Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 39(2); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Mediating Role of Organizational Citizenship Behavior between Organizational Justice and Organizational Effectiveness in Nursing Organizations
- Wall-Yun Park, Sook-Hee Yoon
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2009;39(2):229-236.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.2.229
Published online: April 28, 2009
1Nursing Director, Gimhae Bokum Hospital, Gimhae, Korea.
2Professor, Department of Nursing, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Yoon, Sook-Hee. Department of Nursing, Inje University, 633-165 Gaegeum-dong, Jin-gu, Busan 614-735, Korea. Tel: 82-51-890-6826, Fax: 82-51-894-9840, shyoon0120@hanmail.net
Copyright © 2009 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was a secondary analysis to verify the mediating role of organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) between organizational justice (OJ) and organizational effectiveness (OE) in nursing organizations.
-
Methods
- The RN-BSNs and their colleagues in Seoul and Busan were subjects. The data was collected for 20 days between September 13 and October 2, 2004. Two hundred eighty three data sets were used for the final analysis. The fitness of models were tested using AMOS 5.
-
Results
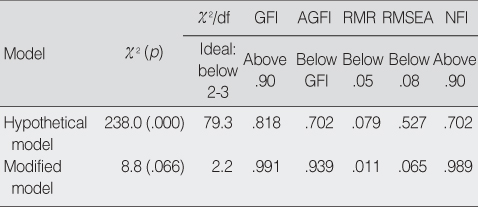
- The fitness of hypothetical model was moderate. Procedural Justice (PJ), Interaction Justice (IJ) and Distributive Justice (DJ) had direct effects on Job Satisfaction (JS), Organizational Commitment (OC) and Turnover Intention (TI) in OE, and indirect effects on JS, OC and TI mediated by OCB. The modified model improved with ideal fitness showed the causal relations among OE. In modified model, PJ, IJ and DJ had direct positive effects on OCB and JS and OC in OE, and indirect effects on JS and OC mediated by OCB. JS and OC in OE had a direct negative effect on TI.
-
Conclusion
- OCB mediated the relationship between OJ and OE, so the nursing managers should enhance OCB of the nurses in order to improve OE.
- 1. Ackfeldt A, Coote LV. A study of organizational citizenship behaviors in a retail setting. Journal of Business Research. 2005;58:151–159.Article
- 2. Amyx D, Bhuian S, Sharma D, Loveland KE. Salesperson corporate ethical values (SCEV) scale: Development and assessment among salespeople. The Journal of Personal Selling. Sales Management. 2008;28:387–401.
- 3. Bies R.J., Moag JS. Lewicki RJ, Sheppard BH, Bazerman MH. Interactional justice: Communication criteria of fairness. Research on negotiation in organizations. 1986;Greenwich, CT, JAI Press. 43–55.
- 4. Bragger JD, Rodriguez-Srednicki O, Kutcher EJ, Indovino L, Rosner E. Work-family conflict, work-family culture, and organizational citizenship behavior among teachers. Journal of Business and Psychology. 2005;20:303–324.ArticlePDF
- 5. Choi DJ, Park DG. The dimensionality and consequences of organizational justice: A meta-analytic review of Korean studies. Korean Journal of Industrial and Organizational Psychology. 2006;19:193–227.
- 6. Eun KS. The influencing factors of organizational commitment and turnover related to the equity perception in the mental hospital employees. 2001;Seoul, Yonsei University Graduate School of Public Health. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 7. Greenberg J. Organizational justice: Yesterday, today and tomorrow. Journal of Management. 1990;16:399–432.ArticlePDF
- 8. Ha NS, Choi J. The Relationship among leadership styles of nurse managers, job satisfaction, organizational commitment and turnover intention. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2002;32:812–822.ArticlePDF
- 9. Jeon HS. A study on the social service workers' organizational citizenship behavior-Focusing on the effects of trust in leader-. 2003;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 10. Jeon HS, Kim MS. Influence of leader-member exchange and organizational commitment on organizational citizenship behavior in nursing organization. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2004;10:97–107.
- 11. Jeon HS. Research on the antecedent and consequences of salesperson job satisfaction-Focused on leadership and organizational citizenship-. Korean Business Review. 2005;18:151–178.
- 12. Kim HG. A study on the effect of the justice perception on organizational citizenship behavior. 2002;Daegu, Kum-oh National Institute of Technology. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 13. Kim MS. Influence of organizational justice and commitment on organizational citizenship behaviors of nurses. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2007;13:481–491.
- 14. Kim YS. A study on the high performance work organization and management performance in hotels-Focused on the intermediate role of organization civilization behavior-. 2004;Seoul, Kyonggi University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 15. Leventhal GS. Gergen KG, Greenberg MS, Wills RH. What should be done with equity theory? New approaches to the study of fairness in social relationships. In: Social exchange: Advances in theory and research. 1980;New York, NY, Plenum Press. 27–55.
- 16. Moon HK, Kim KS. A critical review on OCB studies in Korea. Korean Management Review. 2006;35:609–643.
- 17. Moorman RH. Relationship between organizational justice and organizational citizenship behavior: Do fairness perceptions influence employee citizenship? Journal of Applied Psychology. 1991;76:845–855.Article
- 18. Mowday RT, Steers RM, Porter LW. The management of organizational commitment. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 1979;14:224–247.Article
- 19. Nam SH. A study on the effects of transformational leadership on organizational citizenship behavior in social welfare organizations. 2008;Seoul, Soongsil University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 20. Organ DW. Organizational citizenship behavior: The good soldier syndrome. 1988;Lexington, MA, Lexington Books.
- 21. Park HT. Transformational and transactional leadership styles of the nurses administrators and job satisfaction, organizational commitment in nursing service. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 1997;27:228–241.
- 22. Park SY. Employee's performance of the allocation principles and job satisfaction. The Korean Journal of Industrial and Organizational Psychology. 1993;6:55–91.
- 23. Park WY. The influence of organizational citizenship behavior in the relation of justice and organizational effectiveness perceived by nurses. 2005;Busan, Inje University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 24. Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie SB. A second generation measure of organizational citizenship behavior. 1989;Bloomington, IN, Indiana University.
- 25. Price JL, Muller CW. Handbook of organizational measurement. 1986;Marshfied, MA, Pittman.
- 26. Scarpello V, Campbell JP. Job satisfaction: Are all the parts there? Personal Psychology. 1983;36:577–600.Article
- 27. Song KS, Park BG, Choe MK. A meta-analysis on the determinants and moderators of organizational citizenship behavior. Korean Management Review. 2003;32:1103–1126.
- 28. Vileta BB, Gonzalez JV, Ferrin PF. Person-organization fit, OCB and performance appraisal: Evidence from matched supervisor-Salesperson data set in a Spanish context. Industrial Marketing Management. 2008;37:1005–1019.Article
- 29. Yafang T, Shih-Wang W. The relationship among job satisfaction, organizational citizenship behavior and turnover intention. 2008;Mar;Atlanta, Northeast Decision Sciences Institute.
REFERENCES
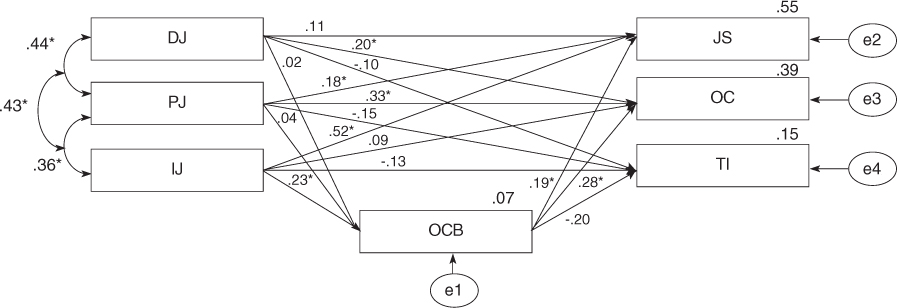
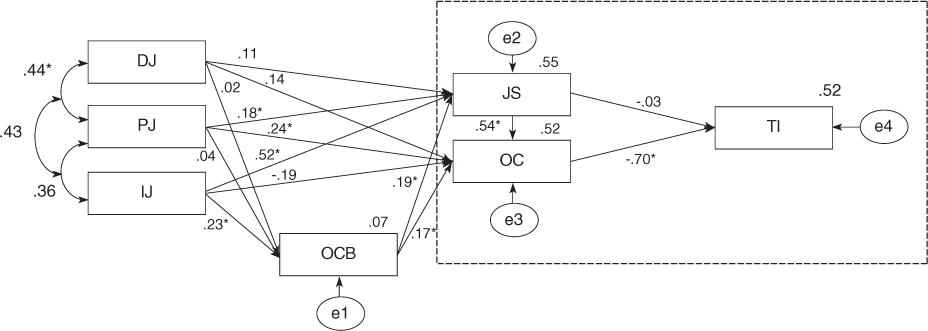
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Organizational commitment of nursing staff: Definition of the concept and specifics of measurement (review of foreign publications)
K. V. Kuzmin, L. E. Petrova, V. S. Kharchenko
Kuban Scientific Medical Bulletin.2025; 32(5): 96. CrossRef - The effect of organizational justice and job involvement on organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) with organizational commitment as mediation variable
Della Restiana Sari, Noermijati, Himmiyatul Amanah Jiwa Juwita
International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science (2147- 4478).2024; 13(5): 421. CrossRef - The impact of organizational justices on organizational success: the mediating role of organizational citizenship behavior
Besfat Engdaw, Melaku Kebede
Cogent Social Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The direct and indirect effect of organizational justice on employee intention to comply with information security policy: The case of Ethiopian banks
Berhanu Aebissa, Gurpreet Dhillon, Million Meshesha
Computers & Security.2023; 130: 103248. CrossRef - Examining the Relationship between Labor Law Compliance and Employee Perceptions, Attitudes and Behaviors
Christine Lovely Red, Mendiola Teng-Calleja
Employee Responsibilities and Rights Journal.2021; 33(4): 337. CrossRef - A Meta-Analytic Path Analysis on the Outcome Variables of Nursing Unit Managers' Transformational Leadership: Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(6): 757. CrossRef - How Leader-Member Exchange Affects Knowledge Sharing Behavior: Understanding the Effects of Commitment and Employee Characteristics
Qi Hao, Yijun Shi, Weiguo Yang
Frontiers in Psychology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - HRM practices and the multifaceted nature of organization performance
Abdallah Taamneh, Abdallah Khalaf Alsaad, Hamzah Elrehail
EuroMed Journal of Business.2018; 13(3): 315. CrossRef - Nurses’ voluntary extra work in the hospital: The role of managers’ decision-making style
Mohammad Amin Bahrami, Marzieh Salehi, Omid Barati, Mohammad Ranjbar Ezzatabadi, Razieh Montazer-alfaraj, Arefeh Dehghani Tafti
International Journal of Healthcare Management.2016; 9(3): 155. CrossRef - Antecedents of organizational citizenship behavior in a sample of Korean manufacturing employees
Paula S Daly, Philip B DuBose, Marion M Owyar-Hosseini, Kibok Baik, Eric M Stark
International Journal of Cross Cultural Management.2015; 15(1): 27. CrossRef - The relationship between South Korean clinical nurses' attitudes toward organizations and voluntary turnover intention: A path analysis
Jong Kyung Kim, Sun Ju Chang
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2015; 21(4): 383. CrossRef - The Influential Factors Related to Organizational Citizenship Behavior of Nurses: With Focus on Authentic Leadership and Organizational Justice
Bora Song, GyeongAe Seomun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(2): 237. CrossRef - Influence of Decentralization, Participation in Decision Making, Job Satisfaction on Nurse Managers' Organizational Commitment
Mi Yu, Kyungsook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2011; 17(3): 357. CrossRef - Organizational Personality Type and Citizenship Behaviors Perceived by Public Health Center Workers in Chonnam Province, Korea
Yoo-Hyang Cho
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2011; 36(1): 47. CrossRef - The Effects of Organizational Justice and Dispositional Affectivity on Job Satisfaction and Intent to Leave among Nurses
Young Hee Yom
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(3): 276. CrossRef
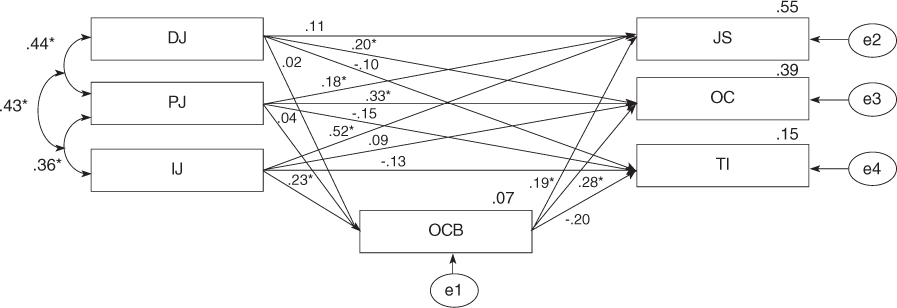
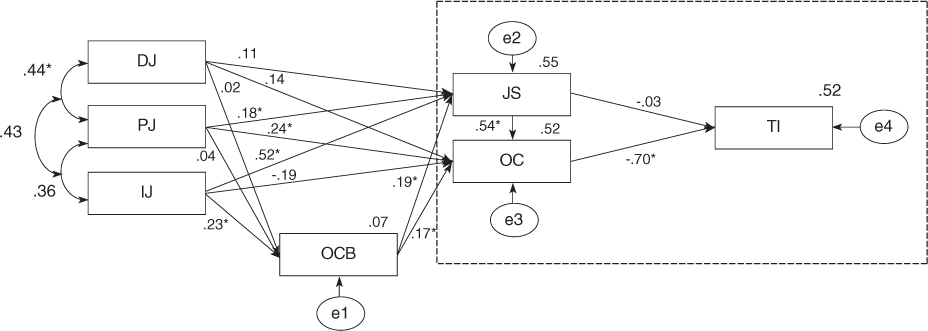
Figure 1
Figure 2
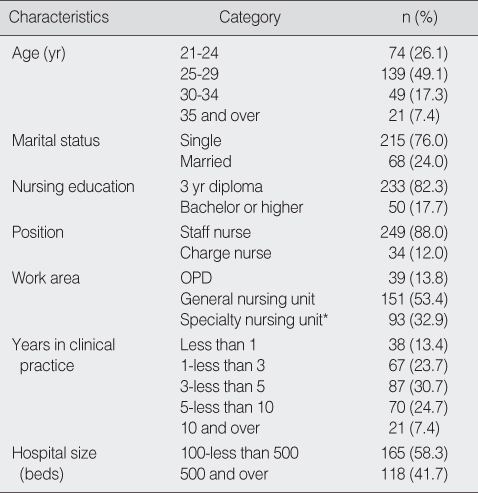
General Characteristics of the Subjects (N=283)
OPD=out patient department.
*Specialty nursing unit includes ICU, CCU, ER, psychiatric ward, pediatric ward.
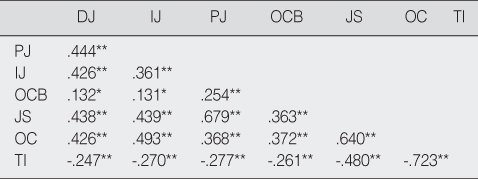
The Correlation of Variables (N=283)
*p<.05; **p<.01.
DJ=Distributive Justice; IJ=Interaction Justice; PJ=Procedural Justice; OCB=Organization Citizenship Behavior; JS=Job Satisfaction; OC= Organizational Commitment; TI=Turnover Intention.
Fitness Index of Models
GFI=goodness of fit index; AGFI=adjusted goodness of fit index; RMR=Root mean square residual; RMSEA=Root mean square error of approximation; NFI=normed fit index.
OPD=out patient department. *Specialty nursing unit includes ICU, CCU, ER, psychiatric ward, pediatric ward.
* DJ=Distributive Justice; IJ=Interaction Justice; PJ=Procedural Justice; OCB=Organization Citizenship Behavior; JS=Job Satisfaction; OC= Organizational Commitment; TI=Turnover Intention.
GFI=goodness of fit index; AGFI=adjusted goodness of fit index; RMR=Root mean square residual; RMSEA=Root mean square error of approximation; NFI=normed fit index.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

