Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Development and psychometric testing of the Perceived Postoperative Care Competency Scale for Nursing Students: a methodological study
- Perihan Şimşek, Gül Çakir Özmen, Melek Ertürk Yavuz, Sema Koçan, Dilek Çilingir
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):81-97. Published online February 24, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
To improve the quality of postoperative care and promote recovery after surgery, it is important that nursing education is competency-based and that competency assessment is an integral part of the educational process. The purpose of this study was to develop a tool to evaluate nursing students’ perceived competence in postoperative care.
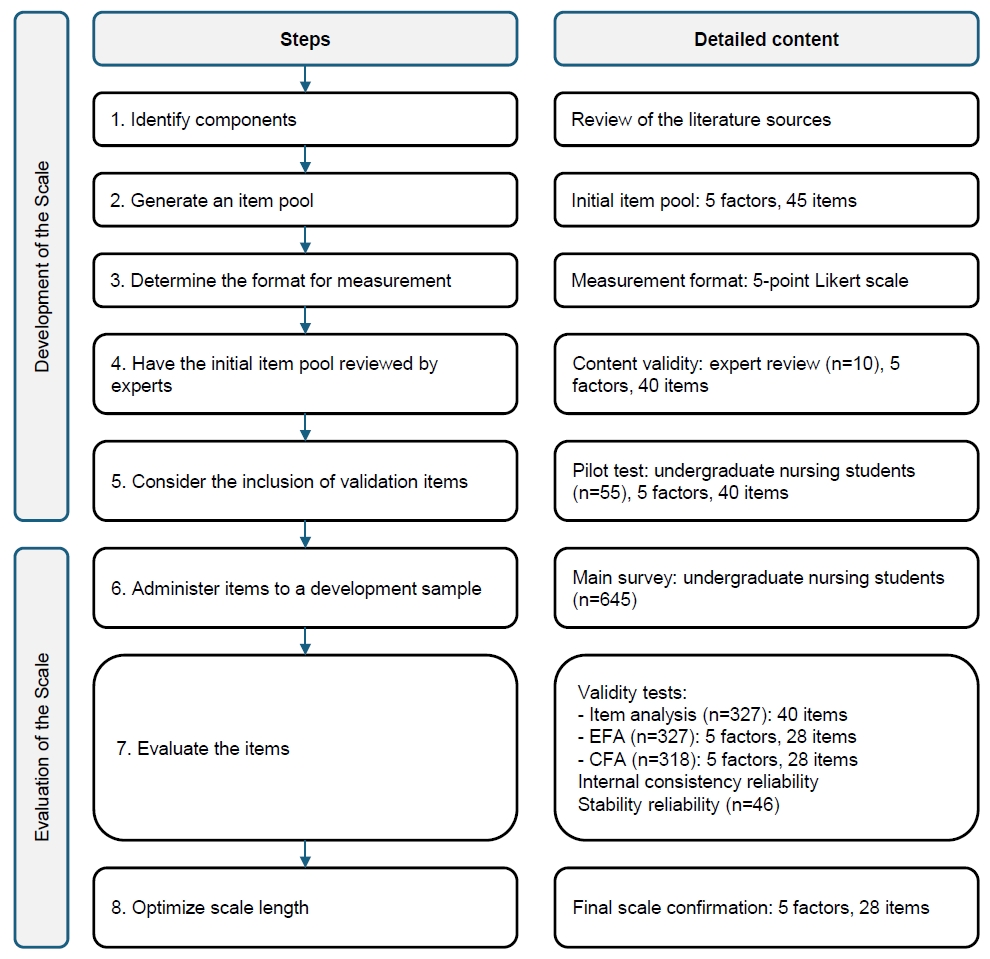
Methods
This cross-sectional methodological study followed DeVellis’s scale development steps and was conducted between December 2022 and March 2023. In this study, 892 students were invited and 703 responded. After exclusions, data from 645 students were analyzed to examine the psychometric structure of the scale using exploratory factor analysis (n=327) and confirmatory factor analysis (n=318). Reliability was assessed by calculating Cronbach’s α coefficients and by test–retest measurement (n=46).
Results
The proposed scale was confirmed to consist of five factors and 28 items (χ2/degrees of freedom=2.25, root mean square error of approximation=.06, normed fit index=.90, and goodness-of-fit index=.85). Cronbach’s α was .97 for the total scale. The data demonstrated high test–retest stability (intraclass correlation coefficient=.88). The scale developed and psychometrically tested in this study revealed a five-factor structure: legal responsibilities and ethical principles (seven items), postoperative nursing care (seven items), interpersonal relations and communication (four items), leadership (six items), and education and professional development (four items).
Conclusion
The scale, which demonstrated very good psychometric properties, would be helpful in assessing perceived postoperative nursing competence among nursing students. This may help students graduate with the necessary knowledge and skills required for postoperative care. However, further research involving larger samples and more diverse cultural contexts is needed to enhance the generalizability of the scale.
- 349 View
- 28 Download

- Psychometric testing of the Korean version of the Undergraduate Nursing Student Academic Satisfaction Scale: a methodological study
- Da-In Park, Joohee Shim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):51-66. Published online February 9, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to translate, cross-culturally adapt, and evaluate the psychometric properties of the Korean version of the Undergraduate Nursing Student Academic Satisfaction Scale (K-UNSASS).
Methods
The K-UNSASS was developed using Brislin’s team-based translation–back-translation approach, with semantic and conceptual equivalence examined. Face validity was assessed, and a pilot test was conducted in November 2022. Content validity was evaluated by an expert panel. Formal data collection was conducted from December 2022 to January 2023. Structural validity was examined using exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses. Reliability was assessed using Cronbach’s alpha and McDonald’s omega coefficients.
Results
A total of 482 full-time nursing students, most of whom were in the fourth year of their nursing program, were included in the psychometric testing. Construct validity supported a four-factor structure accounting for 65.9% of the total variance. After removal of three items with unsatisfactory factor loadings, a 45-item K-UNSASS was established. Confirmatory factor analysis of the 45-item K-UNSASS demonstrated an acceptable model fit, and both Cronbach’s alpha and McDonald’s omega coefficients were .97.
Conclusion
The K-UNSASS demonstrates acceptable reliability and validity for assessing academic satisfaction among Korean nursing students. As a culturally relevant instrument, it supports educational improvement through targeted strategies and program evaluation.
- 497 View
- 45 Download

- Transforming nursing education to enhance integrated nursing competency: a Delphi-based methodological study on symptom-based clinical reasoning
- Jeung-Im Kim, Soyoung Yu, Jin-Hee Park, Ju-Eun Song, Eunjung Ryu, JuHee Lee, YeoJin Im
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):39-50. Published online February 5, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to address the shift toward competency-based education and the planned 2028 “Integrated Nursing” National Licensing Examination (NLE), this study aimed to establish structural alignment among NLE domains, the seven integrated nursing competencies (INCs), and curriculum goals, with a particular focus on implementing symptom-based clinical reasoning (SBCR).
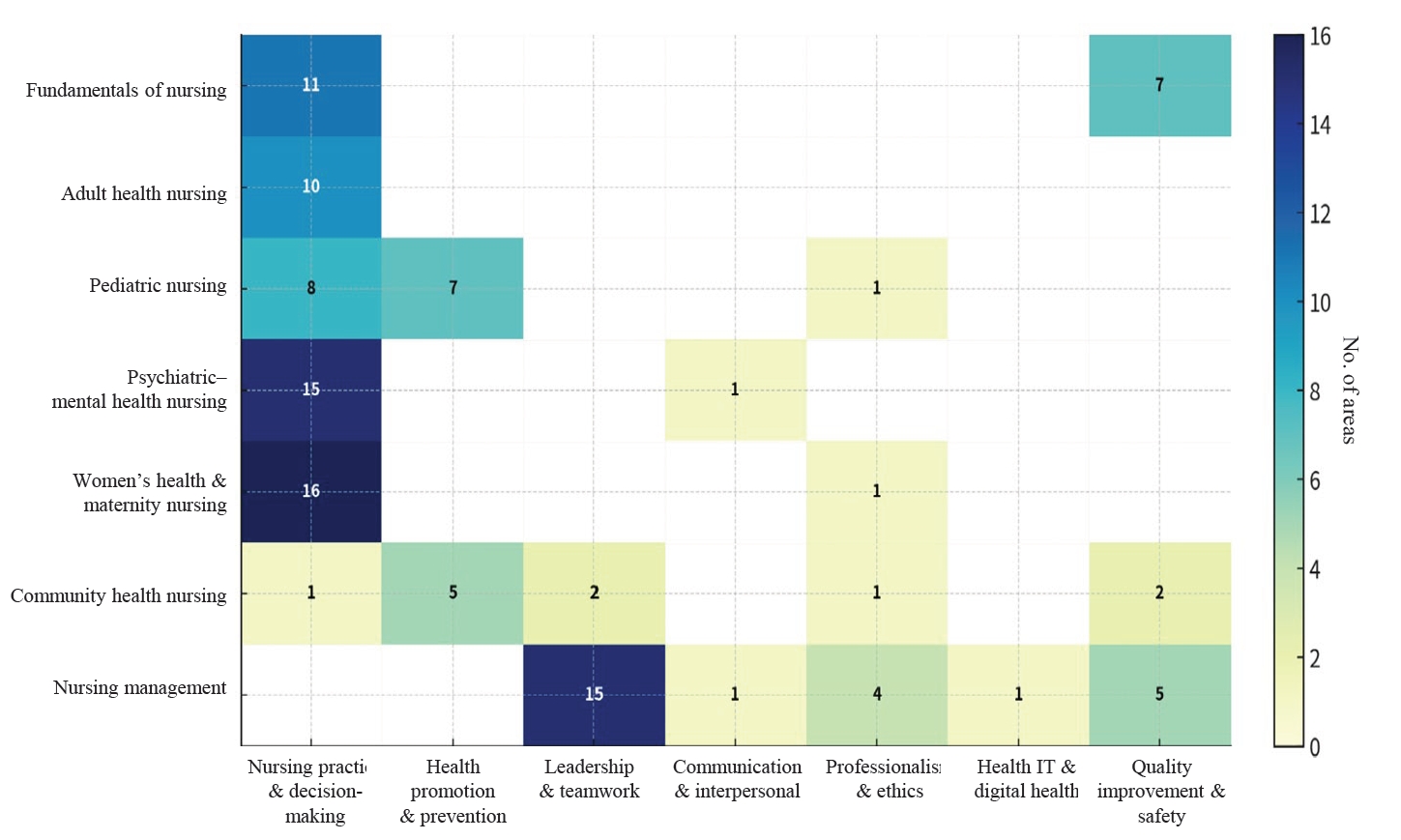
Methods
This Delphi-based methodological study included seven content experts for content validity index (CVI) assessment and 24 nursing education experts who participated in a consensus workshop. The item-level CVI and the scale-level CVI/average were calculated to confirm the linkage between INCs and NLE domains. In addition, qualitative analysis of workshop materials and meeting records was conducted to derive 10 integrated learning topics and to develop an SBCR educational model for the key symptom of headache, grounded in Miller’s Clinical Competence Pyramid (levels 2–4).
Results
The analysis confirmed the validity of integrating the INCs within the overall curriculum structure. The resulting framework delineates staged learning objectives and core clinical questions designed to systematically enhance clinical reasoning, promote safe nursing practice, and support professional reflection within a unified curriculum.
Conclusion
This study provides a practical foundation for nursing curriculum redesign by facilitating a transition from fragmented, subject-based instruction to a holistic, patient-centered SBCR model. This approach aligns with the requirements of the integrated NLE and is expected to contribute to meaningful improvements in actual clinical competency.
- 492 View
- 57 Download

- Comparison of educational needs and priorities for work-related laws between hospital and community-based nurses
- Jeonghyun Kim, Min Kyoung Han, Minjae Lee, Sujin Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):400-412. Published online August 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25049
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the practical utilization of work-related laws in nursing practice and to prioritize educational needs to provide foundational data for improving nurses’ legal competencies.
Methods
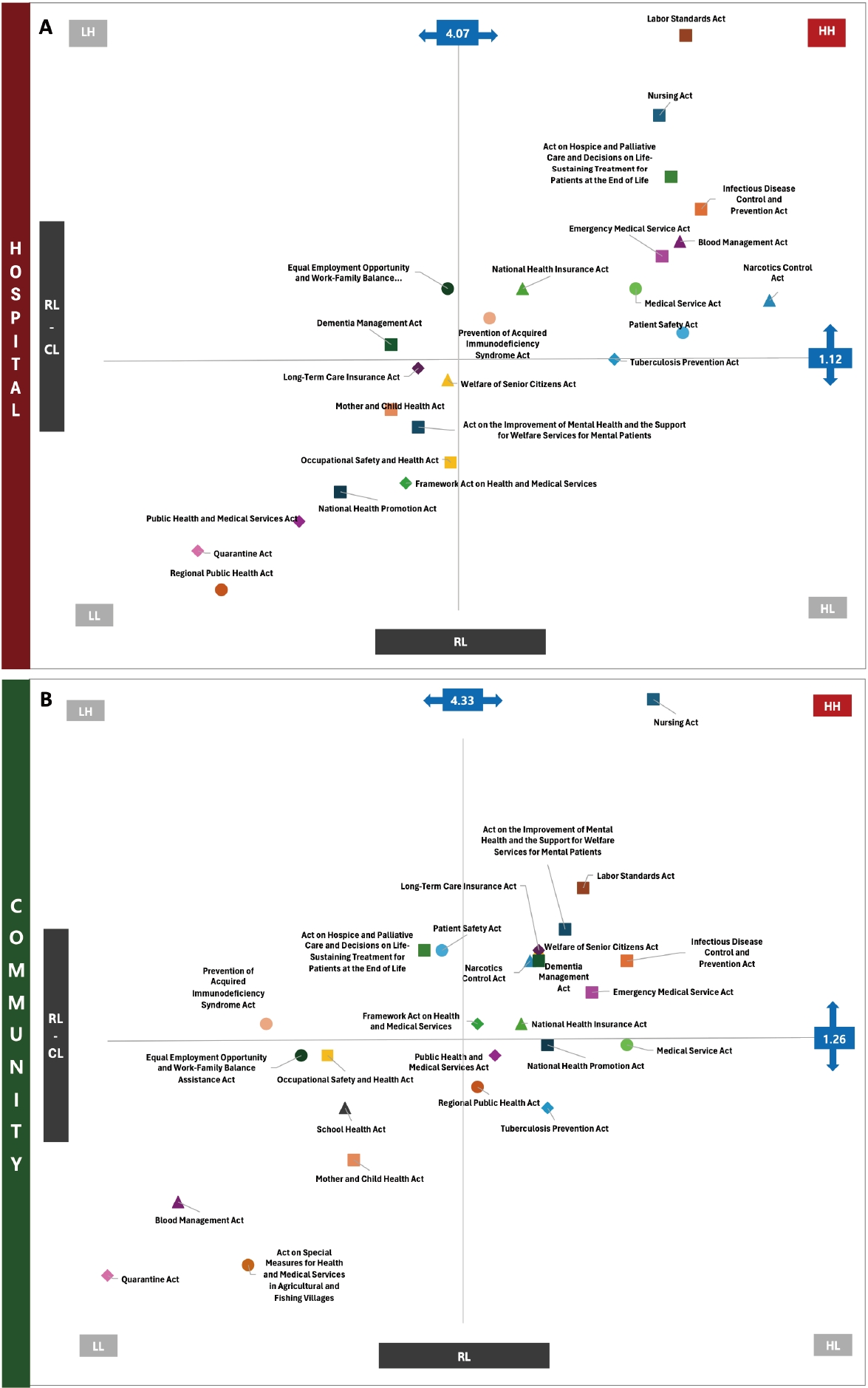
A descriptive survey was employed using an online self-reported questionnaire. Participants included 275 nurses with over 3 years of clinical experience, categorized into hospital and community-based. Convenience sampling was used, and data were collected between January 9 and February 3, 2025. Descriptive statistics and the paired t-test were conducted using IBM SPSS 26.0. Educational needs were analyzed using the Borich Needs Assessment and the Locus for Focus model.
Results
Among participants, 75.6% had received education on work-related laws, and 79.3% of those participants received related education during their undergraduate studies. However, 32.4% of nurses reported experiencing practice related difficulties due to insufficient legal knowledge, particularly related to unclear legal responsibilities and ambiguity in the scope of practice. High educational needs were identified for the Nursing Act and the Labor Standards Act across all workplaces. Hospital nurses emphasized the Hospice and Palliative Care Act and Emergency Medical Services Act, while community-based nurses prioritized the Mental Health Welfare Act, Elderly Welfare Act, and Dementia Management Act.
Conclusion
Nurses’ legal education needs are related to practical applications and their capability to respond appropriately to legal requirements, and these needs vary depending on their work environment and social changes. These findings underscore the necessity of restructuring legal education curricula to improve practical relevance and support nurses’ rights, providing a basis for developing workplace-specific legal education programs.
- 2,103 View
- 151 Download

- Core domains for pre-registered nurses based on program outcomes and licensing competencies
- Soyoung Yu, Hye Young Kim, Jeung-Im Kim, JuHee Lee, Ju-Eun Song, Hyang Yuol Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):249-268. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify core domains for pre-registered nurses by comparing licensing competencies with program outcomes (POs) in undergraduate nursing education. This was accomplished in preparation for the transition of the Korean Nurse Licensing Examination (KNLE) from a tradition seven-subject format to a newly integrated, competency-based single-subject format that reflects current trends in nursing assessment.
Methods
A literature review and survey were conducted. From 828 studies retrieved via PubMed, CINAHL, and Google Scholar using keywords such as “newly graduated registered nurses” and “competency OR competence,” 18 were selected according to pre-established inclusion and exclusion criteria. Documents from national and international nursing organizations were included to extract relevant licensing competencies. We also reviewed POs from all undergraduate nursing schools in South Korea to align educational outcomes with the identified core domains.
Results
The core domains identified were clinical performance and decision-making, professional attitudes and ethics, communication and interpersonal skills, leadership and teamwork, quality improvement and safety, health promotion and prevention, and information technology and digital health. These domains showed strong alignment with POs under the fourth-cycle accreditation standards.
Conclusion
It concludes the seven core domains will be appropriate for evaluating pre-registered nurses in the integrated KNLE. Based on the seven identified core domains, expert consensus should be sought in the next phase to support the development of integrated, competency-based test items grounded in these domains. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Transforming nursing education to enhance integrated nursing competency: a Delphi-based methodological study on symptom-based clinical reasoning
Jeung-Im Kim, Soyoung Yu, Jin-Hee Park, Ju-Eun Song, Eunjung Ryu, JuHee Lee, YeoJin Im
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2026; 56(1): 39. CrossRef
- Transforming nursing education to enhance integrated nursing competency: a Delphi-based methodological study on symptom-based clinical reasoning
- 4,249 View
- 162 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- A non-face-to-face diabetes self-management program based on self-efficacy theory and health literacy: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Jung Hee Lee, Soo Jin Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):165-177. Published online May 23, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to assess the impact of a non-face-to-face diabetes self-management program based on self-efficacy theory and focusing on health literacy.
Methods
A quasi-experimental, nonequivalent control group pre–post design was used. Participants from a community health promotion center were included if they (1) were 30–70 years of age, (2) had type 2 diabetes with glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥6.5%, and (3) had internet access via computers or mobile devices. The 8-week program was developed based on self-efficacy theory, and it included virtual education using an online platform, telephone counseling, videos, and social networking site activities considering health literacy. Fasting blood glucose levels, HbA1c levels, diabetes self-efficacy, social support, depression, and self-management behaviors were assessed. Data were analyzed using the independent t-test, paired t-test, and others.
Results
Post-test results showed that the intervention group had significantly lower fasting blood glucose levels and improved diabetes self-efficacy, social support, and self-management behaviors compared with the control group. An analysis of the pre-to-post changes in scores indicated that the intervention group had significantly greater improvements in fasting blood glucose levels, diabetes self-efficacy, and overall diabetes self-management behaviors than those observed in the control group.
Conclusion
Non-face-to-face programs based on self-efficacy theory that consider health literacy can provide effective diabetes management support to patients when in-person diabetes management at community health centers is challenging.
- 3,479 View
- 253 Download

- Support Needs for Health Promotion of Community-Dwelling People with Disabilities: Perspectives of Operators Managing Disability Supportive Housing
- Hye Jin Nam, Haesun Lee, Han Nah Park, Sujin Lee, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):211-223. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Recent studies have focused on policies aimed at supporting the independence of individuals with disabilities in communities. As part of this initiative, supportive housing, integrated care, and residential spaces offer tailored services based on individual needs and autonomy. The attitudes and knowledge of the administrators supporting supportive housing residents regarding health management can influence the well-being of individuals with disabilities. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the challenges faced by supporting housing workers in enhancing the self-management skills of individuals with disabilities.
Methods
In this qualitative study, focus group interviews were conducted in August 2023 with nine administrators working to support housing in Seoul. Qualitative content analysis was used to analyze the interview data.
Results
The needs and challenges in enhancing the self-management skills of individuals with disabilities were as follows: (1) the complexity of health management challenges, (2) bidirectional strategies for strengthening health management capabilities, and (3) support for systematic health management. Additionally, eight subthemes were derived.
Conclusion
By investigating the difficulties experienced and identifying the necessary support requirements for supportive housing workers, this study seeks to uncover insights and identifies areas for improvement and strategies for health management. This study acknowledges the educational and institutional support necessary to improve the health and quality of life of individuals with disabilities residing in supportive housing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
Haesun Lee, Hye Jin Nam, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(3): 454. CrossRef - Intention to use a health information platform in supportive housing for people with disabilities: An application of the UTAUT model
Bohye Kim, Hye Jin Nam, Haesun Lee, Hannah Park, Ju Young Yoon, Nicola Diviani
PLOS One.2025; 20(10): e0332072. CrossRef - A preliminary study on the development of a chronic disease self-management curriculum for disability support workers: educational needs analysis
Han Nah PARK, Hye Jin NAM, Haesun LEE MSN, Sujin LEE, Bohye KIM, Ju Young YOON
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
- 2,315 View
- 101 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Simulation-Based Education for Caring Patients with COVID-19
- Min Hye Lee, Eun-Young Noh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):397-411. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The role of medical staff gained immense significance in the context of the prolonged coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. However, few studies had explored the impact of simulation-based education on the ability of nursing students to care for the patients of COVID-19. This study provided nursing students with simulation-based education in caring for the patients of COVID-19 and confirmed its effectiveness.
Methods
This study used a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design. The participants were recruited from the nursing departments of two universities in Korea through convenience sampling. A total of 79 participants were included: 37 in the intervention group and 42 in the control group. The intervention group received four sessions of simulation training based on the National League for Nursing Jeffries simulation theory.
Results
The intervention group showed an improvement compared to the control group in terms of knowledge related to coronavirus, confidence in performing infection control skills, and perception of preparedness for caring for the patients of COVID-19, with a high-level of satisfaction and self-confidence in learning. There was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of anxiety.
Conclusion
This simulation is expected to be a significant strategy for alleviating the global burden in terms of staff safety and patient outcomes by improving the competencies of prospective medical staff in responding to pandemics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Utilization and impact of simulation-based education in prelicensure nurse education: An integrative review
Robyn Cant, Colleen Ryan
Journal of Professional Nursing.2026; 63: 6. CrossRef - Building Skills in Infection Prevention Through Simulation: Insights from Nursing Students in Brazil and Peru
Luciene Muniz Braga, Pedro Paulo do Prado-Junior, Andréia Guerra Siman, Talita Prado Simão Miranda, Mara Rúbia Maciel Cardoso do Prado, Luana Vieira Toledo, Rodrigo Siqueira-Batista, Andréia Patrícia Gomes, Yanet Castro Vargas, Luis Alberto Chihuantito-Ab
Nursing Reports.2026; 16(1): 14. CrossRef - Determinants of Standard Precautions Performance Among Nursing Students in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
Se Gyeong Jeon, Eun Jung Kim
Healthcare.2025; 13(21): 2803. CrossRef - Nursing Students’ Perceptions of a Novel Education Approach to Prevention and Control of Healthcare-Associated Infections: Insights from PrevInf Pilot Study
Paulo Santos-Costa, Filipe Paiva-Santos, João Graveto
Nursing Reports.2024; 14(2): 1494. CrossRef
- Utilization and impact of simulation-based education in prelicensure nurse education: An integrative review
- 6,040 View
- 104 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of a Modified Six-Sigma-Methodology-Based Training Program on Core Competencies in Rehabilitation Nurse Specialists
- Jiayi Gu, Lan Luo, Chengjuan Li, Sumin Ma, Fanghua Gong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):412-425. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22122
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Nurses play an important role in ensuring patient rehabilitation and are involved in all aspects of multidimensional rehabilitation. Therefore, strengthening rehabilitation nursing education is vital to ascertain high-quality rehabilitation and optimum outcomes. This study examined the effectiveness of a new teaching reform—a modified Six-Sigma-based training program—against a conventional educational program on rehabilitation specialist nurses’ core competencies, post-training performance, and satisfaction.
Methods
A quasi-randomized controlled trial was conducted to assess the effectiveness of the modified training program. We recruited 56 learners from the 2020 training course at the Hunan Rehabilitation Specialist Nurse Training Base as the control group. Sixty learners from the base’s 2021 training course were recruited as the intervention group. Data were collected in a consistent manner from both groups after the training program was implemented.
Results
Those who underwent the modified training program showed better improvement in all core competencies than those who underwent the conventional training program (p < .05); the scores for theoretical knowledge, clinical nursing lectures, reviews, and nursing case management improved significantly following the teaching reform (p < 0.05). Further, overall satisfaction as well as base management and theoretical teaching satisfaction improved significantly (p < .05).
Conclusion
The modified training program strengthens rehabilitation nurses’ base management abilities; enhances their core competencies; expands their interest in and breadth, depth, and practicability of theoretical courses; and updates the teaching methods. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of bedside comprehensive ability training on teaching and training in operating room
Yi Zhong, Wenjun Bu, Qifan Li, Lili Zheng
Frontiers in Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of rehabilitation nursing training for clinical nurses based on the Kirkpatrick model
Manzhou Yang, Xiuying Zhang, Ruiyang Han, Xiao Ding, Runguo Gao, Qi Jing, Weiqin Cai, Anning Ma, Qianqian Gao, Hongmei Li
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Availability of Six Sigma trials for quality improvement in healthcare: an emerging challenge
Ivan David Lozada-Martinez, Ornella Fiorillo-Moreno, Jessica Manosalva-Sandoval, Yelson Alejandro Picón-Jaimes
International Journal For Quality In Health Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Professional competencies in geriatric nursing for geriatric nurses: a latent profile analysis
Mengxue Wang, Dongdong Li, Jingjing Li, Xiumei Zhang
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A longitudinal assessment of factors affecting training transfer among new clinical nurse specialists
Ardani Latifah Hanum, Qiulan Hu, Wei Wei, Fang Ma
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2024; 11(3): 308. CrossRef
- Effect of bedside comprehensive ability training on teaching and training in operating room
- 2,587 View
- 50 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Effects of Health Education Using Virtual Reality for Adolescents: A Systematic Review and MetaAnalysis
- SoMi Park, ChaeWeon Chung, Gaeun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):177-190. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of health interventions using virtual reality (VR) on improving knowledge, attitudes, and skills; and inducing behavioral change among adolescents.
Methods
This study is a systematic review and meta-analysis following PRISMA guidelines. We searched Cochrane, MEDLINE, Embase, CINAHL, Scopus, Web of Science, and Korean databases between database inception and April 10, 2021. Based on heterogeneity, a random- or fixed-effects model was used, as appropriate, to calculate effect sizes in terms of the standardized mean difference (SMD) and odds ratio (OR). Studies were selected if they verified the effects of health education using VR on adolescents; there was an appropriate control group; and if the effects of education were reported in terms of changes in knowledge, attitudes, skills, or behaviors.
Results
This analysis included six studies (n = 1,086). The intervention groups showed greater responses in knowledge and attitudes (SMD = 0.57, 95% confidence interval (CI) [0.12 to 1.02]), skills related to health behavior (SMD = -0.45, 95% CI [-0.71 to -0.19]), and behavioral change after 12 months (OR = 2.36, 95% CI [1.03 to 5.41]).
Conclusion
The results confirm the effectiveness of health interventions using virtual reality (VR). Although the analysis include a small number of studies, a case can be made for health interventions using VR to be utilized as educational methods and strategies to prevent risky behaviors among adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Implementation of a Childcare-Based Obesity Prevention Program for Vulnerable Families During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons for School Nurses
Jiyoung Park, Gill ten Hoor, Seohyun Won, Gahui Hwang, Sein Hwang, Siew Tiang Lau
The Journal of School Nursing.2025; 41(5): 579. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Virtual Reality Intervention for Reducing Exposure to Endocrine Disruptors in Female Adolescents: A Pilot Study
SoMi Park, Yun Jeong Hwang, ChaeWeon Chung
Journal for Specialists in Pediatric Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Chinese nurses’ perspectives on child-friendly healthcare practice assessment: a qualitative study
Wei Xiao Huang, Mei Chan Chong, Li Yoong Tang, Xiao Xia Liu, Mei Fang, Yun Yun Shen, Xiao Li Guo
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing anatomy education with virtual reality: integrating three-dimensional models for improved learning efficiency and student satisfaction
Shuliang Niu, Jinlong Zhang, Jiang Lin, Binbin Wang, Jie Yan
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Implementation of a Childcare-Based Obesity Prevention Program for Vulnerable Families During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons for School Nurses
- 4,708 View
- 111 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- The Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Readiness for Practice Survey for Nursing Students
- Tae Wha Lee, Yoonjung Ji, Yea Seul Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(6):564-581. Published online December 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22032
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the Readiness for Practice Survey (K-RPS).
Method
The English Readiness for Practice Survey was translated into Korean using the Translation, Review, Adjudication, Pretesting, and Documentation (TRAPD) method. Secondary data analysis was performed using the dataset from the New Nurse e-Cohort study (Panel 2020) in South Korea. This study used a nationally representative sample of 812 senior nursing students. Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses were also conducted. Convergent validity within the items and discriminant validity between factors were assessed to evaluate con-struct validity. Construct validity for hypothesis testing was evaluated using convergent and discriminant validity. Ordinary α was used to assess reliability.
Results
The K-RPS comprises 20 items examining four factors: clinical problem solving, learning experience, professional responsibilities, and professional preparation. Although the convergent validity of the items was successfully verified, discriminant validity between the factors was not. The K-RPS construct validity was verified using a bi-factor model (CMIN/DF 2.20, RMSEA .06, TLI .97, CFI .97, and PGFI .59). The K-RPS was significantly correlated with self-esteem (r = .43, p < .001) and anxiety about clinical practicum (r = - .50, p < .001). Internal consistency was reliable based on an ordinary α of .88.
Conclusion
The K-RPS is both valid and reliable and can be used as a standardized Korean version of the Readiness for Practice measurement tool. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Readiness for Practice among Senior Nursing Students in South Korea: A Cross-sectional Study
Jihye Kim, Kyungmi Lee, Hye Suk Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(1): 54. CrossRef - Readiness for Practice Among Nursing College Graduates: A Cross-Sectional Correlation Study
Kim Jihye, Lee Kyungmi
SAGE Open Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Moderating Effect of Grit on Nursing Education Satisfaction and Readiness for Practice Among Nursing Graduates During COVID-19: A Cross-Sectional Study
Lee Kyungmi, Kim Jihye
Pacific Rim International Journal of Nursing Research.2025; 29(4): 862. CrossRef - The influence of nursing informatics competency, clinical practice self efficacy, and grit on clinical practice readiness of nursing students
Hae Ok Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(4): 440. CrossRef - The mediating effect of transition shock on the relationship between readiness for practice and turnover intention of new graduate nurses in South Korea: A longitudinal study
Taewha Lee, Eunkyung Kim, Yoonjung Ji
Nurse Education Today.2024; 143: 106394. CrossRef
- Readiness for Practice among Senior Nursing Students in South Korea: A Cross-sectional Study
- 4,735 View
- 198 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of Prenatal Education for Environmental Health Behavior Using Cartoon Comics
- Hyun Kyoung Kim, Hee Kyung Kim, Mirim Kim, Seohwa Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(4):478-488. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21083
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and examine the effects of a prenatal program on environmental health behavior using cartoon comics among Korean pregnant women.
Methods
This study used a non-equivalent control group pre-test/post-test design. The program used cartoon comics to explore environmental health behaviors during pregnancy. The program consisted of the following four components: environmental toxicants during pregnancy, avoiding particulate matter during pregnancy, environmental toxicants during baby care, and making a healthy environment for children. In total, 35 pregnant women participated in the study: 18 in the experimental group and 17 in the control group. Data collection and program adaptation were conducted between November 3, 2020 and January 19, 2021. The effect of the prenatal education program was evaluated by t-test and repeated measures ANOVA.
Results
Learning experience (t = - 2.35, p = .025), feasibility (t = - 2.46, p = .019), satisfaction (t = - 2.23, p = .032) were higher in the experimental group than in the control group in the first post-test. Feasibility (t = - 2.40, p = .022) was higher in the experimental group than in the control group in the second post-test. Repeated-measures ANOVA showed significant interactions between time and group in environmental susceptibility (F = 9.31, p < .001), self-efficacy (F = 3.60, p = .033), and community behavior (F = 5.41, p = .007).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates the need for a prenatal education program to promote environmental health perceptions and behavior during pregnancy. We suggest a prenatal class adopting the creative cartoon comics to promote the maternal environmental health behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a diabetes-themed cartoon-based education on disease knowledge and physical activity among Japanese children: a preliminary randomized controlled trial
Yasuhiro Suzuki, Daichi Sugawara, Mika Oki, Hirofumi Takahashi, Takaaki Matsuda, Hiroaki Suzuki, Hitoshi Shimano, Yasushi Hada, Kenji Suzuki
Clinical Pediatric Endocrinology.2026; 35(1): 74. CrossRef - The effect of DECO-MOM mobile application for a prenatal environmental health program on environmental health behaviors: a pilot test
Hae Kyung Jo, Hyun Kyoung Kim
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and evaluation of a quasi-experimental sexual and reproductive health literacy (SRHL) programme for marriage immigrants in South Korea: focus on Vietnamese women
Heeran Chun, Young Sook Lee, Hyeran Yoon
BMJ Public Health.2025; 3(2): e002473. CrossRef - The effects of a YouTube prenatal program on social support, environmental health behavior, and content satisfaction: a quasi-experimental research design
Geum Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Hye Young Min
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Examining the Effectiveness of Interactive Webtoons for Premature Birth Prevention: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial
Sun-Hee Kim, Jennie C De Gagne
JMIR Research Protocols.2024; 13: e58326. CrossRef - Development and effects of a webtoon education program on preventive self-management related to premature labor for women of childbearing age: a randomized controlled trial
Sun-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(3): 250. CrossRef - The effects of environmental prenatal program on environmental health perception and behavior using internet-based intervention in South Korea: A non-randomized controlled study
Hyun Kyoung Kim, Geum Hee Jeong, Hye Young Min, George Vousden
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(11): e0277501. CrossRef
- Effects of a diabetes-themed cartoon-based education on disease knowledge and physical activity among Japanese children: a preliminary randomized controlled trial
- 1,613 View
- 40 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Level of Complete Knowledge on Five Moments of Hand Hygiene among Nurses Working at Integrated Nursing Care Service Wards
- Eunhee Kim, Ihn Sook Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(4):454-464. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21030
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the level of complete knowledge about hand hygiene indications among nurses working at integrated nursing care service wards.
Methods
A total of 127 nurses in eight integrated nursing care service wards completed structured sheets while observing a video based on six scenarios developed by the research team. Complete knowledge level was calculated as the percentage (%) of participants who responded correctly to all questions among participants. Complete knowledge levels according to the scenarios were calculated and compared according to general characteristics using the chi-squared test or Wilcoxon rank-sum test.
Results
The complete knowledge level for each scenario ranged from 7.9% (scenario 6) to 42.5% (scenarios 4 and 5), and no one had complete knowledge of all scenarios. Only 3.1% of participants demonstrated complete knowledge in more than four scenarios, and 26.0% had complete knowledge of four or more hand hygiene moments. Complete knowledge level per scenario did not differ depending on work experience at hospitals and study wards, or prior hand hygiene training in the last year.
Conclusion
As the complete knowledge level regarding hand hygiene moment is very low, it is suggested that regular hand hygiene training should be provided to nurses using video media that reflect real nursing tasks. Thus, they can acquire complete knowledge of when hand hygiene is needed or not during complex nursing work situations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Indication‐based and patient‐based hand hygiene performance among nurses working at a university hospital
Bora Shin, Ihn Sook Jeong
Nursing & Health Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge and Training Needs in Nosocomial Infection among Hospital Staff in the City of Kielce, Poland: A Cross-Sectional Study
Kamila Fortunka, Agnieszka Strzelecka, Grzegorz Król, Paulina Paprocka, Angelika Mańkowska, Agata Lesiak, Urszula Karpeta, Slawomir Okła, Jakub Spałek, Szczepan Kaliniak, Ewelina Piktel, Maciej Karasiński, Bonita Durnaś, Robert Bucki, Hayfa Almutary
Journal of Nursing Management.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Competency Survey of Caregivers in Medical Tourism Special Zone and Other Regions
Dong-Yeop Lee, Sang-Bong Lee, Yeong-Im Park, Jin-Geun Lee, Yoon Hee Park, So Young Lee, Dong-Yoon Kang
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(2): 140. CrossRef
- Indication‐based and patient‐based hand hygiene performance among nurses working at a university hospital
- 3,734 View
- 114 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Comparison of the Effects of Education Only and Exercise Training Combined with Education on Fall Prevention in Adults Aged 70 Years or Older Residing in Elderly Residential Facilities
- Chahwa Hong, Haejung Lee, Misoon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(2):173-187. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20203
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
To compare the effects of education only and exercise training combined with education on fall knowledge, fall efficacy, physical activity, and physical function in adults aged 70 years or older residing in elderly residential facilities.
Method
A three-group pre- and posttest design was utilized: education only (EO; n = 23), education and TheraBand (ET; n = 22), and education and walking (EW; n = 22). Fall education was provided for all three groups. In addition, TheraBand exercise training was provided for the ET and a walking exercise for the EW. Data were collected from November 1st, 2017 to February 15th, 2019 and analyzed with χ2 test, paired t-test, and one-way ANOVA using IBM SPSS/WIN ver. 22.0.
Results
Compared with the EO, the ET and the EW were more effective in terms of fall efficacy, physical activity, and lower extremity muscle strength. The EW showed higher improvement in walking abilities than the EO and the ET.
Conclusion
Exercise training combined with education is more effective in preventing falls among community-dwelling adults aged 70 years or older. When considering fall prevention programs for older adults, both TheraBand and walking exercise training combined with education can be chosen based on the participant’s physical status. Aggressive strategies to improve daily walking are required to maintain walking abilities among community-dwelling adults aged 70 years or older. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Falls caused by balance disorders in the elderly with multiple systems involved: Pathogenic mechanisms and treatment strategies
Liwei Xing, Yi Bao, Binyang Wang, Mingqin Shi, Yuanyuan Wei, Xiaoyi Huang, Youwu Dai, Hongling Shi, Xuesong Gai, Qiu Luo, Yong Yin, Dongdong Qin
Frontiers in Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Falls caused by balance disorders in the elderly with multiple systems involved: Pathogenic mechanisms and treatment strategies
- 2,370 View
- 102 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Nurses and Nursing Students’ Recognition of Good Instruction
- Mina Park, Sujin Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(1):101-115. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.1.101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose: The purpose of this study was to identify and assess from nursing students and nurses in the clinical field what constitute good instruction, through the review of nursing students’ opinions and clinical field demands.
Methods: The study design was used Creswell’s exploratory sequential design by collecting and analyzing qualitative data obtained from interviews and then analysis of quantitative data. The participations were 79 seniors in nursing schools and 85 nurses with less than three years of clinical experience. The data were collected through individual interviews and analyzed based on Elo and Kyngäs’s content analysis method. The quantitative data were collected using the questionnaire developed based on qualitative results and analyzed by SPSS 23.0 program and Importance Performance Analysis (IPA).
Results: The results showed that IPA extracted seven items with high importance but low satisfaction: “nursing fads and trends,” “teacher-learner communication and reflection,” “materials used in clinical settings such as monitoring results and test results,” “special presentations by experienced practitioners,” “instruction assures learners’ comprehension,” “accurate and detailed evaluation standards” and “feedback on homework and exam.”
Conclusion The factors comprising good instruction were verified, and the necessity for additional efforts to improve high importance and low performance factors was noted. Therefore, this study can serve as a guide for nursing education facilities and educators in developing of a thorough education system with excellent instruction designed to achieve an ideal nursing education.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing Learning Flow of Nursing College Students in Online Classes
Soonyang JANG, Inju SEO
THE JOURNAL OF FISHERIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2025; 37(3): 578. CrossRef - Perceptions of Effective Nursing Handover Education
Ji Sun Lee
Nurse Educator.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Expectations and concerns about transitioning to face-to-face learning among Korean nursing students: A mixed methods study
Hyeongsuk Lee, Hye Jin Yoo, Chao Gu
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(1): e0296914. CrossRef - Educational needs of severe trauma treatment simulation based on mixed reality: Applying focus group interviews to military hospital nurses
Seon Mi Jang, Sinwoo Hwang, Yoomi Jung, Eunyoung Jung
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(4): 423. CrossRef - The Effect of the Education Applying Havruta's Method on Communication Competency, Critical Thinking Competency, and Self-leadership of Nursing Students
Jae-Hyun Ha, Hyun-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(3): 337. CrossRef - The mediating effect of self-regulated learning ability on the relationship between experience of good class and problem solving ability of nursing students
Ju Young Park, Chung Hee Woo
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(2): 185. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing Learning Flow of Nursing College Students in Online Classes
- 1,926 View
- 37 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Effects of Spouse-Participated Health Coaching for Male Office Workers with Cardiocerebrovascular Risk Factors
- So Hee Kang, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):748-759. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.748
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to examine the effect of spouses participating in health coaching on stage of the change, health behaviors, and physiological indicators among male office workers with cardiocerebrovascular disease (CVD) risk factors and compare the findings with trainers who provided health coaching only to workers.
Methods A quasi-experimental pretest-posttest design was used. Convenience sampling was used to recruit participants from a manufacturing research and development company in the city of Gyeonggi province. The health coaching program for the experimental group (n=26) included individual counseling sessions according to workers' stage of change, and provision of customized health information materials on CVD prevention to workers and their spouses for 12 weeks through mobile phone and email.
Results After 12 weeks of intervention, the total score for health behavior, and scores on the sub-areas of exercise and health checkups significantly improved in the experimental group, but there were no significant differences in the scores of stage of the change and physical indicators. The results of a paired t-test showed a significant decrease in the body mass index, abdominal circumference, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol and triglyceride values, and a significant increase in the high-density lipoprotein cholesterol value in the experimental group after the intervention.
Conclusion To improve the health of male workers with CVD risk factors in the workplace, sharing health information with their spouses has proven to be more effective than health coaching for only workers. Therefore, it is important to develop strategies to encourage spousal participation when planning workplace health education for changing health-related behaviors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun Jin Kim, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(1): 44. CrossRef - Effects of a Remote Physical Activity Improvement Program on Male Office Workers with Metabolic Syndrome in Their 30s and 40s with Sedentary Behavior: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Kyong Sil Park, Seon Young Hwang
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - An intervention study of a combined intervention of positioning and hand massage in patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation
Yun Kyeong Lee, Mihae Im, Haeryun Cho
Nursing Open.2023; 10(3): 1404. CrossRef
- Effects of a Health Partnership Program Using Mobile Health Application for Male Workers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 1,073 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of a Daily Life-Based Physical Activity Enhancement Program for Middle-Aged Women at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
- Kyung Ae Kim, Seon Young Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):113-125. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of a daily life-based physical activity enhancement program performed by middle-aged women at risk for cardiovascular disease.
Methods This study used a randomized control group pretest-posttest design. Middle-aged women aged 45 to 64 were recruited from two outpatient cardiology departments, and randomly assigned to an experimental group (n=28) and a control group (n=30). For the experimental group, after providing one-on-one counseling and education, we provided customized text messages to motivate them in daily life. To monitor the practice of physical activity, they also used an exercise diary and mobile pedometer for 12 weeks. Subjects' physical activities (MET-min/week) were measured using the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ). Their physiological data were obtained by blood tests using a portable analyzer, and the data were analyzed using the SPSS 21.0/WIN program.
Results There were significant differences in exercise self-efficacy, health behavior, IPAQ score, body fat, body muscle, and fasting blood sugar between the two groups. However, there were no significant differences in total cholesterol, hemoglobin A1c, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and waist-to-hip ratio.
Conclusion Strengthening physical activity in daily life without being limited by cost burden and time and space constraints. Therefore, it is essential to motivate middle-aged women at risk for cardiovascular disease to practice activities that are easily performed in their daily lives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and effectiveness of a mobile-based autonomy support program for the prevention of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged women
Miseon Seo, Eun-Young Jun, Hyunjin Oh
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Remote Physical Activity Improvement Program on Male Office Workers with Metabolic Syndrome in Their 30s and 40s with Sedentary Behavior: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Kyong Sil Park, Seon Young Hwang
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - Effects of Breathing Exercises Using Virtual Reality and Schroth Breathing Exercises on the Lung Function of Adults in Their 20s
Byung-Kon Kim, Wook-Jin Lee
The Journal of Korean Physical Therapy.2024; 36(2): 67. CrossRef - Effectiveness of physical activity monitors in adults: systematic review and meta-analysis
Rasmus Tolstrup Larsen, Vibeke Wagner, Christoffer Bruun Korfitsen, Camilla Keller, Carsten Bogh Juhl, Henning Langberg, Jan Christensen
BMJ.2022; : e068047. CrossRef - Trajectories of subjective health status among married postmenopausal women based on the ecological system theory: a longitudinal analysis using a latent growth model
Eun Jin Kim, Ju-Hee Nho
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(2): 123. CrossRef - Effect and mechanism of tai chi on blood pressure of patients with essential hypertension: a randomized controlled study
Bo LIN, Qiu JIN, Chunhua LIU, Wenhui ZHAO, Runyuan JI
The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of behaviour change interventions on changes in physical activity and anthropometrics in ambulatory hospital settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Stephen Barrett, Stephen Begg, Paul O’Halloran, Owen Howlett, Jack Lawrence, Michael Kingsley
International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors related to the Identification of Middle-Aged Women Who are Disadvantaged by Cardio-cerebrovascular Disease
Moon Jung Kang, Jee Seon Yi, Chang Seung Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(2): 185. CrossRef
- Development and effectiveness of a mobile-based autonomy support program for the prevention of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged women
- 2,377 View
- 47 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- A Comparative Study on Learning Outcomes according to the Integration Sequences of S-PBL in Nursing Students: Randomized Crossover Design
- So Young Yun, Ja Yun Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):92-103. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.92
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to compare the effects of simulation integrated with problem based learning (S-PBL) according to the sequences of problem-based learning (PBL) and high fidelity simulation training (HFS) on knowledge, clinical performance, clinical judgment, self-confidence, and satisfaction in fourth-grade nursing students.
Methods In this randomized crossover design study, four S-PBLs on medical-surgical nursing were applied alternatively to two randomly-assigned groups of 26 senior nursing students for 8 weeks. The collected data were analyzed using an independent t-test.
Results The method of administering PBL prior to HFS led to significantly higher scores on knowledge (t=2.28,
p =.025) as compared to the method of administering HFS prior to PBL. However, the latter method led to significantly higher scores on clinical performance (t=−6.49,p <.001) and clinical judgment (t=−4.71,p <.001) as compared to the method of administering PBL prior to HFS. There were no differences in the effect of the two methods on self-confidence (t=1.53,p =.128) and satisfaction (t=1.28,p =.202).Conclusion The integration sequences of S-PBL was associated with different learning outcomes. Therefore, when implementing S-PBL, it is necessary to consider the educational goal to executes an appropriate sequence of integration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of the Patient’s Severity Classification Competency Promotion Virtual Reality Program of Nursing Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic Period
Eunju Lee, Gyuli Baek, Yeonhui Hwang
Healthcare.2023; 11(8): 1122. CrossRef - The Effect of Mixed Reality-based HoloPatient in Problem-based Learning Contexts
Yun Kang, Insook Lee
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2023; 82: 101438. CrossRef - A Literature Review of Simulation-Based Nursing Education in Korea
Sumee Oh, Jungmin Park
Nursing Reports.2023; 13(1): 506. CrossRef - The Effects of Sequencing Strategies in Teaching Methods on Nursing Students’ Knowledge Acquisition and Knowledge Retention
Wei-Ting Lin, Ching-Yun Yu, Fan-Hao Chou, Shu-Yuan Lin, Bih-O. Lee
Healthcare.2022; 10(3): 430. CrossRef - Learning effects of virtual versus high-fidelity simulations in nursing students: a crossover comparison
SoMi Park, Hea Kung Hur, ChaeWeon Chung
BMC Nursing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The intervention effect of a nursing-media studies convergence problem-based learning (PBL) program to improve nurses’ public image: Changed perceptions of program participants and students attended a PBL presentation
Seungchul Yoo, Seungmi Kang, Jooyeon Ryu
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(1): 59. CrossRef - Comparison of Learning Transfer Using Simulation Problem-Based Learning and Demonstration: An Application of Papanicolaou Smear Nursing Education
Jeongim Lee, Hae Kyoung Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(4): 1765. CrossRef - Effects of S-PBL in Maternity Nursing Clinical Practicum on Learning Attitude, Metacognition, and Critical Thinking in Nursing Students: A Quasi-Experimental Design
Hae Kyoung Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(21): 7866. CrossRef - Comparison of Neck Pain, Shoulder Pain, and Comfort between Buckwheat and Latex Pillows
Ji-Soo Lee, Soo-Kyoung Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2019; 19(2): 107. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of the Patient’s Severity Classification Competency Promotion Virtual Reality Program of Nursing Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic Period
- 1,866 View
- 44 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Clinical Teaching Behavior Inventory (CTBI) for Nurse Preceptors in Korea
- Myun Sook Jung, Eun Gyung Kim, Se Young Kim, Jong Kyung Kim, Sun Ju You
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(5):526-537. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.5.526
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The aim of this study was to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of the Clinical Teaching Behavior Inventory (CTBI).
Methods The English CTBI-23 was translated into Korean with forward and backward translation. Survey data were collected from 280 nurses’ preceptors at five acute-care hospitals in Korea. Content validity, construct validity, and criterion-related validity were evaluated. Cronbach's α was used to assess reliability. SPSS 24.0 and AMOS 22.0 software was used for data analysis.
Results The CTBI Korean version consists of 22 items in six domains, including being committed to teaching, building a learning atmosphere, using appropriate teaching strategies, guiding inter-professional communication, providing feedback and evaluation, and showing concern and support. One of the items in the CTBI was excluded with a standardized factor loading of less than .05. The confirmatory factor analysis supported good fit and reliable scores for the Korean version of the CTBI model. A six-factor structure was validated (χ 2=366.30,
p <.001, CMIN/df=2.0, RMSEA=.06, RMR=.03, SRMR=.05, GFI=.90, IFI=.94, TLI=.92, CFI=.94). The criterion validity of the core competency evaluation tool for preceptors was .77 (p <.001). The Cronbach's α for the overall scale was .93, and the six subscales ranged from .72 to .85.Conclusion The Korean version CTBI-22 is a valid and reliable instrument for identifying the clinical teaching behaviors of preceptors in Korea. The CTBI-22 also could be used as a guide for the effective teaching behavior of preceptors, which can help new nurses adapt to the practicalities of nursing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing preceptor nurses' clinical teaching behavior: A cross-sectional study
Kyeong Hye Kim, Sujin Shin
Nurse Education Today.2025; 146: 106555. CrossRef - The development and validation of a nurse preceptor core competency scale: A culturally compatible methodological study
Tzu-Ting Chen, Chia-Chi Hsiao, Hsing-Ju Lu, Yea-Jyh Chen, Chang-Chiao Hung
Nurse Education Today.2025; 150: 106705. CrossRef - The Effect of Newly Graduated Nurses' Perceived Nursing Practice Readiness, Resilience, and Preceptors' Teaching Behavior on Turnover Intention
Jinhee Kim, Eunhee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(2): 167. CrossRef - Development and psychometric characteristics of military burnout scale
Shi Lei, Ren Fei, Xin Shen, Li Danni, Li Jing, Tian Ye, Wang Yuan
Medicine.2025; 104(44): e45551. CrossRef - Analysis of translation teaching skills in colleges and universities based on deep learning
Yan Liu, Shuhua Li, Dan Cui
Computers in Human Behavior.2024; 157: 108212. CrossRef - An analysis of the educational needs priorities for clinical nurse educators: Utilizing the Borich needs assessment and the locus for focus model
Sujin Shin, Eunmin Hong, Jiyoung Do, Miji Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(4): 405. CrossRef - The relationships between clinical teaching behaviour and transition shock in newly graduated nurses
Bei Yun, Qian Su, Xuchun Ye, Yuhan Wu, Lian Chen, Yamei Zuo, Jia Liu, Lin Han
Nursing Open.2023; 10(4): 2107. CrossRef - Content Analysis of Feedback Journals for New Nurses From Preceptor Nurses Using Text Network Analysis
Shin Hye Ahn, Hye Won Jeong
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2023; 41(10): 780. CrossRef - Exploring the Roles and Outcomes of Nurse Educators in Hospitals: A Scoping Review
Soyoung Kim, Sujin Shin, Inyoung Lee
Korean Medical Education Review.2023; 25(1): 55. CrossRef - Effects of Preceptors’ Clinical Teaching Behavior on the Field Adaptation of New Graduate Nurses: Mediating Effects of Self-Leadership and Resilience
Eunjung Kim, Eungyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(5): 577. CrossRef - Effect of Preceptors' Teaching Behavior on New Graduate Nurses' Intention to Stay: The Mediating Effect of Resilience and Organizational Socialization
Eungyung Kim, Eunha Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(1): 57. CrossRef - Development and Preliminary Evaluation of the Effects of a Preceptor Reflective Practice Program: A Mixed-Method Research
Heui-Seon Kim, Hye-Won Jeong, Deok Ju, Jung-A Lee, Shin-Hye Ahn
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(21): 13755. CrossRef - Types of Role Perception of Preceptors for New Nurses: A Q Methodology Approach
Sukyung Kim, Byoungsook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(3): 204. CrossRef - Effect of Nurses’ Preceptorship Experience in Educating New Graduate Nurses and Preceptor Training Courses on Clinical Teaching Behavior
Kyung Jin Hong, Hyo-Jeong Yoon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(3): 975. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Menorah Park Engagement Scale (K-MPES) for Patients with Dementia
Ye-Na Lee, Eunhye Jeong, Sung Ok Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(2): 200. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Apathy Evaluation Scale Short form for Patients with Dementia
Young-Rim Choi, Ye-Na Lee, Eunhye Jeong, Sung Ok Chang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(2): 164. CrossRef
- Factors influencing preceptor nurses' clinical teaching behavior: A cross-sectional study
- 2,496 View
- 114 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref

- Improving Empathy in Nursing Students: A Comparative Longitudinal Study of Two Curricula
- Celale Tangul Ozcan, Emine Öksüz, Fahriye Oflaz
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(5):497-505. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.497
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to examine changes of empathy levels of nursing student in two different curricula structures, one called “traditional” and the other called “integrated” curricula. The study was a longitudinal design to follow a cohort of nursing students to examine the magnitude of changes in empathy in their education years.
Methods The study was conducted in a public school of nursing giving a baccalaureate degree, which had a fundamental change in their curricula. In all, 81 students from the traditional curricula and 66 students from the integrated curricula completed the study, and data from a total of 147 students were analyzed between 2003 and 2008. The Empathic Communication Skills Scale and the Empathic Tendency Scale were given to the students in the beginning of their freshman year and at the end of the fourth year just before graduation.
Results Although both of the curricula were seemed effective at improving empathic skills of students, especially the scores of students who completed the integrated curricula were higher than the scores of the other group attending the traditional curricula (
p <.05). However, the empathic tendency scores of students in both curricula decreased at the end of fourth year.Conclusion Although undergraduate nursing curricula either traditional or integrated improved empathic skills, it seemed that integrated curricula were more effective than traditional curricula in increasing empathic skills. The more hours and more experiential methods contributed to improved empathy. The decrease in empathic tendency requires further attention of educators and nurse managers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Empathy Scores and Curriculum Integration at Two Different Levels: A Cross-Sectional Study of Final-Year Medical and Dental Students
Amna Faisal, Saira Akhlaq, Naveed Bhatti
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - An Immersive Virtual Reality Simulation Scenario to Improve Empathy in Nursing Students
Rosemary Collier, Rosa Darling, Karen Browne
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Divergent perspectives: A cross-sectional study unveiling disparities in cancer patients' and oncology nurses' perceptions on communication and empathy
Che-Ming Chang, Jhen-Jhen Li, In-Fun Li, Yun-Hsiang Lee
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 76: 102877. CrossRef - The impact of an empathy education programme on empathy, communication skills and emotional competency in nursing students: A quasi-experimental study
Eun Jeong Ko, Eun Ji Seo, Youngjin Lee, Jiyeon Ha, Suno Kim, Jin-Hee Park
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 85: 104364. CrossRef - Empathy and Its Predictive Factors in Undergraduate Health Professional Students: A Longitudinal Cohort Study
Valeria Caponnetto, Elona Gaxhja, Ilda Taka, Elona Prifti, Vittorio Masotta, Ilaria Paoli, Loreto Lancia, Angelo Dante, Cristina Petrucci
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(9): 316. CrossRef - Empathy in Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
Juniarta, Ni Gusti Ayu Eka, Yenni Ferawati Sitanggang
Journal of Holistic Nursing.2024; 42(2_suppl): S59. CrossRef - Nursing Students' Experiences of Empathy in a Virtual Reality Simulation Game
Katri Mattsson, Elina Haavisto, Satu Jumisko-Pyykkö, Jaana-Maija Koivisto
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2024; 42(7): 537. CrossRef - Scale of self-perceived listening, empathy, and presence (LEP) abilities in associate degree nursing students for aging care
Li Chen Weng, Ya-Lie Ku
Geriatric Nursing.2024; 60: 265. CrossRef - Levels and predictors of empathy, self-awareness, and perceived stress among nursing students: a cross sectional study
Shaher H. Hamaideh, Sawsan Abuhammad, Abdallah Abu Khait, Hanan Al-Modallal, Ayman M Hamdan-Mansour, Rami Masa’deh, Saleem Alrjoub
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Rapid Scoping Review: Empathy in Health Sciences Curriculum
Renee Robinson, Kelleen Meluski, Tracy Hellem, Travis Hedwig, Natalie Hansen, Jennifer Adams, Mary Nies, Krista Salazar
Healthcare.2023; 11(10): 1429. CrossRef - A stenography of empathy: Toward a consensual model of the empathic process
J.A. Nasello, J.-M. Triffaux
L'Encéphale.2023; 49(4): 399. CrossRef - Empathy levels among health professional students at a large midwestern public university - a cross-sectional study
Kelsey Wenger, Lauren Reist, Andrea Achenbach, Kimberly Dukes, Michelle Fravel, Laura Knockel, Francis Kuehnle, Jeffrey Reist, Manish Suneja, Chandler Pendleton, Xian Jin Xie, Leonardo Marchini
BMC Medical Education.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Debriefing for Meaningful Learning (DML) Combined with Empathy Map on Prelicensure Nursing Students’ Competency: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Cheng-Yi Huang, Chiu-Hsiang Lee, Pin-Hsi Lin, Wei-Ju Lu, Ruei-Jnen Lin, Ching-Yen Hung, Pei-Ching LI, Chu-Hua Chung
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2023; 81: 101427. CrossRef - The effect of affective learning on alexithymia, empathy, and attitude toward disabled persons in nursing students: A randomized controlled study
Berna Dincer, Demet Inangil
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2022; 58(2): 813. CrossRef - Humanistic caring ability of midwifery students in China and its associated factors: A multi-centre cross-sectional study
Yarui Wang, Xi Zhang, Qinqin Xie, Hua Zhou, Li Cheng
Nurse Education Today.2022; 111: 105276. CrossRef - Teaching empathy in healthcare: an integrative review
José Antonio Cordero da Silva, Cristiane Guerreiro Pereira Abdul Massih, Daniele Azevedo Valente, Danielle Ferreira de Souza, Magda Regiane Lima de Carvalho Monteiro, Raiza Morais Rodrigues
Revista Bioética.2022; 30(4): 715. CrossRef - Enseñar empatía en salud: una revisión integradora
José Antonio Cordero da Silva, Cristiane Guerreiro Pereira Abdul Massih, Daniele Azevedo Valente, Danielle Ferreira de Souza, Magda Regiane Lima de Carvalho Monteiro, Raiza Morais Rodrigues
Revista Bioética.2022; 30(4): 715. CrossRef - Ensino da empatia em saúde: revisão integrativa
José Antonio Cordero da Silva, Cristiane Guerreiro Pereira Abdul Massih, Daniele Azevedo Valente, Danielle Ferreira de Souza, Magda Regiane Lima de Carvalho Monteiro, Raiza Morais Rodrigues
Revista Bioética.2022; 30(4): 715. CrossRef - Turkish adaptation of the Multidimensional Emotional Empathy Scale: A validity and reliability study
Nuray Turan, Hanife Durgun, Hatice Kaya, Türkinaz Aştı
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2021; 57(2): 455. CrossRef - Determining the effect of an intercultural nursing course on empathic skill and intercultural sensitivity levels: An intervention study
Nurhan Çingöl, Mehmet Karakaş, Ebru Çelebi, Seher Zengin
Nurse Education Today.2021; 99: 104782. CrossRef - A Multidisciplinary Scoping Review of Literature Focused on Compassion, Empathy, Emotional Intelligence, or Mindfulness Behaviors and Working with the Public
JJ Pionke, Rebecca Graham
Journal of Library Administration.2021; 61(2): 147. CrossRef - The Effect of Nursing Communication Training on Empathy and Communication Skills of Nursing Students: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Ayfer ÖZTÜRK
OPUS Uluslararası Toplum Araştırmaları Dergisi.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Empathy amongst dental students: An institutional cross‐sectional survey in Poland and Croatia
Ivana Brekalo Prso, Katarzyna Mocny‐Pachońska, Agata Trzcionka, Sonja Pezelj‐Ribaric, Ema Paljevic, Marta Tanasiewicz, Romana Persic Bukmir
European Journal of Dental Education.2020; 24(4): 687. CrossRef - The effect of structured empathy education on empathy competency of undergraduate nursing interns: A quasi-experimental study
Chao Yang, Ya-Li Zhu, Bi-Ying Xia, Ya-Wei Li, Jun Zhang
Nurse Education Today.2020; 85: 104296. CrossRef
- Empathy Scores and Curriculum Integration at Two Different Levels: A Cross-Sectional Study of Final-Year Medical and Dental Students
- 1,756 View
- 19 Download
- 24 Crossref

- Patient Safety Teaching Competency of Nursing Faculty
- Shinae Ahn, Nam-Ju Lee, Haena Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):720-730. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.720
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate patient safety teaching competency of nursing faculty and the extent of teaching patient safety topics in the nursing curriculum.
Methods A national survey was conducted with full-time nursing faculty in 4-year nursing schools. Regional quota sampling method was used. An online survey was sent to 1,028 nursing faculty and 207 of them were completed. Among the 207, we analyzed data from 184 participants. The revised Health Professional Education in Patient Safety Survey was used. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, independent t-test, one-way ANOVA, Pearson's correlation analysis, and multiple linear regression analyses.
Results The faculty's self-confidence was lower than their perceived importance of patient safety education. The mean score of teaching patient safety was 3.52±0.67 out of 5, and the contents were mostly delivered through lectures. The extent of faculty's teaching varied depending on faculty's clinical career, teaching subjects, participation in practicum courses, and previous experience of patient safety education. The significant predictors of the extent of teaching patient safety were the faculty's self-confidence in teaching patient safety (β=.39) during clinical practicum, their perceived importance of patient safety education during lectures (β=.23), and the teaching subject (β=.15).
Conclusion To enhance the competency of nursing faculty for effective patient safety education, a patient safety education program tailored to faculty characteristics should be developed and continuously provided for faculty. In addition, it is necessary to improve patient safety curriculum, strengthen clinical and school linkages, and utilize various education methods in patient safety education.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing patient safety competency in baccalaureate nursing students: A descriptive cross-sectional study
Shinae Ahn
Nurse Education Today.2025; 145: 106498. CrossRef - Transcultural Adaptation and Psychometric Properties of the Persian Version of the Nursing Student Competence Scale (NSCS)
Amir Jalali, Fatemeh Chavoshani, Raheleh Rasad, Niloufar Darvishi, Fatemeh Merati Fashi, Mahbod Khodamorovati, Khalil Moradi
SAGE Open Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing the effects of patient safety education using design thinking and case based learning on nursing students’ competence and professional socialization: A quasi-experimental design
Seongmi Moon, Soo Jung Chang
Heliyon.2024; 10(9): e29942. CrossRef - Analysis of the innovative development path of university civic education based on the era of big data
Xingang Chen, Ye Dong
Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of flipped learning and gamification on nursing students’ patient safety education: A mixed method study
Soo Jung Chang, Geun Myun Kim, Jeong Ah Kim
Heliyon.2024; 10(8): e29538. CrossRef - Experiences of Patient Safety Education and Factors Affecting the Willingness to Participate in Patient Safety in Undergraduate Nursing Students in South Korea
Sun-Hwa Shin, On-Jeon Baek
Healthcare.2023; 12(1): 54. CrossRef - Evaluating a patient safety course for undergraduate nursing students: A quasi-experimental study
Seung Eun Lee, V. Susan Dahinten
Collegian.2023; 30(1): 75. CrossRef - Continuing professional development among social‐ and health‐care educators
Minna Koskimäki, Marja‐Leena Lähteenmäki, Kristina Mikkonen, Maria Kääriäinen, Camilla Koskinen, Hanne Mäki‐Hakola, Tuulikki Sjögren, Meeri Koivula
Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences.2021; 35(2): 668. CrossRef - Nursing Students’ Informal Learning of Patient Safety Management Activities
Nam-Yi Kim
Healthcare.2021; 9(12): 1635. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Self-Efficacy Scale for Nursing Educators’ Role in Sri Lanka
Shyamamala S. Weerasekara, Jina Oh, Haeryun Cho, Mihae Im
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(15): 7773. CrossRef - Developing an integrated curriculum for patient safety in an undergraduate nursing program: a case study
Yoonjung Ji, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Taewha Lee, Mona Choi, Hyejung Lee, Sanghee Kim, Hyunok Kim Do, Sunah Kim, Sang Hui Chu, Jeongok Park, Young Man Kim, Soyoon Park
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of an Informatics System for Nursing Faculty to Improve Patient Safety Teaching Competency
Nam-Ju Lee, Shinae Ahn, Miseon Lee, Haena Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 488. CrossRef - Patient safety education in pre‐registration nursing programmes in South Korea
S. E. Lee, V. Susan Dathinten, H. Do
International Nursing Review.2020; 67(4): 512. CrossRef
- Factors influencing patient safety competency in baccalaureate nursing students: A descriptive cross-sectional study
- 3,864 View
- 79 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

- Development and Effects of Social Learning Theory Based Eye-Health Program for Preschoolers
- Sunghwa Lee, Haejung Lee, Hyungsik Seo, Jaeho Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(4):407-418. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.4.407
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop an eye-health program based on social learning theory (EPST) of preschoolers and evaluate its effectiveness.
Methods A nonequivalent control group pre-post test design was utilized and 141 six-year-old preschoolers and their parents participated (experimental group=69, control group=72) in the study. The EPST in this study included eye-health education and eye exercises. Attention, memory, replay, motivation, reinforcement, and self-efficacy were used as interventional strategies. To examine the effectiveness of EPST, proficiency in eye-health activities, refractive power, and visual acuity were measured before and after the intervention. Data were analyzed with SPSS WIN 21.0 using the Shapiro-Wilk test, χ 2-test, Mann-Whitney U test and Wilcoxon signed rank test.
Results Following the intervention, eye-health activities, refractive power, and visual acuity significantly improved in the experimental group compared to the control group.
Conclusion The results of this study suggest that EPST is effective in improving eye-health activities, refractive power, and visual acuity in preschoolers, and its wider implementation in educational institutions will promise improved eye-health among preschoolers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Social Learning Theory Based Ecological Footprint Awareness Program in 60-72-Month-Old Children: A Randomized Controlled Study
Ayşe Sezer Balci, Kerime Öğüt Düzen, Vildan Yalçın
Child Indicators Research.2025; 18(1): 199. CrossRef - Study of Visual Acuity and Refractive Errors in Multicultural Schoolchildren in Chungcheongnam-do: Focusing on Students Requiring Financial Assistance
Se-Jin Kim, Hyojin Kim
Journal of Korean Ophthalmic Optics Society.2025; 30(2): 83. CrossRef - Eye health behaviors and parental influencing factors among preschool children in Korea: a cross-sectional study
Il Tae Park
Child Health Nursing Research.2025; 31(3): 144. CrossRef - A qualitative content analysis based on an extended parallel process model study of daycare center teacher behaviors concerning the eye health of preschool children
Il Tae Park, Gi Joong Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2024; 30(3): 222. CrossRef - Social cognitive theory-based health promotion in primary care practice: A scoping review
Kazi Faria Islam, Abdul Awal, Hoimonty Mazumder, Ummi Rukaiya Munni, Koushik Majumder, Kohinoor Afroz, Mustari Nailah Tabassum, M. Mahbub Hossain
Heliyon.2023; 9(4): e14889. CrossRef - Relationship between decreased visual acuity and physical activity time in school age children
Hanna Lee, Jeong-Won Han
Frontiers of Nursing.2021; 8(2): 113. CrossRef - Developing and Evaluating an Educational Program for Respiratory Infection Prevention among Rural Elderly Residents in South Korea
Jin Soon Kim, Ji Hye Choi, Myung Soon Kwon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(9): 3057. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Social Learning Theory Based Ecological Footprint Awareness Program in 60-72-Month-Old Children: A Randomized Controlled Study
- 1,870 View
- 24 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Development and Effects of a Coping Skill Training Program for Caregivers in Feeding Difficulty of Older Adults with Dementia in Long-Term Care Facilities
- Hyun Hwa Hong, Mee Ock Gu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):167-181. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.167
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose We developed and tested the effects of a coping skill training program for caregivers in feeding difficulty among older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The subjects comprised 34 caregivers (experimental group: 17, control group: 17) and 40 older adults with dementia (experimental group: 20, control group: 20). The developed program was delivered in 4-hour sessions over 6 weeks (including 2 weeks of lectures and lab practice on feeding difficulty coping skills, and 4 weeks of field practice). Data were collected before, immediately after, and 4 weeks after the program (January 3 to April 6, 2016). The data were analyzed using t-test and repeated measures ANOVA using SPSS/WIN 20.0.
Results Compared to their counterparts in the control group, caregivers in the experimental group showed a significantly greater improvement in feeding knowledge and feeding behavior, while older adults with dementia showed greater improvements in feeding difficulty and Body Mass Index.
Conclusion The study findings indicate that this coping skill training program for caregivers in feeding difficulty is an effective intervention for older adults with dementia in long-term care facilities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influencing factors of depressive and anxiety symptoms among caregivers of Alzheimer's disease patients: A cross-sectional study
Chengfei Duan, Mo Zhu, Xia Li, Ling Yue
Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.2026; 109(3): 1264. CrossRef - Mealtime Support by Direct Care Workers in Long‐Term Care Facilities: Secondary Behavioural Analysis of Videos
Eunju Choi, Leeho Yoo, Soogyung Shin, Dukyoo Jung
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Feasibility of a nurse-led online video intervention for mealtime assistance in dementia care: a quasi-experimental mixed-methods study
Dukyoo Jung, Leeho Yoo, Soogyung Shin, Sukyung Byeon, Hyein Seo, Eunju Choi
BMC Geriatrics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting Mealtime Difficulties in Older Adults with Dementia Living in Long-Term Care Facilities: A Multilevel Model Analysis
Dukyoo Jung, Jennie C. De Gagne, Hyesoon Lee, Leeho Yoo, Jisung Park, Eunju Choi, Yonggang Zhang
Journal of Nursing Management.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of Case-Based Small-Group Learning on Care Workers’ Emergency Coping Abilities
Soon-Ok Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(21): 11458. CrossRef - Eating Difficulties among Older Adults with Dementia in South Korean Long-Term Care Facilities: A Scoping Review
Dukyoo Jung, Kyuri Lee, Eunju Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 470. CrossRef Feasibility of a Mobile Meal Assistance Program for Direct Care Workers in Long-Term Care Facilities in South Korea
Dukyoo Jung, Jennie C De Gagne, Minkyung Lee, Hyesoon Lee, Kyuri Lee, Eunju Choi, Juyoun Chung
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2020; Volume 15: 2019. CrossRef- Informal dementia caregivers’ experiences and perceptions about mealtime care: A qualitative evidence synthesis
Yijing Li, Dan Sun, Xu Zhang, Huanhuan Li, Yingnan Zhao, Dongfei Ma, Zehui Li, Jiao Sun
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2020; 76(12): 3317. CrossRef
- Influencing factors of depressive and anxiety symptoms among caregivers of Alzheimer's disease patients: A cross-sectional study
- 1,075 View
- 19 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Development and Effects of a Children's Sex Education Program for the Parents of Lower Elementary Grade Students
- Eun Mi Lee, Hyunlye Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):222-232. Published online April 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to develop a children's sex education program for the parents of lower elementary grade students and to evaluate its effects on sexual knowledge, gender role attitude, parent efficacy for child's sex education, and marital consistency.
Methods A quasi-experimental with a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The participants were 29 couples (58 parents, experimental group=28, control group=30) from G city. The 5-week (5-session) program was developed based on ‘A theory of protection: parents as sex educators’ and used the case-based small group learning method. Data were collected during July and August 2015. The characteristics of the program developed in the present study were a theoretical-based, client-centered, multi-method.
Results After the intervention, the experimental group showed a significant improvement in sexual knowledge, gender role attitudes, parent efficacy for child's sex education, and marital consistency, compared to the control group. The effect sizes of the program were .64 (knowledge), .65 (gender role attitudes), and .68 (parent efficacy).
Conclusion The results of this study provided implications for the parents as effective sex educator and the role expansion of school health nurses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Parental Attitude Towards Sex Education: A Study of Demographic and Socio-Cultural Determinants in Rural Nigeria
Abdullateef Raji, Lanre Abdul-Rasheed Sulaiman, Moshood Issa, Abubakar Yunusa Muhammed, Ridwan Olabisi Yusuff, Salihu Zakariyyah Abdulbaqi, Sunday Joseph Akor
Sexuality Research and Social Policy.2026; 23(1): 217. CrossRef - A study on the reliability and validity of the Korean version of the parenting outcome expectancy scale for parents of elementary school students
Yoonjung Kim, Jungmin Lee, Ratchneewan Ross
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of parents in hygienic and sexual education of children and adolescents
NO Demchenkov, ED Krasilnikova, NI Sheina, VV Korolik
Российский вестник гигиены.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Children’s Sexual Health Education Program on Knowledge and Attitude of Primary School Health Care Providers
Zahra Barimani Aboksari, Jila Ganji, Nouraddin Mousavinasab, Soghra Khani
Journal of Child Sexual Abuse.2021; 30(5): 563. CrossRef - Comparison of the Effects of Sex Education with Two Methods of Educational Pack and Group Discussion on Awareness in Mothers of Pre-school Children
F Alaee karahroudy, Z Aryaeefar, S Maleki
Journal of Health and Care.2021; 22(4): 339. CrossRef - The significance of understanding psychosexual development and sexuality education for Vietnamese adolescents
Nguyen Thi Lan, Nguyen Huy Huong
International Journal of Research Studies in Education.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Parental Attitude Towards Sex Education: A Study of Demographic and Socio-Cultural Determinants in Rural Nigeria
- 2,520 View
- 27 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Effects of Psychoeducational Intervention for Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):143-163. Published online April 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material Purpose This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis designed to investigate effects of psychoeducational intervention for cancer survivors.
Methods Ten databases were searched. Two reviewers independently performed the selection of the studies, data extraction and assessment. The risk of bias was assessed using Cochrane Collaboration's tool. To estimate the effect size, meta-analysis of the studies was performed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis and RevMan programs.
Results Of 18,781 publications identified, 35 met inclusion criteria, and 25 studies were used to estimate effect size of psychoeducational intervention. Effect sizes (standardized mean difference [SMD]) were heterogeneous and random effects models were used in the analyses. Psychoeducational intervention was effective for quality of life (n=2,410, ES=0.23; 95% CI: 0.09~0.37), coping and self-efficacy (n=179, ES=0.68; 95% CI: 0.26~1.11), anxiety (n=1,786, ES=-0.26; 95% CI: -0.37~-0.15), depression (n=1,910, ES=-0.28; 95% CI: -0.37~-0.18), and psychological distress (n=2,242, ES=-0.31; 95% CI: -0.46~-0.17). Subgroup analysis showed that counseling was the most effective intervention for quality of life, and behavioral therapy was an effective intervention for all positive and negative outcomes. Publication bias was not detected except for psychological distress.
Conclusion Psychoeducational intervention appears to be effective in improving quality of life and coping and self-efficacy, and it is effective in reducing psychological symptoms in cancer survivors. Behavioral therapy, especially, is commonly effective in improving psychosocial outcomes. However, low-quality evidence, variability in the designs of existing studies, and publication bias suggest that additional high-quality trials should be conducted in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with post-treatment smoking among a diverse sample of cancer survivors in the US
Safa Elkefi, Corina T. Lelutiu-Weinberger, Jean-Marie Bruzzese, Alicia K. Matthews
Discover Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Group‐Based Support Interventions for Adolescents and Young Adults With Lymphoma: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Dalnim Cho, Sairah Ahmed, Stella Snyder, Juliet Kroll, Minxing Chen, Michael Roth, Kathrin Milbury
Psycho-Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Mind Health of Persons with Cancer: Psycho-Oncology and Nursing
Park Eun Young
Journal of Clinical Psychooncology.2025; 11(1): 24. CrossRef - Psychosocial interventions for people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and motor neuron disease and their caregivers: a scoping review
Juyeon Oh, Jiwon An, Kyongok Park, Youngok Park
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of telemedicine psychoeducational interventions for adults with non‐oncological chronic disease: A systematic review
Carmen Sánchez‐Gutiérrez, Eugenia Gil‐García, Adriana Rivera‐Sequeiros, José M. López‐Millán
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2022; 78(5): 1267. CrossRef - Cancer-Related Psychological Distress in Lymphoma Survivor: An Italian Cross-Sectional Study
Giulia Agostinelli, Barbara Muzzatti, Samantha Serpentini, Michele Spina, Maria Antonietta Annunziata
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the Advanced Practice Nurse-Led Psychoeducational Program for Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hye Kyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 245. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Led Intervention Programs Based on Goal Attainment Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 699. CrossRef - Effects of Psychosocial Interventions on Physical Function and Depression in Stroke Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jinhyang YANG, Changwan KANG, Hye-Won PARK, Euna PARK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(2): 396. CrossRef - Development of A Nurse-Led Educational Intervention Program in Managing the Nutrition Impact Symptom Cluster in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma following the Medical Research Council Framework
Wenli Xiao, Carmen W Chan, Jinnan Xiao, Cho L Wong, Ka M Chow
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 8(6): 653. CrossRef - Chemotherapy Education and Support: A Model for Use in the Ambulatory Care Setting
Terri Jabaley, Patricia Rizzo, Nina Grenon, Clare Sullivan, Janet Bagley, Maritza Nassif, Renee Siegel, Meghan Underhill-Blazey
Clinical Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 24(4): E43. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for Chronic Pain Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Hee-Sook Kang, Sung-Dong Hwang, Sang-Eun Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(3): 271. CrossRef
- Factors associated with post-treatment smoking among a diverse sample of cancer survivors in the US
- 2,159 View
- 37 Download
- 12 Crossref

- A Study on the Current Status of the Curriculum Operation of the Basic Medical Sciences in Nursing Education
- Myoung Ae Choi, Gi Soo Shin
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(4):975-987. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.4.975
-
 Abstract
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to investigate the current status of curriculum operation of the basic medical sciences in nursing education at college of nursing, department of nursing and junior college of nursing, ultimately to provide the basic data to provide a curriculum of basic medical science in nursing education. 78 professors who were in charge of basic medical science at 22 colleges of nursing and department of nursing, and 20 junior colleges of nursing responded the questionnaire consisted of 22 question items about the status of objectives, lectures, laboratory practice and characteristics of professors, and mailed to the author. The findings of this study were as follows : 1. The subjects of basic medical science were identified as physiology, anatomy, biochemistry, pathology, microbiology, pharmacology in the most colleges of nursing and junior college of nursing. 2. College of nursing and department of nursing(9.1%) and 19 junior colleges of nursing(95%) did not open biochemistry, 1 college of nursing and department of nursing(5%) did not open pathology and pharmacology. 2 Junior colleges of nursing(10%) did not open pharmacology, 1 junior college of nursing(5%) did not open pathology, the other 1 junior college of nursing did not open microbiology. 2. Credits of the subjects were ranged from 1 to 4. Lecture hours of one semester of physiology at school of nursing and junior college of nursing was average 103.6 and average 102.67, that of anatomy was average 127.1 and average 98, that of microbiology was average 109.7 and average 86.33, that of biochemistry was average 105, that of pathology was average 91 and average 94, that of pharmacology was average 86 and average 85.75. 3. Most of schools used 1 textbook for lectures, 3 school of nursing and department of nursing recommended references without using textbook, while all 36 junior colleges of nursing used textbooks. 4. 5 among 10 schools of nursing and department of nursing had a laboratory practice in physiology, 4 among 7 schools in anatomy, 4 among 6 schools in biochemistry, 2 among 6 schools in biochemistry, 2 among 6 schools in pathology, 5 among 6 schools in microbiology. Not all the schools had a laboratory practice in pharmacology. 4 among 9 junior colleges of nursing had a laboratory practice in physiology. 1 among 4 schools in anatomy, 2 among 7 schools in microbiology. Not all the junior college of nursing had a laboratory practice in pathology and pharmacology. 11 among 20 colleges of nursing and department of nursing, 4 among 7 junior schools of nursing used a textbook of laboratory practice. 5. All the subjects as school of nursing and department of nursing responded that content of lectures and laboratory practices of basic medical science should be different from that of medical education, 34 junior schools of nursing responded that content of lecture of basic medical science in nursing education should be different from that of medical education. 33 junior schools of nursing responded that content of practice of basic medical science in nursing education should be different from that of medical education. 6. The final degree of 25 professors who were in charge of basic medical science were doctors of medicine, that of 5 professors were masters of medicine, that of 5 were doctor of pharmacology, that of 2 were a master of pharmacology, that of 1 was physical science. The final degree of 8 professors who were in charge og basic medical science were masters of medicine, 7 doctors of medicine, 4 masters of nursing science, 4 masters of pharmacology, 2 doctors of nursing, 2 doctors of physical science, 2 doctors of pharmacology and 1 master of public health. 9 full professors, 13 associate professors, 11 assistant professors, 3 full time instructors, and 6 part time instructors were in charge of basic medical science at college of nursing and department of nursing, 20 part time instructors, 8 associate professors, 6 assistant professors, and 2 full professors were in charge of has basic medical science at junior college of nursing. Based on these results, curriculum of basic medical science in nursing education should be reviewed deeply based on nursing model.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Establishment of biological nursing science in Korea
Myoung-Ae Choe
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - The Relevance between Pathophysiological Subject and Examination Workbook Items for National Nurse Licensure Examination in South Korea and the United States
Myung Sook Park, Hee Jung Choi, Youn Jung Kim, Hee Kyung Chang, Sun Ju Chang, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2016; 18(4): 264. CrossRef
- Establishment of biological nursing science in Korea
- 739 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- An Effect of Self: Care Education and Level of Resourcefulness on Active Coping in Patients with Chemotherapy
- Soon Rim Suh
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(3):639-647. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.3.639
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identify how internal and external coping resources influenced active coping in the process of stress-coping. The model was established theoretically by comparing and integrating the following theories : Stress-Coping, Self-Care, and Resourcefulness. The subjects consisted of sixty eight patients undergoing chemotherapy(experimental group 34, control group 34) at two general hospitals from January to July, 1995, The results were as follows : After self-care education, the active coping score of the experimental group was significantly higher than that of the control group. The active coping score of the high resourcefulness group was significantly higher than that of the low resourcefulness group. The interaction effect between self-care education and resourcfulness was not significant statistically. Specifically as to such scores of seeking social support, problem-oriented strategy and self care behavior, there were significantly higher in the experimental group and high resourcefulness group than in each of the other groups. Considering them both, self-care education and resourcefulness are effective nursing strategies to promote active coping including self-care. Consequently, the synthesis and testing of theories of stress-coping, self-care, and resoucefulness in this study are mostly proven to enhance the explanation and prediction of the change of active coping including self-care. Therefore the result of this study will contribute in the development of practice theory of nursing. A further study is necessary to reevaluate the interaction effect between self-care education and resourcefulness and to identify the difference between resourcefulness and self-efficacy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Self-Efficacy Promotion Program on Self-Efficacy, Self-Care Behavior, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy
Hea-Kyoung Ko, Geum Ja Park
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2011; 11(2): 136. CrossRef
- Effects of Self-Efficacy Promotion Program on Self-Efficacy, Self-Care Behavior, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy
- 600 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Educational Needs Of Mothers of Nephrotic Syndrome Patients and the Degree of Nurse's Educational Performances Perceived by Mothers
- Mi Hae Sung, Seung Nam Paik
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(2):303-314. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.2.303
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This is descriptive study conducted to identify educational needs of mothers of nephrotic syndrome patients and the degree of nurses' educational performances perceived by mothers who look after mainly nephrotic syndrome patients. The study subjects were composed of 74 mothers of nephrotic syndrome patients whose children were hospitalized in 2 Pediatric wards of University Hospital in Seoul and 1 in Pusan from Jure in 1996 to January in 1997. A questionnaire for this study was item Kikert type 5 point scale, developed on the basis of previous literature and researcher's clinical experience and the reliability of the used instruments was q=.97. The data analysis was done by SAS. t-test, and ANOVA were done to determine the effect of general characteristics of subjects on their educational needs. Pearson correlation was done to measure relations between general characteristics of subjects and their educational needs and Stepwise Multiple Regression was done to test a variable affecting educational needs. The results were as follows. 1. Mean score of educational needs of subjects was 137.06(Maximum 176). The score of the educational needs of home care was the highest, but the question numbers(of that category) are smaller than others. So, the educational need of the diagnosis and treatment was regarded as the highest in contents. 2. The mean score of nurses' educational performances was very low, 74.91(Maximum 176). Nurse's educational performances score in the diagnosis and treatment of the disease ranked as the highest Burt that score in the care during hoapitalization was the highest in contents as the educational needs was. 3. The number of children excepting the patient(r2=.215289, P=.006)and the age of patient(r2=.23770, P=.001) were emerged as important variables affecting the degree of mother's educational need.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Educational Needs for Prevention of Cell Phone Addiction in Korean Adolescents
Hyun Young Koo, Hyun Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(4): 304. CrossRef
- Educational Needs for Prevention of Cell Phone Addiction in Korean Adolescents
- 802 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Sex Knowledge and Need for Sex Education among University Students
- Young Whee Lee, Mi Ra Park, Mi Sook Song, Jin Hee Too, Soon Nam Choi, Yoo Mi Han, Yoon Jung Hwang
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(1):26-35. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.1.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was done to examine knowledge about. and need for sex education among university students in Korea. This Study design was descriptive survey design. The data were collected from 540 university students from June 10 to June 30, 1996, using questionnaires developed by the authors. The results are as follows : Those who had sex education had higher scores in sex knowledge than those had not had sex education. The average score for sex knowledge was 71.9 of a maximum score of 100. Knowledge of sexually transmitted disease was scored highest of 79.8, and knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of the reproductive system was scored lowest at 60.9. The subjects who answered 'yes' about the necessity of sex education numbered 529(98%) and the most important reason given for needing sex education was to cope well with physical and psychological developments. Regarding the content of sex education, a choice of relevant contraceptive methods was given the highest rating. Anatomy and physiology of reproductive system was the least chaser subject as the first priority among five topics. Yet, sex education for university students should include anatomy and physiology of the reproductive system, considering the low level of knowledge on this topic in the subjects of this study and its importance as a part of sex education.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Female College Students’ Sexual Intercourse and Knowledge: A Comparison of Two Cohorts in 2008 and 2018
Gye-Sook Yoo, Na-Hwi Ki, Min-Jeong Kim, Da-Yeon Yang, Ji-Eun Yoon
Korean Journal of family welfare.2019; 24(1): 37. CrossRef
- Female College Students’ Sexual Intercourse and Knowledge: A Comparison of Two Cohorts in 2008 and 2018
- 820 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of the Education on AIDS for Korean Healthe Care Workers
- Soon Bok Chang, C W Lee
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(1):201-211. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.1.201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was an evaluation study of AIDS education program. The purpose of this study was to clarify the education effects on AIDS for health care workers to develop abetter next education program. This study was done by self reporting with a 67 items of structured questionnaire by 431 health care workers included doctors, nurses, laboratory technicians, and health educators. Data were collected at the time of completion of each AIDS education with the help of education program manager. Both the AIDS related knowledge score and the acceptance attitudes score were significantly higher in the male group, in the medical institution employer group, in the group who have met the HIV infected person, who has known the HIV positive person, and the group of laboratory technician, but the AIDS prevention intention score was statistically higher in the group of female and laboratory technician group. The post education scores of AIDS related knowledge, acceptance attitudes, and preventive intention were statistically higher than those of the preeducation. The most increased item among AIDS prevention intention list was 'I will provide the meeting between the HIV infected persons and the public(+21.9%)'. But even the decreased item among AIDS prevention intention list was 'I will advice to female not to have extra marital sexual contact to avoid AIDS(-3.1%)'. It could be concluded that the health care workers were ignorant of vertical transmission of AIDS, they were afraid of disclosing the infection status, and have less AIDS prevention intention. Therefore is needed to take an assessment process before each new education strategy to increase AIDS related the effect of the education on AIDS.
- 393 View
- 0 Download

- The Effect of Structured Patient Education on Knowledge and Behavior about Selfcare in Hemodialysis Patients
- Young Ran Jeong
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(1):120-127. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.1.120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identify the effect of structured patient education on knowledge and behavior about selfcare in hemodialysis patients, and to find the strategy to promote their selfcare behavior. In conclusion, structured patient education in hemodialysis patients was improved the level of knowledge and behavior about selfcare. But there was a little relationship between the knowledge and behavior about selfcare. That is ; structured patient education is the effective nursing intervention to improve their selfcare knowledge and behavior, but further research is needed to find the factor to increase selfcare behavior in hemodialysis patients.
- 412 View
- 1 Download

- The Effect of the Structured Education on the Early Rehabilitation Knowledge and Activity Performance of the C.V.A. Patients
- Hei Jin Lee, Hyang Yun Rhee
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(1):109-119. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.1.109
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study had been attempted to set up the strategies of the nursing which can promote the activity performance for early rehabilitation for the patients by examining the effect of the structured patient education on the early rehabilitation knowledge and activity performance of the C.V.A. patients. The study method had been done by investigating the experiment group and control group in advance through the question papers and interview and observation on 65 patients who had been hospitalized at oriental medicine hospital of K Medical Center form July 1st 1995 to the end of Sep, 1995. The analysis of the collected material had been done for the homogeneity test in which general characters of experiment group and control group had been tested by x2 and the homogeneity test of ADL by t-test. To test the hypothesis the t-test had been given for the difference of the early rehabilitation knowledge and activity performance between the two groups and the correlation between early rehabilitation knowledge and activity performance had been tested by Pearson's Correlation Coefficient. The result of the test of the hypothesis is as the below. 1. The 1st hypothesis "The experiment group which had received the structured education should be higher in the early rehabilitation knowledge than the control group" was supported(t=4.45, p=.000). 2. The 2nd hypothesis "The experiment group which received the structured education should be higher in the early rehabilitation activity performance than the control group" was supported(t=2.11, p=.036). 3. The 3rd hypothesis "The higher the early rehabilitation knowledge of the patient the higher the activity performance degree" was rejected(r=.1546, p=.219). In conclusion, the patients who received the structured showed the increase in the degree of early rehabilitation knowledge and activity performance so, it had been judged that education had been prerequisite in increasing the knowledge and activity performance of early rehabilitation.
- 503 View
- 0 Download

- The Effect of Health Education on the Performance of Health Promoting Behavior in College Students
- Jeong Sook Park, Chung Ja Park, Young Sook Kwon
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(2):359-371. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.2.359
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study has been done for the purpose of testing the effect of health education on the performance of health promoting behavior in college students, and identifying the factors affecting health promoting behaviors. A Nonequivalent control group posttest research design was used. Two hundred thirty college students at K College in T city were studied, Of them, 114 who attended a systematic health education session for three hours a week during one semester were the experimental group. And 116 college students who were chosen of matched sampling of grade, class and sex were the control group. This study was conducted from March 1 to July 2, 1995. The instruments used for this study included a survey of general characteristics, perceived health status, self-esteem, health promoting behavior and health locus of control. Analysis of data was done by use of mean, t-test, Pearson correlation coefficient and multiple regression. The results of this study are summerized as follows; 1) The average item score for the health promoting behavior was low at 2.52. In the sub-categories, the highest degree of performance was 'harmonious relationships', following 'sanitary life', 'self-esteem', 'rest and sleep', and 'emotional support' and the lowest degree was 'professional health management'. 2) Hypothesis 1 that the college students who get health education will have a higher degree of health promoting behavior than the college students who do not get health education was accepted. There was a statistically significant difference between the average of the experimental group, 2.60, and the average of the control group, 2.45.(t=11.30, p=0.0009). 3) Hypothesis 2 that the college students who get health education will have a higher score of perceived health status than college students who do not get the health education was rejected. (t=1.13, p=0.289) 4) Performance of health promoting behavior was positively correlated with self-esteem and grade and negatively correlated with perceived health status. 5) The most important factor affecting performance of health promoting behavior was self-esteem. The following suggestions are made based on the above results; 1) Replication of the research is needed to confirm effects of health education. 2) More effective health education programs need to be deveolped through by modification of teaching methods and content analysis of health education. 3) Other factors affecting health promoting behavior should be identified. 4) Nursing colleges or departments of nursing should make an effort to develop and carry out various health education programs for the health promotion of all college students.
- 566 View
- 4 Download

- Application and Effectiveness of a Preceptorship for the Improvement of Clinical Education
- Won Hee Lee, So Sun Kim, Shin Hi Han, So Yon Lee, Gi Yon Kim
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1995;25(3):581-596. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1995.25.3.581
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Clinical practice in nursing education provides an opportunity for students, through the process of applying theoretical knowledge to practice, and to learn nursing skills as well as being socialized into nursing and as such decrease the reality shock of actual nursing practice. Because of a shortage of nursing faculty, the job of achieving the objectives of the clinical practice had been turned over to the head nurses. This resulted in many problems, such as, unclear location of responsibilities and inadequate feedback from head nurses. Therefore this study was done to introduce and evaluate the use of preceptors as a way to minimize the above problems, and to maximize the achievement of the clinical practice objectives. Using an adaptation of Zerbe's (1991) three-tiered team model, clinical practice was done using a preceptor, a head nurse and a clinical instructor, each with different and well defined roles. The subjects of this study were 67 senior students of the College of Nursing of Y University in Seoul whose clinical practice in adult nursing was carried out between May 1, 1994 and December 8, 1994. There were 22 preceptors who had at least two years of clinical experience and who were recommended by their head nurses. They were given additional education on the philosophy and objectives of the College of Nursing, on communication skills, on the theory and practice of education, and on nursing diagnosis and education evaluation. The role of the preceptor was to work one-to-one with students in their practice. The role of the head nurse was to supervise and evaluate the preceptors. The role of the clinical instructor was to provide the education program for the preceptors, to provide advice and suggestions to the preceptors and to maintain lines of communication with the college. With each of these roles in place, it was thought that the effectiveness and efficiency of the clinical practice could be increased significantly. To evaluate the effectiveness of the precep-torship, the three-tiered model, Lowery's Teacher Evaluation Opinion Form translated and adapted to Korea was used to measure student statisfaction. The Clinical Practice Compentency Evaluation Tool developed by Lee et al was also used to measure student competencies. The results of this study are as follows: 1. The satisfaction with clinical practice was higher with the introduction of the perceptors than it was before they were used. (t=-5.96, p=<.005) 2. The clinical practice competencies were higher with the introduction of the preceptors than it was before they were used(t= -5.13, p<.005) 3. In order to analyze areas not measured by the quantitative tools additional analysis of the open questions was done. The results of this analysis showed that: 1) The students felt positive about their sense of security, confidence, handling of responsbility, and being systematic. They also felt positive about improvements in knowledge, opportunities for direct care, and socialization. 2) The students felt negative about the technical part of their role, lack of knowledge by the preceptor, unprofessional attitudes on the part of the preceptor, difficulty in the role of the professional nurse (student). 3) The preceptors felt positive about their responsibility, motivation, and relationship with the college. 4) The preceptors felt negative about their burden. Introduction of the preceptorship model will lead to change and improvement in the negative factors discussed above, solve problems in the present clinical education system, increase continuity in the education of the students, help with socialization of the students and motivation of the preceptors to upgrade their education and increase their confidence. These objectives must be obtained to further the development of professional nursing, and thus, making the preceptorship a reality is our job for the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Students’ Evaluation of Practice Sites and Preceptors in Pharmacy Experiential Education
Jeong-Hyun Yoon, Hae Sun Suh, Nam Kyung Je
Korean Journal of Clinical Pharmacy.2017; 27(2): 69. CrossRef
- The Students’ Evaluation of Practice Sites and Preceptors in Pharmacy Experiential Education
- 927 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Nursing Education Systems in Korea, China and the United States of America and its Future Directions
- Sung Rae Shin, Kyung Rim Shin, Chun Yu Li
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(7):949-959. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.7.949
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF BACKGROUND: Korea and the People's Republic of China received their nursing traditions from European and the American missionaries in the late 1800's. However, the stages of nursing education development and its standards are not same among countries. Korea, People's Republic of China and the United States have gone through various internal socio-political, hierarchical changes which impact development of its nursing education systems in the past. PURPOSE AND METHODS: In this paper the authors have endeavored to review undergraduate nursing education systems in Korea, China and the United States in consideration with their unique historical social and political background of its development. Result: Korea has two nursing education systems: associate and baccalaureate. China developed three types of nursing education systems: certificate, associate and baccalaureate. The United States, one of the countries, which nurtured the modern nursing education, has four types of nursing education systems: certificate, associate, diploma and baccalaureate. Furthermore, the authors have discussed on several core and common issues to be considered for future directions on nursing education systems for three countries.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The private healthcare setting as a place for educating nurses: A qualitative exploration
Rhoda Meyer, Elize Archer, Susan C. Van Schalkwyk
International Journal of Africa Nursing Sciences.2022; 17: 100483. CrossRef - Stress, Burnout, and Low Self-Efficacy of Nursing Professionals: A Qualitative Inquiry
Luis Miguel Dos Santos
Healthcare.2020; 8(4): 424. CrossRef - Supporting the development of information literacy skills and knowledge in undergraduate nursing students: An integrative review
Margaret Purnell, Bernadette Royal, Lyndall Warton
Nurse Education Today.2020; 95: 104585. CrossRef - The Role of Nurses in Advancing the Objectives of the Global Compacts for Migration and on Refugees
Franklin Shaffer, Mukul Bakhshi, Niamh Farrell, Thomas Álvarez
Nursing Administration Quarterly.2019; 43(1): 10. CrossRef - Global Mobility for Internationally Educated Nurses: Challenges and Regulatory Implications
Franklin A. Shaffer, Julia To Dutka
Journal of Nursing Regulation.2013; 4(3): 11. CrossRef
- The private healthcare setting as a place for educating nurses: A qualitative exploration
- 1,054 View
- 5 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Indoor Environment Management Education for Prevention of Allergic Asthma
- Jee Won Park, Yong Soon Kim, Young Shin Song
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(7):1017-1023. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.7.1017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The objective of this research is to provide the indoor environment management education program for the asthma patients and their families and then analyze the effectiveness in education preventing allergic asthma.
METHODS
A pre-post single group quasi-experimental design was used to provide an education program about correct indoor environment management to a total of 58 households (29 patient households and 29 normal households). The performance rate of correct indoor environment management procedure, amount of house dust mite antigen, allergy subjective symptoms score and knowledge score about indoor environment management were compared before and after the education to test the effectiveness of the education.
RESULTS
Home-visit education in this research had effects in improving subject households' performance rate of indoor environment management procedures, reducing the amount of house dust mite antigen - an important inducing factor of allergy, and reducing perceived subjective symptoms of allergy.
- 569 View
- 0 Download

- An Analysis of Research on Clinical Nursing Education
- In Soo Kwon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(5):706-715. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.5.706
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This literature review was designed to identify a trend of study in clinical nursing education, to propose the idea for further study on an improvement of teaching students in the clinical setting. METHOD: The researches reviewed were 36 (seven in Korea and twenty nine out of Korea) on clinical nursing education in baccalaurate program from 1996 to 2000 from Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing, Journal of Korean Education of Nursing, Journal of Nursing Education, and Nurse Educator. RESULT: The prevailing research design was the nonexperimental(N=21). Subjects were predominantly nursing students(N=24). Structured questionnaire(N=22) was used most often for data collection. Among clinical setting studied, specific area was none in Korea. Research variables in nonexperimental studies were 4 types of student, teacher and teaching method. Independent variables in experimental studies were 7 types of clinical teaching methods, and dependent variables were six types of competence and knowledge of student. Research theme of qualitative research was most in clinical experience of student. CONCLUSION: In Korean, there were the lack of researches in specific clinical area, clinical teacher and teaching method. Accordingly, future studies need to be focused on various clinical areas, clinical teacher, and teaching method to improve the clinical nursing education in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving clinical reasoning competency and communication skills using virtual simulation-based learning focused on a pathophysiological approach in Korea: a quasi-experimental study
Sung Hae Kim, Yoona Choi
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2024; 26(4): 363. CrossRef - Relationships among Knowledge and Skills about Suicide Prevention, Attitudes toward Suicide, and Burnout of Suicide Prevention Work of Nurses at Mental Health Welfare Centers: A Mixed Methods Study
Hee-Ra Dong, Ji Min Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 92. CrossRef - Simulation-based education program on postpartum hemorrhage for nursing students
Miok Kim, Juyoung Ha
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(1): 19. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Metacognition, Communication Skills, and Confidence in the Performance of Core Basic Nursing Skills on Clinical Competency in Nursing Students
Soeun Jang, Soyoung Kim, Namhee Park
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(4): 448. CrossRef - A Comparative Study between American Public Health Nurse Core Competency and Community Health Nursing Practicum in a Province
Hanju Lee, Junghyun Choi, Sa Saeng Hyeon, Chun Mi Kim, Young Ran Chin
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2017; 28(3): 334. CrossRef - The Effects of Clinical Education Program for Nurses in Regional Public Hospital
Yoonhee Shin, Kwanjun Park, Eunkyung Byun, Dongwon Lee, Woong Ju
Health Policy and Management.2016; 26(4): 373. CrossRef - A Study on Learning Experiences and Self-Confidence of Core Nursing Skills in Nursing Practicum among Final Year Nursing Students
Aekyung Han, Dong Sook Cho, Jongsoon Won
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2014; 21(2): 162. CrossRef - Comparison of Blended Practicum Combined E-learning between Cooperative and Individual Learning on Learning Outcomes
Soon Hee Choi, Hyang Sook So, Ja Yun Choi, Sung Hee Yoo, So Young Yun, Myung Hee Kim, Mi Ok Song
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(2): 341. CrossRef - Effects of Family Nursing Practicum Using Role Play on Emotional Intelligence, Communication Ability, and Family Nursing Performance of Nursing Students
Eunok Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(4): 656. CrossRef - Clinical Practice Performance According to Type of Practices and Satisfaction of Clinical Practice in Students at Child Health Nursing
Jisoo Kim, Ae-Ran Lee, Yongsook Eo
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(4): 542. CrossRef - Study on Clinical Education for Nursing in Hospitals in Korea
Jiho Song, Miwon Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(2): 251. CrossRef - Affecting Factors on Clinical Competence of Nursing Students
Hee-Jung Jang, Youn-Kyoung Kwag
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(9): 4380. CrossRef - Trends in Research on Caregivers Hospitalized Children in Korea-Focus on Knowledge Type
In-soo Kwon, Yeong-mi Seo, Ji-youn Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2012; 18(3): 101. CrossRef - Effects of Teaching Method using Standardized Patients on Nursing Competence in Subcutaneous Injection, Self-Directed Learning Readiness, and Problem Solving Ability
Mi-Ran Eom, Hyun-Sook Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Kayeon Seong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(2): 151. CrossRef - Evaluating Learners' Behaviors in a Web-based Instructional Program
Jeonghee Kang
Korean Journal of Medical Education.2007; 19(2): 123. CrossRef
- Improving clinical reasoning competency and communication skills using virtual simulation-based learning focused on a pathophysiological approach in Korea: a quasi-experimental study
- 936 View
- 5 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Information and Social Support Regarding Breastfeeding: A Survey of Mothers in Seoul, South Korea
- Heasook Kim, Andrea Crivelli Kovach
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(7):1151-1159. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.7.1151
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF BACKGROUND: Pediatric societies throughout the world recommend breastfeeding as the optimal form of infant nutrition. This recommendation is based on extensive epidemiologic research that documents the health, developmental, psychological, social, economic, and environmental benefits to infants, mothers, families, and society. The purpose of this study was to examine breastfeeding information and emotional support received by mothers prenatally, hospital breastfeeding practices, and the relationship between information and support received and breastfeeding initiation and planned feeding method post discharge from the hospital.
METHODS
A 36-item questionnaire was distributed during the Spring 2000 to mothers who delivered babies at maternity centers in Seoul, South Korea. A sample of 52 mothers was surveyed at the time of hospital discharge. The questionnaire was developed based on the literature and reviewed by experts including internationally board certified lactation consultants, a nutritionist, and perinatal nurses. The survey instrument consists of five components: sociodemographic information, breastfeeding information received by mothers prenatally, emotional support regarding the mothers' infant feeding choice, breastfeeding initiation and supplementation, and hospital breastfeeding practices.
RESULTS
Fifty-two breastfeeding mothers at three hospitals completed the survey. The majority of the mothers were 26 to 35 years of age, college graduates, married, had uncomplicated vaginal or planned cesarean deliveries, and primiparas. Forty-nine mothers responded that they decided to breastfeed during their pregnancy. Mothers reported that the information they received during pregnancy was provided primarily by their mothers, or friends and other relatives. The majority of mothers reported that others influenced their infant-feeding decision. Forty mothers reported receiving emotional support for their infant feeding choice during their pregnancy with mothers or mothers-in-law and friends providing the greatest support.
DISCUSSION
Women obtain information prenatally about breastfeeding from many sources-family, friends, written materials, prenatal classes, and health care professionals. There are benefits and drawbacks to information received from multiple sources. Additionally, research has shown that a woman's infant-feeding decision is affected by the type of professional and social support the mother receives. Postpartum professional support for new breastfeeding mothers encompasses multiple dimensions ranging from a follow-up telephone call from the hospital nursing staff to referral to a community resource. Prenatal breastfeeding education on a community-wide basis can provide essential information for future mothers, families, and community support networks. Additional research needs to be done exploring the impact of prenatal, postpartum, and post-discharge support for women on breastfeeding initiation and duration rates.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Immediate Skin‐to‐Skin Contact on Exclusive Breastfeeding: An Instrumental Variable Approach
Sangyun Lee, Yongnam Kim
Acta Paediatrica.2025; 114(9): 2367. CrossRef - Postnatal women’s breastfeeding beliefs, practices, and support during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional comparative study across five countries
K. P. Coca, E. Y. Lee, L. Y. Chien, A. C. P. Souza, P. Kittikul, S. A. Hong, Y. S. Chang
International Breastfeeding Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Postpartum Breast-feeding Support by Nurse on the Breast-feeding Prevalence
Gun Ja Jang, Sun Hee Kim, Kyung Soon Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(1): 172. CrossRef
- The Effect of Immediate Skin‐to‐Skin Contact on Exclusive Breastfeeding: An Instrumental Variable Approach
- 799 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- A Study of the Standard Evaluation of Baccalaureate Nursing Education
- Kyung Rim Shin, Yang Heui Ahn, Kyung Sook Park, Yeon Ok Suh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(6):1109-1118. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.6.1109
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to analyze the appraising frame and the accreditation system of universities in both Korea and the United Sates, as well as developing a standard plan to appraise 4 year nursing education institutions in Korea. Research design of this study was descriptive comparative research. The results of the research can be divided into six fields, educational purposes, educational courses, students, faculty, facility equipments and administration finance in Korea. Then the results were further categorized into seven fields : mission and governance, faculty, students, curriculum and instruction, resources, educational effectiveness and integrity. Thus Korean appraising frames were suggested to have eight fields of standard. The fields are philosophy and purposes of educational institution, educational courses and instruction, students, faculty, facility equipments, adminstration finance, educational effectiveness and integrity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Faculty Perceptions of the Improvement and Effort for the Achievement of Quality in Nursing Education through Accreditation in Baccalaureate Nursing Programs
Kon Hee Kim
Korean Medical Education Review.2011; 13(2): 59. CrossRef - Development of Standards and Criteria for Accreditation of Baccalaureate Nursing Education Program
Yang Heui Ahn, Kyung Sook Park, Soon Ok Yang, Kyung Rim Shin, Mi Ja Kim
Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions.2005; 2: 87. CrossRef - Nursing Education on Women’s Health Care in Australia, Japan, South Korea, and Thailand
Vickie A. Lambert, Clinton E. Lambert, John Daly, Patricia M. Davidson, Wipada Kunaviktikul, Kyung Rim Shin
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2004; 15(1): 44. CrossRef
- Faculty Perceptions of the Improvement and Effort for the Achievement of Quality in Nursing Education through Accreditation in Baccalaureate Nursing Programs
- 735 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Development of a CD-ROM and an Educational Program for the Prevention Sexual Harassment and Sexual Violence in Preschool Children
- Kyung Hye Lee, Ja Hyung Lee, Il Ok Kim, Jeong Yi Bae
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(6):1067-1076. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.6.1067
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was to developed to create a CD-ROM and an educational program for the prevention of sexual harassment and violence and to contribute to the perception and add to the coping of the victims of sexual harassment and violence as well as the child, parents, and teachers.
METHOD
The study's methods were literature reviews, surveys, and assessments of the negotiation process for educational needs of sexual harassed and abused children.
RESULT
The sexual harassment and violence prevention program will contain four subjects : 1) sexual development of a preschool child, 2) characteristics of sexual harassment and violence of a preschool child, 3) safe sex, early detection of sexual violence syndrome, and coping strategies. The CD-RON was composed from three sites. The first was a child site, the second was a parent/teacher site, and the third was a game site for evaluations. The child site consisted of 10 possible scenarios of sexual harassment and violence that a child could experience. The parent/teacher site consisted of knowledge and information for prevention and coping strategies for sexual harassment and violence. At the end of each situation question and answer sections that were used for formative evaluation. Also, the game site could be a summative evaluation.
CONCLUSION
The effects of this program and the CD-ROM were based of the promotion of reverence for humanity and gender equality for preschool childen. Eventually, children, parents, and teachers will have prevention and coping ability that will reduce the occurrence of sexual harassment and violence in Korea.
- 475 View
- 2 Download

- The Effect of AIDS Education on Baccalaureate Nursing Students
- Young Ran Han
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(3):467-476. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.3.467
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: to evaluate the effects of AIDS education for baccalaureate nursing students.
METHOD
a one-time AIDS education was delivered to 175 nursing students and knowledge and attitude toward HIV/AIDS were measured before and after the AIDS education using a questionnaire. RESULT: 1) Before the AIDS education, the average knowledge score of the students was 64.30 points out of 103 points while the average attitude score was 25.77 points out of 36 points. 2) Before the AIDS education, school grade, former experience of AIDS education and religion were founded to be the significantly related to the student's knowledge on AIDS. 3) There was a significant increase in AIDS related knowledge (t=-24.21, p=.000). There was also a significant improve- ment in attitude toward HIV/AIDS (t=4.67, p=.000) after the AIDS education. 4) There was a significant correlation between the knowledge and the attitude toward HIV/AIDS before the AIDS education, while no correlations was found between the AIDS knowledge and attitude after the education. CONCLUSION: AIDS education is necessary and effective for baccalaureate nursing students. It is necessary to develop comprehensive AIDS education program to improve the level of knowledge and preventive behavior for HIV/AIDS as well as to allay the fears for AIDS.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of HIV/AIDS Education Program for Professional Graduate Medical School Students by Teaching-Learning Methods
Myoung Hee Seo, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(9): 519. CrossRef - Knowledge and Attitude toward HIV/AIDS among Professional Graduate Medical School Students
Myoung Hee Seo, Seok Hee Jeong, Ja Hyun Shin, Myung In Lee
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(11): 255. CrossRef - The Effects of Supportive Nursing Intervention Using Video-Program of Operating Room Nurses before Operation on Laparoscopic Hysterectomy Patient's Anxiety
Yong-Sook Eo, Nae-Young Lee, Ji-Won Lee, Hyeon-Jun Cha
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(4): 2639. CrossRef - Effect of Sexual Education Program on Female College Student's Sexual Knowledge and Sexual Autonomy
Nami Chun
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2012; 18(2): 108. CrossRef
- The Effect of HIV/AIDS Education Program for Professional Graduate Medical School Students by Teaching-Learning Methods
- 842 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

- The Study on the Development and Effectiveness of Parent Role Education Program
- Kyung Ja Han, Kyung Sook Bang, Mi Kyung Kwon, Jung Soo Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(3):417-431. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.3.417
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the maternal role education program for primiparas in mother-infant interaction, childrearing environ- ment, and infant development. METHOD: A Non-equivalent control group time-series design was used. For the intervention group, programmed parenting education focusing on mother-infant interaction, home environment for infant development, and parent counseling and support was provided via home visits or telephone for twelve months.
RESULT
Significant differences were found in the mother-infant interaction feeding scale at one and three months, but no differences were found in the teaching scale at six and twelve months between the intervention and control groups. Also, the difference in childrearing environment (HOME) between the two groups was significant at three, six, twelve months. In addition, the intervention group showed higher GQ in the Griffiths mental development scale at three and six months. In multiple regression analysis, 22.6% to 43.6% of infant development was explained by HOME, mother-infant interaction, and previous development. CONCLUSION: The maternal role education program proved to be effective in promoting mother-infant interaction, organizing the childrearing environment, and fostering infant development.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of an Early Nursing Intervention Program for Infants' Development and Mother's Child Rearing in Poverty
Kyung-Sook Bang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(6): 796. CrossRef
- Effects of an Early Nursing Intervention Program for Infants' Development and Mother's Child Rearing in Poverty
- 715 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effect of Education for Prevention of Osteoporosis Patients with Bone Fracture
- Hyang Yeon Lee, Sook Young Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(2):194-205. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.2.194
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of the study was to identify the effect of structured patients education had on prevention of osteoporosis, with fracture and the resulting of life style changes in patients. In this study, a non equivalent control group pre and a post test design was employed. Data were collected through an interview process using questionnaires from April to December of 1999. The subjects, consisting of 59 patients with fractures and over 40 years of age, were diagnosed in K University Hospital. This study tested the patients knowledge at three times. The times were before the program 2 weeks into the program, and 6 months after education program. Life style change related to prevention of osteoporosis was shown twice (before and 6 months after the education program) in the experimental group, and control group went without it. The instruments used for this study were developed by literature review according to a reliability test. Data was analyzed using X2 test and t test to determine similarities between the experimental and control groups. The hypothesis was tested using repeated measures of ANOVA, t-test and Pearson correlation coefficients. The results of the study were summarized as follows: 1. The first hypothesis was accepted: a higher level of knowledge about osteoporosis was found in experimental groups who received education than to the control group during the period (F=19.82, p=.0001). 2. The second hypothesis was accepted: a higher level of life style changes about osteoporosis on experimental group were recorded than as compared to control group (t=3.55, p=.001). 3. The third hypothesis was accepted: the higher the knowledge about osteoporosis the higher the level of performance of life style changes about prevention of osteoporosis (r=.600, p=.0001). In conclusion, structured patient education in patient with fractures improved the level of knowledge about osteoporosis and more likely undergo of life style changes 6 months after the education program. Also reeducation would be needed 6 months after program ends. That is structured patient education in pamphlet form would be very effective in nursing intervention that may to result in life style changes. Therefore further research is needed to reinforce the education material and to generalize the education effect.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of a Group Educational Intervention on the Prevention of Osteoporosis in Breast Cancer Patients
Bong Hae Ma, Chai-Soon Park, Hee Chong Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(4): 398. CrossRef - Gender Difference in Osteoporosis Prevalence, Awareness and Treatment: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008~2011
Yunmi Kim, Jung Hwan Kim, Dong Sook Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(2): 293. CrossRef - Study of the Level of Osteoporosis Awareness among Women Dwelling in Urban Area
Miyoung Chung, Kyunghye Hwang, Euysoon Choi
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(4): 362. CrossRef - Decreased Bone Mineral Density and Fractures in Low-Income Korean Women
Kyunghee Yang, Beverly J. McElmurry, Chang G. Park
Health Care for Women International.2006; 27(3): 254. CrossRef
- The Effects of a Group Educational Intervention on the Prevention of Osteoporosis in Breast Cancer Patients
- 852 View
- 6 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Nursing Education between South and North Korea through Verbal Evidence from Defecting North Korean Medical Personnels
- Kyung Rim Shin, Il Ok Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(2):169-179. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.2.169
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Recently, there has been an increasing interchange between South Korea and North Korea. Accordingly, there has been active research to understand the society and culture of North Korea, it has been attempted to have comparative study about nursing education to increase understanding between South and North Korea. In the current educational system, 12 years of education is required for entering a nursing college or university in South Korea, but there are only 10 years for entering nursing college in North Korea. After finishing undergraduate studies one can enter graduate school for a masters degree and or a doctoral degree, but there is a longitudinal relation to medical education in North Korea. Regarding the number of nursing educational institutions, there are 50 BSN programs & 61 Diploma programs in South Korea and 11 Diploma programs in North Korea. In regards to curriculum, South Korea has diverse subjects for general education for freshmen, then is subjects to basic specialities sophomore year, and speciality subject and clinical practices from junior year corresponding to the student's intentions. North Korea has minor subjects for general education and basic specialities in freshmen, speciality subjects sophomore year, speciality subjects and clinical practice in the junior year that may not correspond with the student's intentions. The most outstanding difference in the curriculum is North Korea has various subjects for oriental medicine with clinical application. North Korea also does not teach computer science and English is at a very low level. In clinical practice, South Korea has various settings for clinical practice including community health institutions under the nursing professor or clinical instructor. However, North Korea has limited settings for clinical practice (general hospitals) under a doctor's instruction. Also both South and North Korea have a similar licensing system. Therefore, there must be many more studies regarding North Korea, especially in nursing and nursing education in order to decrease differences and confusion between the Koreas and to prepare for a future unification.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Experiences of Nurses Defecting from North Korea Regarding North Korean Nursing Education and Practice
Jung Hee Jeon, Kon Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2024; 38(2): 234. CrossRef - A North Korean Defector’s Experience With Becoming A Nurse in South Korea
Sang Hui Chu, Jinsook Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2024; 38(2): 220. CrossRef - Development of international nursing standard–based curriculum for North Korean nurses
Younhee Kang, Insook Yang, Eliza Lee, Chohee Bang
International Nursing Review.2022; 69(4): 503. CrossRef - A Review on the Clinical Laboratory Personnel in North Korea
Bon-Kyeong Koo, Sei Ick Joo, Dai-Joong Kim, In-Ho Jang
The Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2020; 52(1): 83. CrossRef
- Experiences of Nurses Defecting from North Korea Regarding North Korean Nursing Education and Practice
- 918 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Hospital Breastfeeding Policies and Practices in South Korea: A Comparison with the WHO/UNICEF Ten Steps
- Andrea Crivelli Kovach, Heasook Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(7):1752-1767. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.7.1752
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF BACKGROUND: The purpose of this study was to describe breastfeeding policies and practices among hospitals in South Korea and the degree to which the hospitals are implementing the WHO/UNICEF Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative.
METHODS
A cross-sectional survey of 34 hospitals was used to collect data. Quantitative and qualitative information and insights into current breastfeeding policies and practices were derived from responses of maternal and child health personnel at each hospital. One questionnaire per hospital was completed with personnel from all sections of maternity services, labor and delivery, nursery, and postpartum, contributing information needed to create a composite picture of the hospital's breastfeeding policies and practices.
RESULTS
Most hospitals were classified as either high or moderately high implementers on four of the Ten Steps: printed information distributed to breastfeeding mothers, oral breastfeeding instruction given to mothers, infant supplementation, and infant feeding schedules. The remaining steps, including key practices like staff instruction, breastfeeding initiation, rooming-in, and hospital postpartum support are being partially implemented by the majority of hospitals in this study.
CONCLUSIONS
Areas identified as needing the greatest attention by hospitals were health care staff training, breastfeeding initiation, supplementation, rooming-in, breastfeeding policy, and postpartum support for the breastfeeding mother.
- 658 View
- 1 Download

- Preliminary Analysis for Predicting Changes in Pain and Depression after Implementing the Rheumatoid Health Promotion Program
- Hyun Soo Oh, Wha Sook Seo
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(7):1615-1626. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.7.1615
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was performed to evaluate the effect of 7-week comprehensive health promotion program for RA patients (CHPPRA) on changes in pain and depression. In addition, it was also examined that this effect was generated by changes in patients' health promoting strategies (positive self-image, positive thinking, problem solving, communication, pain management, stress management, exercise, and knowledge about RA) learned through CHPPRA. Twenty-eight out-patients of RA clinic in a university hospital participated for this study. The results are as followers. Changes in exercise, self-concept, positive thinking, problem solving, depression, and pain management were significant predictors to explain relieving pain level. Since all of these variables had positive standardized beta weights (betas), it can be interpreted that increasing level of these health promoting strategies may induce pain improvement. Changes in positive thinking, communication skill, exercise, self-concept, pain management, and knowledge about the disease were significant predictors to explain positive change in depression. Since all of the significant variables except the change in knowledge about the disease had positive standardized beta weights (betas), it can be interpreted that increasing level of these health promoting strategies may induce improving depression level. However, our results showed that the higher level of the knowledge about the disease was, the worse depression was.
- 482 View
- 2 Download

- A Study of the Effects on the Korean Adolescents' Sexual Role Identity and Attitude by the Audio-Visual Program for Sexual Education
- Young Hae Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(6):1556-1568. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.6.1556
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The aims of this study were to identify the effects on sexual role identity and sexual attitude of the A-V programed sexual education on Oct. 1. 1997 through Sep. 30, 2000. The program was focused on the formation of the desirable sexual activity, attitude and androgyny sexual role identity of the Korean adolescents, and that was the 25 minute VTR media "Our sexuality is healthful". This study was non equivalent post-test only quasi-experimental design, and the subjects were 530 middle school boys in Busan, Korea. After the manipulation, the change of sexual role identity and sexual attitude was analysed. Outcome measures were middle school boys' sexual role identity toward KSRI on a seven-point Likert scale and sexual attitudes toward SAS on a five-point Likert scale. The data was analysed by SPSS WIN. The results were summarized as follows: 1) The experimental group who was exposed to the A-V media produced by the author showed the higher score of androgyny sexual role identity than the control group who didn't watch the A-V program. 2) The experimental group showed the higher rate of the androgyny than the control group, On the other hand, their rate of the masculinity turned out to be lower than the latter group. 3) The experimental group didn't show the difference of SAS score from the control group. In conclusion, "Our sexuality is Healthful" A-V program for sexual education brought about the significant change of sexual role identity of the middle school boys, but didn't affect their attitude toward sexual activity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Typology: Older Women and Gender Role Identity
Myung-Ae Kim, Euna Park, Sung-Hee Ko
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(3): 289. CrossRef - Effects of a CD-ROM Educational Program on Sexual Knowledge and Attitude
YOUNG-HEE YOM, LEE KYU EUN
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2005; 23(4): 214. CrossRef
- A Typology: Older Women and Gender Role Identity
- 762 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Survey on the Difference in Perceptions on Educational Need in Patients with Epilepsy and Medical Personnel
- Mi Ri Choi, Yeon Hee Kim, Yeon Ja So, Sun Moo Yun, Guen Suk Lee, Sang Sun Leem, Geum Sun Kim, S Mi Choi-Kwon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(6):1400-1410. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.6.1400
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: To determine whether there is a discrepancy between the medical professions perception of what patients should know and that of the patients themselves, we studied patients need to be informed about different aspects of epilepsy and compared findings with medical personnels perceptions of the issue.
METHODS
Our study population consisted of 39 patients with epilepsy from the inpatient epilepsy unit, and 51patients from the outpatients clinic of the S. University Hospital between July and November 1997. However, the patients who declined to participate or who were not able to understand the directions and content of the questionnaire were excluded. The medical personnel participated in this study were 56 residents or nurses who were working in either Neurology or Neuro surgery Units. The questionnaire consisted of 6 categories with a total of 79 questions. The responses were indicated on a 5point Likert scale with 5 indicating the highest need . The data were analyzed with descriptive statistics, students t-tests, and chi-square.
RESULTS
Of the 90 patients and 56 medical personnel studied, the need for lifestyle information such as smoking, drinking, sleep, driving, employment, and marriage was significantly higher from medical personnel than that of the patients(p=0.00). Regarding medical knowledge about epilepsy, the patients group had higher scores in the need for information on the structure of the brain (p=0.00), whereas medical personnel had higher scores on the symptoms of epilepsy. There was no correlation between the length of epilepsy and the need for information on every item on the questionnaire. The patients had higher rank regarding diet, although it was not significantly different from the medical personnel. Regarding antiepileptic drugs and what to do when there is an attack, medical personnel scored higher. The items on which the patients group scored higher than 4.5 were the possibility of inheritance, the factors that might reduce the number of attacks, the period of usage of AED, and the food they have to avoid or the food they have to take to reduce seizure attacks.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study indicates that the patients group requires higher educational need in the structure of the brain, diet, and surgical treatment, but less in lifestyles and what to do when there is an attack. The educational program for the patients with epilepsy should emphasize medical knowledge with regard to brain anatomy, what to eat and what to avoid, and details of surgical treatment.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Difference in Perceptions of Educational Need Between Epilepsy Patients and Medical Personnel
Smi Choi‐Kwon, Sun Moo Yoon, Mi Ri Choi, Dong‐Wha Kang, Sang Kun Lee
Epilepsia.2001; 42(6): 785. CrossRef
- The Difference in Perceptions of Educational Need Between Epilepsy Patients and Medical Personnel
- 770 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Educational Needs of a Mother when Nurturing Children
- Kyung Hee Yoo
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(4):905-916. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.4.905
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to investigate the educational needs of a mother when nurturing children from neonates to the schoolage. A total of 657 subjects responded to the survey about the level of educational needs when nurturing children. The subjects of the study constituted of 401 mothers who visited the health center for immunization and 256 mothers who visited the pediatric outpatient department or whose children were hospitalized in pediatrics. This instrument had 64 items about nurturing children from neonates to the schoolage and one item had a score range of one to four. In data analysis, SPSSWIN 9.0 program was utilized for descriptive statistics. The results were as follows. 1) Mothers who had the neonates represented the highest educational needs about parental-neonates attachments with 3.47 of mean score compared to neonatal convulsion(3.44), management of common colds(3.44), nutrition(3.44), fever control (3.42). 2) Mothers who had infancy represented the highest educational needs about management of common colds with 3.34 of mean score compared to psychosocial developments (3.23), management of foreign bodies (3.22), feeding the food(3.19), playing with the infant(3.16). 3) Mothers who had toddlers represented the highest educational needs about psychosocial developments with 3.35 of mean score compared to discipline for children(3.34), management of teeth (3.29), management of common colds (3.21), management of accidents(3.20). 4) Mothers who had the a child in preschool represented the highest educational needs about psychosocial developments with 3.53 of mean score compared to management of accidents(3.23), discipline for children (3.00). 5) Mothers who had the child in secondary school represented the highest educational needs about psychosocial developments with 3.42 of mean score compared to management of teeth(3.13), management of accidents (3.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quality Evaluation of Online Health Information Related to Young Child
Hyun-Mi Son, Minji Je, Young-Sil Sohn
Child Health Nursing Research.2018; 24(1): 91. CrossRef - Effects of an Early Nursing Intervention Program for Infants' Development and Mother's Child Rearing in Poverty
Kyung-Sook Bang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(6): 796. CrossRef
- Quality Evaluation of Online Health Information Related to Young Child
- 690 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Development of the Education Program and It Effect on Osteoporosis and Life Style among Women
- Young Soon Byun, Ok Soo Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):764-775. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.764
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to develop the educational program based on the self-efficacy theory of Bandura(1986) and to identify the effect of the program among women. For this purpose a non-equivalent control group, and a pretest- posttest design was used between the experimental and the control group. The subjects in this study were female and were over the age 40, 37 in the experimental group and 46 in the control group. In this study, the educational program was developed to increase the level of osteoporosis self efficacy and to prevent osteoporosis. The program consisted of watching, videotapes, telephone contact, lectures, and small group discussions. This study was conducted to determine whether the 6 month educational program would increase osteoporosis self- efficacy, thus modifying life styles related to osteoporosis increas BMD. The instruments utilized in this study were the Lifestyle Questionnaire, and the Osteoporosis Self-Efficacy Scale. Also, bone marrow density (BMD) on the left wrist was measured by DTX-200. The findings are as follows: 1. A significant decrease in BMD was observed in the control group. By contrast, no significant change in BMD was observed in the experimental group. 2. The Osteoporosis Self-Efficacy was not significantly changed in both the experimental and control groups. 3. In the experimental group, the number of exercise participants and their exercise times were significantly increased. Also the amount of caffeine intake was significantly decreased.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study of Factors Influencing the Bone Mineral Density on Premenopausal Women: Using the 2011 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
Young-Mi Chun, Sun-Hee Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(12): 6246. CrossRef - Structural Model for Osteoporosis Preventive Behaviors in Postmenopausal Women: Focused on their Own BMD Awareness
Young Joo Park, Sook Ja Lee, Nah Mee Shin, Hyun Cheol Kang, Sun Haeng Kim, Tak Kim, Song I Jeon, In hae Cho
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(5): 527. CrossRef - Decreased Bone Mineral Density and Fractures in Low-Income Korean Women
Kyunghee Yang, Beverly J. McElmurry, Chang G. Park
Health Care for Women International.2006; 27(3): 254. CrossRef
- A Study of Factors Influencing the Bone Mineral Density on Premenopausal Women: Using the 2011 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
- 739 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


