Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 42(4); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Characteristics of Eating Behavior in Elders with Dementia residing in Long-Term Care Facilities
- Kyoung Min Lee, Jun-Ah Song
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2012;42(4):466-476.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.4.466
Published online: August 31, 2012
1Department of Nursing, DongKang College, Gwangju, Korea.
2College of Nursing, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Lee, Kyoung Min. Department of Nursing, DongKang College, 50 Dongmundaero, Buk-gu, Gwangju 500-714 , Korea. Tel: +82-62-520-2289, Fax: +82-62-520-2368, muesayou@naver.com
© 2012 Korean Society of Nursing Science
- 985 Views
- 5 Download
- 7 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to explore characteristics of eating behavior according to level of functional status of elders with dementia (EWD), and to examine feeding time, change in food intake and body mass index (BMI) according to eating behavior.
-
Methods
- Participants were 149 EWD residing in long-term care facilities located in Seoul or Gyeonggi province and evaluated using the Mini-Mental State Exam-Korean version, Korean version-Activities of Daily Living, and Eating Behavior Scale (EBS). Feeding time, change in food intake, and BMI were also measured. Data were analyzed using SPSS 17.0, specifically descriptive statistics, ANOVA, and Chi-square test.
-
Results
- Participants' mean EBS score was 10.43±6.01 and half of them (54.4%) needed moderate or total assistance while eating. The EBS score was significantly lower for elders with severe dementia compared to those with mild or moderate dementia; and elders with severe ADL dependence compared to those with mild or moderate ADL dependence. Lower EBS scores were related to longer feeding time, a greater the rate of participants with decreased food intake and 'underweight' BMI.
-
Conclusion
- Nursing intervention programs which are designed for EWD are needed to maintain functional eating skills and prevent negative consequences in this population.
- 1. Alzheimer's Society. Food for thought. 2000;London, Author.
- 2. Blandford G, Watkins LB, Mulvihill MN, Taylor B. Vellas B, Rivière S. Assessing abnormal feeding behavior in dementia: A taxonomy and initial findings. In: Weight loss and eating behavior disorders in Alzheimer's disease. 1998;Paris, SERDI Publishing Company. 49–66.
- 3. Chang CC, Lin LC. Effects of a feeding skills training programme on nursing assistants and dementia patients. Journal of Clinical Nursing. 2005;14:1185–1192. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2005.01240.x.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Chang CC, Roberts BL. Feeding difficulty in older adults with dementia. Journal of Clinical Nursing. 2008;17:2266–2274. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2007.02275.x.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Cho MJ, Kim GU, Kim MH, Kim MD, Kim BJ, Kim SG, et al. Nationwide study on the prevalence of dementia in Korean elders. 2008;Seoul, Seoul National University Hospital.
- 6. Cho YH. Family caregivers' needs for a professional help by the symptom level of senile dementia. 2007;Seoul, Yonsei University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 7. Colodny N. Comparison of dysphagics and nondysphagics on pulse oximetry during oral feeding. Dysphagia. 2000;15:68–73. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s004550010003.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Crogan NL, Shultz JA, Adams CE, Massey LK. Barriers to nutrition care for nursing home residents. Journal of Gerontological Nursing. 2001;27(12):25–31.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Durnbaugh T, Haley B, Roberts S. Assessing problem feeding behaviors in mid-stage Alzheimer's disease. Geriatric Nursing. 1996;17:63–67. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0197-4572(96)80170-4.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. "Mini-mental state": A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research. 1975;12:189–198. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6.PubMed
- 11. Han HJ, Kim NC. Mini-nutritional assessment of elders in rural areas. Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing. 2007;9:22–28.
- 12. Kang Y, Kim M, Lee E. The relationship of perceived health status, activities of daily living and nutrition status in the community-dwelling Korean elderly. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008;38:122–130.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. A study on the improvement of long-term care system for the elderly. 2008;Seoul, Author.
- 14. Korean National Statistical Office. The elderly persons statistics. 2009;Daejeon, Author.
- 15. Lee J. A study on nutrient intakes of demented elderly with general diet in geriatric hospital. 2006;Seoul, Dankook University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 16. Lin LC, Watson R, Lee YC, Chou YC, Wu SC. Edinburgh Feeding Evaluation in Dementia (EdFED) scale: Cross-cultural validation of the Chinese version. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2008;62:116–123. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2008.04596.x.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Magri F, Borza A, del Vecchio S, Chytiris S, Cuzzoni G, Busconi L, et al. Nutritional assessment of demented patients: A descriptive study. Aging Clinical and Experimental Research. 2003;15:148–153.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 18. National Health Insurance Corporation. A determining system for the category of need in long-term care insurance system. 2009;Seoul, Author.
- 19. Omran ML, Salem P. Diagnosing undernutrition. Clinics in Geriatric Medicine. 2002;18:719–736.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Park JH, Kwon YC. Korean version of Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE-K) Part I: Development of the test for the elderly. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 1989;28:125–135.
- 21. Park YH, Suh EE. The risk of malnutrition, depression, and the perceived health status of older adults. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2007;37:941–948.ArticlePDF
- 22. Rivière S, Gillette-Guyonnet S, Andrieu S, Nourhashemi F, Lauque S, Cantet C, et al. Cognitive function and caregiver burden: Predictive factors for eating behaviour disorders in Alzheimer's disease. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2002;17:950–955. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/gps.724.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Tully MW, Matrakas KL, Muir J, Musallam K. The Eating Behavior Scale. A simple method of assessing functional ability in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Gerontological Nursing. 1997;23(7):9–15.Article
- 24. Wang SY. Weight loss and metabolic changes in dementia. The journal of nutrition, health and aging. 2002;6:201–205.
- 25. Watson R. Eating difficulty in older people with dementia. Nursing Older People. 2002;14(3):21–25.ArticlePubMed
- 26. White HK. Nutrition in advanced Alzheimer's disease. North Carolina Medical Journal. 2005;66:307–312.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Won CW, Yang KY, Rho YG, Kim SY, Lee E, Yoon JL, et al. The Development of Korean Activities of Daily Living (K-ADL) and Korean Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (K-IADL) Scale. Journal of the Korean Geriatrics Society. 2002;6:107–120.
- 28. Zec RF, Landreth ES, Vicari SK, Belman J, Feldman E, Andrise A, et al. Alzheimer Disease Assessment Scale: A subtest analysis. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders. 1992;6:164–181.PubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Development of mealtime difficulty scale for older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities
Dukyoo Jung, Eunju Choi, Leeho Yoo, Hyesoon Lee
BMC Geriatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with eating performance in older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities: a cross-sectional study
Dukyoo Jung, Jennie C. De Gagne, Hyesoon Lee, Minkyung Lee
BMC Geriatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Eating Difficulties among Older Adults with Dementia in South Korean Long-Term Care Facilities: A Scoping Review
Dukyoo Jung, Kyuri Lee, Eunju Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 470. CrossRef Feasibility of a Mobile Meal Assistance Program for Direct Care Workers in Long-Term Care Facilities in South Korea
Dukyoo Jung, Jennie C De Gagne, Minkyung Lee, Hyesoon Lee, Kyuri Lee, Eunju Choi, Juyoun Chung
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2020; Volume 15: 2019. CrossRef- High feeding dependence prevalence in residents living in Italian nursing homes requires new policies: Findings from a regionally based cross-sectional study
Alvisa Palese, Luca Grassetti, Davide Bandera, Ranieri Zuttion, Barbara Ferrario, Sandra Ponta, Mark Hayter, Roger Watson
Health Policy.2018; 122(3): 301. CrossRef - Factors associated with Feeding Difficulty in Long-term Care Facility Older Adults with Dementia
Jeong Lee, Se Ang Ryu
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2017; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - Feeding Difficulty and its influencing factors of Elders with Dementia in Long-term Care Facilities
Hyun-Hwa Hong, Mee-Ock Gu
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(2): 1240. CrossRef
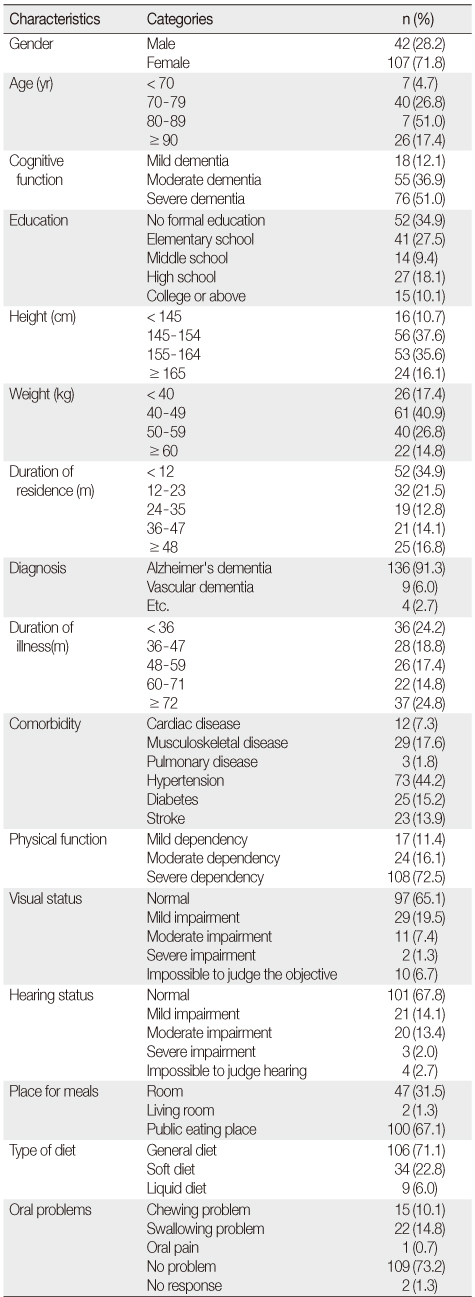
General Characteristics of Participants (N=149)
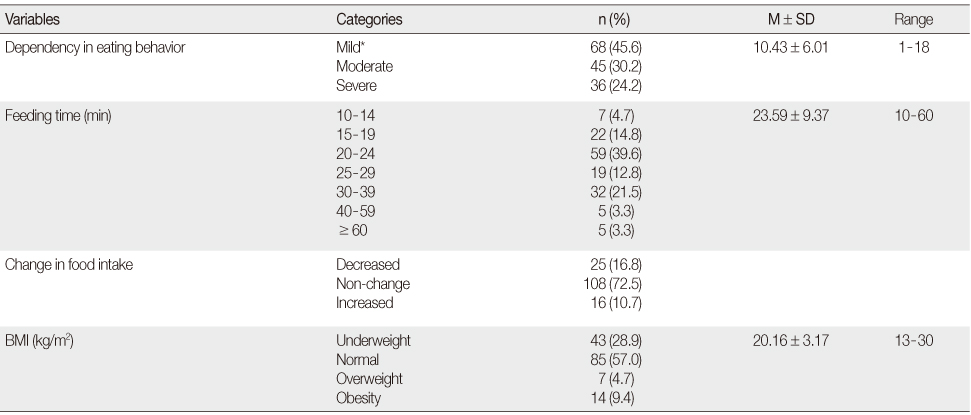
Eating Behavior, Feeding Time, Change in Food Intake, and BMI of Participants (N=149)
BMI=Body Mass Index.
*Including 18 persons: Completely independent in eating behavior.
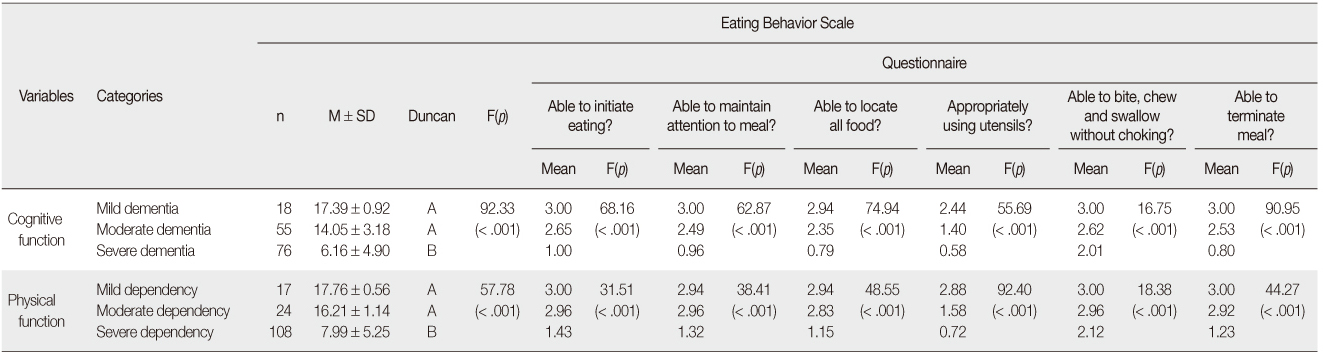
Eating Behavior of Participants according to the Level of Function Status (N=149)
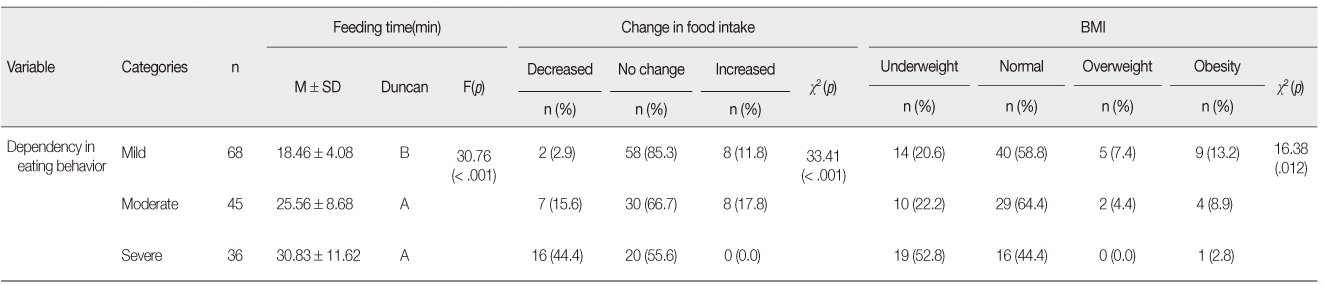
Feeding Time, Change in Food Intake, and BMI according to Eating Behavior of Participants (N=149)
BMI=Body Mass Index.
BMI=Body Mass Index. *Including 18 persons: Completely independent in eating behavior.
BMI=Body Mass Index.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

