Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Variables influencing digital health literacy in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Jin Hwa Park, Eun Ju Mun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):651-667. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
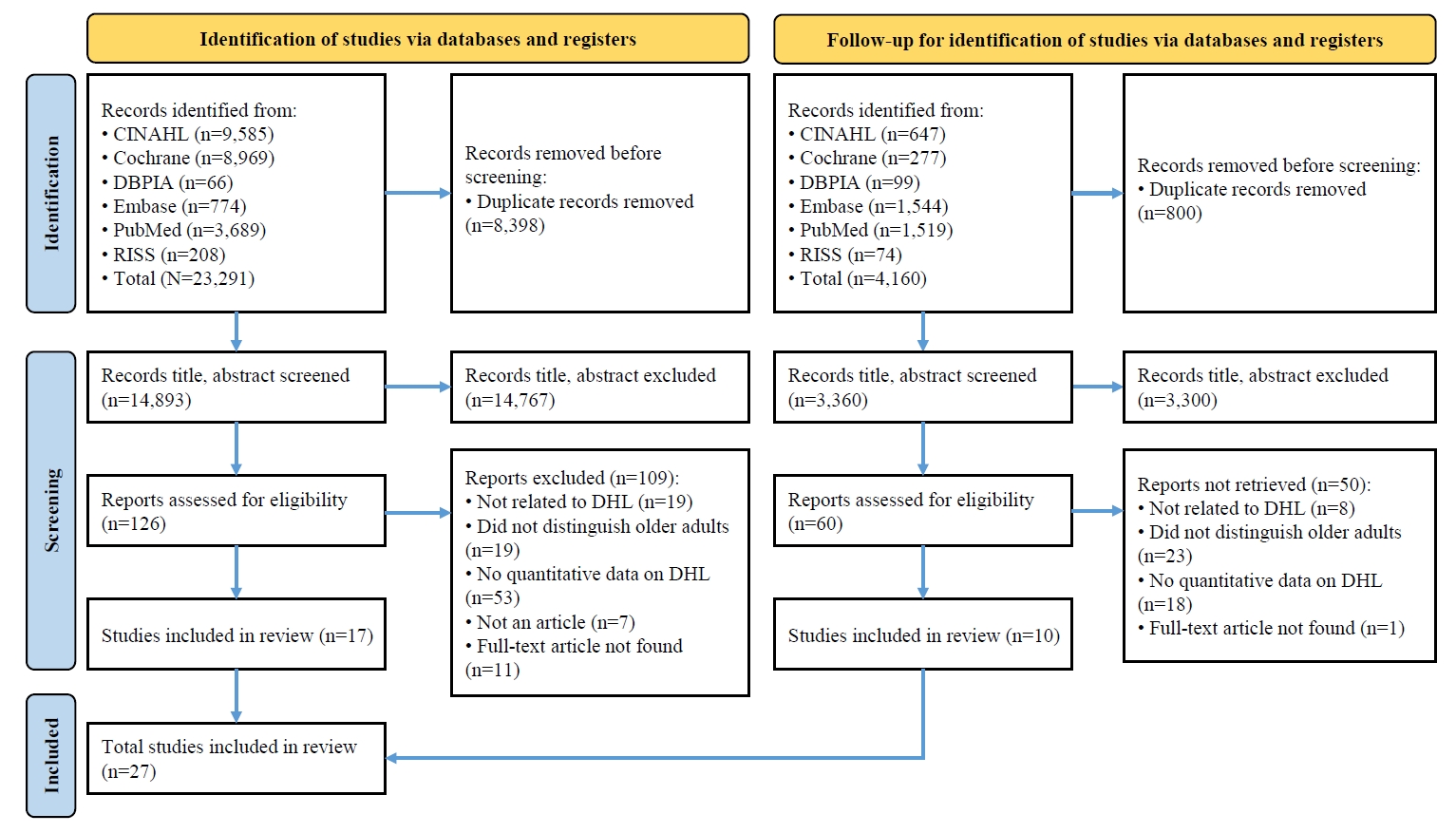
This study aimed to synthesize existing evidence on digital health literacy (DHL) among older adults and to estimate the associations between related influencing factors through a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines. Literature searches were performed across PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, RISS, and DBPIA. The search and screening process was conducted from December 24, 2023, to March 31, 2025. Effect sizes (ESr) using correlation coefficient for each variable were calculated, and meta-analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel and R version 4.3.1.
Results
Forty-seven variables were identified, including two demographic, six physical, six behavioral, 23 psychosocial, and 10 cognitive factors. Meta-analysis results showed that physical, behavioral, psychosocial, and cognitive factors had significant effects on DHL. Among these, digital information level (ESr=.62; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55 to 0.69) within the cognitive domain and technophobia (ESr=−.55; 95% CI, −0.47 to −0.40) within the psychosocial domain demonstrated the largest ESr.
Conclusion
Among factors influencing DHL, digital information level and technophobia showed the strongest associations. These findings suggest that improving DHL in older adults requires a dual approach targeting both cognitive and psychosocial dimensions—enhancing digital information skills while reducing technophobia—to effectively support digital engagement and health empowerment in this population (PROSPERO registration number: CRD42023487486).
- 1,385 View
- 157 Download

- Multidimensional factors influencing the completion of advance directives among community-dwelling older Koreans
- Hee-Ju Ji, Soong-Nang Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):543-556. Published online November 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25098
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
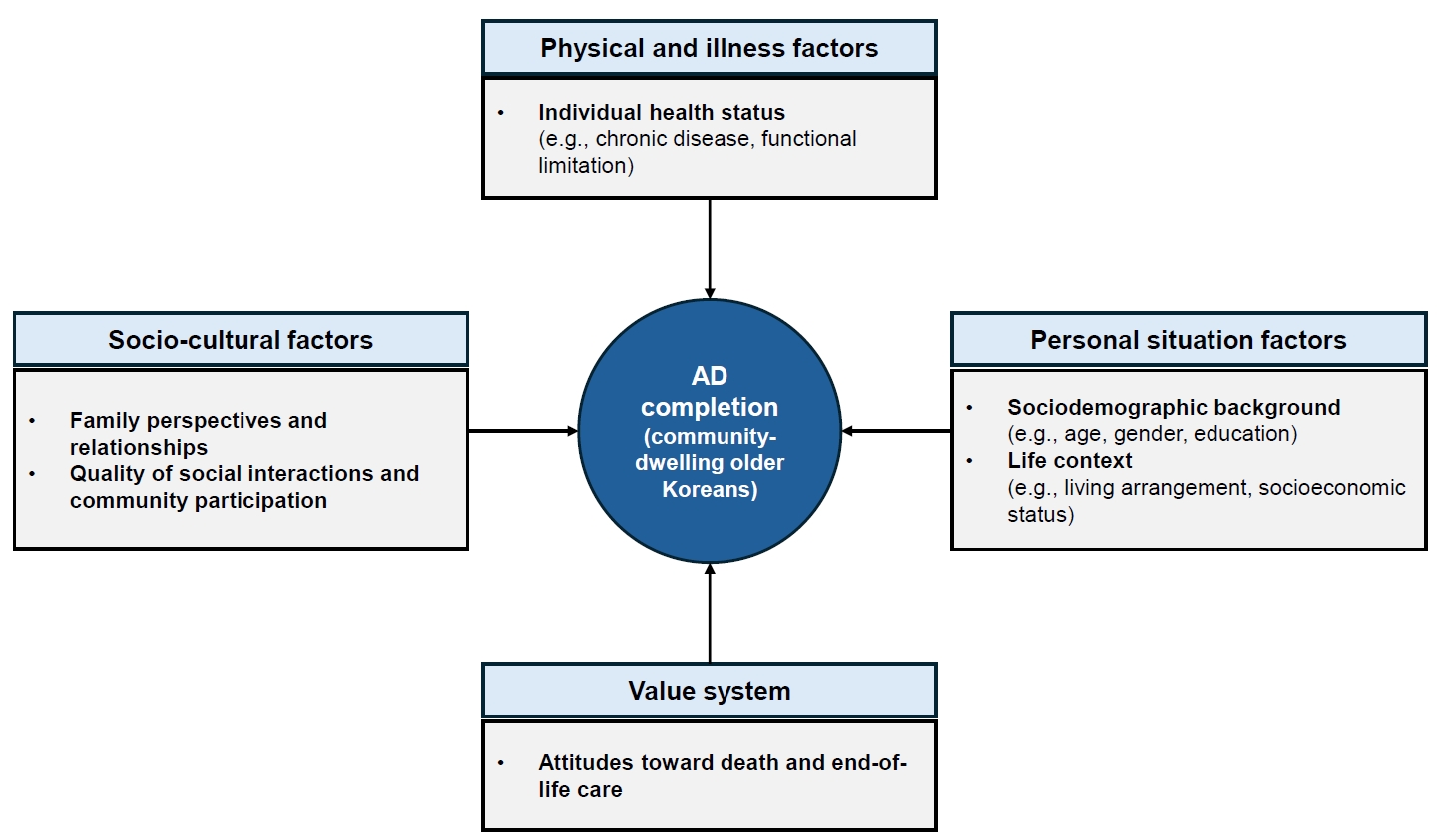
This study aimed to examine the multidimensional factors associated with the completion of advance directives (ADs) among community-dwelling older Koreans, guided by conceptual frameworks developed in Asian contexts.
Methods
Data from the 2023 National Survey of Older Koreans (sixth wave) were analyzed for 9,951 community-dwelling older Koreans aged 65 years or older. Complex sample cross-tabulation and binary logistic regression analyses were conducted.
Results
In total, 11.1% of community-dwelling older Koreans had completed an AD. Significant factors associated with AD completion were identified across four domains—personal situation: age, educational level, religion, and housing preference in the event of poor health; socio-cultural: presence of children, participation in social activities and satisfaction with social relationships; physical and illness: the number of chronic diseases; and value system: awareness of hospice and palliative services, participation in death preparedness education, and documentation of organ donation.
Conclusion
Among older Koreans, AD completion represents more than a documentation process; it reflects a complex decision-making process shaped by their values and life circumstances, underscoring the need for supportive interventions. As the highest AD completion rates are found among older adults, related policies should be aligned with older adult-centered policy frameworks.
- 1,557 View
- 157 Download

- Effects of an agro-healing program on depression, stress, and cognitive function in older adults: a quasi-experimental study
- Gyu Yeon Park, Kwang Ok Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):342-352. Published online August 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25058
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
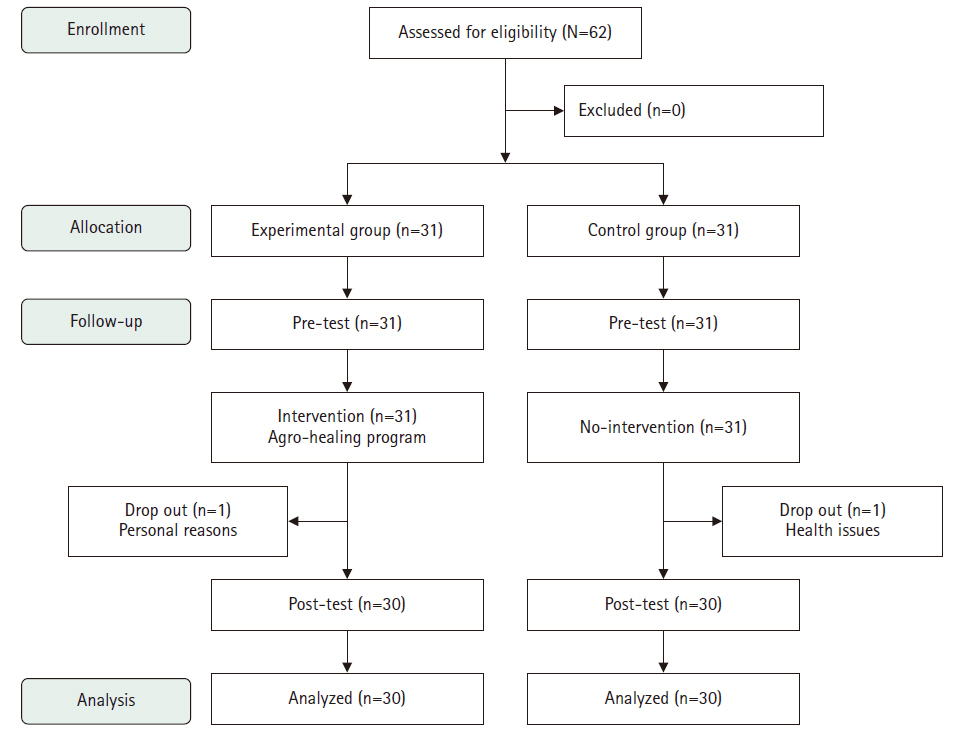
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of an agro-healing program on depression, stress, and cognitive function in older adults.
Methods
A quasi-experimental, nonequivalent control group pretest–posttest design was used. The study was conducted from July 16 to September 6, 2024. Sixty-two individuals aged 65 or older residing in Gimcheon, Gyeongsangbuk-do, were recruited according to the selection criteria (31 in the experimental group and 31 in the control group). The final analysis included 30 participants in each group. The program was delivered by one main instructor (a healing farmer) and three assistants. The pretest assessed general characteristics, the Geriatric Depression Scale Short Form-Korean Version, Stress Response Inventory-Modified Form, and Cognitive Impairment Screening Test. The experimental group participated in the agro-healing program once a week for 90 minutes over 8 weeks. The posttest included the same measurements as the pretest. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS ver. 23.0.
Results
The experimental group, which participated in the healing agriculture program, showed reduced depression (F=7.97, p=.007) and stress (F=282.70, p<.001) and improved cognitive function (F=10.12, p=.002) compared to the control group.
Conclusion
The findings suggest that the agro-healing program is an effective intervention for reducing depression and stress and improving cognitive function in older adults. We propose its use to promote health and prevent dementia in this population.
- 2,859 View
- 233 Download

- Development of a scale to measure fear of falling in older adults: a psychometric validation study
- Dayeon Lee, Sunghee H Tak
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):413-424. Published online August 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25036
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
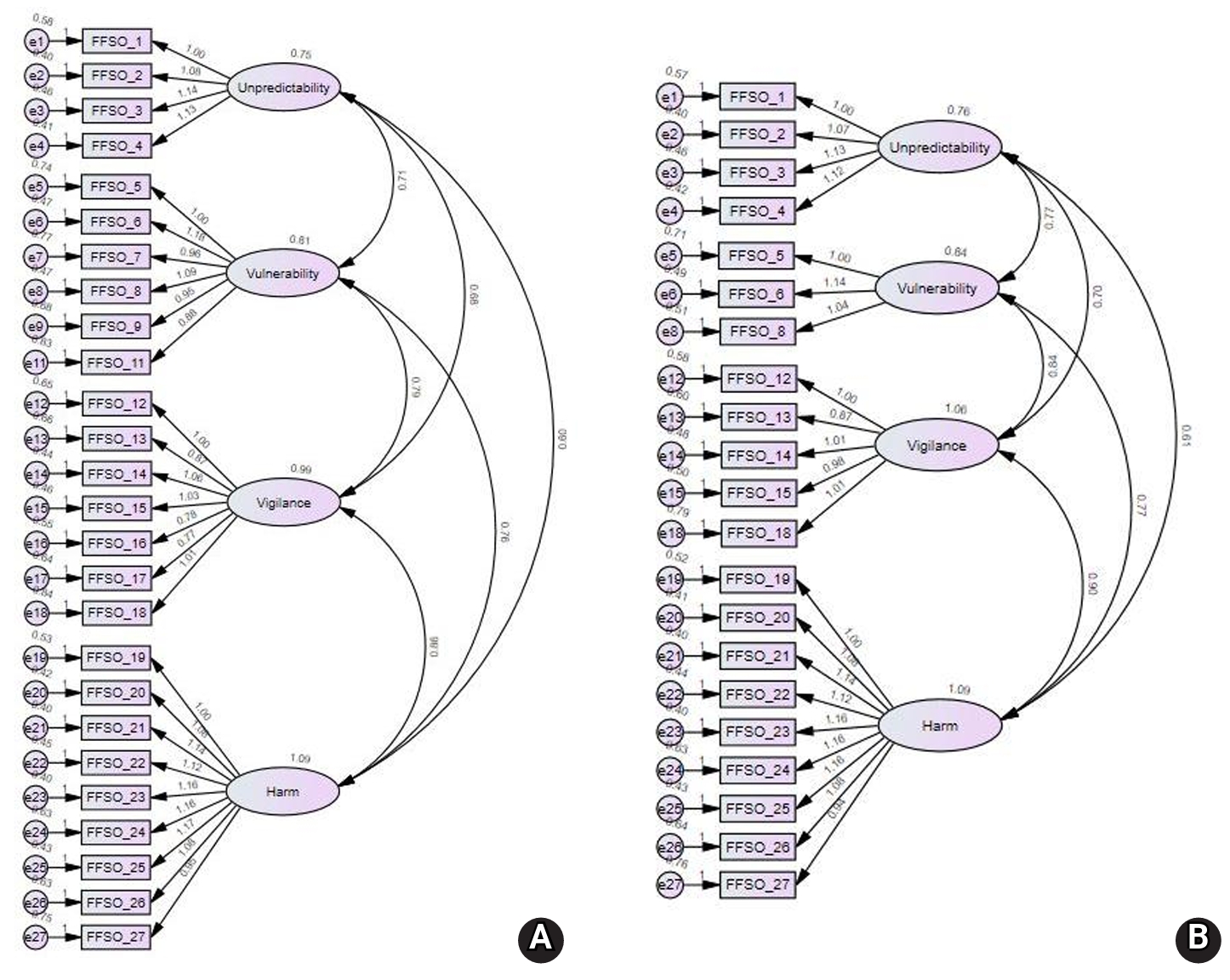
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure fear of falling in older adults and to validate its reliability and validity.
Methods
In total, 31 initial items were developed by referring to expressions from previous studies and items from existing instruments. After verifying content validity through expert evaluation, the remaining 27 items were used to construct a survey. Data from 252 participants recruited at three senior welfare centers in the metropolitan area were analyzed to examine item analysis, construct validity, convergent validity, discriminant validity, and reliability. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was conducted to test construct validity. The correlation with the Korean version of the Falls Efficacy Scale-International (KFES-I) was used to assess convergent validity. Cronbach’s alpha was calculated to determine reliability.
Results
The final instrument consisted of 21 items. CFA confirmed acceptable model fit. Convergent validity was also acceptable and discriminant validity was partially supported. Correlations with the KFES-I ranged from .54 to .63. The Cronbach’s alpha coefficients for the total score and all factors ranged from .84 to .97.
Conclusion
The Fear of Falling Scale for Older Adults developed in this study is a validated tool capable of measuring various dimensions of fear of falling. It provides a foundation for accurately assessing fear of falling in older adults and addressing its specific aspects.
- 1,357 View
- 166 Download

- Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
- Haesun Lee, Hye Jin Nam, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):454-467. Published online August 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
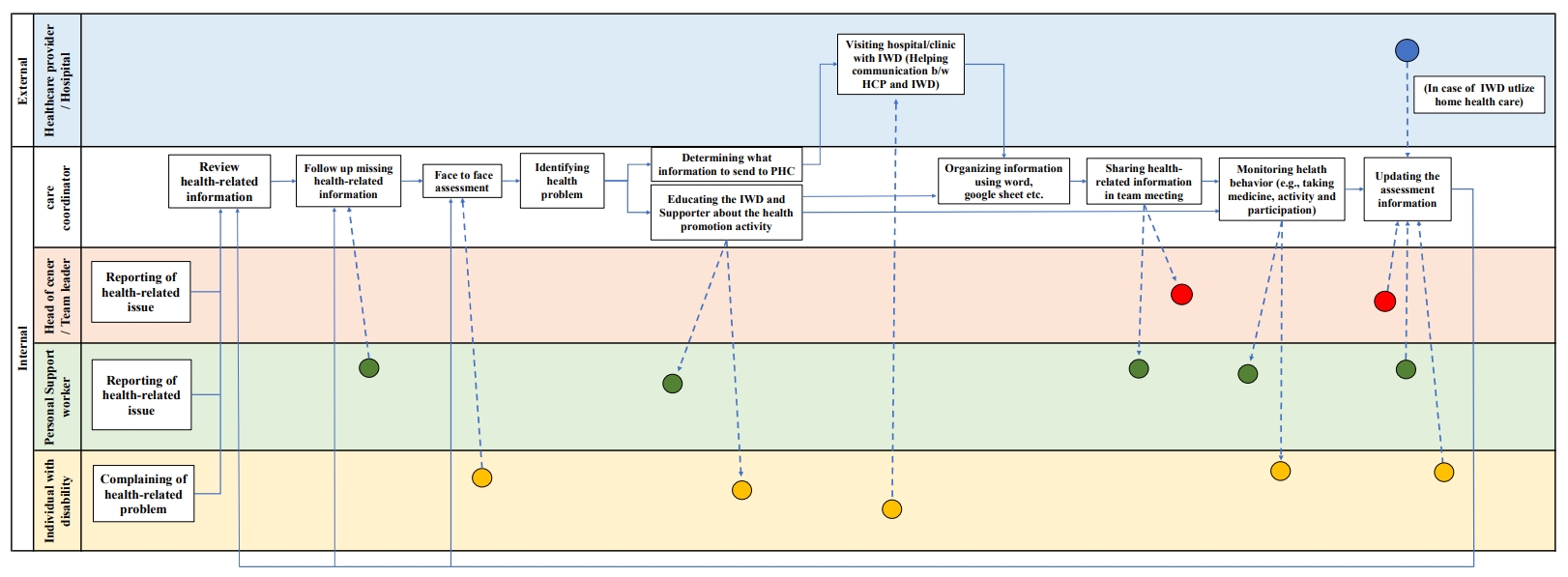
This study conducted a work-system analysis using the Systems Engineering Initiative for Patient Safety (SEIPS) framework to assess the flow of health-related information, and the current status of health management tasks for individuals with disabilities (IWD) in supportive housing.
Methods
This qualitative study utilized focus groups. Participants included a head of supportive housing, a team leader, a care coordinator and three personal support workers for IWD. Semi-structured interviews were guided by the SEIPS framework to explore the components of persons, tasks, tools and technology, organization, and environments.
Results
This study identified five key themes within the five SEIPS components: (1) disparities in role identity and health literacy among staff, (2) challenges in health care support reflecting a person-centered approach, (3) barriers in health-related information exchange and communication tools, (4) needs for organizational strategies or information communication, and (5) needs for integrating health-related information across external healthcare institutions. Additionally, 10 sub-themes were identified.
Conclusions
These findings provide a comprehensive system-wide perspective and offer insights into the systematic approaches needed to improve healthcare processes and structures within disability supportive housing. Specifically, healthcare providers and effective tools for integrating health-related information are identified as critical components.
- 1,448 View
- 89 Download

- Effectiveness of a mobile application for tracking symptoms and enhancing symptom management among breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy in Bangkok, Thailand: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Duangrat Kaveenuntachai, Supawan Jaiboon, Bualuang Sumdaengrit, Chureeporn Silaguntsuti, Arveewan Vittayatigonnasak, Pornchan Sailamai
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):178-190. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25011
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study evaluated the effectiveness of a mobile application in tracking symptoms and improving symptom management and quality of life (QoL) among breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in Thailand.
Methods
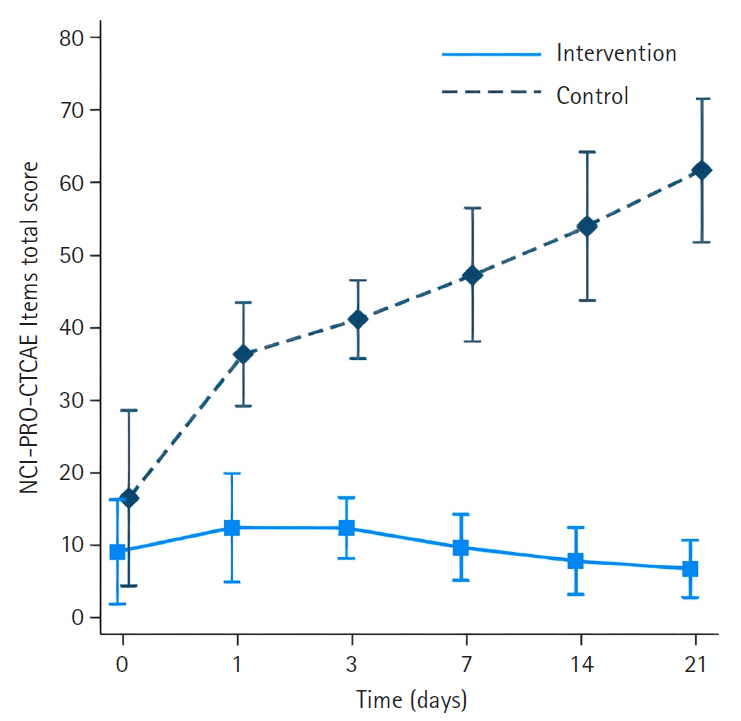
A non-randomized controlled trial was used, with 25 participants in the intervention group and 25 in the control group. Research instruments included a demographic data form, the NCI-PRO-CTCAE Items-Thai-Thailand version 1.0, and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Core Questionnaire and Breast Cancer-Specific Module.
Results
The intervention group had significantly less severe side effects than the control group, with mean differences of –23.33 (95% confidence interval [CI], –27.82 to –18.83) on day 1, –28.18 (95% CI, –33.22 to –23.14) on day 3, –34.63 (95% CI, –40.18 to –29.08) on day 7, –42.56 (95% CI, –48.72 to –36.40) on day 14, and –51.31 (95% CI, –58.13 to –44.48) on day 21 (p<.001 for all). On day 21, participants in the intervention group reported significantly higher scores in the Global Health QoL and Functional Scales compared to the control group (p<.001). Additionally, intervention group participants reported lower scores on the Symptom Scales and higher scores on the Functional Scales than those in the control group (p<.001).
Conclusion
The ChemoPro application helped manage chemotherapy-related symptoms and was associated with improved symptom monitoring and QoL. Nonetheless, the study was limited by a small sample size and restriction to Android users. Future research with larger and more diverse populations is recommended before broader implementation in clinical practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of a digital health intervention on the supportive care needs and quality of life in Mexican patients with breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial
Saúl Eduardo Contreras-Sánchez, Svetlana V. Doubova, Rocío Grajales-Álvarez, Ricardo Villalobos-Valencia, Abdel Karim Dip-Borunda, José Gustavo Nuñez-Cerrillo, Alma Diana Huerta-López, Álvaro José Montiel-Jarquín, Arturo García-Galicia, Enrique Isay Talam
BMC Cancer.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effectiveness of a digital health intervention on the supportive care needs and quality of life in Mexican patients with breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial
- 4,258 View
- 215 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Successful aging among the elderly with mild cognitive impairment facing the crisis of old age: a grounded theory study
- Haeyun Shin, Suhye Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):301-316. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to understand experiences of successful aging experience in older adults with mild cognitive impairment.
Methods
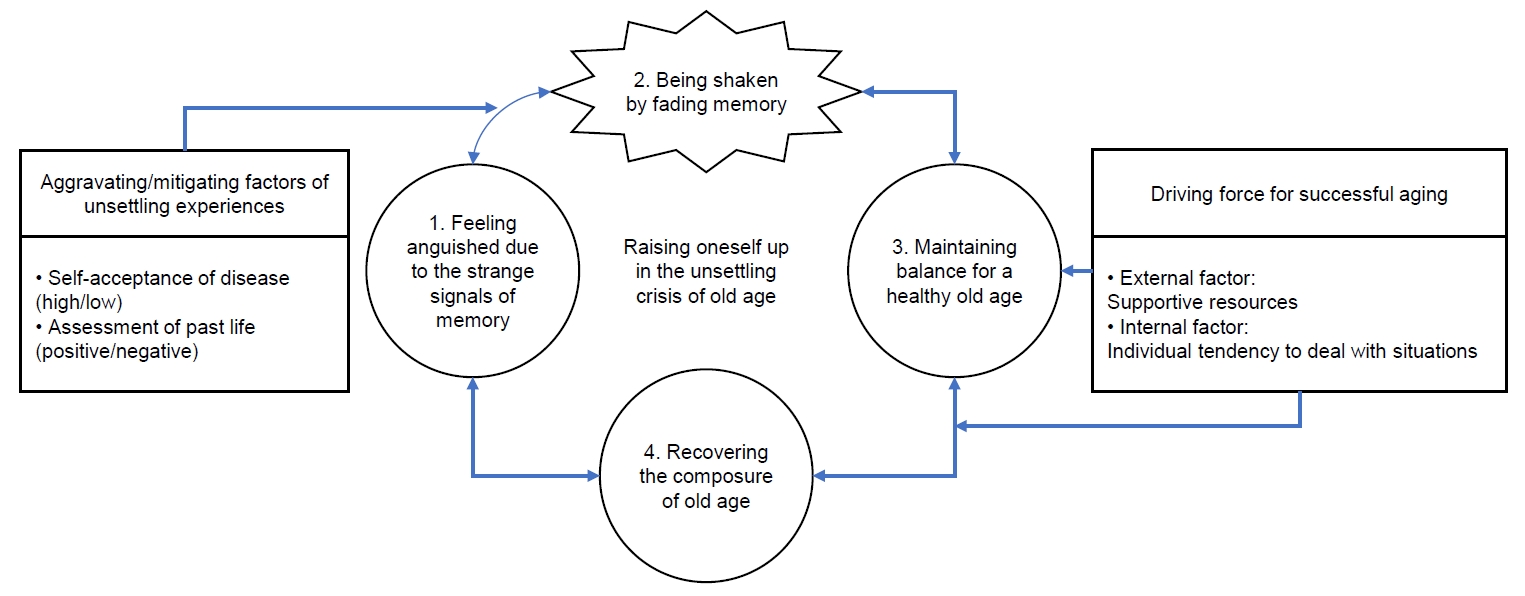
The participants were 15 older adults with mild cognitive impairment who had experienced successful aging. Data were collected from January to October 2021 through individual deep, unstructured interviews. Data analysis was performed using Charmaz’s grounded theory method. In addition, the consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research checklist was used to ensure the quality of the study.
Results
The key category representing experiences of successful aging experience in older adults with mild cognitive impairment was “raising oneself up in the unsettling crisis of old age.” Four stages were derived: “feeling anguished due to the strange signals of memory,” “being shaken by fading memory,” “maintaining balance for a healthy old age,” and “recovering the composure of old age.”
Conclusion
Participants tried to successfully achieve aging while implementing their own plans and strategies in the midst of the challenges of old age, when the mind and body were unsettled by mild cognitive impairment. The results of this study provide a deep understanding of experiences of successful aging in older adults with mild cognitive impairment, potentially contributing to the development and implement of nursing intervention programs to promote the successful pursuit of aging in this population.
- 2,256 View
- 113 Download

- A non-face-to-face diabetes self-management program based on self-efficacy theory and health literacy: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Jung Hee Lee, Soo Jin Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):165-177. Published online May 23, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to assess the impact of a non-face-to-face diabetes self-management program based on self-efficacy theory and focusing on health literacy.
Methods
A quasi-experimental, nonequivalent control group pre–post design was used. Participants from a community health promotion center were included if they (1) were 30–70 years of age, (2) had type 2 diabetes with glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥6.5%, and (3) had internet access via computers or mobile devices. The 8-week program was developed based on self-efficacy theory, and it included virtual education using an online platform, telephone counseling, videos, and social networking site activities considering health literacy. Fasting blood glucose levels, HbA1c levels, diabetes self-efficacy, social support, depression, and self-management behaviors were assessed. Data were analyzed using the independent t-test, paired t-test, and others.
Results
Post-test results showed that the intervention group had significantly lower fasting blood glucose levels and improved diabetes self-efficacy, social support, and self-management behaviors compared with the control group. An analysis of the pre-to-post changes in scores indicated that the intervention group had significantly greater improvements in fasting blood glucose levels, diabetes self-efficacy, and overall diabetes self-management behaviors than those observed in the control group.
Conclusion
Non-face-to-face programs based on self-efficacy theory that consider health literacy can provide effective diabetes management support to patients when in-person diabetes management at community health centers is challenging.
- 3,341 View
- 243 Download

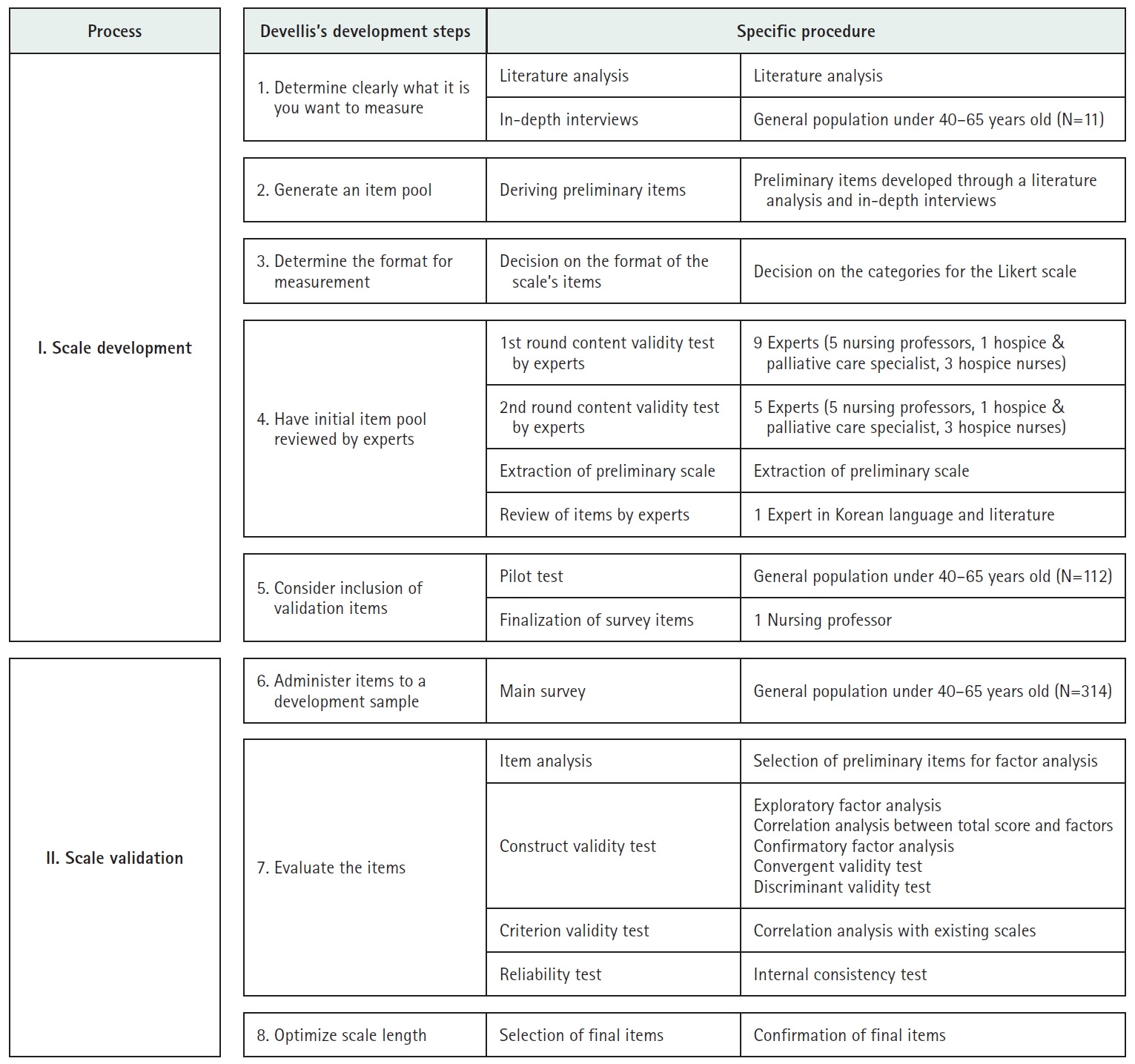
- Development of a well-dying awareness scale for middle-aged adults in Korea: a mixed-methods study
- Yu Jin Jung, Eun Joung Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):285-300. Published online March 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a valid and reliable tool to measure awareness of well-dying among middle-aged adults.
Methods
A mixed-methods approach was adopted, consisting of a qualitative phase to identify the characteristics of well-dying and a quantitative phase to validate the instrument with middle-aged participants. Initially, 76 items were generated through a literature review and in-depth interviews, and these were reduced to 35 items through expert validation. A pilot survey was conducted with 112 individuals aged 40–65, selected via quota sampling from 17 administrative regions in South Korea. Based on the pilot survey results, the instrument was refined to 32 items for the main survey. The main survey included 314 participants recruited through quota sampling in Busan and Ulsan Metropolitan Cities and Gyeongsang Region. Exploratory factor analysis (EFA), confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), and reliability testing were performed to validate the instrument.
Results
The final scale comprised 23 items across six factors. EFA demonstrated an explanatory power of 69.1%, with factor loadings ranging from 0.53 to 0.88. CFA confirmed the instrument’s validity, and reliability was established with a Cronbach’s α of .93.
Conclusion
This instrument is a validated and reliable tool for measuring middle-aged individuals’ awareness of well-dying. It can serve as an effective resource for evaluating and assessing well-dying awareness in the middle-aged population.
- 2,915 View
- 200 Download

- Nomogram for predicting changes in cognitive function in community dwelling older adults with mild cognitive impairment based on Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing Panel Data: a retrospective study
- Hyuk Joon Kim, Hye Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):50-63. Published online February 7, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24059
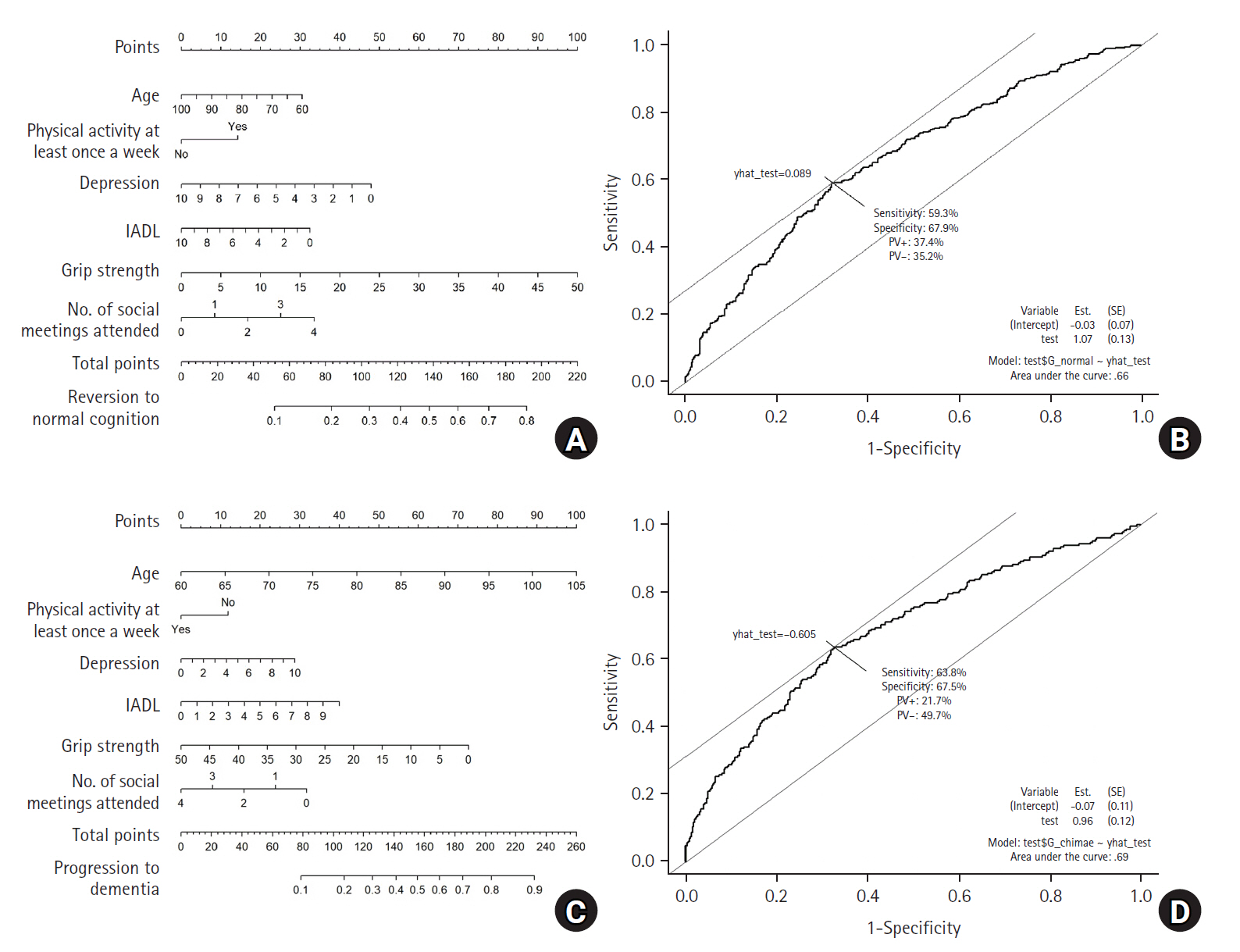
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify factors associated with normal cognitive reversion and progression to dementia in older adults with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) residing in the community and to develop a nomogram.
Methods
This longitudinal study used secondary data from the Korea Longitudinal Study of Ageing Panel Data (2006–2018). The study included 1,262 participants aged 60 or older, with initial Mini-Mental State Examination scores ranging from 18 to 23. Data were analyzed using the Rao-Scott chi-square test, panel binary logistic regression, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve in Stata ver. 17.0 (Stata Corp.).
Results
The rate of reversion from MCI to normal cognition was 37.0% after 2 years and 32.9% after 12 years. The rate of progression to dementia was 18.0% after 2 years and 30.2% after 12 years. In the nomogram for reversion to normal cognition, the most significant influences were grip strength, depression, number of meetings, age, and regular exercise, with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of .66. In contrast, in the nomogram for progression to dementia, the most significant influences were age, grip strength, instrumental activities of daily living, number of social meetings attended, depression, and regular exercise, with an AUC of .69.
Conclusion
These nomograms can serve as an effective intervention tool for preventing dementia in the field of community health care since they can serve as a visual technique for presenting information on risk to individuals with MCI. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Longitudinal Relationship Between Physical Functions and Cognitive Functions Among Middle-Aged and Older Adults in Primary Care
Nan Hu, Wupeng Yin, Rabeya Illyas Noon, Noof Alabdullatif
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2025; 22(6): 908. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Nomogram Predicting Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults
Sook Kyoung Park, Hyuk Joo Kim, Young-Me Lee, Hye Young Kim
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Emotional Labor on Burnout in Nurses: Focusing on the Moderating Effects of Social Intelligence and Emotional Intelligence
Kyung Ran Lee, Jeoung Mi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(1): 22. CrossRef
- The Longitudinal Relationship Between Physical Functions and Cognitive Functions Among Middle-Aged and Older Adults in Primary Care
- 3,511 View
- 212 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Analysis of the Adequacy of Nurse Staffing Level through the Estimation of Nursing Activity Hours and Implementation of Focus Group Interviews in a Tertiary Hospital: Using a Mixed-Method Design
- Hyun-Joo Kim, Sun-Hee Lee, Jai-Jung Lee, Sun-Suk Seong, Hee Yang, Hyang-Yuol Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):237-249. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22142
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the adequacy of current nurse staffing levels by identifying nursing activities and workload.
Methods
The study used a mixed-method design. A nursing activity survey was conducted using the work sampling method over 2 working days with 119 general ward nurses. A focus group interview was conducted with 12 nurses. Quantitative and qualitative data were analyzed using SPSS 20.0 and content analysis, respectively.
Results
The most amount of time was spent on medication (in direct nursing) and electronic medical record documentation (in indirect nursing). The appropriate nurse-to-patient ratio is 1:7.7 for the day shift, 1:9.0 for the evening shift, and 1:11.9 for the night shift. However, the current nurse-to-patient ratio is 1:9.4, 1:11.0, and 1:13.8 for the day, evening, and night shifts, respectively. Therefore, the current nurse staffing level is insufficient for the workload. In the focus group interview, the main reasons cited for being unable to complete tasks within working hours were communication and coordination, and the nursing electronic medical record. The essential nursing activities of basic nursing and emotional support were overlooked owing to a heavy workload. Therefore, an adequate nurse staffing level should be higher than the measured quantitative workload.
Conclusion
These results suggest the general wards of tertiary hospitals should evaluate the adequacy of their current nurse staffing and allocate sufficient nurses to improve patient safety and nursing care quality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nurses' Experience Working with Substitute Nurses
Hye Mi Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 208. CrossRef
- Nurses' Experience Working with Substitute Nurses
- 3,042 View
- 262 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Experiences of Transitional Care for Medicaid Case Managers
- Yunhee Hwang, Gaeon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(5):556-569. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23031
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This phenomenological study tried to understand the essence of the transitional care experience of medicaid case managers and its structural meaning. In addition, it was attempted to establish a system of transitional care and seek support measures for medicaid case managers.
Methods
The participants of this study were 7 medicaid case managers who had spent more than 1 year and 6 months in medicaid pilot project. Data were collected with individual in-depth interviews from June to December 2021. The data were analyzed by Giorgi's phenomenological analysis method.
Results
The seven constituents derived from the results of this study were 'struggle to establish a living environment', 'dedication to supporting independent living', 'anxiety about safety', 'pressure on care responsibilities', ‘distress in building the pilot project’, 'pride in role', and 'expectation for improvement'.
Conclusion
The study results provide a comprehensive understanding of the transition care reality for medicaid case managers. They also shed light on managers’ perceptions and attitudes. These findings can serve as fundamental information for establishing support measures for medicaid case managers and transitional care systems.
- 1,800 View
- 31 Download

- An Investigation of the Cumulative Effects of Depressive Symptoms on the Cognitive Function in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Analysis of the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging
- Eunmi Kim, Jinkyung Oh, Iksoo Huh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):453-467. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated the cumulative effects of depressive symptoms on cognitive function over time in community-dwelling older adults. Methods: Data were investigated from 2,533 community-dwelling older adults who participated in the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (KLoSA) from the 5th (2014) to the 8th wave (2020). The association between cumulative depressive symptoms and cognitive function was identified through multiple regression analysis. Results: When the multiple regression analysis was conducted from each wave, the current depressive symptoms scores and cognitive function scores were negatively associated, regardless of the waves (B5th = - 0.26, B6th = - 0.26, B7th = - 0.26, and B8th = - 0.27; all p < .001). Further, when all the previous depressive symptoms scores were added as explanatory variables in the 8th wave, the current one (B8th = - 0.09, p < .001) and the previous ones (B5th = - 0.11, B6th = - 0.09, and B7th = - 0.13; all p < .001) were also negatively associated with the cognitive function score. The delta R2 , which indicates the difference between the model’s R2 with and without the depressive symptoms scores, was greater in the model with all the previous and current depressive symptoms scores (6.4%) than in the model with only the current depressive symptoms score (3.6%). Conclusion: Depressive symptoms in older adults have a long-term impact. This results in an accumulated adverse effect on the cognitive function. Therefore, to prevent cognitive decline in older adults, we suggest detecting their depressive symptoms early and providing continuous intervention to reduce exposure to long-term depressive symptoms. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Systematic identification and quantification of factors and their interactions with age, sex, and panel wave influencing cognitive function in Korean older adults
Eunmi Kim, Jinkyung Oh, Jungsoo Gim, Iksoo Huh
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Systematic identification and quantification of factors and their interactions with age, sex, and panel wave influencing cognitive function in Korean older adults
- 2,263 View
- 56 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of Self-Efficacy for HIV Disease Management Skills
- Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Mi-So Shim, Seoyoung Baek, Namhee Kim, Min Kyung Park, Youngjin Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(3):295-308. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23016
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study evaluated the validity and reliability of Shively and colleagues’ self-efficacy for HIV disease management skills (HIVSE) among Korean participants.
Methods
The original HIV-SE questionnaire, comprising 34 items, was translated into Korean using a translation and back-translation process. To enhance clarity and eliminate redundancy, the author and expert committee engaged in multiple discussions and integrated two items with similar meanings into a single item. Further, four HIV nurse experts tested content validity. Survey data were collected from 227 individuals diagnosed with HIV from five Korean hospitals. Construct validity was verified through confirmatory factor analysis. Criterion validity was evaluated using Pearson’s correlation coefficients with the new general self-efficacy scale. Internal consistency reliability and test-retest were examined for reliability.
Results
The Korean version of HIV-SE (K-HIV-SE) comprises 33 items across six domains: “managing depression/mood,” “managing medications,” “managing symptoms,” “communicating with a healthcare provider,” “getting support/help,” and “managing fatigue.” The fitness of the modified model was acceptable (minimum value of the discrepancy function/degree of freedom = 2.49, root mean square error of approximation = .08, goodnessof-fit index = .76, adjusted goodness-of-fit index = .71, Tucker-Lewis index = .84, and comparative fit index = .86). The internal consistency reliability (Cronbach’s α = .91) and test-retest reliability (intraclass correlation coefficient = .73) were good. The criterion validity of the K-HIV-SE was .59 (p < .001).
Conclusion
This study suggests that the K-HIV-SE is useful for efficiently assessing self-efficacy for HIV disease management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Providing 2 Types of mHealth Interventions to Support Self-Management Among People Living With HIV: Randomized Clinical Trial
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Seoyoung Baek, Sooyoung Kwon, Ji Min Kim, Jun Yong Choi, Jae-Phil Choi
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2025; 13: e60905. CrossRef - Factors associated with health-related quality of life among people living with HIV in South Korea: Tobit regression analysis
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, SangA Lee, Mi-So Shim, Youngjin Lee, Seoyoung Baek, Claus Kadelka
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(5): e0303568. CrossRef - Three cycles of mobile app design to improve HIV self-management: A development and evaluation study
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Seoyoung Baek, Mi-So Shim, SangA Lee, Ji Min Kim, Jong Yae Yoon, Jin Kim, JunYong Choi, Jae-Phil Choi
DIGITAL HEALTH.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Providing 2 Types of mHealth Interventions to Support Self-Management Among People Living With HIV: Randomized Clinical Trial
- 2,917 View
- 64 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Association between Visual Impairment and Nutritional Risk among Older Adults with Diabetes: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study
- Eunjin Yang, Kyung Hee Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):167-176. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22141
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Despite the high prevalence of visual impairment caused by diabetic retinopathy and nutritional problems among older adults with diabetes, evidence regarding factors related to nutritional risk in this population is limited. Therefore, this study aimed to identify the correlates of nutritional risk among older adults with diabetes, focusing on visual impairment.
Methods
This study was a secondary data analysis of the 2020 National Survey of Older Koreans aged 65 years and above. The sample comprised 2,376 older adults with diabetes, and complex sample ANOVA and Rao–Scott chi-square tests were used to compare the groups according to visual impairment. Complex-sample logistic regression analyses were conducted to verify the association between visual impairment and nutritional risk.
Results
Older adults with diabetes, who also have severe visual impairment, are more likely to have nutritional risk status than those without impairment after controlling for covariates (odds ratio [OR] = 2.44, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.16~5.13). Among the covariates, depression (OR = 3.58, 95% CI 2.60~4.94), dependent activities of daily living status (OR = 2.79, 95% CI 1.60~4.86), and experience of hospitalization during the past year (OR = 2.51, 95% CI 1.57~4.03) were strongly associated with nutritional risk.
Conclusion
Severe visual impairment increases the nutritional risk among older adults with diabetes. Therefore, it is essential to prevent visual impairment due to exacerbation of diabetes through appropriate management. Additionally, tailored nutritional interventions for visually impaired older adults with diabetes that consider visual characteristics are required. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of Alcohol Drinking with Chronic Diseases among Korean Men with Severe Vision Disorders
Sunmee YUN-WELCH, Sunhee KIM, Jeehoon LEE, Mieun YUN, Geumseon LEE
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2025; 25(4): 147. CrossRef - Insights into the associated risk factors of malnutrition among nursing home residents: A longitudinal study
Johanna de Almeida Mello, Emilie Schoebrechts, Patricia Ann Ivonne Vandenbulcke, Anja Declercq, Jan De Lepeleire, Christophe Matthys, Dominique Declerck, Joke Duyck
Clinical Nutrition.2024; 43(11): 166. CrossRef - Frailty and Visual Impairment in Elderly Individuals: Improving Outcomes and Modulating Cognitive Decline Through Collaborative Care Between Geriatricians and Ophthalmologists
Daniel Dinarvand, Johann Panthakey, Ahmed Hassan, Mohamed H. Ahmed
Diseases.2024; 12(11): 273. CrossRef - Malnutrition Risk in Community-Dwelling Older Adults with Dual Sensory Declines: Focusing on Social Determinants of Health
Ha Na Jeong
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2024; 35: 325. CrossRef
- Associations of Alcohol Drinking with Chronic Diseases among Korean Men with Severe Vision Disorders
- 2,619 View
- 62 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of Clinical Nurses’ Job Crafting on Organizational Effectiveness Based on Job DemandsResource Model
- Eun Young Lee, Eungyung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):129-143. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22138
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the mediating effects of clinical nurses’ job crafting on organizational effectiveness based on the job demands-resources model proposed by Bakker and Demerouti (2017).
Methods
The participants consisted of 393 nurses working in nursing units of a tertiary general hospital located in Cheongju region. The data, collected using questionnaire from August 9 to August 20, 2021, were analyzed using SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 27.0.
Results
The goodness-of-fit (GoF) test results on the modified model (χ 2 = 2.7, GFI = .94, SRMR = .03, RMSEA = .06, NFI = .92, CFI = .94, TLI = .92, AGFI = .90), indicated that the GoF index satisfied the recommended level. Regarding the effects of each variable on organizational effectiveness, job crafting showed statistically significant direct (β = .48, p < .001), indirect (β = .23, p < .001), and total effects (β = .71, p < .001). Burnout showed statistically significant direct effect (β = - .17, p < .001). Work engagement showed statistically significant direct (β = .41, p < .001) and total effects (β = .41, p < .001). The factors explaining organizational effectiveness were job crafting, burnout, and work engagement, which had an explanatory power of 76.7%.
Conclusion
Nurses’ job crafting is an important mediating factor for enhancing the organizational effectiveness of nursing organizations. Hospitals should develop job-crafting success cases and related education and training programs as a strategy for enhancing the job crafting of nurses and, consequently organizational effectiveness. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hospital Nurses’ Professional Quality of Life Model: A Cross‐Sectional Study Based on the Expanded Job Demands‐Resources Model
Younghee Kim, Mi Yu, Jacopo Fiorini
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of grit and job crafting on organizational commitment and job satisfaction among hospital nurses in Korea
Mi-Suk Hyun
Medicine.2025; 104(45): e45890. CrossRef - Effects of Attitude Toward Interdepartmental Transfer, Career Growth Opportunity, and Role Breadth Self-Efficacy on Job Crafting among Nurses with Transfer Experience
Yu Jin Lee, Chung Hee Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 497. CrossRef - Job Crafting as the Missing Link: Understanding Its Role in Nurses’ Work Engagement
Kyungjin Lee, Ja Kyung Seo, Seung Eun Lee, Yunhong Liu
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Commitment to Organizational Change in Clinical Nurses: A Structural Model Applying Lewin's Change Theory
Mihwa Hong, Sujeong Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 38. CrossRef
- Hospital Nurses’ Professional Quality of Life Model: A Cross‐Sectional Study Based on the Expanded Job Demands‐Resources Model
- 3,956 View
- 169 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Lived Experience of Middle-Aged Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
- Young-suk Seo, Sunhee Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(6):598-607. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22086
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This qualitative study aimed to explore the lived and true meaning of experiences of middle-aged patients with complex regional pain syndrome.
Methods
The participants were 10 men and women aged 40 to 60 years who received outpatient treatment at a university hospital, could communicate, and agreed to participate in the study. Data were collected through individual interviews using open and semi-structured questions from September 2019 to July 2021 and were analyzed using the content analysis method suggested by Hsieh and Shannon (2005).
Results
As a result of this study, 42 summarized semantic units related to life experience, 15 subthemes, and seven themes were derived. The seven themes were “pressed by severe pain,” “frustrated because I cannot be part of the community,” “distressed because people do not recognize my disease,” “sad about conflicts with family,” “unmotivated because of desperate life,” “appreciating for support,” and “putting oneself together and living daily life.” Conclusion: The vivid experiences of the participants derived in this study are the basic data for developing treatment guidelines. In the future, we propose a study on life and family care experiences according to the developmental characteristics of the life cycle of patients with complex regional pain syndrome and develop and apply programs to support patients and their families. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Experiences of diagnosis and treatment for upper limb Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: a qualitative analysis
Grace S Griffiths, Bronwyn L Thompson, Deborah L Snell, Jennifer A Dunn
Pain Medicine.2023; 24(12): 1355. CrossRef
- Experiences of diagnosis and treatment for upper limb Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: a qualitative analysis
- 1,763 View
- 37 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- The Development of Automated Personalized Self-Care (APSC) Program for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Gaeun Park, Haejung Lee, Ah Reum Khang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(5):535-549. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22046
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The study aimed to design and develop an automated personalized self-care (APSC) program for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The secondary aim was to present a clinical protocol as a mixed-method research to test the program effects.
Methods
The APSC program was developed in the order of analysis, design, implementation, and evaluation according to the software development life cycle, and was guided by the self-regulatory theory. The content validity, heuristics, and usability of the program were verified by experts and patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Results
The APSC program was developed based on goal setting, education, monitoring, and feedback components corresponding to the phases of forethought, performance/volitional control, and self-reflection of self-regulatory theory. Using the mobile application, the participants are able to learn from educational materials, monitor their health behaviors, receive weekly-automated personalized goals and feedback messages, and use an automated conversation system to solve the problems related to self-care. The ongoing two-year study utilizes a mixed method design, with 180 patients having type 2 diabetes mellitus randomized to receive either the intervention or usual care. The participants will be reviewed for self-care self-efficacy, health behaviors, and health outcomes at 6, 12, 18, and 24 months. Participants in the intervention group will be interviewed about their experiences.
Conclusion
The APSC program can serve as an effective tool for facilitating diabetes health behaviors by improving patients’ self-care self-efficacy and self-regulation for self-care. However, the clinical effectiveness of this program requires further investigation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of mHealth-Based Self-Management Interventions on Self-Efficacy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Junhee Ahn, Youngran Yang, Ji Young Kim, Jihyon Pahn, Yura Jang
The Science of Diabetes Self-Management and Care.2025; 51(5): 517. CrossRef - Impact of Mobile App-Based Self-Monitoring Engagement on Self-Care Self-Efficacy, Health Behaviors, and Hemoglobin A1c Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial
Gaeun Park, Haejung Lee, Min Jin Lee, Ahreum Khang
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2025; 47(12): 1180. CrossRef - A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Da-Jung Kim
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2025; 21(5): 234. CrossRef - Adherence-based experiences with a personalized self-care program for type 2 diabetes in South Korea: a mixed-methods study
Haejung Lee, DaeEun Lee, Mihwan Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(4): 706. CrossRef - Participation experience in self-care program for type 2 diabetes: A mixed-methods study
Mihwan Kim, Haejung Lee, Gaeun Park, Ah Reum Khang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(1): 31. CrossRef - Long‐Term Effects of an Automated Personalized Self‐Care Program for Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Haejung Lee, Gaeun Park, DaeEun Lee, Ah Reum Khang, Min Jin Lee
Nursing & Health Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Automated Personalized Self-care Program for Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Pilot Trial
Gaeun Park, Haejung Lee, Yoonju Lee, Myoung Soo Kim, Sunyoung Jung, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(2): 114. CrossRef - Healthcare coaching program for youth with type 1 diabetes in South Korea: a pilot study
Dae Eun Lee, Haejung Lee, Chong Kun Cheon, Ju Young Yoon
Child Health Nursing Research.2024; 30(1): 17. CrossRef - The Association between the Low-density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol to High-density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol Ratio and the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Adults: A Secondary Data Analysis Using a Community-based Cohort Study in Korea
Bo-Kyoung Cha
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(1): 66. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of mHealth-Based Self-Management Interventions on Self-Efficacy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 3,884 View
- 114 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- A Longitudinal Study of the Reciprocal Relationship between Depression and Income among Korean Older Men and Women
- Jeong Lee, Gyeong-Suk Jeon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):451-463. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the reciprocal relationships between depression and income, and gender differences in these relationships among older adults in South Korea.
Methods
Using 2015 to 2019 of the Korea Welfare Panel Study (KoWePS), we studied 6,070 older adults (2,394 men and 3,676 women) aged 60 years over in 2015. The generalized estimating equation was employed to explore the effect of an individual income on depression and the reverse causal link-that of depression on income.
Results
The study found the reciprocal relationships between income and depression. Income has a significant impact on depression. Higher-income was linked to decreased risks of the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression (CES-D) scores among older adults (B = - 0.121, p < 0.001). Estimates of the reverse causal link show that higher CES-D scores were also linked to income reduction among Korean older adults (B = - 0.007, p < 0.001). In addition, we also observed gender differences in the impact of income on depression but not in the reverse causal link. Income has more detrimental to psychological consequence for older men (B = - 0.108, p < 0.001) than older women (B = - 0.057, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
The finding implies that both psychological and social protection policies for the elderly are needed in view of gender perspective. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factors of depression among the baby boomer generation: A cross-sectional study using the 2022 Korean Community Health Survey
Kyoung Mi Kim, Hye Jung Jun
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(3): 308. CrossRef
- Risk factors of depression among the baby boomer generation: A cross-sectional study using the 2022 Korean Community Health Survey
- 1,976 View
- 35 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Influence of Social Capital on Depression of Older Adults Living in Rural Area: A Cross-Sectional Study Using the 2019 Korea Community Health Survey
- Minho Jung, Jinhyun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):144-156. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21239
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the influence of social capital on the depression of older adults living in rural areas.
Methods
Data sets were obtained from the 2019 Korea Community Health Survey. The participants were 39,390 older adults over 65 years old living in rural areas. Indicators of social capital included trust, reciprocity, network, and social participation. Depression—the dependent variable—was measured using the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9). Hierarchical ordinal logistic regression was conducted to identify factors associated with depression after adjusting the data numbers to 102,601 by applying the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE).
Results
The independent variables—indicators of social capital—exhibited significant association with the depression of older adults. The odds ratios of depression were higher in groups without social capital variables.
Conclusion
To reduce depression, we recommend increasing social capital. Factors identified in this study need to be considered in older adult depression intervention programs and policies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Perceived Stress on Depression among Middle-aged Adults with Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: Exploring the Mediating Role of Social Capital through a Descriptive Correlational Study
Kyung Ae Kim, Mi Ran Bang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(1): 50. CrossRef - An Observational Study on the Association Between Nutritional Intake and Mental Health Among Older Adults in Rural Areas
Kyeongmin Jang
Nursing & Health Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Modelo de regresión ordinal para pronóstico de la depresión en el adulto mayor peruano
Lilian Roxana Paredes López
UCV Hacer.2025; 14(2): 32. CrossRef - Moderating effects of social capital on the relationship between fear of falling and depressive symptoms among community-dwelling older adults
Yeong-Mi Seo, Eun Sook Lee
Archives of Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction model of weight control experience in men with obesity in their 30 s and 40 s using decision tree analysis
Myeunghee Han
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between human capital and depression among middle-aged rural adults: The multiple-parallel mediating effects of social capital
Soo Mi Jang, Hyung Mi Ha
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2023; 40(1): 33. CrossRef
- The Effects of Perceived Stress on Depression among Middle-aged Adults with Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: Exploring the Mediating Role of Social Capital through a Descriptive Correlational Study
- 2,546 View
- 108 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Couple Satisfaction Index
- Suk-Sun Kim, Minji Gil, Daeun Kim, Sunhai Kim, Dayeon Heo, Nan Young Moon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):228-227. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21177
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The study aimed to translate the Couple Satisfaction Index (CSI 32) into Korean, to evaluate the reliability and validity of CSI 32 and short-form (CSI 16, 4) in the Korean context, and to determine a cut-off score for Korean couples.
Methods
Korean Versions of the Couple Satisfaction Index (K-CSI) 32 was translated, back-translated, and reviewed by five bilingual experts. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was conducted with data from a sample of 218 couples (N = 436) to test construct validity. Validity and reliability were evaluated. The receiver’s operating characteristics curve analysis was used to obtain the cut-off score.
Results
The construct validities of K-CSI 32, 16, and 4 were verified using one-factor structures. The results of CFA showed a slightly better fit for K-CSI 16 and 4 than for K-CSI 32. Convergent validity was supported by significant positive correlations of K-CSI with Kansas Marital Satisfaction Scale, Dyadic Adjustment Scale, and Family Relationship Assessment Scale. Moreover, the significant differences in K-CSI between normal and depressive group demonstrated known-group validity. Cut-off scores of 105.5 on K-CSI 32, 50.25 on K-CSI 16, and 13.25 on K-CSI 4 were validated to identify distressed couple relationships.
Conclusion
For clinical practice, the reliable and valid K-CSI 32 has the potential to measure changes in couple satisfaction after couple therapy or interventions. Applying K-CSI 32 may facilitate research on couple and family relationships in nursing and contribute to the discussion on the role of couple satisfaction in mental health. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating Effects of Parental Family Adaptation on the Quality of Life of Children With Down Syndrome: A Study of Father–Mother Dyads
Seung Hyeon Yang, Chang Gi Park, Eun Kyoung Choi
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Online coaching blended couple‐oriented intervention for preventing depression among Korean middle adulthood: A feasibility study
Minji Gil, Suk‐Sun Kim, Daeun Kim, Sunhai Kim
Family Process.2023; 62(4): 1478. CrossRef
- Mediating Effects of Parental Family Adaptation on the Quality of Life of Children With Down Syndrome: A Study of Father–Mother Dyads
- 5,320 View
- 188 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Willingness to Use and Appropriate Payable Cost for Visiting Nurse Service for the Elderly in the Community
- Soyoung Seo, Soong-nang Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):105-119. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21193
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to measure willingness to use (WTU) and appropriate payable cost of visiting nurse service for the elderly and explore their impact factors.
Methods
The study included 752 participants selected from data that were completed in 2017 for the elderly aged over 60 nationwide. Logit and Tobit regression analysis were performed to confirm the influencing factors.
Results
The study found that 39.1% of the elderly in the community were WTU the visiting nurse service, and they reported that the cost per visit was 12,650 Korean Won. The factors influencing WTU were having less than moderate subjective health status (OR = 1.63, p = .011), being part of a social participating groups (OR = 1.50, p = .046), or participation in senior health promotion programs (SHPPs) (OR = 1.96, p = .003). The cost was also influenced by less than moderate subjective health status (β = 4.37, p = .021), being part of a social participating groups (β = 4.41, p = .028), or participation in SHPPs (β = 4.87, p = .023). Additionally, elderly people living alone who were used as covariates were highly WTU (OR = 2.20, p = .029).
Conclusion
This study provides evidence to predict demand for visiting nurse service and reflects consumer value in setting the service cost. This is the first study to derive cost from consumers' perspective regarding the service for the elderly. As it is the result of an open-ended survey, follow-up studies are needed to estimate more reliable and reasonable results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health and Environmental Monitoring Services for Smart Healthy Cities : Current Practices and Challenges in Local Government Plans
Dong-ah Choi, Yun-jeong Song, Andy Hong
Journal of Korea Planning Association.2024; 59(5): 147. CrossRef
- Health and Environmental Monitoring Services for Smart Healthy Cities : Current Practices and Challenges in Local Government Plans
- 2,860 View
- 52 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Healthcare Considerations for Special Populations during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review
- Jeung-Im Kim, YeoJin Im, Ju-Eun Song, Sun Joo Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):511-524. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has emerged as a threat to human health and public safety. People of all ages are susceptible to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection. However, the clinical manifestations of this infection differ by age. This study purposes to describe healthcare considerations for special populations, such as children, pregnant and lactating women, and older adults, who may have unique healthcare needs, in the pandemic situation. To realize the research purpose, we conducted a review of the practice guidelines of public documents and qualified studies that were published online/offline during a specific period. The review identified current knowledge on care for newborns, children in schools, pregnant women (from antenatal to postpartum care), and older adults suffering from high-risk conditions. Subsequently, we summarize vaccination guidance for special populations and, finally, discuss the issues currently affecting special populations. Therefore, this current knowledge on care for special populations helps nurses to provide accurate information on vaccinations aimed at preventing COVID-19 and protecting the masses from infection. Currently, the scarcity of information on COVID-19 variants necessitates further research on measures to reduce pandemic spread.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Global and Regional Burden of Vaccine‐Associated Transverse Myelitis and Potentially Associated With Vaccines From 1967 to 2023: An Analysis of the International Pharmacovigilance Data
Jae E. Lee, Hyesu Jo, Hanseul Cho, Jiyeon Oh, Yi Deun Jeong, Sooji Lee, Jaeyu Park, Hyeon Jin Kim, Yejun Son, Soeun Kim, Hayeon Lee, Louis Jacob, Damiano Pizzol, Ho Geol Woo, Jiyoung Hwang, Dong Keon Yon
Journal of Medical Virology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Preliminary Exploratory Bibliometric Study on COVID-19 and Pregnancy
Fatima Aguirre-Vegas, Jakeline Ramos-Aliaga, Maria E Guerrero, Juan Alvitez, Abigail Temoche, Frank Mayta-Tovalino
Journal of South Asian Federation of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.2025; 17(5): 618. CrossRef - The Use of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange in the Treatment of a Pregnant Woman with COVID-19 Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Sy Duong-Quy, Duc Huynh-Truong-Anh, Thanh Nguyen-Thi-Kim, Tien Nguyen-Quang, Thanh Nguyen-Chi, Nhi Nguyen-Thi-Y, Van Duong-Thi-Thanh, Carine Ngo, Timothy Craig
Pulmonary Therapy.2022; 8(2): 233. CrossRef
- Global and Regional Burden of Vaccine‐Associated Transverse Myelitis and Potentially Associated With Vaccines From 1967 to 2023: An Analysis of the International Pharmacovigilance Data
- 2,227 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- The Effects of Programs on Body-Image Improvement in Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Hyun Jung Yun, Kyoungsan Seo, Dallong Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):597-616. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study’s objective was to investigate the effects of programs that improve adolescents’ body image, using a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
A literature search was performed in eleven electronic databases, using preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis guidelines. Population characteristics, contents of the programs, and measured outcomes were systematically reviewed from 21 selected studies. To estimate the size of the effects, meta-analysis was conducted using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software.
Results
The contents of the programs that aimed to improve body image included physical, psychological, interpersonal, and sociocultural interventions. Sixteen studies were meta-analyzed to estimate the effect size of body-image improvement programs. Results showed that the program for body-image improvement had significant effects on body satisfaction (effect size [ES] = 0.56, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.23 to 0.89), and body dissatisfaction (ES = - 0.15, 95% CI = - 0.23 to - 0.08).
Conclusion
The program for body image improvement in adolescents includes a combination of physical, psychological, interpersonal relationship, and socio-cultural dimensions. The program that seeks to improve body image appears to be effective at increasing body satisfaction, and at reducing body dissatisfaction in adolescents. Thus, it is necessary to develop and apply multidimensional programs for adolescents to have a positive body image. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 청소년의 신체상과 행복감 간의 관계: 가족 의사소통으로 조절된 자아존중감의 매개역할*
종일 여
Journal of Family Relations.2025; 30(1): 55. CrossRef
- 청소년의 신체상과 행복감 간의 관계: 가족 의사소통으로 조절된 자아존중감의 매개역할*
- 2,886 View
- 62 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Self-Efficacy for Managing Chronic Disease 6-Item Scale
- Sook-Nam Kim, Hyun-Ju Lee, So-Young Kim, Nayoon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):617-629. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21069
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aim of this study was to examine the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the self-efficacy for managing chronic disease 6-item scale (SECD-6-K).
Methods
The English version of the Self-Efficacy for Managing Chronic Disease 6-item Scale first underwent forward and backward translation procedures. The SECD-6-K was then used to collect data from 350 adults diagnosed with chronic diseases. Content, construct, convergent, discriminant, and criterion validity were all evaluated. Reliability was assessed using Cronbach’s α. SPSS 25.0 and the data were analyzed using AMOS 26.0 software.
Results
The SECD-6-K consists of six items in two domains: disease management and health behavior. The results for construct, convergent, and discriminant validity were good. Exploratory factor analysis produced eigen values between 2.27 and 3.28, with factors total explained cumulative variance of 91.1%. Confirmatory factor analysis supported goodness of fit and reliability for the modified SECD-6-K model. The criterion validity also showed significant correlation with both the Patient Health Questionnaire and 12-item Short-Form Health Survey version 2. Finally, reliability was found to be excellent.
Conclusion
This study identified the high reliability and validity of SECD-6-K. The SECD-6-K is an appropriate tool for determining Korean patients’ self-efficacy in managing their chronic conditions. Therefore, this scale may be used in clinical settings as well as in educational and research settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Generic instruments for assessing self-management abilities and behaviors in patients with chronic diseases: a COnsensus-based standards for the selection of health measurement INstruments (COSMIN)-based systematic review
Ke Liu, Guangyan Meng, Caixia Li, Shuyi Wang, Xianwen Fan, Qirong Chen
Quality of Life Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Path Analysis of Factors Influencing Health-Related Quality of Life for Community-Dwelling Vulnerable Older Adults with Chronic Diseases in Korea
Hyun-Ju Lee
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2025; 36: 315. CrossRef - Development of a self-care scale for women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a methodological approach
Miok Kim
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Short Form of Core Competencies Scale of Nursing Care for Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Sung Hae Kim, Seyong Lee, Sang Hee Kim, Jung Ok Choi, Gie Ok Noh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(4): 184. CrossRef - Factors influencing self-management behaviors in older people with multiple chronic conditions based on the individual and family self-management theory: A cross-sectional study
Youngji Seo, Sunyoung Jung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(3): 332. CrossRef - Psychometric property of the Japanese version of self-efficacy for managing chronic disease scale in individuals with chronic diseases
Megumi Hazumi, Mayumi Kataoka, Ayako Nakashita, Kentaro Usuda, Michi Miyake, Chiaki Kamikawa, Daisuke Nishi, Naoaki Kuroda
Heliyon.2024; 10(22): e40218. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the self-efficacy scale for chronic disease management (SEMCD-S) in older Colombian adults
Lorena Cudris-Torres, Stefano Vinaccia Alpi, Álvaro Barrios-Núñez, Natali Gaviria Arrieta, Martha Luz Gómez Campuzano, Giselle Olivella-López, Juan Hernández-Lalinde, Valmore Bermúdez, Olaiza Lobato Pérez, Jorge Armando Niño-Vega, Jorge Navarro-Obeid, Rom
BMC Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ambulatory Chemotherapy (Portable Infusion Pump Use) Video Education on Knowledge, Self-efficacy and Anxiety of Colorectal Cancer Patients
Eun Hee Choi, Eun Young Park, Young A Park, You Hee Son, Myung Jin Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(3): 193. CrossRef
- Generic instruments for assessing self-management abilities and behaviors in patients with chronic diseases: a COnsensus-based standards for the selection of health measurement INstruments (COSMIN)-based systematic review
- 4,549 View
- 215 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- The Lived Experience of Body Alteration and Body Image with Regard to Immediate Breast Reconstruction among Women with Breast Cancer
- Jeonghee Ahn, Eunyoung E. Suh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(2):245-259. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21028
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to explore the lived experience of body alteration and body image with regard to immediate breast reconstruction among women with breast cancer.
Methods
Data were collected from July to December 2020 through individual in-depth interviews with 15 women who had undergone immediate breast reconstruction due to breast cancer. Verbatim transcripts were analyzed using Colaizzi’s phenomenological analysis.
Results
The following four theme clusters emerged. First, “revalued meaning of breasts due to cancer” illustrated the fact that cancer removal surgery brought the participants to reconsider the meaning of their breasts. Second, “had no choice but breast reconstruction” demonstrated the participants’ decision-making process of not wanting to lose breasts. Third, “unsatisfied breasts despite reconstruction” portrayed the distress due to the unexpected surgical outcomes. Finally, “restarted everyday routines with the altered body” described the healing process of the participants by accepting their changed body.
Conclusion
In Korea, where family-centeredness and fidelity are highly valued, women perceived their breasts not only as a symbol of femininity but as the mediator connecting the self to family. Despite the distress related to imperfect breasts, the participants were thankful for their reconstructed breasts. Breast reconstruction helped them return to daily life as the psychological trauma of breast cancer was healed. The participants rebuilt their body image by accepting their scarred new body. This may allow health professionals to provide constructive and culturally appropriate counseling in advance by providing insight into women’s perception of their body image with regard to breast reconstruction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mental health in female breast cancer survivors post-mastectomy: A structural model based on Roy's adaptation model
Hyeng Sook Yoon, Eunjung Ryu
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100820. CrossRef - Categorising Subjective Perceptions of Middle-Aged Breast Cancer Patients Using Q Methodology
Min-Jeung Shim, Song-Yi Lee, Oh-Sun Ha
Healthcare.2024; 12(18): 1873. CrossRef - Body Acceptance Scale for Women with Breast Cancer: Development and Validation of a Measurement
Jeonghee Ahn, Eunyoung E. Suh
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2023; 39(5): 151486. CrossRef - Influence of body image on quality of life in breast cancer patients undergoing breast reconstruction: Mediating of self‐esteem
Yunhee Jang, Mihyeon Seong, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(17-18): 6366. CrossRef - Body acceptance in women with breast cancer: A concept analysis using a hybrid model
Jeonghee Ahn, Eunyoung E. Suh
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 62: 102269. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta-analysis on the prepectoral single-stage breast reconstruction
Jiameng Liu, Xiaobin Zheng, Shunguo Lin, Hui Han, Chunsen Xu
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(7): 5659. CrossRef
- Mental health in female breast cancer survivors post-mastectomy: A structural model based on Roy's adaptation model
- 2,513 View
- 86 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Face Mask Usage, Knowledge and Behavior of Face Mask Usage in Older Adults Living Alone in the COVID-19 Era
- A-Reum Han, Yeon-Hwan Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(2):203-216. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20252
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study analyzed the current status of face mask usage. It also identified factors related to the knowledge and behavior regarding the same among older adults living alone during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
This descriptive study was conducted via a telephone survey involving 283 older adults living alone in S City from March to April 2020. Knowledge and behavior pertaining to face mask usage were measured using Hilda Ho’s Face Mask Use Scale; reliability of the measurement was Kuder-Richardson formula-20 = .62, Cronbach’s α = .92. Data were analyzed using descriptive analysis, independent t-test, Pearson’s correlation coefficient, and multiple linear regression.
Results
Older adults used one mask for 3.55 days on an average. The knowledge level was 9.97 (± 1.84) out of 12 and behavior level was 15.49 (± 1.55) out of 16. Level of education (β = - .31, p < .001), living region (β = .13, p = .017), personal income (β = .12, p = .041) significantly affected the face mask usage-related knowledge, and living region (β = .15, p = .010) significantly affected the face mask usage-related behavior.
Conclusion
Older adults living alone are aware of the effects of using face masks. However, their mask usage is inappropriate, for example, the prolonged use of the same mask. Considering the low level of face mask usage-related knowledge, it is necessary to develop customized education programs and infectious disease prevention strategies for older adults possessing low educational levels living alone in urban-rural complex areas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A comparative cross-cultural study of fear of COVID-19 in Persian and Turkmen elderly populations
Maliheh Makhtum, Naser Behnampour, Akram Sanagoo, Hossein Nasiri, Leila Jouybari
Journal of Research Development in Nursing and Midwifery.2023; 20(1): 11. CrossRef - Influencing factors on self-care of older adults living alone in a community during COVID-19: A cross-sectional study
Heeyoung Woo, Minkyung Gu
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - The association between depression and non‐compliance with COVID‐19 preventive behaviors in South Korean older adults stratified by sex
Jae Jun Lee, Namhee Kim, Min Kyung Park, Hyunju Ji, Gwang Suk Kim
International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with Depression in Older Adults Living Alone during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Eun Hye Hong, Kyung Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(4): 418. CrossRef
- A comparative cross-cultural study of fear of COVID-19 in Persian and Turkmen elderly populations
- 1,623 View
- 15 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Diabetes Self-Management Experience of Patients with Diabetes: Focused on the Visually Impaired
- Sun Ju Chang, Kyoung-eun Lee, Eunjin Yang, Hee Jung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):92-104. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20231
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to understand and describe the diabetes self-management experience of visually impaired people with diabetes.
Methods
Ten participants were recruited through a website used by the visually impaired from February to March 2020. Data were collected through two focus group interviews conducted in June 2020; each group consisted of five participants. All interviews were recorded with the consent of the participants and transcribed verbatim. The transcribed data were analyzed using qualitative content analysis.
Results
Seven categories were as follows; a two-faced, lifelong companion, an unprepared encounter, struggle to live, love-hate relationship with family, strategies to adapt, lessening attention to self-management, the desire to learn properly.
Conclusion
It can be concluded that the visually impaired have fewer opportunities for receiving diabetes self-management education than general diabetic patients. Consequently, plans to improve the education available to such patients are required. Additionally, psychological counseling and diabetes education for patients’ families are necessary, and improving the perception of medical workers regarding the visually impaired will be prove useful. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetes care for people experiencing homelessness in the UK: insights from a national survey of frontline professionals and the development of an integrated care model
Daniela Oehring, Martha Paisi, Mona Nasser, Theo Jackson, Ryan Young, Lynne Wooff, Helen Partridge, Jacqueline Conaty, Samantha Dorney-Smith
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Widening disparities in the national prevalence of diabetes mellitus for people with disabilities in South Korea
I. Hwang, S.Y. Kim, Y.Y. Kim, J.H. Park
Public Health.2024; 226: 173. CrossRef - A Tailored Intervention for Improving Diabetes Self-care Among Adults With Visual Impairment: A Pilot Study
Hee Jung Kim, Kyoung-eun Lee, Eunjin Yang, Sun Ju Chang
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2024; 48(6): 394. CrossRef - The Impact of Visual Impairment on Healthcare Use among Four Medical Institution Types: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study in Korea
Boyoung Jeon, Heejo Koo, Hee Kyoung Choi, Euna Han
Yonsei Medical Journal.2023; 64(7): 455. CrossRef - Association between Visual Impairment and Nutritional Risk among Older Adults with Diabetes: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study
Eunjin Yang, Kyung Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(2): 167. CrossRef - Who are the most vulnerable populations for primary care? Avoidable hospitalizations across individuals with different types of disabilities in South Korea
S. Kim, B. Jeon
Public Health.2023; 217: 138. CrossRef - Factors Associated With Diabetes Self-Care Behaviors of People With Visual Impairment: A Cross-Sectional Study
Sun Ju Chang, Hee Jung Kim, Kyoung-eun Lee, Eunjin Yang
The Science of Diabetes Self-Management and Care.2022; 48(5): 324. CrossRef
- Diabetes care for people experiencing homelessness in the UK: insights from a national survey of frontline professionals and the development of an integrated care model
- 2,704 View
- 54 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Family’s Perception of Proxy Decision Making to Authorize Do Not Resuscitate Order of Elderly Patients in Long Term Care Facility: A Q-Methodological Study
- Hyeon Jin Cho, Jiyeon Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):15-26. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20188
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to distinguish and describe the types of perceptions of do not resuscitate (DNR) proxy decisions among families of elderly patients in a long-term care facility.
Methods
This exploratory study applied Q-methodology, which focuses on individual subjectivity. Thirty-four Q-statements were selected from 130 Q-populations formed based on the results of in-depth interviews and literature reviews. The P-samples were 34 families of elderly patients in a long-term care hospital in Busan, Korea. They categorized the Q-statements using a 9-point scale. Using the PC-QUANL program, factor analysis was performed with the P-samples along an axis.
Results
The families’ perceptions of the DNR proxy decision were categorized into three types. Type I, rational acceptance, valued consensus among family members based on comprehensive support from medical staff. Type II, psychological burden, involved hesitance in making a DNR proxy decision because of negative emotions and psychological conflict. Type III, discreet decisions, valued the patients’ right to self-determination and desire for a legitimate proxy decision. Type I included 18 participants, which was the most common type, and types II and III each included eight participants.
Conclusion
Families’ perceptions of DNR proxy decisions vary, requiring tailored care and intervention. We suggest developing and providing interventions that may psychologically support families. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Subjectivity study on health conservation of elderly hemodialysis patients
Eunji Yim, Mijin Yun, Sohyune Sok
BMC Geriatrics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Types of Empathy Among Certified Caregivers of Older Adults with Dementia
So-Hyeong Sim, Geun Myun Kim, Eun Joo Kim, Soo Jung Chang
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2023; Volume 16: 2715. CrossRef
- Subjectivity study on health conservation of elderly hemodialysis patients
- 1,483 View
- 32 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Actor and Partner Effects of Couple’s Daily Stress and Dyadic Coping on Marital Satisfaction
- Su Kyung Won, Kyoung Ok Seol
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(6):813-821. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20162
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the actor and partner effects of daily stress and dyadic coping on marital satisfaction using the Actor-Partner Interdependence Mediational Model (APIeM).
Methods
Participants were 314 couples who met the study’s eligibility criteria. Data were collected from March to April 2016 through apartment and cooperative company communities in Seoul. Two APIeMs of positive and negative dyadic coping were analyzed using SPSS 20.0 and Mplus 7.4. All measures were self-administered.
Results
Daily stress and positive and negative dyadic coping in both spouses had direct actor effects on their marital satisfaction. Daily stress in both spouses had an indirect actor effect on marital satisfaction through their positive and negative dyadic coping. The husband’s daily stress had an indirect partner effect on the wife’s marital satisfaction through his positive dyadic coping, while the wife’s positive dyadic coping had a direct partner effect on the husband’s marital satisfaction. The husband’s daily stress had an indirect partner effect on the wife’s marital satisfaction through his negative dyadic coping, while the wife’s negative dyadic coping had a direct partner effect on the husband’s marital satisfaction.
Conclusion
Dyadic coping is an effective way to deal with couple’s daily hassles as it increase their satisfaction in marriage. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of risk factors for co-morbid anxiety and depression in pregnant women
Wei Zhang, Ling Li, Xiabidan Tuxunjiang, Bahedana Sailike, Xiaoting Wang, Weicui Meng, Sufeila Shalayiding, Ting Jiang
Psychiatry Research.2025; 344: 116323. CrossRef - Pregnant Women’s Dyadic Coping and Associated Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study Utilizing Latent Profile Analysis
Shiqiong Yan, Wenzhuo Fan, Yonghong Ma, Sijia Xie, Rong Li, Yao Lan, Linli Xie, Jie Jing
International Journal of Women's Health.2024; Volume 16: 1009. CrossRef - Spouse Burnout and Marriage Satisfaction in Married Individuals: The Mediating Role of Psychologıcal Well-being
Bülent Şen, Nergüz Bulut Serin, Kadriye Karagülmez
Batı Anadolu Eğitim Bilimleri Dergisi.2024; 15(2): 1266. CrossRef - Dyadic coping and associated factors in women with high-risk pregnancy and their spouses: Do they interact?
Mengjie Liu, Yu Fang, Mengshi Liu, Min Wu, Jingshuo Zhang, Tianchen Niu, Xiaoman Zhang
Midwifery.2024; 134: 104006. CrossRef - 중년부부의 문제해결 유형과 결혼만족도의 관계
수산나 주, 미선 강, 인혜 정, 서진 조
Journal of Family Relations.2023; 28(1): 33. CrossRef - Relationship between Chinese middle-aged and old couples' Confucian coping thinking and marital quality
Zhiguang Fan, Hanwei Wu, Min Tao, Lei Chen
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of avoidant attachment on marital satisfaction of Chinese married people: Multiple mediating effect of spousal support and coping tendency
Lian Xiong, Caihua Zhou, Liangshi Yan, Pan Zhao, Mengting Deng, Yan Hu
Acta Psychologica.2022; 228: 103640. CrossRef - Interrelation of Attachment and Coping Behavior In Adults
E.V. Kuftyak
Counseling Psychology and Psychotherapy.2021; 29(1): 28. CrossRef
- Analysis of risk factors for co-morbid anxiety and depression in pregnant women
- 1,589 View
- 45 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Predictive Model for Quality of Life of the Older Men Living Alone
- Su Jin Kim, Gyeong-Suk Jeon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(6):799-812. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to construct and test a predictive model that explains and predicts the quality of life in older men living alone.
Methods
A self-report questionnaire was used to collect data from 334 older adult men living along aged 65 years or over living in Jeollanam-do provinces. The endogenous variables were depression, self-rated health, instrumental activity of daily life, health promotion behaviors, the number of social participation activities and quality of life. Data were analyzed using the SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0 programs.
Results
The final model with 14 of the 8 analysed paths showed a good fit to the empiri cal data: χ2= 173.26(p < .001, df = 53),normed χ2= 3.27, GFI = .92, NFI = .90, CFI = .93, TLI = .89, RMSEA = .08 and SRMR = .06. Activities had direct effect on quality of life of older men living alone and social support had both direct and indirect effects. Meanwhile, function and socioeconomic status showed only indirect effects.The variables included in the eight significant paths explained 83.7% of variance in the prediction model.
Conclusion
Instrumental activities of daily living and social support effect directly on quality of life in the older men living alone. Findings suggest that health care providers including community nurses need to provide social support as well as empowerment programs of instrumental activities of daily living and health promotion for improving quality of life of the older men living alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changes in the health status and health-related quality of life of community-dwelling older adults living alone: one-year follow-up from a cohort study
Hana Ko, Belong Cho, Kyung-Choon Lim, Soong-Nang Jang, Sun Ju Chang, Yu Mi Yi, Hye Ryung Cho, So Im Ryu, Eun-Young Noh, Yeon-Hwan Park
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influencing factors on self-care of older adults living alone in a community during COVID-19: A cross-sectional study
Heeyoung Woo, Minkyung Gu
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - A novel nomogram to stratify quality of life among advanced cancer patients with spinal metastatic disease after examining demographics, dietary habits, therapeutic interventions, and mental health status
Yue Li, Ze Long, Xiuju Wang, Mingxing Lei, Chunzi Liu, Xiaolin Shi, Yaosheng Liu
BMC Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Associated Factors with Health-related Quality of Life among Older Adults with Diabetes in Korea
Eun-Kyung Lee, Sun-Young Jung
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2022; 25(2): 61. CrossRef
- Changes in the health status and health-related quality of life of community-dwelling older adults living alone: one-year follow-up from a cohort study
- 2,081 View
- 34 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- The Disease Management Experience of Patients with Asthma: Grounded Theory Approach
- Bohye Kim, Oksoo Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(5):714-727. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20139
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aim of this study was to develop a situation-specific theory to explain the disease management experience of patients with asthma.
Methods
Twenty participants with asthma were selected using the theoretical sampling method. The data were acquired through in-depth interviews conducted from June to October 2018 and analyzed using the grounded theory approach of Strauss and Corbin.
Results
In total, 69 concepts, 30 subcategories, and 13 categories were generated to explain the disease management experience of patients with asthma. The core category of the disease management experience of patients with asthma was ‘management of the disease to prevent aggravation of symptoms over the lifetime’. The disease management process of asthma patients included three steps: the ‘cognition phase’, the ‘adjustment phase’, and the ‘maintenance phase’. However, some patients remained in the ‘stagnation phase’ of disease management, which represents the result of the continual pursuit of risky health behavior. There were three types of disease management experiences among patients with asthma: ‘self-managing’, ‘partially self-managing’, and ‘avoidant’.
Conclusion
This study shows that patients with asthma must lead their disease management process to prevent exacerbation of their symptoms. It is imperative to develop nursing strategies and establish policies for effective disease management of patients with asthma based on their individual disease management processes and types. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Qualitative Research in Healthcare: Data Analysis
Dasom Im, Jeehye Pyo, Haneul Lee, Hyeran Jung, Minsu Ock
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(2): 100. CrossRef
- Qualitative Research in Healthcare: Data Analysis
- 1,710 View
- 50 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Qualitative Study on the Experience of Patients with Meniere Disease
- Woo Joung Joung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(5):699-713. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20115
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to understand and describe the experiences of patients with Meniere disease.
Methods
Data were collected from February 19, 2019, to February 5, 2020, through individual in-depth interviews with 13 Meniere patients. Verbatim transcripts were analyzed using Colaizzi’s phenomenological analysis.
Results
The experiences of patients with Meniere disease were clustered into the following four themes from 22 meaning units: 1) Complex unfamiliar symptoms that shatter both balance of the body and peace of the heart; 2) A disease that medical treatment and health professionals cannot cure; 3) Suffering hardships that cannot be understood by non-Meniere sufferers; and 4) Making daily efforts to become healthier. Symptoms of Meniere disease are life-shattering and depressing because they are neither visible nor easily curable. Over time, as they accepted the reality of living with the disease, the participants would shift their focus from complete symptomatic cure to leading a healthy and more balanced life.
Conclusion
This study shows that Meniere disease has a pervasive impact on all aspects of the patients’ lives. Patients are prone to experiencing restrictions in their social functioning and activities. They also experience psychosocial problems due to the unseen nature of their symptoms. This study elucidates the experiences of Meniere patients and the need for nursing intervention to help improve their quality of life and ability to self-manage. Lastly, this study shows the need for a coordinated interdisciplinary approach to raising public awareness of the disease.
- 2,454 View
- 27 Download

- Effects of BeHaS Program on Health Behavior, Physiologic Index and Self-Esteem of the Elderly Living Alone with Metabolic Syndrome Based on Community Based Participatory Research
- Jong Im Kim, Sun Ae Kim, Keumok Park, Jiyoung Kim, Lina Lee, Si Wan Choi, Bon Jeong Ku
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(4):571-582. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19261
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to determine the effects of a 12-week metabolic syndrome BeHaS (Be Happy and Strong) program in elderly people with metabolic syndrome living alone, based on a community-based participatory research (CBPR).
Methods
A nonequivalent control group pre-posttest design was used, and the participants were 43 elderly people living alone (experimental group 24, control group 19). The experimental group received a one-hour program per week and two individual health consultations during 12 weeks. The control group received two sessions about the metabolic syndrome and two individual health consultations. The effects of health behavior, blood pressure, blood sugar levels, abdominal circumference, triglycerides, and self-esteem were evaluated. The data were analyzed using the independent t-test and Mann-Whitney U test.
Results
The health behavior with respect to the metabolic syndrome in the experimental group increased significantly (t = - 3.19, p = .002). Both diastolic blood pressure and abdominal circumference decreased in the experimental group (t = 2.00, p = .028 and t = 3.91, p < .001). No significant differences were observed between the groups in systolic blood pressure, fasting blood sugar levels, triglycerides, and self-esteem.
Conclusion
The 12-week metabolic syndrome BeHaS program using community resources improves the health of elderly people with metabolic syndrome living alone. Based on these findings, further studies on the effectiveness of the metabolic syndrome BeHaS program and the experiences of those who participated in the CBPR are warranted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and effects of a customized integrated health management program for older adults living alone: A nonequivalent control-group pre-posttest design
Mooyong Cho
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(3): 295. CrossRef - Exploring the Impact of Smart Mobility and ICT Solutions on Older Adults’ Mobility: A Systematic Literature Review
Chengyuan An
IEEE Access.2024; 12: 159056. CrossRef - 노인 대사증후군에 효과적인 중재: 체계적 문헌고찰과 메타분석
서현 이, 슬 구, 유미 서, 선화 반
Public Health Weekly Report.2023; 16(48): 1633. CrossRef - Comparison of the Effects of Education Only and Exercise Training Combined with Education on Fall Prevention in Adults Aged 70 Years or Older Residing in Elderly Residential Facilities
Chahwa Hong, Haejung Lee, Misoon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(2): 173. CrossRef
- Development and effects of a customized integrated health management program for older adults living alone: A nonequivalent control-group pre-posttest design
- 1,504 View
- 36 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Development and Validation of the Self-Care for Aspiration Pneumonia Prevention Scale in the Community Dwelling Elderly with Risk of Dysphasia
- Eun Young Yang, Shin-Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):474-486. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20041
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop and validate a Korean version of the Self-Care for Aspiration Pneumonia Prevention(SCAPP-K) scale in older adults at risk of dysphasia.
Methods
The Hertz and Baas model of scale development and validation was used. Inthe development stage, items were generated via literature review and interviews with medical experts, older adults, and caregivers. Tenexperts assessed the items for content validity. Subsequently, 12 older adults participated in a pilot test to determine the comprehensibilityand appropriateness of the SCAPP-K scale. The validation stage involved a cross-sectional survey with 203 older adults for exploratoryfactor analysis (EFA) and 200 older adults for confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) and to determine convergent and discriminant validity. Totest the validity and reliability of the scale, EFA using principal component analysis with varimax rotation and CFA were conducted, andconvergent and discriminant validity as well as internal consistency reliability were determined.
Results
As a result of EFA, three self-carefactors (knowledge, resources, behaviors) with 21 items were validated. The CFA and convergent and discriminant validity indicated theapplicability of the three-factor self-care scale. The reliability of the SCAPP-K scale was acceptable, with Cronbach’s a=.87~.91.
Conclusion
The SCAPP-K scale has acceptable validity and reliability and can contribute to clinical practice, research, and education to improveself-care for the prevention of aspiration pneumonia in older adults at risk of dysphasia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cause-specific mortality in Korea during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic
Jinwook Bahk, Kyunghee Jung-Choi
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022110. CrossRef - Translation of the Chinese version of the Self‐Care for Aspiration Pneumonia Prevention Scale and its validation among Chinese community dwelling elderly with risk of dysphasia
Zhen Yang, Fengmin Chen, Yibo Zhang, Sien Pan, Yingying Lu, Huijun Zhang
Nursing Open.2022; 9(3): 1902. CrossRef - Development and validation of a self-care scale for older adults undergoing hip fracture surgery: the HFS-SC
Eun-Jeong Jeon, Kyeong-Yae Sohng, Hye-Ah Yeom
BMC Nursing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on the characterization, biocompatibility and efficacy of sponge brush products for oral care
Song-Yi Yang, Ji-Won Choi, Sang-Hwan Oh
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2021; 48(1): 27. CrossRef
- Cause-specific mortality in Korea during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic
- 2,217 View
- 77 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Health Behavior Related to Particulate Matter in Older Adults
- Min Kyung Park, Gwang Suk Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):431-443. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate health behavior related to particulate matter (PM) in older adults and examine the factors affectingit.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey design was used. Data were collected from 150 voluntary older adult participants from Songpa-gu inSeoul. The survey questions measured service perception and experience related to PM, risk perception related to PM, attitude toward riskof PM, and health behavior related to PM.
Results
The average score for health behavior related to PM was 79.37, ranging from 51 to 115.There was a significant positive correlation between health behavior related to PM and risk perception related to PM (r=.58, p <.001) as wellas between health behavior related to PM and attitude toward risk of PM (r=.70, p<.001). Multiple linear regression revealed that healthbehavior related to PM was predicted by levels of the existence of disease related to PM (β=.14, p=.019), service experience related to PM(b=.20, p=.021), risk perception related to PM (b=.20, p=.019), and attitude toward risk of PM (b=.44, p<.001). The model including thesevariables accounted for 47.0% of health behavior related to PM.
Conclusion
Korean older adults have the low level of health behaviorrelated to PM. The findings of this study emphasize that risk perception and attitude toward risk of PM should be evaluated, and theunderlying diseases related to PM and their service experience should be considered in developing intervention to improve health behaviorrelated to PM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Validation of the Dust Exposure Reduction Behavior Scale
Sung Woo Hwang, Hyun Kyoung Kim
Sage Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Graduate Students’ Perception and Behavior Related to Climate Change and Health: A Secondary Data Analysis
Min Kyung Park, Seoyoung Baek, Da Woon Jeong, Gwang Suk Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(1): 71. CrossRef - The association between depression and non‐compliance with COVID‐19 preventive behaviors in South Korean older adults stratified by sex
Jae Jun Lee, Namhee Kim, Min Kyung Park, Hyunju Ji, Gwang Suk Kim
International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation between Particulate Matter Concentrations in Rural Villages in Wanju-gun and the Air Pollution Monitoring Network
Minji Lee, Dongphil Choi, Kyungsu Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2022; 33(1): 139. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Augmented Reality-Based Education on Fine Dust for the Elderly
Jung-Rim Huh, Kon-Joon Bhang
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2021; 22(6): 979. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on the Policy for Facilitating of Health Behaviors Related to Particulate Matter: Using Topic and Semantic Network Analysis of Media Text
Hye Min Byun, You Jin Park, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(1): 68. CrossRef - Environmental Factors Related to Non-compliant Health Behaviors in Urban-Dwelling Elderly
Minkyung Park, Jisu Park, Sunhye Moon, Heejung Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(4): 361. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Particulate Matter-Related Health Behaviors of Patients with Pulmonary Disease
Joohee Ham, SeungHye Choi, Smi Choi-Kwon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(5): 504. CrossRef
- Development and Validation of the Dust Exposure Reduction Behavior Scale
- 1,362 View
- 29 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Development and Effect of a Fall Prevention Program Based on the King's Goal Attainment Theory for Fall High-Risk Elderly Patients in Long-Term Care Hospital
- Bom Mi Park, Ho Sihn Ryu, Kyeung Eun Kwon, Chun Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):203-214. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.203
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study to develop a fringed fall prevention program based on King's goal attainment theory and education. This study is applied to the personal, interpersonal, and social systems of fall high-risk patients to test its effects.
Methods This study was a nonequivalent control group pre- and post-test design. There were 52 fall high-risk patients in the experimental group and 45 in the control group. The experimental group received six sessions, with the group sessions lasting 60 minutes and the individual sessions lasting 20~30 minutes. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, an χ2-test, a paired sample t-test, and a Wilcoxon signed-ranks test utilizing IBM SPSS software.
Results For the 3-month intervention period, the fall prevention program was found to be particularly effective for patients in the experimental group (from 3.38 to 1.69 per 1000 patient days;
p =.044), as opposed to the control group (from 1.94 to 1.49 per 1000 patient days;p =.300). For the 6-month follow up period, the fall prevention program was again found to be effective for patients in the experimental group (from 3.26 to 0.76 per 1000 patient days;p =.049) compared to the control group (from 1.98 to 1.01 per 1000 patient days;p =.368).Conclusion These results indicate that the fringed fall prevention program is very effective in reducing falls, not only during the intervention period, but also after the intervention period has ended. We can therefore recommend this program for use concerning fall high-risk patients in long-term care hospitals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent advances in the identification of related factors and preventive strategies of hip fracture
Yaohui Yu, Yudan Wang, Xiaoli Hou, Faming Tian
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Falls in Patients of Medical Institutions in South Korea: A Literature Review
Jongwon Choi, Woochol Joseph Choi
Physical Therapy Korea.2023; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of a Fall Prevention Program Based on Goal Attainment Theory for Homebound Older Adults With Osteoarthritis of the Lower Extremities
Chunhee Lee, Heeok Park
Orthopaedic Nursing.2022; 41(6): 414. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Led Intervention Programs Based on Goal Attainment Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 699. CrossRef - EFFECTIVENESS OF EDUCATIONAL INTERVENTIONS FOR FALL PREVENTION: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Maria Aline Moreira Ximenes, Maria Girlane Sousa Albuquerque Brandão, Thiago Moura de Araújo, Nelson Miguel Galindo Neto, Lívia Moreira Barros, Joselany Áfio Caetano
Texto & Contexto - Enfermagem.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Application Value of Rehabilitation Nursing in Patients with Stroke Based on the Theory of Interactive Standard: A Randomized Controlled Study
Ningning Li, Jun Wang, Mei Zheng, Qunying Ge, Mozaniel Oliveira
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - A prospective cohort study of the risk factors for new falls and fragility fractures in self-caring elderly patients aged 80 years and over
Jian Zhou, Bo Liu, Ming-Zhao Qin, Jin-Ping Liu
BMC Geriatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Fall Prevention Program Based on King’s Theory of Goal Attainment in Long-Term Care Hospitals: An Experimental Study
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 715. CrossRef - Development of Fall Inducement System based on Pedestrian Biological Data for Fall Reproduction
Jong-il Lee, Jong-Boo Han, Jae Wan Koo, Seokjae Lee, Dong-Seop Sohn, Kap-Ho Seo
Journal of Korea Robotics Society.2020; 15(3): 286. CrossRef
- Recent advances in the identification of related factors and preventive strategies of hip fracture
- 3,095 View
- 106 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Effects of a Web-Based Korean Triage and Acuity Scale Learning Program on Triage Self-Efficacy and Triage Performance Ability for Nurses in Emergency Department
- Hyo-Jin Kim, Hee-Young Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):171-180. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.171
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The Korean Triage and Acuity Scale (KTAS) is a tool used to classify the severity and urgency of emergency department (ED) patients, focusing on their symptoms. In consideration of the importance of the KTAS, a web-based learning program has emerged as a new mode of education; it enables ED triage nurses to access it anytime and anywhere, and according to their own learning abilities. This study aimed to develop a web-based KTAS learning program and evaluate its effects on self-efficacy and triage performance ability in ED nurses.
Methods A quasi-experimental design with a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest was used. The conceptual framework was Bandura's self-efficacy theory. There were 30 participants in the experimental group and 29 in the control group. The experimental group attended an orientation and 4 sessions of a web-based KTAS learning program. The learning program lasted 280 minutes over five weeks, consisting of 40 minutes of orientation and four 60-minute sessions.
Results The scores of self-efficacy, triage performance ability in KTAS level, and chief complaints significantly increased in the experimental group compared to the control group. In addition, the numbers of under-triage in KTAS significantly decreased in the experimental group in comparison to the control group.
Conclusion The results suggest that the learning program was effective in improving ED nurses' level of self-efficacy and triage performance ability (KTAS level and KTAS chief complaint). Accordingly, the web-based KTAS learning program can be applied as an education intervention to improve ED nurses' triage skill.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimizing triage education for emergency room nurses: A scoping review
Hui Ju Shin, Subin Park, Hyun Joo Lee
Nurse Education Today.2025; 144: 106452. CrossRef - Strategies to improve the quality of nurse triage in emergency departments: A systematic review
Simon Ouellet, Maria Cécilia Gallani, Guillaume Fontaine, Éric Mercier, Alexandra Lapierre, Fabian Severino, Céline Gélinas, Mélanie Bérubé
International Emergency Nursing.2025; 81: 101639. CrossRef - Construction of learning objectives and content for emergency triage nurses in tertiary general hospitals: A Delphi study
Linyuan Zhang, Bo Gao, Fang He, Chao Wu, Juan Du, Li Zhang, Juan Liang, Hongjuan Lang
Nurse Education in Practice.2024; 80: 104145. CrossRef - Effectiveness of the Patient’s Severity Classification Competency Promotion Virtual Reality Program of Nursing Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic Period
Eunju Lee, Gyuli Baek, Yeonhui Hwang
Healthcare.2023; 11(8): 1122. CrossRef - Effects on Triage Competency Based on Nursing Task Performance and Self-Efficacy of Nurses in Regional Emergency Medical Institutions
Su Jin Kim, Su Ol Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(3): 304. CrossRef - The Effect of Competency-Based Triage Education Application on Emergency Nurses’ Triage Competency and Performance
Sun-Hee Moon, In-Young Cho
Healthcare.2022; 10(4): 596. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Patient Satisfaction in an Emergency Department Based on the Use of the Korea Triage and Acuity Scale
Keun Hee Park, Min Yoon, Myoung Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(3): 338. CrossRef - Factors associated with the undertriage of patients with abdominal pain in an emergency room
Boo Young Oh, Kisook Kim
International Emergency Nursing.2021; 54: 100933. CrossRef - Facilitators and Barriers of the Triage Process based on Emergency Nurses’ Experience with the Korean Triage and Acuity Scale: A Qualitative Content Analysis
Sun-Hee Moon, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Deok Ju
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(4): 255. CrossRef - Effect of problem-based learning on severity classification agreement by triage nurses
Kyeongmin Jang, Eunmi Jo, Kyoung Jun Song
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Remote Diagnosis System of Uremia Complicated with Sleep Disorder and Effectiveness of Nursing Intervention
Yiqian Wang, Jing Zhu, Jun Cao, Dan Zheng, Lihua Wang, Yuvaraja Teekaraman
Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Comparing the Effect of Web-based Networking Education and Lectures on Learning of Hospital Triage in Nursing Students in Armed Forces Universities of the Islamic Republic of Iran in the Covid-19 Pandemic
Ashkan Morovati, Zahra Farsi, Nahid Rajai, Seyede Azam Sajadi
Military Caring Sciences.2021; 8(2): 127. CrossRef
- Optimizing triage education for emergency room nurses: A scoping review
- 2,403 View
- 47 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref

- Evaluation of Validity of the Korean Triage and Acuity Scale
- Heejung Choi, Jong Sun Ok, Soo Young An
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):26-35. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The aim of this study was to identify the predictive validity of the Korean Triage and Acuity Scale (KTAS).
Methods This methodological study used data from National Emergency Department Information System for 2016. The KTAS disposition and emergency treatment results for emergency patients aged 15 years and older were analyzed to evaluate its predictive validity through its sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value.
Results In case of death in the emergency department, or where the intensive care unit admission was considered an emergency, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of the KTAS were 0.916, 0.581, 0.097, and 0.993, respectively. In case of death in the emergency department, or where the intensive or non-intensive care unit admission was considered an emergency, the sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value, and negative predictive value were 0.700, 0.642, 0.391, and 0.867, respectively.
Conclusion The results of this study showed that the KTAS had high sensitivity but low specificity. It is necessary to constantly review and revise the KTAS level classification because it still results in a few errors of under and over-triage. Nevertheless, this study is meaningful in that it was an evaluation of the KTAS for the total cases of adult patients who sought help at regional and local emergency medical centers in 2016.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prognostic Implications of KTAS Levels 2 and 3 in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Single-center Retrospective Study
Sujin Koo, Seongeun Lee, Jae Young Park, JeongKyu Lee, Keon Yeup Kim, Hyunsun Oh, Jeonghoon Ahn, Bum Joon Kim
Journal of the Korean Neurological Association.2026; 44(1): 27. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Mistriage Based on the Korean Triage and Acuity Scale: A Retrospective Cross‐Sectional Study
Nayeon Yi, Dain Baik
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2025; 57(5): 860. CrossRef - Clinical features and mortality risk factors in hospitalized heart failure patient during the COVID-19 pandemic: A South Korea national emergency department study
Soo Young An, Jong Sun Ok, Sung Hea Kim
Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health.2025; 35: 102144. CrossRef - Transfer versus direct-visit patients in medically underserved emergency departments: a retrospective cohort study
Kyongmin Sun, Youjin Lee, Jungsil Lee
BMC Emergency Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive validity of resource-adjusted Korean Triage and Acuity Scale in pediatric gastrointestinal tract foreign body patients
Jin Hee Lee, Jin Hee Jung, Hyun Noh, Mi Jin Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of storage duration on outcome of patients receiving red blood cell in emergency department
Yu-Kyung Koo, Sol Ji Choi, Soon Sung Kwon, Jinwoo Myung, Sinyoung Kim, Incheol Park, Hyun Soo Chung
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inter hospital external validation of interpretable machine learning based triage score for the emergency department using common data model
Jae Yong Yu, Doyeop Kim, Sunyoung Yoon, Taerim Kim, SeJin Heo, Hansol Chang, Gab Soo Han, Kyung Won Jeong, Rae Woong Park, Jun Myung Gwon, Feng Xie, Marcus Eng Hock Ong, Yih Yng Ng, Hyung Joon Joo, Won Chul Cha
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A novel deep learning algorithm for real-time prediction of clinical deterioration in the emergency department for a multimodal clinical decision support system
Arom Choi, Kwanhyung Lee, Heejung Hyun, Kwang Joon Kim, Byungeun Ahn, Kyung Hyun Lee, Sangchul Hahn, So Yeon Choi, Ji Hoon Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Validity of the Korean triage and acuity scale in older patients compared to the adult group
Ho Sub Chung, Myeong Namgung, Dong Hoon Lee, Yoon Hee Choi, Sung Jin Bae
Experimental Gerontology.2023; 175: 112136. CrossRef - Predictive indicators for determining red blood cell transfusion strategies in the emergency department
Junhyup Song, Sinyoung Kim, Hyun Soo Chung, Incheol Park, Soon Sung Kwon, Jinwoo Myung
European Journal of Emergency Medicine.2023; 30(4): 260. CrossRef - Development and Validation of Simple Age-Adjusted Objectified Korean Triage and Acuity Scale for Adult Patients Visiting the Emergency Department
Seung Wook Kim, Yong Won Kim, Yong Hun Min, Kui Ja Lee, Hyo Ju Choi, Dong Won Kim, You Hwan Jo, Dong Keon Lee
Yonsei Medical Journal.2022; 63(3): 272. CrossRef - Baseline and clinical characteristics of older adults admitted to the intensive care unit through the emergency room: Analysis based on age groups
Ye Lim Lee, Sang Ook Ha, Young Sun Park, Jeong Hyeon Yi, Sun Beom Hur, Ki Ho Lee, Ki Yong Hong, Ju Young Sin, Duk Hwan Kim, Jun Kwon Cha, Jin Hyuck Kim
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine.2021; 28(2): 85. CrossRef - Long-term impact of coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on emergency department utilization in a metropolitan emergency department in Korea
Seung Yeon Hwang, Jae Kwang Lee, Hyun Sik Ryu, Seong Soo Park, Jun Young Choi, Hye Ji Lee, Seung Ho Hur, Yeong Geun Park, Hyun Soo Choi
Pediatric Emergency Medicine Journal.2021; 8(2): 57. CrossRef - Modification and Validation of a Complaint-Oriented Emergency Department Triage System: A Multicenter Observational Study
Dong Hyun Choi, Won Pyo Hong, Kyoung Jun Song, Tae Han Kim, Sang Do Shin, Ki Jeong Hong, Jeong Ho Park, Joo Jeong
Yonsei Medical Journal.2021; 62(12): 1145. CrossRef - Pediatric Emergency Department Utilization and Coronavirus Disease in Daegu, Korea
Kyung Mi Jang, Ji Young Ahn, Hee Joung Choi, Sukhee Lee, Dongsub Kim, Dong Won Lee, Jae Young Choe
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with School Nurses’ Triage Competency in South Korea
Jaehee Yoon, Heesook Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(16): 8279. CrossRef - Characteristics of children with trauma compared to those with disease in the emergency department: a Korean single regional emergency medical center study
Yosub Hwang, Ha Young Jo, Hye Won Yoo, Young Mi Kim, Hye-Young Kim
Pediatric Emergency Medicine Journal.2020; 7(2): 108. CrossRef - Alert Override Patterns With a Medication Clinical Decision Support System in an Academic Emergency Department: Retrospective Descriptive Study
Junsang Yoo, Jeonghoon Lee, Poong-Lyul Rhee, Dong Kyung Chang, Mira Kang, Jong Soo Choi, David W Bates, Won Chul Cha
JMIR Medical Informatics.2020; 8(11): e23351. CrossRef
- Prognostic Implications of KTAS Levels 2 and 3 in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Single-center Retrospective Study
- 5,183 View
- 107 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref

- Latent Class Analysis for Health-Related Quality of Life in the Middle-Aged Male in South Korea
- Youngsuk Cho, Dong Moon Yeum
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):104-112. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to identify types of quality of life (QoL) based on the 5 dimensions of EQ-5D and predict factors affecting types of QoL.
Methods This study was a secondary analysis using data from the Korean Health Panel Survey- II(2012). Participants were 2,071 middle-aged men who had completed the additional survey in 2012 and the data were analyzed using SPSS 20.0 and Mplus 5.21 for latent analysis.
Results Three latent classes of QoL were identified: serious (2.4% of the sample), threatened (15.5%), and stable types (82.0%). The types and characteristics of QoL among the latent classes differed. On comparing latent type 1 with latent type 2, the socioeconomic status (
p <.05), employment status (p <.05), and subjective health status (p <.001) were found to be significant. On comparing latent type 1 with latent type 3, the socioeconomic status (p <.05), current smoking status (p <.001), and subjective health status (p <.001) were found to be significant. On comparing latent type 2 with latent type 3, the socioeconomic status (p <.05), subjective health status (p <.001), stress (p <.001) were found to be significant.Conclusion The results showed significant heterogeneity in types of QoL and the predictors of QoL by types were different. These findings provide basic information for developing nursing interventions to improve QoL. Specific characteristics depending on the subtypes should be considered during the development of interventions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Heterogeneity and associated factors of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome health behaviors: a latent class analysis
Ying liu, Yunmei Guo, Rui Ding, Xin Yan, Huiwen Tan, Xueting Wang, Yousha Wang, LianHong Wang
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sociodemographic and Health Characteristics Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Men and Women Aged ≥50 Years
Goeun Chung, Hye-Sun Jung, Hye-Jin Kim
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2021; 19(3): 159. CrossRef - Health related quality of life in patient with type 2 diabetes: The role of household food insecurity on latent class membership
Abbas Abbasi-Ghahramanloo, Hamid Reza Baradaran, Masoudreza Sohrabi, Kamyar Mansori, Ali Gholami
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(4): 473. CrossRef - Analysis of the Types and Affecting Factors of Older People's Health-related Quality of Life, Using Latent Class Analysis
Sun-Hee Jang, Dong-Moon Yeum
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(2): 212. CrossRef
- Heterogeneity and associated factors of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome health behaviors: a latent class analysis
- 1,269 View
- 12 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Development of the Korean Geriatric Loneliness Scale (KGLS)
- Si Eun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(5):643-654. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.5.643
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop and psychometrically test the Korean Geriatric Loneliness Scale (KGLS).
Methods The initial items were based on in-depth interviews with 10 older adults. Psychometric testing was then conducted with 322 community-dwelling older adults aged 65 or older. Content, construct, and criterion-related validity, classification in cutoff point, internal consistency reliability, and test-retest reliability were used for the analysis.
Results Exploratory factor analysis showed three factors, including 15 items explaining 91.6% of the total variance. The three distinct factors were loneliness associated with family relationships (34.3%), social loneliness (32.4%), and a lack of belonging (24.9%). As a result of confirmatory factor analysis, 14 items in the three-factor structure were validated. Receiver operating characteristic analysis demonstrated that the KGLS’ cutoff point of 32 was associated with a sensitivity of 71.0%, specificity of 80.2%, and area under the curve of .83. Reliability, as verified by the test-retest intraclass correlation coefficient, was .89, and Cronbach's α was .90.
Conclusion As its validity and reliability have been verified through various methods, the KGLS can contribute to assessing loneliness in South Korean older adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of the Smawell Mobile App on Psychological and Biological Factors in the Middle Aged and Older Adults Living Alone
Kyung Sook Kim, Miok Kim, Mi Hee Han
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2022; 31(2): 171. CrossRef - Impact of Frailty, Depression, and Loneliness on Ego-Integrity in Community-Dwelling Elderly
Seon Ju Song, Sung Hee Ko, Ji Young Kim, Hyun Kyung Kim
STRESS.2022; 30(3): 139. CrossRef - A Structural Model of Life Satisfaction for Middle Aged or Older People Living Alone
Kyung Sook Kim, Miok Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(1): 96. CrossRef - Impacts of the Depression among the Elderly in the South Korea Community in COVID-19 Pandemic
Boo Deuk Suh, Kyoung Hee Kwon
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(1): 54. CrossRef - Applying Latent Profile Analysis to Identify Lifestyle Profiles and Their Association with Loneliness and Quality of Life among Community-Dwelling Middle- and Older-Aged Adults in South Korea
Kang-Hyun Park, Eun-Young Yoo, Jongbae Kim, Ickpyo Hong, Jae-Shin Lee, Ji-Hyuk Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(23): 12374. CrossRef
- Effects of the Smawell Mobile App on Psychological and Biological Factors in the Middle Aged and Older Adults Living Alone
- 3,605 View
- 104 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Identification of Knowledge Structure of Pain Management Nursing Research Applying Text Network Analysis
- Chan Sook Park, Eun-Jun Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(5):538-549. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.5.538
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to explore and compare the knowledge structure of pain management nursing research, between Korea and other countries, applying a text network analysis.
Methods 321 Korean and 6,685 international study abstracts of pain management, published from 2004 to 2017, were collected. Keywords and meaningful morphemes from the abstracts were analyzed and refined, and their co-occurrence matrix was generated. Two networks of 140 and 424 keywords, respectively, of domestic and international studies were analyzed using NetMiner 4.3 software for degree centrality, closeness centrality, betweenness centrality, and eigenvector community analysis.
Results In both Korean and international studies, the most important, core-keywords were “pain,” “patient,” “pain management,” “registered nurses,” “care,” “cancer,” “need,” “analgesia,” “assessment,” and “surgery.” While some keywords like “education,” “knowledge,” and “patient-controlled analgesia” found to be important in Korean studies; “treatment,” “hospice palliative care,” and “children” were critical keywords in international studies. Three common sub-topic groups found in Korean and international studies were “pain and accompanying symptoms,” “target groups of pain management,” and “RNs’ performance of pain management.” It is only in recent years (2016~17), that keywords such as “performance,” “attitude,” “depression,” and “sleep” have become more important in Korean studies than, while keywords such as “assessment,” “intervention,” “analgesia,” and “chronic pain” have become important in international studies.
Conclusion It is suggested that Korean pain-management researchers should expand their concerns to children and adolescents, the elderly, patients with chronic pain, patients in diverse healthcare settings, and patients’ use of opioid analgesia. Moreover, researchers need to approach pain-management with a quality of life perspective rather than a mere focus on individual symptoms.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the Knowledge Structure of Research for Nurse Preceptor Training Programs Using Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Sun Hee Seon, Hye Won Jeong, Ja Yun Choi
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of clinical nurse educators’ mentoring feedback on new nurse journals at a tertiary hospital in South Korea: utilizing text network analysis
Shinhye Ahn, Hye Won Jeong
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Pediatric Pain Education Research: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Jinkyung Park, Anna Lee, Namsu Kim, Kyounghae Kim
Pain Management Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Temporal Exploration of New Nurses’ Field Adaptation Using Text Network Analysis
Shin Hye Ahn, Hye Won Jeong, Seong Gyeong Yang, Ue Seok Jung, Myoung Lee Choi, Heui Seon Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 358. CrossRef - Content Analysis of Patient Safety Incident Reports Using Text Mining: A Secondary Data Analysis
On-Jeon Baek, Ho Jin Moon, Hyosun Kim, Sun-Hwa Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(4): 298. CrossRef - Text Network Analysis of Research Topics and Trends on Simulations Using Virtual Patients in Nursing Education
Miok Song, Jeong Eun Moon, Aeri Jang
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2023; 41(9): 639. CrossRef - National Petition Analysis Related to Nursing: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
HyunJung Ko, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee, Hee Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 635. CrossRef - Research trends over 10 years (2010-2021) in infant and toddler rearing behavior by family caregivers in South Korea: text network and topic modeling
In-Hye Song, Kyung-Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(3): 182. CrossRef - Content Analysis of Feedback Journals for New Nurses From Preceptor Nurses Using Text Network Analysis
Shin Hye Ahn, Hye Won Jeong
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2023; 41(10): 780. CrossRef - Capturing New Nurses' Experiences and Supporting Critical Thinking
Sun Hee Seon, Hye Won Jeong, Deok Ju, Jung A. Lee, Shin Hye Ahn
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2023; 41(6): 434. CrossRef - Images of Nurses Appeared in Media Reports Before and After Outbreak of COVID-19: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Min Young Park, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Eun Jee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 291. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Nurses’ Performance of Cancer Pain Management in a Tertiary Hospital
Minhwa Kang, Minjeong Seo
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2022; 25(3): 99. CrossRef - Knowledge Structure of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Health Information on Health-Related Websites and Patients’ Needs in the Literature Using Text Network Analysis
Ja Yun Choi, Su Yeon Lim, So Young Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(6): 720. CrossRef - Trends of Nursing Research on Accidental Falls: A Topic Modeling Analysis
Yeji Seo, Kyunghee Kim, Ji-Su Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 3963. CrossRef - An Identification of the Knowledge Structure on the Resilience of Caregivers of People with Dementia using a Text Network Analysis
Eun Young Kim, Sung Ok Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(1): 66. CrossRef - Identification of the Knowledge Structure of Cancer Survivors’ Return to Work and Quality of Life: A Text Network Analysis
Kisook Kim, Ki-Seong Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(24): 9368. CrossRef - Effect of Knowledge and Attitudes of Cancer Pain Management and Patient-Centered Care on Performance of Cancer Pain Management among Nurses at an Oncology Unit
Mikyung Kim, Yun Mi Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(1): 57. CrossRef - Knowledge Structure of Nursing Studies on Heart Failure Patients in South Korea through Text Network Analysis
Seang Ryu, Hyunyoung Park, Yun-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(4): 409. CrossRef
- Exploring the Knowledge Structure of Research for Nurse Preceptor Training Programs Using Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
- 3,320 View
- 34 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref

- The Development and Evaluation of a Health Literacy-Adapted Self-Management Intervention for Elderly Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
- Yoon Sun Kim, Young Sook Tae, Kwuy-Im Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):472-485. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.472
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to develop and evaluate the effectiveness of an adapted health literacy self-management intervention for elderly cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
Methods The intervention in this study was systematically developed through the six stages of Intervention Mapping Protocol and was based on Fransen et al's causal pathway model. A quasi-experimental trial was conducted on a total of 52 elderly patients (26 in an experimental group and 26 in a control group) undergoing chemotherapy in Korea. The intervention consisted of seven sessions over 5 weeks. The experimental tool for this study was an adapted health literacy self-management intervention, which was designed to promote a reduction in the symptom experience and distress of elderly cancer patients through the promotion of self-management behavior. To develop efficient educational materials, the participants’ health literacy was measured. To educate participants, clear communication and the teach-back method were used. In addition, for the improvement of self-efficacy, four sources were utilized. For the promotion of self-management behavior, five self-management skills were strengthened. Data were collected before and after the intervention from June 4 to September 14, 2018. The data were analyzed with SPSS/WIN 21.0.
Results Following the intervention, self-management knowledge and behavior and, self-efficacy significantly improved in experimental group. Symptom experience and distress decreased in the experimental group compared to the control group.
Conclusion The self-management intervention presented in this study was found to be effective in increasing self-management knowledge and behavior and, self-efficacy, and ultimately in reducing symptom experience and distress for elderly patients undergoing chemotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Self‐Management Education for Deaf Individuals With Hypertension: A Quasi‐Experimental Study
Gi Won Choi, Hee Jung Kim, Yujin Park, Ha Na Jeong, Sun Ju Chang
Research in Nursing & Health.2025; 48(6): 724. CrossRef - The Effect of Group Education Reflecting Unmet Needs on Knowledge of Chemotherapy for Patients and Their Families Undergoing Chemotherapy: A One Group Pre-Post Design
Seyoung Lee, Hoyoung Kim, Nayeon Kim, Misun Yi, Ayoung Lee, Seonmi Cho, Minsun Nam, Juhee Cho
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(1): 42. CrossRef - Health Information Seeking Pathways and Factors Influencing Health Literacy Among Cancer Patients: Based on Data from the 2nd Korean Health Panel 2021
Yun-La Hur, Eun-Jeong Hong
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(3): 155. CrossRef - The Effects of Chemotherapy Education Reflecting Educational Needs on Self-Care Knowledge and Performance in Female Cancer Patients: A Non-Equivalent Control Group Pretest-Posttest Design
Jin Hee Jun, Se-Na Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(3): 103. CrossRef - Effectiveness of teach‐back for chronic kidney disease patient education: A systematic review
Hemamali M. H. Jagodage, Amanda McGuire, Charrlotte Seib, Ann Bonner
Journal of Renal Care.2024; 50(2): 92. CrossRef - Effects of Telephone-based Self-care Intervention for Gynecologic Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Boyeon Lee, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(2): 216. CrossRef - Analysis of Telephone Counseling of Patients in Chemotherapy Using Text Mining Technique
Seoyeon Kim, Jihyun Jung, Heiyoung Kang, Jeehye Bae, Kayoung Sim, Miyoung Yoo, Eunyoung, E. Suh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 46. CrossRef - Evaluating a theory-based intervention for improving eHealth literacy in older adults: a single group, pretest–posttest design
Sun Ju Chang, Kyoung-eun Lee, Eunjin Yang, Hyunju Ryu
BMC Geriatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the teach-back method among cancer patients: a systematic review of the literature
Seonhwa Choi, Jahyun Choi
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(12): 7259. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Self‐Management Education for Deaf Individuals With Hypertension: A Quasi‐Experimental Study
- 2,939 View
- 90 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Experiences of Ego Integrity Recovery in Elderly Cancer Patients: Grounded Theory Approach
- Han-Gyo Choi, Hye-Ah Yeom
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):349-360. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.349
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to derive a substantive theory on lived experiences of elderly cancer patients.
Methods The data were collected from February to March 2018 through in-depth personal interviews with 14 elderly cancer patients. The collected data were analyzed based on Corbin and Strauss's grounded theory.
Results The core category was “the journey to find balance in daily lives as a cancer patient by recovering disturbed ego integrity.” The core phenomenon was “shattered by suffering from cancer,” and the causal conditions were “physical change” and “limitations in daily life.” The contextual conditions were “decreased self-esteem,” “feelings of guilt toward the family,” and the sense of “economic burden.” The participants’ action and interaction strategies were “maintaining or avoiding social relations,” “seeking meaning of the illness,” “falling into despair,” and “strengthening the willingness to battle the cancer.” The intervening conditions were “support from health care providers and family,” “dissatisfaction with health care providers,” “spiritual help from religion,” and “the improvement or worsening of health conditions.” The consequences were “having a new insight for life,” “living positively along with cancer illness,” and “the loss of willingness to live.” A summary of the series of processes includes the “crisis stage,” “reorganizing stage,” and the “ego integration stage.”
Conclusion This study explored the holistic process of ego integrity impairment and the recovery experience of elderly cancer patients. This study is expected to be used as a basis for the development of nursing interventions that can support patients when coping with all stages of their cancer illness trajectory.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Decision-making experiences regarding kidney transplant among older adults in South Korea: A qualitative descriptive study
Hye Jin Chong, Min Kyeong Jang, Hyun Kyung Kim
Patient Education and Counseling.2024; 119: 108044. CrossRef - Living experiences of older patients with cancer amid the COVID-19 pandemic: A phenomenological study
Yong Hwan Hyeon, Kyoung Ja Moon
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(1): 54. CrossRef - Relationship between Communication Competence, Empathy and Geriatric Nursing Practice of Nurses Caring for Elderly Cancer Patients at a General Hospital: Focusing on Veterans Hospital
Eun Sil Park, Jeong Hye Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(2): 94. CrossRef - Qualitative Research in Healthcare: Data Analysis
Dasom Im, Jeehye Pyo, Haneul Lee, Hyeran Jung, Minsu Ock
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(2): 100. CrossRef - Decision-Making Experience of Older Patients with Cancer in Choosing Treatment: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis Study
Eun Young Kim, Se Jin Hong
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(4): 418. CrossRef - Identifying optimal care coordination strategies for older adults with cancer
Han-Gyo Choi, Hye-Ah Yeom
Geriatric Nursing.2021; 42(6): 1349. CrossRef - Hermeneutic Phenomenological Study on the Lived Experience of Illness among Older Females with Cancer in South Korea
Miseon Bang, Suhye Kwon, Seonnyeo Kim, Haeyun Shin, Eunyoung Seo
Asian Oncology Nursing.2020; 20(2): 110. CrossRef - Experiences of Inpatients Living with Lung Cancer in South Korea
Hae Ok Kim, Hyeon Jeong Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2020; 20(1): 28. CrossRef - Good Nursing Experience of Patients with Cancer in a Korean Cancer Hospital
Eunyoung E. Suh, Hye Jin Yoo, Jeong Hee Hong, In Gak Kwon, Hyunju Song
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2020; 13(3): 51. CrossRef
- Decision-making experiences regarding kidney transplant among older adults in South Korea: A qualitative descriptive study
- 1,427 View
- 25 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Reversals in Decisions about Life-Sustaining Treatment and Associated Factors among Older Patients with Terminal Stage of Cardiopulmonary Disease
- Jung-Ja Choi, Su Hyun Kim, Shin-Woo Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):329-339. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.329
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the frequency, patterns, and factors of reversals in decisions about life-sustaining treatment (LST) among older patients with terminal-stage chronic cardiopulmonary disease.
Methods This was a retrospective correlational descriptive study based on medical chart review. De-identified patient electronic medical record data were collected from 124 deceased older patients with terminal-stage cardiopulmonary disease who had made reversals of LST decisions in an academic tertiary hospital in 2015. Data were extracted about the reversed LST decisions, LST treatments applied before death, and patients’ demographic and clinical factors. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to identify the factors associated with the reversal to higher intensity of LST treatment.
Results The use of inotropic agents was the most frequently reversed LST treatment, followed by cardiopulmonary resuscitation, intubation, ventilator therapy, and hemodialysis. Inconsistency between the last LST decisions and actual treatments occurred most often in hemodialysis. One-third of the reversals in LST decisions were made toward higher intensity of LST treatment. Patients who had lung diseases (vs. heart diseases); were single, divorced, or bereaved (vs. married); and had an acquaintance as a primary decision maker (vs. the patients themselves) were significantly more likely to reverse the LST decisions to higher intensity of LST treatment.
Conclusion This study demonstrated the complex and turmoil situation of the LST decision-making process among older patients with terminal-stage cardiopulmonary disease and suggests the importance of support for patients and families in their LST decision-making process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characteristics of Life-Sustaining Treatment Decisions: National Data Analysis in South Korea
Jiyeon Choi, Heejung Jeon, Ilhak Lee
Asian Bioethics Review.2024; 16(1): 33. CrossRef - Decision and Practice of End-of-Life Care in Lung Disease Patients with Physicians Orders for Life Sustaining Treatment
Yu Mi Oh, Yoon Na Kang, Soo Jung Han, Jeong Hye Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2023; 26(1): 7. CrossRef - Same, same, but different? A longitudinal, mixed-methods study of stability in values and preferences for future end-of-life care among community-dwelling, older adults
Malin Eneslätt, Gert Helgesson, Carol Tishelman
BMC Palliative Care.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Preferences for life-sustaining treatment in Korean adults: a cross-sectional study
HyunChul Youn, Suk-young Lee, Han-yong Jung, Shin-Gyeom Kim, Seung‑Hyun Kim, Hyun-Ghang Jeong
BMJ Open.2021; 11(1): e039470. CrossRef - Life-Sustaining Treatment in End-Stage Liver Disease Patients: Patients’ Decisions and Results
Hyun Jung Jung, Jeong Yun Park
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2020; 23(2): 85. CrossRef
- Characteristics of Life-Sustaining Treatment Decisions: National Data Analysis in South Korea
- 1,164 View
- 9 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Mediation Effect of Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Perceived Self-Management Support and Health-Related Quality of Life among Cancer Survivors
- Bo Gyeong Lee, Tae Sook Lee, Soo Hyun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):298-306. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.298
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to examine the levels of perceived self-management support, self-efficacy for self-management, and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in cancer survivors, and to identify the mediating effect of self-efficacy in the relationship between perceived self-management support and HRQoL.
Methods This study used a descriptive correlational design. Two hundred and four cancer survivors who had completed treatment participated in the study. Measurements included the Patient Assessment of Chronic Illness Care Scale, the Korean version of the Cancer Survivors’ Self-Efficacy Scale, and the Medical Outcomes Study Short Form-36. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson's correlation coefficient analysis, and multiple regression analysis using Baron and Kenny's method for mediation.
Results The mean score for perceived self-management support was 3.35 out of 5 points, self-efficacy was 7.26 out of 10 points, and HRQoL was 65.90 out of 100 points. Perceived self-management support was significantly positively correlated with self-efficacy (r=.29,
p <.001) and HRQoL (r=.27,p <.001). Self-efficacy was also significantly correlated with HRQoL (r=.59,p <.001). Furthermore, self-efficacy (β=.55,p <.001) had a complete mediating effect on the relationship between perceived self-management support and HRQoL (Z=3.88,p <.001).Conclusion The impact of perceived self-management support on HRQoL in cancer survivors was mediated by self-efficacy for self-management. This suggests that strategies for enhancing self-efficacy in cancer survivors should be considered when developing self-management interventions for improving their HRQoL.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated With Quality of Life Among Posttreatment Cancer Survivors in Korea
Soo Hyun Kim, Yu Hyeon Choe, Jingyeong Choi, Ji Young Park, Eun Yi
Cancer Nursing.2025; 48(1): E47. CrossRef - Effects of Symptom Burden, Self-Efficacy, and Stigma on Cancer Coping in Patients with primary Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy
Ah-Reum Han, Euna Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(3): 158. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Symptom Experience and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Enhee Jo, Ju-Young Park, Young Jun Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(3): 315. CrossRef - An Integrated Review of Health Care in Child and Adolescent Cancer Survivors Based on Roy’s Adaptation Model
Hye Jin Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(2): 82. CrossRef - Trajectories of quality of life in breast cancer survivors during the first year after treatment: a longitudinal study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ji Young Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
BMC Women's Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of perceived chronic illness management support, health literacy, and social support on the care burden of families caring for older people with multiple chronic conditions at home: A cross-sectional study
Eun Sil Lee, Mi Young Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(1): 76. CrossRef - Effects of Uncertainty, Appraisal of Uncertainty, and Self-Efficacy on the Quality of Life of Elderly Patients with Lung Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy: Based on Mishel’s Theory of Uncertainty
Min-Kyung Hwang, Hee-Kyung Kim, Ki-Hyeong Lee
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1051. CrossRef - Between Personality Traits and Postpartum Depression: The Mediated Role of Maternal Self-Efficacy
Lingli Han, Ji Zhang, Jingxuan Yang, Xiaoyu Yang, Hua Bai
Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment.2022; Volume 18: 597. CrossRef - A Structural Model of Quality of Life in Patients after Colorectal Cancer Surgery
Jeong Won Yeom, Yeon Ok Suh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(5): 2564. CrossRef - The influence of Digital Informatization Level, Self-efficacy, and Social Support on Digital Health Literacy in the Elderly with Cancer
Hye Su Kim, Ji Hyun Sung
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(4): 255. CrossRef - The Correlation Between Quality of Life and Positive Psychological Resources in Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis
Xinxin Zhao, Siqi Tong, Ye Yang
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrated, cross-sectoral psycho-oncology (isPO): a new form of care for newly diagnosed cancer patients in Germany
Michael Kusch, Hildegard Labouvie, Vera Schiewer, Natalie Talalaev, Jan C. Cwik, Sonja Bussmann, Lusine Vaganian, Alexander L. Gerlach, Antje Dresen, Natalia Cecon, Sandra Salm, Theresia Krieger, Holger Pfaff, Clarissa Lemmen, Lisa Derendorf, Stephanie St
BMC Health Services Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Self-efficacy, post-traumatic growth, and quality of life of pediatric cancer survivors: A cross-sectional study
Yeunhee Kwak, Yoonjung Kim, Eun Seok Choi, Ho Joon Im
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 54: 102019. CrossRef - Determinants of quality of life in women immediately following the completion of primary treatment of breast cancer: A cross-sectional study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ji Young Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae, Ka Ming Chow
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(10): e0258447. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of patient assessment of chronic illness care among Korean cancer survivors
Soo Hyun Kim, Bo Gyeong Lee, Yu Hyeon Choe, Francesca Chiesi
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0256119. CrossRef - Mediating and Moderating Factors of Adherence to Nutrition and Physical Activity Guidelines, Breastfeeding Experience, and Spousal Support on the Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors
Nam Mi Kang, Won-Ho Hahn, Suyeon Park, Jung Eun Lee, Young Bum Yoo, Chung Ja Ryoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7532. CrossRef
- Factors Associated With Quality of Life Among Posttreatment Cancer Survivors in Korea
- 1,928 View
- 41 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref

- Prediction Modeling on Family Life Satisfaction of Old Adults Living at Home
- Young Mi Huh, Sohyune Sok
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(5):534-544. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.534
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to construct and test a structural model on family life satisfaction of aged individuals living at home. The conceptual model was based on Bandura's self-efficacy and social cognitive theories (1977; 1986) and Bowen's (1976) family systems theory.
Methods From January 25 to March 5, 2016, 227 older adults living at home completed a structured questionnaire. Data were analyzed to calculate the direct and indirect effects of factors affecting family life satisfaction. SPSS WIN 20.0 and AMOS 20.0 were used.
Results The hypothetical model was a good fit for the data. The model fit indices were χ2=78.05, χ2/df=1.35, RMSR=.02, GFI=.98, AGFI=.96, NFI=.94, CFI=.98, and RMSEA=. 05. Family life satisfaction was positively affected by perceived collective family efficacy, status of physical health, family communication, and family support. Depression resulted in a significant negative effect. Family differentiation had a significant indirect effect on family life satisfaction. The model explained 76% of variance in family life satisfaction.
Conclusion Perceived collective family efficacy, status of physical health, depression, family differentiation, family communication, and family support were significant factors explaining family life satisfaction among older adults staying at home. Further research should be conducted to seek intervention strategies to improve family life satisfaction among older adults living at home by focusing on the respective contributing factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between family support and life satisfaction in hypertensive patients: the multiple mediating roles of self-esteem and self-care
Han Wu, Haijun Zhang, Congzhi Wang, Tian Pan, Yue Zhao, Xiang Chen, Lin Zhang
Geriatric Nursing.2026; 69: 103799. CrossRef - The Effect of Pain Catastrophizing on Depression among Older Korean Adults with Chronic Pain: The Mediating Role of Chronic Pain Interference and Sleep Quality
Kyoung-eun Lee, Hyunju Ryu, Sun Ju Chang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(23): 8716. CrossRef
- The relationship between family support and life satisfaction in hypertensive patients: the multiple mediating roles of self-esteem and self-care
- 1,115 View
- 14 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Psychoeducational Approach to Distress Management of Newly Diagnosed Patients with Breast Cancer
- Jin-Hee Park, Mison Chun, Yong Sik Jung, Sun Hyoung Bae, Young-Mi Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):669-678. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.669
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of integrated psychoeducational program for distress management of newly diagnosed patients with breast cancer.
Methods A quasi-experimental trial was conducted. The participants consisted of 47 female patients with breast cancer assigned to an intervention group (n=25) and control group (n=22). The intervention group participated in integrated psychoeducational program, consisting of individual face-to-face education and telephone-delivered health-coaching sessions. Data were collected at three time points: pre-intervention (T1), post-intervention (T2), and 6-month follow-up (T3). Study instruments were Distress thermometer, Supportive Care Needs Survey Short Form 34 and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast.
Results Compared with the control group, breast cancer patients in the intervention group reported lower distress and supportive care needs than the control group. The intervention group reported higher quality of life (QOL) overall and higher emotional well-being than the control group.
Conclusion These findings indicate that the integrated psychoeducational program is an effective intervention for reducing distress and supportive care needs and increasing QOL of newly diagnosed patients with breast cancer. Oncology nurses need to provide psychoeducational intervention to support patients with breast cancer in managing their distress and helping them adjust to their life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
Young-Hee Je, Kyoung-Ah Kang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Tailored Psychoeducational Intervention for Patients With Advanced Cancer in Indonesia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Nurul Huda, Made Satya Nugraha Gautama, Wan Nishfa Dewi, Agung Waluyo, Hsiu Ju Chang, Malissa Kay Shaw
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2025; 57(5): 848. CrossRef - Evidence on the benefits of mind-body Qigong exercise in women with breast cancer
Michel Marcos Dalmedico, Jackson Adriano Canavarro Ribeiro, Juliana Londero Silva Avila, Prisley Pereira de Oliveira, Paula Karina Hembecker, Sergio Ossamu Ioshii
Fisioterapia em Movimento.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychological Distress and Influencing Factors in Newly Diagnosed Patients with Breast Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Min Hee Hur, Yu Jin Jeong
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(4): 311. CrossRef - Effects of Psychosocial Interventions for Patients with Breast Cancer: A Meta-analysis
Kyu-Sic Hwang, Kuy-Haeng Lee, Chan-Mo Yang, Hye-Jin Lee, Sang-Yeol Lee
Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience.2023; 21(1): 118. CrossRef - The development of a lifestyle modification mobile application, “Health for You” for overweight and obese breast cancer survivors in Korea
Su-Jin Seo, Ju-Hee Nho, Youngsam Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(3): 243. CrossRef - Development and Effect of the Integrated Health Promotion Program for Cancer Survivors Living at Home
Hee Sang Yoon, Eun A Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(1): 51. CrossRef - Adjustment to life with metastatic cancer through psychodrama group therapy: A qualitative study in Turkey
Songül Kamışlı, Bahar Gökler
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2021; 57(2): 488. CrossRef - Integration of longitudinal psychoeducation programmes during the phases of diagnosis, management and survivorship of breast cancer patients: A narrative review
Athena Michaelides, Constantina Constantinou
Journal of Cancer Policy.2020; 23: 100214. CrossRef - Quality of Life in Patients Undergoing Mastectomy for Breast Cancer
Kavitha Konnakkaparambil Ramakrishnan, Sreekumar Damodaran
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2020; 7(28): 1368. CrossRef - Mediating and Moderating Factors of Adherence to Nutrition and Physical Activity Guidelines, Breastfeeding Experience, and Spousal Support on the Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors
Nam Mi Kang, Won-Ho Hahn, Suyeon Park, Jung Eun Lee, Young Bum Yoo, Chung Ja Ryoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7532. CrossRef - Uncertainty and unmet care needs before and after surgery in patients with gastric cancer: A survey study
Ji Yea Lee, Yeonsoo Jang, Sanghee Kim, Woo Jin Hyung
Nursing & Health Sciences.2020; 22(2): 427. CrossRef - Effects of Different Exercise Interventions on Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Tetiana Odynets, Yuriy Briskin, Valentina Todorova
Integrative Cancer Therapies.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
- 1,836 View
- 41 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Development and Effects of Combined Exercise Program for Older Adults with Sarcopenia Based on Transtheoretical Model
- Seoyoun Park, Mee Ock Gu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):656-668. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.656
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop and examine the effects of combined exercise program for older adults with sarcopenia based on transtheoretical model (TTM).
Methods A non-equivalent control group with a pretest-posttest design was used. The subjects consisted of 43 older adults with sarcopenia in precontemplation stage, contemplation stage and preparation stage of TTM (experimental group: 22, control group: 21). The developed program consisted of 36 sessions for 12 weeks including combined exercise (60 minutes) and TTM based strategies for enhancing exercise behavior (10 minutes) per session. Data were collected before, immediately after the program between July 31 to October 27, 2017. The data were analyzed using independent t-test, Mann-Whitney U test with SPSS/WIN 18.0.
Results Compared with their counterparts in the control groups, older adults with sarcopenia in the experimental group showed a significantly greater improvement in process of exercise behavior change, pros and cons of decisional balance for exercise behavior, exercise self-efficacy, parameters of muscle, and the level of physical performance.
Conclusion The study findings indicate that this combined exercise program for older adults with sarcopenia based on TTM model was effective and can be recommended as a nursing intervention for older adults with sarcopenia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current status of nutrition education media and its utilization in providing customized nutrition information for older adults in Korea: a scoping review based on the transtheoretical model and food literacy
Seojin Yun, Jiwon An, Kirang Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 175. CrossRef - Research Progress of Body Composition Changes in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
鹏霞 张
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(08): 7181. CrossRef - Systematic Review of Diagnostic Tools and Interventions for Sarcopenia
Moon Joo Cheong, Yeonseok Kang, Sungchul Kim, Hyung Won Kang
Healthcare.2022; 10(2): 199. CrossRef - Research of Home-Based Exercise Program Development and Effect Analysis: Prevention of Sarcopenia in Hemiplegic Disorder
Myung Nam Ha, Gyoo Yeong Cho
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2021; 24(2): 97. CrossRef - Effects of a 12-Week Transtheoretical Model–Based Exercise Training Program in Chinese Postoperative Bariatric Patients: a Randomized Controlled Trial
Ziqi Ren, Hanfei Zhu, Tianzi Zhang, Hongxia Hua, Kang Zhao, Ningli Yang, Hui Liang, Qin Xu
Obesity Surgery.2021; 31(10): 4436. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Physical Activity Promotion Programs for Elderly Patients Hospitalized in Long-term Care Hospital
Se In Ryu, Aekyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(4): 400. CrossRef - Study on the Relationship between Hand Grip Strength, Depression, Somatic Symptoms and Health-related Quality of Life of the Elderly in Rural Area
Sun-Sook Moon, Chang Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2020; 23(1): 80. CrossRef
- Current status of nutrition education media and its utilization in providing customized nutrition information for older adults in Korea: a scoping review based on the transtheoretical model and food literacy
- 3,008 View
- 82 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Development of a Triage Competency Scale for Emergency Nurses
- Sun Hee Moon, Yeon Hwan Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):362-374. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.362
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to develop a triage competency scale (TCS) for emergency nurses, and to evaluate its validity and reliability.
Methods Preliminary items were derived based on the attributes and indicators elicited from a concept analysis study on triage competency. Ten experts assessed whether the preliminary items belonged to the construct factor and determined the appropriateness of each item. A revised questionnaire was administered to 250 nurses in 18 emergency departments to evaluate the reliability and validity of the scale. Data analysis comprised item analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, contrasted group validity, and criterion-related validity, including criterion-related validity of the problem solving method using video scenarios.
Results The item analysis and confirmatory factor analysis yielded 5 factors with 30 items; the fit index of the derived model was good (χ 2/
df =2.46, Root Mean squared Residual=.04, Root Mean Squared Error of Approximation=.08). Additionally, contrasted group validity was assessed. Participants were classified as novice, advanced beginner, competent, and proficient, and significant differences were observed in the mean score for each group (F=6.02,p =.001). With reference to criterion-related validity, there was a positive correlation between scores on the TCS and the Clinical Decision Making in Nursing Scale (r=.48,p <.001). Further, the total score on the problem solving method using video scenarios was positively correlated with the TCS score (r=.13,p =.04). The Cronbach's α of the final model was .91.Conclusion Our TCS is useful for the objective assessment of triage competency among emergency nurses and the evaluation of triage education programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Patient Satisfaction With the Level of Competence of the Triage Nurse in Hospital Emergency Departments
Meritxell López Hernández, Montserrat Puig‐Llobet, Sergio Higon Fernández, Marta Franco Freirut, Yolanda Moreno Mateos, Jordi Galimany Masclans
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025; 34(9): 3893. CrossRef - Effects of Critical Thinking Disposition, Clinical Judgement, and Nurse–Physician Collaboration on Triage Competency Among Triage Nurses
Ji-Won Song, Hyung-Ran Park
Healthcare.2025; 13(4): 405. CrossRef - The Impact of the Nursing Professionalism and Triage Competency of Emergency Department Nurses on Disaster Nursing Competency
Hyo Jin Im, Ju Young Ha
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2025; 39(1): 19. CrossRef - Effects of Disaster Nursing Education Based on the Korean Triage and Acuity Scale (KTAS): Focus on Competency in Emergency Patient Triage, Core Competencies in Disaster Nursing, Confidence in Disaster Nursing, and Self-efficacy
Yoonhee Seok, Hye-Ryeon Park
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2025; 13(1): 83. CrossRef - Influence of work stress, clinical decision-making ability, and teamwork on triage competency among emergency room nurses in Korea: a cross-sectional study
Seon-Hyeong Kim, Ae-Ri Jung
Journal of Acute Care Surgery.2025; 15(2): 60. CrossRef - Validation of the Persian Triage Decision-Making Inventory (TDMI): a cross-cultural adaptation study
Mahdi Nabi Foodani, Amir Hossein Goudarzian, Özkan Görgülü, Kelly Jo Cone, Khosro Shakeri, Zahra Abbasi Dolatabadi
BMC Emergency Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of risk prediction models for high-risk patients with non-traumatic acute abdominal pain: a prospective observational study
Rui Li, Xiao-Hui Wei, Xiao-Qin Li, Ai-Hua Dong, Dan-Nan Ai, Li-Jin Zhou, Yan Yang
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Triage—clinical reasoning on emergency nursing competency: a multiple linear mediation effect
Won-Oak Oh, Myung-Jin Jung
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Korean Triage and Acuity Scale education using role-playing and its effects on triage competency: A quasi-experimental design
Yon Hee Seo, Sun-Og Lim, Vanessa Carels
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(10): e0311892. CrossRef - Construction of learning objectives and content for emergency triage nurses in tertiary general hospitals: A Delphi study
Linyuan Zhang, Bo Gao, Fang He, Chao Wu, Juan Du, Li Zhang, Juan Liang, Hongjuan Lang
Nurse Education in Practice.2024; 80: 104145. CrossRef - Concept analysis of psychiatric nursing competency in psychiatric nursing
Hwa-Bok Choi
Archives of Psychiatric Nursing.2024; 52: 130. CrossRef - Enhancing triage accuracy in emergency nurses: The impact of a game-based triage educational app
Sun-Hee Moon, Su Ol Kim
International Emergency Nursing.2024; 72: 101398. CrossRef - Emergency nurses’ communication experiences with patients and their families during the COVID-19 pandemic: A qualitative study
Soyoung Shin, Hye Jin Yoo
International Emergency Nursing.2023; 66: 101240. CrossRef - Influence of Emergency Department Nurses' Grit, Self-Leadership, and Communication on Their Triage Competencies: A Descriptive Survey Study
Gwiseon Jeong, Hyeongsuk Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(4): 356. CrossRef - Factors affecting triage competence among emergency room nurses: A cross‐sectional study
Seokhwa Hwang, Sujin Shin
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(13-14): 3589. CrossRef - Professional Self-Concept, Job Stress, and Triage Competency Among Emergency Nurses: Secondary Data Analysis of a Cross-Sectional Survey
You-Jin Cho, Young-Ran Han, Yeo-Won Jeong
Journal of Emergency Nursing.2022; 48(3): 288. CrossRef - The Effect of Competency-Based Triage Education Application on Emergency Nurses’ Triage Competency and Performance
Sun-Hee Moon, In-Young Cho
Healthcare.2022; 10(4): 596. CrossRef - Factors Associated with School Nurses’ Triage Competency in South Korea
Jaehee Yoon, Heesook Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(16): 8279. CrossRef - Development of emergency nursing care competency scale for school nurses
Jaehee Yoon
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with the undertriage of patients with abdominal pain in an emergency room
Boo Young Oh, Kisook Kim
International Emergency Nursing.2021; 54: 100933. CrossRef - Development and validity of the Korea psychiatric triage algorithm
Jeongmin Ha, Kyeongmin Jang, Misuk An
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Patient Satisfaction With the Level of Competence of the Triage Nurse in Hospital Emergency Departments
- 3,022 View
- 116 Download
- 21 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


