Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Lessons from the US Advanced Practice Registered Nurse system
- Eun-Ok Im, Dongmi Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):492-505. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This review compares the development of South Korea’s Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) system the well-established APRN system in the United States and provides recommendations for future improvements to the APRN system in South Korea.
Methods
To compare the APRN systems between the two countries, an integrative literature review was conducted using multiple databases and professional nursing organization documents and reports from both the United States and South Korea.
Results
Issues were identified in five major domains: (1) research evidence, (2) education and training, (3) the scope of practice, (4) financial mechanisms, and (5) public awareness and acceptance.
Conclusion
Recommendations are made in four areas: (1) building evidence to support APRN programs; (2) strengthening APRN education; (3) establishing legal support and reimbursement mechanisms; and (4) improving public awareness and acceptance of APRNs.
- 652 View
- 96 Download

- Variables influencing digital health literacy in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Jin Hwa Park, Eun Ju Mun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):651-667. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to synthesize existing evidence on digital health literacy (DHL) among older adults and to estimate the associations between related influencing factors through a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.
Methods
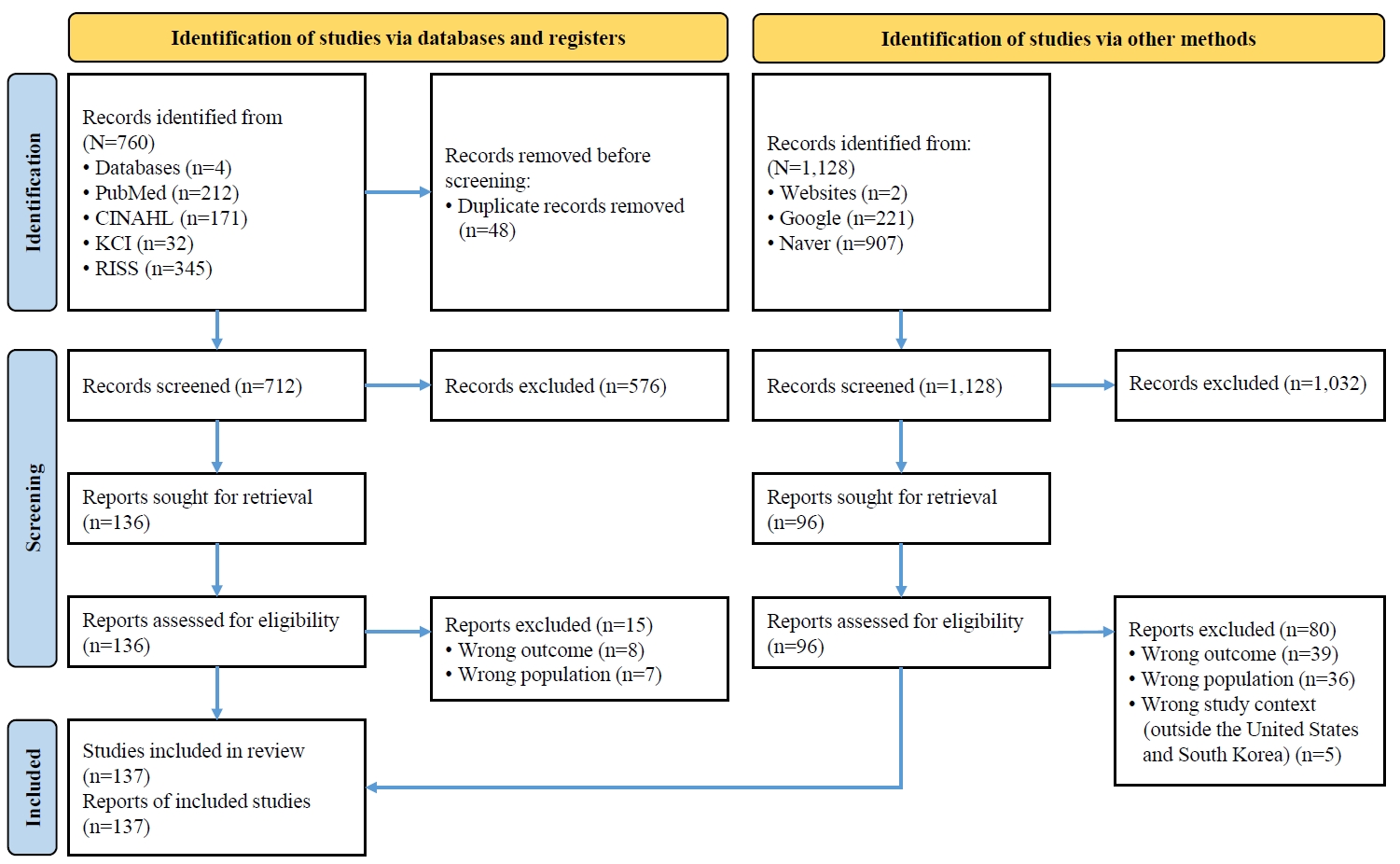
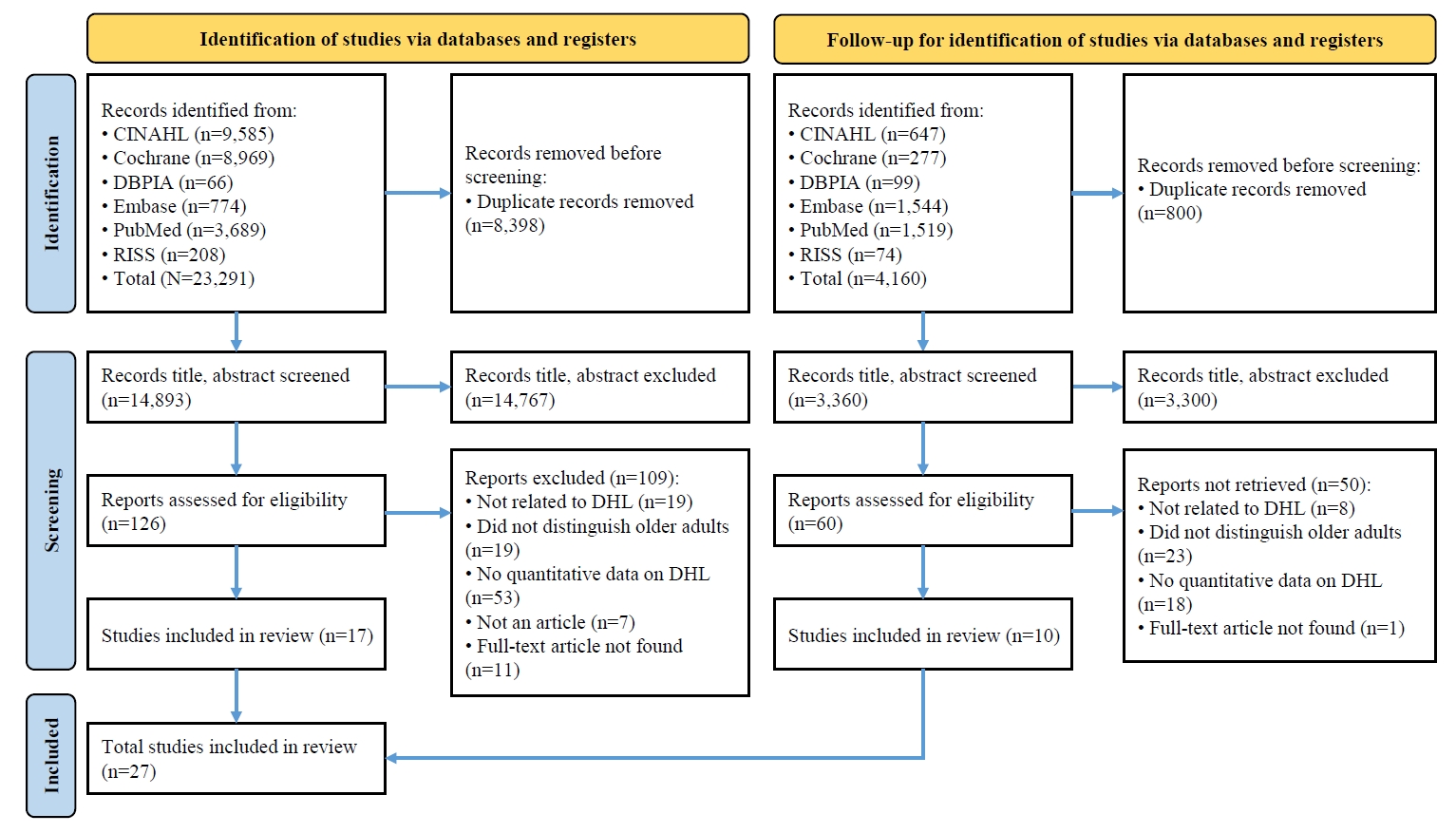
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines. Literature searches were performed across PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, RISS, and DBPIA. The search and screening process was conducted from December 24, 2023, to March 31, 2025. Effect sizes (ESr) using correlation coefficient for each variable were calculated, and meta-analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel and R version 4.3.1.
Results
Forty-seven variables were identified, including two demographic, six physical, six behavioral, 23 psychosocial, and 10 cognitive factors. Meta-analysis results showed that physical, behavioral, psychosocial, and cognitive factors had significant effects on DHL. Among these, digital information level (ESr=.62; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55 to 0.69) within the cognitive domain and technophobia (ESr=−.55; 95% CI, −0.47 to −0.40) within the psychosocial domain demonstrated the largest ESr.
Conclusion
Among factors influencing DHL, digital information level and technophobia showed the strongest associations. These findings suggest that improving DHL in older adults requires a dual approach targeting both cognitive and psychosocial dimensions—enhancing digital information skills while reducing technophobia—to effectively support digital engagement and health empowerment in this population (PROSPERO registration number: CRD42023487486).
- 1,000 View
- 84 Download

- Multidimensional factors influencing the completion of advance directives among community-dwelling older Koreans
- Hee-Ju Ji, Soong-Nang Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):543-556. Published online November 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25098
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
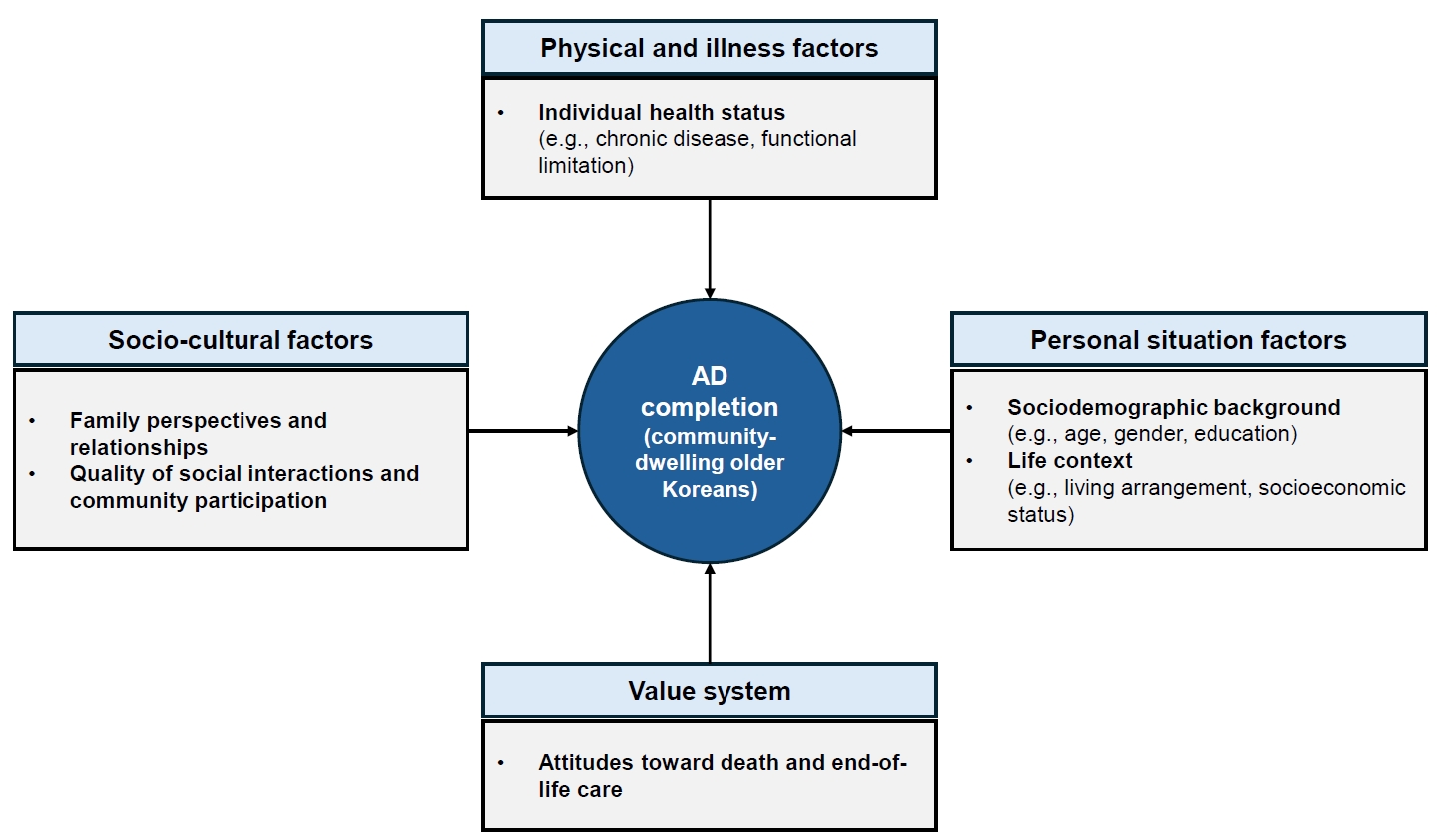
This study aimed to examine the multidimensional factors associated with the completion of advance directives (ADs) among community-dwelling older Koreans, guided by conceptual frameworks developed in Asian contexts.
Methods
Data from the 2023 National Survey of Older Koreans (sixth wave) were analyzed for 9,951 community-dwelling older Koreans aged 65 years or older. Complex sample cross-tabulation and binary logistic regression analyses were conducted.
Results
In total, 11.1% of community-dwelling older Koreans had completed an AD. Significant factors associated with AD completion were identified across four domains—personal situation: age, educational level, religion, and housing preference in the event of poor health; socio-cultural: presence of children, participation in social activities and satisfaction with social relationships; physical and illness: the number of chronic diseases; and value system: awareness of hospice and palliative services, participation in death preparedness education, and documentation of organ donation.
Conclusion
Among older Koreans, AD completion represents more than a documentation process; it reflects a complex decision-making process shaped by their values and life circumstances, underscoring the need for supportive interventions. As the highest AD completion rates are found among older adults, related policies should be aligned with older adult-centered policy frameworks.
- 1,167 View
- 89 Download

- Comparison of educational needs and priorities for work-related laws between hospital and community-based nurses
- Jeonghyun Kim, Min Kyoung Han, Minjae Lee, Sujin Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):400-412. Published online August 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25049
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the practical utilization of work-related laws in nursing practice and to prioritize educational needs to provide foundational data for improving nurses’ legal competencies.
Methods
A descriptive survey was employed using an online self-reported questionnaire. Participants included 275 nurses with over 3 years of clinical experience, categorized into hospital and community-based. Convenience sampling was used, and data were collected between January 9 and February 3, 2025. Descriptive statistics and the paired t-test were conducted using IBM SPSS 26.0. Educational needs were analyzed using the Borich Needs Assessment and the Locus for Focus model.
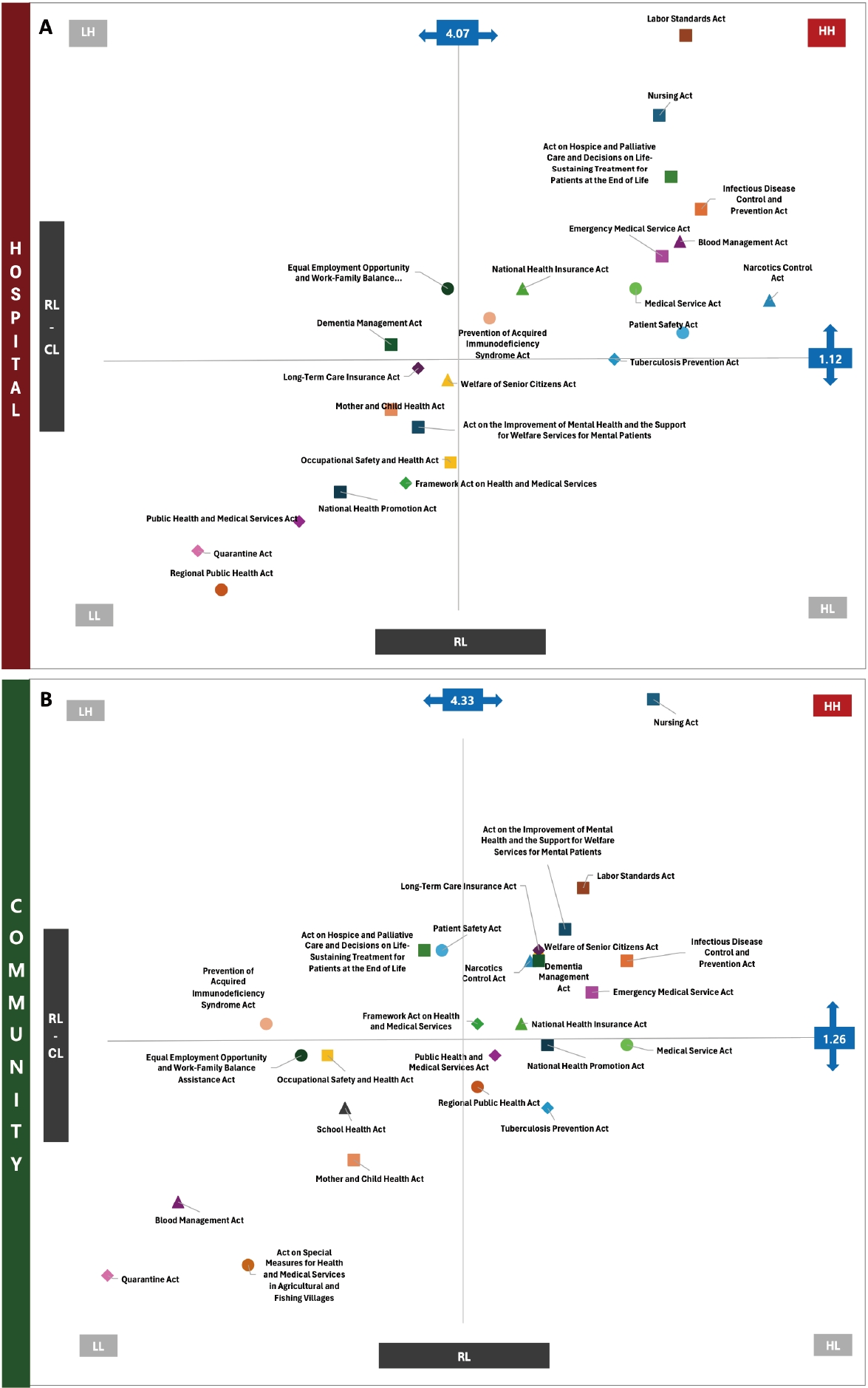
Results
Among participants, 75.6% had received education on work-related laws, and 79.3% of those participants received related education during their undergraduate studies. However, 32.4% of nurses reported experiencing practice related difficulties due to insufficient legal knowledge, particularly related to unclear legal responsibilities and ambiguity in the scope of practice. High educational needs were identified for the Nursing Act and the Labor Standards Act across all workplaces. Hospital nurses emphasized the Hospice and Palliative Care Act and Emergency Medical Services Act, while community-based nurses prioritized the Mental Health Welfare Act, Elderly Welfare Act, and Dementia Management Act.
Conclusion
Nurses’ legal education needs are related to practical applications and their capability to respond appropriately to legal requirements, and these needs vary depending on their work environment and social changes. These findings underscore the necessity of restructuring legal education curricula to improve practical relevance and support nurses’ rights, providing a basis for developing workplace-specific legal education programs.
- 1,869 View
- 133 Download

- Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
- Haesun Lee, Hye Jin Nam, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):454-467. Published online August 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
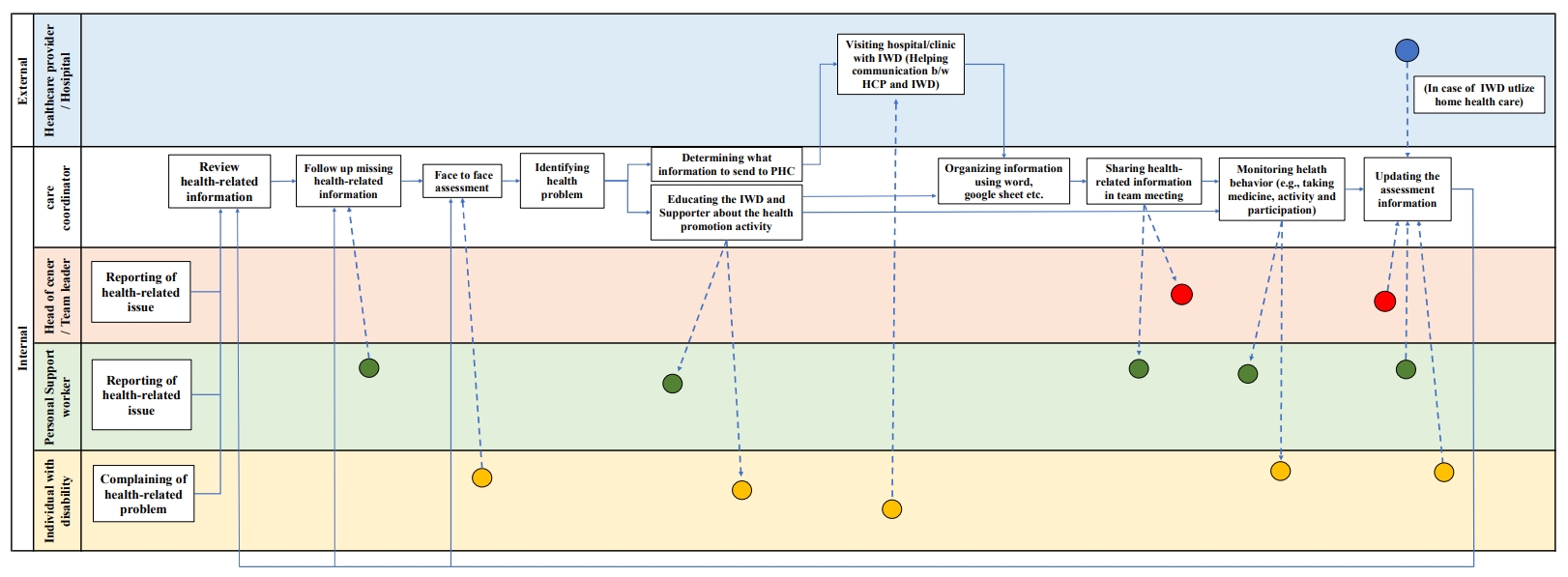
This study conducted a work-system analysis using the Systems Engineering Initiative for Patient Safety (SEIPS) framework to assess the flow of health-related information, and the current status of health management tasks for individuals with disabilities (IWD) in supportive housing.
Methods
This qualitative study utilized focus groups. Participants included a head of supportive housing, a team leader, a care coordinator and three personal support workers for IWD. Semi-structured interviews were guided by the SEIPS framework to explore the components of persons, tasks, tools and technology, organization, and environments.
Results
This study identified five key themes within the five SEIPS components: (1) disparities in role identity and health literacy among staff, (2) challenges in health care support reflecting a person-centered approach, (3) barriers in health-related information exchange and communication tools, (4) needs for organizational strategies or information communication, and (5) needs for integrating health-related information across external healthcare institutions. Additionally, 10 sub-themes were identified.
Conclusions
These findings provide a comprehensive system-wide perspective and offer insights into the systematic approaches needed to improve healthcare processes and structures within disability supportive housing. Specifically, healthcare providers and effective tools for integrating health-related information are identified as critical components.
- 1,285 View
- 73 Download

- A non-face-to-face diabetes self-management program based on self-efficacy theory and health literacy: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Jung Hee Lee, Soo Jin Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):165-177. Published online May 23, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
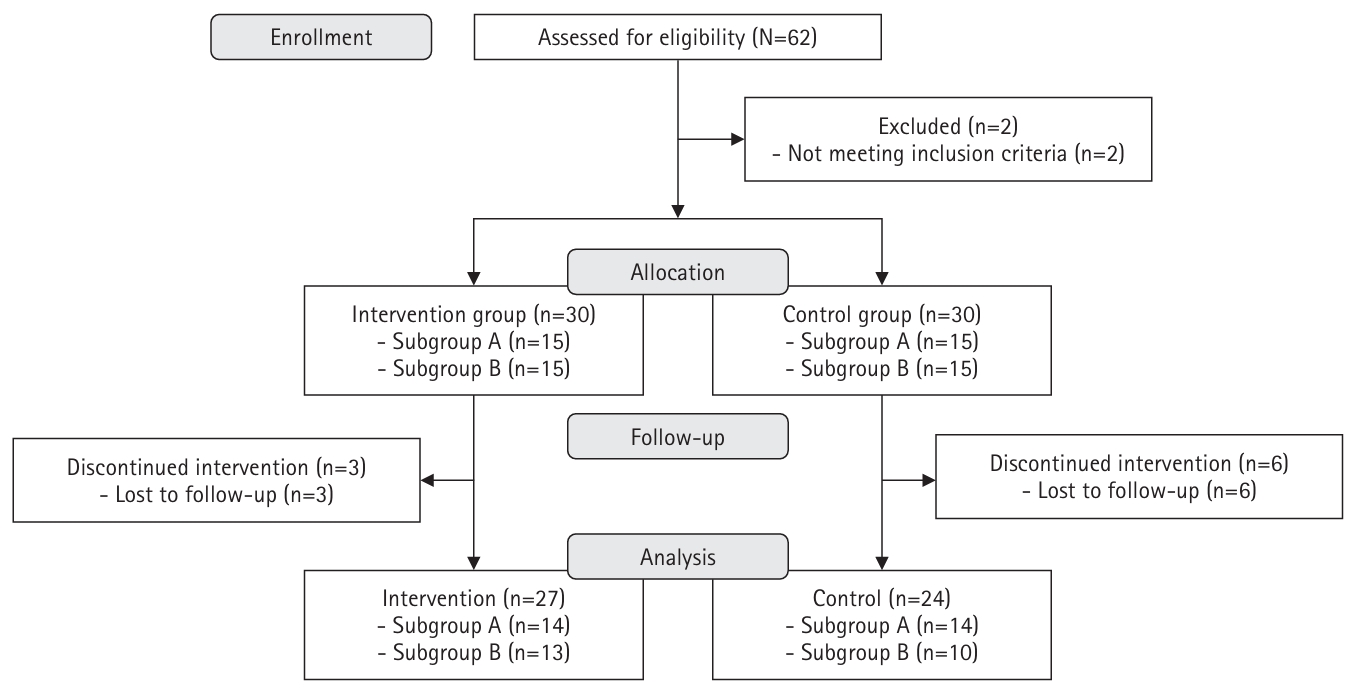
This study aimed to assess the impact of a non-face-to-face diabetes self-management program based on self-efficacy theory and focusing on health literacy.
Methods
A quasi-experimental, nonequivalent control group pre–post design was used. Participants from a community health promotion center were included if they (1) were 30–70 years of age, (2) had type 2 diabetes with glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥6.5%, and (3) had internet access via computers or mobile devices. The 8-week program was developed based on self-efficacy theory, and it included virtual education using an online platform, telephone counseling, videos, and social networking site activities considering health literacy. Fasting blood glucose levels, HbA1c levels, diabetes self-efficacy, social support, depression, and self-management behaviors were assessed. Data were analyzed using the independent t-test, paired t-test, and others.
Results
Post-test results showed that the intervention group had significantly lower fasting blood glucose levels and improved diabetes self-efficacy, social support, and self-management behaviors compared with the control group. An analysis of the pre-to-post changes in scores indicated that the intervention group had significantly greater improvements in fasting blood glucose levels, diabetes self-efficacy, and overall diabetes self-management behaviors than those observed in the control group.
Conclusion
Non-face-to-face programs based on self-efficacy theory that consider health literacy can provide effective diabetes management support to patients when in-person diabetes management at community health centers is challenging.
- 3,045 View
- 226 Download

- Development and effects of a media-based reproductive health promotion program for male high school students at male high school: a quasi-experimental study
- Joon-Young Lee, Yeoungsuk Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):34-49. Published online February 20, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24050
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
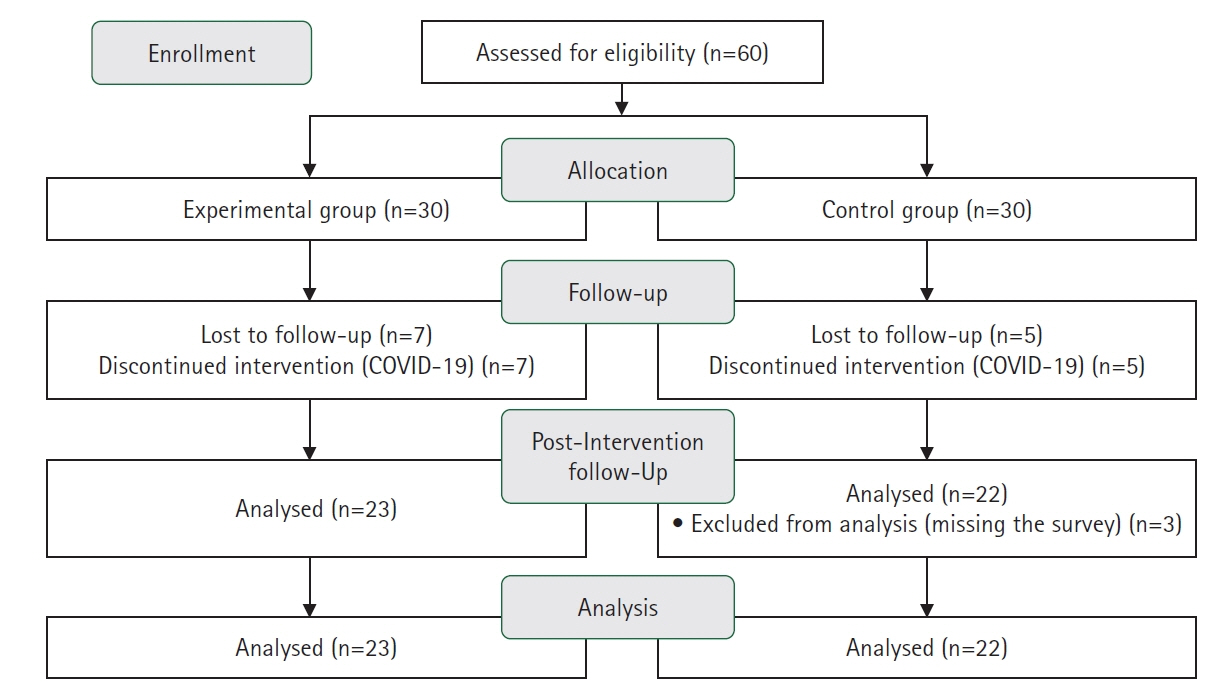
This quasi-experimental study was conducted to develop a media-based reproductive health promotion program (MRHPP) among male high school students and to evaluate its effectiveness.
Methods
The ADDIE model (analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation model) was used to develop the MRHPP based on Ajzen’s theory of planned behavior. The research was conducted using a non-equivalent control group with a pretest-posttest design (experimental group=23; control group=22). The program consisted of six sessions and was conducted twice a week. The participants were assessed through a pre-test, post-test immediately after training (post-test 1), and follow-up after 4 weeks (post-test 2) by using questionnaires. The collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, the independent t-test, chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, and repeated-measures analysis of variance.
Results
The analysis of the group-by-time interaction showed statistically significant differences in attitudes toward reproductive health behavior (RHB) (F=4.09, p=.049), subjective norms of RHB (F=5.31, p=.026), and intention to engage in RHB (F=3.78, p=.016). The effect sizes for attitudes, subjective norms, and intention to engage in RHB ranged from 0.75 (medium) to 1.02 (large) (p<.001) at post-test 1, and those for attitudes and subjective norms of RHB ranged from 0.36 (small) to 0.69 (medium) (p<.001) at post-test 2.
Conclusion
The MRHPP was demonstrated to be an effective intervention for promoting reproductive health behavior among male high school students.
- 2,415 View
- 229 Download

- Examination of Predicting Factors for COVID-19 Vaccination Behaviors of University Students Utilizing the Theory of Planned Behavior
- Yeon Jeong Heo, Hye-Jin Hyun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):178-192. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24020
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the predictive factors of COVID-19 vaccination behavior by evaluating the moderating effect of perceived behavioral control on the theory of planned behavior.
Methods
Data were collected from August 6 to August 31, 2022 from 235 college students (aged 20~29 years) across 12 universities using a structured web-based survey. Statistical analyses were conducted using the SPSS and AMOS software.
Results
Attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccination, subjective norms, and intention to be vaccinated significantly influenced COVID-19 vaccination behavior. Attitudes and subjective norms indirectly affected COVID-19 vaccination behavior through intention to vaccinate, whereas intention to vaccinate had a direct effect. The moderating effect of perceived behavioral control on the relationship between subjective norms and intention to vaccinate was significant.
Conclusion
Interventions that foster a positive attitude toward COVID-19 vaccination and bolster subjective norms and perceived behavioral control can boost the intention to be vaccinated and facilitate the uptake of COVID-19 vaccination.
- 1,426 View
- 41 Download

- Support Needs for Health Promotion of Community-Dwelling People with Disabilities: Perspectives of Operators Managing Disability Supportive Housing
- Hye Jin Nam, Haesun Lee, Han Nah Park, Sujin Lee, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):211-223. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Recent studies have focused on policies aimed at supporting the independence of individuals with disabilities in communities. As part of this initiative, supportive housing, integrated care, and residential spaces offer tailored services based on individual needs and autonomy. The attitudes and knowledge of the administrators supporting supportive housing residents regarding health management can influence the well-being of individuals with disabilities. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the challenges faced by supporting housing workers in enhancing the self-management skills of individuals with disabilities.
Methods
In this qualitative study, focus group interviews were conducted in August 2023 with nine administrators working to support housing in Seoul. Qualitative content analysis was used to analyze the interview data.
Results
The needs and challenges in enhancing the self-management skills of individuals with disabilities were as follows: (1) the complexity of health management challenges, (2) bidirectional strategies for strengthening health management capabilities, and (3) support for systematic health management. Additionally, eight subthemes were derived.
Conclusion
By investigating the difficulties experienced and identifying the necessary support requirements for supportive housing workers, this study seeks to uncover insights and identifies areas for improvement and strategies for health management. This study acknowledges the educational and institutional support necessary to improve the health and quality of life of individuals with disabilities residing in supportive housing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
Haesun Lee, Hye Jin Nam, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(3): 454. CrossRef - Intention to use a health information platform in supportive housing for people with disabilities: An application of the UTAUT model
Bohye Kim, Hye Jin Nam, Haesun Lee, Hannah Park, Ju Young Yoon, Nicola Diviani
PLOS One.2025; 20(10): e0332072. CrossRef
- Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
- 2,131 View
- 96 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Influence of Illness Uncertainty on Health Behavior in Individuals with Coronary Artery Disease: A Path Analysis
- Hyesun Jeong, Yesul Lee, Jin Sup Park, Yoonju Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):162-177. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the influence of uncertainty-related factors on the health behavior of individuals with coronary artery disease (CAD) based on Mishel’s uncertainty in illness theory (UIT).
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional study and path analysis to investigate uncertainty and factors related to health behavior. The study participants were 228 CAD patients who visited the outpatient cardiology department between September 2020 and June 2021. We used SPSS 25.0 and AMOS 25.0 software to analyze the data.
Results
The final model demonstrated a good fit with the data. Eleven of the twelve paths were significant. Uncertainty positively affected danger and negatively affected self-efficacy and opportunity. Danger had a positive effect on perceived risk. Opportunity positively affected social support, self-efficacy, perceived benefit and intention, whereas it negatively affected perceived risk. Social support, self-efficacy, perceived benefit and intention had a positive effect on health behavior. We found that perceived benefit and intention had the most significant direct effects, whereas self-efficacy indirectly affected the relationship between uncertainty and health behavior.
Conclusion
The path model is suitable for predicting the health behavior of CAD patients who experience uncertainty. When patients experience uncertainty, interventions to increase their self-efficacy are required first. Additionally, we need to develop programs that quickly shift to appraisal uncertainty as an opportunity, increase perceived benefits of health behavior, and improve intentions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health uncertainty: Scale development and its effect on health behaviors
Rui Ren, Su Tao, Yuhua Ouyang, Wenchong Du
Journal of Health Psychology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Self-Care, Resilience, and Uncertainty in Patients After Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
Eun-Hye Park, JiYeon Choi, Phill Ja Kim, Jiyeon Lee
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Coping Profiles and Cardiac Health Behavior among Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: A Latent Profile Analysis
Yesul Lee, Yoonju Lee, Jeong Cheon Choe, Hyesun Jeong, Sunyoung Jung
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(3): 228. CrossRef
- Health uncertainty: Scale development and its effect on health behaviors
- 3,422 View
- 162 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- The Effects of Stress Vulnerability and Parental Burnout on Mental Health in Women with Early School-Age Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Mediating Effect of Spirituality
- Mijung Yeom, Min Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):106-117. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23150
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the effects of stress vulnerability and parental burnout on the mental health of women with early schoolaged children, with a focus on the mediating role of spirituality.
Methods
A survey was conducted among 171 women with early schoolaged children in Gyeonggi Province, Gangwon Province, and Seoul. Data were collected from September to December 2022 using the Korean-Symptom Check List 95, the Parental Burnout Assessment, and the Spirituality Assessment Scale. The data were analyzed using structural equation modeling with SPSS/WIN 22.0 and AMOS 20.0.
Results
The study model demonstrated a good fit, explaining 40.5% of the variance in mental health through stress vulnerability, parental burnout, and spirituality. Spirituality had a significant direct impact on mental health. Additionally, participants’ spirituality directly influenced their mental health, while stress vulnerability and parental burnout indirectly affected their mental health and were mediated through spirituality.
Conclusion
Stress vulnerability and parental burnout are negatively associated with mental health, while spirituality partially mediates these effects. Implementing a program to promote spirituality is suggested to assist mothers in recognizing the value and meaning of parenting activities during nursing interventions for mental health.
- 2,092 View
- 64 Download

- Structural Equation Modeling of Health Promotion Behavior on Migrant Workers: A Multi-Group Analysis Based on the Period of Residence
- Hanna Jeong, Youngsuk Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):73-92. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study developed and tested a hypothetical model of health promotion behavior on migrant workers based on the Health Promotion Model and the Health Literacy Skills Framework.
Methods
Data were collected from 298 migrant workers in 9 regions across the country from December 2020 to March 2021. The exogenous variables were e-health literacy, occupational stress, acculturation, and social support. The endogenous variables were perceived benefits of action, self-efficacy, and health promotion behavior. Data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 25.0, AMOS 20.0, and R-4.0.3 program.
Results
The model fit was appropriate. Social support had the most significant direct impact on the health promotion behavior of migrant workers. Perceived benefits of action and self-efficacy played a mediating role in the relationship among e-health literacy, social support, and health promotion behavior. Based on multi-group analysis, the migrant worker group with less than 5 years of residency had a more statistically significant effect on the relationship between perceived benefits of action and health promotion behavior than those with over 5 years.
Conclusion
Providing social support as a critical administrative strategy to enhance the health promotion behavior of migrant workers is necessary. Furthermore, when developing an intervention program utilizing the internal mechanism between social support and health promotion behavior, a self-efficacy-enhancing strategy is considered to be more effective. Additionally, educating migrant workers with short-term residence of less than 5 years about the benefits of health behaviors is essential. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing cardiovascular health behaviors among Korean-Chinese migrant workers with metabolic syndrome using mixed methods
Yu Zhu Zhang, Seon Young Hwang
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated With Physical Activity in Home‐Based Rehabilitation Patients With Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Prospective Longitudinal Study
Heng‐Ying Fang, Ying‐Hua Pan, Yi‐Heng Zhang, Yu‐Hua Deng, Xiao‐Wen Li, Lei Huang, Hui‐Ting Gu, Yue Ding, Xin‐Xin Hu, Mu Liu, Rui‐Chong Wang, MeiFen Zhang
Musculoskeletal Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Factors influencing cardiovascular health behaviors among Korean-Chinese migrant workers with metabolic syndrome using mixed methods
- 2,595 View
- 100 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Eun Jin Kim, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):44-58. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23090
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to apply a health partnership program using commercially available mobile health apps to improve cardiovascular risk factors in male employees and verify its effectiveness.
Methods
Using a randomized control group pretest-posttest design, male employees with cardiovascular risk factors from five small and medium-sized workplaces were randomly assigned to an experimental group (n = 32) and a control group (n = 31). The experimental group was encouraged to use three mobile health apps for 12 weeks to acquire the necessary cardiovascular disease-related information and practice strengthening training, walking, and diet management appropriate to their level. They also received feedback on their weekly activities and motivational text messages from health partners. Hypotheses were tested using the SPSS WIN 22.0.
Results
The experimental group showed a significant difference compared to the control group in terms of their perception of mobile health app (p < .05), self-efficacy for exercise and diet, self-management partnership, and cardiovascular disease prevention health behavior (p < .001). In particular, there were significant decreases in the body mass index, ratio, serum fasting blood sugar, total cholesterol, and triglyceride in the experimental group (p < .001); however, there was no significant difference in high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol.
Conclusion
Intervention using mobile apps based on partnership with health managers is effective in improving the objective cardiovascular risk index in male employees; therefore, such intervention should be continuously used as a useful lifestyle modification strategy in the workplace. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adherence to a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Yura Shin, Jina Choo, Songwhi Noh
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Adherence to a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
- 3,468 View
- 205 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effects of the Infant Health Promotion Program for Mothers with Their Firstborn Infants
- Chae-Min Yoon, Mi-Ae You
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):666-677. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23056
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study was intended to evaluate the effects of an Infant Health Promotion Program (IHPP) for mothers with their firstborn infants.
Methods
This study employed a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design. The participants consisted of 17 mothers with their firstborn infants in the experimental group and 17 in the control group from two women’s hospitals. The experimental group received eight sessions of the program for four weeks. The collected data were analyzed using the chi-square test and repeated-measures ANOVA using an SPSS/WIN ver. 22.0.
Results
The experimental group receiving the program had statistically significant higher levels of infant health promotion knowledge (F = 22.91, p < .001), social support (F = 27.64, p < .001), maternal role confidence (F = 8.25, p = .005) and health promotion behavior for infants (F = 16.85, p < .001) than the control group. The experimental group had a statistically significant lower level of parenting stress than the control group (F = 29.93, p < .001).
Conclusion
The study’s findings indicate that the IHPP is effective in improving health promotion knowledge, social support, and maternal role confidence and decreasing parenting stress among mothers with their firstborn infants. A method of delivering intervention, focused on readily accessible online platforms, coupled with intervention strategies grounded in the theory of self-efficacy, proves to be an advantageous approach for this particular target group. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Mothers’ Smartphone Use, eHealth Literacy, Maternal Role Performance Confidence, and Online Social Support on Health Promotion Behavior for Infants and Toddlers
Se-Young JUNG, So Yeon PARK
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2024; 24(3): 134. CrossRef - A qualitative study on the oral health of mobile platform workers: focus on tooth brushing experience
Jae-In Ryu, Na-Yeon Tak
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2024; 48(2): 40. CrossRef
- The Impact of Mothers’ Smartphone Use, eHealth Literacy, Maternal Role Performance Confidence, and Online Social Support on Health Promotion Behavior for Infants and Toddlers
- 1,328 View
- 31 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Caring Program for Health Promotion among Women Who Have Experienced Trauma: A QuasiExperimental Pilot Study
- Goun Kim, Heejung Kim, Jeongok Park, Hee Sun Kang, Soojin Kim, Sunah Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(5):500-513. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Women are more vulnerable to post-traumatic stress (PTS) than men, causing several health problems. Nurses should understand and work with women who have experienced trauma and provide interventions to promote their physical, social, and mental health.
Methods
This quasi-experimental pilot study used a one-group pre-test/post-test design. Data were collected from 14 women recruited between December 2019 and May 2020 from a self-sufficiency support center in South Korea for sexually-exploited women who had experienced trauma. The program consisted of six one-on-one intervention sessions per week for six weeks. Each session averaged 60~120 minutes. Participants were assessed at pre-test, post-test, and one-month follow-up. Changes in outcome variables over time were analyzed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank and Friedman tests.
Results
The caring program for health promotion was divided into six sessions: understanding the self, sharing traumatic events and negative emotions, reframing the meaning of traumatic events, identifying thoughts and physical and emotional responses, developing health promotion activities, and maintaining a positive attitude during the process of change. As a result of the caring program, PTS (F = 36.33, p < .001), depression (F = 24.45, p < .001), health-promoting behaviors (F = 7.06, p = .004), and self-esteem (F = 19.74, p < .001) among the participants differed significantly at pre-test, post-test, and follow-up.
Conclusion
This study provides foundational information for the implementation of a theory-driven program by nurses in clinical and community settings to provide comprehensive care for women who have experienced trauma. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Effectiveness of an Interpersonal Relationship Improvement Program for Inpatients with Chronic Schizophrenia: Quasi-experimental/Non-randomised Evaluation
Jae-Eun Choi, Jeongyee Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(2): 188. CrossRef - Prediction and Feature Selection of Mastectomy-Related Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Using Machine Learning Among Breast Cancer Patients in Bangladesh
Syed Billal Hossain, Md. Mizanoor Rahman, Kapashia Binte Giash, Md. Hazrat Ali, Mst. Asma Akter, A.B.M. Alauddin Chowdhury
Cancer Informatics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Development and Effectiveness of an Interpersonal Relationship Improvement Program for Inpatients with Chronic Schizophrenia: Quasi-experimental/Non-randomised Evaluation
- 2,294 View
- 63 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Exploring Spatial Variations and Factors associated with Walking Practice in Korea: An Empirical Study based on Geographically Weighted Regression
- Eunjoo Kim, Yeongseo Lee, Ju Young Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):426-438. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23045
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Walking practice is a representative indicator of the level of physical activity of local residents. Although the world health organization addressed reduction in prevalence of insufficient physical activity as a global target, the rate of walking practice in Korea has not improved and there are large regional disparities. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the spatial variations of walking practice and its associated factors in Korea.
Methods
A secondary analysis was conducted using Community Health Outcome and Health Determinants Database 1.3 from Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A total of 229 districts was included in the analysis. We compared the ordinary least squares (OLS) and the geographically weighted regression (GWR) to explore the associated factors of walking practice. MGWR 2.2.1 software was used to explore the spatial distribution of walking practice and modeling the GWR.
Results
Walking practice had spatial variations across the country. The results showed that the GWR model had better accommodation of spatial autocorrelation than the OLS model. The GWR results indicated that different predictors of walking practice across regions of Korea.
Conclusion
The findings of this study may provide insight to nursing researchers, health professionals, and policy makers in planning health programs to promote walking practices in their respective communities.
- 1,006 View
- 37 Download

- Internal Structure of the Health-Related Quality of Life Instrument with 8-Items in a Nationally Representative Population
- Eun-Hyun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(3):359-369. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study evaluated the internal structure (structural validity, internal consistency, and measurement invariance) of the Health-Related Quality of Life Instrument with Eight Items (HINT-8), developed to measure Korean people’s health-related quality of life.
Methods
A secondary analysis was conducted using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, involving 6,167 adults aged over 18 years. The structural validity of the HINT-8 was assessed using exploratory graph analysis and confirmatory factor analysis. Internal consistency and measurement invariance were analyzed using McDonald’s omega (ω) and multigroup confirmatory factor analysis, respectively.
Results
The HINT-8 had a single dimension and good internal consistency (ω = .804). The one-dimension HINT-8 ex-hibited matric invariance but not scalar invariance across sociodemographic groups (sex, age, education, and marital status). Further, it exhibited scalar or partial scalar invariance across medical condition groups (hypertension, diabetes, depressive symptoms, and cancer).
Conclusion
The study finds that the HINT-8 demonstrated satisfactory structural validity and internal consistency, indicating its suitability for practice and research. However, the HINT-8 scores cannot be compared across different groups regarding sex, age, education, and marital status, as the interpretation varies within each sociodemographic category. Conversely, interpretation of the HINT-8 is consistent for individuals with and without hypertension, diabetes, depressive symptom, and cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between obstructive sleep Apnea–Related factors and HINT-8 utility scores in adults: a secondary analysis of the 2023 Korea National health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES)
Mima Park, Seon-Ha Kim
Quality of Life Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The Predictors of Dietary Supplement Use Among Women With Musculoskeletal Disease: A Population-Based Complex Sample Designed Study
Myoungjin Kwon, Sun Ae Kim, Youngshin Song
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Network Analysis of Quality of Life Among Older Adults With Arthritis
Dahee Wi, Chang G. Park, Jiae Lee, Eunjin Kim, Yoonjung Kim
International Journal of Older People Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Network analysis of quality of life among young and middle-aged Korean cancer survivors
Yoonjung Kim, Dahee Wi, Eunjin Kim, Jiae Lee
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100684. CrossRef - Quality of Life Based on the Experience of Psychological Counseling in Adults with Depressive Symptoms
Jihyeon Seo, Jihye Lim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2025; 50(1): 39. CrossRef - Validation of the health-related quality of life instrument with 8 items for assessing health-related quality of life in patients with oropharyngeal cancer: a comparison with the EQ-5D-5L
Gyeong-U Hong, Bon Seok Koo, Min-Ju Kim, Woo-Jeong Sim, Ah-Yeon Lee, Ji-Eun An, Su-Yeon Yu, Sei Young Lee, Soo Hyun Lee
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative effectiveness and safety of herbal medicine therapy for low back pain and radiculopathy caused by lumbar intervertebral disc herniation: a study protocol for a pragmatic randomized controlled trial
Jung-Hyun Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha, Won-Suk Sung, Eun-Jung Kim, Yeoncheol Park, Yonghyeon Baek, Sang-Soo Nam, Byung-Kwan Seo
Frontiers in Neurology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the health behavior and nutrition status of young-old women according to the vitality in their quality of life: based on the 2019, 2021 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jiyoung Jeong, Yoon Jung Yang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(5): 496. CrossRef
- Association between obstructive sleep Apnea–Related factors and HINT-8 utility scores in adults: a secondary analysis of the 2023 Korea National health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES)
- 4,440 View
- 126 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Effects of Health Education Using Virtual Reality for Adolescents: A Systematic Review and MetaAnalysis
- SoMi Park, ChaeWeon Chung, Gaeun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):177-190. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of health interventions using virtual reality (VR) on improving knowledge, attitudes, and skills; and inducing behavioral change among adolescents.
Methods
This study is a systematic review and meta-analysis following PRISMA guidelines. We searched Cochrane, MEDLINE, Embase, CINAHL, Scopus, Web of Science, and Korean databases between database inception and April 10, 2021. Based on heterogeneity, a random- or fixed-effects model was used, as appropriate, to calculate effect sizes in terms of the standardized mean difference (SMD) and odds ratio (OR). Studies were selected if they verified the effects of health education using VR on adolescents; there was an appropriate control group; and if the effects of education were reported in terms of changes in knowledge, attitudes, skills, or behaviors.
Results
This analysis included six studies (n = 1,086). The intervention groups showed greater responses in knowledge and attitudes (SMD = 0.57, 95% confidence interval (CI) [0.12 to 1.02]), skills related to health behavior (SMD = -0.45, 95% CI [-0.71 to -0.19]), and behavioral change after 12 months (OR = 2.36, 95% CI [1.03 to 5.41]).
Conclusion
The results confirm the effectiveness of health interventions using virtual reality (VR). Although the analysis include a small number of studies, a case can be made for health interventions using VR to be utilized as educational methods and strategies to prevent risky behaviors among adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Implementation of a Childcare-Based Obesity Prevention Program for Vulnerable Families During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons for School Nurses
Jiyoung Park, Gill ten Hoor, Seohyun Won, Gahui Hwang, Sein Hwang, Siew Tiang Lau
The Journal of School Nursing.2025; 41(5): 579. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Virtual Reality Intervention for Reducing Exposure to Endocrine Disruptors in Female Adolescents: A Pilot Study
SoMi Park, Yun Jeong Hwang, ChaeWeon Chung
Journal for Specialists in Pediatric Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Chinese nurses’ perspectives on child-friendly healthcare practice assessment: a qualitative study
Wei Xiao Huang, Mei Chan Chong, Li Yoong Tang, Xiao Xia Liu, Mei Fang, Yun Yun Shen, Xiao Li Guo
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing anatomy education with virtual reality: integrating three-dimensional models for improved learning efficiency and student satisfaction
Shuliang Niu, Jinlong Zhang, Jiang Lin, Binbin Wang, Jie Yan
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Implementation of a Childcare-Based Obesity Prevention Program for Vulnerable Families During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons for School Nurses
- 4,284 View
- 99 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Pathway Analysis on the Effects of Nursing Informatics Competency, Nursing Care Left Undone, and Nurse Reported Quality of Care on Nursing Productivity among Clinical Nurses
- Mi Yu, Se Young Kim, Ji Min Ryu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):236-248. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22110
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Nursing informatics competency is used to manage and improve the delivery of safe, high-quality, and efficient healthcare services in accordance with best practices and professional and regulatory standards. This study examined the relationship between nursing informatics competency (NIC), nursing care left undone, and nurse reported quality of care (NQoC) and nursing productivity. A path model for their effects on nursing productivity among clinical nurses was also established.
Methods
Data were collected using structured questionnaires answered by 192 nurses working in a tertiary hospital located in J city, Korea, and analyzed using SPSS/WIN 23.0 and AMOS 21.0 program.
Results
The fit indices of the alternative path model satisfied recommended levels χ2 = .11 (p= .741), normed χ2 (χ2/df) = .11, SRMR = .01, RMSEA = .00, GFI = 1.00, NFI = 1.00, AIC = 18.11. Among the variables, NIC (β = .44, p < .001), NQoC (β = .35, p < .001) had a direct effect on nursing productivity. Due to the mediating effect of NQoC on the relationship between NIC and nursing productivity, the effect size was .14 (95% CI .08~.24). Meanwhile, nursing care left undone through NQoC in the relationship between NIC and nursing productivity, has a significant mediation effect (estimate .01, 95% CI .00~.03). The explanatory power of variables was 44.0%.
Conclusion
Education and training for enhancing NIC should be provided to improve nursing productivity, quality of care and to reduce missed nursing care. Furthermore, monitoring the quality of nursing care and using it as a productivity index is essential. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Information Literacy Competencies and Associated Variables among Korean Nursing Students
Shin Hyang Kim, Jong Mi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 358. CrossRef - The impact of nursing informatics competency, social influence, and medical information culture on nurses’ intention to use new medical technology in general hospitals
Jeong Ho Ji, Kyungja Kang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(4): 484. CrossRef - Effects of digital literacy and nursing informatics competency as job resources on nurses’ burnout and work engagement: a cross-sectional study
Jeehae Chung, Hyesil Jung, Sang Mi Park, Kyeongmin Lee
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Care Left Undone by Cancer Ward Nurses
Chung Hee Woo, Yeon Joo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 594. CrossRef
- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Information Literacy Competencies and Associated Variables among Korean Nursing Students
- 2,811 View
- 122 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Determinants of Problem Drinking by Regional Variation among Adult Males in Single-Person Households: Geographically Weighted Regression Model Analysis
- Junggeun Ahn, Heeseung Choi, Jiu Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):101-114. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22131
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify regional differences in problem drinking among adult males in single-person households and predict the determinants.
Methods
This study used data from the 2019 Community Health Survey. Geographically weighted regression analysis was performed on 8,625 adult males in single-person households who had been consuming alcohol for the past year. The Si-Gun-Gu was selected as the spatial unit.
Results
The top 10 regions for problem drinking among adult males in single-person households were located in the Jeju-do and Jeollanam-do areas near the southern coast, whereas the bottom 10 regions were located in the Incheon and northern Gyeonggi-do areas. Smoking, economic activity, and educational level were common factors affecting problem drinking among this population. Among the determinants of regional disparities in problem drinking among adult males in single-person households, personal factors included age, smoking, depression level, economic activity, educational level, and leisure activity, while regional factors included population and karaoke venue ratio.
Conclusion
Problem drinking among adult males in single-person households varies by region, and the variables affecting each particular area differ. Therefore, it is necessary to develop interventions tailored to individuals and regions that reflect the characteristics of each region by prioritizing smoking, economic activity, and educational level as the common factors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of factors associated with unmet dental care needs using geographically weighted regression
Ji-Yeon Lim, Sang-Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2025; 49(2): 72. CrossRef
- Analysis of factors associated with unmet dental care needs using geographically weighted regression
- 1,531 View
- 41 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Preventive Behaviors for COVID-19 in Undergraduate Nursing Students: A Cross-Sectional Descriptive Study
- Jeong Sil Choi, Kyung Mi Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(6):554-563. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22047
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to determine how undergraduate nursing students’ knowledge and health beliefs affected their COVID-19-related infection-prevention behaviors.
Methods
This study used a descriptive survey. A total of 188 undergraduate nursing students from two universities in South Korea participated in this study. The data were collected from June 2020 to August 2020. Factors influencing infection-prevention behaviors were identified using multiple regression analysis.
Results
The participants’ mean knowledge level regarding COVID-19 was 84.05 ± 11.78 out of 100. The average health belief score was 2.80 ± 0.32 points out of 5. COVID-19-related preventive health behaviors were correlated with experiences of searching for COVID-19 information (r = .22, p < .01), perceived severity (r = .24, p < .01), perceived benefits (r = .29, p < .01), cues to action (r = .30, p < .01), knowledge (r = .27, p < .01), and perceived barriers (r = - .19, p < .05). Factors that significantly affected COVID-19-related preventive health behaviors were the participants’ years of study, experiences regarding COVID-19 prevention education, perceived severity, perceived barriers, and cues to action.
Conclusion
COVID-19-related preventive health behaviors are promoted by increasing awareness about the disease and promoting COVID-19 education in nursing curriculums. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The multiple mediating effects of health beliefs on the relationship between infection control knowledge and infection-preventive behaviors among health science college students
Yoonmi Lee, Hyejin Kim, Jieun Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(2): 196. CrossRef - Effect of an educational intervention on nursing students’ knowledge about COVID-19 and compliance with standard and transmission-based precautions: a quasi-experimental study
Ana Beatriz de Almeida Lima, Cristine Maria Pereira Gusmão, Lais do Espirito Santo Lima, Daniel de Macedo Rocha, Mayra Gonçalves Menegueti, Ana Cristina de Oliveira e Silva, Renata Karina Reis
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing factors related to perceived control and preventive behaviors from COVID‐19 between Japanese and American nursing students: A cross‐sectional study
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Kosuke Niitsu, Kazuko Naruse, Tomomi Oki, Erika Ota, Mabel C. Ezeonwu
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The multiple mediating effects of health beliefs on the relationship between infection control knowledge and infection-preventive behaviors among health science college students
- 1,995 View
- 33 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Moderating the Effects of Health Behaviors on Sexual Intercourse among Adolescents: A CrossSectional Study Using the 2020 Adolescent Health Behavior Survey
- Eunmi Lee, Youngran Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(5):499-510. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22080
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated the association between adolescent health behaviors (drinking, smoking, and drug use) and sexual intercourse, as well as the moderating effects of economic status, cohabitation with parents, and school type, among adolescents in Korea.
Methods
Secondary data from the 16th Adolescent Health Behavior Survey (2020) were used. A total of 395 schools and 54,948 middle and high school students participated in the study. Complex sample frequency analysis, the Rao–Scott test, and complex sample logistic regression analyses were performed.
Results
Sexual intercourse rates for men and women were 5.8% and 3.3%, respectively. Approximately 7.3% of high school students and 1.8% of middle school students reported having had sexual relations. Drinking (odds ratio [OR] = 3.15, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 2.82~3.52), smoking (OR = 6.75, 95% CI = 5.90~7.71), and drug use (OR = 3.03, 95% CI = 2.23~4.11) significantly increased the risk of sexual intercourse. Economic status and school type had moderating effects on the association between drinking and sexual intercourse.
Conclusion
Adolescent drinking, smoking, and drug use are associated with a higher risk of sexual experience. Thus, to reduce this risk, controlling alcohol consumption, smoking, and drug use is necessary. In addition, programs for healthy lifestyles and sexual intercourse should be differentiated according to the school type and the economic conditions of the adolescents’ households. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Public discourse on substance use behavior as a driver of public policy: a scoping review of South Korean academic and official literature
Meekang Sung, Jihye Han, Carrie G. Wade, Vaughan W. Rees
Addiction Research & Theory.2025; 33(4): 312. CrossRef
- Public discourse on substance use behavior as a driver of public policy: a scoping review of South Korean academic and official literature
- 3,065 View
- 16 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- A Longitudinal Study of the Reciprocal Relationship between Depression and Income among Korean Older Men and Women
- Jeong Lee, Gyeong-Suk Jeon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):451-463. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the reciprocal relationships between depression and income, and gender differences in these relationships among older adults in South Korea.
Methods
Using 2015 to 2019 of the Korea Welfare Panel Study (KoWePS), we studied 6,070 older adults (2,394 men and 3,676 women) aged 60 years over in 2015. The generalized estimating equation was employed to explore the effect of an individual income on depression and the reverse causal link-that of depression on income.
Results
The study found the reciprocal relationships between income and depression. Income has a significant impact on depression. Higher-income was linked to decreased risks of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression (CES-D) scores among older adults (B = - 0.121, p < 0.001). Estimates of the reverse causal link show that higher CES-D scores were also linked to income reduction among Korean older adults (B = - 0.007, p < 0.001). In addition, we also observed gender differences in the impact of income on depression but not in the reverse causal link. Income has more detrimental to psychological consequence for older men (B = - 0.108, p < 0.001) than older women (B = - 0.057, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
The finding implies that both psychological and social protection policies for the elderly are needed in view of gender perspective. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factors of depression among the baby boomer generation: A cross-sectional study using the 2022 Korean Community Health Survey
Kyoung Mi Kim, Hye Jung Jun
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(3): 308. CrossRef
- Risk factors of depression among the baby boomer generation: A cross-sectional study using the 2022 Korean Community Health Survey
- 1,863 View
- 34 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of an Integrated Health Management Program for Psychiatric Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
- Yun Bock Kwak, Ji Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):261-277. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study developed an integrated health management program for metabolic syndrome in psychiatric patients and examined its effects on self-efficacy, healthy lifestyle, physiological indicators, knowledge of metabolic syndrome, attitudes toward healthy behavior, and social support.
Methods
A non-equivalent control group pretest posttest design was used. The participants were 65 psychiatric patients with metabolic syndrome in psychiatric rehabilitation centers, with 33 in the experimental group and 32 in the control group. The experimental group participants engaged in daily mobile application and walking exercises three times a week for more than 40 minutes over 8 weeks, while those in the control group were provided education booklets. The outcomes were measured using self-report questionnaires, anthropometrics, and blood analyses. Intervention effects were analyzed using the independent t-test, Mann—Whitney U test, ANCOVA, and Ranked ANCOVA.
Results
The experimental group showed a significant increase in self-efficacy (F = 8.85, p = .004, ηp2 = .13) and knowledge of metabolic syndrome (t = 2.60, p = .012, d = 0.60) compared to the control group. Additionally, the experimental group demonstrated a significant decrease in waist circumference (Z = - 2.34, p = .009, d = 0.58) and body mass index (Z = - 1.91, p = .028, d = 0.47) compared to the control group.
Conclusion
The integrated health management program for psychiatric patients with metabolic syndrome is effective in improving self-efficacy and knowledge of metabolic syndrome and decreasing physiological indicators such as waist circumference and body mass index. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- User evaluation of a mobile education application for the management of metabolic syndrome among cancer survivors
Ji-Su Kim, Minhae Kim, Yeji Seo
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 63: 102276. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Web-Based Self-Management Program for Korean Adult Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Based on the Information–Motivation–Behavioral Skills Model
Seohyeon Hwang, Woori Na, Dayoung Oh, Cheongmin Sohn
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(12): 6915. CrossRef - Effect of Patient Safety Training Program of Nurses in Operating Room
Peijia Zhang, Xin Liao, Jie Luo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(4): 378. CrossRef
- User evaluation of a mobile education application for the management of metabolic syndrome among cancer survivors
- 2,500 View
- 99 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- A Prediction Model of Exercise Level in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Moon Ja Kim, Eun Nam Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):157-172. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21238
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to construct and test a hypothetical model to explain the predictive factors and causal pathways for exercise levels in patients with ankylosing spondylitis based on the self-determination theory. A conceptual framework was constructed assuming that autonomy support by health care providers would satisfy the three basic psychological needs of patients, which would increase their autonomous motivation for exercise, resulting in its initiation and continuation.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 221 patients with ankylosing spondylitis who were visiting rheumatology clinics in two tertiary hospitals. Health Care Climate Questionnaire-exercise regularly, Basic Psychological Needs Satisfaction scale, Behavior Regulation in Exercise Questionnaire-2, and exercise level were used to collect data.
Results
The fitness of the hypothetical model met the recommended level (χ2/df ≤ 3, SRMR ≤ .08, RMSEA ≤ .08, GFI ≥ .90, AGFI ≥ .85, NFI ≥ .90, TLI ≥ .90, CFI ≥ .90). The model effect analysis revealed that autonomy support by health care providers had a positive effect on patients' autonomy, competence, relatedness, autonomous motivation, and exercise level. Competence and relatedness had positive effects on autonomous motivation and exercise level, respectively. Autonomous motivation had a positive effect on exercise level.
Conclusion
The predictive factors of exercise level in patients with ankylosing spondylitis were autonomous motivation, health care providers' autonomy support, competence, and relatedness. Considering these factors, we recommend the development of an effective program for improving exercise levels in these patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Structural Equation Model for Low Back Pain Management Behavior in Patients With Spinal Disease
Raewan Kim, Aekyung Kim
Pain Management Nursing.2025; 26(1): e107. CrossRef - Exercise and adults with hemophilia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Doo Young Kim, Mi Yang Jeon, Young Eun, Da In Jeong
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2024; 26(1): 1. CrossRef
- A Structural Equation Model for Low Back Pain Management Behavior in Patients With Spinal Disease
- 1,213 View
- 28 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Experience of Peer Support Work among People with Mental Illness in the Community: A Grounded Theory Approach
- Myung Sun Hyun, Hyunlye Kim, Kyoung A Nam, Su Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):187-201. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21208
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study discovered a substantive theory of the experience and process of peer support work among people with mental illness.
Methods
The participants were members of community-based mental health facilities and had been working as peer supporters for more than six months. The data were collected through in-depth interviews with twelve participants and analyzed using Corbin and Strauss’s grounded theory approach.
Results
The core category was “becoming a healer going with patients in the journey of recovery,” and the core phenomenon was “identity confusion as a peer supporter.” The causal conditions were “starting peer support work without certainty” and “standing at the boundary between the therapist and patient.” The intervening conditions were “willingness to become a successful peer supporter,” “feeling a sense of homogeneity with the patient,” “accepting the mental illness,” and “support from people around.” The action and interaction strategies were “letting go of greed,” “being open about oneself,” “developing professional skills,” “maintaining wellness in the body and mind,” and “being with the patient.” The consequences were “becoming a useful person,” “changing attitude toward life,” “expansion of the sense of self-existence,” “recovering from mental illness,” and “discovering a role as peer supporter.” Finally, the substantive theory of “becoming a healer going with patients in the journey of recovery” was derived.
Conclusion
This study provides a holistic understanding of peer support work and the implications of interventions to help people with mental illness in a person-centered recovery process. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A model for the involvement of service users as instructors into the psychiatric nursing curriculum in Korea: A qualitative study on participation experience
Suyoun Ahn, Soyoung Shin, Jaewon Joung
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(4): 917. CrossRef - Experience of Mental Health Professionals Collaborating with Peer Supporters in a Community Mental Health Service Team
Sowon Lee, Boyoung Kim, Chung Kil Park
International Journal of Mental Health Promotion.2024; 26(4): 251. CrossRef - Experience of Peer Supporters for Patients with Schizophrenia
Hae Kyung Jo, Se Na Ryu
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(3): 280. CrossRef
- A model for the involvement of service users as instructors into the psychiatric nursing curriculum in Korea: A qualitative study on participation experience
- 2,384 View
- 42 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Interorganizational Networks for Smoking Prevention and Cessation: A Blockmodeling Approach
- Eun-Jun Park, Hyeongsu Kim, Kun Sei Lee, Junghee Cho, Jin Hyeong Kim, Ho Jin Jeong, Ji An Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):202-213. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined characteristics and patterns of interorganizational networks for smoking prevention and cessation in Korea.
Methods
We surveyed two community health centers, ninety-five hospitals or clinics, ninety- two pharmacies, and sixty-five health welfare organizations in two districts of Seoul in 2020. Data on the organizations’ characteristics of smoking cessation and interorganizational activities for information sharing, client referral, and program collaboration were collected and analyzed using network statistics and blockmodeling.
Results
Network size was in the order of information sharing, client referral, and program collaboration networks. Network patterns for interorganizational activities on information sharing, client referral, and program collaboration among four organizations were similar between the two districts. Community health centers provided information and received clients from a majority of the organizations. Their interactions were not unidirectional but mutual with other organizations. Pharmacies were involved in information sharing with health welfare organizations and client referrals to hospitals or clinics. Health welfare organizations were primarily connected with the community health centers for client referrals and program collaboration.
Conclusion
A community health center is the lead agency in interorganizational activities for smoking prevention and cessation. However, hospitals or clinics, pharmacies, and health welfare organizations also participate in interorganizational networks for smoking prevention and cessation with diverse roles. This study would be evidence for developing future interorganizational networks for smoking prevention and cessation.
- 726 View
- 19 Download

- Willingness to Use and Appropriate Payable Cost for Visiting Nurse Service for the Elderly in the Community
- Soyoung Seo, Soong-nang Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):105-119. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21193
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to measure willingness to use (WTU) and appropriate payable cost of visiting nurse service for the elderly and explore their impact factors.
Methods
The study included 752 participants selected from data that were completed in 2017 for the elderly aged over 60 nationwide. Logit and Tobit regression analysis were performed to confirm the influencing factors.
Results
The study found that 39.1% of the elderly in the community were WTU the visiting nurse service, and they reported that the cost per visit was 12,650 Korean Won. The factors influencing WTU were having less than moderate subjective health status (OR = 1.63, p = .011), being part of a social participating groups (OR = 1.50, p = .046), or participation in senior health promotion programs (SHPPs) (OR = 1.96, p = .003). The cost was also influenced by less than moderate subjective health status (β = 4.37, p = .021), being part of a social participating groups (β = 4.41, p = .028), or participation in SHPPs (β = 4.87, p = .023). Additionally, elderly people living alone who were used as covariates were highly WTU (OR = 2.20, p = .029).
Conclusion
This study provides evidence to predict demand for visiting nurse service and reflects consumer value in setting the service cost. This is the first study to derive cost from consumers' perspective regarding the service for the elderly. As it is the result of an open-ended survey, follow-up studies are needed to estimate more reliable and reasonable results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health and Environmental Monitoring Services for Smart Healthy Cities : Current Practices and Challenges in Local Government Plans
Dong-ah Choi, Yun-jeong Song, Andy Hong
Journal of Korea Planning Association.2024; 59(5): 147. CrossRef
- Health and Environmental Monitoring Services for Smart Healthy Cities : Current Practices and Challenges in Local Government Plans
- 2,762 View
- 52 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of Health Empowerment Scale for North Korean Women Defectors
- Semi Lim, Younhee Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):80-91. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21174
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study developed an instrument to evaluate the health empowerment of North Korean women refugees and examined its validity and reliability.
Methods
Through literature review and focused group interviews, 66 preliminary items with three constructs, including perceived control, perceived competence, and goal internalization were selected based on Menon’s psychological health empowerment model. A questionnaire survey was conducted with 239 North Korean women refugees in the community from August 31 to September 4, 2020. Content, construct, convergent, and discriminative validity were evaluated. Cronbach’s α was used to evaluate the reli-ability of scale.
Results
The final instrument consisted of 31 items with three factors that were identified through confirmatory factor analysis. The convergent validity showed that the correlation coefficient was .52 (p < .001), which confirmed the validity of the developed measurement tool. Cronbach’s α for all the items was .94, and Cronbach's α for the factors was .76~.91.
Conclusion
This health empowerment scale has been developed to include aspects of health empowerment, provide a conceptual framework, and offer objective indicators to evaluate the effectiveness of a health education program.
- 1,082 View
- 31 Download

- Effectiveness of the Infectious Disease (COVID-19) Simulation Module Program on Nursing Students: Disaster Nursing Scenarios
- Won Ju Hwang, Jungyeon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):648-660. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21164
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop an emerging infectious disease (COVID-19) simulation module for nursing students and verify its effectiveness.
Methods
A one-group pretest–posttest quasi-experimental study was conducted with 78 under-graduate nursing students. A simulation module was developed based on the Jeffries simulation model. It consisted of pre-simulation lectures on disaster nursing including infectious disease pandemics, practice, and debriefings with serial tests. The scenarios contained pre-hospital settings, home visits, arrival to the emergency department, and follow-up home visits for rehabilitation.
Results
Disaster preparedness showed a statistically significant improvement, as did competencies in disaster nursing. Confidence in disaster nursing increased, as did willingness to participate in disaster response. However, critical thinking did not show significant differences between time points, and neither did triage scores.
Conclusion
The developed simulation program targeting an infectious disease disaster positively impacts disaster preparedness, disaster nursing competency, and confidence in disaster nursing, among nursing students. Further studies are required to develop a high-fidelity module for nursing students and medical personnel. Based on the current pandemic, we suggest developing more scenarios with virtual reality simulations, as disaster simulation nursing education is required now more than ever. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The development of disaster preparedness education for public: a scoping review
Ling Guo, Mingwang Fang, Li Liu, Haiyan Chong, Wen Zeng, Xiuying Hu
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sustainable Disaster Nursing Education Through Functional Exercises and Simulation: Effects on Knowledge, Problem-Solving, and Learning Outcomes
Myongsun Cho, Miyoung Kwon
Sustainability.2025; 17(20): 9165. CrossRef - The effect of repeated simulation-based disaster education on nursing students’ self-efficacy in disaster response
Ebru Konal Korkmaz, Aynur Uysal Toraman
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Implementation of a Mobile-Integrated Simulation for COVID-19 Nursing Practice: A Randomized Controlled Pretest–Posttest Experimental Design
Sun-Hwa Lee, Jeong-Sil Choi
Healthcare.2024; 12(4): 419. CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Simulation-Based Disaster Nursing Education Program for Nursing Students Using Standardized Patients
Yeon Mi PARK, Won Ju HWANG
Journal of Nursing Research.2024; 32(1): e314. CrossRef - Enhancing Disaster Triage Competencies through Simulation-Based Training: An Interventional Study among Undergraduate Nursing Students
Amal Hamdi, Abdulellah Al Thobaity
Sustainability.2023; 15(21): 15513. CrossRef - Development and testing effectiveness of a simulation program to control COVID-19 infections in nursing students
Kino Kang, Mihae Im, Miyoung Jang, Jaewoon Lee, Okjong Lee
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2023; 16(2): 54. CrossRef - Implementation and Evaluation of a Virtual Reality-Based Cognitive Assessment and Rehabilitation Simulation Course in Undergraduate Nursing Students: A Pre-Post Study
Guichen Li, Lan Gao, Huiru Yin, Yong Jia, Xueyan Zhang, Huimin Tian, Lufang Zheng, Yiming Qiu, Xin Li, Li Chen
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2023; 81: 101430. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Simulation-Based Education for Caring Patients with COVID-19
Min Hye Lee, Eun-Young Noh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(4): 397. CrossRef - Effectiveness of multiple scenario simulations of acute and critical care for undergraduate nursing students: A quasi-experimental design
Yu-Ling Chang, Ming-Ju Hsieh, Tsui-Hsia Feng, Shu-Ting Shang, Yun-Fang Tsai
Nurse Education Today.2022; 118: 105526. CrossRef - Systematic Bibliometric Analysis of Research Hotspots and Trends on the Application of Virtual Reality in Nursing
Junqiang Zhao, Yi Lu, Fujun Zhou, Ruping Mao, Fangqin Fei
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fourth Industrial Revolution and Nursing Research
Young Whee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 1. CrossRef
- The development of disaster preparedness education for public: a scoping review
- 2,650 View
- 65 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Assessment of Health Literacy in Breast and Cervical Cancer Screening
- Hye Sook Shin, Eunlim Chi, Hae-Ra Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):769-781. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21108
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Health literacy is a significant determinant of health and health behaviors such as cancer screening. Despite its significance, there are limited instruments available to assess health literacy targeting Koreans. The purpose of this study was to test the psychometric properties of Korean translation of a validated health literacy instrument in cancer screening—Korean version of assessment of health literacy in breast and cervical cancer screening (K-AHL-C).
Methods
A total of 555 women aged 20~65 participated in the online survey study. Of 52 items addressing five domains included in the original version, we focused on 36 items addressing three key domains closely associated with cancer screening: familiarity, health navigation, and comprehension.
Results
During content validation, two items from the health navigation domain were removed, yielding 34 items. Using Rasch analysis and confirmatory factor analysis, we found the evidence of construct validity of K-AHL-C. The Korean version was also significantly correlated with measures of Functional Health Literacy scale, cancer prevention behaviors, and subjective health status, suggesting convergent validities respectively. Finally, K-AHL-C had acceptable reliability coefficients (α) ranging from 0.71 to 0.92 for each domain and the total scale.
Conclusion
These psychometric properties support the K-AHL-C is a valid and reliable instrument for measuring Koreans’ health literacy in cancer screening. Also it is expected to use the instrument to detect breast and cervical cancer early and improve the screening rate, and ultimately to contribute to the promotion of women's health and women's health nursing practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Web-Based Delivery of an Effective Church-Based Intervention Program to Promote Cancer Screening (Community-based Health litEracy-focused intervention for breast and cervical Cancer Control) Among Korean Immigrant Women in the United States: Randomized Co
Hae-Ra Han, Yoon-Jae Lee, Deborah Min, Joyline Chepkorir, DaSol Amy Hwang, Steve Chae
JMIR Human Factors.2025; 12: e66092. CrossRef - Associations and gender differences between OHI-seeking behaviors and eHealth literacy among Chinese university students
Jie Chen, Hua Tian
Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Health Information Seeking Pathways and Factors Influencing Health Literacy Among Cancer Patients: Based on Data from the 2nd Korean Health Panel 2021
Yun-La Hur, Eun-Jeong Hong
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(3): 155. CrossRef - A Psychometric Validation of the Korean Version of Disaster Response Self-Efficacy Scale for Nursing Students
Sung Hae Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(4): 2804. CrossRef - Health literacy measures in South Korea: A scoping review
Heeran Chun, Su Hyun Kim, Eunja Park
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(4): 39. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Climate, Health, and Nursing Tool
Da Woon Jeong, Gwang Suk Kim, Min Kyung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(2): 173. CrossRef
- Web-Based Delivery of an Effective Church-Based Intervention Program to Promote Cancer Screening (Community-based Health litEracy-focused intervention for breast and cervical Cancer Control) Among Korean Immigrant Women in the United States: Randomized Co
- 2,457 View
- 48 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Knowledge Structure of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Health Information on HealthRelated Websites and Patients’ Needs in the Literature Using Text Network Analysis
- Ja Yun Choi, Su Yeon Lim, So Young Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):720-731. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21086
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the knowledge structure of health information (HI) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Methods
Keywords or meaningful morphemes from HI presented on five health-related websites (HRWs) of one national HI institute and four hospitals, as well as HI needs among patients presented in nine literature, were reviewed, refined, and analyzed using text network analysis and their co-occurrence matrix was generated. Two networks of 61 and 35 keywords, respectively, were analyzed for degree, closeness, and betweenness centrality, as well as betweenness community analysis.
Results
The most common keywords pertaining to HI on HRWs were lung, inhaler, smoking, dyspnea, and infection, focusing COPD treatment. In contrast, HI needs among patients were lung, medication, support, symptom, and smoking cessation, expanding to disease management. Two common sub-topic groups in HI on HRWs were COPD overview and medication administration, whereas three common sub-topic groups in HI needs among patients in the literature were COPD overview, self-management, and emotional management.
Conclusion
The knowledge structure of HI on HRWs is medically oriented, while patients need supportive information. Thus, the support system for self-management and emotional management on HRWs must be informed according to the structure of patients’ needs for HI. Healthcare providers should consider presenting COPD patient-centered information on HRWs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Da-Jung Kim
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2025; 21(5): 234. CrossRef - Development of pictogram‐based content of self‐management health information for Korean patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Ja Yun Choi, Eui Jeong Ryu, Xin Jin
International Journal of Older People Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of the feature genes involved in cytokine release syndrome in COVID-19
Bing Yang, Meijun Pan, Kai Feng, Xue Wu, Fang Yang, Peng Yang, Salman Sadullah Usmani
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(1): e0296030. CrossRef - Content Analysis of Feedback Journals for New Nurses From Preceptor Nurses Using Text Network Analysis
Shin Hye Ahn, Hye Won Jeong
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2023; 41(10): 780. CrossRef - Research trends over 10 years (2010-2021) in infant and toddler rearing behavior by family caregivers in South Korea: text network and topic modeling
In-Hye Song, Kyung-Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(3): 182. CrossRef - A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis of Self-management Experiences of Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Euna PARK, Jeong-Soo KIM
THE JOURNAL OF FISHERIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2022; 34(5): 794. CrossRef
- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- 1,682 View
- 14 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Job Analysis of Nurse Care Coordinators for Chronic Illness Management in Primary Care Settings: Using Developing a Curriculum Process
- Ju-Hee Hwang, Yong-Jun Choi, Mi-Sook Kim, Seng-Eun Yi, Yong-Soon Park, Ji-Hyang Kim, Ju-Young Yoon, Dong-Soo Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):758-768. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21065
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to conduct a job analysis of nurse carecoordinators and to identify the frequency, importance and difficulty of each task of their job.
Methods
A committee for developing a curriculum (DACUM) was formed and members of the committee defined nurse care coordinators’ jobs and enumerated the duties, tasks and task elements by applying the DACUM technique. Then nurse care coordinators enrolled in the pilot project evaluated the frequency, importance and difficulty of each task.
Results
From the job descriptions of nurse care coordinators, we identified 12 duties and 42 tasks. Each task comprised 1~5 task elements. Among tasks, ‘assess the patient’s general health status’ was carried out most frequently. Nurse care coordinators perceived that ‘check vital signs’ and ‘strengthen patient competence to promote health behaviors’ were more important than all other tasks. The most difficult task was ‘develop professionalism as a nurse care coordinator’.
Conclusion
The nurse care coordinators' roles developed in this study will serve as the key guidelines for human resource management of care coordinators. Further, job specifications for nurse care coordinators need to be developed, which is necessary for designing education and training programs. We also need to integrate primary health care as an essential component in nursing education. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Job Analysis of Nurses Working at Dementia Care Centers Using DACUM
Yong-Sun Shin, Jong-Eun Lee
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2025; 36: 21. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Care Coordination for Chronic Disease Patients with a Usual Source of Care
Hyunsang Kwon, Ju Young Yoon
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2025; 36: 339. CrossRef - Job analysis of vaccination health workers at public health centers and sub‐centers
No‐Yai Park, Chung‐Min Cho, Eun‐Hyun Lee, Jeong‐Mo Park, Young‐Ran Lee, Jeong‐Ik Hong, Geun‐Yong Kwon
Public Health Nursing.2024; 41(4): 723. CrossRef - Development and Analysis of the Job Description for Dementia Care Center Nurses in Korea Using Developing a Curriculum (DACUM)
Hana Ko, SuJung Jung
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2023; 49(10): 29. CrossRef - Analysis of flow rate and pressure in syringe-based wound irrigation using Bernoulli's equation
Hanna Lee, Ye-kyung Lee, Ji-Yun Park, Jeong-won Han
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Preliminary Study for the Curriculum Development of Community Care Coordinators: Educational Needs Analysis
Han Nah Park, Ju Young Yoon, Soong-Nang Jang, Hye Jin Nam
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(2): 153. CrossRef
- Job Analysis of Nurses Working at Dementia Care Centers Using DACUM
- 2,258 View
- 52 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Information and General Guidance for Healthcare Professionals in the Fourth Wave of COVID-19
- Jeung-Im Kim, Mi Yu, Soyoung Yu, Jin-Hee Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(4):395-407. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21137
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The COVID-19 curve seesawed and reached the fourth pandemic in July 2021. Since the first three waves, the focus has been on achieving herd immunity through vaccination while a lot of manpower is used for quarantine. However, we have not been able to prevent the fourth wave. The causes are thought to be related to people who doubt the safety of the vaccine and refuse it or violate quarantine guidelines such as social distancing. This study examined guidelines for preventing and controlling COVID-19, the accuracy of vaccination-related information, and described quarantine measures including for those who completed vaccination. In conclusion, prevention and vaccination are the most effective countermeasures against COVID-19. We recommend people vaccination with self-quarantine. Also, it is necessary to make large investments to protect and support nurses in future pandemics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Halal Indonesia: creating global nation branding through communication and diplomacy
Nurprapti Wahyu Widyastuti, Marchela Rahesta, Isti Nursih Wahyuni
Jurnal Studi Komunikasi (Indonesian Journal of Communications Studies).2025; 9(2): 577. CrossRef - COVİD-19 Pandemisinde Diş Hekimlerinin Dezenfeksiyon, Antisepsi ve Sterilizasyon Uygulamalarına Bakışı
Pelin ÖZMEN, Serdar SÜTCÜ, Haluk KÖSE
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2023; 12(3): 348. CrossRef - The thoughts of parents to vaccinate their children against COVID‐19: An assessment of situations that may affect them
Melike Y. Çelik
Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Nursing.2022; 35(2): 189. CrossRef - Vaccination process evaluation at COVID-19 vaccination centers in Lebanon: a national study
Abeer Zeitoun, Souheil Hallit, Maya Helali, Sirine Chehade, Carla Allam, Aya Ibrahim, Hani Dimassi, Rita Karam
Journal of Pharmaceutical Policy and Practice.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Theoretical effectiveness of steam inhalation against SARS-CoV-2 infection: updates on clinical trials, mechanism of actions, and traditional approaches
Md. Nafees Rahman Chowdhury, Yasin Arafat Alif, Safaet Alam, Nazim Uddin Emon, Fahmida Tasnim Richi, S. M. Neamul Kabir Zihad, Md. Tohidul Islam Taki, Mohammad A. Rashid
Heliyon.2022; 8(1): e08816. CrossRef - Experience of Nurses in Charge of COVID-19 Screening at General Hospitals in Korea
Boo Young Ha, Yun-Sook Bae, Han Sol Ryu, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 66. CrossRef - Effectiveness and Utility of Virtual Reality Infection Control Simulation for Children With COVID-19: Quasi-Experimental Study
Mi Yu, Mi Ran Yang
JMIR Serious Games.2022; 10(2): e36707. CrossRef - Healthcare Considerations for Special Populations during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review
Jeung-Im Kim, YeoJin Im, Ju-Eun Song, Sun Joo Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(5): 511. CrossRef
- Halal Indonesia: creating global nation branding through communication and diplomacy
- 2,543 View
- 15 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of Prenatal Education for Environmental Health Behavior Using Cartoon Comics
- Hyun Kyoung Kim, Hee Kyung Kim, Mirim Kim, Seohwa Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(4):478-488. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21083
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and examine the effects of a prenatal program on environmental health behavior using cartoon comics among Korean pregnant women.
Methods
This study used a non-equivalent control group pre-test/post-test design. The program used cartoon comics to explore environmental health behaviors during pregnancy. The program consisted of the following four components: environmental toxicants during pregnancy, avoiding particulate matter during pregnancy, environmental toxicants during baby care, and making a healthy environment for children. In total, 35 pregnant women participated in the study: 18 in the experimental group and 17 in the control group. Data collection and program adaptation were conducted between November 3, 2020 and January 19, 2021. The effect of the prenatal education program was evaluated by t-test and repeated measures ANOVA.
Results
Learning experience (t = - 2.35, p = .025), feasibility (t = - 2.46, p = .019), satisfaction (t = - 2.23, p = .032) were higher in the experimental group than in the control group in the first post-test. Feasibility (t = - 2.40, p = .022) was higher in the experimental group than in the control group in the second post-test. Repeated-measures ANOVA showed significant interactions between time and group in environmental susceptibility (F = 9.31, p < .001), self-efficacy (F = 3.60, p = .033), and community behavior (F = 5.41, p = .007).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates the need for a prenatal education program to promote environmental health perceptions and behavior during pregnancy. We suggest a prenatal class adopting the creative cartoon comics to promote the maternal environmental health behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a diabetes-themed cartoon-based education on disease knowledge and physical activity among Japanese children: a preliminary randomized controlled trial
Yasuhiro Suzuki, Daichi Sugawara, Mika Oki, Hirofumi Takahashi, Takaaki Matsuda, Hiroaki Suzuki, Hitoshi Shimano, Yasushi Hada, Kenji Suzuki
Clinical Pediatric Endocrinology.2026; 35(1): 74. CrossRef - The effect of DECO-MOM mobile application for a prenatal environmental health program on environmental health behaviors: a pilot test
Hae Kyung Jo, Hyun Kyoung Kim
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and evaluation of a quasi-experimental sexual and reproductive health literacy (SRHL) programme for marriage immigrants in South Korea: focus on Vietnamese women
Heeran Chun, Young Sook Lee, Hyeran Yoon
BMJ Public Health.2025; 3(2): e002473. CrossRef - The effects of a YouTube prenatal program on social support, environmental health behavior, and content satisfaction: a quasi-experimental research design
Geum Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Hye Young Min
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Examining the Effectiveness of Interactive Webtoons for Premature Birth Prevention: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial
Sun-Hee Kim, Jennie C De Gagne
JMIR Research Protocols.2024; 13: e58326. CrossRef - Development and effects of a webtoon education program on preventive self-management related to premature labor for women of childbearing age: a randomized controlled trial
Sun-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(3): 250. CrossRef - The effects of environmental prenatal program on environmental health perception and behavior using internet-based intervention in South Korea: A non-randomized controlled study
Hyun Kyoung Kim, Geum Hee Jeong, Hye Young Min, George Vousden
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(11): e0277501. CrossRef
- Effects of a diabetes-themed cartoon-based education on disease knowledge and physical activity among Japanese children: a preliminary randomized controlled trial
- 1,401 View
- 39 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Information Resource Network Analysis of Factors Influencing Breastfeeding Planning and Duration
- Eunyoung Lee, Insook Cho, Seong Jin Cho, Eunju Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(2):232-244. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20280
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the modifiable factors affecting breastfeeding planning and duration among healthy mothers and their use of breastfeeding information resources.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey was conducted in a community setting. Four hundreds participants were recruited at five pediatric clinics and three community health centers located in Paju-si and Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, between January and May 2019. Based on the breastfeeding decision-making model, driven by Martens and Young’s work, the survey items consisted of demographics, childbirth and breastfeeding characteristics, and breastfeeding information resources. In the analysis, 389 responses were used in the t-test, ANOVA, and logistic regression. Information resource networks were compared before and after childbirth including a subgroup analysis depending on the breastfeeding duration.
Results
The modifiable factors affecting breastfeeding planning and duration were antenatal and postpartum breastfeeding education and the provision of information in the hospital. The frequency of Internet use and websites visited were notable and potentially modifiable factors, which were also observed in the networks showing different relationship patterns according to participant subgroups and times. The childbirth event increased the centralization of the network in the planned group, while the network of the non-planned group was more diffused after childbirth. The network of the short-term breastfeeding group was characterized by a more centralized pattern and the resources of high betweenness centrality than the long-term group.
Conclusion
Breastfeeding education is a consistent factor that affects breastfeeding behavior. A well-designed internet-based approach would be an effective nursing intervention to meet the needs of women seeking breastfeeding information and changing their behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Survey on the Status of Breastfeeding in Korean Medical Institution Workers
Tae Hyeong Kim, Sung-Hoon Chung, Jun Hwan Kim, Youngmin Ahn, Son Moon Shin, Woo Ryoung Lee, Eui Kyung Choi, Juyoung Lee, Hye-Jung Shin, Euiseok Jung, Ju Sun Heo, Jin A Lee, Soon Min Lee, Seong Phil Bae, Jeonglyn Song, Chae-Young Kim, Dae Yong Yi
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Multi-Center Educational Research Regarding Breastfeeding for Pediatrics Residents in Korea
Yong-Sung Choi, Sung-Hoon Chung, Eun Sun Kim, Eun Hee Lee, Euiseok Jung, So Yeon Lee, Wooryoung Lee, Hye Sun Yoon, Yong Joo Kim, Ji Kyoung Park, Son Moon Shin, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim
Neonatal Medicine.2022; 29(1): 28. CrossRef - Breastfeeding Success Experience of Primiparas
Sun Ok Lee, Sung Soon Na, Hee Sook Kim, Kyung Eui Bae, Mi Sun Youn, Eun Ju Oh
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2022; 26(4): 254. CrossRef - Breastfeeding experiences of women with gestational diabetes
Seungmi Park, Soo-Young Yu
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 274. CrossRef
- Survey on the Status of Breastfeeding in Korean Medical Institution Workers
- 1,427 View
- 22 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Sub-Health Status Survey and Influential Factor Analysis in Chinese during Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic
- Yanbin Pan, Jianlong Yan, Wanxian Lu, Miaohang Shan
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):5-14. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate sub-health status (SHS) of people living in China during the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) COVID-19 pandemic. COVID-19 is a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) infection-induced acute infectious disease, which is featured by universal susceptibility and strong infectivity, and SHS (a status of low quality health) refers to a status of low-quality health. COVID-19 has gradually developed into a global pandemic, making the public in a high stress situation in physiological, psychological and social states in the short term.
Methods
From March 6 to 11, 2020, a large-scale cross-sectional survey was conducted by convenient sampling, and SHS assessment scale was used in the questionnaire. The ordinal logistic regression analysis was used to identify the factors affecting SHS.
Results
In this study, 17,078 questionnaires were delivered with 16,820 effective questionnaires collected, and 10,715 subjects (63.7%) were found with SHS, with moderate SHS primarily. Physiological sub-scale scored the highest, followed by psychological and social sub-scales. Ordinal logistic regression analysis indicated that man, only-child, workers and farmers were risk factors of SHS. Protective factors of SHS included living in rural areas and townships, laid-off retirees and education degree.
Conclusion
It shows many people in China place in a poor health status during COVID-19 pandemic. It is necessary that relevant departments pay more attention to people with poor health such as men, only-child, urban people, workers and farmers, and groups with high education degree during and after pandemic stabilization. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Immunomodulatory effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum CCFM8661 + stachyose on cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression mice
Weiwei Ma, Hang Sun, Lian Lian, Lidong Guo, Yanyan Wang, Lili Huang
Frontiers in Immunology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Tourism Motivation and Perceived Value on Tourists’ Behavioral Intention Toward Forest Health Tourism: The Moderating Role of Attitude
Yujiao Zhao, Jun Yang, Juanru Song, Yiqing Lu
Sustainability.2025; 17(2): 713. CrossRef - Analysis of sub-health status and related factors in medical students in the Chinese Mainland from the perspective of health ecology
Yifan Jiang, Xuan Wang, Min Zhang, Zhiyong Xu, Yibo Wu, Liang Chen
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimized Implementation Strategies for Traditional Chinese Medicine Management Interventions in Sub-Healthy Elderly Population and Their Impact on Quality of Life Enhancement
Huifen Liu, Bing Xu
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2025; Volume 20: 1481. CrossRef - Polygonatum sibiricum, a tonic and functional food, ameliorates poor lifestyle-induced sub-health by regulating gut microbiota and kynurenine metabolism
Bingqing Yu, Menglin Shi, Jie Su, Jingjing Yu, Hengpu Zhou, Qiwei Lin, Suhong Chen, Guiyuan Lv, Meiqiu Yan
Journal of Agriculture and Food Research.2025; 24: 102413. CrossRef - Summary of Outpatient Visits for Characteristic Nursing in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Junrui Ma, Hushan Zhang, Jialan Wang, Jie Gao, Dandan Fan, Yanping Qian, Zhuo Chen, Ruifang Bao, Lihua Yin, Guangyi Xiong
Holistic Nursing Practice.2024; 38(3): 164. CrossRef - Relationship chains of subhealth physical examination indicators: a cross-sectional study using the PLS-SEM approach
Yu Wang, Jindi Lou, Jun Li, Yulin Shi, Tao Jiang, Liping Tu, Jiatuo Xu
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Multi-objective optimization and nonlinear dynamics for sub-healthy COVID-19 epidemic model subject to self-diffusion and cross-diffusion
Yunbo Tu, Xinzhu Meng, Abdullah Khames Alzahrani, Tonghua Zhang
Chaos, Solitons & Fractals.2023; 175: 113920. CrossRef - Measurement properties of the EQ-5D-5L in sub-health: evidence based on primary health care workers in China
Yueyue Liu, Chuchuan Wan, Xiaoyu Xi
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Immunomodulatory effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum CCFM8661 + stachyose on cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression mice
- 1,602 View
- 13 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Health Behavior Compliance in Adult Moyamoya Patients
- Bo Eun Kim, Ju-Eun Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):80-91. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify factors influencing health behavior compliance in adult patients with moyamoya.
Methods
A descriptive correlation study was conducted to investigate the factors influencing health behavior compliance. Participants were 142 adult patients diagnosed with moyamoya disease who were hospitalized or visited an outpatient clinic in the Gyeonggi province. Data were collected from December 16, 2019 to April 14, 2020 using self-report questionnaires and analyzed using the IBM SPSS 26.0 Win software.
Results
The hierarchical multiple regression analysis demonstrated that self-efficacy (β = .60, p < .001), social support (β = .13, p = .032), and age (β = .21, p = .005) affected the health behavior of adults with moyamoya disease. These 3 variables explained 62.0% of the variance of health behavior compliance, and the most influential factor was self-efficacy.
Conclusion
Based on the results of this study, it concludes that nursing interventions should be focused on self-efficacy and social support to improve health behavior compliance with adult patients diagnosed with moyamoya disease. For that, various strategies to enhance self-efficacy and social support should be developed and actively applied in the clinical setting for adult moyamoya patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictors of self-care performance in patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms
Hae-Na Woo, Yong-Cheol Lim, Joo Hee Lee, Sun Hyoung Bae
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Predictors of self-care performance in patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms
- 1,353 View
- 24 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- An Exploratory Study on the Policy for Facilitating of Health Behaviors Related to Particulate Matter: Using Topic and Semantic Network Analysis of Media Text
- Hye Min Byun, You Jin Park, Eun Kyoung Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):68-79. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20213
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to analyze the mass and social media contents and structures related to particulate matter before and after the policy enforcement of the comprehensive countermeasures for particulate matter, derive nursing implications, and provide a basis for designing health policies.
Methods
After crawling online news articles and posts on social networking sites before and after policy enforcement with particulate matter as keywords, we conducted topic and semantic network analysis using TEXTOM, R, and UCINET 6.
Results
In topic analysis, behavior tips was the common main topic in both media before and after the policy enforcement. After the policy enforcement, influence on health disappeared from the main topics due to increased reports about reduction measures and government in mass media, whereas influence on health appeared as the main topic in social media. However semantic network analysis confirmed that social media had much number of nodes and links and lower centrality than mass media, leaving substantial information that was not organically connected and unstructured.
Conclusion
Understanding of particulate matter policy and implications influence health, as well as gaps in the needs and use of health information, should be integrated with leadership and supports in the nurses’ care of vulnerable patients and public health promotion. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Online community users’ perceptions of particulate matter in South Korea through topic modeling and semantic network analysis
Hansol Choi, Yong Pyo Kim, Yungwook Kim, Ji Yi Lee, Hyemi Lee
Environmental Advances.2025; 20: 100641. CrossRef - Changes in Public Sentiment under the Background of Major Emergencies—Taking the Shanghai Epidemic as an Example
Bowen Zhang, Jinping Lin, Man Luo, Changxian Zeng, Jiajia Feng, Meiqi Zhou, Fuying Deng
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(19): 12594. CrossRef
- Online community users’ perceptions of particulate matter in South Korea through topic modeling and semantic network analysis
- 1,368 View
- 17 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Disease Prevention Knowledge, Anxiety, and Professional Identity during COVID-19 Pandemic in Nursing Students in Zhengzhou, China
- Yuyan Sun, Dongyang Wang, Ziting Han, Jie Gao, Shanshan Zhu, Huimin Zhang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(4):533-540. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate nursing students’ understanding of the prevention of COVID-19, as well as their anxiety towards the disease and their perception of their professional identity in the wake of the pandemic, in Zhengzhou, China.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was designed to investigate 474 nursing students by cluster sampling using a stratified questionnaire from February 15 to March 31, 2020. Multiple linear regression was used to identify the factors affecting professional identity. Binary and multiple logistic regression were used to identify the factors affecting anxiety.
Results
Responders with a high level of understanding of COVID-19 and frequent use of behavioral strategies for its prevention comprised 93.2% and 30.0% of the cohort, respectively. Professional identity was significantly associated with gender and anxiety (p < .050). The prevalence of anxiety among nursing students was 12.4%. Male (odds ratio [OR] = 2.39; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.26~4.52), sophomores (OR = 5.30; 95% CI = 1.61~7.45), and infrequent use of prevention measures (OR = 3.49; 95% CI = 1.16~5.19) had a significant effect on anxiety.
Conclusion
Anxiety during the COVID-19 epidemic gives an adverse effect on the professional identity of nursing in students. Nursing education institutions need to provide psychological counseling services for nursing students, in addition to improving their teaching of COVID-19 prevention strategies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Global prevalence of different levels of anxiety and stress symptoms in healthcare students: A meta-analysis and meta-regression
Ying Xuan Loh, Ying Lau, Wen Wei Ang, Shean Ern Shannen Lee, Siew Tiang Lau
Annals of General Psychiatry.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Anatomical dissection influences emotions of podiatry students
Alicia Mohedano‐Moriano, Carmen Romo‐Barrientos, Alicia Flores‐Cuadrado, Isabel Ubeda‐Bañon, Jaime Gonzalez‐Gonzalez, Maria Teresa Gil Ruiz, Daniel Saiz‐Sanchez, Veronica Astillero‐Lopez, Felix Marcos‐Tejedor, Alino Martinez‐Marcos, Antonio Viñuela, Juan
Journal of Foot and Ankle Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Hand Hygiene Practices and Educational Interventions Among Indonesian Nursing Students: An Analysis Using ATP Wipe Tests and Hand Hygiene Checkers
Mayumi Sato, Syahrul, Tantut Susanto, Fithria, Naoki Hokama, Ruka Saito, Andi Muhammad Fiqri Muslih Djaya, Hiroshi Sugimoto
Journal of Rural Community Nursing Practice.2025; 3(1): 60. CrossRef - The transformation of ambivalent professional identity of nursing students following clinical placement in China: A qualitative study from the perspectives of the “post-00s” generation
Jingyi Chen, Xiao Zhang, Yidan Yang, Rong Hu
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 86: 104387. CrossRef - Resilience, perceived control, and intention to receive additional vaccines for COVID‐19 among healthcare university students: Mediating role of knowledge of vaccine and infection‐preventive behaviors
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Erika Ota, Tomomi Oki, Kazuko Naruse
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The influences of nursing students’ prevention and control practice behaviours on emerging and re-emerging respiratory viral illnesses: An integrative review and narrative synthesis
Gift A. Mutsonziwa, Paul Glew, Rona Pillay
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 88: 104564. CrossRef - Ser enfermeiro na perspectiva de estudantes de enfermagem do nordeste brasileiro no contexto pandemico
Thais Araujo da Silva, Ruth Silva dos Santos, Nayhara Rayanna Gomes da Silva, Ryanne Carolynne Marques Gomes Mendes
Journal of Nursing and Health.2025; 15(2): e1528145. CrossRef - Kayseri İlinde Öğrenim Gören Paramedik Öğrencilerinin Mesleki Kaygı Düzeyinin Belirlenmesi
Emre Bulbul, Etem Hızaler, Mehmet Doğan
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2025; 6(1): 8. CrossRef - Nursing Students’ Perceptions of Factors Influencing Nursing Intentions toward COVID-19 Patients
Nari Lee, Hae Ran Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 285. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of the training on “Home care of COVID-19 positive/suspicious patients” given to nursing students: A quasi-experimental study
Hande Sabandüzen, Öznur Kavaklı
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of alexithymia, anxiety, social pressure, and academic burnout on depression in Chinese university students: an analysis based on SEM
Mingyang Sun, Ming Piao, Zhaona Jia
BMC Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between anxiety and academic identity and the motivation to study nursing and midwifery in the covid-19 pandemic: A structural model
Ashraf Khoramirad, Sarallah Shojaei, Heydar Ghaderi, Zahra Abedini
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Holistic Approach to Nursing Students’ Changing Life and Anxiety in the Pandemic: A Descriptive Cross Sectional Study Utilizing Positive Psychotherapy
Ayşe Kuzu Durmaz, Ferhan Açıkgöz, Çiğdem Şen Tepe
Journal of Higher Education and Science.2024; 14(2): 349. CrossRef - The Mediating Role of Psychological Resilience in Chinese Nursing Students’ Professional Identity and Learning Burnout
Liu Zhang, Qin Zhang, ShuWen Li, YuHong Li, GuoCui Wu, Ying Chen, YunNa Zhou
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(4): 509. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Nurses’ Perceptions of Spirituality and Spiritual Care and Their Attitudes Towards the Nursing Profession
İbrahim Nas, Gülay İpekçoban
Gümüşhane Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2024; 13(2): 542. CrossRef - Anxiety in Nursing Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Aroa García-Rivas, María Begoña Martos-Cabrera, María José Membrive Jiménez, Raimundo Aguayo-Estremera, Nora Suleiman Martos, Luis Albendín-García, José L. Gómez-Urquiza
Healthcare.2024; 12(16): 1575. CrossRef - Work environment as perceived by nursing interns and its relation to their professional identity
Habiba A.A. Gadallah, Sahar H.A. El Banan, Faten S.A. Ahmed
Egyptian Nursing Journal.2024; 21(2): 129. CrossRef - Assesment of Occupational Anxiety of Emergency Aid and Disaster Management Students
Cüneyt Çalışkan, Kerem Kınık
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2024; 5(1): 51. CrossRef - COVID-19 Perceptions, Avoidance and Vaccine Attitudes of Nursing Students: Case of Türkiye
Gülşen ULAŞ KARAAHMETOĞLU, Zeynep ARABACI
Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Fakültesi Elektronik Dergisi.2024; : 111. CrossRef - COVID-19 Pandemi Süreci Uzaktan Eğitim Döneminde Hemşirelik Öğrencilerinde Anksiyete ve Klinik Performans Öz-Yeterlilik Algısı İlişkisi
Yeliz AKKUŞ, Nihal BOSTANCI DAŞTAN
Sağlık Bilimlerinde Değer.2024; 14(1): 106. CrossRef - Comparing factors related to perceived control and preventive behaviors from COVID‐19 between Japanese and American nursing students: A cross‐sectional study
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Kosuke Niitsu, Kazuko Naruse, Tomomi Oki, Erika Ota, Mabel C. Ezeonwu
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sağlık Hizmetleri Meslek Yüksekokulu Öğrencilerinin Mesleğe Yönelik Kaygı Düzeylerinin Belirlenmesi
Dilan AKTEPE COŞAR, Nuray BİNGÖL, Hatice DEMİRAĞ
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2023; 4(2): 66. CrossRef - Satisfied with teaching? Psychometric properties of the Teaching Satisfaction Scale
Tyrone B. Pretorius, Anita Padmanabhanunni, Kyle M. Jackson, Brendon D. Faroa
African Journal of Psychological Assessment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Risk Factors for Anxiety Symptoms among Student Nurses in Gauteng Province of South Africa
Maleke Manana, Sam Thembelihle Ntuli, Kebogile Mokwena, Kgomotso Maaga
Behavioral Sciences.2023; 13(8): 630. CrossRef - Factors related to mental health effect among nursing students in Japan and the United States during the coronavirus pandemic: A cross‐sectional study
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Kosuke Niitsu, Kazuko Naruse, Tomomi Oki, Erika Ota, Mabel C. Ezeonwu
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(1): 186. CrossRef - Effects of a Nursing Simulation Learning Module on Clinical Reasoning Competence, Clinical Competence, Performance Confidence, and Anxiety in COVID-19 Patient-Care for Nursing Students
Ye-Eun Kim, Hee-Young Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(1): 87. CrossRef - Research Progress of Chinese Nursing Students’ Professional Identity during COVID-19
毓 徐
Nursing Science.2023; 12(01): 7. CrossRef - Prevalence and levels of burnout in nursing students: A systematic review with meta-analysis
José L. Gómez-Urquiza, Almudena Velando-Soriano, María José Membrive-Jiménez, Lucia Ramírez-Baena, Raimundo Aguayo-Estremera, Elena Ortega-Campos, Guillermo A. Cañadas-De la Fuente
Nurse Education in Practice.2023; 72: 103753. CrossRef - Psychological impacts of transition to distance learning due to COVID‐19 on nursing students
Ahmad Rayan
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(3): 767. CrossRef - COMPARISON OF TWO DIFFERENT TECHNIQUES FOR TEACHING LEARNING SKILLS: EVALUATION IN THE PERIOD OF PANDEMIC
Sevim ÇELİK, Elif KARAHAN, Sibel ALTINTAŞ, Özge UÇAR
International Journal of Health Services Research and Policy.2023; 8(2): 114. CrossRef - How has the COVID-19 pandemic influenced nursing students' academic experience and career choices? A qualitative descriptive analysis
Masamitsu Kobayashi, Yuji Koga, Jun Kako, Takahiro Kakeda, Hana Kiyohara, Yasutaka Kimura, Michiko Ishida, Michihiro Tsubaki, Yoko Nishida, Kimie Harada, Yuki Wakiguchi, Yoji Endo, Yoshiyasu Ito, Shinsuke Sasaki, Kohei Kajiwara, Seiji Hamanishi, Makoto Ya
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2023; 18(1): 30. CrossRef - Perceived social support and professional identity in nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic era: the mediating effects of self-efficacy and the moderating role of anxiety
Zhi-Hui Zhao, Jin-Yi Guo, Jie Zhou, Jia Qiao, Shu-Wen Yue, Yan-Qiong Ouyang, Sharon R. Redding, Rong Wang, Zhong-Xiang Cai
BMC Medical Education.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Anxiety, depression, and stress prevalence among college students during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Chunyi Wang, Wen Wen, Haifu Zhang, Jie Ni, Jingjie Jiang, Yongran Cheng, Mengyun Zhou, Lan Ye, Zhanhui Feng, Zhongjun Ge, Hong Luo, Mingwei Wang, Xingwei Zhang, Wenmin Liu
Journal of American College Health.2023; 71(7): 2123. CrossRef - Factors associated with mental health among undergraduate nursing students early in the COVID-19 pandemic: an integrative review
Keiko Sugimoto, Rieko K. Fukuzawa, Ganchimeg Togoobaatar, Chang G. Park, Susan C. Vonderheid
International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - PANDEMİ SÜRECİNDE KLİNİK UYGULAMA YAPAMAYAN İLK VE ACİL YARDIM ÖĞRENCİLERİNİN MESLEKİ YAŞAM İLE İLGİLİ KAYGI DÜZEYLERİNİN VE İLİŞKİLİ FAKTÖRLERİN BELİRLENMESİ
Elif KILIÇ GÜNER, Özge AKBABA, Elanur YILMAZ KARABULUTLU, Havva ÖZTÜRK
Hastane Öncesi Dergisi.2023; 7(3): 331. CrossRef - Hemşirelik Öğrencilerinin Mesleğe Yönelik Tutumu ile COVID-19 Enfeksiyonu Korkusu Arasındaki İlişki
Süreyya Bulut, Nihal Taşkıran
Hacettepe Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Fakültesi Dergisi.2023; 10(3): 207. CrossRef - Investigation of the Stress Level and Coping Behaviors of Nursing Students, and Their Thoughts on Professional Life in COVİD-19 Pandemic
Belkız KIZILTAN, Nurgül KAPLAN, Seda UZUNALİ
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2023; 4(1): 26. CrossRef - The development and effects of a COVID-19 nursing education program for nursing students
Hyewon Choi, Hyunju Kang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 368. CrossRef - Hemşirelik Son Sınıf Öğrencilerinin Mezuniyet Sonrası Covid-19 Kliniklerinde Çalışmaya İlişkin Görüşleri: Nitel Bir Çalışma
Ilknur TURA, Sevilay ERDEN
Hemşirelik Bilimi Dergisi.2022; 5(3): 149. CrossRef - The multidimensionality of anxiety among nursing students during COVID‐19 pandemic: A cross‐sectional study
Rizal Angelo N. Grande, Daniel Joseph E. Berdida, Rolan Rodolfo Jr C. Paulino, Eric A. Anies, Reinhard Roland T. Ebol, Roger R. Molina
Nursing Forum.2022; 57(2): 267. CrossRef - Identity Matters: Validation of the Professional Identification Scale in a Sample of Teachers in South Africa During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Tyrone B. Pretorius, Anita Padmanabhanunni, Serena Ann Isaacs
Trends in Psychology.2022; 32(4): 1426. CrossRef - The study of psychological traits among Chinese college students during the COVID-19 campus lockdown
Haibo Xu, Zhen Wang, Lixin Peng, Yanyan Mi, Ping Zeng, Xin Liu
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Perceived professional identity and related factors in Iranian nursing students: a cross-sectional study
Tahereh Gilvari, Hassan Babamohamadi, Fatemeh Paknazar
BMC Nursing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Nursing students’ experiences of mental wellness during the COVID-19 pandemic: A phenomenological study
Dana Laczko, Alex Hodson, Melissa Dykhuizen, Kelsey Knipple, Kassandra Norman, Paula Hand-Cortes
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2022; 17(4): 392. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Infection Control Performance of School Health Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic in South Korea
Mi-Ra Yim, Boyoung Kim
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2022; Volume 15: 805. CrossRef - The Beneficial Effects of Professional Identity: The Mediating Role of Teaching Identification in the Relationship between Role Stress and Psychological Distress during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Tyrone Brian Pretorius, Anita Padmanabhanunni
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(18): 11339. CrossRef - Being a Nursing Student In a Pandemic: Fear of COVID-19 and Clinical Practice
Pınar TUNÇ TUNA, Halil İbrahim TUNA, Birsel MOLU, Alev YILDIRIM KESKİN
Genel Tıp Dergisi.2022; 32(5): 506. CrossRef - Mental Health Among Medical Students During COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Qingwen Jia, Yi Qu, Huiyuan Sun, Huisheng Huo, Hongxia Yin, Dianping You
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge and attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccination among student nurses from Saudi Arabia
Romeo Mostoles Jr, Richard Maestrado, Joyce Buta, Salman Alsaqri, Evalynn Rondilla, Hamdan Mohammad Albaqawi
Jurnal Ners.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of anxiety symptoms among Chinese university students amid the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Xiaohang Wang, Quzhi Liu
Heliyon.2022; 8(8): e10117. CrossRef - Has the COVID-19 pandemic affected nursing students’ career self-efficacy and professional calling? The mediating impact of professional identity
Li Yang, Mengfan Xu, Jinke Kuang, Kexin Zhou, Xuemei Zhu, Lingna Kong, Li QI, Heng Liu
BMC Medical Education.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research on Health Education Strategies for Improving Student Knowledge on Infectious Disease Prevention
Shailly Gupta , Manashree Mane , Debashree Priyadarshini , Ajab Singh Choudhary
Health Leadership and Quality of Life.2022; 1: 126. CrossRef - Relationship between nursing students’ attitudes toward nursing profession and online learning satisfaction during COVID-19 lockdown
Maša Černelič-Bizjak, Petra Dolenc, Ali B. Mahmoud
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(11): e0277198. CrossRef - Anxiety and fear of COVID‐19 among nursing students during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A descriptive correlation study
Nilgun Kuru Alici, Ebru Ozturk Copur
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2022; 58(1): 141. CrossRef - Professional Identity of 0.24 Million Medical Students in China Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Three Waves of National Cross-Sectional Studies
Chen Yu, Qiao Liu, Weimin Wang, Ana Xie, Jue Liu
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Attitudes of Nursing Students towards Vaccination and Other Preventive Measures for Limitation of COVID-19 Pandemic: Cross-Sectional Study in Three European Countries
Nevenka Kregar Velikonja, Beata Dobrowolska, Sanja Stanisavljević, Karmen Erjavec, Vislava Globevnik Velikonja, Ivan Verdenik
Healthcare.2021; 9(7): 781. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Preventive Practice of International Students in South Korea against COVID-19 during the Pandemic
Gun Ja Jang, Ginam Jang, Sangjin Ko
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(5): 2259. CrossRef - Perceived Control, Preventative Health Behaviors, and the Mental Health of Nursing Students During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Kazuko Naruse, Tomomi Oki, Kosuke Niitsu, Mabel C. Ezeonwu
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Individual and Joint Effects of Cumulative Confirmed Cases and Attention Level of COVID-19 on Medical Students' Professional Identity: A National Cross-Sectional Study in China
Qiao Liu, Chen Yu, Ana Xie, Weimin Wang, Jue Liu
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of mental health problems and sleep disturbances in nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mulyadi Mulyadi, Santo Imanuel Tonapa, Suwandi Luneto, Wei-Ting Lin, Bih-O Lee
Nurse Education in Practice.2021; 57: 103228. CrossRef - Transition in learning during COVID‐19: Student nurse anxiety, stress, and resource support
Anita Fitzgerald, Sharon Konrad
Nursing Forum.2021; 56(2): 298. CrossRef - Nursing Students in Crisis Mode
Bella Savitsky, Yifat Findling, Anat Ereli, Tova Hendel
Nurse Educator.2021; 46(3): E33. CrossRef - Impact of Anxiety on Readiness for COVID-19 Vaccination among Polish Nursing Undergraduate Students: Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study
Joanna Gotlib, Mariusz Jaworski, Dominik Wawrzuta, Tomasz Sobierajski, Mariusz Panczyk
Vaccines.2021; 9(12): 1385. CrossRef
- Global prevalence of different levels of anxiety and stress symptoms in healthcare students: A meta-analysis and meta-regression
- 2,315 View
- 18 Download
- 47 Web of Science
- 63 Crossref

- Effects of BeHaS Program on Health Behavior, Physiologic Index and Self-Esteem of the Elderly Living Alone with Metabolic Syndrome Based on Community Based Participatory Research
- Jong Im Kim, Sun Ae Kim, Keumok Park, Jiyoung Kim, Lina Lee, Si Wan Choi, Bon Jeong Ku
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(4):571-582. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19261
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to determine the effects of a 12-week metabolic syndrome BeHaS (Be Happy and Strong) program in elderly people with metabolic syndrome living alone, based on a community-based participatory research (CBPR).
Methods
A nonequivalent control group pre-posttest design was used, and the participants were 43 elderly people living alone (experimental group 24, control group 19). The experimental group received a one-hour program per week and two individual health consultations during 12 weeks. The control group received two sessions about the metabolic syndrome and two individual health consultations. The effects of health behavior, blood pressure, blood sugar levels, abdominal circumference, triglycerides, and self-esteem were evaluated. The data were analyzed using the independent t-test and Mann-Whitney U test.
Results
The health behavior with respect to the metabolic syndrome in the experimental group increased significantly (t = - 3.19, p = .002). Both diastolic blood pressure and abdominal circumference decreased in the experimental group (t = 2.00, p = .028 and t = 3.91, p < .001). No significant differences were observed between the groups in systolic blood pressure, fasting blood sugar levels, triglycerides, and self-esteem.
Conclusion
The 12-week metabolic syndrome BeHaS program using community resources improves the health of elderly people with metabolic syndrome living alone. Based on these findings, further studies on the effectiveness of the metabolic syndrome BeHaS program and the experiences of those who participated in the CBPR are warranted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and effects of a customized integrated health management program for older adults living alone: A nonequivalent control-group pre-posttest design
Mooyong Cho
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(3): 295. CrossRef - Exploring the Impact of Smart Mobility and ICT Solutions on Older Adults’ Mobility: A Systematic Literature Review
Chengyuan An
IEEE Access.2024; 12: 159056. CrossRef - 노인 대사증후군에 효과적인 중재: 체계적 문헌고찰과 메타분석
서현 이, 슬 구, 유미 서, 선화 반
Public Health Weekly Report.2023; 16(48): 1633. CrossRef - Comparison of the Effects of Education Only and Exercise Training Combined with Education on Fall Prevention in Adults Aged 70 Years or Older Residing in Elderly Residential Facilities
Chahwa Hong, Haejung Lee, Misoon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(2): 173. CrossRef
- Development and effects of a customized integrated health management program for older adults living alone: A nonequivalent control-group pre-posttest design
- 1,357 View
- 34 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Health Behavior Related to Particulate Matter in Older Adults
- Min Kyung Park, Gwang Suk Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):431-443. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate health behavior related to particulate matter (PM) in older adults and examine the factors affectingit.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey design was used. Data were collected from 150 voluntary older adult participants from Songpa-gu inSeoul. The survey questions measured service perception and experience related to PM, risk perception related to PM, attitude toward riskof PM, and health behavior related to PM.
Results
The average score for health behavior related to PM was 79.37, ranging from 51 to 115.There was a significant positive correlation between health behavior related to PM and risk perception related to PM (r=.58, p <.001) as wellas between health behavior related to PM and attitude toward risk of PM (r=.70, p<.001). Multiple linear regression revealed that healthbehavior related to PM was predicted by levels of the existence of disease related to PM (β=.14, p=.019), service experience related to PM(b=.20, p=.021), risk perception related to PM (b=.20, p=.019), and attitude toward risk of PM (b=.44, p<.001). The model including thesevariables accounted for 47.0% of health behavior related to PM.
Conclusion
Korean older adults have the low level of health behaviorrelated to PM. The findings of this study emphasize that risk perception and attitude toward risk of PM should be evaluated, and theunderlying diseases related to PM and their service experience should be considered in developing intervention to improve health behaviorrelated to PM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Validation of the Dust Exposure Reduction Behavior Scale
Sung Woo Hwang, Hyun Kyoung Kim
Sage Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Graduate Students’ Perception and Behavior Related to Climate Change and Health: A Secondary Data Analysis
Min Kyung Park, Seoyoung Baek, Da Woon Jeong, Gwang Suk Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(1): 71. CrossRef - The association between depression and non‐compliance with COVID‐19 preventive behaviors in South Korean older adults stratified by sex
Jae Jun Lee, Namhee Kim, Min Kyung Park, Hyunju Ji, Gwang Suk Kim
International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation between Particulate Matter Concentrations in Rural Villages in Wanju-gun and the Air Pollution Monitoring Network
Minji Lee, Dongphil Choi, Kyungsu Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(1): 139. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Augmented Reality-Based Education on Fine Dust for the Elderly
Jung-Rim Huh, Kon-Joon Bhang
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2021; 22(6): 979. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on the Policy for Facilitating of Health Behaviors Related to Particulate Matter: Using Topic and Semantic Network Analysis of Media Text
Hye Min Byun, You Jin Park, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(1): 68. CrossRef - Environmental Factors Related to Non-compliant Health Behaviors in Urban-Dwelling Elderly
Minkyung Park, Jisu Park, Sunhye Moon, Heejung Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(4): 361. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Particulate Matter-Related Health Behaviors of Patients with Pulmonary Disease
Joohee Ham, SeungHye Choi, Smi Choi-Kwon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(5): 504. CrossRef
- Development and Validation of the Dust Exposure Reduction Behavior Scale
- 1,268 View
- 27 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Effects of Oral Gargling with Aroma Solution in Psychiatric Inpatients: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
- Yun Ah Jung, Hee Sook Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(2):200-209. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.2.200
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of oral gargling with an aromatic solution on xerostomia, objective oral status, and oral health-related quality of life in psychiatric inpatients.
Methods
A nonequivalent control group with a non-synchronized design was used in this study. The experimental group (n=34) received oral gargling with an aroma solution, while the control group (n=33) gargled with 0.9% normal saline. Dependent variables were measured at pre-, post-, and follow-up test. Data were analyzed using an c2-test, Fisher’s exact probability test, t-tests, and repeated measures ANOVA using SPSS/WIN v.21.0.
Results
After the intervention, significant differences were revealed in xerostomia (F=15.30, p <.001), objective oral status (F=38.44, p <.001), and oral health-related quality of life (F=62.70, p <.001) with an interaction effect between group and time.
Conclusion
These findings indicate that gargling with an aroma solution is more effective than 0.9% normal saline for the oral health of psychiatric inpatients. Therefore gargling with an aroma can be safely recommended as a brief, economical, and positive intervention in clinical settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of sugar-free cola solution based on the ICOCFAS score in oral care of non-artificial airway patients with severe neurological conditions
Qingmei Wang, Yuanyuan Fan, Mei Chen, Ping Chen
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of aromatherapy-based oral care on oral conditions, salivary pH, and halitosis in older adults with dementia: Pilot study
Ae Kyung Chang, Bo kyoung Kim, Ah Young Kim
Geriatric Nursing.2023; 53: 109. CrossRef
- Application of sugar-free cola solution based on the ICOCFAS score in oral care of non-artificial airway patients with severe neurological conditions
- 1,190 View
- 16 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of Suicide Prevention Nursing Competency Programs for Visiting Nurses
- Jung Eun Kim, Suk-Sun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(1):14-25. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.1.14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose: The purpose of this study was to develop a suicide prevention nursing competency program for visiting nurses, and to examine the effect of this program on suicide prevention-related knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors.
Methods: A total of 66 visiting nurses were recruited from 10 public health centers and divided equally into the experimental and control group. For the experimental group, the suicide prevention nursing competency program was provided twice a week for 120 minutes across 3 weeks. Participants were asked questions related to suicide prevention knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors at pre, post, and 1 month after the intervention. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, a t-test, repeated measure ANOVA, and Friedman test.
Results: There were significant differences in knowledge and behaviors at the measured time periods, and significant differences in attitudes and behaviors between the two groups. There were also significant interactions between groups and times in attitudes and behaviors. These results suggest that the effects of the program were persistent until the 1-month follow-up.
Conclusion The developed suicide prevention nursing competency program is effective in evidence-based education for visiting nurses to increase suicide prevention-related knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gatekeeper competencies for suicide prevention among Korean social work students: a path model of the relationship between education and gatekeeper intention
Jungyai Ko
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating the Longitudinal Efficacy of Suicide CARE (a Korean Standard Gatekeeper Training Program) in a General Community Sample: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Jinmi Seol, Hwa-Young Lee, Sang Min Lee, Seon Wan Ki, Sung Joon Cho, Kang Seob Oh, Jong-Woo Paik
Psychiatry Investigation.2024; 21(12): 1329. CrossRef - Factors Related to Nursing Practices of General Visiting Nurses for Clients With Suicidal Ideation in Japan
Tomoko Chijiiwa, Kayoko Ishimura, Mutsuo Deguchi
Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services.2023; 61(1): 47. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Gatekeeper Training for Families of People With Mental Disorders in Korea: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Deuk-Kweon You, Jeoung-Mo Son, Tae-Yeon Hwang
Psychiatry Investigation.2023; 20(12): 1185. CrossRef - Effectiveness of an Educational Intervention on Clinical Competency among Mental Health Nurses Working at a Government Mental Health Hospital: A Quasi-experimental Study
Manal S.J. Alzahrani, Loujain S. Sharif
The Open Nursing Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationships among Knowledge and Skills about Suicide Prevention, Attitudes toward Suicide, and Burnout of Suicide Prevention Work of Nurses at Mental Health Welfare Centers: A Mixed Methods Study
Hee-Ra Dong, Ji Min Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 92. CrossRef - How Should We Approach Nurse Suicide in Korea: With the Aspect of Prevention-Intervention-Postvention Management
Hyoung Suk Kim, Hyun Ji Bae, Kyeong Hwa Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(4): 408. CrossRef
- Gatekeeper competencies for suicide prevention among Korean social work students: a path model of the relationship between education and gatekeeper intention
- 2,634 View
- 70 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Prediction Model for Nursing Work Outcome of Nurses - Focused on Positive Psychological Capital
- Soon Neum Lee, Jung A Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(1):1-13. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose: The purpose of this study was to construct and test a structural equation model on nursing work outcomes based on Youssef and Luthans’ positive psychological capital and integrated conceptual framework of work performance.
Methods: This study used a structured questionnaire administered to 340 nurses. Data were analyzed using structural equation modeling.
Results: Positive psychological capital showed indirect and direct effects on job satisfaction, retention intention, organizational citizenship behavior, and nursing performance. While, the nursing work environment had direct and indirect effects on job satisfaction and nursing performance, it only had indirect effects on intention to work and organizational citizenship behavior. Additionally, a mediating effect on retention intention and organizational citizenship behavior was found between job satisfaction and nursing performance variables.
Conclusion: The nursing organization needs to build a supportive work environment and reinforce positive psychological capital to improve nursing performance. Additionally, it needs to actively manage the necessary parameters involved in the stages of job satisfaction, retention intention, nursing performance, and organizational citizenship behavior of nurses. The findings propose the continuous management of nursing personnel based on nurses’ attitude outcome, behavioral intention, behavioral outcome, and stage of role performance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of the Empowering Leadership of Nurse Unit Managers on Patient Safety Nursing Activities: Double Mediating Effects of Positive Psychological Capital and Work Engagement
Jin-Young Park, Eungyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 516. CrossRef - Social Support and Psychological Capital Mediate the Effect of Personalities on the Mental Health of Professional Staff in China During COVID-19 Pandemic
Yongcheng Yao, Jie Tang, Zhenzhen Li, Shuyan Chen, Haixia Du, Lingeng Lu
Psychology Research and Behavior Management.2024; Volume 17: 3443. CrossRef - Individual‐level positive psychological capital that enhances managers' transformational leadership effectiveness on nurse career success
Sujin Jung, Kihye Han, Kyeongsug Kim
International Nursing Review.2024; 71(4): 977. CrossRef - Effect of Transition Shock on Intention to Stay in Newly Graduated Nurses : The Mediating Effect of Positive Psychological Capital
Hyuna Kam, Chanhee Kim, Yeonok Yoon, Heeyoung Shin, Junghwa Lee, Myoungohk Kim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(3): 25. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Performance of Intensive Care Unit Nurses: Role of Clinical Reasoning Competence, Positive Psychological Capital, and Nursing Work Environment
MiRim Heo, Haena Jang
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(2): 83. CrossRef - Effect of positive psychological capital on burnout in public hospital nurses: Mediating effect of compassion fatigue is greater than compassion satisfaction
Sin Ah Kim, Sung Reul Kim, Hye Young Kim
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychological capital and organizational citizenship behavior among nurses during the COVID-19 epidemic: mediation of organizational commitment
Li Zeng, Fen Feng, Man Jin, Wanqing Xie, Xin Li, Lan Li, Yihang Peng, Jialin Wang
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Nurses’ Workplace Bullying, Social Interaction Anxiety and Positive Psychological Capital on Nursing Performance
Hyang Mi Kim, Sun Hee Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(3): 331. CrossRef - BİLİNÇLİ FARKINDALIK VE ÇALIŞAN İYİ OLUŞU ARASINDAKİ İLİŞKİDE PSİKOLOJİK SERMAYENİN ARACILIK ROLÜ: HEMŞİRELER ÜZERİNE BİR İNCELEME
Emrehan KÜÇÜK, Selin METİN CAMGÖZ
Mehmet Akif Ersoy Üniversitesi İktisadi ve İdari Bilimler Fakültesi Dergisi.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Moderating Effect of Organizational Justice on the Relationship between Self-Efficacy and Nursing Performance in Clinical Nurses
Ju-Ra Kim, Yukyung Ko, Youngjin Lee, Chun-Ja Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(5): 511. CrossRef - Effects of Positive Psychological Capital, Job Crafting and Job Satisfaction on Intention of Retention in Hospital Nurses
Eun-Ah Lee, Yeongmi Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(5): 586. CrossRef - Investigation of the relationship between psychological resilience and job performance in Turkish nurses during the Covid‐19 pandemic in terms of descriptive characteristics
Haydar Hoşgör, Mevlüt Yaman
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(1): 44. CrossRef - How Nurses Perceived Their Work-Environments and Its Related Nursing Management Perspectives during the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Investigatory Study
Elsa Vitale
Psych.2022; 4(4): 747. CrossRef - Influence of gender role conflict, resilience, and nursing organizational culture on nursing work performance among clinical nurses
Ji Eon Han, Nam Hee Park, Jeonghyun Cho
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(3): 248. CrossRef - Influences of Type D Personality, Positive Psychological Capital, and Emotional Labor on the Burnout of Psychiatric Nurses
Seung Mi Park, Myung Ha Lee, Ji Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2020; 29(2): 133. CrossRef
- Impact of the Empowering Leadership of Nurse Unit Managers on Patient Safety Nursing Activities: Double Mediating Effects of Positive Psychological Capital and Work Engagement
- 2,684 View
- 81 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- Factors Relating to the Quality of Care for Nursing Home Residents in Korea: Using the Delphi Method
- Juh Hyun Shin, Eun Mee Kim, Ji Yeon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):783-794. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.783
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study identified factors related to the quality of care in nursing homes, and elicited consensus opinions from experts on nursing homes.
Methods A Delphi questionnaire was developed based on a review of the literature using the keywords “nursing homes,” “workforce,” and “quality of care.” A total of two Delphi surveys were conducted with 14 experts. The important and urgent factors related to the quality of care for nursing home residents emerged.
Results A consensus was achieved on the important and urgent factors relating to the quality of care. The related factors were grouped into four sections: Organizational Characteristics, Staffing Characteristics, the Long-Term Care Market and Legal and Policy Issues, and Nursing Processes. In total, 23 items were important factors and 26 items were urgent factors relating to the quality of care. In addition, the unanimous advocacy by the experts for increased hours per resident day for registered nurses (RNs, 41 minutes 59 seconds) was much higher than the current hours per resident day of RNs in Korea.
Conclusion To provide optimal care for residents in nursing homes in Korea, the mandatory and essential placement of RNs with professional knowledge and skills is paramount.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of special nursing units in nursing homes on healthcare utilization and cost: A case-control study using propensity score matching
Eunhee Cho, Eun-Young Kim, Kyung Hee Lee, Hye-Ryoung Kim, Seonhwa Choi, Yea Seul Yoon, EunKyo Kim, Seok-Jae Heo, Se Young Jung, Jiyoon Jang
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2023; 147: 104587. CrossRef - Effects of registered nurse staffing levels, work environment, and education levels on adverse events in nursing homes
Seonhwa Choi, Eunhee Cho, Eunkyo Kim, Kyongeun Lee, Soo Jung Chang
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cost of Care and Pattern of Medical Care Use in the Last Year of Life among Long-Term Care Insurance Beneficiaries in South Korea: Using National Claims Data
Sunjoo Boo, Jungah Lee, Hyunjin Oh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(23): 9078. CrossRef - Impact of Nurse Staffing, Skill Mix and Stability on Resident Health Outcomes in Korean Nursing Homes
Juh Hyun Shin, Gui Yun Choi, Jiyeon Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2020; 22(4): 291. CrossRef - The Effects of Long-term Care Hospitals' Nurse Staffing Level on Patient Outcomes: Differences according to Region
Kyung Jin Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 354. CrossRef
- The effects of special nursing units in nursing homes on healthcare utilization and cost: A case-control study using propensity score matching
- 1,856 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Effects of Spouse-Participated Health Coaching for Male Office Workers with Cardiocerebrovascular Risk Factors
- So Hee Kang, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):748-759. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.748
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to examine the effect of spouses participating in health coaching on stage of the change, health behaviors, and physiological indicators among male office workers with cardiocerebrovascular disease (CVD) risk factors and compare the findings with trainers who provided health coaching only to workers.
Methods A quasi-experimental pretest-posttest design was used. Convenience sampling was used to recruit participants from a manufacturing research and development company in the city of Gyeonggi province. The health coaching program for the experimental group (n=26) included individual counseling sessions according to workers' stage of change, and provision of customized health information materials on CVD prevention to workers and their spouses for 12 weeks through mobile phone and email.
Results After 12 weeks of intervention, the total score for health behavior, and scores on the sub-areas of exercise and health checkups significantly improved in the experimental group, but there were no significant differences in the scores of stage of the change and physical indicators. The results of a paired t-test showed a significant decrease in the body mass index, abdominal circumference, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol and triglyceride values, and a significant increase in the high-density lipoprotein cholesterol value in the experimental group after the intervention.
Conclusion To improve the health of male workers with CVD risk factors in the workplace, sharing health information with their spouses has proven to be more effective than health coaching for only workers. Therefore, it is important to develop strategies to encourage spousal participation when planning workplace health education for changing health-related behaviors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun Jin Kim, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(1): 44. CrossRef - Effects of a Remote Physical Activity Improvement Program on Male Office Workers with Metabolic Syndrome in Their 30s and 40s with Sedentary Behavior: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Kyong Sil Park, Seon Young Hwang
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - An intervention study of a combined intervention of positioning and hand massage in patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation
Yun Kyeong Lee, Mihae Im, Haeryun Cho
Nursing Open.2023; 10(3): 1404. CrossRef
- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 966 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Public Reporting on the Quality Ratings of Nursing Homes in the Republic of Korea
- Hyang Yuol Lee, Juh Hyun Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):161-170. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.161
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Quality ratings could provide vital information to help people in choosing a nursing home.
Purpose This study investigated factors aligned with quality ratings of nursing homes.
Methods We employed a cross-sectional descriptive design to assess publicly available data on 1,354 nursing homes with 30 or more beds in the Republic of Korea. After excluding 289 nursing homes with no reported quality-evaluation ratings, we analyzed the 2015 data of 1,065 nursing homes. To prevent multicollinearity among independent variables, we carefully selected the final set of variables based on clinical and theoretical meaningfulness to direct nursing care. Quality, the ordinal outcome, was scored from 1 to 5 with a higher score indicating higher quality of the organization. We constructed a multivariate ordered logistic regression model.
Results Higher quality ratings of nursing homes was significantly related to the number of unoccupied beds (OR=0.99,
p =.024), registered nurses (RNs) (OR=1.30,p =.003), qualified care workers (OR=1.03,p =.011), cognitive-improvement programs (OR=1.05,p =.024), and other programs for residents' activities (OR=1.09,p <.001).Conclusion The number of RNs had the strongest influence on the publicly reported quality rating, while the rating of qualified care workers demonstrated little effect and that of nursing assistants had no effect. The number of RNs could be used as a crucial indicator for high-quality homes; more resident-engaging programs also demonstrated better quality of nursing home care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Performance indicators on long-term care for older people in 43 high- and middle-income countries: literature review, web search and expert consultation
Mircha Poldrugovac, Joost D. Wammes, Véronique L. L. C. Bos, Erica Barbazza, Damir Ivanković, Hanneke Merten, Janet L. MacNeil Vroomen, Niek S. Klazinga, Dionne S. Kringos
BMC Health Services Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficiency and equity of elderly care service resource allocation in China, 2014–2022
Min Bao, Rongji Ma, Jianqian Chao
Health Policy and Technology.2025; 14(3): 101016. CrossRef - Institutional and individual factors influencing urinary tract infections and pressure injuries in Korean nursing home residents: A multilevel analysis of National Health Insurance Service Data
Hee Seung Lee, Jung Suk Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(4): 349. CrossRef - Nurse staffing and adverse events in residential aged care: Retrospective multi-site analysis
Dorika Nhongo, Annie Holt, Tracy Flenady, Amanda Rebar, Kasia Bail
Collegian.2023; 30(2): 343. CrossRef - Nursing Management-Associated Factors Associated with Urinary Tract Infection in Residents from Nursing Home Based on LTCfocus Database
Wei Wang, Hui Wang
Urologia Internationalis.2022; 106(7): 744. CrossRef - Effects of registered nurse staffing levels, work environment, and education levels on adverse events in nursing homes
Seonhwa Choi, Eunhee Cho, Eunkyo Kim, Kyongeun Lee, Soo Jung Chang
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Increasing Registered Nurse Hours Per Resident Day for Improved Nursing Home Residents’ Outcomes Using a Longitudinal Study
Juh Hyun Shin, Rosemary Anne Renaut, Mark Reiser, Ji Yeon Lee, Ty Yi Tang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(2): 402. CrossRef
- Performance indicators on long-term care for older people in 43 high- and middle-income countries: literature review, web search and expert consultation
- 2,201 View
- 11 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of a Daily Life-Based Physical Activity Enhancement Program for Middle-Aged Women at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
- Kyung Ae Kim, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):113-125. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of a daily life-based physical activity enhancement program performed by middle-aged women at risk for cardiovascular disease.
Methods This study used a randomized control group pretest-posttest design. Middle-aged women aged 45 to 64 were recruited from two outpatient cardiology departments, and randomly assigned to an experimental group (n=28) and a control group (n=30). For the experimental group, after providing one-on-one counseling and education, we provided customized text messages to motivate them in daily life. To monitor the practice of physical activity, they also used an exercise diary and mobile pedometer for 12 weeks. Subjects' physical activities (MET-min/week) were measured using the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ). Their physiological data were obtained by blood tests using a portable analyzer, and the data were analyzed using the SPSS 21.0/WIN program.
Results There were significant differences in exercise self-efficacy, health behavior, IPAQ score, body fat, body muscle, and fasting blood sugar between the two groups. However, there were no significant differences in total cholesterol, hemoglobin A1c, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and waist-to-hip ratio.
Conclusion Strengthening physical activity in daily life without being limited by cost burden and time and space constraints. Therefore, it is essential to motivate middle-aged women at risk for cardiovascular disease to practice activities that are easily performed in their daily lives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and effectiveness of a mobile-based autonomy support program for the prevention of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged women
Miseon Seo, Eun-Young Jun, Hyunjin Oh
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Remote Physical Activity Improvement Program on Male Office Workers with Metabolic Syndrome in Their 30s and 40s with Sedentary Behavior: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Kyong Sil Park, Seon Young Hwang
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - Effects of Breathing Exercises Using Virtual Reality and Schroth Breathing Exercises on the Lung Function of Adults in Their 20s
Byung-Kon Kim, Wook-Jin Lee
The Journal of Korean Physical Therapy.2024; 36(2): 67. CrossRef - Effectiveness of physical activity monitors in adults: systematic review and meta-analysis
Rasmus Tolstrup Larsen, Vibeke Wagner, Christoffer Bruun Korfitsen, Camilla Keller, Carsten Bogh Juhl, Henning Langberg, Jan Christensen
BMJ.2022; : e068047. CrossRef - Trajectories of subjective health status among married postmenopausal women based on the ecological system theory: a longitudinal analysis using a latent growth model
Eun Jin Kim, Ju-Hee Nho
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(2): 123. CrossRef - Effect and mechanism of tai chi on blood pressure of patients with essential hypertension: a randomized controlled study
Bo LIN, Qiu JIN, Chunhua LIU, Wenhui ZHAO, Runyuan JI
The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of behaviour change interventions on changes in physical activity and anthropometrics in ambulatory hospital settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Stephen Barrett, Stephen Begg, Paul O’Halloran, Owen Howlett, Jack Lawrence, Michael Kingsley
International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors related to the Identification of Middle-Aged Women Who are Disadvantaged by Cardio-cerebrovascular Disease
Moon Jung Kang, Jee Seon Yi, Chang Seung Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(2): 185. CrossRef
- Development and effectiveness of a mobile-based autonomy support program for the prevention of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged women
- 2,174 View
- 43 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Influencing Factors and Consequences of Near Miss Experience in Nurses’ Medication Error
- Jin Hee Park, Eun Nam Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(5):631-642. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.5.631
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to predict the influencing factors and the consequences of near miss in nurses’ medication error based upon Salazar & Primomo's ecological system theory.
Methods A convenience sample of 198 nurses was recruited for the cross-sectional survey design. Data were collected from July to September 2016. Using the collected data, the developed model was verified by structural equation modeling analysis using SPSS and AMOS program.
Results For the fitness of the hypothetical model, the results showed that χ 2 (χ 2=258.50,
p <.001) was not fit, but standardized χ 2 (χ 2/df=2.35) was a good fit for this model. Additionally, absolute fit index RMR=.06, RMSEA=.08, GFI=.86, AGFI=.81 reached the recommended level, but the Incremental fit index TLI=.82, CFI=.85 was not enough to reach to the recommended level. With the path diagram of the hypothetical model, caution (β=-.29p <.001), patient safety culture (β=-.20,p =.041), and work load (β=.18,p =.037) had a significant effect on the near miss experiences in nurses’ medication error, while fatigue (β=-.06,p =.575) did not affect it. Moreover, the near miss experience had a significant effect on work productivity (β=-.25,p =.001).Conclusion These results have shown that to decrease the near miss experience by nurses and increase their work productivity in hospital environments would require both personal and organizational effort.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of aroma inhalation on the quality of sleep, professional quality of life, and near-misses in medication errors among emergency room nurses on night duty in Korea: a randomized controlled trial
Jungha Son, Chul-Gyu Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(1): 25. CrossRef - Effects of Clinical Nurses’ Communication Ability, Critical Reflection Competency, and Nursing Professional Self-efficacy
on Medication Safety Competency
Seongyoun Jang, Sujin Shin
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2025; 13(1): 43. CrossRef - The effect of a clinical decision-making program for preventing high-alert medication errors among intensive care unit nurses in South Korea: a quasi-experimental study with a nonequivalent control group design
Se Yeong Park, SoMi Park, Ga Young Kim, Seung Ah Hong, Hyang Ok Choi, Sunyoung Moon
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(3): 366. CrossRef - A comparative study of back pain, task-load and presenteeism in nursing homes
Hye Young Shim, Jin H. Park, Sook Hee Jeong
Disability and Rehabilitation: Assistive Technology.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Nursing near miss: a concept analysis
Dan Zhou, Sisi Guo, Qin Tan, Xuerong Lin
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association of Job Stress, Quality of Sleep, and the Experience of Near-Miss Errors among Nurses in General Hospitals
Seong-Kyeong Kwak, Jin-Soo Ahn, Yeon-Ha Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(6): 699. CrossRef - Association between Nurses’ Perceptions of Patient Safety Culture, Willingness to Report Near Misses, Critical Thinking Disposition, and Nursing Care Activities for Patient Safety
Da Eun Lee, Bo Gyeong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 283. CrossRef - The associations of psychological burnout and time factors on medication errors in rotating shift nurses in Korea: A cross sectional descriptive study
Cheongin Im, Suyoung Song, Kyoungja Kim
Nursing Open.2023; 10(8): 5550. CrossRef - Clinical nurses’ recovery experiences after adverse events in South Korea: A qualitative study
Hyoung Eun Chang, Haena Jang, Yong Ik Bak
Collegian.2022; 29(4): 456. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Nursing Work Interruption Scale
Eun-Jeong Yu, Eun-Nam Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(20): 13487. CrossRef - Relationship between Clinical Nurses' Job Stress and Medication Safety Performance: Mediating Effect of Fatigue
Se Yeong Park, Hea Kung Hur
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 283. CrossRef - A Study on Factors Affecting Near Misses by Nurses in Small-Medium Sized Hospitals
San-Na Lee, Seon-Ha Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(2): 75. CrossRef - Impact of Hospital Nurses’ Perception on Clinical Alarms and Patient Safety Culture on Alarm Management Practice
Soo-Joung Lee, Yun-Mi Lee, Eun Ji Seo, Youn-Jung Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4018. CrossRef - Factors causing medication errors in an electronic reporting system
Seonhee Yoon, Kyeongyae Sohng
Nursing Open.2021; 8(6): 3251. CrossRef
- The effects of aroma inhalation on the quality of sleep, professional quality of life, and near-misses in medication errors among emergency room nurses on night duty in Korea: a randomized controlled trial
- 2,348 View
- 141 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


