Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 46(6); 2016 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effects of Home Care Services Use by Older Adults on Family Caregiver Distress
- Jiyeon Kim, Hongsoo Kim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2016;46(6):836-847.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.6.836
Published online: December 30, 2016
1College of Nursing, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
2Graduate School of Public Health, Department of Public Health Science·Institute of Aging·Institute of Health and Environment, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kim, Hongsoo. Graduate School of Public Health, Seoul National University, 1 Gwanak-gu, Seoul 08826, Korea. Tel: +82-2-880-2723, Fax: +82-2-762-9105, hk65@snu.ac.kr
© 2016 Korean Society of Nursing Science
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NoDerivs License. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/) If the original work is properly cited and retained without any modification or reproduction, it can be used and re-distributed in any format and medium.
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to examine the association between utilization of home care services under the national long-term care insurance system and family caregiver distress.
-
Methods
- A secondary data analysis was conducted in this study using data collected in 2011 and 2012 from the Korean version of International Resident Assessment Instrument (interRAI) Home Care assessment system. The study sample included 228 clients receiving community based home care and their family caregivers in Korea. Descriptive statistics, χ2 test, t-test, and Heckman selection model analysis were conducted using SAS 9.3.
-
Results
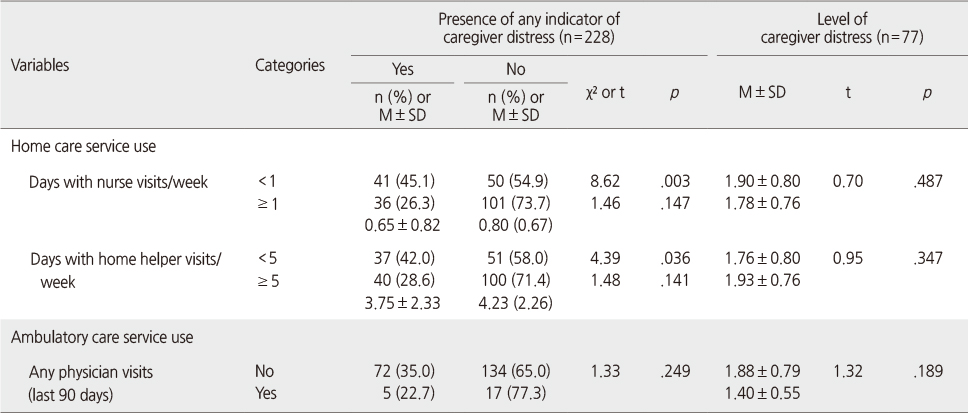
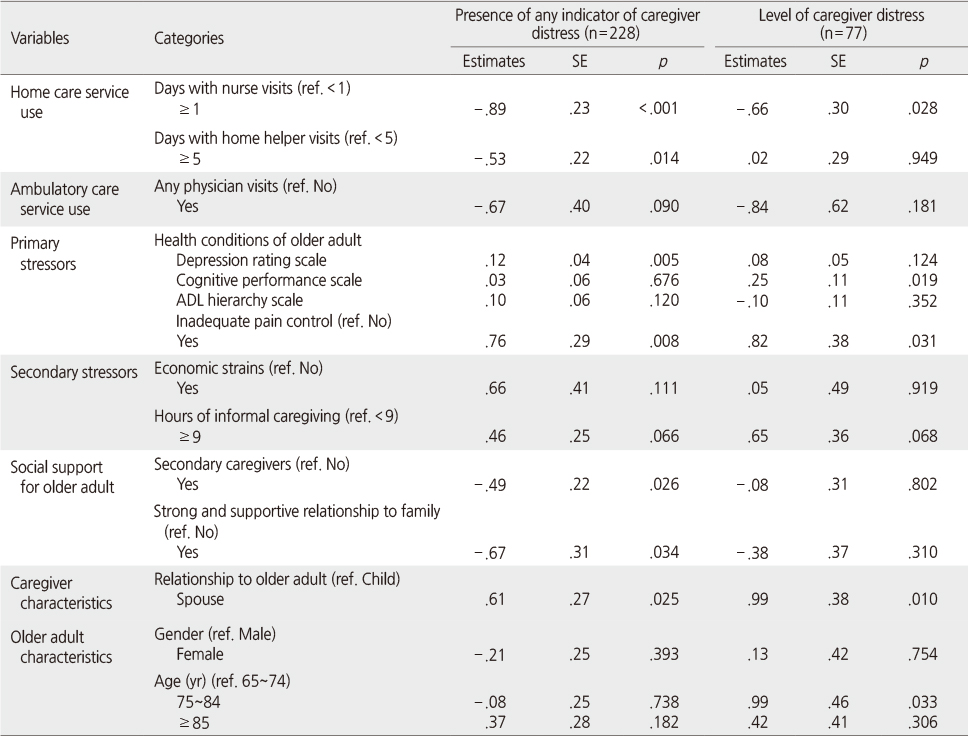
- Presence of family caregiver distress was significantly associated with days of nurse visits (β=-.89, p=<.001) and home helper visits (β=-.53, p=.014). Level of caregiver distress was also significantly associated with days of nurse visits (β=-.66, p=.028). Other factors which were significantly associated with caregiver distress were depression, cognitive function, inadequate pain control, social support for older adult, and caregiver relationship to the older adult.
-
Conclusion
- The results of this study show that visiting nurse service and appropriate support programs for Older Adults and family caregivers experiencing caregiver distress should be developed and provided to families based on the health care needs of older adults and their family caregivers for effective and sustainable home care.
This manuscript is a revision of the first author's master's thesis from Seoul National University.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (Grant number: 2010-0002802).
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
- 1. Chung KH, Oh YH, Kang EN, Kim JW, Sunwoo D, Oh MA. A survey of Korean older persons. Sejong: Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korean Institute of Health and Social Welfare; 2014.Report No.: Policy Report 2014-61.
- 2. Yang NJ, Choi IH. The impact of the Korean long-term care insurance system on its family caregivers: Focusing on family caregiving arrangement. Korean J Soc Welf Stud. 2013;44(3):31–56. Article
- 3. Hirdes JP, Freeman S, Smith TF, Stolee P. Predictors of caregiver distress among palliative home care clients in Ontario: Evidence based on the interRAI palliative care. Palliat Support Care. 2012;10(3):155–163. ArticlePubMed
- 4. Lee YK. Development of reward system for family carer in elderly long-term care insurance. Health Welf Policy Forum. 2010;165:96–104.
- 5. Han EJ, Kang IO, Kwon J. A study of determinants on institutionalization of elderly using home care services. J Korean Gerontol Soc. 2011;31(2):259–276.
- 6. Yaffe K, Fox P, Newcomer R, Sands L, Lindquist K, Dane K, et al. Patient and caregiver characteristics and nursing home placement in patients with dementia. JAMA. 2002;287(16):2090–2097. ArticlePubMed
- 7. Bainbridge D, Krueger P, Lohfeld L, Brazil K. Stress processes in caring for an end-of-life family member: Application of a theoretical model. Aging Ment Health. 2009;13(4):537–545. ArticlePubMed
- 8. Kumamoto K, Arai Y, Zarit SH. Use of home care services effectively reduces feelings of burden among family caregivers of disabled elderly in Japan: Preliminary results. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2006;21(2):163–170. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Han EJ, Na YK, Lee JS, Kwon J. Factors to influence the family caregivers' burden with the community-dwelling elderly under long-term care insurance system: Comparison among sub-dimensions. Korea Soc Policy Rev. 2015;22(2):61–96. Article
- 10. National Health Insurance Service. 2014 long term care insurance statistical yearbook. Seoul: Author; 2015.
- 11. Moorman SM, Macdonald C. Medically complex home care and caregiver strain. Gerontologist. 2013;53(3):407–417. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Han EJ, Lee JM, Kwon JH, Shin SB, Lee JS. Factors related to family caregivers’ burden with the community-dwelling disabled elderly under the long-term care insurance system. Health Policy Manag. 2014;24(1):71–84. Article
- 13. Morris JN, Fries BE, Bernabei R, Steel K, Ikegami N, Carpenter I. InterRAI home care (HC) assessment form and user's manual: Version 9.1. Kim H . Washington, DC: Inter-RAI; 2009.
- 14. Kim H, Jung YI, Sung M, Lee JY, Yoon JY, Yoon JL. Reliability of the interRAI long term care facilities (LTCF) and interRAI home care (HC). Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2015;15(2):220–228. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Pearlin LI, Mullan JT, Semple SJ, Skaff MM. Caregiving and the stress process: An overview of concepts and their measures. Gerontologist. 1990;30(5):583–594. ArticlePubMed
- 16. Han SJ, Lee S, Kim JY, Kim H. Factors associated with family caregiver burden for patients with dementia: A literature review. J Korean Gerontol Nurs. 2014;16(3):242–254. Article
- 17. Onder G, Finne-Soveri H, Soldato M, Liperoti R, Lattanzio F, Bernabei R, et al. Distress of caregivers of older adults receiving home care in European countries: Results from the aged in home care study. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2009;17(10):899–906. ArticlePubMed
- 18. Soldato M, Liperoti R, Landi F, Carpenter IG, Bernabei R, Onder G. Patient depression and caregiver attitudes: Results from the aged in home care study. J Affect Disord. 2008;106(1-2):107–115. ArticlePubMed
- 19. Choi IH, Kim EJ, Chung SY, Yang NJ. The impact of the Korean long-term care insurance system on the beneficiaries and their family caregivers: Focusing on quality of life and family relationships. Seoul: Korean Women's Development Institute; 2011. p. 1–283.
- 20. Burrows AB, Morris JN, Simon SE, Hirdes JP, Phillips C. Development of a minimum data set-based depression rating scale for use in nursing homes. Age Ageing. 2000;29(2):165–172. ArticlePubMed
- 21. Morris JN, Fries BE, Mehr DR, Hawes C, Phillips C, Mor V, et al. MDS cognitive performance scale. J Gerontol. 1994;49(4):M174–M182. PubMed
- 22. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. The impact of caring on family carers. In: Colombo F, Llena-Nozal A, Mercier J, Tjadens F, editors. Help Wanted?: Providing and paying for long-term care. Paris, FR: OECD Publishing; 2011. p. 85–120.
- 23. Nahm CH. Sample selection biases in sociological studies. Korean J Soc. 1998;32:99–136.
- 24. Arai Y, Kumamoto K, Washio M, Ueda T, Miura H, Kudo K. Factors related to feelings of burden among caregivers looking after impaired elderly in Japan under the long-term care insurance system. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2004;58(4):396–402. ArticlePubMed
- 25. National Health Insurance Service. 2012 long term care insurance statistical yearbook. Seoul: Author; 2013.
- 26. Riggs JS, Madigan EA, Fortinsky RH. Home health care nursing visit intensity and heart failure patient outcomes. Home Health Care Manag Pract. 2011;23(6):412–420. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 27. Lim JY, Kim EJ, Choi KW, Lee JS, Noh WJ. Analysis of barriers and activating factors of visiting nursing in long-term care insurance. J Korea Contents Assoc. 2012;12(8):283–299. Article
- 28. Lee JS, Hwang RI, Han EJ. Trends in home-visit nursing care by agencies' characteristics under the national long-term care insurance system. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2012;23(4):415–426. Article
- 29. Cho E, Cho E, Kim SS. Effects of family relationship on burden of family caregivers of older adult with dementia. J Korean Gerontol Soc. 2010;30(2):421–437.
- 30. Rinaldi P, Spazzafumo L, Mastriforti R, Mattioli P, Marvardi M, Polidori MC, et al. Predictors of high level of burden and distress in caregivers of demented patients: Results of an Italian multicenter study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2005;20(2):168–174. ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Career Disruption and Employment Status of Korean Family Caregivers of Older Adults Using Home-Based Care
Minah Lee
Nursing Reports.2024; 14(3): 1587. CrossRef - Effect of perceived chronic illness management support, health literacy, and social support on the care burden of families caring for older people with multiple chronic conditions at home: A cross-sectional study
Eun Sil Lee, Mi Young Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(1): 76. CrossRef - Korean primary health care program for people with disabilities: do they really want home-based primary care?
Hye-Jin Kim, Jae-Young Lim, Soong-Nang Jang
BMC Health Services Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Use of Home Care Services Reduces Care-Related Strain in Long-Distance Caregivers
Francesca B Falzarano, Verena Cimarolli, Kathrin Boerner, Karen L Siedlecki, Amy Horowitz, Suzanne Meeks
The Gerontologist.2022; 62(2): 252. CrossRef - Comparing the Needs of Family Caregivers and Program Providers in Long-Term Care in Terms of Family Support Program
Myonghwa Park, Younghye Go, Miri Jeong, Eun-Jeong Han
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(1): 14. CrossRef - Development and Application of Cost Management Program for Visiting Nursing Centers Using Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing
Juhang Kim, Ji Young Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 586. CrossRef
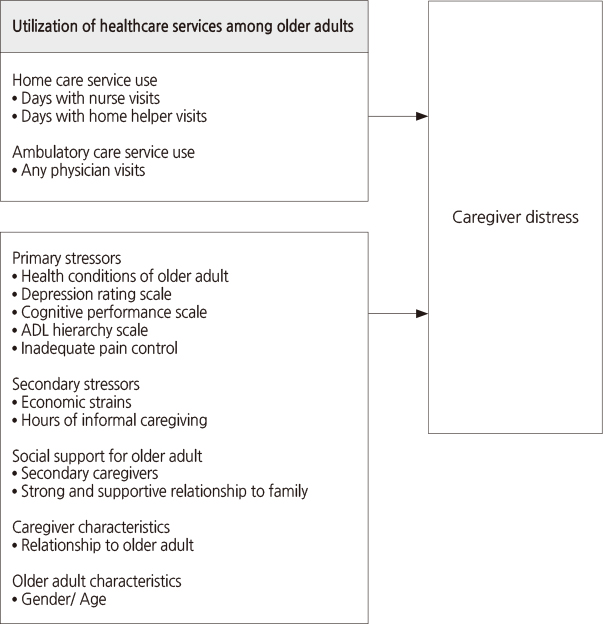
Figure 1
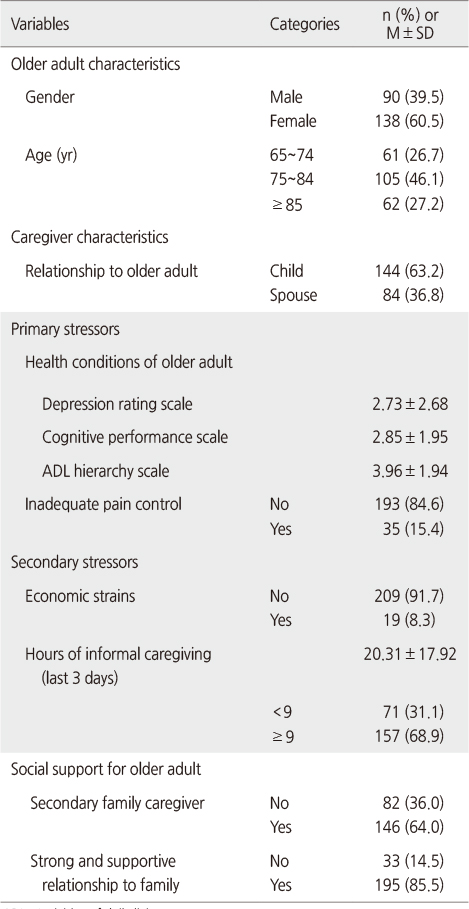
General Characteristics of Participants (N=228)
ADL=Activities of daily living.
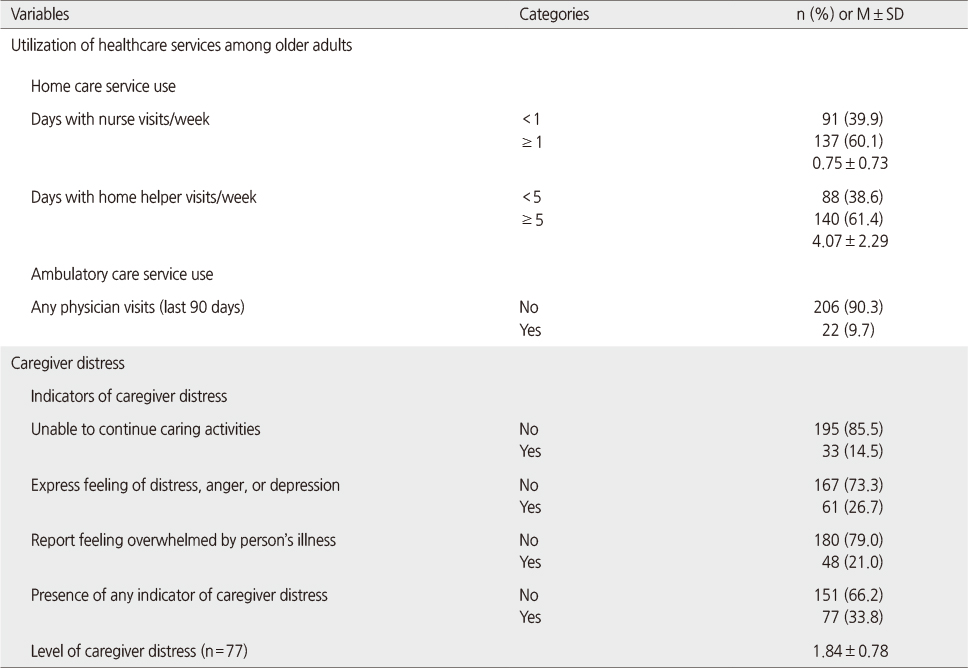
Characteristics of Healthcare Services for Older Adults and Caregiver Distress (N=228)
Caregiver Distress by Utilization of Healthcare Services among Older Adults (N=228)
Heckman Selection Model Analysis of Caregiver Distress (N=228)
ADL=Activities of Daily Living
ADL=Activities of daily living.
ADL=Activities of Daily Living
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

