Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Development and evaluation of a question-answering chatbot to provide information for patients with coronary artery disease after percutaneous coronary intervention
- Geunhee Lee, Yun Hee Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):153-164. Published online May 13, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24128
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
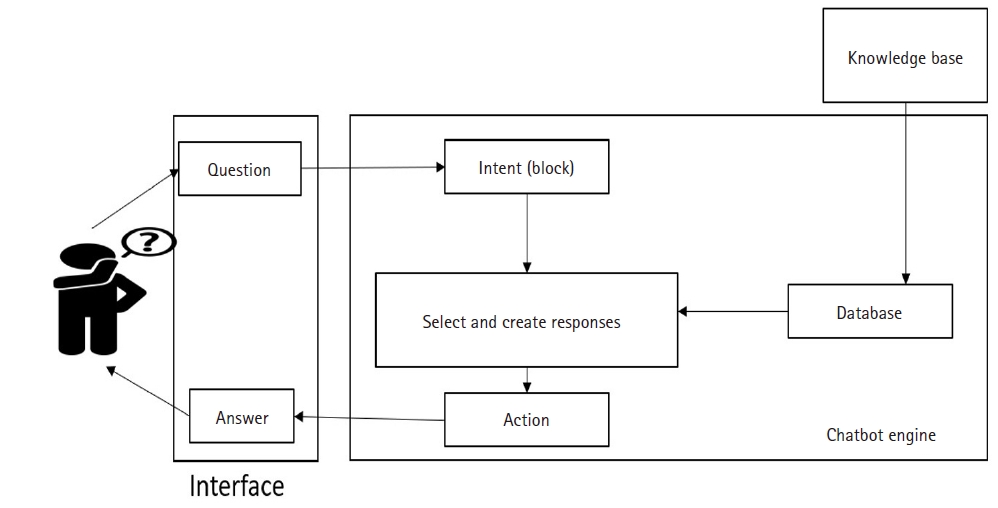
This study aimed to develop a question-answering chatbot that provides accurate and consistent answers to questions that may arise during the recovery process of patients with coronary artery disease after percutaneous coronary intervention, and to evaluate the chatbot.
Methods
The chatbot was developed through the stages of analysis, design, implementation, and evaluation. It was evaluated by five experts, and the user experience was evaluated by 27 patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention. Furthermore, chatbot utilization was analyzed based on user experience logs.
Results
The chatbot was constructed as a question-answering database that included three categories: coronary artery disease, percutaneous coronary intervention, and post-intervention management. The question-answering chatbot, referred to as the “Cardiovascular Strong” channel, has been launched and implemented. An expert evaluation of the chatbot revealed no usability issues or necessary modifications. The overall result of the user experience evaluation was 4.26 points. Based on the user experience log, the question-answer accuracy was 84.6%, and medications during post-intervention management were the most frequently searched topic, accounting for 110 cases (20.8%) out of a total of 528.
Conclusion
The chatbot that was developed to provide information via real-time answers to questions after the intervention can be easily accessed in clinical settings with no time or space constraints. It also will contribute to providing accurate disease-related information via the familiar KakaoTalk platform. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Generative AI at the Bedside: An Integrative Review of Applications and Implications in Clinical Nursing Practice
Adrianna L. Watson, Carmel Bond, Helen Aveyard, Graeme D. Smith, Debra Jackson
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Generative AI at the Bedside: An Integrative Review of Applications and Implications in Clinical Nursing Practice
- 2,371 View
- 249 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Formative versus reflective measurement models in nursing research: a secondary data analysis of a cross-sectional study in Korea
- Eun Seo Park, Young Il Cho, Hyo Jin Kim, YeoJin Im, Dong Hee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):107-118. Published online February 19, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24095
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
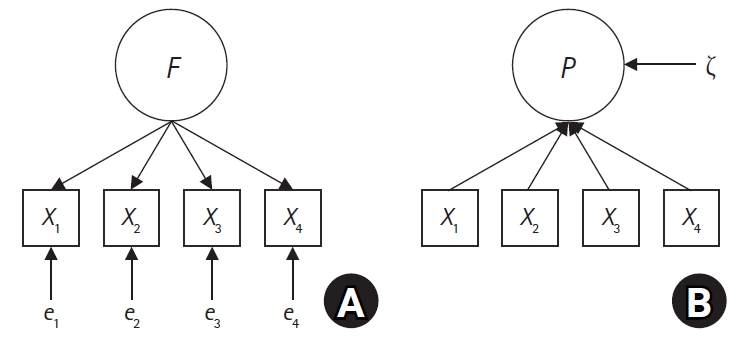
This study aimed to empirically verify the impact of measurement model selection on research outcomes and their interpretation through an analysis of children’s emotional and social problems measured by the Pediatric Symptom Checklist (PSC) using both reflective and formative measurement models. These models were represented by covariance-based structural equation modeling (CB-SEM) and partial least squares SEM (PLS-SEM), respectively.
Methods
This secondary data analysis evaluated children’s emotional and social problems as both reflective and formative constructs. Reflective models were analyzed using CB-SEM, while formative models were assessed using PLS-SEM. Comparisons between these two approaches were based on model fit and parameter estimates.
Results
In the CB-SEM analysis, which assumed a reflective measurement model, a model was not identified due to inadequate fit indices and a Heywood case, indicating improper model specification. In contrast, the PLS-SEM analysis, assuming a formative measurement model, demonstrated adequate reliability and validity with significant path coefficients, supporting the appropriateness of the formative model for the PSC.
Conclusion
The findings indicate that the PSC is more appropriately analyzed as a formative measurement model using PLS-SEM, rather than as a reflective model using CB-SEM. This study highlights the necessity of selecting an appropriate measurement model based on the theoretical and empirical characteristics of constructs in nursing research. Future research should ensure that the nature of measurement variables is accurately reflected in the choice of statistical models to improve the validity of research outcomes.
- 2,269 View
- 141 Download

- Effects of Non-Pharmacological Interventions on Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Patients Underwent Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Sojeong Jo, Haejung Lee, Gaeun Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):311-328. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24019
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
In this study a systematic review and meta-analysis investigated the impact of non-pharmacological interventions on major adverse cardiac events (MACE) in patients with coronary artery disease who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Methods
A literature search was performed using PubMed, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, and Cumulative Index to Nursing & Allied Health Literature databases up to November 2023. The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2.0 tool. Effect sizes and 95% confidence intervals were calculated using R software (version 4.3.2).
Results
Eighteen randomized studies, involving 2,898 participants, were included. Of these, 16 studies with 2,697 participants provided quantitative data. Non-pharmacological interventions (education, exercise, and comprehensive) significantly reduced the risk of angina, heart failure, myocardial infarction, restenosis, cardiovascular-related readmission, and cardiovascular-related death. The subgroup meta-analysis showed that combined interventions were effective in reducing the occurrence of myocardial infarction (MI), and individual and group-based interventions had significant effects on reducing the occurrence of MACE. In interventions lasting seven months or longer, occurrence of decreased by 0.16 times, and mortality related to cardiovascular disease decreased by 0.44 times, showing that interventions lasting seven months or more were more effective in reducing MI and cardiovascular disease-related mortality.
Conclusion
Further investigations are required to assess the cost-effectiveness of these interventions in patients undergoing PCI and validate their short- and long-term effects. This systematic review underscores the potential of non-pharmacological interventions in decreasing the incidence of MACE and highlights the importance of continued research in this area (PROSPERO registration number: CRD42023462690).
- 3,018 View
- 218 Download

- Effects of a Pre-Conception Care Program in Women with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Mixed-Methods Study Including a Randomized Controlled Trial
- Young Jin Lee, Hae Won Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Suk-Kyun Yang, Ji-Yeon Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):386-402. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to conduct a pre-conception care program for women of childbearing age with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in Korea and verify its effects on self-efficacy for IBD management, IBD-related pregnancy knowledge, and IBD-related pregnancy anxiety. It also aimed to explore the changes in participants through the program.
Methods
A convergent mixed-methods study design was adopted. In the quantitative phase, 35 women (17 and 18 in the intervention and control group, respectively) participated. The intervention group attended a program that included small-group sessions and individual tele-coaching. To confirm the effects, data were collected before and one and four weeks after the intervention. In the qualitative stage, focus group interviews and tele-coaching were conducted with the intervention group.
Results
After the program ended, significant differences were observed over time between the intervention and control groups for self-efficacy for IBD management (Wald χ2 = 4.41, p = .036), IBD-related pregnancy knowledge (Wald χ2 = 13.80, p < .001) and IBD-related pregnancy anxiety (Wald χ2 = 8.61, p = .003). Qualitative data analysis revealed the following themes: (1) improving confidence in IBD management and awareness for planned pregnancy; (2) improving IBD awareness related to pregnancy and childbirth; and (3) relieving anxiety about and actively facing pregnancy.
Conclusion
This study is meaningful in that, to the best of our knowledge, it is the first to develop a pre-conception care program for women diagnosed with IBD and confirm its effectiveness. Furthermore, this program is expected to be suitable for patient counseling and education in clinical practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The experiences of fertility concerns in women with inflammatory bowel disease of childbearing age: a descriptive qualitative study
Lewei Tu, Qiaoyu Wu, Mengxiao Jiang, Meihao Wei, Ying Wang, Ying Xiao
BMC Gastroenterology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Health Literacy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review of Health Outcomes, Predictors and Barriers
Caterina Mercuri, Rita Nocerino, Vincenzo Bosco, Teresa Rea, Vincenza Giordano, Michele Virgolesi, Patrizia Doldo, Silvio Simeone
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(23): 8577. CrossRef
- The experiences of fertility concerns in women with inflammatory bowel disease of childbearing age: a descriptive qualitative study
- 2,421 View
- 93 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Influence of Illness Uncertainty on Health Behavior in Individuals with Coronary Artery Disease: A Path Analysis
- Hyesun Jeong, Yesul Lee, Jin Sup Park, Yoonju Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):162-177. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the influence of uncertainty-related factors on the health behavior of individuals with coronary artery disease (CAD) based on Mishel’s uncertainty in illness theory (UIT).
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional study and path analysis to investigate uncertainty and factors related to health behavior. The study participants were 228 CAD patients who visited the outpatient cardiology department between September 2020 and June 2021. We used SPSS 25.0 and AMOS 25.0 software to analyze the data.
Results
The final model demonstrated a good fit with the data. Eleven of the twelve paths were significant. Uncertainty positively affected danger and negatively affected self-efficacy and opportunity. Danger had a positive effect on perceived risk. Opportunity positively affected social support, self-efficacy, perceived benefit and intention, whereas it negatively affected perceived risk. Social support, self-efficacy, perceived benefit and intention had a positive effect on health behavior. We found that perceived benefit and intention had the most significant direct effects, whereas self-efficacy indirectly affected the relationship between uncertainty and health behavior.
Conclusion
The path model is suitable for predicting the health behavior of CAD patients who experience uncertainty. When patients experience uncertainty, interventions to increase their self-efficacy are required first. Additionally, we need to develop programs that quickly shift to appraisal uncertainty as an opportunity, increase perceived benefits of health behavior, and improve intentions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health uncertainty: Scale development and its effect on health behaviors
Rui Ren, Su Tao, Yuhua Ouyang, Wenchong Du
Journal of Health Psychology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Self-Care, Resilience, and Uncertainty in Patients After Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
Eun-Hye Park, JiYeon Choi, Phill Ja Kim, Jiyeon Lee
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Coping Profiles and Cardiac Health Behavior among Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: A Latent Profile Analysis
Yesul Lee, Yoonju Lee, Jeong Cheon Choe, Hyesun Jeong, Sunyoung Jung
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(3): 228. CrossRef
- Health uncertainty: Scale development and its effect on health behaviors
- 3,622 View
- 175 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Eun Jin Kim, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):44-58. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23090
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to apply a health partnership program using commercially available mobile health apps to improve cardiovascular risk factors in male employees and verify its effectiveness.
Methods
Using a randomized control group pretest-posttest design, male employees with cardiovascular risk factors from five small and medium-sized workplaces were randomly assigned to an experimental group (n = 32) and a control group (n = 31). The experimental group was encouraged to use three mobile health apps for 12 weeks to acquire the necessary cardiovascular disease-related information and practice strengthening training, walking, and diet management appropriate to their level. They also received feedback on their weekly activities and motivational text messages from health partners. Hypotheses were tested using the SPSS WIN 22.0.
Results
The experimental group showed a significant difference compared to the control group in terms of their perception of mobile health app (p < .05), self-efficacy for exercise and diet, self-management partnership, and cardiovascular disease prevention health behavior (p < .001). In particular, there were significant decreases in the body mass index, ratio, serum fasting blood sugar, total cholesterol, and triglyceride in the experimental group (p < .001); however, there was no significant difference in high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol.
Conclusion
Intervention using mobile apps based on partnership with health managers is effective in improving the objective cardiovascular risk index in male employees; therefore, such intervention should be continuously used as a useful lifestyle modification strategy in the workplace. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adherence to a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Yura Shin, Jina Choo, Songwhi Noh
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Adherence to a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
- 3,647 View
- 208 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of Self-Efficacy for HIV Disease Management Skills
- Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Mi-So Shim, Seoyoung Baek, Namhee Kim, Min Kyung Park, Youngjin Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(3):295-308. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23016
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study evaluated the validity and reliability of Shively and colleagues’ self-efficacy for HIV disease management skills (HIVSE) among Korean participants.
Methods
The original HIV-SE questionnaire, comprising 34 items, was translated into Korean using a translation and back-translation process. To enhance clarity and eliminate redundancy, the author and expert committee engaged in multiple discussions and integrated two items with similar meanings into a single item. Further, four HIV nurse experts tested content validity. Survey data were collected from 227 individuals diagnosed with HIV from five Korean hospitals. Construct validity was verified through confirmatory factor analysis. Criterion validity was evaluated using Pearson’s correlation coefficients with the new general self-efficacy scale. Internal consistency reliability and test-retest were examined for reliability.
Results
The Korean version of HIV-SE (K-HIV-SE) comprises 33 items across six domains: “managing depression/mood,” “managing medications,” “managing symptoms,” “communicating with a healthcare provider,” “getting support/help,” and “managing fatigue.” The fitness of the modified model was acceptable (minimum value of the discrepancy function/degree of freedom = 2.49, root mean square error of approximation = .08, goodnessof-fit index = .76, adjusted goodness-of-fit index = .71, Tucker-Lewis index = .84, and comparative fit index = .86). The internal consistency reliability (Cronbach’s α = .91) and test-retest reliability (intraclass correlation coefficient = .73) were good. The criterion validity of the K-HIV-SE was .59 (p < .001).
Conclusion
This study suggests that the K-HIV-SE is useful for efficiently assessing self-efficacy for HIV disease management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Providing 2 Types of mHealth Interventions to Support Self-Management Among People Living With HIV: Randomized Clinical Trial
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Seoyoung Baek, Sooyoung Kwon, Ji Min Kim, Jun Yong Choi, Jae-Phil Choi
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2025; 13: e60905. CrossRef - Factors associated with health-related quality of life among people living with HIV in South Korea: Tobit regression analysis
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, SangA Lee, Mi-So Shim, Youngjin Lee, Seoyoung Baek, Claus Kadelka
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(5): e0303568. CrossRef - Three cycles of mobile app design to improve HIV self-management: A development and evaluation study
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Seoyoung Baek, Mi-So Shim, SangA Lee, Ji Min Kim, Jong Yae Yoon, Jin Kim, JunYong Choi, Jae-Phil Choi
DIGITAL HEALTH.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Providing 2 Types of mHealth Interventions to Support Self-Management Among People Living With HIV: Randomized Clinical Trial
- 2,918 View
- 64 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of Motivational Interviewing Pulmonary Rehabilitation Program Based on Self-Determination Theory for Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Jun Hee Jang, Hye Sook Min
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):191-207. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22093
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a motivational interviewing pulmonary rehabilitation program based on self-determination theory to maintain pulmonary rehabilitation-related health behaviors in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The program was developed by reviewing the literature on pulmonary rehabilitation guidelines, drawing on the self-determinism theory to establish its contents, recruiting experts to test its validity, and conducting a preliminary survey.
Methods
A quasi-experimental design was used to confirm the effect of the program. The participants were outpatients diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease at three general hospitals in Busan. There were 33 subjects: 15 in the experimental group and 18 in the control group. The experimental group performed a motivational interviewing pulmonary rehabilitation program which comprised 11 sessions delivered over 10 weeks. The outcomes were measured using basic psychological needs, dyspnea, 6-minute walking distance, and functional status. Intervention effects were analyzed using repeated-measures ANOVA.
Results
The analysis revealed significant differences between the experimental and control groups in competence among the subdomains of basic psychological needs, dyspnea during exercise, and functional status.
Conclusion
The developed program affects physical conditions and can be applied as an effective clinical nursing intervention to continuously improve the pulmonary rehabilitation behavior of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating Effect of Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Symptom Experience and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Enhee Jo, Ju-Young Park, Young Jun Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(3): 315. CrossRef
- Mediating Effect of Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Symptom Experience and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- 2,574 View
- 133 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of Self-Care Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Inventory (SC-COPD) and Self-Care Self-Efficacy Scale (SCES-COPD)
- Ja Yun Choi, So Young Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(5):522-534. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22062
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the Self-Care in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Inventory (SC-COPDI) and the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Self-Care Self-Efficacy Scale (SCES-COPD). The SC-COPDI consists of the Self-Care Maintenance Scale (SCMES), Self-Care Monitoring Scale (SCMOS), and Self-Care Management Scale (SCMAS).
Methods
The original tool was translated using a back-translation process. Participants were 241 patients with COPD at the Chonnam National University Hospital in Korea. The construct validity was verified through confirmatory factor analysis, and reliability was verified using Cronbach’s α.
Results
The SCMES consisted of 10 items of three factors―one of four factors was deleted from the original tool. In the SC-MOS, there were six items of two factors after two items were deleted from the original tool. The SCMAS consisted of the original 10 items of three factors. The SCES-COPD consisted of six items of two factors, with one item removed from the original tool. The model fit indices of all tools were good, and the construct validity was confirmed. Cronbach’s α of SCMES was .72, SCMOS was .90, SCMAS was .81, and SCES-COPD was .85.
Conclusion
The Korean version of SC-COPDI and SCES-COPD are valid and reliable instruments for measuring selfcare in people with COPD. These instruments can be used in self-care studies of COPD patients in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Ruminative Thinking on Breathlessness Catastrophizing With Elderly COPD Patients: The Mediating Role of Self‐Efficacy
Yuye Zhang, Qiufang Li, Xiaokai Wang, Tianci Xiao, Chenmeng Wei, Na Song, Lamei Liu
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025; 34(11): 4854. CrossRef - The influence of depression, social support, and uncertainty on self-management compliance in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases: A descriptive survey study
Han-na Jang, Jeong-soo Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(3): 318. CrossRef - Enhancing deep learning models for predicting smoking Status using clinical data in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Sehyun Cho, Hyeonseok Jin, Kyungbaek Kim, Sola Cho, Ja Yun Choi
DIGITAL HEALTH.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influences of Illness Uncertainty, Health Literacy, and Self-Care on Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Min Jin Chu, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 530. CrossRef - E-health literacy and attitudes toward internet health information in relation to self-care adherence among Korean patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a cross-sectional study
Na Yeong Park, Insook Lee
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric testing of the cross-culturally adapted Thai version of the Self-Care Self-Efficacy Scale version 3.0 in individuals with chronic illnesses
Chennet Phonphet, Jom Suwanno, Chonchanok Bunsuk, Wanna Kumanjan, Ladda Thiamwong
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2024; 11(4): 473. CrossRef
- Impact of Ruminative Thinking on Breathlessness Catastrophizing With Elderly COPD Patients: The Mediating Role of Self‐Efficacy
- 2,647 View
- 72 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Knowledge Structure of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Health Information on HealthRelated Websites and Patients’ Needs in the Literature Using Text Network Analysis
- Ja Yun Choi, Su Yeon Lim, So Young Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):720-731. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21086
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the knowledge structure of health information (HI) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Methods
Keywords or meaningful morphemes from HI presented on five health-related websites (HRWs) of one national HI institute and four hospitals, as well as HI needs among patients presented in nine literature, were reviewed, refined, and analyzed using text network analysis and their co-occurrence matrix was generated. Two networks of 61 and 35 keywords, respectively, were analyzed for degree, closeness, and betweenness centrality, as well as betweenness community analysis.
Results
The most common keywords pertaining to HI on HRWs were lung, inhaler, smoking, dyspnea, and infection, focusing COPD treatment. In contrast, HI needs among patients were lung, medication, support, symptom, and smoking cessation, expanding to disease management. Two common sub-topic groups in HI on HRWs were COPD overview and medication administration, whereas three common sub-topic groups in HI needs among patients in the literature were COPD overview, self-management, and emotional management.
Conclusion
The knowledge structure of HI on HRWs is medically oriented, while patients need supportive information. Thus, the support system for self-management and emotional management on HRWs must be informed according to the structure of patients’ needs for HI. Healthcare providers should consider presenting COPD patient-centered information on HRWs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Da-Jung Kim
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2025; 21(5): 234. CrossRef - Development of pictogram‐based content of self‐management health information for Korean patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Ja Yun Choi, Eui Jeong Ryu, Xin Jin
International Journal of Older People Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of the feature genes involved in cytokine release syndrome in COVID-19
Bing Yang, Meijun Pan, Kai Feng, Xue Wu, Fang Yang, Peng Yang, Salman Sadullah Usmani
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(1): e0296030. CrossRef - Content Analysis of Feedback Journals for New Nurses From Preceptor Nurses Using Text Network Analysis
Shin Hye Ahn, Hye Won Jeong
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2023; 41(10): 780. CrossRef - Research trends over 10 years (2010-2021) in infant and toddler rearing behavior by family caregivers in South Korea: text network and topic modeling
In-Hye Song, Kyung-Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(3): 182. CrossRef - A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis of Self-management Experiences of Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Euna PARK, Jeong-Soo KIM
THE JOURNAL OF FISHERIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2022; 34(5): 794. CrossRef
- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- 1,795 View
- 14 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Job Analysis of Nurse Care Coordinators for Chronic Illness Management in Primary Care Settings: Using Developing a Curriculum Process
- Ju-Hee Hwang, Yong-Jun Choi, Mi-Sook Kim, Seng-Eun Yi, Yong-Soon Park, Ji-Hyang Kim, Ju-Young Yoon, Dong-Soo Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):758-768. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21065
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to conduct a job analysis of nurse carecoordinators and to identify the frequency, importance and difficulty of each task of their job.
Methods
A committee for developing a curriculum (DACUM) was formed and members of the committee defined nurse care coordinators’ jobs and enumerated the duties, tasks and task elements by applying the DACUM technique. Then nurse care coordinators enrolled in the pilot project evaluated the frequency, importance and difficulty of each task.
Results
From the job descriptions of nurse care coordinators, we identified 12 duties and 42 tasks. Each task comprised 1~5 task elements. Among tasks, ‘assess the patient’s general health status’ was carried out most frequently. Nurse care coordinators perceived that ‘check vital signs’ and ‘strengthen patient competence to promote health behaviors’ were more important than all other tasks. The most difficult task was ‘develop professionalism as a nurse care coordinator’.
Conclusion
The nurse care coordinators' roles developed in this study will serve as the key guidelines for human resource management of care coordinators. Further, job specifications for nurse care coordinators need to be developed, which is necessary for designing education and training programs. We also need to integrate primary health care as an essential component in nursing education. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Job Analysis of Nurses Working at Dementia Care Centers Using DACUM
Yong-Sun Shin, Jong-Eun Lee
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2025; 36: 21. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Care Coordination for Chronic Disease Patients with a Usual Source of Care
Hyunsang Kwon, Ju Young Yoon
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2025; 36: 339. CrossRef - Job analysis of vaccination health workers at public health centers and sub‐centers
No‐Yai Park, Chung‐Min Cho, Eun‐Hyun Lee, Jeong‐Mo Park, Young‐Ran Lee, Jeong‐Ik Hong, Geun‐Yong Kwon
Public Health Nursing.2024; 41(4): 723. CrossRef - Development and Analysis of the Job Description for Dementia Care Center Nurses in Korea Using Developing a Curriculum (DACUM)
Hana Ko, SuJung Jung
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2023; 49(10): 29. CrossRef - Analysis of flow rate and pressure in syringe-based wound irrigation using Bernoulli's equation
Hanna Lee, Ye-kyung Lee, Ji-Yun Park, Jeong-won Han
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Preliminary Study for the Curriculum Development of Community Care Coordinators: Educational Needs Analysis
Han Nah Park, Ju Young Yoon, Soong-Nang Jang, Hye Jin Nam
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(2): 153. CrossRef
- Job Analysis of Nurses Working at Dementia Care Centers Using DACUM
- 2,382 View
- 57 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Factors Influencing the COVID-19 Vaccination Intentions in Nurses: Korea, February 2021
- Ju Young Park, Jiyeon Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):537-548. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21110
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the factors influencing COVID-19 vaccination intentions in nurses.
Methods
The participants were 184 nurses in Korea. Data were collected using a Google Form online survey method in February, 2021, and analyzed using an independent t-test, one-way ANOVA, Pearson correlation, and multiple regression analysis with the SPSS/WIN 26.0 program.
Results
COVID-19 vaccination intention in nurses was correlated significantly with vaccine hesitancy (r = .58, p < .001), risk perception of COVID-19 (r = .22, p = .003), perception of vaccination as a professional duty (r = .59, p < .001), and attitude towards workplace infection control policies (r = .20, p = .007). Vaccine hesitancy (β = .40, p < .001) and the perception of vaccination as a professional duty (β = .44, p < .001) significantly influenced COVID-19 vaccination intention. The model developed in this study explained 50% of the variation in COVID-19 vaccination intention.
Conclusion
Improving the perception of vaccination as a professional duty and lowering vaccine hesitancy may enhance nurses’ COVID-19 vaccination intention. Above all, it is necessary to provide programs to encourage voluntary recognition of vaccination as a professional duty and develop strategies to reduce hesitancy toward COVID-19 vaccinations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Related to Length of Stay for COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Study
Hoosun Cho, Eunsu Kim
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2025; 36: 221. CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance and Associated Factors among General Population
Jung-Whan Lee
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2024; 49(1): 19. CrossRef - Nurses' vaccination acceptance and related factors in the initial stage of COVID-19 vaccination in Korea: a cross-sectional study
Kyoung Ha Kim, Jae Sim Jeong
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2024; 26(3): 240. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the COVID-19 Vaccination Intentions in Parents for Their Children Aged 5~11: Korea, April 2022
In Suk Choi, Eun A Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(2): 208. CrossRef - Factors influencing COVID-19 vaccination intention among parents of children aged 5-11 years in South Korea: a cross-sectional study
Jung Hwa Kang, Yunsoo Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(3): 237. CrossRef - Nurses’ Intentions for COVID-19 Vaccination in South Korea in 2022
Byung Yun Song, Sun Hee Choi, Dong Yeon Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(1): 125. CrossRef - The Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of the 5C Psychological Antecedents of Vaccination Scale
SuYeon Bae, HeeJu Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(3): 324. CrossRef - Adapting and Validating the COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy and Vaccine Conspiracy Beliefs Scales in Korea
Hyesung Ock, Mihyeon Seong, Insook Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(11): 2274. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Clinical Nurse’s Intention for Acquiring Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccination
YeonHui Choe, Jieun Cha
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(1): 48. CrossRef - Confidence in a Vaccine against COVID-19 among Registered Nurses in Barcelona, Spain across Two Time Periods
David Palma, Anna Hernández, Camila A. Picchio, Glòria Jodar, Paola Galbany-Estragués, Pere Simón, Montserrat Guillaumes, Elia Diez, Cristina Rius
Vaccines.2022; 10(6): 873. CrossRef
- Factors Related to Length of Stay for COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Study
- 1,307 View
- 11 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Self-Efficacy for Managing Chronic Disease 6-Item Scale
- Sook-Nam Kim, Hyun-Ju Lee, So-Young Kim, Nayoon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):617-629. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21069
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aim of this study was to examine the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the self-efficacy for managing chronic disease 6-item scale (SECD-6-K).
Methods
The English version of the Self-Efficacy for Managing Chronic Disease 6-item Scale first underwent forward and backward translation procedures. The SECD-6-K was then used to collect data from 350 adults diagnosed with chronic diseases. Content, construct, convergent, discriminant, and criterion validity were all evaluated. Reliability was assessed using Cronbach’s α. SPSS 25.0 and the data were analyzed using AMOS 26.0 software.
Results
The SECD-6-K consists of six items in two domains: disease management and health behavior. The results for construct, convergent, and discriminant validity were good. Exploratory factor analysis produced eigen values between 2.27 and 3.28, with factors total explained cumulative variance of 91.1%. Confirmatory factor analysis supported goodness of fit and reliability for the modified SECD-6-K model. The criterion validity also showed significant correlation with both the Patient Health Questionnaire and 12-item Short-Form Health Survey version 2. Finally, reliability was found to be excellent.
Conclusion
This study identified the high reliability and validity of SECD-6-K. The SECD-6-K is an appropriate tool for determining Korean patients’ self-efficacy in managing their chronic conditions. Therefore, this scale may be used in clinical settings as well as in educational and research settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Generic instruments for assessing self-management abilities and behaviors in patients with chronic diseases: a COnsensus-based standards for the selection of health measurement INstruments (COSMIN)-based systematic review
Ke Liu, Guangyan Meng, Caixia Li, Shuyi Wang, Xianwen Fan, Qirong Chen
Quality of Life Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Path Analysis of Factors Influencing Health-Related Quality of Life for Community-Dwelling Vulnerable Older Adults with Chronic Diseases in Korea
Hyun-Ju Lee
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2025; 36: 315. CrossRef - Development of a self-care scale for women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a methodological approach
Miok Kim
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Short Form of Core Competencies Scale of Nursing Care for Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Sung Hae Kim, Seyong Lee, Sang Hee Kim, Jung Ok Choi, Gie Ok Noh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(4): 184. CrossRef - Factors influencing self-management behaviors in older people with multiple chronic conditions based on the individual and family self-management theory: A cross-sectional study
Youngji Seo, Sunyoung Jung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(3): 332. CrossRef - Psychometric property of the Japanese version of self-efficacy for managing chronic disease scale in individuals with chronic diseases
Megumi Hazumi, Mayumi Kataoka, Ayako Nakashita, Kentaro Usuda, Michi Miyake, Chiaki Kamikawa, Daisuke Nishi, Naoaki Kuroda
Heliyon.2024; 10(22): e40218. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the self-efficacy scale for chronic disease management (SEMCD-S) in older Colombian adults
Lorena Cudris-Torres, Stefano Vinaccia Alpi, Álvaro Barrios-Núñez, Natali Gaviria Arrieta, Martha Luz Gómez Campuzano, Giselle Olivella-López, Juan Hernández-Lalinde, Valmore Bermúdez, Olaiza Lobato Pérez, Jorge Armando Niño-Vega, Jorge Navarro-Obeid, Rom
BMC Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ambulatory Chemotherapy (Portable Infusion Pump Use) Video Education on Knowledge, Self-efficacy and Anxiety of Colorectal Cancer Patients
Eun Hee Choi, Eun Young Park, Young A Park, You Hee Son, Myung Jin Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(3): 193. CrossRef
- Generic instruments for assessing self-management abilities and behaviors in patients with chronic diseases: a COnsensus-based standards for the selection of health measurement INstruments (COSMIN)-based systematic review
- 4,549 View
- 215 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Health Behavior Compliance in Adult Moyamoya Patients
- Bo Eun Kim, Ju-Eun Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):80-91. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify factors influencing health behavior compliance in adult patients with moyamoya.
Methods
A descriptive correlation study was conducted to investigate the factors influencing health behavior compliance. Participants were 142 adult patients diagnosed with moyamoya disease who were hospitalized or visited an outpatient clinic in the Gyeonggi province. Data were collected from December 16, 2019 to April 14, 2020 using self-report questionnaires and analyzed using the IBM SPSS 26.0 Win software.
Results
The hierarchical multiple regression analysis demonstrated that self-efficacy (β = .60, p < .001), social support (β = .13, p = .032), and age (β = .21, p = .005) affected the health behavior of adults with moyamoya disease. These 3 variables explained 62.0% of the variance of health behavior compliance, and the most influential factor was self-efficacy.
Conclusion
Based on the results of this study, it concludes that nursing interventions should be focused on self-efficacy and social support to improve health behavior compliance with adult patients diagnosed with moyamoya disease. For that, various strategies to enhance self-efficacy and social support should be developed and actively applied in the clinical setting for adult moyamoya patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictors of self-care performance in patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms
Hae-Na Woo, Yong-Cheol Lim, Joo Hee Lee, Sun Hyoung Bae
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Predictors of self-care performance in patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms
- 1,464 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- The Disease Management Experience of Patients with Asthma: Grounded Theory Approach
- Bohye Kim, Oksoo Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(5):714-727. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20139
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aim of this study was to develop a situation-specific theory to explain the disease management experience of patients with asthma.
Methods
Twenty participants with asthma were selected using the theoretical sampling method. The data were acquired through in-depth interviews conducted from June to October 2018 and analyzed using the grounded theory approach of Strauss and Corbin.
Results
In total, 69 concepts, 30 subcategories, and 13 categories were generated to explain the disease management experience of patients with asthma. The core category of the disease management experience of patients with asthma was ‘management of the disease to prevent aggravation of symptoms over the lifetime’. The disease management process of asthma patients included three steps: the ‘cognition phase’, the ‘adjustment phase’, and the ‘maintenance phase’. However, some patients remained in the ‘stagnation phase’ of disease management, which represents the result of the continual pursuit of risky health behavior. There were three types of disease management experiences among patients with asthma: ‘self-managing’, ‘partially self-managing’, and ‘avoidant’.
Conclusion
This study shows that patients with asthma must lead their disease management process to prevent exacerbation of their symptoms. It is imperative to develop nursing strategies and establish policies for effective disease management of patients with asthma based on their individual disease management processes and types. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Qualitative Research in Healthcare: Data Analysis
Dasom Im, Jeehye Pyo, Haneul Lee, Hyeran Jung, Minsu Ock
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(2): 100. CrossRef
- Qualitative Research in Healthcare: Data Analysis
- 1,711 View
- 50 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Qualitative Study on the Experience of Patients with Meniere Disease
- Woo Joung Joung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(5):699-713. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20115
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to understand and describe the experiences of patients with Meniere disease.
Methods
Data were collected from February 19, 2019, to February 5, 2020, through individual in-depth interviews with 13 Meniere patients. Verbatim transcripts were analyzed using Colaizzi’s phenomenological analysis.
Results
The experiences of patients with Meniere disease were clustered into the following four themes from 22 meaning units: 1) Complex unfamiliar symptoms that shatter both balance of the body and peace of the heart; 2) A disease that medical treatment and health professionals cannot cure; 3) Suffering hardships that cannot be understood by non-Meniere sufferers; and 4) Making daily efforts to become healthier. Symptoms of Meniere disease are life-shattering and depressing because they are neither visible nor easily curable. Over time, as they accepted the reality of living with the disease, the participants would shift their focus from complete symptomatic cure to leading a healthy and more balanced life.
Conclusion
This study shows that Meniere disease has a pervasive impact on all aspects of the patients’ lives. Patients are prone to experiencing restrictions in their social functioning and activities. They also experience psychosocial problems due to the unseen nature of their symptoms. This study elucidates the experiences of Meniere patients and the need for nursing intervention to help improve their quality of life and ability to self-manage. Lastly, this study shows the need for a coordinated interdisciplinary approach to raising public awareness of the disease.
- 2,456 View
- 27 Download

- Continuity of Care in Chronic Diseases: A Concept Analysis by Literature Review
- Jingjing Hu, Yuexia Wang, Xiaoxi Li
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(4):513-522. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20079
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to utilize concept analysis to obtain a better understanding of the concept of “continuity of care” in chronic diseases.
Methods
The concept of continuity of care was analyzed using the Walker and Avant method. Covering literature in English from 1930 to 2018, the data sources included CINAHL Complete, Academic Search Complete, MEDLINE, PsyARTICLES, Health Source: Nursing/ Academic Edition, Google Scholar, Science Direct, and the Cochrane Library.
Results
A comprehensive definition of concept of continuity of care was developed based on a systematic search and synthesis. The key defining attributes were identified as (a) care over time, (b) the relationship between an individual patient and a care team, (c) information transfer, (d) coordination, and (e) meeting changing needs. The antecedents of continuity of care were having a chronic disease, inexperienced with disease management, a poorly coordinated healthcare system, and medical care limitations. The consequences of continuity of care were decreasing hospital admissions, reducing costs, reducing emergency room visits, improving the quality of life, improving patient satisfaction, and delivering good healthcare.
Conclusion
The thorough concept analysis provides insight into the nature of “continuity of care” in chronic diseases and also helps ground the concept in healthcare. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preferred reporting items for concept analysis in nursing: a systematic review
Abdulqadir J Nashwan, Jibin Kunjavara, George Joy, Kalpana Singh, Moustaq Karim Khan Rony, Kamarudeen Mannethodi, Sirwan Khalid Ahmed
Journal of Research in Nursing.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Patient-Centered Care in Family Medicine: Strategies for Continuity and Comprehensive Care for Older Adults – A Mixed-Methods Study
Abdulaziz Alodhialah, Ashwaq Almutairi, Mohammed Almutairi
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2025; Volume 20: 985. CrossRef - Roy adaptation model-based nursing combined with transitional care for enhancing mental health and quality of life after cancer surgery: results from a randomized controlled study
Lijie Yuan, Ying Fu
Perioperative Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Patient perceptions of relational continuity in England: insights from two cross-sectional surveys
Bolanle Odebiyi, Jonathan Gibson, Mhorag Goff, Ali MK Hindi, Jonathan Hammond, Katherine Checkland, Matt Sutton, Sally Jacobs
BJGP Open.2025; : BJGPO.2024.0267. CrossRef - Primary Care Utilization and Prehospital Emergency Demand Among Patients with Multimorbidity in Spain
Enrique Coca-Boronat, José Miguel Morales-Asencio, Daniel Coca-Gallen, Laura Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, Inmaculada Lupiáñez-Pérez, Cristina Guerra-Marmolejo, José Sáenz-Gómez, Bibiana Pérez-Ardanaz
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(11): 377. CrossRef - Evaluation of a telemedicine pilot project for hypertension in Korea: a nationwide real-world data study
Jeong-Yeon Kim, Yeryeon Jung, Seongwoo Seo, Youseok Kim, Min Jung Ko, Hun-Sung Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2025; 47: e2025048. CrossRef - The meaning of continuity of care from the perspective of older people with complex care needs–A scoping review
Ingrid Djukanovic, Amanda Hellström, Anna Wolke, Kristina Schildmeijer
Geriatric Nursing.2024; 55: 354. CrossRef - Care needs of chronically ill patients with intellectual disabilities in Dutch general practice: patients’ and providers’ perspectives
Milou van den Bemd, Monique Koks-Leensen, Maarten Cuypers, Geraline L. Leusink, Bianca Schalk, Erik W. M. A. Bischoff
BMC Health Services Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - KRONİK HASTALIĞI OLAN YETİŞKİN BİREYLERİN 6 ŞUBAT 2023 KAHRAMANMARAŞ MERKEZLİ DEPREMLER SONRASI HASTALIK YÖNETİMİNE İLİŞKİN DENEYİMLERİ: NİTEL BİR ARAŞTIRMA
Uğur Doğan, Murat Tamer
Kocatepe Tıp Dergisi.2024; 25(4): 429. CrossRef - Measuring patients' experiences of continuity of care in a primary care context—Development and evaluation of a patient‐reported experience measure
Linda Ljungholm, Kristofer Årestedt, Cecilia Fagerström, Ingrid Djukanovic, Mirjam Ekstedt
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2024; 80(1): 387. CrossRef - Assessing multidisciplinary follow-up pattern efficiency and cost in follow-up care for patients in cervical spondylosis surgery: a non-randomized controlled study
Zhongmin Fu, Yan Xie, Peifang Li, Menghui Gao, Jiali Chen, Ning Ning
Frontiers in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lessons Learned From a Retrospective Analysis of Medicolegal Risks for Physicians Treated Adolescents and Young Adults With Medical Complexity
Rana Aslanova, Laura Payant, Richard Liu, Karen Pacheco, Jacqueline H. Fortier, Gary E. Garber
Journal of Adolescent Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Implementation and evaluation of a complex intervention to improve information availability at the interface between inpatient and outpatient care in older patients with multimorbidity and polypharmacy (HYPERION-TransCare) — study protocol for a pilot and
Astrid-Alexandra Klein, Jenny Petermann, Franziska Brosse, Steve Piller, Martin Kramer, Maria Hanf, Truc Sophia Dinh, Sylvia Schulz-Rothe, Jennifer Engler, Karola Mergenthal, Hanna M. Seidling, Sophia Klasing, Nina Timmesfeld, Marjan van den Akker, Karen
Pilot and Feasibility Studies.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Young adults with eating disorders perspectives on educational resources to support the transition into adult medicine: a thematic analysis
Jennifer Mooney, Anna Dominic, Alyona Lewis, Roger Chafe
Journal of Eating Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of medical care linkage-continuous management mode in patients with posterior circulation cerebral infarction undergoing endovascular interventional therapy
Fen-Xia Zhu, Qian Ye
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(29): 10478. CrossRef - Effect of continuous nursing on angina attack and quality of life in patients with coronary artery disease
Xiaohuan Zhou, Yamin Yuan, Zhanglin Wang, Ke Zhang, Weiwei Fan, Yawei Zhang, Pu Ma
Medicine.2021; 100(5): e24536. CrossRef - Sårbar sammenheng i helse- og omsorgstjenesten til eldre pasienter
Maren Kristine Raknes Sogstad, Astrid Bergland
Tidsskrift for omsorgsforskning.2021; 7(2): 9. CrossRef - CONTINUIDADE DE CUIDADOS DE REABILITAÇÃO ENTRE CONTEXTOS DE SAÚDE: ESTUDO DE CASO
Rui Pedro Silva, Elisabeth Sousa
Revista Portuguesa de Enfermagem de Reabilitação.2020; 3(Sup 1): 70. CrossRef
- Preferred reporting items for concept analysis in nursing: a systematic review
- 4,611 View
- 178 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref

- Effects of Spouse-Participated Health Coaching for Male Office Workers with Cardiocerebrovascular Risk Factors
- So Hee Kang, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):748-759. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.748
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to examine the effect of spouses participating in health coaching on stage of the change, health behaviors, and physiological indicators among male office workers with cardiocerebrovascular disease (CVD) risk factors and compare the findings with trainers who provided health coaching only to workers.
Methods A quasi-experimental pretest-posttest design was used. Convenience sampling was used to recruit participants from a manufacturing research and development company in the city of Gyeonggi province. The health coaching program for the experimental group (n=26) included individual counseling sessions according to workers' stage of change, and provision of customized health information materials on CVD prevention to workers and their spouses for 12 weeks through mobile phone and email.
Results After 12 weeks of intervention, the total score for health behavior, and scores on the sub-areas of exercise and health checkups significantly improved in the experimental group, but there were no significant differences in the scores of stage of the change and physical indicators. The results of a paired t-test showed a significant decrease in the body mass index, abdominal circumference, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol and triglyceride values, and a significant increase in the high-density lipoprotein cholesterol value in the experimental group after the intervention.
Conclusion To improve the health of male workers with CVD risk factors in the workplace, sharing health information with their spouses has proven to be more effective than health coaching for only workers. Therefore, it is important to develop strategies to encourage spousal participation when planning workplace health education for changing health-related behaviors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun Jin Kim, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(1): 44. CrossRef - Effects of a Remote Physical Activity Improvement Program on Male Office Workers with Metabolic Syndrome in Their 30s and 40s with Sedentary Behavior: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Kyong Sil Park, Seon Young Hwang
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - An intervention study of a combined intervention of positioning and hand massage in patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation
Yun Kyeong Lee, Mihae Im, Haeryun Cho
Nursing Open.2023; 10(3): 1404. CrossRef
- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 1,035 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of a Daily Life-Based Physical Activity Enhancement Program for Middle-Aged Women at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
- Kyung Ae Kim, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):113-125. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of a daily life-based physical activity enhancement program performed by middle-aged women at risk for cardiovascular disease.
Methods This study used a randomized control group pretest-posttest design. Middle-aged women aged 45 to 64 were recruited from two outpatient cardiology departments, and randomly assigned to an experimental group (n=28) and a control group (n=30). For the experimental group, after providing one-on-one counseling and education, we provided customized text messages to motivate them in daily life. To monitor the practice of physical activity, they also used an exercise diary and mobile pedometer for 12 weeks. Subjects' physical activities (MET-min/week) were measured using the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ). Their physiological data were obtained by blood tests using a portable analyzer, and the data were analyzed using the SPSS 21.0/WIN program.
Results There were significant differences in exercise self-efficacy, health behavior, IPAQ score, body fat, body muscle, and fasting blood sugar between the two groups. However, there were no significant differences in total cholesterol, hemoglobin A1c, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and waist-to-hip ratio.
Conclusion Strengthening physical activity in daily life without being limited by cost burden and time and space constraints. Therefore, it is essential to motivate middle-aged women at risk for cardiovascular disease to practice activities that are easily performed in their daily lives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and effectiveness of a mobile-based autonomy support program for the prevention of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged women
Miseon Seo, Eun-Young Jun, Hyunjin Oh
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Remote Physical Activity Improvement Program on Male Office Workers with Metabolic Syndrome in Their 30s and 40s with Sedentary Behavior: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Kyong Sil Park, Seon Young Hwang
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - Effects of Breathing Exercises Using Virtual Reality and Schroth Breathing Exercises on the Lung Function of Adults in Their 20s
Byung-Kon Kim, Wook-Jin Lee
The Journal of Korean Physical Therapy.2024; 36(2): 67. CrossRef - Effectiveness of physical activity monitors in adults: systematic review and meta-analysis
Rasmus Tolstrup Larsen, Vibeke Wagner, Christoffer Bruun Korfitsen, Camilla Keller, Carsten Bogh Juhl, Henning Langberg, Jan Christensen
BMJ.2022; : e068047. CrossRef - Trajectories of subjective health status among married postmenopausal women based on the ecological system theory: a longitudinal analysis using a latent growth model
Eun Jin Kim, Ju-Hee Nho
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(2): 123. CrossRef - Effect and mechanism of tai chi on blood pressure of patients with essential hypertension: a randomized controlled study
Bo LIN, Qiu JIN, Chunhua LIU, Wenhui ZHAO, Runyuan JI
The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of behaviour change interventions on changes in physical activity and anthropometrics in ambulatory hospital settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Stephen Barrett, Stephen Begg, Paul O’Halloran, Owen Howlett, Jack Lawrence, Michael Kingsley
International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors related to the Identification of Middle-Aged Women Who are Disadvantaged by Cardio-cerebrovascular Disease
Moon Jung Kang, Jee Seon Yi, Chang Seung Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(2): 185. CrossRef
- Development and effectiveness of a mobile-based autonomy support program for the prevention of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged women
- 2,297 View
- 46 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Comparison of Effects of Oral Health Program and Walking Exercise Program on Health Outcomes for Pregnant Women
- Hae-jin Park, Haejung Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(5):506-520. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.506
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose To compare the effects of the Interaction Model of Client Health Behavior (IMCHB)-based oral health program (OHP) and walking exercise program (WEP) on oral health behaviors, periodontal disease, physical activity, and psychological indicators (depression, stress, and quality of life) in pregnant women.
Methods A nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design was adopted to compare the effects of a 12-week OHP and WEP on pregnant women (n=65). Pregnant women were randomly assigned to the oral health group (OHG; n=23), walking exercise group (WEG; n=21), or control group (CG; n=21). Data were analyzed by the χ2-test, Fisher's exact test, Scheffe test, and repeated measures ANOVA, using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences for Windows (version 21.0).
Results The OHG and WEG showed significant improvements in oral health behaviors, periodontal disease, and psychological indicators as compared to the CG. The WEG showed significant improvement in physical activity as compared to the OHG and CG.
Conclusion These findings indicate that the IMCHB-based OHP and WEP were effective in improving periodontal disease, physical activity, and psychological indicators. However, further studies are needed to identify the positive effects of the OHP and WEP on birth outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Physical Activity as a Mediatior in the Relationship Between Oral Health Status and Prevalence of Diabetes in Older Adults
Min-Jun Kim, Taewan Kim, Youngyun Jin, Donghyun Kim
Exercise Science.2025; 34(1): 35. CrossRef - Physical Activity as a Mediator in the Relationship Between Oral health status and Depression Prevalence in Older Adults
Min-Jun Kim, Taewan Kim, Yoonhwan Kim, Donghyun Kim
Exercise Science.2025; 34(2): 188. CrossRef - Twenty-first century knowledge mapping on oral diseases and physical activity/exercise, trends, gaps, and future perspectives: a bibliometric review
Thamires Campos Gomes, José Lucas Gomes Moura, Daiane Claydes Baia-da-Silva, Rafael Rodrigues Lima, Patrícia de Almeida Rodrigues
Frontiers in Sports and Active Living.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Review of domestic and international intervention studies to improve oral health in pregnant women
Jun-Yeong Kwon, Hyoung-Joo Kim, Hanna Gu, Hee-Jung Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2024; 48(3): 155. CrossRef - Secondary prevention of coronary heart disease: The effect of a nursing intervention using Cox's interaction model of client health behaviour
Qianqian Shen, Pingping He, Min Wen, Juping Yu, Yeshi Chen, Junyi Li, Xinping Ouyang
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2021; 77(10): 4104. CrossRef - Theoretical evaluation of Cox’s interaction model of client health behavior for health promotion in adult
women
Youlim Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Gi Wook Ryu
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(2): 120. CrossRef
- Physical Activity as a Mediatior in the Relationship Between Oral Health Status and Prevalence of Diabetes in Older Adults
- 1,414 View
- 27 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Self-Management Experiences of the Adolescents with Chronic Kidney Disease
- Sug Young Lee, Heesun Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):266-278. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.266
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The aim of this study was to develop a substantive theory on self-management conducted by the adolescents with chronic kidney disease from their lived experience.
Methods Data was collected through in-depth interviews from May to December in 2015 with thirteen adolescents with chronic kidney disease. The data collected were analyzed on the basis of Strauss and Corbin's grounded theory.
Results The core of the category found in this study was “overcoming the unstable sense of self- control and integrating disease experience into their life”. The causal conditions triggering the central phenomenon were “restriction in daily life” and “manifestation and aggravation of symptom”. The central phenomenon in the experience of self-management within the adolescents with chronic kidney disease was “unstable sense of self control”. The intervening condition for unstable self control were “micro system support” and “motivational resources”. This study found that the adolescents with chronic kidney disease followed a series of strategies when they faced the central phenomenon, including; passive coping, reappraisal of illness, active coping, compliance with treatment, controlling physical activity, and adjusting school life. With these strategic approaches, the adolescents with chronic kidney disease could maintain their active lifestyles and achieve their health behaviors. The process of self-management by these adolescents passed through four phases; limited experience caused by diseases, effort for normalization, reorganizing their daily lives, and integration with daily lives and self-management.
Conclusion This Study explored the process and experience of self-management of adolescents with chronic kidney disease. These findings can be used for basis for developing substantive theory and nursing intervention strategy for adolescents with chronic kidney diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with healthcare transition readiness for adolescents with chronic conditions: A cross-sectional study
Hye Seung Hong, YeoJin Im
Journal of Child Health Care.2025; 29(3): 658. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Self-management in Children with Chronic Kidney Diseases through Walker and Avant’s Method
Sug Young Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(1): 105. CrossRef - Patient and Caregiver Perspectives on Diet and Nutrition for Children With CKD: A Systematic Review of Qualitative Studies
Ao Zhang, Anita van Zwieten, Anastasia Hughes, Siah Kim, Kelly Lambert, Luca G. Torrisi, Allison Jaure, Chandana Guha
American Journal of Kidney Diseases.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Phenomenological Study of the Lived Illness Experience of Adolescents with Chronic Glomerular Disease
Sug Young Lee
Children.2025; 12(12): 1671. CrossRef - Validity and reliability of the Korean caregiver contribution to self-care chronic illness inventory
Juhee Lee, Eunyoung Kim, Misook Chung, Insun Yeom
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Health Behavior and Social-Emotional Health Status of School-Aged Children According to their Experience with Atopic Dermatitis Diagnosis: Based on the 12th (2019) Panel Study on Korean Children
Da-Jeong Kum, Kyung-Sook Bang
Children.2023; 10(2): 288. CrossRef - Illness Experiences of Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
Ji Eun Kim, Ilaria Campesi
Journal of Diabetes Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Physical activity and the ‘pediatric inactivity triad’ in children living with chronic kidney disease: a narrative review
Thomas J. Wilkinson, Lauren L. O’Mahoney, Patrick Highton, Joao L. Viana, Heitor S. Ribeiro, Courtney J. Lightfoot, Ffion Curtis, Kamlesh Khunti
Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factor analysis of the Korean version of the Illness Cognition Questionnaire for adolescents with chronic illness
Dasuel Lee, Dae‐Chul Jeong, Nack‐Gyun Chung, Sunhee Lee
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Factors associated with healthcare transition readiness for adolescents with chronic conditions: A cross-sectional study
- 1,752 View
- 13 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Non-Pharmacologic Interventions in Chemotherapy Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Pok-Ja Oh, You Lim Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):123-142. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of non-pharmacologic interventions in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN).
Methods PubMed, Cochrane Library CENTRAL, EMBASE, CINAHL, and several Korean databases (Until August 2017) were searched. The main search strategy combined terms for peripheral neuropathy and presence of neoplasms. The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane's Risk of Bias tool for randomized studies and the Risk of Bias Assessment tool for non-randomized studies. To estimate the effect size, a meta-analysis of the studies was performed using the Rev Man 5.3 program of the Cochrane Library random-effects models were used in the analyses.
Results Twenty-two studies with a total of 954 participants met the inclusion criteria. Of the 22 studies, 12 were used to estimate the effect size of the non-pharmacologic interventions. The non-pharmacologic interventions used in patients with CIPN were exercise, acupuncture, massage, and foot bath. The acupuncture significantly reduced CIPN symptoms and signs (d=-0.71) and CIPN pain (d=-0.73) (
p <.001). Massage and foot bath were also effective in reducing CIPN symptoms (d=-0.68; 95% CI=-1.05, -0.30;p <.001; I2=19%).Exercis-es were effective in improving muscle strength and endurance(d=-0.55) and quality of life (d=-2.96), but they were not significantly effective in improving CIPN.Conclusion Although these results provide little evidence of the effectiveness of acupuncture, massage, and foot bath in the treatment of CIPN, they suggest that these interventions can reduce CIPN symptoms in patients with cancer. However, the findings of this study should be interpreted with caution as there is a relative lack of data in this field, and additional well-designed studies are needed. PROSPERO registration: CRD42017076278.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effectiveness and Safety of Nurse-Led Auricular Acupressure on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Among Patients With Breast Cancer
Mi Sook Jung, Mijung Kim, Eun Hee Sohn, Jin Sun Lee
Cancer Nursing.2025; 48(2): E64. CrossRef - Effects of acupuncture-related intervention on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and quality of life: An umbrella review
Mei-Ling Yeh, Chin-Che Hsu, Matthew Lin, Chuan-Ju Lin, Jaung-Geng Lin
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2025; 89: 103131. CrossRef - Effects of Swanson theory-based auricular acupressure on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, and broader health-related outcomes in patients with breast cancer: A randomized controlled trial
Yuanyuan Mi, Ying Chen, Jing Li, Xinxin Liu, Zhengrong Li, Quanlian Ye, Jinli Guo, Yuanfei Liu
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100729. CrossRef - Traditional herbal medicine for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis with association rule analysis
Eun Hye Kim, Hayun Jin, Su Hyeon Lee, Seong Woo Yoon
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Acupuncture-related interventions improve chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Mei-Ling Yeh, Ru-Wen Liao, Pin-Hsuan Yeh, Chuan-Ju Lin, Yu-Jen Wang
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Exercise Intervention on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Symptoms in Cancer Patients: A Meta-analysis
Nan Wu, Hongshi Cao, Shiyuan Du, Yulu Chen, Xinxin Wang, Jiong Li, Xin Peng
Cancer Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effectiveness and safety of acupuncture/electroacupuncture for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Li-Xia Pei, Yue Yi, Jing Guo, Lu Chen, Jin-Yong Zhou, Xiao-Liang Wu, Jian-Hua Sun, Hao Chen
Acupuncture in Medicine.2023; 41(2): 73. CrossRef - Effects of Footbath on Postoperative Pain and Sleep Quality in Patients With Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease: A Randomized Controlled Study
Seher Ünver, Ülkü Çolakoğlu, Ahmet Tolgay Akıncı
Journal of Neuroscience Nursing.2023; 55(4): 125. CrossRef - Non-pharmacological therapy for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Xia Zhang, Ao Wang, Miaowei Wang, Guo Li, Quan Wei
BMC Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Manual Therapy on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Eunsang Lee, Hyunjoong Kim
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - The impact of peripheral neuropathy symptoms, self-care ability, and disturbances to daily life on quality of life among gynecological cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: a cross-sectional survey
Sohee Mun, Hyojung Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(4): 296. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Mobile Application-based Self-Management Program for Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Colorectal Cancer Patients
Pok-Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(3): 258. CrossRef - Treatment and diagnosis of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: An update
Allison D. Desforges, Chance M. Hebert, Allyson L. Spence, Bailey Reid, Hemangini A. Dhaibar, Diana Cruz-Topete, Elyse M. Cornett, Alan David Kaye, Ivan Urits, Omar Viswanath
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 147: 112671. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in children and adolescent cancer patients
Nicolette Tay, E-Liisa Laakso, Daniel Schweitzer, Raelene Endersby, Irina Vetter, Hana Starobova
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Case Report of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Treated with Modified
Guibi-tang
Su Bin Park, Jee-Hyun Yoon, Eun Hye Kim, Seong Woo Yoon
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2022; 43(3): 451. CrossRef - Kanser Tedavisi Alan Çocuklarda Kemoterapiyle İlişkili Periferik Nöropatinin Değerlendirilmesinde Hemşirenin Rolü
Bilge ÖZDEMİR, Gülçin ÖZALP GERÇEKER
Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Fakültesi Elektronik Dergisi.2022; 15(3): 369. CrossRef - Non-Pharmacological Self-Management Strategies for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in People with Advanced Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Megan Crichton, Patsy M. Yates, Oluwaseyifunmi Andi Agbejule, Amy Spooner, Raymond J. Chan, Nicolas H. Hart
Nutrients.2022; 14(12): 2403. CrossRef - The Effects of Foot Reflexology on the Physical Symptoms of Cancer Patients
Young-Ran Yeun, Yi-Sub Kwak, Hye-Young Kim
Exercise Science.2021; 30(1): 8. CrossRef - A Case Report of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Treated with Warm Needling
Jee-Hyun Yoon, Su Bin Park, Jee Young Lee, Eun Hye Kim, Seong Woo Yoon
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2021; 42(2): 114. CrossRef - The Effect of Self-Acupressure on Peripheral Neuropathy, Disturbance in Daily Activity, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients undergoing Chemotherapy
Su Young Kim, Jeong Sook Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(3): 129. CrossRef - Effects of Exercise on Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yu Hyeon Choe, Da Hye Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(5): 458. CrossRef - Effects of pain neuroscience education on kinesiophobia in patients with chronic pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Hyunjoong Kim, Seungwon Lee
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2020; 9(4): 309. CrossRef - Prescribing for persistent cancer pain: focus on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy
Martin Galligan
Journal of Prescribing Practice.2020; 2(4): 176. CrossRef - Effects of Nonpharmacological Interventions in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: An Overview of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Jie Hao, Xiaoshu Zhu, Alan Bensoussan
Integrative Cancer Therapies.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical study on concurrent use of electro-acupuncture or Chuna manual therapy with pregabalin for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: safety and effectiveness (open-labeled, parallel, randomized controlled trial, assessor-blinded)
Jin-Hyun Lee, Tae jin Cho, Min Geun Park, Ji-Hoon Kim, Sung Kyu Song, Shin-Young Park, Yun-Young Sunwoo, Ilkyun Lee, Tae-Yong Park
Medicine.2020; 99(3): e18830. CrossRef - The Experience of Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy in People with Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Eun Sook Choi, Jin Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(2): 81. CrossRef - Acupuncture therapy improves health-related quality of life in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Po-Chun Hsieh, Mei-Chen Yang, Yao-Kuang Wu, Hsin-Yi Chen, I-Shiang Tzeng, Pei-Shan Hsu, Chang-Ti Lee, Chien-Lin Chen, Chou-Chin Lan
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2019; 35: 208. CrossRef - Acupuncture for the Relief of Chronic Pain: A Synthesis of Systematic Reviews
Carole A. Paley, Mark I. Johnson
Medicina.2019; 56(1): 6. CrossRef - Evidence, safety and recommendations for when to use acupuncture for treating cancer related symptoms: a narrative review
Stephen Birch, Myeong Soo Lee, Terje Alraek, Tae-Hun Kim
Integrative Medicine Research.2019; 8(3): 160. CrossRef - Physiotherapy management of chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy in a gynecological condition through clinical reasoning process: A case study
K. M. Amran Hossain, Mohammad Anwar Hossain, Feroz Ahmed Mamin, Ehsanur Rahman, Nasrin Afroz, Nusrat Jahan Sonia, Shati Aziz Khan
Edorium Journal of Disability and Rehabilitation.2018; 4(2): 1. CrossRef - Research Trend about Complementary and Alternative Therapy in Korea using Text Network Analysis
Hae Ree Sung, Jung Lim Lee, Youngji Kim, Jeong Sig Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2018; 21(2): 61. CrossRef - Síntesis de la evidencia científica en acupuntura
Juan Muñoz-Ortego, Jorge Vas, Betina Nishishinya Aquino, Beltrán Carrillo, Alberto Pérez Samartín, Cristina Verástegui, Rafael Cobos
Revista Internacional de Acupuntura.2018; 12(4): 97. CrossRef
- The Effectiveness and Safety of Nurse-Led Auricular Acupressure on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Among Patients With Breast Cancer
- 3,363 View
- 81 Download
- 32 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling on Successful Aging in Elders with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on Selection-Optimization-Compensation Strategy
- Young Mi Jang, Rhayun Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(4):488-498. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.4.488
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The focus of the study was on the selection-optimization-compensation (SOC) strategy to predict successful aging mediated by dyspnea symptoms in older adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The model was constructed based on the hypotheses that coping strategy and social support of the elders predict successful aging through the SOC strategies.
Methods Participants were 218 outpatients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease recruited for the study. Data collection was done from March 25 to September 11, 2015, and analyzed using SPSSWIN 22.0 and AMOS 21.0.
Results The hypothetical model appeared to be fit to the data. Seven of eight hypotheses selected for hypothetical model were statistically significant. The SOC strategy has only significant indirect effects through dyspnea symptoms on successful aging. Coping strategy, social support, SOC strategies and dyspnea symptoms explained 62% of variance in successful aging.
Conclusion The SOC strategies with social support and dyspnea symptoms significantly explained successful aging among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nursing strategies should be focused on social support and coping strategies to optimize SOC strategies so that older adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are able to manage dyspnea symptoms and eventually achieve successful aging.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A structural equation modeling analysis of successful aging in older adults with osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional descriptive study
Jeong Hwa Kum
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(2): 131. CrossRef - Development of a scale to measure selection, optimization, compensation (SOC) strategy in late middle-aged women: a methodological study
Do-Young Lee, Gie Ok Noh
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(3): 216. CrossRef - Factors contributing to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients' functional performance: Structural equation modelling based on theory of unpleasant symptoms
Hye Suk Jun, Younhee Kang
Nursing Open.2023; 10(5): 3132. CrossRef - Experiences on Self Management of Aged Men with Mild Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Jeong-Soo KIM
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(3): 758. CrossRef - The Relationships among Social Support, Bowel Function Symptoms and Uncertainty in Rectal Cancer Patients
Kyungmi Lee, Semi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 421. CrossRef - Life experience of older women with chronic conditions: Flow and Balance as a coping resource
Sanghee Lee, Jinmoo Heo
Educational Gerontology.2019; 45(4): 259. CrossRef
- A structural equation modeling analysis of successful aging in older adults with osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional descriptive study
- 1,108 View
- 13 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Prevention Stages for Sexually Transmitted Diseases of College Students
- Soon Bok Chang
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(2):423-432. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.2.423
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This is a descriptive study to understand the preventive stage for STDs to provide a basis for sex education for college students. The colleges were selected by quota sampling in five representative cities in Korea, but the1,691 college students were selected by convenient sampling in the cities nationwide, and the data were collected by self-reporting using questionnaire consisting of 33 items. The results were as follows : 1. Their mean ages were 21.8 for female and 23.3 for male students, 2. 78.0% of the males and 46.5% of the females permitted premarital sex, 57.1% of male and 10.3% of female college students had experienced sexual intercourse, 7.1% of males and 2.4% of females had experienced pregnancy, 10.3% of males and 3.4% of females had been infected with STDs, 72.1% of male and 13.8% of female didn't use condoms at the time of infection. 3. Most of the factors related to STDs infection, such as drinking, smoking, frequency of sexual intercourse, pregnancy, knowledge of STDs, the score of STDs prevention were statistically higher in the male student group than in the female group. 4. The student's mean score of knowledge about STDs was similar between the male group(7.80)and the female group(7.84) with a possible score range from 0-18. 5. Only fifteen percent of male and 9.6% of female students expressed that they will do something to prevent STD. 6. The group having the experience of sexual intercourse(t=3.924, P=.048) and the group of having experience of contracting STDs(t=16.638, P=.000) had shown statistically higher STDs prevention score than the group not having that kind of experience, but the group not having experience with pregnancy didn't show any difference from the group not having experience with pregnancy. Considering that 57.1% of males and 10.3% of females had sexual intercourse experience, 78% of male and 46.5% of female permitted premarital sex, 10.3% of male and 3.4% of female had been infected with STDs. It could be concluded that the college students were ignorant about the prevention of STDs and had unrealistic stage of the STDs prevention. Therefore, enforcement of education for the prevention of STDs including the dynamics of the sexual intercourse and STDs infection is needed.
- 483 View
- 2 Download

- Factors Influencing Functional Status in People with Chronic Lung Disease
- Eui Geum Oh, Cho Ja Kim, Won Hee Lee, So Sun Kim, Bo Eun Kwon, Yeon Soo Chang, Ji Yeon Lee, Young Jin Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(5):643-653. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.5.643
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to identify factors that influence the functional status of chronic lung disease patients. METHOD: A descriptive, correlational study design was used. The study was conducted at the outpatient respiratory clinic of the large university hospital in Korea. A convenience sample of 128 chronic lung patients (age = 64.2 yrs; 106 COPD, 17 bronchiectasis, 5 DILD) with mean FEV1 64.4 % predicted. Functional status was measured with SIP. Physical variables (FEV1% predicted, dyspnea, fatigue, pulmonary symptom distress), psychological variables (mood, stress), and situational variable (sleep quality) were examined. Dyspnea was measured by the BDI, fatigue was measured with the MFI. Mood was measured with the modified Korean version of POMS. Sleep quality was measured with the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. Potential independent variables for the regression were age, gender, years since diagnosis, FEV1% predicted, dyspnea, fatigue, pulmonary symptom distress, stress, and sleep quality. RESULT: In general, functional status was relatively good. In regression analysis, functional status were significantly influenced by dyspnea, mood, age and fatigue. These variables explained 70 % of the variances in functional status. CONCLUSION: The results suggest that psychophysiologic symptom management should be a focus to enhance the functional status in this group.
- 428 View
- 2 Download

- Predictors of Intention to Quit Smoking among Patient with Coronary Heart Disease
- Eun Kyung Kim, Mae Ja Kim, Mi Ryung Song
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(3):355-363. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.3.355
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to examine the level of intention to quit smoking and to identify factors influencing intention to quit among patients with coronary heart disease. Method: The subjects consisted of 80 male patients with coronary heart disease (angina pectoris, myocardial infarction) at three hospitals in Seoul. The data were collected with self reporting in a structured questionnaire. Stepwise multiple regression was used to identify predictors of intention to quit. Included variables were attitudes toward smoking cessation, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, usefulness of smoking cessation, and previous attempts to quit. RESULT: 1. The mean score for intention to quit was 11.1(+/-6.1) which was lower than median score of the scale. 2. There were significant correlations between the all predictive variables and the intention to quit(r=.24-.48, p<.05). 3. usefulness of smoking cessation, perceived behavioral control, and previous attempts to quit explained 34.6% of the variance for intention to quit. CONCLUSION: usefulness of smoking cessation, perceived behavioral control, and previous attempts to quit were identified as important variables in explaining the intention to quit smoking among patients with coronary heart disease. Thus, it is necessary to try to enhance this factors for increasing intention to quit among patients with coronary heart disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing Intention to Quit Smoking in Stroke Patients: Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior
Jin-hyun Bae, Eun Su Do, Young Soo Seo
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2014; 16(1): 49. CrossRef - Predictors of Intention to Quit Smoking in Elderly Smokers following a Stroke
Eun Su Do, Young-Sook Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2014; 21(1): 48. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing Intention to Quit Smoking in Stroke Patients: Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior
- 747 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of a Occupational Health Promotion Program for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease
- Jee Won Park, Yong Soon Kim, Gi Yon Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(2):196-205. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.2.196
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purposes of this study was to evaluate an occupational health promotion program for the prevention of cardiovascular disease. METHOD: This study employed a quasi-experimental non-equivalent pre and post test to evaluate the program. The subjects of this study were 48 employees selected by convenience sampling who were suspected of having hypertension and hyperlipidemia in routine physical examinations and who were working in A University Hospital in Suwon. 25 subjects were assigned to the experimental group and 23 to the control group. Data collection was done using questionnaries before and after the subjects used the program. RESULTS: The results of this study showed that systolic blood pressure, ALT, gamma-GTP in the experimental group was lower than that of the control group. There were significant differences between two groups in the percentage of 'irregularity of diet' and in health behavior compliance. There were significant differences between the two groups in the number of complaints of symptoms after using the program. CONCLUSION: This study shows that there were no obvious differences between the two groups in all areas, but this program had a positive effect on health behavior changes. It is expected that employees' lifestyles can be changed through continuous health promotion programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Comprehensive Lifestyle Improvement Program for Middle-aged Women with Cardio-cerebrovascular Disease-related Risk Factors
Mi-Kyoung Park, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(2): 111. CrossRef - Effects of a Tailored Health Promotion Program to Reduce Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Among Middle-Aged and Advanced-Age Bus Drivers
Gyu-Seok Hwang, Jae-Wook Choi, Seoung-Hyung Choi, Seoung-Gil Lee, Kyung-Hee Kim, Yong-Min Cho, Chungsik Yoon
Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health.2012; 24(1): 117. CrossRef - The Effects of a Worksite On-line Health Education Program on Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors and Nutrient Intakes of Male Workers
Ji-Yeon Kang, Sang-Woon Cho, Ji-Young Lee, Sook-Hee Sung, Yoo-Kyoung Park, Yun-Mi Paek, Tae-In Choi
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2010; 43(1): 57. CrossRef
- Effects of a Comprehensive Lifestyle Improvement Program for Middle-aged Women with Cardio-cerebrovascular Disease-related Risk Factors
- 818 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Influencing Factors on Health Behavior of Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
- Young Whee Lee, Hwa Soon Kim, Eui Young Cho
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(1):40-49. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.1.40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to investigate the influencing factors on health behavior among patients with coronary artery disease.
METHOD
The subjects were 95 patients who visited the out-patient department of a university hospital for follow-up. The four health belief concepts (motivation, benefit, barrier, seriousness), general self-efficacy, health behaviors on medication, diet, exercise, stress management, smoking, and drinking were measured.
RESULT
There were significant differences in the health behavior scores of subjects according to family support and the experience of surgical procedure. Subjects were found to have a high degree of compliance in taking medication. However subjects reported the lowest degree of compliance in regular exercise. In the multiple regression analysis, surgical procedure and motivation were significant predictors to explain diet. Motivation and barrier were significant predictors to explain exercise. Self-efficacy, motivation and family support were significant predictors to explain stress management. Family support and seriousness explained 16% of variance in drinking. Also, family support explained 30% of variance in smoking.
CONCLUSION
Since predicting factors on each health behavior indicator were different, then nurses should consider these differences to construct strategy enhancing patient's recovery.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on Breast Cancer Patients’ Commitment to a Plan for Exercise based on Health Beliefs
Hyoung Sook Park, Yun Seo Jung, Young Mi Kim, Jae Hyun Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(1): 64. CrossRef - Influence of Disease-related Knowledge, Depression, and Family Support on Health Behaviors in Older Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Ji Mi Mun, So Young Shin
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2019; 21(3): 155. CrossRef - Effects of Spouse-Participated Health Coaching for Male Office Workers with Cardiocerebrovascular Risk Factors
So Hee Kang, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(6): 748. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of the Resilience on the Relationship between Type D Personality and Compliance in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Mi Young Cheon, Jiyeon Kang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(1): 61. CrossRef - Comparison of Health Behavior Change Before and After the Percutaneous Coronary Intervention among Coronary Artery Disease Patients
Jung-Hun Lee, Kyeong-Soo Lee, Tae-Yoon Hwang
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2016; 41(3): 140. CrossRef - Health Literacy and Health Behavior Compliance in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Eun-Young Jung, Sun-Kyung Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(3): 251. CrossRef - Influences of Knowledge, Self-efficacy, and Social Support on Sick Role Behavior in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Soonhee Kim, Sunhee Lee
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(2): 228. CrossRef - Relationships of Factors Affecting Self-care Compliance in Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients Following Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Eun Suk Shin, Seon Young Hwang, Myung Ho Jeong, Eun Sook Lee
Asian Nursing Research.2013; 7(4): 205. CrossRef - Knowledge, Health Belief, and Preventive Behavioral Intention related to Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) of the Patients with Lower Limb Musculoskeletal System Disorders
Hye Jin Yang, Hee-Young Kang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(4): 531. CrossRef - Predictors of Compliance in Hypertensive Patients
Eun Sil Min, Myung-Haeng Hur
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(4): 474. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Behavior Compliance of Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
Ji-Soon Kang, Hyun-Sook Kang, Eun-Kyoung Yun, Hyun-Rim Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(2): 191. CrossRef - Development of the Japanese Version FFS (Family Functioning Scale): Reliability and Validity for Family on Child-Fostering Phase
Mitsuko Kanzaki, Chifumi Otaki, Kazue Maeda, Taeko Hori, Akemi Take, Hiroko Otsuka, Taeko Noguchi, Sumiko Maehara
Journal of Japan Academy of Nursing Science.2012; 32(1): 50. CrossRef - The relationship between the patient's health beliefs and the implementation of functional movement rehabilitation and ability to perform ADL in stroke patients
Byeong-Mu Mun, Yeon-Seop Lee, Byung-Hoon Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(7): 3057. CrossRef - The Development and Effects of an Integrated Symptom Management Program for Prevention of Recurrent Cardiac Events after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Youn-Jung Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(2): 217. CrossRef
- A Study on Breast Cancer Patients’ Commitment to a Plan for Exercise based on Health Beliefs
- 745 View
- 3 Download
- 14 Crossref

- A Structural Model for Health Promoting Behaviors in Patients with Chronic Respiratory Disease
- Young Joo Park, So In Kim, Pyoung Sook Lee, Soon Yong Khim, Sook Ja Lee, Eun Sook Park, Ho Shin Ryu, Sung Ok Chang, Kuem Sun Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(3):477-491. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.3.477
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was designed to construct a structural model for health promoting behavior in patients with chronic respiratory disease. A hypothetical model was developed based on the literature review. METHOD: Data was collected by questionnaires from 235 patients with chronic respiratory disease in a General Hospital in Seoul. Data analysis was done using SAS 6.12 for descriptive statistics and the PC-LISREL 8.13 Program for Covariance Structural Analysis. RESULT: The results are as follows : 1. The fit of the hypothetical model to the data was moderate. It was modified by excluding 2 path and including free parameters and 3 path to it. The modified model with path showed a good fitness to the empirical data(X2=80.20, P=0.05, GFI=0.95, AGFI=0.88, NNFI=0.95, NFI=0.96, RMSR=0.01, RMSEA =0.06). 2. The perceived benefits, self-efficacy, and a plan of action were found to have significant direct effects on the health promoting behavior in patients with chronic respiratory disease. 3. The health perception, self-esteem, and activity related to affect were found to have indirect effects on the health promoting behavior in patients with chronic respiratory disease. CONCLUSION: The modified model of this study is considered appropriate in explaining and predicting health promoting behavior in patients with chronic respiratory disease. Therefore, it can effectively be used as a reference model for further studies and suggested direction in nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Predictive Model of Health Promotion Behavior in Obese School-Age Children
Mi Suk Jeon, Hyeon-Ok Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(2): 264. CrossRef - Exercise self-efficacy, exercise benefits and barriers, and commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean women with osteoporosis and osteoarthritis
Yun Hee Shin, Hea Kung Hur, Nola J. Pender, Hee Jung Jang, Moon-Sil Kim
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2006; 43(1): 3. CrossRef - Test of the health promotion model as a causal model of commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean adults with chronic disease
YunHee Shin, SangKyun Yun, Nola J. Pender, HeeJung Jang
Research in Nursing & Health.2005; 28(2): 117. CrossRef - Using methodological triangulation for cultural verification of commitment to a plan for exercise scale among Korean adults with chronic diseases
YunHee Shin, Nola J. Pender, SangKyun Yun
Research in Nursing & Health.2003; 26(4): 312. CrossRef
- A Predictive Model of Health Promotion Behavior in Obese School-Age Children
- 727 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- A Structural Model Based on Pender's Model for Quality of Life of Chronic Gastric Disease
- Eun Sook Park, So In Kim, Pyoung Sook Lee, Soon Yong Khim, Sook Ja Lee, Young Joo Park, Ho Shin Ryu, Sung Ok Chang, Kuem Sun Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(1):107-125. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.1.107
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was designed to construct a structural model for quality of life of chronic gastric disease. The hypothetical model was developed based on the literature review and Pender's health promotion model. Data were collected by questionnaires from 459 patients with chronic gastric disease in a General Hospital from July 1999 to August 2000 in Seoul. Data analysis was done with SAS 6.12 for descriptive statistics and PC-LISREL 8.13 Program for Covariance structural analysis. The results are as follows : 1. The fit of the hypothetical model to the data was moderate, thus it was modified by excluding 1 path and including free parameters and 2 path to it. The modified model with path showed a good fitness to the empirical data (Chi2=934.87, p<.0001, GFI=0.88, AGFI=0.83, NNFI=0.86, RMSR =0.02, RMSEA=0.07). 2. The perceived barrier, health promoting behavior, self-efficacy, and self-esteem were found to have significant direct effects on the quality of life. 3. The health concept, health perception, emotional state, and social support were found to have indirect effects on quality of life of chronic gastric disease. In conclusion, the derived model in this study is considered appropriate in explaining and predicting quality of life of chronic gastric disease. Therefore it can effectively be used as a reference model for further studies and suggested direction in nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exercise self-efficacy, exercise benefits and barriers, and commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean women with osteoporosis and osteoarthritis
Yun Hee Shin, Hea Kung Hur, Nola J. Pender, Hee Jung Jang, Moon-Sil Kim
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2006; 43(1): 3. CrossRef - Structural Model for Quality of Life of Patients With Chronic Cardiovascular Disease in Korea
Kuem Sun Han, Sook Ja Lee, Eun Sook Park, Young-Joo Park, Kang Hyun Cheol
Nursing Research.2005; 54(2): 85???96. CrossRef - Test of the health promotion model as a causal model of commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean adults with chronic disease
YunHee Shin, SangKyun Yun, Nola J. Pender, HeeJung Jang
Research in Nursing & Health.2005; 28(2): 117. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life in People with Chronic Illness in Korea
KuemSun Han, PyoungSook Lee, SookJa Lee, EunSook Park
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2003; 35(2): 139. CrossRef - Using methodological triangulation for cultural verification of commitment to a plan for exercise scale among Korean adults with chronic diseases
YunHee Shin, Nola J. Pender, SangKyun Yun
Research in Nursing & Health.2003; 26(4): 312. CrossRef
- Exercise self-efficacy, exercise benefits and barriers, and commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean women with osteoporosis and osteoarthritis
- 696 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Perceived Exercise Self-Efficacy and Exercise Benefits/Barriers of Korean Adults with Chronic Diseases
- Yun Hee Shin, Hee Jung Jang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(4):869-879. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.4.869
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to assess the perceived exercise self-efficacy and exercise benefits/barriers of Korean adults with chronic diseases, and the relationship between the two variables. For the study, 249 Korean adults with chronic diseases with ages ranging from 18 to 79 years were recruited from hospitals or health centers in five Korean cities and surrounding rural areas. The research instruments were the scales that researchers psychometrically verified the Exercise Self-Efficacy Scale, developed by Bandura (1997), and the Exercise Benefits/ Barriers Scale, developed by Sechrist, Walker, and Pender(1987). Results of descriptive analysis showed that Korean adults with chronic diseases perceived relatively low exercise self-efficacy and relatively high exercise benefits/ barriers. Exercise self-efficacy was significantly correlated with gender, education, regular exercise, and exercise benefits/barriers was significantly correlated with gender, regular exercise. Pearson correlation coefficient showed the significant relationship between the two variables. Further researches, which are a study to evaluate a causal structure for Pender's Health Promotion Model and an intervention study to increase physical activity of chronic patients, are recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing Physical Activity after Discharge from Hospital for Total Hip Arthroplasty Patients
Ju Young Kim, Mi Yang Jeon
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2022; 11(4): 535. CrossRef - A Pilot Primary Stroke Prevention Program for Elderly Korean Americans
Minjeong An, Eun-Shim Nahm, Marianne Shaughnessy, Carla L. Storr, Hae-Ra Han, JuHee Lee
Journal of Neuroscience Nursing.2018; 50(6): 327. CrossRef - The Relationship between Health Belief and Exercise Compliance among Elderly Adults at Senior Centers
Kyung Im Lee, Young Eun
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(2): 79. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Exercise Behavior of the Male Manual Worker and Office Worker based on Health Promotion Model
SeungKyoung Yang, Yeongmi Ha, Mi-Ra Jung
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2015; 24(3): 235. CrossRef - The Effects of Task-Oriented Training Program on Balance, Activities of Daily Living Performance and Self-Efficacy in Stroke Patients : A Pilot Study
Jinuk Choi, Soonhee Kang
Journal of The Korean Society of Integrative Medicine.2013; 1(4): 15. CrossRef - Influences of oral health behaviors according to oral health education experiences in middle school students
Mi-Sook Cho, Min-Kyung Park, Kyeung-Ae Jang
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2013; 13(4): 639. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Fear of Falling in Stroke Patients
Hee-Sook Jeong, Eun-Nam Lee, Sam-Sook Kim
Journal of muscle and joint health.2011; 18(2): 215. CrossRef - A Predictive Model on Health Promotion Behavior in Women who Immigrate for Marriage
Namok Jeong, Myung Ha Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(5): 695. CrossRef - Gender differences in physical activity and its determinants in rural adults in Korea
Hyun Kyung Kim, Mi Ja Kim, Chang Gi Park, Hyeon Ok Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2010; 19(5-6): 876. CrossRef - Health Locus of Control, Exercise Self-efficacy, and Exercise Benefits/Barriers of Female College Students
Ju Young Ha
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(2): 116. CrossRef - Effects of the Exercise Self-Efficacy and Exercise Benefits/Barriers on doing Regular Exercise of the Elderly
Eun-Hee Hwang, Yeo-Sook Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(3): 428. CrossRef - Exercise self-efficacy, exercise benefits and barriers, and commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean women with osteoporosis and osteoarthritis
Yun Hee Shin, Hea Kung Hur, Nola J. Pender, Hee Jung Jang, Moon-Sil Kim
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2006; 43(1): 3. CrossRef - Test of the health promotion model as a causal model of commitment to a plan for exercise among Korean adults with chronic disease
YunHee Shin, SangKyun Yun, Nola J. Pender, HeeJung Jang
Research in Nursing & Health.2005; 28(2): 117. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing Physical Activity after Discharge from Hospital for Total Hip Arthroplasty Patients
- 822 View
- 9 Download
- 13 Crossref

- A Study on the Circadian Blood Pressure Rhythm of Diabetic Patients
- Hwa Soon Kim, Wha Sook Suh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):741-749. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.741
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was performed to investigate the relationship between reversed circadian blood pressure and risk factors of peripheral vascular disease in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) subjects. The subjects in this study were 18 NIDDM patients who were hospitalized in a medical unit of an university medical center located in Incheon, Korea, between November, 1998 and March, 1999. Blood pressure was measured with a mercury sphygmomanometer by 2 trained examiners every 2 hours during 24 hours. NIDDM subjects were divided into a dipper group and non-dipper group. Dippers are defined as those who show a mean nighttime blood pressure(BP) drop of more than 10% compared with daytime BP. Non-dippers are defined as those who show a mean nighttime BP drop of less than 10%, or an elevation in BP compared with daytime BP. Daytime BP included values obtained between 6 a.m. and 10 p.m. Night time BP included values obtained between 10 p.m. and 6 a.m. Data was analyzed by SPSS/PC package. Chi-square( 2) test was used for the comparison of sex between The dipper group and non-dipper group. Mann-Whitney test was used for comparisons of values of the risk factors of peripheral vascular disease and the frequency of complications of diabetes between the dipper group and non-dipper group. The results are as follows. There were no significant differences in daytime systolic, diastolic, and mean blood pressures between the dipper group and non-dipper group. However, night time systolic, diastolic, and mean blood pressures in the non-dipper group were significantly nigher than those in the dipper group (p=.021). There were no differences in sex, age, body, weight, duration of diabetes, serum lipid levels, BUN and HbA1c between the two groups. On the contrary, 87.5% of non-dipper group subjects showed having hypertension, 30% of dipper group subjects showed having hypertension and this difference was statistically significant (p=.018). All of the non-dipper group subjects (N=8) showed having at least one diabetic complication. However, 40% of the dipper group subjects (N=10) showed having no diabetic complication at all and this difference was also statistically significant (p=.049). There were no significant differences in frequency of nephropathy, neuropathy and retinopathy between the dipper group and non-dipper group.
- 513 View
- 2 Download

- Lifestyles Effects on Stroke Risk in Different Regions in Korea
- Smi Choi-Kwon, Eun Kyung Kim, Mi Yang Jeon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(3):729-738. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.3.729
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Stroke is a leading cause of death in Korea. Early measurement to prevent stroke are extremely important since it has no cure. Korean might have different risk factors since their dietary habit and socio-economical status differ from most western countries. However, the risk factors for stroke in Korea have not yet been identified. Moreover, the lifestyle of health Korean adults has not been investigated. In this study we investigate the life of health adults living in Seoul and rural areas and compare the life style of the two. METHODS: One hundred seventy one subjects were studies. Among the subjects studied, 128 were from Seoul, the other 43 were from the country area. The age of the subjects was limited to over 40 years. Blood pressure, fast blood sugar, and cholesterol were measured. The subjects' height, weight, body mass index total body fat, skinfolds thickness of triceps, subscapular and abdomen were measured to determine obesity. Using a structured interview, we assessed : sodium intake, physical activity and exercise, consumption of vegetables, fat, fish and fruits. The results of the two groups were compared. RESULTS: There were no statistical differences in age and education between the two groups of subjects. The mean age of the subjects were 66 years old. The subjects residing in rural areas had a higher intake of sodium(p<0.05), lower physical active(P<0.05), and higher BMI and body fat(p<0.05) as compared to the subjects in Seoul. Subjects with hypertension were between 24% and 33% and the prevalence of hypertension was the highest was the highest when compared to the prevalence of DM, or hypercholesterolemia. However, the prevalence of hypertension, DM, hypercholesterolemia, were not significantly different in these areas. CONCLUSION: our results show that subjects living in rural areas eat more salty food, exercise less and tend to be obese. The finding of this study lead to speculation that Korean living in rural areas have less information about the effects diet of diet on health than city dwellers do. General health and nutrition education programs aimed at the prevention of stoke and other such conditions for rural area Korean may close the risk factor gap between rural and urban dwellers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Korean Version of Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly (K-PASE)
Myoung-Ae Choe, Jeungim Kim, Mi-yang Jeon, Young-Ran Chae
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(1): 47. CrossRef - Echocardiographic Plains Reflecting Total Amount of Epicardial Adipose Tissue as Risk Factor of Coronary Artery Disease
Jung-Won Hwang, Un-Jung Choi, Sung-Gyun Ahn, Hong-Seok Lim, Soo-Jin Kang, Byoung-Joo Choi, So-Yeon Choi, Myeong-Ho Yoon, Gyo-Seung Hwang, Seung-Jea Tahk, Joon-Han Shin, Doo-Kyung Kang
Journal of Cardiovascular Ultrasound.2008; 16(1): 17. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Korean Version of Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly (K-PASE)
- 784 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Actual Physical Symptom and Stress in Caregivers of Patients with Cerebrovascular Disease
- Hee Seoung Kim, Hyeoun Ae Park, Mi Jeong Oh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(3):695-704. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.3.695
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study amis for examines the actual physical symptom and stress in caregivers of patients with cerebrovascular disease. The data were collected by a survey conducted from August to September, 1997 which included 65 caregivers of cerebrovascular disease patient in 4 hospitals located in Seoul. The caregiver's stress was measured by Choi(1992)'s instrument and the actual physical symptoms were investigated. The data were analyzed using ANOV, Scheffe test, pearson correlation coefficient and stepwise multiple regression. The results were as follows : 1. The mean number of caregiver's physical symptom was 3.5. There were significantly higher number of physical symptom in women, those of who have a religious affiliation, those of two perceive their own health status perceived s bad, and those of two perceived their patients disease condition as serious than in their counterparts. Also, the number of caregiver's physical symptom was significantly higher in caregivers whose patients have a paralysis symptom and the disease onset as spontaneous. 2. The average of caregiver's stress was 57.9. The caregiver's stress was the highest in between the ages of 50 and 59. There were also significantly higher level of stress in women, those of two perceived the disease condition of their patient as serious than in counterparts. 3. The most common caregiver's physical symptom was fatigue(87.7%). This was followed by insomnia(58.5%) and muscle (47.4%). 4. Caregiver's physical symptom was positively correlated with caregiver's stress and negatively correlated with patient's activity of daily life. 5. The most important variable affecting the caregiver's physical symptom was patient's activity of daily life which accounted for 12.7% of the total variance in stepwise multiple regression analysis. The most important variable affecting the caregiver's stress was the patient disease condition perceived by the caregiver that accounted for 12.1% of the total variance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life of Family Caregivers of Patient with Lung Cancer
Ju-Young Park
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2010; 10(2): 129. CrossRef
- Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life of Family Caregivers of Patient with Lung Cancer
- 624 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Correlations between Weight, Body Mass Index(BMI) and Risk Factors of Coronary Artery Disease in Men and Women in their Forties and Fifties
- Hee Seung Kim, Hye Sun Jeong, Kyung Sil Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(1):184-192. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.1.184
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was done to examine the correlations between weight, BMI and risk factors of coronary heart disease in men and women in their forties and fifties. The subjects were 412 adults, who had regular health examinations between January and December of 1996 at S-Hospital in Seoul. The data were analyzed using ANOVA, Scheffe test, and Pearson correlation coefficient. The results are as follows : 1. The men between 50 and 59 years of age had higher levels for BMI, weight, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, triglyceride, fasting blood sugar, plasminogen activator-1, and hemoglobin A1C than the group of women in their forties. Yet, HDL-cholesterol was lower than in the former group. 2. In the group of men in their forties, weight was significantly correlated to diastolic blood pressure(r=.22), LDL-cholesterol(r=.20), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1(r=.35) HDL-cholesterol(r=-.19). Their BMI was significantly corrected to systolic blood pressure(r=.27), diastolic blood pressure(r=.33), total cholesterol(r=.23), LDL-cholesterol(r=.26), plasminogen activator-1(r=.36) and HDL-cholesterol(r=-.25). 3. As for the group of women in their forties weight was significantly correlated to systolic blood pressure(r=.20), diastolic blood pressure(r=.22), triglyceride(r=.32), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1(r=.30) and HDL-cholesterol(r=-.37). Their BMI was significantly correlated to diastolic blood pressure(r=.25) triglyceride(r=.47), plasminogen activator-1(r=.35), fibrinogen(r=.27) and HDL-cholesterol(r=-.47). 4. In the group of men in their fifties, weight was significantly correlated to total cholesterol(r=.32), LDL-cholesterol(r=.29), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1(r=.26). Their BMI was significantly correlated to systolic blood pressure(r=.24), diastolic blood pressure(r=.22), total cholesterol(r=.34), LDL-cholesterol(r=.32), and plasminogen activator-1(r=.25). 5. In the group of women in their fifties, weight was significantly correlated to diastolic blood pressure(r=.33), total cholesterol(r=.21), LDL-cholesterol(r=.20), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1(r=.43) and HDL-cholesterol(r=-.21). Their BMI was significantly corrected to systolic blood pressure(r=.25), diastolic blood pressure(r=.40), total cholesterol(r=.24), LDL-cholesterol(r=.24), triglyceride(r=.22), and HDL-cholesterol(r=-.30). The above findings indicate that the BMI was more predictive than weight as a risk factor for coronary artery disease for men and women in their forties and fifties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Morbidity and mortality rates in women with heart disease: Lessons in gender differences from Korea
Myoung-Ae Choe, Kyungeh An
Contemporary Nurse.2003; 14(2): 158. CrossRef
- Morbidity and mortality rates in women with heart disease: Lessons in gender differences from Korea
- 593 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Predictors of Coronary Heart Disease Risk in Healthy Men and Women
- Kyeung Ae Kim, Jung Soon Kim, Myoung Soo Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(7):1039-1048. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.7.1039
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF OBJECTIVES: The purpose of this study was to identify predictors of coronary heart disease risk factors in healthy men and women. METHOD: The subjects of this study were 346 people (173 men and women aged 20 years and over) who received health screenings. Data was collected from December 1, 2005 to February 28, 2006. The FANTASTIC Lifestyle Assessment Inventory except smoking and the Framingham risk score of subjects were investigated. Data was analyzed by descriptive analysis, t-test, ANOVA, pearson correlation coefficients and stepwise multiple regression using the SPSS 10.0 program. RESULTS: The mean score of the lifestyle of the women (64.24) was higher than that of the men (59.12). The mean score of the risk of coronary heart disease of the men (5.28%) was higher than that of the women (0.28%). The framingham risk for men was significantly related to lifestyle such as dietary habit, use of caffeine and drugs, anxiety and depression, job satisfaction, and closeness with family. The main predictors of framingham risk for men and women were 'use of caffeine and drugs', and 'menopause' which explained 16.5%, and 30.7% respectively. CONCLUSION: Since lifestyles can be changed with effort, coronary heart disease can be prevented while people are healthy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ATTITUDE TO HEALTH, PREVENTION AND MEDICAL CARE: GENDER ASPECT
А. Akimov, M. Kayumova, A. Novoselov, E. Lebedev, M. Bessonova
Vrach.2023; 34(6): 45. CrossRef - Factors Associated With Cardiovascular Disease Prevention Behavior Among Office Workers Based on an Ecological Model
Jihyon Pahn, Youngran Yang
Sage Open.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors related to Coronary Artery Disease in Korean Adults: Based on the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013~2015
Sook Young Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2018; 21(1): 33. CrossRef - GENDER-RELATED CHARACTERISTICS OF AFFECTIVE DISORDERS IN PATIENTS WITH ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
S. Yu. Mukhtarenko, T. M. Murataliev, Yu. N. Nekludova, Z. T. Radzhapova, V. K. Zventsova
The Clinician.2017; 11(2): 49. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Factors Influencing The Framingham Risk Score-Coronary Heart Disease by BMI
Kwang-Ok Park, Ji-Yeong Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(4): 248. CrossRef - The framingham risk score, diet, and inflammatory markers in Korean men with metabolic syndrome
Cheongmin Sohn, Juyong Kim, Wookyung Bae
Nutrition Research and Practice.2012; 6(3): 246. CrossRef
- ATTITUDE TO HEALTH, PREVENTION AND MEDICAL CARE: GENDER ASPECT
- 860 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Effects of a Nurse Presence Program on Suicide Prevention for Elders with a Chronic Disease
- Kae Hwa Jo
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(7):1027-1038. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.7.1027
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to identify the effects of a nurse presence program on suicide prevention for elders with chronic disease. METHOD: The subjects were recruited from two different elderly institutions located in D city and K province, Korea. Twenty subjects in the control group received no intervention and nineteen subjects in the experimental group received a nurse presence program. RESULT: There were more significant decreases in suicide ideation, and the cortisol level and increases in life satisfaction in the experimental group compared to the control group. CONCLUSION: According to the above results, a nurse presence program for elders with a chronic disease decreased stressful events like suicide ideation and increased self esteem through therapeutic interaction. These findings suggest that this program can be used as an efficient independent nursing intervention for elders in a critical situation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Depression and Suicide Prevention Program for Vulnerable Community-Dwelling Elderly Women
Jae-Soon Yoo, Hyun-Sook Kim, Hyon-Jin Yon
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(5): 2882. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse Presence Program on Anxiety and Physiological Indicators in Patients with Gynecological Surgery
Yun Jeong Kim, Kae Hwa Jo
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2014; 16(4): 326. CrossRef - Power Analysis in Experimental Designs with t test Analysis
Jeong-Hee Kang, Kyung-Sook Bang, Sung-Hee Ko
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2009; 15(1): 120. CrossRef
- The Effect of Depression and Suicide Prevention Program for Vulnerable Community-Dwelling Elderly Women
- 908 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Development and Effects of a Self-management Program for Patients with Parkinson's Disease
- Kyeong Yae Sohng, Jung Soon Moon, Kwang Soo Lee, Dong Won Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(6):891-901. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.6.891
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was done to develop and examine the effects of a self-management program (SMP) on physical, psychological functions, and symptoms in patients with Parkinson's disease(PD). METHODS: In a two-group pre-and post-test design, a total of 40 patients were assigned to the experimental group(21) or the control group (19). The experimental group received eight weekly 2-hour sessions for 10-15 literate adults of all ages, while the control group did not receive any intervention. RESULTS: The experimental group showed significant improvements in muscle strength, balance, self-efficacy, depression, quality of life(QL), quality of sleep, and discomfort of constipation. It also reduced the number of participants using assistive walking devices. There were no significant changes in fear of falling and duration of sleep. CONCLUSION: The eight week SMP in patients with PD was found to be significantly effective in enhancing muscle strength, balance, self-efficacy, QL, and quality of sleep. It also decreased depression, discomfort of constipation, and assistive walking devices. These results suggest that a SMP can have effects on physical, psychological functions and symptoms in patients with PD. Further research with a larger sample and for a longer follow up period is needed to expand our understanding of the effects of a SMP for patients with PD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of mobile health intervention for self-management on self-efficacy, motor and non-motor symptoms, self-management, and quality of life in people with Parkinson's disease: Randomized controlled trial
Yusun Park, Sung Reul Kim, Hui Young So, Sungyang Jo, Seung Hyun Lee, Yun su Hwang, Mi Sun Kim, Sun Ju Chung
Geriatric Nursing.2022; 46: 90. CrossRef - Effects of Environmental Enrichment on Neurotrophins in an MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Animal Model: A Randomized Trial
Hyeyoung Cho, Kyoungah Kang
Biological Research For Nursing.2020; 22(4): 506. CrossRef - Clinical effectiveness of acupuncture on Parkinson disease
Sook-Hyun Lee, Sabina Lim
Medicine.2017; 96(3): e5836. CrossRef - A Meta-Analysis of Nonpharmacological Interventions for People With Parkinson’s Disease
JuHee Lee, MoonKi Choi, Yonju Yoo
Clinical Nursing Research.2017; 26(5): 608. CrossRef - Factors associated with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms for Patients with Parkinson's Disease
Hyo Jeong Song, Ji Hoon Kang, Eun Joo Lee, Jung-Sik Huh, Young-Joo Kim, Chul Soo Kim, Myung Ja Kim, Seung Kyo Chaung, Hye Ja Park, Hyung Chang Kang, Keun Heau Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(1): 116. CrossRef
- Effect of mobile health intervention for self-management on self-efficacy, motor and non-motor symptoms, self-management, and quality of life in people with Parkinson's disease: Randomized controlled trial
- 995 View
- 23 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Influencing Factors on Fatigue in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- So Youn Bang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(6):855-862. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.6.855
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to identify the factors influencing fatigue in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. METHODS: A descriptive correlational study design was used. A convenience sample of 125 subjects was recruited from the outpatient respiratory clinic at a large university hospital. Data was collected from June to October, 2005 using structured questionnaires, an oxygen saturation test, a 6-minute walking test, and a pulmonary function test. RESULTS: Subjects had a slightly low degree of fatigue. The fatigue showed a significant correlation with emotion(r= .589, p= .000), dyspnea(r= .304, p= .001), self-efficacy (r= -.278, p= .002), and symptom experience(r= .238, p= .008). Emotion(34.7%) and dyspnea(5.8%) were significant predictors to explain fatigue. CONCLUSION: This study provides comprehensive understanding of the influencing factors on fatigue in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nursing interventions to decrease negative emotion and dyspnea for management of fatigue is suggested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease among Nonsmokers: Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2010–2012)
Heeyoung Oh, Ye-Eun Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2016; 7(6): 385. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Health‐Related Quality of Life of Korean Patients with Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease
Jisu Kim, Kisook Kim
Public Health Nursing.2015; 32(3): 191. CrossRef
- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease among Nonsmokers: Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2010–2012)
- 658 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Subjective and Objective Caregiver Burden in Parkinson's Disease
- Keum Soon Kim, Bog Ja Kim, Kyung Hee Kim, Myoung Ae Choe, Myungsun Yi, Yang Sook Hah, Sun Ju Chung, So Hi Kwon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(2):242-248. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.2.242
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor disabilities and increasing dependence on others for daily life activities with consequent impact on patients' and caregivers' quality of life. The aim of this study was to elucidate the burden on primary caregivers of patients with PD, and identify related factors.
Methods A cross-sectional descriptive study. Seventy-six primary caregivers of PD patients in a neurology outpatient clinic, Seoul, Korea completed structured questionnaires, of which 68 were analyzed. The structured self-report questionnaire included (1) demographic information on the caregivers, (2) information regarding the disease characteristics of the patients, and (3) the subjective and objective caregiver burdens as assessed on Montgomery, Gonyea, & Hooyman's scale.
Results The mean age of the caregivers was 54.56 years, and spouses represented the largest proportion(47.0%). Caregivers of PD patients experienced high levels of burden (mean scores on the subjective and objective burdens were 45.22 and 34.90, respectively), which were comparable to the caregiver burdens in stroke, and higher than the caregiver burdens in general chronic disease. Older caregivers and spousal caregivers experienced significantly higher burdens (p=.004 and p=.019, respectively). A greater motor disability and higher modified Hoehn and Yahr grade were related to higher caregiver burden (p=.001 and p=.018, respectively).
Conclusion Caring for PD patients is associated with a high level of caregiver burden. Therefore, healthcare professionals should identify the burden of caregivers who look after PD patients and develop comprehensive management strategies both for patients and their caregivers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perceptions of workload in caregivers involved in the care of patients with Parkinson’s disease: an exploratory - correlational study
Elsa Vitale, Luana Conte, Rosita Pasquadibisceglie, Antonino Calabrò, Cosimo Leone, Maicol Carvello, Roberto Lupo
Journal of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2024; 72(3): 122. CrossRef - Development of the Forman Parkinson’s Disease Symptom Checklist
Bushra Akram, Ivan Suneel
Journal of Professional & Applied Psychology .2022; 3(3): 356. CrossRef - Effects of Multimodal Rehabilitation on the Activities of Daily Living, Quality of Life, and Burden of Care for Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Control Study
Hyun-Se Choi, Seung-Hyun Cho
Healthcare.2022; 10(10): 1888. CrossRef - Parkinson's Disease Caregiver Strain in Singapore
Siok-Bee Tan, Allison F. Williams, Eng-King Tan, Richard B. Clark, Meg E. Morris
Frontiers in Neurology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychological distress and perceived burden in caregivers of persons with autism spectrum disorder
Eman Khamis Alnazly, Amjed Abojedi
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2019; 55(3): 501. CrossRef - Caregiver Burden, Spirituality, and Psychological Well-Being of Parents Having Children with Thalassemia
Jawaria Anum, Rabia Dasti
Journal of Religion and Health.2016; 55(3): 941. CrossRef - Predictors of Depression Among Caregivers of Older Adults With Severe Mental Illness
Sherry M. Cummings, Nancy P. Kropf
Journal of Gerontological Social Work.2015; 58(3): 253. CrossRef - The Relationship among Caregiver Burden, Demographic Variables, and the Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease—A Systematic Review of Studies Using Various Caregiver Burden Instruments
Ingrid Leiknes, Unn-Tone Lien, Elisabeth Severinsson
Open Journal of Nursing.2015; 05(10): 855. CrossRef - A Structural Model of Health-Related Quality of Life in Parkinson’s Disease Patients
JuHee Lee, MoonKi Choi, Dukyoo Jung, Young H. Sohn, JinYong Hong
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2015; 37(8): 1062. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Caregiver Burden in Caregivers of Patients with Parkinson's Disease
Dong Won Kim, Eun Sook Bae
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(3): 283. CrossRef - Factors Related to Family Caregivers' Burden with the Community-Dwelling Disabled Elderly under the Long-Term Care Insurance System
Eun-Jeong Han, Jung-Myun Lee, Jin-Hee Kwon, Seul-Bi Shin, Jung-Suk Lee
Health Policy and Management.2014; 24(1): 71. CrossRef - Family caregivers experiences of provided home care to persons with Parkinsons disease
Ingrid Leiknes, Sevald Høye
Nordisk sygeplejeforskning.2012; 2(1): 29. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life in Caregivers of People with Parkinson's Disease and Implications for Clinical Guidelines
D. Morley, S. Dummett, M. Peters, L. Kelly, P. Hewitson, J. Dawson, R. Fitzpatrick, C. Jenkinson
Parkinson's Disease.2012; 2012: 1. CrossRef
- Perceptions of workload in caregivers involved in the care of patients with Parkinson’s disease: an exploratory - correlational study
- 1,105 View
- 9 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Comparison of Cardiovascular Risk Profile Clusters Among Industrial Workers
- Seon Young Hwang, Ji Hyun Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(8):1500-1507. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.8.1500
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify subgroups of the physical and behavioral risk profiles for cardiovascular disease among industrial workers, and to examine predicting factors for the subgroups.
Sample and Methods Health records of 2,616 male and female workers aged 19-56 years who were employed in an airplane manufacturing industry were analyzed. Data were analyzed using the Latent class cluster analysis.
Results Four different clusters (two high-risk groups, one low-risk group, and one normal group) were found and these clusters were significantly different by age, gender, and work type (p<.05). The two high-risk groups had higher chances of drinking alcohol, elevated BMI, FBS, total cholesterol, having hypertension, and were significantly older, and had relatively high chances of being day workers rather than other groups. The low-risk group had higher chances of drinking alcohol, higher BMI and total cholesterols compared to normal group, and highest portions of current smokers and shift workers in the four clusters and their mean BP was within prehypertension criteria.
Conclusion Industrial nurses should guide the lifestyle behaviors and risk factors of the high risk groups for CVD and need to intervene early for behavioral change for the low-risk group who are young and shift workers. Age, and work environment should be considered in planning for targeted preventive interventions for industrial workers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated with Blue-collar Workers' Risk Perception of Cardiovascular Disease
Won Ju Hwang, OiSaeng Hong, Mi Ja Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(7): 1095. CrossRef
- Factors Associated with Blue-collar Workers' Risk Perception of Cardiovascular Disease
- 770 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effects of a Sex Education Program on Knowledge Related to Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Sexual Autonomy among University Students
- Yun Hee Shin, Young Kyung Chun, Sung Mi Cho, Ye Ryung Cho
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(7):1304-1313. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.7.1304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of a sex education program, which was based on the Health Belief Model, on knowledge related to sexually transmitted diseases and sexual autonomy among university students.
Methods A non-equivalent control group, pretest-posttest design was used. The four session program was delivered to 18 students during 4 weeks; the control group consisted of 23 students. The theme of the first session was “sex, gender, and sexuality: all our concern”, “dangerous sex” for the second session, “safe sex” for the third session, and “right sex for you and me” for the fourth session.
Results At follow-up, the knowledge related to sexually transmitted diseases and sexual autonomy were significantly greater in the intervention group than in the control group.
Conclusion A sex education program with several sessions within the theoretical frame of HBM was effective to improve knowledge related to sexually transmitted diseases and sexual autonomy. The results suggest the potential of a systematic sexual education program to teach healthy sex and to extend the program for other various populations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- User-centered design to enhance university students’ sex and menstrual education in South Korea: randomized controlled trial
Hana Kim, Ji Woon Ko, Doyon Kim, Nagyeom Yoon, Jisan Lee
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - An Integrative Literature Review on Sex Education Programs for Korean College Students
Hyewon Shin, Jung Lee, Hye Min
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(1): 78. CrossRef - Gender Difference in Mediating Effects of Self-Efficacy for the Prevention of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) among College Students' STD Knowledge, Susceptibility, and Sexual Autonomy
Mijeong Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(4): 482. CrossRef - Affecting Factors Sexual Experience Among College Students
Ae Hwa Jaung, Yu Jin Jung, Min Young Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(1): 555. CrossRef - Effects of sexual autonomy enhancement program for university students in South Korea
Ju-Eun Song, So Mi Park, Jeongok Park, Hyun Ju Chae
Journal of Public Health.2014; 22(2): 165. CrossRef - Knowledge on Cardiovascular Prevention and Nicotine Dependency among Smoking Male College Students
Seon Young Hwang, Kyongok Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(2): 75. CrossRef - Effect of Sexual Education Program on Female College Student's Sexual Knowledge and Sexual Autonomy
Nami Chun
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2012; 18(2): 108. CrossRef - Self-Efficacy and Sexual Autonomy among University Students
Kyung-Won Kim, Kyeong-Hwa Kang, Geum-Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2012; 26(1): 51. CrossRef - A Mentoring Program for the Promotion of Sexual Health Among Korean Adolescents
YunHee Shin, Lynn Rew
Journal of Pediatric Health Care.2010; 24(5): 292. CrossRef
- User-centered design to enhance university students’ sex and menstrual education in South Korea: randomized controlled trial
- 871 View
- 14 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Development and Testing of a Sexually Transmitted Diseases Prevention Program in At-Risk Prostitutes
- Yang Heui Ahn, Gi Nam Jin
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(5):868-878. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.5.868
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of the study was to test the effectiveness of an 8 session intervention program to prevent sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) among at-risk prostitutes.
Methods An experimental research design was employed. Subjects were 59 prostitutes (29 in the control group and 30 in the experimental group) who agreed to participate in this study. An STD Prevention Framework derived from Cox's Interaction Model of Client Health Behavior guided the overall intervention and the components. The intervention had 8 sessions with STD-prevention strategies and was led by Public Health Nurses. Analysis included change scores, χ2-test, and t-test.
Results The results revealed significant increase in feelings and skills of condom use, peer belief on condom use, condom use practice, and satisfaction with service at public health centers (PHC) on STDs knowledge and skills in the experimental group. However, newly contracted STDs were not significant statistically between groups.
Conclusion The 8 session STDs prevention program showed a effect on emotions, skills and behaviors of condom use even withthe limitation of methodological rigors because of subject-specific conditions. In the future, a capacity-building model based on collaborating networks among community-based organizations will be needed to develop in effective STDs prevention.
- 585 View
- 1 Download

- Prospective Study on the Relating Factors to the Stages of Change in Smoking Cessation and Barriers in Coronary Artery Disease Patients
- Hwa Soon Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(1):27-36. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.1.27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The main purpose of this study was to investigate that the stages of change in smoking cessation behavior among coronary artery disease patients for six months progressed following the stages of change suggested by the transtheoretical model.
Method Subjects for this descriptive survey were 59 coronary disease patients who were smoking or who had stopped smoking for less than six months.
Result In the baseline, the distribution of the subjects' stages of change was as follows: pre-contemplation stage 25.4%, contemplation stage 25.4%, preparation stage 22%, and action stage 27.1%. After six months, more subjects in the contemplation(33.3%) and preparation stages(30.8%) progressed to the action stage than those of the pre-contemplation stage(0%). Eighty-one percent of the subjects in the action stage at baseline progressed to the maintenance stage. The relationship between the numbers of smoking cessation attempts for six months and stages of change at baseline was significant(p=.001). However, the relationships between self-efficacy and nicotine dependence at baseline and progression in stages of change after six months were not significant.
Conclusion Progression in the stages of change for six months among subjects corresponded to the stages of change suggested by the transtheoretical model. Hence, future development and evaluation of intervention programs should be tailored individually considering each patient's stage of change.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Personal Training Is a Great Way for Psychotherapists to Empathize With Their Clients
Geon Ho Bahn
Psychoanalysis.2024; 35(3): 29. CrossRef - Body Fat Percentage and Natural Killer Cell Activity of Breast and Rectal Cancer Patients after Diagnosis but before Treatment
Dal Sook Kim, Myung Hee Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(2): 321. CrossRef
- Personal Training Is a Great Way for Psychotherapists to Empathize With Their Clients
- 649 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Prevalence and Associated Factors of Falls among People with Parkinson's Disease
- Kyeong Yae Sohng, Jung Soon Moon, Kwang Soo Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(6):1081-1091. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.6.1081
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to identify the risk factors associated with falls among patients with Parkinson's Disease(PD).
Method A retrospective study design was used through the collection of physiological and physical health, and psychosocial functions.
Results Of the 100 participants, fifty-nine(59%) reported one or more falls and seventy-one(71%) reported one or more near-falls. Anaverage 34.7 falls and 150.3 near-falls were reported in the previous year per person. Stage of PD, foot problems, balance, fear of falling, and activities of daily living were significantly associated with an increased risk of falls.
Conclusion The findings confirm the high risk of falling in PD patients. Also these results have implications for developing fall prevention programs for PD patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comparative Study of Older Adults’ Perceptions on Housing for Fall Prevention among Older Adults with and without Falls
Chang-Yin Liu, Hyun Joo Kwon, Jiyoung Oh
Journal of the Korean Housing Association.2025; 36(3): 025. CrossRef - Changes of Balance Ability according to the Stability of Shoes in Elderly Woman and Female University Student
Yu-jin Song, Gyeong-hun Min, Deok-yong Jeong, Seon-young Yook, Yun-young Choi, Kyung-yoon Bae, Ki Hun Cho
The Journal of Korean Academy of Physical Therapy Science.2019; 26(3): 70. CrossRef - Risk factors of falls among inpatients with cancer
M.D. Jun, K.M. Lee, S.A. Park
International Nursing Review.2018; 65(2): 254. CrossRef - A Literature Review of Parkinson's Disease Rating, Balance, Fall and Gait Scales
Chang-Hwan Kim, Mi-Young Kim, Bee-Oh Lim
Korean Journal of Sport Biomechanics.2015; 25(4): 441. CrossRef - Fall Risk Factors and Characteristics of an Acute Hospital Setting across Clinical Departments
In-Sil Jang, Sun-Gyo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2014; 21(3): 264. CrossRef - Effects of Hoehn-Yahr Scale on the Activation of Lower-Extremity Muscles during Walking with Parkinson's Patients
Chang-Hwan Kim, Mi-Young Kim, Je-Heon Moon, Bee-Oh Lim
Korean Journal of Sport Biomechanics.2014; 24(3): 287. CrossRef - Analysis of Lower Extremity Muscle Activities in Parkinson's Patients for Improving to Stop Task
Chang-Soo Yang, Bee-Oh Lim
Korean Journal of Sport Biomechanics.2012; 22(3): 333. CrossRef - Factors associated with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms for Patients with Parkinson's Disease
Hyo Jeong Song, Ji Hoon Kang, Eun Joo Lee, Jung-Sik Huh, Young-Joo Kim, Chul Soo Kim, Myung Ja Kim, Seung Kyo Chaung, Hye Ja Park, Hyung Chang Kang, Keun Heau Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(1): 116. CrossRef - Falls Risk Factors of Inpatients
Eun-Kyung Kim, Jae Chang Lee, Mi-Ran Eom
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 676. CrossRef
- A Comparative Study of Older Adults’ Perceptions on Housing for Fall Prevention among Older Adults with and without Falls
- 762 View
- 8 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Decisional Balances and the Process of Change in Smoking Cessation in Patients with Coronary Artery Diseases
- Haeng Mi Son
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(8):1171-1177. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.8.1171
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Despite many smoking cessation programs, many patients with CAD continue to smoke or re-smoke. The processes of change and self-change for smoking cessation is emphasized. The purpose of present study was to investigate decisional balances and processes of change according to stages of change for smoking cessation in the patients with CAD.
Methods This descriptive study was performed using the self-reported questionnaires from 157 male patients with CAD who have smoking experiences. The questionnaires consisted of decisional balances toward smoking (pros/cons) and processes of change including 7 factors.
Results 45.2% of the subjects had myocardial infarction and 54.8% for angina pectoris. Major stages of change were maintenance, contemplation, and precontemplation in 62%, 14%, and 18% respectively. The mean score of pros smoking was 31.07 and cons smoking was 32.52. The mean scores of processes of change were high in all 7 factors, especially in self determination. The pros smoking in precontemplation stage was significantly higher than those in other stages. Between contemplation and precontemplation stages, processes of change showed significant differences in stimulus control, self determination, information management, and dramatic relief.
Conclusion This study suggests that decisional balances and processes of change are stage-specific. As this study, smoking cessation program in the patients with CAD must put priority on the patients group in precontemplation and contemplation stages, and stress self determination and dramatic relief.
- 526 View
- 2 Download

- The Effects of a Pulmonary Rehabilitation Program for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients
- Suk Jung Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(7):1008-1017. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.7.1008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was designed to investigate the effects of a pulmonary rehabilitation program for patients with COPD.
Method 37 subjects, who had a FEV1/FVC below 70%, participated. 18 were assigned to the experimental group and 19 to the control group. The program consisted of individualized education program and exercise program for 6weeks, 3times a week. Data was collected through questionnaire surveys of general characteristics, anxiety and depression, blood tests for lactic acid and cardiopulmonary exercise tests, and also using bicycle ergometer, for exercise capacity. As for data analyses, paired and unpaired t-test and x2-test were adopted using an SPSS program.
Result The result revealed that the increase in VT, peak VO2, VEmax, HRmax and Wmax, at the maximal exercise, were significantly high in the experimental group. However, the anxiety and depression scores were not significantly high in the experimental group.
Conclusion The pulmonary rehabilitation program was effective in increasing cardiopulmonary endurance in patients with COPD. Accordingly, we should seriously consider an individualized pulmonary rehabilitation program as a nursing intervention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Developing a Home-based Self-management Support Intervention for Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Hee-Young Song
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2015; 18(2): 75. CrossRef - The Effects on the Pulmonary Function of Normal Adults Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation Respiration Pattern Exercise
KyoChul Seo, MiSuk Cho
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2014; 26(10): 1579. CrossRef
- Developing a Home-based Self-management Support Intervention for Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- 810 View
- 27 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of a Short-term Home-based Pulmonary Rehabilitation Program in Patients with Chronic Lung Disease
- Eui Geum Oh, Sun Hee Kim, Hee Ok Park, So Yon Bang, Chun Hwa Lee, So Hee Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(5):570-579. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.5.570
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study is to exam the effects of a short-term pulmonary program on lung function, exercise tolerance, and quality of life in chronic lung patients.
Method Randomized controlled pre-post test design was used. The outcome measures were forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1, % predicted), 6 min walking distance (6MWD), Borg score after 6MWD, and Chronic Respiratory Disease Questionnaire (CRDQ). Experimental group performed the 4-week home-based pulmonary rehabilitation program composed of inspiratory muscle training, upper and lower extremity exercise, relaxation, and telephone visit. Patients in control group were only given education about self-management strategies. Thirty four patients with moderate-to-severe respiratory impairment were recruited, and 28 patients (19 in experiments, 15 in control) completed the study.
Result Significant improvements in lung function, exercise tolerance, and health related quality of life were found only in the experiment group.
Conclusion This study yielded evidence for the potential and beneficial effects of home-based pulmonary rehabilitation program in patients with moderate to severe chronic lung disease. The program could be adequately utilized for improvement of health related quality of life in chronic lung patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Embedding Pulmonary Rehabilitation for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in the Home and Community Setting: A Rapid Review
Túlio Medina Dutra de Oliveira, Adriano Luiz Pereira, Giovani Bernardo Costa, Liliane P. de Souza Mendes, Leonardo Barbosa de Almeida, Marcelo Velloso, Carla Malaguti
Frontiers in Rehabilitation Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Systematic Review of Home based Pulmonary Rehabilitation in COPD Patients: Randomized Controlled Trials
Min Hee Ahn, Ja Yun Choi, Yun Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2016; 19(2): 82. CrossRef - Developing a Home-based Self-management Support Intervention for Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Hee-Young Song
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2015; 18(2): 75. CrossRef
- Embedding Pulmonary Rehabilitation for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in the Home and Community Setting: A Rapid Review
- 799 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Effects of Self-Efficacy Promoting Cardiac Rehabilitation Program on Self-Efficacy, Health Behavior, and Quality of Life
- Kyung Ja Song
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(4):510-518. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.4.510
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Ischemic heart disease results from athesclerotic changes of the coronary artery. These changes are aggravated by hypercholesterolemia, smoking, obesity, lack of exercise, coronary-prone personality, and stress. Because these risk factors affect not only the prevalence of the ischemic heart disease but also recurrence of the disease, cardiac rehabilitation programs were introduced to help patients with ischemic heart disease reduce risk factors. Diverse cardiac rehabilitation programs are needed to motivate participation in cardiac rehabilitation and to enhance patients' quality of life.
Objectives To examine the effect of a self-efficacy promoting cardiac rehabiltation program on self-efficacy, health behavior and quality of life of patients with ischemic heart disease.
Methods Data were collected from 45 hospitalized ischemic heart disease patients. Medical records were reviewed to obtain demographic and clinical characteristics. Data regarding self-efficacy, health behavior, and quality of life were obtained from interviews using structured questionnaires. The nonequivalent control group non-synchronized design was used to conduct this study. One session of conventional group education was given to patients in the control group while they were in the hospital. Patients in the experimental group participated in a newly developed cardiac rehabilitation program. It focused on strengthening selfefficacy with four self-efficacy sources - performance accomplishment, vicarious experiences, verbal persuasion and physical status using two individualized in-hospital education sessions and four weekly telephone counseling follow-up calls after discharge.
Results Four weeks after discharge, the increment of total self-efficacy score was significantly higher in the experimental group than in the control group (
p <.01). There was also a significant difference in the total quality of life scores increments between the two groups (p <.01). However, no significant changes were noted in the increments of total health behavior scores between the two groups.Conclusion A cardiac rehabilitation program focusing on promoting self-efficacy was effective in improving self-efficacy, and quality of life of patients with ischemic heart disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Topics of Self-efficacy in Nursing from 2013 to 2022: A Bibliometric Analysis
Qian Cao, Yue Hu, Wan-Ting Cai
Asian Nursing Research.2025; 19(4): 371. CrossRef - Feasibility and preliminary effectiveness of a patient-centered self-care intervention for adults with coronary heart disease in a low resource setting
Rukhsana Perveen, Muhammad Saqib Rabbani, Samina Kausar, Kainat Asmat
Preventive Medicine Reports.2025; 59: 103246. CrossRef - The effects of self-efficacy, a health-promoting lifestyle, and social support on resilience of patients receiving percutaneous coronary intervention: A descriptive survey study
Su-Jin Kim, Jeong-soo Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(4): 403. CrossRef - Social support and self-efficacy multiply mediate the relationship between medical coping style and resilience in patients with type A aortic dissection
Miaoxuan Hong, Rong Zhang, Jin Zhu, Wenxuan Tan
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of risk factor-tailored autonomy enhancement education in the first-time middle-aged patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a randomized controlled trial
In Ae Uhm, Seon Young Hwang
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Barriers and Facilitators to Delivering Inpatient Cardiac Rehabilitation: A Scoping Review
Marina Wasilewski, Abirami Vijayakumar, Zara Szigeti, Sahana Sathakaran, Kuan-Wen Wang, Adam Saporta, Sander L Hitzig
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2023; Volume 16: 2361. CrossRef - The Influence of Knowledge of Coronary Artery Disease and Self-Efficacy on Health Behavior Compliance among Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
A Ram Kil, Yong Soon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(1): 57. CrossRef - Effect of Educational intervention based on Health Belief Model on promoting preventive behaviours of urinary tract infections in mothers with children under 6-Years of age
Zahra Bazargani, Fatemeh Sarikhani, Sadegh Karami Darenjani, Mehdi Amirkhani, Pooyan Afzali Harsini, Ali Khani Jeihooni
BMC Women's Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Self-Efficacy and Health Status in Coronary Artery Disease Patients
Wantiyah Wantiyah, Mochamad Riko Saputra, Fitrio Deviantony
Jurnal Ners.2020; 15(1): 14. CrossRef - The Effects of Smart Program for Patients Who Underwent Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (SP-PCI) on Disease-Related Knowledge, Health Behavior, and Quality of Life: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
Jueun Lee, Haejung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(6): 756. CrossRef - Long-term effects of nurse-led individualized education on middle-aged patients with acute coronary synrome: a quasi-experimental study
Jae Lan Shim, Seon Young Hwang
BMC Nursing.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness of Tailored Education and Counseling Program for Patients with Coronary Artery Disease undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
So-Yeon Kim, Min Young Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(5): 547. CrossRef - Risk Factor–tailored Small Group Education for Patients with First-time Acute Coronary Syndrome
Seon Young Hwang, Jin Shil Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(4): 291. CrossRef - Relationships of Factors Affecting Self-care Compliance in Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients Following Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Eun Suk Shin, Seon Young Hwang, Myung Ho Jeong, Eun Sook Lee
Asian Nursing Research.2013; 7(4): 205. CrossRef
- Research Topics of Self-efficacy in Nursing from 2013 to 2022: A Bibliometric Analysis
- 960 View
- 22 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Development of a Scale to Measure Self-Care for Korean Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Jeong Ja Jun, Ae Kyung Kim, Sang Ok Choi, Jung Hee Ae, Mi Kyung Choi, Sun A Jang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(1):9-16. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.1.9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
Purpose The objective of this study was the development and validation of a scale to measure the self-care of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD) in Korea.
Method Self-care scale was developed based on the self-care activities patients had to carry out in order to manage their COPD. The original scale contained 34 items rated along a five-point Likert scale and was reviewed by 18 professional nurses and 10 Korean patients with COPD for content validity. Subsequently, patients with COPD were asked to complete this 23-item scale and further tests were done with the 125 useable responses.
Result Factor analysis identified eight factors- “maintaining a clean air way”, “taking medication”, “support from family”, “preventing infection”, “managing symptoms”, “breathing exercising”, and “taking in nutrition”. The internal consistency of the total scale was Cronbach's alpha=0.7226. These eight factors explained 60.8% of total variance. There was correlation among Korean Self-Care Scale score, administration level, and knowledge level but there was no correlation to patients' satisfaction with medical services.
Conclusion The 23 item questionnaire positively identified 8 areas defined important for COPD patients. Further studies are required to see how these can be integrated into patient education.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of self-management education using pictogram-based content of health information on outcomes in Korean patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A randomized controlled trial
Ja Yun Choi, Eui Jeong Ryu, Xin Jin
Geriatric Nursing.2023; 54: 324. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of Self-Care Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Inventory (SC-COPD) and Self-Care Self-Efficacy Scale (SCES-COPD)
Ja Yun Choi, So Young Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(5): 522. CrossRef - Self‐management model based on information–motivation–behavioral skills model in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Kyeung Eun Lim, Sung Reul Kim, Hye Young Kim, So Ri Kim, Yong Chul Lee
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2022; 78(12): 4092. CrossRef - The Effects of Primary Stroke Prevention Program on the Knowledge of Stroke, Stroke Symptom Coping Behavior and Self Management of Stroke Risk Group
Eun-Jeong Kim, Jeong-Hyeon Kong
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(11): 7925. CrossRef - Relationship of Knowledge, Attitude, Correct Metered Dose Inhaler Use, and Self-management Compliance among Patients with COPD
Min-Hee An, Ja-Yun Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(2): 160. CrossRef
- Effect of self-management education using pictogram-based content of health information on outcomes in Korean patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A randomized controlled trial
- 1,023 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


