Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 45(1); 2015 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effect of Muscle Strength Training on Urinary Incontinence and Physical Function: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Long-term Care Facilities
- Hyekyung Kang, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2015;45(1):35-45.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.35
Published online: February 27, 2015
College of Nursing, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to : Kang, Hyekyung. 409-2 ho, Elderly Nursing Lab, Collage of Nursing, Hanyang University, 222 Wangsomni-ro, Seongdong-gu, Seoul 133-791, Korea. Tel: +82-10-5074-9830, Fax: +82-2-2220-4711, kangfung@hanyang.ac.kr
© 2015 Korean Society of Nursing Science
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NoDerivs License. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/) If the original work is properly cited and retained without any modification or reproduction, it can be used and re-distributed in any format and medium.
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was done to determine whether muscle strength training programs have an impact on improving symptoms of urinary incontinence (UI) and physical function among elderly women with UI who reside in long-term care facilities.
-
Methods
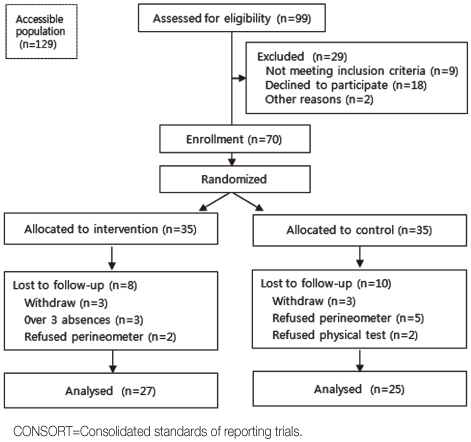
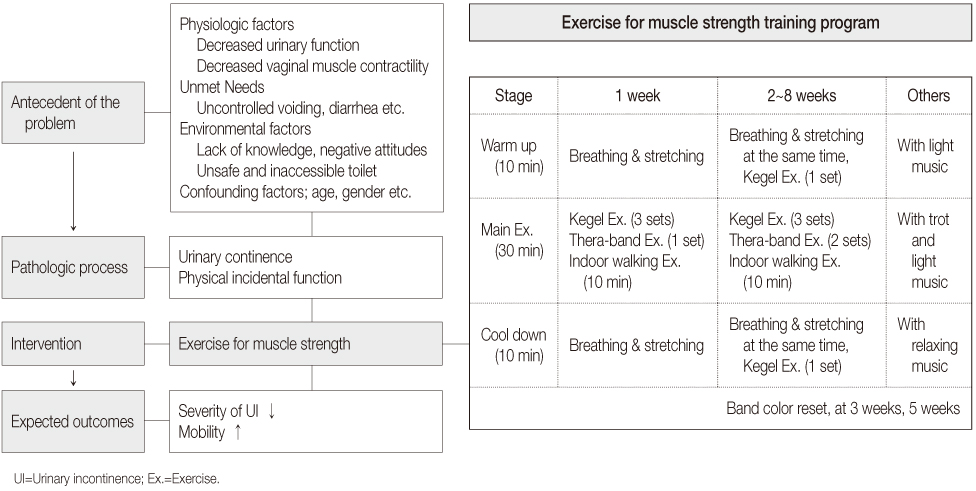
- A randomized controlled trial was conducted. Participants had to be over 65 years, score over 15 score on the mini-mental state examination, and be able to walk alone or with an assistant. Seventy residents were randomly allocated to either the training group (n=35) or control group (n=35). The program consisted of 50 minutes, twice a week for 8 weeks, and included Kegel's exercise, Thera-band training and indoor walking. Main outcomes were UI symptoms, peak vaginal pressure and physical functions measured with timed up and go test (TUG), one leg standing test (OLST), activities of daily living (ADL) and grip strength. Changes in outcome measurements were calculated from baseline to 4 weeks and to 8 weeks using repeated measures ANOVA.
-
Results
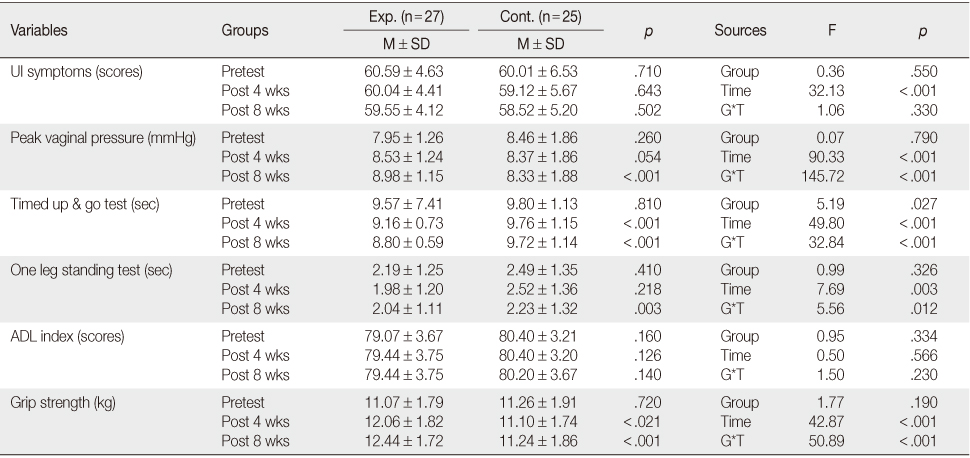
- There were significant differences in peak vaginal pressure (p<.001), TUG (p<.001), OLST (p=.012) and grip strength (p<.001) in the interaction between groups and time.
-
Conclusion
- Future studies are suggested to confirm the effect of muscle strength training in long-term care facilities where elderly women with UI reside.
This manuscript is based on a part of the first author's doctoral dissertation from Hanyang University.
- 1. Health Quality Ontario. Behavioural interventions for urinary incontinence in community-dwelling seniors: An evidence-based analysis. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2008;8(3):1–52.
- 2. Kim MS, Lee SH. Prevalence rate and associated factors of urinary incontinence among nursing home residents. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2008;38(1):92–100. Article
- 3. Korean Continence Society. Geriatric incontinence [Internet]. Suwon, Author. 2007;cited 2013 November 11. Available from: http://www.kocon.or.kr/patient/pt5.html
- 4. Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: Report from the standardisation sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn. 2002;21(2):167–178. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Sands LP, Wang Y, McCabe GP, Jennings K, Eng C, Covinsky KE. Rates of acute care admissions for frail older people living with met versus unmet activity of daily living needs. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54(2):339–344. ArticlePubMed
- 6. Tibaek S, Gard G, Klarskov P, Iversen HK, Dehlendorff C, Jensen R. Are activity limitations associated with lower urinary tract symptoms in stroke patients? A cross-sectional, clinical survey. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2009;43(5):383–389. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00365590903013919ArticlePubMed
- 7. Thirugnanasothy S. Managing urinary incontinence in older people. BMJ. 2010;341:c3835ArticlePubMed
- 8. Tibaek S, Gard G, Jensen R. Pelvic floor muscle training is effective in women with urinary incontinence after stroke: A randomised, controlled and blinded study. Neurourol Urodyn. 2005;24(4):348–357. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Malmstrom TK, Andresen EM, Wolinsky FD, Schootman M, Miller JP, Miller DK. Urinary and fecal incontinence and quality of life in African Americans. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;58(10):1941–1945. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Landefeld CS, Bowers BJ, Feld AD, Hartmann KE, Hoffman E, Ingber MJ, et al. National Institutes of Health state-of-the-science conference statement: Prevention of fecal and urinary incontinence in adults. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148(6):449–458.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Amend B, Kruck S, Bedke J, Ritter R, Arenas da Silva L, Chapple C, et al. Urinary incontinence in the elderly: What can and should be done. Urologe A. 2013;52(6):805–812. PubMed
- 12. Saxer S, de Bie RA, Dassen T, Halfens RJ. Nurses' knowledge and practice about urinary incontinence in nursing home care. Nurse Educ Today. 2008;28(8):926–934. ArticlePubMed
- 13. Durrant J, Snape J. Urinary incontinence in nursing homes for older people. Age Ageing. 2003;32(1):12–18.ArticlePubMed
- 14. van Houten P, Achterberg W, Ribbe M. Urinary incontinence in disabled elderly women: A randomized clinical trial on the effect of training mobility and toileting skills to achieve independent toileting. Gerontology. 2007;53(4):205–210. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Vinsnes AG, Helbostad JL, Nyrønning S, Harkless GE, Granbo R, Seim A. Effect of physical training on urinary incontinence: A randomized parallel group trial in nursing homes. Clin Interv Aging. 2012;7:45–50. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Pereira VS, Correia GN, Driusso P. Individual and group pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment in female stress urinary incontinence: A randomized controlled pilot study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2011;159(2):465–471. ArticlePubMed
- 17. Rice J, Keogh JWL. Power training: Can it improve functional performance in older adults? A systematic review. Int J Exerc Sci. 2009;2(2):131–151.Article
- 18. Inouye SK, Studenski S, Tinetti ME, Kuchel GA. Geriatric syndromes: Clinical, research, and policy implications of a core geriatric concept. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2007;55(5):780–791. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 19. Song MS, Yoo YK, Choi CH, Kim NC. Effects of nordic walking on body composition, muscle strength, and lipid profile in elderly women. Asian Nurs Res. 2013;7(1):1–7. Article
- 20. Offermans MP, Du Moulin MF, Hamers JP, Dassen T, Halfens RJ. Prevalence of urinary incontinence and associated risk factors in nursing home residents: A systematic review. Neurourol Urodyn. 2009;28(4):288–294. ArticlePubMed
- 21. Ouslander JG, Griffiths PC, McConnell E, Riolo L, Kutner M, Schnelle J. Functional incidental training: A randomized, controlled, crossover trial in Veterans Affairs nursing homes. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53(7):1091–1100.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Baker WL, Karan S, Kenny AM. Effect of dehydroepiandrosterone on muscle strength and physical function in older adults: A systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(6):997–1002. ArticlePubMed
- 23. Park SY, Shin IS. Muscle strengthening effects of exercise programs for preventing falls among the elderly in Korea: A meta-analysis. J Korean Acad Univ Trained Phys Ther. 2011;18(3):38–48.
- 24. Han JW, Kim TH, Jhoo JH, Park JH, Kim JL, Ryu SH, et al. A normative study of the mini-mental state examination for dementia screening (MMSE-DS) and its short form(SMMSE-DS) in the Korean elderly. J Korean Geriatr Psychiatry. 2010;14(1):27–37.
- 25. Lim CG, Lee KS. The study on the balance reaction and physical activity of dementia patients. J Korea Acad Industr Coop Soc. 2011;12(11):5087–5093. Article
- 26. Choi IH. The effects of pelvic floor muscle exercise on urinary symptoms and quality of life in women with stress urinary incontinence. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2008;19(1):46–56.
- 27. Bø K. Pelvic floor muscle strength and response to pelvic floor muscle training for stress urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2003;22(7):654–658. ArticlePubMed
- 28. Academy of Geriatric Physical Therapy. Section on geriatrics recommended outcome measures for medicare functional limitation/severity reporting [Internet]. Madison, WI, Author. 2013;cited 2013 December 2. Available from: http://www.geriatricspt.org/userfiles/files/SoGJoint-Report-March-2013.pdf
- 29. Kim SY, Won CW, Rho YG. The validity and reliability of Korean version of bathel ADL index. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2004;25(7):534–541.
- 30. Kim HG, Nam HK. The effect of thera band exercise on muscle flexibility, balance ability, muscle strength in elderly women. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2011;22(4):451–457. Article
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Interventions for treating urinary incontinence in older women: a network meta-analysis
Giovana Vesentini, Nicole O'Connor, Mélanie Le Berre, Ashraf F Nabhan, Adrian Wagg, Sheila A Wallace, Chantale Dumoulin
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - What is the impact of a multi‐component exercise intervention on the cure rate of urinary incontinence among older women living in the community?
Rachele Ricci, Pinar Avsar, Zena Moore, Tom O'Connor, Linda Nugent, Declan Patton
Lifestyle Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Multisite Study on the Effect of a Urinary Incontinence Self-Management Program on Community-Dwelling Older Women in Korea
Sunah Park, Aeyoung So
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2024; 51(1): 61. CrossRef - The Sustainable Care Model for an Ageing Population in Vietnam: Evidence from a Systematic Review
Loi Tan Nguyen, Phouthakannha Nantharath, Eungoo Kang
Sustainability.2022; 14(5): 2518. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Muscle Strength of the Elderly Without Activity Restrictions By Gender
Myoungjin Kwon, Moonkyoung Park, Hyun Joo Kim, Jong Im Kim, Sun Ae Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(1): 43. CrossRef - Long-Term Effects of a Self-management Program for Older Women With Urinary Incontinence in Rural Korea
Aeyoung So, Jennie C. De Gagne, Sunah Park
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2019; 46(1): 55. CrossRef - Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women
Chantale Dumoulin, Licia P Cacciari, E Jean C Hay-Smith
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of an Exercise Program for Preventing Urinary Incontinence among Community-Dwelling Elderly Females Living Alone
Mi Sook Song, Sunjoo Boo
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(2): 247. CrossRef - The Development of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation Medical Devices for The Treatment of Non-implantable Urinary Incontinence
Jae-Yong Lee, Chang-Doo Lee, Ki-Jin Kwon
The Transactions of the Korean Institute of Electrical Engineers P.2015; 64(3): 175. CrossRef
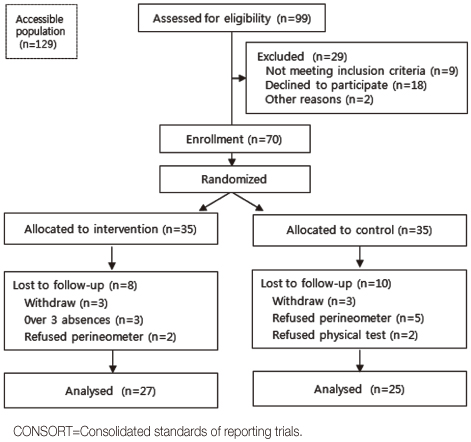
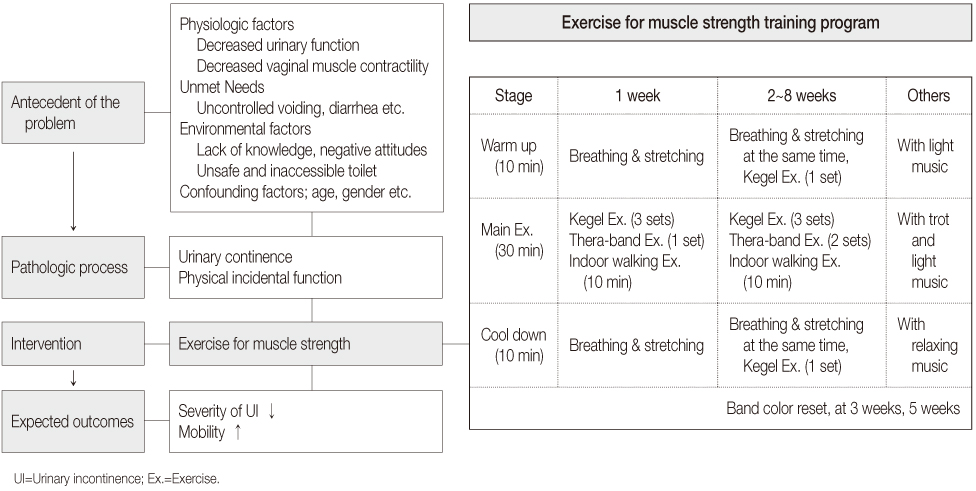
Figure 1
Figure 2
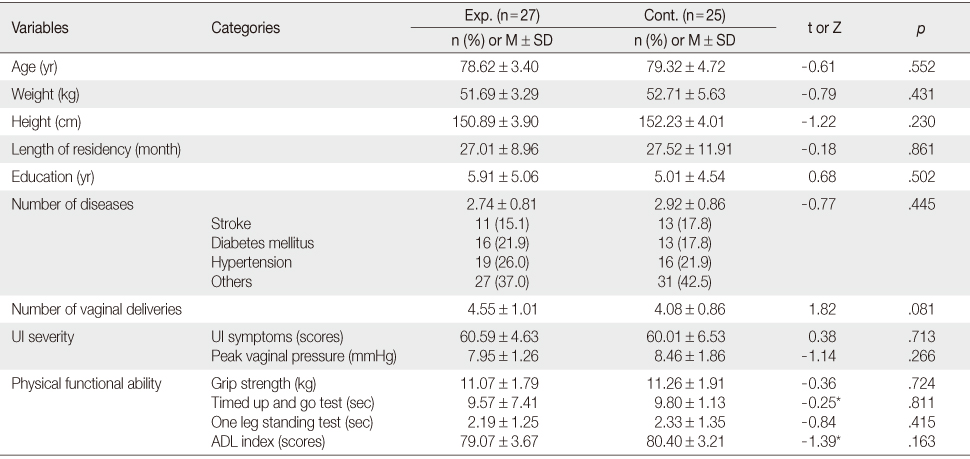
Homogeneity of General Characteristics and Dependent Variables for Participants (N=52)
*Mann-Whitney U test; Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; UI=Urinary incontinence; ADL=Activities of daily living.
Changes in Urinary Incontinence and Physical Functions by Application of the Muscle Strength Training Program (N=52)
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; UI=Urinary incontinence; ADL=Activities of daily living; G*T=Interactions between group and time.
*Mann-Whitney U test; Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; UI=Urinary incontinence; ADL=Activities of daily living.
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; UI=Urinary incontinence; ADL=Activities of daily living; G*T=Interactions between group and time.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

