Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Mediating effect of grit on the influence of nurses’ silence behavior on medication safety competence: a cross-sectional study
- Haengsuk Kim, Wanju Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):81-92. Published online February 20, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24088
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study investigated the mediating effect of grit in the relationship between silence behavior and medication safety competence among nurses.
Methods
The study included 166 nurses from four university hospitals and general hospitals in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do, South Korea. Data were collected from March 1 to 10, 2024, using self-report questionnaires. Data were analyzed using the t-test, analysis of variance, Scheffé’s test, and Pearson’s correlation coefficients with IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 23.0 (IBM Corp.). A mediation analysis was performed using Hayes’s PROCESS macro model 4 and the bootstrapping method.
Results
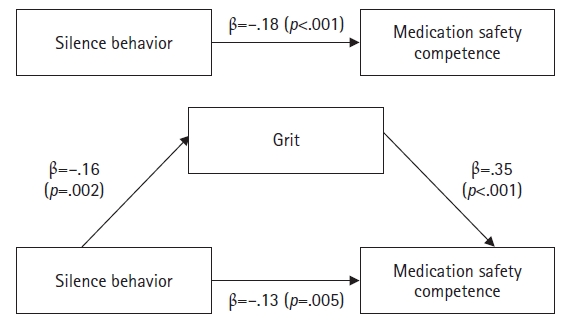
Medication safety competence showed significant correlations with silence behavior (r=–.21, p=.008) and grit (r=.43, p<.001). Furthermore, grit partially mediated the relationship between silence behavior and medication safety competence.
Conclusion
This study indicates that grit is a significant mediator in the relationship between silence behavior and medication safety competence. Therefore, an integrated approach that reduces silence behavior and promotes grit is essential for strengthening nurses’ medication safety competence. Ultimately, these strategies will help ensure patient safety by improving medication safety competence.
- 5,405 View
- 468 Download

- A Predictive Model of Resilience in Mothers of Children with Developmental Disabilities
- Youyoung Cho, Hyeonok Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):407-420. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21235
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This structural model study was constructed and verified a hypothetical model to examine the effects of parenting stress, social resources, family resources, and positive coping on resilience among mothers of children with developmental disabilities.
Methods
Data were collected using self‐report structured questionnaires, from October 19 to October 30, 2018, with 214 mothers caring for chil-dren with developmental disabilities under the age of 20 years.
Results
In the fitness test results of the hypothesis model, with the fit index χ 2 (p) = 69.27 (< .001), and the normed fit indices (χ 2 = 1.87, GFI = .94, CFI = .97, NFI = .93, and TLI = .95, RMSEA = .06, SRMR = .06), this study satisfies the good fitness in standards. There are seven statistically significant paths among the 10 paths set in the hypotheti-cal model. The explanatory power of parenting stress and social resources, which affects the family resources was 41.4%, the explanato-ry power of parenting stress, social resources, and family resources affecting the positive coping was 58.9%, and the explanatory power of parenting stress, social resources, family resources, and positive coping affecting resilience was 55.5%.
Conclusion
Positive coping, family resources, and social resources of mothers of children with developmental disabilities directly affect their resilience, and parenting stress indirectly affects it. Therefore, to improve the resilience of mothers of children with developmental disabilities, it is necessary to develop a systematic nursing intervention that considers parenting stress, social resources, family resources, and positive coping. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ÖZEL GEREKSİNİMLİ ÇOCUK ANNELERİ: MUĞLA-MENTEŞE ÖRNEĞİ
Ebru Açık Turguter
Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Edebiyat Fakültesi Dergisi.2025; 12(1): 320. CrossRef - Factors influencing the family management of children with atopic dermatitis: an integrative review
Sunyeob Choi, Hyewon Shin
Child Health Nursing Research.2025; 31(4): 187. CrossRef
- ÖZEL GEREKSİNİMLİ ÇOCUK ANNELERİ: MUĞLA-MENTEŞE ÖRNEĞİ
- 2,765 View
- 77 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of Resilience Enhancement Program Applying Mindfulness Meditation in Patients with Ileostomy
- Jee Hye Shin, Ja Yun Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):334-346. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21019
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop a resilience enhancement program applying mindfulness meditation (REP-MM) and evaluate the effects of the program on post-traumatic stress (PTS), resilience, and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in patients with ileostomy.
Methods
The REP-MM was developed by combining the resilience enhancement program with mindfulness meditation according to four patterns. The program was developed through identifying patients’ needs, reviewing relevant literature, developing a preliminary program, and testing content validity and user evaluation. The participants were 55 patients with ileostomy. We conveniently assigned 27 patients to the experimental group and 28 to the control group. The study was conducted in conducted in a hospital from January 22 to May 30, 2019. The REPMM was provided to the experimental group, and conventional ileostomy care was provided to the control group using a nonequivalent control-group pretest-posttest design. Results: ANCOVA revealed that the levels of PTS (F = 321.64, p < .001), resilience (F = 111.86, p < .001), and HRQoL (F = 31.08, p < .001) in the experimental group were higher than those in the control group when comparing pretest to posttest changes.
Conclusion
The REP-MM is effective in PTS, resilience, and HRQoL in patients suffering from post-stoma creation crisis. The REP-MM can induce positive self-recognition changes in patients with ileostomy through dispositional, situational, relational, and philosophical interventions. We suggest nurses reduce PTS and improve resilience and HRQoL in patients with ileostomy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Meditation Techniques in Treating Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
David W. Orme-Johnson, Vernon A. Barnes, Brian Rees, Jean Tobin, Kenneth G. Walton
Medicina.2024; 60(12): 2050. CrossRef - The experiences of Chinese colorectal cancer survivors in marital intimacy after ostomy creation: A qualitative study
Xixi Du, Suchira Chaiviboontham, Bualuang Sumdaengrit
Belitung Nursing Journal.2024; 10(2): 222. CrossRef - Analysis on effect of psychological nursing combined with extended care for improving negative emotions and self-care ability in patients with colorectal cancer and enterostomy: A retrospective study
Fang Liu, Kun Yao, Xiaoxiang Liu
Medicine.2024; 103(21): e38165. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Healthcare Empowerment Program for Patients with Temporary Ileostomy
Jin Mi Kim, Jeong Sook Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(6): 616. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Meditation Techniques in Treating Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1,725 View
- 32 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Relationship of Workplace Violence to Turnover Intention in Hospital Nurses: Resilience as a Mediator
- Hyun-Jung Kang, Jaeyong Shin, Eun-Hyun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(5):728-736. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20147
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the relationship between workplace violence and turnover intention, and the mediation effect of resilience on the relationship in hospital nurses.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional study. A total of 237 registered nurses were recruited from three hospitals in South Korea from April to May 2019. Participants were invited to complete self-reported questionnaires that measure workplace violence, turnover intention, resilience, and demographic information. The data obtained were analyzed using multiple regression and a simple mediation model applying the PROCESS macro with 95% bias-corrected bootstrap confidence interval (5,000 bootstrap resampling).
Results
After controlling demographic covariates, workplace violence significantly accounted for the variance of turnover intention. It was also demonstrated that resilience partially mediated the relationship between workplace violence and turnover intention in hospital nurses. A 73.8% of nurses had experienced workplace violence (such as attack on personality, attack on professional status, isolation from work, or direct attack). Conclusion: Workplace violence directly influences turnover intention of nurses and indirectly influences it through resilience. Therefore, hospital administrators need to develop and provide a workplace violence preventive program and resilience enhancement program to decrease nurses’ turnover intention, and leaving. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of nurses’ caring behaviors and personality traits on workplace violence
Hongjuan Chang, Xin Liu, Mengmeng Hu, Rui Zeng, Chun Zhang, Huanhuan Luo
Frontiers in Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The mediating role of psychological resilience in the relationship between workplace violence and job stress among healthcare workers
Vasfiye Bayram Değer, Sema Çifçi, Havva Kaçan
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Hemşirelerin İş Yerinde Yaşadıkları Psikolojik Şiddet ile Psikolojik Sağlamlılıkları Arasındaki İlişki
Fatma GÜNDOGDU, Aybüke ULAŞ, Ecem TAŞ, Vildan ÇARDAK, İrem Yaren ŞANDIR, Muhammed DURMAZ, Mehmet Salim ECER
Ordu Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Çalışmaları Dergisi.2023; 6(3): 608. CrossRef - The relationship between workplace violence, emotional exhaustion, job satisfaction and turnover intention among nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic
Özlem Gedik, Refika Ülke Şimdi, Şerife Kıbrıs, Derya Kara (Sivuk)
Journal of Research in Nursing.2023; 28(6-7): 448. CrossRef - Associations among the workplace violence, burnout, depressive symptoms, suicidality, and turnover intention in training physicians: a network analysis of nationwide survey
Je-Yeon Yun, Sun Jung Myung, Kyung Sik Kim
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing the effect of nursing stress factors on turnover intention among newly recruited nurses in hospitals in China
Lulin Zhou, Arielle Doris Kachie Tetgoum, Prince Ewudzie Quansah, Joseph Owusu‐Marfo
Nursing Open.2022; 9(6): 2697. CrossRef - The influence of experienced violence and the clinical learning environment on vocational identity in nursing students
Mira Lee, Hee Ok Park, Insook Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 321. CrossRef - Factors Affecting on Turnover Intentions of Emergency Department Nurses who have Experienced Verbal Abuse
Gyoo-Yeong CHO, Mi-Kyung SEO
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(2): 314. CrossRef - Effects of the Resilience of Nurses in Long-Term Care Hospitals during on Job Stress COVID-19 Pandemic: Mediating Effects of Nursing Professionalism
Bom-Mi Park, Jiyeon Jung
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(19): 10327. CrossRef - Nurses' Voices: Autumn 2020
Jeung-Im Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 644. CrossRef
- The impact of nurses’ caring behaviors and personality traits on workplace violence
- 1,499 View
- 55 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Symptom Distress and Coping in Young Korean Breast Cancer Survivors: The Mediating Effects of Social Support and Resilience
- Ji Hyun Lee, Hye Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):241-253. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to test the mediating effect of social support and resilience on the relationship between symptom distress and coping in young Korean breast cancer survivors.
Methods A purposive sample of 209 young breast-cancer survivors (mean age 39.9) was recruited for a cross-sectional survey, and the data were collected between June and October 2015. The instruments used in this study were the Memorial Symptom Assessment Scale-Short Form, the Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support, 10-item Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale, and Cancer Coping Questionnaire. The collected data were then analyzed using the SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 23.0 programs.
Results Symptom distress was found to have a significant indirect effect on coping (beta=-.32,
p =.002), but not a significant direct effect (beta=.06,p =.577). Additionally, based on the values obtained for the squared multiple correlation, symptom distress, social support, and resilience were found to explain 46.4% of the total variance of coping.Conclusion Based on the results of this study, it can be suggested that in order to enhance young breast cancer survivors’ ability to cope with the distress they commonly feel, intervention methods that strengthen resilience and provide social support should be developed and made available to them.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sexual well-being in cancer care services: the role of body image and coping strategies
Judith Partouche-Sebban, Saeedeh Rezaee Vessal, Youssef Souak, Aymen Ammari, Alain Toledano
Journal of Services Marketing.2026; : 1. CrossRef - How Online Patient-Provider Communication Alleviates Psychological Distress Among Patients with Chronic Diseases: The Role of Perceived Patient-Centered Communication and Adaptive Coping Strategies
Bingqing Ling, Yu Zheng
Health Communication.2025; 40(8): 1559. CrossRef - Factors Associated With Not Returning to Work Among Breast Cancer Survivors
Leni Merdawati, Hui-Chen Lin, Chieh-Hsin Pan, Hui-Chuan Huang
Workplace Health & Safety.2025; 73(5): 216. CrossRef - Factors affecting resilience among young breast cancer survivors: A cross-sectional study
Hye Young Min, Yoonjung Kim, Hae Jeong An
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 75: 102837. CrossRef - Latent classes of health‐promoting lifestyle in breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in China: A cross‐sectional survey
Meixuan Song, Qiuyao He, Juan Yang, Jinyu Zhang
Nursing Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Postmastectomy Pain Syndrome: A Narrative Review
Sajad Ahmad Salati, Lamees Alsulaim, Mariyyah H Alharbi, Norah H Alharbi, Thana M Alsenaid, Shoug A Alaodah, Abdulsalam S Alsuhaibani, Khalid A Albaqami
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the CALM intervention on resilience in Chinese patients with early breast cancer: a randomized trial
Shaochun Liu, Runze Huang, Anlong Li, Sheng Yu, Senbang Yao, Jian Xu, Lingxue Tang, Wen Li, Chen Gan, Huaidong Cheng
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2023; 149(20): 18005. CrossRef - Perceived social support and depressive symptoms in Chinese patients with ovarian cancer and the mediating role of resilience:a cross-sectional study
Xiaoyan Pang, Fangmei Li, Lei Dou, Yichang Tian, Yi Zhang
Current Psychology.2023; 42(24): 20485. CrossRef - Resilience-related Breast Cancer: A Concept Analysis
Fitria Endah Janitra, Nur Aini, Anggi Lukman Wicaksana
Nurse Media Journal of Nursing.2023; 13(1): 31. CrossRef - Factors influencing the coping strategies of liver cancer patients undergoing transarterial chemoembolization
Su‐Chih Chen, Shu‐Fang Wu, Tsae‐Jyy Wang, John Rosenberg, Yu‐Ying Lu, Shu‐Yuan Liang
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Perceived social support and coping style as mediators between resilience and health-related quality of life in women newly diagnosed with breast cancer: a cross-sectional study
Kaina Zhou, Fan Ning, Xiao Wang, Wen Wang, Dongfang Han, Xiaomei Li
BMC Women's Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Determinants of quality of life in women immediately following the completion of primary treatment of breast cancer: A cross-sectional study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ji Young Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae, Ka Ming Chow
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(10): e0258447. CrossRef - A Mobile Healing Program Using Virtual Reality for Sexual Violence Survivors: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study
Mi‐ran Lee, Chiyoung Cha
Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing.2021; 18(1): 50. CrossRef - Factors related to the resilience and mental health of adult cancer patients: a systematic review
Saori Tamura, Kumi Suzuki, Yuri Ito, Akiko Fukawa
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(7): 3471. CrossRef - Resilience in women with breast cancer: A systematic review
Ibane Aizpurua-Perez, Joana Perez-Tejada
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 49: 101854. CrossRef - Individual resilience in adult cancer care: A concept analysis
Dan Luo, Manuela Eicher, Kate White
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2020; 102: 103467. CrossRef - Relationship between cancer stigma, social support, coping strategies and psychosocial adjustment among breast cancer survivors
No Eul Kang, Hye Young Kim, Ji Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2020; 29(21-22): 4368. CrossRef - Effects of cyclic adjustment training delivered via a mobile device on psychological resilience, depression, and anxiety in Chinese post-surgical breast cancer patients
Kaina Zhou, Jin Li, Xiaomei Li
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2019; 178(1): 95. CrossRef
- Sexual well-being in cancer care services: the role of body image and coping strategies
- 1,975 View
- 22 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Post Traumatic Stress Disorder in Crime Scene Investigators
- Seon Mi Nho, Eun A Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(1):39-48. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.1.39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to verify the relationships among social support, resilience and post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and especially to identify factors influencing PTSD in police crime scene investigators.
Methods A cross-sectional design was used, with a convenience sample of 226 police crime scene investigators from 7 Metropolitan Police Agencies. Data were collected through self-report questionnaires during July and August, 2015. Data were analyzed using t-test, χ2-test, Fisher's exact test, and binary logistic regression analysis with SPSS/WIN 21.0 program.
Results The mean score for PTSD in police crime scene investigators was 13.69. 11 points. Of the crime scene investigators 181 (80.1%) were in the low-risk group and 45 (19.9%) in high-risk group. Social support (t=5.68,
p <.001) and resilience (t=5.47,p <.001) were higher in the low-risk group compared to the high-risk group. Logistic regression analysis showed that resilience (OR=4.74, 95% CI: 1.57~14.35), and social support (OR=2.13, 95% CI: 1.23~3.69) are effect factors for PTSD low group.Conclusion For effective improvement of PTSD in police crime scene investigators, intervention programs including social support and strategies to increase should be established.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing nursing students' attitudes toward autopsies in South Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive study
Seonmi Nho, Hanna Choi
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(1): 85. CrossRef - An Exploration of the Personal Experiences of Forensic Scene Investigators’ Daily Work: An Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis
Zoe Alexander, Juliane A. Kloess, Michael Larkin
Journal of Police and Criminal Psychology.2025; 40(3): 529. CrossRef - A price paid? A review of the research on the impact of investigating serious crime on the wellbeing of police staff
Ashley Cartwright, Jason Roach
The Police Journal: Theory, Practice and Principles.2022; 95(1): 109. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in Critical Care Nurses based on Lazarus & Folkman's Stress, Appraisal-Coping Model
Hye Gyeong Kim, Ja Yun Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(1): 88. CrossRef - Emotions and Cognition in International Criminal Justice: An Exploration from Cognitive Biases to Emotional Intelligence
Moa Lidén
Forensic Science International: Mind and Law.2020; 1: 100037. CrossRef - PTSD Symptoms Experienced and Coping Tactics Used by Crime Scene Investigators in the United States
Joseph A. Rosansky, Jeffery Cook, Harold Rosenberg, Jon E. Sprague
Journal of Forensic Sciences.2019; 64(5): 1444. CrossRef - Influence of Post-traumatic Stress Disorders on Quality of Life among Patients with Ostomy: Focused on the Mediating Effect of Resilience
Jee Hye Shin, Hyang Sook So, Eun A Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(6): 657. CrossRef
- Factors influencing nursing students' attitudes toward autopsies in South Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive study
- 1,641 View
- 20 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of a Positive Psychotherapy Program on Positive Affect, Interpersonal Relations, Resilience, and Mental Health Recovery in Community-Dwelling People with Schizophrenia
- Jinhee Kim, Hyunjoo Na
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(5):638-650. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.5.638
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose Recently, the interest in positive psychotherapy is growing, which can help to encourage positive relationships and develop strengths of people. This study was conducted to investigate the effects of a positive psychotherapy program on positive affect, interpersonal relations, resilience, and mental health recovery in community-dwelling people with schizophrenia.
Methods The research was conducted using a randomized control group pretest-posttest design. A total of 57 adults with schizophrenia participated in this study. The study participants in experimental group received a positive psychotherapy program (n=28) and the participants in control group received only the usual treatment in community centers (n=29). The positive psychotherapy program was provided for 5 weeks (of 10 sessions, held twice/week, for 60 minutes). The study outcomes included positive affect, interpersonal relations, resilience, and mental health recovery. The collected data were analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA for examining study hypothesis.
Results Results showed that interpersonal relations (F=11.83,
p =.001) and resilience (F=9.62,p =.003) significantly increased in the experimental group compared to the control group. Although experimental group showed a slight increase in positive affect, it was not significant.Conclusion The study findings confirm that the positive psychotherapy program is effective for improving interpersonal relations and resilience of community-dwelling people with schizophrenia. Based on the findings, we believe that the positive psychotherapy program would be acceptable and helpful to improve recovery of mental health in schizophrenia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors that influence hospitalization stress in patients with chronic schizophrenia: A cross‐sectional study in psychiatric hospitals
Sumin Chai, Goun Kim
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 32(1): 102. CrossRef - Positive mental health interventions for people with schizophrenia: A scoping review
Catarina Nogueira, Emanuel Dias Pereira, Joana Catarina Ferreira Coelho, Antonio Rafael Moreno-Poyato, Carlos Alberto Cruz Sequeira
Schizophrenia Research.2025; 276: 40. CrossRef - The effects of positive psychology theory in the rehabilitation nursing of Chinese patients with schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Yu Hong, Yanjun Huang, Junhong Jiang, Qiuhua Liu, Jing Hu, Wenfei Tan, Jinying Deng, Xintian Wang
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Stigma and Self-Management in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Cross-Sectional Study
Seulgi Ryu, Yeon-Hwan Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(4): 425. CrossRef - The Effect of Resiliency Training on Mental Health and Resilience of Pregnant Women with Unwanted Pregnancy: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Marjan Naderpour, Maryam Moradi, Sedigheh Shariat Moghani, Seyed Ali Kimiaei, Jamshid Jamali, Masoumeh Hashemian, Mahla Salarfard
Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research.2024; 29(2): 231. CrossRef - The power of virtual connections: A randomized controlled trial of online positive psychotherapy training on effective communication skills of nursing students
Kübra Gülırmak Güler, Serap Güleç Keskin, Eda Albayrak
Nurse Education in Practice.2024; 77: 103967. CrossRef - The Mediating Role of Positive Thinking on the Relationship Between Depression and Functional Recovery in Community-Dwelling People With Schizophrenia
Won Hee Jun, Hyunjoo Na
Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services.2023; 61(2): 44. CrossRef - The Effects of Positive Psychological Capital and Organizational Justice on Job Embeddedness of Clinical Nurses
Youn Shin Lee, Heeyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(3): 228. CrossRef - Effects of cultural adaptation resilience promotion program for mothers-in-law in multicultural families
Sang-Hwa Lee, Dong-Hee Kim, Kyoungrim Kang, Omnia Samir El Seifi
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(9): e0274224. CrossRef - Positive psychology interventions to improve well-being and symptoms in people on the schizophrenia spectrum: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Isabela Pina, Catarina de M. Braga, Túlio F.R. de Oliveira, Camila N. de Santana, Rodrigo C. Marques, Leonardo Machado
Brazilian Journal of Psychiatry.2021; 43(4): 430. CrossRef - Effects of a mental fitness positive psychology intervention program on inpatients with schizophrenia in South Korea: A feasibility study
Se Jin Kang, Sung Hee Ko, Ji Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2020; 56(1): 6. CrossRef - Recovery from schizophrenia
Antonio Vita, Stefano Barlati
Current Opinion in Psychiatry.2018; 31(3): 246. CrossRef
- Factors that influence hospitalization stress in patients with chronic schizophrenia: A cross‐sectional study in psychiatric hospitals
- 2,094 View
- 69 Download
- 12 Crossref

- The Effects of Violence Coping Program Based on Middle-Range Theory of Resilience on Emergency Room Nurses’ Resilience, Violence Coping, Nursing Competency and Burnout
- Seung Min Lee, Kyung Mi Sung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(3):332-344. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.3.332
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of a violence coping program (VCP) based on Polk's middle-range theory of resilience on nursing competency, resilience, burnout, and the ability to cope with violence in nurses working in emergency rooms.
Methods A quasi-experimental study, with a nonequivalent control group and a pretest-posttest design, was conducted. Participants were 36 nurses who worked in emergency rooms and had experienced violence; 18 nurses from D hospital and 18 nurses from C hospital were assigned to the experimental and control groups, respectively. The experimental group received the VCP twice per week for 8 weeks.
Results Levels of resilience,
F =59.41,p <.001, active coping behavior, c2=33.09,p <.001, and nursing competency,F =59.41p <.001, increased significantly and levels of passive coping behavior, c2=22.92,p <.001, and burnout,F =52.74,p <.001, decreased significantly in the experimental group.Conclusion The results suggest that the VCP could be an effective strategy for reducing burnout and improving resilience, active coping behavior, and nursing competency. Therefore, it would be a useful intervention for improving the quality of nursing care provided in emergency rooms.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations Between Workplace Violence and Work Performance Among Nurses: A Longitudinal Study Based on Affective Events Theory
Yifei Pei, Yiping Xiao, Xuan Zhang, Yan'e Lu, Meng Sun, Ran Lyu, Fenglin Cao
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2026; 35(2): 756. CrossRef - ОСОБЛИВОСТІ ПСИХОЛОГІЧНОЇ СТІЙКОСТІ МЕДСЕСТЕР РІЗНИХ ВІДДІЛЕНЬ
Н. Д. Дейнека, М. І. Марущак, О. Є. Оксенюк, В. М. Стернік, О. П. Мялюк
Медсестринство.2025; (1): 16. CrossRef - Effects of a Remote Videoconferencing-based Expressive Writing Program on Posttraumatic Stress, Resilience, and Post-traumatic Growth among Traumatized Nurses
Nam Hee Chae, Ji Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(2): 152. CrossRef - Relationship Between Illness Uncertainty and Family Resilience Among Caregivers of Stroke Patients in Chinese Nuclear Families: The Mediating Role of Perceived Stress
Qian Li, Caifeng Luo, Jianqin Ye, Zekun Bian, Weiyi Sun, Man Zhou, Mingzhu Rong
Patient Preference and Adherence.2024; Volume 18: 1095. CrossRef - Mixed‐methods study protocol for exploring the perception of nurses' resilience in the COVID‐19 pandemic: Designing, implementing and evaluation of intervention
Tooba Hoseini Azizi, Nahid Dehghan Nayeri, Alun C. Jackson, Fatemeh Bahramnezhad
Nursing Open.2023; 10(6): 4111. CrossRef - Psychological Intervention to Promote Resilience in Nurses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Suk-Jung Han, Young-Ran Yeun
Healthcare.2023; 12(1): 73. CrossRef - The Influence of Infection Control Knowledge, Emergency Nursing Competency, and Infection Prevention Environment on Burnout among Psychiatric Nurses Caring for Patients with COVID-19
Hyeran Cho, Suyon Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(4): 482. CrossRef - Interventions to reduce burnout among clinical nurses: systematic review and meta-analysis
Miran Lee, Chiyoung Cha
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Needs assessment of a home-visit safety management training program for visiting nurses
Eunjoo Kim, Hyori Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 138. CrossRef - Relationships between Violence Experience, Resilience, and the Nursing Performance of Emergency Room Nurses in South Korea
Sarang Kim, Minkyung Gu, Sohyune Sok
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(5): 2617. CrossRef - Verbal violence and turnover intention among new nurses in Korea: A time‐lagged survey
Ae Kyung Chang, Ah Young Kim
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(6): 1823. CrossRef - Clinical nurses’ experiences of workplace verbal violence: a phenomenological study
Min Soo Woo, Hyoung Suk Kim, Jeung-Im Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(2): 154. CrossRef - Recent advancements in microfluidic chip biosensor detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria: a review
Fang Mi, Cunming Hu, Ying Wang, Li Wang, Fei Peng, PengFei Geng, Ming Guan
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry.2022; 414(9): 2883. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Psychological Burnout in Nurses Caring for Terminal Cancer Patients
Na-Ri Seo, Hyun-E Yeom
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2022; 25(4): 159. CrossRef - Predictors of compassion fatigue, burnout, and compassion satisfaction among emergency nurses: A cross-sectional survey
Hairong Yu, Anhua Qiao, Li Gui
International Emergency Nursing.2021; 55: 100961. CrossRef - Effects of Hospital-Based Violence-Prevention and Coping Programs on Nurses' Violence Experience, Violence Responses, Self-Efficacy, and Organizational Commitment
Yu Jeong Yang, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 550. CrossRef - Relationship of Workplace Violence to Turnover Intention in Hospital Nurses: Resilience as a Mediator
Hyun-Jung Kang, Jaeyong Shin, Eun-Hyun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 728. CrossRef - Impact of Traumatic Events and Resilience on the Professional Quality of Life among Clinical Nurses
Dan-Bi Yoo, Hye-Ja Park, Phill-Ja Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2019; 22(1): 27. CrossRef - Effectiveness of interventions to reduce occupational stress among emergency department staff: a systematic review protocol
Hui (Grace) Xu, Kathryn Kynoch, Anthony Tuckett, Robert Eley, Peter Newcombe
JBI Database of Systematic Reviews and Implementation Reports.2019; 17(4): 513. CrossRef - Mediating effects of workplace violence on the relationships between emotional labour and burnout among clinical nurses
Hyejin Kim, Ji‐Su Kim, Kwisoon Choe, Yeunhee Kwak, Jae‐seok Song
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2018; 74(10): 2331. CrossRef - Resilience and Coping After Hospital Mergers
Cynthia Russo, Oriana Calo, Georgia Harrison, Kathleen Mahoney, Kathleen Evanovich Zavotsky
Clinical Nurse Specialist.2018; 32(2): 97. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Empathy and Resilience on the Relationship between Terminal Care Stress and Performance for Nurses in a Tertiary Hospital
Heui Yeoung Kim, Keum Hee Nam, Su Hye Kwon
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2017; 20(4): 253. CrossRef
- Associations Between Workplace Violence and Work Performance Among Nurses: A Longitudinal Study Based on Affective Events Theory
- 1,693 View
- 64 Download
- 22 Crossref

- The Structural Equation Model on Resilience of Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy
- Jeong Ha Yang, Ok Soo Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(3):327-337. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.327
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to construct and test a structural equation model on resilience of breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy.
Methods Participants were 204 patients with breast cancer who received chemotherapy treatment. They participated in a structured interview, which included social support, depression, symptom experience, self-efficacy, hope, resilience, and infection prevention behaviors. Data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 20.0 and AMOS 18.0.
Results Lower depression (γ=-.33,
p =.020) and symptom experience (γ=-.31,p =.012) and higher self-efficacy (γ=.32,p =.005) and hope (γ=.48,p =.016) were influenced by higher social support. Greater resilience was influenced by lower symptom experience (β=-.18,p =.016), higher self-efficacy (β=.49,p =.023), and higher hope (β=.46,p =.012), and these predictors explained 66.7% of variance in resilience. Greater resilience (β=.54,p =.009) made an impact on greater infection prevention behaviors. Resilience mediated the relations of symptom experience (β=-.10p =.013), self-efficacy (β=.27,p =.006) and hope (β=.25,p =.009) with infection prevention behaviors. These predictors explained 24.9% of variance in infection prevention behaviors.Conclusion The findings of the study suggest that breast cancer patientsw ith greater resilience who are receiving chemotherapy participate in increased infection prevention behaviors. Further research should be conducted to seek intervention strategies that improve breast cancer patients' resilience.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Structural Equation Model of Resilience in Patients Undergoing Lung Cancer Surgery During the Acute Survival Phase: A Cross-Sectional Study
Miri Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(2): 174. CrossRef - Understanding Intention Triggers in Early Autism Screening Promotion: The Role of Narrative and Framing
Lingfei Wang, Will Grant, Xinyi Jin, Guoyan Wang
Health Communication.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Effects of Telephone-based Self-care Intervention for Gynecologic Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Boyeon Lee, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(2): 216. CrossRef - Adaptación a la enfermedad, resiliencia y optimismo en mujeres con cáncer de mama
Marlen Simancas Fernández, Carla Zapata Rueda, Gonzalo Galván Patrignani, Jose Carlos Celedón Rivero, Juan Hernández Padilla
Revista Colombiana de Psiquiatría.2023; 52(4): 280. CrossRef - Adaptation to the disease, resilience and optimism in woman with breast cancer
Marlen Simancas Fernández, Carla Zapata Rueda, Gonzalo Galván Patrignani, Jose Carlos Celedón Rivero, Juan Hernández Padilla
Revista Colombiana de Psiquiatría (English ed.).2023; 52(4): 280. CrossRef - Positive personal resources and psychological distress during the COVID-19 pandemic: resilience, optimism, hope, courage, trait mindfulness, and self-efficacy in breast cancer patients and survivors
Francesca Chiesi, Deborah Vizza, Moira Valente, Rosy Bruno, Chloe Lau, Maria Rosita Campagna, Melania Lo Iacono, Francesco Bruno
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(8): 7005. CrossRef - A menopausal transition model based on transition theory
Jisoon Kim, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(3): 210. CrossRef - Development and Effect of the Integrated Health Promotion Program for Cancer Survivors Living at Home
Hee Sang Yoon, Eun A Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(1): 51. CrossRef - Resilience in Patients With Lung Cancer
Jie Zhang, Yizhen Yin, Anni Wang, Hui Li, Juan Li, Silan Yang, Yuchen Wu, Jingping Zhang
Cancer Nursing.2021; 44(6): 465. CrossRef - Mediator Roles of Social Support and Hope in the Relationship Between Body Image Distress and Resilience in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Treatment: A Modeling Analysis
Hsin-Tien Hsu, Chiung-Hui Juan, Jyu-Lin Chen, Hsiu-Fen Hsieh
Frontiers in Psychology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Structure Equation Modeling for Resilience in Patients with Breast Cancer
Dong Rim Hyun, So Yeun Jun, Chang Wan Jun, Sue Kyung Sohn
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(2): 87. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Resilience among Korean adolescents and young adult survivors of childhood cancer
Yoon Jung Shin, Eui Geum Oh
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 53: 101977. CrossRef - Self-efficacy, Hope as Mediators Between Positive Coping and Resilience Among Patients With Gastric Cancer Before the First Chemotherapy
Xiaoting Wu, Haibo Xu, Xiaomin Zhang, Shiyu Han, Liuna Ge, Xiaohui Li, Xinqiong Zhang
Cancer Nursing.2021; 44(1): 79. CrossRef - The relationship between resilience, anxiety and depression among patients with mild symptoms of COVID‐19 in China: A cross‐sectional study
Jie Zhang, Zhen Yang, Xiao Wang, Juan Li, Lili Dong, Fusheng Wang, Yifei Li, Ruihong Wei, Jingping Zhang
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2020; 29(21-22): 4020. CrossRef - Relationship between Self-efficacy and Resilience among Patients with Colorectal Cancer with Stoma: Mediating Effects of Family Support and Medical Staff Support
Mi Na Yun, Kyoung Mi Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(6): 599. CrossRef - Relationship between cancer stigma, social support, coping strategies and psychosocial adjustment among breast cancer survivors
No Eul Kang, Hye Young Kim, Ji Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2020; 29(21-22): 4368. CrossRef - Resilience and Its Predictors Among Chinese Liver Cancer Patients Undergoing Transarterial Chemoembolization
Caixia Li, Huijuan Lu, Wei Qin, Xiaorong Li, Jingxian Yu, Fang Fang
Cancer Nursing.2019; 42(5): E1. CrossRef - Resilience in Koreans With Cancer
Shin-Young Lee, Haeok Lee, Jacqueline Fawcett, Jeong-Hwan Park
Journal of Hospice & Palliative Nursing.2019; 21(5): 358. CrossRef - Examining spiritual support among African American and Caucasian Alzheimer's caregivers: A risk and resilience study
Scott E. Wilks, Wanda R. Spurlock, Sandra C. Brown, Bettina C. Teegen, Jennifer R. Geiger
Geriatric Nursing.2018; 39(6): 663. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Resilience in Hospitalized Patients with Stroke
Jong Kyung Lee, Ji Yeong Yun
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(4): 385. CrossRef - Effects of a Group Coaching Program on Depression, Anxiety and Hope in Women with Breast Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy
So Ryoung Seong, Moon-kyung Cho, Jeeyoon Kim, Yeo Ok Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2017; 17(3): 188. CrossRef
- A Structural Equation Model of Resilience in Patients Undergoing Lung Cancer Surgery During the Acute Survival Phase: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 1,542 View
- 23 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Development and Application of an Overcoming Compassion Fatigue Program for Emergency Nurses
- Yeong Ah Kim, Jeong Sook Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(2):260-270. Published online April 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.2.260
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to develop a program to help emergency nurses overcome compassion fatigue, and to analyze the effects of the program.
Methods A nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. There were 14 participants in the experimental group and 18 subjects in the control group. The program was comprised of five, weekly 80-minute sessions including understanding and assessment of compassion fatigue, enhancing positive affect, balancing work-life, planning self care, training in relaxation techniques and cognitive restructuring, and getting social support. Research variables were ego-resiliency, compassion satisfaction and compassion fatigue of the ProQOL 5, and salivary cortisol. Data were analyzed using Chi-square test, independent t-test, and paired t-test.
Results The first hypothesis, "There will be a difference in scores for ego resiliency between the experimental group and the control group". was not supported. The second hypothesis, "There will be a difference in scores for compassion satisfaction between the experimental group and the control group" was supported (t=2.15,
p =.046). The third hypothesis, "There will be a difference in scores for compassion fatigue between the experimental group and the control group" was not supported.Conclusion The first program for emergency nurses to overcome compassion fatigue in Korea was effective in increasing emergency nurses' compassion satisfaction and decreasing salivary cortisol level in the experimental group. Therefore, this program for overcoming compassion fatigue is useful to increase emergency nurses' compassion satisfaction. However replication studies of short-term intensive program reflecting emergency nurses' opinion are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of a Compassion Fatigue Intervention on Nurses’ Professional Quality of Life: A Single Group Study
Priyanka Singh, Nanda Kumar Paniyadi, Jaison Jacob, Anuradha Kumari, Roshna Lytton, Dishani Harh
Indian Journal of Palliative Care.2025; 31: 342. CrossRef - Effect of positive psychological capital on burnout in public hospital nurses: Mediating effect of compassion fatigue is greater than compassion satisfaction
Sin Ah Kim, Sung Reul Kim, Hye Young Kim
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Occupational Stress- Addressing Woes of the Nurses in a Burn Unit
Kajal Gupta, Monaliza Monaliza, Karobi Das, Ramesh Kumar Sharma
Hospital Topics.2023; 101(3): 184. CrossRef - Interventions to reduce burnout among clinical nurses: systematic review and meta-analysis
Miran Lee, Chiyoung Cha
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychological Intervention to Promote Resilience in Nurses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Suk-Jung Han, Young-Ran Yeun
Healthcare.2023; 12(1): 73. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Turnover Intention of Clinical Nurses in a Tertiary Hospital: Focusing on Fatigue, Nursing Professionalism, and Compassion Satisfaction
Jiyeon Song, Minjeong An
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2022; 25(1): 40. CrossRef - Рrofessional burnout of naval personel and ways of its psychophysiological correction: a review
P. A. Soshkin, A. G. Zaytsev, D. S. Zabrodskiy
Marine Medicine.2022; 8(2): 19. CrossRef - The Effectiveness and Safety of Mind-Body Modalities for Mental Health of Nurses in Hospital Setting: A Systematic Review
Su-Eun Jung, Da-Jung Ha, Jung-Hyun Park, Boram Lee, Myo-Sung Kim, Kyo-Lin Sim, Yung-Hyun Choi, Chan-Young Kwon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(16): 8855. CrossRef - Effect of Expressive Writing on Professional Quality of Life and Resilience among Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Danbi You, Hye-Ja Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(3): 276. CrossRef - Sociological conceptualizations of compassion fatigue: Expanding our understanding
Christian Vaccaro, Melissa Swauger, Shayna Morrison, Alex Heckert
Sociology Compass.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Cognitive-Behavioral Stress Management Program on Psychosocial Stress, Mood State, and Ways of Coping for Emergency Department Nurses
Ja-Hyun Kim, Kuem-Sun Han
Korean Journal of Stress Research.2021; 29(2): 87. CrossRef - Effect of a compassion fatigue resiliency program on nurses’ professional quality of life, perceived stress, resilience: A randomized controlled trial
Tuğba Pehlivan, Perihan Güner
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2020; 76(12): 3584. CrossRef - The effects of empathy and self concept on problem solving: Focusing on the mediating effect of communication of nursing students
Young Hui Hwang, Sun Jung Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(4): 348. CrossRef - Effectiveness of interventions to reduce occupational stress among emergency department staff: a systematic review protocol
Hui (Grace) Xu, Kathryn Kynoch, Anthony Tuckett, Robert Eley, Peter Newcombe
JBI Database of Systematic Reviews and Implementation Reports.2019; 17(4): 513. CrossRef - Compassion satisfaction and compassion fatigue among medical social workers in Korea: the role of empathy
Jaehee Yi, Min Ah Kim, Kwonho Choi, Brian A. Droubay, Soohyun Kim
Social Work in Health Care.2019; 58(10): 970. CrossRef - Prevention Actions of Burnout Syndrome in Nurses: An Integrating Literature Review
Sidney Medeiros de Oliveira, Luiz Vinicius de Alcantara Sousa, Maria do Socorro Vieira Gadelha, Vânia Barbosa do Nascimento
Clinical Practice & Epidemiology in Mental Health.2019; 15(1): 64. CrossRef - The Effects of Violence Coping Program Based on Middle-Range Theory of Resilience on Emergency Room Nurses' Resilience, Violence Coping, Nursing Competency and Burnout
Seung Min Lee, Kyung Mi Sung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(3): 332. CrossRef
- Effect of a Compassion Fatigue Intervention on Nurses’ Professional Quality of Life: A Single Group Study
- 1,931 View
- 58 Download
- 17 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Forgiveness Therapy on Resilience, Self-esteem, and Spirituality of Wives of Alcoholics
- Hee Kyung Kim, Mihyoung Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(3):237-247. Published online June 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.3.237
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose In this study the effects of forgiveness therapy on the resilience, self-esteem, and spirituality of wives of men suffering from alcohol abuse was examined.
Methods The study design was a quasi-experimental design. Forgiveness therapy was conducted once a week for 12 weeks. Data were obtained from March 2012 to December 2013. Participants were chosen from women in two Alcohol Counseling Centers. Of the 29 participants, 16 were assigned to the experimental group and 13 to the control group. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-test, χ2-test, and repeated measure ANOVA.
Results There were statistically significantly differences for resilience, self-esteem, and spirituality between the experimental and control groups. Forgiveness therapy improved the resilience, self-esteem, and spirituality in the experimental group compared to the control group (
p <.05). In follow-up tests, the experimental group had a statistically significantly increase only in self-esteem.Conclusion This study results show that forgiveness therapy is effective in improving resilience, self-esteem, and spirituality in wives of men suffering from alcohol abuse. Therefore, forgiveness therapy can be considered a useful nursing intervention to promote improvements in emotional stability and provide pain relief for these wives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ergenler ve Genç Yetişkinler İçin İçsel Manevi Değerler Ölçeğinin Geliştirilmesi: Minnettarlık Affedicilik ve Sabır Güçlerinin Değerlendirilmesi
Olcan Aslan, Ömer Faruk Kabakçı
Bilimname.2025; (53): 71. CrossRef - Effect of forgiveness-based bibliotherapy on forgiveness, self-esteem and psychological symptoms in nursing students: A randomized controlled study
Dilek Avci, Sila Kuzu
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2025; 20(4): e1176. CrossRef - Ser mulher em relacionamento com homens que vivenciam o adoecimento pelo uso de álcool: revisão integrativa
Laiza Carvalho Costa, Maria Lidiany Tributino de Sousa, George Gonçalves Machado
Ciência & Saúde Coletiva.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Ser mujer en relación con hombres que viven enfermedad por el consumo de alcohol: revisión integrativa
Laiza Carvalho Costa, Maria Lidiany Tributino de Sousa, George Gonçalves Machado
Ciência & Saúde Coletiva.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Being women in relationship with men who experience illness due to the use of alcohol: integrative review
Laiza Carvalho Costa, Maria Lidiany Tributino de Sousa, George Gonçalves Machado
Ciência & Saúde Coletiva.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Subjective well-being: self-forgiveness, coping self-efficacy, mindfulness, and the role of resilience?
Feridun Kaya, Hatice Odacı
British Journal of Guidance & Counselling.2024; 52(4): 628. CrossRef - Spirituality, forgiveness and self-esteem throughout adulthood in France
Agli Océane, Bailly Nathalie, Cuervo-Lombard Christine-Vanessa
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics Plus.2024; 1(4): 100098. CrossRef - FORGIVENESS AND RESILIENCE: A CASE OF ADOLESCENTS WITH BROKEN HOME DIVORCE
Tut Wuri Tri Lestari, Arthur Huwae
Counsenesia Indonesian Journal Of Guidance and Counseling.2023; 4(1): 8. CrossRef - Psychosocial Interventions to Improve Psychological, Social and Physical Wellbeing in Family Members Affected by an Adult Relative’s Substance Use: A Systematic Search and Review of the Evidence
Ruth McGovern, Debbie Smart, Hayley Alderson, Vera Araújo-Soares, Jamie Brown, Penny Buykx, Vivienne Evans, Kate Fleming, Matt Hickman, John Macleod, Petra Meier, Eileen Kaner
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(4): 1793. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Forgiveness of Wives of Alcoholics
Hee Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2021; 30(1): 42. CrossRef - FORGIVENESS, SELF-ESTEEM, AND RESILIENCE IN ADULT VICTIMS OF BULLYING
Dinu Hafidh Muvariz, Hanifah Nur Fitriani, Indah Nisrina, Fuad Nashori
al-Balagh : Jurnal Dakwah dan Komunikasi.2020; 5(2): 165. CrossRef - Self-Forgiveness as a Critical Factor in Addiction and Recovery: A 12-Step Model Perspective
Jon R. Webb, Loren L. Toussaint
Alcoholism Treatment Quarterly.2018; 36(1): 15. CrossRef - Effects of the Self-transcendence Enhancement Program among Patients with Drug Addiction: A Mixed Method Research
Younsil Kim, Suk-Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2017; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - Self-Esteem, Self-Stigma, and Stigmatization among People with Mental Illness in Japan Who Have Work Experience
Hatsumi Yoshii, Kouhei Akazawa, Hidemitsu Saito
Psychology.2016; 07(08): 1174. CrossRef - Effects of Forgiveness Therapy Program on Self-esteem, Anger, and Forgiveness in People who Abuse Alcohol
Sun Ja Kang, Soo Jin Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2015; 24(4): 300. CrossRef
- Ergenler ve Genç Yetişkinler İçin İçsel Manevi Değerler Ölçeğinin Geliştirilmesi: Minnettarlık Affedicilik ve Sabır Güçlerinin Değerlendirilmesi
- 1,313 View
- 9 Download
- 15 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


