Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Development of an end-of-life care competency scale for nurses in long-term care hospitals: a psychometric validation study
- Sookyeon Son, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):598-612. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure end-of-life care (EOLC) competency among nurses working in long-term care hospitals and to evaluate its validity and reliability.
Methods
Preliminary items were developed based on attributes and indicators identified through a conceptual analysis of EOLC competency. The initial version of the scale was refined through expert content validity assessment, item revision, and a pilot test. The main survey was conducted among 460 nurses in long-term care hospitals, and 409 valid responses were analyzed after excluding 51 incomplete or invalid cases. Data were analyzed using software-assisted item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses, and assessments of convergent, discriminant, and criterion-related validity, as well as reliability testing.
Results
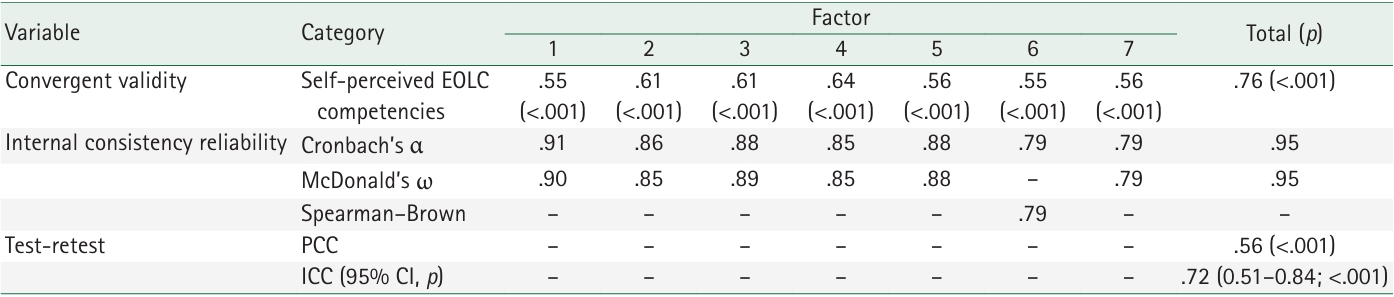
The initial 55 items were reduced to a final set of 30 items across seven dimensions. Model fit indices indicated good construct validity (χ²/degrees of freedom=1.91, standardized root mean square residual=.06, root mean square error of approximation=.07, Tucker-Lewis index=.90, comparative fit index=.91), with a total explained variance of 70.2%. The scale demonstrated strong criterion-related validity (r=.76, p<.001), high internal consistency (Cronbach’s α=.95; McDonald’s ω=.95), acceptable test–retest reliability (r=.56, p<.001), and an intraclass correlation coefficient of .72 (95% confidence interval, .51–.84; p<.001).
Conclusion
The developed scale is a valid and reliable instrument for assessing EOLC competency among nurses in long-term care hospitals. It can be effectively utilized for educational assessment, training evaluation, and the measurement of program effectiveness in end-of-life care.
- 980 View
- 122 Download

- Development and Effects of a Person-Centered Fall Prevention Program for Older Adults with Dementia in Long-Term Care Hospitals: For Older Adults with Dementia and Caregivers in LongTerm Care Hospitals
- Jeong Ok Lim, Mee Ock Gu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):341-358. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21230
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the effects of a person-centered fall prevention program for older adults with dementia in long-term care hospitals.
Methods
A nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The study sample included 42 older adults with dementia (experimental group: 21, control group: 21) and 42 caregivers (experimental group: 21, control group: 21). The program comprised 48 sessions held over 12 weeks and included exercise intervention with resistance and balance, dance walking (45~60 min, three times/week), cognitive and emotional intervention (35~50 min, once per week), and person-centered fall prevention education (10 min, once per week). The program for caregivers consisted of six educational sessions (i.e., fall prevention competency enhancement and person-centered care strategy education, 80 min, once per week) for six weeks. Data were collected before participation and 12 weeks after program completion from February 18 to May 12, 2019. Data analysis was conducted using the chi-square test, t-test, and Mann―Whitney U test with SPSS/WIN 21.0.
Results
The experimental group of older adults with dementia showed significant improvement in physical and cognitive functions, and a decrease in depression, and behavioral and psychological symptoms, when compared with the control group. caregivers in the experimental group exhibited significant improvement in fall-related knowledge and person-centered care of older adults with dementia compared to the control group.
Conclusion
The study findings indicate that this program was effective as a nursing intervention for fall prevention among older adults with dementia in long-term care hospitals. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influencing factors of depressive and anxiety symptoms among caregivers of Alzheimer's disease patients: A cross-sectional study
Chengfei Duan, Mo Zhu, Xia Li, Ling Yue
Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.2026; 109(3): 1264. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Fall Incidents at Long-term Care Hospitals: Using Data from the Korea Patient Safety Reporting and Learning System
Soojin Chung, Jeongim Lee
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2025; 50(1): 96. CrossRef - Current Trends of Exercise Programs for Improving Cognitive Function in Older Adults
Jae-Hyun Lee, Wooyeon Jo, Jaeho Jin, Yaxiong Zheng, Soyoon Lee, Se-Yeon Jang, Minseo Kim, Young-Jin Moon, Hye Gwang Jeong, Sang Ki Lee
Exercise Science.2024; 33(3): 254. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Dementia Care Competence among Care Staff: A Mixed-Methods Systematic Review Protocol
Jinfeng Zhu, Jing Wang, Bo Zhang, Xi Zhang, Hui Wu
Healthcare.2024; 12(11): 1155. CrossRef - Falls in Patients of Medical Institutions in South Korea: A Literature Review
Jongwon Choi, Woochol Joseph Choi
Physical Therapy Korea.2023; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - A Study on Emotions to Improve the Quality of Life of South Korean Senior Patients Residing in Convalescent Hospitals
Aeju Kim, Yucheon Kim, Jongtae Rhee, Songyi Lee, Youngil Jeong, Jeongeun Lee, Youngeun Yoo, Haechan Kim, Hyeonji So, Junhyeong Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(21): 14480. CrossRef
- Influencing factors of depressive and anxiety symptoms among caregivers of Alzheimer's disease patients: A cross-sectional study
- 2,866 View
- 180 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Factors Relating to the Quality of Care for Nursing Home Residents in Korea: Using the Delphi Method
- Juh Hyun Shin, Eun Mee Kim, Ji Yeon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):783-794. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.783
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study identified factors related to the quality of care in nursing homes, and elicited consensus opinions from experts on nursing homes.
Methods A Delphi questionnaire was developed based on a review of the literature using the keywords “nursing homes,” “workforce,” and “quality of care.” A total of two Delphi surveys were conducted with 14 experts. The important and urgent factors related to the quality of care for nursing home residents emerged.
Results A consensus was achieved on the important and urgent factors relating to the quality of care. The related factors were grouped into four sections: Organizational Characteristics, Staffing Characteristics, the Long-Term Care Market and Legal and Policy Issues, and Nursing Processes. In total, 23 items were important factors and 26 items were urgent factors relating to the quality of care. In addition, the unanimous advocacy by the experts for increased hours per resident day for registered nurses (RNs, 41 minutes 59 seconds) was much higher than the current hours per resident day of RNs in Korea.
Conclusion To provide optimal care for residents in nursing homes in Korea, the mandatory and essential placement of RNs with professional knowledge and skills is paramount.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of special nursing units in nursing homes on healthcare utilization and cost: A case-control study using propensity score matching
Eunhee Cho, Eun-Young Kim, Kyung Hee Lee, Hye-Ryoung Kim, Seonhwa Choi, Yea Seul Yoon, EunKyo Kim, Seok-Jae Heo, Se Young Jung, Jiyoon Jang
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2023; 147: 104587. CrossRef - Effects of registered nurse staffing levels, work environment, and education levels on adverse events in nursing homes
Seonhwa Choi, Eunhee Cho, Eunkyo Kim, Kyongeun Lee, Soo Jung Chang
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cost of Care and Pattern of Medical Care Use in the Last Year of Life among Long-Term Care Insurance Beneficiaries in South Korea: Using National Claims Data
Sunjoo Boo, Jungah Lee, Hyunjin Oh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(23): 9078. CrossRef - Impact of Nurse Staffing, Skill Mix and Stability on Resident Health Outcomes in Korean Nursing Homes
Juh Hyun Shin, Gui Yun Choi, Jiyeon Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2020; 22(4): 291. CrossRef - The Effects of Long-term Care Hospitals' Nurse Staffing Level on Patient Outcomes: Differences according to Region
Kyung Jin Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 354. CrossRef
- The effects of special nursing units in nursing homes on healthcare utilization and cost: A case-control study using propensity score matching
- 1,999 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Development and Effect of a Fall Prevention Program Based on the King's Goal Attainment Theory for Fall High-Risk Elderly Patients in Long-Term Care Hospital
- Bom Mi Park, Ho Sihn Ryu, Kyeung Eun Kwon, Chun Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):203-214. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.203
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study to develop a fringed fall prevention program based on King's goal attainment theory and education. This study is applied to the personal, interpersonal, and social systems of fall high-risk patients to test its effects.
Methods This study was a nonequivalent control group pre- and post-test design. There were 52 fall high-risk patients in the experimental group and 45 in the control group. The experimental group received six sessions, with the group sessions lasting 60 minutes and the individual sessions lasting 20~30 minutes. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, an χ2-test, a paired sample t-test, and a Wilcoxon signed-ranks test utilizing IBM SPSS software.
Results For the 3-month intervention period, the fall prevention program was found to be particularly effective for patients in the experimental group (from 3.38 to 1.69 per 1000 patient days;
p =.044), as opposed to the control group (from 1.94 to 1.49 per 1000 patient days;p =.300). For the 6-month follow up period, the fall prevention program was again found to be effective for patients in the experimental group (from 3.26 to 0.76 per 1000 patient days;p =.049) compared to the control group (from 1.98 to 1.01 per 1000 patient days;p =.368).Conclusion These results indicate that the fringed fall prevention program is very effective in reducing falls, not only during the intervention period, but also after the intervention period has ended. We can therefore recommend this program for use concerning fall high-risk patients in long-term care hospitals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent advances in the identification of related factors and preventive strategies of hip fracture
Yaohui Yu, Yudan Wang, Xiaoli Hou, Faming Tian
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Falls in Patients of Medical Institutions in South Korea: A Literature Review
Jongwon Choi, Woochol Joseph Choi
Physical Therapy Korea.2023; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of a Fall Prevention Program Based on Goal Attainment Theory for Homebound Older Adults With Osteoarthritis of the Lower Extremities
Chunhee Lee, Heeok Park
Orthopaedic Nursing.2022; 41(6): 414. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Led Intervention Programs Based on Goal Attainment Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 699. CrossRef - EFFECTIVENESS OF EDUCATIONAL INTERVENTIONS FOR FALL PREVENTION: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Maria Aline Moreira Ximenes, Maria Girlane Sousa Albuquerque Brandão, Thiago Moura de Araújo, Nelson Miguel Galindo Neto, Lívia Moreira Barros, Joselany Áfio Caetano
Texto & Contexto - Enfermagem.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Application Value of Rehabilitation Nursing in Patients with Stroke Based on the Theory of Interactive Standard: A Randomized Controlled Study
Ningning Li, Jun Wang, Mei Zheng, Qunying Ge, Mozaniel Oliveira
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - A prospective cohort study of the risk factors for new falls and fragility fractures in self-caring elderly patients aged 80 years and over
Jian Zhou, Bo Liu, Ming-Zhao Qin, Jin-Ping Liu
BMC Geriatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Fall Prevention Program Based on King’s Theory of Goal Attainment in Long-Term Care Hospitals: An Experimental Study
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 715. CrossRef - Development of Fall Inducement System based on Pedestrian Biological Data for Fall Reproduction
Jong-il Lee, Jong-Boo Han, Jae Wan Koo, Seokjae Lee, Dong-Seop Sohn, Kap-Ho Seo
Journal of Korea Robotics Society.2020; 15(3): 286. CrossRef
- Recent advances in the identification of related factors and preventive strategies of hip fracture
- 3,096 View
- 106 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Development and Effects of a Coping Skill Training Program for Caregivers in Feeding Difficulty of Older Adults with Dementia in Long-Term Care Facilities
- Hyun Hwa Hong, Mee Ock Gu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):167-181. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.167
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose We developed and tested the effects of a coping skill training program for caregivers in feeding difficulty among older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The subjects comprised 34 caregivers (experimental group: 17, control group: 17) and 40 older adults with dementia (experimental group: 20, control group: 20). The developed program was delivered in 4-hour sessions over 6 weeks (including 2 weeks of lectures and lab practice on feeding difficulty coping skills, and 4 weeks of field practice). Data were collected before, immediately after, and 4 weeks after the program (January 3 to April 6, 2016). The data were analyzed using t-test and repeated measures ANOVA using SPSS/WIN 20.0.
Results Compared to their counterparts in the control group, caregivers in the experimental group showed a significantly greater improvement in feeding knowledge and feeding behavior, while older adults with dementia showed greater improvements in feeding difficulty and Body Mass Index.
Conclusion The study findings indicate that this coping skill training program for caregivers in feeding difficulty is an effective intervention for older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influencing factors of depressive and anxiety symptoms among caregivers of Alzheimer's disease patients: A cross-sectional study
Chengfei Duan, Mo Zhu, Xia Li, Ling Yue
Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.2026; 109(3): 1264. CrossRef - Mealtime Support by Direct Care Workers in Long‐Term Care Facilities: Secondary Behavioural Analysis of Videos
Eunju Choi, Leeho Yoo, Soogyung Shin, Dukyoo Jung
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Feasibility of a nurse-led online video intervention for mealtime assistance in dementia care: a quasi-experimental mixed-methods study
Dukyoo Jung, Leeho Yoo, Soogyung Shin, Sukyung Byeon, Hyein Seo, Eunju Choi
BMC Geriatrics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting Mealtime Difficulties in Older Adults with Dementia Living in Long-Term Care Facilities: A Multilevel Model Analysis
Dukyoo Jung, Jennie C. De Gagne, Hyesoon Lee, Leeho Yoo, Jisung Park, Eunju Choi, Yonggang Zhang
Journal of Nursing Management.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of Case-Based Small-Group Learning on Care Workers’ Emergency Coping Abilities
Soon-Ok Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(21): 11458. CrossRef - Eating Difficulties among Older Adults with Dementia in South Korean Long-Term Care Facilities: A Scoping Review
Dukyoo Jung, Kyuri Lee, Eunju Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 470. CrossRef Feasibility of a Mobile Meal Assistance Program for Direct Care Workers in Long-Term Care Facilities in South Korea
Dukyoo Jung, Jennie C De Gagne, Minkyung Lee, Hyesoon Lee, Kyuri Lee, Eunju Choi, Juyoun Chung
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2020; Volume 15: 2019. CrossRef- Informal dementia caregivers’ experiences and perceptions about mealtime care: A qualitative evidence synthesis
Yijing Li, Dan Sun, Xu Zhang, Huanhuan Li, Yingnan Zhao, Dongfei Ma, Zehui Li, Jiao Sun
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2020; 76(12): 3317. CrossRef
- Influencing factors of depressive and anxiety symptoms among caregivers of Alzheimer's disease patients: A cross-sectional study
- 1,035 View
- 19 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Predictors of Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia: Based on the Model of Multi-Dimensional Behavior
- Jeong Eun Yang, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):143-153. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify factors predicting behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) in persons with dementia. Factors including the patient, caregiver, and environment based on the multi-dimensional behavioral model were tested.
Methods The subjects of the study were 139 pairs of persons with dementia and their caregivers selected from four geriatric long-term care facilities located in S city, G province, Korea. Data analysis included descriptive statistics, inverse normal transformations, Pearson correlation coefficients, Spearman's correlation coefficients and hierarchical multiple regression with the SPSS Statistics 22.0 for Windows program.
Results Mean score for BPSD was 40.16. Depression (β=.42,
p <.001), exposure to noise in the evening noise (β=-.20,p =.014), and gender (β=.17,p =.042) were factors predicting BPSD in long-term care facilities, which explained 25.2% of the variance in the model.Conclusion To decrease BPSD in persons with dementia, integrated nursing interventions should consider factors of the patient, caregiver, and environment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The influence path of caregivers’ positive aspects, expressed emotion and coping style on behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia
Shuang Zhang, Xiumei Ying, Shuyan Fang, Wenxia Wang, Xiangning Zhu, Yueyang Dong, Meng He, An Chang, Jiao Sun
Geriatric Nursing.2022; 44: 143. CrossRef
- The influence path of caregivers’ positive aspects, expressed emotion and coping style on behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia
- 1,147 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Study on the Forecast of Bed Demand for Institutional Long-term Care in Taegu, Korea
- Myung Hi Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):437-451. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.437
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to estimate the forecast of bed demand for institutional long-term care for the elderly persons in Taegu Metropolitan City. The study subject was the total 1,877 elderly persons over age 65 living in Taegu. Among them 1,441 elderly persons were sampled from community and 436 were from the elderly admitted 5 general hospitals. Data collection was carried out by interview from 25 August to 25 December 1997. The measuring instrument of this study was the modified tool of CARE, MAI, PCTC, and ADL which were examined for validity and reliability. In order to forecast bed demand of Nursing Home, this study revised prediction techniques suggested by Robin. The results were as follows : 1. OLDi of Taegu City were 122,202 by the year 1998 and number of Low-Income Elderly Persons were 3,210. 2. The Level I : Senior Citizen Home AQi * ASTAYi ADEMi = --------------- 365 * AOCUi . AQi = OLDi * LADLi * NASi * ALONi * LIADLi * AUTILi Predicted number of bed demand for Home Based Elderly Persons were 4,210 and Low-Income Elderly Persons were 1,081 and Total Elderly Persons were 5,291 by the year 1998, 6,343 by the year 2000 and 8,351 by the 2005. 3. The Level II : Nursing Home (BQ1i+BQ2i) * BSTAYi BDEMi = ----------------------- 365 * BOCUi . BQ1i = OLDi * HADLi * ALONi * HIADLi BQ2i = OLDi * HADLi * FAMi * OBEDi Predicted number of demand for Total Elderly Persons were 668 by the year 1998, 802 by the year 2000 and 1,055 by the 2005. 4. The Level III : Nursing Home COLDi * HDISi * CUTILi * CSTAYi CDEMi = ------------------------------------ + CQi/10 365 * COCUi Predicted number of demand for Total Elderly Persons were 1,899 by the year 1998, 2,311 by the year 2000 and 3,003 by the 2005. 5. Predicted number of bed demand of long-term care facilities in the year 1998 according to Levels were 4.3% among elderly persons in Taegu by Level I, 0.5% by Level II and 1.5% by Level III. Number of elderly persons in current long-term care facilities were 458 in LevelI I,284 in Level II. 6. Deficit number of bed demand of long-term care facilities were 4,833 in Level I, 384 in Level II , 1,899 in Level III for the elderly persons in Taegu Metropolitan City.
- 433 View
- 0 Download

- Functional Status of Stroke Patients among Different Long-Term Care Settings
- Eun Young Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(2):372-378. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.2.372
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to measure the functional status of stroke patients cared for in different long-term care settings.
Method We assessed all stroke patients in two home health care agencies, four nursing homes and one geriatric hospital in Korea (n=171) using the Resident Assessment Instrument (RAI), which comprises Activity of Daily Living (ADL), urine incontinence, bowel incontinence, a Cognitive Performance Scale (CPS),and being understood and understanding others. Data was collected by face-to-face surveys with patients.
Results The mean ADL score, urine incontinence score, bowel incontinence score, CPS, and being understood score and understanding others score were lowest for the patients receiving home health care, and highest for the patients in nursing homes. Low scores described poor and high scores good functional status. The results showed significant differences in physical and cognitive function scores between the three groups of patients.
Conclusion This study suggests that there may be large differences between the patients in these three types of long-term care settings. These findings can be used to help develop and implement efficient long-term care programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and potential determinants of musculoskeletal disease symptoms among care workers in long‐term care facilities in South Korea
Myung‐Sook Park, Mi Yu, Su‐Jeong Yu, Kyung‐Ja Kang, Hyun‐Mi Seo
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2014; 11(3): 211. CrossRef - The Long-term Care Utilization of the Elderly with Dementia, Stroke, and Multimorbidity in Korea
Boyoung Jeon, Soonman Kwon, Hongsoo Kim
Health Policy and Management.2013; 23(1): 90. CrossRef
- Prevalence and potential determinants of musculoskeletal disease symptoms among care workers in long‐term care facilities in South Korea
- 751 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- On the Feasibility of a RUG-III based Payment System for Long-Term Care Facilities in Korea
- Eun Kyung Kim, Ha Young Park, Chang Yup Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(2):278-289. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.2.278
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to classify the elderly in long-term care facilities using the Resource Utilization Group(RUG-III) and to examine the feasibility of a payment method based on the RUG-III classification system in Korea.
Method This study measured resident characteristics using a Resident Assessment Instrument-Minimum Data Set(RAI-MDS) and staff time. Data was collected from 530 elderly residents over sixty, residing in long-term care facilities. Resource use for individual patients was measured by a wage-weighted sum of staff time and the total time spent with the patient by nurses, aides, and physiotherapists.
Result The subjects were classified into 4 groups out of 7 major groups. The group of Clinically Complex was the largest (46.3%), and then Reduced Physical Function(27.2%), Behavior Problems (17.0%), and Impaired Cognition (9.4%) followed. Homogeneity of the RUG-III groups was examined by total coefficient of variation of resource use. The results showed homogeneity of resource use within RUG-III groups. Also, the difference in resource use among RUG major groups was statistically significant (p<0.001), and it also showed a hierarchy pattern as resource use increases in the same RUG group with an increase of severity levels(ADL).
Conclusion The results of this study showed that the RUG-III classification system differentiates resources provided to elderly in long-term care facilities in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of the Cost and Case-mix of Post-acute Stroke Patients in China Using Quantile Regression and the Decision-tree Models
Mengjia Zhi, Linlin Hu, Fangli Geng, Ningjun Shao, Yuanli Liu
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2022; Volume 15: 1113. CrossRef - Development of a Web-based Education Program for Nurses working in Nursing Homes on Human Rights of Older Adults
Ki-Kyong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(4): 463. CrossRef - Relationship between Resource Utilization and Long-term Care Classification Level for Residents in Nursing Homes
Min Kyung Lee, Eun-Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(6): 903. CrossRef - Effects of Case Management using Resident Assessment Instrument-Home Care (RAI-HC) in Home Health Services for Older People
Kyung Ja June, Ji Yun Lee, Jong Lull Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(3): 366. CrossRef
- Analysis of the Cost and Case-mix of Post-acute Stroke Patients in China Using Quantile Regression and the Decision-tree Models
- 724 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Resource use of the Elderly in Long-term Care Hospital using RUG-III
- Eun Kyung Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(2):275-283. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.2.275
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to classify elderly in long-term care hospitals for using Resource Utilization Group(RUG-III) and to consider feasibility of payment method based on RUG-III classification system in Korea.
Method This study designed by measuring resident characteristics using the Resident Assessment Instrument-Minimum Data Set(RAI-MDS) and staff time. The data were collected from 382 elderly over sixty-year old, inpatient in the five long-term care hospitals. Staff time was converted into standard time based on the average wage of nurse and aids.
Result The subjects were classified into 4 groups. The group of Clinically Complex was the largest(46.3%), Reduced Physical Function(27.2%), Behavior Problem(17.0%), and Impaired Cognition(9.4%). The average resource use for one resident in terms of care time(nurses, aids) was 183.7 minutes a day. Relative resource use was expressed as a case mix index(CMI) calculated as a proportion of mean resource use. The CMI of Clinically Complex group was the largest(1.10), and then Reduced Physical Function(0.93), Behavior Problem(0.93), and Impaired Cognition(0.83) followed. The difference of the resource use showed statistical significance between major groups(p<0.0001).
Conclusion The results of this study showed that the RUG-III classification system differentiates resources provided to elderly in long-term care hospitals in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Overview of International Staff Time Measurement Validation Studies of the RUG-III Case-mix System
Luke A Turcotte, Jeff Poss, Brant Fries, John P Hirdes
Health Services Insights.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- An Overview of International Staff Time Measurement Validation Studies of the RUG-III Case-mix System
- 775 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

-
The Effect of Dongchimi Juice Containing Kimchi
Lactobacillus on the Oral Health of Patients at a Long-Term Care Hospital: Comparison with Chlorhexidine Solution - Seung-Ah Lee, Dongsuk Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(4):540-550. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.4.540
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The aim of this study was to identify the effect of Dongchimi juice containing kimchi
Lactobacillus as an oral hygiene agent and to compare it with that of chlorhexidine solution (0.12% dilution).Methods This study employed a pretest-posttest experimental design in which a single group of patients was exposed to two different treatments over a period of time. The study included 32 patients hospitalized at a longterm care hospital in Korea. Data were collected between August 12, 2016 and September 28, 2016. The patients first used chlorhexidine solution as an oral care agent for 1 week. After an interval of 2 weeks, they used Dongchimi juice for 1 week. Each agent was applied 2 times a day depending on the protocol. The oral status of the patients was measured using Beck's Oral Exam Guide (OEG) scores. The number of pathogens in the oral cavity was counted by culture, and the patients’ subjective satisfaction score for each oral agent was measured using a visual analogue scale. T-test and Mann-Whitney test were performed to identify significant differences between Dongchimi juice and chlorhexidine solution by using PASW Statistics for Windows, Version 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Results The OEG score was not statistically different with the use of chlorhexidine solution and Dongchimi juice. However, decreasing number of pathogens and the subjective satisfaction score were higher with Dongchimi juice than with the chlorhexidine solution.
Conclusion These findings support the use of Dongchimi juice containing kimchi
Lactobacillus as an oral hygiene agent for Korean patients.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Honey-based Oral Care on Oral Health of Patients With Stroke Undergoing Rehabilitation: A Randomized Controlled Trial
A-Ra Cho, Hyunmi Son, Gyumin Han
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(3): 215. CrossRef - Health Benefits of Kimchi, Sauerkraut, and Other Fermented Foods of the Genus Brassica
Sabina Fijan, Polona Fijan, Lei Wei, Maria L. Marco
Applied Microbiology.2024; 4(3): 1165. CrossRef - The impact of aromatherapy-based oral care on oral conditions, salivary pH, and halitosis in older adults with dementia: Pilot study
Ae Kyung Chang, Bo kyoung Kim, Ah Young Kim
Geriatric Nursing.2023; 53: 109. CrossRef - Effects of Oral Probiotics on Subjective Halitosis, Oral Health, and Psychosocial Health of College Students: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
Dong-Suk Lee, Myoungsuk Kim, Seoul-Hee Nam, Mi-Sun Kang, Seung-Ah Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(3): 1143. CrossRef - Reduction of Halitosis by a Tablet ContainingWeissella cibariaCMU: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
Dong-Suk Lee, Seung-Ah Lee, Myoungsuk Kim, Seoul-Hee Nam, Mi-Sun Kang
Journal of Medicinal Food.2020; 23(6): 649. CrossRef
- Effect of Honey-based Oral Care on Oral Health of Patients With Stroke Undergoing Rehabilitation: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 1,171 View
- 12 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Effects of Home Care Services Use by Older Adults on Family Caregiver Distress
- Jiyeon Kim, Hongsoo Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(6):836-847. Published online December 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.6.836
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the association between utilization of home care services under the national long-term care insurance system and family caregiver distress.
Methods A secondary data analysis was conducted in this study using data collected in 2011 and 2012 from the Korean version of International Resident Assessment Instrument (interRAI) Home Care assessment system. The study sample included 228 clients receiving community based home care and their family caregivers in Korea. Descriptive statistics, χ2 test, t-test, and Heckman selection model analysis were conducted using SAS 9.3.
Results Presence of family caregiver distress was significantly associated with days of nurse visits (β=-.89,
p =<.001) and home helper visits (β=-.53,p =.014). Level of caregiver distress was also significantly associated with days of nurse visits (β=-.66,p =.028). Other factors which were significantly associated with caregiver distress were depression, cognitive function, inadequate pain control, social support for older adult, and caregiver relationship to the older adult.Conclusion The results of this study show that visiting nurse service and appropriate support programs for Older Adults and family caregivers experiencing caregiver distress should be developed and provided to families based on the health care needs of older adults and their family caregivers for effective and sustainable home care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Career Disruption and Employment Status of Korean Family Caregivers of Older Adults Using Home-Based Care
Minah Lee
Nursing Reports.2024; 14(3): 1587. CrossRef - Effect of perceived chronic illness management support, health literacy, and social support on the care burden of families caring for older people with multiple chronic conditions at home: A cross-sectional study
Eun Sil Lee, Mi Young Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(1): 76. CrossRef - Korean primary health care program for people with disabilities: do they really want home-based primary care?
Hye-Jin Kim, Jae-Young Lim, Soong-Nang Jang
BMC Health Services Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Use of Home Care Services Reduces Care-Related Strain in Long-Distance Caregivers
Francesca B Falzarano, Verena Cimarolli, Kathrin Boerner, Karen L Siedlecki, Amy Horowitz, Suzanne Meeks
The Gerontologist.2022; 62(2): 252. CrossRef - Comparing the Needs of Family Caregivers and Program Providers in Long-Term Care in Terms of Family Support Program
Myonghwa Park, Younghye Go, Miri Jeong, Eun-Jeong Han
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(1): 14. CrossRef - Development and Application of Cost Management Program for Visiting Nursing Centers Using Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing
Juhang Kim, Ji Young Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 586. CrossRef
- Career Disruption and Employment Status of Korean Family Caregivers of Older Adults Using Home-Based Care
- 1,507 View
- 10 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Person-centered Care Assessment Tool in Long-term Care Facilities in Korea
- Young Ran Tak, Hae Young Woo, Sun Young You, Ji Hye Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(3):412-419. Published online June 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.3.412
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The aim of this study was to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the Person-centered Care Assessment Tool (P-CAT).
Methods The English P-CAT was translated into Korean with forward and backward translation. Survey data were collected from 458 staff in 17 long-term care facilities in Korea. Construct validity and criterion related validity were evaluated. Cronbach's alpha was used to assess reliability.
Results The Korean version of P-CAT was shown to be valid homogeneously by factor, item and content analysis. Internal consistency reliability was satisfactory in which the values of factor 1, factor 2 and the total scale were .84, .77 and .86 respectively. Exploratory factor analysis supported the construct validity with a two-factor solution. Factor loadings of the 13 items ranged in .34~.80. Criterion validity to the Person-centered Climate Questionnaire-staff (PCQ-S) was .74 (
p <.001).Conclusion The Korean version of the P-CAT was found to be an applicable instrument with satisfactory reliability and validity for further use in measuring successful person-centered care in long-term care facilities for older persons.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing the validity of social measures on human rights awareness: a dual-method approach integrating exploratory factor analysis and latent profile analysis
Song-Iee Hong, So Youn Chung, Yoewon Yoon
Journal of Elder Abuse & Neglect.2026; 38(1): 1. CrossRef - Person‐Centered Care Assessment Tool: French Validation and Structural Invariance in Nursing Home Staff
Jérôme Erkes, Clarisse Madiouni, Cécile Bourgeois, David Edvardsson, Valérie Vitou, Sophie Bayard
International Journal of Older People Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of perceptions of a good death, person-centered care, and empathy competency on end-of-life care among long-term care facilities' nursing staff and mediating effects of empathy competency: A descriptive study
Eunmi An, Taewha Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(2): 187. CrossRef - Effect of Emotional Intelligence on Personal and Professional Success: A Quantitative Study
Abdul-Monim Batiha, Abeer S. Aseeri, Mohammed ALBashtawy, Kamel A. Saleh, Omar M. Khraisat, Fadwa Alhalaiqa
The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing.2025; 56(6): 251. CrossRef - Factors influencing person-centered care among nurses in long-term care hospitals in South Korea: a cross-sectional study
Suhye Kwon, Hyochol Brian Ahn, Miseon Bang
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(3): 412. CrossRef - Trends in Person-Centered Nursing Research among Geriatric Nursing Staff in South Korea: A Scoping Review
Sohee Yoo, Duckhee Chae, Sooyeon Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2025; 39(3): 309. CrossRef - Emotional Touch Nursing Competencies Model of the Fourth Industrial Revolution: Instrument Validation Study
Sun-Young Jung, Ji-Hyeon Lee
Asian/Pacific Island Nursing Journal.2024; 8: e67928. CrossRef - Information-Motivation-Behavioral Skill model-based physical restraint education program for nursing care providers in long-term care hospitals: A quasi-experimental repeated measures non-equivalent control group design
Sukhyun Jun, Haejung Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(3): 288. CrossRef - Person-centered care assessment tool with a focus on quality healthcare: a systematic review of psychometric properties
Lluna Maria Bru-Luna, Manuel Martí-Vilar, César Merino-Soto, José Livia-Segovia, Juan Garduño-Espinosa, Filiberto Toledano-Toledano
BMC Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a Tool to Measure Slow Nursing for Older Adults in Long-term Care Hospitals: A Methodological Study
Hyeon Mi Woo
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(3): 212. CrossRef - Evaluating person-centered care in residential care facilities from the perspective of caregivers in South Korea: a survey
Young-Ran Chin, Hyo Young Lee
BMC Health Services Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of the Indonesian version of the Person‐centered Care Assessment Tool
Woro Mustika Weni, Megumi Shimizu, Chiaki Ando‐Ohmura, Yuki Ohashi, David Edvardsson, Annica Backman, Rebecca Baxter, Noortje Kloos, Akiko Ozaki
International Journal of Older People Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Attitude toward Dementia and Nursing Practice Environment on Person-centered Care in Long-term Care Hospital Nurses
Su Hyun Jang, Hyun Hee Shin
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(4): 306. CrossRef - Factors influencing shared decision-making in long-term care facilities
Da Eun Kim, Min Jung Kim
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Performance of Person-centered Care Among Nurses in Designated COVID-19 Hospitals
Hyun-Joung Yun, Jaehee Jeon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(4): 413. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling of Person-Centered Nursing in Hospital Nurses
Yeon Hee Bae, Hye-Ah Yeom
Healthcare.2022; 10(3): 514. CrossRef - Person-Centered Care Practice, Patient Safety Competence, and Patient Safety Nursing Activities of Nurses Working in Geriatric Hospitals
Ayoung Huh, Juh Hyun Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(10): 5169. CrossRef - A Comparative Review of the Design Guidelines for Dementia-Friendly Care Environments in Terms of ‘Person-Centered Care’ Approach
Su-Kyung Lee, Yoon-Kyung Choi
KIEAE Journal.2021; 21(1): 81. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Person-Centered Practice Inventory-Staff for Nurses
Sohyun Kim, Sunghee H Tak
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(3): 363. CrossRef - Reliability Generalization Study of the Person-Centered Care Assessment Tool
Lluna María Bru-Luna, Manuel Martí-Vilar, César Merino-Soto, José Livia
Frontiers in Psychology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of the Chinese version of the Person-Centred Care Assessment Tool
Cai Le, Ke Ma, Pingfen Tang, David Edvardsson, Lina Behm, Jie Zhang, Jiqun Yang, Haiyan Fu, Gerd Ahlström
BMJ Open.2020; 10(7): e031580. CrossRef - A Concept Analysis on Patient-Centered Care in Hospitalized Older Adults with Multimorbidity
Youn-Jung Son, Heun-Keung Yoon
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(2): 61. CrossRef - Factors associated with Person-centered Care for Elderly in Long-term Care Hospital Nurses
So Bun Kim, Youngrye Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(6): 618. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of an Instrument Assessing Advance Directives for Nurse
Hojung Cheon, Eunha Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2019; 22(3): 134. CrossRef - Influence of Moral Sensitivity and Nursing Practice Environment in Person-centered Care in Long-term Care Hospital Nurses
Eun-Mi Park, Jin-Hwa Park
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2018; 20(2): 109. CrossRef - Testing Reliability and Validity of the Person-centered Climate Questionnaire-staff version in Korean for Long-term Care Facilities
Hae Sagong, Da Eun Kim, Soyoung Bae, Ga Eon Lee, David Edvardsson, Ju Young Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(1): 11. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Measurement to Assess Person-centered Critical Care Nursing
Jiyeon Kang, Young Shin Cho, Yeon Jin Jeong, Soo Gyeong Kim, Seonyoung Yun, Miyoung Shim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(3): 323. CrossRef - Effects of Perceptions regarding Purpose in Life and Good Death on Caring Behaviors of Formal Caregivers of Community-dwelling Older Adults with Dementia
Chun-Gill Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2018; 20(2): 57. CrossRef - A Review of the Korean Nursing Research Literature with Focus on Quantitative Measurement of Caring
Jeong-Hee Kim, Young Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(2): 155. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Korean Person-centered Climate Questionnaire-resident Version
Ju Young Yoon, Da Eun Kim, Soyoung Bae, Edvardsson David, Sun Ju Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2018; 20(1): 10. CrossRef - Factors related to aggressive behaviors among older adults in nursing homes of Korea: A cross-sectional survey study
Hyoungshim Choi, Young-Il Jung, Hongsoo Kim
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2018; 88: 9. CrossRef - Person-centered Care and Nursing Service Quality of Nurses in Long-term Care Hospitals
Hae Sagong, Ga Eon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 309. CrossRef
- Enhancing the validity of social measures on human rights awareness: a dual-method approach integrating exploratory factor analysis and latent profile analysis
- 2,421 View
- 64 Download
- 32 Crossref

- Effect of Muscle Strength Training on Urinary Incontinence and Physical Function: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Long-term Care Facilities
- Hyekyung Kang, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(1):35-45. Published online February 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to determine whether muscle strength training programs have an impact on improving symptoms of urinary incontinence (UI) and physical function among elderly women with UI who reside in long-term care facilities.
Methods A randomized controlled trial was conducted. Participants had to be over 65 years, score over 15 score on the mini-mental state examination, and be able to walk alone or with an assistant. Seventy residents were randomly allocated to either the training group (n=35) or control group (n=35). The program consisted of 50 minutes, twice a week for 8 weeks, and included Kegel's exercise, Thera-band training and indoor walking. Main outcomes were UI symptoms, peak vaginal pressure and physical functions measured with timed up and go test (TUG), one leg standing test (OLST), activities of daily living (ADL) and grip strength. Changes in outcome measurements were calculated from baseline to 4 weeks and to 8 weeks using repeated measures ANOVA.
Results There were significant differences in peak vaginal pressure (
p <.001), TUG (p <.001), OLST (p =.012) and grip strength (p <.001) in the interaction between groups and time.Conclusion Future studies are suggested to confirm the effect of muscle strength training in long-term care facilities where elderly women with UI reside.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Interventions for treating urinary incontinence in older women: a network meta-analysis
Giovana Vesentini, Nicole O'Connor, Mélanie Le Berre, Ashraf F Nabhan, Adrian Wagg, Sheila A Wallace, Chantale Dumoulin
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - What is the impact of a multi‐component exercise intervention on the cure rate of urinary incontinence among older women living in the community?
Rachele Ricci, Pinar Avsar, Zena Moore, Tom O'Connor, Linda Nugent, Declan Patton
Lifestyle Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Multisite Study on the Effect of a Urinary Incontinence Self-Management Program on Community-Dwelling Older Women in Korea
Sunah Park, Aeyoung So
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2024; 51(1): 61. CrossRef - The Sustainable Care Model for an Ageing Population in Vietnam: Evidence from a Systematic Review
Loi Tan Nguyen, Phouthakannha Nantharath, Eungoo Kang
Sustainability.2022; 14(5): 2518. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Muscle Strength of the Elderly Without Activity Restrictions By Gender
Myoungjin Kwon, Moonkyoung Park, Hyun Joo Kim, Jong Im Kim, Sun Ae Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(1): 43. CrossRef - Long-Term Effects of a Self-management Program for Older Women With Urinary Incontinence in Rural Korea
Aeyoung So, Jennie C. De Gagne, Sunah Park
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2019; 46(1): 55. CrossRef - Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women
Chantale Dumoulin, Licia P Cacciari, E Jean C Hay-Smith
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of an Exercise Program for Preventing Urinary Incontinence among Community-Dwelling Elderly Females Living Alone
Mi Sook Song, Sunjoo Boo
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(2): 247. CrossRef - The Development of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation Medical Devices for The Treatment of Non-implantable Urinary Incontinence
Jae-Yong Lee, Chang-Doo Lee, Ki-Jin Kwon
The Transactions of the Korean Institute of Electrical Engineers P.2015; 64(3): 175. CrossRef
- Interventions for treating urinary incontinence in older women: a network meta-analysis
- 1,695 View
- 46 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Association between Efficiency and Quality of Health Care in South Korea Long-term Care Hospitals: Using the Data Envelopment Analysis and Matrix Analysis
- Minsung Sohn, Mankyu Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(4):418-427. Published online August 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.4.418
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Objectives of this study were to investigate the association between efficiency and quality of health care in Long-term Care Hospitals (LTCH) and determine related factors that would enable achievement of both high efficiency and high quality at the same time.
Methods Major data sources were the "2012 Korean Assessment of Propriety by Long-term Care Hospitals" obtained from the Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service. Cost variables were supplemented by a National Tax Service accounting document. First, data envelopment analysis was performed by generating efficiency scores for each LTCH. Second, matrix analysis was conducted to ascertain association between efficiency and quality. Lastly, kruskal-wallis and mann-whitney tests were conducted to identify related factors.
Results First, efficiency and quality of care are not in a relationship of trade-offs; thus, LTCH can be confident that high efficiency-high quality can be achieved. Second, LTCH with a large number of beds, longer tenure of medical personnel, and adequate levels of investment were more likely to have improved quality as well as efficiency.
Conclusion It is essential to enforce legal standards appropriate to the facilities, reduce turnover of nursing staff, and invest properly in human resources. These consequences will help LTCH to maintain the balance of high efficiency-high quality in the long-run.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimising efficiency and patient-centredness in general hospitals: insights from data envelopment and matrix analysis
Hyunseo Lee, Minsung Sohn, Mankyu Choi
Journal of Health Organization and Management.2025; 39(6): 974. CrossRef - Financial Performance and Its Determinants in Korean Long-term Care Hospitals
Geun-Chan Lee
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2025; 19(3): 1. CrossRef - The influence of professional competency, professional commitment, and nursing organizational culture on the person-centered practice of nurses in long-term care hospitals: A cross-sectional study
Yoon Saeng Choi, Su Hyun Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(2): 116. CrossRef - Uzun Dönemli Bakım Etkinliğinin Değerlendirilmesi: OECD Ülkeleri Üzerinde Bir Araştırma
Yasin ÇİLHOROZ, İlknur ARSLAN ÇİLHOROZ
Karadeniz Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi.2022; 14(26): 70. CrossRef - Regional Differences and Influencing Factors of Allocation Efficiency of Rural Public Health Resources in China
Tao Liu, Jixia Li, Juan Chen, Shaolei Yang
Healthcare.2020; 8(3): 270. CrossRef - Has the long-term care insurance resolved disparities in mortality for older Koreans? examination of service type and income level
Minsung Sohn, Patricia O'Campo, Carles Muntaner, Haejoo Chung, Mankyu Choi
Social Science & Medicine.2020; 247: 112812. CrossRef - Efficiency Analysis of East Asian Zinc Smelters and the Effects of Capacity and Bonus Zinc on Efficiency
Ha Sung Park, Daecheol Kim
Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity.2019; 5(1): 4. CrossRef - Difference in Recognition of Internal Customer Service Quality of Outsourcing Staff in Hospital Using IPA
Sung-Soo Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2018; 43(1): 80. CrossRef - Relationship between Medical Service Specialization and Operational Performance in Hospitals: Focusing on Length of Stay and Medical Expense
Hai-Won Yoo, Kyoung-Hoon Kim
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2016; 10(1): 1. CrossRef - Person-centered Care and Nursing Service Quality of Nurses in Long-term Care Hospitals
Hae Sagong, Ga Eon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 309. CrossRef - A Study on Fitness Evaluation for Major Education of Competency Unit Element by the Development and Application of Subject Contents Based on NCS of Health Majoring Students at Junior Colleges
Min-Ja Kim, Hee-Jung Yang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(8): 508. CrossRef
- Optimising efficiency and patient-centredness in general hospitals: insights from data envelopment and matrix analysis
- 1,382 View
- 16 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Characteristics of Eating Behavior in Elders with Dementia residing in Long-Term Care Facilities
- Kyoung Min Lee, Jun-Ah Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(4):466-476. Published online August 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.4.466
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore characteristics of eating behavior according to level of functional status of elders with dementia (EWD), and to examine feeding time, change in food intake and body mass index (BMI) according to eating behavior.
Methods Participants were 149 EWD residing in long-term care facilities located in Seoul or Gyeonggi province and evaluated using the Mini-Mental State Exam-Korean version, Korean version-Activities of Daily Living, and Eating Behavior Scale (EBS). Feeding time, change in food intake, and BMI were also measured. Data were analyzed using SPSS 17.0, specifically descriptive statistics, ANOVA, and Chi-square test.
Results Participants' mean EBS score was 10.43±6.01 and half of them (54.4%) needed moderate or total assistance while eating. The EBS score was significantly lower for elders with severe dementia compared to those with mild or moderate dementia; and elders with severe ADL dependence compared to those with mild or moderate ADL dependence. Lower EBS scores were related to longer feeding time, a greater the rate of participants with decreased food intake and 'underweight' BMI.
Conclusion Nursing intervention programs which are designed for EWD are needed to maintain functional eating skills and prevent negative consequences in this population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of mealtime difficulty scale for older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities
Dukyoo Jung, Eunju Choi, Leeho Yoo, Hyesoon Lee
BMC Geriatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with eating performance in older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities: a cross-sectional study
Dukyoo Jung, Jennie C. De Gagne, Hyesoon Lee, Minkyung Lee
BMC Geriatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Eating Difficulties among Older Adults with Dementia in South Korean Long-Term Care Facilities: A Scoping Review
Dukyoo Jung, Kyuri Lee, Eunju Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 470. CrossRef Feasibility of a Mobile Meal Assistance Program for Direct Care Workers in Long-Term Care Facilities in South Korea
Dukyoo Jung, Jennie C De Gagne, Minkyung Lee, Hyesoon Lee, Kyuri Lee, Eunju Choi, Juyoun Chung
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2020; Volume 15: 2019. CrossRef- High feeding dependence prevalence in residents living in Italian nursing homes requires new policies: Findings from a regionally based cross-sectional study
Alvisa Palese, Luca Grassetti, Davide Bandera, Ranieri Zuttion, Barbara Ferrario, Sandra Ponta, Mark Hayter, Roger Watson
Health Policy.2018; 122(3): 301. CrossRef - Factors associated with Feeding Difficulty in Long-term Care Facility Older Adults with Dementia
Jeong Lee, Se Ang Ryu
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2017; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - Feeding Difficulty and its influencing factors of Elders with Dementia in Long-term Care Facilities
Hyun-Hwa Hong, Mee-Ock Gu
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(2): 1240. CrossRef
- Development of mealtime difficulty scale for older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities
- 986 View
- 5 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Caregiver Burden in Caring for Elders Before and After Long-term Care Service in Korea
- Hung Sa Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(2):236-247. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.2.236
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Purposes of this study were: evaluation of family burden of caring for elders who receive long term care services, and examination of differences in burden before and after the introduction of long term care service in Korea.
Methods Data were collected by questionnaires from 416 caregivers of elders who were registered with the Long Term Care Insurance Corporation in six cities. Data were collected in September, 2010 and analyzed using descriptive statistics, paired t-test, and ANOVA with the Scheffe test, and stepwise multiple regression.
Results Family burden decreased significantly after long-term care service was initiated. Subjective burden decreased from 2.93 to 2.69 (t=11.78,
p <.001), and objective burden, from 3.40 to 3.10 (t=12.73,p <.001). Stepwise multiple regression analysis revealed that factors affecting subjective burden were family relations (F=13.60,p =.003), age (F=5.47,p =.019), job (F=6.98,p =.008), and education (F=4.59,p =.032), and that factors affecting objective burden were living together (F=17.66,p <.001), job (F=13.34,p =.003), monthly income (F=6.61,p =.010), and type of service (F=6.62,p =.010).Conclusion The results of this first study to investigate caregiver burden after the Korean Long-term Care Insurance System was begun provide positive information for the development of strategies to decrease family burden in long term care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Sleep Quality between Families of Dementia Patients and General Population in Community: Analysis with the Korea Community Health Survey
Mina Kim, Young-Hoon Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(3): 139. CrossRef - Registered Nurses’ Experiences of End-of-Life Care in Nursing Homes of South Korea: A Qualitative Study
Soo-Jung Chang
Healthcare.2022; 10(11): 2213. CrossRef - Study on the Nutrient Intake and Dietary Quality of Elderly Residents on Various Meal Types in Long-Term Care Facility
Hee-Sook Lim, Eun Bi Oh, Yoo Kyoung Park, Hae-Yun Chung
Journal of the East Asian Society of Dietary Life.2020; 30(2): 172. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Family Caregivers' Burden and Depression in Home-based Long-Term Care Service under the Long-Term Care Insurance System
Hung Sa Lee, Chunmi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(4): 530. CrossRef - Effect of Family Caregiving on Depression in the First 3 Months After Spinal Cord Injury
Min-Gu Kang, Chul-Hyun Kim, Eunhee Park, Jae-Won Huh, Won-Jong Yang, Tae-Woo Nam, Yu-Sun Min, Tae-Du Jung
Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine.2018; 42(1): 130. CrossRef - Relationship between caregiving burden and depression in caregivers of individuals with intellectual disabilities in Korea
Su-Jung Nam, Eun-Young Park
Journal of Mental Health.2017; 26(1): 50. CrossRef - The Effect of Post-Stroke Depression on Rehabilitation Outcome and the Impact of Caregiver Type as a Factor of Post-Stroke Depression
Dong-Heun Ahn, Yung-Jin Lee, Ji-Hun Jeong, Yong-Rok Kim, Jong-Bum Park
Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine.2015; 39(1): 74. CrossRef - Factors Related to Family Caregivers' Burden with the Community-Dwelling Disabled Elderly under the Long-Term Care Insurance System
Eun-Jeong Han, Jung-Myun Lee, Jin-Hee Kwon, Seul-Bi Shin, Jung-Suk Lee
Health Policy and Management.2014; 24(1): 71. CrossRef
- Comparison of Sleep Quality between Families of Dementia Patients and General Population in Community: Analysis with the Korea Community Health Survey
- 2,325 View
- 10 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Factors Impacting the Physical Function of Older Adults in Korean Long-Term Care Hospitals
- Ji-Yun Lee, Eun-Young Kim, Eunhee Cho
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(6):780-787. Published online December 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.6.780
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to examine activities of daily living (ADL) of older adults admitted to Korean long-term care hospitals (LTCHs), and to explore the patient and organizational factors that have an impact on the ADL of this population.
Methods A secondary analysis of the Korean minimum data set (K-MDS) of patients (N=14,369) and of the profiles of LTCHs (N=358) from the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service was done between January and July 2008. The outcome variable was ADL score 6 months after baseline assessment. Multi-level linear regression was employed to explore the patient and organizational factors that affected ADL scores.
Results Of the patients, 45.4% had a baseline ADL score of between 31 and 40, with a score of 40 indicating that the patient was entirely dependent for all items. None of the organizational characteristics were significantly associated with effects on the ADLs of older adults who had been in a LTHC for at least 6 months. However, patient characteristics, such as age, baseline ADL, frequency of physical therapy, urinary incontinence, fecal incontinence, pressure ulcers, and having a tube or catheter, were significantly associated with ADL 6 months after baseline.
Conclusion In order to maintain and improve the ADL of older adults in LTCHs, we should develop strategies to prevent urinary and fecal incontinence, pressure ulcers, unnecessary tubes or catheters, providing adequate physical therapy. Additional studies should include more detailed information regarding nursing staff, including RN hours for direct care, education level and turnover.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Just visiting: A qualitative study of Australian allied health professionals' experiences working in residential aged care facilities during the COVID‐19 pandemic
Isabelle Meulenbroeks, Karla Seaman, Magdalena Z. Raban, Nasir Wabe, Johanna Westbrook
Australasian Journal on Ageing.2023; 42(4): 690. CrossRef - Allied health in residential aged care: Using routinely collected data to improve funding opportunities
Isabelle Meulenbroeks, Karla Seaman, Magdalena Z. Raban, Johanna Westbrook
Australasian Journal on Ageing.2023; 42(1): 221. CrossRef - Therapy-based allied health delivery in residential aged care, trends, factors, and outcomes: a systematic review
Isabelle Meulenbroeks, Magdalena Z. Raban, Karla Seaman, Johanna Westbrook
BMC Geriatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of registered nurse staffing on quality of care and resident outcomes in nursing homes
Eunhee Cho, In Sook Kim, Tae Wha Lee, Gwang Suk Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Deulle Min
Geriatric Nursing.2020; 41(6): 685. CrossRef - Nationwide survey of continence status among older adult residents living in long‐term care facilities in Japan: The prevalence and associated risk factors of incontinence and effect of comprehensive care on continence status
Motofumi Suzuki, Jiro Okochi, Katsuya Iijima, Taro Murata, Haruki Kume
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2020; 20(4): 285. CrossRef - Ultrasound‐assisted prompted voiding care for managing urinary incontinence in nursing homes: A randomized clinical trial
Motofumi Suzuki, Hideyo Miyazaki, Jun Kamei, Mikako Yoshida, Tamami Taniguchi, Kaoru Nishimura, Yasuhiko Igawa, Hiromi Sanada, Yukio Homma
Neurourology and Urodynamics.2019; 38(2): 757. CrossRef - Longitudinal associations of nursing staff turnover with patient outcomes in long-term care hospitals in Korea
Yoonseo Kim, Kihye Han
Journal of Nursing Management.2018; 26(5): 518. CrossRef - Ultrasound‐assisted prompted voiding for management of urinary incontinence of nursing home residents: Efficacy and feasibility
Motofumi Suzuki, Yasuhiro Iguchi, Yasuhiko Igawa, Mikako Yoshida, Hiromi Sanada, Hideyo Miyazaki, Yukio Homma
International Journal of Urology.2016; 23(9): 786. CrossRef - Impact of Nurse Staffing Level and Oral Care on Hospital Acquired Pneumonia in Long-term Care Hospitals
Jung Mi Chae, Hyunjong Song, Gunseog Kang, Ji Yun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(2): 174. CrossRef - Nursing outcomes of inpatient on level of nursing staffing in long term care hospitals
Eun Hee Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2015; 26(3): 715. CrossRef - Impact of Nurse, Nurses' Aid Staffing and Turnover Rate on Inpatient Health Outcomes in Long Term Care Hospitals
Yunmi Kim, Ji Yun Lee, Hyuncheol Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(1): 21. CrossRef
- Just visiting: A qualitative study of Australian allied health professionals' experiences working in residential aged care facilities during the COVID‐19 pandemic
- 1,403 View
- 4 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Effects of Multisensory Stimulation Using Familiarity: Persons with Dementia in Long-term Care Facility in Korea
- Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(4):528-538. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.4.528
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of the study was to examine the effects of multisensory stimulation (MSS) using familiarity on persons with dementia (PWDs) residing in nursing homes in Korea.
Methods A nonequivalent control group with pre and posttests was used. Fifty one PWDs were included if they: 1) were over 65 yr old, 2) were diagnosed with dementia, 3) had no visual or speech impairments, 4) were able to communicate, and 5) had spent more than one month in a nursing home. The experimental group (n=25) received a 55 min MSS program twice a week for 10 weeks. The outcome variables included were cognition, activities of daily living, grip strength, depression, wandering, and aggressive behaviors. Repeated ANOVA was used for data analysis.
Results There were no significant differences in demographics or the main variables at pretest. Cognition, depression, wandering, and aggressive behaviors were significant over time between the two groups. Grip strength was only significant when accounting for interaction between group and time.
Conclusion An intervention of MSS using familiarity was marginally effective in improving cognition, depression, wandering, and aggression. Future study is suggested with a larger sample and longer treatment to retest the effects of MSS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of multisensory environment/stimulation therapy on adults with cognitive impairment and/or special needs: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Meret Helbling, Marie‐Laure Grandjean, Murali Srinivasan
Special Care in Dentistry.2024; 44(2): 381. CrossRef - Personally tailored activities for improving psychosocial outcomes for people with dementia in long-term care
Ralph Möhler, Stella Calo, Anna Renom, Helena Renom, Gabriele Meyer
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomization controlled and nonrandomized controlled studies on nurse‐led nonpharmacological interventions to improve cognition in people with dementia
Yujin Suh, Sumi Lee, Go‐Eun Kim, JuHee Lee
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(13-14): 3155. CrossRef - Non-pharmacological Intervention for Wandering Behavior in Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Yoojin Kim, Eunhee Cho
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(3): 321. CrossRef - A pragmatic trial testing a tailored non pharmacologic therapies on nocturnal behavioral and psychological symptoms associated with dementia
Thierry Bautrant, Caroline Franqui, Hossein Clément, Maurice Rabault, Faima Masseboeuf, Manon Pastore, Magali Pardo, Yannick Brandi, Nicolas Drouin, Anne-Daphnée Brice, Michel Grino
Geriatric Nursing.2022; 43: 85. CrossRef - The Development of Wholeness Program for Effects Dementia-Buffering Testing of the Demented Elderly
Hye-Jeon Hong
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2018; 57(1): 405. CrossRef - Personally tailored activities for improving psychosocial outcomes for people with dementia in long-term care
Ralph Möhler, Anna Renom, Helena Renom, Gabriele Meyer
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of an educational tooth-brushing program using priming in an elderly population with dementia residing in nursing homes
Gwi-Ryung Son Hong, Jung-Soo Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2016; 40(3): 149. CrossRef - Non-pharmacological interventions for agitation in dementia: systematic review of randomised controlled trials
Gill Livingston, Lynsey Kelly, Elanor Lewis-Holmes, Gianluca Baio, Stephen Morris, Nishma Patel, Rumana Z. Omar, Cornelius Katona, Claudia Cooper
British Journal of Psychiatry.2014; 205(6): 436. CrossRef
- Effects of multisensory environment/stimulation therapy on adults with cognitive impairment and/or special needs: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
- 1,334 View
- 30 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Relationship between Resource Utilization and Long-term Care Classification Level for Residents in Nursing Homes
- Min Kyung Lee, Eun-Kyung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(6):903-912. Published online December 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.6.903
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to examine whether the level of classification for long-term care service under long-term care insurance reflects resource utilization level for residents in nursing homes.
Methods From 2 long-term care facilities, the researchers selected 95 participants and identified description and time of care services provided by nurses, certified caregivers, physical therapists and social workers during a 24-hr-period.
Results Resource utilization level was: 281.04 for level 1, 301.05 for level 2 and 270.87 for level 3. Resource utilization was not correlated with level. Differences in resource utilization within the same level were similar with the coefficient of variance, 22.7-27.1%. Physical function was the most influential factor on long-term care scores (r=.88,
p <.001). The level for long-term care service did not reflect differences in resource utilization level of residents on long-term care insurance.Conclusion The results of this study indicate that present grading for long-term care service needs to be reconsidered. Further study is needed to adjust the long-term care classification system to reflect the level of resource utilization for care recipients on the long-term care insurance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of resource utilization by physical function, cognitive function, and behavioral symptoms of residents in long-term care facilities: A cross-sectional study
Eun-Jeong Han, Seonhwa Lee, JungSuk Lee, Myonghwa Park
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(4): 432. CrossRef - Comparison of Utilized Resource Volumes by Grade of Seniors in Long-Term Care Facilities
Eun-Jeong Han, Seonhwa Lee, Rahil Hwang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(1): 96. CrossRef - Research on Disability Grading Based on ICF Functional Framework: Empirical Evidence From Zhejiang Province, China
Huan Liu
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of aerobic exercise based korean traditional dance on vascular health, muscle strength and balance in the elderly with dementia
Mi Yang Jeon, Chi Yang Yoon, Mi Jeong Jin, Dong Hyun Yi, Hyeon Cheol Jeong
The Journal of Korean Academy of Physical Therapy Science.2020; 27(3): 12. CrossRef - Incidence of hip fracture among long-term care insurance beneficiaries with dementia: comparison of home care and institutional care services
Juyeong Kim, Young Choi, Eun-Cheol Park
BMC Geriatrics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Does long‐term care insurance reduce the burden of medical costs? A retrospective elderly cohort study
Jae Woo Choi, Eun‐Cheol Park, Sang Gyu Lee, Sohee Park, Hwang‐Gun Ryu, Tae Hyun Kim
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2018; 18(12): 1641. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Care Behavior of Certified Care Assistants for Older Adults with Dementia
Ji-yeon Kim, Sunghee H Tak
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2018; 20(3): 185. CrossRef - Demand and willing to pay for oral hygiene service in long-term care insurance of elderly
Han-Nah Kim, Gi-Yon Kim, Hie-Jin Noh, Nam-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2018; 42(4): 204. CrossRef - Incidence of Pressure Ulcers During Home and Institutional Care Among Long-Term Care Insurance Beneficiaries With Dementia Using the Korean Elderly Cohort
Juyeong Kim, Young Choi, Jaeyong Shin, Suk-Yong Jang, Kyeong Hee Cho, Jin Young Nam, Eun-Cheol Park
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2017; 18(7): 638.e1. CrossRef - Factors Associated with the Changes in Activities of Daily Living in Older Adults with Stroke: A Comparison of Home Care and Institutional Care
Woon-Sook Jung, Eun-Shil Yim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 388. CrossRef - Cognitive Function, Behavioral Problems, and Physical Function in Long‐Term Care Insurance Beneficiaries with Dementia in South Korea: Comparison of Home Care and Institutional Care Services
Tae Wha Lee, Eunsil Yim, Eunhee Cho, Jane Chung
Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.2014; 62(8): 1467. CrossRef - Cognitive Function and Activity of Daily Living of Older Adults Using Long-term Care Service
Hyun-Sook Chang, Hung Sa Lee
Korean Journal of Health Policy and Administration.2012; 22(4): 522. CrossRef
- Comparison of resource utilization by physical function, cognitive function, and behavioral symptoms of residents in long-term care facilities: A cross-sectional study
- 1,262 View
- 4 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Estimation of Nursing Costs Based on Nurse Visit Time for Long-Term Care Services
- Eun-Kyung Kim, Yun Mi Kim, Myung Ae Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(3):349-358. Published online June 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.3.349
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to estimate nursing costs and to establish appropriate nursing fees for long-term care services for community elders.
Methods Seven nurses participated in data collection related to visiting time by nurses for 1,100 elders. Data on material costs and management costs were collected from 5 visiting nursing agencies. The nursing costs were classified into 3 groups based on the nurse's visit time under the current reimbursement system of long-term care insurance.
Results The average nursing cost per minute was 246 won. The material costs were 3,214 won, management costs, 10,707 won, transportation costs, 7,605 won, and capital costs, 5,635 won per visit. As a result, the average cost of nursing services per visit by classification of nursing time were 41,036 won (care time <30 min), 46,005 won (care time 30-59 min), and 57,321 won (care time over 60 min).
Conclusion The results of the study indicate that the fees for nurse visits currently being charged for long-term care insurance should be increased. Also these results will contribute to baseline data for establishing appropriate nursing fees for long-term care services to maintain quality nursing and management in visiting nursing agencies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Plan for Invigoration of Visiting Nursing Center in Long-Term Care Insurance for the Elderly - Through SWOT Analysis -
Do Hwa Byeon
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2015; 29(2): 203. CrossRef - Activity-Based Costing Analysis of Nursing Activities in General Hospital Wards
Ho-Soon Yoon, Jinhyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(4): 449. CrossRef - Trends in Home-visit Nursing Care by Agencies' Characteristics under the National Long-term Care Insurance System
Jung Suk Lee, Rah Il Hwang, Eun Jeong Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(4): 415. CrossRef - Korean and United States: Comparison of Costs of Nursing Interventions
Sung-Jung Hong, Eun-Joo Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(4): 358. CrossRef - The Characteristics and Service Utilization of Home Nursing Care Beneficiaries Under the Korean Long Term Care Insurance
Jung-Suk Lee, Eun-Jeong Han, Im-Ok Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2011; 22(1): 33. CrossRef
- Plan for Invigoration of Visiting Nursing Center in Long-Term Care Insurance for the Elderly - Through SWOT Analysis -
- 1,906 View
- 1 Download
- 5 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


