Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse articles > Previous issues
Research Papers
- Development and evaluation of a question-answering chatbot to provide information for patients with coronary artery disease after percutaneous coronary intervention
- Geunhee Lee, Yun Hee Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):153-164. Published online May 13, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24128
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
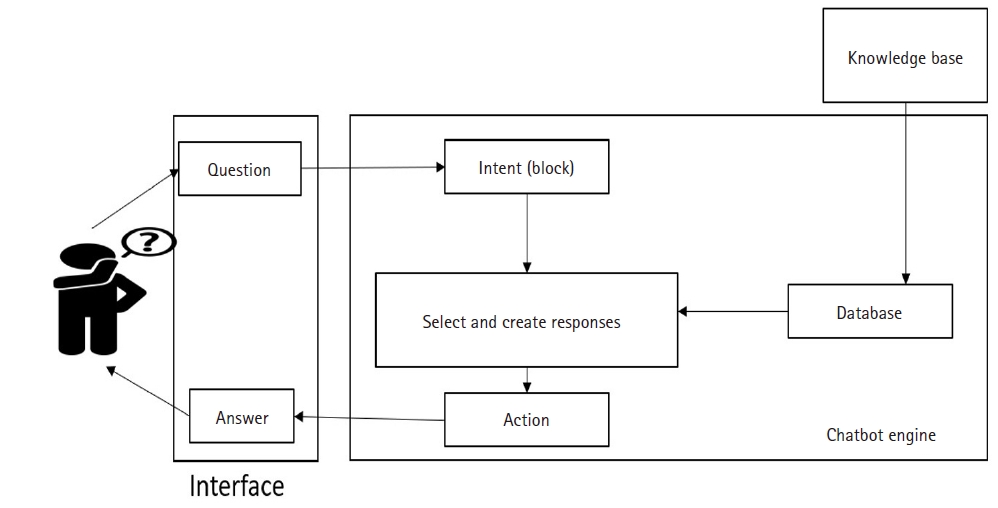
This study aimed to develop a question-answering chatbot that provides accurate and consistent answers to questions that may arise during the recovery process of patients with coronary artery disease after percutaneous coronary intervention, and to evaluate the chatbot.
Methods
The chatbot was developed through the stages of analysis, design, implementation, and evaluation. It was evaluated by five experts, and the user experience was evaluated by 27 patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention. Furthermore, chatbot utilization was analyzed based on user experience logs.
Results
The chatbot was constructed as a question-answering database that included three categories: coronary artery disease, percutaneous coronary intervention, and post-intervention management. The question-answering chatbot, referred to as the “Cardiovascular Strong” channel, has been launched and implemented. An expert evaluation of the chatbot revealed no usability issues or necessary modifications. The overall result of the user experience evaluation was 4.26 points. Based on the user experience log, the question-answer accuracy was 84.6%, and medications during post-intervention management were the most frequently searched topic, accounting for 110 cases (20.8%) out of a total of 528.
Conclusion
The chatbot that was developed to provide information via real-time answers to questions after the intervention can be easily accessed in clinical settings with no time or space constraints. It also will contribute to providing accurate disease-related information via the familiar KakaoTalk platform. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Generative AI at the Bedside: An Integrative Review of Applications and Implications in Clinical Nursing Practice
Adrianna L. Watson, Carmel Bond, Helen Aveyard, Graeme D. Smith, Debra Jackson
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Generative AI at the Bedside: An Integrative Review of Applications and Implications in Clinical Nursing Practice
- 2,365 View
- 249 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- A non-face-to-face diabetes self-management program based on self-efficacy theory and health literacy: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Jung Hee Lee, Soo Jin Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):165-177. Published online May 23, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to assess the impact of a non-face-to-face diabetes self-management program based on self-efficacy theory and focusing on health literacy.
Methods
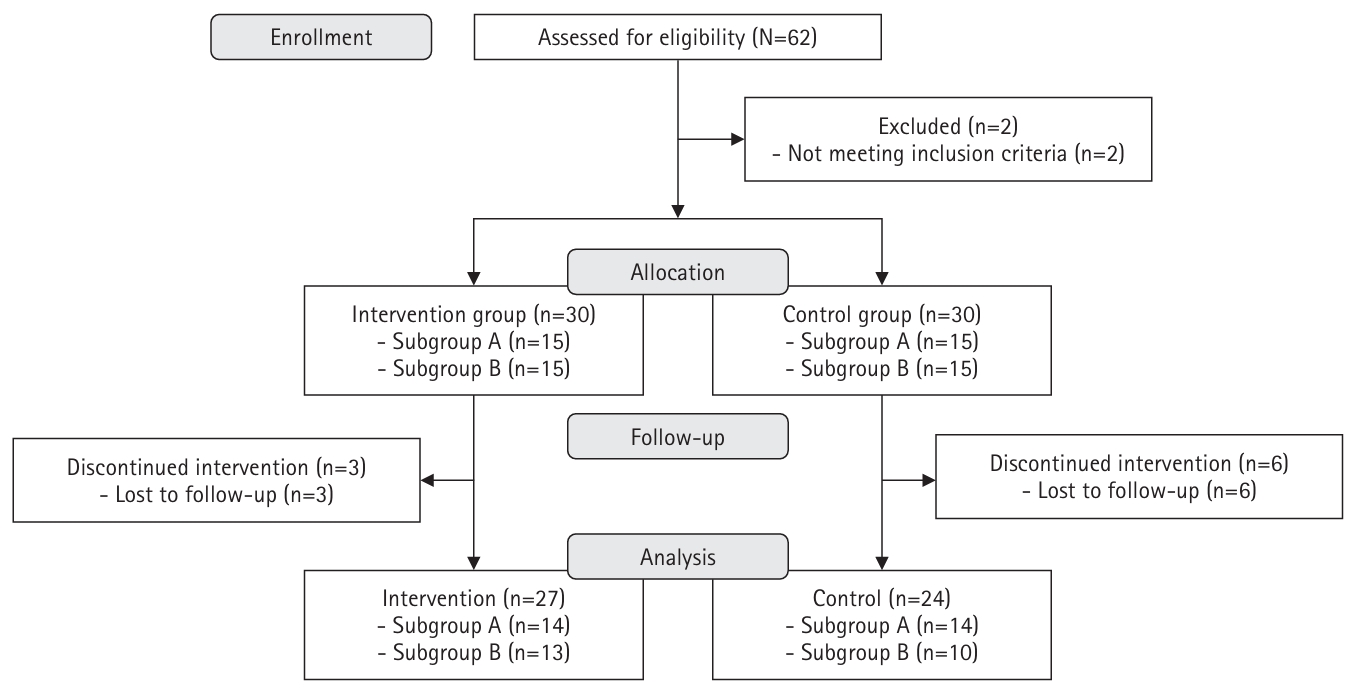
A quasi-experimental, nonequivalent control group pre–post design was used. Participants from a community health promotion center were included if they (1) were 30–70 years of age, (2) had type 2 diabetes with glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥6.5%, and (3) had internet access via computers or mobile devices. The 8-week program was developed based on self-efficacy theory, and it included virtual education using an online platform, telephone counseling, videos, and social networking site activities considering health literacy. Fasting blood glucose levels, HbA1c levels, diabetes self-efficacy, social support, depression, and self-management behaviors were assessed. Data were analyzed using the independent t-test, paired t-test, and others.
Results
Post-test results showed that the intervention group had significantly lower fasting blood glucose levels and improved diabetes self-efficacy, social support, and self-management behaviors compared with the control group. An analysis of the pre-to-post changes in scores indicated that the intervention group had significantly greater improvements in fasting blood glucose levels, diabetes self-efficacy, and overall diabetes self-management behaviors than those observed in the control group.
Conclusion
Non-face-to-face programs based on self-efficacy theory that consider health literacy can provide effective diabetes management support to patients when in-person diabetes management at community health centers is challenging.
- 3,339 View
- 243 Download

- Effectiveness of a mobile application for tracking symptoms and enhancing symptom management among breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy in Bangkok, Thailand: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Duangrat Kaveenuntachai, Supawan Jaiboon, Bualuang Sumdaengrit, Chureeporn Silaguntsuti, Arveewan Vittayatigonnasak, Pornchan Sailamai
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):178-190. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25011
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study evaluated the effectiveness of a mobile application in tracking symptoms and improving symptom management and quality of life (QoL) among breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in Thailand.
Methods
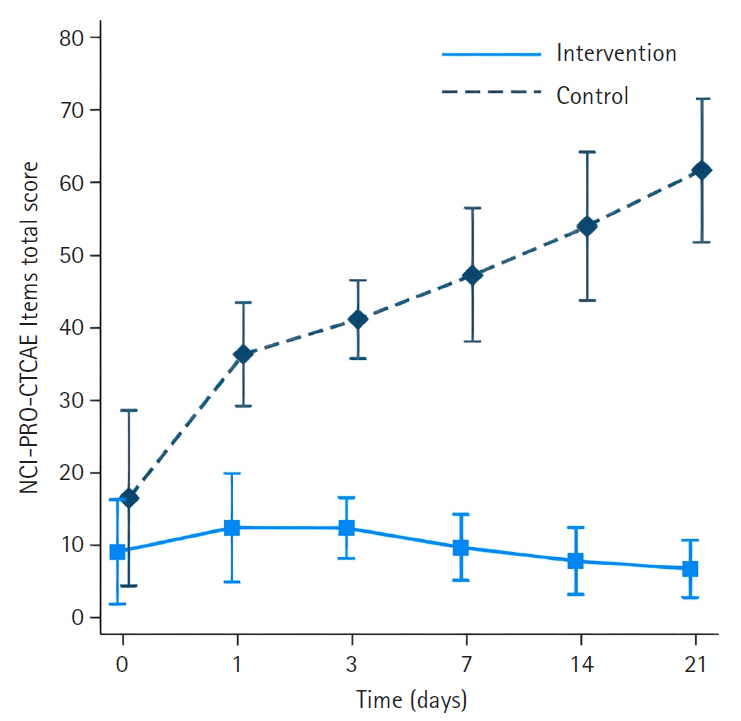
A non-randomized controlled trial was used, with 25 participants in the intervention group and 25 in the control group. Research instruments included a demographic data form, the NCI-PRO-CTCAE Items-Thai-Thailand version 1.0, and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Core Questionnaire and Breast Cancer-Specific Module.
Results
The intervention group had significantly less severe side effects than the control group, with mean differences of –23.33 (95% confidence interval [CI], –27.82 to –18.83) on day 1, –28.18 (95% CI, –33.22 to –23.14) on day 3, –34.63 (95% CI, –40.18 to –29.08) on day 7, –42.56 (95% CI, –48.72 to –36.40) on day 14, and –51.31 (95% CI, –58.13 to –44.48) on day 21 (p<.001 for all). On day 21, participants in the intervention group reported significantly higher scores in the Global Health QoL and Functional Scales compared to the control group (p<.001). Additionally, intervention group participants reported lower scores on the Symptom Scales and higher scores on the Functional Scales than those in the control group (p<.001).
Conclusion
The ChemoPro application helped manage chemotherapy-related symptoms and was associated with improved symptom monitoring and QoL. Nonetheless, the study was limited by a small sample size and restriction to Android users. Future research with larger and more diverse populations is recommended before broader implementation in clinical practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of a digital health intervention on the supportive care needs and quality of life in Mexican patients with breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial
Saúl Eduardo Contreras-Sánchez, Svetlana V. Doubova, Rocío Grajales-Álvarez, Ricardo Villalobos-Valencia, Abdel Karim Dip-Borunda, José Gustavo Nuñez-Cerrillo, Alma Diana Huerta-López, Álvaro José Montiel-Jarquín, Arturo García-Galicia, Enrique Isay Talam
BMC Cancer.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effectiveness of a digital health intervention on the supportive care needs and quality of life in Mexican patients with breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial
- 4,253 View
- 215 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effects of a lifestyle intervention for men in infertile couples in South Korea: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Yun Mi Kim, Ju-Hee Nho
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):191-204. Published online April 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of an interaction model of client health behavior (IMCHB)-based lifestyle intervention on health-promoting behaviors, infertility stress, fertility-related quality of life, and semen quality in men in infertile couples.
Methods
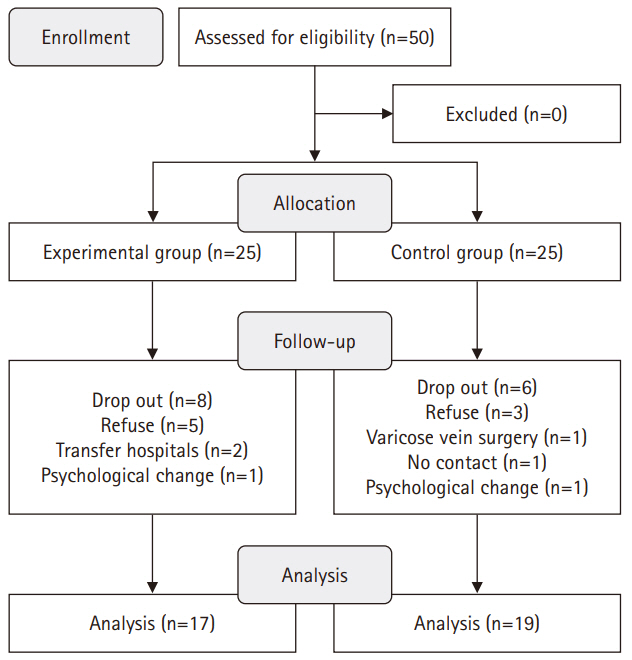
This study used a quasi-experimental, non-equivalent control group, pretest-posttest design, with participants divided into an experimental group (n=17) and a control group (n=19). The 16-session, 8-week intervention included components such as reproductive health education, physical activity, nutritional management, and stress management. Data collection occurred between July 1, 2021 and September 27, 2022. The outcomes measured included health-promoting behaviors, infertility stress, fertility-related quality of life, and sperm quality (volume, total motility, immobility, concentration, and normal morphology).
Results
The experimental group showed significant improvements in health-promoting behaviors (z=–2.27, p=.023) and reductions in infertility stress (t=–2.40, p=.022) compared to the control group. Total sperm motility (F=4.39, p=.045) and normal morphology (z=2.86, p=.017) were also significantly higher in the experimental group than in the control group.
Conclusion
The IMCHB-based lifestyle intervention significantly increased health-promoting behaviors, reduced infertility stress, and improved key sperm parameters, indicating its effectiveness in supporting the reproductive health of men in infertile couples. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychological Stress and Male Infertility: Oxidative Stress as the Common Downstream Pathway
Aris Kaltsas, Stamatis Papaharitou, Fotios Dimitriadis, Michael Chrisofos, Nikolaos Sofikitis
Biomedicines.2026; 14(2): 259. CrossRef
- Psychological Stress and Male Infertility: Oxidative Stress as the Common Downstream Pathway
- 3,652 View
- 139 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Triglyceride-glucose parameters as predictors of diabetes mellitus incidence in Korean adults: a secondary analysis of a Prospective Cohort Study
- Yu Jin Park, Miseon Shin, Hyun Seon Jeon, Eun Hee Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):205-221. Published online April 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24108
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
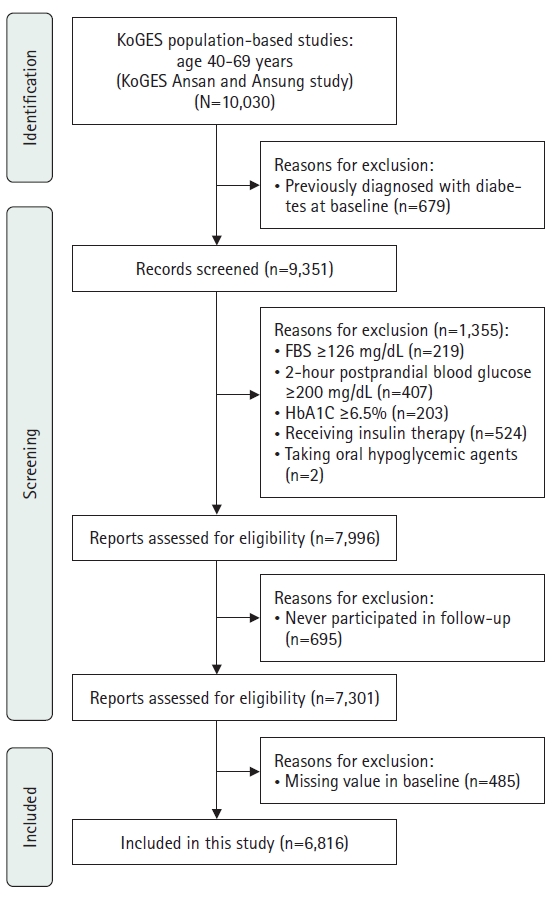
This study aimed to evaluate the association between triglyceride-glucose (TyG)–related parameters and the incidence of diabetes mellitus in Korean adults. Data were obtained from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES).
Methods
This secondary analysis examined data from 6,816 adults aged 40–69 years who participated in the KoGES from 2001 to 2020. TyG–related parameters, including the TyG index, TyG–body mass index (TyG–BMI), TyG–waist circumference (TyG–WC), and TyG–waist-to-height ratio (TyG–WHtR), were assessed. Cox proportional hazards models were employed to determine the association between these parameters and the incidence of diabetes mellitus, with adjustments made for demographic, lifestyle, and health-related characteristics.
Results
Higher levels of all TyG–related parameters were significantly associated with an increased risk of developing diabetes mellitus. Specifically, participants in the highest quartile of the TyG index, TyG–BMI, TyG–WC, and TyG–WHtR exhibited significantly higher hazard ratios for diabetes mellitus incidence compared with those in the lowest quartile (p<.001 for all). Notably, the TyG index demonstrated a stronger predictive value for diabetes mellitus than traditional measures such as the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance.
Conclusion
TyG–related parameters are robust predictors of diabetes mellitus incidence in Korean adults. These findings support the incorporation of TyG–related measures into clinical settings for the early identification and intervention of high-risk populations. Utilizing these parameters for early diagnosis and preventive strategies may significantly enhance diabetes mellitus management.
- 2,438 View
- 154 Download

- Impact of smoking on diabetes complications: a secondary analysis of the Korean National Health Insurance Service-health screening cohort (2002–2019)
- Seonmi Yeom, Youngran Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):222-235. Published online April 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24109
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
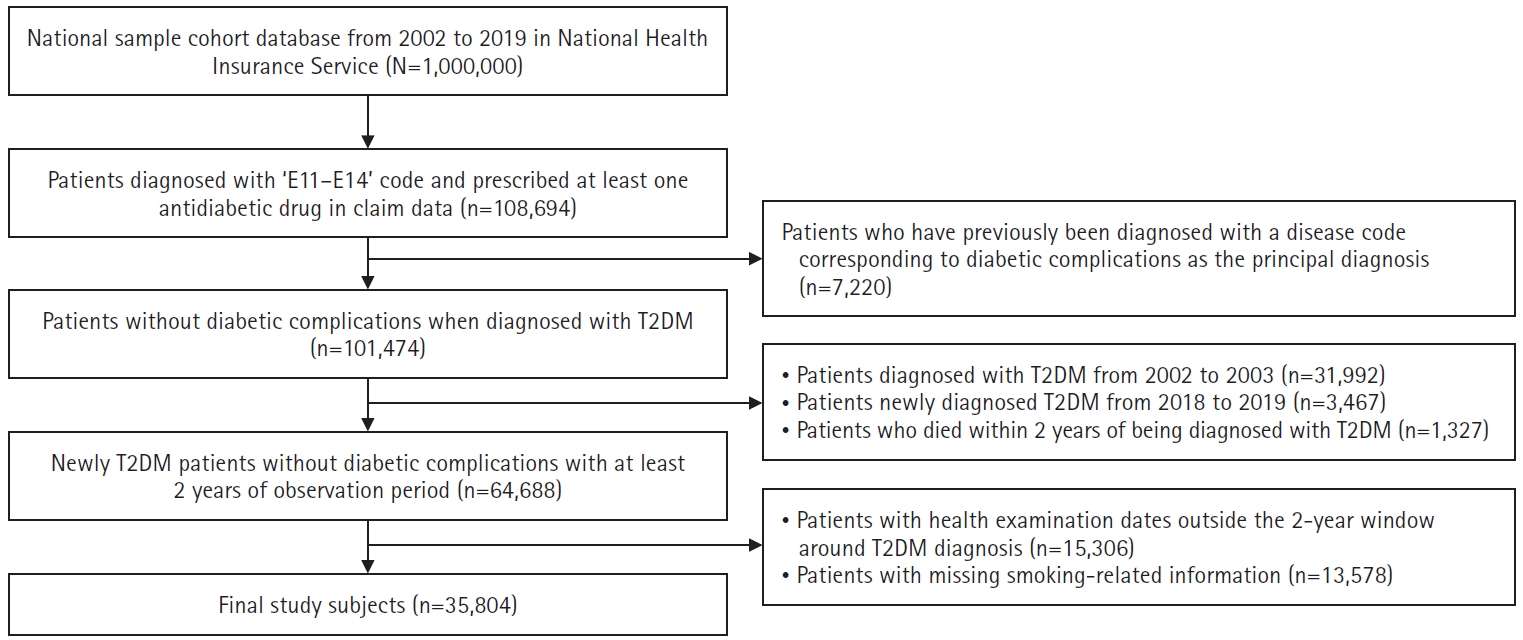
This study aimed to examine the effects of smoking on the incidence of macrovascular and microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods
We analyzed 35,804 patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes between 2004 and 2017 using the Korean National Health Insurance Service–National Health Screening Cohort (2002–2019). Smoking status was categorized into never, former, and current smoking, with further classification based on duration of smoking and daily smoking amount. We conducted survival analysis using a Cox proportional hazards model.
Results
Both former and current smokers had significantly elevated risks of macrovascular complications compared to non-smokers, with hazard ratios (HRs) of 1.60 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.49–1.66) and 1.10 (95% CI, 1.08–1.17), respectively. Long-term smokers (over 30 years) had significantly higher risks of both macrovascular (HR, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.29–1.42) and microvascular complications (HR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.30–1.42). Heavy smokers (over 2 packs/day) more frequently developed macrovascular (HR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.30–1.64) and microvascular (HR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.60–1.98) complications than never smokers. Notably, former smokers had increased risks of developing neuropathy (HR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.31–1.49), nephropathy (HR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.16–1.39), and retinopathy (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.39–1.60).
Conclusion
Patients with type 2 diabetes and a history of smoking are at higher risk of developing macrovascular and microvascular complications. Smoking cessation, along with reducing smoking duration and amount, is crucial for lowering these risks.
- 2,099 View
- 120 Download

- Analysis of the relative importance of key factors in nursing workforce management for pandemic response in general hospitals and long-term care hospitals
- Jeong Eun Cha, Eun Kyoung Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):236-248. Published online May 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
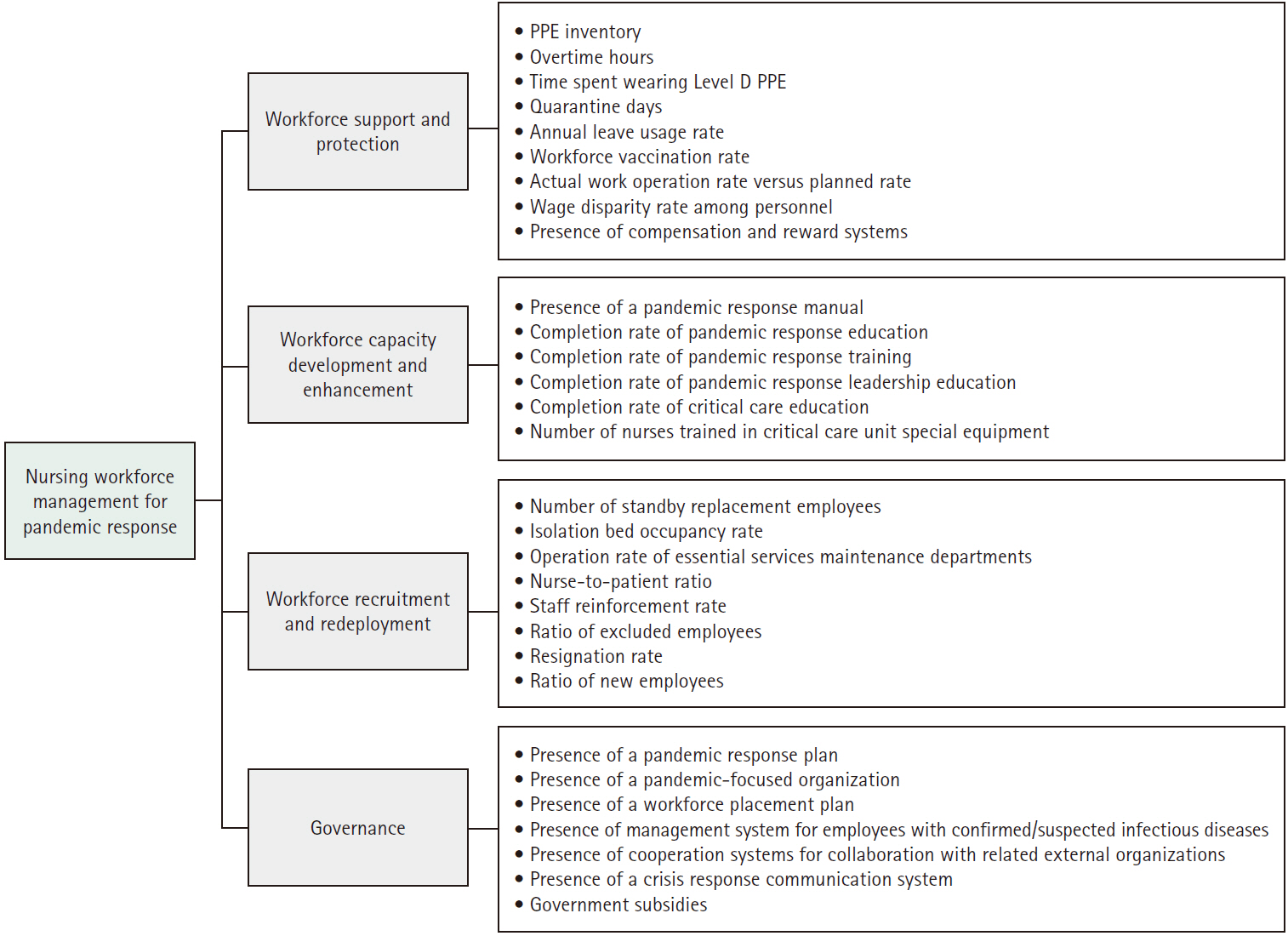
This study aimed to identify the key factors in nursing workforce management for pandemic response in general hospitals and long-term care hospitals and to analyze the relative importance of these factors.
Methods
A validity test was conducted with experts to select four categories and 30 key factors related to nursing workforce management for pandemic response. Surveys were collected from 25 nursing managers in general hospitals and 21 nursing managers in long-term care hospitals, and the relative importance of the key factors was analyzed using the analytic hierarchy process method.
Results
Differences were found between the two groups in the relative importance of nursing workforce management for pandemic response. Specifically, the highest-ranking category was “workforce recruitment and redeployment” for general hospitals, but “workforce support and protection” for long-term care hospitals. The most important factor regarding nursing workforce management was the “nurse-to-patient ratio” for both general and long-term care hospitals.
Conclusion
General and long-term care hospitals need to establish nursing workforce management strategies to effectively respond to pandemics with appropriate consideration of the relative importance and prioritization of key factors based on hospital characteristics.
- 1,952 View
- 74 Download

- Core domains for pre-registered nurses based on program outcomes and licensing competencies
- Soyoung Yu, Hye Young Kim, Jeung-Im Kim, JuHee Lee, Ju-Eun Song, Hyang Yuol Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):249-268. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify core domains for pre-registered nurses by comparing licensing competencies with program outcomes (POs) in undergraduate nursing education. This was accomplished in preparation for the transition of the Korean Nurse Licensing Examination (KNLE) from a tradition seven-subject format to a newly integrated, competency-based single-subject format that reflects current trends in nursing assessment.
Methods
A literature review and survey were conducted. From 828 studies retrieved via PubMed, CINAHL, and Google Scholar using keywords such as “newly graduated registered nurses” and “competency OR competence,” 18 were selected according to pre-established inclusion and exclusion criteria. Documents from national and international nursing organizations were included to extract relevant licensing competencies. We also reviewed POs from all undergraduate nursing schools in South Korea to align educational outcomes with the identified core domains.
Results
The core domains identified were clinical performance and decision-making, professional attitudes and ethics, communication and interpersonal skills, leadership and teamwork, quality improvement and safety, health promotion and prevention, and information technology and digital health. These domains showed strong alignment with POs under the fourth-cycle accreditation standards.
Conclusion
It concludes the seven core domains will be appropriate for evaluating pre-registered nurses in the integrated KNLE. Based on the seven identified core domains, expert consensus should be sought in the next phase to support the development of integrated, competency-based test items grounded in these domains.
- 4,067 View
- 156 Download

- Development of a communication self-efficacy scale for nurses: a psychometric validation study
- Kuem Sun Han, Jihye Shin, Soo Yeon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):269-284. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24129
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This methodological study was conducted to develop a scale to measure communication self-efficacy in nurses and examine its validity and reliability.
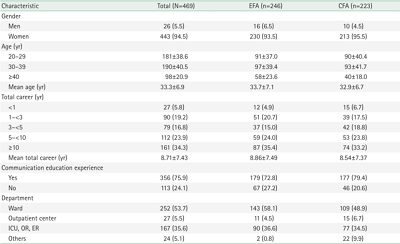
Methods
We selected 54 initial items from literature reviews and interviews with 10 clinical nurses. Thirty-two preliminary items were derived from consultations with 10 experts. To verify the scale’s factor structure, we conducted exploratory factor analysis (EFA), and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) among 469 nurses. Data were analyzed using item analysis, EFA, CFA, discriminant validity, convergent validity, and internal consistency using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 29.0 (IBM Corp.) and IBM SPSS AMOS ver. 20.0 (IBM Corp.).
Results
The scale consisted of 18 items with three factors (ability to apply therapeutic communication skills, crisis management capabilities, and communication competence), which explained 46.1% of the total variance. Convergent validity and discriminant validity were confirmed for the factors. CFA supported the fit of the measurement model comprising three factors (standardized root mean square residual=.04, root mean square error of approximation=.03, goodness of fit index=.92, Tucker-Lewis index=.97, comparative fit index=.98, normed fit index=.89, critical N=216). Internal consistency was confirmed by a Cronbach’s α coefficient of .91.
Conclusion
The communication self-efficacy scale for nurses is expected to measure communication self-efficacy among nurses. It will be useful for improving nurses’ professional communication abilities.
- 3,570 View
- 272 Download

- Development of a well-dying awareness scale for middle-aged adults in Korea: a mixed-methods study
- Yu Jin Jung, Eun Joung Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):285-300. Published online March 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a valid and reliable tool to measure awareness of well-dying among middle-aged adults.
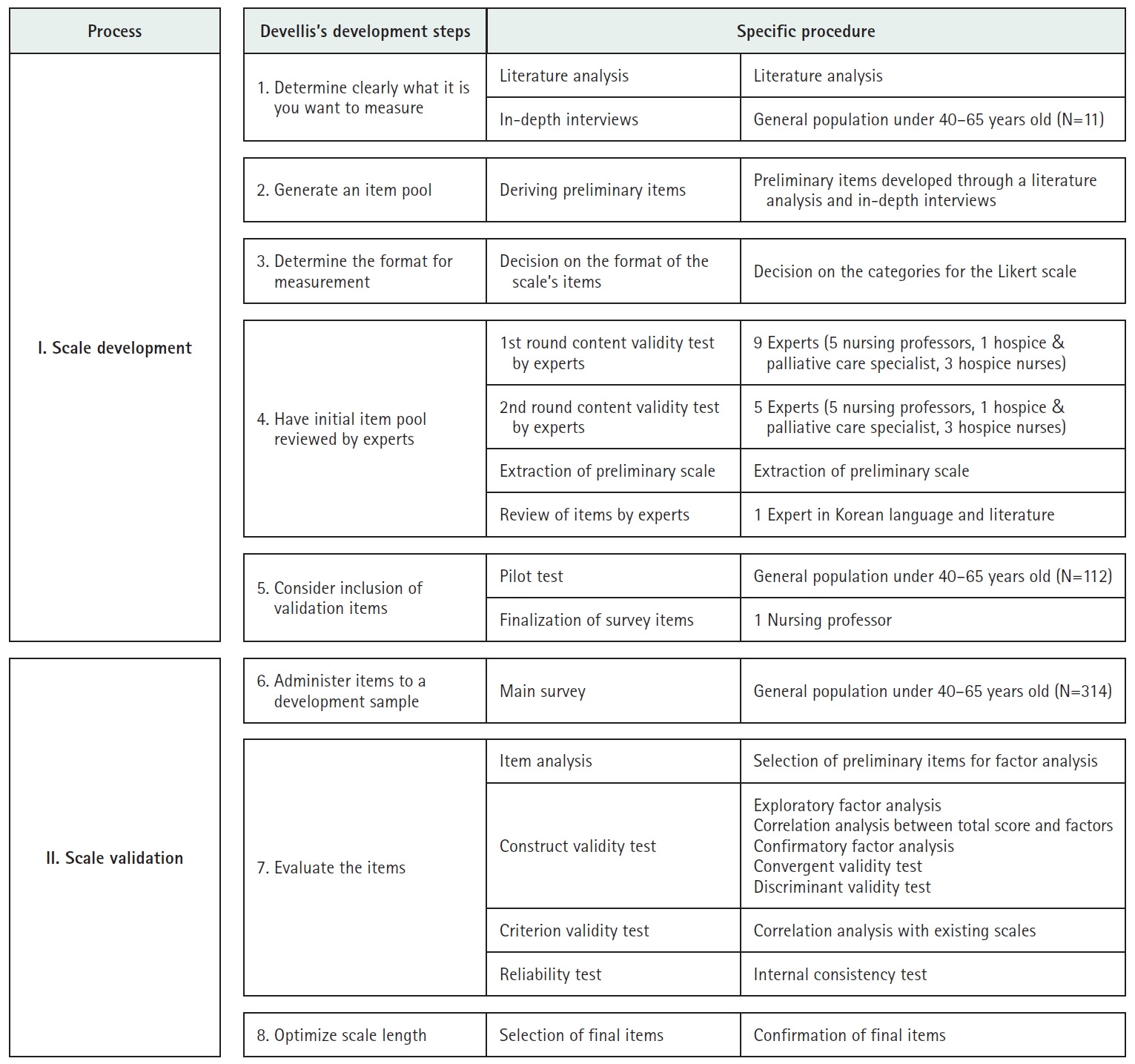
Methods
A mixed-methods approach was adopted, consisting of a qualitative phase to identify the characteristics of well-dying and a quantitative phase to validate the instrument with middle-aged participants. Initially, 76 items were generated through a literature review and in-depth interviews, and these were reduced to 35 items through expert validation. A pilot survey was conducted with 112 individuals aged 40–65, selected via quota sampling from 17 administrative regions in South Korea. Based on the pilot survey results, the instrument was refined to 32 items for the main survey. The main survey included 314 participants recruited through quota sampling in Busan and Ulsan Metropolitan Cities and Gyeongsang Region. Exploratory factor analysis (EFA), confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), and reliability testing were performed to validate the instrument.
Results
The final scale comprised 23 items across six factors. EFA demonstrated an explanatory power of 69.1%, with factor loadings ranging from 0.53 to 0.88. CFA confirmed the instrument’s validity, and reliability was established with a Cronbach’s α of .93.
Conclusion
This instrument is a validated and reliable tool for measuring middle-aged individuals’ awareness of well-dying. It can serve as an effective resource for evaluating and assessing well-dying awareness in the middle-aged population.
- 2,910 View
- 200 Download

- Successful aging among the elderly with mild cognitive impairment facing the crisis of old age: a grounded theory study
- Haeyun Shin, Suhye Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):301-316. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to understand experiences of successful aging experience in older adults with mild cognitive impairment.
Methods
The participants were 15 older adults with mild cognitive impairment who had experienced successful aging. Data were collected from January to October 2021 through individual deep, unstructured interviews. Data analysis was performed using Charmaz’s grounded theory method. In addition, the consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research checklist was used to ensure the quality of the study.
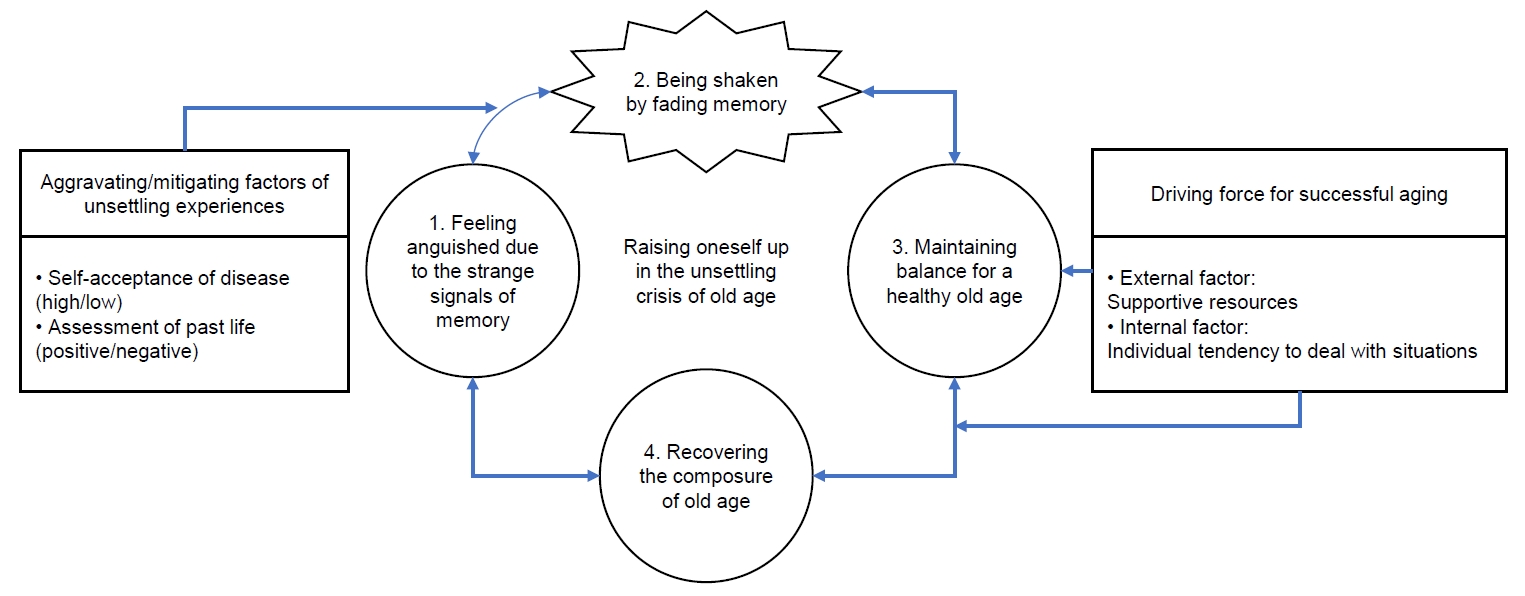
Results
The key category representing experiences of successful aging experience in older adults with mild cognitive impairment was “raising oneself up in the unsettling crisis of old age.” Four stages were derived: “feeling anguished due to the strange signals of memory,” “being shaken by fading memory,” “maintaining balance for a healthy old age,” and “recovering the composure of old age.”
Conclusion
Participants tried to successfully achieve aging while implementing their own plans and strategies in the midst of the challenges of old age, when the mind and body were unsettled by mild cognitive impairment. The results of this study provide a deep understanding of experiences of successful aging in older adults with mild cognitive impairment, potentially contributing to the development and implement of nursing intervention programs to promote the successful pursuit of aging in this population.
- 2,254 View
- 113 Download

Review Paper
- A review of domestic and international contexts for establishing a communication platform for early-career nurse scientists
- Jeung-Im Kim, Jin-Hee Park, Hye Young Kim, Mi Yu, Sun Joo Jang, Yeonsoo Jang, Sangeun Jun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):317-325. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25041
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
As nursing continues to advance through digital health, clinical specialization, and interdisciplinary research, early-career nurse scientists are central to advancing innovation. However, Korea lacks a structured platform to support their research, collaboration, and career development. This review aimed to identify the needs of early-career nurse scientists and examine international best practices to guide the creation of an effective communication platform.
Methods
This study involved a secondary analysis of the final report from the project “Establishment of a communication platform for young nursing scientists,” carried out by the Korean Society of Nursing Science. The report comprises data from focus group interviews with domestic graduate students and early-career researchers, a literature review of international communication and support systems, and a global policy analysis related to young nursing scientists. Based on this report, the present review synthesizes key findings and draws implications for the development of a communication platform in Korea.
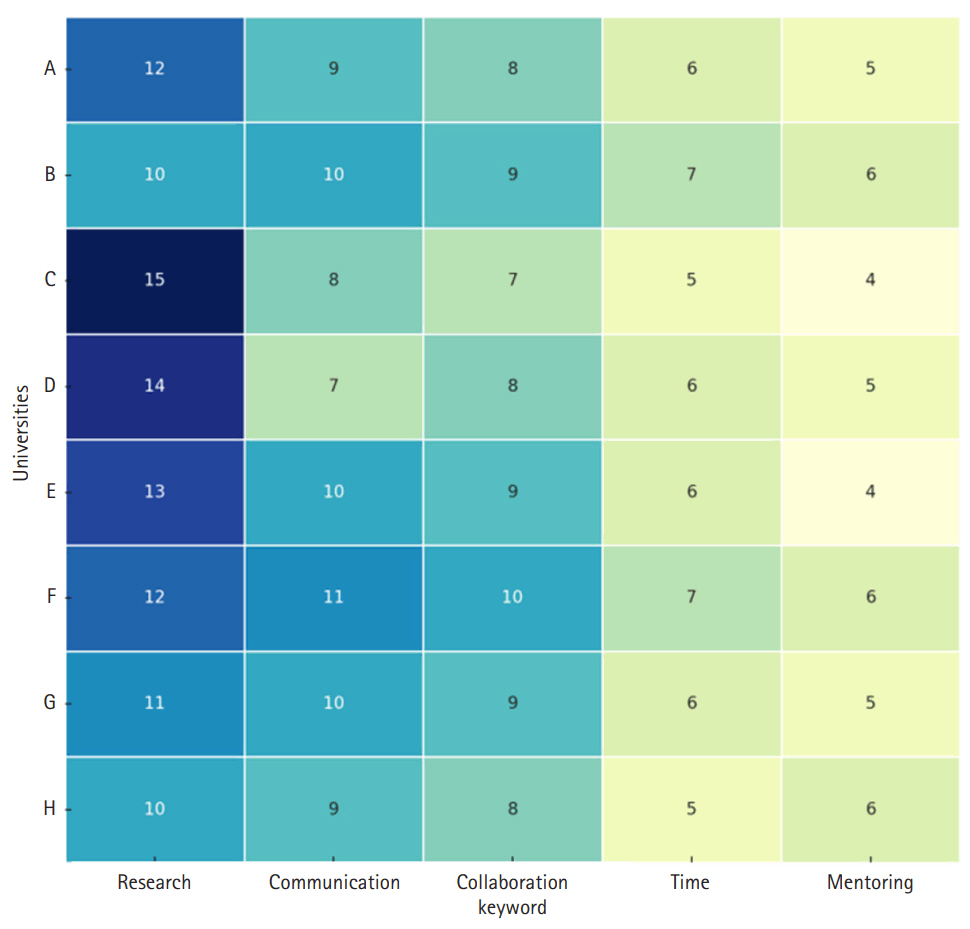
Results
International examples, such as grant writing programs, mentoring initiatives, and digital collaboration hubs, showed positive outcomes in strengthening research capacity and promoting the professional growth of nurse scientists. Based on these findings, key considerations for platform development include: (1) establishing clear leadership and a participatory governance model; (2) providing demand-driven content such as research guides, mentoring, and mental health resources; (3) implementing mechanisms to ensure sustainability, content quality, and user data protection; and (4) designing an integrated platform that fosters synergy across research, policy development, education, and global networking.
Conclusion
A digital platform for early-career nurse scientists should function not merely as an information portal, but also as dynamic infrastructure for collaboration, mentorship, and growth. It is recommended that the Korean Society of Nursing Science spearhead this initiative, with governmental support, to enhance the research capacity and expand the global engagement of Korean nursing scientists.
- 2,370 View
- 80 Download

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION



 First
First Prev
Prev


