Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effects of presenteeism on turnover intention in clinical nurses through the serial mediating roles of missed nursing care and job satisfaction: a cross-sectional predictive correlational study
- Hyeonseon Cheon, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyung Kim, Hyoung Eun Chang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):584-597. Published online November 10, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25015
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
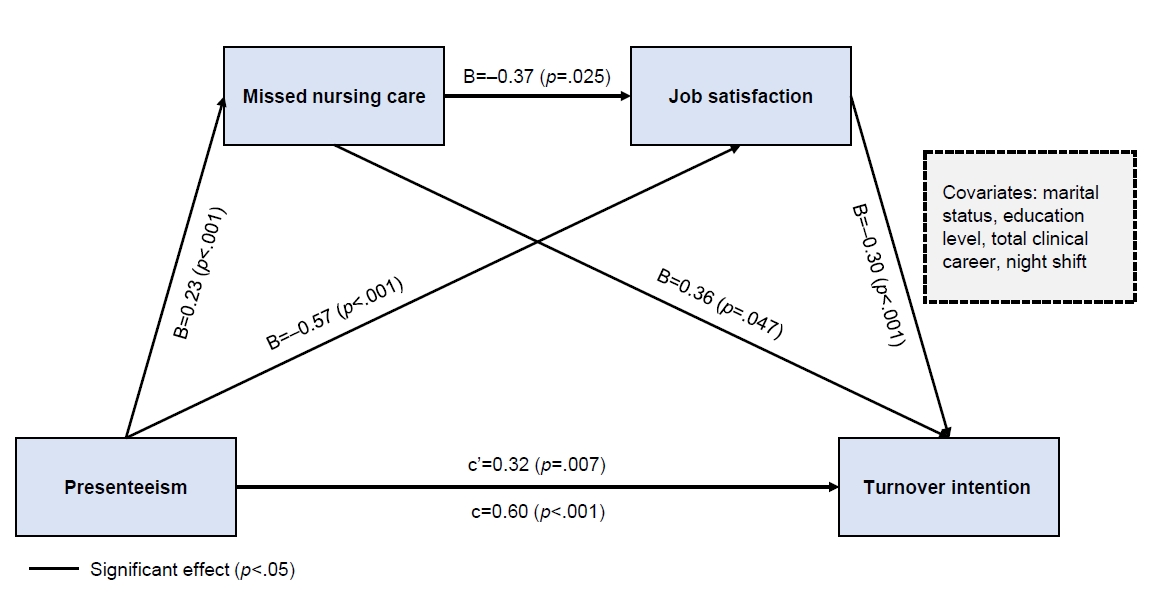
This study aimed to investigate the two-mediator serial mediation effect of missed nursing care and job satisfaction on the relationship between presenteeism and turnover intention in clinical nurses.
Methods
A cross-sectional predictive correlational study was conducted, and the participants were 208 clinical nurses working in advanced general hospitals in South Korea. Data were collected from October 6 to November 7, 2023 using self-reported questionnaires, including general characteristics, presenteeism, missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS/WIN ver. 29.0 and PROCESS macro ver. 4.2.
Results
Missed nursing care and job satisfaction exhibited a double mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. In addition, missed nursing care showed a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Job satisfaction had a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Presenteeism had a direct effect on missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Missed nursing care exerted a direct effect on job satisfaction and turnover intention among clinical nurses. Job satisfaction had a direct effect on turnover intention.
Conclusion
To reduce nurses’ turnover intention, it is essential to develop and implement programs focused on preventing presenteeism. Additionally, organizational initiatives should prioritize active support for nurses’ health management, alleviating the shortage of nursing staff, augmenting job satisfaction, and improving the overall working environment.
- 1,677 View
- 228 Download

- Effects of Leadership Styles of Nursing Managers on Turnover Intention of Hospital Nurses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Yunjeong Cho, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Young Man Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(5):479-498. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22039
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine effect sizes of leadership styles of nursing managers on turnover intention of hospital nurses.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the PRISMA and MOOSE guidelines. Participants were nurses working in hospitals. The intervention involved nursing managers’ leadership styles; the outcome assessed was nurses’ turnover intention. This was an observational study design. Eleven databases were searched to obtain articles published in Korean or English. Of the 14,428 articles reviewed, 21 were included in systematic review and meta-analysis. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis and R software programs were used.
Results
The total effect size r (ESr) was - 0.25 (95% confidence interval: - 0.29 to - 0.20). Effect sizes of each leadership style on turnover intention were as follows: ethical leadership (ESr = - 0.34), transformational leadership (ESr = - 0.28), authentic leadership (ESr = - 0.23), transactional leadership (ESr = - 0.21), and passive avoidant leadership (ESr = 0.13). Ethical leadership was the most effective style in decreasing turnover intention of hospital nurses.
Conclusion
Positive leadership styles of nurse managers effectively decrease turnover intention of hospital nurses, and negative leadership styles of nurse managers effectively increase turnover intention of hospital nurses. The ethical leadership style is the most effective in decreasing turnover intention of hospital nurses; however, it requires careful interpretation as its effects are reported by only two studies. This study contributes to addressing the high turnover rate of hospital nurses and developing positive leadership styles of nurse managers in hospital settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of organizational communication and grit on turnover intention of rehabilitation hospital nurses: A cross-sectional correlation study
Inji Ha, Heeok Park, Ji Hun Joung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(1): 35. CrossRef - Influence of Leadership Styles on Turnover Intentions in Technology Startups
Sheeza Fayyaz, Saima Majeed
Journal of Professional & Applied Psychology .2025; 6(1): 36. CrossRef - Protecting Workers From Rude Customers to Enhance Organizational Identification in Emotional Labor Environments: A Study With Call Center Agents
Hyojeong Kim, Nagesh N Murthy, Anurag Agarwal, Kwangtae Park
Production and Operations Management.2025; 34(10): 3250. CrossRef - Humanistic nursing care management strategies: from formulation to implementation
Jing Lv, Yajie Su, Hongmei Tang, Xiaolin Jiang, Xiaojuan Chen
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - When Leadership Drives Nurses Away: Empirical Research Qualitative on High Turnover Rates Reasons
Saleem Al‐Rjoub
Nursing Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between different leadership styles of nursing managers and nurses’ turnover intention in hospitals: an integrative review
Alicia Jimenez-Caceres, Anna Agusti-Boada, Conxi Caro-Benito, Olga Monistrol
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Structured Subjective Readiness in Situational Leadership: Validating the 4D Model as an Associative Predictor
Dino Giergia, Nikola Drašković, Mario Fraculj
Administrative Sciences.2025; 15(12): 488. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Leader-Member Exchange on the Ethical Leadership of Nursing Unit Managers and Turnover Intention of Clinical Nurses: A Nationwide Survey using Proportional Quota Sampling
Jihun Kim, Sunmi Kim, Nara Han, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(1): 42. CrossRef - Effects of Resilience, Nursing Managers’ Empowering Leadership on Turnover Intention among New Nurses: Mediating role of Transition Shock
Hyun Jin Jung, Hyun Kyung Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 212. CrossRef - Investigation of the relationship between nurses' perception of toxic leadership and their organizational trust levels and turnover intentions
Sultan Türkmen Keskin, Meltem Özduyan Kiliç
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2024; 80(5): 1859. CrossRef - The structural relationship of job stress, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention among youth sports education leaders in Korea
Myung Kyu Jung, Tae Gyeom Jung, Min Woo Jeon, Ji Hae Lee
Frontiers in Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Patient Safety Management System, Leadership, and Communication Types on Nurse’ Patient Safety Management Activities
Eunji Lee, Haejung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 367. CrossRef - Nursing-sensitive Indicators in East Asian Hospitals: A Scoping Review
Jae Jun Lee, Won Jin Seo, Dong Ah Park, Hwa Yeong Oh, Seung Eun Lee
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2024; 30(2): 88. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nurses Turnover in Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Review
Abdulmajeed M. Albalawi, Glezzeelyne P. Pascua, Sameer A. Alsaleh, Walaa Sabry, Sitti Nursa Ahajan, Jeseela Abdulla, Amal Abdulalim, Suad S. Salih, Sulaiman Al Sabei
Nursing Forum.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Unit Managers’ Authentic Leadership, Transformational Leadership, and Transactional Leadership on Turnover Intention in Advanced Beginner Nurses: Mediation Effects of Positive Psychological Capital
Eun Jeong Kim, Eungyung Kim, Son Ja Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 409. CrossRef - Factors related to the organizational silence of Korean nurses: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Kyungja Kang, Jeong-Hee Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(3): 302. CrossRef
- The effect of organizational communication and grit on turnover intention of rehabilitation hospital nurses: A cross-sectional correlation study
- 7,988 View
- 508 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref

- Relationships among Non-Nursing Tasks, Nursing Care Left Undone, Nurse Outcomes and Medical Errors in Integrated Nursing Care Wards in Small and Medium-Sized General Hospitals
- Ju-Young Park, Jee-In Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):27-39. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the degree of non-nursing tasks and nursing care left undone in integrated nursing care wards, and examine their relationships with nurses’ burnout, job satisfaction, turnover intentions, and medical errors.
Methods
A cross-sectional questionnaire survey was conducted. Data were collected using self-report questionnaires from 346 nurses working in 20 wards of seven small and medium-sized general hospitals, and analyzed using multiple regression and multiple logistic regression analysis with the SPSS WIN 25.0 program.
Results
The mean score for non-nursing tasks was 7.32±1.71, and that for nursing care left undone was 4.42 ± 3.67. An increase in non-nursing tasks (β = .12, p = .021) and nursing care left undone (β = .18, p < .001) led to an increase in nurses’ burnout (F = 6.26, p < .001). As nursing care left undone (β = .13, p = .018) increased, their turnover intentions also (F = 3.96, p < .001) increased, and more medical errors occurred (odds ratio 1.08, 95% confidence interval 1.02~1.15).
Conclusion
Non-nursing tasks and nursing care left undone are positively associated with nurses’ burnout, turnover intentions, and the occurrence of medical errors. Therefore, it is important to reduce non-nursing tasks and nursing care left undone in order to deliver high quality nursing care and in turn increase patient safety. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- First Integration of a Service Robot and a Communication Application into a Nursing Isolation Setting – An Observational Study Evaluating Walking Distances, Stress and Radiation Doses
Angelika Warmbein, Laura Sehn, Ivanka Rathgeber, Janesca Seif, Christoph Ohneberg, Nicole Stöbich, Astrid Delker, Christian Zach, Inge Eberl, Uli Fischer
International Journal of Social Robotics.2025; 17(9): 1809. CrossRef - Effects of a mobile simulation program for nursing delegation: A randomised controlled trial
Haena Lim, Yeojin Yi
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 83: 104283. CrossRef - Study of Nurses' Malpractice Tendencies and Burnout Levels
Leman Şenturan, Gizem Kaya, Tuba Emirtaş
Research in Nursing & Health.2025; 48(3): 385. CrossRef - The relationship between job stress and the perception of patient safety culture among Palestinian hospital nurses
Loai M. Zabin, Jamal Qaddumi, Sajed Faisal Ghawadra
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Grit, Teamwork, Organizational Communication Competence, Perception of Patient Safety Culture on Patient Safety Nursing Activities in Integrated Nursing Care Units
Jeeseon Kim, Haejung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 237. CrossRef - Non-Value-Added Activities and Non-Nursing Tasks Affecting Nursing Task Efficiency: A Scoping Review
Mi Ha Chung, Yongah Kim, Na Yeong Kim, Min Ju Kim, Hyeon Jin Kim, Ju Hee Park, Ji In Park, Su Yeon Bae, Heajin Bae, Eunjeong Lee, Min Young Jeon, Suyoung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 405. CrossRef - Relationships bewteen Non-nursing Tasks, Missed Nursing Care, Patient Safety Nursing Activities, and Medical Errors in Nurses
Tae-Ryun Lee, Jee-In Hwang
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2025; 31(2): 2. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Care Left Undone by Cancer Ward Nurses
Chung Hee Woo, Yeon Joo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 594. CrossRef - A phenomenological study of the experiences of nurses working in integrated nursing care wards in Korea
Young-mi Cho, Sun-hui Kim
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationships among Nursing Skill Mix, Missed Nursing Care, and Adverse Events in Small and Medium-Sized Hospital Comprehensive Nursing Care Wards
Yoon Sook Cho, Hyoung Eun Chang, Hyunjung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(2): 163. CrossRef - Exploring the causes and consequences of non-nursing tasks among nurses in Jordan: An in-depth qualitative investigation
Ayman Abed Aldarawsheh, Ahmad Rajeh Saifan, Murad Adnan Sawalha, Enas A. Assaf, Intima Alrimawi, Rami A. Elshatarat, Zyad T. Saleh, Wesam T. Almagharbeh, Nermen A. Mohamed, Mudathir M. Eltayeb
Applied Nursing Research.2024; 77: 151791. CrossRef - Influence of Work Environment, Missed Nursing Care, and Non-Nursing Tasks of Hospital Nurses on Job Stress
Ji Yeong Park, Kyoung Ja Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 246. CrossRef - A comparative analysis of nurses' reported number of patients and perceived appropriate number of patients in integrated nursing care services
Hyunjeong Kwon, Jinhyun Kim
Nursing & Health Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a virtual reality application‐based education programme on patient safety management for nursing students: A pre‐test–post‐test study
Jae Woo Oh, Ji Eun Kim
Nursing Open.2023; 10(12): 7622. CrossRef - The Effect of Missed Nursing Care on Adverse Event Experiences, Patient Safety Management Activity, Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention in Nurses: A Nationwide Survey using Proportional Quota Sampling
Myung Jin Choi, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 490. CrossRef - Pathway Analysis on the Effects of Nursing Informatics Competency, Nursing Care Left Undone, and Nurse Reported Quality of Care on Nursing Productivity among Clinical Nurses
Mi Yu, Se Young Kim, Ji Min Ryu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(2): 236. CrossRef - Competency Survey of Caregivers in Medical Tourism Special Zone and Other Regions
Dong-Yeop Lee, Sang-Bong Lee, Yeong-Im Park, Jin-Geun Lee, Yoon Hee Park, So Young Lee, Dong-Yoon Kang
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(2): 140. CrossRef - Influence of the Team Effectiveness of Nursing Units on Nursing Care Left Undone and Nurse-Reported Quality of Care
Se Young Kim, Young Ko
Healthcare.2023; 11(10): 1380. CrossRef - The Impact of Performance of Non-Nursing Tasks on the Attitudes of Nursing Students toward Nursing Profession
Ibrahim Rawhi Ayasreh, Ferial Hayajneh, Rana Al Awamleh
Nurse Media Journal of Nursing.2022; 12(2): 151. CrossRef - Clinical Application Value of Group‐Sharing Nursing Management Based on Case Analysis
Jing Mei, Yifan Wu, Jie Hu, Min Li, Mohammad Farukh Hashmi
Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Burnout on Quality of Care Using Donabedian’s Framework
Kathleen M. White, Dorothy Dulko, Bonnie DiPietro
Nursing Clinics of North America.2022; 57(1): 115. CrossRef - Emotional Labor, Burnout, Medical Error, and Turnover Intention among South Korean Nursing Staff in a University Hospital Setting
Chan-Young Kwon, Boram Lee, O-Jin Kwon, Myo-Sung Kim, Kyo-Lin Sim, Yung-Hyun Choi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(19): 10111. CrossRef - Integrated and Person-Centered Nursing in the Era of the 4th Industrial Revolution
Hyoung Suk Kim, Sun Joo Jang, Jeung-Im Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(3): 261. CrossRef - Analysis of Nurses' Work Experience in Comprehensive Nursing Care Units of Small and Medium-sized Hospitals
Mi Ryeong Song, Su Hyang Ryu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 419. CrossRef
- First Integration of a Service Robot and a Communication Application into a Nursing Isolation Setting – An Observational Study Evaluating Walking Distances, Stress and Radiation Doses
- 4,393 View
- 199 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 24 Crossref

- Relationship of Workplace Violence to Turnover Intention in Hospital Nurses: Resilience as a Mediator
- Hyun-Jung Kang, Jaeyong Shin, Eun-Hyun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(5):728-736. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20147
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the relationship between workplace violence and turnover intention, and the mediation effect of resilience on the relationship in hospital nurses.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional study. A total of 237 registered nurses were recruited from three hospitals in South Korea from April to May 2019. Participants were invited to complete self-reported questionnaires that measure workplace violence, turnover intention, resilience, and demographic information. The data obtained were analyzed using multiple regression and a simple mediation model applying the PROCESS macro with 95% bias-corrected bootstrap confidence interval (5,000 bootstrap resampling).
Results
After controlling demographic covariates, workplace violence significantly accounted for the variance of turnover intention. It was also demonstrated that resilience partially mediated the relationship between workplace violence and turnover intention in hospital nurses. A 73.8% of nurses had experienced workplace violence (such as attack on personality, attack on professional status, isolation from work, or direct attack). Conclusion: Workplace violence directly influences turnover intention of nurses and indirectly influences it through resilience. Therefore, hospital administrators need to develop and provide a workplace violence preventive program and resilience enhancement program to decrease nurses’ turnover intention, and leaving. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of nurses’ caring behaviors and personality traits on workplace violence
Hongjuan Chang, Xin Liu, Mengmeng Hu, Rui Zeng, Chun Zhang, Huanhuan Luo
Frontiers in Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The mediating role of psychological resilience in the relationship between workplace violence and job stress among healthcare workers
Vasfiye Bayram Değer, Sema Çifçi, Havva Kaçan
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Hemşirelerin İş Yerinde Yaşadıkları Psikolojik Şiddet ile Psikolojik Sağlamlılıkları Arasındaki İlişki
Fatma GÜNDOGDU, Aybüke ULAŞ, Ecem TAŞ, Vildan ÇARDAK, İrem Yaren ŞANDIR, Muhammed DURMAZ, Mehmet Salim ECER
Ordu Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Çalışmaları Dergisi.2023; 6(3): 608. CrossRef - The relationship between workplace violence, emotional exhaustion, job satisfaction and turnover intention among nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic
Özlem Gedik, Refika Ülke Şimdi, Şerife Kıbrıs, Derya Kara (Sivuk)
Journal of Research in Nursing.2023; 28(6-7): 448. CrossRef - Associations among the workplace violence, burnout, depressive symptoms, suicidality, and turnover intention in training physicians: a network analysis of nationwide survey
Je-Yeon Yun, Sun Jung Myung, Kyung Sik Kim
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing the effect of nursing stress factors on turnover intention among newly recruited nurses in hospitals in China
Lulin Zhou, Arielle Doris Kachie Tetgoum, Prince Ewudzie Quansah, Joseph Owusu‐Marfo
Nursing Open.2022; 9(6): 2697. CrossRef - The influence of experienced violence and the clinical learning environment on vocational identity in nursing students
Mira Lee, Hee Ok Park, Insook Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 321. CrossRef - Factors Affecting on Turnover Intentions of Emergency Department Nurses who have Experienced Verbal Abuse
Gyoo-Yeong CHO, Mi-Kyung SEO
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(2): 314. CrossRef - Effects of the Resilience of Nurses in Long-Term Care Hospitals during on Job Stress COVID-19 Pandemic: Mediating Effects of Nursing Professionalism
Bom-Mi Park, Jiyeon Jung
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(19): 10327. CrossRef - Nurses' Voices: Autumn 2020
Jeung-Im Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 644. CrossRef
- The impact of nurses’ caring behaviors and personality traits on workplace violence
- 1,588 View
- 57 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- The Influence of Grit on Turnover Intention of University Hospital Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Job Involvement
- Ji Yeong Jeong, Youn Sook Seo, Jung Hoon Choi, Seong Hee Kim, Min Sook Lee, Sung Hwa Hong, Jung Suk Choi, Da Eun Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):181-190. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.181
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to confirm the mediating effect of job involvement in the relationship between grit and turnover intention among nurses working at university hospitals.
Methods Participants included 437 nurses from university hospitals located in C city, Gyeongnam. Data were collected from January 8 to 19, 2018, using self-report questionnaires. Data were analyzed using the t-test, analysis of variance, Scheffe's test, Pearson's correlation coefficient, and multiple regression, with the SPSS/22.0 program. A mediation analysis was performed according to the Baron and Kenny, and bootstrapping methods.
Results There were significant relationships between grit and job involvement (r=.40,
p <.001), grit and turnover intention (r=−.29,p <.001), and turnover intention and job involvement (r=−.52,p <.001). Job involvement showed partial mediating effects in the relationship between grit and turnover intention.Conclusion Grit increased job involvement and lowered turnover intention. Therefore, to reduce nurses' turnover intention, it is necessary to develop a program and strategies to increase their grit.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Workplace Spirituality and Self‐Efficacy on Quality of Life Among Cancer Survivors: Empirical Quantitative Research
Seulgi Kang, Yoonjung Kim, Hyeji Shin
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025; 81(5): 2438. CrossRef - Mediating effect of grit on the influence of nurses’ silence behavior on medication safety competence: a cross-sectional study
Haengsuk Kim, Wanju Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(1): 81. CrossRef - Success doesn’t come to you, you go to it: the role of self-perceived employability among engineering graduates
Arun Aggarwal, Amit Mittal, Ishani Sharma, Pawan Kumar Chand, Amruta Deshpande
Industrial and Commercial Training.2025; 57(4): 361. CrossRef - The associations of grit, self-leadership, and followership with competency in evidence-based practice among nurses in Korea: a descriptive correlational study
Ha-young Kim, Jin-il Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(2): 244. CrossRef - Effects of Grit and Nursing Work Environment on Work Engagement in Clinical Nurses
Young Ju Kim, Hye Young Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 312. CrossRef - Exploring personal, community, and societal conditions associated with South Korean new graduate nurses’ organizational socialization: a cross-sectional survey study
Jihye Song, Jeongsuk Lee, Youmin Cho, Ahyoung Jeon, Moonhee Gang
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Free Will Belief and Nurses’ Job Performance: The Mediating Roles of Grit and Positive Affect
Wei Liu, Song Wang
International Nursing Review.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Attitude Toward Interdepartmental Transfer, Career Growth Opportunity, and Role Breadth Self-Efficacy on Job Crafting among Nurses with Transfer Experience
Yu Jin Lee, Chung Hee Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 497. CrossRef - Effects of Grit and Retention Intention on Work Performance among Operating Room Nurses
Ae-Kyung Jang, Jun-Hee Lee, Kyeong-Soo Lee, Tae-Yoon Hwang
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2025; 39(3): 381. CrossRef - Effects of grit, calling, and resilience on the retention intention of general hospital nurses
Gi Ran Lee, Imsun Lee, Mihee Chung, Jiyeon Ha
International Nursing Review.2024; 71(4): 766. CrossRef - Relationship between the sense of nursing professional pride and adversity quotient, grit levels among nurses in blood purification centers: a multicenter cross-sectional study
Wenbin Xu, Lin Li, Qian Jiang, Yiqian Fang, Qian Yang
Frontiers in Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Experiences of Newly Graduated Nurses Trained by Clinical Nurse Educators
Yeon Hee Kim, Young Sun Jung, Kyoung Hui Lee, Eun Ji Chang
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2024; 9(1): 34. CrossRef - The influence of grit on nurse job satisfaction: Mediating effects of perceived stress and moderating effects of optimism
Cui Yang, Lu Yang, Dongmei Wu
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of grit on the work engagement of nurses: The mediating effects of positive psychological capital and burnout
Mi Kyung Park, Won Hwa Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 161. CrossRef - Grit among Nursing Students at Private Nursing Institute of Karachi Pakistan
Muhammad Ishaq, Afsha Bibi, Fazal Khaliq, Ashfaq Ahmad
Pakistan Journal of Health Sciences.2023; : 115. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Grit on the Relationship between Work Environment and Intention to Stay at Work among Regional Trauma Center Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study
Ji Sun Yang, Myung Jin Jang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(2): 107. CrossRef - Similarity in functional connectome architecture predicts teenage grit
Sujin Park, Daeun Park, M Justin Kim
Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Gratitude Disposition, Social Support, and Occupational Stress of Clinical Nurses on Grit
Ha-Na Lee, Hwee Wee
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(1): 56. CrossRef - Effects of Nurses' Grit on the Nursing Performance: Multiple Mediating Effects of Work Engagement and Job Crafting
Jeong-Lim Ryu, So-Hyoung Hong, Yoon Seo Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 468. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Nurse Retention Intention: With a Focus on Shift Nurses in South Korea
Eun-Young Cho, Hwee Wee
Healthcare.2023; 11(8): 1167. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Passion Continuation Program based on GRIT Theory for Nurses in COVID-19 Pandemic: A Non-Randomized Experimental Study
Do-Young Lee, Nam-Joo Je, Yoon Jung Kim, Chunseon Jang, Hyun-Ju Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(3): 357. CrossRef - Antecedents and Consequences of Grit Among Working Adults: A Transpersonal Psychology Perspective
Devanshi Agrawal, Surekha Chukkali, Sabah Singh
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a scale to measure the psychological resources of grit in adults
Sarah E. Schimschal, Denis Visentin, Rachel Kornhaber, Tony Barnett, Michelle Cleary
Nursing & Health Sciences.2022; 24(3): 752. CrossRef - Effect of Nurses’ Grit on Nursing Job Performance and the Double Mediating Effect of Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment
Hyun-Kuk Cho, Boyoung Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(2): 396. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on the Mediating Effect of Clinical Competence in the Relationship Between Grit and Field Adaptation in Newly Graduated Nurses
Eunhee Shin
SAGE Open Nursing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Pediatric nurses' grit and nursing intention during the COVID-19 pandemic: Mediating and moderating effects of mindset and psychological collectivism
Young Soo Chu, Won-Oak Oh, Il Tae Park, Anna Lee, Myung-Jin Jung
Child Health Nursing Research.2021; 27(4): 395. CrossRef - Grit and Meaning in Life of Chinese Nurses: The Chain Mediating Effect of Social Support and Hope
Lei Yang, Dongmei Wu
Frontiers in Psychology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Grit-S in Chinese Nurses
Changjiu He, Dongmei Wu, Lu Yang, Lei Yang, Yuchuan Yue
Frontiers in Psychology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influences of Grit, Emotional Labor and Organizational Intimacy on Nurses' Intention to Stay in Comprehensive Nursing Care Service Units
Dae Yeon Lee, Sook Young Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2020; 23(2): 149. CrossRef - Studying the effects of future-oriented factors and turnover when threatened
Sean McGinley, Nathaniel Discepoli Line, Wei Wei, Taylor Peyton
International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management.2020; 32(8): 2737. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Clinical Nurses Grit Scale (CN-GRIT)
Hyosun Park, Kyungmi Lee, Nayeon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(1): 55. CrossRef - The Relationship between Occupational Stress and Burnout among Firefighters: Mediating of Grit
Yun Ah Jung, Myung Soo Oh, Hee Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2020; 29(2): 96. CrossRef - Mediation Effects of Calling and Role Breadth Self-efficacy on the Relationship between Supportive Supervision and Job Crafting of Nurses in General Hospitals
Sujeong Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(3): 251. CrossRef - Effects of Grit and Critical Thinking Disposition on Nursing Students’
Clinical Competence
Sook-Hee Cho, Kyung-Soon Yun
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2020; 14(2): 117. CrossRef - The Impact of Grit on University Student’s Core Competency in Dental Hygiene Students
Soo-Auk Park, Young-Sik Cho
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2019; 19(3): 170. CrossRef
- The Effects of Workplace Spirituality and Self‐Efficacy on Quality of Life Among Cancer Survivors: Empirical Quantitative Research
- 2,616 View
- 76 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 35 Crossref

- The Effects of Hospitals’ Family Friendly Management on Married Female Nurses’ Retention Intention: Focused on the Mediating Effects of Work-Family Interface
- Jin Hwa Lee, Jee-In Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):386-397. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.386
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study examined the effect of hospitals’ family-friendly management on married female nurses’ retention intention. The focus was the mediating effects of the work-family interface (work-family conflict, work-family enrichment and work-family balance).
Methods This study was a cross-sectional study. The participants were 307 nurses working at five public and five private hospitals with more than 200 beds in Seoul. Data were collected using structured questionnaires from September 10 to September 17, 2018 and analyzed with SPSS 24.0. Data were analyzed using an independent t-test, a one-way ANOVA, Pearson's correlation coefficients, and multiple regression following the Baron and Kenny method and Sobel test for mediation.
Results There were significant correlations among family-friendly management, the work-family interface, and retention intention. Work-family conflict showed a partial mediating effect on the relationship between family-friendly management and retention intention. Work-family enrichment showed a partial mediating effect on the relationship between family-friendly management and retention intention. Work-family balance showed a partial mediating effect on the relationship between family-friendly management and retention intention.
Conclusion These findings indicate that both hospitals’ family-friendly management and nurses’ work-family interface are important factors associated with nurses’ retention intention. Therefore, hospitals should actively implement family-friendly management for nurses and establish strategies to enhance nurses’ work-family interface for effective human resource management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How parenting-related characteristics influence parenting stress among nurses with young children in the Seoul metropolitan area, South Korea: a cross-sectional study
Minhwa Hwang, Nagyeong Lee, Gunjeong Lee
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Retention Intention of Female Nurses Raising Young and School-Age Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Ha Neul Lee, Suyon Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 504. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of Instruments Measuring Dyadic Communication and Environment in Dementia Care: A Systematic Review
Sohyun Kim, Wen Liu, Patricia Heyn
The Gerontologist.2023; 63(1): 52. CrossRef - Disaster Preparedness and Associated Factors Among Emergency Nurses in Guangdong Province, China: A Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study
Jia Wang, Xinglan Sun, Sihui Lu, Fen Wang, Meijuan Wan, Hanxi Chen, Yibing Tan
Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Causes and Effects of Burnout Experienced by Insurance Review Nurses: Focus Group Interview
Eun Sil Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyung Kim, Myoung Hee Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(5): 545. CrossRef - Nurses’ Clinical Work Experience during Pregnancy
Hyunjung Lee, Hyoung Eun Chang, Jiyeon Ha
Healthcare.2020; 9(1): 16. CrossRef
- How parenting-related characteristics influence parenting stress among nurses with young children in the Seoul metropolitan area, South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- 1,279 View
- 34 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- The Effect of Nurse's Emotional Labor on Turnover Intention: Mediation Effect of Burnout and Moderated Mediation Effect of Authentic Leadership
- Soo Yang Na, Hanjong Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):286-297. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.286
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose To investigate the effect of nurses’ emotional labor on their turnover intention that was mediated by burnout and to examine the moderated mediation effect of authentic leadership.
Methods A total of 227 nurses working at two general hospitals in Seoul were recruited from March 21 to May 6 in 2016. Emotional labor including surface acting and deep acting; burnout factors such as emotional exhaustion and personal accomplishment; and turnover intention were assessed. The data were analyzed using SPSS 22.0 and SPSS PROCESS macro.
Results Surface acting significantly increased emotional exhaustion and reduced personal accomplishment. Deep acting significantly increased personal accomplishment. Emotional exhaustion significantly increased turnover intention. Conversely, personal accomplishment significantly reduced turnover intention. Surface acting had an indirect effect on turnover intention that was mediated by emotional exhaustion. Deep acting had an indirect effect on turnover intention that was mediated by personal accomplishment. Authentic leadership had a moderated mediation effect on the relationship between surface acting and turnover intention that was mediated by emotional exhaustion.
Conclusion The findings of this study indicate that the establishment of strong authentic leadership by head nurses would help nurses reduce their burnout and turnover intention. Conducting intervention studies would be also important to promote better work environments that would enable nurses to fortify the positive aspect of emotional labor and to reduce their burnout levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigation of professional values education's effect on pediatric nurses' perception of professional values, emotional labour behaviours and burnout levels: A randomised controlled trial
Nazmiye Yirik, Şerife Tutar
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2026; 87: 99. CrossRef - Effect of a Nursing Practice Environment, Nursing Performance on Retention Intention: Focused on the Mediating Effects of Nursing Professional Pride
Shin Hee Kim, Mi Sook Oh, Yun Bok Kwak
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(1): 64. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Burnout of Nurses in Comprehensive Nursing Care Service Wards: Focusing on Positive Psychological Capital, Role Conflict, and Authentic Leadership
Jung Wha Park, Kyoung Ja Kim, Ji Young Im, Ji Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 345. CrossRef - The Relationship between School Managers' Authentic Leadership Behaviors and Teachers' Emotional Labor Behaviors
Mehmet Akif Köse, Esra Töre
İZÜ Eğitim Dergisi.2024; 6(1): 1. CrossRef - Servant leadership and nurses' deep acting: a moderated mediation model
Shu-Chen Susan Chang, Anyi Chung, Shu Yu Chen, Chu Yen Lin, I-Heng Chen
Journal of Organizational Change Management.2024; 37(3): 546. CrossRef - Association between Emotional Labor and Work Absence Due to Dental Treatment in Korean Workers
Ji-Young Son, Se-Hwan Jung, Jae-In Ryu, Dong-Hun Han
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2024; 24(4): 350. CrossRef - Turnover intention and its related factors of clinical research coordinator in Hunan, China: a cross-sectional study
Juan Li, JinHua Li, ZhengDi She, LiWen Guo, ShanZhi Gu, Wen Lu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - How surface acting affects turnover intention among family doctors in rural China: the mediating role of emotional exhaustion and the moderating role of occupational commitment
Anqi Wang, Changhai Tang, Lifang Zhou, Haiyuan Lv, Jia Song, Zhongming Chen, Wenqiang Yin
Human Resources for Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Effect of Emotional Labor on Turnover Intention and the Moderating Role of Perceived Organizational Support: Evidence from Korean Firefighters
Jaeyoung Lim, Kuk-Kyoung Moon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(5): 4379. CrossRef - Key Factors for Enhancing Home Care Workers’ Intention to Stay by Multiple-Criteria Decision Analysis
Wei Hsu, Fang-Ping Shih
Healthcare.2023; 11(5): 750. CrossRef - The relationship between job burnout and intention to change occupation in the accounting profession: the mediating role of psychological well-being
Lum Çollaku, Muhamet Aliu, Skender Ahmeti
Management Research Review.2023; 46(12): 1694. CrossRef - The effect of organizational justice on young nurses’ turnover intention: The mediating roles of organizational climate and emotional labour
Yue Su, Zhe Jiang, Ran Meng, Guangli Lu, Chaoran Chen
Nurse Education in Practice.2023; 72: 103723. CrossRef - Authentic leadership in nurses’ professional practice: an integrative review
Ellen Daiane Biavatti de Oliviera Algeri, Rosemary Silva da Silveira, Jamila Geri Tomaschewski Barlem, Maria Claudia Medeiros Dantas de Rubim Costa, Danubia Andressa da Silva Stigger, Cristiane de Sá Dan
Revista Brasileira de Enfermagem.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of burnout and its dimensions on turnover intention among nurses: A meta‐analytic review
Ahmet Hakan Özkan
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(3): 660. CrossRef - A liderança autêntica no exercício profissional do enfermeiro: uma revisão integrativa
Ellen Daiane Biavatti de Oliviera Algeri, Rosemary Silva da Silveira, Jamila Geri Tomaschewski Barlem, Maria Claudia Medeiros Dantas de Rubim Costa, Danubia Andressa da Silva Stigger, Cristiane de Sá Dan
Revista Brasileira de Enfermagem.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of burnout and its dimensions on turnover intention among nurses: a meta-analytic review
AHmet Hakan Özkan
Kybernetes.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of professional identity, job satisfaction and burnout with turnover intention among general practitioners in China: evidence from a national survey
Tao Zhang, Jing Feng, Heng Jiang, Xin Shen, Bo Pu, Yong Gan
BMC Health Services Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Collegial surface acting emotional labour, burnout and intention to leave in novice and pre‐retirement nurses in the United Kingdom: A cross‐sectional study
Catherine Theodosius, Christina Koulouglioti, Paula Kersten, Claire Rosten
Nursing Open.2021; 8(1): 463. CrossRef - The Experience of Emotional Labor and Its Related Factors among Nurses in General Hospital Settings in Republic of Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Da-Jung Ha, Jung-Hyun Park, Su-Eun Jung, Boram Lee, Myo-Sung Kim, Kyo-Lin Sim, Yung-Hyun Choi, Chan-Young Kwon
Sustainability.2021; 13(21): 11634. CrossRef
- Investigation of professional values education's effect on pediatric nurses' perception of professional values, emotional labour behaviours and burnout levels: A randomised controlled trial
- 2,673 View
- 86 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref

- Patterns and Influential Factors of Inter-Regional Migration of New and Experienced Nurses in 2011~2015
- Bohyun Park, Se Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(5):676-688. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.5.676
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyze the migration patterns of new nurses and experienced nurses and to identify the factors influencing inter-regional migration for solving regional imbalances of clinical nurses in South Korea.
Methods This study involved a secondary analysis of data from the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA). Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and multiple logistic regression analysis.
Results New nurses tended to migrate from Kyunggi to Seoul. However, experienced nurses tended to migrate from Seoul and Chungchung to Kyunggi. Significant predictors of inter-regional migration among new nurses were location and nurse staffing grade of hospitals. Significant predictors of inter-regional migration among experienced nurses were location, hospital type, nurse staffing grade, ownership of hospitals and age of nurses.
Conclusion Inter-regional migration occupied a small portion of total hospital movement among clinical nurses. The regional imbalances of nurses were not caused by the migration from non-metropolitan areas to Seoul. Nurse shortage problems in the small and medium hospitals of the non-metropolitan area can be solved only through improvement of work environment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ideation Model for Healthcare Workforce Management in the Philippine Context
Jose Abantao, Jose Marlon Refuncion, Marife Lacaba
Journal of Interdisciplinary Perspectives.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Turnover Rates and Factors Associated With Turnover: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Retention Period of Clinical Nurses in Korea Using National Data
Yunmi Kim, Hyun-Young Kim
Policy, Politics, & Nursing Practice.2024; 25(2): 83. CrossRef - A Study on the Outflow Intention of Nursing Students in Non-Metropolitan Area: Honam Region
Purum Kang, A Young Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(3): 234. CrossRef - Impact evaluation of nurse staffing policy reform in Korea: A quasi‐experimental study
Jinseon Yi, Jinhyun Kim
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 3457. CrossRef - Re-employment Hospital Types of Early Career Nurses and Changes in Work-Life Balance
Eun-Young Kim, Yun-Kyung Oh
STRESS.2022; 30(3): 163. CrossRef - Retention Rates and the Associated Risk Factors of Turnover among Newly Hired Nurses at South Korean Hospitals: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Yunmi Kim, Hyun-Young Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(19): 10013. CrossRef - Emotional Labor Strategies, Stress, and Burnout Among Hospital Nurses: A Path Analysis
Ji‐Soo Kim
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2020; 52(1): 105. CrossRef - Nursing stress factors affecting turnover intention among hospital nurses
Eun‐Kyoung Lee, Ji‐Soo Kim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Organizational Justice, Organizational Culture and Emotional Intelligence on Intention of Retention in Reemployed Nurses
Yu Ri Jung, So Young Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 501. CrossRef - Intention to leave among staff nurses in small‐ and medium‐sized hospitals
Jeong Hye Park, Min Jung Park, Hye Young Hwang
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2019; 28(9-10): 1856. CrossRef - Why newly graduated nurses in South Korea leave their first job in a short time? A survival analysis
Eunhee Lee
Human Resources for Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Students' Choices of a Place of Employment
Sun Ju You, Jong Kyung Kim, Myun Sook Jung, Se Young Kim, Eun Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2018; 18(4): 184. CrossRef
- Ideation Model for Healthcare Workforce Management in the Philippine Context
- 1,685 View
- 13 Download
- 12 Crossref

- The Relationship Among Leadership Styles of Nurse Managers, Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment, and Turnover Intention
- Na Sun Ha, Jung Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(6):812-822. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.6.812
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The Purpose of this study was to identify the relationship among leadership style of nurse managers, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention. METHOD: The subjects were 468 nurses and 19 head nurses who were working at the 3 general hospitals in seoul. The data were collected from July 6 to September 14, 2001 by the structured questionnaires. For data analysis, descriptive statistics, ANOVA, Pearson correlation coefficient, and stepwise multiple regression with SAS package were used. RESULT: 1) The score of the nurse managers' transformational leadership perceived by surbodinates' were higher than that of the nurse managers' transactional leadership. Among 5 subdimensions of the leadership styles perceived by surbodinates', the scores of 'charisma' and 'intellectual stimulation' were highest and 'management by exception' were lowest. 2) 'Charisma', 'intellectual stimulation', 'individual consideration' and 'contingent reward' were positively related to all of variables except 'turnover intention'. 'Management by exception' was negatively related to all of variables and was positively related to 'turnover intention'. 3) 'Job satisfaction' was positively related to 'organizational commitment' and 'Job satisfaction', 'organizational commitment' were negatively related to 'turnover intention'. 4) As a result of stepwise multiple regression analysis, the key determinants of 'turnover intention' were 'organizational commitment' and this explained 44.4% of the total variance of it.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between nurse managers' leadership style and patients' perception of the quality of the care provided by nurses: Cross sectional survey
F. Zaghini, J. Fiorini, M. Piredda, R. Fida, A. Sili
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2020; 101: 103446. CrossRef - Perception of Healthcare Accreditation System on Patient Safety Management Activities and Nursing Performance of Regional Public Hospital Nurses
Myung Ju Kang, Kyung Hee Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(4): 416. CrossRef - Leadership Experience of Clinical Nurses: Applying Focus Group Interviews
Byoung-Sook Lee, Yong-Sook Eo, Mi-Aie Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(5): 671. CrossRef - The Effects of Positive Psychological Capital, Organizational Commitment, Customer Orientation in Clinical Nurses
In Suk Kim, Ryu Bin Seo, Bok Nam Kim, A Ri Min
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(1): 10. CrossRef - The relationship between South Korean clinical nurses' attitudes toward organizations and voluntary turnover intention: A path analysis
Jong Kyung Kim, Sun Ju Chang
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2015; 21(4): 383. CrossRef - The Effects of the Organizational Socialization Education Program on Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment and Turnover Intention of New Nurses
Gum-Hee Choi
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2014; 8(3): 89. CrossRef - A Phenomenological Study on Oncology Adaptation Experiences of New Nurses
Hye Ran Kim, In Soo Kwon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(2): 127. CrossRef - Assessing the Influence of Managerial Coaching on Employee Outcomes
Sewon Kim
Human Resource Development Quarterly.2014; 25(1): 59. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling on Nursing Productivity of Nurses in Korea
Se Young Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Heon Man Lim, Mi Young Lee, Kwang-Ok Park, Kyoung A Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(1): 20. CrossRef - Effects of Nurses' Perception of Servant Leadership on Leader Effectiveness, Satisfaction and Additional Effort: Focused on the Mediating Effects of Leader Trust and Value Congruence
Sang Sook Han, Nam Eun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(1): 85. CrossRef - A Model on Turnover Intention of Chief Nurse Officers
Kwang-Ok Park, Jong Kyung Kim, Se Young Kim, Sunju Chang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(1): 9. CrossRef - Relationship Between Organizational Communication Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment among Hospital Nurses
Kyeong Hwa Kang, Yong Hee Han, Soo Jin Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2012; 18(1): 13. CrossRef - Influence of Decentralization, Participation in Decision Making, Job Satisfaction on Nurse Managers' Organizational Commitment
Mi Yu, Kyungsook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2011; 17(3): 357. CrossRef - Role of internal marketing, organizational commitment, and job stress in discerning the turnover intention of Korean nurses
Haejung LEE, Myoung‐Soo KIM, Jung‐A YOON
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2011; 8(1): 87. CrossRef - Relationship between Critical Thinking Disposition, Clinical Decision Making and Job Satisfaction of Cancer Center Nurses
Sam Chul Jung, Dukyoo Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2011; 17(4): 443. CrossRef - Influence of Clinical Nurse Specialists' Emotional Intelligence on Their Organizational Commitment and Turnover Intention
Young Hee Sung, Moon Sook Hwang, Kyeong Sug Kim, Na Mi Chun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(3): 259. CrossRef - New Nurse Turnover Intention and Influencing Factors
Sang Sook Han, In Soon Sohn, Nam Eun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(6): 878. CrossRef - The Mediating Role of Organizational Citizenship Behavior between Organizational Justice and Organizational Effectiveness in Nursing Organizations
Wall-Yun Park, Sook-Hee Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(2): 229. CrossRef
- The relationship between nurse managers' leadership style and patients' perception of the quality of the care provided by nurses: Cross sectional survey
- 1,188 View
- 16 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Predictors of Nurse Turnover: Model Development and Testing
- Richard Redman, Sung Hyun Cho, Shake Ketefian, Oi Saeng Hong
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(7):1667-1678. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.7.1667
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF BACKGROUND: The phenomenon of nursing turnover has been explained by organizational commitment, job satisfaction, or intent to stay in previous studies; yet the combined contribution of these factors to nurse turnover has not been examined. OBJECTIVES: The purpose of this study was to develop and test a turnover model which included professionalism, job-related variables, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and intent to stay.
METHOD
A total of 424 registered nurses in a university hospital completed a self-administered questionnaire including Professionalism Scale, Job Diagnostic Survey, Nurse Assessment Survey, and intention to stay. Nurses were classified as to whether they remained in or had left the organization 18 months after the survey. Multiple regression and logistic regression analyses were conducted to test the model.
RESULTS
Overall job satisfaction and intent to stay were the most important determinants of nursing turnover. Organizational commitment positively affected intent to stay and indirectly decreased turnover through intent to stay. Satisfaction with coworkers and supervisor were the most important factors in explaining overall job satisfaction. Satisfaction with pay, autonomy, and feedback from job also positively affected overall job satisfaction.
CONCLUSION
Using the results of the tested model nurse managers and administrators could predict turnover by monitoring its determinants, and ultimately reduce the turnover rate through early intervention.
- 566 View
- 3 Download

- Turnover Experience of Male Nurses
- Hyunsu Kim, Jeongseop Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(1):25-38. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.1.25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The aim of this study was to identify turnover experiences of men in nursing and to derive a substantive theory on the turnover experience of men who are nurses.
Methods Data were collected through in-depth interviews with 13 men who had worked as a nurse for 1 year or more, and had a turnover experience during that period. Collected data were analyzed on the basis of Strauss and Corbin's grounded theory.
Results The core category in the turnover experiences of the respondents was ‘seeking a stable place for me’. In the analysis of the core category, types of ‘contentment’, ‘seeking’, ‘survival’ and ‘confusion’ were identified. The sequential stages of these nurses’ turnover experience were ‘confrontation’, ‘incertitude’, ‘retrying’ and ‘realization’. However, when a problem arose in the process, they returned to the stage of confusion. Thus, these stages could occur in a circular fashion.
Conclusion These findings provide a deep understanding of the turnover experience of men in nursing and offers new information about how they adapt to nursing practice. The findings should be useful as foundational data for men who hope to become nurses and also for managers responsible for nurses who are men.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Male nurses’ adaptation experiences after turnover to community institutions in Korea: A grounded theory methodology
Ja-Sook Kim, Suhyun Kim, Hyang-In Cho Chung, Sally Mohammed Farghaly
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(5): e0302819. CrossRef - Turnover Rates and Factors Associated With Turnover: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Retention Period of Clinical Nurses in Korea Using National Data
Yunmi Kim, Hyun-Young Kim
Policy, Politics, & Nursing Practice.2024; 25(2): 83. CrossRef - A survival analysis approach to determine factors associated with non-retention of newly hired health workers in Iran
Vahid Ghavami, Seyed Saeed Tabatabaee
BMC Health Services Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing work engagement among male nurses: A structural equation model
Chao Wu, Si‐zhe Cheng, Jing Wu, Yin‐juan Zhang, Ya‐wei Lin, Lu Li, Juan Du, Yu‐hai Zhang, Hong‐juan Lang
Nursing Open.2023; 10(12): 7749. CrossRef - Turnover intention and retention of newly licensed nurses in their first job: A longitudinal study
Hyoung Eun Chang, Sung‐Hyun Cho
International Nursing Review.2023; 70(3): 338. CrossRef - Clinical Work and Life of Mid-Career Male Nurses: A Qualitative Study
Soo-Yong Shin, Eun-Ju Lim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(12): 6224. CrossRef - Analysis of Male and Female Nurses’ Attitudes toward Nurse Uniforms in South Korea: The Functional, Expressive, and Aesthetic (FEA) Framework
Seon Mi Jang, Sae Eun Lee, Jeong-Ju Yoo
International Journal of Costume and Fashion.2021; 21(1): 25. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Turnover Intention among Male Nurses in Korea
Su Ol Kim, Sun-Hee Moon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(18): 9862. CrossRef - Factors associated with the nurses’ intent to stay in China, Japan, and Korea: an integrative review
Ting Xue, Wen-Bin Jiang, Meng-Di Ma, Jie Zhang, Ming-Hui Lu, Yong-Mei Jiang
Frontiers of Nursing.2020; 7(3): 269. CrossRef - Why newly graduated nurses in South Korea leave their first job in a short time? A survival analysis
Eunhee Lee
Human Resources for Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Subjectivity About Turnover Intention Among Male Nurses in South Korea: A Q-Methodological Study
Ick-Jee Kim, Hyung-Wha Shim
Asian Nursing Research.2018; 12(2): 113. CrossRef - Win-Win Partnership in the Clinical Setting: Female Nurses' Adaptive Experience to Male Nurses
Hyunsu Kim, Eun Jin Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(5): 423. CrossRef
- Male nurses’ adaptation experiences after turnover to community institutions in Korea: A grounded theory methodology
- 2,373 View
- 25 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Association between Emotional Labor, Emotional Dissonance, Burnout and Turnover Intention in Clinical Nurses: A Multiple-Group Path Analysis across Job Satisfaction
- Chi-Yun Back, Dae-Sung Hyun, Sei-Jin Chang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(6):770-780. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.6.770
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to investigate the influence of emotional labor, emotional dissonance, and burnout on nurse's turnover intention and examine the effect of job satisfaction on the relationships among emotional labor, emotional dissonance, burnout, and turnover intention.
Methods The sample consisted of 350 nurses recruited from 6 general hospitals in 2 cities in Korea. A multiple-group analysis was utilized. Data were analyzed using SPSS statistics 23 and AMOS 20.
Results In the path analysis, turnover intention was directly related to burnout in clinical nurses who had a high job satisfaction (b=.24,
p =.003), while it was indirectly related to emotional dissonance (b=.13,p =.002). In the multiple-group path analysis, turnover intention was directly related to emotional dissonance (b=.18,p =.033) and burnout (b=.26,p =.002) for nurses with low job satisfaction.Conclusion These results indicate that manuals and guidelines to alleviate the negative effects of emotional labor, emotional dissonance, and burnout, and to increase job satisfaction are strongly required to reduce turnover intention in nurses at the organizational level as well as at the individual level.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of work–family conflict on teachers’ turnover intention: the mediating role of emotional labor
Yang yang Zhou, Man Jiang
Cogent Education.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the nursing practice environment, slow nursing, and living a calling on geriatric nursing stress among general hospital nurses in South Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive study
Chung Hee Woo
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2026; 28(1): 157. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Resilience on the Relationship Between Job Stress and the Professional Quality of Life of Hospice and Palliative Care Nurses: A Multicenter Cross-sectional Study
Eunhee Jo, Soon-Jung Hwang, Hyang-Suk Kwon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(3): 241. CrossRef - Emotional dissonance and burnout among child welfare workers: The moderating role of social support from colleagues, supervisors, and organization
Morten Birkeland Nielsen, Håkon A. Johannessen, Jan Olav Christensen, Live Bakke Finne
Journal of Social Work.2023; 23(4): 615. CrossRef - Emotional labor and job satisfaction among nurses: The mediating effect of nurse–patient relationship
Yi-wei Xu, Ling Fan
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Professional Quality of Life, Work-Related Stress, and Job Satisfaction among Nurses in Saudi Arabia: A Structural Equation Modelling Approach
Emad Shdaifat, Noha Al-Shdayfat, Najla Al-Ansari, Jonathan Haughton
Journal of Environmental and Public Health.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - A structural equation model of organizational commitment by hospital nurses: The moderating effect of each generation through multi-group analysis
Jeong Hye Chae, Young Suk Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(3): 305. CrossRef - Emotional Labor, Burnout, Medical Error, and Turnover Intention among South Korean Nursing Staff in a University Hospital Setting
Chan-Young Kwon, Boram Lee, O-Jin Kwon, Myo-Sung Kim, Kyo-Lin Sim, Yung-Hyun Choi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(19): 10111. CrossRef - The Experience of Emotional Labor and Its Related Factors among Nurses in General Hospital Settings in Republic of Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Da-Jung Ha, Jung-Hyun Park, Su-Eun Jung, Boram Lee, Myo-Sung Kim, Kyo-Lin Sim, Yung-Hyun Choi, Chan-Young Kwon
Sustainability.2021; 13(21): 11634. CrossRef - Health-Related Symptoms and Working Conditions on Vulnerability to Presenteeism Among Nurses in South Korea
Jee-Seon Yi, Eungyung Kim, Hyeoneui Kim
Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health.2021; 33(8): 880. CrossRef - Effects of Hospital Characteristics on Employment Rate, Working Period and Retirement of Ward Nurses in Korea: A Retrospective Cohort Study Based on HIRAS Data
Hee-Jung Seo, Gi Yon Kim, Sei-Jin Chang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(6): 837. CrossRef - The Influence of Mistreatment by Patients on Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention among Chinese Nurses: A Three-Wave Survey
Lei Qi, Xin Wei, Yuhan Li, Bing Liu, Zikun Xu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(4): 1256. CrossRef - Emotional Labor Strategies, Stress, and Burnout Among Hospital Nurses: A Path Analysis
Ji‐Soo Kim
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2020; 52(1): 105. CrossRef - Nursing stress factors affecting turnover intention among hospital nurses
Eun‐Kyoung Lee, Ji‐Soo Kim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of the Tromsø Social Intelligence Scale
Sook Kyoung Park, Ya Ki Yang, Eunju Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(2): 165. CrossRef - Nurses' organizational communication satisfaction, emotional labor, and prosocial service behavior: A cross‐sectional study
Youngsoo Kim, Sun Joo Jang
Nursing & Health Sciences.2019; 21(2): 223. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Mindfulness in the Relationship between Self-Esteem and Burnout among Clinical Nurses
Hanju Bea, Heekyung Chang, Young Eun
Stress.2018; 26(3): 243. CrossRef
- The impact of work–family conflict on teachers’ turnover intention: the mediating role of emotional labor
- 1,556 View
- 35 Download
- 17 Crossref

- Predictors of Turnover among New Nurses using Multilevel Survival Analysis
- Suhee Kim, Kyongeun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(5):733-743. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.5.733
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine factors influencing new graduate nurse turnover.
Methods This study was carried out as a secondary analysis of data from the 2010 Graduates Occupational Mobility Survey (GOMS). A total of 323 nurses were selected for analysis concerning reasons for turnover. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and multilevel survival analysis.
Results About 24.5% of new nurses left their first job within 1 year of starting their jobs. Significant predictors of turnover among new nurse were job status, monthly income, job satisfaction, the number of hospitals in region, and the number of nurses per 100 beds.
Conclusion New graduate nurses are vulnerable to turnover. In order to achieve the best health of the nation, policy approaches and further studies regarding reducing new graduate nurse turnover are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and Moderating Factors of Turnover Rate and Turnover Intention Among Nurses Worldwide: A Meta-Analysis
Dluha Mafula, Hidayat Arifin, Ruey Chen, Chien-Mei Sung, Chiu-Kuei Lee, Kai-Jo Chiang, Kondwani Joseph Banda, Kuei-Ru Chou
Journal of Nursing Regulation.2025; 15(4): 20. CrossRef - Educational and professional needs of newly graduated nurses during transition to practice: an integrative review
Hadi Jafarimanesh, Shahrzad Ghiyasvandian, Bret Lyman, Hossein Ghanaati, Masoumeh Zakerimoghadam
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting turnover intention among newly graduated nurses in South Korea: a decision tree analysis
Mikyung Moon, Hyunwook Kang
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Individual and environmental factors that influence longevity of newcomers to nursing and midwifery: a scoping review
Janie Alison Brown, Tanya Capper, Desley Hegney, Helen Donovan, Moira Williamson, Pauline Calleja, Terena Solomons, Sally Wilson
JBI Evidence Synthesis.2024; 22(5): 753. CrossRef - Assessing the impacts of nurse staffing and work schedules on nurse turnover: A systematic review
Sung‐Heui BAE
International Nursing Review.2024; 71(1): 168. CrossRef - Factors associated with practice readiness among newly qualified nurses in their first two years of practice
Siew Hoon Lim, Shin Yuh Ang, Fazila Aloweni, Kee Chen Elaine Siow, Sabrina Bee Leng Koh, Tracy Carol Ayre
Nurse Education Today.2024; 136: 106143. CrossRef - South Korean Nurse Residency Program for New Graduates: A Posttest Study
Jihye Song, Kyunghee Kim, Yunjung Jang
The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing.2024; 55(8): 393. CrossRef - Socializing into a Profession with High Early Turnover: Nursing Students’ Expectations for Leader-Member Relationships
Jennifer K. Ptacek, Leah M. Omilion-Hodges
Health Communication.2024; 39(11): 2402. CrossRef - An examination of the career decision-making self-efficacy of final-year nursing students
Edah Anyango, Esther Adama, Janie Brown, Irene Ngune
Nurse Education Today.2024; 138: 106196. CrossRef - Association of Work Schedules With Nurse Turnover: A Cross-Sectional National Study
Sung-Heui Bae
International Journal of Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive assessment of factors contributing to the actual turnover of newly licensed registered nurses working in acute care hospitals: a systematic review
Sung-Heui Bae
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Turnover intention and retention of newly licensed nurses in their first job: A longitudinal study
Hyoung Eun Chang, Sung‐Hyun Cho
International Nursing Review.2023; 70(3): 338. CrossRef - Factors Influencing RNs' Intention to Stay in Nursing Homes: Multilevel Modeling Approach
Sunyeob Choi, Jiyeon Lee
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2023; 49(7): 40. CrossRef - Factors associated with difficulty in adapting and intent to leave among new graduate nurses in South Korea
Sun-young Park, Heejung Kim, Chenjuan Ma
Health Care Management Review.2022; 47(2): 168. CrossRef - Why Nurses Are Leaving Veterans Affairs Hospitals?
Dongjin Oh, Keon-Hyung Lee
Armed Forces & Society.2022; 48(4): 760. CrossRef - Re-employment Hospital Types of Early Career Nurses and Changes in Work-Life Balance
Eun-Young Kim, Yun-Kyung Oh
STRESS.2022; 30(3): 163. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Re-Employment of Newly Graduated Nurses: Longitudinal Study
Yun Kyung Oh, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(2): 162. CrossRef - Predictors of actual turnover among nurses working in Korean hospitals: A nationwide longitudinal survey study
Sung‐Heui Bae, Mijung Cho, Oksoo Kim, Yanghee Pang, Chiyoung Cha, Heeja Jung, Sue Kim, Hyunseon Jeong
Journal of Nursing Management.2021; 29(7): 2102. CrossRef - The Effect of Neighborhood Characteristics and Friends' Smoking Status on the Habitual Smoking Onset in Adolescents
You-Jung Choi, Gwang Suk Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(1): 54. CrossRef - Nurse turnover: A longitudinal survival analysis of the Korea Nurses' Health Study
Young Taek Kim, Oksoo Kim, Chiyoung Cha, Yanghee Pang, Choa Sung
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2021; 77(10): 4089. CrossRef - Factors associated with the nurses’ intent to stay in China, Japan, and Korea: an integrative review
Ting Xue, Wen-Bin Jiang, Meng-Di Ma, Jie Zhang, Ming-Hui Lu, Yong-Mei Jiang
Frontiers of Nursing.2020; 7(3): 269. CrossRef - Exploring barriers and facilitators for successful transition in new graduate nurses: A mixed methods study
Ju Hee Kim, Hye Sook Shin
Journal of Professional Nursing.2020; 36(6): 560. CrossRef - Turnover Rates and Factors Influencing Turnover of Korean Acute Care Hospital Nurses: A Retrospective Study Based on Survival Analysis
Bohyun Park, Yukyung Ko
Asian Nursing Research.2020; 14(5): 293. CrossRef - Effects of Head Nurses' Authentic Leadership, Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment Perceived by Newly Licenced Nurses on Turnover Intention
Eun Min An, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 428. CrossRef - Relationships among demands at work, aggression, and verbal abuse among registered nurses in South Korea
Hyoung Eun Chang, Mi Youn Park, Haena Jang, Shinae Ahn, Hyo-Jeong Yoon
Nursing Outlook.2019; 67(5): 567. CrossRef - Survey on the Education System for New Graduate Nurses in Hospitals: Focusing on the Preceptorship
Sujin Shin, Young Woo Park, Mijung Kim, Jeonghyun Kim, Inyoung Lee
Korean Medical Education Review.2019; 21(2): 112. CrossRef - The effect of quality of work life and job control on organizational indifference and turnover intention of nurses: a cross-sectional questionnaire survey
Narjes Alsadat Nasabi, Peivand Bastani
Central European Journal of Nursing and Midwifery.2018; 9(4): 915. CrossRef - Predictors of Turnover Intention among Nurses in Small and Medium-sized Hospitals
Jeong Hye Park, Hye Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(5): 471. CrossRef - Patterns and Influential Factors of Inter-Regional Migration of New and Experienced Nurses in 2011~2015
Bohyun Park, Se Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(5): 676. CrossRef
- Prevalence and Moderating Factors of Turnover Rate and Turnover Intention Among Nurses Worldwide: A Meta-Analysis
- 2,531 View
- 38 Download
- 29 Crossref

- Influences of Hospital Nurses' perceived reciprocity and Emotional Labor on Quality of Nursing Service and Intent to Leave
- Mi-Aie Lee, Eunjeong Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(3):364-374. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.364
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was performed to investigate the relationship among reciprocity, emotional labor, nursing service quality and intent to leave, and to identify factors influencing nursing service quality and intent to leave.
Methods This study was a cross-sectional survey. Participants were 300 nurses working at five general hospitals in two provincial cities in Gyeongsang Province, Korea. From May 1 to June 30, 2014, data were collected using structured questionnaires and analyzed with SPSS/PC ver 20.0 programs.
Results There were relationships between reciprocity and nursing service quality, and intent to leave, and between emotional labor and intent to leave. Participants' general characteristics, reciprocity and emotional labor explained 48.4% of variance in nursing service quality and participants' general characteristics and these two independent variables explained 31.9% of intent to leave.
Conclusion These findings indicate that from the perception of hospital nurses, reciprocity and emotional labor are both very important factors to improve the quality of nursing service and decrease the intent to leave. So nursing managers should try to develop various personnel management programs focused on human emotions, and create a mutual respectable organizational culture and work environment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and Moderating Factors of Turnover Rate and Turnover Intention Among Nurses Worldwide: A Meta-Analysis
Dluha Mafula, Hidayat Arifin, Ruey Chen, Chien-Mei Sung, Chiu-Kuei Lee, Kai-Jo Chiang, Kondwani Joseph Banda, Kuei-Ru Chou
Journal of Nursing Regulation.2025; 15(4): 20. CrossRef - Impact of Structural Empowerment, Thriving at Work, and Caregiver Reciprocity on the Psychological Empowerment of Home Care Workers in South Korea
Heekyung Chang, Youngjoo Do, Jinyeong Ahn, Yumi Kim
Healthcare.2025; 13(15): 1809. CrossRef - Does emotional labor affect nurses suffering from workplace violence? A moderated mediation model
Hakan Erkutlu, Jamel Chafra, Hatice Ucak, Rahsan Kolutek
Journal of Aggression, Conflict and Peace Research.2024; 16(1): 28. CrossRef - Effect of Nursing Practice Environment on Intent to Leave in Hospital Nurses: Focused on the Mediating Effect of Reciprocity
So Young Lee, Mi-Aie Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 201. CrossRef - Negative emotional status and influencing factors among young employees in center of disease control and prevention
Lu Han, Qiyu Li, Yu Zhang, Tuo Liu, Ran Niu, Qi Wang, Lina Zhao
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Experience of Emotional Labor and Its Related Factors among Nurses in General Hospital Settings in Republic of Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Da-Jung Ha, Jung-Hyun Park, Su-Eun Jung, Boram Lee, Myo-Sung Kim, Kyo-Lin Sim, Yung-Hyun Choi, Chan-Young Kwon
Sustainability.2021; 13(21): 11634. CrossRef - Nurses' organizational communication satisfaction, emotional labor, and prosocial service behavior: A cross‐sectional study
Youngsoo Kim, Sun Joo Jang
Nursing & Health Sciences.2019; 21(2): 223. CrossRef - The Effect of Nurse's Emotional Labor on Turnover Intention: Mediation Effect of Burnout and Moderated Mediation Effect of Authentic Leadership
Soo Yang Na, Hanjong Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(3): 286. CrossRef - Influences of Interpersonal Problems and Character of Nurses on Quality of Nursing Service
Eun-Yi Yeom, Kawoun Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(5): 445. CrossRef
- Prevalence and Moderating Factors of Turnover Rate and Turnover Intention Among Nurses Worldwide: A Meta-Analysis
- 1,343 View
- 13 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Impact of Nurse, Nurses' Aid Staffing and Turnover Rate on Inpatient Health Outcomes in Long Term Care Hospitals
- Yunmi Kim, Ji Yun Lee, Hyuncheol Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(1):21-30. Published online February 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.1.21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to explore the impact of registered nurse/nurses' aid (RN/NA) staffing and turnover rate on inpatient health outcomes in long term care hospitals.
Methods A secondary analysis was done of national data from the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Services including evaluation of long term care hospitals in October-December 2010 and hospital general characteristics in July-September 2010. Final analysis of data from 610 hospitals included RN/NA staffing, turnover rate of nursing staff and 5 patient health outcome indicators.
Results Finding showed that, when variables of organization and community level were controlled, patients per RN was a significant indicator of decline in ADL for patients with dementia, and new pressure ulcer development in the high risk group and worsening of pressure ulcers. Patients per NA was a significant indicator for new pressure ulcer development in the low risk group. Turnover rate was not significant for any variable.
Conclusion To maintain and improve patient health outcomes of ADL and pressure ulcers, policies should be developed to increase the staffing level of RN. Studies are also needed to examine causal relation of NA staffing level, RN staffing level and patient health outcomes with consideration of the details of nursing practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Experience of turnover to long-term care hospital nurse: A phenomenological qualitative research
Inhee Choo, Milim Cho, Eunha Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(4): 392. CrossRef - Physical Therapy Provider Continuity Predicts Functional Improvements in Inpatient Rehabilitation
Mitchell D. Adam, Debra K. Ness, John H. Hollman
Journal of Neurologic Physical Therapy.2023; 47(2): 91. CrossRef - The effect of the reformed nurse staffing policy on employment of nurses in Korea
Jinhyun Kim, Sungjae Kim, Eunhee Lee, Hyunjeong Kwon, Jayon Lee, Hyunji Bae
Nursing Open.2021; 8(5): 2850. CrossRef - Nurses’ Clinical Work Experience during Pregnancy
Hyunjung Lee, Hyoung Eun Chang, Jiyeon Ha
Healthcare.2020; 9(1): 16. CrossRef - Exploring Nurses' Perceptions of Nursing Home Care in South Korea: A Qualitative Study
Eunhee Cho, Hyejin Kim, Soo Jung Chang, Hyang Kim, Jeongah Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2020; 22(2): 85. CrossRef - The Effects of Long-term Care Hospitals' Nurse Staffing Level on Patient Outcomes: Differences according to Region
Kyung Jin Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 354. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on the Job Stress, Burnout and Nursing Performance of Nurses in Comprehensive Nursing Care Service Wards and Nurses in General Wards
Youn Sil Kim, Jung Ae Park, Eun Koung Seo
Stress.2019; 27(1): 46. CrossRef - Experiences of Long-term Care Hospital Nurses Caring for Elders with Dementia
Eun Kyoung Suh, Hye Ryoung Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2019; 21(2): 99. CrossRef - Longitudinal associations of nursing staff turnover with patient outcomes in long-term care hospitals in Korea
Yoonseo Kim, Kihye Han
Journal of Nursing Management.2018; 26(5): 518. CrossRef - Influence of Nurses' Work Environment, Organizational Commitment, and Nursing Professionalism on Turnover Intention of Nurses in Long Term Care Hospitals
Hyun Suk Joo, Won Hee Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(4): 265. CrossRef - Importance, Performance and Rates of Nurse Performance of Nursing Interventions in Long-term Care Hospitals
Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Myung Ha Lee, Hyun Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(4): 359. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis Research of Inpatient Satisfaction with Nursing on Comprehensive Nursing Service Units & General Units and Nurses' Work Stress
Su Mi Jung, Sook Hee Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(3): 229. CrossRef - Delegation of Nursing Activities in Long-term Care Hospitals
Eun Ju Jang, Su Hyun Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2017; 19(2): 101. CrossRef - Effects of Empathy and Attitude in Caring for Elders by Nurses in Geriatric Nursing Practice in Long-term Care Hospitals
Young Kyoung Kim, Suhye Kwon
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2017; 19(3): 203. CrossRef - Predictors of Turnover among New Nurses using Multilevel Survival Analysis
Suhee Kim, Kyongeun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(5): 733. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nurse Turnover Intention of Senior Convalescence Hospitals in the Metropolitan Area
Youn Sun Hwang, Eunyoung Cho
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(3): 156. CrossRef - Nursing outcomes of inpatient on level of nursing staffing in long term care hospitals
Eun Hee Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2015; 26(3): 715. CrossRef - The Effects of Emotional Labor and Job Involvement on Turnover Intention of Nurses in Long-term Care Hospitals
Su-Jeong Kang, Suhye Kwon
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2015; 24(4): 290. CrossRef
- The Experience of turnover to long-term care hospital nurse: A phenomenological qualitative research
- 1,634 View
- 20 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Effects of Nurses' Mentoring on Turnover Intention: Focused on the Mediating Effects Role Stress and Burnout
- Sangsook Han, Ohsook Kim, Yunsu Joo, Eunduck Choi, Jeongwon Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(5):605-612. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.5.605
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the casual relationship between nurses' mentoring and turnover intention and to verify the goodness of fit between a hypothetical model and actual data in order to suggest an adequate model.
Methods The survey was conducted with 434 nurses working in general hospitals in Seoul. Data were collected during February 2013, and analyzed with SPSS Windows 18.0 and AMOS 7.0.
Results Mentoring was found to have a direct effect on decrease in role stress. Role stress had a direct effect on increase in burnout and mentoring, with role stress as a mediator, there was an indirect effect on burnout. Burnout had a direct effect on increase in turnover intention, and role stress, with burnout as a mediator, and mentoring, through role stress and burnout, an indirect effect was found on increase in turnover intention.
Conclusion The results of this study indicate that nursing managers should put effort into reducing role stress and burnout, while seeking to establish a more efficient mentoring system so that for nurses, there will be a lowering of turnover intention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of horizontal violence among nurses on patient safety: Mediation of organisational communication satisfaction and moderated mediation of organisational silence
Eun Young Doo, Sujin Choi
Journal of Nursing Management.2021; 29(3): 526. CrossRef - Trends in Turnover Research on Korean Nurses: Based on 8 Journals Published by Member Societies under the Korean Academy of Nursing Science, 2006-2015
Hyo Geun Geun
The Open Nursing Journal.2019; 13(1): 92. CrossRef - Prevalence of burnout in mental health nurses and related factors: a systematic review and meta‐analysis
Isabel María López‐López, José Luis Gómez‐Urquiza, Gustavo Raúl Cañadas, Emilia Inmaculada De la Fuente, Luis Albendín‐García, Guillermo Arturo Cañadas‐De la Fuente
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(5): 1035. CrossRef - Job burnout and turnover intention among nurses in China: the mediating effects of positive emotion
Li-Feng Yang, Jing-Ying Liu, Yan-Hui Liu
Frontiers of Nursing.2018; 5(1): 43. CrossRef - Attitude, Role Perception and Nursing Stress on Life Sustaining Treatment among Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Su Jeong Lee, Hye Young Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(2): 131. CrossRef - Don’t abandon hope all ye who enter here: The protective role of formal mentoring and learning processes on burnout in correctional officers
M.L. Farnese, B. Barbieri, B. Bellò, P.T. Bartone
Work.2017; 58(3): 319. CrossRef - Effect of Nurses' Mentoring Function and Organizational Citizen Behavior on Nursing Performance
Kyung-Hee Park, Jeong Won Han
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(2): 179. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Turnover Intention in Pediatric Nurses
Min Suk Im, Young Eun Lee
Child Health Nursing Research.2016; 22(1): 37. CrossRef - The effect of perceived organisational support on burnout among community health nurses in China: the mediating role of professional self-concept
Xiaoyi Cao, Lin Chen, Lang Tian, Yongshu Diao
Journal of Nursing Management.2016; 24(1): E77. CrossRef - Covariance Structure Analysis on the Impact of Job Stress, Fatigue Symptoms and Job Satisfaction on Turnover Intention among Dental Hygienists
Se-Young Han, Young-Chae Cho
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(7): 629. CrossRef - Effect of professional self‐concept on burnout among community health nurses in Chengdu, China: the mediator role of organisational commitment
Xiaoyi Cao, Lin Chen, Lang Tian, Yongshu Diao, Xiuying Hu
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2015; 24(19-20): 2907. CrossRef - Literature Review of Structural Equation Models for Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention in Korea
Eunhye Kim, Jinhyun Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2014; 11(2): 109. CrossRef
- Effects of horizontal violence among nurses on patient safety: Mediation of organisational communication satisfaction and moderated mediation of organisational silence
- 1,197 View
- 14 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Effects of Nurses' Social Capital on Turnover Intention: Focused on the Mediating Effects Organizational Commitment and Organizational Cynicism
- Jeongwon Han, Heeyoung Woo, Eunsil Ju, Sohee Lim, Sangsook Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(4):517-525. Published online August 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.4.517
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the casual relationship between nurses' social capital and turnover intention and to verify the goodness of fit between a hypothetical model and actual data in order to suggest the best model.
Methods This survey was conducted with 315 nurses working in general hospitals in Seoul. Data were collected from December 1 to December 30, 2011, and analyzed using SPSS Windows 18.0 and AMOS 16.0.
Results Nurses' social capital was found to have a direct effect on reducting organization cynicism and increasing organizational commitment. Nurses' organizational cynicism and organizational commitment were found to have a direct effect on turnover intention, but social capital did not have a direct effect on turnover intention. However, social capital had a partial and indirect effect on turnover intention through mediating organizational cynicism and organizational commitment.
Conclusion Results of this study indicate that nurse managers should put increased effort in reducing nurses' organizational cynicism and improving their organizational commitment, two contrary parameters. At the same time managers need to develop plans to establish social capital more efficiently so that nurses have lower turnover intention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Roles of Relational Leadership and Employee Satisfaction in the Linkage Between Social Capital and Employee Turnover: A Moderated‐Mediation Analysis
James Aditchere, R. Angmortey
Journal of Public Affairs.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Price of silence, isolation, and cynicism: The impact on occupational frustration
Omar Durrah, Wafa Rashid Alalyani, Kamaal Allil, Ayman Al Shehab, Shooq Al Rawas, Ali Hubais, Souzan Hannawi
Heliyon.2023; 9(11): e22278. CrossRef - Duygusal Emeğin İşten Ayrılma Niyetine Etkisinde Örgütsel Bağlılığın Aracılık Rolü: Yiyecek İçecek İşletmeleri Üzerinde Bir Araştırma
Mehmet POLAT
GSI Journals Serie A: Advancements in Tourism Recreation and Sports Sciences.2022; 5(2): 145. CrossRef - The Association Between Unit-Level Workplace Social Capital and Intention to Leave Among Employees in Health Care Settings: A Cross-Sectional Multilevel Study
Mako Iida, Kazuhiro Watanabe, Emiko Ando, Kanami Tsuno, Akiomi Inoue, Sumiko Kurioka, Norito Kawakami
Journal of Occupational & Environmental Medicine.2020; 62(5): e186. CrossRef - Positive Psychological Capital Mediates the Association between Burnout and Nursing Performance Outcomes among Hospital Nurses
Minjeong An, Eun Suk Shin, Myoung Yi Choi, Yeonhu Lee, Yoon Young Hwang, Miran Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(16): 5988. CrossRef - Paternalistic Leadership, Organizational Cynicism, and Intention to Quit One’s Job in Nursing
Cuma Sungur, Özlem Özer, Meltem Saygili, Özgür Uğurluoğlu
Hospital Topics.2019; 97(4): 139. CrossRef - Occupational therapy practitioners’ ratings of job satisfaction factors through a lens of social capital
Vicki C. Mason, Mary L. Hennigan
Occupational Therapy In Health Care.2019; 33(1): 88. CrossRef - Effects of Underemployment Perception of Chinese Hotel Employees on Turnover Intention and Organizational Cynicism
우양, 김영현
Tourism Research.2018; 43(3): 141. CrossRef - The Quintessence of Organizational Commitment and Organizational Cynicism
Aida Margelytė-Pleskienė, Jolita Vveinhardt
Management of Organizations: Systematic Research.2018; 80(1): 67. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Organizational Commitment in the Relationship between Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention for Staff Nurses Working with Alternative Shift System in the Medical-Surgical Units
cho hang nan, Song, Chi Eun, 박애란
Global Health and Nursing (글로벌 건강과 간호).2018; 8(1): 1. CrossRef - RETRACTED: The Mediating Effect of Social Capital on the Relationship Between Public Health Managers' Transformational Leadership and Public Health Nurses' Organizational Empowerment in Korea Public Health
Soo Young Jun
Asian Nursing Research.2017; 11(4): 246. CrossRef - Influence of type D personality on job stress and job satisfaction in clinical nurses: the mediating effects of compassion fatigue, burnout, and compassion satisfaction
Yeon Hee Kim, Sung Reul Kim, Yeo Ok Kim, Ji Young Kim, Hyun Kyung Kim, Hye Young Kim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2017; 73(4): 905. CrossRef - Effects of Nurses' Social Capital and Job Engagement on Nursing Performance: Focused on the Mediating effects of Organizational Citizenship Behavior
Mi Soon Ko, Hyunsook Zin Lee, Myung Suk Koh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(1): 42. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Social capital between Transformational leadership and Organizational Commitment of Nurses in Hospitals
Soon-gu Kim, Young-sook Seo
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(2): 282. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of a Korean version of Leader Rapport Management
Jeong-Won Han, Nam-Eun Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(2): 129. CrossRef - The effect of social capital on job satisfaction and quality of care among hospital nurses in South Korea
Ji In Shin, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2016; 24(7): 934. CrossRef - A Study on the Relationship Between Schools’ Health and Teachers’ Organizational Commitment
Ali Asghar Hayat, Naeimeh Kohoulat, Javad Kojuri, Hatam Faraji
International Journal of School Health.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Introducing Routine Measurement of Healthcare Worker's Well-being as a Leading Indicator for Proactive Safety Management Systems Based on Resilience Engineering
Bobbie N. Ray-Sannerud, Stephen Leyshon, Vibeke B. Vallevik
Procedia Manufacturing.2015; 3: 319. CrossRef - Literature Review of Structural Equation Models for Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention in Korea
Eunhye Kim, Jinhyun Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2014; 11(2): 109. CrossRef - Effects of Decision Making Competency, Nursing Professionalism, and Job Satisfaction on Turnover Impulse among Nurses
Heun Keung Yoon, Jihea Choi, Eun-young Lee, Haeyoung Lee, Mijeong Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(5): 658. CrossRef
- The Roles of Relational Leadership and Employee Satisfaction in the Linkage Between Social Capital and Employee Turnover: A Moderated‐Mediation Analysis
- 1,268 View
- 9 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Development and Testing of a Nurse Turnover Intention Scale (NTIS)
- Eun Ja Yeun, Heejeong Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(2):256-266. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.2.256
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a measurement tool of nurse's turnover intention.
Methods Data were collected from questionnaires completed by 678 nurses who worked in 3 university hospitals in South Korea and analyzed using the SPSS 18.0 and AMOS 18 programs. Thirty-seven preliminary items were selected from 161 basic items extracted via a literature review and in depth interviews with 6 hospital nurses. Three steps with factor analysis were undertaken to verify the reliability and validity of the preliminary instruments. Finally, confirmative factor analysis was carried out.
Results As a result of the analysis, 3 factors including 10 items were selected. Cronbach's Alpha for the 10 items was .83, for job satisfaction (4 items), .78, for interpersonal relationships (3 items), .80, and for work performance (3 items), .74, which was stable.
Conclusion This study is meaningful because through it a scale reflecting Korean culture was developed to measure turnover intention in nurses. Further studies that test the psychometrics of this scale in more diverse samples are warranted.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and Moderating Factors of Turnover Rate and Turnover Intention Among Nurses Worldwide: A Meta-Analysis
Dluha Mafula, Hidayat Arifin, Ruey Chen, Chien-Mei Sung, Chiu-Kuei Lee, Kai-Jo Chiang, Kondwani Joseph Banda, Kuei-Ru Chou
Journal of Nursing Regulation.2025; 15(4): 20. CrossRef - Turnover intention, collaboration and competences of intensive care unit nurses: A descriptive correlational study
Miyase Avcı, Ahmet Avcı
Applied Nursing Research.2025; 82: 151930. CrossRef - Impact of Professional Quality of Life on Turnover Intention among General Hospital Nurses: A Comparative Study Using Linear and Nonlinear Analysis Methods
Mi-Jin Park, Il-Ok Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(1): 132. CrossRef - The effect of nurses’ individual and occupational characteristics and perceptions of hierarchical career plateau on their turnover intention: A cross-sectional study
Şehrinaz Polat, Tuğba Yeşilyurt Sevim, Hanife Tiryaki Şen, Roaa Sabri Gassas
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(4): e0316895. CrossRef - The effects of communication competence, meaning of work, and work-life balance on turnover intention in Generation Z nurses in South Korea: A cross-sectional study
Kyu-Yeon Jeong, MiRa Yun, Eun-Hi Choi
Applied Nursing Research.2025; 83: 151952. CrossRef - Investigation of the relationship between work motivation, work performance and turnover intention of surgical nurses: a cross-sectional study
Nihal Celikturk Doruker, Gulver Hacioglu, Birgul Nurulke, Leyla Ceylan
Applied Nursing Research.2025; 83: 151960. CrossRef - Influence of COVID-19–Induced Anxiety on Job Turnover Intention among Emergency Room Nurses during the COVID-19 Pandemic, the Mediating Effect of Needs Satisfaction: A Cross-Sectional Study
YuJin Seo, Myung Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(2): 104. CrossRef - Relationships Between Nurses' Personal and Professional Characteristics and Career Decision Regret, Occupational Stress and Turnover Intention: A Descriptive Cross‐Sectional Study
Şehrinaz Polat, Aslı Yeşil
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Job Satisfaction, Quality of Life, and Turnover Intention Among Nurses: A Comparative Study of Pattern-Based and Rotating Shift Schedules
Yu Jin Jung, Haejin Kim
Healthcare.2025; 13(20): 2551. CrossRef - Effects of Person-Environment Fit, Career Commitment, and Organizational Silence on Turnover Intention among Shift-Working Nurses
Gyeong-Hee Bae, Ji-Won Kim
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2025; 19(3): 43. CrossRef - The Influence of Work-Life Balance and Job Embeddedness on Turnover Intention among Nurses Caring for Cancer Patients
Jin-young Park, Yeunhee Kwak, Jiwoo Jung, Seoung-Wha Lim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2025; 18(3): 28. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of the Chinese version of the nurse turnover intention scale: a translation and validation study
Wenguang Xie, Xinyue Zhao, Xiaoyu Liu, Xinchen Yang, Yulu Deng, Yangyang Zhang, Chao Zhang, Yanyan Gong
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Resilience, Nursing Managers’ Empowering Leadership on Turnover Intention among New Nurses: Mediating role of Transition Shock
Hyun Jin Jung, Hyun Kyung Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 212. CrossRef - Impact of Emotional Labor and Positive Psychological Capital on the Turnover Intention of Nurses Caring for Patients with COVID-19: A Descriptive Survey Study
Mira Kwon, Yeoungsuk Song, Majd T. Mrayyan
Journal of Nursing Management.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Effect of Work-Family Conflict on Turnover Intention among Married Female Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Nursing Work Environment
Min Gyeong Jeong, So Young Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 451. CrossRef - The mediating and moderating role of recovery experience between occupational stress and turnover intention in nurses caring for patients with COVID‐19
Junghoon Lee, Junekyu Kim, Hong‐A Lim, Yeoungsuk Song
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2024; 33(4): 1470. CrossRef - Effects of Job Crafting, Burnout, and Job Satisfaction on Nurses' Turnover Intention: A Path Analysis
Mihee Chung, Sujeong Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(2): 281. CrossRef - The Effect of Missed Nursing Care on Adverse Event Experiences, Patient Safety Management Activity, Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention in Nurses: A Nationwide Survey using Proportional Quota Sampling
Myung Jin Choi, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 490. CrossRef - The adaptation of the Nurse Turnover Intention Scale into Turkish: A validity and reliability study
Arife Şanlıalp Zeyrek, Özlem Fidan, Nesrin Çunkuş Köktaş
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Job Satisfaction on the Relationship between Nursing Practice Environment and Turnover Intention of Nurses in a National Forensic Psychiatic Hospital
Moonhee Gang, Donghyeon Gwak
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(3): 307. CrossRef - Impact of workplace bullying and resilience on new nurses' turnover intention in tertiary hospitals
Gyu Li Baek, EunJu Lee
Nursing & Health Sciences.2022; 24(4): 801. CrossRef - The Factors That Affect Turnover Intention According to Clinical Experience: A Focus on Organizational Justice and Nursing Core Competency
Hanna Choi, Sujin Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(6): 3515. CrossRef - Modeling the mediation roles in the relationship between job satisfaction and organizational commitment of public sector forest engineers in Turkey
Yaşar Selman Gültekin
Journal of Forest Research.2022; 27(4): 255. CrossRef - Effects of Ego-Resiliency on Interpersonal Problems among Nursing Students: The Mediating Effects of Aggression
Sona Lee, Hye Young Ahn, Hye Seon Choi
Healthcare.2022; 10(12): 2455. CrossRef - A meta‐analysis on predictors of turnover intention of hospital nurses in South Korea (2000–2020)
Hyeoneui Kim, Eun Gyung Kim
Nursing Open.2021; 8(5): 2406. CrossRef - Emotional Labor, Burnout, Medical Error, and Turnover Intention among South Korean Nursing Staff in a University Hospital Setting
Chan-Young Kwon, Boram Lee, O-Jin Kwon, Myo-Sung Kim, Kyo-Lin Sim, Yung-Hyun Choi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(19): 10111. CrossRef - Effect of Verbal Violence on the Turnover Intention among Operating Room Nurses: Focusing on the Moderating Effects of Social Support and Coping
Ae-Sook Kim, Eun Hee Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(5): 433. CrossRef - Effects of Workplace Bullying and Empowerment on Nurses' Turnover Intention
Yesul Lee, Yoonju Lee, Ju-Young Ha, Minjeong Jo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - Factors associated with the nurses’ intent to stay in China, Japan, and Korea: an integrative review
Ting Xue, Wen-Bin Jiang, Meng-Di Ma, Jie Zhang, Ming-Hui Lu, Yong-Mei Jiang
Frontiers of Nursing.2020; 7(3): 269. CrossRef - Impact of nurse staffing on intent to leave, job satisfaction, and occupational injuries in Korean hospitals: A cross‐sectional study
Sujin Shin, Seung Jin Oh, Jeonghyun Kim, Inyoung Lee, Sung‐Heui Bae
Nursing & Health Sciences.2020; 22(3): 658. CrossRef - Influence of Secondary Trauma Stress, and Vocation on Turnover Intention of Nurses in Regional Trauma Centers
Hyun-Gwan Lee, Ji-Soo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(1): 65. CrossRef - Nursing stress factors affecting turnover intention among hospital nurses
Eun‐Kyoung Lee, Ji‐Soo Kim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship of Workplace Violence to Turnover Intention in Hospital Nurses: Resilience as a Mediator
Hyun-Jung Kang, Jaeyong Shin, Eun-Hyun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 728. CrossRef - Relationship between Types of Role Conflict and Turnover Intention in Nurses Working at Rehabilitation Hospitals
Bo Young Kim, Joo yun Lee
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2019; 22(2): 142. CrossRef - Trends in Turnover Research on Korean Nurses: Based on 8 Journals Published by Member Societies under the Korean Academy of Nursing Science, 2006-2015
Hyo Geun Geun
The Open Nursing Journal.2019; 13(1): 92. CrossRef - Influence of Communication Competency and Nursing Work Environment on Job Satisfaction in Hospital Nurses
Bongjeong Kim, Soon Young Lee, Gyeong Ju An, Guna Lee, Hyun Jung Yun
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2019; 44(2): 189. CrossRef - Effects of Emotional Development Therapy (EDT) on Stress, Fatigue, Sleep, and Heart Rate Variability (HRV) in Nurses
Mi-Young Jeong, Nam-Sook Seo
Korean Journal of Stress Research.2018; 26(1): 60. CrossRef - Pediatric Nurses’ Perceptions related to End-of-Life Care and Turnover Intention
Sook Young Baek, Sook Jung Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2018; 24(4): 353. CrossRef - Influences of Interpersonal Problems and Character of Nurses on Quality of Nursing Service
Eun-Yi Yeom, Kawoun Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(5): 445. CrossRef - Relationship of Gender Role Conflict and Job Satisfaction to Turnover Intention for Men in Nursing
Ha-Man Hwang, Myung Ja Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(1): 32. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Articles Published in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration for 3 Years (2013~2015): The Application of Text Network Analysis
Tae Wha Lee, Kwang-Ok Park, GyeongAe Seomun, Miyoung Kim, Jee-In Hwang, Soyoung Yu, Seok Hee Jeong, Min Jung, Mikyung Moon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(1): 101. CrossRef - Factors Affecting on Turnover Intentions among Operating Room Nurses
Yeo-Jin Kim, Keum-Sook Park, Eun-Ja Yang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(12): 352. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention: A Cross-sectional Survey
Eun-Ja Yeun, Young-Mi Kwon, Mi-Soon Je, Jeong-Hwa An
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2016; 16(1): 94. CrossRef - Interpersonal Relations, Hope, Professional Self-concept and Turnover Intention according to Adult Attachment Styles in Early Stage Nurses
Eun Jin Oh, Se Young Lee, Kyung Mi Sung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(4): 491. CrossRef
- Prevalence and Moderating Factors of Turnover Rate and Turnover Intention Among Nurses Worldwide: A Meta-Analysis
- 3,960 View
- 230 Download
- 44 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling on Nursing Productivity of Nurses in Korea
- Se Young Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Heon Man Lim, Mi Young Lee, Kwang-Ok Park, Kyoung A Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(1):20-29. Published online February 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.1.20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to propose and test a predictive model that could explain and predict nursing productivity.
Methods A survey using a structured questionnaire was conducted with 360 nurses in Korea. The data were analyzed using SPSS Windows 18.0 and AMOS 19.0 program.
Results Based on the constructed model, burnout and organizational commitment were found to have direct effects on nurses' turnover intention and nursing productivity. While nursing work environment was found to have indirect effects on nurses' turnover intention and nursing productivity.
Conclusion This structural equational model is a comprehensive theoretical model that explains the related factors and their relationship with nursing productivity. Comprehensive organizational interventions to improve nursing productivity should focus on improving the nursing work environment. Findings from this study can be used to design appropriate strategies to decrease nurse turnover in Korea. Further studies are needed to prospectively verify these causal relationships with larger samples.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of Self-Efficacy for HIV Disease Management Skills
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Mi-So Shim, Seoyoung Baek, Namhee Kim, Min Kyung Park, Youngjin Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(3): 295. CrossRef - Effect of Job Embeddedness on Turnover Intention of Nurses in Long Term Care Hospitals: The Mediating Effect of Nursing Work Environment
Sun Mi Ha, Yeong Ju Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 439. CrossRef - A Meta-Analytic Path Analysis on the Outcome Variables of Nursing Unit Managers' Transformational Leadership: Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(6): 757. CrossRef - Clinical nurses’ beliefs, knowledge, organizational readiness and level of implementation of evidence-based practice: The first step to creating an evidence-based practice culture
Jae Yong Yoo, Jin Hee Kim, Jin Sun Kim, Hyun Lye Kim, Jung Suk Ki, Tim Schultz
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(12): e0226742. CrossRef - Relationship among Nursing Professionalism, Nursing Work Environment, and Patient Safety Nursing Activities in General Hospital Nurses
Mi-Aie Lee, Sunjoo Kang, Hye Sun Hyun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2019; 25(4): 317. CrossRef - Influence of Emotional Intelligence, Communication, and Organizational Commitment on Nursing Productivity among Korean Nurses
Hyo Geun Geun, Eunok Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(2): 226. CrossRef - Impact of Burnout on Organizational Outcomes, the Influence of Legal Demands: The Case of Ecuadorian Physicians
Paola Ochoa
Frontiers in Psychology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Nurses' Social Capital and Job Engagement on Nursing Performance: Focused on the Mediating effects of Organizational Citizenship Behavior
Mi Soon Ko, Hyunsook Zin Lee, Myung Suk Koh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(1): 42. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Social capital between Transformational leadership and Organizational Commitment of Nurses in Hospitals
Soon-gu Kim, Young-sook Seo
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(2): 282. CrossRef - Relationship of between Task Performance, Job Satisfaction, and Organizational Contribution of Dental Hygienists
Jun-Yeong Kwon, Su-Young Lee
Journal of dental hygiene science.2016; 16(4): 302. CrossRef - A Path Analysis of Variables Influencing customer orientation of Hospital Nurses
Eun-Su Do, Young-Sook Seo
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(1): 275. CrossRef - Nurses' Perception of Organizational Commitment, Nursing Work Environment, and Social Support in a General Hospital
Sook Bin Im, Mi Young Lee, Se Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(1): 1. CrossRef - Literature Review of Structural Equation Models for Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention in Korea
Eunhye Kim, Jinhyun Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2014; 11(2): 109. CrossRef - Clinical Nurses' Experience of Positive Organizational Culture
Young-Hee Yom, Sang Mi Noh, Kyung Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(5): 469. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Intensive Care Units Nursing Workload
Mohammad Karim Bahadori, Ramin Ravangard, Mehdi Raadabadi, Seyed Masod Mosavi, Mohammad Gholami Fesharaki, Fardin Mehrabian
Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Hospital Nurses' Recognition of the Team System and Effects on the Nursing Organizational Team System
Kwang-ok Park, Sung Hee Park, Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(4): 414. CrossRef
- Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of Self-Efficacy for HIV Disease Management Skills
- 1,613 View
- 10 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Relationships between Compassion Fatigue, Burnout, and Turnover Intention in Korean Hospital Nurses
- Kiwol Sung, Youngsook Seo, Jee Hee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(7):1087-1094. Published online December 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.7.1087
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to identify relationships between compassion fatigue, burnout, and turnover intention in Korean hospital nurses.
Methods In total, 142 hospital nurses were surveyed as part of data collection. Data related to compassion fatigue, burnout, and turnover intention were collected using a questionnaire between May 2011 and September 2011. The data analysis was performed using PASW 19.0 program, which included one-way ANOVA, independent t-tests, Pearson's correlation coefficient, and hierarchical regression analysis.
Results This study detected a positive correlation between compassion fatigue and burnout(r=.37,
p <.001), and turnover intention(r=.55,p <.001). Compassion fatigue accounted for 29.6% of the variance for turnover intention among Korean hospital nurses.Conclusion The results indicate that it is necessary to reduce compassion fatigue, and turnover intention among Korean hospital nurses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Self-compassion and secondary traumatic stress in pediatric oncology/hematology nurses
Tuğba Şahin Tokatlıoğlu, Perihan Güner
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2026; 86: 191. CrossRef - Compassion Fatigue, Compassion Satisfaction and Mindfulness Among Healthcare Professionals: A Meta-Analysis of Correlational Studies and Randomized Controlled Trials
A.C.M. Li, F.H.N. Chio, W.W.S. Mak, T.H. Fong, S.H.W. Chan, Y.H.R. Tran, K. Kakani
Social Science & Medicine.2025; : 117749. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Compassion Fatigue and Anxiety Levels of Nurses After Working in COVID-19 Isolation Ward
Sahar Jasim Mohammed Mohammed, Hilal Altundal Duru
Sage Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurses’ professional quality of life and job satisfaction in Jordan
Khaldoun M. Hamdan, Rabia S. Allari, Nadiah A. Baghdadi, Shaherah Yousef Andargeery, Abdullah M. Haymour, Evan Sabrah, Abeer M. Shaheen
Frontiers in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study on Compassion Fatigue in Health Workers During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Mehmet Akif Çakmak, Tahsin İlhan
Uluslararası Türk Eğitim Bilimleri Dergisi.2024; 12(2): 584. CrossRef - The effect of thanatophobia and professional commitment on compassion fatigue in nurses in Türkiye: Cross sectional study
Gönül Gökçay, Yeliz Akkuş
HEALTH SCIENCES QUARTERLY.2024; 4(1): 41. CrossRef - Psychosocial Care Competencies and Compassion Fatigue in Intensive Care Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abdullah Gerçek, Ayşe Okanlı, Mustafa Durmuş
Yoğun Bakım Hemşireliği Dergisi.2024; 28(2): 93. CrossRef - SAĞLIK ÇALIŞANLARININ İŞ STRESİNİN İŞTEN AYRILMA NİYETİ ÜZERİNE ETKİSİNDE MERHAMET YORGUNLUĞUNUN ARACILIK ROLÜ
Cuma Sungur, İnci Fatma Kurtulgan, Fatoş Mutlu Ağgül
Dicle Üniversitesi İktisadi ve İdari Bilimler Fakültesi Dergisi.2024; 14(28): 895. CrossRef - The relationships among factors affecting compassion fatigue, compassion satisfaction, and burnout in Japanese nurses: A cross‐sectional study
Kumiko Kishimoto, Kenichi Asano
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sağlık Çalışanlarında İşten Ayrılma Niyeti: Bibliyometrik Bir Analiz
Buse METE
MEYAD Akademi.2023; 4(1): 41. CrossRef - A Bibliometric Analysis of the Association Between Compassion Fatigue and Psychological Resilience From 2008 to 2021
Li-Juan Yi, Yi Liu, Ling Tang, Liang Cheng, Guo-Hao Wang, Su-Wen Hu, Xiao-Ling Liu, Xu Tian, Maria F. Jiménez-Herrera
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations among professional quality of life dimensions, burnout, nursing practice environment, and turnover intention in newly graduated nurses
Shu Gong, Jin Li, Xiangdong Tang, Xiaoyi Cao
Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing.2022; 19(2): 138. CrossRef - Alleviating the impact of SNS fatigue on user discontinuance
One-Ki Daniel Lee, Seoyoun Lee, Woojong Suh, Younghoon Chang
Industrial Management & Data Systems.2022; 122(1): 292. CrossRef - Compassion fatigue in mental health nurses: A systematic review
Cameron Marshman, Alison Hansen, Ian Munro
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2022; 29(4): 529. CrossRef - Predictors of Professional Quality of Life in Veterinary Professionals
Vanessa I. Rohlf, Rebekah Scotney, Holly Monaghan, Pauleen Bennett
Journal of Veterinary Medical Education.2022; 49(3): 372. CrossRef - The Impact of Burnout on Police Officers’ Performance and Turnover Intention: The Moderating Role of Compassion Satisfaction
Gabriela Pedro Gomes, Neuza Ribeiro, Daniel Roque Gomes
Administrative Sciences.2022; 12(3): 92. CrossRef - The effect of nurses' compassion on burnout: A cross‐sectional study
Emine Kaplan Serin, Ahmet Özdemir, Kevser Işik
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2021; 57(1): 371. CrossRef - Relationships between resilience, empathy, compassion fatigue, work engagement and turnover intention in haemodialysis nurses: A cross‐sectional study
Xiaoyi Cao, Lin Chen
Journal of Nursing Management.2021; 29(5): 1054. CrossRef - Assessing Compassion in Korean Population: Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of Sussex-Oxford Compassion Scales
Jiyoung Kim, Jang-Won Seo
Frontiers in Psychology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Sağlık Çalışanlarında Duygusal Emek Gösterimlerine İlişkin Çok Değişkenli Bir Araştırma: Bursa Örneği
Bilal EZİLMEZ, Umut EROĞLU
TroyAcademy.2021; 6(3): 888. CrossRef - Oncology nurses’ compassion fatigue, burn out and compassion satisfaction
Reem Ahmad Jarrad, Sawsan Hammad
Annals of General Psychiatry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Secondary Trauma Stress, and Vocation on Turnover Intention of Nurses in Regional Trauma Centers
Hyun-Gwan Lee, Ji-Soo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(1): 65. CrossRef - Compassion satisfaction and fatigue in cardiovascular nurses: A cross-sectional descriptive study
Sima Babaei, Marzieh Haratian
Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research.2020; 25(3): 212. CrossRef - Balancing empathy: Can professors have too much?
Aditi Rabindra Sachdev, Caitlin M. Lapine, Anmol Sachdeva
Industrial and Organizational Psychology.2020; 13(4): 479. CrossRef - Development and Validation of an Empirical Model to Study the Mediating Role of Empathic School Leadership in the Motivation of High School Students in India
Debarshi Roy
Metamorphosis: A Journal of Management Research.2020; 19(1): 7. CrossRef - Impact of Traumatic Events and Resilience on the Professional Quality of Life among Clinical Nurses
Dan-Bi Yoo, Hye-Ja Park, Phill-Ja Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2019; 22(1): 27. CrossRef - The Professional Quality of Life Among Health-Care Providers and its Related Factors
Zohreh Keshavarz, Maryam Gorji, Zeinab Houshyar, Zeinab Talebi Tamajani, Jeno Martin
Asian Journal of Social Health and Behavior.2019; 2(1): 32. CrossRef - Secondary traumatic stress experiences of nurses caring for cancer patients
Neslihan Partlak Günüşen, Besti Üstün, Pınar Serçekuş Ak, Dilek Büyükkaya Besen
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Compassion Fatigue and Satisfaction: Influence on Turnover Among Oncology Nurses at an Urban Cancer Center
Diana Wells-English, Jeannie Giese, Joseph Price
Clinical Journal of Oncology Nursing.2019; 23(5): 487. CrossRef - Development and Psychometric Assessment of Risk Factors of Compassion Fatigue Inventory in Nurses
Mahdieh Sabery, Mansoureh Zagheri Tafreshi, Meimanat Hosseini, Jamileh Mohtashami, Abbas Ebadi
Journal of Nursing Measurement.2019; 27(2): E62. CrossRef - Compassion Fatigue, Secondary Traumatic Stress, and Vicarious Traumatization: a Qualitative Review and Research Agenda
Rachel S. Rauvola, Dulce M. Vega, Kristi N. Lavigne
Occupational Health Science.2019; 3(3): 297. CrossRef - The Emotional Cost of Caring for Others
Marlene Walden, Greg Adams, Elissa Annesley-Dewinter, Shasha Bai, Nici Belknap, Amy Eichenlaub, Angela Green, Amy Huett, Katie Lea, Austin Lovenstein, Amy Ramick, Mary Salassi-Scotter, Tammy Webb, Valerie Wessel
JONA: The Journal of Nursing Administration.2018; 48(11): 545. CrossRef - Compassion satisfaction and fatigue: an investigation into levels being reported by radiotherapy students
David Flinton, Pam Cherry, Richard Thorne, Liam Mannion, Chris O’Sullivan, Ricardo Khine
Journal of Radiotherapy in Practice.2018; 17(4): 364. CrossRef - Secondary Traumatic Stress and Burnout Among Muslim Nurses Caring for Chronically Ill Children in a Turkish Hospital
Neslihan Partlak Günüşen, Marian Wilson, Burcu Aksoy
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2018; 29(2): 146. CrossRef - Compassion fatigue: A meta-narrative review of the healthcare literature
Shane Sinclair, Shelley Raffin-Bouchal, Lorraine Venturato, Jane Mijovic-Kondejewski, Lorraine Smith-MacDonald
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2017; 69: 9. CrossRef - Occupational Burnout Syndrome in the nursing context: an integrative literature review
Mateus Estevam Medeiros-Costa, Regina Heloísa Maciel, Denise Pereira do Rêgo, Lucimar Lucas de Lima, Maria Eliziane Pinto da Silva, Julyana Gomes Freitas
Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Turnover Intention in Clinical Nurses: Compassion Fatigue, Coping, Social Support, and Job Satisfaction
Young Hee Yang, Jong Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(5): 562. CrossRef - Understanding Compassion Fatigue in Healthcare Providers: A Review of Current Literature
Claire Sorenson, Beth Bolick, Karen Wright, Rebekah Hamilton
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2016; 48(5): 456. CrossRef - Understanding compassion fatigue: understanding compassion
Kathleen Ledoux
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2015; 71(9): 2041. CrossRef - Preparing Students for the Emotional Challenges of Nursing: An Integrative Review
Patricia A. Dwyer, Susan M. Hunter Revell
Journal of Nursing Education.2015; 54(1): 7. CrossRef
- Self-compassion and secondary traumatic stress in pediatric oncology/hematology nurses
- 2,426 View
- 33 Download
- 40 Crossref

- A Model on Turnover Intention of Chief Nurse Officers
- Kwang-Ok Park, Jong Kyung Kim, Se Young Kim, Sunju Chang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(1):9-18. Published online February 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.1.9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to test the turnover intention model for chief nurse officers in general hospitals. The variables for the study included job stress, social support, job satisfaction, and organization commitment.
Methods A predictive, non-experimental design was used with a sample of 144 chief nurse officers from 144 general hospitals. Data were collected using self-administered questionnaires and analyzed using SPSS, AMOS program.
Results The overall fitness of the hypothetical model to the data was good (χ2=16.80,
p =.052, GFI=.96, AGFI=.90, NFI=.97, CFI=.99). Job stress, social support, job satisfaction, and organization commitment explained 59.0% of the variance in turnover intention by chief nurse officers. Both organization commitment and social support directly influenced turnover intention for chief nurse officers, and job stress and job satisfaction indirectly influenced turnover intention.Conclusion The results imply that chief nurse officers in hospitals need social support and management of job stress to increase job satisfaction and organization commitment, and lower turnover intention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nurse Staffing, Work Hours, Mandatory Overtime, and Turnover in Acute Care Hospitals Affect Nurse Job Satisfaction, Intent to Leave, and Burnout: A Cross-Sectional Study
Sung-Heui Bae
International Journal of Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mediating effects of workgroup processes on the relationship between nurse turnover and nurse outcomes in hospitals
Sung-Heui Bae, Suin Kim, Hwasook Myung
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationships among Non-Nursing Tasks, Nursing Care Left Undone, Nurse Outcomes and Medical Errors in Integrated Nursing Care Wards in Small and Medium-Sized General Hospitals
Ju-Young Park, Jee-In Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(1): 27. CrossRef - Assessing the Presence of Post-Traumatic Stress and Turnover Intention Among Nurses Post–Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Outbreak: The Importance of Supervisor Support
Heeja Jung, Sun Young Jung, Mi Hyang Lee, Mi Sun Kim
Workplace Health & Safety.2020; 68(7): 337. CrossRef - The Convergence Study of Interpersonal Caring Behaviors on Anger, Job Stress and Social Support in Nurses
Jin-Ah Han, Mi-Jin Kim
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(3): 87. CrossRef - Influences of Customer Orientation, Emotional Labor, Unit Manager-nurse Exchange and Relational Bonds on Nurses' Turnover Intension
Young-Soon Kim, Kyung-Yeon Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(4): 396. CrossRef - Literature Review of Structural Equation Models for Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention in Korea
Eunhye Kim, Jinhyun Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2014; 11(2): 109. CrossRef - Effects of Nurses' Social Capital on Turnover Intention: Focused on the Mediating Effects Organizational Commitment and Organizational Cynicism
Jeongwon Han, Heeyoung Woo, Eunsil Ju, Sohee Lim, Sangsook Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(4): 517. CrossRef - The Effects of DISC Behavior Styles of Office Workers on Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment and Job Performance
Yun-Young Kim, Young-Hwa Baek, Ki-Hyun Park, Jong-Hyang Yoo, Eun-Su Jang
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2012; 21(2): 98. CrossRef
- Nurse Staffing, Work Hours, Mandatory Overtime, and Turnover in Acute Care Hospitals Affect Nurse Job Satisfaction, Intent to Leave, and Burnout: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 1,262 View
- 9 Download
- 9 Crossref

- A Predictive Model on Turnover Intention of Nurses in Korea
- Sook Ja Moon, Sang Sook Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(5):633-641. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.5.633
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to propose and test a predictive model that could explain and predict Korean nurses' turnover intentions.
Methods A survey using a structured questionnaire was conducted with 445 nurses in Korea. Six instruments were used in this model. The data were analyzed using SPSS 15.0 and Amos 7.0 program.
Results Based on the constructed model, organizational commitment, and burnout were found to have a significant direct effect on turnover intention of nurses. In addition, factors such as empowerment, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment were found to indirectly affect turnover intention of nurse. The final modified model yielded χ2=402.30,
p <.001), χ2/df=2.94, RMSEA=0.07, RMR=0.03, GFI=0.90, AGF=0.87, NFI=0.88, CFI=0.92 and good fit indices.Conclusion This structural equational model is a comprehensive theoretical model that explains the related factors and their relationship with turnover intention in Korean nurses. Findings from this study can be used to design appropriate strategies to further decrease the nurses' turnover intention in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Instruments to measure nurses' intention-to-stay in the profession: A systematic literature review
Myrthe van der Zanden, Saba Hinrichs-Krapels, Christa Niehot, Anna Teeuw, Swasti Madan, Naomi van der Linden
International Journal of Nursing Studies Advances.2026; 10: 100496. CrossRef - The effect of organizational communication and grit on turnover intention of rehabilitation hospital nurses: A cross-sectional correlation study
Inji Ha, Heeok Park, Ji Hun Joung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(1): 35. CrossRef - The Influence of Socio-Cognitive Mindfulness, Job Stress and Social Support on Turnover Intention in General Hospital Nurses
Chun Ha Kim, Mikyoung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(2): 155. CrossRef - The Effects of Presenteeism, Burnout, and Nursing Performance on Retention Intention among Nurses at an Intensive Care Unit
Seung-Hee Lee, Na Rin Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 269. CrossRef - Effect of Nursing Professionalism on Turnover Intention among Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Job Embeddedness
Ja In Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyoung Eun Chang, Sunmi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 446. CrossRef - The Effects of Nurses’ Dispatch Work Characteristics on Job Embeddedness, Organizational Commitment, and Turnover Intention
Eejee Jung, Gunjeong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 560. CrossRef - The need for attention to mental health of nursing staff during COVID-19 pandemic as their basic human right
Sina Abdollahzade, Sima Rafiei, Saber Souri
International Journal of Human Rights in Healthcare.2024; 17(2): 145. CrossRef - Relationship between organizational commitment, working environment, and burnout in clinical nurses
Mona Alinejad-Naeini, Mahin Ghasemi, Mohammad Saeed Mirzaee, Farshad Heidari-Beni
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Nursing Practice Environment on Intent to Leave in Hospital Nurses: Focused on the Mediating Effect of Reciprocity
So Young Lee, Mi-Aie Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 201. CrossRef - Effect of the Nursing Work Environment on Turnover Intention: Serial Mediation Effects of Career Motivation and Job Satisfaction
Young Deok Park, Sun Ju You
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(5): 529. CrossRef - The Effect of Nurses’ Perceived Leader-Member Exchange on Psychological Ownership, Job Engagement, and Turnover Intention
Eun Ah Cho, Myun Sook Jung, Eun Ju Heo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(3): 298. CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Unit Managers’ Authentic Leadership, Transformational Leadership, and Transactional Leadership on Turnover Intention in Advanced Beginner Nurses: Mediation Effects of Positive Psychological Capital
Eun Jeong Kim, Eungyung Kim, Son Ja Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 409. CrossRef - Psychological capital and employee job attitudes: the critical significance of work-life balance
Zahoor Ahmad Parray, Tanveer Ahmad Shah, Shahbaz Ul Islam
Evidence-based HRM: a Global Forum for Empirical Scholarship.2023; 11(3): 483. CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Work Environment, Need Satisfaction, and Depression on Turnover Intention in Korea
Sun-Hwa Shin, On-Jeon Baek, Eun-Hye Lee
Healthcare.2023; 11(12): 1698. CrossRef - Comparative Study on Work-Life Balance, Nursing Work Environment, Nursing Organizational Culture, and Job Satisfaction before Turnover among Nurses Leaving Hospital: Current Clinical Nurses versus Non-clinical Nurses
Yejin Seo, Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 385. CrossRef - The mediating effect of workplace incivility on organization culture in South Korea: A descriptive correlational analysis of the turnover intention of nurses
Yoon Heui Lee, Jumi Lee, Soo‐Kyoung Lee
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2022; 54(3): 367. CrossRef - Effect of an Age-Stratified Working Environment and Hospital Characteristics on Nurse Turnover
Yoseb Lee, Jeong Lim Kim, So Hee Kim, Jungmi Chae
Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service Research.2022; 2(1): 106. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling of Nurses’ Turnover Intention Based on Affective Events Theory
Eun Ha Choi, Eun Gyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 27(5): 399. CrossRef - Correlation between Stress and Anxiety to Viral Epidemics (SAVE) and Burnout among Korean Dental Hygienists during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study
Seul-Ah Lee, Jung-Eun Park, Jong-Hwa Jang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(6): 3668. CrossRef - Effects of Meaning of Work, Job Embeddedness, and Workplace Bullying on Turnover Intention of Nurses in a University Hospital
Young Suk Sim, Gui Sook Shim, Bong Hi Sim, Joo Hyun Sung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(4): 227. CrossRef - Job satisfaction and turnover intention of preventive medicine workers in northern Vietnam: Is there any relationship?
Quynh Anh Nguyen, Anh Dung Tran
Health Services Insights.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the factors of turnover intention of dental hygienists in dental hospitals
Jung Hwa Lee, Na Na Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2021; 45(2): 92. CrossRef - Effects of Clinical Nurses’ Workplace Bullying, Empathic Ability, and Resilience on Job Satisfaction
Mi Young Lee, Youngrye Park
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2021; 14(2): 57. CrossRef - Nurses’ turnover intention in secondary hospitals in China: A structural equation modelling approach
Yong‐ai Zhang, Xiao‐na Zhang, Na Xu, EunKyoung Yun
Journal of Nursing Management.2021; 29(7): 2216. CrossRef - Psychological Capital Mediates the Association between Job Stress and Burnout of among Korean Psychiatric Nurses
Sooyeong Kim, YoungRan Kweon
Healthcare.2020; 8(3): 199. CrossRef - Influence of Job Embeddedness and Resilience on Turnover Intention in Dental Hygienists
Ji-Min Hwang, Ji-Hyoung Han
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2020; 20(3): 171. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Burnout in the Association Between Emotional Labor and Turnover Intention in Korean Clinical Nurses
Chi-Yun Back, Dae-Sung Hyun, Da-Yee Jeung, Sei-Jin Chang
Safety and Health at Work.2020; 11(1): 88. CrossRef - A study on the intent to leave and stay among hospital nurses in Korea: A cross‐sectional survey
Mi‐Aie Lee, Young‐Hee Ju, So‐Hee Lim
Journal of Nursing Management.2020; 28(2): 332. CrossRef - Effects of recognition of flexible work systems, organizational commitment, and quality of life on turnover intentions of healthcare nurses
Myoungjin Kwon
Technology and Health Care.2019; 27(5): 499. CrossRef - Influence of Resilience and Job Embeddedness on Turnover Intention in General Hospital Nurses
Kyoung Ja Ko, Soo-Kyoung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2019; 25(4): 362. CrossRef - Relationship between Career Plateau, Career Planning, Social Support, and Turnover Intention in Nurses
Jeonga Ko, Heeyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(1): 97. CrossRef - Effect of Nurses' Emotional Labor on Customer Orientation and Service Delivery: The Mediating Effects of Work Engagement and Burnout
Sang-Sook Han, Jeong-Won Han, Yun-Hyung Kim
Safety and Health at Work.2018; 9(4): 441. CrossRef - Effects of Group Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy on the Nurses' Job Stress, Burnout, Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment and Turnover Intention
Hye-Lyun Kim, Sook-Hee Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(4): 432. CrossRef - Turnover Experience of Male Nurses
Hyunsu Kim, Jeongseop Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(1): 25. CrossRef - The mediating effect of emotional intelligence between emotional labour, job stress, burnout and nurses' turnover intention
Eunyoung Hong, Young Sook Lee
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2016; 22(6): 625. CrossRef - The effect of social capital on job satisfaction and quality of care among hospital nurses in South Korea
Ji In Shin, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2016; 24(7): 934. CrossRef - Influences of Customer Orientation, Emotional Labor, Unit Manager-nurse Exchange and Relational Bonds on Nurses' Turnover Intension
Young-Soon Kim, Kyung-Yeon Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(4): 396. CrossRef - The Influence of Job Characteristics and Job Stress on Children's Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention
Se-Young Kim, Seong-Hee Back
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2016; 16(4): 100. CrossRef - Factors Affecting on Turnover Intentions among Operating Room Nurses
Yeo-Jin Kim, Keum-Sook Park, Eun-Ja Yang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(12): 352. CrossRef - Influence of the Emotional Intelligence, Communication Competence and Stress coping on Turnover Intention in Psychiatric Nurses
Hye-Seung Kang, Yoon-Young Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(1): 141. CrossRef - Influences of Hospital Nurses' perceived reciprocity and Emotional Labor on Quality of Nursing Service and Intent to Leave
Mi-Aie Lee, Eunjeong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(3): 364. CrossRef - Relationships among Nursing Work Environment, Job Embeddedness, and Turnover Intention in Nurses
Hae Jin Ko, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(3): 279. CrossRef - Impact of Unit-level Nurse Practice Environment on Nurse Turnover Intention
Youngjin Lee, GyeongAe Seomun
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(6): 355. CrossRef - Structural equation modeling on nurses' emotional labor including antecedents and consequences
Miyeon Kim, Heejung Choi
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2016; 27(1): 143. CrossRef - Influence of Job Embeddedness Factors on Turnover Intention of Nurses in Small and Medium Sized General Hospitals
Yun-Sook Kim, Seang Ryu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(2): 158. CrossRef - Effects of Job Participation on Intention to Leave among Physicians Working in Public Health Center
Hyunjong Song, Hyong Won Cho, Sok-Goo Lee, Hyunkyung Park
Health Policy and Management.2016; 26(3): 219. CrossRef - The Influence of Emotional Labor, Job Stress, and Burnout on Turnover Intention of Care Worker's at Long-Term Care Hospitals
Soon-Chul Youn, Suhye Kwon, Hyo-Jeong Kang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(5): 428. CrossRef - A Predictive Model on North Korean Refugees' Adaptation to South Korean Society: Resilience in Response to Psychological Trauma
So-Hee Lim, Sang-Sook Han
Asian Nursing Research.2016; 10(2): 164. CrossRef - A Structural Model of Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention: Focusing on Organizational Characteristics, Job Satisfaction, and Job Embeddedness
Mi Ja Yoo, Jong Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(3): 292. CrossRef - Perceptions of Medical Personnel toward Burnout using Q Methodology
Eun Ja Yeun, Young Mi Kwon, Young Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(1): 57. CrossRef - Effects of role stress on nurses' turnover intentions: The mediating effects of organizational commitment and burnout
Sang‐Sook Han, Jeong‐Won Han, Young‐Suk An, So‐Hee Lim
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2015; 12(4): 287. CrossRef - A Study on Self-Esteem, Nursing Professional Values and Organizational Commitment in a Diploma Nursing Students
Ho-Jin Cho, Jong-Yul Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(12): 8498. CrossRef - The Structural Modeling for Nurses' Interpersonal Competence within an Organization
Jieun Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(4): 366. CrossRef - Perceptions on Fixed Night Shift System and Turnover Intention of General Hospital Nurses
Mi-Aie Lee, Hye-Jin Cho, Sung-Hee Ahn, Hyo-Ju Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(5): 519. CrossRef - Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment and Turnover Intention among Male Nurses
Min Kweon Ahn, Myung Ha Lee, Hyun Kyung Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(2): 203. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Turnover Intentions among the Newcomers in the Construction of Landscape Architecture
Do-Gyun Kim, Il Ryu
Journal of the Korean Institute of Landscape Architecture.2015; 43(2): 73. CrossRef - A Phenomenological Study on the Turnover Experience of Novice Nurses Working in General Hospital
Bo-Mi Im, Jong-Min Park, Mi-Jin Kim, Su-Yeon Kim, Jeong-Ho Maeng, Lu-Li Lee, Kyung-Ah Kang
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2015; 24(4): 313. CrossRef - Phenomenological Study on Burnout Experience of Clinical Nurses Who have Turnover Intention
Jeung-Im Kim, Haeng-Mi Son, In Hee Park, Hee Jin Shin, Ji hyun Park, Mi Ock Cho, Seongui Kim, Mi Ock Yu
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2015; 21(4): 297. CrossRef - The comparative study on changes in job satisfaction and turnover intention according to the convergence mediating factors and the level of emotional labor in dental hygienists
Mi-sook Choi, Dong-ha Ji
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2015; 6(6): 27. CrossRef - Effects of Emotional Labor and Communication Competence on Turnover Intention in Nurses
Se Hyang Kim, Mi-Aie Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(3): 332. CrossRef - Mediation and Moderation Effects of Job Embeddedness between Nursing Performance and Turnover Intention of Nurses
Eun Hee Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(8): 5042. CrossRef - Influence of Workplace Bullying and Leader-Member Exchange on Turnover Intention among Nurses
Mi Ra Han, Jeung Ah Gu, Il Young Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(4): 383. CrossRef - Job Stress, Organizational Commitment, Way of Coping and Turnover Intention among Korean Visiting Nurses
In-Hee Choi, Young-Hae Chung, In-Hyae Park, Young-Ae Choi
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2013; 22(2): 149. CrossRef - The Experiences of Turnover Intention in Early Stage Nurses
Se Young Lee, Eun Jin Oh, Kyung Mi Sung
journal of east-west nursing research.2013; 19(2): 168. CrossRef - Effects of Nurses' Social Capital on Turnover Intention: Focused on the Mediating Effects Organizational Commitment and Organizational Cynicism
Jeongwon Han, Heeyoung Woo, Eunsil Ju, Sohee Lim, Sangsook Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(4): 517. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling on Nursing Productivity of Nurses in Korea
Se Young Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Heon Man Lim, Mi Young Lee, Kwang-Ok Park, Kyoung A Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(1): 20. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Organizational Commitment and Turnover Intention of Hospital Nurses: Focused on the Mediating Effects of Person-environment Fit
Hyang Sook Seok
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(3): 361. CrossRef - Effects of Nurses' Mentoring on Turnover Intention: Focused on the Mediating Effects Role Stress and Burnout
Sangsook Han, Ohsook Kim, Yunsu Joo, Eunduck Choi, Jeongwon Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(5): 605. CrossRef - A Path Analysis of Variables Influencing Turnover Intention Among Healthcare Providers
Jung-Hee Song, Ji-Yeon An
Journal of muscle and joint health.2012; 19(2): 142. CrossRef
- Instruments to measure nurses' intention-to-stay in the profession: A systematic literature review
- 2,262 View
- 57 Download
- 69 Crossref

- New Nurse Turnover Intention and Influencing Factors
- Sang Sook Han, In Soon Sohn, Nam Eun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(6):878-887. Published online December 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.6.878
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The study was done to identify turnover intention in new nurses according to characteristics of the nurses and other factors affecting turnover and to provide data to set up a strategy to reduce the turnover.
Methods Data were collected from 1,077 new nurses who had less than 12 months employment experience and worked in one of 188 hospitals. Eight research instruments were used. Data analysis was done using SPSS WIN 15.0 program.
Results Several factors influence new nurse turnover intention. The average score for turnover intention was 2.12. The scores for subscales were self efficacy, 3.76, nursing performance, 3.90, job satisfaction, 2.09, organization commitment, 1.28, stress, 1.32, burnout, 2.82 and nursing organizational culture, 3.29. Turnover intention was related to self efficacy, nursing performance, job satisfaction, organization commitment, stress, burnout, nursing organizational culture, duration of in-class training, duration of on the job training, number of hospital beds, length of employment and duration of employment in current workplace. The predicting factors for turnover intention were burnout, stress, duration of employment in the current workplace, self efficacy and nursing performance. Those factors explained 51.6% of turnover intention.
Conclusion New nurse turnover intention can be reduced by mitigating the factors affecting this intention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of self-efficacy and professional identity on Japanese early childhood education and care (ECEC) teachers’ absenteeism tendency and turnover intention
Yuko Matsuda, Shoko Hamada
Education 3-13.2026; 54(3): 652. CrossRef - Care Workers’ Turnover Intentions Associated With Workplace Abuse: The Role of Work-Related Stress and Job Satisfaction
Sunghyun Ko, Yeonjung Lee
The International Journal of Aging and Human Development.2025; 100(2): 248. CrossRef - Factors influencing perceived preceptor empathy and nursing practice readiness on field adaptation of new nurses in South Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive study
Kyeungyeun Jang, Hanna Choi
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(1): 94. CrossRef - Factors influencing delirium nursing competency among nurses in integrated nursing care wards in South Korea: a cross-sectional study
Jeeyoung Yeon, Gisoo Shin
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(2): 256. CrossRef - Impact of Grit, Teamwork, Organizational Communication Competence, Perception of Patient Safety Culture on Patient Safety Nursing Activities in Integrated Nursing Care Units
Jeeseon Kim, Haejung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 237. CrossRef - Organizational commitment of nursing staff: Definition of the concept and specifics of measurement (review of foreign publications)
K. V. Kuzmin, L. E. Petrova, V. S. Kharchenko
Kuban Scientific Medical Bulletin.2025; 32(5): 96. CrossRef - Predicting turnover intention among newly graduated nurses in South Korea: a decision tree analysis
Mikyung Moon, Hyunwook Kang
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Individual and environmental factors that influence longevity of newcomers to nursing and midwifery: a scoping review
Janie Alison Brown, Tanya Capper, Desley Hegney, Helen Donovan, Moira Williamson, Pauline Calleja, Terena Solomons, Sally Wilson
JBI Evidence Synthesis.2024; 22(5): 753. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Intensive Care Unit Nurses’ Competency in Delirium Care in A Tertiary General Hospital
Mi Ran Lim, Gyoo Yeong Cho
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(3): 37. CrossRef - The educational needs of virtual reality simulation training for novice nurses’ adaptation to clinical practice: A mixed methods study
Mikyoung Lee, Jeong Hee Eom, Jinyoung Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(4): 339. CrossRef - The mediating effect of job motivation on the relationship between career barriers and nurses’ turnover intention
Tuğba Yeşilyurt, Nilgün Göktepe, Şehrinaz Polat
Collegian.2023; 30(6): 821. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Employee Performance on the Relationship Between Emotional Labour and Intent to Leave Among Nurses
Bayram Sahin, Gülnur Ilgun, Seda Sonmez
Journal of Health Management.2023; 25(2): 299. CrossRef - The Experiences of Overcoming Turnover Intention among Experienced Nurses
Min Jeong Kwon, Kyung Mi Sung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(1): 32. CrossRef - Effects of job embeddedness and nursing working environment on turnover intention among trauma centre nurses: A cross‐sectional study
Hye Ju Lee, Soo‐Kyoung Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2915. CrossRef - Effect of an Age-Stratified Working Environment and Hospital Characteristics on Nurse Turnover
Yoseb Lee, Jeong Lim Kim, So Hee Kim, Jungmi Chae
Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service Research.2022; 2(1): 106. CrossRef - Turnover intention and related factors among resident physicians in China under the standardised residency training programme: a cross-sectional survey
Xiaoting Sun, Mengmeng Zhang, Zhanghong Lu, Zhaoyu Zhang, Jialin Charlie Zheng, Liming Cheng, Lianhua Zeng, Yingli Qian, Lei Huang
BMJ Open.2022; 12(4): e061922. CrossRef - Differences in the effects of organisational climate on burnout according to nurses’ level of experience
Naoko Tsukamoto, Mikiko Kudo, Yukiko Katagiri, Aya Watanabe, Yuka Funaki, Akemi Hirata
Journal of Nursing Management.2021; 29(2): 194. CrossRef - The Effect of Coronavirus Stress on Job Burnout in Nurses with the Moderating Role of Psychological Capital
Mohsen Arefnejad, Fariborz Fathi Chegeni, Mostafa Omidnejad
Journal of Ergonomics.2021; 9(2): 58. CrossRef - Occupational identity, job satisfaction and their effects on turnover intention among Chinese Paediatricians: a cross-sectional study
Wanjun Deng, Zhichun Feng, Xinying Yao, Tingting Yang, Jun Jiang, Bin Wang, Lan Lin, Wenhao Zhong, Oudong Xia
BMC Health Services Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction Model for Nursing Work Outcome of Nurses: Focused on Positive Psychological Capital
Soon Neum Lee, Jung A Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of Head Nurses' Authentic Leadership, Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment Perceived by Newly Licenced Nurses on Turnover Intention
Eun Min An, Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 428. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of an Education Program Based on Whole Brain Model for Novice Nurses
Moo Cho
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(1): 36. CrossRef - Developing Nursing Standard Guidelines for Nurses in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: A Delphi Study
Hanna Lee, Da-Jung Kim, Jeong-Won Han
Healthcare.2020; 8(3): 320. CrossRef - The Effect of Appreciative Inquiry on Positive Psychological Capital and Organizational Commitment of New Nurses
Hyunju Kim, Young Hee Yi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2019; 12(3): 13. CrossRef - The Effect of Work-Life Balance on Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention of Hospital Nurses: Compared to Female Wage Workers
Dong Min Son, Young-Il Jung
Stress.2019; 27(3): 268. CrossRef - The role of job satisfaction, work engagement, self-efficacy and agentic capacities on nurses' turnover intention and patient satisfaction
Silvia De Simone, Anna Planta, Gianfranco Cicotto
Applied Nursing Research.2018; 39: 130. CrossRef - Impact of resilience and job involvement on turnover intention of new graduate nurses using structural equation modeling
Mi Yu, Haeyoung Lee
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2018; 15(4): 351. CrossRef - The protective role of self-efficacy against workplace incivility and burnout in nursing
Roberta Fida, Heather K. Spence Laschinger, Michael P. Leiter
Health Care Management Review.2018; 43(1): 21. CrossRef - The stress experience of nurses who are reemployed after career interruption
Eun-Jin Soun, Jae-Hyeon Eom, Eun-Sook Nam, Young-Ran Chae, Myung-Sook Kil, Eun-Ha Park
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(5): 125. CrossRef - Predictors of Turnover among New Nurses using Multilevel Survival Analysis
Suhee Kim, Kyongeun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(5): 733. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Turnover Intention for New Graduate Nurses in Three Transition Periods for Job and Work Environment Satisfaction
Mi Yu, Kyung Ja Kang
The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing.2016; 47(3): 120. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Turnover Intention in Pediatric Nurses
Min Suk Im, Young Eun Lee
Child Health Nursing Research.2016; 22(1): 37. CrossRef - Influence of Head Nurses' Ethical Leadership on Job Satisfaction among Staff Nurses: Mediating Effect of Affective Commitment
Min Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(5): 553. CrossRef - Clinical Competence and Organizational Socialization according to Communication Style of Preceptors as Perceived by New Nurses*
Young Choon Park, Hyoung Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2016; 23(1): 42. CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Professionalism and Job Involvement on Turnover Intention among New Graduate Nurses
Hye Yun Jeoung, Se Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(5): 531. CrossRef - A Study on Self-Esteem, Nursing Professional Values and Organizational Commitment in a Diploma Nursing Students
Ho-Jin Cho, Jong-Yul Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(12): 8498. CrossRef - The Effects of Fear of Negative Evaluation, Cognitive Emotional Regulation on Field Adaptation of New Graduate Nurses
Kwi-Nam Jeong, Haw-Jin Lee, Hae-Jin Kwon
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(10): 6895. CrossRef - Resilience and Organizational Socialization in New Nurses
So Yeonn Park, Yunhee Kwon, Yeong Sook Park
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2015; 15(2): 324. CrossRef - A Study on Satisfaction, Job Stress, Burnout, Organizational Citizenship and Productivity of Hospital Nurses
Hyun-min Ko, Shinyoung Gwak, Kyung Chang
Journal of the Korea Safety Management and Science.2015; 17(4): 181. CrossRef - The relationship between South Korean clinical nurses' attitudes toward organizations and voluntary turnover intention: A path analysis
Jong Kyung Kim, Sun Ju Chang
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2015; 21(4): 383. CrossRef - Relation of Compassionate Competence to Burnout, Job Stress, Turnover Intention, Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment for Oncology Nurses in Korea
Sun-A Park, Seung-Hee Ahn
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2015; 16(13): 5463. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Turnover Intentions among the Newcomers in the Construction of Landscape Architecture
Do-Gyun Kim, Il Ryu
Journal of the Korean Institute of Landscape Architecture.2015; 43(2): 73. CrossRef - A Phenomenological Study on the Turnover Experience of Novice Nurses Working in General Hospital
Bo-Mi Im, Jong-Min Park, Mi-Jin Kim, Su-Yeon Kim, Jeong-Ho Maeng, Lu-Li Lee, Kyung-Ah Kang
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2015; 24(4): 313. CrossRef - Job Stress, Burnout, Nursing Organizational Culture and Turnover Intention among Nurses
Young-Ran Yeun
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(8): 4981. CrossRef - Content Analysis of Communication between Nurses during Preceptorship
Yeon Ok Jeoung, Song Chol Park, Jeong Kun Jin, Joo Young Kim, Ji Uhn Lee, Soon Young Park, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 23(2): 82. CrossRef - A Study on the Development and Evaluation of Hospital Communication (Hospital Adaptation) Program for New Graduate Nurses
Mi-Jee Koo, Kyoung-Nam Kim
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2014; 8(4): 1. CrossRef - Experience of Turnover in New Nurses
Sun Ae Kim, Hye Won Jeon
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(3): 644. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nurse Turnover Intention in Small and Medium Sized Hospitals in the Metropolitan Area
Youn Sun Hwang, Kyeong Hwa Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(5): 576. CrossRef - Effect of Self-leadership Recognized by Newly-employed Nurses on Job Satisfaction: Mediating Effect of Organizational Commitment
Yeon Hee Choi, Hyeon Mi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 23(4): 242. CrossRef - Relationship among Essentials of Fundamental Nursing Skills Performance, Stress from Work and Work Capability of New Clinical Nurses
Soon Sik Bang, Il-Ok Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(4): 628. CrossRef - Impact of organisational characteristics on turnover intention among care workers in nursing homes in Korea: a structural equation model
Jong Goon Ha, Ji Man Kim, Won Ju Hwang, Sang Gyu Lee
Australian Health Review.2014; 38(4): 425. CrossRef - The Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Stress Coping of Nurses
Hyoung-Sook Park, Jae-Hyun Ha, Mee-Hun Lee, Hyun-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2014; 21(4): 466. CrossRef - Volunteer activity, sociality, and morality in the dental hygiene students
Hye-Kyung Lee
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2014; 14(6): 927. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Organizational Commitment and Turnover Intention of Hospital Nurses: Focused on the Mediating Effects of Person-environment Fit
Hyang Sook Seok
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(3): 361. CrossRef - Lived Experiences of New Graduate Nurses
Yeonok Suh, Kyungwoo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(2): 227. CrossRef - The Experiences of Turnover Intention in Early Stage Nurses
Se Young Lee, Eun Jin Oh, Kyung Mi Sung
journal of east-west nursing research.2013; 19(2): 168. CrossRef - Current Situation and the Forecast of the Supply and Demand of the Nursing Workforce in Korea
Boon Han Kim, Bok Yae Chung, Jin Kyung Kim, Ae-young Lee, Seon Young Hwang, Joon Ah Cho, Jung A Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(6): 701. CrossRef - Current Situation and the Forecast of the Supply and Demand of the Nursing Workforce in Korea
Boon Han Kim, Bok Yae Chung, Jin Kyung Kim, Ae Young Lee, Seon Young Hwang, Joon Ah Cho, Jung A Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(6): 701. CrossRef - Educational Needs in the Development of a Simulation Based Program on Neonatal Emergency Care for Nursing Students
So-Young Yoo, Sung-Hee Kim, Ja-Hyung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2012; 18(4): 170. CrossRef - Development of OSCE by Nurse Managers of One University-Affiliated Hospital for Skill Test of Nurse Recruitment Process
Mi-Hyun Han, Joo-Soon Choi, Seok-Gun Park
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(6): 2625. CrossRef - Newly Graduated Nurses' Job Satisfaction: Comparison with Allied Hospital Professionals, Social Workers, and Elementary School Teachers
Mihyun Park, Ji Yun Lee, Sung-Hyun Cho
Asian Nursing Research.2012; 6(3): 85. CrossRef - Turnover intention of graduate nurses in South Korea
Haejung LEE, Yeonjung LIM, Hee Young JUNG, Youn‐Wha SHIN
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2012; 9(1): 63. CrossRef - A study on satisfaction in major and job esteem based on volunteering experience of college students in the department of dental hygiene and nursing
Mi-A Shin, Kwon-Suk Ahn
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2012; 12(6): 1090. CrossRef - The Effects of Preceptors' Transformational Leadership on Job Stress and Clinical Performance among New Graduate Nurses
Hee Young Kim, Jong Park, So Yeon Ryu, Seong Woo Choi, Mi Ah Han
Health Policy and Management.2012; 22(3): 347. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse's Organizational Conflict on Organizational Commitment and Labor Union Commitment in University Hospitals
Soon Min, Hye Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2012; 18(4): 374. CrossRef - A Study on Nursing Students' Job-esteem, Work Values, and Satisfaction of Their Major
Bong-Hee Son, Young-Mi Kim, In-Gyeong Jun
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2011; 20(3): 240. CrossRef - Influence of Clinical Nurses' Emotional Intelligence on their Career Commitment and Turnover Intention : Moderating Role of Career Commitment
Su-Jeong Han
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2011; 11(7): 418. CrossRef - Influence of Nursing Organizational Culture on Empowerment as Perceived by New Nurses
Yang Yoeb Seo, Hyeon Ok Ju
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2011; 17(1): 88. CrossRef - Effects of the In-Home Visitation Care Facility Directors' Leadership Types on Organizational Effectiveness and the Moderating Role of Organizational Trust
Myeong-Suk Kim, Soo-Il Choi
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2010; 10(9): 327. CrossRef
- Impact of self-efficacy and professional identity on Japanese early childhood education and care (ECEC) teachers’ absenteeism tendency and turnover intention
- 3,135 View
- 50 Download
- 69 Crossref

- The Mediating Role of Organizational Citizenship Behavior between Organizational Justice and Organizational Effectiveness in Nursing Organizations
- Wall-Yun Park, Sook-Hee Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(2):229-236. Published online April 28, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.2.229
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was a secondary analysis to verify the mediating role of organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) between organizational justice (OJ) and organizational effectiveness (OE) in nursing organizations.
Methods The RN-BSNs and their colleagues in Seoul and Busan were subjects. The data was collected for 20 days between September 13 and October 2, 2004. Two hundred eighty three data sets were used for the final analysis. The fitness of models were tested using AMOS 5.
Results The fitness of hypothetical model was moderate. Procedural Justice (PJ), Interaction Justice (IJ) and Distributive Justice (DJ) had direct effects on Job Satisfaction (JS), Organizational Commitment (OC) and Turnover Intention (TI) in OE, and indirect effects on JS, OC and TI mediated by OCB. The modified model improved with ideal fitness showed the causal relations among OE. In modified model, PJ, IJ and DJ had direct positive effects on OCB and JS and OC in OE, and indirect effects on JS and OC mediated by OCB. JS and OC in OE had a direct negative effect on TI.
Conclusion OCB mediated the relationship between OJ and OE, so the nursing managers should enhance OCB of the nurses in order to improve OE.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Organizational commitment of nursing staff: Definition of the concept and specifics of measurement (review of foreign publications)
K. V. Kuzmin, L. E. Petrova, V. S. Kharchenko
Kuban Scientific Medical Bulletin.2025; 32(5): 96. CrossRef - The effect of organizational justice and job involvement on organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) with organizational commitment as mediation variable
Della Restiana Sari, Noermijati, Himmiyatul Amanah Jiwa Juwita
International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science (2147- 4478).2024; 13(5): 421. CrossRef - The impact of organizational justices on organizational success: the mediating role of organizational citizenship behavior
Besfat Engdaw, Melaku Kebede
Cogent Social Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The direct and indirect effect of organizational justice on employee intention to comply with information security policy: The case of Ethiopian banks
Berhanu Aebissa, Gurpreet Dhillon, Million Meshesha
Computers & Security.2023; 130: 103248. CrossRef - Examining the Relationship between Labor Law Compliance and Employee Perceptions, Attitudes and Behaviors
Christine Lovely Red, Mendiola Teng-Calleja
Employee Responsibilities and Rights Journal.2021; 33(4): 337. CrossRef - A Meta-Analytic Path Analysis on the Outcome Variables of Nursing Unit Managers' Transformational Leadership: Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(6): 757. CrossRef - How Leader-Member Exchange Affects Knowledge Sharing Behavior: Understanding the Effects of Commitment and Employee Characteristics
Qi Hao, Yijun Shi, Weiguo Yang
Frontiers in Psychology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - HRM practices and the multifaceted nature of organization performance
Abdallah Taamneh, Abdallah Khalaf Alsaad, Hamzah Elrehail
EuroMed Journal of Business.2018; 13(3): 315. CrossRef - Nurses’ voluntary extra work in the hospital: The role of managers’ decision-making style
Mohammad Amin Bahrami, Marzieh Salehi, Omid Barati, Mohammad Ranjbar Ezzatabadi, Razieh Montazer-alfaraj, Arefeh Dehghani Tafti
International Journal of Healthcare Management.2016; 9(3): 155. CrossRef - Antecedents of organizational citizenship behavior in a sample of Korean manufacturing employees
Paula S Daly, Philip B DuBose, Marion M Owyar-Hosseini, Kibok Baik, Eric M Stark
International Journal of Cross Cultural Management.2015; 15(1): 27. CrossRef - The relationship between South Korean clinical nurses' attitudes toward organizations and voluntary turnover intention: A path analysis
Jong Kyung Kim, Sun Ju Chang
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2015; 21(4): 383. CrossRef - The Influential Factors Related to Organizational Citizenship Behavior of Nurses: With Focus on Authentic Leadership and Organizational Justice
Bora Song, GyeongAe Seomun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(2): 237. CrossRef - Influence of Decentralization, Participation in Decision Making, Job Satisfaction on Nurse Managers' Organizational Commitment
Mi Yu, Kyungsook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2011; 17(3): 357. CrossRef - Organizational Personality Type and Citizenship Behaviors Perceived by Public Health Center Workers in Chonnam Province, Korea
Yoo-Hyang Cho
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2011; 36(1): 47. CrossRef - The Effects of Organizational Justice and Dispositional Affectivity on Job Satisfaction and Intent to Leave among Nurses
Young Hee Yom
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(3): 276. CrossRef
- Organizational commitment of nursing staff: Definition of the concept and specifics of measurement (review of foreign publications)
- 1,191 View
- 7 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Experiences of Nurse Turnover
- Yun-Jung Lee, Kwuy-Bun Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(2):248-257. Published online April 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.2.248
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was designed to search for nursing intervention strategies centering around the meaning structure of the nurse's turnover experience by applying phenomenological methods.
Methods The participants were 6 nurses in small and medium sized hospitals who had experienced at least 1 turnover. Data were collected used MP3 records. The data analysis was done by Giorgi (1985) method.
Results The results were divided into the following categories: 1) Careless decision: wrong decisions, imprudent desire, insufficient patience, unclear future, 2) Inappropriate working environment: irregular working hours, high workload, poor working environment, insufficient understanding of related divisions, lack of opinion collection, low salary, 3) Interpersonal relations problems: discord with colleagues, difficulty in relationships with others, difficulty in daily lives, 4) Lack of specialization: feeling of inertia, lack of role identification, lack of self identification, 5) Inappropriate coping: regret with clinical challenges, difficulty with a new environment, repentance, expectation, relative humility, 6) New self-dignity: expectation, new challenge, relaxing lives, decisions based on future-oriented confidence.
Conclusion The finding of this study will offer profound information on the nurse's turnover experience and provide basic raw materials for improving the quality of nursing performance and contribute to the development of hospital organization.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nurses' Hospital Selection within a Dual Labor Market Framework: The Dilemma of Professional Identity
Hyun-Ji Bae, Hyoung Suk Kim, Hwal Lan Bang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(1): 14. CrossRef - Why Nurses Are Leaving Veterans Affairs Hospitals?
Dongjin Oh, Keon-Hyung Lee
Armed Forces & Society.2022; 48(4): 760. CrossRef - Mental disorders among workers in the healthcare industry: 2014 national health insurance data
Min-Seok Kim, Taeshik Kim, Dongwook Lee, Ji-hoo Yook, Yun-Chul Hong, Seung-Yup Lee, Jin-Ha Yoon, Mo-Yeol Kang
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Turnover Experience of Male Nurses
Hyunsu Kim, Jeongseop Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(1): 25. CrossRef - Effects of Nurses' Social Capital and Job Engagement on Nursing Performance: Focused on the Mediating effects of Organizational Citizenship Behavior
Mi Soon Ko, Hyunsook Zin Lee, Myung Suk Koh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(1): 42. CrossRef - Work Experiences of Delivery Room Nurses: A Phenomenological Study
Yunjung Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2017; 23(2): 78. CrossRef - Predictors of Turnover among New Nurses using Multilevel Survival Analysis
Suhee Kim, Kyongeun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(5): 733. CrossRef - Perceived Emotional Labor of Clinical Nurse from the Persons Concerned
Ji-hyun Back, Myung Hee Kim, Sungmin Kim
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(3): 148. CrossRef - The stress experience of nurses who are reemployed after career interruption
Eun-Jin Soun, Jae-Hyeon Eom, Eun-Sook Nam, Young-Ran Chae, Myung-Sook Kil, Eun-Ha Park
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(5): 125. CrossRef - Effects of professional self-concept, self efficacy on the job satisfaction in general hospital nurses
Eun Jin Park, Ji Young Han, Na Young Jo
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2016; 27(1): 191. CrossRef - The convergence study of Experience of Turnover in new graduate nurses within one year
Young-Mi Kim, Sang-Nam Kim
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(4): 97. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of a Korean version of Leader Rapport Management
Jeong-Won Han, Nam-Eun Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(2): 129. CrossRef - Influence of Job Embeddedness Factors on Turnover Intention of Nurses in Small and Medium Sized General Hospitals
Yun-Sook Kim, Seang Ryu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(2): 158. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Turnover Intentions among the Newcomers in the Construction of Landscape Architecture
Do-Gyun Kim, Il Ryu
Journal of the Korean Institute of Landscape Architecture.2015; 43(2): 73. CrossRef - A study of convergence perception of successful aging, turnover intention and retirement plans of hospital nurses
Hyeon-Jeom Hur, Young-Chae Kwon
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(8): 337. CrossRef - Organizational Socialization and Intention to Leave in Operating Room Nurses Working at Secondary General University Hospitals
Su Jung Yoon, Hye-Ja Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(1): 88. CrossRef - Phenomenological Study on Burnout Experience of Clinical Nurses Who have Turnover Intention
Jeung-Im Kim, Haeng-Mi Son, In Hee Park, Hee Jin Shin, Ji hyun Park, Mi Ock Cho, Seongui Kim, Mi Ock Yu
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2015; 21(4): 297. CrossRef - KoreanWorkEnvironmentScales forClinicalNurses
Jong‐Kyung Kim, Se‐Young Kim, Mi Yu, Myung Ja Kim, Kyoung‐A Lee
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2015; 12(1): 54. CrossRef - Qualitative Study on Clinical Nurses' Intention to Stay in Hospital
Kwang-Ok Park, Jong Kyung Kim, Se Young Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(6): 681. CrossRef - A study on the relevance among Self efficacy, Major satisfaction, Nursing ethics values in Nursing Students before Clinical Practice
Soon-Young Yun, Minsuk Kim
Journal of Digital Convergence.2014; 12(2): 363. CrossRef - Nursing professionalism, Job satisfaction and Turnover intention of nurses in small and medium-sized hospitals - Focused on "I" City
Young-Sil Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(5): 2695. CrossRef - Nurses' Self-image Perceived by Clinical Nurses: An Application of Q-Methodology
Eun-Ho Ha, Kyoung Soon Hyun
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(1): 117. CrossRef - Content Analysis of Communication between Nurses during Preceptorship
Yeon Ok Jeoung, Song Chol Park, Jeong Kun Jin, Joo Young Kim, Ji Uhn Lee, Soon Young Park, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 23(2): 82. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Empowerment, Job Stress, and Organizational Commitment in Relation-oriented Nursing Organization Culture and Turnover Intention of Clinical Nurses
Soon Jeong Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(3): 372. CrossRef - Process of Overcoming Turnover Intention in Career Nurses
Ha Yoon Cheong, Sun Hee Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(3): 414. CrossRef - Literature review of effect of work pattern (day shift and night shift) on worker's health
Ki-Youn Kim, Man-Su Cho, Won-Mo Gal
Journal of the Korea Safety Management and Science.2013; 15(2): 1. CrossRef - Job Stress, Organizational Commitment, Way of Coping and Turnover Intention among Korean Visiting Nurses
In-Hee Choi, Young-Hae Chung, In-Hyae Park, Young-Ae Choi
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2013; 22(2): 149. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling on Nursing Productivity of Nurses in Korea
Se Young Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Heon Man Lim, Mi Young Lee, Kwang-Ok Park, Kyoung A Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(1): 20. CrossRef - Nursing Activity, Job Stress, and Job Satisfaction of Nurses in Community Mental Health Facilities
Hyunjung Lim, Moonhee Gang, Kyongok Oh
The Journal of Digital Policy and Management.2013; 11(12): 507. CrossRef - The Experiences of Turnover Intention in Early Stage Nurses
Se Young Lee, Eun Jin Oh, Kyung Mi Sung
journal of east-west nursing research.2013; 19(2): 168. CrossRef - Factors to Affect Turnover Intention of Nurse: Focusing on Personal, Situational and Interpersonal Relation Variables
Sook Bin Im, Mi-Kyoung Cho, Myoung Lyun Heo
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2013; 22(4): 314. CrossRef - Impact of Unit-level Nurse Practice Environment on Nurse Turnover Intention in the Small and Medium Sized Hospitals
Jeong Ok Kwon, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2012; 18(4): 414. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Turnover Intention of Nurses in Small-medium sized Hospitals
Ki No Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2012; 18(2): 155. CrossRef - A Study on Nursing Students' Job-esteem, Work Values, and Satisfaction of Their Major
Bong-Hee Son, Young-Mi Kim, In-Gyeong Jun
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2011; 20(3): 240. CrossRef - Occupational Health Nurses' Role Experiences
Kyung-Ja June, Hea-Ju Joo, Young-Mi Kim
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2011; 20(3): 250. CrossRef - Perceived Hurts and Forgiveness in Clinical Nurses - The Status and Influencing Variables -
Ki-Wol Sung, Kae-Hwa Jo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(4): 428. CrossRef - Re-employment Experience of Nurses Who Have Left the Profession
Young Soon Byeon, Miyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 768. CrossRef
- Nurses' Hospital Selection within a Dual Labor Market Framework: The Dilemma of Professional Identity
- 1,421 View
- 6 Download
- 37 Crossref

- The Effect of Assertiveness Training on Communication Related Factors and Personnel Turnover Rate among Hospital Nurses
- Myung Ja Kang, Haejung Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(5):681-690. Published online August 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.5.681
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of assertiveness training on nurses' assertive behaviors, interpersonal relations, communication conflicts, conflict management style and personnel turnover rate.
Method A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used in this study. Nurses were assigned into the experimental or control groups, each consisting of 39 nurses. Data was collected between January to March 2004. An ‘Assertiveness Training Program’ for Nurses developed by Park was used for the study. To emphasize assertiveness practice, 5 practice sessions utilizing ABCDE principles were added to Park's program. To examine the effects of the program, differences between the two groups in assertive behaviors, interpersonal relations, communication conflicts, conflict management style and personnel turnover rate were analyzed using ANCOVA.
Results The assertiveness training was effective in improving the nurses' assertiveness behaviors, but was not effective in improving interpersonal relations, reducing the subjects' communication conflicts, changing the conflict management style or reducing their personnel turnover rate.
Conclusion There have been many studies about factors affecting nurses' personnel turnover rates, but few have been done about methods of intervention to reduce the personnel turnover rate. Thus, this study provides a significant contribution in attempting such an intervention from nursing management perspectives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of speak-up training programs for clinical nurses: A scoping review
Eunhee Lee, Jennie C. De Gagne, Paige S. Randall, Hyokyung Kim, Branti Tuttle
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2022; 136: 104375. CrossRef - The Experience of Emotional Labor and Its Related Factors among Nurses in General Hospital Settings in Republic of Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Da-Jung Ha, Jung-Hyun Park, Su-Eun Jung, Boram Lee, Myo-Sung Kim, Kyo-Lin Sim, Yung-Hyun Choi, Chan-Young Kwon
Sustainability.2021; 13(21): 11634. CrossRef - Assess the Level of Assertiveness among BSc Nursing Final Year Students in a Selected Nursing College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
C Sumathi, J Van Vagula Devi, V Prathiba Sivakumar
Pondicherry Journal of Nursing.2020; 13(2): 33. CrossRef - The Effect of Assertiveness Program on Clinical Competence of Intensive Care Units Nurses; A Randomized Clinical Trial
Samira Abbasi, Reza Masoudi, Leili Rabiei, Koroush Shahbazi
Avicenna Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Care.2019; 27(5): 293. CrossRef - Effects of SBAR Program on Communication Clarity, Clinical Competence and Self-efficacy for Nurses in Cancer Hospitals
Youn Hwa Kim, Yooun Sook Choi, Hye Young Jun, Myung Ja Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2016; 19(1): 20. CrossRef - Content Analysis of Communication between Nurses during Preceptorship
Yeon Ok Jeoung, Song Chol Park, Jeong Kun Jin, Joo Young Kim, Ji Uhn Lee, Soon Young Park, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 23(2): 82. CrossRef - Moral Distress, Moral Sensitivity and Ethical Climate of Nurses Working in Psychiatric Wards
Dabok Noh, Sunah Kim, Sanghee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2013; 22(4): 307. CrossRef - Turnover intention of graduate nurses in South Korea
Haejung LEE, Yeonjung LIM, Hee Young JUNG, Youn‐Wha SHIN
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2012; 9(1): 63. CrossRef - Work Stress, Turnover Intention and Burnout among Nurses in Neonatal Intensive Care Units
Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2011; 17(1): 115. CrossRef - Comparison of Anger Expression, Assertive Behavior, and Self-esteem between a Nursing Student Group and an Educational Student Group
Ki-Wol Sung, Oh-Gye Kwag, Won-Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(1): 1. CrossRef - A Phenomenological Study on the Experience of Hurt and Forgiveness of Clinical Nurses in Korea after Loss of Employment
Kae-Hwa Jo, Ki-Wol Sung, Yeong-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(4): 561. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of speak-up training programs for clinical nurses: A scoping review
- 1,318 View
- 9 Download
- 11 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


