personal situation: age, educational level, religion, and housing preference in the event of poor health; socio-cultural: presence of children, participation in social activities and satisfaction with social relationships; physical and illness: the number of chronic diseases; and value system: awareness of hospice and palliative services, participation in death preparedness education, and documentation of organ donation.
Conclusion
Among older Koreans, AD completion represents more than a documentation process; it reflects a complex decision-making process shaped by their values and life circumstances, underscoring the need for supportive interventions. As the highest AD completion rates are found among older adults, related policies should be aligned with older adult-centered policy frameworks.
- 1,376 View
- 126 Download

- Effects of an integrated healthcare program for postpartum women: a quasi-experimental study
- Eun Suk Hwang, Ju-Hee Nho
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):506-518. Published online November 7, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25076
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and evaluate an integrated healthcare program for postpartum mothers based on Cox’s interaction model of client health behavior.
Methods
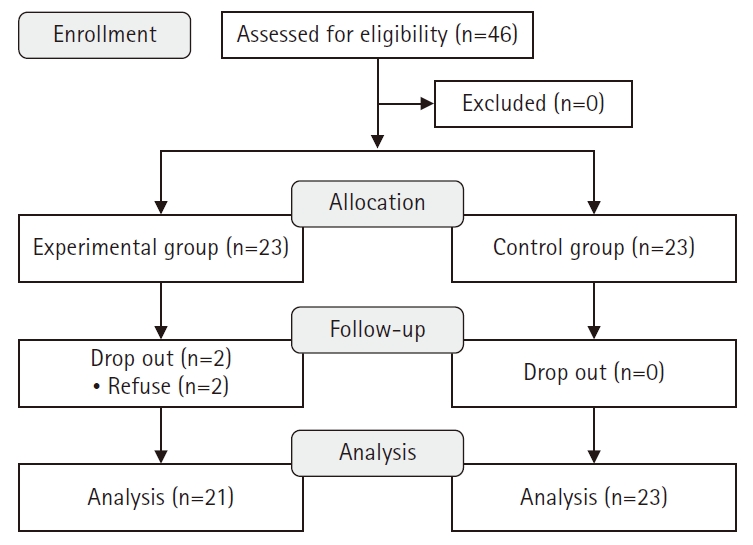
A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The integrated healthcare program was administered 6 times over 2 weeks to postpartum mothers in the experimental group (n=21), while the control group (n=23) received standard care. Data were collected from June 3 to July 15, 2024, through structured questionnaires measuring postpartum fatigue, depression, marital intimacy, and mother-infant attachment. Analyses were conducted using IBM SPSS ver. 23.0.
Results
The experimental group showed significantly lower postpartum fatigue (Z=–2.00, p=.023), a significantly proportion of improvement in postpartum depression (χ2=10.32, p=.012), and a significant increase in mother-infant attachment (t=1.70, p=.048) compared to the control group. However, there was no significant difference in marital intimacy between groups (Z=–0.46, p=.326).
Conclusion
These results suggest that an integrated health management program including physical health, psychological stability, and relational support can be used as an effective nursing intervention to promote health in postpartum mothers. Therefore, additional research is warranted that expands and applies integrated programs for postpartum mothers in various environments in postpartum care centers and communities.
- 1,483 View
- 190 Download

- The effects of a lifestyle intervention for men in infertile couples in South Korea: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Yun Mi Kim, Ju-Hee Nho
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):191-204. Published online April 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of an interaction model of client health behavior (IMCHB)-based lifestyle intervention on health-promoting behaviors, infertility stress, fertility-related quality of life, and semen quality in men in infertile couples.
Methods
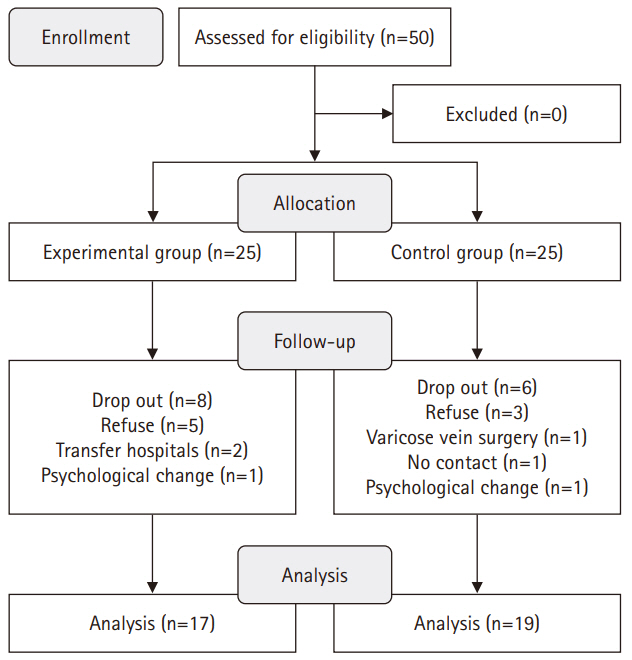
This study used a quasi-experimental, non-equivalent control group, pretest-posttest design, with participants divided into an experimental group (n=17) and a control group (n=19). The 16-session, 8-week intervention included components such as reproductive health education, physical activity, nutritional management, and stress management. Data collection occurred between July 1, 2021 and September 27, 2022. The outcomes measured included health-promoting behaviors, infertility stress, fertility-related quality of life, and sperm quality (volume, total motility, immobility, concentration, and normal morphology).
Results
The experimental group showed significant improvements in health-promoting behaviors (z=–2.27, p=.023) and reductions in infertility stress (t=–2.40, p=.022) compared to the control group. Total sperm motility (F=4.39, p=.045) and normal morphology (z=2.86, p=.017) were also significantly higher in the experimental group than in the control group.
Conclusion
The IMCHB-based lifestyle intervention significantly increased health-promoting behaviors, reduced infertility stress, and improved key sperm parameters, indicating its effectiveness in supporting the reproductive health of men in infertile couples. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychological Stress and Male Infertility: Oxidative Stress as the Common Downstream Pathway
Aris Kaltsas, Stamatis Papaharitou, Fotios Dimitriadis, Michael Chrisofos, Nikolaos Sofikitis
Biomedicines.2026; 14(2): 259. CrossRef
- Psychological Stress and Male Infertility: Oxidative Stress as the Common Downstream Pathway
- 3,517 View
- 132 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A qualitative meta-synthesis of the essence of patient experiences of dialysis
- Soyoung Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh, Yoonhee Seok
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):119-136. Published online February 19, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24102
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to understand the experiences of dialysis and their meaning among patients with chronic kidney disease through a meta-synthesis of the existing literature. Since 2010, the prevalence of end-stage renal disease has doubled in South Korea, which has the sixth-highest incidence worldwide. Although most kidney disease patients undergo dialysis to attenuate disease-related symptoms and prolong their lives, the implications of dialysis on their lives, together with the role played by patients’ significant others, remain underexplored. Similarly, existing research has not considered both patients with hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
Methods
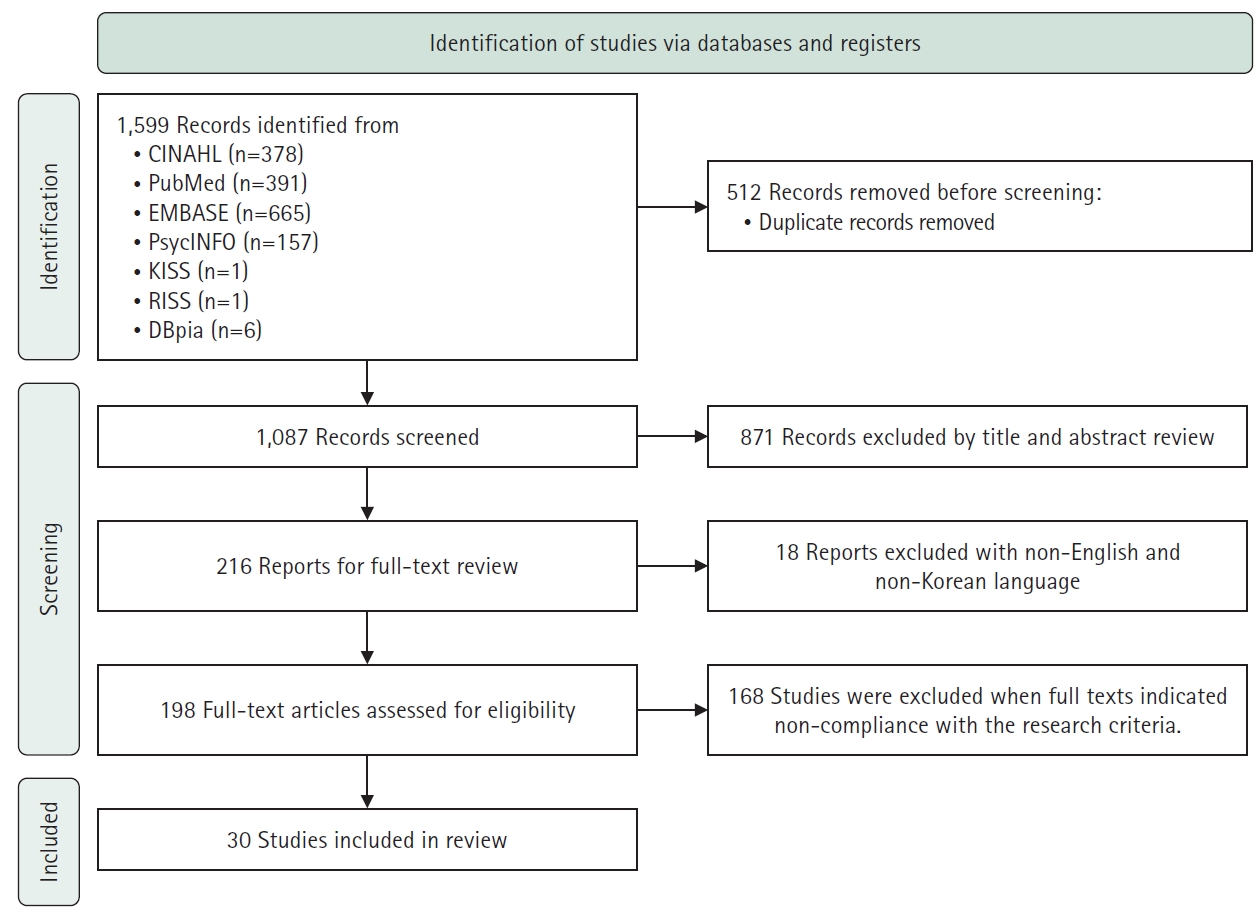
In this meta-synthesis, seven electronic databases (PubMed, CINAHL, EMBASE, PsycINFO, DBpia, KISS, and RISS) were searched for the terms “dialysis” and “qualitative.” Thirty qualitative studies were selected for examination.
Results
The overriding theme observed in the studies was “I do not have much time left.”–navigating the dual realities of one’s limited existence, while other key themes were: (1) the inevitable experience of the troubles of dialysis, (2) life is extended, but deteriorating in every aspect, (3) accepting dialysis with a positive outlook for life, and (4) essential support experienced in an exhausting life.
Conclusion
These findings are important for the design and delivery of practical and tailored nursing interventions to help patients overcome the various challenges related to dialysis treatment, and improve their quality of life.
- 3,284 View
- 157 Download

- Association between Resilience, Professional Quality of Life, and Caring Behavior in Oncology Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Misun Jeon, Sue Kim, Sanghee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):597-609. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23058
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The degree of caring behavior of oncology nurses is a crucial factor in the care provided to patients with cancer. In this study, we aimed to investigate factors related to oncology nurses’ caring behavior, including their resilience and professional quality of life.
Methods
A cross-sectional descriptive study was conducted with 107 oncology nurses at an urban tertiary hospital from May 18 to 24, 2015. We used a self-report questionnaire to measure resilience, professional quality of life, and degree of caring behavior. Data analysis included descriptive statistics, correlations, and multiple regression analysis using SPSS/WIN 20.0.
Results
Oncology nurses presented with low levels of resilience and caring behavior, and high levels of compassion satisfaction, burnout, and secondary traumatic stress. There was a statistically significant relationship between the degree of caring behavior, resilience (r = .43, p < .001), compassion satisfaction (r = .51, p < .001), and burnout (r = - .42, p < .001), as well as between secondary traumatic stress and burnout (r = .34, p < .001). Factors associated with oncology nurses’ degree of caring behavior were compassion satisfaction (t = 6.00, p < .001) and educational level (t = 3.45, p = .001).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that oncology nurses’ degree of caring behavior is related to their professional quality of life and education. These findings suggest that enhancing oncology nurses’ healthy coping strategies at both the individual and organizational levels can further develop holistic nursing care. Additionally, it is necessary to examine the factors affecting nurses’ compassion satisfaction and to try to promote this aspect. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Mediating Role of Resilience Between Empathy and Professional Competence Among Emergency Nurses in the West Bank, Palestine: Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling
Anas Shehadeh, Ahmad Shuhaiber, Malakeh Z. Malak, Ahmad Ayed, Hisham Zahran
International Nursing Review.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Burnout among health professionals working in oncology: current evidence and challenges for future research
Javier Martinez-Calderon, Cristina García-Muñoz
Current Opinion in Oncology.2025; 37(4): 302. CrossRef - Personal and work-related factors associated with nurse resilience: An updated systematic review using meta-analysis and narrative synthesis
Fiona Yu, Deborah Raphael, Lisa Mackay, Melody Smith, Ritin Fernandez
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2025; 166: 105054. CrossRef - Impact of an oncology training program on nursing personnel knowledge: A pilot study
Sara Gabriela Yeverino-Castro, Francisco Zamora-Rosales, Rodrigo Álvarez-Calderon , Oswaldo Enrique Sánchez-Dávila , Erika Evangelina Coronado-Cerda , Sonia Esquivel Ochotorena
Revista de Estudios e Investigación en Psicología y Educación.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Compassion fatigue, psychological resilience, moral sensitivity, and humanistic caring ability in clinical nurses: a structural equation model
Shuqi Zhai, Qinqin Liu, Congcong Dai, Yifan Lu, Huanhuan Zhang, Jie Liu, Chaoran Chen
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Impact of Resilience on Professional Quality of Life Among Oncology Nurses
Asma Al Yahyaei, Wafa Al Jabri, Nabiha Al Hasni, Zainab Al Kindi, Sulaiman Al Sabei, Omar Al Omari, Joshua Muliira, Foroozan Atashzadeh-Shoorideh
Nursing Forum.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of the Quranic Teachings on the Resilience and Caring Behaviors of Nursing Students Amid Crises Such as the COVID-19 Pandemic
Maryam Shaygan, Fatemeh Vizeshfar, Azadeh Amiri, Marzieh Kargar Jahromi
International Perspectives in Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Professional Quality of Life in Nursing: The Role of Psychological Resources—A Cross-Sectional Study
Lovorka Brajković, Dora Korać, Vanja Kopilaš
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(12): 434. CrossRef - Connectedness to Nature and Professional Quality of Life Among Nurses in South Korea in the Context of COVID-19
Hyeon Sik Chu, Young Ran Tak, Hanyi Lee
HERD: Health Environments Research & Design Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study on Moral Distress, Compassion Fatigue, Compassion Satisfaction, and Their Predictors among Nurses Caring for Patients with Cancer
Soomin Hong, Yesol Kim, Mi Sook Jung, Yoonjung Lee, Hyunju Hong, Mijin Jeon, Mee-Young Cho, Jiyeon Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(4): 217. CrossRef - Mindful self-care among oncology nurses in China: a latent profile analysis
Yan Shi, Peng Wang, Lamei Liu, Mengmeng Li
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The mediating role of compassion fatigue between perceived organization support and caring behavior among outpatient nurses in China: a cross-sectional study
Xingxing Liu, Fang He, Tian Tian, Jun Zhang, Yuanjiao Ji, Yuexia Zhong
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Critical Role of Nursing in Identifying and Managing Care Fatigue Among Hospitalized Patients
Haya Semah D Alreshidi, Alanazi, Maryam Munadi, May Farhan Salem Alanazi, Hamidah Matrouk Alruwaili, Alruwaili, Rehab Mulhi A, Awatif Rakyan Murayr Alruwaili, Huda Alshawi J Alruwaili, Adhwaa Alohaylim Aldaghmani, Almatrafi, Rawan Wadi S, Hana M
International Journal of Computational and Experimental Science and Engineering.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Mediating Role of Resilience Between Empathy and Professional Competence Among Emergency Nurses in the West Bank, Palestine: Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling
- 4,664 View
- 198 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

- Internal Structure of the Health-Related Quality of Life Instrument with 8-Items in a Nationally Representative Population
- Eun-Hyun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(3):359-369. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study evaluated the internal structure (structural validity, internal consistency, and measurement invariance) of the Health-Related Quality of Life Instrument with Eight Items (HINT-8), developed to measure Korean people’s health-related quality of life.
Methods
A secondary analysis was conducted using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, involving 6,167 adults aged over 18 years. The structural validity of the HINT-8 was assessed using exploratory graph analysis and confirmatory factor analysis. Internal consistency and measurement invariance were analyzed using McDonald’s omega (ω) and multigroup confirmatory factor analysis, respectively.
Results
The HINT-8 had a single dimension and good internal consistency (ω = .804). The one-dimension HINT-8 ex-hibited matric invariance but not scalar invariance across sociodemographic groups (sex, age, education, and marital status). Further, it exhibited scalar or partial scalar invariance across medical condition groups (hypertension, diabetes, depressive symptoms, and cancer).
Conclusion
The study finds that the HINT-8 demonstrated satisfactory structural validity and internal consistency, indicating its suitability for practice and research. However, the HINT-8 scores cannot be compared across different groups regarding sex, age, education, and marital status, as the interpretation varies within each sociodemographic category. Conversely, interpretation of the HINT-8 is consistent for individuals with and without hypertension, diabetes, depressive symptom, and cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between obstructive sleep Apnea–Related factors and HINT-8 utility scores in adults: a secondary analysis of the 2023 Korea National health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES)
Mima Park, Seon-Ha Kim
Quality of Life Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk Factors and Quality of Life in Patients With Geographic Atrophy, a Late Stage of Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Findings From the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yeji Kim, Yun Tae Kim, Mingui Kong, Jae Hui Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The Predictors of Dietary Supplement Use Among Women With Musculoskeletal Disease: A Population-Based Complex Sample Designed Study
Myoungjin Kwon, Sun Ae Kim, Youngshin Song
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Network Analysis of Quality of Life Among Older Adults With Arthritis
Dahee Wi, Chang G. Park, Jiae Lee, Eunjin Kim, Yoonjung Kim
International Journal of Older People Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Network analysis of quality of life among young and middle-aged Korean cancer survivors
Yoonjung Kim, Dahee Wi, Eunjin Kim, Jiae Lee
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100684. CrossRef - Quality of Life Based on the Experience of Psychological Counseling in Adults with Depressive Symptoms
Jihyeon Seo, Jihye Lim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2025; 50(1): 39. CrossRef - Validation of the health-related quality of life instrument with 8 items for assessing health-related quality of life in patients with oropharyngeal cancer: a comparison with the EQ-5D-5L
Gyeong-U Hong, Bon Seok Koo, Min-Ju Kim, Woo-Jeong Sim, Ah-Yeon Lee, Ji-Eun An, Su-Yeon Yu, Sei Young Lee, Soo Hyun Lee
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative effectiveness and safety of herbal medicine therapy for low back pain and radiculopathy caused by lumbar intervertebral disc herniation: a study protocol for a pragmatic randomized controlled trial
Jung-Hyun Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha, Won-Suk Sung, Eun-Jung Kim, Yeoncheol Park, Yonghyeon Baek, Sang-Soo Nam, Byung-Kwan Seo
Frontiers in Neurology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the health behavior and nutrition status of young-old women according to the vitality in their quality of life: based on the 2019, 2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jiyoung Jeong, Yoon Jung Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(5): 496. CrossRef
- Association between obstructive sleep Apnea–Related factors and HINT-8 utility scores in adults: a secondary analysis of the 2023 Korea National health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES)
- 4,542 View
- 132 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Factors Affecting the Quality of Life in Low-Income Older Adults with Sarcopenia: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Ju-Hee Nho, Eun Jin Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):1-11. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22126
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the factors influencing quality of life (QoL) of low-income older adults (LOAs) with sarcopenia.
Methods
A convenience sample of 125 older adults was recruited from Jeonbuk Province, South Korea. Data were collected using a self-report questionnaire that included nutritional status, the Depression Anxiety Stress Scale-21, and the World Health Organization Quality of Life Instrument-Older Adults Module. Additionally, grip strength and appendicular skeletal muscle mass, were evaluated, along with the short physical performance battery.
Results
Sarcopenia and severe sarcopenia were observed in 43.2% and 56.8% of participants, respectively. Using multiple regression analysis, depression (β = - .40, p < .001), nutritional status (β = .24, p = .003), and anxiety (β = - .15, p = .042) were identified as factors affecting the QoL of the older adults in low-income groups with sarcopenia, the explanatory power of these variables was 44%.
Conclusion
The results of this study can be used to develop a nursing intervention program and establish policies to improve depression, anxiety, and nutritional status to enhance QoL of LOAs with sarcopenia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing health-related quality of life in older adult women with sarcopenia: analysis of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
Sol Hyun Lee, Ju-Hee Nho, Hye Young Kim, Eun Jee Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(4): 328. CrossRef
- Factors influencing health-related quality of life in older adult women with sarcopenia: analysis of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
- 2,229 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of Acculturative Stress on Multicultural Adolescents’ Life Satisfaction: Sequential Multiple Mediating Effects of Bicultural Acceptance Attitude, Self-Esteem, and Social Withdrawal -Using the 2016 Multicultural Adolescents Panel Study-
- Soo Mi Kim, Hyeon Ok Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):324-340. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22030
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study determined acculturative stress’ effect on the life satisfaction of multicultural adolescents based on Roy’s Adaptation Model and some earlier studies. Further, it examined the sequential multiple mediating effects of bicultural acceptance attitude, self-esteem, and social withdrawal on life satisfaction.
Methods
Participants included 1,163 multicultural adolescents who participated in the sixth Multicultural Adolescents Panel Study. A hypothesis test was conducted using Hayes’ Process Macro Model 81.
Results
Life satisfaction increased with a decline in acculturative stress. Each of bicultural acceptance attitude, self-esteem, and social withdrawal had a single mediating effect on the relationship between acculturative stress and life satisfaction in multicultural adolescents. The sequential multiple mediating effects of bicultural acceptance attitude and self-esteem were confirmed significant after their impact on the relationship between acculturative stress and life satisfaction was analyzed. Bicultural acceptance attitude and social withdrawal were found to have a significant sequential multiple mediating effect on the relationship, as well.
Conclusion
This study’s results demonstrate that acculturative stress reduction is critical to improving multicultural adolescents’ life satisfaction. Bicultural acceptance attitude, self-esteem, and social withdrawal have a single mediating or sequential multiple mediating effect on the relationship between multicultural adolescents’ acculturative stress and life satisfaction. The findings, which highlight mediating effects, indicate that by increasing bicultural acceptance attitude and self-esteem, and reducing social withdrawal, multicultural adolescents’ life satisfaction can be improved. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between parents’ country of birth and multicultural adolescents’ psychological well-being in South Korea: A study on depression, worries, life satisfaction, and social withdrawal
Abdullatif Ghafary, Jaeyong Shin, Sang Sook Beck, Jieun Jang, Rajaguru Vasuki, So Yoon Kim, Hanif Abdul Rahman
PLOS Mental Health.2025; 2(6): e0000356. CrossRef - Acculturative Stress and Psychosocial Well-Being of Multicultural Youth in South Korea: The Moderating Role of Host Culture Identity
Cheolwoo Park, Hannah B. Bayne
International Journal for the Advancement of Counselling.2024; 46(3): 465. CrossRef - Bicultural Acceptance Attitude as a Protective Factor Against the Effect of Acculturative Stress on Life Satisfaction Among Korean Multicultural Adolescents
Jong-Hye Park, Sung-Man Bae
Applied Research in Quality of Life.2024; 19(4): 1811. CrossRef - The influence of bullying victimization on acculturation and life satisfaction among children from multicultural families in South Korea
Jinho Kim, Eric Fong
Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies.2024; 50(18): 4718. CrossRef - The Influence of Support Services for Multicultural Adolescents on
School Adjustment and the Moderated Mediation Effect of Bicultural Attitude
by Social Support
Rae-Hyuck Lee, Jae-Kyoung Lee
Korean Journal of family welfare.2024; 29(1): 149. CrossRef
- Association between parents’ country of birth and multicultural adolescents’ psychological well-being in South Korea: A study on depression, worries, life satisfaction, and social withdrawal
- 3,171 View
- 130 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling for Quality of Life of Mothers of Children with Developmental Disabilities: Focusing on the Self-Help Model
- Mi Ran Yang, Mi Yu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):308-323. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22013
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to construct and test a predictive model for the quality of life (QOL) in mothers of children with developmental disabilities (DB). The hypothesized model included severity of illness, distress, uncertainty, self-help, and parenting efficacy as influencing factors, QOL as a consequence based on the Braden’s Self-Help Model.
Methods
The data were collected through a direct and online surveys from 206 mothers in 8 locations, including welfare or daycare centers, developmental treatment centers, and The Parents’ Coalition for the Disabled located in two provinces of Korea. Data were analysed using SPSS/WIN 23.0 and AMOS 21.0 program.
Results
The fit indices of the predictive model satisfied recommended levels; χ2 = 165.79 (p < .001), normed χ2 (χ2 /df) = 2.44, RMR = .04, RMSEA = .08, GFI = .90, AGFI = .85, NFI = .91, TLI = .93, CFI = .95. Among the variables, distress (β = - .46, p < .001), parenting efficacy (β = .22, p < .001), and self-help (β = .17, p = .018) had direct effects on QOL. Severity of illness (β = - .61, p = .010) and uncertainty (β = - .08, p = .014) showed indirect effects. The explanatory power of variables was 61.0%.
Conclusion
The study results confirm the utility of Braden’s Self-Help Model. They provide a theoretical basis for improving QOL in mothers of children with DB. Nursing intervention strategies that can relieve mothers’ distress and uncertainty related to disease and enhance parenting efficacy and self-help behavior should be considered. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with uncertainty in parents of children with developmental disabilities: A scoping review
Heejung Choi, GyeongAe Seomun, Jeongeun Song
Disability and Health Journal.2026; 19(1): 101962. CrossRef - Moderating role of informational support in the relationship between credible authority and parental uncertainty in developmental disabilities: a preliminary study
Heejung Choi, GyeongAe Seomun, Sung-Min Son
Disability and Rehabilitation.2025; 47(20): 5237. CrossRef - Adaptation and validation of the Korean version of the parental perception of uncertainty scale (K-PPUS) in parents of children with developmental disabilities
Heejung Choi, GyeongAe Seomun
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2025; 82: 47. CrossRef - Pilot Study to Develop the Korean Screening Index of Early Development-Parent Form
Hyo-Jeong Jeon, Eun-Kyoung Goh, Min-Jung Kim, Eun-Seol Kim
Korean Journal of Child Studies.2025; 46(2): 37. CrossRef - Exploring parental uncertainty and information needs for children with developmental disabilities: A qualitative study
Heejung Choi
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2025; 84: 328. CrossRef - The impact of maternal adverse childhood experiences on children's quality of life: the moderating role of self-esteem and the mediating role of maternal quality of life
Eunjeong Cho, Yeon Jeong Heo, Eunha Ryoo, Hye Jin Kim
Frontiers in Global Women's Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Relation among Uncertainty, Social Support, Care Burden of Mothers having Children with Developmental Disabilities
Kyoung Eun Jeong, Min Hyun Suk
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2023; 34: 117. CrossRef
- Factors associated with uncertainty in parents of children with developmental disabilities: A scoping review
- 1,457 View
- 44 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of the Advanced Practice Nurse-Led Psychoeducational Program for Colorectal Cancer Survivors
- Hye Kyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):245-260. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21207
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the effects of an advanced practice nurse-led psychoeducational program on distress, anxiety, depression, coping with cancer (CWC), health promotion behavior (HPB), and quality of life (QOL) among colorectal cancer survivors.
Methods
This study was designed as a quasi-experimental study with a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest. The participants were survivors of colorectal cancer who underwent follow-up care. There were 39 survivors: 19 in the experimental group and 20 in the control group. The experimental group performed a psychoeducational program for 120 minutes per session, once a week for a total of six weeks, while the control group received routine education and counseling. Distress, anxiety, depression, CWC, HPB, and QOL were investigated before, immediately after, and 4 weeks after the intervention. The data were analyzed with SPSS/WIN ver. 24.0, using repeated measures ANOVA.
Results
There were significant interactions between time and group for distress and anxiety. In addition, CWC interacted with the total of CWC and interpersonal coping, and QOL interacted with the total of QOL and functional status. However, there were no significant differences in the depression or HPB scores.
Conclusion
Based on the results of this study, we expect that this program can be used as an effective intervention for colorectal cancer survivors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tailored psychoeducation for multiple myeloma patients: a step toward enhancing quality of life and health outcomes
Yoorin Cho, Yang Sook Yoo
Health Education Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a mobile-based return to work program for decent return to work, fatigue, stress, and quality of working life among cancer survivors
Kisook Kim, Hyohyeon Yoon
Journal of Cancer Survivorship.2025; 19(2): 713. CrossRef - Elevating Elderly Cancer Care: A Systematic Review of Advanced Practice Nursing’s Role in Senior Oncology Patients’ Quality of Life
Cristian-David Useche-Guerrero, María-de-los-Ángeles Merino-Godoy, Eva-María Barroso-Márquez, Emilia Isabel Martins Teixeira da Costa, Rafaela Camacho Bejarano, Francisco-Javier Gago-Valiente, Rizal Angelo Grande
Journal of Nursing Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Psycho-education Interventions on Colorectal Cancer Patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
XiaoYing Zhang, HuangQin Liu, LiYing Lin, Huimin Xiao
Journal of Cancer Education.2023; 38(5): 1413. CrossRef - How should the healthcare system support cancer survivors? Survivors’ and health professionals’ expectations and perception on comprehensive cancer survivorship care in Korea: a qualitative study
Su Jung Lee, Dal-Lae Jin, Young Ae Kim, Hyun-Ju Seo, Seok-Jun Yoon
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer Survivorship Care and Roles of Oncology Nurses
Eun Young Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(3): 121. CrossRef
- Tailored psychoeducation for multiple myeloma patients: a step toward enhancing quality of life and health outcomes
- 1,885 View
- 90 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of Resilience Enhancement Program Applying Mindfulness Meditation in Patients with Ileostomy
- Jee Hye Shin, Ja Yun Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):334-346. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21019
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop a resilience enhancement program applying mindfulness meditation (REP-MM) and evaluate the effects of the program on post-traumatic stress (PTS), resilience, and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in patients with ileostomy.
Methods
The REP-MM was developed by combining the resilience enhancement program with mindfulness meditation according to four patterns. The program was developed through identifying patients’ needs, reviewing relevant literature, developing a preliminary program, and testing content validity and user evaluation. The participants were 55 patients with ileostomy. We conveniently assigned 27 patients to the experimental group and 28 to the control group. The study was conducted in conducted in a hospital from January 22 to May 30, 2019. The REPMM was provided to the experimental group, and conventional ileostomy care was provided to the control group using a nonequivalent control-group pretest-posttest design. Results: ANCOVA revealed that the levels of PTS (F = 321.64, p < .001), resilience (F = 111.86, p < .001), and HRQoL (F = 31.08, p < .001) in the experimental group were higher than those in the control group when comparing pretest to posttest changes.
Conclusion
The REP-MM is effective in PTS, resilience, and HRQoL in patients suffering from post-stoma creation crisis. The REP-MM can induce positive self-recognition changes in patients with ileostomy through dispositional, situational, relational, and philosophical interventions. We suggest nurses reduce PTS and improve resilience and HRQoL in patients with ileostomy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Meditation Techniques in Treating Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
David W. Orme-Johnson, Vernon A. Barnes, Brian Rees, Jean Tobin, Kenneth G. Walton
Medicina.2024; 60(12): 2050. CrossRef - The experiences of Chinese colorectal cancer survivors in marital intimacy after ostomy creation: A qualitative study
Xixi Du, Suchira Chaiviboontham, Bualuang Sumdaengrit
Belitung Nursing Journal.2024; 10(2): 222. CrossRef - Analysis on effect of psychological nursing combined with extended care for improving negative emotions and self-care ability in patients with colorectal cancer and enterostomy: A retrospective study
Fang Liu, Kun Yao, Xiaoxiang Liu
Medicine.2024; 103(21): e38165. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Healthcare Empowerment Program for Patients with Temporary Ileostomy
Jin Mi Kim, Jeong Sook Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(6): 616. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Meditation Techniques in Treating Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1,659 View
- 31 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Actor and Partner Effects of Couple’s Daily Stress and Dyadic Coping on Marital Satisfaction
- Su Kyung Won, Kyoung Ok Seol
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(6):813-821. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20162
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the actor and partner effects of daily stress and dyadic coping on marital satisfaction using the Actor-Partner Interdependence Mediational Model (APIeM).
Methods
Participants were 314 couples who met the study’s eligibility criteria. Data were collected from March to April 2016 through apartment and cooperative company communities in Seoul. Two APIeMs of positive and negative dyadic coping were analyzed using SPSS 20.0 and Mplus 7.4. All measures were self-administered.
Results
Daily stress and positive and negative dyadic coping in both spouses had direct actor effects on their marital satisfaction. Daily stress in both spouses had an indirect actor effect on marital satisfaction through their positive and negative dyadic coping. The husband’s daily stress had an indirect partner effect on the wife’s marital satisfaction through his positive dyadic coping, while the wife’s positive dyadic coping had a direct partner effect on the husband’s marital satisfaction. The husband’s daily stress had an indirect partner effect on the wife’s marital satisfaction through his negative dyadic coping, while the wife’s negative dyadic coping had a direct partner effect on the husband’s marital satisfaction.
Conclusion
Dyadic coping is an effective way to deal with couple’s daily hassles as it increase their satisfaction in marriage. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of risk factors for co-morbid anxiety and depression in pregnant women
Wei Zhang, Ling Li, Xiabidan Tuxunjiang, Bahedana Sailike, Xiaoting Wang, Weicui Meng, Sufeila Shalayiding, Ting Jiang
Psychiatry Research.2025; 344: 116323. CrossRef - Pregnant Women’s Dyadic Coping and Associated Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study Utilizing Latent Profile Analysis
Shiqiong Yan, Wenzhuo Fan, Yonghong Ma, Sijia Xie, Rong Li, Yao Lan, Linli Xie, Jie Jing
International Journal of Women's Health.2024; Volume 16: 1009. CrossRef - Spouse Burnout and Marriage Satisfaction in Married Individuals: The Mediating Role of Psychologıcal Well-being
Bülent Şen, Nergüz Bulut Serin, Kadriye Karagülmez
Batı Anadolu Eğitim Bilimleri Dergisi.2024; 15(2): 1266. CrossRef - Dyadic coping and associated factors in women with high-risk pregnancy and their spouses: Do they interact?
Mengjie Liu, Yu Fang, Mengshi Liu, Min Wu, Jingshuo Zhang, Tianchen Niu, Xiaoman Zhang
Midwifery.2024; 134: 104006. CrossRef - 중년부부의 문제해결 유형과 결혼만족도의 관계
수산나 주, 미선 강, 인혜 정, 서진 조
Journal of Family Relations.2023; 28(1): 33. CrossRef - Relationship between Chinese middle-aged and old couples' Confucian coping thinking and marital quality
Zhiguang Fan, Hanwei Wu, Min Tao, Lei Chen
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of avoidant attachment on marital satisfaction of Chinese married people: Multiple mediating effect of spousal support and coping tendency
Lian Xiong, Caihua Zhou, Liangshi Yan, Pan Zhao, Mengting Deng, Yan Hu
Acta Psychologica.2022; 228: 103640. CrossRef - Interrelation of Attachment and Coping Behavior In Adults
E.V. Kuftyak
Counseling Psychology and Psychotherapy.2021; 29(1): 28. CrossRef
- Analysis of risk factors for co-morbid anxiety and depression in pregnant women
- 1,545 View
- 42 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Predictive Model for Quality of Life of the Older Men Living Alone
- Su Jin Kim, Gyeong-Suk Jeon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(6):799-812. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to construct and test a predictive model that explains and predicts the quality of life in older men living alone.
Methods
A self-report questionnaire was used to collect data from 334 older adult men living along aged 65 years or over living in Jeollanam-do provinces. The endogenous variables were depression, self-rated health, instrumental activity of daily life, health promotion behaviors, the number of social participation activities and quality of life. Data were analyzed using the SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0 programs.
Results
The final model with 14 of the 8 analysed paths showed a good fit to the empiri cal data: χ2= 173.26(p < .001, df = 53),normed χ2= 3.27, GFI = .92, NFI = .90, CFI = .93, TLI = .89, RMSEA = .08 and SRMR = .06. Activities had direct effect on quality of life of older men living alone and social support had both direct and indirect effects. Meanwhile, function and socioeconomic status showed only indirect effects.The variables included in the eight significant paths explained 83.7% of variance in the prediction model.
Conclusion
Instrumental activities of daily living and social support effect directly on quality of life in the older men living alone. Findings suggest that health care providers including community nurses need to provide social support as well as empowerment programs of instrumental activities of daily living and health promotion for improving quality of life of the older men living alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changes in the health status and health-related quality of life of community-dwelling older adults living alone: one-year follow-up from a cohort study
Hana Ko, Belong Cho, Kyung-Choon Lim, Soong-Nang Jang, Sun Ju Chang, Yu Mi Yi, Hye Ryung Cho, So Im Ryu, Eun-Young Noh, Yeon-Hwan Park
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influencing factors on self-care of older adults living alone in a community during COVID-19: A cross-sectional study
Heeyoung Woo, Minkyung Gu
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - A novel nomogram to stratify quality of life among advanced cancer patients with spinal metastatic disease after examining demographics, dietary habits, therapeutic interventions, and mental health status
Yue Li, Ze Long, Xiuju Wang, Mingxing Lei, Chunzi Liu, Xiaolin Shi, Yaosheng Liu
BMC Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Associated Factors with Health-related Quality of Life among Older Adults with Diabetes in Korea
Eun-Kyung Lee, Sun-Young Jung
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2022; 25(2): 61. CrossRef
- Changes in the health status and health-related quality of life of community-dwelling older adults living alone: one-year follow-up from a cohort study
- 2,002 View
- 32 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- A Structural Equation Model of Health-Related Quality of Life among Older Women Following Bilateral Total Knee Replacement
- Hyun Ok Lee, Jae Soon Yoo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(4):554-570. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19216
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and test a structural equation model of health-related quality of life among older women following bilateral total knee replacement based on a literature review and Wilson and Cleary’s model of health-related quality of life.
Methods
One hundred ninety three women who were diagnosed with osteoarthritis, were older than 65 years, and were between 13 weeks and 12 months of having a bilateral total knee replacement were recruited from an outpatient clinic. Data were collected from July 2017 to April 2018 using a structured questionnaire and medical records. Data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 22.0, AMOS 22.0, and Smart PLS 3.2.4.
Results
The fitness of the hypothetical model was good, with coefficients of determination (R2 ) ranging between .28 and .75 and predictive relevance (Q2 ) between .26 and .73. The standardized root mean square residual of the model fit indices for the hypothetical model was .04; which explained 64.2% of physical and 62.5% of mental health-related quality of life. Self-efficacy, symptom status, functional status, and general health perceptions had a significant direct effect on physical health-related quality of life, while social support, symptom status, and general health perceptions had a significant direct effect on participants’ mental-health-related quality of life.
Conclusion
To improve the physical and mental quality of life of older women who receive bilateral knee replacement, nursing-based intervention strategies that reduce symptoms, improve functional status, and increase health perceptions, self-efficacy, and social support are needed. The most important factor is the symptom status. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Path Analysis of Factors Influencing Health-Related Quality of Life for Community-Dwelling Vulnerable Older Adults with Chronic Diseases in Korea
Hyun-Ju Lee
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2025; 36: 315. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life for older patients with chronic low back pain: A structural equation modeling study
Suin Lee, Eun-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(3): 248. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life in female patients with reumatoid arthritis: a structural equation model
Bukyung Kim, Mi-Hae Sung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(2): 91. CrossRef - Effect of Oral Tranexamic Acid on the Blood Transfusion Rate and the Incidence of Deep Vein Thromboembolism in Patients after TKA
Bingqian Chen, Xiaohong Qu, Xiaowen Fang, Xuesong Wang, Guoxiu Ke, Xiaonan Xi
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Relationship between Uncertainty and Health-related Quality of Life in Elderly Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty: The Mediating Effects of Sense of Coherence and Social Support
Min-Yi Song, Min-Jeong Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(3): 284. CrossRef - The Effect of Focusing Manner on Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Pain: The Sequential Mediating Effects of Social Support and Self-efficacy
Song Hee Yoon, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(2): 248. CrossRef
- Path Analysis of Factors Influencing Health-Related Quality of Life for Community-Dwelling Vulnerable Older Adults with Chronic Diseases in Korea
- 2,101 View
- 56 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Prevalence of Menstrual Disorders according to Body Mass Index and Lifestyle Factors: The National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort in Korea, 2009~2016
- SoMi Park, Tae Woong Yoon, Dae Ryong Kang, ChaeWeon Chung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):401-410. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20054
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study was performed to identify the prevalence of menstrual disorders in Korean women based on body mass index (BMI)and lifestyle factors, by utilizing the Korean National Health Insurance Database.
Methods
A retrospective observational study designwas used for the secondary data analysis. Data of women aged 15 to 49 years who were diagnosed with menstrual disorders were extractedfrom The National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort in Korea from 2009 to 2016. The age-standardizedprevalence rate of menstrual disorders was calculated using SAS version 9.4, and a Chi-square test and Cochran-Armitage test were performed.
Results
In total, 2,219,445 cases were extracted from the database. The prevalence of menstrual disorders significantly increasedfrom 8.6% to 11.6% (Z=135.16, p for trend <.001) over the past eight years. In particular, it was higher in underweight womenthan in women with normal weight across all years (Z=-4.18~-14.72, p <.001). Moreover, statistically significant differences in the prevalenceof menstrual disorders were found to be associated with drinking and smoking in all years and with physical activity levels in part(p <.05~.001).
Conclusion
These findings present compelling evidence on the prevalence of menstrual disorders based on a national database.Since the prevalence of menstrual disorders has steadily increased and differs based on BMI and lifestyle factors, educational andclinical interventions are necessary to promote risk awareness and appropriate behavioral changes among Korean women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Menstrual Disorders in Korean Women
Ye-Lin Kim, Jun Young Chang, Suejin Kim, Mira Yoon, Jae-Na Ha, Kang Hyun Um, Boeun Lee, Kyoung Sook Jeong
Healthcare.2025; 13(6): 606. CrossRef - Menstrual Disorders Are Associated With Depressive Symptoms Among Women of Reproductive Age: Findings From the Korean Women’s Health Survey for Sexual and Reproductive Health
Kyunghee Han, Sihan Song, Bo Mi Song, Eunja Park, Joong-Yeon Lim, Hyun-Young Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Disease Experience in Women with PCOS: A Qualitative Content Analysis
Miok Kim, Su Jeong Yi
Healthcare.2025; 13(24): 3243. CrossRef - Factors associated with regularity and length of menstrual cycle: Korea Nurses’ Health Study
Sihan Song, Hansol Choi, Yanghee Pang, Oksoo Kim, Hyun-Young Park
BMC Women's Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Body mass index, menstruation, acne, and hirsutism of polycystic ovary syndrome in women: A cross-sectional study
Jung-Hee Kim, Oksoo Kim, Heeja Jung, Yanghee Pang, Hyunju Dan
Health Care for Women International.2022; 43(1-3): 85. CrossRef
- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Menstrual Disorders in Korean Women
- 2,126 View
- 59 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Menopause-Specific Quality of Life
- Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Young-Mi Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):487-500. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20049
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of Menopause-Specific Quality of Life (MENQOL).
Methods
The MENQOL was translated into Korean according to algorithm of linguistic validation process. A total of 308 menopausal womenwere recruited and assessed using the Korean version of MENQOL (MENQOL-K), the World Health Organization Quality of Life BriefVersion (WHOQOL-BREF), and Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale (CES-D-K). In estimating reliability, internal consistencyreliability coefficients were calculated. Validity was evaluated through criterion validity and construct validity with confirmatory factor analysesusing SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 25.0 software.
Results
In item analyses, the “increased facial hair” symptom was excluded because of thelow contribution of MENQOL-K. The confirmatory factor analysis supported good fit and reliable scores for MENQOL-K model, and thefour-factor structure was validated (x2=553.28, p <.001, NC=1.84, RMSEA=.05, AGIF=.85, AIC=765.28). The MENQOL-K consists of 28 itemsin 4 domains, including vasomotor (3 items), psychosocial (7 items), physical (15 items), and sexual subscales (3 items). There was an acceptablecriterion validity with moderately significant correlation between MENQOL-K and WHOQOL-BREF. The Cronbach’s a for the 4subsacles ranged from .80 to .93.
Conclusion
The MENQOL-K is a valid and reliable scale to measure condition-specific quality of life forperimenopausal and postmenopausal women. It can be used to assess the impact of menopausal symptoms on the quality of life of Koreanwomen in clinical trials. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Examining the relationship between symptoms and quality of life related to menopausal period of women with gynecologic cancer: a cross-sectional study
Ahsen Demirhan Kayacik, Gulsah Kok
Supportive Care in Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The 3-dimensionel Ovarian Volume Assessment to Evaluate Whether Menopausal Related Symptoms and Hormone Levels Correlate with the Ovarian Volume
Gizem Işık Solmaz, İsmail Güler, Esra İşçi Bostancı, Serhan Can İşcan, Nuray Bozkurt, Mehmet Anıl Onan
Gazi Medical Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Longitudinal analysis of alcohol consumption pattern and menopause‐specific quality of life in middle‐aged women undergoing the menopausal transition
Ria Kwon, Yoosoo Chang, Yoonyoung Jang, Ga‐young Lim, Yoo‐Jung Kim, Seungho Ryu
Addiction.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Aerobic Exercise Vs Surya Namaskar on Quality of Life in Postmenopausal Women Using Menopause Specific Quality of Life (MENQOL) Questionnaire
Dr. Dhanashree P. Shinde (PT), Alphina E. Jules
International Journal of Advanced Research in Science, Communication and Technology.2025; : 51. CrossRef - Longitudinal patterns and group heterogeneity of depressive symptoms during menopausal transition in middle-aged Korean women
Yoonyoung Jang, Yoosoo Chang, Junhee Park, Sang Won Jeon, Byungtae Seo, Jae Ho Park, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Seungho Ryu
Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Early-onset vasomotor symptoms and development of depressive symptoms among premenopausal women
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Jungeun Park, Yoosun Cho, Chanmin Kim, Min-Jung Kwon, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-young Lim, Jiin Ahn, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 354: 376. CrossRef - Association between Menopausal Women’s Quality of Life and Aging Anxiety: The Role of Life Satisfaction and Depression
Seunghee Lee, Mijung Jang, Dohhee Kim, KyooSang Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(8): 1189. CrossRef - Vasomotor and other menopause symptoms and the prevalence of ideal cardiovascular health metrics among premenopausal stage women
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Yoosun Cho, Min-Jung Kwon, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Menopause.2023; 30(7): 750. CrossRef - Research trends in the Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing from 2011 to 2021: a quantitative content analysis
Ju-Hee Nho, Sookkyoung Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(2): 128. CrossRef - Low anti-Müllerian hormone levels are associated with an increased risk of incident early-onset vasomotor symptoms among premenopausal women
SunJu NamGoung, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Hoon Kim, In Young Cho, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Hye Rin Choi, Jeonggyu Kang, Kye-Hyun Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Hyun-Young Park, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Min-Jung Kwon, Seungho Ryu
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - High low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level is associated with an increased risk of incident early-onset vasomotor symptoms
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Jeonggyu Kang, Min-Jung Kwon, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Ideal Cardiovascular Health Metrics and Risk of Incident Early-Onset Vasomotor Symptoms Among Premenopausal Women
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Yoosun Cho, Jeonggyu Kang, Min-Jung Kwon, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(9): 2666. CrossRef - Alcohol Consumption Patterns and Risk of Early-Onset Vasomotor Symptoms in Premenopausal Women
Ria Kwon, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Yoosun Cho, Hye Rin Choi, Ga-Young Lim, Jeonggyu Kang, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Sanjay Rampal, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Nutrients.2022; 14(11): 2276. CrossRef - Metabolically healthy and unhealthy obesity and risk of vasomotor symptoms in premenopausal women: cross‐sectional and cohort studies
Sunju Namgoung, Yoosoo Chang, Chae‐Yeon Woo, Yejin Kim, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga‐Young Lim, Hye Rin Choi, Kye‐Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun‐Young Park, Seungho Ryu
BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology.2022; 129(11): 1926. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Risk of Early-Onset Vasomotor Symptoms in Lean and Overweight Premenopausal Women
Yoosun Cho, Yoosoo Chang, Hye Rin Choi, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Jiin Ahn, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Sanjay Rampal, Juhee Cho, Hyun-Young Park, Eliseo Guallar, Seungho Ryu
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2805. CrossRef
- Examining the relationship between symptoms and quality of life related to menopausal period of women with gynecologic cancer: a cross-sectional study
- 3,259 View
- 126 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- Effect of Lifestyle Intervention Program for Overweight and Obesity Pregnant Women
- Hye Kyung Choi, Hyeon Ok Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):459-473. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19228
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study was conducted to identify the effects of a lifestyle intervention program on weight gain, dietary habits, fatigue andpregnancy stress, blood pressure, and neonatal birth weight, using Cox’s interaction model of client health behavior for overweight andobese women.
Methods
This was a quasi-experimental research with a non-equivalent control group pre-post test design. A total of 52patients who met the selection criteria, including 25 in the experimental group and 27 in the control group, were the subjects of the study;they comprised overweight and obese pregnant women who were receiving prenatal care at A and B women’s hospital in J province. Thelifestyle intervention program ran for 12 weeks in total and consisted of interactions involving affective support, health information, andprofessional/technical competencies. The data collection period was from February 1, 2017 to August 31, 2017.
Results
This study showeddifferences in the appropriate weight gain rate (x2=6.17, p=.013), suppression of an increase in fatigue (t=-2.32, pp =.012), and an increasein pregnancy stress (t=-1.87, p=.034). Yet, no differences in physical activity, dietary habits change, blood pressure, and neonatal birthweight (p>.05) were found.
Conclusion
The study findings indicate that this program could be an effective intervention for the control ofappropriate weight gain, fatigue, and pregnancy stress. Therefore, a lifestyle intervention program based on Cox’s interaction model of clienthealth behavior could be an efficient strategy for a positive health outcome of overweight and obesity pregnant women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of an integrated healthcare program for postpartum women: a quasi-experimental study
Eun Suk Hwang, Ju-Hee Nho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(4): 506. CrossRef - Literature Review on Lifestyle Intervention Program for Adults in Korea
Keun-Young Yang
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2023; 24(8): 1815. CrossRef - Research Trends of Lifestyle Intervention for Women With Obesity: A Text Network Analysis
Sook Kyoung Park, Ju-Hee Nho
Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.2023; 13(1): 44. CrossRef
- Effects of an integrated healthcare program for postpartum women: a quasi-experimental study
- 1,780 View
- 25 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- A Meta-Analysis on the Effects of Mind-Body Therapy on Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Eun Hui Choi, Moon Ja Kim, Eun Nam Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):385-400. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19224
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Previous randomized controlled trials (RCT) found that mind-body therapy can improve the health outcomes of patients with irritablebowel syndrome (IBS). The purpose of this meta-analysis was to identify the combined effects of mind-body therapy on patients’ IBSsymptoms, quality of life, anxiety, and depression.
Methods
A systematic literature search was conducted using various databases such asPubMed, EMBASE, CINAHL CENTRAL, DBpia, RISS, and KISS. The primary outcome variables were IBS symptoms and quality of life; the secondaryoutcome variables were anxiety and depression. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis version 3.0 was used to analyze the extracted data.The effect size was calculated using standardized mean difference (SMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results
Eleven final RCTs wereused for this meta-analysis. Mind-body therapy was found to have a significant effect on the IBS patients’ symptoms (SMD, -0.63; 95% CI,-0.77 to -0.48), quality of life (SMD, 1.03; 95% CI, 0.40 to 1.66), anxiety (SMD, -0.28; 95% CI, -0.47 to -0.09), and depression (SMD,-0.31; 95% CI, -0.06 to -0.12).
Conclusion
This meta-analysis reveals that mind-body therapy significantly improves IBS patients’ symptoms,quality of life, anxiety, and depression. The results suggest that, in the future, appropriate mind-body therapy should be applied toKoreans suffering from IBS. Moreover, the therapy’s long-term effects should be assessed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of walking exercise on cognitive and physical functions: meta-analysis of older adults
Mi Jin Lee, Hee Ju Ro, Jung Kee Choi, So Yeon Kim
Forest Science and Technology.2024; 20(2): 201. CrossRef - Effects of Non-Pharmacological Interventions on Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Patients Underwent Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sojeong Jo, Haejung Lee, Gaeun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 311. CrossRef - The Effect of Laughter Therapy on Physical and Mental Health: Systematic Review
Elif ÜNER, Ayşe SEZER BALCI, Hasibe KADIOĞLU
Halk Sağlığı Hemşireliği Dergisi.2022; 4(3): 251. CrossRef - RESEARCH ARTICLE: Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback: Managing Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction by Improving Autonomic Homeostasis
Richard Gevirtz
Biofeedback.2022; 50(4): 100. CrossRef - Effects of Korean forest healing programs on stress in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
So-Yeon Kim, Jungkee Choi
Forest Science and Technology.2021; 17(4): 206. CrossRef
- Effects of walking exercise on cognitive and physical functions: meta-analysis of older adults
- 1,924 View
- 25 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Development and Effects of Smartphone App-Based Walking Exercise Program for Taxi Drivers: Based on Bandura’s Self Efficacy Theory
- Yun Ha Choi, Min-Jeong Chae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(2):242-254. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.2.242
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of smart-phone app-based walking exercise programs for taxi drivers on self-efficacy and outcome expectations for exercise, health-related quality of life, walking as an exercise, and physiological indexes.
Methods
A nonequivalent control group with a pre-post-test design was used. The subjects were recruited in G metropolitan city. Subjects were assigned to the experimental (n=31) or control groups (n=30). The smart phone app-based walking exercise program consisted of educations via the app, twelve short message services, and one individual telephone counseling session, which was spread over 12 weeks.
Results
Self-efficacy, outcome expectations, and health-related quality of life had significantly higher pre-post test differences in scores in the experimental group. Additionally, blood pressure, body mass index, and waist circumference had significantly decreased prepost- test difference levels in the experimental group. Walking as an exercise (which consisted of days walked, number of steps walked, and amount of time walked) had significantly increased in the experimental group after 7~12 weeks in the period following the intervention program rather than 1~6 weeks after the program.
Conclusion
The smart phone app-based walking exercise program based on the self-efficacy theory demonstrates a significant effect on improving self-efficacy, outcome expectations physical activities, and health-related quality of life for taxi drivers. Therefore, it is recommended to actively use the program as a tool to promote self-efficacy, physical activities, and health behaviors in taxi drivers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring physical therapists’ approach to addressing home exercise program-related low self-efficacy: knowledge, strategies, and barriers
Mariana Wingood, Patricia M. Bamonti, Justin B. Moore, Kelsey J. Picha
Disability and Rehabilitation.2025; 47(8): 2065. CrossRef - Intervención educativa en la actividad física de médicos residentes durante la pandemia COVID-19. Estudio cuasiexperimental
Paola María Moreno-Pesquera, Clara Lilia Varela-Tapia, Hermelinda Hernández-Amaro, Daniel Martínez-Barro
Revista Mexicana de Medicina Física y Rehabilitación.2025; 37(1-2): 21. CrossRef - A Mobile App for Comprehensive Symptom Management in People With Parkinson’s Disease
JuHee Lee, Yujin Suh, Eunyoung Kim, Subin Yoo, Yielin Kim
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2024; 42(4): 289. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Mobile Application to Prevent Recurrent Stroke by Enhancing Self-management on Health Outcomes for Stroke Survivors
Young Ju Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Hyun Goo Kang
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2024; 42(1): 53. CrossRef - mHealth Interventions to Promote Physical Activity of Adults in Korea: Health Equity-Focused Systematic Review
Hana Kim, Jisan Lee
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(Suppl 1): S1. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of a mHealth Program Using Wearable Devices and Health Coaching among Bus Drivers for Promoting Physical Activity
Yeongmi Ha, Sang-Ho Lee, Suyeon Lee, Yeojoo Chae
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(3): 332. CrossRef - Effect of the SNS-Based Physical Activity-Related Psychological Intervention on Physical Activity and Psychological Constructs among Inactive University Students
Youngho Kim, Jonghwa Lee
International Journal of Clinical and Health Psychology.2022; 22(2): 100299. CrossRef - PERFORMANCE OF PHYSICAL EXERCISE IN SEDENTARY PEOPLE’S AUTONOMY
Zaiyong Shou
Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte.2022; 28(6): 785. CrossRef - An eHealth intervention (ManGuard) to reduce cardiovascular disease risk in male taxi drivers: protocol for a feasibility randomised controlled trial
James McMahon, David R. Thompson, Kevin Brazil, Chantal F. Ski
Pilot and Feasibility Studies.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Mobile Wellness Program for Nurses with Rotating Shifts during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Pilot Cluster-Randomized Trial
Yeongmi Ha, Sang-Ho Lee, Dong-Ha Lee, Young-Hun Kang, Woonjoo Choi, Jinung An
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(2): 1014. CrossRef - Co-Design of an eHealth Intervention to Reduce Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Male Taxi Drivers: ManGuard
James McMahon, David R. Thompson, Kevin Brazil, Chantal F. Ski
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(22): 15278. CrossRef
- Exploring physical therapists’ approach to addressing home exercise program-related low self-efficacy: knowledge, strategies, and barriers
- 2,203 View
- 43 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- Applying Extended Theory of Planned Behavior for Lung Cancer Patients Undergone Pulmonary Resection: Effects on Self-Efficacy for Exercise, Physical Activities, Physical Function, and Quality of Life
- Yeonjung Lim, Haejung Lee, Do Hyung Kim, Yeong Dae Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(1):66-80. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.1.66
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose: This study aims to examine the effects of nursing interventions based on the Extended Theory of Planned Behavior (ETPB) regarding self-efficacy for exercise (SEE), physical activity (PA), physical function (PF), and quality of life (QOL) in patients with lung cancer who have undergone pulmonary resection.
Methods: This quasi-experimental study was conducted between July 2015 and June 2018 in two university-affiliated hospitals. The intervention included pre-operative patient education, goal setting (action and coping planning), and feedback (behavior intention and perceived behavioral control). The intervention group (IG) (n=51) received nursing interventions from the day before surgery to 12 months after lung resection, while the comparison group (CG) (n=36) received usual care. SEE, PA, PF (dyspnea, functional status, and 6-minute walking distance [6MWD]), and QOL were measured before surgery and at one, three, six, and 12 months after surgery. Data were analyzed using the χ2 test, Fisher’s exact test, Mann-Whitney U test, t-test, and generalized estimation equations (GEE).
Results: There were significant differences between the two groups regarding SEE (χ2=13.53,
p =.009), PA (χ2=9.51,p =.049), functional status (χ2=10.55,p =.032), and 6MWD (χ2=15.62,p =.004). Although there were no time or group effects, the QOL mental component (Z=-2.78,p =.005) of the IG was higher than that of the CG one month after surgery. Interventions did not affect dyspnea or the QOL physical component.Conclusion The intervention of this study was effective in improving SEE, PA, functional status, and 6MWD of lung cancer patients after lung resection. Further extended investigations that utilize ETPB are warranted to confirm these results.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- [Retracted] Dynamic Changes and Influencing Factors for the Quality of Life in Nursing Care after Lung Cancer Resection
Shuzhen Hu, Aihong Fang, Mohammad Farukh Hashmi
Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on influence factors of public participation willingness in substation project based on integrated TPB-NAM model
Xin Ma, Junpeng Li, Fuli Guo, Caocao Cui, Tengfei Chen, Fan Xv, Wenbin Wang
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- [Retracted] Dynamic Changes and Influencing Factors for the Quality of Life in Nursing Care after Lung Cancer Resection
- 2,483 View
- 101 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Latent Class Analysis for Health-Related Quality of Life in the Middle-Aged Male in South Korea
- Youngsuk Cho, Dong Moon Yeum
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):104-112. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to identify types of quality of life (QoL) based on the 5 dimensions of EQ-5D and predict factors affecting types of QoL.
Methods This study was a secondary analysis using data from the Korean Health Panel Survey- II(2012). Participants were 2,071 middle-aged men who had completed the additional survey in 2012 and the data were analyzed using SPSS 20.0 and Mplus 5.21 for latent analysis.
Results Three latent classes of QoL were identified: serious (2.4% of the sample), threatened (15.5%), and stable types (82.0%). The types and characteristics of QoL among the latent classes differed. On comparing latent type 1 with latent type 2, the socioeconomic status (
p <.05), employment status (p <.05), and subjective health status (p <.001) were found to be significant. On comparing latent type 1 with latent type 3, the socioeconomic status (p <.05), current smoking status (p <.001), and subjective health status (p <.001) were found to be significant. On comparing latent type 2 with latent type 3, the socioeconomic status (p <.05), subjective health status (p <.001), stress (p <.001) were found to be significant.Conclusion The results showed significant heterogeneity in types of QoL and the predictors of QoL by types were different. These findings provide basic information for developing nursing interventions to improve QoL. Specific characteristics depending on the subtypes should be considered during the development of interventions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Heterogeneity and associated factors of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome health behaviors: a latent class analysis
Ying liu, Yunmei Guo, Rui Ding, Xin Yan, Huiwen Tan, Xueting Wang, Yousha Wang, LianHong Wang
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sociodemographic and Health Characteristics Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Men and Women Aged ≥50 Years
Goeun Chung, Hye-Sun Jung, Hye-Jin Kim
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2021; 19(3): 159. CrossRef - Health related quality of life in patient with type 2 diabetes: The role of household food insecurity on latent class membership
Abbas Abbasi-Ghahramanloo, Hamid Reza Baradaran, Masoudreza Sohrabi, Kamyar Mansori, Ali Gholami
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(4): 473. CrossRef - Analysis of the Types and Affecting Factors of Older People's Health-related Quality of Life, Using Latent Class Analysis
Sun-Hee Jang, Dong-Moon Yeum
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(2): 212. CrossRef
- Heterogeneity and associated factors of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome health behaviors: a latent class analysis
- 1,227 View
- 9 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- A Structural Model for Chemotherapy Related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients
- Jung Ran Lee, Pok Ja Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):375-385. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.375
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to develop and test a structural model for chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment of breast cancer patients based on a literature review and Hess and Insel's chemotherapy-related cognitive change model.
Methods The Participants consisted of 250 patients who were ≥19 years of age. The assessment tools included the Menopause Rating Scale, Symptom Experience Scale, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, Everyday Cognition, and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast Cancer. Data were analyzed using the SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0 programs.
Results The modified model was a good fit for the data. The model fit indices were χ 2=423.18 (
p <.001), χ 2/df=3.38, CFI=.91, NFI=.91, TLI=.89, SRMR=.05, RMSEA=.09, and AIC=515.18. Chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment was directly influenced by menopausal symptoms (β=.38,p =.002), depression and anxiety (β=.25,p =.002), and symptom experiences (β=.19,p =.012). These predictors explained 47.7% of the variance in chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment. Depression and anxiety mediated the relations among menopausal symptoms, symptom experiences, and with chemotherapy related cognitive impairment. Depression and anxiety (β=-.51,p =.001), symptom experiences (β=-.27,p =.001), menopausal symptoms (β=-.22,p =.008), and chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment (β=-.15,p =.024) had direct effects on the quality of life and these variables explained 91.3%.Conclusion These results suggest that chemotherapy-related toxicity is highly associated with cognitive decline and quality of life in women with breast cancer. Depression and anxiety increased vulnerability to cognitive impairment after chemotherapy. Nursing intervention is needed to relieve chemotherapy-related toxicity and psychological factor as well as cognitive decline for quality of life in patients undergoing chemotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
Young-Hee Je, Kyoung-Ah Kang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - Impact of social support on cognitive function in patients with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy: The chain-mediating role of fatigue and depression
Yuanqi Ding, Qingmei Huang, Fulei Wu, Yang Yang, Ling Wang, Xuqian Zong, Xiaoyan Yu, Changrong Yuan
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100743. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Oncofertility in Gynecological Cancer Patients: Application of Mixed Methods Study
Minji Kim, Juyoung Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 418. CrossRef - Relationships Between Chemotherapy-Related Cognitive Impairment, Self-Care Ability, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study
Nan Wu, Ze Luan, Zijun Zhou, He Wang, Shiyuan Du, Yulu Chen, Xinxin Wang, Jiong Li, Xin Peng
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2024; 40(5): 151690. CrossRef - Effects of different exercise interventions on chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment in patients with breast cancer: a study protocol for systematic review and network meta-analysis
Yu Dong, Hao Huang, Aiping Wang
BMJ Open.2024; 14(4): e078934. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Self-reported Memory Problems of Adult Cancer Survivors Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
Sangjin Ko
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(1): 51. CrossRef - Impact of nonpharmacological interventions on cognitive impairment in women with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jin-Hee Park, Su Jin Jung, Lena J. Lee, Junghyun Rhu, Sun Hyoung Bae
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(4): 100212. CrossRef - Impact of discriminant factors on the comfort-care of nurses caring for trans-arterial chemoembolisation patients
Myoung Soo Kim, Ju-Yeon Uhm
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(9): 7773. CrossRef - Brain morphological alterations and their correlation to tumor differentiation and duration in patients with lung cancer after platinum chemotherapy
Pin Lv, Guolin Ma, Wenqian Chen, Renyuan Liu, Xiaoyan Xin, Jiaming Lu, Shu Su, Ming Li, ShangWen Yang, Yiming Ma, Ping Rong, Ningyu Dong, Qian Chen, Xin Zhang, Xiaowei Han, Bing Zhang
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Rehabilitation on Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Clinical Study
Teresa Paolucci, Aristide Saggino, Francesco Agostini, Marco Paoloni, Andrea Bernetti, Massimiliano Mangone, Valter Santilli, Raoul Saggini, Marco Tommasi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(16): 8585. CrossRef
- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
- 1,726 View
- 23 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Reversals in Decisions about Life-Sustaining Treatment and Associated Factors among Older Patients with Terminal Stage of Cardiopulmonary Disease
- Jung-Ja Choi, Su Hyun Kim, Shin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):329-339. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.329
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the frequency, patterns, and factors of reversals in decisions about life-sustaining treatment (LST) among older patients with terminal-stage chronic cardiopulmonary disease.
Methods This was a retrospective correlational descriptive study based on medical chart review. De-identified patient electronic medical record data were collected from 124 deceased older patients with terminal-stage cardiopulmonary disease who had made reversals of LST decisions in an academic tertiary hospital in 2015. Data were extracted about the reversed LST decisions, LST treatments applied before death, and patients’ demographic and clinical factors. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to identify the factors associated with the reversal to higher intensity of LST treatment.
Results The use of inotropic agents was the most frequently reversed LST treatment, followed by cardiopulmonary resuscitation, intubation, ventilator therapy, and hemodialysis. Inconsistency between the last LST decisions and actual treatments occurred most often in hemodialysis. One-third of the reversals in LST decisions were made toward higher intensity of LST treatment. Patients who had lung diseases (vs. heart diseases); were single, divorced, or bereaved (vs. married); and had an acquaintance as a primary decision maker (vs. the patients themselves) were significantly more likely to reverse the LST decisions to higher intensity of LST treatment.
Conclusion This study demonstrated the complex and turmoil situation of the LST decision-making process among older patients with terminal-stage cardiopulmonary disease and suggests the importance of support for patients and families in their LST decision-making process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characteristics of Life-Sustaining Treatment Decisions: National Data Analysis in South Korea
Jiyeon Choi, Heejung Jeon, Ilhak Lee
Asian Bioethics Review.2024; 16(1): 33. CrossRef - Decision and Practice of End-of-Life Care in Lung Disease Patients with Physicians Orders for Life Sustaining Treatment
Yu Mi Oh, Yoon Na Kang, Soo Jung Han, Jeong Hye Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2023; 26(1): 7. CrossRef - Same, same, but different? A longitudinal, mixed-methods study of stability in values and preferences for future end-of-life care among community-dwelling, older adults
Malin Eneslätt, Gert Helgesson, Carol Tishelman
BMC Palliative Care.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Preferences for life-sustaining treatment in Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
HyunChul Youn, Suk-young Lee, Han-yong Jung, Shin-Gyeom Kim, Seung‑Hyun Kim, Hyun-Ghang Jeong
BMJ Open.2021; 11(1): e039470. CrossRef - Life-Sustaining Treatment in End-Stage Liver Disease Patients: Patients’ Decisions and Results
Hyun Jung Jung, Jeong Yun Park
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2020; 23(2): 85. CrossRef
- Characteristics of Life-Sustaining Treatment Decisions: National Data Analysis in South Korea
- 1,121 View
- 9 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Mediation Effect of Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Perceived Self-Management Support and Health-Related Quality of Life among Cancer Survivors
- Bo Gyeong Lee, Tae Sook Lee, Soo Hyun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):298-306. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.298
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to examine the levels of perceived self-management support, self-efficacy for self-management, and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in cancer survivors, and to identify the mediating effect of self-efficacy in the relationship between perceived self-management support and HRQoL.
Methods This study used a descriptive correlational design. Two hundred and four cancer survivors who had completed treatment participated in the study. Measurements included the Patient Assessment of Chronic Illness Care Scale, the Korean version of the Cancer Survivors’ Self-Efficacy Scale, and the Medical Outcomes Study Short Form-36. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson's correlation coefficient analysis, and multiple regression analysis using Baron and Kenny's method for mediation.
Results The mean score for perceived self-management support was 3.35 out of 5 points, self-efficacy was 7.26 out of 10 points, and HRQoL was 65.90 out of 100 points. Perceived self-management support was significantly positively correlated with self-efficacy (r=.29,
p <.001) and HRQoL (r=.27,p <.001). Self-efficacy was also significantly correlated with HRQoL (r=.59,p <.001). Furthermore, self-efficacy (β=.55,p <.001) had a complete mediating effect on the relationship between perceived self-management support and HRQoL (Z=3.88,p <.001).Conclusion The impact of perceived self-management support on HRQoL in cancer survivors was mediated by self-efficacy for self-management. This suggests that strategies for enhancing self-efficacy in cancer survivors should be considered when developing self-management interventions for improving their HRQoL.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated With Quality of Life Among Posttreatment Cancer Survivors in Korea
Soo Hyun Kim, Yu Hyeon Choe, Jingyeong Choi, Ji Young Park, Eun Yi
Cancer Nursing.2025; 48(1): E47. CrossRef - Effects of Symptom Burden, Self-Efficacy, and Stigma on Cancer Coping in Patients with primary Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy
Ah-Reum Han, Euna Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(3): 158. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Symptom Experience and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Enhee Jo, Ju-Young Park, Young Jun Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(3): 315. CrossRef - An Integrated Review of Health Care in Child and Adolescent Cancer Survivors Based on Roy’s Adaptation Model
Hye Jin Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(2): 82. CrossRef - Trajectories of quality of life in breast cancer survivors during the first year after treatment: a longitudinal study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ji Young Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
BMC Women's Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of perceived chronic illness management support, health literacy, and social support on the care burden of families caring for older people with multiple chronic conditions at home: A cross-sectional study
Eun Sil Lee, Mi Young Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(1): 76. CrossRef - Effects of Uncertainty, Appraisal of Uncertainty, and Self-Efficacy on the Quality of Life of Elderly Patients with Lung Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy: Based on Mishel’s Theory of Uncertainty
Min-Kyung Hwang, Hee-Kyung Kim, Ki-Hyeong Lee
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1051. CrossRef - Between Personality Traits and Postpartum Depression: The Mediated Role of Maternal Self-Efficacy
Lingli Han, Ji Zhang, Jingxuan Yang, Xiaoyu Yang, Hua Bai
Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment.2022; Volume 18: 597. CrossRef - A Structural Model of Quality of Life in Patients after Colorectal Cancer Surgery
Jeong Won Yeom, Yeon Ok Suh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(5): 2564. CrossRef - The influence of Digital Informatization Level, Self-efficacy, and Social Support on Digital Health Literacy in the Elderly with Cancer
Hye Su Kim, Ji Hyun Sung
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(4): 255. CrossRef - The Correlation Between Quality of Life and Positive Psychological Resources in Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis
Xinxin Zhao, Siqi Tong, Ye Yang
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrated, cross-sectoral psycho-oncology (isPO): a new form of care for newly diagnosed cancer patients in Germany
Michael Kusch, Hildegard Labouvie, Vera Schiewer, Natalie Talalaev, Jan C. Cwik, Sonja Bussmann, Lusine Vaganian, Alexander L. Gerlach, Antje Dresen, Natalia Cecon, Sandra Salm, Theresia Krieger, Holger Pfaff, Clarissa Lemmen, Lisa Derendorf, Stephanie St
BMC Health Services Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Self-efficacy, post-traumatic growth, and quality of life of pediatric cancer survivors: A cross-sectional study
Yeunhee Kwak, Yoonjung Kim, Eun Seok Choi, Ho Joon Im
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 54: 102019. CrossRef - Determinants of quality of life in women immediately following the completion of primary treatment of breast cancer: A cross-sectional study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ji Young Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae, Ka Ming Chow
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(10): e0258447. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of patient assessment of chronic illness care among Korean cancer survivors
Soo Hyun Kim, Bo Gyeong Lee, Yu Hyeon Choe, Francesca Chiesi
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0256119. CrossRef - Mediating and Moderating Factors of Adherence to Nutrition and Physical Activity Guidelines, Breastfeeding Experience, and Spousal Support on the Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors
Nam Mi Kang, Won-Ho Hahn, Suyeon Park, Jung Eun Lee, Young Bum Yoo, Chung Ja Ryoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7532. CrossRef
- Factors Associated With Quality of Life Among Posttreatment Cancer Survivors in Korea
- 1,861 View
- 41 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref

- The Effect of the Intergenerational Exchange Program for Older Adults and Young Children in the Community Using the Traditional Play
- Min-Jung Choi, Kyeong-Yae Sohng
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):743-753. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.743
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to explore the effects of a community-based first and third Intergenerational Exchange Program (IGEP) on older adults’ health-related quality of life (HRQoL), loneliness, depression, and walking speed, and on 4~5-year-old preschool children's learning-related social skills.
Methods This study employed a non-equivalent control group pre-post-test design. The experimental group included 42 older adults and 42 children who participated in the IGEP for 8 weeks, and the control group included 39 older adults. The experimental group participated in the IGEP once a week for 8 weeks. It comprised a traditional play program based on the intergroup contact theory.
Results Compared to the control group, there was a significant increase in scores on the HRQoL-Visual analogue scale (VAS) and a decrease in loneliness and depression in older adults in the experimental group (
p <.05). Children who participated in the IGEP showed an improvement in their learning-related social skills (p <.001).Conclusion These results confirm that the IGEP is an effective intervention to improve HRQoL-VAS, loneliness, and depression among older adults and learning-related social skills among preschool children in the community.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Intergenerational Interaction on Older Adults Depends on Children’s Developmental Stages; Observational Evaluation in Facilities for Geriatric Health Service
Rie Fukuoka, Shinji Kimura, Toru Nabika
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(1): 836. CrossRef - Intergenerational Taekwondo Program: A Narrative Review and Practical Intervention Proposal
Yongseop Kim, Junhyoung Kim, Jung-Min Lee, Dong-Chul Seo, Hyun Chul Jung
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(9): 5247. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study Exploring Negative Affect in Older Adults Residing in Long-Term Care Facilities
Zhen Chen, Hongxia Zhang, Jinhua Zhang, Suqing Li, Yanmei Zhao
Research and Theory for Nursing Practice.2022; 36(3): 301. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Intergenerational Interaction on Older Adults Depends on Children’s Developmental Stages; Observational Evaluation in Facilities for Geriatric Health Service
- 1,540 View
- 45 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Psychoeducational Approach to Distress Management of Newly Diagnosed Patients with Breast Cancer
- Jin-Hee Park, Mison Chun, Yong Sik Jung, Sun Hyoung Bae, Young-Mi Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):669-678. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.669
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of integrated psychoeducational program for distress management of newly diagnosed patients with breast cancer.
Methods A quasi-experimental trial was conducted. The participants consisted of 47 female patients with breast cancer assigned to an intervention group (n=25) and control group (n=22). The intervention group participated in integrated psychoeducational program, consisting of individual face-to-face education and telephone-delivered health-coaching sessions. Data were collected at three time points: pre-intervention (T1), post-intervention (T2), and 6-month follow-up (T3). Study instruments were Distress thermometer, Supportive Care Needs Survey Short Form 34 and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast.
Results Compared with the control group, breast cancer patients in the intervention group reported lower distress and supportive care needs than the control group. The intervention group reported higher quality of life (QOL) overall and higher emotional well-being than the control group.
Conclusion These findings indicate that the integrated psychoeducational program is an effective intervention for reducing distress and supportive care needs and increasing QOL of newly diagnosed patients with breast cancer. Oncology nurses need to provide psychoeducational intervention to support patients with breast cancer in managing their distress and helping them adjust to their life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
Young-Hee Je, Kyoung-Ah Kang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Tailored Psychoeducational Intervention for Patients With Advanced Cancer in Indonesia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Nurul Huda, Made Satya Nugraha Gautama, Wan Nishfa Dewi, Agung Waluyo, Hsiu Ju Chang, Malissa Kay Shaw
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2025; 57(5): 848. CrossRef - Evidence on the benefits of mind-body Qigong exercise in women with breast cancer
Michel Marcos Dalmedico, Jackson Adriano Canavarro Ribeiro, Juliana Londero Silva Avila, Prisley Pereira de Oliveira, Paula Karina Hembecker, Sergio Ossamu Ioshii
Fisioterapia em Movimento.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychological Distress and Influencing Factors in Newly Diagnosed Patients with Breast Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Min Hee Hur, Yu Jin Jeong
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(4): 311. CrossRef - Effects of Psychosocial Interventions for Patients with Breast Cancer: A Meta-analysis
Kyu-Sic Hwang, Kuy-Haeng Lee, Chan-Mo Yang, Hye-Jin Lee, Sang-Yeol Lee
Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience.2023; 21(1): 118. CrossRef - The development of a lifestyle modification mobile application, “Health for You” for overweight and obese breast cancer survivors in Korea
Su-Jin Seo, Ju-Hee Nho, Youngsam Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(3): 243. CrossRef - Development and Effect of the Integrated Health Promotion Program for Cancer Survivors Living at Home
Hee Sang Yoon, Eun A Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(1): 51. CrossRef - Adjustment to life with metastatic cancer through psychodrama group therapy: A qualitative study in Turkey
Songül Kamışlı, Bahar Gökler
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2021; 57(2): 488. CrossRef - Integration of longitudinal psychoeducation programmes during the phases of diagnosis, management and survivorship of breast cancer patients: A narrative review
Athena Michaelides, Constantina Constantinou
Journal of Cancer Policy.2020; 23: 100214. CrossRef - Quality of Life in Patients Undergoing Mastectomy for Breast Cancer
Kavitha Konnakkaparambil Ramakrishnan, Sreekumar Damodaran
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2020; 7(28): 1368. CrossRef - Mediating and Moderating Factors of Adherence to Nutrition and Physical Activity Guidelines, Breastfeeding Experience, and Spousal Support on the Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors
Nam Mi Kang, Won-Ho Hahn, Suyeon Park, Jung Eun Lee, Young Bum Yoo, Chung Ja Ryoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7532. CrossRef - Uncertainty and unmet care needs before and after surgery in patients with gastric cancer: A survey study
Ji Yea Lee, Yeonsoo Jang, Sanghee Kim, Woo Jin Hyung
Nursing & Health Sciences.2020; 22(2): 427. CrossRef - Effects of Different Exercise Interventions on Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Tetiana Odynets, Yuriy Briskin, Valentina Todorova
Integrative Cancer Therapies.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
- 1,780 View
- 41 Download
- 13 Crossref

- An Ethnography on the Healthy Life of the Aged Women Participating the Senior Centers
- Eunha Kim, Jinhyang Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):349-361. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.349
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This ethnography was performed to explore patterns and meanings of healthy life among aged women using senior centers.
Methods The informants were 21 individuals aged 65 years and older at 2 community-based senior centers. Data were collected from iterative fieldwork through in-depth interviews and participant observations and analyzed using text analysis and taxonomic methods developed by Spradley. Field notes were used with follow-up interviews and dialogue between authors to enhance interpretation.
Results Patterns of healthy life among aged women using senior centers were categorized by age groups within the context of the four cultural elements of taking care of the body, relationality, temporality, and spatiality: active and passive control, maintenance of interdependence and individuality, expansion and maintenance of the daily routine, unity of peer relations and sustenance of family relations, spending time productively and tediously, and complementary and alternative space of the family relations.
Conclusion The informants in this study demonstrated healthy life by maintaining and strengthening continuous relationships developed in the senior centers without being isolated from the family and society. Patterns of their healthy life differed across age groups within the socio-cultural context. Therefore, interventions should be tailored to address age groups and community needs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Qualitative Study on the Exercise Experiences and Health Perceptions of Older Women
Young Hye Jeong
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2025; 36(4): 645. CrossRef
- Qualitative Study on the Exercise Experiences and Health Perceptions of Older Women
- 1,204 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Structural Equation Model of Health-Related Quality of Life in School Age Children with Asthma
- Yunsoo Kim, Ho Ran Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(1):96-108. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.1.96
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to construct and test a hypothetical model of the quality of life of school-age children with asthma based on the health-related quality of life model by Wilson and Cleary.
Methods Data were collected from 205 pairs of pediatric outpatients diagnosed with asthma and their parents in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do from July 2016 to April 2017. The exogenous variables were asthma knowledge, number of accompanying allergic diseases, and social support. The endogenous variables were asthma self-efficacy, asthma symptom control, perceived health status, parental quality of life, and children's quality of life. For data analysis, descriptive statistics, factor analysis, and structural equation modeling were performed.
Results Eighteen of the twenty-four hypotheses selected for the hypothetical model were attentive and supported statistically. Quality of life was explained by asthma self-efficacy, asthma symptom control, perceived health, parental quality of life, and asthma knowledge with 83.5%.
Conclusion Strategies for promoting self-efficacy and enforcing asthma knowledge will be helpful for the improvement of health-related quality of life with school-aged asthmatic children.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adaptation of the ‘’Food Allergy Self-Efficacy Scale for Parents’’(FASE-P) to Turkish: a validity and reliability study
Nilay Çalışkan, Şeyma Genç, Güler Yıldırım, Hamit Bologur, Hilal Güngör, Merve Karaca Şahin, Muhammed Fatih Erbay, Şefika İlknur Kökcü Karadağ, Özlem Terzi, Deniz Özçeker
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics.2024; 66(5): 534. CrossRef - Perception of quality of life in school-age children born before 32 weeks of gestational age
Amaia Merino-Hernández, Agustin Muñoz-Cutillas, Cristina Ramos-Navarro, Sara Bellón-Alonso, Juan Luis Rodríguez-Cimadevilla, Noelia González-Pacheco, Manuel Sánchez-Luna
European Journal of Pediatrics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Structural Equation Model of Health-Related Quality of Life among Older Women Following Bilateral Total Knee Replacement
Hyun Ok Lee, Jae Soon Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(4): 554. CrossRef - Effect of Functional Adjustment Procedure on Pain, Dysfunction and, Health-related Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain
Chang-Wook Bae, Jae-Bum Lee
Journal of The Korean Society of Physical Medicine.2020; 15(2): 109. CrossRef - Analysis of the Dimensions of Quality of Life in Colombian University Students: Structural Equation Analysis
Juan-Cancio Arcila-Arango, Manuel Castro-Sánchez, Sebastian Espoz-Lazo, Cristian Cofre-Bolados, Maria Luisa Zagalaz-Sánchez, Pedro Valdivia-Moral
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(10): 3578. CrossRef
- Adaptation of the ‘’Food Allergy Self-Efficacy Scale for Parents’’(FASE-P) to Turkish: a validity and reliability study
- 1,403 View
- 15 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Impact of Uncertainty on the Quality of Life of Young Breast Cancer Patients: Focusing on Mediating Effect of Marital Intimacy
- Yeong Kyong Oh, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(1):50-58. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.1.50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the mediating effect of marital intimacy on the impact of uncertainty on the quality of life (QoL) of young breast cancer patients.
Methods This study used a pathway analysis with 154 young breast cancer cases in their early diagnosis stage at a medical center in Korea. Data were collected from November 2016 to February 2017 and analyzed using correlation analysis and pathway analysis.
Results Uncertainty, marital intimacy, and 4 sub-scales of QoL showed a significant correlation. Marital intimacy was directly affected by uncertainty (b=-.39,
p =.013) and 4 sub-scales of QoL were also affected by uncertainty. Among the 4 sub-scales of QoL, physical well-being (PWB) (b=.17,p =.026), social well-being (SWB) (b=.49,p =.010), and functional well-being (FWB) (b=.38,p =.009) were affected by marital intimacy but emotional well-being (EWB) was not affected by it. The mediating effect of marital intimacy on the impact of uncertainty on QoL was confirmed. Marital intimacy showed a significant indirect effect on PWB (b=-.07,p =.024), SWB (b=-.19,p =.008), and FWB (b=-.15,p =.005), and it means that marital intimacy has a partial mediating effect on the impact of uncertainty on PWB, SWB, and FWB.Conclusion Effects of uncertainty on QoL was mediated by marital intimacy of young breast cancer patients in their early diagnosis stage. It suggests that marital intimacy needs to be considered in providing nursing intervention for young breast cancer patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Incertidumbre en mujeres diagnosticadas con cáncer de mama: estudio transversal
Rosa Herminia Pastuña-Doicela, Olivia Inés Sanhueza-Alvarado
Escola Anna Nery.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Uncertainty in women diagnosed with breast cancer: a cross-sectional study
Rosa Herminia Pastuña-Doicela, Olivia Inés Sanhueza-Alvarado
Escola Anna Nery.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Body change stress, sexual function, and marital intimacy in korean patients with breast cancer receiving adjuvant chemotherapy: A cross-sectional study
Hyesoon Lee, Hyeon Gyeong Yoon
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(5): 100228. CrossRef - Factors influencing the supportive care needs of female patients with genital cancer in South Korea
Yu-Jung Son, Keum-Hee Nam, JaeLan Shim
Medicine.2023; 102(51): e36650. CrossRef - An explanatory model of quality of life in high-risk pregnant women in Korea: a structural equation model
Mihyeon Park, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(4): 302. CrossRef - Impacts of Uncertainty and Social Support on the Quality of Life of Breast Cancer Survivors after Chemotherapy: Based on Self-help Group Participants
Hyenam Hwang, Yoonshin Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2023; 23(4): 177. CrossRef - A hermeneutic phenomenological study on the disease experience among young women with breast cancer
Jeonghee Ahn, Kyoung-eun Lee
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(10): 100310. CrossRef - Psychological variables associated with quality of life in patients with head and neck cancer: the role of body image distress
Silvia Cerea, Maria Sansoni, Giovanni Scarzello, Elena Groff, Marta Ghisi
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(11): 9127. CrossRef - Relationships among sexual function, marital intimacy, type D personality and quality of life in patients with ovarian cancer, with spouses
Ju‐Hee Nho, Sung Reul Kim, Won Ku Choi
European Journal of Cancer Care.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Relationships among Social Support, Bowel Function Symptoms and Uncertainty in Rectal Cancer Patients
Kyungmi Lee, Semi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 421. CrossRef - The development of a lifestyle modification mobile application, “Health for You” for overweight and obese breast cancer survivors in Korea
Su-Jin Seo, Ju-Hee Nho, Youngsam Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(3): 243. CrossRef - Mediating and Moderating Factors of Adherence to Nutrition and Physical Activity Guidelines, Breastfeeding Experience, and Spousal Support on the Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors
Nam Mi Kang, Won-Ho Hahn, Suyeon Park, Jung Eun Lee, Young Bum Yoo, Chung Ja Ryoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7532. CrossRef - Effects of uncertainty and spousal support on infertility-related quality of life in women undergoing assisted reproductive technologies
Hye Shin Lee, Sunjoo Boo, Jeong-Ah Ahn, Ju-Eun Song
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(1): 72. CrossRef - Impact of Psycho-Social Factors on Fatigue among Breast Cancer Patients Who Are Currently Undergoing Radiotherapy
Hyesun Park, Kisook Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(17): 6092. CrossRef - Health care Utilization of Cancer patient Women at Nursing Hospital
Hye-Sun Park, Kyung-Sook Park
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2018; 19(11): 2139. CrossRef
- Incertidumbre en mujeres diagnosticadas con cáncer de mama: estudio transversal
- 1,283 View
- 14 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Effects of Active Mandibular Exercise for Mouth Opening Limitation Patients after Maxillomandibular Fixation Release: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
- Hyo Jin Jang, Myung Hee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(1):26-37. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.1.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of active mandibular exercise (AME) in patients with limited mouth opening after maxillomandibular fixation (MMF) release.
Methods The study used a quasi-experimental, nonequivalent control group and a pre test-post test design. Sixty-two patients with Maxillomandibular Fixation Release were assigned to the experimental (n=31) or control group (n=31). The AME was performed in the experimental group for 4 weeks. The exercise AME consisted of maximal mouth opening, lateral excursion and protrusive movement. These movements were repeated ten times a day. After the final exercise of the day, the number of tongue blades used for mouth opening was noted. The effect of AME was evaluated after MMF release at different time intervals: a) immediately, b) after 1 week, c) after 2 weeks, d) after 4 weeks, and e) after 12 weeks. The exercise was assessed using the following criteria: a) mandibular movements, b) pain scores associated with maximal mouth opening, c) discomfort scores associated with range of movement, and d) daily life activities that involve opening the mouth.
Results The experimental group showed significant improvement regarding the range of mandibular movements (maximal mouth opening (F=23.60,
p <.001), lateral excursion to the right side (F=5.25,p =.002), lateral excursion to the left side (F=5.97,p =.001), protrusive movement (F=5.51,p =.001)), pain score (F=39.59,p <.001), discomfort score (F=9.38,p <.001). Daily life activities that involve opening the mouth were more favorable compared to those in the control group.Conclusion The AME in patients after MMF release is helpful for increasing mandibular movement range, decreasing pain and discomfort, and improving day life activities that involve opening the mouth. Therefore, AME is highly recommended as an effective nursing intervention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of early active mandibular exercise in early recovery of mandibular movement and quality of life after orthognathic surgery: a single-centre randomised clinical trial
Hyo-Jin Jang, Jae-Min Song, Yong-Il Kim, Sung-Hun Kim, Seong-Sik Kim, Youn-Kyung Choi
British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2025; 63(9): 650. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Physical Therapy in Orthognathic Surgery Patients: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
Gonzalo Navarro-Fernández, Alfonso Gil-Martínez, Marta Diaz-Saez, Ignacio Elizagaray-Garcia, Paloma Pili-Mayayo, Julian Ocampo-Vargas, Hector Beltran-Alacreu
Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology.2023; 8(1): 17. CrossRef - Is it worth applying self-irrigation after third molar extraction? A randomised controlled trial
Hyo-Jin Jang, Youn-Kyung Choi, Eun-Young Kwon, Won-Hyuk Choi, Jae-Min Song
British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2022; 60(7): 877. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of early active mandibular exercise in early recovery of mandibular movement and quality of life after orthognathic surgery: a single-centre randomised clinical trial
- 1,072 View
- 15 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Effects of Mobile Social Networking Service-Based Cognitive Behavior Therapy on Insomnia in Nurses
- Ji Eun Kim, Suk-Sun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(4):476-487. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.4.476
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to examine the effects of cognitive behavior therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) based on the mobile social networking service (SNS) on dysfunctional beliefs and attitudes about sleep, sleep quality, daytime sleepiness, depression, and quality of life among rotating-shift nurses in a hospital in Korea.
Methods A nonequivalent control group pre-post test design was used. The participants included 55 nurses with rotating three-shift work (25 in the experimental group and 30 in the control group). For the experimental group, CBT-I using mobile SNS was provided once a week for 60 minutes over six weeks. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, χ2-test, independent samples t-test, and Mann-whitney U test with the SPSS 21.0 program.
Results In the homogeneity test of the general characteristics and study variables, there were no significant differences between the two groups. Nurses in the experimental group had significantly lower scores on dysfunctional beliefs and attitudes regarding sleep and sleepiness than nurses in the control group. Nurses in the experimental group had significantly higher scores on sleep quality and quality of life than nurses in the control group.
Conclusion These findings indicate that using the mobile SNS-based CBT-I is feasible and has significant and positive treatment-related effects on rotating-shift nurses' irrational thoughts and beliefs in association with sleep, sleep quality, daytime sleepiness, and quality of life. These contribute to expanding our knowledge of rotating-shift nurses' sleep issues and their preferences for intervention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia in Patients with Alcohol Use Disorder: An Experimental Study
Sook Kyoung Park, Eun Ju Song, Keun Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(2): 211. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Quality of Life of Clinical Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Seul-Ki Park, Kyoung-Sook Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(3): 1752. CrossRef - Effectiveness of sleep interventions for rotating night shift workers: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Bo Min Jeon, Su Hyun Kim, Seung Hwa Shin
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of the type of delivery of cognitive‐behavioral therapy for healthcare workers: A systematic review
In Gyu Yoo
Journal of Clinical Psychology.2022; 78(2): 149. CrossRef - Effects of cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) on quality of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Zainab Alimoradi, Elahe Jafari, Anders Broström, Maurice M. Ohayon, Chung-Ying Lin, Mark D. Griffiths, Kerstin Blom, Susanna Jernelöv, Viktor Kaldo, Amir H. Pakpour
Sleep Medicine Reviews.2022; 64: 101646. CrossRef - Rotating between day and night shifts: Factors influencing sleep patterns of hospital nurses
Seunghwa Shin, SuHyun Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2021; 30(21-22): 3182. CrossRef - Sleep quality among shift-work nurses: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jiwon Kang, Wonjung Noh, Youngjin Lee
Applied Nursing Research.2020; 52: 151227. CrossRef
- Effects of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia in Patients with Alcohol Use Disorder: An Experimental Study
- 1,995 View
- 52 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Experience of Becoming a Father of a High Risk Premature Infant
- Jeong Eon Park, Byoung Sook Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):277-288. Published online April 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.277
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was performed to identify the experience of becoming a father of a high risk premature infant.
Methods Grounded theory was used for this research. The participants were 12 fathers who had premature infants lighter than 2,500g of birth weight, less than 37 weeks of gestational age and having stayed 2 weeks or longer in a NICU right after birth. Theoretical sampling was done to identify participants and indepth interviews were done for the data collection. For data analysis, the process suggested by Corbin and Strauss was used.
Results For these participants the core phenomenon of the experience of becoming a father of a high risk premature infant was ‘striving through with belief and patience’. The phenomenon was ‘being frustrated in an unrealistic shock’. Contextual conditions were ‘uncertainty in the health status of the premature baby’ and ‘no one to ask for help’ and intervening conditions were ‘possibility in the health recovery of the premature baby’ and ‘assistance from significant others’. Action/interaction strategies were ‘withstanding with belief in the baby’ and ‘enduring with willpower as head of the family’ and the consequence was ‘becoming a guardian of the family’.
Conclusion For the participants, the process of becoming the father of a high risk premature infant was striving through the situation with belief in their babies' ability to overcome the crisis and waiting for the babies' recovery with patience.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Topics and Trends in Neonatal Family-Centered Care
In Young Cho, Cho Hee Kim
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - An Integrated Review of Transitional Care for Families of Pre-Term Infants
Jeong Soon Kim, Hae Ran Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(22): 2287. CrossRef - The experience of fathers whose infants were hospitalized in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit in South Korea: A scoping review
Jiyeon Lee, Sunyeob Choi
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2023; 72: 36. CrossRef - Perceptions of fatherhood and confidence regarding neonatal care among fathers of high-risk neonates in South Korea: a descriptive study
Jin Won Lee, Sunhee Lee
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(3): 229. CrossRef - Changes in Strauss & Corbin's Grounded Theory
Ji Eun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 505. CrossRef - Parenting Experience of Prematurity Parents Based on Grounded Theory
Jeong Soon Kim
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2019; 23(4): 232. CrossRef - Experiences of Mothers of Premature Infants Receiving Rehabilitation Therapy
Hyun-Ju Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2018; 24(3): 298. CrossRef
- Topics and Trends in Neonatal Family-Centered Care
- 1,236 View
- 19 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Correlational Study on Management of Menopause, Marital Satisfaction, and Quality of Life in Middle-aged Women
- Jung Hee Yeo
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(2):261-269. Published online April 6, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.2.261
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to examine the correlations among management of menopause, marital satisfaction, and quality of life in middle-aged women.
Method The sample was 158 middle-aged women who were 40-64 years. Data were collected from June 14 to July 10, 2003 using questionnaires and were analyzed by using the SPSS 10.0 PC+ program.
Result The level of marital satisfaction was related positively to the level of quality of life(r=.504, p<.01) and management of menopause(r=.315, p<.01). In addition, there were significant correlations between the level of quality of life and management of menopause(r=.251, <.01). In stepwise multiple regression analysis, 25.9% of the variance in quality of life was explained by marital satisfaction.
Conclusion Marital satisfaction and management of menopause serve to improve the quality of life of middle-aged women. It is necessary to develop an effective intervention program to improve marital satisfaction and management of menopause.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Determinants of Quality of Life (QoL) in Female Caregivers in Elderly Care Facilities in Korea
Hee-Kyung Kim, Hye-Suk Oh
Behavioral Sciences.2024; 14(1): 53. CrossRef - The Effects of Personal Psychological Variables, Family Variables, and Job Satisfaction on the Psychological Well-being of Middle-aged Men
Seon Hye Woo, Jung Min Kim, Han Sol Jo
Journal of Korean Home Management Association.2016; 34(6): 15. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling on Healthy Menopausal Transition
Eunyoung Hong, Young Sil Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(1): 64. CrossRef - Effects of Sanhujori and Menopausal Adaptation on Health-related QOL in Middle-aged Women
Moon-Jeong Kim, Kyung-Ja Kang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2014; 20(1): 62. CrossRef - Women Religious and Married Women's Attitudes toward Menopause and Menopausal Symptoms
Myung-Sook Yoo
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(2): 186. CrossRef - Lifestyle, Depression, and Health Related Quality of Life among Women in Jeju Province
Young Rye Park, Hwee Wee, Soo Jin Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(2): 148. CrossRef
- Determinants of Quality of Life (QoL) in Female Caregivers in Elderly Care Facilities in Korea
- 627 View
- 5 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Predicting Quality of Life in People with Cancer
- Pok Ja Oh
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(4):901-911. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.4.901
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study is to provide a basis for nursing intervention strategies to promote quality of life in cancer patients. Therefore the study is designed to evaluate the effectiveness of perceived health status, self-esteem, health locus of control, self-efficacy, perceived susceptibility/severity, health promoting behaviors, and hope for quality of life. The sample was composed of 164 stomach cancer patients who visited outpatient clinics at a university hospital in Seoul. The following instruments were used in the study after some adaptation : Lawstone and others' Health Self-rating Scale, Rosenberg's Self-esteem Scale, Wallston and others' Multidimensional Health Locus of Control Scale, Sherer and Maddux's Self-efficacy Scale, Moon's Health Beliefs Scale, Welker and others' Health Promoting Lifestyle Profile, Nowotney's Hope scale and Noh's Quality of Life Scale. Data were analyzed using a SAS program for Pearson correlation coefficients descriptive correlational statistics and stepwise multiple regression. The results are as follows : 1. The scores on the quality of life scale ranged from 115 to 243 with a mean of 177.84(SD : 25.35). The mean scores(range 1-5) on the different dimensions were : emotional state 3.37 ; economic life 3.47 ; physical state and function 3.52 ; self-esteem 3.66 ; relationship with neighbors 3.73 ; family relationships 3.80. 2. There was a significant correlation between all the predictive variables and the quality of life(r=.20 -.65, p<.01). 3. Stepwise multiple regression analysis showed that : 1) Self-esteem was the main predictor of quality of life and accounted from 46.9% of the variance in quality of life. 2) Perceived health status, hope and perceived susceptibility/severity accounted for 11.8%, 8.3%, 1.5% of the variance in quality of life respectively. 3) Self-esteem, perceived health status, hope and perceived susceptibility/severity combined accounted for 68.5% of the variance in quality of life. In conclusion, self-esteem, perceived health status, hope and perceived susceptibility / severity were identified as important variables in the quality of life of cancer patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of denture use on the quality of life of cancer patients over 40 years of age: The 6th-7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013–2018)
A-Jung Lee, Mi-Ra Lee, Min-Kyung Kang
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2024; 24(2): 141. CrossRef - The Influence of Resilience on the Quality of Life of Patients with non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Soon Hee Shim, Jeong Hye Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(1): 47. CrossRef - Effects of Holistic Hospice Nursing Intervention Program on Self Esteem and Spiritual Well-being for Inpatients of Hospice Palliative Care Unit
Sung-Eun Choi, N. Eun-Sil Kang
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2009; 12(4): 209. CrossRef
- Effects of denture use on the quality of life of cancer patients over 40 years of age: The 6th-7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013–2018)
- 563 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- An Effect of Nursing-Logotherapy on Purpose in Life and Finding Meaning, and Hope of the patients of Mental Illness
- Jong Ji Lee
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(4):727-739. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.4.727
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to present an effective nursing intervention for helping the patients of mental illness by determining the effect of nursing-logotherapy on purpose in life and finding meaning, and hope of the patients of mental illness by developing and applicating program of nursing-logotherapy. The data was collected from March to September in 1995, and its subjects were the patients of mental illness who was appropriate to the standard of this study among the patients of mental illness who hospitalized into Neuro-Psychiatric ward of M. and B. hospital located in Pusan area. They were all 60 subjects, thirty of them for an experimental group and the rest for a control group. The research design was an equivalent control group pre-test and post-test design as an quasiexpe-rimental research and the conceptual framework was an interpersonal model. The data analysis was computerized by using SP-SS/PC+ and hypothesis testing was done with 2-way ANCOVA and simple correlation. Results were summarized as follows : 1. There were significant changes of purpose in life and finding meaning in an experimental group before and after treatment and a control group before and after. 2. There were significant changes of hope in an experimental group before and after treatment and a control group before and after. 3. The positive correlation between purpose in life and finding meaning and hope of the patients of mental illness were observed. Consequently, nursing-logotherapy could significantly increase the purpose in life and finding meaning, and of hope, so it could be said an effective nursing intervention for helping the healing of the patients of mental illness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Meaning in Life and Social Support on Posttraumatic Growth in Pancreatic Cancer Survivors
Youjin Kim, Boyoung Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2021; 30(4): 330. CrossRef
- Effects of Meaning in Life and Social Support on Posttraumatic Growth in Pancreatic Cancer Survivors
- 641 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Study on Self-esteem, Coping Type and the Quality of Life in Mothers of Handicapped Children
- Mi Kyung Sim
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(3):673-682. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.3.673
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between self-esteem and quality of life(QOL) and between coping type and quality of life (QOL) in mothers of handicapped children and further to identify the level of self-esteem and quality of life of the subjects. The subjects of this study were the 51 mothers of handicapped children who were registered in two special schools in Taejon. The data were collected using a questionnaire and the period of the data collection was from April 18th to May 26th, 1997. The instruments for this study were Resenberg's self-esteem scale, Folkman and Lazarus's Ways of Coping Checklist(WCC) and the quality of life scale designed by Ro, You Ja. The results were analyzed using SPSS/PC+. Data analysis included the descriptive correlational statistics of ANOVA, Pearson Correlational Coefficient, and t-test. The results are as follows : 1. The level of self-esteem showed a mean score 34.51 and the level of QOL, a mean score 137.55. An Active type of coping was used more often than a passive one. 2. The level of self-esteem differed according to monthly income and was significantly higher in mothers of children with acquired handicaps than those of children with congenital handicaps. The level of QOL differed according to monthly income. 3. There was positive correlation between health status and self-esteem(r=.355, p<.05), and between health status and QOL(r=.367, p<.01). 4. Test for hypothesis ; Hypothesis 1, "The higher the level of self-esteem in mothers of handicapped children, the higher their level of quality of life will be." was supported(r=.755, p<.001). Hypothesis 2, "The QOL level for the active coping group as compared to the passive coping group will be higher." was not supported.
- 369 View
- 0 Download

- Effects of a Program to Promote Self-Efficacy and Hope on the Self: Care Behaviors and the Quality of Life in Patients with Leukemia
- Pok Ja Oh, Eun Ok Lee, Young Sook Tae, Dong Choon Um
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(3):627-638. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.3.627
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Most patients having leukemia suffer severely from emotional turmoil due to the generalized perception that cancer will be fatal. The conventional chemotherapy results in side effects such as severe bone marrow depression which interfere with self-care management, vital for improvement in their condition. Bandura's theory of the self-efficacy suggests that self-efficacy can be enforced by performance attainments, vicarious experiences, verbal persuasion and the release of emotional arousal. Self-efficacy can be enforced by a program of vicarious experiences and verbal persuasion, while the emotional arousal can be relieved through a hope promotion program. If once self-efficacy increases, the patient's self-care behaviors and the quality of life will also increase. The purpose of this study was to empirically test the effects of a program, to promote self-efficacy and hope, on self-care behaviors and quality of life in patients having leukemia. In this study, three types of approaches to enhance self-efficacy and hope were used : 1) a 20-minute long slide/tape for vagarious experiences ; 2) a 10-minute long telephone call coaching for verbal persuasion ; and 3)two booklets for information about the symptoms of leukemia and treatment modalities and hope promotion. Thirsty one patients were recruited in the experimental group and 29 in the control group with a nonequivalent pretest-posttest design. The subjects were patients with leukemia undergoing chemotherapy. Sherer and Maddux's self-efficacy scale, Nowotny's hope scale, and Padilla's quality of life scale were employed with some modifications. A self-care behavior scale was developed by the researchers. Statistical analyses including paired t-test, Chi-square, ANCOVA and ANOVA, were used. The results are as follows : The levels of self-efficacy, self-care behavior and quality of life were higher in the experimental group than in the control group after four weeks of intervention(F=28.71, P=.0001 ; F=63.35, P=.0001 ; F=16.57, P=.0001). After ten weeks of intervention, all of the dependent variables(self-efficacy, self-care behavior, hope and quality of life) in the experimental group were higher than in the control group(F=74.12, P=.0001 ; F=108.34, P=.0001 ; F=13.11, P=.001 ; F=43.52, P=.0001). In conclusion, self-care behavior and quality of life increased mainly through an increase an increase in self-efficacy, while increases in hope took more time and effort.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The development and initial validation of the self-care belief and behavior questionnaire
Julia A. Najm, Diana M. Morelen
Journal of Human Behavior in the Social Environment.2025; 35(6): 936. CrossRef - Fatigue, Self-Care Behavior, and Quality of Life in Patients Undergoing Home-Based Chemotherapy with a Disposable Elastomeric Infusion Pump
Koh-Woon Choi, Suk-Jung Han
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(4): 229. CrossRef - The Effects of Chemotherapy Education Reflecting Educational Needs on Self-Care Knowledge and Performance in Female Cancer Patients: A Non-Equivalent Control Group Pretest-Posttest Design
Jin Hee Jun, Se-Na Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(3): 103. CrossRef - Validation of the Korean Version of the Health Care Climate Questionnaire among Cancer Survivors
Hyun-E Yeom, Jungmin Lee, Young-Joo Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 323. CrossRef - Relationship between Health Literacy and Self-care Behavior in Patients with Stomach Cancer after Gastrectomy: Mediating Effects of Subjective Health Status and Specific Self-efficacy
Min Jung Kim, Yong Soon Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 259. CrossRef - The Development and Evaluation of a Health Literacy-Adapted Self-Management Intervention for Elderly Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Yoon Sun Kim, Young Sook Tae, Kwuy-Im Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(4): 472. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life of Cancer Patients Hospitalized in Long-term Care Hospitals
A Young Jang, Jeong Sook Park
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2018; 20(1): 35. CrossRef - The Effect of Patient Education Interventions on Distress, Self-Care Knowledge and Self-Care Behavior of Oncology Patients: A Meta-Analysis
Pok-Ja Oh, Hyeong-Ji Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(4): 257. CrossRef - Effects of Self-Efficacy Promotion Program on Self-Efficacy, Self-Care Behavior, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy
Hea-Kyoung Ko, Geum Ja Park
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2011; 11(2): 136. CrossRef
- The development and initial validation of the self-care belief and behavior questionnaire
- 778 View
- 15 Download
- 9 Crossref

- A Structural Model for Quality of Life in Individuals with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Hyun Soo Oh, Young Ran Kim
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(3):614-626. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.3.614
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The main purposes of the study were to develop and test a model which explains the dynamic relationship among factors reported as affecting to the quality of life of individuals with rheumatoid arthritis and to examine the relationship between self-help response and quality of life. Data for the study were collected from March 1996 to December 1996 from 153 female patients who regularly visited a clinic for people with rheumatism. The Patients were introduced to the investigators by nurses who worked at that clinic, and then the investigator interviewed the patients for 30 to 40 minutes to collect the data. Instruments used in the study were modified self-report questionnaires from the ones which were already developed in previous studies of from related literature. Data analysis were performed using LISREL(Lineal Structural Relations) 8 Program to test whether the proposed hypothesized model fit the collected data. To test fitablity of the hypothesized model both a general fit measure and a detailed fit measure were used. Based on the test results from the various fit measures, the hypothesized model was found to be well suited to the real data. As characteristics related to illness becomes severe, the feasibility for uncertainty about the illness tend to increase, but, the direct effects from the illness characteristics(such as level of physical symptoms, sense of social-psychologic change, limitations of action) as they are related to the other intrinsic variables(self-efficacy or self-help behavior and quality of life), were found to be not significant. It was found that uncertainty had a direct effect on self-efficacy but did not have a direct effect on self-help behavior or quality of life. Also, it is noted that self-efficacy had a positive effect on self-help behavior and quality of life and there was a bilateral relationship between self-efficacy and self-help behavior. Lastly, the hypothesis proposed from the theoretical model in this study was supported basis of the results that self-help behavior provides both direct and positive effects to quality of life. Particularity, since a bilateral relationship was also found between self-help behavior and quality of life in the modified model, as self-help behavior increased, so did quality of life. And, reversely, as quality of life increased, so did self-help behavior. In conclusion, the results of this study suggest that focusing on both acquirement and reinforcement of adjustment factors or self-help behavior is more efficient than focusing on the characteristics of illness in establishing the strategies for improving quality of life of individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health-related quality of life in female patients with reumatoid arthritis: a structural equation model
Bukyung Kim, Mi-Hae Sung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(2): 91. CrossRef - Factors Related to Quality of Life among Older Adults who Had Arthritis: Limited Daily Activities and Physical Activity
Jee-Seon Yi
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2023; 12(4): 431. CrossRef - Health-related Quality of Life in Korean Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Association with Pain, Disease Activity, Disability in Activities of Daily Living and Depression
Dong Choon Uhm, Eun Sook Nam, Ho Yeon Lee, Eun Bong Lee, Young Im Yoon, Gong Ju Chai
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(3): 434. CrossRef
- Health-related quality of life in female patients with reumatoid arthritis: a structural equation model
- 642 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Study on Health Promoting Lifestyle of the Elderly
- Young Shin Song, Mi Ra Lee, Eun Kyong Ahn
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(3):541-549. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.3.541
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was done to describe health promoting lifestyle and determine affecting factors in elderly based on the Heath Promotion Model by Pender. Cognitive-perceptual factors that were included in this study were self-efficacy and hardiness. Modifying factors were demographic characteristics(sex, age, partner, previous illness, education level, income and religion). The specific purpose of this study was to examine the relationships of self-efficacy, hardiness and the demographic chasteristics to health promoting lifestyle and to determine causal factors affecting the elderly. The subjects were a volunteer sample of 98 elderly in one city in? The instruments for this study were Health Promoting Lifestyle Profile(47items, 4scale), Health Related Hardiness Scale(22items, 6scale), general Self-Efficacy Scale((13items, 5scale). Frequency, percentage, t-test, ANOVA, Pearson's correlation coefficient and Stepwise Multiple regression technique with SAS program were used to analyze the data. The Results of the study are follows ; 1) The average item score for the health promoting lifestyle was 2.63, the highest score on the subscales was interpersonal support(M=3.3), followed by self-actualization(M=2.9), nutrition (M=2.8), stress management(M=2.7), health responsibility(m=2.1) with the lowest being exercise(M=2.0). 2) A significant difference between education level, income, religion and health promoting lifestyle were found. 3) All of the subscales on health promoting lifestyle were positively related to total hardiness(r=0.330, p<0.001). The hardiness subscale of control was positively related to self-actualization(r=0.276, p<0.01), and commitment was positively related to self-actualization(r=0.315, p<0.001), exercise/nutrition(r=0.245, p<0.01), interpersonal support(r=0.278, p<0.01), stress management(r=0.250, p<0.01). Challenge was positively related to self-actualization(r=0.315, p<0.001), exercise/nutrition((r=0.245, p<0.01). There was no significant correlation between self-efficacy and all of the subscales of health promoting lifestyle. Self-efficacy showed a significant correlation only with control(r=0.469, p<0.001), committment(r=0.507, p<0.001), Challenge(r=0.489, p<0.001). 4) Committment, self-efficacy and income explained 25.01% of the variance for the total health promoting lifestyle. The results of this study show that commitment, self efficacy and income predicted the health promoting lifestyle of the elderly. So health promoting programs that increase committment and self-efficacy should be developed to promote a healthy lifestyle of the elderly, especially those who have low income.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ego Integrity of the Elderly - Focusing on Mediator of Self-actualization -
김고은, 신은주
Korean Journal of Gerontological Social Welfare.2016; 71(3): 109. CrossRef
- Ego Integrity of the Elderly - Focusing on Mediator of Self-actualization -
- 554 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Changes in Fatigue and the Quality of Life of Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy
- Eun Sook Lee, Jucia Jo
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(3):489-502. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.3.489
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Quality of life(QOL) and fatigue in cancer patients receiving the radiotherapy was assessed. The subjects were 46 cancer patients who daily attended the radiotherapy department. Assessment was done on four occasions ; the first assessment was done on the treatment simulation visit, the second one was four week after treatment started, the third one at the completion of treatment and the last assessment was done between six and eight week following treatment. The results are as follows : The fatigue scores of the patients at each stage of assessment ranged from 5.49 points to 7.67 points and highest score was recorded at the third assessment hat is, at the completion of treatment. The fatigue points showed an increase from the 1st. to 3rd. stage. However, at the 4th. stage, fatigue points decreased to the level at the first stage, fatigue points decreased to the level at the first stage of assessment. QOL were assessed in three areas namely, physical, emotional and social/functional. The QOL scores in the physical area showed the highest score, followed by social/functional and emotional areas. The QOL scores decreased gradually to the third. stage of assessment thereafter recovered to the level of the first. stage. Correlation between QOL and fatigue scores during the treatment indicated that the level of QOL decreased as the level of fatigue increased. In particular, fatigue persisted after completion of the treatment and showed a significantly negative correlation with QOL. The present study strongly suggests that a strategy to restore the emotional well being level of the patient should be devised in order to improve QOL and reduce fatigue of patients receiving radiotherapy.
- 391 View
- 1 Download

- A Study, on the Quality, of Life, Family, Support and Hope of Hospitalized and Home Care Cancer Patients
- Kae Wha Jo, Myung Ja Kim
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(2):353-363. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.2.353
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF With the occurrence of cancer, most cancer patients experience various emotional changes such as anxiety, depression, and emotional shock. Especially in our country, cancer has been recognized as an incurable disease resulting in death. The number of cancer patients increases daily. But as the survival rate of cancer patients is also increasing, there is a need to find the better methods of nursing care for cancer patients. The purposes of this paper are as follows : 1) To understand family support and hope and quality of life for the cancer patient both during hospitalization and at home. 2) To determine the relationship between family support, hope and quality of life. To examine the problems, we used a questionnaire and obtained data form the records of 45 home care and 94 hospitalized(in 3 university hospitals) Patients in Taegu area from the period of June 15 to August 15, 1996. SPSS /PC was used for the data analysis and the statistical methods used were the T-test and ANOVA. The results of this paper are as follow : 1 ) In the aspect of family support, there is no difference between hospitalized and home care cancer patients(t=1.63, P>0.01 ). 2) In the aspect of hope, hospitalized cancer patients have a higher score than home care cancer patients (t=3.08, P>0.01 ) 3) In the aspect of quality of life, hospitalized cancer patients have a higher score than home care patients(t=2.96, P<.01). 4) There is a correlation between quality of life and hope with a correlation coefficient r=0.5199 and P=0.000. In addition. the correlation coefficient between quality of life and family support is 4179 with P =0.000. 5) The family support of the cancer patient is influenced by sex(F=9.1863, P<0.01), education(F=4.3641, P<0.01) and the level of life (F=5.5002, P<0.01 ). 6) The hope of cancer patients is influenced by the number of hospitalizations (F=3.6413, P<.05), education(F=B.01 13, P<.01 ) and the level of life (F=5.0649, P <.01 ). 7) The quality of life of cancer patients is influenced by the number of hospitalization( F=5.1167, P<0.05), education( F=3.1590, P<0.01 ) and the level of life (F=5.6942, P<1.01 ).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Influences of Family Support on the Meaning of Life in Cancer Patients
Min Jung Kim, Min Sung Kim
Journal of Families and Better Life.2023; 41(2): 19. CrossRef - Needs of Hospice Care and Quality of Life for Cancer Patients
In Sun Suh, Mi Hwa Shin, Se Hwa Hong
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2010; 13(2): 89. CrossRef
- The Influences of Family Support on the Meaning of Life in Cancer Patients
- 572 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Predictors of health Promoting Lifestyle for the Korean Immigrants in the U.S.A
- Myung Ja Kim, Hyo Jeong Song
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(2):341-352. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.2.341
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The study was to examine the relationships among health promoting lifestyle, level of anxiety, and perceived health status and to reveal those variables affecting health promoting lifestyle in Korean immigrants in the United States. The subjects were 425 adults chosen from Korean religious and social organizations located in New York from April 25th through July 5th, 1996. Data analyses were conducted by using pearson correlation coefficients, t-test, ANOVA, and stepwise multiple regression. The results were as follows : Health promoting lifestyle was significantly different according to age, religion, occupation, and the length of residence in the US. Those insured and those with no chronic conditions revealed a significantly higher score in health promoting lifestyle. Significant differences in the level of anxiety were found according to education, marital status, occupation, family income, and the length of residence. Those with no chronic conditions experienced a significantly lower level of anxiety. In the subscales of the health promoting lifestyle profile, self-actualization and interpersonal relationship revealed higher scores, whereas the scores of stress management, health responsibility, and exercise were lower. Those subjects whose perceived health status was very good, showed the lowest level of anxiety and the highest score on the health promoting lifestyle profile. Negative correlations were observed between the health promoting lifestyle profile and the level of anxiety, and between the perceived health status and the level of anxiety. Health promoting lifestyle was significantly predicted by the level of anxiety(22.0%), age(2.0%), health insurance(1.1%), respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of yoga exercise on maximum oxygen uptake, cortisol level, and creatine kinase myocardial bond activity in female patients with skeletal muscle pain syndrome
Min-Sung Ha, Yeong-Ho Baek, Jong-Won Kim, Do-Yeon Kim
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2015; 27(5): 1451. CrossRef
- Effects of yoga exercise on maximum oxygen uptake, cortisol level, and creatine kinase myocardial bond activity in female patients with skeletal muscle pain syndrome
- 585 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Determinants of Health Promoting Lifestyle of College Students
- Mi Ra Lee
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(1):156-168. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.1.156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was undertaken in order to examine the relationship of self-efficacy, control, perceived health status, self-esteem, social support, and demographic characteristics to health promoting lifestyle of college students, and to determine factors affecting health promoting lifestyle of college students. The subjects were 92 students of one university in Taejon. The instruments used for this study were a survey of general characteristics, health promoting lifestyle(44 items), self-efficacy (28 items), self-esteem(10 items), control(8 items), perceived health status( 1 item), and social support(12 items) Analysis of data was done by use of mean, percentage, t-test, ANOVA, Pearson correlation coefficient and stepwise regression with SAS program. The results of this study are as follows. 1) The average item score for the health promoting lifestyles was low at 2.30. n the sub-categories, the highest degree of performance was interpersonal support(2.90), and the lowest degree was exercise(1.67). 2) Male students showed a significant higher score in exercise subscale than female students. Students who had more income had higher scores in self actualization subscale. Students who's family had experienced severe disease had higher scores in health responsibility and interpersonal support subscale. Students who had experienced exercise had higher scores interpersonal support, and stress management subscale. 3) Significant correlation between perceived health status and self-efficacy, perceived health status and self-esteem, control and self-efficacy, control and self-esteem, control and social support, self-esteem and self-efficacy was found. 4) Self-efficacy and control revealed significant correlations with total health promoting lifestyle and all subscales of health promoting lifestyle except self actualization. A significant correlation between perceived health status and self actualization subscale was found. Self-esteem revealed significant correlations only with self actualization and interpersonal support subscale. 5) Significant correlations were found between most of the subscales of total health promoting lifestyle. 6) Self-efficacy was the highest factor predicting health promoting lifestyles of college students (30.55%). Self-efficacy and control accounted for 36.55% in health promoting lifestyle of college students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health Promotion Behavior of Chinese International Students in Korea Including Acculturation Factors: A Structural Equation Model
Sun Jung Kim, Il Young Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2016; 10(1): 25. CrossRef - Effects of a Health Education Program based on Social Cognitive Theory on the Health Promotion of University Students with Metabolic Syndrome
Hee-Gerl Kim, Jinhwa Lee, Jiyun Kim, Hyunju Park, Hyun Sook Oh, Won Jae Lee, Eun Aae Kim, Hye Kyung Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(4): 451. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Promotion Lifestyles and Self-esteem of Korean and Chinese Nursing Students.
Hee Cho, Suk Jeong Lee, Ren Shan Cui
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2010; 19(1): 22. CrossRef - The Relations among ADL, Self-efficacy, Physical Activity and Cognitive Function in Korean Elders
Myoung Ja Wang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(1): 101. CrossRef - HEALTH-PROMOTING BEHAVIORS OF Older Adults Compared to Young and Middle-Aged Adults in Korea
Mee Ock Gu, Young Eun
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2002; 28(5): 46. CrossRef
- Health Promotion Behavior of Chinese International Students in Korea Including Acculturation Factors: A Structural Equation Model
- 696 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- An Exploration of the Life Experiences of Patients with Chronic Pain: Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Hea Kyung Hur
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(1):13-25. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.1.13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rheumatoid Arthritis(RA), a chronic and systemic inflammatory disorder, is characterized by joint pain, swelling and stiffness. Patients with RA suffer from joint pain and overall pain. The painful and disabling consequences of RA are accompanied by a variety of affective, cognitive, and behavioral changes. The purpose of this paper was to explore and describe the life experiences of RA patients by eliciting verbal description of their experiences. Participants were nine persons who were diagnosed with RA, and had if for more than six months. They were asked open ended and descriptive questions in order for them to talk about their experiences in their own terms. Interviews were tape recorded and transcribed verbatim. The transcripts were analyzed by Colaizzi method. From the protocols, 213 significant statements about life experience were organized into 83 formulating meanings which were then grouped into five theme clusters. The major themes that emerged from the analysis were 'Emotional Disturbances', 'Trying to Adapt to the Progress of Treatment', ' Change of Role Performances', 'Experiences related to Family'. The result of this study showed that RA patients and families need nursing care based on a deep understanding of their lived experiences in everyday life. Nurses and other health workers must develop rehabilitation programs that focus on the pain control, functional independence and psychosocial factors.
- 369 View
- 0 Download

- A Structural Model for Health Promotion and Quality of Life in People with Cancer
- Pok Ja Oh
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(3):632-652. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.3.632
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF It has been noted that a genetic alteration of cells influenced by unhealthy lifestyle in addition to a series of other carcinogens increases the incidence of various neoplasmic diseases. Therefore the importance of a lifestyle that minimizes such an impact on health should be emphasized. Since stomach cancer, the most common neoplasmic disease in Korea, is related to personal lifestyle and as there is a possibility of its recurrence, patients with stomach cancer need to lead a healthy lifestyle. Also the quality of life which patients experience is negatively affected by the side effects of treatments and the possibility of recurrence. Therefore an effective nursing intervention to enhance quality of life and encourage healthy lifestyle is needed. The purpose of this study is to provide a basis for nursing intervention strategies to promote health and thus enhance quality of life. A hypothetical model for this purpose was constructed based on Pender's Health Promotion Model and Becker's Health Belief Model, with the inclusion of some influential factors such as hope for quality of life and health promoting behavior. The aims of study were to: 1) evaluate the effectiveness of patient's cognitive-perceptual factors on health promoting behaviors and quality of life; 2) examine the causal relationships among perceived benefit, perceived barrier, perceived susceptibility and severity, internal locus of control, perceived health status, hope, health concept, self efficacy, self esteem, health promoting behaviors and quality of life; 3) build and test a global hypothetical model. The subjects for this study were 164 patients who were being treated for stomach cancer were approached in the outpatient clinic on a University Hospital. The data from the completed questionnaires were analyzed using Linear Structural Relationships (LISREL). The results of research are as follows: 1) Hypothetical model and the modified model showed a good fit to the empirical data, revealing considerable explanational power for health promoting behaviors(54.9%) and quality of life(87.6%) 2) Self efficacy and hope had significant effects on health promoting behaviors. Of these, hope was affected indirectly through self efficacy and self esteem. 3) Perceived health status, hope and self esteem had significant direct effect on the quality of life. Of these variables, perceived health status was the most essential factor affecting general satisfaction in life. 4) Self-efficacy, as a mediating variable, was positively affected by perceived benifit and hope. 5) Self-esteem, as a mediating variable, was positively affected by perceived health status and hope. 6) Hope was the main variable affecting self efficacy, self esteem, health promoting behaviors and quality of life. The derived model in this study could effectively be used as a reference model for further study and could suggests a direction for nursing practices.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tailored psychoeducation for multiple myeloma patients: a step toward enhancing quality of life and health outcomes
Yoorin Cho, Yang Sook Yoo
Health Education Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality of life patterns and its association with predictors among non-muscle invasive bladder cancer survivors: A latent profile analysis
Jeongok Park, Young Deuk Choi, Kyoungjin Lee, Miae Seo, Ahyoung Cho, Sejeong Lee, Keum-hee Nam
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 9(6): 100063. CrossRef - Posttraumatic Growth and Health Promotion Behavior in Patients with Cancer: The Mediating Effect of Spiritual Well-Being
Shunji Piao, Pok Ja Oh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(1): 33. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Posttraumatic Growth of Gynecologic Oncology Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Sun Jeong Yun, Hye Young Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(4): 409. CrossRef - Psychosocial Adjustment in Korean Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hyejin Sun, Jia Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(5): 545. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Characteristics of Cancer Patients and Cancer Survivors
So Young Baek, Ja Yun Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(1): 11. CrossRef - Self-Efficacy, Self-Care Behavior, Posttraumatic Growth, and Quality of Life in Patients with Cancer according to Disease Characteristics
Jinho Choi, Sunyoung Lee, Byungduck An
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2016; 19(2): 170. CrossRef - A Predictive Model of Quality of Life for Stomach Cancer Patients with Gastrectomy
Young Suk Kim, Young Sook Tae
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(6): 613. CrossRef - The Effects of Posttraumatic Growth and Meaning in Life on Health Promotion Behavior in Cancer Patients
Sun-Hee Jang, Hae-Rang Lee, Hyung-Nam Yeu, Soon-Ock Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(2): 100. CrossRef - The Influencing Factors on Quality of Life among Breast Cancer Survivors
Yoon Sun Kim, Young Sook Tae
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2011; 11(3): 221. CrossRef
- Tailored psychoeducation for multiple myeloma patients: a step toward enhancing quality of life and health outcomes
- 827 View
- 10 Download
- 10 Crossref

- An Effect of Muscle Strengthening Exercise Program on Muscle Strength, Pain, Depression, Self-efficacy, and Quality of Life of Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis
- Mi Ra Lee
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(3):556-575. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.3.556
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In an attempt to investigate the effect of a muscle strengthening exercise program on muscle strength, pain, depression, self-efficacy and quality of life of patients with knee osteoarthritis, a pre-experiment, one group pre-test and post-test design, was planned. Muscle strengthening exercise was carried out from May 22 through August 14, 1995 at isokinetic exercise room in rehabilitation department of University Hospital in Taejon. The subjects were seven female clients conveniently sampled from University Hospital located in Taejon, between 39 and 61 years of age, who had a osteoarthritis in knee. Muscle strengthening exercise program was composed of three sessions per week, one isokinetic exercise at angular velocity of 60degrees and 180degrees with Cybex isokinetic dynamometer and two resistance home exercise sessions with elastic band. Data were analyzed with frequency, percentage of change, Friedman test, Duncan test using SAS program. Results were obtained as follows: 1) Flexion and extension muscle strength at angular velocity of 60degrees and 180degrees were increased after 12weeks' exercise than those of before experiment. But exept flexion muscle strength at angular velocity of 180degrees (F=3.34, P=0.0261), there was no statistically significant difference among muscle strengths, which is measured every 3 weeks. 2) Pain was decreased after 6weeks' exercise than that of before experiment, and after 12weeks' exercise than that of 6weeks' exercise. There was statistically significant difference(F=4.28, P= 0.0396). 3) Depression was increased after 6weeks' exercise than that of before experiment, and after 12weeks' execise than that of 6weeks' exercise. There was no statistically significant difference between before experiment and after 6weeks' exercise. But, there was statistically significant difference between after 6weeks' exercise and 12weeks' exercise (F=9.38, P=0.0035). 4) Self-efficacy was decreased after 6weeks' exercise than that of before exercise. But, it was increased after 12weeks' exercise than that of before exercise and after 6weeks' exercise. But there was no statistically significant difference (F=1.46, P=0.2706). 5) Quality of life was increased after Gweeks' exercise than that of before exercise, and after 6weeks' exercise than that of 12weeks' exercise. But there was no statistically significant differ-ence(F=1.06, P=0.3816). Thus, the significant of muscle strengthening exercise for the improvement of muscle strength, pain, depression, is verified. But, this study was a preexperiment with small size subjects. So, controlled experimental study is necessary to determine the effect of this muscle strengthening exercise program on muscle strength, pain, depression, self-efficacy, and quality of life of patients with knee osteoarthritis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of elastic band exercises and nutritional education on frailty, strength, and nutritional intake in elderly women
Yena Bong, Wook Song
Physical Activity and Nutrition.2020; 24(1): 37. CrossRef - The Relationship between Job Stress and Depression in Opticians in Seoul, Korea
Semi Kim, Jihye Ahn, Moonsung Choi
Journal of Korean Ophthalmic Optics Society.2019; 24(3): 223. CrossRef - Retracted:Effects of Exercise Program on Physical Fitness, Depression, and Self‐Efficacy of Low‐Income Elderly Women in South Korea
Kyung Rim Shin, Younhee Kang, Hyo Jung Park, Margaret Heitkemper
Public Health Nursing.2009; 26(6): 523. CrossRef
- The effects of elastic band exercises and nutritional education on frailty, strength, and nutritional intake in elderly women
- 736 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Development of Meaning in Life Measurement Tool
- Jeong Ji Lee, Kyung Il Shin, Soon Ock Choi, Sook Nam Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(7):1039-1048. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.7.1039
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to develop an instrument to measure meaning in life based on Frankl's theory of logotherapy. Data were collected from August to October, 1999 by means of questionnaires developed by researchers. The subjects were 351 adults living in Busan and Kyoung Nam province. The study was conducted as follows: 1) A conceptual framework was identified based on the extensive review of relevant literatures and interviews with adults and professionals in psychology, philosophy, theology, and nursing. 2) The 76 items, 4-points scale were developed. 3) The scale was tested on 351 adults to assess the reliability and validity, and factor analysis was done. 4) 63 items were established based on this testing and ten factors were extracted. These factors were labeled as self-awareness and self-acceptance, futuristic aspiration, valuelessness, purpose in life, contentedness with life, role awareness, experience of love, love in family, commitment, self- transcendence. Cronbach's alpha of the 63 items was .950. Comparative studies to assess construct validity and repetitive studies to heighten generalizability are needed. This tool can be utilized to measure Korean's meaning in life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- الفراغ الوجودي لدى المطلقات في لواء البادية الشمالية /الأردن
هند المهلهل, فواز المومني
مجلة جامعة الشارقة للعلوم الانسانية والاجتماعية.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- الفراغ الوجودي لدى المطلقات في لواء البادية الشمالية /الأردن
- 648 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Age at Menopause and Related Factors in Korean Women
- Young Joo Park, Hesook Suzie Kim, Hyun Choel Kang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(7):1024-1031. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.7.1024
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This cross-sectional design was to identify the age at menopause of Korean women using a national sample, and to examine relationships between age at menopause and the anthropometric, sociodemographic, biological and life style behavioral factors. Two thousand eight hundred seven naturally postmenopausal women aged between 41-65 years were recruited by self-selection from 7 metropolitans and 6 provinces in Korea from Dec. 20, 1998 to April 30, 1999. The age at menopause of Korean women was 49.2 years (mean) and 50.0 years (median). The range of age at menopause was 33.0 to 61.0 years. The significant influencing factors on age at menopause were body mass index, mother's and sister's age at menopause, alcohol use, physical activity, coffee preference, and residential area. The menopausal age of Korean women has slightly increased compared to a previous study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exposure to the one-child policy and fertility among chinese immigrants to the US
Siyuan Lin, Laura Argys, Susan Averett
Review of Economics of the Household.2025; 23(3): 969. CrossRef - Menopause Across Asia: A Comprehensive Meta-analysis of Age and Influencing Factors
Prabhat Kumar Agrawal, Amit Varshney, Siddhant Dev, Ruchika Garg, Ashish Gautam, Nikhil Pursnani, Sandipta Kumar Panda, Nidhi Agastya
Journal of Mid-life Health.2025; 16(3): 257. CrossRef - Functional Effects of Sericin on Bone Health and D-Serine Regulation in Estrogen-Deficient Rats
Hyun-Seung Kim, Xiangguo Che, Shihyun Kim, Jongho Choi, Joon Ha Lee, You-Young Jo, Seong-Gon Kim, Je-Yong Choi, Ji-Hyeon Oh
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(18): 10247. CrossRef - Nonpharmacological Intervention Effects on Middle-Aged Women with Menopausal Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ji-Hyun Kim, Hea-Jin Yu
Healthcare.2025; 13(24): 3206. CrossRef - Longitudinal patterns and group heterogeneity of depressive symptoms during menopausal transition in middle-aged Korean women
Yoonyoung Jang, Yoosoo Chang, Junhee Park, Sang Won Jeon, Byungtae Seo, Jae Ho Park, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Seungho Ryu
Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Regular Use of Analgesics before Cancer Diagnosis and Occurrence of Mood Disorders
Hyun Sook Oh, Subin Noh, Hwa Jeong Seo
Nursing Reports.2024; 14(3): 1828. CrossRef - Study on depletion of ovarian function and late‐life chronic diseases in India
Sampurna Kundu, Sanghmitra Sheel Acharya
International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics.2023; 162(3): 1057. CrossRef - Exposure to the One-Child Policy and Fertility Among Chinese Immigrants to the Us
Siyuan Lin, Laura Argys, Susan Averett
SSRN Electronic Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Iron Deficiency in Korean Patients With Heart Failure
Jin Joo Park, Minjae Yoon, Hyoung-Won Cho, Sang-Eun Lee, Jin-Oh Choi, Byung-Su Yoo, Seok-Min Kang, Dong-Ju Choi
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of early age at menopause on disease outcomes in postmenopausal women with rheumatoid arthritis: a large observational cohort study of Korean patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Eun Hye Park, Eun Ha Kang, Yun Jong Lee, You-Jung Ha
RMD Open.2023; 9(1): e002722. CrossRef - Osteoporosis Associated with Breast Cancer Treatments Based on Types of Hormonal Therapy: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Korean National Sample Data
Yen Min Wang, Yu-Cheol Lim, Deok-Sang Hwang, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha, Ye-Seul Lee
Medicina.2023; 59(9): 1505. CrossRef - Measured sodium excretion is associated with cardiovascular outcomes in non-dialysis CKD patients: results from the KNOW-CKD study
Seong Cheol Kang, Minjung Kang, Hyunjin Ryu, Seonmi Kim, Ji Hye Kim, Eunjeong Kang, Yujin Jeong, Jayoun Kim, Yong-Soo Kim, Soo Wan Kim, Yeong Hoon Kim, Kook-Hwan Oh
Frontiers in Nephrology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of tiotropium on the risk of coronary heart disease in patients with COPD: a nationwide cohort study
Jiyoung Shin, Jin Hwa Lee
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined Effects of Unhealthy Lifestyle Behaviors on Metabolic Syndrome among Postmenopausal Women
Jin-Suk Ra, Hyesun Kim
Healthcare.2021; 9(7): 848. CrossRef - Ovarian Function Preservation in Patients With Cervical Cancer Undergoing Hysterectomy and Ovarian Transposition Before Pelvic Radiotherapy
Wonguen Jung, Yun H. Kim, Kyung S. Kim
Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Clinical Impact of Body Mass Index on Breast Cancer in Korea: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Jae Hwan Jeong, Hak Min Lee, Hai Young Son, Ilkyun Lee
Journal of Breast Disease.2020; 8(1): 51. CrossRef - Beneficial Effects of Breastfeeding on the Prevention of Metabolic Syndrome Among Postmenopausal Women
Jin Suk Ra, Soon Ok Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2020; 14(3): 173. CrossRef - Neck Circumference and Cerebral Gray Matter Volume
Chol Shin, Regina E.Y. Kim, Robert J. Thomas, Chang-Ho Yun, Seung Ku Lee, Robert D. Abbott
Alzheimer Disease & Associated Disorders.2020; 34(4): 306. CrossRef - Inhaled corticosteroids in COPD and the risk for coronary heart disease: a nationwide cohort study
Jiyoung Shin, Hee-Young Yoon, Yu Min Lee, Eunhee Ha, Jin Hwa Lee
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends of Premature and Early Menopause: a Comparative Study of the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Seung-Ah Choe, Joohon Sung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Urinary bisphenol A, phthalate metabolites, and obesity: do gender and menopausal status matter?
Jung-eun Lim, BongKyoo Choi, Sun Ha Jee
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2020; 27(27): 34300. CrossRef - Association between lower urinary tract symptoms and cardiovascular risk scores in ostensibly healthy women
Hyun Young Lee, Ji Eun Moon, Hwa Yeon Sun, Seung Whan Doo, Won Jae Yang, Yun Seob Song, So‐Ryoung Lee, Byoung‐Won Park, Jae Heon Kim
BJU International.2019; 123(4): 669. CrossRef - Higher Pro-Inflammatory Dietary Score is Associated with Higher Hyperuricemia Risk: Results from the Case-Controlled Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study_Cardiovascular Disease Association Study
Hye Sun Kim, Minji Kwon, Hyun Yi Lee, Nitin Shivappa, James R. Hébert, Cheongmin Sohn, Woori Na, Mi Kyung Kim
Nutrients.2019; 11(8): 1803. CrossRef - Association between obesity type and obstructive coronary artery disease in stable symptomatic postmenopausal women: data from the KoRean wOmen'S chest pain rEgistry (KoROSE)
Jun Hwan Cho, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Myung-A Kim, Sohee Oh, Mina Kim, Seong Mi Park, Hyun Ju Yoon, Mi Seung Shin, Kyung-Soon Hong, Gil Ja Shin, Wan-Joo Shim
Menopause.2019; 26(11): 1272. CrossRef - Obesity and colorectal adenomatous polyps: A cross-sectional study in Korean adults
Ji Young Lee, Sang Mi Kwak, Seung-Kwon Myung, Sun Ha Jee
Obesity.2014; 22(2): 518. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Risk Factors for Intracranial Cerebral Atherosclerosis Among Asymptomatic Subjects
Young-Suk Kim, Jin-Woo Hong, Woo-Sang Jung, Seong-Uk Park, Jung-Mi Park, Sung-Il Cho, Young-min Bu, Sang-Kwan Moon
Gender Medicine.2011; 8(1): 14. CrossRef - Cortisol, estradiol-17β, and progesterone secretion within the first hour after awakening in women with regular menstrual cycles
Ryun S Ahn, Jee H Choi, Bum C Choi, Jung H Kim, Sung H Lee, Simon S Sung
Journal of Endocrinology.2011; 211(3): 285. CrossRef
- Exposure to the one-child policy and fertility among chinese immigrants to the US
- 3,083 View
- 24 Download
- 27 Crossref

- Social Support, Stressful Life Events, and Health Behaviors of Korean Undergraduate Students
- Young Joo Park, Sook Ja Lee, Ka Sil Oh, Kyoung Ok Oh, Jeong Ah Kim, Hee Soon Kim, Sang Soon Choi, Sung Eun Yi, Choo Ja Chung, Hoa Yun Jun
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(6):792-802. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.6.792
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This cross-sectional study was designed to explore the relationship among social support, experienced stressful life events and health behaviors of Korean undergraduate students, and validate the mediator effect of social support. METHOD: One thousand four hundred fifty-three undergraduate students were randomly selected from five universities located in the middle area of Korea. RESULT: The health behaviors of Korean undergraduates tend to have unhealthy patterns. In the case of the students living without family, experiencing more stressful life events and perceiving lower social support, health behaviors are poor. The relationship between perceived social supports, the frequency of the experienced stressful life events and the score of health behavior patterns is statistically significant. After controlling the effect of social support, the correlation coefficient between the frequency of experienced stressful life events and the score of health behavior patterns was slightly lower. The score of health behaviors between the group with an extremely high score of social support and the group with an extremely low score were statistically significantly different. CONCLUSION: Future studies need to be pursued to develop various strategies such as a health education programs and counseling programs for health maintenance and health promotion of undergraduates.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Affecting the Eating Behavior Disorders of Korean College Students
Mi-Kyoung Cho, Mi Young Kim, Gisoo Shin
The Open Nursing Journal.2021; 15(1): 55. CrossRef - Relationship between Health Literacy and Self-care Behavior in Patients with Stomach Cancer after Gastrectomy: Mediating Effects of Subjective Health Status and Specific Self-efficacy
Min Jung Kim, Yong Soon Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 259. CrossRef - Cultural fit of emotions and health implications: A psychosocial resources model
Jiah Yoo, Yuri Miyamoto
Social and Personality Psychology Compass.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - What Causes Health Promotion Behaviors in College Students?
Mi Young Kim, Yu Jeong Kim
The Open Nursing Journal.2018; 12(1): 106. CrossRef - The Sugars Intake through Processed Foods and Its Related Factors in College Students
Eun Kyung Shin, Young Taek Doo
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2016; 41(2): 85. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Behavior, Stress and Stress Coping Type between Undergraduate Nursing Students and Female Students in Other Majors
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2015; 21(1): 28. CrossRef - A Relevance on Health Perception, Health Knowledge and Health Promotion Behavior of the University students
Sun-Jung KIm, Eun-Young Jung
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(8): 5394. CrossRef - An Influencing Health Promoting Behavior of Perceived Health Status and Self-Efficacy according to major of college students
Hee-Joo Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(2): 989. CrossRef - Influence of Negative Emotion on the Suicidal Ideation in University Student: Mediated Moderating Effect of Explosive Behavior through Gender
Goo-Churl Jeong
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(12): 775. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Promotion Behaviors of College Students
Hwanhui Sim, Misook Kim, Kyeongsook Jeong, Jeeun Heo, Eunjung Choi
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(3): 97. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Depression of Korean Female University Students
Kyung-Sook Lee, Chin-Kang Koh, Joo Hyun Kim, Haeng-Mi Son, Mi Ryeong Song, Su Jeong Yu, Kyung Sook Cho
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(2): 112. CrossRef - Depression Cognition and Health Promoting Behaviors of Smoking and Non-smoking College Students
Mi-Ok Kim, Mi Yu, Se-Jin Ju, Kyeong-Suk Kim, Jung-Hyun Choi, Hee-Jeong Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(3): 35. CrossRef
- Factors Affecting the Eating Behavior Disorders of Korean College Students
- 919 View
- 2 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Factors Influencing on Quality of Life in Aged Women with Chronic Pain
- Jung Tae Son, Sun Rim Suh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(5):735-742. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.5.735
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was conducted to identify the pain characteristics, family support and physical functioning and to determine predictors of the quality of life in aged women with chronic pain. METHOD: The questionnaires were collected through direct interview by a trained research assistant from July 2 to August 24, 2001. Subjects were 108 women clients with chronic pain over 65 years of age. Data analyzed frequency, percentage, mean, Pearson's correlation, ANOVA and stepwise multiple regression by SAS. RESULT: Care providers were mostly spouses and daughters in law. Care providers who took care of elderly for a few hours a day had the highest percentile. Aged women had persistently had chronic pain of moderate intensity and was moderately satisfied with pain management. The mean score of disability due to pain was 3 on a 10 point scale. The mean scores of physical function and quality of life were moderate and there were negative correlations between pain characteristics, physical functioning, and quality of life at the range from r=-.46 to r=-.83. Satisfaction with care, duration of pain, disability due to pain, and physical functioning accounted for 56% of the variance in perceived quality of life for aged women with chronic pain. Disability due to pain was the most predictable variable of quality of life and physical function was the second . CONCLUSION: The results suggest that care by family, education in pain control, prevention of disability, and maintenance of physical function are important to improve and maintain quality of life in aged women with chronic pain. Therefore, there is a need for program development that enhance family support and nursing intervention that focuses on active pain control.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Liquid Soap Manufactured with Vegetable Fatty Acid and Essential Oil by Hand on the Foot Skin of the Elderly
Mi-Young Gu, Soo-Yean Oh, Hwa-Jung Choi
Journal of the Korean Society of Cosmetology.2022; 28(2): 233. CrossRef - Pain, Wisdom and Health Conservation in Older Adults with Chronic Diseases
Kiwol Sung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2014; 16(1): 85. CrossRef - Effects of Tai Chi Exercise on Physical Fitness and Quality of Life in Elderly Women
Jung Ah Park, Sook Young Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2014; 17(1): 38. CrossRef - Factors contributing to the use of complementary and alternative medicine in rural older women with chronic pain in South Korea
Saunjoo L. Yoon, Jeong-Hee Kim
Applied Nursing Research.2013; 26(4): 186. CrossRef - Relationship between Low Back Pain and Health-Related Quality of Life among Some Elderly
Kyeong-Ae Oh, Jong Park, Dae-Jung Jeon, Mi-Ah Han, Seong-Woo Choi
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2012; 37(3): 156. CrossRef - Relationships among the Pain Belief, Pain Coping, and Pain Disability of Patients with Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain
Sung-Nam Choi, Jeong-Hwa Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2012; 15(1): 30. CrossRef - Alternative View of Health Behavior: The Experience of Older Korean Women
Jin Hyang Yang, Bok Sun Yang
Qualitative Health Research.2011; 21(3): 324. CrossRef - EFFICACY OF QI-THERAPY (EXTERNAL QIGONG) FOR ELDERLY PEOPLE WITH CHRONIC PAIN
KYUNG HEE YANG, YOUNG HEE KIM, MYEONG SOO LEE
International Journal of Neuroscience.2005; 115(7): 949. CrossRef
- Effects of Liquid Soap Manufactured with Vegetable Fatty Acid and Essential Oil by Hand on the Foot Skin of the Elderly
- 635 View
- 2 Download
- 8 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


