Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Mediating effect of grit on the influence of nurses’ silence behavior on medication safety competence: a cross-sectional study
- Haengsuk Kim, Wanju Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):81-92. Published online February 20, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24088
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
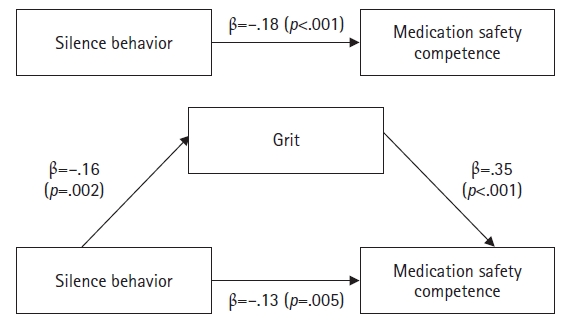
This study investigated the mediating effect of grit in the relationship between silence behavior and medication safety competence among nurses.
Methods
The study included 166 nurses from four university hospitals and general hospitals in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do, South Korea. Data were collected from March 1 to 10, 2024, using self-report questionnaires. Data were analyzed using the t-test, analysis of variance, Scheffé’s test, and Pearson’s correlation coefficients with IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 23.0 (IBM Corp.). A mediation analysis was performed using Hayes’s PROCESS macro model 4 and the bootstrapping method.
Results
Medication safety competence showed significant correlations with silence behavior (r=–.21, p=.008) and grit (r=.43, p<.001). Furthermore, grit partially mediated the relationship between silence behavior and medication safety competence.
Conclusion
This study indicates that grit is a significant mediator in the relationship between silence behavior and medication safety competence. Therefore, an integrated approach that reduces silence behavior and promotes grit is essential for strengthening nurses’ medication safety competence. Ultimately, these strategies will help ensure patient safety by improving medication safety competence.
- 5,404 View
- 468 Download

- Structural Topic Modeling Analysis of Patient Safety Interest among Health Consumers in Social Media
- Nari Kim, Nam-Ju Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):266-278. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23156
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate healthcare consumers’ interest in patient safety on social media using structural topic modeling (STM) and to identify changes in interest over time.
Methods
Analyzing 105,727 posts from Naver news comments, blogs, internet cafés, and Twitter between 2010 and 2022, this study deployed a Python script for data collection and preprocessing. STM analysis was conducted using R, with the documents’ publication years serving as metadata to trace the evolution of discussions on patient safety.
Results
The analysis identified a total of 13 distinct topics, organized into three primary communities: (1) “Demand for systemic improvement of medical accidents,” underscoring the need for legal and regulatory reform to enhance accountability; (2) “Efforts of the government and organizations for safety management,” highlighting proactive risk mitigation strategies; and (3) “Medical accidents exposed in the media,” reflecting widespread concerns over medical negligence and its repercussions. These findings indicate pervasive concerns regarding medical accountability and transparency among healthcare consumers.
Conclusion
The findings emphasize the importance of transparent healthcare policies and practices that openly address patient safety incidents. There is clear advocacy for policy reforms aimed at increasing the accountability and transparency of healthcare providers. Moreover, this study highlights the significance of educational and engagement initiatives involving healthcare consumers in fostering a culture of patient safety. Integrating consumer perspectives into patient safety strategies is crucial for developing a robust safety culture in healthcare. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- From Posts to Protection: Understanding User-Generated Safety Content on Reddit
Mashael Yousef Almoqbel
International Journal of Computational and Experimental Science and Engineering.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- From Posts to Protection: Understanding User-Generated Safety Content on Reddit
- 2,165 View
- 70 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Patient Safety Management Activities of Korean Nurses: A Meta-Analytic Path Analysis
- Seohee Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):363-377. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22022
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to test a hypothetical model of Korean nurses’ patient safety management activities using meta-analytic path analysis.
Methods
A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-analytic path analysis were conducted following the PRISMA and MOOSE guidelines. Seventy-four studies for the meta-analysis and 92 for the meta-analytic path analysis were included. The R software program (Version 3.6.3) was used for data analysis.
Results
Four variables out of 49 relevant variables were selected in the meta-analysis. These four variables showed large effect sizes (ESr = .54) or median effect sizes (ESr = .33∼.40) with the highest k (number of studies) in the individual, job, and organizational categories. The hypothetical model for the meta-analytic path analysis was established using these variables and patient safety management activities. Twelve hypothetical paths were set and tested. Finally, the perception of the importance of patient safety management and patient safety competency directly affected patient safety management activities. In addition, self-efficacy, the perception of the importance of patient safety management, patient safety competency, and patient safety culture, indirectly affected patient safety management activities.
Conclusion
Self-efficacy, the perception of the importance of patient safety management, patient safety competency, and the organization’s patient safety culture should be enhanced to improve nurses’ patient safety management activities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and validation of patient safety educational booklet to empower anesthesia process owners to improve safety compliance before, during and after anesthesia
Fatemeh Asadi, Azam Saei, Shanam Sedigh Maroufi, Jamileh Abolghasemi
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a patient safety management protocol for nurses in long-term care hospitals
Soon-Ock Kim
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Clinical Nurses' Patient Safety Competency, Psychological Safety, and Nursing Unit Manager's Safety-Specific Transformational Leadership on Intention to Report Near Misses
Young hyun Cho, Seung Eun Lee, Mi Jeong Kwak, Hyun Joo Lee
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2025; 31(2): 60. CrossRef - The influencing factors of pediatric nurses’ perception of patient safety culture and partnership with patients’ parents on patient safety nursing activities in South Korea: a descriptive study
Seo Jin Lee, Young Ran Han
Child Health Nursing Research.2024; 30(4): 255. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Nurse Collaboration and Nurse-Physician Collaboration on Nursing Performance in Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Patient Safety Management Activities
JaHyun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Sunmi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 343. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Job Satisfaction between Nurses’ Perceptions of Patient Safety Culture and Their Safety Nursing Activities
I Jung Han, Young Ran Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(1): 46. CrossRef - The Effects of Professional Autonomy, Job Satisfaction, and Perceived Patient-Safety Culture on Nurses' Patient-Safety Management Activities: A Cross-Sectional Study
Bokja Koak, Junglim Seo, Eunji Song, Haneul Shin, Jaehee Jeon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(2): 117. CrossRef
- Development and validation of patient safety educational booklet to empower anesthesia process owners to improve safety compliance before, during and after anesthesia
- 3,901 View
- 196 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Effect of Patient Safety Training Program of Nurses in Operating Room
- Peijia Zhang, Xin Liao, Jie Luo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):378-390. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study developed an in-service training program for patient safety and aimed to evaluate the impact of the program on nurses in the operating room (OR).
Methods
A pretest–posttest self-controlled survey was conducted on OR nurses from May 6 to June 14, 2020. An in-service training program for patient safety was developed on the basis of the knowledge–attitude–practice (KAP) theory through various teaching methods. The levels of safety attitude, cognition, and attitudes toward the adverse event reporting of nurses were compared to evaluate the effect of the program. Nurses who attended the training were surveyed one week before the training (pretest) and two weeks after the training (posttest).
Results
A total of 84 nurses participated in the study. After the training, the scores of safety attitude, cognition, and attitudes toward adverse event reporting of nurses showed a significant increase relative to the scores before the training (p < .001). The effects of safety training on the total score and the dimensions of safety attitude, cognition, and attitudes toward nurses’ adverse event reporting were above the moderate level.
Conclusion
The proposed patient safety training program based on KAP theory improves the safety attitude of OR nurses. Further studies are required to develop an interprofessional patient safety training program. In addition to strength training, hospital managers need to focus on the aspects of workflow, management system, department culture, and other means to promote safety culture. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Implementation strategies by leaders and health professionals to improve the safety climate in the operating room: a scoping review
Rosilene Alves Ferreira, Eduardo José Ferreira Santos, Olga Maria Pimenta Lopes Ribeiro, Danielle Mendonça Henrique, Flavia Giron Camerini, Andressa Aline Bernardo Bueno, Soraia Cristina de Abreu Pereira, Vivian Schutz, Marcia Valeria Rosa Lima, Cintia Si
BMJ Open.2026; 16(1): e109055. CrossRef - Correlation analysis of satisfaction with subspecialty management model in operating rooms: a cross-sectional survey in China
W. Wang, J. Shen, Y. Ma, Y. Chen, R. Gong, Q. Qian, Y. Sun
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Counting Error Prevention Training on Operating Room Nurses’ Counting Error Prevention Awareness and Perceptions of Patient Safety
Myung Jin JANG, Mi Kyung HONG, Mi Jeong LEE, Kyung A LEE, Yang Ok KIM, Jin A JEON, Hana KO
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2024; 24(1): 20. CrossRef
- Implementation strategies by leaders and health professionals to improve the safety climate in the operating room: a scoping review
- 5,022 View
- 201 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of Second Victim Experiences after Patient Safety Incidents on Nursing Practice Changes in Korean Clinical Nurses: The Mediating Effects of Coping Behaviors
- Seohee Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(4):489-504. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21089
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study was investigated the mediating effect of coping behaviors in the relationship between the second victim experiences after patient safety incidents and the nursing practice changes.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey was performed using structured questionnaires. Participants were 218 clinical nurses in general tertiary hospitals in South Korea. Data were collected through an online survey and snowball sampling from August 11 to September 6 2020. Data were analyzed using SPSS 23.0 program. A mediation analysis was performed using multiple regression and a simple mediation model applying the PROCESS macro with 95% bias-corrected bootstrap confidence interval.
Results
The mean scores of second victim experiences was 3.41/5. Approach coping (β = .55, p < .001) and the avoidant coping (β = - .23, p = .001) showed mediation effects in the relationship between second victim experiences and constructive change in nursing practice. Avoidant coping (β = .29, p < .001) showed a mediation effect in the relationship between second victim experiences and defensive change in nursing practice.
Conclusion
Coping behaviors has a mediating effect on the relationship between second victim experiences and nursing practice changes. To ensure that nurses do not experience second victim, medical institutions should have a culture of patient safety that employs a systematic approach rather than blame individuals. They also need to develop strategies that enhance approach coping and reducing avoidant coping to induce nurses’ constructive practice changes in clinical nurses in experiencing second victims due to patient safety incidents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influences of Clinical Nurses’ Second Victim Experience after Patient Safety Incidents, Individual and Organizational Support, and Job Satisfaction on Turnover Intention
Hyeran Kang, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2026; 32(1): 58. CrossRef - Factors influencing negative outcomes for nurses who experience patient safety incidents: An integrative review
Hanseulgi Lee, Nam‐Ju Lee, Nari Kim
International Nursing Review.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - How does just culture reduce negative work outcomes through second victim distress and demand for support in clinical nurses? A path analysis
Seohee Jeong, Sunmi Kim, Hyoung Eun Chang, Seok Hee Jeong
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Nursing Practice Among Clinical Nurses After Experiencing a Patient Safety Incident: Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling
Sunmi Kim, Seohee Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong, Majd Mrayyan
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of Nurses' Reporting Level by the Types of Patient Safety Incidents
Ju-Hee Kang, Yeojin Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 434. CrossRef - The Relationship of Medication Safety Competence, Second Victim Experiences, Second Victim Support, and Negative Work Outcomes among Clinical Nurses
Ahlim Chang, Youngjin Lee, Minkyung Kang, Ji Yea Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 493. CrossRef - “Learn from Errors”: Post-traumatic growth among second victims
Huanhuan Huang, Tong Liu, Ying Peng, Xingyao Du, Qi Huang, Qinghua Zhao, Mingzhao Xiao, Yetao Luo, Shuangjiang Zheng
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurse Leader Perspectives and Experiences on Caregiver Support Following a Serious Medical Error
Marie M. Prothero, Madeline Sorhus, Katherine Huefner
JONA: The Journal of Nursing Administration.2024; 54(12): 664. CrossRef - Prevalence of the second victim phenomenon among intensive care unit nurses and the support provided by their organizations
Maria Kappes, Pilar Delgado‐Hito, Verónica Riquelme Contreras, Marta Romero‐García
Nursing in Critical Care.2023; 28(6): 1022. CrossRef - The mediating role of coping styles in the relationship between second victim experience and professional quality of life among nurses: a cross-sectional study
Xizhao Li, Chong Chin Che, Yamin Li, Ling Wang, Mei Chan Chong
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations among workplace incivility, stress coping, and nursing performance in hospital nurses: A path analysis
Eun Ha Kim, Yeojin Yi
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2023; 55(4): 834. CrossRef - Influence of Clinical Nurses’ Second-Victim Experience and Second-Victim Support in Relation to Patient Safety Incidents on Their Work-Related Outcomes
Su Jin Jung, Youngjin Lee, Sun Hyoung Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(4): 331. CrossRef - Profiles of second victim symptoms and desired support strategies among Korean nurses: A latent profile analysis
Eun Young Choi, Jeehee Pyo, Minsu Ock, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2022; 78(9): 2872. CrossRef
- Influences of Clinical Nurses’ Second Victim Experience after Patient Safety Incidents, Individual and Organizational Support, and Job Satisfaction on Turnover Intention
- 3,495 View
- 81 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

- Analysis of Subgroups with Lower Level of Patient Safety Perceptions Using Decision-Tree Analysis
- Sun Hwa Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(5):686-698. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20044
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study was aimed to investigate experiences, perceptions, and educational needs related to patient safety and the factors affecting these perceptions.
Methods
Study design was a descriptive survey conducted in November 2019. A sample of 1,187 Koreans aged 20-80 years participated in the online survey. Based on previous research, the questionnaire used patient safety-related and educational requirement items, and the Patient Safety Perception Scale. Descriptive statistics and a decision tree analysis were performed using SPSS 25.0.
Results
The average patient safety perception was 71.71 (± 9.21). Approximately 95.9% of the participants reported a need for patient safety education, and 88.0% answered that they would participate in such education. The most influential factors in the group with low patient safety perceptions were the recognition of patient safety activities, age, preference of accredited hospitals, experience of patient safety problems, and willingness to participate in patient safety education.
Conclusion
It was confirmed that the vulnerable group for patient safety perception is not aware of patient safety activities and did not prefer an accredited hospital. To prevent patient safety accidents and establish a culture of patient safety, appropriate educational strategies must be provided to the general public. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Structural Topic Modeling Analysis of Patient Safety Interest among Health Consumers in Social Media
Nari Kim, Nam-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(2): 266. CrossRef - Analysis of Factors Related to Domestic Patient Safety Incidents Using Decision Tree Technique
Jieun Shin, Ji-Hoon Lee, Nam-Yi Kim
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2023; Volume 16: 1467. CrossRef - Smoking Awareness and Intention to Quit Smoking in Smoking Female Workers: Secondary Data Analysis
Eun-Hye Lee, Sun-Hwa Shin, Goo-Churl Jeong
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(5): 2841. CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness of a Patient Safety Education Program for Inpatients
Sun Hwa Shin, Mi Jung Kim, Ho Jin Moon, Eun Hye Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(6): 3262. CrossRef
- Structural Topic Modeling Analysis of Patient Safety Interest among Health Consumers in Social Media
- 1,252 View
- 15 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Predictors of Blood and Body Fluid Exposure and Mediating Effects of Infection Prevention Behavior in Shift-Working Nurses: Application of Analysis Method for Zero-Inflated Count Data
- Jae Geum Ryu, Choi-Kwon Smi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(5):658-670. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20025
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the predictors of blood and body fluid exposure (BBFE) in multifaceted individual (sleep disturbance and fatigue), occupational (occupational stress), and organizational (hospital safety climate) factors, as well as infection prevention behavior. We also aimed to test the mediating effect of infection prevention behavior in relation to multifaceted factors and the frequency of BBFE.
Methods
This study was based on a secondary data analysis, using data of 246 nurses from the Shift Work Nurses’ Health and Turnover study. Based on the characteristics of zero-inflated and over-dispersed count data of frequencies of BBFE, the data were analyzed to calculate zero-inflated negative binomial regression within a generalized linear model and to test the mediating effect using SPSS 25.0, Stata 14.1, and PROCESS macro.
Results
We found that the frequency of BBFE increased in subjects with disturbed sleep (IRR = 1.87, p = .049), and the probability of non-BBFE increased in subjects showing higher infection prevention behavior (IRR = 15.05, p = .006) and a hospital safety climate (IRR = 28.46, p = .018). We also found that infection prevention behavior had mediating effects on the occupational stress-BBFE and hospital safety climate-BBFE relationships.
Conclusion
Sleep disturbance is an important risk factor related to frequency of BBFE, whereas preventive factors are infection prevention behavior and hospital safety climate. We suggest individual and systemic efforts to improve sleep, occupational stress, and hospital safety climate to prevent BBFE occurrence. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of an infection control competency scale for clinical nurses: an instrument design study
Yong Hwan Hyeon, Kyoung Ja Moon
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Work Characteristics and Needlestick-Injury Status of Dental Hygienists
Yeon-Soon Park, Jeong-Hyun Lee, Jin-Soo Kim, Kyoung-Ok Yun, Sung-Suk Bae
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2024; 24(3): 190. CrossRef - Smartphone‐based home workout program for shift‐work nurses working during the COVID‐19 pandemic
Yunmi Baek, Kihye Han, Jieun Kim, Hae Young Yoo
Nursing & Health Sciences.2022; 24(3): 708. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Role Clarity between Clinical Decision-Making Abilities and Job Stress for Advanced Practice Nurses at Tertiary Hospitals
Min Young Kim, Jeong Hye Kim, Su Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2022; 15(2): 27. CrossRef
- Development of an infection control competency scale for clinical nurses: an instrument design study
- 1,552 View
- 40 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of Electronic Health Record Data-Driven Predictive Models for Pressure Ulcers
- Seul Ki Park, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Hee Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(5):575-585. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.5.575
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop predictive models for pressure ulcer incidence using electronic health record (EHR) data and to compare their predictive validity performance indicators with that of the Braden Scale used in the study hospital.
Methods A retrospective case-control study was conducted in a tertiary teaching hospital in Korea. Data of 202 pressure ulcer patients and 14,705 non-pressure ulcer patients admitted between January 2015 and May 2016 were extracted from the EHRs. Three predictive models for pressure ulcer incidence were developed using logistic regression, Cox proportional hazards regression, and decision tree modeling. The predictive validity performance indicators of the three models were compared with those of the Braden Scale.
Results The logistic regression model was most efficient with a high area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUC) estimate of 0.97, followed by the decision tree model (AUC 0.95), Cox proportional hazards regression model (AUC 0.95), and the Braden Scale (AUC 0.82). Decreased mobility was the most significant factor in the logistic regression and Cox proportional hazards models, and the endotracheal tube was the most important factor in the decision tree model.
Conclusion Predictive validity performance indicators of the Braden Scale were lower than those of the logistic regression, Cox proportional hazards regression, and decision tree models. The models developed in this study can be used to develop a clinical decision support system that automatically assesses risk for pressure ulcers to aid nurses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of an educational intervention on pressure ulcer documentation among tertiary hospital nurses in Jordan
Emran A Abu Aqoulah, Rosliza Abaul Manaf, Suriani Ismail, Salam Bani Hani, Aya Al-Ali
British Journal of Nursing.2025; 34(12): S30. CrossRef - Application of Air Pillows and Left‐Right Lateral Tilt Position to Prevent Increased Risk of Pressure Injuries in Bedridden Patients in the ICU: A Quasi‐Experimental Study
Nur Chayati, Wantonoro Wantonoro, Mahsuna Alfianti, Tiara Marthias
Health Science Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a Pressure Injury Machine Learning Prediction Model and Integration into Clinical Practice: A Prediction Model Development and Validation Study
Ju Hee Lee, Jae Yong Yu, So Yun Shim, Kyung Mi Yeom, Hyun A Ha, Se Yong Jekal, Ki Tae Moon, Joo Hee Park, Sook Hyun Park, Jeong Hee Hong, Mi Ra Song, Won Chul Cha
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(3): 191. CrossRef - Could we prove the nursing outcomes utilising clinical data warehouse? Effectiveness of pressure ulcer intervention in Korean tertiary hospital
Moonsook Kim, Se Yeon Park, Meihua Piao, Earom Lim, Soon Hwa Yoo, Minju Ryu, Hyo Yeon Lee, Hyejin Won
International Wound Journal.2023; 20(1): 201. CrossRef - Data‐driven approach to predicting the risk of pressure injury: A retrospective analysis based on changes in patient conditions
Yinji Jin, Ji‐Sun Back, Sun Ho Im, Jong Hyo Oh, Sun‐Mi Lee
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(19-20): 7273. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Pressure Injury Among Critically Ill Patients in a Coronary Care Unit
Eunji Ko, Seunghye Choi
Advances in Skin & Wound Care.2022; 35(10): 1. CrossRef - Data-Driven Learning Teaching Model of College English Based on Mega Data Analysis
Jie Zhang, Tongguang Ni
Scientific Programming.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef
- Effect of an educational intervention on pressure ulcer documentation among tertiary hospital nurses in Jordan
- 2,152 View
- 55 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Patient Safety Teaching Competency of Nursing Faculty
- Shinae Ahn, Nam-Ju Lee, Haena Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):720-730. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.720
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate patient safety teaching competency of nursing faculty and the extent of teaching patient safety topics in the nursing curriculum.
Methods A national survey was conducted with full-time nursing faculty in 4-year nursing schools. Regional quota sampling method was used. An online survey was sent to 1,028 nursing faculty and 207 of them were completed. Among the 207, we analyzed data from 184 participants. The revised Health Professional Education in Patient Safety Survey was used. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, independent t-test, one-way ANOVA, Pearson's correlation analysis, and multiple linear regression analyses.
Results The faculty's self-confidence was lower than their perceived importance of patient safety education. The mean score of teaching patient safety was 3.52±0.67 out of 5, and the contents were mostly delivered through lectures. The extent of faculty's teaching varied depending on faculty's clinical career, teaching subjects, participation in practicum courses, and previous experience of patient safety education. The significant predictors of the extent of teaching patient safety were the faculty's self-confidence in teaching patient safety (β=.39) during clinical practicum, their perceived importance of patient safety education during lectures (β=.23), and the teaching subject (β=.15).
Conclusion To enhance the competency of nursing faculty for effective patient safety education, a patient safety education program tailored to faculty characteristics should be developed and continuously provided for faculty. In addition, it is necessary to improve patient safety curriculum, strengthen clinical and school linkages, and utilize various education methods in patient safety education.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing patient safety competency in baccalaureate nursing students: A descriptive cross-sectional study
Shinae Ahn
Nurse Education Today.2025; 145: 106498. CrossRef - Transcultural Adaptation and Psychometric Properties of the Persian Version of the Nursing Student Competence Scale (NSCS)
Amir Jalali, Fatemeh Chavoshani, Raheleh Rasad, Niloufar Darvishi, Fatemeh Merati Fashi, Mahbod Khodamorovati, Khalil Moradi
SAGE Open Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing the effects of patient safety education using design thinking and case based learning on nursing students’ competence and professional socialization: A quasi-experimental design
Seongmi Moon, Soo Jung Chang
Heliyon.2024; 10(9): e29942. CrossRef - Analysis of the innovative development path of university civic education based on the era of big data
Xingang Chen, Ye Dong
Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of flipped learning and gamification on nursing students’ patient safety education: A mixed method study
Soo Jung Chang, Geun Myun Kim, Jeong Ah Kim
Heliyon.2024; 10(8): e29538. CrossRef - Experiences of Patient Safety Education and Factors Affecting the Willingness to Participate in Patient Safety in Undergraduate Nursing Students in South Korea
Sun-Hwa Shin, On-Jeon Baek
Healthcare.2023; 12(1): 54. CrossRef - Evaluating a patient safety course for undergraduate nursing students: A quasi-experimental study
Seung Eun Lee, V. Susan Dahinten
Collegian.2023; 30(1): 75. CrossRef - Continuing professional development among social‐ and health‐care educators
Minna Koskimäki, Marja‐Leena Lähteenmäki, Kristina Mikkonen, Maria Kääriäinen, Camilla Koskinen, Hanne Mäki‐Hakola, Tuulikki Sjögren, Meeri Koivula
Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences.2021; 35(2): 668. CrossRef - Nursing Students’ Informal Learning of Patient Safety Management Activities
Nam-Yi Kim
Healthcare.2021; 9(12): 1635. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Self-Efficacy Scale for Nursing Educators’ Role in Sri Lanka
Shyamamala S. Weerasekara, Jina Oh, Haeryun Cho, Mihae Im
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(15): 7773. CrossRef - Developing an integrated curriculum for patient safety in an undergraduate nursing program: a case study
Yoonjung Ji, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Taewha Lee, Mona Choi, Hyejung Lee, Sanghee Kim, Hyunok Kim Do, Sunah Kim, Sang Hui Chu, Jeongok Park, Young Man Kim, Soyoon Park
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of an Informatics System for Nursing Faculty to Improve Patient Safety Teaching Competency
Nam-Ju Lee, Shinae Ahn, Miseon Lee, Haena Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 488. CrossRef - Patient safety education in pre‐registration nursing programmes in South Korea
S. E. Lee, V. Susan Dathinten, H. Do
International Nursing Review.2020; 67(4): 512. CrossRef
- Factors influencing patient safety competency in baccalaureate nursing students: A descriptive cross-sectional study
- 3,782 View
- 76 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

- Development and Effect Analysis of Web-Based Instruction Program to Prevent Elementary School Students from Safety Accidents
- Eun Soon Chung, Ihn Sook Jeong, Mi Gyoung Song
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(3):485-494. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.3.485
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was aimed to develop a WBI(Web Based Instruction) program on safety for 3rd grade elementary school students and to test the effects of it.
Method The WBI program was developed using Macromedia flash MX, Adobe Illustrator 10.0 and Adobe Photoshop 7.0. The web site was http://www.safeschool. co.kr. The effect of it was tested from Mar 24, to Apr 30, 2003. The subjects were 144 students enrolled in the 3rd grade of an elementary school in Gyungju. The experimental group received the WBI program lessons while each control group received textbook-based lessons with visual presenters and maps, 3 times. Data was analyzed with descriptive statistics, and χ2 test, t-test, and repeated measure ANOVA.
Result First, the WBI group reported a longer effect on knowledge and practice of accident prevention than the textbook-based lessons, indicating that the WBI is more effective. Second, the WBI group was better motivated to learn the accident prevention lessons, showing that the WBI is effective. As a result, the WBI group had total longer effects on knowledge, practice and motivation of accident prevention than the textbook-based instruction.
Conclusion We recommend that this WBI program be used in each class to provide more effective safety instruction in elementary schools.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of mHealth–Safe Kids Hospital for the prevention of hospitalized children safety incidents: A randomized controlled trial
Il Tae Park, Won‐Oak Oh, Gwang‐Cheon Jang, Jihee Han
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2021; 53(5): 623. CrossRef - Effects of a Structure-centered Cooperative Learning Safety Education Program based on Blended Learning for Elementary School Students
Jeong Hye Seong
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(1): 57. CrossRef - The Development of Web-Based Ventilator Management Education Program
Young-Soon Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(11): 5284. CrossRef - Development of a Web-based Senescence Preparation Education Program for Successful Aging for Middle-aged Adults
Young-Mi Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(6): 831. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of mHealth–Safe Kids Hospital for the prevention of hospitalized children safety incidents: A randomized controlled trial
- 949 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Characteristics and Risk Factors for Falls in Tertiary Hospital Inpatients
- Eun-Ju Choi, Young-Shin Lee, Eun-Jung Yang, Ji-Hui Kim, Yeon-Hee Kim, Hyeoun-Ae Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(3):420-430. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.3.420
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The aim of this study was to explore characteristics of and risk factors for accidental inpatient falls.
Methods Participants were classified as fallers or non-fallers based on the fall history of inpatients in a tertiary hospital in Seoul between June 2014 and May 2015. Data on falls were obtained from the fall report forms and data on risk factors were obtained from the electronic nursing records. Characteristics of fallers and non-fallers were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Risk factors for falls were identified using univariate analyses and logistic regression analysis.
Results Average length of stay prior to the fall was 21.52 days and average age of fallers was 61.37 years. Most falls occurred during the night shifts and in the bedroom and were due to sudden leg weakness during ambulation. It was found that gender, BMI, physical problems such elimination, gait, vision and hearing and medications such as sleeping pills, antiarrhythmics, vasodilators, and muscle relaxant were statistically significant factors affecting falls.
Conclusion The findings show that there are significant risk factors such as BMI and history of surgery which are not part of fall assessment tools. There are also items on fall assessment tools which are not found to be significant such as mental status, emotional unstability, dizziness, and impairment of urination. Therefore, these various risk factors should be examined in the fall risk assessments and these risk factors should be considered in the development of fall assessment tools.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perceptions and practices of rehabilitation specialist nurses in fall management: a qualitative study
Heli Zhang, Jianfen Luo, Xiaotian Zhang, Yuting Jiang, Xiaoyu Sun, Qi Tang, Xin Wang, Baohua Li
Frontiers in Public Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of intrinsic and extrinsic fall risk factors in hospitals, long-term facilities, and homes: A narrative review
A.C. Dondi, K.G. Davis
Human Factors in Healthcare.2026; 9: 100125. CrossRef - Prevalence of bed falls among inpatients in Iranian hospitals: A meta-analysis
Parvaneh Isfahani, Mohammad Sarani, Mina Salajegheh, Somayeh Samani, Aliyeh Bazi, Mahdieh Poodineh Moghadam, Fatemeh Boulagh, Mahnaz Afshari
Human Factors in Healthcare.2025; 7: 100093. CrossRef - Evaluation of Risk Factors for Fall Incidence Based on Statistical Analysis
Da Hye Moon, Tae-Hoon Kim, Myoung-Nam Lim, Seon-Sook Han
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2025; 22(5): 748. CrossRef - Experiences of nurse managers in preventing and managing inpatient falls: a qualitative descriptive study
Erge Jia, Yan Kang, Runv Zhou, Weiying Zhang, Xueyan Li
BMJ Open.2025; 15(12): e106509. CrossRef - Sensitivity of Fall Risk Perception and Associated Factors in Hospitalized Patients with Mental Disorders
Ji Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim, Yusun Park, Jin Kyeong Ko, Eunmi Ra
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(5): 443. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Fall Risk Perception Questionnaire-Short Version for Inpatients in Acute Care Hospitals
Jeeeun Choi, Sujin Lee, Eunjin Park, Sangha Ku, Sunhwa Kim, Wonhye Yu, Eunmi Jeong, Sukhee Park, Yusun Park, Hye Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(2): 151. CrossRef - The Impact of Physical Performance and Fear of Falling on Fall Risk in Hemodialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jiwon Choi, Sun-Kyung Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(1): 63. CrossRef - The Impact of Possible Sarcopenia and Obesity on the Risk of Falls in Hospitalized Older Patients
Kahyun Kim, Dukyoo Jung
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2023; 26(1): 18. CrossRef - Analysis of Data on Accidental Falls from the Hospital Incident Reporting in a General Hospital
Yu-ri Jang, Jeong Yun Park
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2023; 29(1): 15. CrossRef - Predication of Falls in Hospitalized Cancer Patients
Jun-Nyun Kim, Sun-Hwa Beak, Bo-Seop Lee, Mi-Ra Han
Asian Oncology Nursing.2023; 23(2): 56. CrossRef - Nurses’ Burden of Elimination Care: Sequential Explanatory Mixed-Methods Design
Se Young Jung, Hui-Woun Moon, Da Som Me Park, Sumi Sung, Hyesil Jung
International Journal of General Medicine.2023; Volume 16: 4067. CrossRef - Clinical study of falls among inpatients with hematological diseases and exploration of risk prediction models
Jing Wang, Bin Chen, Fang Xu, Qin Chen, Jing Yue, Jingjing Wen, Fang Zhao, Min Gou, Ya Zhang
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Clinical Data Warehouse Analysis of Risk Factors for Inpatient Falls in a Tertiary Hospital: A Case-Control Study
Eunok Kwon, Sun Ju Chang, Mikyung Kwon
Journal of Patient Safety.2023; 19(8): 501. CrossRef - Z-drugs and falls in nursing home patients: data from the INCUR study
Sarah Damanti, Moreno Tresoldi, Philipe de Souto Barreto, Yves Rolland, Matteo Cesari
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2022; 34(12): 3145. CrossRef - The Fall Risk Screening Scale Is Suitable for Evaluating Adult Patient Fall
Li-Chen Chen, Yung-Chao Shen, Lun-Hui Ho, Whei-Mei Shih
Healthcare.2022; 10(3): 510. CrossRef - Comparisons of Fall Prevention Activities Using Electronic Nursing Records: A Case-Control Study
Hyesil Jung, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Ho-Young Lee
Journal of Patient Safety.2022; 18(3): 145. CrossRef - Risk Factors according to Fall Risk Level in General Hospital Inpatients
Yeon Hwa Lee, Myo Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(1): 35. CrossRef - Development and validation of the fall risk perception questionnaire for patients in acute care hospitals
Jieun Choi, Se Min Choi, Jeong Sin Lee, Soon Seok Seo, Ja Yeon Kim, Hye Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2021; 30(3-4): 406. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Degree of Harm from Fall Incidents in Hospitals
Shinae Ahn, Da Eun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(5): 334. CrossRef - A Machine Learning–Based Fall Risk Assessment Model for Inpatients
Chia-Hui Liu, Ya-Han Hu, Yu-Hsiu Lin
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2021; 39(8): 450. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Falls in High- and Low-Risk Patients in a Tertiary Hospital in Korea
Young-Shin Lee, Eun-Ju Choi, Yeon-Hee Kim, Hyeoun-Ae Park
Journal of Patient Safety.2020; 16(4): e376. CrossRef - Impact of Hearing Loss on Patient Falls in the Inpatient Setting
Victoria L. Tiase, Kui Tang, David K. Vawdrey, Rosanne Raso, Jason S. Adelman, Shao Ping Yu, Jo R. Applebaum, Anil K. Lalwani
American Journal of Preventive Medicine.2020; 58(6): 839. CrossRef - Improving Prediction of Fall Risk Using Electronic Health Record Data With Various Types and Sources at Multiple Times
Hyesil Jung, Hyeoun-Ae Park, Hee Hwang
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2020; 38(3): 157. CrossRef - Triggers and Outcomes of Falls in Hematology Patients: Analysis of Electronic Health Records
Min Kyung Jung, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2019; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - Incidence of Falls and Risk Factors of Falls in Inpatients
Soo-Jin Yoon, Chun-Kyon Lee, In-Sun Jin, Jung-Gu Kang
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2018; 24(2): 2. CrossRef
- Perceptions and practices of rehabilitation specialist nurses in fall management: a qualitative study
- 2,667 View
- 44 Download
- 26 Crossref

- Application and Developmental Strategies for Community-Based Injury Prevention Programs of the International Safe Communities Movement in Korea
- Jeongyee Bae, Joonpil Cho, Seong-il Cho, Minyeong Kwak, Taehyen Lee, Christina Aram Bae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(6):910-918. Published online December 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.6.910
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose Safety of humans is an important factor that affects health overall, and injuries are one of the major public-health problems in the world. The purposes of this study were to describe the International safe Community movement which contributes to the injury prevention and safety promotion all over the world, and to identify out the application and developmental strategies for Korea.
Methods A review was done of previous research, reviews, and reports on the history, concepts, basic principles, and recommendations for actions of the Safe Community.
Results For this study, the application strategies of the International Safe Community movement in Korea were examined to deduce the strengths of the safe Community program. Community-based injury prevention work according to the International Safe Community model is a successful and cost-effective way of reducing injuries in the community.
Conclusion Through the International Safe Community program, communities are able to realize a healthy community and achieve improved quality of lives for the people, which is the ultimate objective of the Safe Community model. In addition, it will contribute to the economic vitalization and gain through energy and enhancement of productivity of people.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Classifying strategies for building community health movements: a guide for implementers
Felicia Jia Hui Chan, Alyssa Yenyi Chan, Wen Xi Zhuang, Priyanka Rajendram, Joseph Jie Hui Quek, Weng Mooi Tan, Yoek Ling Yong, Clarice Liying Song, Zoe Jane-Lara Hildon
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Agenda Setting for the Safe Community Program in Iran: A Retrospective Policy Analysis Using Kingdon’s Multiple Streams Model
NourolHoda Fakhrzad, Mohsen Barouni, Reza Goudarzi, Vahid Yazdi-Feyzabadi
Health and Development Journal.2025; 13(4): 203. CrossRef - THE SAFE COMMUNITY CONCEPT – A SUCCESSFUL TOOL FOR INJURY PREVENTION AND SAFETY PROMOTION
Birutė Strukčinskienė, Sabine Distl, Sigitas Griškonis
Visuomenės sveikata.2019; 28(7): 41. CrossRef - Iranian Designated Safe Communities: A Quantitative Analysis
Jafar Sadegh Tabrizi, Homayoun Sadeghi Bazargani, Reza Mohammadi, Mohammad Saadati
Trauma Monthly.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Classifying strategies for building community health movements: a guide for implementers
- 862 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Operating Room Nurses' Experiences of Securing for Patient Safety
- Kwang-Ok Park, Jong Kyung Kim, Myoung-Sook Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(5):761-772. Published online October 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.5.761
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to evaluate the experience of securing patient safety in hospital operating rooms.
Methods Experiential data were collected from 15 operating room nurses through in-depth interviews. The main question was "Could you describe your experience with patient safety in the operating room?". Qualitative data from the field and transcribed notes were analyzed using Strauss and Corbin's grounded theory methodology.
Results The core category of experience with patient safety in the operating room was 'trying to maintain principles of patient safety during high-risk surgical procedures'. The participants used two interactional strategies: 'attempt continuous improvement', 'immersion in operation with sharing issues of patient safety'.
Conclusion The results indicate that the important factors for ensuring the safety of patients in the operating room are manpower, education, and a system for patient safety. Successful and safe surgery requires communication, teamwork and recognition of the importance of patient safety by the surgical team.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- AMELİYATHANEDE STAJ YAPAN ÖĞRENCİLERİN STAJLARINA İLİŞKİN GÖRÜŞLERİNİN İNCELENMESİ
Gül Özlem Yıldırım, Bektaş Sarı
İnönü Üniversitesi Sağlık Hizmetleri Meslek Yüksek Okulu Dergisi.2024; 12(2): 735. CrossRef - Influences of Teamwork and Job Burnout on Patient Safety Management Activities among Operating Room Nurses
Ayoung Kim, Haein Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(5): 605. CrossRef - Effects of Patient Safety Culture on Nurse Burnout in the Operating Room
Ye Sol Lee, Chin Kang Koh
Stress.2020; 28(3): 118. CrossRef - Development of a protocol for procedures utilizing local anaesthesia and moderate sedation in the operating room
Eunha Ryoo, Soyoung Yu
Perioperative Care and Operating Room Management.2020; 20: 100100. CrossRef - Experience of Communication for Patient Safety by Perioperative Nurses
Shinae Ahn, Nam-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2019; 25(4): 329. CrossRef - Effect of Nurses' Perception of Patient Safety Culture on Reporting of Patient Safety Events
Sun Aee Kim, Eun-Mi Kim, Ju-Ry Lee, Eui Geum Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(4): 319. CrossRef - The Impact of Safety Climate and Fatigue on Safety Performance of Operating Room Nurses
U-Eun Choi, Hyun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(5): 471. CrossRef
- AMELİYATHANEDE STAJ YAPAN ÖĞRENCİLERİN STAJLARINA İLİŞKİN GÖRÜŞLERİNİN İNCELENMESİ
- 1,822 View
- 41 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Factors related to Nurses' Patient Identification Behavior and the Moderating Effect of Person-organization Value Congruence Climate within Nursing Units
- Young Mee Kim, Seung-Wan Kang, Se Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(2):198-208. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.2.198
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This research was an empirical study designed to identify precursors and interaction effects related to nurses' patient identification behavior. A multilevel analysis methodology was used.
Methods A self-report survey was administered to registered nurses (RNs) of a university hospital in South Korea. Of the questionnaires, 1114 were analyzed.
Results The individual-level factors that had a significantly positive association with patient identification behavior were person-organization value congruence, organizational commitment, occupational commitment, tenure at the hospital, and tenure at the unit. Significantly negative group-level precursors of patient identification behavior were burnout climate and the number of RNs. Two interaction effects of the person-organization value congruence climate were identified. The first was a group-level moderating effect in which the negative relationship between the number of RNs and patient identification behavior was weaker when the nursing unit's value congruence climate was high. The second was a cross-level moderating effect in which the positive relationship between tenure at the unit and patient identification behavior was weaker when value congruence climate was high.
Conclusion This study simultaneously tested both individual-level and group-level factors that potentially influence patient identification behavior and identified the moderating role of person-organization value congruence climate. Implications of these results are discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Content Analysis of Patient Safety Incident Reports Using Text Mining: A Secondary Data Analysis
On-Jeon Baek, Ho Jin Moon, Hyosun Kim, Sun-Hwa Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(4): 298. CrossRef - Compare Value Congruence of Nurse-Patient Assignment with Work Performance in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Hye Min Kim, Dong Yeon Kim, Ji Young Kim, Ga Young Kim, Seol Hee Moon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(5): 355. CrossRef - Structural empowerment and nurses’ patient identification behaviors: a cross-sectional study
Young Mee Kim, Se Young Kim
International Journal of Health Care Quality Assurance.2019; 32(5): 832. CrossRef
- Content Analysis of Patient Safety Incident Reports Using Text Mining: A Secondary Data Analysis
- 1,005 View
- 9 Download
- 3 Crossref

- A Structural Model for the Practice of Life Safety Behavior in School-age Children
- Myung-Ock Chae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(2):119-128. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.2.119
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study is an examination of the paths in which the primary factors of anxiety, impulsiveness, knowledge of life safety practice, attitudes towards life safety practice, interpersonal support, and self-efficacy from Pender's Health Promotion Model influence the practice of life safety behavior in school-age children.
Methods The sample consisted of 489 5th and 6th grade students recruited from five elementary schools in Seoul City and four provinces, South Korea. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, correlations, factor analysis, and structural equation modeling.
Results Attitudes towards life safety practice, interpersonal support, self-efficacy and impulsiveness directly influenced practice of life safety behavior. Anxiety did not have a direct influence on practice of life safety behavior, but indirectly affected it. In this modified model, 52.0% of the practice of life safety behavior was explained by the primary factors.
Conclusion To facilitate the practice life safety behaviors in late childhood, a positive attitude towards life safety needs to be developed along with decreasing impulsiveness and enhancing self-efficacy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study of Effect of Disability Prevention Program Acquired by People with Disabilities are Performed : centered on Elementary School Students
Yeon-Jung Kim
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(5): 369. CrossRef - Effects of Academic Stress and Self-Esteem on Practice of Life Safety Behaviors in School-Age Children
Myung-Ock Chae
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(4): 2713. CrossRef
- A Study of Effect of Disability Prevention Program Acquired by People with Disabilities are Performed : centered on Elementary School Students
- 1,070 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Development and Validation of the Korean Patient Safety Culture Scale for Nursing Homes
- Sook Hee Yoon, Byungsoo Kim, Se Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(3):379-388. Published online June 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.3.379
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a tool to evaluate patient safety culture in nursing homes and to test its validity and reliability.
Methods A preliminary tool was developed through interviews with focus group, content validity tests, and a pilot study. A nationwide survey was conducted from February to April, 2011, using self-report questionnaires. Participants were 982 employees in nursing homes. Data were analyzed using Cronbach's alpha, item analysis, factor analysis, and multitrait/multi-Item analysis.
Results From the results of the analysis, 27 final items were selected from 49 items on the preliminary tool. Items with low correlation with total scale were excluded. The 4 factors sorted by factor analysis contributed 63.4% of the variance in the total scale. The factors were labeled as leadership, organizational system, working attitude, management practice. Cronbach's alpha for internal consistency was .95 and the range for the 4 factors was from .86 to .93.
Conclusion The results of this study indicate that the Korean Patient Safety Culture Scale has reliability and validity and is suitable for evaluation of patient safety culture in Korean nursing homes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated With Registered Nurses’ Safety Nursing Activities in Nursing Homes
Jiyeon Lee, Sunyeob Choi
Asian Nursing Research.2025; 19(1): 19. CrossRef - Factors Associated with the Patient Safety Activities among Home-Visit Caregiver: A Cross-Sectional Study
Soon-hee Cho, Sujin Kang, Youngji Kim
Annals of Geriatric Medicine and Research.2025; 29(2): 159. CrossRef - Institutional factors affecting patient safety culture and resident safety activities in long-term care facilities
Deulle Min
Geriatric Nursing.2025; 65: 103520. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of a Korean-language version of the Nursing Home Survey on Patient Safety Culture (K-NHSPSC)
Seung Eun Lee, So Young Park
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of the resident safety activity questionnaire for long-term care facility staff
Deulle Min, Suhee Kim
Geriatric Nursing.2024; 56: 278. CrossRef - The mediating effect of patient safety culture on the relationship between professionalism, self-leadership, and compliance with infection prevention activity against emerging respiratory infectious disease among nurses working in geriatric long-term care
Sun Young Jeong, Min Sun Song, Heeja Jung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(4): 360. CrossRef - Study of Patient Safety Culture Awareness of Radiological Technologists in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Laboratories
Min-Seo Park, Dong-Ha Lee, Hyun-Jin Jo, Hea-Youn Cho, Yeong-Cheol Heo
Journal of the Korean Society of MR Technology.2024; 34(1): 9. CrossRef - Developing a Cross-National Disability Measure for Older Adult Populations across Korea, China, and Japan
Sanghun Nam, Mi Jung Lee, Ickpyo Hong
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(16): 10338. CrossRef - Patient safety measurement tools used in nursing homes: a systematic literature review
Kyoung-A Kim, Jungeun Lee, Dahee Kim, Deulle Min
BMC Health Services Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Communication Self-efficacy and Perception of Patient Safety Culture on Experience of Nursing Errors among Operating Room Nurses
Jiin Seo, Yujeong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(3): 181. CrossRef - Analysis of Subgroups with Lower Level of Patient Safety Perceptions Using Decision-Tree Analysis
Sun Hwa Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 686. CrossRef - Clinical Nurses' Safety Management Experiences with Older Patients
Hyunmee Cho, Suhye Kwon, Younhyang Lee, Yunjeong Kim, Jungmi Kang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2020; 22(2): 105. CrossRef - Why Do They Stay? Intention to Stay among Registered Nurses in Nursing Homes
Ji Yeon Lee, Juh Hyun Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(22): 8485. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Patient Safety Perception Scale for hospitalized Patients
Kyung Ja Kim, Eun Hee Lee, Sun Hwa Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(4): 404. CrossRef - Characteristics and Mortality Risk Factors in Geriatric Hospital Patients visiting One Region-wide Emergency Department
Kyoung Wan Kim, Soongnang Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 327. CrossRef - Awareness of Hospital Safety Culture and Safety Activities of Workers in a Tertiary Care Hospital
Eun-Ho Ha, Kyoung-Soon Hyun, Jin-Young Cho
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2016; 22(2): 191. CrossRef - A realist analysis of hospital patient safety in Wales: applied learning for alternative contexts from a multisite case study
Andrea Herepath, Martin Kitchener, Justin Waring
Health Services and Delivery Research.2015; 3(40): 1. CrossRef - Influence of Safety Culture Perception, Safety Control and Safety Management Activities as Perceived for Nurses in Nursing Home
Young-Sook Seo, Eun-Su Do
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(9): 303. CrossRef - Perception of Workers on Patient Safety Culture and Degree of Patient Safety in Nursing Homes in Korea
Sook Hee Yoon, Se Young Kim, XiangLian Wu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(3): 247. CrossRef
- Factors Associated With Registered Nurses’ Safety Nursing Activities in Nursing Homes
- 1,867 View
- 21 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Medication Error Management Climate and Perception for System Use according to Construction of Medication Error Prevention System
- Myoung Soo Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(4):568-578. Published online August 12, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.4.568
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this cross-sectional study was to examine current status of IT-based medication error prevention system construction and the relationships among system construction, medication error management climate and perception for system use.
Methods The participants were 124 patient safety chief managers working for 124 hospitals with over 300 beds in Korea. The characteristics of the participants, construction status and perception of systems (electric pharmacopoeia, electric drug dosage calculation system, computer-based patient safety reporting and bar-code system) and medication error management climate were measured in this study. The data were collected between June and August 2011. Descriptive statistics, partial Pearson correlation and MANCOVA were used for data analysis.
Results Electric pharmacopoeia were constructed in 67.7% of participating hospitals, computer-based patient safety reporting systems were constructed in 50.8%, electric drug dosage calculation systems were in use in 32.3%. Bar-code systems showed up the lowest construction rate at 16.1% of Korean hospitals. Higher rates of construction of IT-based medication error prevention systems resulted in greater safety and a more positive error management climate prevailed.
Conclusion The supportive strategies for improving perception for use of IT-based systems would add to system construction, and positive error management climate would be more easily promoted.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Validation of the Medication Safety Competence Scale for Nurses
JinKyung Park, GyeongAe Seomun
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2021; 43(7): 686. CrossRef - Mediating role of the perceived benefits of using a medication safety system in the relationship between transformational leadership and the medication-error management climate
Myoung Soo Kim, Ji Hye Seok, Bo Min Kim
Journal of Research in Nursing.2020; 25(1): 22. CrossRef - Perception of Patient Safety Risk Factors and Performance Level of Safety Care Activities among Hospital Nurses
Young Shin Son, Young Whee Lee, Young Shin Kim, Eun Jeong Song, Hye Ryun Lee, Ju Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2018; 24(2): 190. CrossRef - Impact of Safety Climate Perception and Barriers to Adverse Drug Reaction Reporting on Clinical Nurses' Monitoring Practice for Adverse Drug Reactions
Hyun Jin Kim, Seon Young Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(2): 115. CrossRef - Preventing Medication Error Based on Knowledge Management Against Adverse Event
Apriyani Puji Hastuti, Nursalam Nursalam, Mira Triharini
Jurnal Ners.2017; 12(1): 133. CrossRef - Reporting of medication administration errors by nurses in South Korean hospitals
Eunjoo Lee
International Journal for Quality in Health Care.2017; 29(5): 728. CrossRef - Provider risk factors for medication administration error alerts: analyses of a large‐scale closed‐loop medication administration system using RFID and barcode
Yeonsoo Hwang, Dukyong Yoon, Eun Kyoung Ahn, Hee Hwang, Rae Woong Park
Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety.2016; 25(12): 1387. CrossRef - Discriminating Power of Organization Related Variables on Intention to Medication Error Reporting
Myoung Soo Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2016; 41(2): 155. CrossRef - The Mediating and Moderating Roles of Safety-specific Transformational Leadership on the Relationship between Barrier to and Intention of Reporting Medication Errors
Myoung Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(6): 673. CrossRef - Development of a Medication Error Prevention System and Its Influence on Patient Safety Culture and Initiatives
Myoung-Soo Kim, Hyun-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - Reducing the waiting time of parkinson's patients in outpatient pharmacy by improving EMR and workflow
Dan-Hee Choi, Ji-Yoon Yim, Yong-Hwa Lee
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2014; 20(1): 28. CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness of Smartphone Application for the Medication Confirmation of High-alert Medications
Myoung Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(3): 253. CrossRef - Role of Transformational-leadership in the Relationship between Medication Error Management Climate and Error Reporting Intention of Nurse
Myoung Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(6): 633. CrossRef - Role of Transformational-leadership in the Relationship between Medication Error Management Climate and Error Reporting Intention of Nurse
Myoung Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(6): 633. CrossRef - Canonical Correlation between Drug Dosage Calculation Error Prevention Competence of Nurses and Medication Safety Organizational Climate
Myoung Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(6): 569. CrossRef
- Development and Validation of the Medication Safety Competence Scale for Nurses
- 1,702 View
- 19 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Concept Analysis of Patient Safety
- Mi Ran Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(1):1-8. Published online February 28, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to investigate the clear concept of patient safety and obtain theoretical evidences.
Methods Research was conducted using Walker & Avant's conceptual analysis process.
Results Patient safety was defined as an activity that minimizes and removes possible errors and injuries to patients. It includes a basic desire to secure the patient's right to safety, and the legal regulations and duties of medical teams. The results of the establishment of a safety culture are patient-centered medical treatment and caring. Antecedents were found to be open and clear communications, continuous education and training for health care personnel, sufficient allocation of qualified personnel, cooperation among departments, improvements in the recognition of patient safety. Consequences were found to be the provision of high quality medical care and treatment, and increase in patient satisfaction.
Conclusion Patient safety as defined by the results of this study will contribute to the foundation of institutionalization of the pursuit of patient safety and creation of a hospital culture focusing on patient safety as a first priority.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A review of the relationship between patient safety culture and safety activities: A systematic review focusing on the Korean version of the Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture 1.0
Hana Kim, Mijeong Park, Jeongeun Kim, Jisan Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(1): 65. CrossRef - A concept analysis of vicarious resilience in mental health nursing
Nora Ghalib AlOtaibi
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2024; 11(4): 485. CrossRef - Patient Safety Competence Nursing Experience of Nurse : A meta-synthesis Study
Jin Lee, SunHwa Park, Mi-Seon Kim
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2024; 12(1): 17. CrossRef - Development of a Patient Safety Simulation Program for New Nurses in the Intensive Care Unit
Su Jin Jung, Jin-Hee Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 100. CrossRef - Factors Related to the Severity of Patient Safety Incidents in Operating Rooms in South Korea
Minjung Ryu, Jun Su Park, Bomgyeol Kim, Suk-Yong Jang, Sang Gyu Lee, Tae Hyun Kim
Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service Research.2024; 4(2): 149. CrossRef - Influence of Nursing Students’ Competencies Who Participated in Simulation Training on Competency with Evidence-based Practice
Yeon Jeong Su
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2024; 12(1): 33. CrossRef - Association between Nurses’ Perceptions of Patient Safety Culture, Willingness to Report Near Misses, Critical Thinking Disposition, and Nursing Care Activities for Patient Safety
Da Eun Lee, Bo Gyeong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 283. CrossRef - Effects of Nurses' Incident Reporting Attitude, Perception of Importance on Patient Safety Management, and Patient Safety Culture on the Reporting of Patient Safety Events
Eun Suk Ko, Kyung Ja Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(3): 309. CrossRef - The Effect of Patient Safety Experience on Patient Satisfaction of Patients Using Outpatient Health Services in Hospitals/Clinics
Soojin Chung, Bomi An
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(3): 252. CrossRef - Measures to Strengthen Patient Safety Management Competencies for Patient Safety Coordinators: A Qualitative Research
Hee-Jin Kim, Mi-Young Kim
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2023; 29(2): 2. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a virtual reality application‐based education programme on patient safety management for nursing students: A pre‐test–post‐test study
Jae Woo Oh, Ji Eun Kim
Nursing Open.2023; 10(12): 7622. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Job Satisfaction between Nurses’ Perceptions of Patient Safety Culture and Their Safety Nursing Activities
I Jung Han, Young Ran Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(1): 46. CrossRef - Patient safety interprofessional education program using medical error scenarios for undergraduate nursing and medical students in Korea
Hea Kung Hur, Ki Kyong Kim, Young Mi Lim, Junghee Kim, Kyung Hye Park, Yon Chul Park
Journal of Interprofessional Care.2023; 37(6): 944. CrossRef - Patient Understanding of Patient Safety: Based on Results from Focus Group Discussion
Jeehye Im, Minsu Ock
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2022; 28(2): 50. CrossRef - Relationship between Clinical Nurses' Job Stress and Medication Safety Performance: Mediating Effect of Fatigue
Se Yeong Park, Hea Kung Hur
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 283. CrossRef - A Study on Factors Affecting Near Misses by Nurses in Small-Medium Sized Hospitals
San-Na Lee, Seon-Ha Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(2): 75. CrossRef - Development of a patient safety care activity scale for clinical nurses in Korea
Ya Ki Yang
Archives of Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors affecting patient safety culture in terms of compliance with preventing bloodborne pathogens among general hospital nurses
Na Young Kim, Kyoung Ja Moon
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative study on patient safety attitude between nurses and doctors in operating rooms
Eunok Kwon, Young Woo Kim, Seo Won Kim, Sujeong Jeon, Eunsook Lee, Hye-Young Kang, Seungnam Nam, Mihyeong Kim
Journal of International Medical Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Mobile Application for Safety Incident Prevention among Hospitalized Korean Children: A pilot Study of Feasibility and Acceptability
Jihee Han, Won-Oak Oh, Il Tae Park, Anna Lee
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2020; 51: e69. CrossRef - Comparison of Shift Satisfaction, Sleep, Fatigue, Quality of Life, and Patient Safety Incidents Between Two-Shift and Three-Shift Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Min Jin Chae, Su Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2020; 13(2): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of Subgroups with Lower Level of Patient Safety Perceptions Using Decision-Tree Analysis
Sun Hwa Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 686. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Patient Safety Management Activity of Nursing Students: A Quantile Regression Approach
Myungsuk Kang, Yeonsoo Jang, Ui Rim Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(3): 230. CrossRef - Relationships between dental hygienists’ work environment and patient safety culture
Eun-Mi Choi, So-Jung Mun, Won-Gyun Chung, Hie-Jin Noh
BMC Health Services Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The Causal Relationships among Staff Nurses' Job Stress Factors, Patient Safety Culture Perception and Patient Safety Nursing Activities in a University Hospital
Mi-Kyung Kim, Sang-Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2019; 25(4): 340. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Safety Care Activities of Hospital Nurses
Ya Ki Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2019; 26(3): 188. CrossRef - Analysis of Factors Affecting Dental Hygiene Students’ Attitudes toward Patient Safety and Performing Confidence
Kyung-Yi Chung
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2018; 18(5): 288. CrossRef - Patient Safety Care Activity in Small-Medium Sized Hospital Nurses Patient Safety Care Activity among Nurses in Small-Medium Sized General Hospitals
Yuna Paik, Youngji Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2018; 21(1): 51. CrossRef - Perception of Importance of Patient Safety Management, Patient Safety Culture and Safety Performance in Hospital Managerial Performance of Hospital Nurses
Mi Yeon Park, Eun A Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(1): 40. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Patient Safety Perception Scale for hospitalized Patients
Kyung Ja Kim, Eun Hee Lee, Sun Hwa Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(4): 404. CrossRef - Effect of Hospital Nurses' Perceptions of Organizational Health and Patient Safety Culture on Patient Safety Nursing Activities
Mi-Young Han, Myun-Sook Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(2): 127. CrossRef - The Effects of Smartphone Application to Educate Patient on Patient Safety in Hospitalized Surgical Patients
Hyo Jin Choi, Eunjoo Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(2): 154. CrossRef - Perception of Healthcare Accreditation System on Patient Safety Management Activities and Nursing Performance of Regional Public Hospital Nurses
Myung Ju Kang, Kyung Hee Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(4): 416. CrossRef - Development of Hospital Nurses' Job Description based on DACUM Method: Focusing on General Ward and Intensive Care Unit
Sun Mi Lee, Yeon Hee Kim, Yu Mi Shim, Jin Sun Choi, Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(5): 535. CrossRef - Effects of Psychiatric Nurses' Perception of the Healthcare Accreditation System and Safety Climate on Patient Safety Management Activities
Junghee Jang, Sung Hee Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2016; 25(4): 375. CrossRef - The Impact of Safety Climate and Fatigue on Safety Performance of Operating Room Nurses
U-Eun Choi, Hyun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(5): 471. CrossRef - Perception and Work Performance of Patient Safety among Nurses Working in Long-term Care Hospitals
Ok Nyun Moon, Young Im Kim, Hyo Geun Geun
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(2): 118. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Nursing Students' Practice of Patient Safety Management in Clinical Practicum
Seung Hye Choi, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(2): 184. CrossRef - The Attitude of Patient Safety and Patient Safety Management Activity in Nursing Students
Seong-Soo Huh, Hee-Young Kang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(8): 5458. CrossRef - Defining attributes of patient safety through a concept analysis
Linda Kim, Courtney H. Lyder, Donna McNeese‐Smith, Linda Searle Leach, Jack Needleman
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2015; 71(11): 2490. CrossRef - Analysis of Effects of Chemotherapy using Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) on Patient Safety and Safe Nursing
Nam Young Yang, Mi Hyang Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(3): 254. CrossRef - Influence of Safety Culture Perception, Safety Control and Safety Management Activities as Perceived for Nurses in Nursing Home
Young-Sook Seo, Eun-Su Do
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(9): 303. CrossRef - Operating Room Nurses' Experiences of Securing for Patient Safety
Kwang-Ok Park, Jong Kyung Kim, Myoung-Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(5): 761. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on Perception of Patient Safety Culture and Safety Care Activities: Comparing University Hospital Nurses and Small Hospital Nurses
Bo Kyoung Cha, Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(4): 405. CrossRef - Accuracy and Satisfaction with IVIC300 (Intravenous infusion controller)
Jung Hee Park, Nam Young Yang, Moon Jun Na, Young Jin Go, Ki Suk Kim, Young Aue Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(1): 114. CrossRef - Knowledge, Attitude, and Confidence on Patient Safety of Undergraduate Nursing Students
Jeonghye Park, Myonghwa Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(1): 5. CrossRef - A Pediatric Fall-Risk Assessment Tool for Hospitalized Children.
Hyeon Ju Shin, Young Nam Kim, Ju Hee Kim, In Sook Son, Kyung Sook Bang
Child Health Nursing Research.2014; 20(3): 215. CrossRef - A Survey on Perception Level of the Radiological Technologist's about Culture of Patient Safety
Min-Cheol Jeon, Young-Il Kim, Jae-Uk Jang, Man-Seok Han, Sun-Youl Seo
Journal of Digital Convergence.2014; 12(2): 423. CrossRef - Perception of Patient Safety Culture and Safety Care Activity of Entry-level Nurses
Seong-Suk Cho, Moon Hee Gang
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2013; 22(1): 24. CrossRef - Application of the hospital survey on patient safety culture (HSOPSC) to dentistry
Eun Suk An, Ho Sung Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2013; 37(4): 216. CrossRef - Development of a Perception of Importance on Patient Safety Management Scale (PI-PSM)for Hospital Employee
Mi Jeong Park, In Sook Kim, Young Lim Ham
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2013; 13(5): 332. CrossRef - Impact of Nurses' Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment on Patient Safety Management Activities in Tertiary Hospitals
Hyun Hee Gong, Youn-Jung Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(4): 453. CrossRef - Comparative studies in Perception of Patient safety culture of Nurses and Dental hygienist
Mi-Young Kim, Young-Mi Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(11): 5196. CrossRef
- A review of the relationship between patient safety culture and safety activities: A systematic review focusing on the Korean version of the Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture 1.0
- 3,298 View
- 95 Download
- 53 Crossref

- The Effectiveness of Error Reporting Promoting Strategy on Nurse's Attitude, Patient Safety Culture, Intention to Report and Reporting Rate
- Myoungsoo Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(2):172-181. Published online April 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.2.172
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the impact of strategies to promote reporting of errors on nurses' attitude to reporting errors, organizational culture related to patient safety, intention to report and reporting rate in hospital nurses.
Methods A nonequivalent control group non-synchronized design was used for this study. The program was developed and then administered to the experimental group for 12 weeks. Data were analyzed using descriptive analysis, χ2-test, t-test, and ANCOVA with the SPSS 12.0 program.
Results After the intervention, the experimental group showed significantly higher scores for nurses' attitude to reporting errors (experimental: 20.73 vs control: 20.52, F=5.483,
p =.021) and reporting rate (experimental: 3.40 vs control: 1.33, F=1998.083,p <.001). There was no significant difference in some categories for organizational culture and intention to report.Conclusion The study findings indicate that strategies that promote reporting of errors play an important role in producing positive attitudes to reporting errors and improving behavior of reporting. Further advanced strategies for reporting errors that can lead to improved patient safety should be developed and applied in a broad range of hospitals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Influence of Age and Experience on Safety Climate Perceptions Among Healthcare Staff in Operating, Interventional Radiology, and Hybrid Operating Rooms: A Cross-Sectional Study
Johanna Rhodin, Sofia Erestam, May Bazzi, Jenny Milton, Sofia Strömberg, Monica Pettersson
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2026; Volume 19: 1. CrossRef - The mediating role of moral courage in the relationship between ethical leadership and error reporting behavior among nurses in Saudi Arabia: a structural equation modeling approach
Ebtisam A. Elhihi, Khadija Lafi Aljarary, Maha Alahmadi, Jawaher Bakor Adam, Ohud Atiah Almwualllad, Marwan S. Hawsawei, Abdulmajid Ahmad Hamza, Ibrahim Abdullatif Ibrahim
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Nursing Professionalism, Ethical Sensitivity, and the Clinical Learning Environment on Nursing Students' Intention to Report Near Misses and Adverse Events
Sookhee Yoon, Ha-Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(2): 209. CrossRef - Safety voice concept clean-up: Examining the voice that challenges us to be safer
Jeanne Paul, Colin Pilbeam, Anna Smallwood
Safety Science.2025; 191: 106931. CrossRef - Fostering a safe horizon: Nursing organizational culture as a mediator between medication safety climate and reporting intentions for high-alert medication errors among pediatric nursing care
Abdelaziz Hendy, Rasha Kadri Ibrahim, Hosny Maher Sultan, Hanan F. Alharbi, Zeinab Al-Kurdi, Naglaa Hassan Abuelzahab, Taliaa Mohsen Al-Yafeai, Ahmad Ahmeda, Zainab Attia Abdallah, Wesam Taher Almagharbeh, Ghada Ahmed Hassan
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2025; 85: 103. CrossRef - Impact of Clinical Nurses' Patient Safety Competency, Psychological Safety, and Nursing Unit Manager's Safety-Specific Transformational Leadership on Intention to Report Near Misses
Young hyun Cho, Seung Eun Lee, Mi Jeong Kwak, Hyun Joo Lee
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2025; 31(2): 60. CrossRef - Attitudes towards patient safety among physicians and nurses in Iranian governmental teaching hospitals: a cross-sectional survey
Edris Kakemam, Farzaneh Miri, Sevda Sadeghpour, Alireza Mirzaei, Jalal Saeidpour
BMJ Open.2024; 14(11): e089328. CrossRef - Exploring research trends in nursing organizational culture using topic modeling
Eun-Jun Park, Chan Sook Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2024; 30(4): 371. CrossRef - Testing the association between the enabling and enacting factors of patient safety culture and patient safety: structural equation modelling
Seung Eun Lee, V. Susan Dahinten, Jong Hyun Lee
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Job Crafting and Perception of Patient Safety Culture with Patient Safety Management Activities among Hospital Nurses
Jung Sook Kim, Ji-Soo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(4): 382. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Willingness to Medical Error-reporting of Nursing Students
Eunsim Kim, Juyoun Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(4): 440. CrossRef - Psychological Safety as a Mediator of the Relationship Between Inclusive Leadership and Nurse Voice Behaviors and Error Reporting
Seung Eun Lee, V. Susan Dahinten
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2021; 53(6): 737. CrossRef - The influence of nurse leadership style on the culture of patient safety incident reporting: a systematic review
Yusriawati Yusuf, Andi Masyitha Irwan
British Journal of Healthcare Management.2021; 27(6): 1. CrossRef - A Phenomenological Study on Nurses' Experience of Near Miss in Medication Administration
Jin Hee Park, Kyoung Ran Kong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(3): 127. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Clinical Nurses’ Intention to Report Medication Administration Errors
Seul Hee Lee, Eun Ji Seo
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2021; 14(3): 62. CrossRef - The impact of patient safety culture and the leader coaching behaviour of nurses on the intention to report errors: a cross-sectional survey
Zahra Chegini, Edris Kakemam, Mohammad Asghari Jafarabadi, Ali Janati
BMC Nursing.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Patient safety culture among nurses working in Palestinian governmental hospital: a pathway to a new policy
Nasser Ibrahim Abu-El-Noor, Mysoon Khalil Abu-El-Noor, Yousef Zuheir Abuowda, Maha Alfaqawi, Bettina Böttcher
BMC Health Services Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Barriers to reporting of patient safety incidents in tertiary hospitals: A qualitative study of nurses and resident physicians in South Korea
Won Lee, So Yoon Kim, Sang‐il Lee, Sun Gyo Lee, Hyung Chul Kim, Insook Kim
The International Journal of Health Planning and Management.2018; 33(4): 1178. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Nursing Students’ Perception on Pediatric Patient Safety Culture and Nursing Activity
Eunsook Park, Won-Oak Oh, Mirim Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2017; 23(4): 534. CrossRef - The Relationships Among Perceived Patients' Safety Culture, Intention to Report Errors, and Leader Coaching Behavior of Nurses in Korea: A Pilot Study
YuKyung Ko, Soyoung Yu
Journal of Patient Safety.2017; 13(3): 175. CrossRef - Discriminating Power of Organization Related Variables on Intention to Medication Error Reporting
Myoung Soo Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2016; 41(2): 155. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on Perception of Patient Safety Culture and Safety Care Activities: Comparing University Hospital Nurses and Small Hospital Nurses
Bo Kyoung Cha, Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(4): 405. CrossRef - The Mediating and Moderating Roles of Safety-specific Transformational Leadership on the Relationship between Barrier to and Intention of Reporting Medication Errors
Myoung Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(6): 673. CrossRef - Assessing Safety Attitudes among Healthcare Providers after a Hospital-Wide High-Risk Patient Care Program
Sang Mo Je, Hyun Jong Kim, Je Sung You, Sung Phil Chung, Junho Cho, Jin Hee Lee, Hahn Shick Lee, Hyun Soo Chung
Yonsei Medical Journal.2014; 55(2): 523. CrossRef - Canonical correlation between organizational characteristics and barrier to medication error reporting of nurses
Min-Jeong Kim, Myoung Soo Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(2): 979. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Korean Patient Safety Culture Scale for Nursing Homes
Sook Hee Yoon, Byungsoo Kim, Se Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(3): 379. CrossRef - Role of Transformational-leadership in the Relationship between Medication Error Management Climate and Error Reporting Intention of Nurse
Myoung Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(6): 633. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Patient Safety Reporting Promoting Education Program
Myoung-Soo Kim, Yun-Hee Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(1): 284. CrossRef
- The Influence of Age and Experience on Safety Climate Perceptions Among Healthcare Staff in Operating, Interventional Radiology, and Hybrid Operating Rooms: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 1,812 View
- 65 Download
- 28 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


