Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Perspectives of parents, teachers, and community leaders on adolescent sexual behavior across ecological contexts in Cambodia: a qualitative study
- Youngran Yang, Gloria Park
- Received October 31, 2025 Accepted January 24, 2026 Published online February 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25146 [Epub ahead of print]
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study investigated the perspectives of parents, teachers, and community leaders regarding adolescents’ sexual behavior in Cambodia.
Methods
Grounded in the ‘ecological framework of adolescent health,’ this study employed a descriptive qualitative approach to explore the perspectives of key stakeholders, including 12 parents, eight teachers, and four community leaders. Drawing on in-depth, semi-structured individual and focus group interviews, the study examined risk and protective factors related to risky sexual behavior across family, school, community, social, cultural, and policy contexts. Data collection was conducted from December 5, 2022 to January 31, 2023.
Results
The integrated thematic analysis revealed six main themes. Parents positioned themselves as anxious protectors but struggled with limited opportunities for open conversation; teachers acted as observe-and-warn mediators, constrained by institutional authority, curricular boundaries, and rapidly shifting youth culture; and community leaders interpreted emerging trends through the lens of social change, eroding traditions, and weakening collective governance. Across groups, participants acknowledged the limitations of unilateral action and advocated for multilevel, collaborative solutions that bridge families, schools, and broader communities.
Conclusion
The study concluded that adolescent sexual behaviors should be understood from diverse perspectives. This finding highlights the need for culturally appropriate and sensitive measures supported by multisectoral systems operating at the family, school, community, civil society (e.g., non-governmental organizations), and national levels.
- 131 View
- 1 Download

- Factors influencing smartphone overdependence in university students: an ecological model: a descriptive study
- Jeong Soon Yu, Myung Soon Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):64-80. Published online February 20, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24092
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
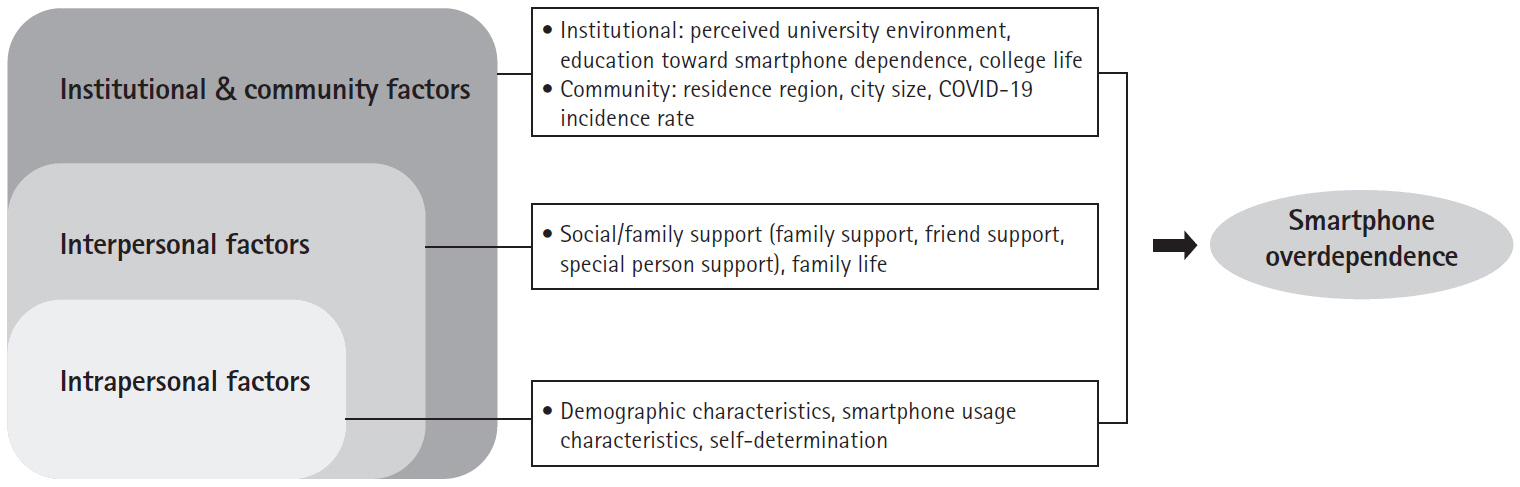
This study investigated the factors influencing smartphone overdependence in university students using an ecological model and descriptive research.
Methods
Data were collected from 482 students at 13 universities in the six regions in South Korea from October 20, 2020, to March 25, 2021. Data analysis involved descriptive statistics, the chi-square test, the independent samples t-test, analysis of variance, and hierarchical multiple regression.
Results
The significant ecological factors influencing smartphone overdependence included self-awareness of smartphone overdependence (β=.33, p<.001), autonomy (β=–.25, p<.001), average daily smartphone usage time (β=.18, p<.001), gender (β=.15, p=.001), college year (β=.15, p=.020), forming relationships with others as a motivation for smartphone use (β=–.15, p=.008), friend support (β=.14, p=.006), and age (β=–.12, p=.047). The model explained 34.9% of the variance.
Conclusion
The study emphasized the role of personal and interpersonal factors, in smartphone overdependence among university students. Tailored intervention strategies are necessary to address smartphone overdependence, considering the unique characteristics of students’ environments. A significant aspect of this study is that it provides an explanation of the multidimensional factors contributing to smartphone overdependence among university students, including intrapersonal, interpersonal, and environmental influences.
- 3,715 View
- 195 Download

- Mediating effect of grit on the influence of nurses’ silence behavior on medication safety competence: a cross-sectional study
- Haengsuk Kim, Wanju Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):81-92. Published online February 20, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24088
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
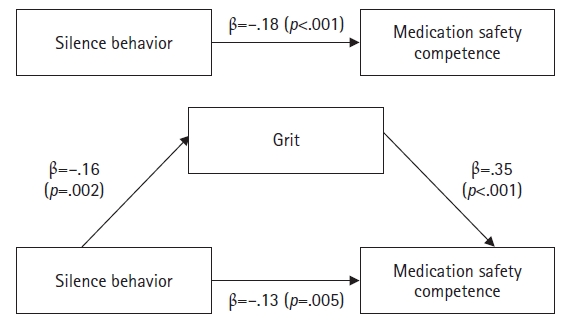
This study investigated the mediating effect of grit in the relationship between silence behavior and medication safety competence among nurses.
Methods
The study included 166 nurses from four university hospitals and general hospitals in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do, South Korea. Data were collected from March 1 to 10, 2024, using self-report questionnaires. Data were analyzed using the t-test, analysis of variance, Scheffé’s test, and Pearson’s correlation coefficients with IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 23.0 (IBM Corp.). A mediation analysis was performed using Hayes’s PROCESS macro model 4 and the bootstrapping method.
Results
Medication safety competence showed significant correlations with silence behavior (r=–.21, p=.008) and grit (r=.43, p<.001). Furthermore, grit partially mediated the relationship between silence behavior and medication safety competence.
Conclusion
This study indicates that grit is a significant mediator in the relationship between silence behavior and medication safety competence. Therefore, an integrated approach that reduces silence behavior and promotes grit is essential for strengthening nurses’ medication safety competence. Ultimately, these strategies will help ensure patient safety by improving medication safety competence.
- 5,403 View
- 468 Download

- Examination of Predicting Factors for COVID-19 Vaccination Behaviors of University Students Utilizing the Theory of Planned Behavior
- Yeon Jeong Heo, Hye-Jin Hyun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):178-192. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24020
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the predictive factors of COVID-19 vaccination behavior by evaluating the moderating effect of perceived behavioral control on the theory of planned behavior.
Methods
Data were collected from August 6 to August 31, 2022 from 235 college students (aged 20~29 years) across 12 universities using a structured web-based survey. Statistical analyses were conducted using the SPSS and AMOS software.
Results
Attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccination, subjective norms, and intention to be vaccinated significantly influenced COVID-19 vaccination behavior. Attitudes and subjective norms indirectly affected COVID-19 vaccination behavior through intention to vaccinate, whereas intention to vaccinate had a direct effect. The moderating effect of perceived behavioral control on the relationship between subjective norms and intention to vaccinate was significant.
Conclusion
Interventions that foster a positive attitude toward COVID-19 vaccination and bolster subjective norms and perceived behavioral control can boost the intention to be vaccinated and facilitate the uptake of COVID-19 vaccination.
- 1,559 View
- 43 Download

- Development of the Hospital Nurses’ Silence Behavior Scale
- Soojin Chung, Jee-In Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):279-295. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23138
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure hospital nurses’ silence behavior and examine its validity and reliability.
Methods
A total of 52 preliminary items on hospital nurses’ silence behavior were selected using a content validity test by seven experts on 53 candidate items derived from a literature review and in-depth interviews with 14 nurses. A total of 405 hospital nurses participated in a psychometric testing. Data analysis comprised item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses, and convergent and discriminant validity tests. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used for assessing concurrent validity, and Cronbach’s alpha was used for the reliability test.
Results
The final scale consisted of nine factors with 31 items, exhibiting acceptable model fit indices, convergent validity, and discriminant validity. The score of the entire scale was positively correlated with the ‘Organizational Silence Scale (OSS)-the issues on which nurses remain silent’ (r = .60, p < .001) and ‘OSS-the reasons why nurses remain silent’ (r = .68, p < .001). Cronbach’s α of the scale was .92, and α of each subscale ranged from .71 to .90.
Conclusion
The Hospital Nurses’ Silence Behavior Scale is a useful tool for assessing multifaceted silence behavior among nurses. It can provide basic data for developing better communication strategies among nurses and other hospital staff. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating Effect of Emotional Labour on the Role Pressure and Silence Behaviour of Nurses
Lianci He, Jianhua Liu, Rong Sun, Yuan Deng, Ling Tang, Shaochuan Chen
Evaluation & the Health Professions.2026; 49(1): 3. CrossRef - Mediating effect of grit on the influence of nurses’ silence behavior on medication safety competence: a cross-sectional study
Haengsuk Kim, Wanju Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(1): 81. CrossRef - Influence of Clinical Nurses’ Organizational Silence on Organizational Citizenship Behavior: Mediating Effect of Organizational Commitment Moderated by Organizational Justice
Shin Ae Hwang, Haeyoung Min
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 416. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation and translation of the Persian version of the Organizational Silence Behavior Scale (OSBS-P) for clinical nurses
Alireza Mirzaei, Mobina Jamshidinia, Mehrzad Aghabarari, Pouya Dolat Abadi, Reza Nemati-Vakilabad, Ehsan Namaziandost
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(12): e0314155. CrossRef
- Mediating Effect of Emotional Labour on the Role Pressure and Silence Behaviour of Nurses
- 4,735 View
- 280 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Influence of Illness Uncertainty on Health Behavior in Individuals with Coronary Artery Disease: A Path Analysis
- Hyesun Jeong, Yesul Lee, Jin Sup Park, Yoonju Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):162-177. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the influence of uncertainty-related factors on the health behavior of individuals with coronary artery disease (CAD) based on Mishel’s uncertainty in illness theory (UIT).
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional study and path analysis to investigate uncertainty and factors related to health behavior. The study participants were 228 CAD patients who visited the outpatient cardiology department between September 2020 and June 2021. We used SPSS 25.0 and AMOS 25.0 software to analyze the data.
Results
The final model demonstrated a good fit with the data. Eleven of the twelve paths were significant. Uncertainty positively affected danger and negatively affected self-efficacy and opportunity. Danger had a positive effect on perceived risk. Opportunity positively affected social support, self-efficacy, perceived benefit and intention, whereas it negatively affected perceived risk. Social support, self-efficacy, perceived benefit and intention had a positive effect on health behavior. We found that perceived benefit and intention had the most significant direct effects, whereas self-efficacy indirectly affected the relationship between uncertainty and health behavior.
Conclusion
The path model is suitable for predicting the health behavior of CAD patients who experience uncertainty. When patients experience uncertainty, interventions to increase their self-efficacy are required first. Additionally, we need to develop programs that quickly shift to appraisal uncertainty as an opportunity, increase perceived benefits of health behavior, and improve intentions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health uncertainty: Scale development and its effect on health behaviors
Rui Ren, Su Tao, Yuhua Ouyang, Wenchong Du
Journal of Health Psychology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Self-Care, Resilience, and Uncertainty in Patients After Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
Eun-Hye Park, JiYeon Choi, Phill Ja Kim, Jiyeon Lee
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Coping Profiles and Cardiac Health Behavior among Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: A Latent Profile Analysis
Yesul Lee, Yoonju Lee, Jeong Cheon Choe, Hyesun Jeong, Sunyoung Jung
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(3): 228. CrossRef
- Health uncertainty: Scale development and its effect on health behaviors
- 3,620 View
- 175 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Eun Jin Kim, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):44-58. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23090
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to apply a health partnership program using commercially available mobile health apps to improve cardiovascular risk factors in male employees and verify its effectiveness.
Methods
Using a randomized control group pretest-posttest design, male employees with cardiovascular risk factors from five small and medium-sized workplaces were randomly assigned to an experimental group (n = 32) and a control group (n = 31). The experimental group was encouraged to use three mobile health apps for 12 weeks to acquire the necessary cardiovascular disease-related information and practice strengthening training, walking, and diet management appropriate to their level. They also received feedback on their weekly activities and motivational text messages from health partners. Hypotheses were tested using the SPSS WIN 22.0.
Results
The experimental group showed a significant difference compared to the control group in terms of their perception of mobile health app (p < .05), self-efficacy for exercise and diet, self-management partnership, and cardiovascular disease prevention health behavior (p < .001). In particular, there were significant decreases in the body mass index, ratio, serum fasting blood sugar, total cholesterol, and triglyceride in the experimental group (p < .001); however, there was no significant difference in high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol.
Conclusion
Intervention using mobile apps based on partnership with health managers is effective in improving the objective cardiovascular risk index in male employees; therefore, such intervention should be continuously used as a useful lifestyle modification strategy in the workplace. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adherence to a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Yura Shin, Jina Choo, Songwhi Noh
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Adherence to a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
- 3,644 View
- 208 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Development of Nursing Clinical Judgment Scale
- Shi Nae Kwon, Hyojung Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):652-665. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23042
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a nursing clinical judgment scale (NCJS) and verify its validity and reliability in assessing the clinical judgment of nurses.
Methods
A preliminary instrument of the NCJS comprising 38 items was first developed from attributes and indicators derived from a literature review and an in-depth/focus interview with 12 clinical nurses. The preliminary tool was finalized after 7 experts conducted a content validity test based on a data from a preliminary survey of 30 hospital nurses in Korea. Data were collected from 443 ward, intensive care unit, emergency room nurses who voluntarily participated in the survey through offline and online for the verification of the construct validity and reliability of the scale.
Results
The final scale comprised 23 items scored on a 5-point Likert scale. Six factors – integrated data analysis, evaluation and reflection on interventions, evidence on interventions, collaboration among health professionals, patient-centered nursing, and collaboration among nurse colleagues – accounted for 64.9% of the total variance. Confirmatory factor analysis supported the fit of the measurement model, comprising six factors (root mean square error of approximation = .07, standardized root mean square residual = .04, comparative fit index = .90). Cronbach’s α for all the items was .92.
Conclusion
The NCJS is a valid and reliable tool that fully reflects the characteristics of clinical practice, and it can be used effectively to evaluate the clinical judgment of Korean nurses. Future research should reflect the variables influencing clinical judgment and develop an action plan to improve it. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How the nursing work environment moderates the relationship between clinical judgment and person-centered care among intensive care unit nurses
Mi Hwa Seo, Eun A. Kim, Hae Ran Kim, Mohammad Jamil Rababa
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(1): e0316654. CrossRef - Effects of Critical Thinking Disposition, Clinical Judgement, and Nurse–Physician Collaboration on Triage Competency Among Triage Nurses
Ji-Won Song, Hyung-Ran Park
Healthcare.2025; 13(4): 405. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a virtual reality nursing simulation for pediatric pneumonia care: a Korean pilot study using a single-group pre-post test design
Eun Joo Kim, Seong Kwang Kim, Sung Sook Song
Child Health Nursing Research.2025; 31(4): 198. CrossRef - The Influence of Clinical Nurses' Clinical Judgment, Nursing Work Environment and Ethical Nursing Competence on Patient Safety Nursing Activities
Eunseo Hong, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2025; 39(3): 368. CrossRef
- How the nursing work environment moderates the relationship between clinical judgment and person-centered care among intensive care unit nurses
- 4,830 View
- 293 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Adolescents’ Experiences of Non-Suicidal Self-Injury: An Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis Study
- Jung A Ko, Ji Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(5):538-555. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23075
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This qualitative study used interpretative phenomenological analysis and photovoice methods to explore the meaning of non-suicidal self-injury experienced by adolescents.
Methods
Participants were adolescents enrolled in middle and high schools in Gyeonggi-do and Jeollabuk-do who were selected through snowball sampling. Six participants had repeatedly engaged in self-injurious behavior for over a year. Data were collected through in-depth interviews and the photovoice method between November 2020 and July 2021. The collected data were analyzed using six steps of interpretative phenomenological analysis.
Results
The results yielded 5 main themes and 18 subthemes. The main themes were ‘a silent cry to an indifferent world’, ‘a heartache that one endures with scars’, ‘an inescapable cycle’, ‘filling the space in one’s heart’, and ‘healing the wounds’. The study findings revealed that the self-injurious behavior of adolescents began as a consequence of feeling lost and struggling with conflicts at home and school, which helped them relieve tension and pain. Nonetheless, inflicting self-injury only left signs of regret and remorse, which became a trace that the participants wanted to hide. However, the wounds healed after receiving attention and support from others. They were determined to stop engaging in repeated self-injurious behaviors and made efforts to do so.
Conclusion
This study can be used as a basis for the development of educational programs to prevent non-suicidal self-injury in adolescents. Additionally, it can inform nursing interventions that focus on building support systems to help adolescents who attempt self-injury. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Collaborative Immersive Virtual Environments in Geography Education on Climate Zones: A UX Case Study
Martina Střechová, Michal Černý, Čeněk Šašinka, Zdeněk Stachoň, Alžběta Šašinková, František Holubec, Hana Švédová
ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information.2025; 14(12): 455. CrossRef - Experiences of Male Nursing Students in Women's Health Nursing Practicum: A Mixed-Methods Study Using Photovoice
Na Won An, Na Kyoung Lee
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2024; 9(2): 104. CrossRef
- Collaborative Immersive Virtual Environments in Geography Education on Climate Zones: A UX Case Study
- 6,404 View
- 122 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Exploring Spatial Variations and Factors associated with Walking Practice in Korea: An Empirical Study based on Geographically Weighted Regression
- Eunjoo Kim, Yeongseo Lee, Ju Young Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):426-438. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23045
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Walking practice is a representative indicator of the level of physical activity of local residents. Although the world health organization addressed reduction in prevalence of insufficient physical activity as a global target, the rate of walking practice in Korea has not improved and there are large regional disparities. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the spatial variations of walking practice and its associated factors in Korea.
Methods
A secondary analysis was conducted using Community Health Outcome and Health Determinants Database 1.3 from Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A total of 229 districts was included in the analysis. We compared the ordinary least squares (OLS) and the geographically weighted regression (GWR) to explore the associated factors of walking practice. MGWR 2.2.1 software was used to explore the spatial distribution of walking practice and modeling the GWR.
Results
Walking practice had spatial variations across the country. The results showed that the GWR model had better accommodation of spatial autocorrelation than the OLS model. The GWR results indicated that different predictors of walking practice across regions of Korea.
Conclusion
The findings of this study may provide insight to nursing researchers, health professionals, and policy makers in planning health programs to promote walking practices in their respective communities.
- 1,110 View
- 41 Download

- Factors Affecting Radiation Protective Behaviors in Perioperative Nurses Applying the Theory of Planned Behavior: Path Analysis
- Se Young Jang, Hee Sun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Young Man Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):222-235. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22099
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aim of this study was to identify the factors explaining protective behaviors against radiation exposure in perioperative nurses based on the theory of planned behavior.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional study. A total of 229 perioperative nurses participated between October 3 and October 20, 2021. Data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 23.0 and AMOS 23.0 software. The three exogenous variables (attitude toward radiation protective behaviors, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control) and two endogenous variables (radiation protective intention and radiation protective behaviors) were surveyed.
Results
The hypothetical model fit the data (χ2/df = 1.18, SRMR = .02, TLI = .98, CFI = .99, RMSEA = .03). Radiation protective intention (β = .24, p = .001) and attitude toward radiation protective behaviors (β = .32, p = .002) had direct effects on radiation protective behaviors. Subjective norm (β = .43, p = .002) and perceived behavior control (β = .24, p = .003) had direct effects on radiation protective intention, which explained 38.0% of the variance. Subjective norm (β = .10, p = .001) and perceived behavior control (β = .06, p = .002) had indirect effects via radiation protective intention on radiation protective behaviors. Attitude toward radiation protective behaviors, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control were the significant factors explaining 49.0% of the variance in radiation protective behaviors.
Conclusion
This study shows that the theory of planned behavior can be used to effectively predict radiation protective behaviors in perioperative nurses. Radiation safety guidelines or education programs to enhance perioperative nurses’ protective behaviors should focus on radiation protective intention, attitude toward radiation protective behaviors, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health Protective Behavior in Occupational Health Practice: A Concept Analysis
Fenggang Liu, Juanjuan Wang, Weeraporn Suthakorn, Li Liao
Health Science Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors related to preventive measures towards PM2.5 exposure: A systematic review
Jeevan Bhatta, Orapin Laosee, Cheerawit Rattanapan
Global Transitions.2024; 6: 212. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Radiation Protection Behavior of Nurses in Intensive Care Units
Seo Jeong Kim, Yun Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(3): 1. CrossRef - A Review of the Relationship between Health Behaviors and Career Adaptability among University Students
Dongming Jia, Xia Yuan
Journal of Medicine and Health Science.2024; 2(4): 43. CrossRef
- Health Protective Behavior in Occupational Health Practice: A Concept Analysis
- 2,609 View
- 98 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Moderating the Effects of Health Behaviors on Sexual Intercourse among Adolescents: A CrossSectional Study Using the 2020 Adolescent Health Behavior Survey
- Eunmi Lee, Youngran Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(5):499-510. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22080
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated the association between adolescent health behaviors (drinking, smoking, and drug use) and sexual intercourse, as well as the moderating effects of economic status, cohabitation with parents, and school type, among adolescents in Korea.
Methods
Secondary data from the 16th Adolescent Health Behavior Survey (2020) were used. A total of 395 schools and 54,948 middle and high school students participated in the study. Complex sample frequency analysis, the Rao–Scott test, and complex sample logistic regression analyses were performed.
Results
Sexual intercourse rates for men and women were 5.8% and 3.3%, respectively. Approximately 7.3% of high school students and 1.8% of middle school students reported having had sexual relations. Drinking (odds ratio [OR] = 3.15, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 2.82~3.52), smoking (OR = 6.75, 95% CI = 5.90~7.71), and drug use (OR = 3.03, 95% CI = 2.23~4.11) significantly increased the risk of sexual intercourse. Economic status and school type had moderating effects on the association between drinking and sexual intercourse.
Conclusion
Adolescent drinking, smoking, and drug use are associated with a higher risk of sexual experience. Thus, to reduce this risk, controlling alcohol consumption, smoking, and drug use is necessary. In addition, programs for healthy lifestyles and sexual intercourse should be differentiated according to the school type and the economic conditions of the adolescents’ households. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Public discourse on substance use behavior as a driver of public policy: a scoping review of South Korean academic and official literature
Meekang Sung, Jihye Han, Carrie G. Wade, Vaughan W. Rees
Addiction Research & Theory.2025; 33(4): 312. CrossRef
- Public discourse on substance use behavior as a driver of public policy: a scoping review of South Korean academic and official literature
- 3,319 View
- 18 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- The Influence of Parental Self-Esteem on Late School-Aged Children’s Media Device Addiction: The Mediating Effect of Marital Conflict and Children’s Self-Esteem
- Dayeon Heo, Suk-Sun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):421-434. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22036
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the effect of parental self-esteem on late school-aged children’s media device addiction by mediating marital conflict and children’s self-esteem.
Methods
This study used data from the 11th (2018) Panel Study on Korean Children. The participants consisted of 1,082 family triads (fathers, mothers, and children). Data were collected using the Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale, Marital Conflict Scale, and K-Internet Addiction Scale. The data were analyzed using structural equation modeling with SPSS/WIN 27.0 and Mplus 8.7.
Results
The final model showed a good fit for the data. Children’s media device addiction was directly related to mothers’ self-esteem, mothers’ marital conflict, and children’s self-esteem. Fathers’ self-esteem had a significant indirect effect on children’s media device addiction by mediating both fathers’ and mothers’ marital conflict. In addition, mothers’ self-esteem had a significant indirect effect on children’s media device addiction by mediating mothers’ marital conflict.
Conclusion
The findings indicates that self-esteem and marital conflict for both fathers and mothers have a significant effect on children’s media device addiction. It suggests that more attention might be given to fathers and mothers in developing interventions to prevent children’s media device addiction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A longitudinal study of the relationship between parents’ self-esteem and children’s digital media addiction: Testing the mediating roles of children’s self-esteem and aggression
Il Bong Mun, Seyoung Lee
The Social Science Journal.2025; 62(3): 802. CrossRef
- A longitudinal study of the relationship between parents’ self-esteem and children’s digital media addiction: Testing the mediating roles of children’s self-esteem and aggression
- 1,414 View
- 36 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of an Integrated Health Management Program for Psychiatric Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
- Yun Bock Kwak, Ji Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):261-277. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study developed an integrated health management program for metabolic syndrome in psychiatric patients and examined its effects on self-efficacy, healthy lifestyle, physiological indicators, knowledge of metabolic syndrome, attitudes toward healthy behavior, and social support.
Methods
A non-equivalent control group pretest posttest design was used. The participants were 65 psychiatric patients with metabolic syndrome in psychiatric rehabilitation centers, with 33 in the experimental group and 32 in the control group. The experimental group participants engaged in daily mobile application and walking exercises three times a week for more than 40 minutes over 8 weeks, while those in the control group were provided education booklets. The outcomes were measured using self-report questionnaires, anthropometrics, and blood analyses. Intervention effects were analyzed using the independent t-test, Mann—Whitney U test, ANCOVA, and Ranked ANCOVA.
Results
The experimental group showed a significant increase in self-efficacy (F = 8.85, p = .004, ηp2 = .13) and knowledge of metabolic syndrome (t = 2.60, p = .012, d = 0.60) compared to the control group. Additionally, the experimental group demonstrated a significant decrease in waist circumference (Z = - 2.34, p = .009, d = 0.58) and body mass index (Z = - 1.91, p = .028, d = 0.47) compared to the control group.
Conclusion
The integrated health management program for psychiatric patients with metabolic syndrome is effective in improving self-efficacy and knowledge of metabolic syndrome and decreasing physiological indicators such as waist circumference and body mass index. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- User evaluation of a mobile education application for the management of metabolic syndrome among cancer survivors
Ji-Su Kim, Minhae Kim, Yeji Seo
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 63: 102276. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Web-Based Self-Management Program for Korean Adult Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Based on the Information–Motivation–Behavioral Skills Model
Seohyeon Hwang, Woori Na, Dayoung Oh, Cheongmin Sohn
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(12): 6915. CrossRef - Effect of Patient Safety Training Program of Nurses in Operating Room
Peijia Zhang, Xin Liao, Jie Luo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(4): 378. CrossRef
- User evaluation of a mobile education application for the management of metabolic syndrome among cancer survivors
- 2,650 View
- 105 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of Virtual Reality Program for Alleviating Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia Patients
- Seon-Min Park, Seung-Yi Choi, Jung-Hee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):121-133. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the impact of a virtual reality intervention program based on psychological needs on behavioral and psychological symptoms, apathy, and quality of life (QOL) in patients with dementia or mild cognitive impairment living in nursing facilities.
Methods
This study is nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design of quasi-experimental study. The study collected data from November 18, 2020 to July 24, 2021 from patients with dementia or mild cognitive impairment (30 in the experimental group and 30 in the control group) at three nursing facilities in G city using self-reporting and caregiver-informant reporting methods. The analysis employed the chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, paired t-test, independent t-test, Wilcoxon signed rank test, Mann–Whitney U, repeated measures ANOVA, GEE, using SPSS/WIN 27.0.
Results
The severity of behavioral and psychological symptoms (Wald χ2 = 2.68, p = .102) and the care burden of caregivers (Wald χ2 = 1.72, p = .190) were not significant and was no significant time and group interaction effect (Wald χ2 = 0.63, p = .426, Wald χ2 = 0.52, p =. 471). The difference in apathy and QOL score were statistically significant for the group-time interaction (F = 43.65, p < .001; F = 4.35, p= .041).
Conclusion
The virtual reality intervention program of this study shows a positive effect on the apathy reduction and QOL of patients with dementia or mild cognitive impairment residing in nursing facilities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effectiveness of nursing interventions for elderly dementia patients based on virtual reality technology: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jun Wen, Hong Yan, Siyu Wang, Jialan Xu, Zitong Zhou
Ageing Research Reviews.2024; 93: 102135. CrossRef - Development of the “living well” concept for older people with dementia
Jiyoung Kim, Nayeon Shin
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The effectiveness of nursing interventions for elderly dementia patients based on virtual reality technology: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- 2,135 View
- 104 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- A Prediction Model of Exercise Level in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Moon Ja Kim, Eun Nam Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):157-172. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21238
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to construct and test a hypothetical model to explain the predictive factors and causal pathways for exercise levels in patients with ankylosing spondylitis based on the self-determination theory. A conceptual framework was constructed assuming that autonomy support by health care providers would satisfy the three basic psychological needs of patients, which would increase their autonomous motivation for exercise, resulting in its initiation and continuation.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 221 patients with ankylosing spondylitis who were visiting rheumatology clinics in two tertiary hospitals. Health Care Climate Questionnaire-exercise regularly, Basic Psychological Needs Satisfaction scale, Behavior Regulation in Exercise Questionnaire-2, and exercise level were used to collect data.
Results
The fitness of the hypothetical model met the recommended level (χ2/df ≤ 3, SRMR ≤ .08, RMSEA ≤ .08, GFI ≥ .90, AGFI ≥ .85, NFI ≥ .90, TLI ≥ .90, CFI ≥ .90). The model effect analysis revealed that autonomy support by health care providers had a positive effect on patients' autonomy, competence, relatedness, autonomous motivation, and exercise level. Competence and relatedness had positive effects on autonomous motivation and exercise level, respectively. Autonomous motivation had a positive effect on exercise level.
Conclusion
The predictive factors of exercise level in patients with ankylosing spondylitis were autonomous motivation, health care providers' autonomy support, competence, and relatedness. Considering these factors, we recommend the development of an effective program for improving exercise levels in these patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Structural Equation Model for Low Back Pain Management Behavior in Patients With Spinal Disease
Raewan Kim, Aekyung Kim
Pain Management Nursing.2025; 26(1): e107. CrossRef - Exercise and adults with hemophilia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Doo Young Kim, Mi Yang Jeon, Young Eun, Da In Jeong
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2024; 26(1): 1. CrossRef
- A Structural Equation Model for Low Back Pain Management Behavior in Patients With Spinal Disease
- 1,287 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Climate, Health, and Nursing Tool
- Da Woon Jeong, Gwang Suk Kim, Min Kyung Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):173-186. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21211
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Climate change has various negative effects on human health, which has resulted in increased burden on the health care system. Nurses contribute significantly to assessing climate-related health risks and creating a healthy environment. This study aimed to evaluate the reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Climate, Health, and Nursing Tool (K-CHANT) to measure nurses’ awareness, motivation, concern, and behaviors at work and at home regarding climate change and health.
Methods
The 22 items of English CHANT were translated into Korean with forward-backward translation techniques. Internal consistency reliability, test-retest reliability, and construct validity using confirmatory factor analysis were performed using SPSS WIN (25.0) and AMOS (26.0). Survey data were collected from 220 master’s, doctoral, and post-doctoral nursing students.
Results
The K-CHANT consists of 20 items across 5 domains.Two items of the original CHANT were excluded because of low content validity index and standardized regression weights. The internal consistency reliability of the K-CHANT, assessed by Cronbach’s αá was .81, with an intraclass correlation coefficient of .66~.90. The five subscales model was validated by confirmatory factor analysis (SRMR < .08, RMSEA < .08, AGFI > .70, CFI > .70).
Conclusion
The K-CHANT has satisfactory construct validity and reliability to measure nurses’ awareness, motivation, concern, and behaviors at work and at home regarding climate change and health. Future research should examine nurses’ perceptions and behaviors related to the health effects of climate change and develop an action plan to improve it. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nurses' Perceptions and Behaviours Regarding Climate Change and Health: A Quantile Regression Analysis
Min Kyung Park, Seoyoung Baek, Da Woon Jeong, Gwang Suk Kim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025; 81(12): 8218. CrossRef - Exploring influences of environmental information, beliefs and self‐efficacy on nurses' climate health behaviours and their relationships
Jeongmin Yi, Yeojin Yi
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025; 81(12): 8160. CrossRef - Climate change perceptions and behaviors among Korean nurses: The role of organizational initiatives
Dukhyun Back, Kihye Han, Jieun Kim, Hyang Baek
Nursing Outlook.2025; 73(3): 102383. CrossRef - Preparedness of nurses for climate change: questionnaire development and preliminary validation
Pui Hing Chau, Tiffany L.T. Yu, Yan Hu, Yasna K. Palmeiro Silva, Eileen Gilder, Michelle Cole, Roinah Ngunyulu, Chia-Chin Lin
International Journal of Nursing Studies Advances.2025; 8: 100337. CrossRef - Nurses' educational needs regarding climate change and health by type of institutions: A descriptive cross-sectional study
Min Kyung Park, Gwang Suk Kim, Da Woon Jeong, Seoyoung Baek
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 87: 104473. CrossRef - İklim, Sağlık ve Hemşirelik Ölçeğinin Türkçeye Uyarlanması, Geçerlik ve Güvenirliğinin İncelenmesi
Özden Buse Yalçin, Betül Aktaş
Hemşirelik Bilimi Dergisi.2025; 8(2): 231. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Turkish Version of the Climate and Health Tool (CHAT) for Health Professionals: A Validity and Reliability Study
Arzu Bulut, Hande Demirtaş
Evaluation & the Health Professions.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evidencia de validez y fiabilidad de la Climate and Health Tool (CHANT): versión en español adaptada a la zona tropical latinoamericana
Ericka Carolina Murillo-Rodríguez, Diego Leal-Chaves
Revista Facultad Nacional de Salud Pública.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Climate change and nursing research: a scoping review
Claire A Richards, Ann Dyer, Melissa Vera, Julie Postma
Environmental Research: Health.2025; 3(4): 042001. CrossRef - Measuring Nurses’ Knowledge and Awareness of Climate Change and Climate-Associated Diseases: Systematic Review of Existing Instruments
Omar Portela Dos Santos, Élodie Perruchoud, Filipa Pereira, Paulo Alves, Henk Verloo
Nursing Reports.2024; 14(4): 2850. CrossRef - Validation of the Sustainability Attitudes in Nursing Survey-2 for nurses: A cross-sectional study
Sophia J. Chung, Sun Joo Jang, Haeyoung Lee
Nurse Education in Practice.2024; 75: 103898. CrossRef - Factors affecting environmental sustainability attitudes among nurses – Focusing on climate change cognition and behaviours: A cross‐sectional study
Sophia J. Chung, Haeyoung Lee, Sun Joo Jang
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors related to perceptions of climate health impact and climate action: Focusing on the Health Belief Model
Hansol Lee, Jaehee Kim, Yuri Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2024; 41(2): 31. CrossRef - Climate Change and Nursing
Yoomi Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(4): 475. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Dignity in Care Scale of Terminally Ill Patients for Nurses
Yun Sil Ahn, Pok Ja Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(3): 340. CrossRef - Climate, Health, and Nursing Tool (CHANT): A confirmatory factor analysis
Anna Winquist, Elizabeth C. Schenk, Cara Cook, Shanda Demorest, Ekaterina Burduli
Public Health Nursing.2023; 40(2): 306. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Graduate Students’ Perception and Behavior Related to Climate Change and Health: A Secondary Data Analysis
Min Kyung Park, Seoyoung Baek, Da Woon Jeong, Gwang Suk Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(1): 71. CrossRef
- Nurses' Perceptions and Behaviours Regarding Climate Change and Health: A Quantile Regression Analysis
- 2,650 View
- 119 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref

- Effects of Second Victim Experiences after Patient Safety Incidents on Nursing Practice Changes in Korean Clinical Nurses: The Mediating Effects of Coping Behaviors
- Seohee Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(4):489-504. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21089
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study was investigated the mediating effect of coping behaviors in the relationship between the second victim experiences after patient safety incidents and the nursing practice changes.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey was performed using structured questionnaires. Participants were 218 clinical nurses in general tertiary hospitals in South Korea. Data were collected through an online survey and snowball sampling from August 11 to September 6 2020. Data were analyzed using SPSS 23.0 program. A mediation analysis was performed using multiple regression and a simple mediation model applying the PROCESS macro with 95% bias-corrected bootstrap confidence interval.
Results
The mean scores of second victim experiences was 3.41/5. Approach coping (β = .55, p < .001) and the avoidant coping (β = - .23, p = .001) showed mediation effects in the relationship between second victim experiences and constructive change in nursing practice. Avoidant coping (β = .29, p < .001) showed a mediation effect in the relationship between second victim experiences and defensive change in nursing practice.
Conclusion
Coping behaviors has a mediating effect on the relationship between second victim experiences and nursing practice changes. To ensure that nurses do not experience second victim, medical institutions should have a culture of patient safety that employs a systematic approach rather than blame individuals. They also need to develop strategies that enhance approach coping and reducing avoidant coping to induce nurses’ constructive practice changes in clinical nurses in experiencing second victims due to patient safety incidents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influences of Clinical Nurses’ Second Victim Experience after Patient Safety Incidents, Individual and Organizational Support, and Job Satisfaction on Turnover Intention
Hyeran Kang, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2026; 32(1): 58. CrossRef - Factors influencing negative outcomes for nurses who experience patient safety incidents: An integrative review
Hanseulgi Lee, Nam‐Ju Lee, Nari Kim
International Nursing Review.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - How does just culture reduce negative work outcomes through second victim distress and demand for support in clinical nurses? A path analysis
Seohee Jeong, Sunmi Kim, Hyoung Eun Chang, Seok Hee Jeong
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Nursing Practice Among Clinical Nurses After Experiencing a Patient Safety Incident: Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling
Sunmi Kim, Seohee Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong, Majd Mrayyan
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of Nurses' Reporting Level by the Types of Patient Safety Incidents
Ju-Hee Kang, Yeojin Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 434. CrossRef - The Relationship of Medication Safety Competence, Second Victim Experiences, Second Victim Support, and Negative Work Outcomes among Clinical Nurses
Ahlim Chang, Youngjin Lee, Minkyung Kang, Ji Yea Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 493. CrossRef - “Learn from Errors”: Post-traumatic growth among second victims
Huanhuan Huang, Tong Liu, Ying Peng, Xingyao Du, Qi Huang, Qinghua Zhao, Mingzhao Xiao, Yetao Luo, Shuangjiang Zheng
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurse Leader Perspectives and Experiences on Caregiver Support Following a Serious Medical Error
Marie M. Prothero, Madeline Sorhus, Katherine Huefner
JONA: The Journal of Nursing Administration.2024; 54(12): 664. CrossRef - Prevalence of the second victim phenomenon among intensive care unit nurses and the support provided by their organizations
Maria Kappes, Pilar Delgado‐Hito, Verónica Riquelme Contreras, Marta Romero‐García
Nursing in Critical Care.2023; 28(6): 1022. CrossRef - The mediating role of coping styles in the relationship between second victim experience and professional quality of life among nurses: a cross-sectional study
Xizhao Li, Chong Chin Che, Yamin Li, Ling Wang, Mei Chan Chong
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations among workplace incivility, stress coping, and nursing performance in hospital nurses: A path analysis
Eun Ha Kim, Yeojin Yi
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2023; 55(4): 834. CrossRef - Influence of Clinical Nurses’ Second-Victim Experience and Second-Victim Support in Relation to Patient Safety Incidents on Their Work-Related Outcomes
Su Jin Jung, Youngjin Lee, Sun Hyoung Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(4): 331. CrossRef - Profiles of second victim symptoms and desired support strategies among Korean nurses: A latent profile analysis
Eun Young Choi, Jeehee Pyo, Minsu Ock, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2022; 78(9): 2872. CrossRef
- Influences of Clinical Nurses’ Second Victim Experience after Patient Safety Incidents, Individual and Organizational Support, and Job Satisfaction on Turnover Intention
- 3,494 View
- 81 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

- Effects of a Cognitive Behavior Therapy Program for Patients with Fibromyalgia Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Kyoung Ran Kong, Eun Nam Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):347-362. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21025
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study developed a cognitive behavioral therapy program aimed at altering the physical condition, emotions, and behaviors of fibromyalgia patients, and confirmed the program’s clinical applicability. The program was developed by analyzing previous studies conducting in-depth interviews with fibromyalgia patients, drawing on cognitive behavior theory to establish the program contents, recruiting experts to test its validity, and conducting a preliminary survey.
Methods
To confirm the program’s effect, this study used a randomized controlled trial design. The participants were outpatients diagnosed with fibromyalgia in Dong-A University Hospital, Busan. The 30 patients in the experimental group took part in the program, which comprised 8 sessions (90 to 120 minutes) based on cognitive behavior theory, delivered over 8 weeks. Hypothesis testing was carried out using the repeated measures ANOVA.
Results
The analysis revealed significant differences between the experimental and control groups in positive automatic thoughts, pain, fatigue, depression, and interpersonal relationships. However, there was no significant difference between the groups in terms of sleep disorders and negative automatic thoughts.
Conclusion
This program is a positive effect on physical condition, emotions, and behaviors. It is thus expected to be used to help fibromyalgia patients improve their disease conditions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How do people with fibromyalgia interpret ambiguous cues in empathy-related healthcare scenarios?
Maria Planes Alias, David J Moore, Nicholas Fallon, Katie Herron, Charlotte Krahé
The Journal of Pain.2026; 40: 106181. CrossRef - Changes in Dental Caries Risk among Middle School Students Using an ICT-Based Caries Management Program
An-Na Yeo, Yu-Min Kang, Su-Young Lee
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2025; 25(1): 42. CrossRef - Effects of pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions for the management of sleep problems in people with fibromyalgia: a multi-methods evidence synthesis
Mari Imamura, Clare Robertson, Jemma Hudson, Daniel Whibley, Lorna Aucott, Katie Gillies, Marcus Beasley, Martin J Stevens, Paul Manson, Debra Dulake, Abhishek Abhishek, Nicole KY Tang, Gary J Macfarlane, Miriam Brazzelli
Health Technology Assessment.2025; : 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Positive Psychotherapy on Pain Perception, Daily Functioning, and Mental Health in Patients With Fibromyalgia
Hamide Erol, Aysel Karaca
Pain Management Nursing.2025; 26(6): e550. CrossRef - Effects of a Internet-Based Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Program for Adolescents with Diabulimia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Hye-Ryeon Park, Hyeon Ok Ju
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(4): 320. CrossRef - Proposal for a Cognitive Reconstruction Program for Female College Students Experiencing Body Dissatisfaction
Hyun Ju Lee, Helen Ha, Yuan Mei Cui, Jee Hyun Lee, Min Ju Kang
Human Ecology Research.2024; 62(2): 369. CrossRef
- How do people with fibromyalgia interpret ambiguous cues in empathy-related healthcare scenarios?
- 1,679 View
- 79 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Influences of Autonomic Function, Salivary Cortisol and Physical Activity on Cognitive Functions in Institutionalized Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: Based on Neurovisceral Integration Model
- Minhee Suh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):294-304. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20282
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate objectively measured physical activity (PA) in institutionalized older adults with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and to elucidate the influence of autonomic nervous function, salivary cortisol, and PA on cognitive functions based on neurovisceral integration model.
Methods
Overall cognitive function was evaluated using the mini-mental state examination (MMSE) and executive function was evaluated using semantic verbal fluency test and clock drawing test. Actigraph for PA, HRV and sAA for autonomous function, and the geriatric depression scale for depression were used. Saliva specimens were collected in the morning for sAA and cortisol.
Results
Ninety-eight older adults from four regional geriatric hospitals participated in the study. They took 4,499 steps per day on average. They spent 753.93 minutes and 23.12 minutes on average in sedentary and moderate-to-vigorous activity, respectively. In the multiple regression analysis, lower salivary cortisol level (β = - .33, p = .041) and greater step counts (β = .37, p = .029) significantly improved MMSE score. Greater step count (β = .27, p = .016) also exerted a significant influence on verbal fluency, and greater sAA (β = .35, p = .026) was significantly associated with a better clock drawing test result.
Conclusion
Salivary cortisol, sAA and physical activity were significantly associated with cognitive functions. To prevent older adults from developing dementia, strategies are needed to increase their overall PA amount by decreasing sedentary time and to decrease salivary cortisol for cognitive function, and to maintain their sympathetic nervous activity for executive function. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between physical activity levels, sedentary time, and mild cognitive impairment in older adults
Wei Chen, Lei Zhang, Palida Abulizi, Ting Zou, Xuan Xiang, Ruikai Wu, Xiaohui Zhou
Frontiers in Public Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Rest-activity circadian rhythm in hospitalized older adults with mild cognitive impairment in Korea and its relationship with salivary alpha amylase: an exploratory study
Minhee Suh, Jihye Choi
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(4): 306. CrossRef - Circadian Rhythm Changes in Healthy Aging and Mild Cognitive Impairment
Ahmadreza Keihani, Ahmad Mayeli, Fabio Ferrarelli
Advanced Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in stress pathways as a possible mechanism of aerobic exercise training on brain health: a scoping review of existing studies
Cristina Molina-Hidalgo, Chelsea M. Stillman, Audrey M. Collins, Daniel Velazquez-Diaz, Hayley S. Ripperger, Jermon A. Drake, Peter J. Gianaros, Anna L. Marsland, Kirk I. Erickson
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between physical activity levels, sedentary time, and mild cognitive impairment in older adults
- 1,719 View
- 30 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Drinking Reduction Program Focused on Self-Determination Enhancement for College Students with Problematic Drinking
- Jin-Kyoung Ma, Moon-Sook Yoo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):265-279. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20247
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the impact of a drinking reduction program on drinking motivation, drinking refusal self-efficacy, and problematic drinking behaviors in college students with problematic drinking habits.
Methods
This study incorporated a non-equivalent control group prepost-test design. Study participants included 58 college students who scored 12 or more in the AUDIT-K test (Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test-Korean version) (experimental group: 30; control group: 28). The intervention consisted of eight sessions and was conducted once a week. It was designed to promote autonomy, competence, and relatedness-the three elements of basic psychological needs in self-determination theory. The participants were assessed before the intervention, immediately after, and four weeks post intervention. Data were collected from October 12 to December 31, 2017. The analysis employed the chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, independent t-test, and repeated measures ANOVA using SPSS/WIN 22.0.
Results
The mean age of participants was 21.8 years. There were 30 men (51.7%) and 28 women (48.3%). The differences in drinking motivation, drinking refusal self-efficacy, and problematic drinking behaviors were statistically significant for the group by time interaction (F = 42.56, p < .001; F = 54.96, p < .001; F = 39.90, p < .001, respectively). Conclusion: The findings indicate that the intervention effectively decreases drinking motivation, increases drinking refusal self-efficacy, and decreases problematic drinking behaviors. It can be an efficient strategy for college students with problematic drinking habits to enhance their self-determination ability. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of an intervention based on self-determination theory on self-health management capabilities of middle-aged women in rural areas through the concept of leisure cafeteria
Yang Jun Park, Heui Sug Jo, Hyang Hee Hwang, Yukyung Park
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(1): 59. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Self-Determination Improvement Program for Preventing Non-Suicidal Self-Injury in Adolescents: A Pilot Study
Jae Woon Lee, In Sook Kim, Ji Won Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(4): 506. CrossRef
- Effects of an intervention based on self-determination theory on self-health management capabilities of middle-aged women in rural areas through the concept of leisure cafeteria
- 1,785 View
- 49 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Information Resource Network Analysis of Factors Influencing Breastfeeding Planning and Duration
- Eunyoung Lee, Insook Cho, Seong Jin Cho, Eunju Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(2):232-244. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20280
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the modifiable factors affecting breastfeeding planning and duration among healthy mothers and their use of breastfeeding information resources.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey was conducted in a community setting. Four hundreds participants were recruited at five pediatric clinics and three community health centers located in Paju-si and Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, between January and May 2019. Based on the breastfeeding decision-making model, driven by Martens and Young’s work, the survey items consisted of demographics, childbirth and breastfeeding characteristics, and breastfeeding information resources. In the analysis, 389 responses were used in the t-test, ANOVA, and logistic regression. Information resource networks were compared before and after childbirth including a subgroup analysis depending on the breastfeeding duration.
Results
The modifiable factors affecting breastfeeding planning and duration were antenatal and postpartum breastfeeding education and the provision of information in the hospital. The frequency of Internet use and websites visited were notable and potentially modifiable factors, which were also observed in the networks showing different relationship patterns according to participant subgroups and times. The childbirth event increased the centralization of the network in the planned group, while the network of the non-planned group was more diffused after childbirth. The network of the short-term breastfeeding group was characterized by a more centralized pattern and the resources of high betweenness centrality than the long-term group.
Conclusion
Breastfeeding education is a consistent factor that affects breastfeeding behavior. A well-designed internet-based approach would be an effective nursing intervention to meet the needs of women seeking breastfeeding information and changing their behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Survey on the Status of Breastfeeding in Korean Medical Institution Workers
Tae Hyeong Kim, Sung-Hoon Chung, Jun Hwan Kim, Youngmin Ahn, Son Moon Shin, Woo Ryoung Lee, Eui Kyung Choi, Juyoung Lee, Hye-Jung Shin, Euiseok Jung, Ju Sun Heo, Jin A Lee, Soon Min Lee, Seong Phil Bae, Jeonglyn Song, Chae-Young Kim, Dae Yong Yi
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Multi-Center Educational Research Regarding Breastfeeding for Pediatrics Residents in Korea
Yong-Sung Choi, Sung-Hoon Chung, Eun Sun Kim, Eun Hee Lee, Euiseok Jung, So Yeon Lee, Wooryoung Lee, Hye Sun Yoon, Yong Joo Kim, Ji Kyoung Park, Son Moon Shin, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim
Neonatal Medicine.2022; 29(1): 28. CrossRef - Breastfeeding Success Experience of Primiparas
Sun Ok Lee, Sung Soon Na, Hee Sook Kim, Kyung Eui Bae, Mi Sun Youn, Eun Ju Oh
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2022; 26(4): 254. CrossRef - Breastfeeding experiences of women with gestational diabetes
Seungmi Park, Soo-Young Yu
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 274. CrossRef
- Survey on the Status of Breastfeeding in Korean Medical Institution Workers
- 1,522 View
- 24 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Face Mask Usage, Knowledge and Behavior of Face Mask Usage in Older Adults Living Alone in the COVID-19 Era
- A-Reum Han, Yeon-Hwan Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(2):203-216. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20252
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study analyzed the current status of face mask usage. It also identified factors related to the knowledge and behavior regarding the same among older adults living alone during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
This descriptive study was conducted via a telephone survey involving 283 older adults living alone in S City from March to April 2020. Knowledge and behavior pertaining to face mask usage were measured using Hilda Ho’s Face Mask Use Scale; reliability of the measurement was Kuder-Richardson formula-20 = .62, Cronbach’s α = .92. Data were analyzed using descriptive analysis, independent t-test, Pearson’s correlation coefficient, and multiple linear regression.
Results
Older adults used one mask for 3.55 days on an average. The knowledge level was 9.97 (± 1.84) out of 12 and behavior level was 15.49 (± 1.55) out of 16. Level of education (β = - .31, p < .001), living region (β = .13, p = .017), personal income (β = .12, p = .041) significantly affected the face mask usage-related knowledge, and living region (β = .15, p = .010) significantly affected the face mask usage-related behavior.
Conclusion
Older adults living alone are aware of the effects of using face masks. However, their mask usage is inappropriate, for example, the prolonged use of the same mask. Considering the low level of face mask usage-related knowledge, it is necessary to develop customized education programs and infectious disease prevention strategies for older adults possessing low educational levels living alone in urban-rural complex areas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A comparative cross-cultural study of fear of COVID-19 in Persian and Turkmen elderly populations
Maliheh Makhtum, Naser Behnampour, Akram Sanagoo, Hossein Nasiri, Leila Jouybari
Journal of Research Development in Nursing and Midwifery.2023; 20(1): 11. CrossRef - Influencing factors on self-care of older adults living alone in a community during COVID-19: A cross-sectional study
Heeyoung Woo, Minkyung Gu
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - The association between depression and non‐compliance with COVID‐19 preventive behaviors in South Korean older adults stratified by sex
Jae Jun Lee, Namhee Kim, Min Kyung Park, Hyunju Ji, Gwang Suk Kim
International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with Depression in Older Adults Living Alone during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Eun Hye Hong, Kyung Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(4): 418. CrossRef
- A comparative cross-cultural study of fear of COVID-19 in Persian and Turkmen elderly populations
- 1,622 View
- 15 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of Program to Promote Obesity Prevention Behaviors on Pre-Schoolers: Focused on Kindergartener in Korea
- Inju Hwang, Kyung-Sook Bang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(2):188-202. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20217
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a program to promote obesity prevention behaviors for pre-schoolers and to confirm the effectiveness of the program in Korea.
Methods
The program comprised 8 sessions for 4 weeks including combined classroom lectures and physical activities. A non-equivalent control group pre-post test study design was used, and seventy two children, aged 5 to 6 years (experimental group: 33, control group: 39) and their parents participated in the study. To examine the effectiveness of the program, children’s knowledge, intake of sugar-added beverages and fruits & vegetables, time of outdoor play and screen time, and parental self-efficacy were measured. Data were analyzed with SPSS/WIN ver. 22.0 and R 4.0.2, using descriptive analysis, chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, the independent t-test, and Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA).
Results
The results showed that the experimental group reported significantly increased knowledge (p < .001) and longer time of outdoor play on weekends (p = .033). However, there were no significant differences in the intake of sugar-added beverages and fruits & vegetables, screen time, and parental self-efficacy in the two groups.
Conclusion
This study confirms the applicability of an obesity prevention intervention at kindergartens in Korea. The results can be used as basic data for the study of childhood obesity prevention in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of health literacy education program for early childhood to prevent smoking hazards
Sangah Lee, Jiye Kim, Jiyoung Lee, Hyekyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(4): 55. CrossRef - The Let’s Eat Healthy and Move at School program for adolescents in South Korea: Program design, implementation, and evaluation plan using intervention mapping
Jiyoung Park, Gill A. Ten Hoor, Seolhyang Baek, Sochung Chung, Yang-Hyun Kim, Gahui Hwang
Child Health Nursing Research.2021; 27(3): 225. CrossRef
- Development of health literacy education program for early childhood to prevent smoking hazards
- 2,524 View
- 108 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Health Behavior Compliance in Adult Moyamoya Patients
- Bo Eun Kim, Ju-Eun Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):80-91. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify factors influencing health behavior compliance in adult patients with moyamoya.
Methods
A descriptive correlation study was conducted to investigate the factors influencing health behavior compliance. Participants were 142 adult patients diagnosed with moyamoya disease who were hospitalized or visited an outpatient clinic in the Gyeonggi province. Data were collected from December 16, 2019 to April 14, 2020 using self-report questionnaires and analyzed using the IBM SPSS 26.0 Win software.
Results
The hierarchical multiple regression analysis demonstrated that self-efficacy (β = .60, p < .001), social support (β = .13, p = .032), and age (β = .21, p = .005) affected the health behavior of adults with moyamoya disease. These 3 variables explained 62.0% of the variance of health behavior compliance, and the most influential factor was self-efficacy.
Conclusion
Based on the results of this study, it concludes that nursing interventions should be focused on self-efficacy and social support to improve health behavior compliance with adult patients diagnosed with moyamoya disease. For that, various strategies to enhance self-efficacy and social support should be developed and actively applied in the clinical setting for adult moyamoya patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictors of self-care performance in patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms
Hae-Na Woo, Yong-Cheol Lim, Joo Hee Lee, Sun Hyoung Bae
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Predictors of self-care performance in patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms
- 1,463 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- An Exploratory Study on the Policy for Facilitating of Health Behaviors Related to Particulate Matter: Using Topic and Semantic Network Analysis of Media Text
- Hye Min Byun, You Jin Park, Eun Kyoung Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):68-79. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20213
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to analyze the mass and social media contents and structures related to particulate matter before and after the policy enforcement of the comprehensive countermeasures for particulate matter, derive nursing implications, and provide a basis for designing health policies.
Methods
After crawling online news articles and posts on social networking sites before and after policy enforcement with particulate matter as keywords, we conducted topic and semantic network analysis using TEXTOM, R, and UCINET 6.
Results
In topic analysis, behavior tips was the common main topic in both media before and after the policy enforcement. After the policy enforcement, influence on health disappeared from the main topics due to increased reports about reduction measures and government in mass media, whereas influence on health appeared as the main topic in social media. However semantic network analysis confirmed that social media had much number of nodes and links and lower centrality than mass media, leaving substantial information that was not organically connected and unstructured.
Conclusion
Understanding of particulate matter policy and implications influence health, as well as gaps in the needs and use of health information, should be integrated with leadership and supports in the nurses’ care of vulnerable patients and public health promotion. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Online community users’ perceptions of particulate matter in South Korea through topic modeling and semantic network analysis
Hansol Choi, Yong Pyo Kim, Yungwook Kim, Ji Yi Lee, Hyemi Lee
Environmental Advances.2025; 20: 100641. CrossRef - Changes in Public Sentiment under the Background of Major Emergencies—Taking the Shanghai Epidemic as an Example
Bowen Zhang, Jinping Lin, Man Luo, Changxian Zeng, Jiajia Feng, Meiqi Zhou, Fuying Deng
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(19): 12594. CrossRef
- Online community users’ perceptions of particulate matter in South Korea through topic modeling and semantic network analysis
- 1,450 View
- 17 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Identifying Trajectories of Behavioral Problems in Children with Allergic Diseases: Secondary Data Analysis of the 5th to 7th Panel Study of Korean Children
- Miseon Son, Eunsun Ji
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(6):822-836. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20177
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify latent classes of behavioral problem trajectories in children with allergic diseases and investigate their predictors.
Methods
This study used data from the 5th to 7th Panel Study of Korean Children. The participants included 840 children aged 4~6 years with allergic diseases. Statistical analyses were conducted using latent class growth analysis and multinomial logistic regression.
Results
The trajectories of both internalizing and externalizing behavioral problems in children with allergic diseases were classified into five groups, that is deteriorative, recovering, changing 1 (decreasing-increasing), changing 2 (increasing-decreasing), and low state persistent group. For the internalizing behavioral problems, predictors were temperament, father’s education, family interaction, and disconnection in peer interaction. For the externalizing behavioral problems, predictors child’s gender, temperament, marital conflict, parenting stress, family interaction, and parenting environment.
Conclusion
Deteriorative group has high-risk behavioral problems in children with allergic diseases. We suggest to provide interventions considering latent problem trajectories based on ecological environments for allergic children.
- 961 View
- 11 Download

- Development of a Coping Scale for Infertility-Women (CSI-W)
- Miok Kim, Jung-Mi Ko
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(5):671-685. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20038
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop a Coping Scale for Infertility-Women (CSI-W).
Methods
The initial items were based on an extensive literature review and in-depth interviews with seven infertile women. Forty-three items were derived from a pilot survey. Data were collected from 216 women who had experienced intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in-vitro fertilization (IVF) more than once. The data were analyzed to verify the reliability and validity of the scale.
Results
Seven factors containing 28 items (four factors containing 17 items for active coping and three factors containing 11 items for passive coping) were extracted from the exploratory factor analysis to verify the construct validity. The four factors of active coping were confrontation, self-control, seeking social support (spouse), and seeking social support (colleagues and experts). The three factors of passive coping were distancing, escape, and avoidance. These items were verified through convergent, discriminant, and concurrent validity testing. The internal consistency reliability was acceptable (active coping: Cronbach’s a = .78; passive coping: Cronbach’s a = .81).
Conclusion
As its validity and reliability have been verified through various methods, the CSI-W can contribute to assessing the coping strategies of infertile women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing the Intention for Continual Fertility Treatments by the Women Undergoing Assisted Reproductive Technology Procedures: A Cross-Sectional Study
Miok Kim, Minkyung Kim, Minkyung Ban
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(1): 59. CrossRef - Design and psychometric evaluation of the collaborative coping with infertility questionnaire in candidate of assisted reproductive techniques
Marzie Reisi, Ashraf Kazemi
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Types and Characteristics of Stress Coping in Women Undergoing Infertility Treatment in Korea
Yumi Choi, So-Hyun Moon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(3): 2648. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing the Intention for Continual Fertility Treatments by the Women Undergoing Assisted Reproductive Technology Procedures: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 2,316 View
- 45 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of BeHaS Program on Health Behavior, Physiologic Index and Self-Esteem of the Elderly Living Alone with Metabolic Syndrome Based on Community Based Participatory Research
- Jong Im Kim, Sun Ae Kim, Keumok Park, Jiyoung Kim, Lina Lee, Si Wan Choi, Bon Jeong Ku
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(4):571-582. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19261
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to determine the effects of a 12-week metabolic syndrome BeHaS (Be Happy and Strong) program in elderly people with metabolic syndrome living alone, based on a community-based participatory research (CBPR).
Methods
A nonequivalent control group pre-posttest design was used, and the participants were 43 elderly people living alone (experimental group 24, control group 19). The experimental group received a one-hour program per week and two individual health consultations during 12 weeks. The control group received two sessions about the metabolic syndrome and two individual health consultations. The effects of health behavior, blood pressure, blood sugar levels, abdominal circumference, triglycerides, and self-esteem were evaluated. The data were analyzed using the independent t-test and Mann-Whitney U test.
Results
The health behavior with respect to the metabolic syndrome in the experimental group increased significantly (t = - 3.19, p = .002). Both diastolic blood pressure and abdominal circumference decreased in the experimental group (t = 2.00, p = .028 and t = 3.91, p < .001). No significant differences were observed between the groups in systolic blood pressure, fasting blood sugar levels, triglycerides, and self-esteem.
Conclusion
The 12-week metabolic syndrome BeHaS program using community resources improves the health of elderly people with metabolic syndrome living alone. Based on these findings, further studies on the effectiveness of the metabolic syndrome BeHaS program and the experiences of those who participated in the CBPR are warranted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and effects of a customized integrated health management program for older adults living alone: A nonequivalent control-group pre-posttest design
Mooyong Cho
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(3): 295. CrossRef - Exploring the Impact of Smart Mobility and ICT Solutions on Older Adults’ Mobility: A Systematic Literature Review
Chengyuan An
IEEE Access.2024; 12: 159056. CrossRef - 노인 대사증후군에 효과적인 중재: 체계적 문헌고찰과 메타분석
서현 이, 슬 구, 유미 서, 선화 반
Public Health Weekly Report.2023; 16(48): 1633. CrossRef - Comparison of the Effects of Education Only and Exercise Training Combined with Education on Fall Prevention in Adults Aged 70 Years or Older Residing in Elderly Residential Facilities
Chahwa Hong, Haejung Lee, Misoon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(2): 173. CrossRef
- Development and effects of a customized integrated health management program for older adults living alone: A nonequivalent control-group pre-posttest design
- 1,503 View
- 36 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Health Behavior Related to Particulate Matter in Older Adults
- Min Kyung Park, Gwang Suk Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):431-443. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate health behavior related to particulate matter (PM) in older adults and examine the factors affectingit.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey design was used. Data were collected from 150 voluntary older adult participants from Songpa-gu inSeoul. The survey questions measured service perception and experience related to PM, risk perception related to PM, attitude toward riskof PM, and health behavior related to PM.
Results
The average score for health behavior related to PM was 79.37, ranging from 51 to 115.There was a significant positive correlation between health behavior related to PM and risk perception related to PM (r=.58, p <.001) as wellas between health behavior related to PM and attitude toward risk of PM (r=.70, p<.001). Multiple linear regression revealed that healthbehavior related to PM was predicted by levels of the existence of disease related to PM (β=.14, p=.019), service experience related to PM(b=.20, p=.021), risk perception related to PM (b=.20, p=.019), and attitude toward risk of PM (b=.44, p<.001). The model including thesevariables accounted for 47.0% of health behavior related to PM.
Conclusion
Korean older adults have the low level of health behaviorrelated to PM. The findings of this study emphasize that risk perception and attitude toward risk of PM should be evaluated, and theunderlying diseases related to PM and their service experience should be considered in developing intervention to improve health behaviorrelated to PM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Validation of the Dust Exposure Reduction Behavior Scale
Sung Woo Hwang, Hyun Kyoung Kim
Sage Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Graduate Students’ Perception and Behavior Related to Climate Change and Health: A Secondary Data Analysis
Min Kyung Park, Seoyoung Baek, Da Woon Jeong, Gwang Suk Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(1): 71. CrossRef - The association between depression and non‐compliance with COVID‐19 preventive behaviors in South Korean older adults stratified by sex
Jae Jun Lee, Namhee Kim, Min Kyung Park, Hyunju Ji, Gwang Suk Kim
International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation between Particulate Matter Concentrations in Rural Villages in Wanju-gun and the Air Pollution Monitoring Network
Minji Lee, Dongphil Choi, Kyungsu Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(1): 139. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Augmented Reality-Based Education on Fine Dust for the Elderly
Jung-Rim Huh, Kon-Joon Bhang
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2021; 22(6): 979. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on the Policy for Facilitating of Health Behaviors Related to Particulate Matter: Using Topic and Semantic Network Analysis of Media Text
Hye Min Byun, You Jin Park, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(1): 68. CrossRef - Environmental Factors Related to Non-compliant Health Behaviors in Urban-Dwelling Elderly
Minkyung Park, Jisu Park, Sunhye Moon, Heejung Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(4): 361. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Particulate Matter-Related Health Behaviors of Patients with Pulmonary Disease
Joohee Ham, SeungHye Choi, Smi Choi-Kwon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(5): 504. CrossRef
- Development and Validation of the Dust Exposure Reduction Behavior Scale
- 1,360 View
- 29 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Parental Factors Associated with Smartphone Overuse in Preschoolers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Gumhee Lee, Sungjae Kim, Heajin Yu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):349-368. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19186
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify parental factors associated with smartphone overuse in preschoolers.
Methods
A systematic reviewwas conducted according to PRISMA guidelines. Relevant studies published in peer-reviewed journals from 2009 to June 2019 were identifiedthrough systematic search in 10 electronic databases (PubMed, CINAHL, Cochrane Central, EMBASE, Web of Science, NDSL, KISS, KMbase,KoreaMed, and RISS). Standardized effect sizes were calculated to quantify the associations of parental factors with smartphoneoveruse in preschoolers using meta-analysis.
Results
A total of 30 cross-sectional studies involving 7,943 participants met the inclusioncriteria. The following were negatively correlated with smartphone overuse in preschoolers: mother’s parenting self-efficacy (r =-.35),mother-child attachment (r =-.28), mother’s positive parenting behavior (r =-.28), mother’s positive parenting attitude (r =-.25), and father’sparenting involvement (r =-.15). Further, maternal factors such as smartphone addiction tendency (r =.41), parenting stress (r =.40), negativeparenting behavior (r =.35), negative parenting attitude (r =.14), smartphone usage time (r =.26), employment status (r =.18), and age(r =.12) were positively correlated with smartphone overuse in preschoolers.
Conclusion
Several parental factors influence smartphoneoveruse in preschoolers. These findings emphasize the need to assess and enhance the parental factors identified in this study to preventsmartphone overuse in preschoolers. Accordingly, we recommend the development of preventive interventions to strengthen parent-relatedprotective factors and mitigate risk factors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sequential Dual Mediating Effects of Smartphone Dependence and Aggression on the Relationship Between Negative Parenting Attitudes and Depressive Symptoms Among Adolescents
Jihun Na, Sungkyu Lee, Hyeyeon Sung, Jinho Jhone
Child & Family Social Work.2026; 31(1): 23. CrossRef - FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH SMARTPHONE OVERDEPENDENCE IN PRESCHOOL CHILDREN AND ITS EFFECT ON SOCIAL BEHAVIORAL PROBLEMS
Leyla Çakmak, Fikriye Aksoy Boğanak, Nurettin Menteş, Mustafa Volkan
Sağlık ve Sosyal Refah Araştırmaları Dergisi.2025; 7(1): 43. CrossRef - Empowering Parents: The Impact of a Parenting Practice-Based Care Module on Preventing Internet Gaming Disorder in Elementary School Children
Nur Hidaayah, Esti Yunitasari, Hanik Endang Nihayati
Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research.2025; 30(2): 211. CrossRef - Parent-Child Relationships and Children’s Addiction to Smartphones: A Review of International Studies
Victor P. Sheinov
RUDN Journal of Psychology and Pedagogics.2025; 22(1): 75. CrossRef - Effects of digitalization in preschool education on the creative and cognitive development of children
Yiyi Chen, Zihe Ding
Education and Information Technologies.2024; 29(16): 21567. CrossRef - Clinical Manifestations’ Spectrum of Smartphone Addiction: Moving from an Addiction toward a Clinical Syndrome
Mudar Alwazzeh, Muhdammad Harfouch, Manal Ahmed Hasan, Safi Alqatari, Abir Hamad AlSaid, Marwan Jabr Alwazzeh
Clinical Practice & Epidemiology in Mental Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The experiences of counselors caring for children and adolescents with problematic smartphone use
Jaewon Joung, Eunhee Oh, Eun Jee Lee
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of emotion coaching group programme for mothers of preschool children with smart device overdependence: a mixed methods study
Gumhee Lee, Sungjae Kim
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence, determinants and consequences of problematic smartphone use among preschoolers (3–5 years) from Dhaka, Bangladesh: A cross-sectional investigation
Faruq Abdulla, Md. Moyazzem Hossain, Mohammed Nazmul Huq, Abdul Hai, Azizur Rahman, Russell Kabir, Farhana Jahan Peya, Sinigdha Islam, Hafiz T.A. Khan
Journal of Affective Disorders.2023; 329: 413. CrossRef - Factors related to the organizational silence of Korean nurses: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Kyungja Kang, Jeong-Hee Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(3): 302. CrossRef - What Do Mothers Consider When Choosing Screen Media Programs for Their Infants?
Yoon Kyung Kim, Dongmee Lee, Ju Hee Park
Family and Environment Research.2022; 60(1): 115. CrossRef - Relationship between Mother’s emotional intelligence, negative parenting behaviour, Preschooler’s attachment instability, and smart device overdependence
Gumhee Lee, Sungjae Kim
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Related to Smartphone Overdependence in Mothers of Preschoolers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Gumhee Lee, Eunjin Yang
Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services.2022; 60(3): 40. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Online-Based Leisure Between Parenting Attitudes and Children’s Smartphone Dependency
Yoonju Cho
Korean Journal of Child Studies.2021; 42(6): 695. CrossRef - Pathway from Maternal Parenting Efficacy, Inappropriate Motives for Allowing Smart Devices, and Smart Device Dependency to Preschoolers’ Ability to Understand Minds
Yun Mi Park, Min Ju Kang
Korean Journal of Child Studies.2020; 41(6): 9. CrossRef
- Sequential Dual Mediating Effects of Smartphone Dependence and Aggression on the Relationship Between Negative Parenting Attitudes and Depressive Symptoms Among Adolescents
- 2,057 View
- 57 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- Development and Effects of Smartphone App-Based Walking Exercise Program for Taxi Drivers: Based on Bandura’s Self Efficacy Theory
- Yun Ha Choi, Min-Jeong Chae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(2):242-254. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.2.242
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of smart-phone app-based walking exercise programs for taxi drivers on self-efficacy and outcome expectations for exercise, health-related quality of life, walking as an exercise, and physiological indexes.
Methods
A nonequivalent control group with a pre-post-test design was used. The subjects were recruited in G metropolitan city. Subjects were assigned to the experimental (n=31) or control groups (n=30). The smart phone app-based walking exercise program consisted of educations via the app, twelve short message services, and one individual telephone counseling session, which was spread over 12 weeks.
Results
Self-efficacy, outcome expectations, and health-related quality of life had significantly higher pre-post test differences in scores in the experimental group. Additionally, blood pressure, body mass index, and waist circumference had significantly decreased prepost- test difference levels in the experimental group. Walking as an exercise (which consisted of days walked, number of steps walked, and amount of time walked) had significantly increased in the experimental group after 7~12 weeks in the period following the intervention program rather than 1~6 weeks after the program.
Conclusion
The smart phone app-based walking exercise program based on the self-efficacy theory demonstrates a significant effect on improving self-efficacy, outcome expectations physical activities, and health-related quality of life for taxi drivers. Therefore, it is recommended to actively use the program as a tool to promote self-efficacy, physical activities, and health behaviors in taxi drivers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring physical therapists’ approach to addressing home exercise program-related low self-efficacy: knowledge, strategies, and barriers
Mariana Wingood, Patricia M. Bamonti, Justin B. Moore, Kelsey J. Picha
Disability and Rehabilitation.2025; 47(8): 2065. CrossRef - Intervención educativa en la actividad física de médicos residentes durante la pandemia COVID-19. Estudio cuasiexperimental
Paola María Moreno-Pesquera, Clara Lilia Varela-Tapia, Hermelinda Hernández-Amaro, Daniel Martínez-Barro
Revista Mexicana de Medicina Física y Rehabilitación.2025; 37(1-2): 21. CrossRef - A Mobile App for Comprehensive Symptom Management in People With Parkinson’s Disease
JuHee Lee, Yujin Suh, Eunyoung Kim, Subin Yoo, Yielin Kim
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2024; 42(4): 289. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Mobile Application to Prevent Recurrent Stroke by Enhancing Self-management on Health Outcomes for Stroke Survivors
Young Ju Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Hyun Goo Kang
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2024; 42(1): 53. CrossRef - mHealth Interventions to Promote Physical Activity of Adults in Korea: Health Equity-Focused Systematic Review
Hana Kim, Jisan Lee
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(Suppl 1): S1. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of a mHealth Program Using Wearable Devices and Health Coaching among Bus Drivers for Promoting Physical Activity
Yeongmi Ha, Sang-Ho Lee, Suyeon Lee, Yeojoo Chae
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(3): 332. CrossRef - Effect of the SNS-Based Physical Activity-Related Psychological Intervention on Physical Activity and Psychological Constructs among Inactive University Students
Youngho Kim, Jonghwa Lee
International Journal of Clinical and Health Psychology.2022; 22(2): 100299. CrossRef - PERFORMANCE OF PHYSICAL EXERCISE IN SEDENTARY PEOPLE’S AUTONOMY
Zaiyong Shou
Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte.2022; 28(6): 785. CrossRef - An eHealth intervention (ManGuard) to reduce cardiovascular disease risk in male taxi drivers: protocol for a feasibility randomised controlled trial
James McMahon, David R. Thompson, Kevin Brazil, Chantal F. Ski
Pilot and Feasibility Studies.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Mobile Wellness Program for Nurses with Rotating Shifts during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Pilot Cluster-Randomized Trial
Yeongmi Ha, Sang-Ho Lee, Dong-Ha Lee, Young-Hun Kang, Woonjoo Choi, Jinung An
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(2): 1014. CrossRef - Co-Design of an eHealth Intervention to Reduce Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Male Taxi Drivers: ManGuard
James McMahon, David R. Thompson, Kevin Brazil, Chantal F. Ski
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(22): 15278. CrossRef
- Exploring physical therapists’ approach to addressing home exercise program-related low self-efficacy: knowledge, strategies, and barriers
- 2,272 View
- 45 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- Development of a Scale for Alcohol Drinking Prevention Behavior in Early Elementary School Based on Ajzen’s Theory of Planned Behavior
- Younkyoung Kim, Chong Mi Lee, Seo Young Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(2):210-227. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.2.210
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure variables related to alcohol drinking prevention behavior in early elementary school, based on the theory of planned behavior.
Methods
A scale was developed to measure variables related to alcohol drinking prevention behavior. Initial items for direct evaluation were constructed through a literature review, and those for belief-based indirect measure were generated through interviews with 30 second- and third-grade elementary school students. The collected data from 286 third-grade elementary school students were then subjected to item analysis, exploratory and confirmative factor analysis, criterion-related validity testing, and internal consistency assessment.
Results
The final scale consisted of 35 items. Intention, attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control explained 82.7% of the variance; behavioral beliefs, normative beliefs, and control beliefs explained 65.6% of the variance; and evaluation of outcome, motivation to comply, and power of control beliefs explained 72.8% of the variance. The confirmatory factor analysis indicated that the theoretical models had a satisfactory goodness of fit. Criterion-related validity was confirmed between the direct evaluation variables and the indirect measure variables (attitudes r=.64, p <.001; subjective norms r=.39, p <.001; perceived behavioral control r=.62, p <.001). Cronbach’s a was .89 for the direct evaluation variables and .93 for the indirect measure variables.
Conclusion
The scale developed in this study is valid and reliable. It could be used to measure and explain variables related to alcohol drinking prevention behavior in early elementary school. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a Web-Based Alcohol Prevention Program Linking School-Child-Family for Intermediate Elementary Students
Younkyoung Kim, Chong Mi Lee, Seo Young Kang, Hyunju Yang
Journal of Health Communication.2023; 28(2): 102. CrossRef - Effects of a web‐based alcohol drinking prevention program linking school‐to‐home in elementary students
Younkyoung Kim, Chong Mi Lee, Seo Young Kang
Public Health Nursing.2022; 39(2): 472. CrossRef - Factors influencing nursing students’ care intentions toward emerging infectious diseases patients: A descriptive-predictive study
Seungmi Park, Insun Jang, Soo-Young Yu
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 421. CrossRef
- Development of a Web-Based Alcohol Prevention Program Linking School-Child-Family for Intermediate Elementary Students
- 1,328 View
- 28 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Development and Effect of a Smartphone Overdependence Prevention Program for University Students Based on Self-Determination Theory
- Myung Soon Kwon, Jeong Soon Yu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(1):116-131. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.1.116
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose: This study aimed to develop a smartphone overdependence prevention program for college students based on the self-determination theory (SDT) and evaluate its effectiveness.
Methods: A non-equivalent control group repeated measures design was used for the study. Participants were 64 university freshmen (experimental group: 29, control group: 35). The developed program consists of eight sessions conducted twice a week. The program was designed to promote autonomy, competence, and relatedness the three elements of the basic psychological needs of self-determination theory. The participants were assessed before the program, immediately after, and 1 and 3 months after the program. Data were collected from April 23 to September 14, 2018 and analyzed by performing a Chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, independent t-test, and repeated measures ANOVA using SPSS/WIN 23.0.
Results: This study showed improvement in the basic psychological needs (F=3.90,
p =.010) in the experimental group compared to the control group. Specifically, competence (F=2.93,p =.035), relatedness (F=2.89,p =.045), and self-regulatory ability (F=3.11,p =.028) improved significantly.Conclusion Study findings indicate that the smartphone overdependence prevention program based on the Self-determination theory could be an effective intervention for improving basic psychological needs and self-regulation ability. Therefore, this program could be an efficient strategy for smartphone overdependence prevention in university students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Parental Smartphone Dependency and Its Impact on Child Smartphone Use: Insights From a National Survey
Hyeon Jo, Pil‐Tae Hong, Xin‐Ran Li
Child Abuse Review.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations Between Academic Motivation, Academic Stress, and Mobile Phone Addiction: Mediating Roles of Wisdom
Abolghasem Yaghoobi, Kambiz Karimi, Maryam Asoudeh, Sahar Mohammadi
International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction.2025; 23(4): 2926. CrossRef - Factors influencing smartphone overdependence in university students: an ecological model: a descriptive study
Jeong Soon Yu, Myung Soon Kwon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(1): 64. CrossRef - The Effect of Psychological Needs Satisfaction on Protective Gaming Beliefs and Behaviors
Mu He, Rushui Shan, Jiahui Lu, Kwok Kit Tong
Journal of Media Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Examining the Roles of Problematic Internet Use and Emotional Regulation Self-Efficacy on the Relationship Between Digital Game Addiction and Motivation Among Turkish Adolescents
Öner Çelikkaleli, Rıdvan Ata, Muhammet Mustafa Alpaslan, Zafer Tangülü, Özgür Ulubey
Behavioral Sciences.2025; 15(3): 241. CrossRef - Problematic smartphone use and risk behaviors in adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic
Yeseul Lee, Hyeseon Choi, Yedong Son
BMC Pediatrics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adolescent Smartphone Overdependence in South Korea: A Place-Stratified Evaluation of Conceptually Informed AI/ML Modeling
Andrew H. Kim, Uibin Lee, Yohan Cho, Sangmi Kim, Vatsal Shah
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2025; 22(10): 1515. CrossRef - Davranışsal Bağımlılıklara Yönelik Müdahalelere İlişkin Bir Derleme
Ayşegül SAYAN KARAHAN
AYNA Klinik Psikoloji Dergisi.2023; 10(3): 356. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Self-Determination Improvement Program for Preventing Non-Suicidal Self-Injury in Adolescents: A Pilot Study
Jae Woon Lee, In Sook Kim, Ji Won Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(4): 506. CrossRef - Current prevention strategies and future directions for problem Internet use
Jing Shi, Mark van der Maas, Lu Yu, Qiaolei Jiang, Sarah Agasee, Nigel E Turner
Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences.2022; 48: 101231. CrossRef - Effects of an intervention based on self-determination theory on self-health management capabilities of middle-aged women in rural areas through the concept of leisure cafeteria
Yang Jun Park, Heui Sug Jo, Hyang Hee Hwang, Yukyung Park
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(1): 59. CrossRef - Effects of On-Campus and Off-Campus Smartphone Overdependence Prevention Programs Among University Students
Jeong Soon Yu, Ok Kyung Ham, Myung Soon Kwon
Asian Nursing Research.2022; 16(4): 215. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Drinking Reduction Program Focused on Self-Determination Enhancement for College Students with Problematic Drinking
Jin-Kyoung Ma, Moon-Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(3): 265. CrossRef
- Parental Smartphone Dependency and Its Impact on Child Smartphone Use: Insights From a National Survey
- 2,265 View
- 57 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

- The Effect of a Social Skills Program on Violent Behaviors in Children Aged 60~72 Months
- Tülay Kuzlu Ayyildiz, Güler Cimete
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):771-782. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.771
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose To determine the effects of a child and parent program on developing social skills for preventing violent behaviors in children aged 60~72 months through a specially developed pre and posttest, control group, quasi-experimental study.
Methods A social skills development program based on Gardner's Multiple Intelligence Theory was used. The data were collected using the Social Skills Assessment Scale (SSAS), a Chart to Monitor Verbal and Behavioral Violence in Children, the Parental Attitude Scale and the Parent Interview Form. This quasi-experimental study that included a pretest, posttest, and control group had a sample comprising 67 children and parents, with 36 in the experimental group, and 31 in the control group.
Results Over a six-month period, while the social skill scores of the children in the experimental and control groups increased, their violent behaviors decreased (
p <.050). Increase in social skill scores and decrease in violent behaviors were higher in the experimental than in the control group children (p <.050). The parents in the experimental group stated that they had started to empathize with their children, using “I” language, and applied rules more consistently after the program.Conclusion This program was successful in preventing violent behaviors in children through the development of social skills. Hence, it can be effectively implemented through a teacher/nurse collaboration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cultural diversity in parental physical discipline and children's early social skill development: cross-lagged models in Japan and China
Zhu Zhu, Xiang Li, Tokie Anme
Child Abuse & Neglect.2025; 167: 107607. CrossRef - Effects of School-Based Interventions Implemented by Nurses for Children Aged 3-6 Years: A Systematic Review of Experimental Evidence
Gökçe Algül, Ebru Kılıçarslan
SDÜ Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Cultural diversity in parental physical discipline and children's early social skill development: cross-lagged models in Japan and China
- 2,048 View
- 23 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of Spouse-Participated Health Coaching for Male Office Workers with Cardiocerebrovascular Risk Factors
- So Hee Kang, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):748-759. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.748
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to examine the effect of spouses participating in health coaching on stage of the change, health behaviors, and physiological indicators among male office workers with cardiocerebrovascular disease (CVD) risk factors and compare the findings with trainers who provided health coaching only to workers.
Methods A quasi-experimental pretest-posttest design was used. Convenience sampling was used to recruit participants from a manufacturing research and development company in the city of Gyeonggi province. The health coaching program for the experimental group (n=26) included individual counseling sessions according to workers' stage of change, and provision of customized health information materials on CVD prevention to workers and their spouses for 12 weeks through mobile phone and email.
Results After 12 weeks of intervention, the total score for health behavior, and scores on the sub-areas of exercise and health checkups significantly improved in the experimental group, but there were no significant differences in the scores of stage of the change and physical indicators. The results of a paired t-test showed a significant decrease in the body mass index, abdominal circumference, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol and triglyceride values, and a significant increase in the high-density lipoprotein cholesterol value in the experimental group after the intervention.
Conclusion To improve the health of male workers with CVD risk factors in the workplace, sharing health information with their spouses has proven to be more effective than health coaching for only workers. Therefore, it is important to develop strategies to encourage spousal participation when planning workplace health education for changing health-related behaviors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun Jin Kim, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(1): 44. CrossRef - Effects of a Remote Physical Activity Improvement Program on Male Office Workers with Metabolic Syndrome in Their 30s and 40s with Sedentary Behavior: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Kyong Sil Park, Seon Young Hwang
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - An intervention study of a combined intervention of positioning and hand massage in patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation
Yun Kyeong Lee, Mihae Im, Haeryun Cho
Nursing Open.2023; 10(3): 1404. CrossRef
- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 1,035 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of a Reinforcement Program for Postpartum Care Behavioral Skills of Couples with Their First Baby
- Meera Park, Kyung Min Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):137-148. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.137
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to investigate the effects of a reinforcement program for behavioral skills in postpartum care for couples with their first baby.
Methods The study used a non-equivalent control group and pretest-posttest design. It was conducted from January 14 to April 10, 2016 at a postpartum care center in D city. It analyzed 43 couples (22 in the experimental group and 21 in the control group.) For data analysis, descriptive statistics, test of homogeneity in pretest, independent t-tests, and repeated measures ANOVA were used.
Results For maternal fulfillment of postpartum care and postpartum fatigue, there was no significant difference in the interaction between group and time. In terms of parent-newborns attachment, the interaction between group and time showed a significant difference for mothers (F=13.63,
p =.001) and fathers (F=6.51,p =.001). In marital intimacy, the interaction between group and time showed a significant difference for mothers (F=14.40,p <.001) and fathers (F=9.46,p =.004). In parenting stress, the interaction between group and time showed a significant difference for mothers (F=31.8,p <.001) and fathers (F=11.69,p =.001). A significant difference was found for the mothers' postpartum sleeping hours (F=0.14p =.004).Conclusion This program for behavioral skills in postpartum care, which is based on the information-motivation-behavioral skills model, improves postpartum care, parent-newborn attachment, marital intimacy, parenting stress, and maternal postpartum sleeping, by reinforcing behavioral skills required for postpartum care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of postpartum fatigue, parenting stress, and family support on postpartum depression in Chinese first-time mothers: a cross-sectional study
Feiyan Yi, Sukhee Ahn
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(3): 226. CrossRef - Maternal Health Effects of Internet-Based Education Interventions during the Postpartum Period: A Systematic Review
Jung Mi Chae, Hyun Kyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(1): 116. CrossRef - A Structural Model for Breastfeeding Behavior of First-Time Mothers
Seol Hui Park, Seang Ryu
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2021; 25(3): 184. CrossRef
- Effects of postpartum fatigue, parenting stress, and family support on postpartum depression in Chinese first-time mothers: a cross-sectional study
- 1,527 View
- 15 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of a Daily Life-Based Physical Activity Enhancement Program for Middle-Aged Women at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
- Kyung Ae Kim, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):113-125. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of a daily life-based physical activity enhancement program performed by middle-aged women at risk for cardiovascular disease.
Methods This study used a randomized control group pretest-posttest design. Middle-aged women aged 45 to 64 were recruited from two outpatient cardiology departments, and randomly assigned to an experimental group (n=28) and a control group (n=30). For the experimental group, after providing one-on-one counseling and education, we provided customized text messages to motivate them in daily life. To monitor the practice of physical activity, they also used an exercise diary and mobile pedometer for 12 weeks. Subjects' physical activities (MET-min/week) were measured using the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ). Their physiological data were obtained by blood tests using a portable analyzer, and the data were analyzed using the SPSS 21.0/WIN program.
Results There were significant differences in exercise self-efficacy, health behavior, IPAQ score, body fat, body muscle, and fasting blood sugar between the two groups. However, there were no significant differences in total cholesterol, hemoglobin A1c, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and waist-to-hip ratio.
Conclusion Strengthening physical activity in daily life without being limited by cost burden and time and space constraints. Therefore, it is essential to motivate middle-aged women at risk for cardiovascular disease to practice activities that are easily performed in their daily lives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and effectiveness of a mobile-based autonomy support program for the prevention of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged women
Miseon Seo, Eun-Young Jun, Hyunjin Oh
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Remote Physical Activity Improvement Program on Male Office Workers with Metabolic Syndrome in Their 30s and 40s with Sedentary Behavior: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Kyong Sil Park, Seon Young Hwang
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - Effects of Breathing Exercises Using Virtual Reality and Schroth Breathing Exercises on the Lung Function of Adults in Their 20s
Byung-Kon Kim, Wook-Jin Lee
The Journal of Korean Physical Therapy.2024; 36(2): 67. CrossRef - Effectiveness of physical activity monitors in adults: systematic review and meta-analysis
Rasmus Tolstrup Larsen, Vibeke Wagner, Christoffer Bruun Korfitsen, Camilla Keller, Carsten Bogh Juhl, Henning Langberg, Jan Christensen
BMJ.2022; : e068047. CrossRef - Trajectories of subjective health status among married postmenopausal women based on the ecological system theory: a longitudinal analysis using a latent growth model
Eun Jin Kim, Ju-Hee Nho
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(2): 123. CrossRef - Effect and mechanism of tai chi on blood pressure of patients with essential hypertension: a randomized controlled study
Bo LIN, Qiu JIN, Chunhua LIU, Wenhui ZHAO, Runyuan JI
The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of behaviour change interventions on changes in physical activity and anthropometrics in ambulatory hospital settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Stephen Barrett, Stephen Begg, Paul O’Halloran, Owen Howlett, Jack Lawrence, Michael Kingsley
International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors related to the Identification of Middle-Aged Women Who are Disadvantaged by Cardio-cerebrovascular Disease
Moon Jung Kang, Jee Seon Yi, Chang Seung Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(2): 185. CrossRef
- Development and effectiveness of a mobile-based autonomy support program for the prevention of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged women
- 2,297 View
- 46 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- The Effects of Utilizing Smartphone Application Peer Support on Health Behavior and Body Mass Index among Breast Cancer Survivors
- Gaeun Park, Haejung Lee, Hyun Yul Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(5):550-561. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.5.550
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to identify the effects of utilizing Smartphone Application Peer Support (SAPS) on health behavior and body mass index (BMI) among overweight or obese breast cancer survivors (BCS).
Methods A nonequivalent control group with a non-synchronized design was utilized and 36 participants (experimental group 14, control group 22) were recruited from August 2017 to September 2018. Participants were 40~65 years old, overweight or obese, had completed primary cancer treatment within the 12 months prior to the study, and had not done regular exercise during the last 6 months. The 3-month SAPS consisted of exercise and diet education (once p/2 weeks), peer support (once p/week), and self-monitoring using smartphone applications (5 times p/week). All participants underwent assessments at baseline, right after SAPS, and at 3 months after SAPS. Data were analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA.
Results At the completion of SAPS significant differences were found between groups in motivation for exercise (t=-3.24,
p =.005), physical activity (t=-4.15,p <.001), total calorie intake (t=3.42,p =.002), calories from fat (t=-3.01,p =.005), intake of vegetables (t=-2.83,p =.008), and BMI (t=5.21,p <.001). Significant differences in BMI (t=4.13,p <.001) remained up to 3 months after SAPS completion. No significant differences was shown between groups in self-efficacy for exercise, either immediately after or 3 months after SAPS.Conclusion The SAPS has the potential to improve motivation for exercise, health behavior, and BMI of BCS. However, special efforts are required to encourage participants to complete the intervention and maintain long-term effects for future trials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- EHealth intervention for quality of life in long-term breast cancer survivors: randomized controlled trial
Gustavo Adolfo Pimentel-Parra, Nelia Soto-Ruiz, Paula Escalada-Hernández, Leticia San Martín-Rodríguez, Cristina García-Vivar
JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Mobile App–Based Dietary Interventions Among Cancer Survivors: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Krista Ching Wai Chung, Naomi Takemura, Wendy Wing Tak Lam, Mandy Man Ho, Antoinette Marie Lee, Wynnie Yuen Yee Chan, Daniel Yee Tak Fong
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2025; 13: e65505. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of an App-Based Self-Management Program for Exercise Practice of Breast Cancer Survivors: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
Suyoun Maeng, Jungok Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(2): 250. CrossRef - Effects of an integrated lifestyle intervention for overweight and obese breast cancer survivors: A quasi-experimental study
Su Jin Seo, Ju-Hee Nho
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2024; 73: 102714. CrossRef - User evaluation of a mobile education application for the management of metabolic syndrome among cancer survivors
Ji-Su Kim, Minhae Kim, Yeji Seo
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 63: 102276. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Digital Health on the Quality of Life of Long-Term Breast Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review
Gustavo Adolfo Pimentel-Parra, M. Nelia Soto-Ruiz, Leticia San Martín-Rodríguez, Paula Escalada-Hernández, Cristina García-Vivar
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2023; 39(4): 151418. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a virtual reality application‐based education programme on patient safety management for nursing students: A pre‐test–post‐test study
Jae Woo Oh, Ji Eun Kim
Nursing Open.2023; 10(12): 7622. CrossRef - Effects of smart-care services program for breast cancer survivors
Bok Yae Chung, Sung Jung Hong
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(2): 95. CrossRef - The development of a lifestyle modification mobile application, “Health for You” for overweight and obese breast cancer survivors in Korea
Su-Jin Seo, Ju-Hee Nho, Youngsam Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(3): 243. CrossRef - Peer‐supported lifestyle interventions on body weight, energy intake, and physical activity in adults: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Siew Lim, Wai Kit Lee, Andy Tan, Mingling Chen, Chau Thien Tay, Surbhi Sood, Stephanie Pirotta, Lisa J. Moran, Meena Daivadanam, Ljoudmila Busija, Helen Skouteris, Mamaru A. Awoke, Briony Hill
Obesity Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Application and evaluation of mobile nutrition management service for breast cancer patients
Ji Hee Choi, Seon-Joo Park, Hee Kwon, Hae-Jeung Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(1): 83. CrossRef
- EHealth intervention for quality of life in long-term breast cancer survivors: randomized controlled trial
- 1,532 View
- 25 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Health Promotion Program Using Action Planning Strategy for Young Adults
- Su Hyun Kim, Min Ji Kim, Sang Hee Kim, So Yeon Kim, Chae Yeon Park, Jee Yun Bang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):461-471. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.461
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of a health promotion program utilizing action planning strategy for young adults.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pre-post-test design was used. One hundred three university students participated in the study. Participants in the experimental group (n=51) were provided the health promotion program utilizing action planning strategy for five weeks. The program consisted of weekly sessions that included action planning and group feedback. The control group (n=52) was provided with health information every week for 5 weeks. Program outcomes, including self-efficacy, physical activity health behaviors, total exercise time per week, daily cigarette consumption, frequency of alcohol drinking per month, nutritional health behaviors, and subjective health status, were assessed at baseline and at follow-up after 5 weeks.
Results The participants in the experimental group demonstrated significant increases in self-efficacy, physical activity health behaviors, weekly exercise time, and nutritional health behaviors and significant decreases in daily cigarette consumption than those in the control group.
Conclusion The health promotion program utilizing action planning strategy is a brief and effective intervention to promote health behaviors among young adults. Further investigation is warranted to assess the program's effectiveness among other age groups and populations at high risk for chronic illness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Meta-Analysis of Implementation Intentions Interventions in Promoting Physical Activity among University Students
Sanying Peng, Ahmad Tajuddin Othman, Ahmad Zamri Khairani, Zhuang Zhou, Xiaogang Zhou, Fang Yuan, Jinghong Liang
Sustainability.2023; 15(16): 12457. CrossRef - Validation of Types of Body Pain Areas and Related Factors in the Korean Aged Using Latent Class Analysis
Sang Ye Shin, Eun Suk Lee
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2023; 34: 22. CrossRef - E-Questionnaire on health knowledge, attitudes and practices (KAP-Health) for Brazilian students in distance learning
Jane Biscaia Hartmann, Amanda Tribulato Rego, Julia Vieira Khoury, Marcelo Picinin Bernuci, Mirian Ueda Yamaguchi
Global Health Action.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Meta-Analysis of Implementation Intentions Interventions in Promoting Physical Activity among University Students
- 2,063 View
- 54 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Nutritional Status of Liver Transplantation Recipients and Factors Influencing Nutritional Status
- SinYoung Hwang, Smi Choi-Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):340-348. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.340
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to investigate the nutritional status of liver transplantation (LT) recipients and explore certain factors that influence nutritional status, including dietary patterns and physical activities.
Methods This was a cross-sectional, descriptive study. The subjects included 211 LT recipients at a medical center outpatient clinic located in Seoul, Korea. The nutritional status, dietary patterns, and physical activities of each subject were measured using the body mass index (BMI), Mini Dietary Assessment (MDA), and Global Physical Activity Questionnaire. Independent t-test, one-way analysis of variance, and multiple linear regression analysis were used to analyze the data.
Results The percentages of living and deceased donor LTs were 81.0% and 19.0%, respectively. The mean BMIs pre- and post-LT were 23.88 and 23.16 kg/m2, respectively, and the average MDA score was 36.55. More than 60.0% of the subjects had a moderate or high level of physical activity. In multivariate analysis, a higher BMI before LT (β=.72,
p <.001), a lower Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) score (β=-.18,p <.001), and being male (β=-.10,p =.024) contributed to better nutritional status post-LT. Patients within six months of LT were less engaged in muscle exercises than those post six months of LT (p =.020).Conclusion LT recipients in Korea have good nutritional status and a good level of physical activity. To improve recipients’ post-LT nutritional status, the pre-LT nutritional status should be considered, particularly in those with a higher MELD score. In addition, physical activity including muscle-strengthening exercises should be encouraged from an earlier stage.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional Intake after Liver Transplant: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Lynsey N. Spillman, Angela M. Madden, Holly Richardson, Fumiaki Imamura, Danielle Jones, Marilyn Nash, Hong Kai Lim, Holly N. Hellawell, Kirsten L. Rennie, Linda M. Oude Griep, Michael Allison, Simon J. Griffin
Nutrients.2023; 15(11): 2487. CrossRef - Impact of Self-esteem and Social support on Self-care Performance in Liver Transplantation Recipients
Hyun Jung Jung, Young-Ju Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2020; 23(2): 132. CrossRef
- Nutritional Intake after Liver Transplant: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1,103 View
- 14 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Development and Validation of the Communication Behavior Scale for Nurses Caring for People with Dementia
- Jihye Lee, Moonhee Gang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):1-13. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop and validate the Communication Behavior Scale for nurses caring for people with Dementia (CBS-D).
Methods Based on communication accommodation theory, the initial items were generated through a literature review and interviews with 20 experts. Content and face validity of the initial items were assessed. Data from 486 nurses caring for people with dementia were analyzed using item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, criterion-related validity, and internal consistency.
Results The final scale consisted of 18 items and four factors (discourse response management, interpersonal control, emotional expression, and interpretability) that explained 57.6% of the variance. Confirmatory factor analysis indicated that the theoretical model with 18 items satisfied all goodness-of-fit parameters. Criterion-related validity was shown by the Global Interpersonal Communication Competence Scale (
r =.506,p <.001). Cronbach's alpha for the total scale was .88.Conclusion The CBS-D can be used to measure the communication behavior of nurses caring for people with dementia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a communication self-efficacy scale for nurses: a psychometric validation study
Kuem Sun Han, Jihye Shin, Soo Yeon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(2): 269. CrossRef - The influence of socio-cognitive mindfulness, moral sensitivity and dementia communication behaviors on dementia nursing performance of nurses in long-term care hospitals: a cross-sectional study
Hyun Ju Bong, Mikyoung Lee
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing shared decision-making in long-term care facilities
Da Eun Kim, Min Jung Kim
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nursing students' experiences as dementia partners in volunteer activities: An inductive content analysis
Dooree Kim, Yunhee Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(2): 146. CrossRef
- Development of a communication self-efficacy scale for nurses: a psychometric validation study
- 2,261 View
- 65 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling of Self-Care Behaviors in Kidney Transplant Patients Based on Self-Determination Theory
- Hye Won Jeong, Hyang Sook So
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):731-742. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.731
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to test a hypothesis explaining direct and indirect relationships among the factors affecting self-care behaviors of kidney transplant patients, based on self-determination theory.
Methods Data were collected from 222 outpatients with kidney transplantation. The endogenous and exogenous variables of the hypothetical model consisted of healthcare provider's autonomy support, duration after kidney transplantation, basic psychological need satisfaction, autonomous and controlled motivation, depression, and self-care behaviors. Collected data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 24.0 and AMOS 24.0.
Results The hypothetical model demonstrated a good fit: RMSEA=.06, SRMR=.04, TLI=.94, CFI=.97. Statistically significant explanatory variables for the self-care behaviors of kidney transplant patients were duration after transplantation and basic psychological need satisfaction. Healthcare provider's autonomy support was indirectly significant, while autonomous motivation, controlled motivation and depression were not statistically significant for self-care behaviors. The variables accounted for 59.5% of the self-care behaviors of kidney transplant patients.
Conclusion It is necessary to develop an autonomy support program for healthcare providers to enhance the self-care behaviors of kidney transplant patients. Preventing the deterioration of self-care behaviors will be possible by conducting this program at one year and six years post-transplantation. In addition, the results suggest the need to developing personalized autonomy support programs for healthcare providers that can meet the basic psychological need satisfaction of kidney transplant patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Influence of Sleep Disorder, Depression, and Resilience on Self-care Performance in Hemodialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
Eun-Young Hong, Hun Ha Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(3): 287. CrossRef - Associations between Health Literacy, Autonomy Support, and Health Behavior Adherence in Premature Coronary Artery Disease Patients: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Seong Rae Cho, Yeojin Yi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(4): 436. CrossRef - Predictors of self-care in kidney transplant patients according to preoperative dialysis: A comparative study
Hyeiyeon Im, Hye-Young Jang
Heliyon.2024; 10(24): e40237. CrossRef - Validation of the Korean Version of the Health Care Climate Questionnaire among Cancer Survivors
Hyun-E Yeom, Jungmin Lee, Young-Joo Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 323. CrossRef - Causal Model of Autonomous Motivation to Modify Dietary Behavior among People with Early-stage Chronic Kidney Disease
Anucha Taiwong, Tipaporn Wonghongkul, Chiraporn Tachaudomdach, Chomphoonut Srirat
Pacific Rim International Journal of Nursing Research.2024; 28(2): 280. CrossRef - Factors influencing the self-management of kidney transplant patients based on self-determination theory: a cross-sectional study
Mi Kyung Sim, Sun Young Son, Man Ki Ju
Korean Journal of Transplantation.2022; 36(1): 37. CrossRef - Factors associated with health-related quality of life in kidney transplant recipients in Korea
Younghui Hwang, Misook Kim, Kyoungok Min, Frank JMF Dor
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(3): e0247934. CrossRef - A Predictive Model of Sleep Quality of the Older Adults with Low Back Pain
Misoon Lee, Haejung Lee, Sookyung Hyun, Seon-Hwa Ban
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(4): 305. CrossRef - Feasibility and preliminary effects of a theory-based self-management program for kidney transplant recipients: A pilot study
Hye Won Jeong, Chi Eun Song, Minjeong An, Lucy E. Selman
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(6): e0248947. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Self-Care Behaviors of Renal Dialysis Patients
Yoonjung Kim, Sanggeon Park
STRESS.2019; 27(4): 320. CrossRef
- The Influence of Sleep Disorder, Depression, and Resilience on Self-care Performance in Hemodialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 1,331 View
- 30 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Differences in Factors Associated with Depressive Symptoms between Urban and Rural Female Adolescents in Korea
- Gyuyoung Lee, Ok Kyung Ham, Bo Gyeong Lee, Abuan Micah Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(4):475-484. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.4.475
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose To examine the prevalence of depressive symptoms and differentiate factors associated with them in urban and rural areas by applying the Ecological Models of Health Behavior.
Methods We employed a cross-sectional design and convenience sample of 460 female adolescents. The instruments included the Adolescent Mental-Health Problem-Behavior Questionnaire (AMPQ-II) and the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI).
Results Depressive symptoms were confirmed in 15.7% of urban adolescents and 22.9% of rural adolescents (
p <.05). In the urban group, perception of health and stress associated with school performance were significantly associated with depressive symptoms. In the rural group, aca-demic/internet related problems and rule violations were significantly associated with depressive symptoms (p <.05). General life happiness, worry/ anxiety, and mood/suicidal ideation were common factors in both urban and rural areas (p <.05).Conclusion Multiple factors were associated with depressive symptoms, and those significant factors differed between urban and rural female youths. Accordingly, tailored approaches are required considering urban and rural differences. The approaches should include intrapersonal, interpersonal, and organizational levels of interventions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rural Suicide: A Systematic Review and Recommendations
Tyler R. Pritchard, Jennifer L. Buckle, Kristel Thomassin, Stephen P. Lewis
Clinical Psychological Science.2025; 13(1): 3. CrossRef - Urban-Rural Differences in the Prevalence of Depressive Symptoms in Korean Adults
Ji-An Jeong, Sun A Kim, Jung Ho Yang, Min-Ho Shin
Chonnam Medical Journal.2023; 59(2): 128. CrossRef - Urbanicity and depression: A global meta-analysis
Colin Xu, Lucille Miao, Devon Turner, Robert DeRubeis
Journal of Affective Disorders.2023; 340: 299. CrossRef - Short Video-Based Mental Health Intervention for Depressive Symptoms in Junior High School Students: A Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial
Yuting Yang, Hao Wang, Wen Sha, Xiaoqin Guo, Wei Deng, Jingyi Wang, Chaowei Fu
Psychology Research and Behavior Management.2023; Volume 16: 4169. CrossRef - Association between mental health and executive dysfunction and the moderating effect of urban–rural subpopulation in general adolescents from Shangrao, China: a population-based cross-sectional study
Qingmin Lin, Cody Abbey, Yunting Zhang, Guanghai Wang, Jinkui Lu, Sarah-Eve Dill, Qi Jiang, M K Singh, Xinshu She, Huan Wang, Scott Rozelle, Fan Jiang
BMJ Open.2022; 12(8): e060270. CrossRef - Measuring Happiness in Adolescent Samples: A Systematic Review
Justė Lukoševičiūtė, Gita Argustaitė-Zailskienė, Kastytis Šmigelskas
Children.2022; 9(2): 227. CrossRef - Effects of Life Skill Training on the School Violence Attitudes and Behavior Among Elementary School Children
Jae Yeon Lee, Ok Kyung Ham, Hyun Soo Oh, Eun Jin Lee, Young Ko, Bongjeong Kim
The Journal of School Nursing.2022; 38(4): 336. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Obesity in Urban and Rural Adolescents: Demographic, Socioeconomic Characteristics, Health Behavior and Health Education
Gyu-Young Lee, Youn-Joo Um
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(5): 2405. CrossRef - Sociodemographic characteristics associated with adolescent depression in urban and rural areas of Hubei province: a cross-sectional analysis
Guo Li, Junhua Mei, Jing You, Jinfeng Miao, Xiaoyan Song, Wenzhe Sun, Yan Lan, Xiuli Qiu, Zhou Zhu
BMC Psychiatry.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Rural Suicide: A Systematic Review and Recommendations
- 2,087 View
- 10 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Effects of Group Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy on the Nurses’ Job Stress, Burnout, Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment and Turnover Intention
- Hye-Lyun Kim, Sook-Hee Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(4):432-442. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.4.432
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to develop a Group REBT program with group counseling for nurses and test the effect of group counseling on their job stress, burnout, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention.
Methods A quasi-experimental study with nonequivalent control group design was employed to identify the effect of the Group REBT program on nurses’ job stress, burnout, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention. Data were collected from 47 participants from two hospitals. The data from the experimental (n=23) and control (n=24) groups were analyzed from January 5 to April 3, 2015. The Group REBT program was conducted eight tmes in all, once a week, with each session lasting 180 minutes. The effect of experimental intervention was measured for each group using a series of structured questionnaires at each of the phases: Pre-intervention, post-intervention (immediately after intervention), and post-intervention (four weeks after intervention). Following this, the significance of the changes in the scores was tested.
Results The scores of the experimental group, which received the Group REBT program, were compared with those of the control group; the hypotheses were supported in terms of job stress (F=8.85,
p <.001), burnout (F=5.62,p =.022), job satisfaction (F=2.70,p =.042), organizational commitment (F=2.97,p =.048), and turnover intention (F=4.60,p =.012).Conclusion The Group REBT program was shown to be an effective intervention that could reduce nurses’ job stress and burnout and increase job satisfaction and organizational commitment. Therefore, the Group REBT program can be adopted by nursing organizations to strategically decrease nurses’ turnover intention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing Organizational Socialization in New Nurses: A Focus on Job Stress, Resilience, and Nursing Performance
Kyungok Park, Yeoungsuk Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(1): 118. CrossRef - Finding the paths between job demand–resources and turnover intention of community mental health nurses in Korea
Eunmi Hwang, Yeojin Yi
International Nursing Review.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the potential dimensions and influencing factors of nurses’ sense of professional achievement in “Internet + Nursing Services”
Jing Wu, Zhixia Zhang, Juanjuan Li, Heng Li, Niannian Zhang, Lili Gao, Congcong He, Xuan Wang
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Mental health interventions affecting university faculty: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Dalal Hammoudi Halat, Waqas Sami, Abderrezzaq Soltani, Ahmed Malki
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The moderating effects of positive thinking on the relationship between job stress and turnover intention
Khahan Na-Nan
Evidence-based HRM: a Global Forum for Empirical Scholarship.2024; 12(3): 531. CrossRef - Interventions to reduce burnout among clinical nurses: systematic review and meta-analysis
Miran Lee, Chiyoung Cha
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A systematic mapping review on the use of Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) with athletes
Anna Jordana, Martin J. Turner, Yago Ramis, Miquel Torregrossa
International Review of Sport and Exercise Psychology.2023; 16(1): 231. CrossRef - Psychological capital, work stress and burnout among Chinese clinical nurses
Ganjun Song, Lida C Landicho
International Journal of Research Studies in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychological Resilience and Career Success of Female Nurses in Central China: The Mediating Role of Craftsmanship
Huiyuan Xue, Xiaona Si, He Wang, Xiaoren Song, Keke Zhu, Xiaoli Liu, Fen Zhang
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of the second victim's experience and support on the career success of psychiatric nurses: The mediating effect of psychological resilience
Hua Xu, Xiang Cao, Quan‐Xiang Jin, Rui‐Shi Wang, Yan‐Hong Zhang, Zhao‐Hong Chen
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(6): 1559. CrossRef - The effect of a psychoeducation program based on the rational emotional behavioral approach in individuals with multiple sclerosis diagnosis: A randomized controlled trial
Emel Şahin, Serap Güleç Keskin, Murat Terzi
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2022; 58(4): 1449. CrossRef - The Effect of Nurse Support Programs on Job Satisfaction and Organizational Behaviors among Hospital Nurses: A Meta-Analysis
Se Young Kim, Mi-Kyoung Cho
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(24): 17061. CrossRef - Effects of the Anger Management Program for Nurses
Kyoungsun Yun, Yang-Sook Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(4): 247. CrossRef - Nursing management challenges: Effect of quality of work life on depersonalization
P. Yukthamarani Permarupan, Abdullah Al Mamun, Naeem Hayat, Roselina Ahmad Saufi, Naresh Kumar Samy
International Journal of Healthcare Management.2021; 14(4): 1040. CrossRef - Clinical benefits of rational-emotive stress management therapy for job burnout and dysfunctional distress of special education teachers
Liziana N Onuigbo, Charity N Onyishi, Chiedu Eseadi
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2020; 8(12): 2438. CrossRef - Predicting Nurses Burnout through Quality of Work Life and Psychological Empowerment: A Study Towards Sustainable Healthcare Services in Malaysia
P Yukthamarani Permarupan, Abdullah Al Mamun, Naresh Kumar Samy, Roselina Ahmad Saufi, Naeem Hayat
Sustainability.2020; 12(1): 388. CrossRef - Cognitive behavioral therapy for occupational stress among the intensive care unit nurses
MohammadHosein Fadaei, Mahya Torkaman, Naval Heydari, Maryam Kamali, Fariba Ghodsbin
Indian Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2020; 24(3): 178. CrossRef - Effects of Hospital-Based Violence-Prevention and Coping Programs on Nurses' Violence Experience, Violence Responses, Self-Efficacy, and Organizational Commitment
Yu Jeong Yang, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 550. CrossRef - Intervention for burnout among postgraduate chemistry education students
Florence Obiageli Ezeudu, Florence Oboochi Attah, Anthonia Ebere Onah, Tochukwu Longinus Nwangwu, Ekwutosi Monica Nnadi
Journal of International Medical Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of WeChat‐based 'three good things' on turnover intention and coping style in burnout nurses
Yu‐Fang Guo, Virginia Plummer, Wendy Cross, Louisa Lam, Jing‐Ping Zhang
Journal of Nursing Management.2020; 28(7): 1570. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Organizational Commitment in the Relationship between Professional Identity and Job Satisfaction
Seonghyun Yoo, Myoung Soo Kim, Hyoung Sook Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2019; 44(4): 339. CrossRef - Burnout Precursors in Oncology Nurses: A Preliminary Cross-Sectional Study with a Systemic Organizational Analysis
Loris Bonetti, Angela Tolotti, Dario Valcarenghi, Carla Pedrazzani, Serena Barello, Greta Ghizzardi, Guendalina Graffigna, Davide Sari, Monica Bianchi
Sustainability.2019; 11(5): 1246. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing Organizational Socialization in New Nurses: A Focus on Job Stress, Resilience, and Nursing Performance
- 2,544 View
- 68 Download
- 22 Crossref

- Perception on Parental Coping on Unintentional Injury of Their Early Infants and Toddlers: Q Methodological Approach
- Da In Lee, Ho Ran Park, Sun Nam Park, Sungsil Hong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):335-348. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.335
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify parental coping strategies in the face of early infant and toddler injury, and to provide basic data for a parental education program and the most desirable directions it should take.
Methods A Q-methodology to analyze the subjectivity of each item was used. Thirty-four Q-statements were derived from a literature review and interviews. Forty-seven parents were classified into a shape of normal distribution using a 9-point scale. Collected data were analyzed by the pc-QUANL program.
Results Five types of parental coping in early infant and toddler injury were identified. Type I was “hospital treatment focused”, type II was “Improving the safety of the child's environment”, type III was “expression of negative emotion”, type IV was “taking the lead in problem solving”, and type V was “Interrogating the person in charge of the situation in which the injury occurred”.
Conclusion The results of this study indicate that different approaches to educational programs can be used for parents in early childhood injury.
- 879 View
- 5 Download

- Development and Effects of a Coping Skill Training Program for Caregivers in Feeding Difficulty of Older Adults with Dementia in Long-Term Care Facilities
- Hyun Hwa Hong, Mee Ock Gu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):167-181. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.167
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose We developed and tested the effects of a coping skill training program for caregivers in feeding difficulty among older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The subjects comprised 34 caregivers (experimental group: 17, control group: 17) and 40 older adults with dementia (experimental group: 20, control group: 20). The developed program was delivered in 4-hour sessions over 6 weeks (including 2 weeks of lectures and lab practice on feeding difficulty coping skills, and 4 weeks of field practice). Data were collected before, immediately after, and 4 weeks after the program (January 3 to April 6, 2016). The data were analyzed using t-test and repeated measures ANOVA using SPSS/WIN 20.0.
Results Compared to their counterparts in the control group, caregivers in the experimental group showed a significantly greater improvement in feeding knowledge and feeding behavior, while older adults with dementia showed greater improvements in feeding difficulty and Body Mass Index.
Conclusion The study findings indicate that this coping skill training program for caregivers in feeding difficulty is an effective intervention for older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influencing factors of depressive and anxiety symptoms among caregivers of Alzheimer's disease patients: A cross-sectional study
Chengfei Duan, Mo Zhu, Xia Li, Ling Yue
Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.2026; 109(3): 1264. CrossRef - Mealtime Support by Direct Care Workers in Long‐Term Care Facilities: Secondary Behavioural Analysis of Videos
Eunju Choi, Leeho Yoo, Soogyung Shin, Dukyoo Jung
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Feasibility of a nurse-led online video intervention for mealtime assistance in dementia care: a quasi-experimental mixed-methods study
Dukyoo Jung, Leeho Yoo, Soogyung Shin, Sukyung Byeon, Hyein Seo, Eunju Choi
BMC Geriatrics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting Mealtime Difficulties in Older Adults with Dementia Living in Long-Term Care Facilities: A Multilevel Model Analysis
Dukyoo Jung, Jennie C. De Gagne, Hyesoon Lee, Leeho Yoo, Jisung Park, Eunju Choi, Yonggang Zhang
Journal of Nursing Management.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of Case-Based Small-Group Learning on Care Workers’ Emergency Coping Abilities
Soon-Ok Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(21): 11458. CrossRef - Eating Difficulties among Older Adults with Dementia in South Korean Long-Term Care Facilities: A Scoping Review
Dukyoo Jung, Kyuri Lee, Eunju Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 470. CrossRef Feasibility of a Mobile Meal Assistance Program for Direct Care Workers in Long-Term Care Facilities in South Korea
Dukyoo Jung, Jennie C De Gagne, Minkyung Lee, Hyesoon Lee, Kyuri Lee, Eunju Choi, Juyoun Chung
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2020; Volume 15: 2019. CrossRef- Informal dementia caregivers’ experiences and perceptions about mealtime care: A qualitative evidence synthesis
Yijing Li, Dan Sun, Xu Zhang, Huanhuan Li, Yingnan Zhao, Dongfei Ma, Zehui Li, Jiao Sun
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2020; 76(12): 3317. CrossRef
- Influencing factors of depressive and anxiety symptoms among caregivers of Alzheimer's disease patients: A cross-sectional study
- 1,033 View
- 19 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Predictors of Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia: Based on the Model of Multi-Dimensional Behavior
- Jeong Eun Yang, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):143-153. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify factors predicting behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) in persons with dementia. Factors including the patient, caregiver, and environment based on the multi-dimensional behavioral model were tested.
Methods The subjects of the study were 139 pairs of persons with dementia and their caregivers selected from four geriatric long-term care facilities located in S city, G province, Korea. Data analysis included descriptive statistics, inverse normal transformations, Pearson correlation coefficients, Spearman's correlation coefficients and hierarchical multiple regression with the SPSS Statistics 22.0 for Windows program.
Results Mean score for BPSD was 40.16. Depression (β=.42,
p <.001), exposure to noise in the evening noise (β=-.20,p =.014), and gender (β=.17,p =.042) were factors predicting BPSD in long-term care facilities, which explained 25.2% of the variance in the model.Conclusion To decrease BPSD in persons with dementia, integrated nursing interventions should consider factors of the patient, caregiver, and environment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The influence path of caregivers’ positive aspects, expressed emotion and coping style on behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia
Shuang Zhang, Xiumei Ying, Shuyan Fang, Wenxia Wang, Xiangning Zhu, Yueyang Dong, Meng He, An Chang, Jiao Sun
Geriatric Nursing.2022; 44: 143. CrossRef
- The influence path of caregivers’ positive aspects, expressed emotion and coping style on behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia
- 1,146 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of Parenting Stress and Controlling Parenting Attitudes on Problem Behaviors of Preschool Children: Latent Growth Model Analysis
- Jeong Won Han, Hanna Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(1):109-121. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.1.109
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to examine the longitudinal effects of parenting stress and parental control attitudes on problem behaviors in preschool children, using a latent growth model.
Methods Participants were 1,724 pairs of parents and 1,724 preschool children who had completed the panel survey on Korean children (5th~7th survey panels).
Results An analysis of the multivariate latent growth model of parenting stress, parental control attitudes, and children's problem behaviors suggested that the parents’ intercepts for parenting stress influenced their intercepts for parental control attitudes (father: b=.21,
p <.001; mother: b=.55,p <.001). In addition, the slopes for fathers’ parenting stress was the only aspect that affected the slopes for mothers’ parental control attitudes (b=.77,p <.001). Moreover, both the intercepts and slopes of parenting stress and parental control attitudes significantly affected the children's problem behaviors.Conclusion This study is significant as it provides longitudinal evidence of the impact of parenting stress and parental control attitudes on children's problem behaviors. The findings suggest that accurately assessing changes in parenting stress and parental control attitudes and developing intervention programs to reduce them will be effective in reducing problem behaviors in children.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The vicious cycle: The bidirectional influence between maternal parenting stress and mother-child relationships
Youli Wang, Yuxuan Cao, Baocheng Pan, Jingkai Sun, Keman Yuan, Pin Xu, Bowen Xiao, Yan Li
Acta Psychologica.2026; 262: 106035. CrossRef - Nurturing Bonds: Social Support as a Mediator in the Association Between Parenting Stress and the Mother–Child Relationship Among Turkish Mothers
Osman Hatun, Pınar Kütük-Yılmaz, Gülşen Topal-Özgen
The Family Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Infant Temperament and Coparenting Support as Antecedents of French-Canadian Fathers’ Autonomy Support During Toddlerhood
Emma Laflamme, Célia Matte-Gagné, Rose Bourget, Frédérique Fortin
Parenting.2025; 25(4): 449. CrossRef - Unraveling the Longitudinal Relationships Among Parenting Stress, Preschoolers’ Problem Behavior, and Risk of Learning Disorder
Jie Huang, Dongqing Yu, Xiaoxue Tang, Yili Xu, Xiao Zhong, Xiaoqian Lai
Behavioral Sciences.2025; 15(6): 785. CrossRef - COVID-19 and Children’s Mental Health: The Impact of Sociodemographic Variables, Educational Practices and Stressors
Graciana Sanchotene Valandro, Gabriel dos Reis Rodrigues, Angela Helena Marin
Paidéia (Ribeirão Preto).2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Does early skin-to-skin contact have a long-term effect on the emotional and behavioral development of very preterm infants?
Patricia Trautmann-Villalba, Eva Heine, Angela Kribs, Katrin Mehler
Frontiers in Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Relationship Between Parental Attitudes and Parent-Child Relationship
Mine Durmuşoğlu, Tülay İlhan İyi, Cansu Yıldız Taşdemir
Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Buca Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi.2024; (61): 2214. CrossRef - Mothers’ Perceived Co-Parenting and Preschooler’s Problem Behaviors: The Mediating Role of Maternal Parenting Stress and the Moderating Role of Family Resilience
Jingjing Zhu, Shuhui Xiang, Yan Li
Psychology Research and Behavior Management.2024; Volume 17: 891. CrossRef - Okul Öncesi Eğitime Devam Eden 48-72 Aylık Çocukların ve Ailelerin Sürdürülebilirliğe İlişkin Bilgi ve Uygulamaları
Kazım Biber, Caner Börekci
Uludağ Üniversitesi Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi.2024; 37(3): 974. CrossRef - Parental Burnout and Adolescents’ Development: Family Environment, Academic Performance, and Social Adaptation
Wei Wang, Shen Chen, Shengnan Wang, Geyan Shan, Yongxin Li
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(4): 2774. CrossRef - Intrusive parenting in early childhood: A review and meta‐analysis
Zixin Jiang, Xi Liang, Zhengyan Wang, Yige Lin, Linlin Zhang
PsyCh Journal.2023; 12(3): 335. CrossRef - Anxiety, sleep habits and executive function during the COVID-19 pandemic through parents’ perception: a longitudinal study
Ignasi Navarro-Soria, Borja Costa-López, Joshua A. Collado-Valero, Rocío Juárez-Ruiz de Mier, Rocío Lavigne-Cervan
Psicologia: Reflexão e Crítica.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The mediating effects of parenting style on the relationship between parental stress and behavioral problems in girls with precocious puberty in Korea: a cross-sectional study
Ahreum Kwon, Young Il Cho, Hyo Jin Kim, Junghwan Suh, Dong Hee Kim
BMC Pediatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - „Tut sich da denn was? Und wenn ja, was?“ Videodiagnostische Beurteilung elterlicher Interaktionsqualitäten in einer vorschulpsychiatrischen Stichprobe
Clara Hennecke, Marius Janßen
Praxis der Kinderpsychologie und Kinderpsychiatrie.2023; 72(5): 408. CrossRef - The relationship between parental depression and child internalizing and externalizing problems: The roles of parenting stress and child maltreatment
Chen Chen
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychological Need-Based Experiences as Energizing Processes for Mothers’ Identity Formation
Adi Arden, Idit Katz, Ortal Slobodin
Journal of Child and Family Studies.2023; 32(9): 2573. CrossRef - Those in the shadow of the pandemic: impacts of the COVID-19 outbreak on the mental health of children with neurodevelopmental disorders and their parents
Baris Guller, Ferhat Yaylaci, Damla Eyuboglu
International Journal of Developmental Disabilities.2022; 68(6): 943. CrossRef - Mental health effects prevalence in children and adolescents during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A systematic review
Júlia Meller Dias de Oliveira, Luciana Butini, Patrícia Pauletto, Karyn Munyk Lehmkuhl, Cristine Miron Stefani, Michele Bolan, Eliete Guerra, Bruce Dick, Graziela De Luca Canto, Carla Massignan
Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing.2022; 19(2): 130. CrossRef - Children's behavioral problems, screen time, and sleep problems' association with negative and positive parenting strategies during the COVID-19 outbreak in Brazil
T.D.O. Oliveira, D.S. Costa, A. Alvim-Soares, J.J. de Paula, I. Kestelman, A.G. Silva, L.F. Malloy-Diniz, D.M. Miranda
Child Abuse & Neglect.2022; 130: 105345. CrossRef - The Impact of COVID-19 on Cognitive Development and Executive Functioning in Adolescents: A First Exploratory Investigation
Alessandro Frolli, Maria Carla Ricci, Francesca Di Carmine, Agnese Lombardi, Antonia Bosco, Emilio Saviano, Luisa Franzese
Brain Sciences.2021; 11(9): 1222. CrossRef - Helikopter Anne Tutumları: Üniversite Öğrencilerinin Yaşam Doyumları ve Psikolojik İyi Oluşları Üzerindeki Yordayıcı Rolü
Faruk Caner YAM, Hatice KUMCAĞIZ
OPUS Uluslararası Toplum Araştırmaları Dergisi.2021; 17(35): 1946. CrossRef - Consequences of COVID-19 Confinement on Anxiety, Sleep and Executive Functions of Children and Adolescents in Spain
Rocío Lavigne-Cerván, Borja Costa-López, Rocío Juárez-Ruiz de Mier, Marta Real-Fernández, Marta Sánchez-Muñoz de León, Ignasi Navarro-Soria
Frontiers in Psychology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Traumatic Effects of the COVID-19 Outbreak in Middle School Students and Caregivers
Merve Aktaş Terzioğlu, Ahmet Büber
Psychiatry Investigation.2021; 18(6): 553. CrossRef - Effects of Covid-19 confinement on the mental health of children and adolescents in Spain
Juan Pablo Pizarro-Ruiz, Nuria Ordóñez-Camblor
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 on the mental health among children in China with specific reference to emotional and behavioral disorders
Varsha Agarwal, Ganesh L., Sunitha B.K.
International Journal of Human Rights in Healthcare.2021; 14(2): 182. CrossRef - Behavioral and Emotional Disorders in Children during the COVID-19 Epidemic
Wen Yan Jiao, Lin Na Wang, Juan Liu, Shuan Feng Fang, Fu Yong Jiao, Massimo Pettoello-Mantovani, Eli Somekh
The Journal of Pediatrics.2020; 221: 264. CrossRef - The link between mother and child's obsessive-compulsive symptoms: A test of simple and serial mediation models in a healthy community sample
Gabrielle Coppola, Alessandro Costantini, Marvita Goffredo, Domenico Vito Antonio Piazzolla, Cristina Semeraro, Rosalinda Cassibba, Maria Grazia Foschino Barbaro, Francesco Mancini
Journal of Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders.2020; 25: 100510. CrossRef - Longitudinal relationship between the child value, parenting stress, and controlling parenting attitudes and the self‐esteem of children: Applying the actor‐partner interdependence model (APIM) using a latent growth model
Jeong‐Won Han, Hanna Lee
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Behavioral and Emotional Disorders in Children during the COVID-19 Epidemic
Wen Yan Jiao, Lin Na Wang, Juan Liu, Shuan Feng Fang, Fu Yong Jiao, Massimo Pettoello-Mantovani, Eli Somekh
Pediatric pharmacology.2020; 17(3): 230. CrossRef - Stress e competenze genitoriali nelle separazioni giudiziarie. Analisi dei fattori protettivi e di rischio nelle relazioni parentali
Daniela Pajardi, Monia Vagni, Valeria Giostra, Viviana La Spada, Tiziana Maiorano
RICERCHE DI PSICOLOGIA.2019; (4): 693. CrossRef
- The vicious cycle: The bidirectional influence between maternal parenting stress and mother-child relationships
- 2,024 View
- 26 Download
- 30 Crossref

- Effects of Group Counseling Program Based on Goal Attainment Theory for Middle School Students with Emotional and Behavioral Problems
- In Ju Jeong, Soo Jin Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):199-210. Published online April 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.199
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of a group counseling program based on goal attainment theory on self-esteem, interpersonal relationships, and school adjustment of middle school students with emotional and behavioral problems.
Methods Forty-four middle school students with emotional and behavioral problems (22 in the experimental group and 22 in the control group) from G city participated in this study. Data were collected from July 30 to September 24, 2015. The experimental group received the 8-session program, scheduled once a week, with each session lasting 45 minutes. Outcome variables included self-esteem, interpersonal relationship, and school adjustment.
Results There were significant increases for self-esteem (t=3.69,
p =.001), interpersonal relationship (t=8.88,p <.001), and school adjustment (t=4.92,p <.001) in the experimental group compared to the control group.Conclusion These results indicate that the group counseling program based on goal attainment theory is very effective in increasing self-esteem, interpersonal relationship, and school adjustment for middle school students with emotional and behavioral problems. Therefore, it is recommended that the group counseling program based on goal attainment theory be used as an effective psychiatric nursing intervention for mental health promotion and the prevention of mental illness in adolescents.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Therapeutic Communication Program Based on King's Goal Attainment Theory for Nurses in a Hematological Oncology Ward: A Non-equivalent Control Group Pretest–Posttest Study
HyunJung Lee, Bom-Mi Park, Heeju Kim, Jihye Kim, HyunJung Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(4): 412. CrossRef - DEVELOPMENT OF GROUP COUNSELING GUIDE WITH RELAXATION, SYSTEMATIC DESENSITIZATION, AND FLOODING TECHNIQUES TO REDUCE INTERACTION ANXIETY
Eva Kartika Wulan Sari, Leny Latifah
Counsenesia Indonesian Journal Of Guidance and Counseling.2023; 4(2): 148. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Led Intervention Programs Based on Goal Attainment Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 699. CrossRef - Essential Role of Theory in Nursing Research for Advancement of Nursing Science
Soyoung Yu, Ju-Eun Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(4): 391. CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Fall Prevention Program Based on King’s Theory of Goal Attainment in Long-Term Care Hospitals: An Experimental Study
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 715. CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Fall Prevention Program Based on the King's Goal Attainment Theory for Fall High-Risk Elderly Patients in Long-Term Care Hospital
Bom Mi Park, Ho Sihn Ryu, Kyeung Eun Kwon, Chun Young Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(2): 203. CrossRef
- Effects of a Therapeutic Communication Program Based on King's Goal Attainment Theory for Nurses in a Hematological Oncology Ward: A Non-equivalent Control Group Pretest–Posttest Study
- 2,037 View
- 50 Download
- 6 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


