Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Risk factors for the readmission of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hyerim Ji, Sun-Kyung Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):634-650. Published online November 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25072
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
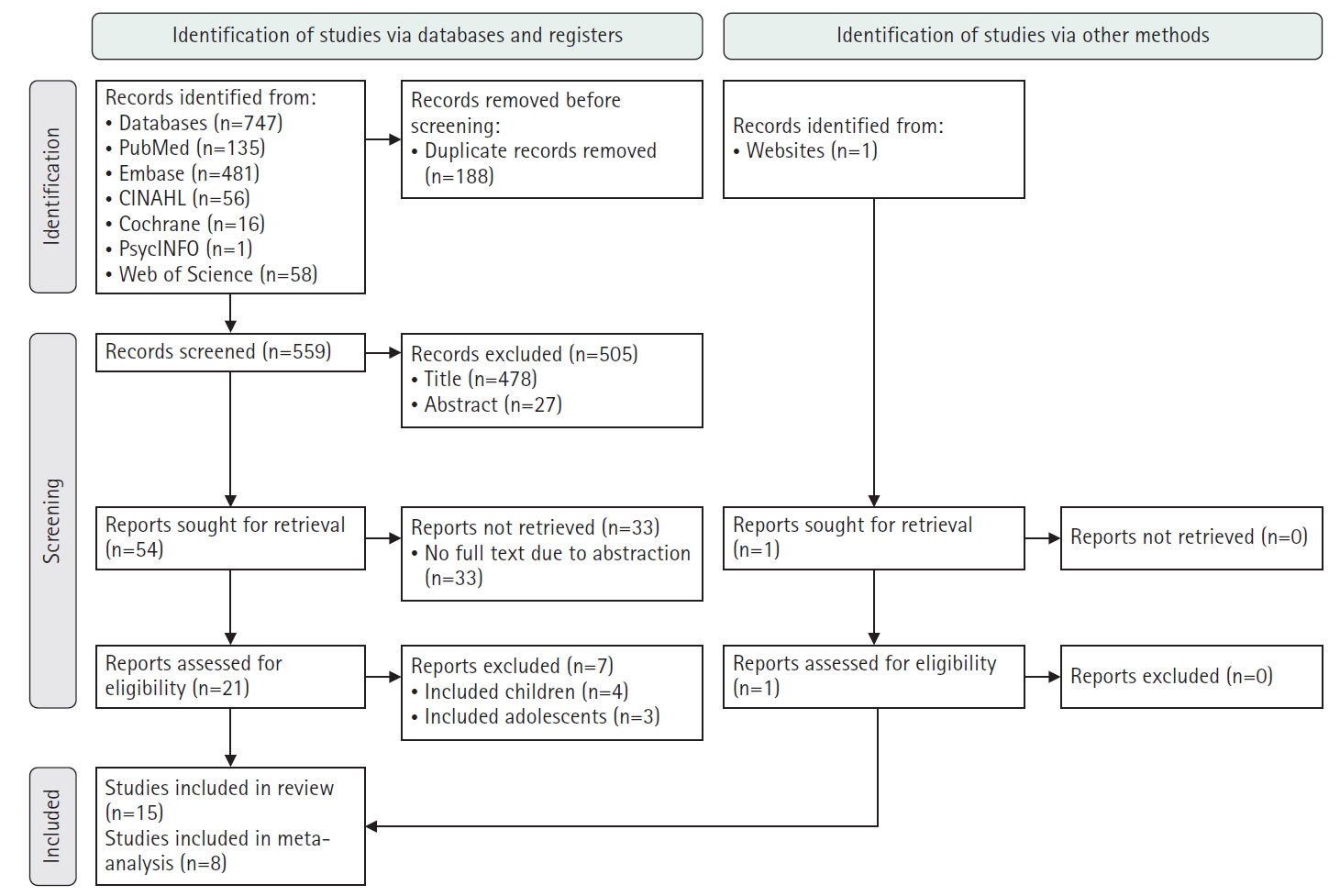
This study aimed to identify risk factors associated with the readmission of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
A systematic literature review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines. Relevant studies were retrieved from international databases (PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Web of Science) and Korean databases (RISS, KoreaMed, KMbase, KISS, and DBpia). Study quality was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Meta-analysis was performed using a random-effects model with the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman adjustment to account for the limited number of studies and heterogeneity.
Results
Fifteen studies were included in the review, and eight were eligible for meta-analysis. From the systematic review, 21 risk factors for DKA readmission were identified and categorized into five domains: demographic, socioeconomic, diabetes-related, comorbidity, and health-behavioral factors. In the meta-analysis, significant risk factors included low income, psychiatric disorders, and discharge against medical advice.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that DKA readmissions result from the complex interplay of multiple clinical and social factors. By identifying these risk factors and suggesting risk-stratification criteria, the findings may support the development of tailored interventions, such as self-management education, integrated mental health care, structured discharge planning, and coordinated post-discharge follow-up.
- 1,183 View
- 170 Download

- Serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression on the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety in high-risk pregnant couples of South Korea
- Mihyeon Park, Sukhee Ahn
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):19-33. Published online February 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24070
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
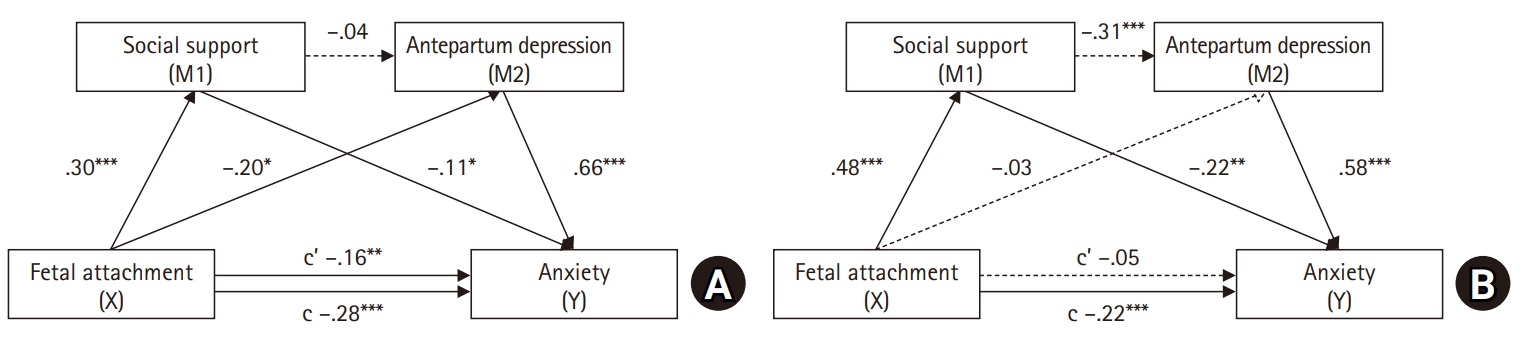
This study examined the direct effects of fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression on anxiety in pregnant women with high-risk pregnancy-related conditions and their husbands. Furthermore, it aimed to explore the serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression in the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety.
Methods
A survey-based study was conducted among pregnant women diagnosed with high-risk pregnancy conditions at 24–32 weeks and their husbands, recruited from a pregnant women’s online community between January 20, 2021 and July 20, 2022. Data were collected from 294 individuals (147 couples) using self-report questionnaires. Correlations between variables were analyzed using the IBM SPSS software ver. 26.0 (IBM Corp.), and the mediation effects were assessed using the PROCESS macro, model 6.
Results
In the maternal model, maternal-fetal attachment directly affected anxiety (p=.005), with antepartum depression partially mediating this relationship (95% confidence interval [CI], –0.26 to –0.01). In the paternal model, paternal-fetal attachment had no direct effect on anxiety (p=.458). However, social support and antepartum depression fully mediated the relationship between paternal-fetal attachment and anxiety (95% CI, –0.14 to –0.03).
Conclusion
The findings indicate that social support in the relationship between fetal attachment and depression in high-risk pregnant women and their partners can have direct or indirect effects on the negative emotions of high-risk pregnant couples. It is necessary to assess the level of anxiety in couples experiencing high-risk pregnancies and provide comprehensive nursing interventions that address fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression in order to reduce anxiety.
- 2,578 View
- 247 Download

- Psychometric Properties of the Fall Risk Perception Questionnaire-Short Version for Inpatients in Acute Care Hospitals
- Jeeeun Choi, Sujin Lee, Eunjin Park, Sangha Ku, Sunhwa Kim, Wonhye Yu, Eunmi Jeong, Sukhee Park, Yusun Park, Hye Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):151-161. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23127
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Patients’ perception of fall risk is a promising new indicator for fall prevention. Therefore, a fall risk perception questionnaire that can be used rapidly and repeatedly in acute care settings is required. This study aimed to develop a short version of the fall risk perception questionnaire (Short-FRPQ) for inpatients.
Methods
For the psychometric measurements, 246 inpatients were recruited from an acute care hospital. The construct (using confirmatory factor analysis and discriminant validity of each item), convergent, and known-group validities were tested to determine the validity of the Short-FRPQ. McDonald’s omega coefficient was used to examine the internal consistency of reliability.
Results
In the confirmatory factor analysis, the fit indices of the Short-FRPQ, comprising 14 items and three factors, appeared to be satisfactory. The Short-FRPQ had a significantly positive correlation with the original scale, the Korean Falls Efficacy Scale-International, and the Morse Fall Scale. The risk of falls group, assessed using the Morse Fall Scale, had a higher score on the Short-FRPQ. McDonald’s omega coefficient was .90.
Conclusion
The Short-FRPQ presents good reliability and validity. As patient participation is essential in fall interventions, evaluating the fall risk perception of inpatients quickly and repeatedly using scales of acceptable validity and reliability is necessary.
- 3,240 View
- 136 Download

- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Eun Jin Kim, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):44-58. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23090
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to apply a health partnership program using commercially available mobile health apps to improve cardiovascular risk factors in male employees and verify its effectiveness.
Methods
Using a randomized control group pretest-posttest design, male employees with cardiovascular risk factors from five small and medium-sized workplaces were randomly assigned to an experimental group (n = 32) and a control group (n = 31). The experimental group was encouraged to use three mobile health apps for 12 weeks to acquire the necessary cardiovascular disease-related information and practice strengthening training, walking, and diet management appropriate to their level. They also received feedback on their weekly activities and motivational text messages from health partners. Hypotheses were tested using the SPSS WIN 22.0.
Results
The experimental group showed a significant difference compared to the control group in terms of their perception of mobile health app (p < .05), self-efficacy for exercise and diet, self-management partnership, and cardiovascular disease prevention health behavior (p < .001). In particular, there were significant decreases in the body mass index, ratio, serum fasting blood sugar, total cholesterol, and triglyceride in the experimental group (p < .001); however, there was no significant difference in high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol.
Conclusion
Intervention using mobile apps based on partnership with health managers is effective in improving the objective cardiovascular risk index in male employees; therefore, such intervention should be continuously used as a useful lifestyle modification strategy in the workplace. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adherence to a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Yura Shin, Jina Choo, Songwhi Noh
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Adherence to a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
- 3,570 View
- 207 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Incidence and Risk Factors of Dyslipidemia after Menopause
- Ihn Sook Jeong, Hae Sun Yun, Myo Sung Kim, Youn Sun Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):214-227. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21188
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study was aimed at investigating the incidence and risk factors of dyslipidemia in menopausal women using a Korean community-based longitudinal study.
Methods
The subjects were 245 postmenopausal women without dyslipidemia who had participated in the Ansan-Ansung cohort study from 2001~2002 (baseline) to 2015~2016 (seventh follow-up visit). The dyslipidemia incidence was measured as incidence proportion (%) and incidence rate per 100 person-years. The predictors of developing dyslipidemia were analyzed with Cox’s proportional hazard model.
Results
The incidence of new dyslipidemia during the follow-up period was 78.4% (192 patients), and 11.9 per 100 person-years. Mean duration from menopause to developing dyslipidemia was 5.3 years in new dyslipidemia cases. The triglyceride/high density lipoprotein (TG/HDL-C) ratio at baseline (hazard ratio = 2.20; 95% confidence interval = 1.39~3.48) was independently associated with developing dyslipidemia.
Conclusion
Dyslipidemia occurs frequently in postmenopausal women, principally within five years after menopause. Therefore, steps must be taken to prevent dyslipidemia immediately after menopause, particularly in women with a high TG/HDL-C ratio at the start of menopause. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of the 5-Year Incidence of Dyslipidemia in the Obese and Nonobese Adult Population: Results of the Yazd Health Study (YaHS)
Parisa Peigan, Masoud Mirzaei, Pedro Marques-Vidal, Mohammadtaghi Sarebanhassanabadi
Advanced Biomedical Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Middle-aged Korean women’s experiences of physical activity during the transition to menopause: a grounded theory approach
Hee Jung Cho, Sukhee Ahn
Women's Health Nursing.2025; 31(3): 215. CrossRef - Middle-aged women’s experiences of physical activity for managing menopausal symptoms: a phenomenological study
Hee Jung Cho, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(2): 104. CrossRef - Relationship between sleep duration and prevalence of hypertension among Korean postmenopausal middle-aged women
Eun Young Hong, Hye Ja Gu
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2023; 40(5): 43. CrossRef - Identification of subgroups with poor lipid control among patients with dyslipidemia using decision tree analysis: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2019 to 2021
Hee Sun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(2): 131. CrossRef
- Comparison of the 5-Year Incidence of Dyslipidemia in the Obese and Nonobese Adult Population: Results of the Yazd Health Study (YaHS)
- 1,542 View
- 32 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Incidence and Predictors of Cataract among People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Using Secondary Data Analysis from the Ansan Cohort of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
- Ihn Sook Jeong, Eun Joo Lee, Myo Sung Kim, Jung Ok Yu, Hae Sun Yun, Jeong Hee Jeong, Youn Sun 6 Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):24-35. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21081
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated the incidence and risk factors of cataract in people with diabetes mellitus (DM) using data from Ansan cohort of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES).
Methods
Data from a total of 329 patients with type 2 DM without cataract who participated in Ansan cohort of the KoGES from baseline survey (2001–2002) to fifth follow-up visit (2011–2012) were examined. The characteristics of the subjects were analyzed with frequency and percentage, and mean and standard deviation. Cataract incidence was measured as incidence proportion (%). For risk factors of cataract, hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were obtained using the Cox proportional hazard model.
Results
The cataract incidence over a 10-year follow-up period was 19.1% (15.1 in males and 25.8 in females), and mean age at the incidence of cataract was 63.48 years (61.58 years in males and 65.31 years in females). Age (HR=1.09, 95% CI=1.05–1.13) and HbA1c (HR=1.21, 95% CI=1.07–1.37) or the duration of DM (HR=1.05, 95% CI=1.00–1.09) were found to be independently associated with cataract development.
Conclusion
Cataract development in people with DM is common, and its likelihood increases with age, HbA1c, and the duration of DM. Considering negative effect of cataract on their quality of life and economic burden, nurses should identify people with DM at a higher risk of cataract development, and plan individual eye examination programs to detect cataract development as early as possible. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mendelian randomization study of causality between 35 blood and urine biomarkers and age-related eye diseases
Jiaqi Chen, Tongtong Chen, Cong Zhao, Zheyu Bao, Hongji Liu
Medicine.2026; 105(5): e47286. CrossRef - Spatiotemporal trend of sensory impairments in China and its provinces from 2011 to 2018: insights from CHARLS
Zhijian Zhang, Zhennan Cai, Cong Li, Shunming Liu, Sheng Li, Lei Liu, Lijun Zhang
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and factors associated with visual impairment in middle-aged and older Chinese population
Hanyuan Ye, Yun Zeng, Hongxia Xiao, Jing Yu, Yun Liu, Shuang Zhang, Bingjie Zhang
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Mendelian randomization study of causality between 35 blood and urine biomarkers and age-related eye diseases
- 1,746 View
- 25 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Development of a Diabetic Foot Ulceration Prediction Model and Nomogram
- Eun Joo Lee, Ihn Sook Jeong, Seung Hun Woo, Hyuk Jae Jung, Eun Jin Han, Chang Wan Kang, Sookyung Hyun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):280-293. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20257
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the risk factors for diabetic foot ulceration (DFU) to develop and evaluate the performance of a DFU prediction model and nomogram among people with diabetes mellitus (DM).
Methods
This unmatched case-control study was conducted with 379 adult patients (118 patients with DM and 261 controls) from four general hospitals in South Korea. Data were collected through a structured questionnaire, foot examination, and review of patients’ electronic health records. Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to build the DFU prediction model and nomogram. Further, their performance was analyzed using the Lemeshow–Hosmer test, concordance statistic (C-statistic), and sensitivity/specificity analyses in training and test samples.
Results
The prediction model was based on risk factors including previous foot ulcer or amputation, peripheral vascular disease, peripheral neuropathy, current smoking, and chronic kidney disease. The calibration of the DFU nomogram was appropriate (χ2 = 5.85, p = .321). The C-statistic of the DFU nomogram was .95 (95% confidence interval .93~.97) for both the training and test samples. For clinical usefulness, the sensitivity and specificity obtained were 88.5% and 85.7%, respectively at 110 points in the training sample. The performance of the nomogram was better in male patients or those having DM for more than 10 years.
Conclusion
The nomogram of the DFU prediction model shows good performance, and is thereby recommended for monitoring the risk of DFU and preventing the occurrence of DFU in people with DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nomogram for Predicting the Risk Factors of Diabetes Mellitus in Middle-Aged Adults: A Secondary Analysis of the 2022 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sook Kyoung Park, Hye Young Kim, Hyuk Joon Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 421. CrossRef - A Simple Nomogram for Predicting Stroke-Associated Pneumonia in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke
Youn-Jung Lee, Hee Jung Jang
Healthcare.2023; 11(23): 3015. CrossRef - Establishment of a Nomogram Model for Predicting Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Events in Diabetic Nephropathy Patients Receiving Maintenance Hemodialysis
Xiaobing Liu, Caili Yan, Xiuxiu Niu, Jiechun Zeng, Fahd Abd Algalil
Applied Bionics and Biomechanics.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Prognostic factors in diabetes: Comparison of Chi-square automatic interaction detector (CHAID) decision tree technology and logistic regression
Hae-Young Choi, Eun-Yeob Kim, Jaeyoung Kim
Medicine.2022; 101(42): e31343. CrossRef
- Nomogram for Predicting the Risk Factors of Diabetes Mellitus in Middle-Aged Adults: A Secondary Analysis of the 2022 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- 1,706 View
- 22 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of Spouse-Participated Health Coaching for Male Office Workers with Cardiocerebrovascular Risk Factors
- So Hee Kang, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):748-759. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.748
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to examine the effect of spouses participating in health coaching on stage of the change, health behaviors, and physiological indicators among male office workers with cardiocerebrovascular disease (CVD) risk factors and compare the findings with trainers who provided health coaching only to workers.
Methods A quasi-experimental pretest-posttest design was used. Convenience sampling was used to recruit participants from a manufacturing research and development company in the city of Gyeonggi province. The health coaching program for the experimental group (n=26) included individual counseling sessions according to workers' stage of change, and provision of customized health information materials on CVD prevention to workers and their spouses for 12 weeks through mobile phone and email.
Results After 12 weeks of intervention, the total score for health behavior, and scores on the sub-areas of exercise and health checkups significantly improved in the experimental group, but there were no significant differences in the scores of stage of the change and physical indicators. The results of a paired t-test showed a significant decrease in the body mass index, abdominal circumference, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol and triglyceride values, and a significant increase in the high-density lipoprotein cholesterol value in the experimental group after the intervention.
Conclusion To improve the health of male workers with CVD risk factors in the workplace, sharing health information with their spouses has proven to be more effective than health coaching for only workers. Therefore, it is important to develop strategies to encourage spousal participation when planning workplace health education for changing health-related behaviors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun Jin Kim, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(1): 44. CrossRef - Effects of a Remote Physical Activity Improvement Program on Male Office Workers with Metabolic Syndrome in Their 30s and 40s with Sedentary Behavior: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Kyong Sil Park, Seon Young Hwang
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - An intervention study of a combined intervention of positioning and hand massage in patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation
Yun Kyeong Lee, Mihae Im, Haeryun Cho
Nursing Open.2023; 10(3): 1404. CrossRef
- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 1,009 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Path Analysis for Delirium on Patient Prognosis in Intensive Care Units
- Sunhee Lee, Sun-Mi Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):724-735. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.724
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to investigate relationship between delirium, risk factors on delirium, and patient prognosis based on Donabedian's structure-process-outcome model.
Methods This study utilized a path analysis design. We extracted data from the electronic medical records containing delirium screening data. Each five hundred data in a delirium and a non-delirium group were randomly selected from electronic medical records of medical and surgical intensive care patients. Data were analyzed using SPSS 20 and AMOS 24.
Results In the final model, admission via emergency department (B=.06,
p =.019), age over 65 years (B=.11,p =.001), unconsciousness (B=.18,p =.001), dependent activities (B=.12,p =.001), abnormal vital signs (B=.12,p =.001), pressure ulcer risk (B=.12,p =.001), enteral nutrition (B=.12,p =.001), and use of restraint (B=.30,p =.001) directly affecting delirium accounted for 56.0% of delirium cases. Delirium had a direct effect on hospital mortality (B=.06,p =.038), hospital length of stay (B=5.06,p =.010), and discharge to another facility (not home) (B=.12,p =.001), also risk factors on delirium indirectly affected patient prognosis through delirium.Conclusion The use of interventions to reduce delirium may improve patient prognosis. To improve the dependency activities and risk of pressure ulcers that directly affect delirium, early ambulation is encouraged, and treatment and nursing interventions to remove the ventilator and drainage tube quickly must be provided to minimize the application of restraint. Further, delirium can be prevented and patient prognosis improved through continuous intervention to stimulate cognitive awareness and monitoring of the onset of delirium. This study also discussed the effects of delirium intervention on the prognosis of patients with delirium and future research in this area.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Does ICU admission dysphagia independently contribute to delirium risk in ischemic stroke patients? Results from a cohort study
Hongtao Cheng, Simeng Song, Yonglan Tang, Shiqi Yuan, Xiaxuan Huang, Yitong Ling, Zichen Wang, Xiaoying Tian, Jun Lyu
BMC Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Preoperative Anxiety and Its Postoperative Associated Factors in Patients Receiving Post Anesthetic Recovery Care at Surgical Intensive Care Unit
Yul Ha Lee, Hye-Ja Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(3): 267. CrossRef - Delirium Experience of the Intensive Care Unit Patients
Jaeyeon Jung, Sujin Jang, Seonmi Jo, Sunhee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(2): 134. CrossRef - The training needs of Korean intensive care unit nurses regarding delirium
Young Sook Roh
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2021; 62: 102954. CrossRef - Effect on Quality of Care of a Delirium Prevention Campaign for Surgical Intensive Care Nurses
Heejeong Kim, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of Nursing Care Quality.2021; 36(4): 361. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis on the Effect of Delirium Prevention Intervention in Korean Intensive Care Units
Jiyeon Kang, Min Jeong Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2021; 14(3): 141. CrossRef
- Does ICU admission dysphagia independently contribute to delirium risk in ischemic stroke patients? Results from a cohort study
- 2,447 View
- 52 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Effects of an Integrated Physical Activity Program for Physically Inactive Workers - Based on the PRECEDE-PROCEED Model -
- Hye-Jin Kim, Jina Choo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):692-707. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.692
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose We aimed to examine the effects of an integrated physical activity (PA) program developed for physically inactive workers on the theoretical basis of the PRECEDE-PROCEED model.
Methods Participants were 268 workers in three departments of L manufacturing unit in South Korea. The three departments were randomly allocated into integration (n=86) (INT), education (n=94) (ED), and control (n=88) (CT) groups. The INT group received self-regulation, support, and policy-environmental strategies of a 12-week integrated PA program, the ED group received self-regulation strategies only, and the CT group did not receive any strategies. After 12 weeks, process evaluation was conducted by using the measures of self-regulation (autonomous vs. controlled regulation), autonomy support, and resource availability; impact evaluation by using PA measures of sitting time, PA expenditure, and compliance; and outcome evaluation by using the measures of cardiometabolic/musculoskeletal health and presenteeism.
Results Among process measures, autonomous regulation did not differ by group, but significantly decreased in the CT group (
p =.006). Among impact measures, PA compliance significantly increased in the INT group compared to the CT group (p =.003). Among outcome measures, the changes in cardiometabolic/musculoskeletal health and presenteeism did not differ by group; however, systolic blood pressure (p =.012) and a presenteeism variable (p =.041) significantly decreased only in the INT group.Conclusion The integrated PA program may have a significant effect on increases in PA compliance and significant tendencies toward improvements in a part of cardiometabolic health and presenteeism for physically inactive workers. Therefore, occupational health nurses may modify and use it as a workplace PA program.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms on Depressive Symptoms and Health-Promoting Behaviors Among Korean Coast Guards: The Mediating Role of Social Support
Hyung-Eun Seo, Mijung Yeom, Hye-Jin Kim
Workplace Health & Safety.2025; 73(5): 236. CrossRef - The characteristics, components, and fidelity of interventions promoting physical activity in people living with musculoskeletal conditions: a systematic review
Alex Thompson, Robert Copeland, Rachel Young, Angela Reilly, Jeff Breckon, Sionnadh McLean
Disability and Rehabilitation.2025; 47(23): 6020. CrossRef - Strategies for preventing presenteeism in nursing
Luís Sousa, Ricardo Mestre, João Tomás, Sandy Severino, Nelson Guerra, Helena José
Management (Montevideo).2025; 3: 147. CrossRef - Use of the PRECEDE–PROCEED Model to Pilot an Occupational Physical Activity Intervention: Tailored Through a Community Partnership
Debra L. Fetherman, Joan Cebrick-Grossman
Workplace Health & Safety.2023; 71(8): 367. CrossRef - Corporate Well-Being Programme in COVID-19 Times. The Mahou San Miguel Case Study
José M. Núñez-Sánchez, Ramón Gómez-Chacón, Carmen Jambrino-Maldonado, Jerónimo García-Fernández
Sustainability.2021; 13(11): 6189. CrossRef - Effects of an Integrated Physical Activity Program for Physically Inactive Workers: Based on the PRECEDE-PROCEED Model
Hye-Jin Kim, Jina Choo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(6): 692. CrossRef
- The Impact of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms on Depressive Symptoms and Health-Promoting Behaviors Among Korean Coast Guards: The Mediating Role of Social Support
- 1,856 View
- 70 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Assessment of Gestational Age using New Ballard Examination in High-Risk Infants
- Young Mee Ahn, Sang Mi Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(2):176-185. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.2.176
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: Knowing the accurate GA is critical in nursing care of high-risk newborns. A descriptive study was performed to examine the reliability and clinical applicability of the new Ballard examination (NBE) in high-risk infants. METHOD: A NBE was performed to measure GA by assessing the neuromuscular and physical maturity in the course of physical examination of a convenient sample of 50 high-risk infants. RESULTS: 1) There was a highly correlation between both the GA by LMP (GA-LMP) and GA by NBE (GA-NBE) (r = .894, p = .000) 2) There was a greater positive relationship in neuromuscular maturity than physical maturity in the GA-NBE of the high-risk newborn (r = .657 versus r = .915, p<. 05). 3) The high-risk infants were thoes with congenital anomalies, prematurity, and RDS(Respiratory Distress Syndrome). Male infants showed a higher neuromuscular maturity, compared to female infants. 4) There was a positive correlation between neuromuscular, physical, total maturity, GA-LMP and GA-NBE in the birth weight, 1 minute Apgar score. CONCLUSION: The study supports the reliability an clinical relevance of NBE in assessment of the accurate GA in high-risk infants.
- 502 View
- 1 Download

- Effects of Motivation-Enhancing Program on Health Behaviors, Cardiovascular Risk factors, and Functional status for Institutionalized Elderly Women
- Rhayun Song, Kyung Ja June, You Ja Ro, Chun Gill Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(5):858-870. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.5.858
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was to compare changes in health behaviors, motivational factors, cardiovascular risk factors, and functional status (SIP) after implementing the 6-month motivation-enhancing program to institutionalized elderly women.
METHODS
Sixty-four elderly women participated. Face to face interviews with blood sampling and anthropometric assessment were conducted at the pretest, 10 weeks and 6 months during the program.
RESULTS
1. The program participants showed significantly better health behaviors over 6 months. The mean motivational level was also significantly improved, especially for perceived benefits, perceived barriers, and emotional salience. 2. The mean of cardiovascular risk factors for the participants was 21.8 at the level of low to moderate risk. After completing the program, total risk score was significantly decreased to 18.7 at 10 weeks, and further to 17.7 at 6 months. A significant reduction was also found in HDL and LDL-cholesterol levels, blood pressure, obesity, inactivity, and stress. 3. The functional status (SIP) was 11% at the baseline and significantly changed in positive direction at 10 weeks (M=9.3) and at 6 month (M=6.3). The significant improvement was also found in physical and psychosocial dimensions and sleep/rest dimension.
CONCLUSION
The motivation enhancing program was effective to reduce cardiovascular risks and to improve the functional status of institutionalized elderly women by motivating them to perform better health behaviors.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Influence of e-Health Literacy, Technostress, and Subjective Health Status on Health Promotion Behaviors among Older Adults
Whang Sun A
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2025; 13(1): 71. CrossRef - The Effects of Health Literacy, Social Support, and Health-Promoting Behaviors on Metabolic Syndrome Among Middle-Aged and Older Women Living in Rural Areas of Republic of Korea
Eun-Kyung Lee, Yong-Sook Eo
Healthcare.2025; 13(24): 3279. CrossRef - The effects of self-efficacy, a health-promoting lifestyle, and social support on resilience of patients receiving percutaneous coronary intervention: A descriptive survey study
Su-Jin Kim, Jeong-soo Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(4): 403. CrossRef - The Role of Health Empowerment on Digital Health Technology Literacy by Generation
Yoongi Chung, Hyerine Shin, Hyejin Kim, Ji-Su Kim
American Journal of Health Behavior.2024; 48(4): 967. CrossRef - Effects of Accelerated Rehabilitation Exercise on the Senior Fitness Test (SFT), Isometric Muscle strength, and Blood Profile in Older Adult Women with Degenerative Knee Osteoarthritis
Ju-ri Lee, Hong-sun Song, Tae-beom Seo, Jong-baek Lee
Korean Journal of Sport Science.2024; : 81. CrossRef - Effects of BeHaS Program on Health Behavior, Physiologic Index and Self-Esteem of the Elderly Living Alone with Metabolic Syndrome Based on Community Based Participatory Research
Jong Im Kim, Sun Ae Kim, Keumok Park, Jiyoung Kim, Lina Lee, Si Wan Choi, Bon Jeong Ku
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(4): 571. CrossRef - Validation of the cardiac health behavior scale for Korean adults with cardiovascular risks or diseases
Rhayun Song, Hyunkyoung Oh, Sukhee Ahn, Sue Moorhead
Applied Nursing Research.2018; 39: 252. CrossRef - Motivation Factors for Stages of Behavioral Change among Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome
Rhayun Song, Moonkyoung Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(1): 60. CrossRef - A structural model of health behavior modification among patients with cardiovascular disease
Hwasoo Goong, Seungmi Ryu, Lijuan Xu
Applied Nursing Research.2016; 29: 70. CrossRef - A Study on IADL, Stress and Motivation on Healthy Lifestyle among Elderly People with Arthritis
Jong Gun Kim, Kyeung Hee Moon, Eun Sun Lim, Jang Hak Yoo
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(3): 209. CrossRef - The Relationship between Health Belief and Exercise Compliance among Elderly Adults at Senior Centers
Kyung Im Lee, Young Eun
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(2): 79. CrossRef - Development of Job Standards for Clinical Nutrition Therapy for Dyslipidemia Patients
Min-Jae Kang, Jung-Sook Seo, Eun-Mi Kim, Mi-Sun Park, Mi-Hye Woo, Dal-Lae Ju, Gyung-Ah Wie, Song-Mi Lee, Jin-A Cha, Cheong-Min Sohn
Clinical Nutrition Research.2015; 4(2): 76. CrossRef - The intake of food and nutrient by the elderly with chronic disease in the Seoul area
Yoo Kyung Park, Yeon Joo Lee, Sang Sun Lee
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2012; 45(6): 531. CrossRef - Effects of a problem‐solving counseling program to facilitate intensified walking on Koreans with type 2 diabetes
Haejung LEE, Myoung‐Soo KIM, Kyung‐Yeon PARK, Hyoung‐Sook PARK, In‐Joo KIM
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2011; 8(2): 129. CrossRef - The Effects of Aerobic Exercise Therapy on Physical Functions in the Elderly
Sook Hee Jung, Kyung Hee Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(2): 252. CrossRef - Health Literacy and Health Status of Korean-Chinese Elderly People Living in Yanbian, China
Chun Yu Li, Ogcheol Lee, Gi Soo Shin, Xian Wen Li
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(3): 386. CrossRef - Effects of the Nutrition Education Program on Self-efficacy, Diet Behavior Pattern and Cardiovascular Risk Factors for the Patients with Cardiovascular Disease
Kyoungok Ju, Heeyoung So
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(1): 64. CrossRef - Effects of Nutrition Education and Exercise Programs on Perceived Dietary Behaviors, Food Intake and Serum Lipid Profiles in Elderly Korean Women Living in Residential Homes
Hee-Seon Kim, Kyung-Ja June, Rhayun Song
Asian Nursing Research.2007; 1(1): 35. CrossRef - Effects of a health-promotion program on cardiovascular risk factors, health behaviors, and life satisfaction in institutionalized elderly women
Chun-Gill Kim, Kyung-Ja June, Rhayun Song
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2003; 40(4): 375. CrossRef
- The Influence of e-Health Literacy, Technostress, and Subjective Health Status on Health Promotion Behaviors among Older Adults
- 884 View
- 20 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Prevalence and Risk Factors for Diabetes Mellitus and Impaired Fasting Glucose of Adults
- Hee Seung Kim, You Ja Ro, Nam Cho Kim, Yang Sook Yoo, Jin Sun Young, Jeong Ah Oh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(6):1479-1487. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.6.1479
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was conducted to draw out prevalence and the risk factors of diabetes mellitus and impaired fasting glucose for adults,(age 30-69). The subjects were 2096 adults, who had regular health examinations between January and December of 1999 at K Hospital in Seoul. The data was analyzed using chi-square test, unpaired t-test and logistic regression. Diabetes Mellitus and impaired fasting glucose were diagnosed by ADA (American Diabetes Association, 1997) criteria. The results were as follows: 1. Mens' prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus was 7.9% and womens' prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus was 3.8%. Mens' prevalence of impaired fasting glucose was 10.4% and womens' prevalence of impaired fasting glucose was 6.5%. Prevalences of Diabetes Mellitus and impaired fasting glucose increased with age. 2. Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus and impaired fasting glucose of obese subjects (relative body weight>=162) was higher than that of overweight subjects (110<=relative body weight<=119) in men and women. 3. The diagnoses of Diabetes Mellitus and impaired fasting glucose increased with systolic blood pressure and triglyceride. 4. Significant factors associated with diabetes in the logistic regression best gut model were age, relative body weight, systolic blood pressure, triglyceride in men, and systolic blood pressure in women. In conclusion, as age, weight, systolic blood pressure and triglyceride get higher, Diabetes Mellitus and impaired fasting glucose prevalence also increases, porportionally.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Relation of Impaired Fasting Glucose and HDL-Cholesterol by Gender and Body Mass Index
Soo-Hee Jin
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2019; 44(1): 8. CrossRef - Effects of Obesity and Family History of Diabetes on the Association ofCETPrs6499861 with HDL-C Level in Korean Populations
Jae Woong Sull, Soriul Kim, Sun Ha Jee
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2019; 8(2): 252. CrossRef - Current Status and Effects of Nutrition Education Programs for Diabetic Patients in Korea
Hae Jin Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(2): 106. CrossRef - Effect of smoking on the association of HHEX (rs5015480) with diabetes among Korean women and heavy smoking men
Jae Woong Sull, Tae Yong Lee, Sun Ha Jee
BMC Medical Genetics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Spatial Distribution of Diabetes Prevalence Rates and Its Relationship with the Regional Characteristics
Eun-Kyung Jo, Eun-Won Seo, Kwang-Soo Lee
Health Policy and Management.2016; 26(1): 30. CrossRef - The Relationship between Factors of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adult Males and the Parents' Family History of Diabetes
Hyung-Su Park, Jin-Gyu Jeong, Jin-Ho Yu
The Journal of the Korea institute of electronic communication sciences.2013; 8(5): 779. CrossRef - Thigh Circumference and Diabetes: Obesity as a Potential Effect Modifier
Keum Ji Jung, Heejin Kimm, Ji Eun Yun, Sun Ha Jee
Journal of Epidemiology.2013; 23(5): 329. CrossRef
- The Relation of Impaired Fasting Glucose and HDL-Cholesterol by Gender and Body Mass Index
- 789 View
- 1 Download
- 7 Crossref

- A Study on the Circadian Blood Pressure Rhythm of Diabetic Patients
- Hwa Soon Kim, Wha Sook Suh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):741-749. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.741
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was performed to investigate the relationship between reversed circadian blood pressure and risk factors of peripheral vascular disease in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) subjects. The subjects in this study were 18 NIDDM patients who were hospitalized in a medical unit of an university medical center located in Incheon, Korea, between November, 1998 and March, 1999. Blood pressure was measured with a mercury sphygmomanometer by 2 trained examiners every 2 hours during 24 hours. NIDDM subjects were divided into a dipper group and non-dipper group. Dippers are defined as those who show a mean nighttime blood pressure(BP) drop of more than 10% compared with daytime BP. Non-dippers are defined as those who show a mean nighttime BP drop of less than 10%, or an elevation in BP compared with daytime BP. Daytime BP included values obtained between 6 a.m. and 10 p.m. Night time BP included values obtained between 10 p.m. and 6 a.m. Data was analyzed by SPSS/PC package. Chi-square( 2) test was used for the comparison of sex between The dipper group and non-dipper group. Mann-Whitney test was used for comparisons of values of the risk factors of peripheral vascular disease and the frequency of complications of diabetes between the dipper group and non-dipper group. The results are as follows. There were no significant differences in daytime systolic, diastolic, and mean blood pressures between the dipper group and non-dipper group. However, night time systolic, diastolic, and mean blood pressures in the non-dipper group were significantly nigher than those in the dipper group (p=.021). There were no differences in sex, age, body, weight, duration of diabetes, serum lipid levels, BUN and HbA1c between the two groups. On the contrary, 87.5% of non-dipper group subjects showed having hypertension, 30% of dipper group subjects showed having hypertension and this difference was statistically significant (p=.018). All of the non-dipper group subjects (N=8) showed having at least one diabetic complication. However, 40% of the dipper group subjects (N=10) showed having no diabetic complication at all and this difference was also statistically significant (p=.049). There were no significant differences in frequency of nephropathy, neuropathy and retinopathy between the dipper group and non-dipper group.
- 486 View
- 2 Download

- Lifestyles Effects on Stroke Risk in Different Regions in Korea
- Smi Choi-Kwon, Eun Kyung Kim, Mi Yang Jeon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(3):729-738. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.3.729
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Stroke is a leading cause of death in Korea. Early measurement to prevent stroke are extremely important since it has no cure. Korean might have different risk factors since their dietary habit and socio-economical status differ from most western countries. However, the risk factors for stroke in Korea have not yet been identified. Moreover, the lifestyle of health Korean adults has not been investigated. In this study we investigate the life of health adults living in Seoul and rural areas and compare the life style of the two. METHODS: One hundred seventy one subjects were studies. Among the subjects studied, 128 were from Seoul, the other 43 were from the country area. The age of the subjects was limited to over 40 years. Blood pressure, fast blood sugar, and cholesterol were measured. The subjects' height, weight, body mass index total body fat, skinfolds thickness of triceps, subscapular and abdomen were measured to determine obesity. Using a structured interview, we assessed : sodium intake, physical activity and exercise, consumption of vegetables, fat, fish and fruits. The results of the two groups were compared. RESULTS: There were no statistical differences in age and education between the two groups of subjects. The mean age of the subjects were 66 years old. The subjects residing in rural areas had a higher intake of sodium(p<0.05), lower physical active(P<0.05), and higher BMI and body fat(p<0.05) as compared to the subjects in Seoul. Subjects with hypertension were between 24% and 33% and the prevalence of hypertension was the highest was the highest when compared to the prevalence of DM, or hypercholesterolemia. However, the prevalence of hypertension, DM, hypercholesterolemia, were not significantly different in these areas. CONCLUSION: our results show that subjects living in rural areas eat more salty food, exercise less and tend to be obese. The finding of this study lead to speculation that Korean living in rural areas have less information about the effects diet of diet on health than city dwellers do. General health and nutrition education programs aimed at the prevention of stoke and other such conditions for rural area Korean may close the risk factor gap between rural and urban dwellers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Korean Version of Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly (K-PASE)
Myoung-Ae Choe, Jeungim Kim, Mi-yang Jeon, Young-Ran Chae
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(1): 47. CrossRef - Echocardiographic Plains Reflecting Total Amount of Epicardial Adipose Tissue as Risk Factor of Coronary Artery Disease
Jung-Won Hwang, Un-Jung Choi, Sung-Gyun Ahn, Hong-Seok Lim, Soo-Jin Kang, Byoung-Joo Choi, So-Yeon Choi, Myeong-Ho Yoon, Gyo-Seung Hwang, Seung-Jea Tahk, Joon-Han Shin, Doo-Kyung Kang
Journal of Cardiovascular Ultrasound.2008; 16(1): 17. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Korean Version of Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly (K-PASE)
- 752 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Nursing Students' Perceptions on Diet and as Environmental Factors Related to Cancer Risk Factors
- Hae Kyung Lee, Seong Joo Cheon, Mi Hye Hwang, Soon Rim Suh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(1):193-200. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.1.193
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identify how students majoring in nursing perceive cause of cancers and the effects of diet for preventing cancers. Data for the study were collected by 651 nursing students, who were registered in the second and third year in three technical colleges and third and fourth year in two universities. The research instruments included items on general characteristics of subjects, items about the degree of perception of the frequency of cancer onset and items on the perception of mortality, risk factors, preventive diets, knowledge, and high risk factor for cancer in specific body areas. The findings of this study are as follows : 1. Almost all subjects(92.8%) reported that the frequency of cancer onset increases and that it is 93.9% for people over 40. Degree of perception about cancer mortality was low at 33.0%. 2. As far as the perception of risk factors for cancer onset was concerned, smoking, stress, heredity, family history, and alcohol were rated high, over 80.0%. Risk factor in clouding, virus, hormones, pesticides were rated as low. 3. As to the perception of risk factor for body area as associated with diet salted and scorched food were rated at 44.5% for stomach cancer, alcohol, 50.4% for liver cancer, smoking, 72.8% for lung cancer, pregnancy times, 25.3%, and marriage age, 23.0% for uterine cancer, and no delivery experience, 40% for breast cancer. 4. The knowledge score for cancer was between 12 and 36, with a mean score of 26.75(SD=4.13). There was a statistically significant difference between experience in caring for cancer patients during clinical practice and knowledge score(t=3.09, p=.002).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Literature Review of Structural Equation Models for Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention in Korea
Eunhye Kim, Jinhyun Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2014; 11(2): 109. CrossRef - Cancer Risk Perception and Cancer Related Health Behavior in College Students
Gye Young Shin, Mee Kyoung Joo
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2010; 10(2): 137. CrossRef
- Literature Review of Structural Equation Models for Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention in Korea
- 688 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Correlations between Weight, Body Mass Index(BMI) and Risk Factors of Coronary Artery Disease in Men and Women in their Forties and Fifties
- Hee Seung Kim, Hye Sun Jeong, Kyung Sil Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(1):184-192. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.1.184
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was done to examine the correlations between weight, BMI and risk factors of coronary heart disease in men and women in their forties and fifties. The subjects were 412 adults, who had regular health examinations between January and December of 1996 at S-Hospital in Seoul. The data were analyzed using ANOVA, Scheffe test, and Pearson correlation coefficient. The results are as follows : 1. The men between 50 and 59 years of age had higher levels for BMI, weight, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, triglyceride, fasting blood sugar, plasminogen activator-1, and hemoglobin A1C than the group of women in their forties. Yet, HDL-cholesterol was lower than in the former group. 2. In the group of men in their forties, weight was significantly correlated to diastolic blood pressure(r=.22), LDL-cholesterol(r=.20), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1(r=.35) HDL-cholesterol(r=-.19). Their BMI was significantly corrected to systolic blood pressure(r=.27), diastolic blood pressure(r=.33), total cholesterol(r=.23), LDL-cholesterol(r=.26), plasminogen activator-1(r=.36) and HDL-cholesterol(r=-.25). 3. As for the group of women in their forties weight was significantly correlated to systolic blood pressure(r=.20), diastolic blood pressure(r=.22), triglyceride(r=.32), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1(r=.30) and HDL-cholesterol(r=-.37). Their BMI was significantly correlated to diastolic blood pressure(r=.25) triglyceride(r=.47), plasminogen activator-1(r=.35), fibrinogen(r=.27) and HDL-cholesterol(r=-.47). 4. In the group of men in their fifties, weight was significantly correlated to total cholesterol(r=.32), LDL-cholesterol(r=.29), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1(r=.26). Their BMI was significantly correlated to systolic blood pressure(r=.24), diastolic blood pressure(r=.22), total cholesterol(r=.34), LDL-cholesterol(r=.32), and plasminogen activator-1(r=.25). 5. In the group of women in their fifties, weight was significantly correlated to diastolic blood pressure(r=.33), total cholesterol(r=.21), LDL-cholesterol(r=.20), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1(r=.43) and HDL-cholesterol(r=-.21). Their BMI was significantly corrected to systolic blood pressure(r=.25), diastolic blood pressure(r=.40), total cholesterol(r=.24), LDL-cholesterol(r=.24), triglyceride(r=.22), and HDL-cholesterol(r=-.30). The above findings indicate that the BMI was more predictive than weight as a risk factor for coronary artery disease for men and women in their forties and fifties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Morbidity and mortality rates in women with heart disease: Lessons in gender differences from Korea
Myoung-Ae Choe, Kyungeh An
Contemporary Nurse.2003; 14(2): 158. CrossRef
- Morbidity and mortality rates in women with heart disease: Lessons in gender differences from Korea
- 565 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Comparison of Cardiovascular Risk Profile Clusters Among Industrial Workers
- Seon Young Hwang, Ji Hyun Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(8):1500-1507. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.8.1500
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify subgroups of the physical and behavioral risk profiles for cardiovascular disease among industrial workers, and to examine predicting factors for the subgroups.
Sample and Methods Health records of 2,616 male and female workers aged 19-56 years who were employed in an airplane manufacturing industry were analyzed. Data were analyzed using the Latent class cluster analysis.
Results Four different clusters (two high-risk groups, one low-risk group, and one normal group) were found and these clusters were significantly different by age, gender, and work type (p<.05). The two high-risk groups had higher chances of drinking alcohol, elevated BMI, FBS, total cholesterol, having hypertension, and were significantly older, and had relatively high chances of being day workers rather than other groups. The low-risk group had higher chances of drinking alcohol, higher BMI and total cholesterols compared to normal group, and highest portions of current smokers and shift workers in the four clusters and their mean BP was within prehypertension criteria.
Conclusion Industrial nurses should guide the lifestyle behaviors and risk factors of the high risk groups for CVD and need to intervene early for behavioral change for the low-risk group who are young and shift workers. Age, and work environment should be considered in planning for targeted preventive interventions for industrial workers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated with Blue-collar Workers' Risk Perception of Cardiovascular Disease
Won Ju Hwang, OiSaeng Hong, Mi Ja Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(7): 1095. CrossRef
- Factors Associated with Blue-collar Workers' Risk Perception of Cardiovascular Disease
- 722 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Risk Factors for Falls among the Community-Dwelling Elderly in Korea
- Kyeong Yae Sohng, Jung Soon Moon, Hae Hiang Song, Kwang Soo Lee, Young Sook Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(8):1483-1490. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.8.1483
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Community-based centres were surveyed to determine the frequency of and risk factors for falls among elderly Koreans. We examined fall-related risk factors, including physiological and physical health, psychosocial functions, self-reported physical capacity and activity, vision, and the use of medication, among 351 elderly people aged 65 years or older, with ambulatory. Forty-two per cent of elderly Korean subjects reported at least one episode of falling in the previous 12 months, 38% of whom had consequences that required either the attention of a physician or hospitalization.
Factors significantly associated with an increased risk of falling were a restricted activity during the previous five years (adjusted OR 1.3), use of alternative therapy (adjusted OR 2.7), low knee flexor and extensor-muscle strength (adjusted OR 1.21 and 1.20), and poor balance with closed eyes (adjusted OR 8.32).
We conclude that falls among older persons living in the community are common in Korea and that indicator of bad health and frailty or variables directly related to neuromuscular impairment are significant predictors of the risk of falling.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Obesity, Physical Performance, Balance Confidence, and Falls in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Results from the Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study
Ga Yang Shim, Myung Chul Yoo, Yunsoo Soh, Jinmann Chon, Chang Won Won
Nutrients.2024; 16(5): 614. CrossRef - Nutrition Risk is Associated With Falls Risk in an Observational Study of Community-Dwelling, Rural, Older Adults
Caitlin D. Eckert, Emily K. Tarleton, Jocelyn Pellerin, Nicole Mooney, Nancy M. Gell
Journal of Aging and Health.2022; 34(6-8): 1125. CrossRef - Clinical Practice Guideline for Frailty Applicable in Primary Care Setting
Hyo-Sun You, Yu-Jin Kwon, Sunyoung Kim, Yang-Hyun Kim, Ye-seul Kim, Yonghwan Kim, Yong-kyun Roh, Byoungjin Park, Young Kyu Park, Chang-Hae Park, Joung Sik Son, Jinyoung Shin, Hyun-Young Shin, Bumjo Oh, Jae-woo Lee, Jae-Yong Shim, Chang Won Won, Ji Won Yoo
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2021; 11(4): 223. CrossRef - Prevalence, Circumstances, and Risk Factors of Falls Among Community Dwelling Members of University of the Third Age
Asmidawati Ashari, Tengku Aizan Hamid, Mohd Rizal Hussain, Rahimah Ibrahim, Keith D. Hill
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The moderating role of social factors in the relationship between an incident of fall and depressive symptoms: a study with a national sample of older adults in South Korea
Min-Kyoung Rhee, Yuri Jang, Soo Young Kim, Sujie Chang
Aging & Mental Health.2021; 25(6): 1086. CrossRef - Clinical Practice Guidelines for Managing Frailty in Community-Dwelling Korean Elderly Adults in Primary Care Settings
Hyo-Sun You, Yu-Jin Kwon, Sunyoung Kim, Yang-Hyun Kim, Ye-seul Kim, Yonghwan Kim, Yong-kyun Roh, Byoungjin Park, Young Kyu Park, Chang-Hae Park, Joung Sik Son, Jinyoung Shin, Hyun-Young Shin, Bumjo Oh, Jae-woo Lee, Jae Yong Shim, Chang Won Won, Ji Won Yoo
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2021; 42(6): 413. CrossRef - Effect of Action Observation Training Using Y-Balance on Balance Capability in Young Adults
Sung Min Son, Kyung Woo Kang
The Journal of Korean Physical Therapy.2020; 32(2): 65. CrossRef - Epidemiology of fall and its socioeconomic risk factors in community-dwelling Korean elderly
Taekyoung Kim, Sang D. Choi, Shuping Xiong, Kyoung-Sae Na
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(6): e0234787. CrossRef - Correlation of the Korean Version of Falls Efficacy Scale-International With Quantitative Balance and Gait Parameters Through Exercise Program in Elderly Men
Bo Ram Ahn, Hyo Jung Kang, Eun Jung Choi, Soo Woong Jang, Hee Sup Chung, Kyung Soo Jeon
Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine.2019; 43(2): 195. CrossRef - Fall-Risk-Increasing Drugs: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: III. Others
Lotta J. Seppala, Esther M.M. van de Glind, Joost G. Daams, Kimberley J. Ploegmakers, Max de Vries, Anne M.A.T. Wermelink, Nathalie van der Velde, Hubert Blain, Jean Bousquet, Gösta Bucht, Maria Angeles Caballero-Mora, Tischa van der Cammen, Patrik Eklund
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2018; 19(4): 372.e1. CrossRef - Analysis of Fall Accidents of Dizzy Patients in a Tertiary Hospital in South Korea (2011-2015)
Sung Kyun Kim, Sung Ho Lee, Seon Heui Lee, Jae Jun Song, Mi Jung Gwak, Hee Seon Lee, Gi Jung Im
Korean Journal of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery.2017; 60(6): 271. CrossRef - Comparison of falls-related physical fitness and fall experience characteristics of the elderly between Ulsan, Korea and Gifu, Japan
Sohee Shin
Korean Journal of Sport Science.2017; : 566. CrossRef - Determining Risk of Falls in Community Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Using Posttest Probability
Michelle M. Lusardi, Stacy Fritz, Addie Middleton, Leslie Allison, Mariana Wingood, Emma Phillips, Michelle Criss, Sangita Verma, Jackie Osborne, Kevin K. Chui
Journal of Geriatric Physical Therapy.2017; 40(1): 1. CrossRef - Evidence-Based Guideline for Fall Prevention in Korea
Kwang-Il Kim, Hye-Kyung Jung, Chang Oh Kim, Soo-Kyung Kim, Hyun-Ho Cho, Dae Yul Kim, Yong-Chan Ha, Sung-Hee Hwang, Chang Won Won, Jae-Young Lim, Hyun Jung Kim, Jae Gyu Kim
Journal of the Korean Geriatrics Society.2016; 20(1): 1. CrossRef - Application of Rasch Analysis to the Korean Version of the Fullerton Advanced Balance Scale
Gyoung-mo Kim
Physical Therapy Korea.2016; 23(1): 46. CrossRef - Usefulness of a 50-meter round walking test for fall prediction in the elderly requiring long-term care
Mizuki Hachiya, Shin Murata, Hiroshi Otao, Takehiko Ihara, Katsuhiko Mizota, Toyoko Asami
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2015; 27(12): 3663. CrossRef - Validation of the Short Form Bobath Memorial Hospital Fall Risk Assessment Scale at a Specialized Geriatric Hospital in Korea
Kyeong-Yae Sohng, Mi Hwa Park, Seung Kyo Chaung, Hye Ja Park
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(3): 495. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Falls in Older Korean Adults: The 2011 Community Health Survey
Eun jin Choi, Sun A Kim, Nu Ri Kim, Jung-Ae Rhee, Yong-Woon Yun, Min-Ho Shin
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2014; 29(11): 1482. CrossRef - Relationship between Self-Perceived Postural Limits and Falls among Hospitalized Stroke Patients
Katsuhiko Takatori, Koji Shomoto, Tomoaki Shimada
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2009; 21(1): 29. CrossRef
- Obesity, Physical Performance, Balance Confidence, and Falls in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Results from the Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study
- 986 View
- 7 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Risk Factors for Sexual Behaviors in Girl's High School Students
- Jung Nam Sohn
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(3):430-439. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.3.430
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine risk factors for sexual behaviors in Korean female high school students.
Method Data was collected by a written questionnaire from June 22 to July 18, 2002 from 522 girls, who were stratified samples from a target population of 63,375 11th grade students from 200 regular high schools and 70 vocational high schools in Seoul, Korea. We conducted multiple regression analysis using the SAS pc+ program.
Result Risk factors for intimate behaviors were association with boy friends, differential association, family attachment, and family abuse experience. These variables cause 68% of intimate behaviors. Risk factors for sexual experiences were differential association, association with boy friend, and family attachment. These variables cause 14% of sexual experiences.
Conclusion Efforts to reduce sexual behaviors in girls should include the possible role of peers and develop peer leader programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of sexual related predicting factors for Female University students in Korea
Jungae Kim
The journal of the convergence on culture technology.2015; 1(1): 15. CrossRef
- Analysis of sexual related predicting factors for Female University students in Korea
- 648 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Maternal Transition in Mothers with High Risk Newborns
- Hyun Jeong Shin
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(2):243-251. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.2.243
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was a comprehensive understanding about maternal transition in mothers with high risk newborns according to the degree of situational meaning.
Method A methodological triangulation that combines qualitative and quantitative methods was used. The situational meaning of a high risk newborn mother was identified using a Family Meaning Attribution Scale. According to the degree of situational meaning, in-depth interviews were conducted at 3 time periods postpartum : between 3-10 days after childbirth, around the time of the newborn's discharge, and between 10-12 weeks after childbirth. Quantitative data was analyzed using descriptive statistics and t-test. Qualitative data was analyzed using Tutty, Rothery, & Grinnell's methodology.
Result The average score of the situational meaning in high the risk newborn mother was 53.57(possible score is between 0-96) and the average score of each item was 1.67. A Maternal transition process in the mother that has a positive situational meaning was conceptualized in three distinctive phases : confusion, accepting, and shaping phases. The Maternal transition process in the mother that has a negative situational meaning was also conceptualized in three distinctive phases : avoiding, conflicting, and accepting phases.
Conclusion It is necessary that the nurses provide high risk newborn mothers with individualized care considering both the situational meaning that is attributed to them and the maternal transition phase that they are faced with.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concept analysis of transition to motherhood: a methodological study
Woon Young Hwang, Sun Yeob Choi, Hae Jeong An
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(1): 8. CrossRef - Effects on Maternal Attachment, Parenting Stress, and Maternal Confidence of Systematic Information for Mothers of Premature Infants.
Hyo Sin Choi, Yeong Hee Shin
Child Health Nursing Research.2013; 19(3): 207. CrossRef - Effects of a Home-based Discharge Program for Mothers of Premature Infants on Oxygen Therapy at Home
Ji Min Lee, Soon Ja Oh, Kyung A Kim, Eun Jung Lee, Ji Yoon Lee, Moon Sook Hwang, Jung Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(2): 144. CrossRef - Life Transition of Mothers of Children with Autism
Ae Ran Lee, Sun Woo Hong, Ji Soo Kim, Se Jin Ju
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(6): 808. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Transitional Care Program for Patients Discharged from Military Hospitals
Seun Young Joe
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(4): 599. CrossRef - Predictors of maternal sensitivity during the early postpartum period
Hyunjeong Shin, Young‐Joo Park, Mi Ja Kim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2006; 55(4): 425. CrossRef
- Concept analysis of transition to motherhood: a methodological study
- 711 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Situational Meaning and Maternal Self-esteem in Mothers with High Risk Newborn
- Hyun Jeong Shin
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(1):93-101. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.1.93
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was designed to explore the relationship of situational meaning with maternal self-esteem in mothers with high risk newborn.
Method The subjects of this study were 82 mothers with high risk newborn. Data were collected using a translated Family Meaning Attribution Scale and Maternal Self-Report Inventory. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-test, Pearson Correlation Coefficients and Stepwise Multiple Regression.
Result The average score of the situational meaning in high risk newborn mothers was 64.01(possible score is between 0-96) and the average score of each item was 1.98. The average score of the maternal self-esteem in high risk newborn mothers was 81.96(possible score is between 26-104) and the average score of each item was 3.15. No significant differences were found in situational meaning according to general characteristics except whether it was a planned pregnancy or not. No significant differences were found in maternal self-esteem according to general characteristics except disease or admission experience during pregnancy. There was significant positive correlation between situational meaning and maternal self-esteem.
Conclusion It is necessary for nurses to provide high risk newborn mothers with care for improving situational meaning that is attributed to the mothers. It can be helpful to improve maternal self-esteem and in the end it will facilitate the maternal transition in mothers with high risk newborn.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploration of the process of maternal role attainment in Iranian mothers with preterm neonate: A grounded theory
Mona Alinejad-Naeini, Mahnaz Shoghi, Hamid Peyrovi
Journal of Human Behavior in the Social Environment.2023; 33(1): 44. CrossRef - Stress, postpartum depression, and anxiety in mothers of neonates admitted in the NICU: A cross-sectional hospital-based study
Dikshita Garg, Suprakash Chaudhury, Daniel Saldanha, Santosh Kumar
Industrial Psychiatry Journal.2023; 32(1): 48. CrossRef - Childbearing culture: a prominent context in the process of maternal role attainment in Iranian mothers with preterm neonates
Mona Alinejad-Naeini, Hamid Peyrovi, Mahnaz Shoghi
Journal of Biosocial Science.2022; 54(6): 1035. CrossRef - The Relationship between Parental Stress and Nurses' Communication as Perceived by Parents of High-risk Newborns
Chang Hee Lee, Mi Heui Jang, Yong Sung Choi, Hyunsook Shin
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(2): 184. CrossRef - Impact of a health education tool on enhancing communication between health providers and parents of neonates in intensive care in Egypt
Mohamed S. Hesham, Yasmin Mansi, Tamer A. Abdelhamid, Rehan M. Saleh
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2016; 79(7): 394. CrossRef - Nursing Needs of the Parents of Infants in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Ji-Sun Park, Kyung-Sook Bang
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2014; 20(2): 136. CrossRef - The conceptual structure of transition to motherhood in the neonatal intensive care unit
Hyunjeong Shin, Rosemary White‐Traut
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2007; 58(1): 90. CrossRef
- Exploration of the process of maternal role attainment in Iranian mothers with preterm neonate: A grounded theory
- 779 View
- 1 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Evaluation of a Community-Based Program for Breast Self-Examination Offered by the Community Health Nurse Practitioners in Korea
- Chung Yul Lee, Hee Soon Kim, Il Sun Ko, Ok Kyung Ham
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(8):1119-1126. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.8.1119
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer among Korean women. Only 14% of urban women and 10% of rural women in Korea, however, participated in breast cancer screening behavior in 1998 (Korean Ministry of Health & Welfare, 1999).
Purpose The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of community-based breast self-examination (BSE) education programs in Korea.
Methods First, breast cancer risk appraisals were done with 1,977 rural women. Of the 1,977 women, nearly 30% (n= 494) had a higher or equal to borderline risk of developing breast cancer. This quasi-experimental study was conducted to target these women with a high or equal to borderline risk of breast cancer. The risk appraisal feedback and breast self-examination education were used as an intervention for breast cancer prevention and early detection.
Results After a 3-month follow-up, 30.5% of the women in the intervention group performed regular BSE compared to 10.2% of women in the control group. The mean knowledge score related to breast cancer and BSE was significantly higher for the women in the intervention group than that in the control group.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of an Ongoing, Community-Based Breast Cancer Prevention Program for Korean American Women
Eun Koh, Ga-Young Choi, Ji Young Cho
Health & Social Work.2016; 41(1): 51. CrossRef - Effects of Tailored Message Education About Breast Cancer Risk Appraisal for Obese Korean Women
SoMi Park, ChaeWeon Chung, Barbara B. Cochrane
Oncology Nursing Forum.2013; 40(6): E382. CrossRef - The effectiveness of a nurse-delivered breast health promotion program on breast cancer screening behaviours in non-adherent Turkish women: A randomized controlled trial
Selda Secginli, Nursen O. Nahcivan
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2011; 48(1): 24. CrossRef - Effects on Nursing Students of Cognition-Behavior Integrated Breast Cancer Prevention Education Using an Interchangeable Nodule Model
So Mi Park, Bo Hwan Kim, Mi Jeong Park, Yang Heui Ahn, Chae Weon Chung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(2): 166. CrossRef - Development of an Integrated Breast Health Program for Prevention of Breast Cancer among Middle-aged Women
Hea Kung Hur, So Mi Park, Chang Hee Kim, Jong-Ku Park, Sang Baek Koh, Gi Yon Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(1): 54. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Mammography Behavior and Intention Among Korean Women
Ok Kyung Ham
Oncology Nursing Forum.2006; 33(1): 113. CrossRef - The Intention of Future Mammography Screening Among Korean Women
Ok Kyung Ham
Journal of Community Health Nursing.2005; 22(1): 1. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of an Ongoing, Community-Based Breast Cancer Prevention Program for Korean American Women
- 714 View
- 1 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Screening for High Risk Population of Dementia and Development of the Preventive Program Using Web
- Jung Soon Kim, Ihn Sook Jeong, Yoon Jin Kim, Sun Kyung Hwang, Byung Chul Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(2):236-245. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.2.236
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to develop a screening model for identifying a high risk group of dementia and to develop and evaluate the web-based prevention program.
Method It was conducted in 5 phases. 1) Data were collected from dementia patients and non-dementia patients in a community. 2) A screening model of the high risk population was constructed. 3) The validity test was performed and the model was confirmed. 4) Four weeks-prevention program was developed. 5) The program was administered, and evaluated the effects.
Result The model consisted of age, illiteracy, history of stroke and hypercholesterolemia. The program was designed with 12 sessions, group health education using web-based individual instruction program, and 12 sessions of low-intensity physical exercise program. After the completion, their self-efficacy, and health behaviors in experimental group were significantly improved over those in the control group. The perceived barrier in the treatment group is significantly decreased.
Conclusion The screening model developed is very simple and can be utilized in diverse community settings. And the web based prevention program will encourage individual learning and timely feedback, therefore it can facilitate their active participation and promote health management behaviors at home.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations Among Health Insurance Type, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and the Risk of Dementia: A Prospective Cohort Study in Korea
So-Hyun Moon, Hyun-Ju Seo, Dong Young Lee, Seong Min Kim, Jeong Min Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(14): 2616. CrossRef - The Effects of Computer - based Attention Program on Cognition and Executive Function in Elderly with Vascular Dementia
Hyojeong Lee, Kyoungok Hwang
Journal of The Korean Society of Integrative Medicine.2014; 2(2): 13. CrossRef - Analysis of Nutrition and Antioxidants of Yak-Kong Chungkukjang Powder Added Black Foods
Hyun-Joo Kong, Heyun-Sook Park, Tae-Hoon Kim, Seung-Ryeul Shin, Ju-Yeon Hong, Kyung-Mi Yang
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2013; 42(11): 1727. CrossRef - Comorbidity and Health Habits of Seoul City Elders with Dementia
Yoon Kyoung Lee, Mi Ra Sung, Dong Young Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(3): 411. CrossRef - Effects of an Exercise Program on Frontal Lobe Cognitive Function in Elders
Mee-Kyung Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(1): 107. CrossRef - A Comparison of the Factors Influencing the Life Satisfaction of the Elderly According to their Cognitive Impairment Level
Rah Il Hwang, Ji Young Lim, Young Whee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 622. CrossRef - Effects of an Exercise Program on Frontal Lobe Cognitive Function in Elders
Mee-Kyung Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(1): 107. CrossRef
- Associations Among Health Insurance Type, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and the Risk of Dementia: A Prospective Cohort Study in Korea
- 634 View
- 3 Download
- 7 Crossref

- A Comparative Study on the Predictive Validity among Pressure Ulcer Risk Assessment Scales
- Young Hee Lee, Ihn Sook Jeong, Seong Sook Jeon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(2):162-169. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.2.162
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to compare the predictive validity of Norton Scale(1962), Cubbin & Jackson Scale(1991), and Song & Choi Scale(1991).
Method Data were collected three times per week from 48-72hours after admission based on the four pressure sore risk assessment scales and a skin assessment tool for pressure sore on 112 intensive care unit(ICU) patients in a educational hospital Ulsan during Dec, 11, 2000 to Feb, 10, 2001. Four indices of validity and area under the curve(AUC) of receiver operating characteristic(ROC) were calculated.
Result Based on the cut off point presented by the developer, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value were as follows : Norton Scale : 97%, 18%, 35%, 93% respectively; Cubbin & Jackson Scale : 89%, 61%, 51%, 92%, respectively; and Song & Choi Scale : 100%, 18%, 36%, 100% respectively. Area under the curves(AUC) of receiver operating characteristic(ROC) were Norton Scale .737, Cubbin & Jackson Scale .826, Song & Choi Scale .683.
Conclusion The Cubbin & Jackson Scale was found to be the most valid pressure sore risk assessment tool. Further studies on patients with chronic conditions may be helpful to validate this finding.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Patient-Level Fall Risk Prediction Using the Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership’s Common Data Model: Pilot Feasibility Study
Hyesil Jung, Sooyoung Yoo, Seok Kim, Eunjeong Heo, Borham Kim, Ho-Young Lee, Hee Hwang
JMIR Medical Informatics.2022; 10(3): e35104. CrossRef - Predictive Validity of the Braden Scale for Pressure Ulcer Risk in Critical Care: A Meta‐Analysis
Min Wei, Ling Wu, Yan Chen, Qiaomei Fu, Wenyue Chen, Dongliang Yang
Nursing in Critical Care.2020; 25(3): 165. CrossRef - Predictive Validity of Pressure Ulcer Risk Assessment Scales among Patients in a Trauma Intensive Care Unit
Ja Eun Choi, Sun-Kyung Hwang
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(2): 26. CrossRef - Testing the Predictive Validity of the Hendrich II Fall Risk Model
Hyesil Jung, Hyeoun-Ae Park
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2018; 40(12): 1785. CrossRef - Automated Pressure Injury Risk Assessment System Incorporated Into an Electronic Health Record System
Yinji Jin, Taixian Jin, Sun-Mi Lee
Nursing Research.2017; 66(6): 462. CrossRef - Longitudinal Evaluation of Johns Hopkins Fall Risk Assessment Tool and Nurses' Experience
Eun Young Hur, Yinji Jin, Taixian Jin, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of Nursing Care Quality.2017; 32(3): 242. CrossRef - Predictive Validity of Pressure Ulcer Risk Assessment Tools for Elderly
Seong-Hi Park, Young-Shin Lee, Young-Mi Kwon
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2016; 38(4): 459. CrossRef - A Meta-analysis of the Timed Up and Go test for Predicting Falls
Seong-Hi Park, On-Seok Lee
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2016; 22(2): 27. CrossRef - Predictive validity of the Braden Scale for pressure ulcer risk in hospitalized patients
Seong-Hi Park, Yun-Kyoung Choi, Chang-Bum Kang
Journal of Tissue Viability.2015; 24(3): 102. CrossRef - Validation of Fall Risk Assessment Scales among Hospitalized Patients in South Korea using Retrospective Data Analysis
Young Ok Kang, Rhayun Song
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(1): 29. CrossRef - Validity of the Morse Fall Scale implemented in an electronic medical record system
Seonhyeon Baek, Jinshi Piao, Yinji Jin, Sun‐Mi Lee
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2014; 23(17-18): 2434. CrossRef - Incidence and Associated Factors of Pressure Ulcers in Newborns
Won-Young Choi, Hyeon-Ok Ju
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2012; 18(4): 177. CrossRef - Predictive Bayesian Network Model Using Electronic Patient Records for Prevention of Hospital-Acquired Pressure Ulcers
In Sook Cho, Eunja Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(3): 423. CrossRef - Braden Scale: evaluation of clinical usefulness in an intensive care unit
InSook Cho, Maengseok Noh
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2010; 66(2): 293. CrossRef
- Patient-Level Fall Risk Prediction Using the Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership’s Common Data Model: Pilot Feasibility Study
- 968 View
- 15 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Analysis of Direct Nursing Activity and Patient Outcomes Related to Graded Fee of Nursing Management for Inpatient
- Seong Hi Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(1):122-129. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.1.122
-
 Abstract
Abstract
Purpose The purpose of this study is to examine the difference of direct nursing activity and patient outcomes as mortality rate, complication rate, readmission rate and length of stay related to graded fee of nursing management for inpatient.
Method The subjects of this study were 44 general hospitals with more than 500 beds. Data totaled to 86,044 claims provided to inpatients in Jan. 2001 requested by an electronic data interchange from a Health Insurance Review Agency. The data was analyzed by SPSS win(ver.10.0) and statistical methods used were frequency, one-way ANOVA, χ2-Test and regression.
Result Synthetic judgment through performance index and 95% confidence interval, direct nursing activity showed to provided adequate quality of nursing care on 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 6th nursing degree. Also, patient outcomes showed difference by graded fee of nursing management for inpatient. Mortality rate of 2nd was the lowest with P.I. 67.9, 3rd, 5th, 6th, 4th in order. In case of complication rate, 2nd, 3rd and 4th were lower than other nursing degree. Readmission rate of 4th and 5th was the lowest. Length of stay of 2nd was the shortest with P.I. 88.3, 3rd, 4th, 5th, 4th, 6th in order.
Conclusion The findings from this study showed that, the higher nurse-to-patient ratio, the greater amount of direct nursing care activity for the patient. Also, the more direct nursing activities influenced a lower mortality rate, complication rate and readmission rate, shorter length of stay.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differences in Medical Use and Patient Outcomes between Patients Admitted to the Integrated Nursing Care Ward and the General Ward
Jeong Eun Mun, Bohyun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 439. CrossRef - Impact on health outcomes of hemodialysis patients based on the experience level of registered nurses in the hemodialysis department: a cross-sectional analysis
EunYoung Jeong
Frontiers in Health Services.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between nurse staffing level and adult nursing-sensitive outcomes in tertiary hospitals of Korea: Retrospective observational study
Chul-Gyu Kim, Kyun-Seop Bae
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2018; 80: 155. CrossRef - Differences of Upgrading Nurse Staffing in Nursing Care Activity, Work Performance Outcomes, and Job Satisfaction
Ju Yeun Kim, Young Whee Lee, Mi Kyoung Chung
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(3): 256. CrossRef - Nursing outcomes of inpatient on level of nursing staffing in long term care hospitals
Eun Hee Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2015; 26(3): 715. CrossRef - Study on Factors Associated with the Rise in Grade of Nursing Management Fee among Korean Hospitals
Hyun-Min Choi, Nam-Kyung Han, Sang-Kyu Lee, Han-Sung Kim, Sungkyoung Choi, Woojin Chung
Health Policy and Management.2015; 25(1): 40. CrossRef - Determinants of Registered Nurse Skill Mix & Staffing Level in Korea
Su-Jin Cho, Jinhyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(1): 10. CrossRef - Analysis on Satisfaction of Nursing Services for Elderly hospitalized in Attended Ward and General Ward
Mee-Suk Wang, In Deok Lee, M.S. Kang, Eun-Kwang Cha, Dae-Ho Choi, Hyeon-Cheol Jeong
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(5): 3014. CrossRef - Activity-Based Costing Analysis of Nursing Activities in General Hospital Wards
Ho-Soon Yoon, Jinhyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(4): 449. CrossRef - A Proposal to Improve Nursing Fee Differentiation Policy for General Hospitals Using Profitability-Analysis in the National Health Insurance
Sungjae Kim, Jinhyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(3): 351. CrossRef - Effects of Hospital Nurse Staffing on in-hospital Mortality, Pneumonia, Sepsis, and Urinary Tract Infection in Surgical Patients
Yunmi Kim, Sung-Hyun Cho, Kyung Ja June, Soon Ae Shin, Jiyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(5): 719. CrossRef - Maternal and Hospital Factors Impacting the Utilization of Rooming-in Care in South Korea: Secondary Analysis of National Health Data
Yunmi Kim, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(5): 593. CrossRef - Inpatient Outcomes by Nurse Staffing Grade in Korea
Su-Jin Cho, Han-Ju Lee, Ju-Yeon Oh, Jin-Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Health Policy and Administration.2011; 21(2): 195. CrossRef - The Effects of Medical Staffing Level on Length of Stay
Hanju Lee, Yu Kyung Ko, Mi-Won Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2011; 17(3): 327. CrossRef - Comparison of Nursing Records of Open Heart Surgery Patients before and after Implementation of Electronic Nursing Record
Insil Lee, Hyeoun-Ae Park
Journal of Korean Society of Medical Informatics.2009; 15(1): 83. CrossRef
- Differences in Medical Use and Patient Outcomes between Patients Admitted to the Integrated Nursing Care Ward and the General Ward
- 892 View
- 0 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Identifying Latent Classes of Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease
- Eunsil Ju, JiSun Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(6):817-827. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.6.817
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to identify latent classes based on major modifiable risk factors for coronary artery disease.
Methods This was a secondary analysis using data from the electronic medical records of 2,022 patients, who were newly diagnosed with coronary artery disease at a university medical center, from January 2010 to December 2015. Data were analyzed using SPSS version 20.0 for descriptive analysis and Mplus version 7.4 for latent class analysis.
Results Four latent classes of risk factors for coronary artery disease were identified in the final model: ‘smoking-drinking’, ‘high-risk for dyslipidemia’, ‘high-risk for metabolic syndrome’, and ‘high-risk for diabetes and malnutrition’. The likelihood of these latent classes varied significantly based on socio-demographic characteristics, including age, gender, educational level, and occupation.
Conclusion The results showed significant heterogeneity in the pattern of risk factors for coronary artery disease. These findings provide helpful data to develop intervention strategies for the effective prevention of coronary artery disease. Specific characteristics depending on the subpopulation should be considered during the development of interventions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Usefulness Evaluation of Laplacian Filter and Fast Non-Local Means Algorithm in Coronary Angiographic Images
Kyeongsoo Jeon, Jiwon Song, Jiwon Hur, Chaeeon Lee, Kang-Hyeon Seo, Youngjin Lee
Journal of Radiological Science and Technology.2025; 48(1): 93. CrossRef - The effect of preoperative training provided to patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery on postoperative comfort
Ayşe Şahin, Figen Dığın
Journal of Surgery and Medicine.2024; 8(6): 00. CrossRef - Profiling the socioeconomic characteristics, dietary intake, and health status of Korean older adults for nutrition plan customization: a comparison of principal component, factor, and cluster analyses
Kyungsook Woo, Kirang Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2024; 46: e2024043. CrossRef - Analysis of the Types and Affecting Factors of Older People's Health-related Quality of Life, Using Latent Class Analysis
Sun-Hee Jang, Dong-Moon Yeum
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(2): 212. CrossRef - Diagnosis and risk stratification of coronary artery disease in Yemeni patients using treadmill test
NouraddenN Aljaber, ShaneiA Shanei, SultanAbdulwadoud Alshoabi, KamalD Alsultan, MoawiaB Gameraddin, KhaledM Al-Sayaghi
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2020; 9(5): 2375. CrossRef - Latent Class Analysis for Health-Related Quality of Life in the Middle-Aged Male in South Korea
Youngsuk Cho, Dong Moon Yeum
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(1): 104. CrossRef
- Usefulness Evaluation of Laplacian Filter and Fast Non-Local Means Algorithm in Coronary Angiographic Images
- 1,114 View
- 9 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Factors Predicting the Interface Pressure Related to Pressure Injury in Intensive Care Unit Patients
- Ji Seon Shine, Soo Jin Kim, Ji Hyun Lee, Mi Yu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(6):794-805. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.6.794
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose Interface pressure is a factor that contributes to the occurrence of pressure injuries. This study aimed to investigate interface pressure at common sites of pressure injury (occipital, gluteal and peritrochanteric areas), to explore the relationships among risk factors, skin condition and interface pressure, and to identify risk factors influencing interface pressure.
Methods A total of 100 patients admitted to the intensive care unit were enrolled at a tertiary teaching hospital in Korea. Interface pressure was recorded by a scanning aid device (PalmQ). Patient data regarding age, pulmonary disease, Braden Scale score, body mass index, serum albumin, hemoglobin, mean blood pressure, body temperature, and oxygen saturation were included as risk factors. Data collected from July to September 2016 were analyzed using binary logistic regression.
Results The mean interface pressure of the occipital, gluteal, and right and left peritrochanteric areas were 37.96 (±14.90), 41.15 (±16.04), 53.44 (±24.67), and 54.33 (±22.80) mmHg, respectively. Predictive factors for pressure injuries in the occipital area were age ≥70 years (OR 3.45, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.19~9.98), serum albumin deficit (OR 2.88, 95% CI: 1.00~8.26) and body temperature ≥36.5oC (OR 3.12, 95% CI: 1.17~8.17); age ≥70 years (OR 2.81, 95% CI: 1.10~7.15) in the right peritrochanteric area; and body temperature ≥36.5oC (OR 2.86, 95% CI: 1.17~6.98) in the left peritrochanteric area.
Conclusion Our findings suggest that old age, hypoalbuminemia, and high body temperature may be contributory factors to increasing interface pressure; therefore, careful assessment and nursing care of these patients are needed to prevent pressure injury. Further studies are needed to establish cutoff values of interface pressure for patients with pressure ulcers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Postoperative Mobility and its Relationship with Surgery-Related Pressure Injuries: Incidence and Risk Factors in Bariatric Surgery Patients
Yasemin Uslu, Rabia Tülübaş, Yakup Akyüz, Mustafa Atabey
Obesity Surgery.2026; 36(1): 128. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Pressure Injury in Mechanically Ventilated Patients in Emergency Intensive Care Units: A Prospective Observational Study
Sun Woo Son, Mi Yu
Nursing in Critical Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Innovative air mattress for the prevention of pressure ulcers in neonates
Tino Adrian Jucker, Simon Annaheim, Elodie Morlec, Martin Camenzind, Anna-Barbara Schlüer, Barbara Brotschi, René Michel Rossi
Journal of Wound Care.2024; 33(9): 652. CrossRef - A Prospective, Randomized, Non-inferiority Trial to Compare the Efficacy of 3% Povidone-Iodine Foam Dressing and Silver Foam Dressing in the Treatment of Pressure Injuries
Kyung Hee Park, Kyuwon Baek, Minkyung Kim, Myoung Jean Ju, Won Hee Jung, Yong Soon Yoon
Journal of Wound Management and Research.2023; 19(1): 13. CrossRef - Characteristics and risk factors of nasal mucosal pressure injury in intensive care units
Ruiling Nan, Yujie Su, Juhong Pei, Haixia Chen, Li He, Xinman Dou, Shuling Nan
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(1-2): 346. CrossRef - Risk Factors of Endotracheal Intubation-Related Pressure Injury among Patients Admitted to the ICU
Lili Qin, Wenjuan Yun, Cheng Hang
Advances in Skin & Wound Care.2021; 34(3): 144. CrossRef - Impact of Pressure Injuries on Patient Outcomes in a Korean Hospital
Yina Han, Yinji Jin, Taixian Jin, Sun-Mi Lee, Ju-Young Lee
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2019; 46(3): 194. CrossRef - The relationship of subepidermal moisture and early stage pressure injury by visual skin assessment
Chul-Gyu Kim, Seungmi Park, Ji Woon Ko, Sungho Jo
Journal of Tissue Viability.2018; 27(3): 130. CrossRef
- Postoperative Mobility and its Relationship with Surgery-Related Pressure Injuries: Incidence and Risk Factors in Bariatric Surgery Patients
- 1,606 View
- 30 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Characteristics and Risk Factors for Falls in Tertiary Hospital Inpatients
- Eun-Ju Choi, Young-Shin Lee, Eun-Jung Yang, Ji-Hui Kim, Yeon-Hee Kim, Hyeoun-Ae Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(3):420-430. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.3.420
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The aim of this study was to explore characteristics of and risk factors for accidental inpatient falls.
Methods Participants were classified as fallers or non-fallers based on the fall history of inpatients in a tertiary hospital in Seoul between June 2014 and May 2015. Data on falls were obtained from the fall report forms and data on risk factors were obtained from the electronic nursing records. Characteristics of fallers and non-fallers were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Risk factors for falls were identified using univariate analyses and logistic regression analysis.
Results Average length of stay prior to the fall was 21.52 days and average age of fallers was 61.37 years. Most falls occurred during the night shifts and in the bedroom and were due to sudden leg weakness during ambulation. It was found that gender, BMI, physical problems such elimination, gait, vision and hearing and medications such as sleeping pills, antiarrhythmics, vasodilators, and muscle relaxant were statistically significant factors affecting falls.
Conclusion The findings show that there are significant risk factors such as BMI and history of surgery which are not part of fall assessment tools. There are also items on fall assessment tools which are not found to be significant such as mental status, emotional unstability, dizziness, and impairment of urination. Therefore, these various risk factors should be examined in the fall risk assessments and these risk factors should be considered in the development of fall assessment tools.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perceptions and practices of rehabilitation specialist nurses in fall management: a qualitative study
Heli Zhang, Jianfen Luo, Xiaotian Zhang, Yuting Jiang, Xiaoyu Sun, Qi Tang, Xin Wang, Baohua Li
Frontiers in Public Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of bed falls among inpatients in Iranian hospitals: A meta-analysis
Parvaneh Isfahani, Mohammad Sarani, Mina Salajegheh, Somayeh Samani, Aliyeh Bazi, Mahdieh Poodineh Moghadam, Fatemeh Boulagh, Mahnaz Afshari
Human Factors in Healthcare.2025; 7: 100093. CrossRef - Evaluation of Risk Factors for Fall Incidence Based on Statistical Analysis
Da Hye Moon, Tae-Hoon Kim, Myoung-Nam Lim, Seon-Sook Han
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2025; 22(5): 748. CrossRef - Experiences of nurse managers in preventing and managing inpatient falls: a qualitative descriptive study
Erge Jia, Yan Kang, Runv Zhou, Weiying Zhang, Xueyan Li
BMJ Open.2025; 15(12): e106509. CrossRef - Sensitivity of Fall Risk Perception and Associated Factors in Hospitalized Patients with Mental Disorders
Ji Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim, Yusun Park, Jin Kyeong Ko, Eunmi Ra
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(5): 443. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Fall Risk Perception Questionnaire-Short Version for Inpatients in Acute Care Hospitals
Jeeeun Choi, Sujin Lee, Eunjin Park, Sangha Ku, Sunhwa Kim, Wonhye Yu, Eunmi Jeong, Sukhee Park, Yusun Park, Hye Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(2): 151. CrossRef - The Impact of Physical Performance and Fear of Falling on Fall Risk in Hemodialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jiwon Choi, Sun-Kyung Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(1): 63. CrossRef - The Impact of Possible Sarcopenia and Obesity on the Risk of Falls in Hospitalized Older Patients
Kahyun Kim, Dukyoo Jung
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2023; 26(1): 18. CrossRef - Analysis of Data on Accidental Falls from the Hospital Incident Reporting in a General Hospital
Yu-ri Jang, Jeong Yun Park
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2023; 29(1): 15. CrossRef - Predication of Falls in Hospitalized Cancer Patients
Jun-Nyun Kim, Sun-Hwa Beak, Bo-Seop Lee, Mi-Ra Han
Asian Oncology Nursing.2023; 23(2): 56. CrossRef - Nurses’ Burden of Elimination Care: Sequential Explanatory Mixed-Methods Design
Se Young Jung, Hui-Woun Moon, Da Som Me Park, Sumi Sung, Hyesil Jung
International Journal of General Medicine.2023; Volume 16: 4067. CrossRef - Clinical study of falls among inpatients with hematological diseases and exploration of risk prediction models
Jing Wang, Bin Chen, Fang Xu, Qin Chen, Jing Yue, Jingjing Wen, Fang Zhao, Min Gou, Ya Zhang
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Clinical Data Warehouse Analysis of Risk Factors for Inpatient Falls in a Tertiary Hospital: A Case-Control Study
Eunok Kwon, Sun Ju Chang, Mikyung Kwon
Journal of Patient Safety.2023; 19(8): 501. CrossRef - Z-drugs and falls in nursing home patients: data from the INCUR study
Sarah Damanti, Moreno Tresoldi, Philipe de Souto Barreto, Yves Rolland, Matteo Cesari
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2022; 34(12): 3145. CrossRef - The Fall Risk Screening Scale Is Suitable for Evaluating Adult Patient Fall
Li-Chen Chen, Yung-Chao Shen, Lun-Hui Ho, Whei-Mei Shih
Healthcare.2022; 10(3): 510. CrossRef - Comparisons of Fall Prevention Activities Using Electronic Nursing Records: A Case-Control Study
Hyesil Jung, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Ho-Young Lee
Journal of Patient Safety.2022; 18(3): 145. CrossRef - Risk Factors according to Fall Risk Level in General Hospital Inpatients
Yeon Hwa Lee, Myo Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(1): 35. CrossRef - Development and validation of the fall risk perception questionnaire for patients in acute care hospitals
Jieun Choi, Se Min Choi, Jeong Sin Lee, Soon Seok Seo, Ja Yeon Kim, Hye Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2021; 30(3-4): 406. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Degree of Harm from Fall Incidents in Hospitals
Shinae Ahn, Da Eun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(5): 334. CrossRef - A Machine Learning–Based Fall Risk Assessment Model for Inpatients
Chia-Hui Liu, Ya-Han Hu, Yu-Hsiu Lin
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2021; 39(8): 450. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Falls in High- and Low-Risk Patients in a Tertiary Hospital in Korea
Young-Shin Lee, Eun-Ju Choi, Yeon-Hee Kim, Hyeoun-Ae Park
Journal of Patient Safety.2020; 16(4): e376. CrossRef - Impact of Hearing Loss on Patient Falls in the Inpatient Setting
Victoria L. Tiase, Kui Tang, David K. Vawdrey, Rosanne Raso, Jason S. Adelman, Shao Ping Yu, Jo R. Applebaum, Anil K. Lalwani
American Journal of Preventive Medicine.2020; 58(6): 839. CrossRef - Improving Prediction of Fall Risk Using Electronic Health Record Data With Various Types and Sources at Multiple Times
Hyesil Jung, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Hee Hwang
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2020; 38(3): 157. CrossRef - Triggers and Outcomes of Falls in Hematology Patients: Analysis of Electronic Health Records
Min Kyung Jung, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2019; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - Incidence of Falls and Risk Factors of Falls in Inpatients
Soo-Jin Yoon, Chun-Kyon Lee, In-Sun Jin, Jung-Gu Kang
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2018; 24(2): 2. CrossRef
- Perceptions and practices of rehabilitation specialist nurses in fall management: a qualitative study
- 2,615 View
- 44 Download
- 25 Crossref

- Ecological Correlates of Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Korean Blue-collar Workers: A Multi-level Study
- Won Ju Hwang, Yunhee Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(6):857-867. Published online December 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.6.857
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate individual and organizational level of cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors associated with CVD risk in Korean blue-collar workers working in small sized companies.
Methods Self-report questionnaires and blood sampling for lipid and glucose were collected from 492 workers in 31 small sized companies in Korea. Multilevel modeling was conducted to estimate effects of related factors at the individual and organizational level.
Results Multilevel regression analysis showed that workers in the workplace having a cafeteria had 1.81 times higher CVD risk after adjusting for factors at the individual level (
p =.022). The explanatory power of variables related to organizational level variances in CVD risk was 17.1%.Conclusion The results of this study indicate that differences in the CVD risk were related to organizational factors. It is necessary to consider not only individual factors but also organizational factors when planning a CVD risk reduction program. The factors caused by having cafeteria in the workplace can be reduced by improvement in the CVD-related risk environment, therefore an organizational-level intervention approach should be available to reduce CVD risk of workers in small sized companies in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multilevel Analysis of Factors Affecting Health-Related Quality of Life of the Elderly
Hyunjung Moon, Sunkyung Cha
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2022; 31(3): 391. CrossRef - Socioeconomic Disparities in Cardiovascular Health in South Korea
Chi-Young Lee, Eun-Ok Im
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2021; 36(1): 8. CrossRef - Health promotion program for office workers with SEM based on the WHO’s healthy workplace framework
Hosihn Ryu, Jiyeon Jung, Jihyun Moon
Health Promotion International.2020; 35(6): 1369. CrossRef - Effects of a Yoga Program in Reducing Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Workers of Small Workplaces: A Pilot Test
Won Ju Hwang, Jin Ah Kim, Ji Sun Ha
Sustainability.2020; 12(23): 10038. CrossRef - An Exploration of Contextual Aspects that Influence Cardiovascular Disease Risks Perceived by Workers in a Small–Medium-Sized Workplace
Jin Ah Kim, Won Ju Hwang, Juhye Jin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(14): 5155. CrossRef - Measurement of Socioeconomic Position in Research on Cardiovascular Health Disparities in Korea: A Systematic Review
Chi-Young Lee, Yong-Hwan Lee
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2019; 52(5): 281. CrossRef - Developing a Health-Promotion Program Based on the Action Research Paradigm to Reduce Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors among Blue Collar Workers
Won Ju Hwang, Jin Ah Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(24): 4958. CrossRef - Regional Factors on the Self-rated Health of Wage Workers
Minjung Kwon, Eunsuk Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(1): 21. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of Interventions for Workers with Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: Using an Ecological Model
Won Ju Hwang, Yunhee Park, Jin Ah Kim
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(1): 41. CrossRef - CVD-related Knowledge, Perception, Belief and Prevention Behaviors of Korean Blue-collar Workers: Needs Assessment for Developing the Intervention Program through Qualitative Approach
Won Ju Hwang, Yunhee Park
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(4): 362. CrossRef
- Multilevel Analysis of Factors Affecting Health-Related Quality of Life of the Elderly
- 1,120 View
- 6 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Trend Analysis in the Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes According to Risk Factors among Korean Adults: Based on the 2001~2009 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
- Young-Ju Kim, Myoung-Nam Lim, Dong-Suk Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(6):743-750. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.6.743
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The objective of this study was to provide a trend analysis of the prevalence of diabetes relative to the socioeconomic, lifestyle, and physiologic risk factors among Korean adults aged over 30 years for a 10-year period using data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Methods Prevalence difference and the slope index of inequality were calculated for each risk factors using binomial regression by considering the repeated cross-sectional features of the data. The prevalence ratio and the relative index of inequality were calculated using log-binomial regression. Linear trend tests were performed using SAS 9.2.
Results Crude prevalence of diabetes increased over the 10-year period, and was higher for men than for women. It was very high for adults 60 years or over, consistently increasing over time. The prevalence among unemployed men, women with higher level of stress, women with hypertension, and adults with serum triglyceride levels over 135 mg/dL increased over the 10-year period in comparison with the respective control group.
Conclusion Considering the rapid economic development and associated lifestyle changes in Korea, action should be taken to control the prevalence of diabetes by both preventing and consistently monitoring these identified risk factors using a public-health approach.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of an Association between Preterm Birth and Parental Educational Level in Japan Using National Data
Tasuku Okui
Children.2023; 10(2): 342. CrossRef - Trends in Diabetes Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment and Control in Yangon Region, Myanmar, Between 2004 and 2014, Two Cross-Sectional Studies
Wai Phyo Aung, Espen Bjertness, Aung Soe Htet, Hein Stigum, Marte Karoline Råberg Kjøllesdal
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(18): 3461. CrossRef - Factors affecting glycated hemoglobin(HbA1c) checkup of diabetic patients by gender: Using the community health survey
Yun-Jeong Kim, Byung-Deog Hwang
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2019; 36(5): 63. CrossRef - Trends in diabetes prevalence among Korean adults based on Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys III–VI
Jae-woo Lee, Hee-Taik Kang, Hyoung-Ji Lim, Byoungjin Park
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 138: 57. CrossRef - Baseline Cardiovascular Characteristics of Adult Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease from the KoreaN Cohort Study for Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease (KNOW-CKD)
Hyoungnae Kim, Tae-Hyun Yoo, Kyu Hun Choi, Kook-Hwan Oh, Joongyub Lee, Soo Wan Kim, Tae Hee Kim, Suah Sung, Seung Hyeok Han
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2017; 32(2): 231. CrossRef - Secular trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in adults in China from 1995 to 2014: A meta‐analysis
Chengyi Han, Ming Zhang, Xinping Luo, Chongjian Wang, Lei Yin, Chao Pang, Tianping Feng, Yongcheng Ren, Bingyuan Wang, Lu Zhang, Linlin Li, Xiangyu Yang, Hongyan Zhang, Yang Zhao, Junmei Zhou, Zhihui Xie, Jingzhi Zhao, Dongsheng Hu
Journal of Diabetes.2017; 9(5): 450. CrossRef - Utilities for Type 2 Diabetes Treatment-Related Attributes in a South Korean and Taiwanese Population
Narayan Rajan, Kristina S. Boye, Meaghan Gibbs, Yoon Ji Lee, Peter Davey, Mark Ball, Steve M. Babineaux
Value in Health Regional Issues.2016; 9: 67. CrossRef - Awareness, treatment and control of type 2 diabetes among Chinese elderly and its changing trend for past decade
Miao Liu, Jianhua Wang, Yao He, Bin Jiang, Lei Wu, Yiyan Wang, Zhang Di, Jing Zeng
BMC Public Health.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes According to Gender among Korean Employees
Sang-A Kim, Woong-Sub Park, Su Jeong Yu, Young Ran Chae, Donghee Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(11): 7589. CrossRef - Association of Family Composition and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults Aged over 45 Years Old
Young-Ju Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(4): 349. CrossRef
- Analysis of an Association between Preterm Birth and Parental Educational Level in Japan Using National Data
- 1,162 View
- 9 Download
- 10 Crossref

- A Path Analysis on Factors Influencing Second Primary Cancer Screening Practices in Stomach, Colon, and Breast Cancer Survivors
- Young Hee Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(2):139-148. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.2.139
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to identify the factors influencing second primary cancer (SPC) screening practice by examining the relationships of physical symptoms, knowledge and attitudes regarding SPC screening, perceived risk, primary cancer type, and demographic factors of cancer survivors.
Methods Participants were 308 survivors of stomach, colon, or breast cancer recruited from 2 university hospitals in Korea. Data were collected using a questionnaire and analyzed using IBM SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 18.0.
Results The proportion of participants taking all cancer screenings according to national guidelines was 40%. They had moderate knowledge and a relatively positive attitude regarding SPC screening and high cancer risk perception. The participants had taken fewer SPC screenings after than before cancer diagnosis. The factors influencing cancer risk perception were age, physical symptoms, knowledge regarding SPC and primary cancer type (stomach). The factors influencing SPC screening practice were age, gender, economic status, knowledge regarding SPC screening, and primary cancer types (colon).
Conclusion It is important for clinical professionals to recognize that survivors of cancer are susceptible to another cancer. Education on SPC screening for these survivors should focus on communicating with and encouraging them to have regular cancer screenings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Integrated Supportive Care Nursing Competence Scale for Cancer Survivors
Eun-Jung Bae, Yun-Hee Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(7): 755. CrossRef - Health Behaviors of Cancer Survivors According to the Employment Status and Occupation: A Cross-Sectional Study
Ka Ryeong Bae, Wi-Young So, Su Jung Lee
Healthcare.2023; 11(22): 2974. CrossRef - Survivors’ health competence mediates the association between wearable activity tracker use and self-rated health: HINTS analysis
Steven De La Torre, Donna Spruijt-Metz, Albert J. Farias
Journal of Cancer Survivorship.2022; 16(6): 1268. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Health Check-up and Cancer Screening Participation among Family Caregivers of Patients with Dementia: A Cross-Sectional Study
Bomgyeol Kim, Yejin Lee, Jin-Won Noh, Tae Hyun Kim
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Supportive Care Needs of Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hyekyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(1): 60. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life among Cancer Survivors: Based on the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) for 2019
Hee Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2021; 24(2): 109. CrossRef - Colorectal cancer screening practices among cancer survivors five years after diagnosis
Adeline Monet, Rajae Touzani, Anne-Déborah Bouhnik, Marc-Karim Bendiane, Julien Mancini
Journal of Public Health.2021; 29(4): 805. CrossRef - An Integrated TK-TD Model for Evaluation of Radix Aconitikusnezoffii (RAK)
Xin Miao, Ren Bu, Yang Liu, Bing Li, Xiaofei Zhang, Haiyan Xing, Gang Li
Pharmacology.2020; 105(11-12): 669. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Characteristics of Cancer Patients and Cancer Survivors
So Young Baek, Ja Yun Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(1): 11. CrossRef - Breast and Cervical Cancer Screening Behavior in Female Cancer Survivors: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007–2012
Eun-Ae Lee, Jinyoung Shin, Eun-Joo Hwang, Jung-Woong Lee
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2017; 38(3): 116. CrossRef - The necessity of analysis of cancer survivor concept in Korea
Jiyoung Kim
Journal of Comprehensive Nursing Research and Care.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The Factors Related to the Non-Practice of Cancer Screening in Cancer Survivors: Based on the 2007-2012 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Song-Ei Yang, Nam-Kyung Han, Sun-Mi Lee, Tae-Hyun Kim, Woojin Chung
Health Policy and Management.2015; 25(3): 162. CrossRef
- Development of Integrated Supportive Care Nursing Competence Scale for Cancer Survivors
- 1,102 View
- 4 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Risk Factors for Pediatric Inpatient Falls
- Myung Sook Cho, Mi Ra Song, Sun Kyung Cha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(5):595-604. Published online October 15, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.5.595
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify risk factors for pediatric inpatients falls.
Methods The study was a matched case-control design. The participants were 279 patients under the age of 6 who were admitted between January 1, 2004 and December 31, 2009. Through chart reviews, 93 pediatric patients who fell and 186 ones who did not fall were paired by gender, age, diagnosis, and length of stay. Five experts evaluated the 38 fall risk factors selected by the researchers.
Results In a general hospital, pediatric patients with secondary diagnosis, tests that need the patient to be moved, intravenous lines, hyperactivity, anxiolytics, sedatives and hypnotics, and general anesthetics showed significance for falls on adjusted-odds ratios. Conditional logistic regression analysis was performed to elucidate the factors that influence pediatric inpatient falls. The probability of falls increased with hyperactivity and general weakness. Patients who didn't have tests that required them to be moved and intravenous line had a higher risk of falls.
Conclusion These findings provide information that is relevant in developing fall risk assessment tools and prevention programs for pediatric inpatient falls.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factors for falls among children aged 0–18 years: a systematic review
Lan Wang, Mao-Lin Qian, Xiao Shan, Xiao-Qin Liu
World Journal of Pediatrics.2022; 18(10): 647. CrossRef - Analysis of Fall Incident Rate among Hospitalized Korean Children Using Big Data
Eun Joo Kim, Anna Lee
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2021; 61: 136. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Fall Prevention Programs for Pediatric Inpatients
Eun-Joo Kim, Geun-Myun Kim, Ji-Young Lim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(11): 5853. CrossRef - An electronic medical record-based fall risk assessment tool for pediatric inpatients in South Korea: Improved sensitivity and specificity
Eun Joo Kim, Ji Young Lim, Geun Myun Kim, Junghyun Min
Child Health Nursing Research.2021; 27(2): 137. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of a Pediatric Fall Risk Assessment Scale for Hospitalized Patients in Taiwan
Ching-Mei Chang, Cheng-Fan Wen, Hsien-Feng Lin
Quality Management in Health Care.2021; 30(2): 121. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Mobile Application for Safety Incident Prevention among Hospitalized Korean Children: A pilot Study of Feasibility and Acceptability
Jihee Han, Won-Oak Oh, Il Tae Park, Anna Lee
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2020; 51: e69. CrossRef - Risk factors of falls among inpatients with cancer
M.D. Jun, K.M. Lee, S.A. Park
International Nursing Review.2018; 65(2): 254. CrossRef - Predictive Factors for Inpatient Falls among Children with Cerebral Palsy
Ebru Alemdaroğlu, Sibel Demir Özbudak, Sibel Mandiroğlu, Seda Alakoç Biçer, Neşe Özgirgin, Halil Uçan
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2017; 32: 25. CrossRef - The Effect of Pediatric Inpatient Fall Prevention Education on Caregivers' Fall-related Knowledge and Preventive Behaviors
So Yeon Park, Hyeon Ok Ju
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2017; 23(4): 398. CrossRef - A Pediatric Fall-Risk Assessment Tool for Hospitalized Children.
Hyeon Ju Shin, Young Nam Kim, Ju Hee Kim, In Sook Son, Kyung Sook Bang
Child Health Nursing Research.2014; 20(3): 215. CrossRef
- Risk factors for falls among children aged 0–18 years: a systematic review
- 1,569 View
- 28 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Effects of Tai Chi on Fall Risk Factors: A Meta-Analysis
- Moonkyoung Park, Rhayun Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(3):341-351. Published online June 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.3.341
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to analyze the effects of Tai Chi on fall-related risk factors through meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials published in English and Korean between 2000 and 2010.
Methods Using health related database and hand search of references and Google, 28 randomized studies were collected from doctoral dissertation and published peer reviewed articles. The Comprehensive Meta-analysis version 2.0 was used for the analysis.
Results The effect sizes for Tai Chi for 3 months were significant with ES=0.54 for static balance, ES=0.24 for dynamic balance, ES=0.69 for balance measured by scale, and ES=0.40 for flexibility, ES=0.48 for muscle strength, ES=0.71 for ADL, and ES=0.37 for fear of falling. Also, the effect sizes of Tai Chi for 6 months were significant for most fall-related variables. The 6 month data for flexibility was not analyzed since only one study was published.
Conclusion The analysis of studies of randomized clinical trials indicate that Tai Chi is effective in improving balance, flexibility, muscle strength, activities of daily living, and fear of falling when applied for 3 or 6 months. The findings provide the objective evidence to apply Tai Chi as a fall preventive intervention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Global research on Chinese martial arts (1974–2025): A bibliometric and visualization-based analysis using Web of Science
Wei Chen, Syahrul Ridhwan Morazuki
Medicine.2025; 104(32): e43769. CrossRef - Effects of Tai-Chi and Running Exercises on Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Biomarkers in Sedentary Middle-Aged Males: A 24-Week Supervised Training Study
Yi Wang, Xian Guo, Liangchao Liu, Minhao Xie, Wing-Kai Lam
Biology.2022; 11(3): 375. CrossRef - Mind-Body Therapies From Traditional Chinese Medicine: Evidence Map
Lissandra Zanovelo Fogaça, Caio Fabio Schlechta Portella, Ricardo Ghelman, Carmen Verônica Mendes Abdala, Mariana Cabral Schveitzer
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Tai Chi for improving balance and reducing falls: An overview of 14 systematic reviews
Dongling Zhong, Qiwei Xiao, Xili Xiao, Yuxi Li, Jing Ye, Lina Xia, Chi Zhang, Juan Li, Hui Zheng, Rongjiang Jin
Annals of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine.2020; 63(6): 505. CrossRef - Exploring the Adaptability of Tai Chi to Stroke Rehabilitation
Inok Hwang, Rhayun Song, Sukhee Ahn, Myung-ah Lee, Peter M. Wayne, Min Kyun Sohn
Rehabilitation Nursing.2019; 44(4): 221. CrossRef - The association between Tai Chi exercise and safe driving performance among older adults: An observational study
Sally Miller, Ruth E. Taylor-Piliae
Journal of Sport and Health Science.2018; 7(1): 83. CrossRef - Adapting Tai Chi for Upper Limb Rehabilitation Post Stroke: A Feasibility Study
Shujuan Pan, Dahlia Kairy, Hélène Corriveau, Michel Tousignant
Medicines.2017; 4(4): 72. CrossRef - The Effects of Tai Chi Practice With Asynchronous Music on Compliance and Fall-Related Risk Factors in Middle-Aged and Older Women: A Pilot Study
Yan Du, Penny Roberts, Qingwen Xu
Journal of Holistic Nursing.2017; 35(2): 142. CrossRef - The Effects of Exercise Intervention for Fall Prevention in Persons with Arthritis: A Meta Analysis
Chun Hee Lee, Heeok Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(6): 587. CrossRef - The correlation between white matter hyperintensity and balance disorder and fall risk: An observational, prospective cohort study
Dong‐Chao Shen, Shuo‐Lin Wu, Yu‐Zhi Shi, Shuo Wang, Yu‐Mei Zhang, Chun‐Xue Wang
Chronic Diseases and Translational Medicine.2016; 2(3): 173. CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Interventions for Fall Prevention in Hospitalized Patients: A Meta-analysis
Yoon Lee Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(4): 469. CrossRef - The effects of Tai‐Chi in conjunction with thera‐band resistance exercise on functional fitness and muscle strength among community‐based older people
Shu‐Fen Lin, Huei‐Chuan Sung, Tzai‐Li Li, Tsung‐Cheng Hsieh, Hsiao‐Chin Lan, Shoa‐Jen Perng, Graeme D. Smith
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2015; 24(9-10): 1357. CrossRef - Recent Literature
Focus on Alternative and Complementary Therapies.2014;[Epub] CrossRef
- Global research on Chinese martial arts (1974–2025): A bibliometric and visualization-based analysis using Web of Science
- 1,276 View
- 1 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Factors Associated with Blue-collar Workers' Risk Perception of Cardiovascular Disease
- Won Ju Hwang, OiSaeng Hong, Mi Ja Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(7):1095-1104. Published online December 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.7.1095
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the contribution of actual cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, as well as, individual, psychosocial, and work-related factors as predictors of CVD risk perception among Korean blue-collar workers.
Methods The participants were 238 Korean blue-collar workers who worked in small companies. Data were collected through a survey; anthropometric and blood pressure measures; and blood sampling for lipid levels.
Results Blue-collar workers had high actual CVD risk and low CVD risk perception. The significant predictors of risk perception included perceived health status, alcohol consumption, knowledge of CVD risk, actual CVD risk, decision latitude, and shift work. The model explained 26% of the variance in CVD risk perception.
Conclusion The result suggests when occupational health nurses are giving routine health examination in small companies, they can enhance CVD risk perception in blue-collar workers by providing essential information about CVD risk factors and personal counseling on the individual worker's CVD risk status.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of perception bias for cardiovascular disease risk on physical activity and dietary habits
Zhiting Guo, Yujia Fu, Xuyang Wang, Aline Aparecida Monroe, Yuping Zhang, Jingfen Jin, Meifen Chen
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2024; 11(5): 505. CrossRef - Work-Life Conflict, Burnout, and Associated Factors Among Hydroelectric Power Plant Employees: A Cross-Sectional Study in Turkey
İrem Medeni, Volkan Medeni, Osman Burak Demirbaş, Mustafa Necmi İlhan
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular disease in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases: The relationship between self-perceived risk and actual risk
Cristiana Sieiro Santos, Maria Miguel Oliveira, Paulo Ney Solari, Pedro Mateus, Maria José Santos, Hector Corominas, Carolina Álvarez Castro, Elvira Díez Álvarez
Reumatología Clínica.2024; 20(5): 229. CrossRef - Cardiovascular disease in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases: The relationship between self-perceived risk and actual risk
Cristiana Sieiro Santos, Maria Miguel Oliveira, Paulo Ney Solari, Pedro Mateus, Maria José Santos, Hector Corominas, Carolina Álvarez Castro, Elvira Díez Álvarez
Reumatología Clínica (English Edition).2024; 20(5): 229. CrossRef - Cardiovascular disease risk perception among community adults in South China: a latent profile analysis
Zhiting Guo, Yong Yuan, Yujia Fu, Nianqi Cui, Qunfei Yu, Erling Guo, Chuanqi Ding, Yuping Zhang, Jingfen Jin
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk perception of non-communicable diseases: A systematic review on its assessment and associated factors
Miaw Yn Jane Ling, Norfazilah Ahmad, Azimatun Noor Aizuddin, Ghobad Moradi
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(6): e0286518. CrossRef - Good general health and lack of family history influence the underestimation of cardiovascular risk: a cross-sectional study
Åsa Grauman, Jorien Veldwijk, Stefan James, Mats Hansson, Liisa Byberg
European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2021; 20(7): 676. CrossRef - Eating control and eating behavior modification to reduce abdominal obesity: a 12-month randomized controlled trial
Soo Kyoung Kim, Norma Patricia Rodriguez Rocha, Hyekyeong Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(1): 38. CrossRef - An Exploration of Contextual Aspects that Influence Cardiovascular Disease Risks Perceived by Workers in a Small–Medium-Sized Workplace
Jin Ah Kim, Won Ju Hwang, Juhye Jin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(14): 5155. CrossRef - Perceptions of the impact of non-standard work schedules on health in Australian graduates: an exploratory study
Meagan E. CROWTHER, Amy C. REYNOLDS, Sally A. FERGUSON, Robert ADAMS
Industrial Health.2020; 58(1): 54. CrossRef - Risk Perception & Risk-Reduction Behavior Model for Blue-Collar Workers: Adapted From the Health Promotion Model
Won Ju Hwang, Mi Jeong Kim
Frontiers in Psychology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Alcohol consumption in Spanish mental health patients vs. working population
Miguel Ruiz-Flores Bistuer, Maria Teofila Vicente-Herrero, Silvia Lladosa-Marco, Ángel Arturo López-González, Luisa Mercedes Capdevila-García
Revista de la Facultad de Medicina.2018; 66(2): 171. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Risk Across Occupational Groups and Industry in a Statewide Study of an Australian Working Population
Helen Louise Kelsall, Palamandadige Harsha Suranga Fernando, Stella May Gwini, Malcolm Ross Sim
Journal of Occupational & Environmental Medicine.2018; 60(3): 286. CrossRef - Psychometric Testing of the Effort-Reward Imbalance–Short Form Among Blue-Collar Workers Employed in Small Industrial Settings in Korea
Won Ju Hwang, Oi Saeng Hong, Dae Ryong Kang
Workplace Health & Safety.2018; 66(12): 597. CrossRef - Evaluating the prevalence, awareness, and control of hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia in Korea using the NHIS-NSC database
Sunjoo Boo, Young Joo Yoon, Hyunjin Oh
Medicine.2018; 97(51): e13713. CrossRef - CVD-related Knowledge, Perception, Belief and Prevention Behaviors of Korean Blue-collar Workers: Needs Assessment for Developing the Intervention Program through Qualitative Approach
Won Ju Hwang, Yunhee Park
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(4): 362. CrossRef - Occupational differences for nutrient intake and physical-activity levels in young and middle-aged men
Eric C. Conchola, Abbie E. Smith-Ryan, Brennan J. Thompson, Eric J. Sobolewski, Eric D. Ryan
Work.2016; 55(1): 187. CrossRef - Association of Work-related Characteristics and Hypertension among White Collar Workers
Chae-Bong Kim, KyooSang Kim
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene.2015; 25(3): 418. CrossRef - Ecological Correlates of Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Korean Blue-collar Workers: A Multi-level Study
Won Ju Hwang, Yunhee Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(6): 857. CrossRef - 10-Year Risk for Cardiovascular Disease Among Male Workers in Small-Sized Industries
Kyongok Park, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2015; 30(3): 267. CrossRef - Casual Dock Work: Profile of Diseases and Injuries and Perception of Influence on Health
Marta Cezar-Vaz, Marlise De Almeida, Clarice Bonow, Laurelize Rocha, Anelise Borges, Diéssica Piexak
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2014; 11(2): 2077. CrossRef - Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Predicting Factors among Small-sized Company Workers
Soo Kyoung Choi, Jeong A Jo, Seon Young Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(2): 244. CrossRef - Actual Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Related Factors
Jong Uk Won, Oi Saeng Hong, Won Ju Hwang
Workplace Health & Safety.2013; 61(4): 163. CrossRef - Grape Polyphenols Increase the Activity of HDL Enzymes in Old and Obese Rats
Andriy L. Zagayko, Ganna B. Kravchenko, Oksana A. Krasilnikova, Yuri O. Ogai
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef - Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of the Metabolic Syndrome in the Korean Workforce
Dae Ryong KANG, Yeongmi HA, Won Ju HWANG
Industrial Health.2013; 51(3): 256. CrossRef - Actual Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Related Factors: A Cross-sectional Study of Korean Blue Collar Workers Employed by Small Businesses
Jong Uk Won, Oi Saeng Hong, Won Ju Hwang
Workplace Health & Safety.2013; 61(4): 163. CrossRef
- The impact of perception bias for cardiovascular disease risk on physical activity and dietary habits
- 1,447 View
- 3 Download
- 26 Crossref

- Risk Factors Influencing Probability and Severity of Elder Abuse in Community-dwelling Older Adults: Applying Zero-inflated Negative Binomial Modeling of Abuse Count Data
- Mi Heui Jang, Chang Gi Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(6):819-832. Published online December 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.6.819
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to identify risk factors that influence the probability and severity of elder abuse in community-dwelling older adults.
Methods This study was a cross-sectional descriptive study. Self-report questionnaires were used to collect data from community-dwelling Koreans, 65 and older (N=416). Logistic regression, negative binomial regression and zero-inflated negative binomial regression model for abuse count data were utilized to determine risk factors for elder abuse.
Results The rate of older adults who experienced any one category of abuse was 32.5%. By zero-inflated negative binomial regression analysis, the experience of verbal-psychological abuse was associated with marital status and family support, while the experience of physical abuse was associated with self-esteem, perceived economic stress and family support. Family support was found to be a salient risk factor of probability of abuse in both verbal-psychological and physical abuse. Self-esteem was found to be a salient risk factor of probability and severity of abuse in physical abuse alone.
Conclusion The findings suggest that tailored prevention and intervention considering both types of elder abuse and target populations might be beneficial for preventative efficiency of elder abuse.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between social network characteristics and falls among older adults living alone: an analysis using Zero-inflated negative binomial regression
Mi-So Shim, Chang Gi Park, Inah Kim
BMC Geriatrics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Probability and Increase of Patients’ Call Bell Use in Integrated Nursing Care Wards
Jiyeong Seong, Sung-Hyun Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(3): 273. CrossRef - Blood Pressure Awareness and Knowledge of Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases in South Korean Women with Hypertension
Yeo Won Jeong
Healthcare.2021; 9(3): 360. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Scaling Experiences of Adolescent Children from Multicultural and Native Families
Eunsuk Ahn, Jin-Young Yang, Ki-Eun Kim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2020; 20(2): 89. CrossRef - Predictors of Blood and Body Fluid Exposure and Mediating Effects of Infection Prevention Behavior in Shift-Working Nurses: Application of Analysis Method for Zero-Inflated Count Data
Jae Geum Ryu, Smi Choi-Kwon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 658. CrossRef - The Relationship between Smartphone Use and Oral Health in Adolescents
Eunsuk Ahn, Ji-Hyoung Han
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2020; 20(1): 44. CrossRef - Fatores associados à violência contra o idoso: uma revisão sistemática da literatura
Maria Angélica Bezerra dos Santos, Rafael da Silveira Moreira, Patrícia Fernanda Faccio, Gabriela Carneiro Gomes, Vanessa de Lima Silva
Ciência & Saúde Coletiva.2020; 25(6): 2153. CrossRef - The Influence of the mother's nationality on adolescent's subjective oral health status-using propensity score matching
Sun Mi Lee, Yun Sin Song, Young Nam Kim, Eunsuk Ahn
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2018; 42(2): 46. CrossRef - Functional Decline and Emotional Elder Abuse: a Population-Based Study of Older Korean Adults
Jooyoung Kong, Haesang Jeon
Journal of Family Violence.2018; 33(1): 17. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Burnout on the Relationship between CCTV Perception and Abusive Behavior of Care Workers in Nursing Homes for the Elderly
전병주
치안정책연구.2017; 31(2): 101. CrossRef - Risk factors of severity of abuse against older women in the home setting: A multinational European study
Liesbeth De Donder, Gert Lang, José Ferreira-Alves, Bridget Penhale, Ilona Tamutiene, Minna-Liisa Luoma
Journal of Women & Aging.2016; 28(6): 540. CrossRef - Research on the Influence of Arts and Culture Education in Childhood and Teenage Years on the Consumption of Arts and Culture: Focus on the Zero-inflated Negative Binomial Model
정지은
Journal of Product Research.2016; 34(2): 67. CrossRef - Neighborhood Environment Associated with Physical Activity among Rural Adults: Applying Zero-Inflated Negative Binominal Regression Modeling
Bongjeong Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2015; 29(3): 488. CrossRef
- Relationship between social network characteristics and falls among older adults living alone: an analysis using Zero-inflated negative binomial regression
- 1,052 View
- 8 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Optimal Time Interval for Position Change for ICU Patients using Foam Mattress Against Pressure Ulcer Risk
- Hyean Jeong Kim, In Sook Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(5):730-737. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.5.730
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to identify the time interval to pressure ulcer and to determine the optimal time interval for position change depending on pressure ulcer risk in patients using foam mattress in intensive care units.
Methods The Braden scale score, occurrence of pressure ulcers and position change intervals were assessed with 56 patients admitted to an intensive care unit from April to November, 2011. The time to pressure ulcer occurrence by Braden scale risk group was analyzed with Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and log rank test. Then, the optimal time interval for position change was calculated with ROC curve.
Results The median time to pressure ulcer occurrence was 5 hours at mild or moderate risk, 3.5 hours at high risk and 3 hours at very high risk on the Braden scale. The optimal time interval for position change was 3 hours at mild and moderate risk, 2 hours at high and very high risk of Braden scale.
Conclusion When foam mattresses are used a slight extension of the time interval for position change can be considered for the patients with mild or moderate pressure ulcer risk but not for patients with high or very high pressure ulcer risk by Braden scale.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of support surface on the prevention of pressure injury in acute care settings: A multi-center prospective observational study
Mi-Ock Shim, Chul-Gyu Kim, Ja Kyung Min, So Yeon Kwak, Hyunhee Ghil, Seungmi Park
Journal of Tissue Viability.2024; 33(4): 652. CrossRef - Predicting the cut‐off point for interface pressure in pressure injury according to the standard hospital mattress and polyurethane foam mattress as support surfaces
Mi Yu, Kyung Hee Park, Jiseon Shin, Ji Hyun Lee
International Wound Journal.2022; 19(6): 1509. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Devices for Prevention and Treatment of Pressure Ulcers: A scoping Review
Soo Youn Jung, Mina Park, Kyoung Ja Moon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(2): 123. CrossRef - Comparing Pressure Injury Incidence Based on Repositioning Intervals and Support Surfaces in Acute Care Settings: A Quasi-Experimental Pragmatic Study
Jeong Sil Choi, Seon Young Hyun, Sun Ju Chang
Advances in Skin & Wound Care.2021; 34(8): 1. CrossRef - Perioperative factors and pressure ulcer development in postoperative ICU patients: a retrospective review
Neha Kumta, Fiona Coyer, Michael David
Journal of Wound Care.2018; 27(8): 475. CrossRef - Improving the quality of nurse‐influenced patient care in the intensive care unit
Lynsey J. Sutton, Rebecca J. Jarden
Nursing in Critical Care.2017; 22(6): 339. CrossRef - The Efficacy of a Viscoelastic Foam Overlay on Prevention of Pressure Injury in Acutely Ill Patients
Kyung Hee Park, Joohee Park
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2017; 44(5): 440. CrossRef - Automated Pressure Injury Risk Assessment System Incorporated Into an Electronic Health Record System
Yinji Jin, Taixian Jin, Sun-Mi Lee
Nursing Research.2017; 66(6): 462. CrossRef - Prophylactic Effect of Transparent Film Dressing on Sacrum and Coccyx in SICU Patients*
Heejeong Kim, Sun-Mi Lee, Hee young Choi, Yu Kyung Min, Yoo Jin Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2016; 23(3): 256. CrossRef - A Phenomenological Study on Illness Experience of Patients with Pressure Ulcer
Misoo Yoo, Myungsun Yi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(5): 515. CrossRef - Reusability of EMR Data for Applying Cubbin and Jackson Pressure Ulcer Risk Assessment Scale in Critical Care Patients
Eunkyung Kim, Mona Choi, JuHee Lee, Young Ah Kim
Healthcare Informatics Research.2013; 19(4): 261. CrossRef
- The effect of support surface on the prevention of pressure injury in acute care settings: A multi-center prospective observational study
- 1,494 View
- 24 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Risk Factors and Features of Critically Ill Patients with Deep Vein Thrombosis in Lower Extremities
- Hwasoon Kim, Ok Min Cho, Hyo Im Cho, Ju Yeun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(3):396-404. Published online June 12, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.3.396
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the features, risk scores and risk factors for deep vein thrombosis in critically ill patients who developed deep vein thrombosis in their lower extremities.
Methods The participants in this prospective descriptive study were 175 adult patients who did not receive any prophylactic medication or mechanical therapy during their admission in the intensive care unit.
Results The mean age was 62.24 (± 17.28) years. Men made up 54.9% of the participating patients. There were significant differences in age, body mass index, and leg swelling between patients who developed deep vein thrombosis and those who did not have deep vein thrombosis. The mean risk score was 6.71(± 2.94) and they had on average 4.01(± 1.35) risk factors. In the multiple logistic regression, body mass index (odds ratio= 1.14) and leg swelling (odds ratio= 6.05) were significant predictors of deep vein thrombosis.
Conclusion Most critically ill patients are in the potentially high risk group for deep vein thrombosis. However, patients who are elderly, obese or have leg edema should be closely assessed and more than one type of active prophylactic intervention should be provided.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Venous Thromboembolism Prevention Education for Elderly Patients with Total Knee Arthroplasty
Mi Hee Lee, Mee Ock Gu
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2019; 26(4): 269. CrossRef - Adaptation and Effects of the Evidence-based IPC Nursing Protocol on Prevention of Postoperative Venous Thromboembolism
Nam Yong Kim, Eun A Kim, Jae Yeun Sim, Soon Hee Jung, Hye Young Kim, Eun Hee Jang, Jee Hye Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(1): 63. CrossRef - Knowledge, Health Belief, and Preventive Behavioral Intention related to Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) of the Patients with Lower Limb Musculoskeletal System Disorders
Hye Jin Yang, Hee-Young Kang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(4): 531. CrossRef
- The Effects of Venous Thromboembolism Prevention Education for Elderly Patients with Total Knee Arthroplasty
- 1,045 View
- 7 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Depression and Risk Factors in Patients with Crohn's Disease
- Ok-Hee Cho, Yang-Sook Yoo, Suk-Kyun Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(2):207-216. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.2.207
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to determine the risk factors among patients with depression with Crohn's disease.
Methods Data were collected by questionnaire from 276 patients who were diagnosed with Crohn's disease at a tertiary hospital located in Seoul. Measurements included patients' demographic characteristics, clinical characteristics, depression level, and health-related quality of life. Data were analyzed using t-test, χ2-test, Wilcoxon rank sum test, and logistic regression analyses.
Results The incidence rate of depression (BDI-II≥14scores) was 31.9% (n=88). Univariate analysis revealed that being a woman, school graduation status, economic status (low), BMI(<18.5Kg/m2), disease duration (≥3 years), CDAI (≥150 scores), frequency of hospital admission (≥2), extra-intestinal manifestation (arthralgia, stomatitis), administration of 5-aminosalicylic acid, and disease related quality of life (SIBDQ<50 scores) were associated with depression. Multivariate analysis revealed that economic status (low), school graduation status, and quality of life (SIBDQ<50 scores) were more likely to report high level of depression.
Conclusion Future research should consider managing depression as an essential component of comprehensive care for patients with Crohn's disease. In addition, further research is needed to develop strategies to better improve quality of life among patients with Crohn's disease who are depressed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mental health and Crohn's disease: evaluating depression through a case-referent study
Juan Manuel Escudero Prados, Antonio Cortés-Rodríguez, Marta Elena Losa-Iglesias, Juan Gómez-Salgado, Ricardo Becerro de Bengoa Vallejo, Miguel Ángel Saavedra-García, Daniel López López, Ana María Jiménez-Cebrián
Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Are Depression and Anxiety Underdiagnosed in Socially Vulnerable Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
Jessica L Sheehan, Ariel A Jordan, Kira L Newman, Laura A Johnson, Dala Eloubeidi, Shirley Cohen-Mekelburg, Jeffrey A Berinstein, Renuka Tipirneni, Peter D R Higgins
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.2024; 30(10): 1696. CrossRef - Prevalence of symptoms of anxiety and depression in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Brigida Barberio, Mohammad Zamani, Christopher J Black, Edoardo V Savarino, Alexander C Ford
The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2021; 6(5): 359. CrossRef - Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Brigida Barberio, Mohammad Zamani, Christopher J. Black, Edoardo V. Savarino, Alexander Ford
SSRN Electronic Journal .2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Depression, Anxiety, Related Risk Factors and Cognitive Distortion in Korean Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Jun Ho Song, Jong Woo Kim, Chi Hyuk Oh, Hyo Jong Kim, Chang Kyun Lee, Won Sub Kang
Psychiatry Investigation.2020; 17(11): 1126. CrossRef - A Model of the Quality of Life in Patients with Crohn’s Disease
Shin Ae Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(4): 333. CrossRef - Is the Chinese medicinal formula Guipi Decoction (归脾汤) effective as an adjunctive treatment for depression? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Chen-xia Sheng, Ze-qi Chen, Han-jin Cui, A-li Yang, Cong Wang, Zhe Wang, Nan-xiang Su, Tao Tang
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine.2017; 23(5): 386. CrossRef - Determinants of Healthcare Utilization Among Veterans with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Mimi C. Tan, Hashem B. El-Serag, Jason K. Hou
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2017; 62(3): 607. CrossRef - The Mental Health State of Quiescent Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients
Sung Chul Park, Yoon Tae Jeen
Gut and Liver.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with Anxiety and Depression in Korean Patients with Inactive Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Min Chul Kim, Yoon Suk Jung, Young Seok Song, Jung In Lee, Jung Ho Park, Chong Il Sohn, Kyu Yong Choi, Dong Il Park
Gut and Liver.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Resilience on Depression and Rehabilitation Motivation in Stroke Patients
Eun Sil Choi, Eun Nam Lee, Jeong Lim Cho
Journal of muscle and joint health.2016; 23(1): 19. CrossRef - Body Image, Self Esteem, and Health related Quality of Life in Patients with Crohn's Disease
Young Jin Lee, Eui Geum Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(4): 383. CrossRef - Factors related to Quality of Life of Patients with Ulcerative Colitis
Yang-Sook Yoo, Miyoung Chung, Ok-Hee Cho
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(2): 129. CrossRef - Psychiatric co-morbidities in Crohn's disease: an often overlooked aspect
Shailendra Kapoor
Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira.2013; 59(2): 100. CrossRef - Psychiatric co-morbidities in Crohn's disease: an often overlooked aspect
Shailendra Kapoor
Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira (English Edition).2013; 59(2): 100. CrossRef
- Mental health and Crohn's disease: evaluating depression through a case-referent study
- 969 View
- 5 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Predictive Bayesian Network Model Using Electronic Patient Records for Prevention of Hospital-Acquired Pressure Ulcers
- In Sook Cho, Eunja Chung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(3):423-431. Published online June 13, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.3.423
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The study was designed to determine the discriminating ability of a Bayesian network (BN) for predicting risk for pressure ulcers.
Methods Analysis was done using a retrospective cohort, nursing records representing 21,114 hospital days, 3,348 patients at risk for ulcers, admitted to the intensive care unit of a tertiary teaching hospital between January 2004 and January 2007. A BN model and two logistic regression (LR) versions, model-I and -II, were compared, varying the nature, number and quality of input variables. Classification competence and case coverage of the models were tested and compared using a threefold cross validation method.
Results Average incidence of ulcers was 6.12%. Of the two LR models, model-I demonstrated better indexes of statistical model fits. The BN model had a sensitivity of 81.95%, specificity of 75.63%, positive and negative predictive values of 35.62% and 96.22% respectively. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) was 85.01% implying moderate to good overall performance, which was similar to LR model-I. However, regarding case coverage, the BN model was 100% compared to 15.88% of LR.
Conclusion Discriminating ability of the BN model was found to be acceptable and case coverage proved to be excellent for clinical use.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the risk prediction model of pressure injuries in hospitalized patient: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Yuxia Ma, Xiang He, Tingting Yang, Yifang Yang, Ziyan Yang, Tian Gao, Fanghong Yan, Boling Yan, Juan Wang, Lin Han
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025; 34(6): 2117. CrossRef - Using nursing data for machine learning-based prediction modeling in intensive care units: A scoping review
Yesol Kim, Mihui Kim, Yeonju Kim, Mona Choi
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2025; 169: 105133. CrossRef - Development of a Pressure Injury Machine Learning Prediction Model and Integration into Clinical Practice: A Prediction Model Development and Validation Study
Ju Hee Lee, Jae Yong Yu, So Yun Shim, Kyung Mi Yeom, Hyun A Ha, Se Yong Jekal, Ki Tae Moon, Joo Hee Park, Sook Hyun Park, Jeong Hee Hong, Mi Ra Song, Won Chul Cha
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(3): 191. CrossRef - The predictive effect of different machine learning algorithms for pressure injuries in hospitalized patients: A network meta-analyses
Chaoran Qu, Weixiang Luo, Zhixiong Zeng, Xiaoxu Lin, Xuemei Gong, Xiujuan Wang, Yu Zhang, Yun Li
Heliyon.2022; 8(11): e11361. CrossRef - Predictive Modeling of Pressure Injury Risk in Patients Admitted to an Intensive Care Unit
Mireia Ladios-Martin, José Fernández-de-Maya, Francisco-Javier Ballesta-López, Adrián Belso-Garzas, Manuel Mas-Asencio, María José Cabañero-Martínez
American Journal of Critical Care.2020; 29(4): e70. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Electronic Health Record Data-Driven Predictive Models for Pressure Ulcers
Seul Ki Park, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Hee Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 575. CrossRef - Development and Comparison of Predictive Models for Pressure Injuries in Surgical Patients
Seul Ki Park, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Hee Hwang
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2019; 46(4): 291. CrossRef - Automated Pressure Injury Risk Assessment System Incorporated Into an Electronic Health Record System
Yinji Jin, Taixian Jin, Sun-Mi Lee
Nursing Research.2017; 66(6): 462. CrossRef - Recommendation of Personalized Surveillance Interval of Colonoscopy via Survival Analysis
Jayeon Gu, Eun Sun Kim, Seoung Bum Kim
Journal of Korean Institute of Industrial Engineers.2016; 42(2): 129. CrossRef - Medical Data Based Clinical Pathway Analysis and Automatic Ganeration System
Hanna Park, In Ho Bae, Yong Oock Kim
The Journal of Korea Information and Communications Society.2014; 39C(6): 497. CrossRef - Reusability of EMR Data for Applying Cubbin and Jackson Pressure Ulcer Risk Assessment Scale in Critical Care Patients
Eunkyung Kim, Mona Choi, JuHee Lee, Young Ah Kim
Healthcare Informatics Research.2013; 19(4): 261. CrossRef - Using EHR data to predict hospital-acquired pressure ulcers: A prospective study of a Bayesian Network model
Insook Cho, Ihnsook Park, Eunman Kim, Eunjoon Lee, David W. Bates
International Journal of Medical Informatics.2013; 82(11): 1059. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the risk prediction model of pressure injuries in hospitalized patient: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
- 1,071 View
- 14 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Development of the Structural Model of Adolescent's Risk Behavior
- Hyun Sook Park, Sun Young Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(3):364-373. Published online June 13, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.3.364
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose In this study the fitness of a path model for the relationship among biological risk disposition, sociocultural risk factors, self-control, parent-adolescent communication, and risk behavior in adolescents was examined.
Methods The participants were 387 adolescents. The data were analyzed with the PASW 18.0 and AMOS 18.0 programs.
Results Sociocultural risk factors, self-control, and parent-adolescent communication showed a direct effect on risk behavior for adolescents, while biological risk disposition and sociocultural risk factor showed an indirect effect on risk behavior for adolescents. The modified path model of adolescents' risk behavior was showed a good fit with the model (χ2/df=2.37, GFI=.95, AGFI=.92, RMSEA=.06 [.05<RMSEA<.07], NNFI=.95, CFI=.97).
Conclusion These results suggest that adolescents' risk behavior can be decreased by reducing biological risk disposition and sociocultural risk factor, and increasing parent-adolescent communication and self-control. Thus there is a need to design intervention programs that emphasizes reducing biological risk disposition and sociocultural risk factor and increasing parent-adolescent communication and self-control in order to decrease adolescents' risk behavior.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Structural Equation Modeling on Clinical Decision Making Ability of Nurses
Min Kyoung Park, Soukyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 601. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Factors Influencing Risk Behaviors of Adolescents Living in Small and Medium-sized Cities and Rural Communities
Hyun Sook Park, Hyun Ju Yeo, Sun Young Jung
Journal of the Korean Society of School Health.2016; 29(3): 256. CrossRef - Association of school, family, and mental health characteristics with suicidal ideation among Korean adolescents
Gyu-Young Lee, Yun-Jung Choi
Research in Nursing & Health.2015; 38(4): 301. CrossRef - Teenagers with Smartphones Exposed to Sexual Content
Jeong-Yim Choi, Donghun Chung
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(4): 445. CrossRef
- Structural Equation Modeling on Clinical Decision Making Ability of Nurses
- 749 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Development of the Competency Model for Prevention of Adolescent Risk Behavior
- Hyun Sook Park, Sun Young Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(2):204-213. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.2.204
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to identify fundamental data on competency reinforcement programs to prevent adolescent risk behavior by developing and examining a competency model.
Methods In this study, competences on prevention of adolescent risk behavior were identified through competency modeling, and a competency model was developed and tested for validity.
Results Competences for prevention of adolescent risk behavior defined by the competency model included the following: self-control, positive mutual understanding between parents and adolescents, and positive connectedness with peer group. Validation of the competency model showed the model to be appropriate.
Conclusion The competency model for prevention of adolescent risk behavior through competency modeling is expected to be the foundation of an integral approach to enhance competency in adolescents and prevent adolescent risk behavior. This kind of approach can be a school-centered, cost-efficient strategy, which not only reduces adolescent risk behavior but also improves quality of adolescent resources.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differences in Health Behavior Profiles of Adolescents in Urban and Rural Areas in a Korean City
Myungah Chae, Kihye Han
Healthcare.2021; 9(3): 282. CrossRef - Comparison of characteristics of risk behaviors and injuries between elderly and young population in Korea: application of convergence educational concept
Yang-Ju Tak
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(5): 289. CrossRef - Construction of the Addiction Prevention Core Competency Model for Preventing Addictive Behavior in Adolescents
Hyun Sook Park, Sun Young Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(6): 714. CrossRef - Effects of Competency Model Based Education Program on Risk Behavior and Competences for Preventing Adolescents' Risk Behavior for Adolescents
Hyun Sook Park, Sun Young Jung, Eun Jin Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(4): 1799. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Health Promotion Competence in Public Health Nurses
Jeong-Soo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2011; 22(3): 281. CrossRef
- Differences in Health Behavior Profiles of Adolescents in Urban and Rural Areas in a Korean City
- 967 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Korea: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Quality of Life
- Young-Mi Jung, Heeyoung Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(2):149-156. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.2.149
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study seeks to examine prevalence, risk factors, and quality of life of Korean adults with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
Methods From the database of the Fourth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV-1, 2008), the researchers selected 1,458 adults over the age of 45. The original study was a population-based epidemiological survey of health and nutrition with a stratified multistage clustered probability design. Prevalence of COPD was computed on the basis of the sampling weight. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, χ2 test, t-test and multiple logistic regression with the SPSS WIN 18.0 and SAS Ver. 9.1 program.
Results The prevalence of COPD was 18.0% among people older than 45 yr. The prevalence of current smokers was 19.7% in this population and 26.3% in individuals with COPD. Age, gender, education, and smoking levels were found to be risk factors for COPD. Significant difference in quality of life was founded between adults with COPD and the healthy controls.
Conclusion The results of this study indicate that COPD is a highly prevalent disease in Korea. To reduce the prevalence of COPD and improve health-related quality of life in patients with COPD, nursing interventions must focus on prevention of risk factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Restrictive Pulmonary Disease in Korean Older Adults
Do-Youn Lee
Journal of The Korean Society of Physical Medicine.2025; 20(1): 99. CrossRef - COPD Prevalence and Risk Factors in Korean Older Adults
Do-Youn Lee
The Journal of Korean Physical Therapy.2025; 37(1): 31. CrossRef - Analysis of Risk Factors for COPD Incidence in Adults Over 40 Years of Age in Korea
Do-Youn Lee
Journal of The Korean Society of Physical Medicine.2024; 19(1): 23. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Symptom Experience and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Enhee Jo, Ju-Young Park, Young Jun Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(3): 315. CrossRef - Inhibitory Effects of GGX on Lung Injury of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (COPD) Mice Model
Tae Hyeon Kim, Won Kyung Yang, Su Won Lee, Seung Hyung Kim, Yee Ran Lyu, Yang Chun Park
Journal of Korean Medicine.2021; 42(3): 56. CrossRef - Qualitative Analysis of the Disease Experience of Korean Older Men With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Kisook Kim, Ji Woon Ko, Sangbong Choi
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2020; 46(2): 49. CrossRef - Novel nomogram based on risk factors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) using a naïve Bayesian classifier model
Ju-Hyun Seo, Jea-Young Lee
Journal of the Korean Statistical Society.2019; 48(2): 278. CrossRef - Factors influencing on health-related quality of life in South Korean with chronic liver disease
Hyun Jin Kim, Hyeonsik Chu, Seonhye Lee
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Gwaruhaengryeon-hwan on COPD and Particulate Matter Induced Lung Injury on a Mouse Model
Chul-wha Lee, Won-kyung Yang, Yee-ran Lyu, Seung-hyeong Kim, Yang-chun Park
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2017; 38(3): 353. CrossRef - Effect of the trunk forward bending angle in sitting position on slow vital capacity
Juncheol Lee, Dongwook Han
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2017; 29(12): 2220. CrossRef - Quality of life and its related factors in patients with Korean chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
So Youn Bang
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2016; 27(5): 1349. CrossRef - Incapacity, Handicap, and Oxidative Stress Markers of Male Smokers With and Without COPD
Syrine Ben Moussa, Sonia Rouatbi, Helmi Ben Saad
Respiratory Care.2016; 61(5): 668. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Health‐Related Quality of Life of Korean Patients with Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease
Jisu Kim, Kisook Kim
Public Health Nursing.2015; 32(3): 191. CrossRef - Effects of Sagan-tang and individual herbs on COPD Mice Model
Jong-Min Han, Won-Kyung Yang, Seung-Hyeong Kim, Yang-Chun Park
Herbal Formula Science.2015; 23(2): 171. CrossRef - Effects of Smoking Status on Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Prevalence in Males 40 years and Older: Findings from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
In Sook Jung, In-Kyung Jung
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2014; 14(4): 155. CrossRef - Factors affecting health status in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Ayse Cil Akinci, Erkan Yildirim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2013; 19(1): 31. CrossRef - Fatigue, anxiety and depression levels, activities of daily living of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Papatya Karakurt, Ayla Ünsal
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2013; 19(2): 221. CrossRef - Gender differences of health behaviors and quality of life of Koreans with asthma
Yeonsoo Jang, Hyera Yoo
Open Journal of Nursing.2013; 03(06): 420. CrossRef - The Development of Infants from Low-Income Families, Parenting Characteristics, and Daily Routines
Hanna Kang, Hyewon Park
Family and Environment Research.2013; 51(6): 613. CrossRef - Effects of Consumer-Centered u-Health Service for the Knowledge, Skill, and Attitude of the Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
JEONGEUN KIM, SUKWHA KIM, HEE-CHAN KIM, KYUNG-HWAN KIM, SEOK-CHUL YANG, CHOON-TAEK LEE, HYOUN-JOONG KONG, KYUNGSOON LEE
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2012; 30(12): 661. CrossRef - Relationship of Knowledge, Attitude, Correct Metered Dose Inhaler Use, and Self-management Compliance among Patients with COPD
Min-Hee An, Ja-Yun Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(2): 160. CrossRef - Quality of Life in the Urban Adults by Age
Jung Sook Choi, EunHee Lee, AeYoung So, Kyung-Sook Lee
Journal of muscle and joint health.2012; 19(3): 362. CrossRef
- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Restrictive Pulmonary Disease in Korean Older Adults
- 1,906 View
- 16 Download
- 22 Crossref

- Comparison for Risk Estimate of Aspiration between the Revised Dysphagia Assessment Tool and Videofluoroscopy in Post-Stroke Patients
- Kyung Hee Moon, Hyun Sook Sohn, Eun Seok Lee, Eun Kyung Paek, Eun Ju Kang, Seung Hee Lee, Na Ri Han, Meen Hye Lee, Deog Young Kim, Chang Gi Park, Ji-Soo Yoo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(3):359-366. Published online June 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.3.359
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to determine the significant factors for risk estimate of aspiration and to evaluate the efficiency of the dysphagia assessment tool.
Methods A consecutive series of 210 stroke patients with aspiration symptoms such as cough and dysphagia who had soft or regular diet without tube feeding were examined. The dysphagia assessment tool for aspiration was compared with videofluoroscopy using Classification and Regression Tree (CART) analysis.
Results In CART analysis, of 34 factors, the significant factors for estimating risk of aspiration were cough during swallowing, oral stasis, facial symmetry, salivary drooling, and cough after swallowing. The risk estimate error of the revised dysphagia assessment tool was 25.2%, equal to that of videofluoroscopy.
Conclusion The results indicate that the dysphagia assessment tool developed and examined in this study was potentially useful in the clinical field and the primary risk estimating factor was cough during swallowing. Oral stasis, facial symmetry, salivary drooling, cough after swallowing were other significant factors, and based on these results, the dysphagia assessment tool for aspiration was revised and complemented.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Screening for aspiration risk associated with dysphagia in acute stroke
Elizabeth Boaden, Jane Burnell, Lucy Hives, Paola Dey, Andrew Clegg, Mary W Lyons, C Elizabeth Lightbody, Margaret A Hurley, Hazel Roddam, Elizabeth McInnes, Anne Alexandrov, Caroline L Watkins
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Utilization of Assessment and Intervention Checklist for Post-stroke Dysphagia
Eun Ha Lee, Ja Yun Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(2): 113. CrossRef
- Screening for aspiration risk associated with dysphagia in acute stroke
- 1,126 View
- 10 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Risk Factors for Surgical Site Infections in Patients Undergoing Craniotomy
- Kyeong-Sook Cha, Ok-Hee Cho, So-Yeon Yoo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(2):298-305. Published online April 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.2.298
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The objectives of this study were to determine the prevalence, incidence, and risk factors for postoperative surgical site infections (SSIs) after craniotomy.
Methods This study was a retrospective case-control study of 103 patients who had craniotomies between March 2007 and December 2008. A retrospective review of prospectively collected databases of consecutive patients who underwent craniotomy was done. SSIs were defined by using the Centers for Disease Control criteria. Twenty-six cases (infection) and 77 controls (no infection) were matched for age, gender and time of surgery. Descriptive analysis, t-test, χ2-test and logistic regression analyses were used for data analysis.
Results The statistical difference between cases and controls was significant for hospital length of stay (>14 days), intensive care unit stay more than 15 days, Glasgrow Coma Scale (GCS) score (≤7 days), extra-ventricular drainage and coexistent infection. Risk factors were identified by logistic regression and included hospital length of stay of more than 14 days (odds ratio [OR]=23.39, 95% confidence interval [CI]=2.53-216.11) and GCS score (≤7 scores) (OR=4.71, 95% CI=1.64-13.50).
Conclusion The results of this study show that patients are at high risk for infection when they have a low level of consciousness or their length hospital stay is long term. Nurses have to take an active and continuous approach to infection control to help with patients having these risk factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An update on a persisting challenge: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the risk factors for surgical site infection post craniotomy
Francesco Magni, Aws Al-Omari, Robert Vardanyan, Arian A. Rad, Susan Honeyman, Alexandros Boukas
American Journal of Infection Control.2024; 52(6): 650. CrossRef - RETRACTED: Comprehensive analysis of risk factors and pathogenetic characteristics associated with surgical site infections following craniotomy procedures
Zhiwei Gu, Chuanjian Tu, Dagang Song, Zhihao Yang, Jiajie Xia
International Wound Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - RETRACTED: A meta‐analysis of the risk factors for neurosurgical surgical site infection following craniotomy
Dechao Sun, Zhuang Ma, Yadong Geng, Chenxu Kong, Zhenjiang Li
International Wound Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Validation of the Risk Prediction Tool for Wound Infection in Abdominal Surgery Patients
Hyun Kyoung Jung, Eun Nam Lee
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2022; 15(3): 75. CrossRef - Association between registered nurse staffing levels and in-hospital mortality in craniotomy patients using Korean National Health Insurance data
Yunmi Kim, Se Young Kim, Kyounga Lee
BMC Nursing.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Logistic Regression Analysis of Risk Factors for Intracranial Infection After Multiple Traumatic Craniotomy and Preventive Measures
Jing Yao, Dong Liu
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2019; 30(7): 1946. CrossRef - Risk factors of neurosurgical site infection after craniotomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Chenyan Fang, Tao Zhu, Ping Zhang, Liang Xia, Caixing Sun
American Journal of Infection Control.2017; 45(11): e123. CrossRef - Infecciones del sistema nervioso central en pacientes críticos con lesión cerebral, con y sin antecedente de manejo neuroquirúrgico
José D. Charry, Fabio Antonio García, Natalia Johana Ortega, Johanna Osorio
Acta Colombiana de Cuidado Intensivo.2015; 15(1): 9. CrossRef - Recent Advances in the Patient Safety and Quality Initiatives Movement
Isaac Yang, Nolan Ung, Daniel T. Nagasawa, Panayiotis Pelargos, Winward Choy, Lawrance K. Chung, Kim Thill, Neil A. Martin, Nasim Afsar-Manesh, Brittany Voth
Neurosurgery Clinics of North America.2015; 26(2): 301. CrossRef - Knowledge, Practice, and Associated Factors towards Prevention of Surgical Site Infection among Nurses Working in Amhara Regional State Referral Hospitals, Northwest Ethiopia
Freahiywot Aklew Teshager, Eshetu Haileselassie Engeda, Workie Zemene Worku
Surgery Research and Practice.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Post-operative central nervous system infections after cranial surgery in China: incidence, causative agents, and risk factors in 1,470 patients
R. Zhan, Y. Zhu, Y. Shen, J. Shen, Y. Tong, H. Yu, L. Wen
European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.2014; 33(5): 861. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Surgical Site Infections According to Electronic Medical Records Data
Young Hee Kim, Young-Hee Yom
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2014; 21(2): 151. CrossRef - Etiología de las infecciones quirúrgicas en pacientes sometidos a craneotomía
Elena Múñez, Antonio Ramos, Teresa Álvarez de Espejo, Josep Vaqué, José Sánchez-Payá, Vicente Pastor, Ángel Asensio
Neurocirugía.2012; 23(2): 54. CrossRef
- An update on a persisting challenge: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the risk factors for surgical site infection post craniotomy
- 1,141 View
- 2 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Development of Outcome Indicators of Urinary Incontinence for Quality Evaluation in Long Term Care Hospitals
- Ju Young Yoon, Ji Yun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(1):110-118. Published online February 28, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.1.110
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose To develop outcome indicators of urinary incontinence to measure quality of care in long term care hospitals in Korea.
Methods The draft indicators of urinary incontinence were developed from a literature review and clinical expert panel. A survey of medical records of 280 patients in 20 hospitals was conducted to test inter-rater reliability. Statistical analysis was done to test risk adjustment criteria, variation between hospitals, and stability of indicators, using assessment data from 77,918 patients in 623 hospitals.
Results The inter-rater reliability of items was high (Kappa range: 0.66-0.92). Severe cognitive impairment (odds ratio [OR]: 3.15, confidence interval [CI]: 3.03-3.26) and total mobility activities of daily living (ADLs) dependency (OR: 4.85, CI: 4.72-4.98) increased the prevalence of urinary incontinence, thus they proved to be significant criteria to stratify high and low risk groups. The prevalence for low risk showed more substantial variation than the high risk group. The indicators were stable over one month.
Conclusion This study demonstrated the feasibility of outcome indicators of urinary incontinence. Improving the reliability of the patient assessment tool and refining the indicators through validation study is a must for future study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Health Assessment Tool for Middle-aged Adults in Long-term Care Settings
Yoon-Jin Park, Nam Cho Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2017; 20(1): 1. CrossRef - Factors Associated with the Changes in Activities of Daily Living in Older Adults with Stroke: A Comparison of Home Care and Institutional Care
Woon-Sook Jung, Eun-Shil Yim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 388. CrossRef - Mobility is the key! Trends and associations of common care problems in German long-term care facilities from 2008 to 2012
Nils A. Lahmann, Antje Tannen, Simone Kuntz, Kathrin Raeder, Gabriela Schmitz, Theo Dassen, Jan Kottner
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2015; 52(1): 167. CrossRef - Comparison of Hospital Standardized Mortality Ratio Using National Hospital Discharge Injury Data
Jong-Ho Park, Yoo-Mi Kim, Sung-Soo Kim, Won-Joong Kim, Sung-Hong Kang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(4): 1739. CrossRef - The impact of organizational factors on the urinary incontinence care quality in long-term care hospitals: A longitudinal correlational study
Ju Young Yoon, Ji Yun Lee, Barbara J. Bowers, David R. Zimmerman
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2012; 49(12): 1544. CrossRef
- Development of Health Assessment Tool for Middle-aged Adults in Long-term Care Settings
- 908 View
- 1 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Work-related Stress and Risk Factors among Korean Employees
- Eun Sook Choi, Yeongmi Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(4):549-561. Published online August 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.4.549
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Work-related stress and risk factors among Korean employees were identified in this study.
Methods Data were obtained from employees aged 20 to 64 using the Korean Working Conditions Survey 2006 (KWCS). Multiple logistic regression analysis using SAS version 9.1 was performed to examine risk factors of work-related stress by gender.
Results The age-adjusted prevalence of work-related stress among male and female employees was 18.4% and 15.1% respectively. After adjustments for multiple variables among both male and female employees, there was a significant relationship between work-related stress and risk factors including education, company size, work time, ergonomic risks, biological·chemical risks, and job demands. The significant variables for male employees were housework load, occupational class, and shift work, and for female employees, type of employment.
Conclusion There is a need to develop and support intensive stress management programs nationally giving consideration to work-related stress associated with working time, physical working environment, and job demands. Based on gender specific approaches, for male employes, stress management programs should be developed with consideration being given to occupational class and shift work. For stress management programs for female employees, consideration needs to be given to permanent employment status, specifically those in small companies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Occupational Stress on the Psychological Well-Being of Healthcare Workers: Basis for Stress Management Interventions
LOVELY V. ECHALAR
International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology (IJISRT).2024; : 391. CrossRef - The association between nutrition label utilization and disease management education among hypertension or diabetes diagnosed in Korea using 2018 Community Health Survey: a cross-sectional study
Miran Jin, Jayeun Kim, Kyuhyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 38. CrossRef - Associations of extended work, higher workloads and emotional work demands with sleep disturbance among night-shift workers
Bo Min Jeon, Su Hyun Kim
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychological stress, smoking, and hazardous drinking behaviors in South Korea: findings from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyunjoon Lee, Harold H. Lee, Augustine Kang, Yoojin Cha, Don Operario
Journal of Substance Use.2021; 26(1): 13. CrossRef - Job Stress and Cardiometabolic Lifestyle Modification Behaviors Among Workers in High-risk and Low-risk Workplaces
Jiyeon Jung, Jina Choo, Sooyeon Park, Jihyun Moon, Songwhi Noh
Journal of Occupational & Environmental Medicine.2021; 63(6): e346. CrossRef - Sex and Gender Differences in Occupational Hazard Exposures: a Scoping Review of the Recent Literature
A. Biswas, S. Harbin, E. Irvin, H. Johnston, M. Begum, M. Tiong, D. Apedaile, M. Koehoorn, P. Smith
Current Environmental Health Reports.2021; 8(4): 267. CrossRef - Effects of a Yoga Program in Reducing Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Workers of Small Workplaces: A Pilot Test
Won Ju Hwang, Jin Ah Kim, Ji Sun Ha
Sustainability.2020; 12(23): 10038. CrossRef - Impacts of family status and gender on the relationships between job demands, job control, and distress
Sehoon Kim, Hyounju Kang, Boreum Ju
European Journal of Training and Development.2019; 43(3-4): 322. CrossRef - Relationship between stress-related psychosocial work factors and suboptimal health among Chinese medical staff: a cross-sectional study
Ying-Zhi Liang, Xi Chu, Shi-Jiao Meng, Jie Zhang, Li-Juan Wu, Yu-Xiang Yan
BMJ Open.2018; 8(3): e018485. CrossRef - Association of stress, depression, and suicidal ideation with subjective oral health status and oral functions in Korean adults aged 35 years or more
Young Sun Kim, Han-Na Kim, Jung-Ha Lee, Se-Yeon Kim, Eun-Joo Jun, Jin-Bom Kim
BMC Oral Health.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Mediating Role of Psychological Capital in Relationship between Occupational Stress and Turnover Intention among Nurses at Veterans Administration Hospitals in Korea
Hee-Yun Yim, Hyun-Ju Seo, Yoonhyung Cho, JinHee Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2017; 11(1): 6. CrossRef - Association between supervisors’ behavior and wage workers’ job stress in Korea: analysis of the fourth Korean working conditions survey
Shin Uk Kang, Byeong Jin Ye, ByoungGwon Kim, Jung Il Kim, Jung Woo Kim
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Job Stress with Health-promoting Behaviors and Health Status in Clinical Nurses
Jung-Suk Kim, Chun-Ja Kim
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(4): 311. CrossRef - The psychosocial status of the family members of rheumatoid arthritis patients in Korea
Sang Wan Chung, You Jung Ha, Eun Ha Kang, Yun Jong Lee, Yeong Wook Song
Rheumatology International.2016; 36(5): 719. CrossRef - A Study on the Characteristics of Injured Workers Rate and Work Environment of Male Workers for over 40 years
Kil-Yong Choi, Kyung-Soo Yang
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2016; 10(1): 131. CrossRef - Effects of an internet-based lifestyle intervention on cardio-metabolic risks and stress in Korean workers with metabolic syndrome: A controlled trial
Chun-Ja Kim, Elizabeth A. Schlenk, Se-Won Kang, Jae-Bum Park
Patient Education and Counseling.2015; 98(1): 111. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on Job Satisfaction of Road Freight Transportation Industry Workers by Type of Employment
Heon Jong YOO, Seung Bum AHN
Journal of Korean Society of Transportation.2015; 33(4): 368. CrossRef - Effect of Obesity and Psychological Stress on Oral Health
Soo-Hwa Kim, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of dental hygiene science.2015; 15(2): 119. CrossRef - Association Night-Shift and Long Working-Hours Effects on Subjective Insomnia in Korean Workers: The Third Korean Working Conditions Survey
Chae-Bong Kim, Tae-Young Jung, Seoung-Min Han
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2015; 9(1): 41. CrossRef - Under and Over Employment and Working Conditions
Kyung Yong Rhee, Se Wook Song, Young Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene.2014; 24(4): 536. CrossRef - Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of the Metabolic Syndrome in the Korean Workforce
Dae Ryong KANG, Yeongmi HA, Won Ju HWANG
Industrial Health.2013; 51(3): 256. CrossRef - Health Status and Affecting Factors related to Job among Korean Women Employees
Eun-Young Hong, Sang-Dol Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(9): 4107. CrossRef - Influence of task demands on occupational stress: Gender differences
Susana García Herrero, Miguel Ángel Mariscal Saldaña, Javier García Rodriguez, Dale O. Ritzel
Journal of Safety Research.2012; 43(5-6): 365. CrossRef - Analysis on Stress and Dietary Attitudes of Male Employees
Mi-Ae Lee, Eun-Ju Lee, Hye-Kyung Soh, Bong-Soon Choi
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2011; 16(3): 337. CrossRef - Spirituality and Stress Responses in Small Industry Employees
Sook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2010; 19(2): 220. CrossRef - Health Behaviors by Job Stress Level in Large-Sized Company with Male and Female Workers
Hyunju Park, Hye-Sun Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(6): 852. CrossRef
- The Effect of Occupational Stress on the Psychological Well-Being of Healthcare Workers: Basis for Stress Management Interventions
- 1,863 View
- 5 Download
- 26 Crossref

- Factors explaining Quality of Life in Individuals with Coronary Artery Disease
- In Sook Park, Rhayun Song, Sukhee Ahn, Hee Young So, Hyun Li Kim, Kyung Ok Joo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2008;38(6):866-873. Published online December 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.6.866
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The study was done to compare quality of life by gender, and to identify factors which explain quality of life in individuals with coronary artery disease.
Methods For the survey, 91 individuals (53 men and 38 women) agreed to participate in the study. Cardiovascular risk factors, systolic blood pressure, body mass index, total cholesterol, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein-cholesterol, and low density lipoprotein-cholesterol, health behavior as well as quality of life, were measured. Descriptive statistics, t-test, correlation and hierarchical multiple regression with SPSS WIN 12.0 were used to analyze the data.
Results Significant gender differences were found for education, smoking status, chronic disease, perceived health status, and quality of life within sub-dimensions. Hierarchical regression analysis showed gender (men), age, perceived health status, cardiovascular risk scores, and health behaviors together explained 40.2% (adjusted R2) of variance in quality of life.
Conclusion As the factors explaining quality of life in individuals with coronary artery disease have been identified as gender (men), age, perceived health status, and health behaviors, health promotion programs designed for this population should focus on these factors for effective behavioral modification, and consequent improvement in quality of life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prediction Model for Health-related Quality of Life in Coronary Artery Disease Patients According to Stress Level
Minju Kim, Ju Youn Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(3): 320. CrossRef - Prevalence of coronary artery disease according to lifestyle characteristics, nutrient intake level, and comorbidities among Koreans aged 40 years and older: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition E
Areum Song, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 457. CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life Based on Comorbidities Among Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease
Jieun Cha, Dallong Han
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2020; 11(4): 194. CrossRef - The Effects of Smart Program for Patients Who Underwent Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (SP-PCI) on Disease-Related Knowledge, Health Behavior, and Quality of Life: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
Jueun Lee, Haejung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(6): 756. CrossRef - Predictors of health-promoting behaviors in Taiwanese patients with coronary artery disease
Ai-Fu Chiou, Shu-Pen Hsu, Huei-Fong Hung
Applied Nursing Research.2016; 30: 1. CrossRef - Effects of position change on lumbar pain and discomfort of Korean patients after invasive percutaneous coronary intervention: a RCT study
Nam Hyun Cha, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2016; 28(10): 2742. CrossRef - Influencing Effects of Type D Personality on Symptom Experiences and Quality of Life in Patients with Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Eun Hee Jo, Sun Hee Han, Myung Ha Lee, Sung Reul Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(5): 536. CrossRef - Relationships of Depression Symptom, Self-Esteem, and Stress to Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Hypertension Registered to a Community Health Center
Mi Ni Choi, Eun-Hyun Lee
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2015; 29(2): 165. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Self Care Education Program for Elderly Patients with Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Gyeong-Jin Jo, Jin-Hyang Yang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(2): 266. CrossRef - The Health Behavioral Experience of Patients with Myocardial Infarction during the Recovery Period
Kyung Ja Kang, Moon Jeong Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(2): 203. CrossRef - Effects of Tai Chi Exercises on Cardiovascular Risks, Recurrence Risk, and Quality of Life in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Rha Yun Song, Moon Kyoung Park, Jin-Ok Cheong, Jae-Hyeong Park, In-Whan Seong
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(5): 515. CrossRef - Teaching Experience of Tai Chi Instructors with Nursing Background
In Sook Park, Rhayun Song
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(1): 10. CrossRef - Postoperative Quality of Life in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Ju-Sung Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2011; 12(3): 1260. CrossRef - Assessment of nurses' nutritional knowledge regarding therapeutic diet regimens
K.A. Park, W.I. Cho, K.J. Song, Y.S. Lee, I.S. Sung, S.M. Choi-Kwon
Nurse Education Today.2011; 31(2): 192. CrossRef - Comparison of Cardiovascular Health Status and Health Behaviors in Korean Women based on Household Income
Young-Joo Park, Nah-Mee Shin, Ji-Won Yoon, Jiwon Choi, Sook-Ja Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(6): 831. CrossRef
- Prediction Model for Health-related Quality of Life in Coronary Artery Disease Patients According to Stress Level
- 916 View
- 2 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Falls Risk Factors of Inpatients
- Eun-Kyung Kim, Jae Chang Lee, Mi-Ran Eom
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2008;38(5):676-684. Published online October 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.5.676
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the risk factors for falls and to suggest data for developing a program for preventing falls.
Methods This was a case-control study in five university hospitals and a general hospital. In total, 216 patients over the age of 18 yr admitted from January 1 to December 31, 2007 participated. One hundred eight patients with experience of falling were matched by gender, age level, diagnosis, and length of stay with 108 patents with no experience of falling admitted on the same unit. A quality assurance coordinator nurse in each hospital examined 35 fall risk factors developed by researchers.
Results In acute hospitals, history of falls, orientation ability, dizziness or vertigo, general weakness, urination problems, transfer/mobility difficulty, walking dependency, impatience, benzodiazepines, diuretics, and vasodilators showed significance on adjusted-odds ratios for fall. Logistic regression analysis was performed to elucidate the factors that influence falls. The probability of falls was increased by dizziness/vertigo, general weakness, and impatience/agitation.
Conclusion This finding can be used as a useful resource in developing nursing intervention programs to predict and prevent the falls of inpatients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Physical Performance and Fear of Falling on Fall Risk in Hemodialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jiwon Choi, Sun-Kyung Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(1): 63. CrossRef - A Clinical Data Warehouse Analysis of Risk Factors for Inpatient Falls in a Tertiary Hospital: A Case-Control Study
Eunok Kwon, Sun Ju Chang, Mikyung Kwon
Journal of Patient Safety.2023; 19(8): 501. CrossRef - Association of medication use with increased fall risk in inpatients: a single-center matched study
Hae-Jin Jeon, Eun-Joo Choi, Min-Jung Kim, Ae-Hee Jung, Sun-Hoi Jung, Hyo-Nam Woo, Kyu-Nam Heo, Ju-Yeun Lee, Hyung-Min Kwon
Journal of Geriatric Neurology.2023; 2(2): 64. CrossRef - Prediction of Falls Risk Using Toe Strength and Force Steadiness based on Deep Learning: A Preliminary Study
Jin Seon Kim, Seong Un Choi, Chang Yeop Keum, Jaehee Lee, Woong Ki Jang, Kwang Suk Lim, Hyungseok Lee, Byeong Hee Kim, Tejin Yoon
Journal of the Korean Society for Precision Engineering.2023; 40(7): 519. CrossRef - The Perceived Knowledge of Fall Prevention in Nurses Working in Acute Care Hospitals in China and the United States
Lin Wang, Li Zhang, Elizabeth Roe, Sally Decker, Gwen Howard, Angela Luth, Kristine Marks, Brenda Whitman
Journal of Patient Safety.2022; 18(2): e580. CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Fall Prevention Program Based on King’s Theory of Goal Attainment in Long-Term Care Hospitals: An Experimental Study
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 715. CrossRef - Comparison of the predictive validity of three fall risk assessment tools and analysis of fall‐risk factors at a tertiary teaching hospital
Eun Hee Cho, Yun Jung Woo, Arum Han, Yoon Chung Chung, Yeon Hee Kim, Hyeoun‐Ae Park
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2020; 29(17-18): 3482. CrossRef - Improving Prediction of Fall Risk Using Electronic Health Record Data With Various Types and Sources at Multiple Times
Hyesil Jung, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Hee Hwang
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2020; 38(3): 157. CrossRef - Triggers and Outcomes of Falls in Hematology Patients: Analysis of Electronic Health Records
Min Kyung Jung, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2019; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - A risk-factor analysis of medical litigation judgments related to fall injuries in Korea
Insook Kim, Seonae Won, Mijin Lee, Won Lee
Medicine, Science and the Law.2018; 58(1): 16. CrossRef - Root Cause Analysis of Falls Occurred and Presenting Fall Prevention Strategies Using Nominal Group Technique
Zhila Najafpour, Ali Movafegh, Arash Rashidian, Mohamadreza Jafari, Ali Akbari Sari, Mohammad Arab
Health Scope.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Structural Analysis of Variables related to Fall Prevention Behavior of Registered Nurses in Small-to-Medium Sized Hospitals
Ji Hyun Park, Jung Tae Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2018; 25(4): 269. CrossRef - Risk factors of falls among inpatients with cancer
M.D. Jun, K.M. Lee, S.A. Park
International Nursing Review.2018; 65(2): 254. CrossRef - Characteristics and Risk Factors for Falls in Tertiary Hospital Inpatients
Eun-Ju Choi, Young-Shin Lee, Eun-Jung Yang, Ji-Hui Kim, Yeon-Hee Kim, Hyeoun-Ae Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(3): 420. CrossRef - Identifying Characteristics of Fall Episodes and Fall-related Risks of Hospitalized Patients
Young Ok Kang, Rhayun Song
Journal of muscle and joint health.2015; 22(3): 149. CrossRef - Fall Risk Factors and Characteristics of an Acute Hospital Setting across Clinical Departments
In-Sil Jang, Sun-Gyo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2014; 21(3): 264. CrossRef - Evaluation of falls by inpatients in an acute care hospital in Korea using the Morse Fall Scale
Yung Hee Sung, Myung Sook Cho, In Gak Kwon, Yoen Yi Jung, Mi Ra Song, Kyunghee Kim, Sungho Won
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2014; 20(5): 510. CrossRef - Fall Risk related Factors in Postmenopausal Women
Jung-Han Lee, Hee Seung Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(5): 533. CrossRef - Effects of Health Belief on Fall Prevention Activities of Emergency Room Nurses
Min Kyoung Park, Hyun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(2): 176. CrossRef - Validation of the Short Form Bobath Memorial Hospital Fall Risk Assessment Scale at a Specialized Geriatric Hospital in Korea
Kyeong-Yae Sohng, Mi Hwa Park, Seung Kyo Chaung, Hye Ja Park
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(3): 495. CrossRef - Fall Risk Factors and Fall Risk Assessment of Inpatients
Yoon Sook Kim, Smi Choi-Kwon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(1): 74. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Pediatric Inpatient Falls
Myung Sook Cho, Mi Ra Song, Sun Kyung Cha
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(5): 595. CrossRef - Safety Consciousness of the Elderly Living Alone
Youngsil Kang, Sun Jae Jung
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(3): 180. CrossRef - The Effects of Fall Prevention Education on the Fall-related Knowledge and Prevention activity of the Elderly Hospitalized in Internal Medicine Department
Myung Sill Chung
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(2): 102. CrossRef - Predictive Effects of Previous Fall History on Accuracy of Fall Risk Assessment Tool in Acute Care Settings
Ihn Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(4): 444. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Patient Safety Reporting Promoting Education Program
Myoung-Soo Kim, Yun-Hee Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(1): 284. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Fear of Falling in Stroke Patients
Hee-Sook Jeong, Eun-Nam Lee, Sam-Sook Kim
Journal of muscle and joint health.2011; 18(2): 215. CrossRef - Current Approaches to Fall Risk Assessment in Nursing Homes
Laura M. Wagner, Vicky Scott, Mara Silver
Geriatric Nursing.2011; 32(4): 238. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Validity of Fall Risk Assessment Scales in Korean Hospitals
Keum Soon Kim, Jin A Kim, Yun-Kyoung Choi, Yu Jeong Kim, Mi Hwa Park, Hyun-Young Kim, Mal Soon Song
Asian Nursing Research.2011; 5(1): 28. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Fall Risk Assessment Tool to Establish Continuous Quality Improvement Process for Inpatients' Falls
Ihn Sook Park, InSook Cho, Eun Man Kim, Min Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2011; 17(4): 484. CrossRef - Defining Reported Errors on Web-based Reporting System Using ICPS From Nine Units in a Korean University Hospital
Chul-Hoon Kim, Myoungsoo Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2009; 3(4): 167. CrossRef
- The Impact of Physical Performance and Fear of Falling on Fall Risk in Hemodialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 1,615 View
- 13 Download
- 31 Crossref

- The Analysis of Type D Personality Research as a Psychosocial Risk Factor in Cardiovascular Disease for Elders with a Chronic Disease
- Eun Kyeung Song, Youn Jung Son
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(1):19-28. Published online February 28, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.1.19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this paper was to examine the relationship between type D personality and cardiovascular disease, and to suggest future research directions.
Methods A literature search was conducted from the following nine databases: 1) MEDLINE, 2) CINAHL, 3) Pubmed Unrestricted, 4) PsycINFO, 5) KISS, 6) RICHIS, 7) RISS4U, and 8) Nanet. The combinations of the words, "type D personality", "personality", "heart", "cardiovascular", and "coronary" were used for keyword searches to find relevant articles. Twenty eight studies were identified.
Results Type D personality has been associated with increased morbidity and mortality in patients with established cardiovascular disease. Type D patients are also at increased risk for impaired quality of life, and seem to benefit less from medical and invasive treatment.
Conclusion There is substantial evidence for a relationship between type D personality and clinical outcomes related to cardiovascular disease. Randomized clinical trials are needed to further evaluate the value of controlling type D personality to improve survival and reduce morbidity in patients with cardiovascular disease. Accumulating evidence from this analysis indicates the urgent need to adopt a personality approach in order to optimize the identification of patients at risk for stress related cardiac events.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations between type D personality, moral disengagement, and cyber aggression among university students
Haeyoung Lee, Sun Joo Jang
Current Psychology.2023; 42(15): 12648. CrossRef - Associations of eating alone with type D personality, depression and rejection sensitivity among South Korean university students
Eunmi Lee, Yujeong Kim, Haeyoung Lee
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2020; 56(2): 256. CrossRef - Impact of Type D Personality on Depression, Anxiety, and Health-related Quality of Life among Coronary Artery Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Sun Hyoung Bae, Jin-Hee Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(3): 219. CrossRef - Comparisons of Clinical Practicum Stress, Depression, and Self-Efficacy among Nursing Students: Focusing on Type D Personality and non-Type D Personality
Mi Hyeon Seong, Ok Sun Kim, Youn Ok Jung, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2017; 26(3): 217. CrossRef - Association among type D personality, non-motor symptoms, and quality of life in Parkinson's disease: A cross-sectional study
Sung Reul Kim, Ji Young Kim, Hyun Kyung Kim, Kyeung Eun Lim, Mi Sun Kim, Sun Ju Chung
Geriatric Nursing.2017; 38(5): 431. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of the Resilience on the Relationship between Type D Personality and Compliance in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Mi Young Cheon, Jiyeon Kang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(1): 61. CrossRef - Does type D personality affect symptom control and quality of life in asthma patients?
Sung Reul Kim, Hyun Kyung Kim, Jeong Hee Kang, Seok Hee Jeong, Hye Young Kim, So Ri Kim, Mi Young Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2015; 24(5-6): 739. CrossRef - The Relationship between Type D Personality and Suicidality in Low-Income, Middle-Aged Adults
Dae Hyun Yoon, Seog Ju Kim, Jong-Ha Lee, Pyo-Min Kim, Doo-Heum Park, Seung Ho Ryu, Jaehak Yu, Jee Hyun Ha
Psychiatry Investigation.2015; 12(1): 16. CrossRef - Effects of Type D Personality on Compassion Fatigue, Burnout, Compassion Satisfaction, and Job Stress in Clinical Nurses
Sung Reul Kim, Hye Young Kim, Jeong Hee Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(3): 272. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Type D Personality of Female Undergraduate Students Majoring in Nursing
Jun Hee Noh, Eun Ju Lim, Yong-Sun Jeong
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(12): 6265. CrossRef - Influence of Type D personality on health‐related quality of life among Korean patients with end‐stage renal disease
Youn‐Jung Son, Mi‐Ae You, Eun Kyeung Song
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2012; 18(3): 260. CrossRef - A Comparison of the Health Status and Health Promoting Behaviors between Type D Personality and Non-Type D Personality in Middle aged Women
Sun Hyoung Bae, Jin-Hee Park, Euigeum Oh
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2011; 17(4): 337. CrossRef - Anti-obesity Effect of Monascus pilosus Mycelial Extract in High Fat Diet-induced Obese Rats
Sang-Il Lee, Jae-Won Kim, Ye-Kyung Lee, Seung-Hwan Yang, In-Ae Lee, Joo-Won Suh, Soon-Dong Kim
Journal of Applied Biological Chemistry.2011; 54(3): 197. CrossRef - Quality of Life and Illness Intrusiveness by Type-D Personality in the Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Haeng-Mi Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(3): 349. CrossRef
- Associations between type D personality, moral disengagement, and cyber aggression among university students
- 1,042 View
- 4 Download
- 14 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


