Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Risk factors for the readmission of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hyerim Ji, Sun-Kyung Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):634-650. Published online November 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25072
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
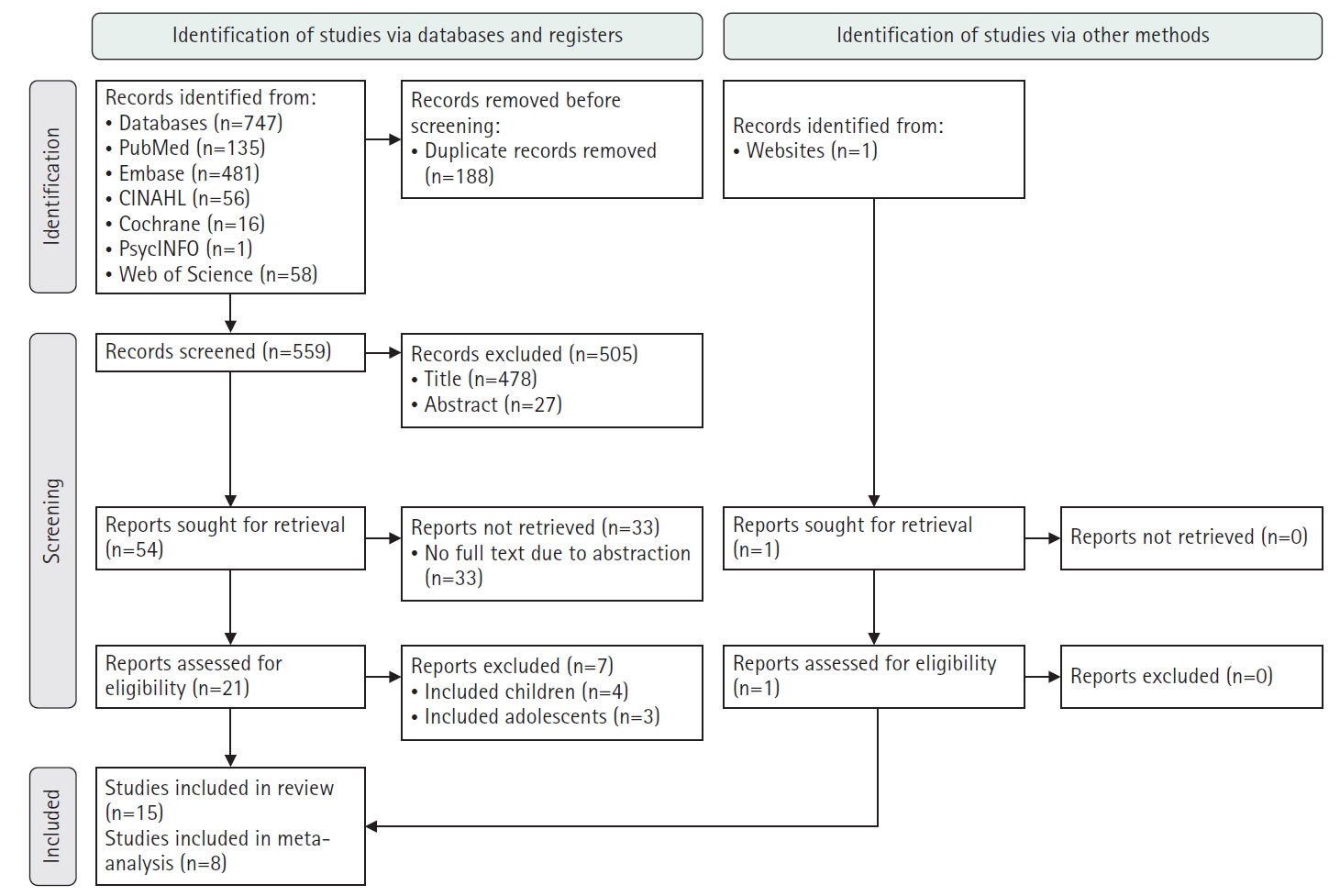
This study aimed to identify risk factors associated with the readmission of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
A systematic literature review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines. Relevant studies were retrieved from international databases (PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Web of Science) and Korean databases (RISS, KoreaMed, KMbase, KISS, and DBpia). Study quality was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Meta-analysis was performed using a random-effects model with the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman adjustment to account for the limited number of studies and heterogeneity.
Results
Fifteen studies were included in the review, and eight were eligible for meta-analysis. From the systematic review, 21 risk factors for DKA readmission were identified and categorized into five domains: demographic, socioeconomic, diabetes-related, comorbidity, and health-behavioral factors. In the meta-analysis, significant risk factors included low income, psychiatric disorders, and discharge against medical advice.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that DKA readmissions result from the complex interplay of multiple clinical and social factors. By identifying these risk factors and suggesting risk-stratification criteria, the findings may support the development of tailored interventions, such as self-management education, integrated mental health care, structured discharge planning, and coordinated post-discharge follow-up.
- 1,316 View
- 193 Download

- Development of the Hybrid Clinical Practicum Environment Scale for Nursing Students
- Seoyoung Yoon, Hye-Ah Yeom
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):340-357. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24016
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a Hybrid Clinical Practicum Environment Scale for Nursing Students (HCPES-NS) and verify its validity and reliability.
Methods
The HCPES-NS was constructed following the DeVellis guidelines. The initial items were written based on a literature review and individual in-depth interviews. Content validity was verified through an expert panel review. To confirm the validity and reliability of the scale, a survey was conducted with 449 nursing students enrolled in 12 nursing colleges. Data were analyzed using item analysis, exploratory factor analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, concurrent validity, and reliability tests.
Results
Factor analysis showed that the HCPES-NS consists of 15 items on five subdomains: clinical site atmosphere, interpersonal relationship, alternative online practicum contents, provision of learning information, and clinical performance facilitation. A higher score indicated a more positive perception of the clinical practicum environment. The concurrent validity of the HCPES-NS was confirmed by its positive correlation with the Clinical Learning Environment Scale (r = .77). The Cronbach’s α reliability of the HCPES-NS was .84.
Conclusion
The HCPES-NS is both valid and reliable. This scale reflects the clinical practicum environment and includes an online practicum factor. It may be used effectively by faculty members and educators to evaluate nursing students’ perceptions of clinical practicum environments. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Environmental and Individual Factors Associated with Clinical Practice Stress in Korean Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
Ui Rim Song
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(4): 355. CrossRef
- Environmental and Individual Factors Associated with Clinical Practice Stress in Korean Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
- 2,964 View
- 96 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Eun Jin Kim, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):44-58. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23090
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to apply a health partnership program using commercially available mobile health apps to improve cardiovascular risk factors in male employees and verify its effectiveness.
Methods
Using a randomized control group pretest-posttest design, male employees with cardiovascular risk factors from five small and medium-sized workplaces were randomly assigned to an experimental group (n = 32) and a control group (n = 31). The experimental group was encouraged to use three mobile health apps for 12 weeks to acquire the necessary cardiovascular disease-related information and practice strengthening training, walking, and diet management appropriate to their level. They also received feedback on their weekly activities and motivational text messages from health partners. Hypotheses were tested using the SPSS WIN 22.0.
Results
The experimental group showed a significant difference compared to the control group in terms of their perception of mobile health app (p < .05), self-efficacy for exercise and diet, self-management partnership, and cardiovascular disease prevention health behavior (p < .001). In particular, there were significant decreases in the body mass index, ratio, serum fasting blood sugar, total cholesterol, and triglyceride in the experimental group (p < .001); however, there was no significant difference in high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol.
Conclusion
Intervention using mobile apps based on partnership with health managers is effective in improving the objective cardiovascular risk index in male employees; therefore, such intervention should be continuously used as a useful lifestyle modification strategy in the workplace. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adherence to a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Yura Shin, Jina Choo, Songwhi Noh
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Adherence to a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
- 3,645 View
- 208 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Development of Nursing Clinical Judgment Scale
- Shi Nae Kwon, Hyojung Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):652-665. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23042
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a nursing clinical judgment scale (NCJS) and verify its validity and reliability in assessing the clinical judgment of nurses.
Methods
A preliminary instrument of the NCJS comprising 38 items was first developed from attributes and indicators derived from a literature review and an in-depth/focus interview with 12 clinical nurses. The preliminary tool was finalized after 7 experts conducted a content validity test based on a data from a preliminary survey of 30 hospital nurses in Korea. Data were collected from 443 ward, intensive care unit, emergency room nurses who voluntarily participated in the survey through offline and online for the verification of the construct validity and reliability of the scale.
Results
The final scale comprised 23 items scored on a 5-point Likert scale. Six factors – integrated data analysis, evaluation and reflection on interventions, evidence on interventions, collaboration among health professionals, patient-centered nursing, and collaboration among nurse colleagues – accounted for 64.9% of the total variance. Confirmatory factor analysis supported the fit of the measurement model, comprising six factors (root mean square error of approximation = .07, standardized root mean square residual = .04, comparative fit index = .90). Cronbach’s α for all the items was .92.
Conclusion
The NCJS is a valid and reliable tool that fully reflects the characteristics of clinical practice, and it can be used effectively to evaluate the clinical judgment of Korean nurses. Future research should reflect the variables influencing clinical judgment and develop an action plan to improve it. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How the nursing work environment moderates the relationship between clinical judgment and person-centered care among intensive care unit nurses
Mi Hwa Seo, Eun A. Kim, Hae Ran Kim, Mohammad Jamil Rababa
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(1): e0316654. CrossRef - Effects of Critical Thinking Disposition, Clinical Judgement, and Nurse–Physician Collaboration on Triage Competency Among Triage Nurses
Ji-Won Song, Hyung-Ran Park
Healthcare.2025; 13(4): 405. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a virtual reality nursing simulation for pediatric pneumonia care: a Korean pilot study using a single-group pre-post test design
Eun Joo Kim, Seong Kwang Kim, Sung Sook Song
Child Health Nursing Research.2025; 31(4): 198. CrossRef - The Influence of Clinical Nurses' Clinical Judgment, Nursing Work Environment and Ethical Nursing Competence on Patient Safety Nursing Activities
Eunseo Hong, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2025; 39(3): 368. CrossRef
- How the nursing work environment moderates the relationship between clinical judgment and person-centered care among intensive care unit nurses
- 4,831 View
- 293 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Development of a Reward Scale for Hospital Nurses
- Sun Hee Kim, Eun-Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(5):525-537. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23057
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and test a reward scale for hospital nurses.
Methods
The initial items were identified through a literature review and focus group interviews with ten hospital nurses. The content validity of the items was evaluated by ten experts. Fifty-one items were derived from the pilot survey. Four hundred eighty-eight nurses participated in the study: 248 for exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and 240 confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). Data were analyzed using item analysis, EFA, CFA, convergent validity, known-group validity, and internal consistency using IBM SPSS Statistics 29.0 and IBM SPSS AMOS 29.0.
Results
The final scale consisted of 31 items and eight factors (decent wage, opportunity to grow and develop, support for special situations, various benefits, flexibility of work, job-related achievement, reflecting career and performance, and recognition), which explained 67.3% of the total variance. The eight-subscale model was validated by CFA. Convergent validity was evaluated by analyzing correlation with intention to leave (r = - .63, p < .001) and job satisfaction (r = .54, p < .001). The known-group validity was evaluated by comparing the reward scales according to age, clinical career, income level and hospital type. The scale was found to be reliable with a Cronbach’s α of .89.
Conclusion
Both the validity and reliability of the reward scale for hospital nurses are verified, which can enhance the understanding of the range of rewards and may assist nurse managers in establishing an effective reward system. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimized nursing management in the Central Sterile Supply Department and Gastroenterology Department: a retrospective controlled study
Dali Wang
American Journal of Translational Research.2024; 16(12): 7480. CrossRef
- Optimized nursing management in the Central Sterile Supply Department and Gastroenterology Department: a retrospective controlled study
- 4,247 View
- 151 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Development and Validation of a Dignity in Care Scale of Terminally Ill Patients for Nurses
- Yun Sil Ahn, Pok Ja Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(3):340-358. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23039
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop an instrument to showcase Dignity in Care of Terminally Ill Patients for Nurses and to examine its validity and reliability.
Methods
A total of 58 preliminary items on dignity in care of terminally ill patients for nurses were selected using content validity analysis and expert opinions on 97 candidate items derived through a literature review and qualitative focus group interviews. Questionnaires were administered to 502 nurses caring for terminally ill cancer patients at hospice and palliative care institutions. The data were analyzed using item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, convergent and discriminant validity, and Pearson correlation for criterion validity, reliability was tested using Cronbach’s alpha.
Results
The final instrument consisted of 25 items, with four factors identified through confirmatory factor analysis. Four factors-ethical values and moral attitudes, interaction-based communication, main-taining comfort, professional insight and competence–accounted for 61.8% of the total variance. Cronbach’s ⍺ for total items was .96, and test-retest reliability of intraclass correlation coefficient was .90.
Conclusion
Since its validity and reliability have been verified through various methods, the Dignity in Care Scale of Terminally Ill Patients for Nurses can be used for develop nursing interventions and improve dignity in care of terminally ill patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cultural adaptation and psychometric validation of the Korean version of the Intensive care unit Dignified Care Questionnaire (IDCQ)
Sejin Kang, So Hyun Park, Youn-Jung Son
BMC Nursing.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Psychometric Testing of the Nurses’ Professional Dignity Scale
Michela Piredda, Maddalena De Maria, Rosario Caruso, Anna Marchetti, Giorgia Petrucci, Anna Cerra, Joyce J. Fitzpatrick, Alessandro Stievano
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(4): 127. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Compassionate Care among Nurses: A Hybrid Model
Ae Kyung Chang, Jin Ah Kim, Yu Kyung Jin, Woo Jung Hong, Yeon Kyung Cho, Ah Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(2): 275. CrossRef - Dignity in Care of Older Patients with Cancer in Korea: A Hybrid Model Concept Analysis
Yun Sil Ahn, Pok-Ja Oh, Gye Jeong Yeom
Healthcare.2025; 13(22): 2935. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Dignity in Care Scale of Terminally Ill Patients for Nurses
Yun Sil Ahn, Pok Ja Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(3): 340. CrossRef
- Cultural adaptation and psychometric validation of the Korean version of the Intensive care unit Dignified Care Questionnaire (IDCQ)
- 3,101 View
- 114 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- The Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of the 5C Psychological Antecedents of Vaccination Scale
- SuYeon Bae, HeeJu Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(3):324-339. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23021
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to valuate the reliability and validity of the Korean version of the 5C Psychological Antecedents of Vaccination (K-5C) scale.
Methods
The English version of the 5C scale was translated into Korean, following the World Health Organization guidelines. Data were collected from 316 community-dwelling adults. Content validity was evaluated using the content validity index, while construct validity was evaluated through confirmatory factor analysis. Convergent validity was examined by assessing the correlation with vaccination attitude, and concurrent validity was evaluated by examining the association with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination status. Internal consistency and test-retest reliability were also evaluated.
Results
Content validity results indicated an item-level content validity index ranging from .83 to 1, and scale-level content validity index, averaging method was .95. Confirmatory factor analysis supported the fit of the measurement model, comprising a five-factor structure with a 15-item questionnaire (RMSEA = .05, SRMR = .05, CFI = .97, TLI = .96). Convergent validity was acceptable with a significant correlation between each sub-scale of the 5C scale and vaccination attitude. In concurrent validity evaluation, confidence, constraints, and collective responsibility of the 5C scale were significant independent predictors of the current COVID-19 vaccination status. Cronbach’s alpha for each subscale ranged from .78 to .88, and the intraclass correlation coefficient for each subscale ranged from .67 to .89.
Conclusion
The Korean version of the 5C scale is a valid and reliable tool to assess the psychological antecedents of vaccination among Korean adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- COVID-19 vaccine acceptance and 5C psychological antecedents amid the omicron surge in South Korea and China
Minjung Lee, Chenyuan Qin, Yubin Lee, Jie Deng, Myoungsoon You, Jue Liu
Vaccine.2025; 43: 126515. CrossRef - Comparative effectiveness of construal-level messaging in the COVID-19 Vaccine Injury Compensation Program in the Republic of Korea: a randomized controlled trial
Jihyun Moon, Se-Hoon Jeong, Young June Choe, Cho Ryok Kang, Taemi Kim, Dooyoung Kim, Jong-Koo Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2025; 16(5): 486. CrossRef - Discriminative Cut-Offs, Concurrent Criterion Validity, and Test–Retest Reliability of the Oxford Vaccine Hesitancy Scale
Jonathan Kantor, Samantha Vanderslott, Michael Morrison, Robert C. Carlisle
Vaccines.2025; 13(12): 1200. CrossRef
- COVID-19 vaccine acceptance and 5C psychological antecedents amid the omicron surge in South Korea and China
- 1,795 View
- 26 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- The Effect of Socioeconomic Status to Depression of Perimenopause Women: Pathway Analysis Using the Reserve Capacity Model
- Mi-Ran Park, Hye Seung Choi, Ju-Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):249-259. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22133
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Based on the Reserve Capacity Model, this study investigated the effects of pre- and postmenopausal women’s socioeconomic status (SES) on depression, focusing on the mediating effects of self-esteem, happiness, and family relationship satisfaction with social network relationships.
Methods
This cross-sectional study involved secondary analysis of national data on 771 perimenopause women gathered from the 16th Korea Welfare Panel Study (KOWEPS) 2021. A path analysis model was constructed to evaluate the relationship between SES, social network satisfaction, self-esteem, perceived health status, and depression. Data were analyzed using ADANCO 2.3.1 and Mplus 8.4.
Results
Although SES had no direct effect on depression, it did affect depression through self-esteem, happiness, and satisfaction with family relationships.
Conclusion
The findings of this study indicate that perimenopausal women’s personal resources—psychosocial variables such as self-esteem and happiness—had a higher effect on depression than tangible reserves like SES. Therefore, interventions for enhancing self-esteem and happiness may prevent depression in perimenopausal women effectively. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Socioeconomic Status on the Health of Menopausal Mothers in Multicultural Families in Korea: A Test of the Reserve Capacity Model
Miran Park, Ju-Young Lee
Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health.2025; 27(2): 277. CrossRef
- Effects of Socioeconomic Status on the Health of Menopausal Mothers in Multicultural Families in Korea: A Test of the Reserve Capacity Model
- 1,913 View
- 44 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Development and Psychometric Evaluation of the Ischemic Stroke Distress Scale (ISDS)
- Jaejin Kang, Yang-Sook Yoo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):12-27. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22090
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure distress in patients with ischemic stroke and verify its validity and reliability.
Methods
Preliminary items were developed from literature review and in-depth interviews. The final preliminary scale was confirmed through a content validity test of eight experts and a preliminary survey of 10 stroke patients. The participants for psychometric testing were 305 stroke patients in the outpatient clinic. Validity and reliability analyses included item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, convergent validity, known-group validity, and internal consistency of the scale.
Results
The final scale consisted of 17 items and 3 factors. The three distinct factors were ‘self-deprecation, worry about future health, and withdrawal from society’ and this structure was validated using a confirmatory factor analysis. Convergent validity was supported by comparison with the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (r = .54, p < .001) and Brief Illness Perception Questionnaire (r = .67, p < .001). Known-groups validity was verified by dividing groups according to ‘duration since diagnosis’ (t = 2.65, p = .009), ‘presence of sequela’ (t = 10.16, p < .001), and ‘awareness of distress’ (t = 12.09, p < .001). The internal consistency of the scale using Cronbach’s α for the total items was .93.
Conclusion
The Ischemic Stroke Distress Scale is a valid and reliable tool that reflects stroke distress effectively. It is expected to be used as a basic tool to develop various intervention strategies to reduce distress in ischemic stroke patients.
- 1,643 View
- 75 Download

- The Reliability and Validity of Korean Version of the Infertility Stigma Scale (K-ISS)
- Miok Kim, Minkyung Ban
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(6):582-597. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22068
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to translate the Infertility Stigma Scale (ISS) into Korean and to evaluate its reliability and validity in the Korean context.
Methods
Data were collected from 350 women who underwent in vitro fertilization (IVF). Data were analyzed using SPSS WIN 25.0 and AMOS 22.0. Content validity was analyzed using the item-level content validity index (I-CVI) and scale-level content validity index/averaging (S-CVI/Ave). The preliminary survey was conducted on 20 women who had experienced IVF at least once to check the level of understanding of the tool and the time required to fill out the questionnaire. Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses were used to test construct validity. Additionally, hypothesis-testing construct validity were tested. Cronbach’s α was used to assess the reliability.
Results
The Korean-ISS (K-ISS) consists of 25 items, excluding two items from the original ISS questionnaire. Exploratory factor analysis identified four factors, which explained 75.6% of the total variance. The four distinct factors were infertility stigma with self-devaluation (56.8%), public stigma (8.1%), social withdrawal (6.5%), and family stigma (4.2%). In the confirmatory factor analysis, the 25 items in the four-factor structure were validated (χ 2 /df ≤ 3, RMSEA ≤ 10). The hypothesis-testing construct validity of K-ISS against FPI (r = .58∼.71, p < .001) and FQI (r = - .49∼- .65, p < .001) was tested and found to be significant. The internal consistency reliability of the K-ISS, assessed using Cronbach’s α, was .97.
Conclusion
The K-ISS has satisfactory construct validity and reliability; therefore, it can help minimize the negative impact of stigma by measuring the stigma associated with women experiencing infertility. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Uncertainty on Depression in Women Undergoing Assisted Reproductive Technology: The Mediating Role of Perceived Stigma and the Moderated Mediation by Spousal Support
Miok Kim
Nursing & Health Sciences.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of the infertility stigma scale short form (ISS-SF): A cross-sectional study
Rong Li, Lan Luo, Nan Qin, Minhui Guan, Enuo Peng, Jia Qu, Guangpeng Wang, Shujuan Zhu, Dan Liu, Shuju Wei, Bing Fu, Jun Lei
Journal of Psychosomatic Research.2025; 194: 112160. CrossRef
- Effects of Uncertainty on Depression in Women Undergoing Assisted Reproductive Technology: The Mediating Role of Perceived Stigma and the Moderated Mediation by Spousal Support
- 1,887 View
- 55 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- The Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Readiness for Practice Survey for Nursing Students
- Tae Wha Lee, Yoonjung Ji, Yea Seul Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(6):564-581. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22032
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the Readiness for Practice Survey (K-RPS).
Method
The English Readiness for Practice Survey was translated into Korean using the Translation, Review, Adjudication, Pretesting, and Documentation (TRAPD) method. Secondary data analysis was performed using the dataset from the New Nurse e-Cohort study (Panel 2020) in South Korea. This study used a nationally representative sample of 812 senior nursing students. Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses were also conducted. Convergent validity within the items and discriminant validity between factors were assessed to evaluate con-struct validity. Construct validity for hypothesis testing was evaluated using convergent and discriminant validity. Ordinary α was used to assess reliability.
Results
The K-RPS comprises 20 items examining four factors: clinical problem solving, learning experience, professional responsibilities, and professional preparation. Although the convergent validity of the items was successfully verified, discriminant validity between the factors was not. The K-RPS construct validity was verified using a bi-factor model (CMIN/DF 2.20, RMSEA .06, TLI .97, CFI .97, and PGFI .59). The K-RPS was significantly correlated with self-esteem (r = .43, p < .001) and anxiety about clinical practicum (r = - .50, p < .001). Internal consistency was reliable based on an ordinary α of .88.
Conclusion
The K-RPS is both valid and reliable and can be used as a standardized Korean version of the Readiness for Practice measurement tool. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Readiness for Practice among Senior Nursing Students in South Korea: A Cross-sectional Study
Jihye Kim, Kyungmi Lee, Hye Suk Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(1): 54. CrossRef - Readiness for Practice Among Nursing College Graduates: A Cross-Sectional Correlation Study
Kim Jihye, Lee Kyungmi
SAGE Open Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Moderating Effect of Grit on Nursing Education Satisfaction and Readiness for Practice Among Nursing Graduates During COVID-19: A Cross-Sectional Study
Lee Kyungmi, Kim Jihye
Pacific Rim International Journal of Nursing Research.2025; 29(4): 862. CrossRef - The influence of nursing informatics competency, clinical practice self efficacy, and grit on clinical practice readiness of nursing students
Hae Ok Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(4): 440. CrossRef - The mediating effect of transition shock on the relationship between readiness for practice and turnover intention of new graduate nurses in South Korea: A longitudinal study
Taewha Lee, Eunkyung Kim, Yoonjung Ji
Nurse Education Today.2024; 143: 106394. CrossRef
- Readiness for Practice among Senior Nursing Students in South Korea: A Cross-sectional Study
- 4,624 View
- 189 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Incidence and Risk Factors of Dyslipidemia after Menopause
- Ihn Sook Jeong, Hae Sun Yun, Myo Sung Kim, Youn Sun Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):214-227. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21188
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study was aimed at investigating the incidence and risk factors of dyslipidemia in menopausal women using a Korean community-based longitudinal study.
Methods
The subjects were 245 postmenopausal women without dyslipidemia who had participated in the Ansan-Ansung cohort study from 2001~2002 (baseline) to 2015~2016 (seventh follow-up visit). The dyslipidemia incidence was measured as incidence proportion (%) and incidence rate per 100 person-years. The predictors of developing dyslipidemia were analyzed with Cox’s proportional hazard model.
Results
The incidence of new dyslipidemia during the follow-up period was 78.4% (192 patients), and 11.9 per 100 person-years. Mean duration from menopause to developing dyslipidemia was 5.3 years in new dyslipidemia cases. The triglyceride/high density lipoprotein (TG/HDL-C) ratio at baseline (hazard ratio = 2.20; 95% confidence interval = 1.39~3.48) was independently associated with developing dyslipidemia.
Conclusion
Dyslipidemia occurs frequently in postmenopausal women, principally within five years after menopause. Therefore, steps must be taken to prevent dyslipidemia immediately after menopause, particularly in women with a high TG/HDL-C ratio at the start of menopause. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of the 5-Year Incidence of Dyslipidemia in the Obese and Nonobese Adult Population: Results of the Yazd Health Study (YaHS)
Parisa Peigan, Masoud Mirzaei, Pedro Marques-Vidal, Mohammadtaghi Sarebanhassanabadi
Advanced Biomedical Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Middle-aged Korean women’s experiences of physical activity during the transition to menopause: a grounded theory approach
Hee Jung Cho, Sukhee Ahn
Women's Health Nursing.2025; 31(3): 215. CrossRef - Middle-aged women’s experiences of physical activity for managing menopausal symptoms: a phenomenological study
Hee Jung Cho, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(2): 104. CrossRef - Relationship between sleep duration and prevalence of hypertension among Korean postmenopausal middle-aged women
Eun Young Hong, Hye Ja Gu
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2023; 40(5): 43. CrossRef - Identification of subgroups with poor lipid control among patients with dyslipidemia using decision tree analysis: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2019 to 2021
Hee Sun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(2): 131. CrossRef
- Comparison of the 5-Year Incidence of Dyslipidemia in the Obese and Nonobese Adult Population: Results of the Yazd Health Study (YaHS)
- 1,595 View
- 32 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Couple Satisfaction Index
- Suk-Sun Kim, Minji Gil, Daeun Kim, Sunhai Kim, Dayeon Heo, Nan Young Moon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):228-227. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21177
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The study aimed to translate the Couple Satisfaction Index (CSI 32) into Korean, to evaluate the reliability and validity of CSI 32 and short-form (CSI 16, 4) in the Korean context, and to determine a cut-off score for Korean couples.
Methods
Korean Versions of the Couple Satisfaction Index (K-CSI) 32 was translated, back-translated, and reviewed by five bilingual experts. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was conducted with data from a sample of 218 couples (N = 436) to test construct validity. Validity and reliability were evaluated. The receiver’s operating characteristics curve analysis was used to obtain the cut-off score.
Results
The construct validities of K-CSI 32, 16, and 4 were verified using one-factor structures. The results of CFA showed a slightly better fit for K-CSI 16 and 4 than for K-CSI 32. Convergent validity was supported by significant positive correlations of K-CSI with Kansas Marital Satisfaction Scale, Dyadic Adjustment Scale, and Family Relationship Assessment Scale. Moreover, the significant differences in K-CSI between normal and depressive group demonstrated known-group validity. Cut-off scores of 105.5 on K-CSI 32, 50.25 on K-CSI 16, and 13.25 on K-CSI 4 were validated to identify distressed couple relationships.
Conclusion
For clinical practice, the reliable and valid K-CSI 32 has the potential to measure changes in couple satisfaction after couple therapy or interventions. Applying K-CSI 32 may facilitate research on couple and family relationships in nursing and contribute to the discussion on the role of couple satisfaction in mental health. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating Effects of Parental Family Adaptation on the Quality of Life of Children With Down Syndrome: A Study of Father–Mother Dyads
Seung Hyeon Yang, Chang Gi Park, Eun Kyoung Choi
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Online coaching blended couple‐oriented intervention for preventing depression among Korean middle adulthood: A feasibility study
Minji Gil, Suk‐Sun Kim, Daeun Kim, Sunhai Kim
Family Process.2023; 62(4): 1478. CrossRef
- Mediating Effects of Parental Family Adaptation on the Quality of Life of Children With Down Syndrome: A Study of Father–Mother Dyads
- 5,320 View
- 188 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- The Development of a Tool for Assessment of Spiritual Distress in Cancer Patients
- Jin Sook Kim, Il-Sun Ko, Su Jin Koh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):52-65. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study was conducted to develop a scale to measure spiritual distress in cancer patients.
Methods
A total of 69 preliminary items for the spiritaul distress assessment tool (SDAT) were compiled, based on a literature review, selection of empirically relevant items through concept analysis of hybrid models, confirmation of content validity by experts, cognitive interviews, and a pretest. Self-administered questionnaires were collected between April 1 and July 31, 2018, from 225 cancer patients at four medical institutions and one nursing home. The data were analyzed using item analysis, exploratory factor analysis, convergent and discriminant validity, and Pearson correlation for criterion validity. Reliability was tested by Cronbash’s α coefficient.
Results
The final version of the SDAT consisted of 20 items. Five-factors, loss of peace, burden of family, avoidance of confronting death, guilt and remorse, regret for not being able to apololgize and forgive were extracted, and showed 62.8% of total variance. The factors were confirmed through convergent and discriminant validity. Criterion validity was confirmed by functional assessment chronic illness therapy spiritual well-being scale 12 (FACIT-Sp12). The overall Cronbach’s α was .91, and the coefficients of each subscale ranged from .78~.83.
Conclusion
The SDAT for cancer patients is valid and reliable. It is suggested that the tool can be used to measure spiritual distress in cancer patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a measurement of doctor-patient communication quality scale
Jiayi Shao, Minhui Wen, Yuqing Zhang, Liping Zhang, Jiangjie Sun
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validity and reliability of the integrated palliative care outcome scale (IPOS) in Korea: a multicenter study of terminally ill cancer patients
So-Jung Park, Yujin Park, Mira Han, Sun-Hyun Kim, In Cheol Hwang, Go-un Woo, Yoo Jeong Lee, Young Sung Kim, Hyun Jung Jho, Yoon Jung Chang
BMC Palliative Care.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Family caregivers’ perceived value of caring for older patient: A hybrid model of concept analysis
Seon-Hye Heo, Hye-Ryoung Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(2): 152. CrossRef - Spiritual Distress in Patients with Dyspnea: A Review of Measurement Tools
Leah McCann Klug
Illness, Crisis & Loss.2023; 31(4): 736. CrossRef
- Development of a measurement of doctor-patient communication quality scale
- 2,438 View
- 77 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Incidence and Predictors of Cataract among People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Using Secondary Data Analysis from the Ansan Cohort of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
- Ihn Sook Jeong, Eun Joo Lee, Myo Sung Kim, Jung Ok Yu, Hae Sun Yun, Jeong Hee Jeong, Youn Sun 6 Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):24-35. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21081
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated the incidence and risk factors of cataract in people with diabetes mellitus (DM) using data from Ansan cohort of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES).
Methods
Data from a total of 329 patients with type 2 DM without cataract who participated in Ansan cohort of the KoGES from baseline survey (2001–2002) to fifth follow-up visit (2011–2012) were examined. The characteristics of the subjects were analyzed with frequency and percentage, and mean and standard deviation. Cataract incidence was measured as incidence proportion (%). For risk factors of cataract, hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were obtained using the Cox proportional hazard model.
Results
The cataract incidence over a 10-year follow-up period was 19.1% (15.1 in males and 25.8 in females), and mean age at the incidence of cataract was 63.48 years (61.58 years in males and 65.31 years in females). Age (HR=1.09, 95% CI=1.05–1.13) and HbA1c (HR=1.21, 95% CI=1.07–1.37) or the duration of DM (HR=1.05, 95% CI=1.00–1.09) were found to be independently associated with cataract development.
Conclusion
Cataract development in people with DM is common, and its likelihood increases with age, HbA1c, and the duration of DM. Considering negative effect of cataract on their quality of life and economic burden, nurses should identify people with DM at a higher risk of cataract development, and plan individual eye examination programs to detect cataract development as early as possible. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mendelian randomization study of causality between 35 blood and urine biomarkers and age-related eye diseases
Jiaqi Chen, Tongtong Chen, Cong Zhao, Zheyu Bao, Hongji Liu
Medicine.2026; 105(5): e47286. CrossRef - Spatiotemporal trend of sensory impairments in China and its provinces from 2011 to 2018: insights from CHARLS
Zhijian Zhang, Zhennan Cai, Cong Li, Shunming Liu, Sheng Li, Lei Liu, Lijun Zhang
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and factors associated with visual impairment in middle-aged and older Chinese population
Hanyuan Ye, Yun Zeng, Hongxia Xiao, Jing Yu, Yun Liu, Shuang Zhang, Bingjie Zhang
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Mendelian randomization study of causality between 35 blood and urine biomarkers and age-related eye diseases
- 1,814 View
- 25 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Turkish Version of the COVID Stress Scale
- Demirgöz Bal Meltem, Dişsiz Melike, Bayri Bingöl Fadime
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):525-536. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21106
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aim of this study was to assess the Turkish adaptation of the COVID Stress Scale (CSS) on the basis of determining the stress caused by the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, and to test its validity and reliability.
Methods
The English CSS was translated into Turkish using forward and backward translation. Data were collected online from 360 participants. Construct validity was evaluated using confirmatory factor analysis, exploratory factor analysis, and content validity. Pearson product-moment correlation, Cronbach’s alpha reliability coefficient, and test-retest methods were used to evaluate reliability.
Results
The Turkish version of the CSS has 36 items consistent with the original scale and has five factors: COVID danger and contamination, socioeconomic consequences of COVID, COVID xenophobia, traumatic stress due to COVID, and compulsive checking for COVID. The construct validity of the Turkish version of the CSS was verified by the adjusted goodness of fit index > .85, and comparative fit index > .95. The content validity index of each item was 91%. The corrected item-total correlations of the scale ranged from .51 to .89. Internal consistency was reliable, with a Cronbach’s α of .93.
Conclusion
The Turkish version of the CSS is valid and reliable. It can be used as a measurement tool for the assessment of COVID-related stress. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Digital equity in nursing research: A methodological review of nursing studies requiring internet connection
Matthew S. Farmer, Drew Herbert, Christa Torrisi, Arthur Zacharjasz, Gerard Castaneda, Takara Schomberg, Michelle Dardis, Nicole Montgomery, Mary E. Melvin
Nursing Outlook.2026; 74(1): 102667. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation and item response theory analysis of the COVID Stress Scales in an older adult population
Kylie A. Arsenault, Ying C. MacNab, Gordon J. G. Asmundson, Thomas Hadjistavropoulos
Aging & Mental Health.2025; 29(4): 726. CrossRef - The long-term impact of the covid-19 pandemic on patients with obsessive–compulsive disorder
Büşra Uçar Bostan, Cana Aksoy Poyraz, Beril Kara Esen, Nazife Gamze Usta Sağlam
Medicine.2025; 104(7): e41562. CrossRef - Is there evidence for factorial invariance of the COVID Stress Scales? an analysis of North American and cross-cultural populations
Blake A. E. Boehme, Laura Kinsman, Steven Taylor, Gordon J. G. Asmundson
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric properties of a brief version of the COVID‐19 Stress Scales (CSS‐B) in young adult undergraduates
Tabatha Thibault, Kara Thompson, Matthew Keough, Marvin Krank, Patricia Conrod, Mackenzie Moore, Sherry H. Stewart
Stress and Health.2023; 39(1): 154. CrossRef - Pandemi Sonrası Yoğun Bakım Hemşirelerinde Covid-19 Stres Düzeyinin Belirlenmesi
Elif PAKLACI, Elif KAYA AYDOĞDU, Besey ÖREN
Yoğun Bakım Hemşireliği Dergisi.2023; 27(3): 138. CrossRef - Initial translation and validation of the Brief Version of the COVID-19 Stress Scales (CSS-B)
Razieh Bandari, Majideh Heravi- Karimooi, Mahsa Tebyanian, Hossein Shahcheragh
Payesh (Health Monitor) Journal.2023; 22(5): 617. CrossRef - Does COVID-19 related symptomatology indicate a transdiagnostic neuropsychiatric disorder? - Multidisciplinary implications
Sari Goldstein Ferber, Gal Shoval, Gil Zalsman, Aron Weller
World Journal of Psychiatry.2022; 12(8): 1004. CrossRef - The adaption of the Chinese version of the COVID Stress Scales as a screening instrument of stress: Psychometric properties during the COVID-19 pandemic
Lu Xia, Qiaoping Lian, Haibo Yang, Daxing Wu
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Digital equity in nursing research: A methodological review of nursing studies requiring internet connection
- 1,234 View
- 5 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Self-Efficacy for Managing Chronic Disease 6-Item Scale
- Sook-Nam Kim, Hyun-Ju Lee, So-Young Kim, Nayoon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):617-629. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21069
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aim of this study was to examine the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the self-efficacy for managing chronic disease 6-item scale (SECD-6-K).
Methods
The English version of the Self-Efficacy for Managing Chronic Disease 6-item Scale first underwent forward and backward translation procedures. The SECD-6-K was then used to collect data from 350 adults diagnosed with chronic diseases. Content, construct, convergent, discriminant, and criterion validity were all evaluated. Reliability was assessed using Cronbach’s α. SPSS 25.0 and the data were analyzed using AMOS 26.0 software.
Results
The SECD-6-K consists of six items in two domains: disease management and health behavior. The results for construct, convergent, and discriminant validity were good. Exploratory factor analysis produced eigen values between 2.27 and 3.28, with factors total explained cumulative variance of 91.1%. Confirmatory factor analysis supported goodness of fit and reliability for the modified SECD-6-K model. The criterion validity also showed significant correlation with both the Patient Health Questionnaire and 12-item Short-Form Health Survey version 2. Finally, reliability was found to be excellent.
Conclusion
This study identified the high reliability and validity of SECD-6-K. The SECD-6-K is an appropriate tool for determining Korean patients’ self-efficacy in managing their chronic conditions. Therefore, this scale may be used in clinical settings as well as in educational and research settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Generic instruments for assessing self-management abilities and behaviors in patients with chronic diseases: a COnsensus-based standards for the selection of health measurement INstruments (COSMIN)-based systematic review
Ke Liu, Guangyan Meng, Caixia Li, Shuyi Wang, Xianwen Fan, Qirong Chen
Quality of Life Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Path Analysis of Factors Influencing Health-Related Quality of Life for Community-Dwelling Vulnerable Older Adults with Chronic Diseases in Korea
Hyun-Ju Lee
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2025; 36: 315. CrossRef - Development of a self-care scale for women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a methodological approach
Miok Kim
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Short Form of Core Competencies Scale of Nursing Care for Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Sung Hae Kim, Seyong Lee, Sang Hee Kim, Jung Ok Choi, Gie Ok Noh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(4): 184. CrossRef - Factors influencing self-management behaviors in older people with multiple chronic conditions based on the individual and family self-management theory: A cross-sectional study
Youngji Seo, Sunyoung Jung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(3): 332. CrossRef - Psychometric property of the Japanese version of self-efficacy for managing chronic disease scale in individuals with chronic diseases
Megumi Hazumi, Mayumi Kataoka, Ayako Nakashita, Kentaro Usuda, Michi Miyake, Chiaki Kamikawa, Daisuke Nishi, Naoaki Kuroda
Heliyon.2024; 10(22): e40218. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the self-efficacy scale for chronic disease management (SEMCD-S) in older Colombian adults
Lorena Cudris-Torres, Stefano Vinaccia Alpi, Álvaro Barrios-Núñez, Natali Gaviria Arrieta, Martha Luz Gómez Campuzano, Giselle Olivella-López, Juan Hernández-Lalinde, Valmore Bermúdez, Olaiza Lobato Pérez, Jorge Armando Niño-Vega, Jorge Navarro-Obeid, Rom
BMC Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ambulatory Chemotherapy (Portable Infusion Pump Use) Video Education on Knowledge, Self-efficacy and Anxiety of Colorectal Cancer Patients
Eun Hee Choi, Eun Young Park, Young A Park, You Hee Son, Myung Jin Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(3): 193. CrossRef
- Generic instruments for assessing self-management abilities and behaviors in patients with chronic diseases: a COnsensus-based standards for the selection of health measurement INstruments (COSMIN)-based systematic review
- 4,549 View
- 215 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Person-Centered Practice Inventory–Staff for Nurses
- Sohyun Kim, Sunghee H Tak
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):363-379. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21027
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of Person-Centered Practice Inventory– Staff (PCPI-S) for nurses.
Methods
The English PCPI-S was translated into Korean with forward and backward translation. Data were collected from 338 nurses at one general hospital in Korea. Construct validity was evaluated with confirmatory factor analysis, convergent validity, and discriminant validity. Known-group validity was also evaluated. Cronbach’s α was used to assess the reliability.
Results
The PCPI-S Korean version consisted of 51 items in three areas: prerequisites, the care environment, and person-centered process. The comparative fit index (CFI) and values of person-centered care process were improved after engagement and having sympathetic presence items were combined as one component. The construct validity of PCPI-S Korean version was verified using four-factor structures (.05 < RMSEA < .10, AGFI > .70, CFI > .70, and AIC). The convergent validity and discriminant validity of the entire PCPI-S question were verified using a two-factor structures (AVE > .50, construct reliability > .70). There was an acceptable known-group validity with a significant correlation between the PCPI-S level and the degree of person-centered care awareness and education. Internal consistency was reliable with Cronbach’s α .95.
Conclusion
The Korean version of PCPI-S is valid and reliable. It can be used as a standardized Korean version of person-centered care measurement tool. Abbreviation: RMSEA = root mean square error of approximation; AGFI = adjusted goodness of fit index; AIC = Akaike information criterion; AVE = average variance extracted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The moderating effects of nurses’ characteristics on the perceptions and practices of family-centered care for chronically ill children and their families in Saudi Arabia
Nada Alqarawi, Eman Alhalal, Ibrahim Alasqah
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric validation and cultural adaptation of the family-centered care Questionnaire-Revised for use among nurses in Saudi Arabia
Nada Alqarawi, Ibrahim Alasqah
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adaptación transcultural y validación del Person-centred Practice Inventory-Staff para la cultura brasileña
Juliana Andrioli Nucci, Edinêis de Brito Guirardello, Ariane Polidoro Dini
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Person-centered Practice Inventory-Staff for Brazilian culture
Juliana Andrioli Nucci, Edinêis de Brito Guirardello, Ariane Polidoro Dini
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adaptação transcultural e validação do Person-centred Practice Inventory-Staff para a cultura brasileira
Juliana Andrioli Nucci, Edinêis de Brito Guirardello, Ariane Polidoro Dini
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Self-Compassion, Burden of BPSD, Communication Behavior, and Nursing Work Environment on Person-Centered Care for Patients with Dementia Among Long-Term Care Hospital Nurses
Yong Min Kim, Mi Heui Jang, Min Jung Sun
Healthcare.2025; 14(1): 15. CrossRef - Impact of Moral Distress, Person-Centred Care, and Nursing Professional Pride on Turnover Intention Among Intensive Care Unit Nurses in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
WonSuk Choi, Younjae Oh
Healthcare.2025; 14(1): 22. CrossRef - Influence of Nursing Professionalism, Nursing Work Environment, and Compassion Competence on Person-Centered Care of Nurses in Comprehensive Nursing Care
Yeon-Jin Lee, Eun-Mi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 572. CrossRef - Person-Centred Care: A Support Strategy for Managing Non-Communicable Diseases
Mateja Lorber, Nataša Mlinar Reljić, Barbara Kegl, Zvonka Fekonja, Gregor Štiglic, Adam Davey, Sergej Kmetec
Healthcare.2024; 12(5): 526. CrossRef - Nurses' practices of children and family-centered care for chronically ill children: A cross-sectional study
Nada Alqarawi, Eman Alhalal
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2024; 77: 172. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Person-Centered Care Among Psychiatric Nurses in Hospitals
Ji Su Lee, Mi Heui Jang, Min Jung Sun
Healthcare.2024; 12(22): 2269. CrossRef - Translation, Cultural Adaptation, and Validation of the Spanish Version of the Person-Centred Practice Inventory-Staff (PCPI-S)
Ana Carvajal-Valcárcel, Edgar Benitez, Marta Lizarbe-Chocarro, María José Galán-Espinilla, Mónica Vázquez-Calatayud, Begoña Errasti-Ibarrondo, Ana Choperena, Brendan McCormack, Vaibhav Tyagi, Virginia La Rosa-Salas
Healthcare.2024; 12(23): 2485. CrossRef - Validation of the Korean Version of Patient-Centered Care Tool: For Outpatients
Yeo Ju Kim, Gunjeong Lee, Sunyeob Choi
Patient Preference and Adherence.2023; Volume 17: 1525. CrossRef - The influence of Critical Reflection Competency, Nursing Work Environment and Job Crafting on Person-Centered Care in Tertiary Hospital Nurses: A Cross-sectional Study
Jinseon Hwang, Sujin Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(3): 245. CrossRef - Translation and transcultural adaptation of the Person-Centred Practice Inventory Staff (PCPI-S) for health professionals in Spain
Begoña Errasti-Ibarrondo, Virginia La Rosa-Salas, Marta Lizarbe-Chocarro, Yvonne Gavela-Ramos, Ana Choperena, Leire Arbea Moreno, Mónica Vázquez-Calatayud, María José Galán-Espinilla, Brendan McCormack, Ana Carvajal-Valcárcel
Anales del Sistema Sanitario de Navarra.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with Person-Centered Care among Hospice Nurses
Sinyoung Kwon, Kyoung Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2022; 25(2): 66. CrossRef - Moral sensitivity and person‐centred care among mental health nurses in South Korea: A cross‐sectional study
Sun Joo Jang, Eun Hye Kim, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2227. CrossRef - Translation and transcultural adaptation of the theoretical Person-Centred Practice Framework to the Spanish context
Ana Choperena, Yvonne Gavela-Ramos, Marta Lizarbe-Chocarro, María José Galán-Espinilla, Begoña Errasti-Ibarrondo, Virginia La Rosa-Salas, Mónica Vázquez-Calatayud, Brendan McCormack, Ana Carvajal-Valcárcel
Anales del Sistema Sanitario de Navarra.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The moderating effects of nurses’ characteristics on the perceptions and practices of family-centered care for chronically ill children and their families in Saudi Arabia
- 3,150 View
- 124 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref

- Development of a Positive Nursing Organizational Culture Measurement Tool
- Mi Jung Kim, Jong Kyung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):305-319. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21014
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop a measurement tool for a positive nursing organizational culture and to verify its reliability and validity.
Methods
A conceptual framework and construct factors were extracted through an extensive literature review and indepth interviews with nurses. The final version of the preliminary tool for the main survey was confirmed by experts through a content validity test and a preliminary survey of 40 nurses. Subsequently, the final tool was developed using a validity and reliability test containing 43 preliminary items. The final version of the tool was used with 327 hospital nurses in the testing phase for the main survey to assess validity and reliability.
Results
From the factor analysis, 4 factors and 26 items were selected. The factors were positive leadership of the nursing unit manager, pursuit of common values, formation of organizational relationships based on trust, and a fair management system. The entire determination coefficient was 67.7%. These factors were verified through convergent, discriminant, and concurrent validity testing. The internal consistency reliability was acceptable (Cronbach’s α = .95).
Conclusion
Both the validity and reliability of the scale were confirmed demonstrating its utility for measuring positive nursing organizational culture. It is expected to be used for education, research, and practical performance policies regarding the nursing organizational culture. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Affecting Workplace Bullying Among Nurses: A Secondary Analysis According to Career Stage
Sun Joo Jang, Haeyoung Lee
Clinical Nursing Research.2026; 35(1): 48. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Workplace Bullying Among Intensive Care Unit Nurses and Their Needs for Improving Organizational Culture: A Mixed‐Methods Study
Eunhye Kim, Sun Joo Jang, Yujeong Kim, Haeyoung Lee, Shashank Kaushik
Journal of Nursing Management.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Grit, Emergency Nursing Competency, and Positive Nursing Organisational Culture on Burnout Among Nurses in the Emergency Department
Su-Young Moon, Hyung-Ran Park
Behavioral Sciences.2025; 15(4): 486. CrossRef - Development and validation of the Cultural Leadership Scale in Nursing (CLS-N): a methodological study
Kadriye Özkol Kılınç, Havva Öztürk
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fostering a safe horizon: Nursing organizational culture as a mediator between medication safety climate and reporting intentions for high-alert medication errors among pediatric nursing care
Abdelaziz Hendy, Rasha Kadri Ibrahim, Hosny Maher Sultan, Hanan F. Alharbi, Zeinab Al-Kurdi, Naglaa Hassan Abuelzahab, Taliaa Mohsen Al-Yafeai, Ahmad Ahmeda, Zainab Attia Abdallah, Wesam Taher Almagharbeh, Ghada Ahmed Hassan
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2025; 85: 103. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Workplace Bullying Perpetration Among Experienced Intensive Care Unit Nurses: A Secondary Analysis Focusing on Narcissistic Personality, Perfectionistic Self‐Presentation, and Mentalization
Sun Joo Jang, Jeehae Chung, Haeyoung Lee, Talat Islam
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of digital literacy and nursing informatics competency as job resources on nurses’ burnout and work engagement: a cross-sectional study
Jeehae Chung, Hyesil Jung, Sang Mi Park, Kyeongmin Lee
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Diversity Management of Nursing Organization on Organizational Commitment: Double Mediating Effect of Diversity Sensitivity Orientation and Positive Nursing Organizational Culture
Hwi Gon Jeon, Keum Seong Jang, Eun A Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 403. CrossRef - Development and validation of a quality of healthy work environment instrument for shift nurses
Sun-Hwa Shin, Eun-Hye Lee
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hospital organisational health as a mediator between positive nursing organisational culture, caring behaviour, and quality of nursing care
Bo Ram Ku, Mi Yu
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Hospital Nurses’ Workplace Bullying Experiences Focusing on Meritocracy Belief, Emotional Intelligence, and Organizational Culture: A Cross‐Sectional Study
Insil Jang, Sun Joo Jang, Sun Ju Chang, Miyuki Takase
Journal of Nursing Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Ethical Nursing Competence and Positive Nursing Organizational Culture on Person-Centered Care in Intensive Care Unit Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Jae Eun Lee, Hye-Young Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(3): 304. CrossRef - Effects of Personality Traits and Mentalization on Workplace Bullying Experiences among Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Sun Joo Jang, Eunhye Kim, Haeyoung Lee, Amanda Jane Henderson
Journal of Nursing Management.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Pathological narcissism, interpersonal cognitive distortions, and workplace bullying among nurses: A cross‐sectional study
Sun Joo Jang, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 3051. CrossRef
- Factors Affecting Workplace Bullying Among Nurses: A Secondary Analysis According to Career Stage
- 3,783 View
- 213 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref

- Development of a Coping Scale for Infertility-Women (CSI-W)
- Miok Kim, Jung-Mi Ko
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(5):671-685. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20038
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop a Coping Scale for Infertility-Women (CSI-W).
Methods
The initial items were based on an extensive literature review and in-depth interviews with seven infertile women. Forty-three items were derived from a pilot survey. Data were collected from 216 women who had experienced intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in-vitro fertilization (IVF) more than once. The data were analyzed to verify the reliability and validity of the scale.
Results
Seven factors containing 28 items (four factors containing 17 items for active coping and three factors containing 11 items for passive coping) were extracted from the exploratory factor analysis to verify the construct validity. The four factors of active coping were confrontation, self-control, seeking social support (spouse), and seeking social support (colleagues and experts). The three factors of passive coping were distancing, escape, and avoidance. These items were verified through convergent, discriminant, and concurrent validity testing. The internal consistency reliability was acceptable (active coping: Cronbach’s a = .78; passive coping: Cronbach’s a = .81).
Conclusion
As its validity and reliability have been verified through various methods, the CSI-W can contribute to assessing the coping strategies of infertile women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing the Intention for Continual Fertility Treatments by the Women Undergoing Assisted Reproductive Technology Procedures: A Cross-Sectional Study
Miok Kim, Minkyung Kim, Minkyung Ban
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(1): 59. CrossRef - Design and psychometric evaluation of the collaborative coping with infertility questionnaire in candidate of assisted reproductive techniques
Marzie Reisi, Ashraf Kazemi
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Types and Characteristics of Stress Coping in Women Undergoing Infertility Treatment in Korea
Yumi Choi, So-Hyun Moon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(3): 2648. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing the Intention for Continual Fertility Treatments by the Women Undergoing Assisted Reproductive Technology Procedures: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 2,316 View
- 45 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Analysis of Research Topics and Trends in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing to Improve Its International Influence
- Soyoung Yu, Jeung-Im Kim, Jin-Hee Park, Sun Joo Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh, Ju-Eun Song, YeoJin Im
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(4):501-512. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20167
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to analyze articles published in the Journal of the Korean Academy of Nursing (JKAN) between 2010 and 2019, along with those published in three international nursing journals, to improve JKAN’s international reputation.
Methods
The overall characteristics of JKAN’s published papers and keywords, study participants, types of nursing interventions and dependent variables, citations, and cited journals were analyzed. Additionally, the keywords and study designs, publication-related characteristics, journal impact factors (JIF), and Eigenfactor scores of International Journal of Nursing Studies (IJNS), International Nursing Review (INR), Nursing & Health Sciences (NHS), and JKAN were analyzed and compared.
Results
Among the four journals, JKAN’s score was the lowest in both the journal impact factor and Eigenfactor score. In particular, while the JIF of INR and NHS has been continuously increasing; JKAN’s JIF has remained static for almost 10 years. The journals which had cited JKAN and those which JKAN had cited were mainly published in Korean.
Conclusion
JKAN still has a low IF and a low ranking among Social Citation Index (E) journals during the past 10 years, as compared to that of four international journals. To enhance JKAN’s status as an international journal, it is necessary to consider publishing it in English and to continuously improve the conditions of other publications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ten-year trends in research designs and keywords: a bibliometric comparison of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and leading international nursing journals
Jin-Hee Park, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Gaeun Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(4): 557. CrossRef - Commemorating the 50th Anniversary of Korean Society of Nursing Science and Contemplating Direction to Move Forward
Kyung-Sook Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 641. CrossRef
- Ten-year trends in research designs and keywords: a bibliometric comparison of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and leading international nursing journals
- 2,418 View
- 28 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Menopause-Specific Quality of Life
- Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Young-Mi Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):487-500. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20049
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of Menopause-Specific Quality of Life (MENQOL).
Methods
The MENQOL was translated into Korean according to algorithm of linguistic validation process. A total of 308 menopausal womenwere recruited and assessed using the Korean version of MENQOL (MENQOL-K), the World Health Organization Quality of Life BriefVersion (WHOQOL-BREF), and Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale (CES-D-K). In estimating reliability, internal consistencyreliability coefficients were calculated. Validity was evaluated through criterion validity and construct validity with confirmatory factor analysesusing SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 25.0 software.
Results
In item analyses, the “increased facial hair” symptom was excluded because of thelow contribution of MENQOL-K. The confirmatory factor analysis supported good fit and reliable scores for MENQOL-K model, and thefour-factor structure was validated (x2=553.28, p <.001, NC=1.84, RMSEA=.05, AGIF=.85, AIC=765.28). The MENQOL-K consists of 28 itemsin 4 domains, including vasomotor (3 items), psychosocial (7 items), physical (15 items), and sexual subscales (3 items). There was an acceptablecriterion validity with moderately significant correlation between MENQOL-K and WHOQOL-BREF. The Cronbach’s a for the 4subsacles ranged from .80 to .93.
Conclusion
The MENQOL-K is a valid and reliable scale to measure condition-specific quality of life forperimenopausal and postmenopausal women. It can be used to assess the impact of menopausal symptoms on the quality of life of Koreanwomen in clinical trials. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Longitudinal analysis of alcohol consumption pattern and menopause‐specific quality of life in middle‐aged women undergoing the menopausal transition
Ria Kwon, Yoosoo Chang, Yoonyoung Jang, Ga‐young Lim, Yoo‐Jung Kim, Seungho Ryu
Addiction.2026; 121(3): 586. CrossRef - Examining the relationship between symptoms and quality of life related to menopausal period of women with gynecologic cancer: a cross-sectional study
Ahsen Demirhan Kayacik, Gulsah Kok
Supportive Care in Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The 3-dimensionel Ovarian Volume Assessment to Evaluate Whether Menopausal Related Symptoms and Hormone Levels Correlate with the Ovarian Volume
Gizem Işık Solmaz, İsmail Güler, Esra İşçi Bostancı, Serhan Can İşcan, Nuray Bozkurt, Mehmet Anıl Onan
Gazi Medical Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Aerobic Exercise Vs Surya Namaskar on Quality of Life in Postmenopausal Women Using Menopause Specific Quality of Life (MENQOL) Questionnaire
Dr. Dhanashree P. Shinde (PT), Alphina E. Jules
International Journal of Advanced Research in Science, Communication and Technology.2025; : 51. CrossRef - Longitudinal patterns and group heterogeneity of depressive symptoms during menopausal transition in middle-aged Korean women
Yoonyoung Jang, Yoosoo Chang, Junhee Park, Sang Won Jeon, Byungtae Seo, Jae Ho Park, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Seungho Ryu
Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Early-onset vasomotor symptoms and development of depressive symptoms among premenopausal women
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Jungeun Park, Yoosun Cho, Chanmin Kim, Min-Jung Kwon, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-young Lim, Jiin Ahn, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 354: 376. CrossRef - Association between Menopausal Women’s Quality of Life and Aging Anxiety: The Role of Life Satisfaction and Depression
Seunghee Lee, Mijung Jang, Dohhee Kim, KyooSang Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(8): 1189. CrossRef - Vasomotor and other menopause symptoms and the prevalence of ideal cardiovascular health metrics among premenopausal stage women
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Yoosun Cho, Min-Jung Kwon, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Menopause.2023; 30(7): 750. CrossRef - Research trends in the Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing from 2011 to 2021: a quantitative content analysis
Ju-Hee Nho, Sookkyoung Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(2): 128. CrossRef - Low anti-Müllerian hormone levels are associated with an increased risk of incident early-onset vasomotor symptoms among premenopausal women
SunJu NamGoung, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Hoon Kim, In Young Cho, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Hye Rin Choi, Jeonggyu Kang, Kye-Hyun Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Hyun-Young Park, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Min-Jung Kwon, Seungho Ryu
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - High low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level is associated with an increased risk of incident early-onset vasomotor symptoms
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Jeonggyu Kang, Min-Jung Kwon, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Ideal Cardiovascular Health Metrics and Risk of Incident Early-Onset Vasomotor Symptoms Among Premenopausal Women
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Yoosun Cho, Jeonggyu Kang, Min-Jung Kwon, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(9): 2666. CrossRef - Alcohol Consumption Patterns and Risk of Early-Onset Vasomotor Symptoms in Premenopausal Women
Ria Kwon, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Yoosun Cho, Hye Rin Choi, Ga-Young Lim, Jeonggyu Kang, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Sanjay Rampal, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Nutrients.2022; 14(11): 2276. CrossRef - Metabolically healthy and unhealthy obesity and risk of vasomotor symptoms in premenopausal women: cross‐sectional and cohort studies
Sunju Namgoung, Yoosoo Chang, Chae‐Yeon Woo, Yejin Kim, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga‐Young Lim, Hye Rin Choi, Kye‐Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun‐Young Park, Seungho Ryu
BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology.2022; 129(11): 1926. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Risk of Early-Onset Vasomotor Symptoms in Lean and Overweight Premenopausal Women
Yoosun Cho, Yoosoo Chang, Hye Rin Choi, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Jiin Ahn, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Sanjay Rampal, Juhee Cho, Hyun-Young Park, Eliseo Guallar, Seungho Ryu
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2805. CrossRef
- Longitudinal analysis of alcohol consumption pattern and menopause‐specific quality of life in middle‐aged women undergoing the menopausal transition
- 3,369 View
- 132 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- Development of Job-Esteem Scale for Korean Nurses
- Hyun Ju Choi, Kwuy Im Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):444-458. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19209
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop the Job Esteem Scale for Korean Nurses (JES-KN) and verify its validity and reliability.
Methods
Preliminary items were based on the attributes and indicators elicited from a concept analysis study on Korean nurses’ job-esteem.The final preliminary tool for the main survey was confirmed through the content validity test of 10 experts and preliminary surveyof 20 hospital nurses. The final preliminary scale was used on 350 hospital nurses in the scale testing phase for the main survey designedto test the validity and reliability of the scale.
Results
The final scale consisted of 28 items and 6 factors, these factor explained 66.6% ofthe total variance. The correlation between the total score and factors ranged from .64 and .84, validating that each sub-factor is suitableto explain job esteem. The correlation coefficient between this scale and the Job Satisfaction Scale for Clinical Nurses ranged from .41 to.70, and the internal consistency for the scale using Cronbach’s a for the total items was .94.
Conclusion
The JES-KN is a valid and reliabletool that reflects the reality of clinical sites accordingly. The JES-KN may well be used effectively to assess and evaluate the job esteem ofKorean nurses. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Weight analysis of Chinese nurses' behaviors to maintain patient dignity and its relationship with job-esteem: a cross-sectional study controlling for agreeableness
Cong Guo, Chunlin Zhang, Cuizhu Zhou, Mengqi Zhu, Lingling Chen, Youran Liu, Yequn Zhang, Jie Wang, Tengfei Liang
Frontiers in Psychology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Ethical Atmosphere and Job‐Esteem on Moral Courage in Psychiatric Nurses
Yan Li, XiangDan Shen, Haishan Quan, Ying Li, Jianhua Li, Zhenzhen Zhang, Xinyang Xing
Nursing & Health Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Work‐Related Stress, Professional Respect, and Psychological Counseling Among Nurses: A Cross‐Sectional Study
Hanif Ullah, Safia Arbab, Sher Alam Khan, Chang-qing Liu, Muhammad Fayaz, Yali Tian, Ka Li, Majed Alamri
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - End-of-Life Care Experiences of Early-Career Intensive Care Unit Nurses : A Qualitative Study
Miju Jung, Sookyeon Son, Jonghyun Park, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2025; 18(3): 98. CrossRef - Occupational stress, respect, and the need for psychological counselling in Chinese nurses: a nationwide cross-sectional study
W. Zhang, X. Ma, S. Yu, X. Zhang, Y. Mu, Y. Li, Q. Xiao, M. Ji
Public Health.2023; 225: 72. CrossRef - The Influence of Gender Equity in Nursing Education Programs on Nurse Job Satisfaction
Joohee Shim, Da-In Park
Healthcare.2023; 11(9): 1318. CrossRef - Effect of COVID-19 Frontline Nurses’ Profession Perception on Their Intention to Stay: The Mediating Role of Job Satisfaction
Ahram Im, Chin Kang Koh
SAGE Open Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Moral courage, job-esteem, and social responsibility in disaster relief nurses
Qiang Yu, Huaqin Wang, Yusheng Tian, Qin Wang, Li Yang, Qiaomei Liu, Yamin Li
Nursing Ethics.2023; 30(7-8): 1051. CrossRef - Development of Nursing Informatics Competence Scale for Korean Clinical Nurses
Seon Mi Jang, Jeongeun Kim
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2022; 40(10): 725. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Health-promoting Behavior of Nurses in Small and Medium-sized Hospitals based on the IMB Model
Jin Hee Jeong, Hye Kyung Lee
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2022; 25(2): 102. CrossRef - Development of the Nurse Occupational Stigma Scale
Lu Yang, Shuangxin Zhang, Jiaqi Leng, Zhiguang Fan, Yi Luo
Psychology Research and Behavior Management.2022; Volume 15: 1627. CrossRef - Why Do They Stay? Intention to Stay among Registered Nurses in Nursing Homes
Ji Yeon Lee, Juh Hyun Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(22): 8485. CrossRef
- Weight analysis of Chinese nurses' behaviors to maintain patient dignity and its relationship with job-esteem: a cross-sectional study controlling for agreeableness
- 2,715 View
- 121 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref

- Development of a Scale for Alcohol Drinking Prevention Behavior in Early Elementary School Based on Ajzen’s Theory of Planned Behavior
- Younkyoung Kim, Chong Mi Lee, Seo Young Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(2):210-227. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.2.210
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure variables related to alcohol drinking prevention behavior in early elementary school, based on the theory of planned behavior.
Methods
A scale was developed to measure variables related to alcohol drinking prevention behavior. Initial items for direct evaluation were constructed through a literature review, and those for belief-based indirect measure were generated through interviews with 30 second- and third-grade elementary school students. The collected data from 286 third-grade elementary school students were then subjected to item analysis, exploratory and confirmative factor analysis, criterion-related validity testing, and internal consistency assessment.
Results
The final scale consisted of 35 items. Intention, attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control explained 82.7% of the variance; behavioral beliefs, normative beliefs, and control beliefs explained 65.6% of the variance; and evaluation of outcome, motivation to comply, and power of control beliefs explained 72.8% of the variance. The confirmatory factor analysis indicated that the theoretical models had a satisfactory goodness of fit. Criterion-related validity was confirmed between the direct evaluation variables and the indirect measure variables (attitudes r=.64, p <.001; subjective norms r=.39, p <.001; perceived behavioral control r=.62, p <.001). Cronbach’s a was .89 for the direct evaluation variables and .93 for the indirect measure variables.
Conclusion
The scale developed in this study is valid and reliable. It could be used to measure and explain variables related to alcohol drinking prevention behavior in early elementary school. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a Web-Based Alcohol Prevention Program Linking School-Child-Family for Intermediate Elementary Students
Younkyoung Kim, Chong Mi Lee, Seo Young Kang, Hyunju Yang
Journal of Health Communication.2023; 28(2): 102. CrossRef - Effects of a web‐based alcohol drinking prevention program linking school‐to‐home in elementary students
Younkyoung Kim, Chong Mi Lee, Seo Young Kang
Public Health Nursing.2022; 39(2): 472. CrossRef - Factors influencing nursing students’ care intentions toward emerging infectious diseases patients: A descriptive-predictive study
Seungmi Park, Insun Jang, Soo-Young Yu
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 421. CrossRef
- Development of a Web-Based Alcohol Prevention Program Linking School-Child-Family for Intermediate Elementary Students
- 1,328 View
- 28 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Development and Validation of the New Version of Spirituality Assessment Scale
- Il-Sun Ko, Soyoung Choi, Jin Sook Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(1):132-146. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.1.132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose: The purpose of this study was to develop a new version of Spirituality Assessment Scale (N-SAS) and verify its reliability and validity.
Methods: The total of 59 preliminary items for the N-SAS were selected through a literature review, two rounds of experts’ content validation, cognitive interviews, and pre-tests. Verification of its reliability and validity was divided into two phases. In Phase I, questionnaires were collected from 219 adults. Reliability was tested using Cronbach’s alpha, validity with item analysis, and exploratory factor analysis. In Phase II, questionnaires developed based on the results of Phase I were collected from 225 adults. Reliability was tested using Cronbach’s alpha, validity with confirmatory factor analysis, and criterion validity.
Results: The final version of the N-SAS comprised two dimensions (vertical and horizontal), four domains (relationship with God; meaning of life and self-integration; self-transcendence; and relationship with others, neighborhoods, and nature), and 44 items were identified. Total Cronbach’s α was .97; those of each subscale ranged from .79 to .98. N-SAS scores were positively correlated with the scores of Howden’s Spiritual Assessment Scale (r=.81,
p <.001).Conclusion Findings suggest that the N-SAS can be used to measure spirituality in adults. The use of N-SAS is expected to facilitate perceiving patient’s spiritual needs and providing spiritual care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing Spirituality and Nursing Performance Ability and Their Effect on the Spiritual Care Competency of Nursing Students
Jinsook Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2025; 39(2): 208. CrossRef - Spiritual Care Expectations Among Cancer and Noncancer Patients With Life-Threatening Illnesses
Kyung-Ah Kang, Shin-Jeong Kim
Cancer Nursing.2024; 47(4): E269. CrossRef - Development of Colleague Solidarity Scale for Nurses
Moon Yeon Kong, Nah-Mee Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 504. CrossRef - Nursing students' rights in clinical practice in South Korea: a hybrid concept-analysis study
Sunghee Park, Mi-Young Choi
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(4): 260. CrossRef - Predictors of end-of-life care stress, calling, and resilience on end-of-life care performance: a descriptive correlational study
Ji-Young Kim, Eun-Hi Choi
BMC Palliative Care.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Development of a Tool for Assessment of Spiritual Distress in Cancer Patients
Jin Sook Kim, Il-Sun Ko, Su Jin Koh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 52. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Nursing Students’ Rights Awareness Scale in Clinical Practice: A Scale Development Study
Sung-Hee Park, Mi-Young Choi
Healthcare.2021; 9(10): 1323. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Versions of the Duke University Religion Index (K-DUREL) and the Daily Spiritual Experience Scale (K-DSES)
Suk-Sun Kim, Daeun Kim, Nan Young Moon, Ahyoung Seo, Minji Gil
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2021; 30(2): 141. CrossRef - Development of the Adult Pandemic Attitude Scale (A-PAS)
Mihyeon Seong, Juyoung Park, Soojin Chung, Sohyune Sok
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(12): 6311. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing Spirituality and Nursing Performance Ability and Their Effect on the Spiritual Care Competency of Nursing Students
- 2,473 View
- 80 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Effects of Spouse-Participated Health Coaching for Male Office Workers with Cardiocerebrovascular Risk Factors
- So Hee Kang, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):748-759. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.748
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to examine the effect of spouses participating in health coaching on stage of the change, health behaviors, and physiological indicators among male office workers with cardiocerebrovascular disease (CVD) risk factors and compare the findings with trainers who provided health coaching only to workers.
Methods A quasi-experimental pretest-posttest design was used. Convenience sampling was used to recruit participants from a manufacturing research and development company in the city of Gyeonggi province. The health coaching program for the experimental group (n=26) included individual counseling sessions according to workers' stage of change, and provision of customized health information materials on CVD prevention to workers and their spouses for 12 weeks through mobile phone and email.
Results After 12 weeks of intervention, the total score for health behavior, and scores on the sub-areas of exercise and health checkups significantly improved in the experimental group, but there were no significant differences in the scores of stage of the change and physical indicators. The results of a paired t-test showed a significant decrease in the body mass index, abdominal circumference, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol and triglyceride values, and a significant increase in the high-density lipoprotein cholesterol value in the experimental group after the intervention.
Conclusion To improve the health of male workers with CVD risk factors in the workplace, sharing health information with their spouses has proven to be more effective than health coaching for only workers. Therefore, it is important to develop strategies to encourage spousal participation when planning workplace health education for changing health-related behaviors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun Jin Kim, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(1): 44. CrossRef - Effects of a Remote Physical Activity Improvement Program on Male Office Workers with Metabolic Syndrome in Their 30s and 40s with Sedentary Behavior: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Kyong Sil Park, Seon Young Hwang
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - An intervention study of a combined intervention of positioning and hand massage in patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation
Yun Kyeong Lee, Mihae Im, Haeryun Cho
Nursing Open.2023; 10(3): 1404. CrossRef
- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 1,035 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Path Analysis for Delirium on Patient Prognosis in Intensive Care Units
- Sunhee Lee, Sun-Mi Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):724-735. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.724
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to investigate relationship between delirium, risk factors on delirium, and patient prognosis based on Donabedian's structure-process-outcome model.
Methods This study utilized a path analysis design. We extracted data from the electronic medical records containing delirium screening data. Each five hundred data in a delirium and a non-delirium group were randomly selected from electronic medical records of medical and surgical intensive care patients. Data were analyzed using SPSS 20 and AMOS 24.
Results In the final model, admission via emergency department (B=.06,
p =.019), age over 65 years (B=.11,p =.001), unconsciousness (B=.18,p =.001), dependent activities (B=.12,p =.001), abnormal vital signs (B=.12,p =.001), pressure ulcer risk (B=.12,p =.001), enteral nutrition (B=.12,p =.001), and use of restraint (B=.30,p =.001) directly affecting delirium accounted for 56.0% of delirium cases. Delirium had a direct effect on hospital mortality (B=.06,p =.038), hospital length of stay (B=5.06,p =.010), and discharge to another facility (not home) (B=.12,p =.001), also risk factors on delirium indirectly affected patient prognosis through delirium.Conclusion The use of interventions to reduce delirium may improve patient prognosis. To improve the dependency activities and risk of pressure ulcers that directly affect delirium, early ambulation is encouraged, and treatment and nursing interventions to remove the ventilator and drainage tube quickly must be provided to minimize the application of restraint. Further, delirium can be prevented and patient prognosis improved through continuous intervention to stimulate cognitive awareness and monitoring of the onset of delirium. This study also discussed the effects of delirium intervention on the prognosis of patients with delirium and future research in this area.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Does ICU admission dysphagia independently contribute to delirium risk in ischemic stroke patients? Results from a cohort study
Hongtao Cheng, Simeng Song, Yonglan Tang, Shiqi Yuan, Xiaxuan Huang, Yitong Ling, Zichen Wang, Xiaoying Tian, Jun Lyu
BMC Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Preoperative Anxiety and Its Postoperative Associated Factors in Patients Receiving Post Anesthetic Recovery Care at Surgical Intensive Care Unit
Yul Ha Lee, Hye-Ja Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(3): 267. CrossRef - Delirium Experience of the Intensive Care Unit Patients
Jaeyeon Jung, Sujin Jang, Seonmi Jo, Sunhee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(2): 134. CrossRef - The training needs of Korean intensive care unit nurses regarding delirium
Young Sook Roh
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2021; 62: 102954. CrossRef - Effect on Quality of Care of a Delirium Prevention Campaign for Surgical Intensive Care Nurses
Heejeong Kim, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of Nursing Care Quality.2021; 36(4): 361. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis on the Effect of Delirium Prevention Intervention in Korean Intensive Care Units
Jiyeon Kang, Min Jeong Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2021; 14(3): 141. CrossRef
- Does ICU admission dysphagia independently contribute to delirium risk in ischemic stroke patients? Results from a cohort study
- 2,511 View
- 53 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Development of the Patient Caring Communication Scale
- Myoung Lyun Heo, Sook Bin Im
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):80-91. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.80
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study attempted to develop a scale that measures the level of patients' recognition of the nurses' care, based on Watson's caring theory, and confirmed its reliability and validity.
Methods The items were developed through a literature review and an expert content validity test. The questionnaires were administered to 285 inpatients of internal medicine and surgical units at two general hospitals. Construct validity was tested using exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, and reliability was tested using Cronbach's alpha.
Results This process resulted in a preliminary scale composed of 34 items; We used item analysis and five exploratory factor analyses, and consequently selected 14 items composed of three factors (respect, genuineness, and relationality). The confirmatory factor analysis verified the model fit and convergent and discriminant validity of the final items; criterion validity was confirmed with the positive correlation with the measurement scale of the patient-perceived quality of nursing . The overall scale reliability had a Cronbach's alpha of .92, which indicated internal consistency and reliability.
Conclusion The developed scale showed content, construct, and criterion validity, and reliability, as well as convergent validity for each item and discriminant validity between the factors. This makes it suitable for use in a diverse range of future studies on nurse communication using structural equation models.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of the Caring Competence Scale for Family Caregivers of Persons With Mental Disorders
Won Hee Jun
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 32(5): 1248. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Therapeutic Communication Scale in Nursing Students
Soolgi Han, Jinhee Yoo, Kyonghwa Kang
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 394. CrossRef - A structural model of nursing students’ performing communication skills
Cho Rong Gil, Kyung Mi Sung
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 148. CrossRef - Nurse’s Evaluation on Health Education in Portuguese Pediatric Hospitals and Primary Care for Children/Young and Parents
Anabela Fonseca Pereira, Joaquim Escola, Vitor Rodrigues, Carlos Almeida
Children.2022; 9(4): 486. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the Korean version of ComOn coaching for oncology nurses
Myoung Soo Kim, Eun-Jung Bae, Ju-Yeon Uhm
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 9(4): 210. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Self-Efficacy for Managing Chronic Disease 6-Item Scale
Sook-Nam Kim, Hyun-Ju Lee, So-Young Kim, Nayoon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(5): 617. CrossRef - Development of the Nursing Start-up Attitude Scale for Student Nurses
Ji Young Lim, Geun Myun Kim, Eun Joo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 388. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Watson Caritas Patient Score
SookBin IM, MiKyoung CHO, MyoungLyun HEO
Journal of Nursing Research.2020; 28(2): e80. CrossRef
- Development of the Caring Competence Scale for Family Caregivers of Persons With Mental Disorders
- 2,982 View
- 134 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Development of the Korean Geriatric Loneliness Scale (KGLS)
- Si Eun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(5):643-654. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.5.643
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop and psychometrically test the Korean Geriatric Loneliness Scale (KGLS).
Methods The initial items were based on in-depth interviews with 10 older adults. Psychometric testing was then conducted with 322 community-dwelling older adults aged 65 or older. Content, construct, and criterion-related validity, classification in cutoff point, internal consistency reliability, and test-retest reliability were used for the analysis.
Results Exploratory factor analysis showed three factors, including 15 items explaining 91.6% of the total variance. The three distinct factors were loneliness associated with family relationships (34.3%), social loneliness (32.4%), and a lack of belonging (24.9%). As a result of confirmatory factor analysis, 14 items in the three-factor structure were validated. Receiver operating characteristic analysis demonstrated that the KGLS’ cutoff point of 32 was associated with a sensitivity of 71.0%, specificity of 80.2%, and area under the curve of .83. Reliability, as verified by the test-retest intraclass correlation coefficient, was .89, and Cronbach's α was .90.
Conclusion As its validity and reliability have been verified through various methods, the KGLS can contribute to assessing loneliness in South Korean older adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of the Smawell Mobile App on Psychological and Biological Factors in the Middle Aged and Older Adults Living Alone
Kyung Sook Kim, Miok Kim, Mi Hee Han
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2022; 31(2): 171. CrossRef - Impact of Frailty, Depression, and Loneliness on Ego-Integrity in Community-Dwelling Elderly
Seon Ju Song, Sung Hee Ko, Ji Young Kim, Hyun Kyung Kim
STRESS.2022; 30(3): 139. CrossRef - A Structural Model of Life Satisfaction for Middle Aged or Older People Living Alone
Kyung Sook Kim, Miok Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(1): 96. CrossRef - Impacts of the Depression among the Elderly in the South Korea Community in COVID-19 Pandemic
Boo Deuk Suh, Kyoung Hee Kwon
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(1): 54. CrossRef - Applying Latent Profile Analysis to Identify Lifestyle Profiles and Their Association with Loneliness and Quality of Life among Community-Dwelling Middle- and Older-Aged Adults in South Korea
Kang-Hyun Park, Eun-Young Yoo, Jongbae Kim, Ickpyo Hong, Jae-Shin Lee, Ji-Hyuk Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(23): 12374. CrossRef
- Effects of the Smawell Mobile App on Psychological and Biological Factors in the Middle Aged and Older Adults Living Alone
- 3,605 View
- 104 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Effects of an Integrated Physical Activity Program for Physically Inactive Workers - Based on the PRECEDE-PROCEED Model -
- Hye-Jin Kim, Jina Choo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):692-707. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.692
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose We aimed to examine the effects of an integrated physical activity (PA) program developed for physically inactive workers on the theoretical basis of the PRECEDE-PROCEED model.
Methods Participants were 268 workers in three departments of L manufacturing unit in South Korea. The three departments were randomly allocated into integration (n=86) (INT), education (n=94) (ED), and control (n=88) (CT) groups. The INT group received self-regulation, support, and policy-environmental strategies of a 12-week integrated PA program, the ED group received self-regulation strategies only, and the CT group did not receive any strategies. After 12 weeks, process evaluation was conducted by using the measures of self-regulation (autonomous vs. controlled regulation), autonomy support, and resource availability; impact evaluation by using PA measures of sitting time, PA expenditure, and compliance; and outcome evaluation by using the measures of cardiometabolic/musculoskeletal health and presenteeism.
Results Among process measures, autonomous regulation did not differ by group, but significantly decreased in the CT group (
p =.006). Among impact measures, PA compliance significantly increased in the INT group compared to the CT group (p =.003). Among outcome measures, the changes in cardiometabolic/musculoskeletal health and presenteeism did not differ by group; however, systolic blood pressure (p =.012) and a presenteeism variable (p =.041) significantly decreased only in the INT group.Conclusion The integrated PA program may have a significant effect on increases in PA compliance and significant tendencies toward improvements in a part of cardiometabolic health and presenteeism for physically inactive workers. Therefore, occupational health nurses may modify and use it as a workplace PA program.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms on Depressive Symptoms and Health-Promoting Behaviors Among Korean Coast Guards: The Mediating Role of Social Support
Hyung-Eun Seo, Mijung Yeom, Hye-Jin Kim
Workplace Health & Safety.2025; 73(5): 236. CrossRef - The characteristics, components, and fidelity of interventions promoting physical activity in people living with musculoskeletal conditions: a systematic review
Alex Thompson, Robert Copeland, Rachel Young, Angela Reilly, Jeff Breckon, Sionnadh McLean
Disability and Rehabilitation.2025; 47(23): 6020. CrossRef - Strategies for preventing presenteeism in nursing
Luís Sousa, Ricardo Mestre, João Tomás, Sandy Severino, Nelson Guerra, Helena José
Management (Montevideo).2025; 3: 147. CrossRef - Use of the PRECEDE–PROCEED Model to Pilot an Occupational Physical Activity Intervention: Tailored Through a Community Partnership
Debra L. Fetherman, Joan Cebrick-Grossman
Workplace Health & Safety.2023; 71(8): 367. CrossRef - Corporate Well-Being Programme in COVID-19 Times. The Mahou San Miguel Case Study
José M. Núñez-Sánchez, Ramón Gómez-Chacón, Carmen Jambrino-Maldonado, Jerónimo García-Fernández
Sustainability.2021; 13(11): 6189. CrossRef - Effects of an Integrated Physical Activity Program for Physically Inactive Workers: Based on the PRECEDE-PROCEED Model
Hye-Jin Kim, Jina Choo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(6): 692. CrossRef
- The Impact of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms on Depressive Symptoms and Health-Promoting Behaviors Among Korean Coast Guards: The Mediating Role of Social Support
- 1,914 View
- 73 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Development of a Triage Competency Scale for Emergency Nurses
- Sun Hee Moon, Yeon Hwan Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):362-374. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.362
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to develop a triage competency scale (TCS) for emergency nurses, and to evaluate its validity and reliability.
Methods Preliminary items were derived based on the attributes and indicators elicited from a concept analysis study on triage competency. Ten experts assessed whether the preliminary items belonged to the construct factor and determined the appropriateness of each item. A revised questionnaire was administered to 250 nurses in 18 emergency departments to evaluate the reliability and validity of the scale. Data analysis comprised item analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, contrasted group validity, and criterion-related validity, including criterion-related validity of the problem solving method using video scenarios.
Results The item analysis and confirmatory factor analysis yielded 5 factors with 30 items; the fit index of the derived model was good (χ 2/
df =2.46, Root Mean squared Residual=.04, Root Mean Squared Error of Approximation=.08). Additionally, contrasted group validity was assessed. Participants were classified as novice, advanced beginner, competent, and proficient, and significant differences were observed in the mean score for each group (F=6.02,p =.001). With reference to criterion-related validity, there was a positive correlation between scores on the TCS and the Clinical Decision Making in Nursing Scale (r=.48,p <.001). Further, the total score on the problem solving method using video scenarios was positively correlated with the TCS score (r=.13,p =.04). The Cronbach's α of the final model was .91.Conclusion Our TCS is useful for the objective assessment of triage competency among emergency nurses and the evaluation of triage education programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Patient Satisfaction With the Level of Competence of the Triage Nurse in Hospital Emergency Departments
Meritxell López Hernández, Montserrat Puig‐Llobet, Sergio Higon Fernández, Marta Franco Freirut, Yolanda Moreno Mateos, Jordi Galimany Masclans
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025; 34(9): 3893. CrossRef - Effects of Critical Thinking Disposition, Clinical Judgement, and Nurse–Physician Collaboration on Triage Competency Among Triage Nurses
Ji-Won Song, Hyung-Ran Park
Healthcare.2025; 13(4): 405. CrossRef - The Impact of the Nursing Professionalism and Triage Competency of Emergency Department Nurses on Disaster Nursing Competency
Hyo Jin Im, Ju Young Ha
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2025; 39(1): 19. CrossRef - Effects of Disaster Nursing Education Based on the Korean Triage and Acuity Scale (KTAS): Focus on Competency in Emergency Patient Triage, Core Competencies in Disaster Nursing, Confidence in Disaster Nursing, and Self-efficacy
Yoonhee Seok, Hye-Ryeon Park
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2025; 13(1): 83. CrossRef - Influence of work stress, clinical decision-making ability, and teamwork on triage competency among emergency room nurses in Korea: a cross-sectional study
Seon-Hyeong Kim, Ae-Ri Jung
Journal of Acute Care Surgery.2025; 15(2): 60. CrossRef - Validation of the Persian Triage Decision-Making Inventory (TDMI): a cross-cultural adaptation study
Mahdi Nabi Foodani, Amir Hossein Goudarzian, Özkan Görgülü, Kelly Jo Cone, Khosro Shakeri, Zahra Abbasi Dolatabadi
BMC Emergency Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of risk prediction models for high-risk patients with non-traumatic acute abdominal pain: a prospective observational study
Rui Li, Xiao-Hui Wei, Xiao-Qin Li, Ai-Hua Dong, Dan-Nan Ai, Li-Jin Zhou, Yan Yang
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Triage—clinical reasoning on emergency nursing competency: a multiple linear mediation effect
Won-Oak Oh, Myung-Jin Jung
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Korean Triage and Acuity Scale education using role-playing and its effects on triage competency: A quasi-experimental design
Yon Hee Seo, Sun-Og Lim, Vanessa Carels
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(10): e0311892. CrossRef - Construction of learning objectives and content for emergency triage nurses in tertiary general hospitals: A Delphi study
Linyuan Zhang, Bo Gao, Fang He, Chao Wu, Juan Du, Li Zhang, Juan Liang, Hongjuan Lang
Nurse Education in Practice.2024; 80: 104145. CrossRef - Concept analysis of psychiatric nursing competency in psychiatric nursing
Hwa-Bok Choi
Archives of Psychiatric Nursing.2024; 52: 130. CrossRef - Enhancing triage accuracy in emergency nurses: The impact of a game-based triage educational app
Sun-Hee Moon, Su Ol Kim
International Emergency Nursing.2024; 72: 101398. CrossRef - Emergency nurses’ communication experiences with patients and their families during the COVID-19 pandemic: A qualitative study
Soyoung Shin, Hye Jin Yoo
International Emergency Nursing.2023; 66: 101240. CrossRef - Influence of Emergency Department Nurses' Grit, Self-Leadership, and Communication on Their Triage Competencies: A Descriptive Survey Study
Gwiseon Jeong, Hyeongsuk Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(4): 356. CrossRef - Factors affecting triage competence among emergency room nurses: A cross‐sectional study
Seokhwa Hwang, Sujin Shin
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(13-14): 3589. CrossRef - Professional Self-Concept, Job Stress, and Triage Competency Among Emergency Nurses: Secondary Data Analysis of a Cross-Sectional Survey
You-Jin Cho, Young-Ran Han, Yeo-Won Jeong
Journal of Emergency Nursing.2022; 48(3): 288. CrossRef - The Effect of Competency-Based Triage Education Application on Emergency Nurses’ Triage Competency and Performance
Sun-Hee Moon, In-Young Cho
Healthcare.2022; 10(4): 596. CrossRef - Factors Associated with School Nurses’ Triage Competency in South Korea
Jaehee Yoon, Heesook Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(16): 8279. CrossRef - Development of emergency nursing care competency scale for school nurses
Jaehee Yoon
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with the undertriage of patients with abdominal pain in an emergency room
Boo Young Oh, Kisook Kim
International Emergency Nursing.2021; 54: 100933. CrossRef - Development and validity of the Korea psychiatric triage algorithm
Jeongmin Ha, Kyeongmin Jang, Misuk An
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Patient Satisfaction With the Level of Competence of the Triage Nurse in Hospital Emergency Departments
- 3,022 View
- 116 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Development and Validation of a Measurement to Assess Person-centered Critical Care Nursing
- Jiyeon Kang, Young Shin Cho, Yeon Jin Jeong, Soo Gyeong Kim, Seonyoung Yun, Miyoung Shim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):323-334. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.323
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a scale to measure person-centered critical care nursing and verify its reliability and validity.
Methods A total of 38 preliminary items on person-centered critical care nursing were selected using content validity analysis of and expert opinion on 72 candidate items derived through literature review and qualitative interviews. We conducted a questionnaire survey with 477 nurses who worked in intensive care units. The collected data were analyzed using exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and confirmative factor analysis (CFA) with SPSS and AMOS 24.0 program.
Results EFA was performed with principal axis factor analysis and Varimax rotation. The 15 items in 4 factors that accounted for 50.8% of the total variance were identified by deleting the items that were not meet the condition that the commonality should be .30 or more and the factor loading over .40. We named the factors as compassion, individuality, respect, and comfort, respectively. The correlation coefficient between this scale and the Caring Perception Scale was
r =.57 (p <.001), which determined concurrent validity. The item-total correlation values ranged from .39 to .63, and the internal consistency for the scale was Cronbach's α=.84.Conclusion The reliability and validity of the 15 item person-centered critical care nursing scale were verified. It is expected that the use of this scale would expand person-centered care in critical care nursing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cultural adaptation and psychometric validation of the Korean version of the Intensive care unit Dignified Care Questionnaire (IDCQ)
Sejin Kang, So Hyun Park, Youn-Jung Son
BMC Nursing.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross‐Cultural Adaptation and Validation of the Yonsei‐Social Play Evaluation Tool (Y‐SPET) for Preschool Children in the United States: A Delphi Study
Sarah Kim, Rachelle Lydell, Sanghee Yoo, Sarah Tucker, Claudia Hilton, Ickpyo Hong
Child: Care, Health and Development.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - How the nursing work environment moderates the relationship between clinical judgment and person-centered care among intensive care unit nurses
Mi Hwa Seo, Eun A. Kim, Hae Ran Kim, Mohammad Jamil Rababa
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(1): e0316654. CrossRef - Development and validation of the nurses’ touch comfort evaluation scale in China
Yaohong Liu, Sainan Qiu, Hao Li, Chong Chen, Renhe Yu, Su’e Yuan
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with good death for end-of-life patients in the intensive care unit based on nurses’ perspectives: A systematic review
Ifa Hafifah, Wasinee Wisesrith, Noraluk Ua-Kit
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2025; 87: 103930. CrossRef - Impact of Interprofessional Communication and Person-centered Care on Perceived Quality of Death in Intensive Care Units by Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study
Hye-Jin Kim, So-Hi Kwon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(2): 153. CrossRef - Trends in person-centered care research: A quantitative content analysis using text network analysis
Dajung Ryu, Hyun Su Lee, Mi Sun Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(2): 141. CrossRef - Workload, Teamwork, Compassion Competence, and Person-centered Critical Care Nursing among Critical Care Nurses
Hyun A Lee, Myung Sun Hyun, Jin-Hee Park, Eun Ji Seo
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2025; 18(2): 14. CrossRef - A Predictive Model for Person-Centered Care in Intensive Care Units in South Korea: A Structural Equation Model
Sunmi Kwon, Kisook Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(4): 467. CrossRef - Analysis of Factors Affecting the Inpatient Satisfaction in Integrated Nursing Care Service Wards using a Healthcare Service Survey Database
Young Shin Cho, Jiwon Hong
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(3): 76. CrossRef - The Influence of Ethical Nursing Competence and Positive Nursing Organizational Culture on Person-Centered Care in Intensive Care Unit Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Jae Eun Lee, Hye-Young Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(3): 304. CrossRef - Emotional Touch Nursing Competencies Model of the Fourth Industrial Revolution: Instrument Validation Study
Sun-Young Jung, Ji-Hyeon Lee
Asian/Pacific Island Nursing Journal.2024; 8: e67928. CrossRef - Development and validation of a patient-centered communication scale for nurses
Youngshin Joo, Yeonsoo Jang, Chang Gi Park, You Lee Yang
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a cyberbullying victimization scale for adolescents in South Korea
JongSerl Chun, Jinyung Kim, Serim Lee
Children and Youth Services Review.2023; 144: 106744. CrossRef - The effect of nursing work environment on slow nursing among long-term care hospital nurses: A descriptive study
Hyeon-mi Woo
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(2): 206. CrossRef - Birey Merkezli Perioperatif Hemşirelik Ölçeği: Türkçe’ye Uyarlama, Geçerlik ve Güvenirlik Çalışması
Nadide YILMAZ ESENBOĞA, Seher YURT
Ege Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Fakültesi Dergisi.2023; 39(1): 21. CrossRef - Comparison of Nursing Needs and Nursing Performance Perceived by Patients and Nurses in Integrated Nursing Care Service Wards in Small and Medium-Sized Hospitals: A Cross-Sectional Descriptive Study
Hee-Sun Choi, Young Shin Cho
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(3): 234. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Person-Centered Care among Nurses in COVID-19 Special Care Units at Tertiary General Hospitals: A Cross-Sectional Descriptive Study
Kisook Kim, Sunmi Kwon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(2): 127. CrossRef - Moral sensitivity and person‐centred care among mental health nurses in South Korea: A cross‐sectional study
Sun Joo Jang, Eun Hye Kim, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2227. CrossRef - Person-Centered Care Experience of Nursing Home Workers: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis Study
Eun Young Kim, Sung Ok Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(1): 33. CrossRef - Intersections of the arts and art therapies in the humanization of care in hospitals: Experiences from the music therapy service of the University Hospital Fundación Santa Fe de Bogotá, Colombia
Mark Ettenberger, Nayibe Paola Calderón Cifuentes
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between person-centred care and the intensive care unit experience of critically ill patients: A multicentre cross-sectional survey
Jiyeon Kang, Minju Lee, Young Shin Cho, Jin-Heon Jeong, Sol A Choi, Jiwon Hong
Australian Critical Care.2022; 35(6): 623. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Communication Competence in the Relationship between Compassion and Patient-Centered Care in Clinical Nurses in South Korea
Miri Jeong, Kawoun Seo
Healthcare.2022; 10(10): 2069. CrossRef - Person-centred care among intensive care unit nurses: A cross-sectional study
Hyuna Youn, Miyoung Lee, Sun Joo Jang
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2022; 73: 103293. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Performance of Person-centered Care Among Nurses in Designated COVID-19 Hospitals
Hyun-Joung Yun, Jaehee Jeon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(4): 413. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Practice for Physical Restraints among Nurses in the Intensive Care Unit
Da Eun Kim, Hye Sook Min
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2022; 15(3): 62. CrossRef - Effectiveness of blood glucose control protocol for open heart surgery patients
Hye Jin Yoo, Eunyoung E. Suh, JaeLan Shim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2021; 77(1): 275. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Patient-Centeredness among Korean Nursing Students: Empathy and Communication Self-Efficacy
Jaehee Jeon, Seunghye Choi
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 727. CrossRef - The Factors Affecting Person-centered Care Nursing in Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Hye Suk Kang, Minjeong Seo
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2021; 14(3): 14. CrossRef - The Effect of a Multifaceted Family Participation Program in an Adult Cardiovascular Surgery ICU*
Hye Jin Yoo, JaeLan Shim
Critical Care Medicine.2021; 49(1): 38. CrossRef - Impact of Job Engagement on the Quality of Nursing Services: The Effect of Person-Centered Nursing in South Korean Nurses
Hyesun Kim, Kawoun Seo
Healthcare.2021; 9(7): 826. CrossRef - The mediating effect of self-efficacy on the relationship between social anxiety and communication ability in nursing students
Mi-Jin You, Hye-Sook Han
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 298. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Person-Centered Practice Inventory-Staff for Nurses
Sohyun Kim, Sunghee H Tak
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(3): 363. CrossRef - The Effects of the Nursing Practice Environment and Self-leadership on Person-centered Care Provided by Oncology Nurses
Sun-Ui Shin, Hyun-E Yeom
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2021; 24(3): 174. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Quality of Dying and Death in Korean Intensive Care Units: Perceptions of Nurses
Haeyoung Lee, Seung-Hye Choi
Healthcare.2021; 9(1): 40. CrossRef - Influencing Factors on Performance of Person-Centered Care among Intensive Care Unit Nurses: An Ecological Perspective
Yein Lee, Yunhee Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(5): 522. CrossRef - Factors affecting to the Person-Centered Care among Critical Care Nurses
Seunghye Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2020; 13(2): 36. CrossRef - Conceptualization of Person-Centered Care in Korean Nursing Literature: A Scoping Review
Ji Yea Lee, Sewon Lee, Eui Geum Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(4): 354. CrossRef - Critical care nurses’ communication experiences with patients and families in an intensive care unit: A qualitative study
Hye Jin Yoo, Oak Bun Lim, Jae Lan Shim, Liza Heslop
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(7): e0235694. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Patient Version of Person-Centered Critical Care Nursing Questionnaire: A Methodological Study
Jiwon Hong, Jiyeon Kang
Sage Open.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a person‐centred care intervention in an intensive care unit: Using mixed methods to examine nurses’ perspectives
Hye Jin Yoo, JaeLan Shim
Journal of Nursing Management.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Relationship between the Work Environment and Person-centered Critical Care Nursing for Intensive Care Nurses
Jiyeon Kang, Yun Mi Lim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(2): 73. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Person-Centered Perioperative Nursing Scale
Soyeung Shin, Jiyeon Kang
Asian Nursing Research.2019; 13(3): 221. CrossRef - The Relationship between Person-Centered Nursing and Family Satisfaction in ICUs
Jiyeon Kang, Eun-Ja Shin
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(3): 1. CrossRef - Development of the Patient Caring Communication Scale
Myoung Lyun Heo, Sook Bin Im
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(1): 80. CrossRef - A Concept Analysis on Patient-Centered Care in Hospitalized Older Adults with Multimorbidity
Youn-Jung Son, Heun-Keung Yoon
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(2): 61. CrossRef - The Meanings of Hands among Clinical Nurses in a Tertiary Hospital
Hye Jin Yoo, Eunyoung E. Suh, Yeon Hee Shin, Jung Sun Choi, Kwang Hee Park, Jung Yoon Kim, Hyunsun Kim, Jiyoung Kang
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(3): 50. CrossRef
- Cultural adaptation and psychometric validation of the Korean version of the Intensive care unit Dignified Care Questionnaire (IDCQ)
- 3,158 View
- 128 Download
- 47 Crossref

- Development of an Instrument to Assess the Quality of Childbirth Care from the Mother's Perspective
- Geum Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Young Hee Kim, Sun-Hee Kim, Sun Hee Lee, Kyung Won Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(1):38-49. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.1.38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to develop an instrument to assess the quality of childbirth care from the perspective of a mother after delivery.
Methods The instrument was developed from a literature review, interviews, and item validation. Thirty-eight items were compiled for the instrument. The data for validity and reliability testing were collected using a questionnaire survey conducted on 270 women who had undergone normal vaginal delivery in Korea and analyzed with descriptive statistics, exploratory factor analysis, and reliability coefficients.
Results The exploratory factor analysis reduced the number of items in the instrument to 28 items that were factored into four subscales: family-centered care, personal care, emotional empowerment, and information provision. With respect to convergence validation, there was positive correlation between this instrument and birth satisfaction scale (r=.34,
p <.001). The internal consistency reliability was acceptable (Cronbach's alpha =.96).Conclusion This instrument could be used as a measure of the quality of nursing care for women who have a normal vaginal delivery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of a continuity of midwifery care model that used a respectful maternal care framework in Korea: a non-randomized study
Geumhee Jeong, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Uri Bang
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Study on Satisfaction of Women Giving Births in Midwifery Birthing Centers and Hospitals
Bu Youn Kim, Sun Hee Lee, Sun Ok Lee
Journal of Korean Maternal and Child Health.2025; 29(4): 218. CrossRef - Maternal Health Effects of Internet-Based Education Interventions during the Postpartum Period: A Systematic Review
Jung Mi Chae, Hyun Kyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(1): 116. CrossRef - Internet-based prenatal interventions for maternal health among pregnant women: A systematic review and meta-analysis
JungMi Chae, Hyun Kyoung Kim
Children and Youth Services Review.2021; 127: 106079. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Prenatal Education for Environmental Health Behavior Using Cartoon Comics
Hyun Kyoung Kim, Hee Kyung Kim, Mirim Kim, Seohwa Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(4): 478. CrossRef - Development and Effect of Nurse-Centered Doula Support Program for Mothers with Natural Childbirth: PILOT TEST
Jimi Park, Ho Ran Park
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2019; 23(4): 269. CrossRef - Comparison of the Quality of Nursing Care as Perceived by Pediatric Nurses and Mothers of Hospitalized Children
So Yeon Yoo, Yae Young Kim, Haeryun Cho
Child Health Nursing Research.2018; 24(4): 373. CrossRef
- Effect of a continuity of midwifery care model that used a respectful maternal care framework in Korea: a non-randomized study
- 1,648 View
- 26 Download
- 7 Crossref

- A Study on the Disturbing Factors Which Work against Therapeutic Atmosphere and Environment on Hospital Wards as Perceived by Patients and Nurses
- Young Hae Kim, Myoung Eun Han
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(1):178-188. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.1.178
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF As a descriptive survey, this study was attempted to get basic data necessary to recognize the factors that disturb the therapeutic atmosphere of hospital wards as perceived by nurses and hospitalized patients, to identify differences between the perceptions of the nurses and of patients. The subjects, 159 patients in Pusan National Hospital and 68 nurses working there were sampled between March 18 and April 13, 1996. The tool used to measure the disturbing factors was an amended form of the one developed by Kim, Mae Ja(1983). The differences between each subject's score for each factor were analyzed using means and SD, and the highest 3 items above the mean score for each factor were collected and compared. The results are described below : 1. Subject's perception of main disturbing factors : patients reported that the main factors were 'loss of role and economic trouble', 'the prognosis of disease', 'the change of daily life' but nurses replied that the main factors were 'the prognosis of disease', 'the communication trouble with the medical team and interpersonal relationships'. 'The change of daily life' was not a perceived factor by nurses, but ranked third by patients. 2. Subject's perception degree of each disturbing factor : (1) among the items related to interpersonal relationship, the patient group reported that the worst disturbance was due to severely ill patients in the same room' but the nurse group regarded 'greed to monopolize wheelchairs or other supplies' as the worst disturbance. (2) among the items related to physical factors, the patient group regarded 'limitations to wash their body, physical pain and limitations in physical activity' as the worst disturbance, but the nurse group regarded 'physical pain', and 'limitations to activity or change of appearance' as the worst disturbance. (3) among the items related to the change of daily activity, the patient group regarded 'the boredom of hospitalization or in favorable diet' as the worst disturbance, but the nurse group regarded 'too much noise or unclean room' as the worst disturbance. (4) among the items related to the communication trouble with medical team, the patient group regarded 'the ignorance of their disease due to poor information, the inability to understand the language of the medical team or the difficulty in seeing physician in time' as the worst disturbance, but the nurse group regarded 'the inability to trust physicians and physician's poor attention to patients' as the worst disturbance.
- 419 View
- 0 Download

- Fatigue and its Related Factors in Patients on Hemodialysis
- Hye Ryoung Kim
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(1):53-72. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.1.53
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The Purpose of this study was to identify characteristics of fatigue and the relationship between fatigue and related factors in patients on hemodialysis. This study was a survey study using a cross-sectional design. The subjects for this study were 101 patients on hemodialysis who were registered in the six hemodialysis clinics among a total of eleven clinics in Seoul. The period of data collection was from February 28, 1995 to May 2, 1995. Data were collected through an interview with a structured packet and the physiological data. The tools used in this study were the Visual Analogue Scale-Fatigue developed by Lee et al(1990) and translated by Lee (1991), the fatigue interview schedule developed by this reseacher, Zung's self rating depression scale (Zung, 1965), the self-efficacy scale developed by Sherer et al(1982) and the Norbeck Social Support Questionnaire (NSSQ) translated by Oh (1984). The collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics (mean, standard deviation, frequency, range), Pearson correlation coefficients and Stepwise multiple regression. The results were as follows: 1. Characteristics of Fatigue of hemodialysis patients: 1) 79 of 101 hemodialysis patients complained fatigue. 2) The mean fatigue score as measured by the VAS-F was 36.2mm. 3) The mean duration of fatigue was 2.9 hours 2. Characteristics of fatigue related factors: 1) The physiologic factor which included Hgb, Hct, BUN, creatinine, potassium and inter-dialytic weight gain deviated from normal range. 2) The psychological factor which included depression and self-efficacy was about the same level as for patients with other chronic diseases. 3) The environmental factor which included social support had wide variation. 3. The relationship between fatigue and related factors: 1) Interdialytic weight gain in the physiological factor was the only valuable with fatigue (p<.05) 2) The relationship between fatigue and the psychological factor of depression showed a positive and strong correlation (p<.05). According to the findings of this study, fatigue was highly correlated with the depression, This indicates that nurses should try to assess and control psychological factors when patients complain of fatigue rather than just considering physiological factors. Nursing has to develop effective nursing interventions to reduce fatigue in patients with chronic diseases using the relationship between fatigue and physiological, psychological and environmental factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Dialysate Flow Rate on Dialysis Adequacy and Fatigue in Hemodialysis Patients
Sun Mi Cha, Hye Sook Min
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(5): 642. CrossRef
- The Effect of Dialysate Flow Rate on Dialysis Adequacy and Fatigue in Hemodialysis Patients
- 697 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Age at Menopause and Related Factors in Korean Women
- Young Joo Park, Hesook Suzie Kim, Hyun Choel Kang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(7):1024-1031. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.7.1024
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This cross-sectional design was to identify the age at menopause of Korean women using a national sample, and to examine relationships between age at menopause and the anthropometric, sociodemographic, biological and life style behavioral factors. Two thousand eight hundred seven naturally postmenopausal women aged between 41-65 years were recruited by self-selection from 7 metropolitans and 6 provinces in Korea from Dec. 20, 1998 to April 30, 1999. The age at menopause of Korean women was 49.2 years (mean) and 50.0 years (median). The range of age at menopause was 33.0 to 61.0 years. The significant influencing factors on age at menopause were body mass index, mother's and sister's age at menopause, alcohol use, physical activity, coffee preference, and residential area. The menopausal age of Korean women has slightly increased compared to a previous study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exposure to the one-child policy and fertility among chinese immigrants to the US
Siyuan Lin, Laura Argys, Susan Averett
Review of Economics of the Household.2025; 23(3): 969. CrossRef - Menopause Across Asia: A Comprehensive Meta-analysis of Age and Influencing Factors
Prabhat Kumar Agrawal, Amit Varshney, Siddhant Dev, Ruchika Garg, Ashish Gautam, Nikhil Pursnani, Sandipta Kumar Panda, Nidhi Agastya
Journal of Mid-life Health.2025; 16(3): 257. CrossRef - Functional Effects of Sericin on Bone Health and D-Serine Regulation in Estrogen-Deficient Rats
Hyun-Seung Kim, Xiangguo Che, Shihyun Kim, Jongho Choi, Joon Ha Lee, You-Young Jo, Seong-Gon Kim, Je-Yong Choi, Ji-Hyeon Oh
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(18): 10247. CrossRef - Nonpharmacological Intervention Effects on Middle-Aged Women with Menopausal Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ji-Hyun Kim, Hea-Jin Yu
Healthcare.2025; 13(24): 3206. CrossRef - Longitudinal patterns and group heterogeneity of depressive symptoms during menopausal transition in middle-aged Korean women
Yoonyoung Jang, Yoosoo Chang, Junhee Park, Sang Won Jeon, Byungtae Seo, Jae Ho Park, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Seungho Ryu
Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Regular Use of Analgesics before Cancer Diagnosis and Occurrence of Mood Disorders
Hyun Sook Oh, Subin Noh, Hwa Jeong Seo
Nursing Reports.2024; 14(3): 1828. CrossRef - Study on depletion of ovarian function and late‐life chronic diseases in India
Sampurna Kundu, Sanghmitra Sheel Acharya
International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics.2023; 162(3): 1057. CrossRef - Exposure to the One-Child Policy and Fertility Among Chinese Immigrants to the Us
Siyuan Lin, Laura Argys, Susan Averett
SSRN Electronic Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Iron Deficiency in Korean Patients With Heart Failure
Jin Joo Park, Minjae Yoon, Hyoung-Won Cho, Sang-Eun Lee, Jin-Oh Choi, Byung-Su Yoo, Seok-Min Kang, Dong-Ju Choi
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of early age at menopause on disease outcomes in postmenopausal women with rheumatoid arthritis: a large observational cohort study of Korean patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Eun Hye Park, Eun Ha Kang, Yun Jong Lee, You-Jung Ha
RMD Open.2023; 9(1): e002722. CrossRef - Osteoporosis Associated with Breast Cancer Treatments Based on Types of Hormonal Therapy: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Korean National Sample Data
Yen Min Wang, Yu-Cheol Lim, Deok-Sang Hwang, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha, Ye-Seul Lee
Medicina.2023; 59(9): 1505. CrossRef - Measured sodium excretion is associated with cardiovascular outcomes in non-dialysis CKD patients: results from the KNOW-CKD study
Seong Cheol Kang, Minjung Kang, Hyunjin Ryu, Seonmi Kim, Ji Hye Kim, Eunjeong Kang, Yujin Jeong, Jayoun Kim, Yong-Soo Kim, Soo Wan Kim, Yeong Hoon Kim, Kook-Hwan Oh
Frontiers in Nephrology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of tiotropium on the risk of coronary heart disease in patients with COPD: a nationwide cohort study
Jiyoung Shin, Jin Hwa Lee
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined Effects of Unhealthy Lifestyle Behaviors on Metabolic Syndrome among Postmenopausal Women
Jin-Suk Ra, Hyesun Kim
Healthcare.2021; 9(7): 848. CrossRef - Ovarian Function Preservation in Patients With Cervical Cancer Undergoing Hysterectomy and Ovarian Transposition Before Pelvic Radiotherapy
Wonguen Jung, Yun H. Kim, Kyung S. Kim
Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Clinical Impact of Body Mass Index on Breast Cancer in Korea: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Jae Hwan Jeong, Hak Min Lee, Hai Young Son, Ilkyun Lee
Journal of Breast Disease.2020; 8(1): 51. CrossRef - Beneficial Effects of Breastfeeding on the Prevention of Metabolic Syndrome Among Postmenopausal Women
Jin Suk Ra, Soon Ok Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2020; 14(3): 173. CrossRef - Neck Circumference and Cerebral Gray Matter Volume
Chol Shin, Regina E.Y. Kim, Robert J. Thomas, Chang-Ho Yun, Seung Ku Lee, Robert D. Abbott
Alzheimer Disease & Associated Disorders.2020; 34(4): 306. CrossRef - Inhaled corticosteroids in COPD and the risk for coronary heart disease: a nationwide cohort study
Jiyoung Shin, Hee-Young Yoon, Yu Min Lee, Eunhee Ha, Jin Hwa Lee
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends of Premature and Early Menopause: a Comparative Study of the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Seung-Ah Choe, Joohon Sung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Urinary bisphenol A, phthalate metabolites, and obesity: do gender and menopausal status matter?
Jung-eun Lim, BongKyoo Choi, Sun Ha Jee
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2020; 27(27): 34300. CrossRef - Association between lower urinary tract symptoms and cardiovascular risk scores in ostensibly healthy women
Hyun Young Lee, Ji Eun Moon, Hwa Yeon Sun, Seung Whan Doo, Won Jae Yang, Yun Seob Song, So‐Ryoung Lee, Byoung‐Won Park, Jae Heon Kim
BJU International.2019; 123(4): 669. CrossRef - Higher Pro-Inflammatory Dietary Score is Associated with Higher Hyperuricemia Risk: Results from the Case-Controlled Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study_Cardiovascular Disease Association Study
Hye Sun Kim, Minji Kwon, Hyun Yi Lee, Nitin Shivappa, James R. Hébert, Cheongmin Sohn, Woori Na, Mi Kyung Kim
Nutrients.2019; 11(8): 1803. CrossRef - Association between obesity type and obstructive coronary artery disease in stable symptomatic postmenopausal women: data from the KoRean wOmen'S chest pain rEgistry (KoROSE)
Jun Hwan Cho, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Myung-A Kim, Sohee Oh, Mina Kim, Seong Mi Park, Hyun Ju Yoon, Mi Seung Shin, Kyung-Soon Hong, Gil Ja Shin, Wan-Joo Shim
Menopause.2019; 26(11): 1272. CrossRef - Obesity and colorectal adenomatous polyps: A cross-sectional study in Korean adults
Ji Young Lee, Sang Mi Kwak, Seung-Kwon Myung, Sun Ha Jee
Obesity.2014; 22(2): 518. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Risk Factors for Intracranial Cerebral Atherosclerosis Among Asymptomatic Subjects
Young-Suk Kim, Jin-Woo Hong, Woo-Sang Jung, Seong-Uk Park, Jung-Mi Park, Sung-Il Cho, Young-min Bu, Sang-Kwan Moon
Gender Medicine.2011; 8(1): 14. CrossRef - Cortisol, estradiol-17β, and progesterone secretion within the first hour after awakening in women with regular menstrual cycles
Ryun S Ahn, Jee H Choi, Bum C Choi, Jung H Kim, Sung H Lee, Simon S Sung
Journal of Endocrinology.2011; 211(3): 285. CrossRef
- Exposure to the one-child policy and fertility among chinese immigrants to the US
- 3,225 View
- 24 Download
- 27 Crossref

- Effects of Motivation-Enhancing Program on Health Behaviors, Cardiovascular Risk factors, and Functional status for Institutionalized Elderly Women
- Rhayun Song, Kyung Ja June, You Ja Ro, Chun Gill Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(5):858-870. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.5.858
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was to compare changes in health behaviors, motivational factors, cardiovascular risk factors, and functional status (SIP) after implementing the 6-month motivation-enhancing program to institutionalized elderly women.
METHODS
Sixty-four elderly women participated. Face to face interviews with blood sampling and anthropometric assessment were conducted at the pretest, 10 weeks and 6 months during the program.
RESULTS
1. The program participants showed significantly better health behaviors over 6 months. The mean motivational level was also significantly improved, especially for perceived benefits, perceived barriers, and emotional salience. 2. The mean of cardiovascular risk factors for the participants was 21.8 at the level of low to moderate risk. After completing the program, total risk score was significantly decreased to 18.7 at 10 weeks, and further to 17.7 at 6 months. A significant reduction was also found in HDL and LDL-cholesterol levels, blood pressure, obesity, inactivity, and stress. 3. The functional status (SIP) was 11% at the baseline and significantly changed in positive direction at 10 weeks (M=9.3) and at 6 month (M=6.3). The significant improvement was also found in physical and psychosocial dimensions and sleep/rest dimension.
CONCLUSION
The motivation enhancing program was effective to reduce cardiovascular risks and to improve the functional status of institutionalized elderly women by motivating them to perform better health behaviors.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Influence of e-Health Literacy, Technostress, and Subjective Health Status on Health Promotion Behaviors among Older Adults
Whang Sun A
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2025; 13(1): 71. CrossRef - The Effects of Health Literacy, Social Support, and Health-Promoting Behaviors on Metabolic Syndrome Among Middle-Aged and Older Women Living in Rural Areas of Republic of Korea
Eun-Kyung Lee, Yong-Sook Eo
Healthcare.2025; 13(24): 3279. CrossRef - The effects of self-efficacy, a health-promoting lifestyle, and social support on resilience of patients receiving percutaneous coronary intervention: A descriptive survey study
Su-Jin Kim, Jeong-soo Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(4): 403. CrossRef - The Role of Health Empowerment on Digital Health Technology Literacy by Generation
Yoongi Chung, Hyerine Shin, Hyejin Kim, Ji-Su Kim
American Journal of Health Behavior.2024; 48(4): 967. CrossRef - Effects of Accelerated Rehabilitation Exercise on the Senior Fitness Test (SFT), Isometric Muscle strength, and Blood Profile in Older Adult Women with Degenerative Knee Osteoarthritis
Ju-ri Lee, Hong-sun Song, Tae-beom Seo, Jong-baek Lee
Korean Journal of Sport Science.2024; : 81. CrossRef - Effects of BeHaS Program on Health Behavior, Physiologic Index and Self-Esteem of the Elderly Living Alone with Metabolic Syndrome Based on Community Based Participatory Research
Jong Im Kim, Sun Ae Kim, Keumok Park, Jiyoung Kim, Lina Lee, Si Wan Choi, Bon Jeong Ku
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(4): 571. CrossRef - Validation of the cardiac health behavior scale for Korean adults with cardiovascular risks or diseases
Rhayun Song, Hyunkyoung Oh, Sukhee Ahn, Sue Moorhead
Applied Nursing Research.2018; 39: 252. CrossRef - Motivation Factors for Stages of Behavioral Change among Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome
Rhayun Song, Moonkyoung Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(1): 60. CrossRef - A structural model of health behavior modification among patients with cardiovascular disease
Hwasoo Goong, Seungmi Ryu, Lijuan Xu
Applied Nursing Research.2016; 29: 70. CrossRef - A Study on IADL, Stress and Motivation on Healthy Lifestyle among Elderly People with Arthritis
Jong Gun Kim, Kyeung Hee Moon, Eun Sun Lim, Jang Hak Yoo
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(3): 209. CrossRef - The Relationship between Health Belief and Exercise Compliance among Elderly Adults at Senior Centers
Kyung Im Lee, Young Eun
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(2): 79. CrossRef - Development of Job Standards for Clinical Nutrition Therapy for Dyslipidemia Patients
Min-Jae Kang, Jung-Sook Seo, Eun-Mi Kim, Mi-Sun Park, Mi-Hye Woo, Dal-Lae Ju, Gyung-Ah Wie, Song-Mi Lee, Jin-A Cha, Cheong-Min Sohn
Clinical Nutrition Research.2015; 4(2): 76. CrossRef - The intake of food and nutrient by the elderly with chronic disease in the Seoul area
Yoo Kyung Park, Yeon Joo Lee, Sang Sun Lee
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2012; 45(6): 531. CrossRef - Effects of a problem‐solving counseling program to facilitate intensified walking on Koreans with type 2 diabetes
Haejung LEE, Myoung‐Soo KIM, Kyung‐Yeon PARK, Hyoung‐Sook PARK, In‐Joo KIM
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2011; 8(2): 129. CrossRef - The Effects of Aerobic Exercise Therapy on Physical Functions in the Elderly
Sook Hee Jung, Kyung Hee Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(2): 252. CrossRef - Health Literacy and Health Status of Korean-Chinese Elderly People Living in Yanbian, China
Chun Yu Li, Ogcheol Lee, Gi Soo Shin, Xian Wen Li
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(3): 386. CrossRef - Effects of the Nutrition Education Program on Self-efficacy, Diet Behavior Pattern and Cardiovascular Risk Factors for the Patients with Cardiovascular Disease
Kyoungok Ju, Heeyoung So
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(1): 64. CrossRef - Effects of Nutrition Education and Exercise Programs on Perceived Dietary Behaviors, Food Intake and Serum Lipid Profiles in Elderly Korean Women Living in Residential Homes
Hee-Seon Kim, Kyung-Ja June, Rhayun Song
Asian Nursing Research.2007; 1(1): 35. CrossRef - Effects of a health-promotion program on cardiovascular risk factors, health behaviors, and life satisfaction in institutionalized elderly women
Chun-Gill Kim, Kyung-Ja June, Rhayun Song
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2003; 40(4): 375. CrossRef
- The Influence of e-Health Literacy, Technostress, and Subjective Health Status on Health Promotion Behaviors among Older Adults
- 923 View
- 20 Download
- 19 Crossref

- A Study on the Elderly Patients Hospitalized by the Fracture from the Fall
- Mi Yang Jeon, Hyeon Cheol Jeong, Myoung Ae Choe
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(3):443-453. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.3.443
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: To identify age, gender, medication, seasons and place of fall, and areas of the fractures from the fall among the hospitalized elderly patients in order to provide the basic data for future fall prevention program for the elderly.
METHODS
This study was conducted for 106 elderly patients admitted into a university hospital by fractures from the fall during the period from January 1, 1999 to December 31, 1999. Data on the age, gender, medication, season and place of the fall, areas of the fracture were collected based on their medical records.
RESULT
The age range of the subjects were from 60 to 96 years old. The subjects were aged between 60-69 years old 49(46.2%), between 70-79 years old 31(29.2%), between 80-89 years old 24(22.6%), and over 90 years old 2(1.9%). Male patients comprised was 34(28.3%), while female patients comprised 76(71.7%). The fall occurred in Winter most frequently 34(32%). The place of the fall included room 81(76.4%), streets 13(12.3%), bathroom 6(5.7%), stair 4(3.8%), and mountain 2(1.9%). Twenty-two subjects (20.8%) had medication regularly, while 84 subjects (79.2%) had no medication. The areas of the fracture from the fall included upper extremities 20(18.9%) and lower extremities 86(81.1%). Radius fracture (7.5%) was the area where the fracture occurred most frequently in upper extremities and femur fracture (52.8%) was the area where the fracture occurred most frequently in lower extremities. A significant difference was found in the fracture area by age, season and place of the fall (p<.05). No significant difference was found in the fracture area by gender and medication. In all age groups, seasons and places of the fall, occurrence of fracture in lower extremity was significantly higher than that in upper extremity.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of patient blood management system and feedback programme on appropriateness of transfusion: An experience of Asia's first Bloodless Medicine Center on a hospital basis
Hyeon Ju Shin, Jong Hun Kim, Yujin Park, Ki Hoon Ahn, Jae Seung Jung, Jong Hoon Park
Transfusion Medicine.2021; 31(1): 55. CrossRef - Development of Motion Platform-Based Exercise Equipment for Rehabilitation Training and Posture Balance
Sung Gwan Park, Joon Hee Kim, Myeong In Seo, Tae Woo Kim, Dong Hwan Kim
Journal of the Korean Society for Precision Engineering.2020; 37(7): 475. CrossRef - Understanding and Prevention of Fall-related Injuries in Older Adults in South Korea: A Systematic Review
Ki-taek Lim, Ji-eun Lee, Ha-eun Park, Su-young Park, Woochol Joseph Choi
Physical Therapy Korea.2019; 26(2): 34. CrossRef - The effects of milk intake and whole-body vibration exercise on bone mineral density in elderly women in nursing homes
So Min Lee, Sungchul Kim, Chae-gil Lim
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2017; 29(7): 1125. CrossRef - Identifying Characteristics of Fall Episodes and Fall-related Risks of Hospitalized Patients
Young Ok Kang, Rhayun Song
Journal of muscle and joint health.2015; 22(3): 149. CrossRef - Effects of a Randomized Controlled Recurrent Fall Prevention Program on Risk Factors for Falls in Frail Elderly Living at Home in Rural Communities
JongEun Yim
Medical Science Monitor.2014; 20: 2283. CrossRef - Basic Study on the Development of Impact Protective Pants and Falls of Elderly Women
Jin Suk Lee, Jung Hyun Park, Jeong Ran Lee
Fashion & Textile Research Journal.2014; 16(6): 945. CrossRef - Study on the Preference Survey for Developing the Fall Impact Protective Clothing - Targeting Women ages of 50s to 70s -
Jung Hyun Park, Jeong Ran Lee
Fashion & Textile Research Journal.2014; 16(1): 101. CrossRef - Gait Analysis on the Elderly Women with Foot Scan
Seong-Suk Kim, Hee-Eun Kim
Fashion & Textile Research Journal.2013; 15(4): 613. CrossRef - Safety Consciousness of the Elderly Living Alone
Youngsil Kang, Sun Jae Jung
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(3): 180. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Recurrent Falls Among Community-dwelling Elderly in Rural Areas
Mi-Yang Jeon, Sun Hee Yang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(12): 6353. CrossRef - Comparison of Comprehensive Health Status and Health-related Quality of Life between Institutionalized Older Adults and Community Dwelling Older Adults
Hye-Jin Hyun, Aekyung Chang, Su Jeong Yu, Yeon-Hwan Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(1): 40. CrossRef - Comparing Effects of Tai Chi Exercise on Pain, Activities of Daily Living, and Fear of Falling in Women with Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Hyun-Kyoung Oh, Suk-Hee Ahn, Rha-Yun Song
Journal of muscle and joint health.2011; 18(2): 137. CrossRef - Activities of Daily Living, Health Related Quality of Life According to the Experience of Falls among the Aged in Community
Seon-Kyung Kim, Jong-Im Kim
Journal of muscle and joint health.2011; 18(2): 227. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of the Exercise Education Programme on Fall Prevention of the Community-dwelling Elderly: A Preliminary Study
Moonyoung Chang, Yan-hua Huang, Heyyoung Jung
Hong Kong Journal of Occupational Therapy.2011; 21(2): 56. CrossRef - Effects of Tai Chi Exercise Program on Physical Fitness, Fall related Perception and Health Status in Institutionalized Elders
MingRen Liu, Heeyoung So
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(4): 620. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Depression in the Relationship between Muscle Strength of Extremities and Falls among Community-Dwelling Elderly
Hyoung-Sook Park, Kyung-Yeon Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 730. CrossRef
- Effect of patient blood management system and feedback programme on appropriateness of transfusion: An experience of Asia's first Bloodless Medicine Center on a hospital basis
- 832 View
- 7 Download
- 17 Crossref

- A Study on the Verification of the Profile of Seo's Elderly Stress Scale (SESS)
- Hyun Mi Seo, Su Jeong Yu, Yang Sook Hah
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(1):94-106. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.1.94
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to verify the use of Seo's Elderly Stress Scale (SESS), which was developed in 1996. Through the modified tool, it is possible to examine the stress of Korean elders and to contribute to the welfare of them. The subjects were 350 elders over 65 years old who live in Seoul, Kwang-Ju, Yang-Ju Gun Kyung-ki Do, Ui-Jong Bu, and Young-Am Kun, Jeun-Ra Nam Do. the data of 331 elders (94%) were analyzed. Data were collected between January and March in 1996 and analyzed using the SPSS Win 8.0. The result are as follows: 1. Items with low correlation with the total items were removed. So 27 items were removed and 37 items remained. This 37 items were death in the family and/or close friends, family member's behavior not meeting expectations, marriage of daughter, marriage of son, friction with daughter- in-law, argument among children, children refuse to live with parent, children leaving home, sex injury or accident, in frequest visits from children and grandchildren, providing care for your daughter or daughter-in-law post-partum, decrease in decision making and authority in home, Lunar new year and the harvest featival, house sitting, working in the house, performing a sacrificial rite, missed birthday, not living with the eldest son, decreased eyesight, decreased strength, decreased memory, sleep pattern changes, thoughts about death, loneliness, decreased hearing, change of dental condition, change in your diet or eating style, difficulty in self care, moving because of disease or aging, argument with friend or neighbour, travel, dealing with the procedure of heritage, loss of money or property, not enough pocket money, hearing on elderly neglect in television or radio, hope of going home and ignorant from others. 2. Overlapped items were discussed by colleagues and were modified. 'marriage of daughter' and 'marriage of son' were modified in 'marriage of children'. 'self injury or accidents' and 'family accidents' were modified in to self or family accidents. 3. Factor analysis was done in order to identify validity and three factors were obtained from the result. The first factor familial relation area, included 17 items. The second factor, physical area, included 9 items. The third factor, psycho-socio-economic area, included 9 items. Cronbach coefficient alpha for the 35 items was .923. 4. Pearson's correlation was .704 between SESS and SOS (Symptoms of Stress) in order to confirm construct validity. Based on the result, the following is suggested; 1. The modified SESS needs to be reverified with elder. 2. Korean elder's health promotion can be made by development of stress intervention which was accurately measured with SESS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The influence of daily stress and resilience on successful ageing
J. Byun, D. Jung
International Nursing Review.2016; 63(3): 482. CrossRef - A Study on IADL, Stress and Motivation on Healthy Lifestyle among Elderly People with Arthritis
Jong Gun Kim, Kyeung Hee Moon, Eun Sun Lim, Jang Hak Yoo
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(3): 209. CrossRef - The factors associated with suicidal ideation among the elderly living alone received the elderly care service in a rural area
Hee-Young Choi, So-Yeon Ryu, Gwang-Il Kwak, Cheol-Won Choi
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2014; 39(2): 81. CrossRef
- The influence of daily stress and resilience on successful ageing
- 749 View
- 14 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Prevalence and Risk Factors for Diabetes Mellitus and Impaired Fasting Glucose of Adults
- Hee Seung Kim, You Ja Ro, Nam Cho Kim, Yang Sook Yoo, Jin Sun Young, Jeong Ah Oh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(6):1479-1487. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.6.1479
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was conducted to draw out prevalence and the risk factors of diabetes mellitus and impaired fasting glucose for adults,(age 30-69). The subjects were 2096 adults, who had regular health examinations between January and December of 1999 at K Hospital in Seoul. The data was analyzed using chi-square test, unpaired t-test and logistic regression. Diabetes Mellitus and impaired fasting glucose were diagnosed by ADA (American Diabetes Association, 1997) criteria. The results were as follows: 1. Mens' prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus was 7.9% and womens' prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus was 3.8%. Mens' prevalence of impaired fasting glucose was 10.4% and womens' prevalence of impaired fasting glucose was 6.5%. Prevalences of Diabetes Mellitus and impaired fasting glucose increased with age. 2. Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus and impaired fasting glucose of obese subjects (relative body weight>=162) was higher than that of overweight subjects (110<=relative body weight<=119) in men and women. 3. The diagnoses of Diabetes Mellitus and impaired fasting glucose increased with systolic blood pressure and triglyceride. 4. Significant factors associated with diabetes in the logistic regression best gut model were age, relative body weight, systolic blood pressure, triglyceride in men, and systolic blood pressure in women. In conclusion, as age, weight, systolic blood pressure and triglyceride get higher, Diabetes Mellitus and impaired fasting glucose prevalence also increases, porportionally.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Relation of Impaired Fasting Glucose and HDL-Cholesterol by Gender and Body Mass Index
Soo-Hee Jin
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2019; 44(1): 8. CrossRef - Effects of Obesity and Family History of Diabetes on the Association ofCETPrs6499861 with HDL-C Level in Korean Populations
Jae Woong Sull, Soriul Kim, Sun Ha Jee
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2019; 8(2): 252. CrossRef - Current Status and Effects of Nutrition Education Programs for Diabetic Patients in Korea
Hae Jin Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(2): 106. CrossRef - Effect of smoking on the association of HHEX (rs5015480) with diabetes among Korean women and heavy smoking men
Jae Woong Sull, Tae Yong Lee, Sun Ha Jee
BMC Medical Genetics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Spatial Distribution of Diabetes Prevalence Rates and Its Relationship with the Regional Characteristics
Eun-Kyung Jo, Eun-Won Seo, Kwang-Soo Lee
Health Policy and Management.2016; 26(1): 30. CrossRef - The Relationship between Factors of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adult Males and the Parents' Family History of Diabetes
Hyung-Su Park, Jin-Gyu Jeong, Jin-Ho Yu
The Journal of the Korea institute of electronic communication sciences.2013; 8(5): 779. CrossRef - Thigh Circumference and Diabetes: Obesity as a Potential Effect Modifier
Keum Ji Jung, Heejin Kimm, Ji Eun Yun, Sun Ha Jee
Journal of Epidemiology.2013; 23(5): 329. CrossRef
- The Relation of Impaired Fasting Glucose and HDL-Cholesterol by Gender and Body Mass Index
- 828 View
- 1 Download
- 7 Crossref

- The Psychological Effect of Hand and Arm Massage on Middle-Aged Women
- Hee Jung Jang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(6):1389-1399. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.6.1389
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Massage therapy is a traditional, alternative and nonphamacological means of promoting rest and relaxation. However, nursing intervention by massage for middle-aged women is rarely practiced by nurses. The purpose of this research was to examine the effects of the hand and arm massage as an independent nursing intervention tool for middle- aged women. The data used in this research were collected from forty-nine subjects using a nonequivalent control group non- synchronized design. Twenty-four persons for the experimental group and Twenty-five persons for the control group were selected from D city and C city from July 1997 to September 2000. Subjects' ages were between forty and fifty-six years old with mean the age of 45.6. Hand and arm massage developed by Cayce and Reilly was applied to the experimental group for a session of 15 minutes two or three times a week for four weeks. The instruments used for the measurement of the subjects' stress, anxiety, depression and the middle-life crisis were Langners's 22-item Screening Score, Spielberger's State Anxiety Inventory, Zung's Self-rating Depression Scale, and Kim's Middle Life Crisis Scale(1988). These psychological factors were measured before and after the implementation of hand and arm massage. The data were analyzed with mean+/-s.d, percent, t-test, and a paired t-test. The results were summarized as follows; 1. Before the treatment, there were no significant differences between the two groups. 2. After the treatment, there were significant differences in the stress and the occurrence of mid life crisis between the two groups. The findings suggest that the use of the hand and arm massage for middle-aged women made significant changes in the level of stress and middle life crisis. Therefore, it is recommended that hand and arm massage be used as an independent nursing intervention tool for middle-aged women. For further research, is needed replication of this concept of research with different subjects in a larger population. Also, it is recommended to investigate the effects of massage with aroma therapy for the berefit of decreasing womens' stress level further.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Sorusangzi Massage on Stress, Fatigue, and Depression in Middle-aged Working Women
Ji On Park, Yun Hee Son, Eun-Hwa Ju
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2017; 15(1): 55. CrossRef - Research Trend on Aromatherapy for Korean Middle-aged Women
Hee-Jung Yong, Hyun Hee Jang, Sung Nae Lee, Soo-Yeon Kim, Young-Sam Kim
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2017; 15(1): 113. CrossRef - Analysis of Studies on Hand Massage Published in Korea: On the Effects of Sleep, Pain, Anxiety and Depression
In-Ja Kim, Yu-Na Cho
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2012; 15(1): 47. CrossRef - Effects of Hand Holding on Self-esteem and Assertiveness in Women Patients with Depression
Mi-Hae Sung, Mi Young Choi, Ok Bong Eum
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2010; 19(2): 154. CrossRef
- Effects of Sorusangzi Massage on Stress, Fatigue, and Depression in Middle-aged Working Women
- 1,047 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- A Study on the Physiological and Psychological Factors related to Successful Weaning from a Mechanical Ventilator
- Cho Ja Kim, Hwasoon Kim, Yeon Soo Jang, Eun Sung Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(4):995-1005. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.4.995
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was performed to identify the physiological and psychological variables related to successful weaning from a mechanical ventilator. The subjects of this study were 22 patients who received mechanical ventilation therapy for more than 3 days in intensive care units. Before the weaning trial, baseline data for following physiologic variables were obtained: spontaneous respiration rate, blood pressure, pulse rate, PaO2, PaCO2, PEEP, static compliance, minute ventilation, tidal volume, rapid shallow breathing index(f/VT), SaO2, PaO2/FiO2 and mean arterial pressure. During spontaneous breathing, physiologic and psychologic variables such as vital signs, ABG, perspiration, chest retraction, paradoxical respiration, dyspnea, anxiety, confidence and efficacy were measured. Successful weaning was defined as sustaining spontaneous respiration over 24 hours after extubation. Weaning failure was defined as the development of more than one of following signs: (1) hypoxemia, (2) CO2 retention or (3) perspiration, tachypnea, chest retraction, tachycardia, arrhythmia, hypotension or hypertension. Subjects (N=18) who successfully weaned from mechanical ventilator were compared with subjects (N=4) who failed. The results are as follows; Eighteen percents of the subjects failed during the weaning trial. Most subjects in the failed group were mechanically ventilated for long-time. This result shows that the success of weaning is more difficult in long-term ventilation patients. In the baseline data that was measured before weaning trial, the mean score of PaO2 in the successfully weaned group was 121mmHg. This is significantly higher than the mean score of PaO2 in the failed group(95mmHg). However, the scores of pH, tidal volume, f/VT, pulse rates, blood pressure, mean airway pressure, SaO2, and PaCO2 were similar between the two groups. Specially the scores of f/VT index as a predominant predictor for successful weaning were not significant (f/VT=44.4) and (f/VT=47). During spontaneous breathing, the scores of dyspnea and anxiety level in the successfully weaned group were less than those of the failed group. On the contrary, the scores of confidence and efficacy in the successful group were greater than those of the failed group. In conclusion, the baseline data that were measured before weaning trial were similar between the both groups, therefore future studies are needed to focus on searching other variables besides physiological parameters related to weaning outcome.
- 534 View
- 0 Download

- A Study on the Circadian Blood Pressure Rhythm of Diabetic Patients
- Hwa Soon Kim, Wha Sook Suh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):741-749. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.741
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was performed to investigate the relationship between reversed circadian blood pressure and risk factors of peripheral vascular disease in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) subjects. The subjects in this study were 18 NIDDM patients who were hospitalized in a medical unit of an university medical center located in Incheon, Korea, between November, 1998 and March, 1999. Blood pressure was measured with a mercury sphygmomanometer by 2 trained examiners every 2 hours during 24 hours. NIDDM subjects were divided into a dipper group and non-dipper group. Dippers are defined as those who show a mean nighttime blood pressure(BP) drop of more than 10% compared with daytime BP. Non-dippers are defined as those who show a mean nighttime BP drop of less than 10%, or an elevation in BP compared with daytime BP. Daytime BP included values obtained between 6 a.m. and 10 p.m. Night time BP included values obtained between 10 p.m. and 6 a.m. Data was analyzed by SPSS/PC package. Chi-square( 2) test was used for the comparison of sex between The dipper group and non-dipper group. Mann-Whitney test was used for comparisons of values of the risk factors of peripheral vascular disease and the frequency of complications of diabetes between the dipper group and non-dipper group. The results are as follows. There were no significant differences in daytime systolic, diastolic, and mean blood pressures between the dipper group and non-dipper group. However, night time systolic, diastolic, and mean blood pressures in the non-dipper group were significantly nigher than those in the dipper group (p=.021). There were no differences in sex, age, body, weight, duration of diabetes, serum lipid levels, BUN and HbA1c between the two groups. On the contrary, 87.5% of non-dipper group subjects showed having hypertension, 30% of dipper group subjects showed having hypertension and this difference was statistically significant (p=.018). All of the non-dipper group subjects (N=8) showed having at least one diabetic complication. However, 40% of the dipper group subjects (N=10) showed having no diabetic complication at all and this difference was also statistically significant (p=.049). There were no significant differences in frequency of nephropathy, neuropathy and retinopathy between the dipper group and non-dipper group.
- 513 View
- 2 Download

- The Reliability and Validity Test of psychosocial Well-being Index(PWI)
- Jeong Hee Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(2):304-313. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.2.304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study is to test the reliability and validity test of PWI to utility of PWI, this newly developed by Sejin Jang which measures stress. The subject were 186 workers in service area. Cronbach's alpha and Guttman split-half coefficient is used to test the reliability of PWI. Factor analysis and the correlation of the GHQ-60, GHQ-30, GHQ-28, GHQ-20, and GHQ-12 with the PWI is used to convergent validity and discriminant validity. The important results of this study are as follows : Cronbach's alpha coefficient of data was 0.894 and Guttman split-half coefficient was 0.7097. The PWI was classified as 13 principle component(eigenvalue>1.0). After exploring 4 factor structure according to previous study result, 4 factors was explained 40.5% out of the total variance. The factor 1 was explained 15.9% and then the rest three factor was 24.6%. Factor 2 and 4 showed good agreement but factor 1 and 3 did not. Depression-related items were classified two factors. Anxiety and depression-related items were loaded unifactor. It was not clear that the PWI was consist of 4 concepts(factors). The correlation of the GHQ-60, GHQ-30, GHQ-28, GHQ-20, and GHQ-12 with the PWI were 0.744~0.905. According to findings of this study, the PWI showed a high degree of validity and reliability. Thus it is recommended to use the PWI in general setting for screening for stress. In addition, it is necessary to clarify the concept of depression and anxiety. In the further study, it may be considered to the factor structure of PWI and studied to two or unidimensional factor structure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Polygenic overlap between subjective well-being and psychiatric disorders and cross-ancestry validation
Jin Young Jung, Yeeun Ahn, Jung-Wook Park, Kyeongmin Jung, Soyeon Kim, Soohyun Lim, Sang-Hyuk Jung, Hyejin Kim, Beomsu Kim, Mi Yeong Hwang, Young Jin Kim , Woong-Yang Park, Aysu Okbay, Kevin S. O’Connell, Ole A. Andreassen, Woojae Myung, Hong-Hee Won
Nature Human Behaviour.2025; 9(6): 1272. CrossRef - The relationship between frailty status and psychosocial indices in older Korean adults
Ji Young Kim, Taesic Lee, Sangbaek Koh
GeroScience.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations Between Psychological Stress and Hand Pain Among Rural and Urban Adults: Findings From the KoGES Community Cohort Study
Sunmi Song, Jennifer E. Graham-Engeland, Junesun Kim
The Journal of Pain.2024; 25(2): 362. CrossRef - Resting-state EEG microstate analysis of internet gaming disorder and alcohol use disorder
Ji Sun Kim, Young Wook Song, Sungkean Kim, Ji-Yoon Lee, So Young Yoo, Joon Hwan Jang, Jung-Seok Choi
Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience.2024; 26(1): 89. CrossRef - Resting-state heart rate variability, level of stress and resilience in internet gaming disorder and alcohol use disorder
Jong Hu Park, So Young Yoo, Hye Yoon Park, Jung-Seok Choi
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychosocial stress accompanied by an unhealthy eating behavior is associated with abdominal obesity in Korean adults: A community-based prospective cohort study
Minji Kim, Yangha Kim
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Kynurenine Pathway and Mediating Role of Stress in Addictive Disorders: A Focus on Alcohol Use Disorder and Internet Gaming Disorder
Joon Hwan Jang, So Young Yoo, Yae Eun Park, Mi-Jung Ji, Hyun-Mee Park, Ji Hyun Back, Ji Yoon Lee, Dai Jin Kim, Ji Eun Lee, Jung-Seok Choi
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Multiple-Kernel Support Vector Machine for Predicting Internet Gaming Disorder Using Multimodal Fusion of PET, EEG, and Clinical Features
Boram Jeong, Jiyoon Lee, Heejung Kim, Seungyeon Gwak, Yu Kyeong Kim, So Young Yoo, Donghwan Lee, Jung-Seok Choi
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation between Preventive Health Behaviors and Psycho-Social Health Based on the Leisure Activities of South Koreans in the COVID-19 Crisis
Young-Jae Kim, Jeong-Hyung Cho
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(11): 4066. CrossRef - Family Factors and Obesity in Relation to Mental Health Among Korean Children and Adolescents
Hye-Mi Noh, Jane Park, Eun-Ju Sung, Young Soo Ju, Hye-Ja Lee, Yoon-Kyoung Jeong, Kyung Hee Park
Journal of Child and Family Studies.2020; 29(5): 1284. CrossRef - Self-Efficacy and Clinical Characteristics in Casual Gamers Compared to Excessive Gaming Users and Non-Gamers in Young Adults
Sun Ju Chung, Joon Hwan Jang, Ji Yoon Lee, Aruem Choi, Bo Mi Kim, Min Kyung Park, Myung Hun Jung, Jung-Seok Choi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(9): 2720. CrossRef - Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Resilience as a Protective Factor in Patients with Internet Gaming Disorder: A Resting-State EEG Coherence Study
Ji-Yoon Lee, Jung-Seok Choi, Jun Kwon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(1): 49. CrossRef - Heritability estimates of individual psychological distress symptoms from genetic variation
Soyeon Kim, Hyeok-Jae Jang, Woojae Myung, Kiwon Kim, Soojin Cha, Hyewon Lee, Sung Kweon Cho, Beomsu Kim, Tae Hyon Ha, Jong-Won Kim, Doh Kwan Kim, Eli Ayumi Stahl, Hong-Hee Won
Journal of Affective Disorders.2019; 252: 413. CrossRef - Relationship between Happiness and Job Satisfaction of Dental Hygienists
Hae-Gyum Ryu
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2017; 17(2): 168. CrossRef - Association of Changes in Mood Status and Psychosocial Well-Being with Depression During Interferon-Based Treatment for Hepatitis C
Jung-Seok Choi, Won Kim, Bo Kyung Sohn, Jun-Young Lee, Hee Yeon Jung, Sohee Oh, Sae Kyoung Joo, Hwi Young Kim, Yong Jin Jung
Psychiatry Investigation.2017; 14(3): 314. CrossRef - Relationship between Exercise Frequency and Stress in Korean Postmenopausal Women
Yoon Jeong Cho, Geon Ho Lee
Korean Journal of Stress Research.2016; 24(3): 161. CrossRef - Changes of quality of life and cognitive function in individuals with Internet gaming disorder
Jae-A Lim, Jun-Young Lee, Hee Yeon Jung, Bo Kyung Sohn, Sam-Wook Choi, Yeon Jin Kim, Dai-Jin Kim, Jung-Seok Choi
Medicine.2016; 95(50): e5695. CrossRef - A Predictive Model on Health Promotion Behavior in Women who Immigrate for Marriage
Namok Jeong, Myung Ha Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(5): 695. CrossRef - Balanced Scorecard for Performance Measurement of a Nursing Organization in a Korean Hospital
Yoonmi Hong, Kyung Ja Hwang, Mi Ja Kim, Chang Gi Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(1): 45. CrossRef - Health Behavioral Patterns Associated with Psychologic Distress Among Middle-Aged Korean Women
Hye-Sook Shin, Jia Lee, Kyung-Hee Lee, Young-A Song
Asian Nursing Research.2007; 1(1): 61. CrossRef - The Impact of Flooding on the Mental Health of Affected People in South Korea
Eun-Hee Chae, Tong Won Kim, Seon-Ja Rhee, Terrence David Henderson
Community Mental Health Journal.2005; 41(6): 633. CrossRef - The Relationship of Work Stress and Family Stress to the Self‐Rated Health of Women Employed in the Industrial Sector in Korea
Gwang Suk Kim, Won Jung Cho, Chung Yul Lee, Lucy N. Marion, Mi Ja Kim
Public Health Nursing.2005; 22(5): 389. CrossRef
- Polygenic overlap between subjective well-being and psychiatric disorders and cross-ancestry validation
- 1,108 View
- 20 Download
- 22 Crossref

- Elderly Sleep Pattern and Disturbing Factors Before and After Hospitalization
- Mi Young Kim, Sung Hee Cho, Sang Mi Lee, Su Jung Jung, Kyung Sook Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(1):61-71. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.1.61
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Sleep is a necessity for survival, Disruption of sleep leads to numerous adverse physiological and psychological consequences. These could be particularly undesirable for older patients, who are subject to many additional factors. But there is limited research related to hospitalized elderly in Korea. The purpose of the study is to explore sleep patterns and disturbing factors of before and after hospitalization, in order to present basic information regarding elderly sleep to develop nursing intervention. The sample consisted of 32 elderly men and women between the ages of 60 and 87 years. Data collection was done from September to November 1997. Measures of sleep patterns and related factors were obtained from self-reported sleep questionnaires. Analysis of data was done by use of t-test, paired t-test, ANOVA, and Pearson Correlation Coefficient. The results of this study were summarized as follows : 1. In comparison between before and after admission of their sleep pattern, "sleep onset" tends to be delayed and nocturnal sleep time was significantly reduced. So, hospitalized elderly reported less total sleep time than before admission. 2. Regarding the sleep disturbing factors, medication(hypnotics : 37.5%), physiological factor(snoring : 59.4%) environmental factor(pillow : 78.1%), emotional factor(anxiety related to disease : 37.5%), and illness factor(fatigue : 34.7%) were reported. 3. Significant differences in gender were found. Men had more disturbances in sleep than women owing to difficulty in falling a sleep and lack of nocturnal sleep. Women consumed more sleep inducing drugs. Significant increase was reported in napping during the day with increasing age. 4. Significant differences between good sleepers and poor sleepers were found for the following variables : nocturnal sleep time, total sleep time, bed time, sleep onset latency time, sleep latency time after nocturnal awakening, time spent in bed upon arousal, environmental factors, and emotional factors. In conclusion, it was found that the quantity and quality of sleep were significantly altered in hospitalized elderly, but adequate strategies for better sleep were not practiced. Further research is needed to develop intervention strategies to promote sleep and to prevent sleep problems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sleep patterns and it's influencing factors of hospitalized elderly in long-term care hospital
Hyo-Yoel Jang, Tae-Im Kim
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2016; 27(3): 773. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Sleep of Disturbance Factors Sleep by Inpatients
Mi-Ryon Lee, Mun-Hee Nam
Journal of Korean Clinical Health Science.2014; 2(3): 176. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Sleep of Elderly Women
Sohyune R. Sok, Jin Yi Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(1): 119. CrossRef - Effects of Eye Protective Device and Ear Protective Device Application on Sleep Disorder with Coronary Disease Patients in CCU
Yoon Jung Koo, Hyo Jung Koh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(4): 582. CrossRef
- Sleep patterns and it's influencing factors of hospitalized elderly in long-term care hospital
- 762 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Lifestyles Effects on Stroke Risk in Different Regions in Korea
- Smi Choi-Kwon, Eun Kyung Kim, Mi Yang Jeon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(3):729-738. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.3.729
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Stroke is a leading cause of death in Korea. Early measurement to prevent stroke are extremely important since it has no cure. Korean might have different risk factors since their dietary habit and socio-economical status differ from most western countries. However, the risk factors for stroke in Korea have not yet been identified. Moreover, the lifestyle of health Korean adults has not been investigated. In this study we investigate the life of health adults living in Seoul and rural areas and compare the life style of the two. METHODS: One hundred seventy one subjects were studies. Among the subjects studied, 128 were from Seoul, the other 43 were from the country area. The age of the subjects was limited to over 40 years. Blood pressure, fast blood sugar, and cholesterol were measured. The subjects' height, weight, body mass index total body fat, skinfolds thickness of triceps, subscapular and abdomen were measured to determine obesity. Using a structured interview, we assessed : sodium intake, physical activity and exercise, consumption of vegetables, fat, fish and fruits. The results of the two groups were compared. RESULTS: There were no statistical differences in age and education between the two groups of subjects. The mean age of the subjects were 66 years old. The subjects residing in rural areas had a higher intake of sodium(p<0.05), lower physical active(P<0.05), and higher BMI and body fat(p<0.05) as compared to the subjects in Seoul. Subjects with hypertension were between 24% and 33% and the prevalence of hypertension was the highest was the highest when compared to the prevalence of DM, or hypercholesterolemia. However, the prevalence of hypertension, DM, hypercholesterolemia, were not significantly different in these areas. CONCLUSION: our results show that subjects living in rural areas eat more salty food, exercise less and tend to be obese. The finding of this study lead to speculation that Korean living in rural areas have less information about the effects diet of diet on health than city dwellers do. General health and nutrition education programs aimed at the prevention of stoke and other such conditions for rural area Korean may close the risk factor gap between rural and urban dwellers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Korean Version of Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly (K-PASE)
Myoung-Ae Choe, Jeungim Kim, Mi-yang Jeon, Young-Ran Chae
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(1): 47. CrossRef - Echocardiographic Plains Reflecting Total Amount of Epicardial Adipose Tissue as Risk Factor of Coronary Artery Disease
Jung-Won Hwang, Un-Jung Choi, Sung-Gyun Ahn, Hong-Seok Lim, Soo-Jin Kang, Byoung-Joo Choi, So-Yeon Choi, Myeong-Ho Yoon, Gyo-Seung Hwang, Seung-Jea Tahk, Joon-Han Shin, Doo-Kyung Kang
Journal of Cardiovascular Ultrasound.2008; 16(1): 17. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Korean Version of Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly (K-PASE)
- 781 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Nursing Students' Perceptions on Diet and as Environmental Factors Related to Cancer Risk Factors
- Hae Kyung Lee, Seong Joo Cheon, Mi Hye Hwang, Soon Rim Suh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(1):193-200. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.1.193
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identify how students majoring in nursing perceive cause of cancers and the effects of diet for preventing cancers. Data for the study were collected by 651 nursing students, who were registered in the second and third year in three technical colleges and third and fourth year in two universities. The research instruments included items on general characteristics of subjects, items about the degree of perception of the frequency of cancer onset and items on the perception of mortality, risk factors, preventive diets, knowledge, and high risk factor for cancer in specific body areas. The findings of this study are as follows : 1. Almost all subjects(92.8%) reported that the frequency of cancer onset increases and that it is 93.9% for people over 40. Degree of perception about cancer mortality was low at 33.0%. 2. As far as the perception of risk factors for cancer onset was concerned, smoking, stress, heredity, family history, and alcohol were rated high, over 80.0%. Risk factor in clouding, virus, hormones, pesticides were rated as low. 3. As to the perception of risk factor for body area as associated with diet salted and scorched food were rated at 44.5% for stomach cancer, alcohol, 50.4% for liver cancer, smoking, 72.8% for lung cancer, pregnancy times, 25.3%, and marriage age, 23.0% for uterine cancer, and no delivery experience, 40% for breast cancer. 4. The knowledge score for cancer was between 12 and 36, with a mean score of 26.75(SD=4.13). There was a statistically significant difference between experience in caring for cancer patients during clinical practice and knowledge score(t=3.09, p=.002).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Literature Review of Structural Equation Models for Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention in Korea
Eunhye Kim, Jinhyun Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2014; 11(2): 109. CrossRef - Cancer Risk Perception and Cancer Related Health Behavior in College Students
Gye Young Shin, Mee Kyoung Joo
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2010; 10(2): 137. CrossRef
- Literature Review of Structural Equation Models for Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention in Korea
- 712 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Discriminative Factor Analysis of Juvenile Delinquency in South Korea
- Hyun Sil Kim, Hun Soo Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(8):1315-1323. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.8.1315
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The present study was intended to compare difference in research variables between delinquent adolescents and student adolescents, and to analyze discriminative factors of delinquent behaviors among Korean adolescents.
Methods The research design of this study was a questionnaire survey. Questionnaires were administered to 2,167 adolescents (1,196 students and 971 delinquents), sampled from 8 middle and high school and 6 juvenile corrective institutions, using the proportional stratified random sampling method. Statistical methods employed were Chi-square, t-test, and logistic regression analysis.
Results The discriminative factors of delinquent behaviors were smoking, alcohol use, other drug use, being sexually abused, viewing time of media violence and pornography. Among these discriminative factors, the factor most strongly associated with delinquency was smoking (odds ratio: 32.32). That is, smoking adolescent has a 32-fold higher possibility of becoming a delinquent adolescent than a non-smoking adolescent.
Conclusions Our findings, that smoking was the strongest discriminative factor of delinquent behavior, suggest that educational strategies to prevent adolescent smoking may reduce the rate of juvenile delinquency. Antismoking educational efforts are therefore urgently needed in South Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Public discourse on substance use behavior as a driver of public policy: a scoping review of South Korean academic and official literature
Meekang Sung, Jihye Han, Carrie G. Wade, Vaughan W. Rees
Addiction Research & Theory.2025; 33(4): 312. CrossRef - Parental Management on Juvenile Delinquency through Low Self-control And Misperception
Hyunin Baek, Carlos E. Posadas, Dae-Hoon Kwak
Deviant Behavior.2023; 44(4): 510. CrossRef - The Consequences of Maltreatment on Children’s Lives
Deborah Fry, Amalee McCoy, Diane Swales
Trauma, Violence, & Abuse.2012; 13(4): 209. CrossRef
- Public discourse on substance use behavior as a driver of public policy: a scoping review of South Korean academic and official literature
- 900 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Developing an Instrument to Measure Climacteric Symptoms among Korean and Japanese Women
- AeRi Song, Kazuyo Oishi, Euy Hoon Suh, Harumi Miyahara, Hisayoshi Nakajima, Yuko Nakao, Miyuki Araki, Makiko Yamasaki
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(4):637-644. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.4.637
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to construct a measurement instrument for climacteric symptoms among Korean and Japanese women.
Methods From Dec. 1st of 2003 to March 30th of 2004, in-depth interviews were made with 26 women (15 in Jinju, Korea and 11 in Nagasaki, Japan) aged from 45 to 59 years who had not taken hormone replacement therapy to relieve the climacteric symptoms. A draft questionnaire with 45 items was constructed on the basis of the interview data and literature review. Three obstetricians, three PhDs in nursing science, and a chief nurse who was exclusively in charge of the climacteric management, examined the draft questionnaire to evaluate content validity. After deletions 39 items remained for a preliminary questionnaire. A survey was conducted by using a convenient sampling method in Jinju of Korea and Nagasaki of Japan during the period from April 1st, 2004 to July 10th, 2005.
Results Factor analysis identified 4 factors, which were “mental and psychological symptoms”, “physical symp-toms”, “loss of autonomic nervous system symptoms”, “sexual symptoms”. These four factors explained 46.9% of total variance.
Conclusions The results demonstrated that climacteric symptom scale was multidimensional, and the reliability and validity of the scale was supported.
- 562 View
- 2 Download

- Comparison of Cardiovascular Risk Profile Clusters Among Industrial Workers
- Seon Young Hwang, Ji Hyun Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(8):1500-1507. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.8.1500
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify subgroups of the physical and behavioral risk profiles for cardiovascular disease among industrial workers, and to examine predicting factors for the subgroups.
Sample and Methods Health records of 2,616 male and female workers aged 19-56 years who were employed in an airplane manufacturing industry were analyzed. Data were analyzed using the Latent class cluster analysis.
Results Four different clusters (two high-risk groups, one low-risk group, and one normal group) were found and these clusters were significantly different by age, gender, and work type (p<.05). The two high-risk groups had higher chances of drinking alcohol, elevated BMI, FBS, total cholesterol, having hypertension, and were significantly older, and had relatively high chances of being day workers rather than other groups. The low-risk group had higher chances of drinking alcohol, higher BMI and total cholesterols compared to normal group, and highest portions of current smokers and shift workers in the four clusters and their mean BP was within prehypertension criteria.
Conclusion Industrial nurses should guide the lifestyle behaviors and risk factors of the high risk groups for CVD and need to intervene early for behavioral change for the low-risk group who are young and shift workers. Age, and work environment should be considered in planning for targeted preventive interventions for industrial workers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated with Blue-collar Workers' Risk Perception of Cardiovascular Disease
Won Ju Hwang, OiSaeng Hong, Mi Ja Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(7): 1095. CrossRef
- Factors Associated with Blue-collar Workers' Risk Perception of Cardiovascular Disease
- 770 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


