Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Variables associated with compliance with standard precautions among hospital nurses: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Song Hee Park, Seok Hee Jeong, Chang Seop Lee, Young Man Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):1-26. Published online February 27, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Purpose
This study aimed to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis to identify variables associated with standard precautions compliance among hospital nurses and to comprehensively examine their effect sizes.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were reported in accordance with the PRISMA and MOOSE guidelines. Studies published in English or Korean were retrieved from KMbase, KoreaMed, KISS, ScienceON, RISS, Nanet, DBpia, PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, and CENTRAL. Data collection was conducted from July 6 to July 16, 2024. To ensure a comprehensive search, no restrictions were placed on the publication period, and studies published up to June 2024 were included in the literature search. Analyses were performed using R ver. 4.4.1.
Results
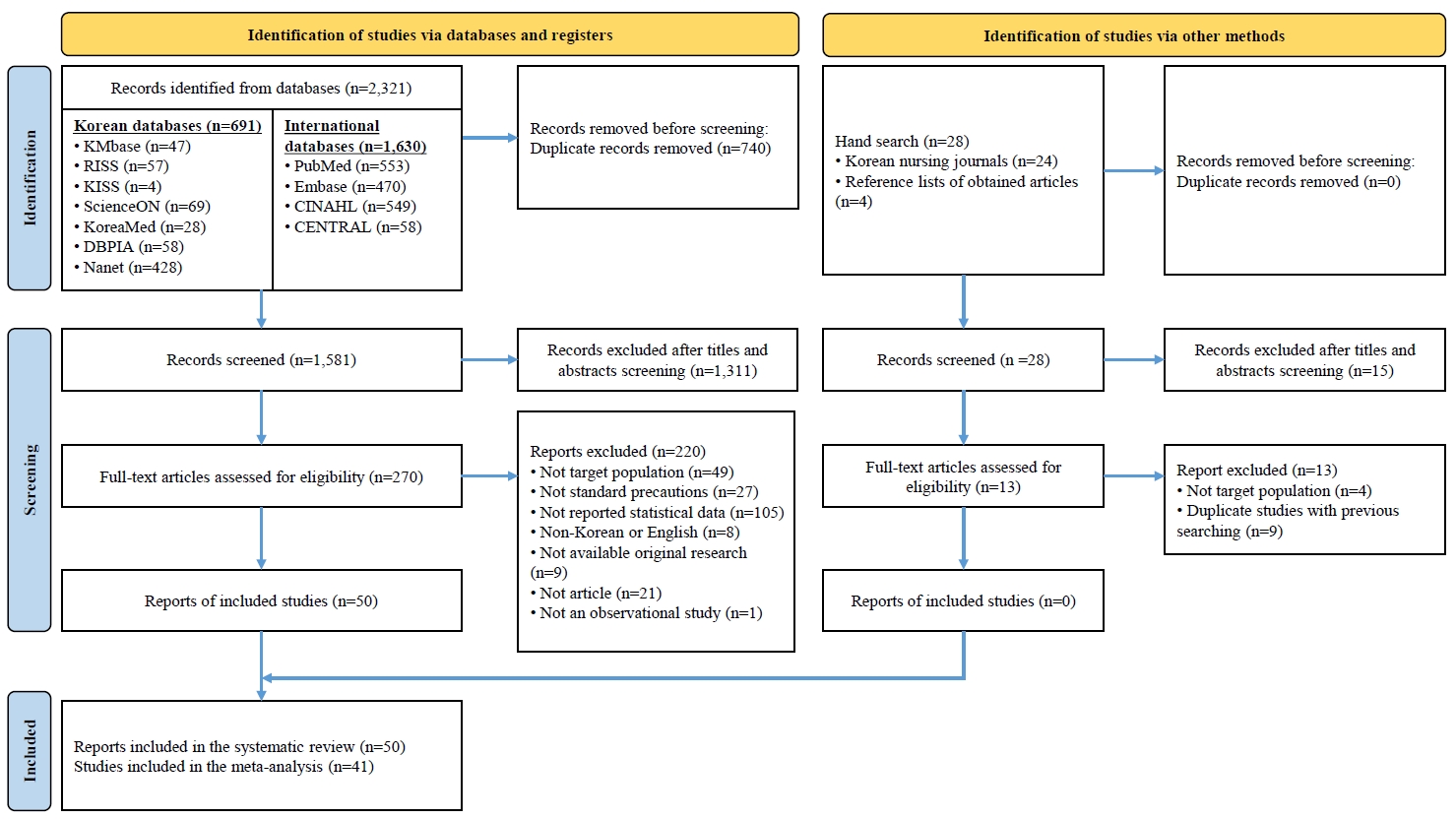
Of the 2,321 studies screened, 50 were included in the systematic review and 41 were included in the meta-analysis. Variables were categorized according to the ecological model. Among individual-level factors, variables with medium correlation effect sizes (ESr ≥.30) included self-efficacy (ESr=.41; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.24 to 0.56), perceived barriers (ESr=−.35; 95% CI, −0.59 to −0.05), cues to action (ESr=.34; 95% CI, 0.07 to 0.57), and perceived benefits (ESr=.30; 95% CI, 0.13 to 0.46). Among organizational factors, organizational culture for infection control (ESr=.47; 95% CI, 0.39 to 0.54) and patient safety culture (ESr=.44; 95% CI, 0.35 to 0.53) demonstrated medium effect sizes. Other statistically significant variables with small effect sizes were also identified. No variables were identified within the interpersonal, community, or public policy domains.
Conclusion
This study identified self-efficacy and organizational culture for infection control as key determinants of compliance with standard precautions. Strengthening these factors may reduce healthcare-associated infections and promote safer nursing care (PROSPERO registration number: CRD42024566518).
- 3 View
- 0 Download

- Variables influencing digital health literacy in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Jin Hwa Park, Eun Ju Mun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):651-667. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to synthesize existing evidence on digital health literacy (DHL) among older adults and to estimate the associations between related influencing factors through a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines. Literature searches were performed across PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, RISS, and DBPIA. The search and screening process was conducted from December 24, 2023, to March 31, 2025. Effect sizes (ESr) using correlation coefficient for each variable were calculated, and meta-analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel and R version 4.3.1.
Results
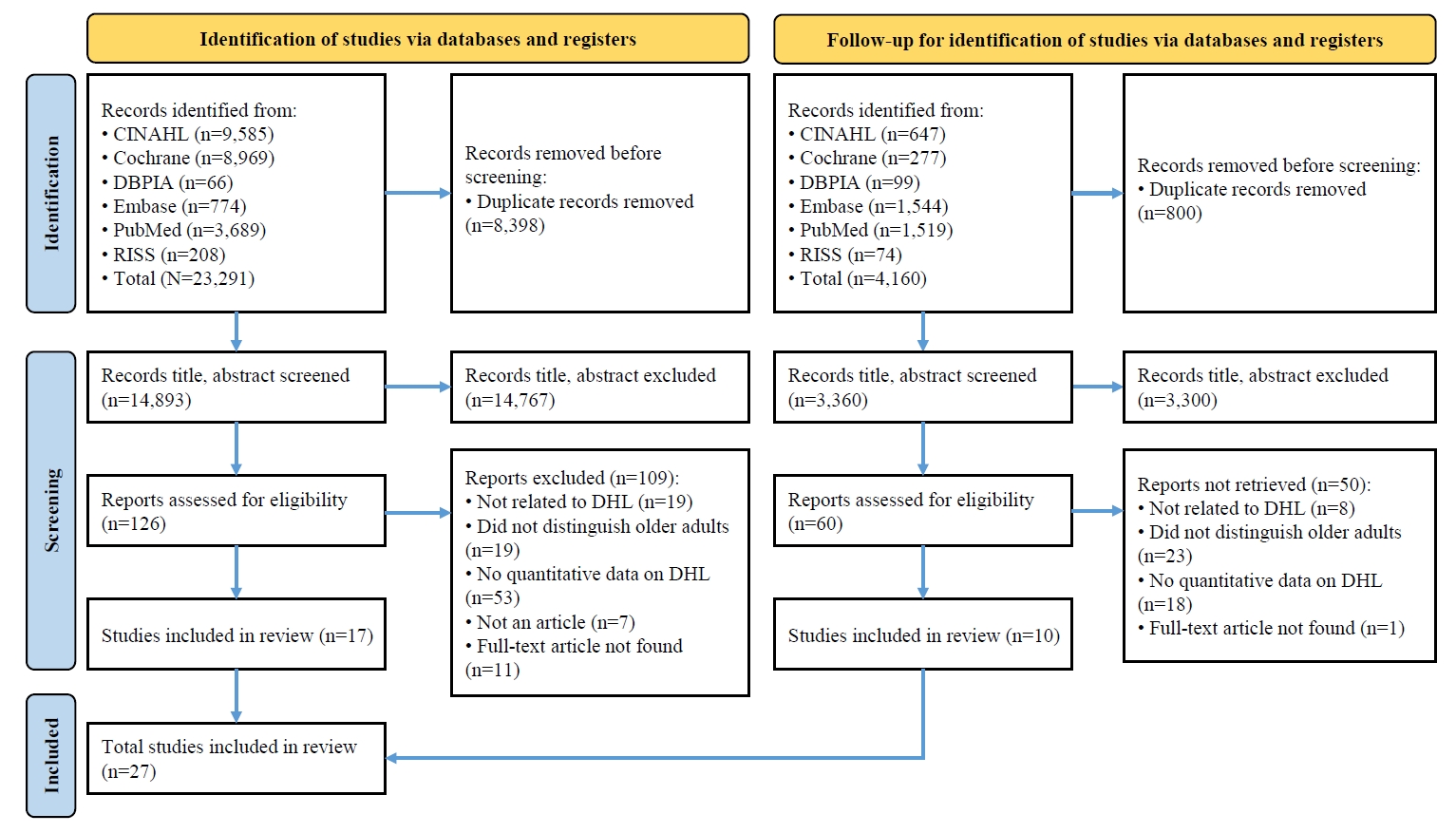
Forty-seven variables were identified, including two demographic, six physical, six behavioral, 23 psychosocial, and 10 cognitive factors. Meta-analysis results showed that physical, behavioral, psychosocial, and cognitive factors had significant effects on DHL. Among these, digital information level (ESr=.62; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55 to 0.69) within the cognitive domain and technophobia (ESr=−.55; 95% CI, −0.47 to −0.40) within the psychosocial domain demonstrated the largest ESr.
Conclusion
Among factors influencing DHL, digital information level and technophobia showed the strongest associations. These findings suggest that improving DHL in older adults requires a dual approach targeting both cognitive and psychosocial dimensions—enhancing digital information skills while reducing technophobia—to effectively support digital engagement and health empowerment in this population (PROSPERO registration number: CRD42023487486).
- 1,383 View
- 156 Download

- Risk factors for the readmission of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hyerim Ji, Sun-Kyung Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):634-650. Published online November 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25072
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify risk factors associated with the readmission of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
A systematic literature review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines. Relevant studies were retrieved from international databases (PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Web of Science) and Korean databases (RISS, KoreaMed, KMbase, KISS, and DBpia). Study quality was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Meta-analysis was performed using a random-effects model with the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman adjustment to account for the limited number of studies and heterogeneity.
Results
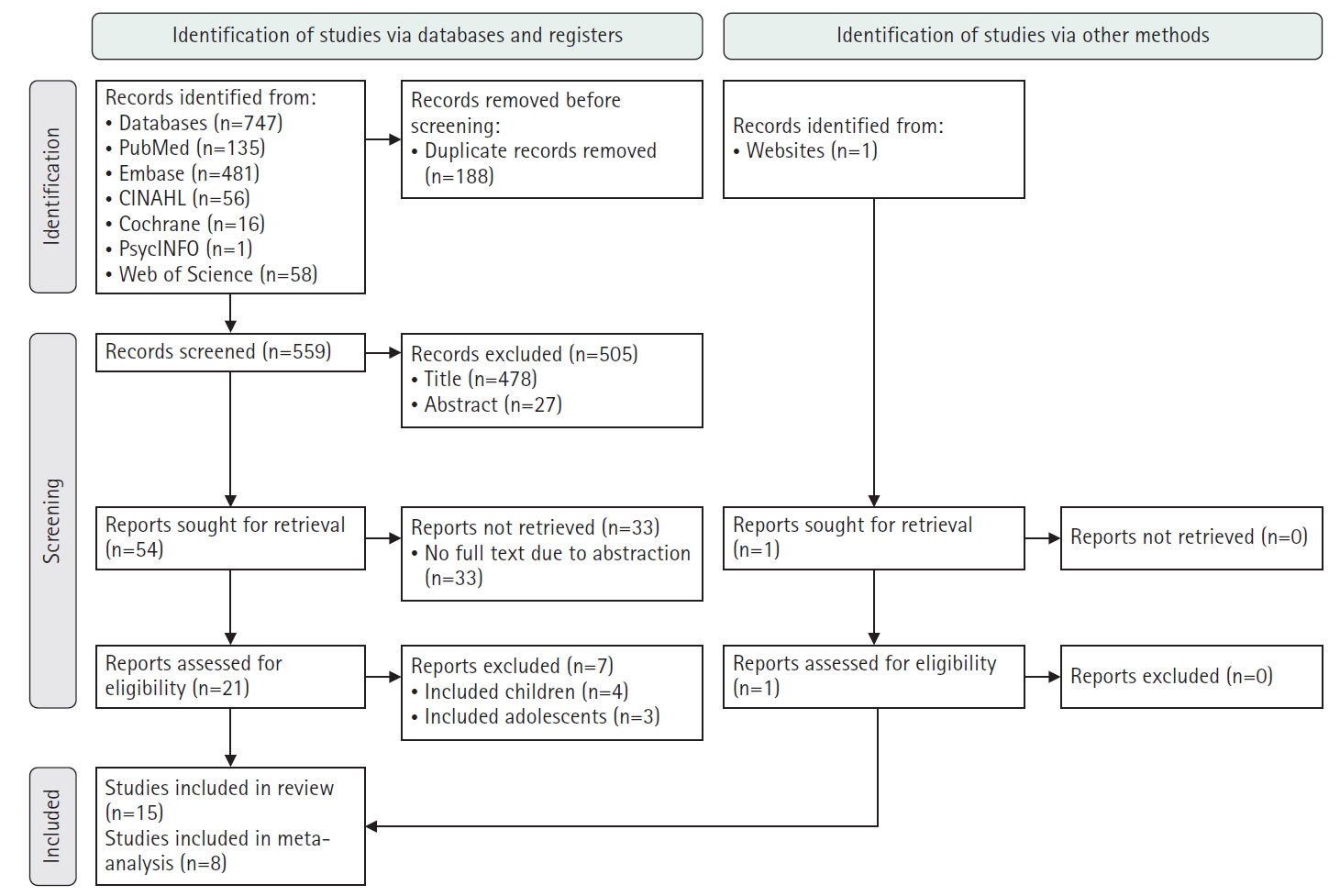
Fifteen studies were included in the review, and eight were eligible for meta-analysis. From the systematic review, 21 risk factors for DKA readmission were identified and categorized into five domains: demographic, socioeconomic, diabetes-related, comorbidity, and health-behavioral factors. In the meta-analysis, significant risk factors included low income, psychiatric disorders, and discharge against medical advice.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that DKA readmissions result from the complex interplay of multiple clinical and social factors. By identifying these risk factors and suggesting risk-stratification criteria, the findings may support the development of tailored interventions, such as self-management education, integrated mental health care, structured discharge planning, and coordinated post-discharge follow-up.
- 1,315 View
- 192 Download

- Research trends in generative artificial intelligence in nursing: a scoping review
- Myung Jin Choi, Myoung Hee Seo, Jihun Kim, Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):468-487. Published online August 5, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) has yet to be comprehensively analyzed in the nursing literature. This study aimed to identify research trends in generative AI within the nursing field through a scoping review and propose strategies for its effective utilization in nursing.
Methods
A scoping review was conducted following Arksey and O’Malley’s six-stage framework. The inclusion criteria included: (1) studies conducted in nursing; (2) research related to generative AI; and (3) original research articles, theses, communications, editorials, letters, or commentaries published in academic journals. Database used PubMed, Embase, CENTRAL, CINAHL, KMbase, KoreaMed, KISS, ScienceON, RISS, DBpia, and 27 nursing-specific journals.
Results
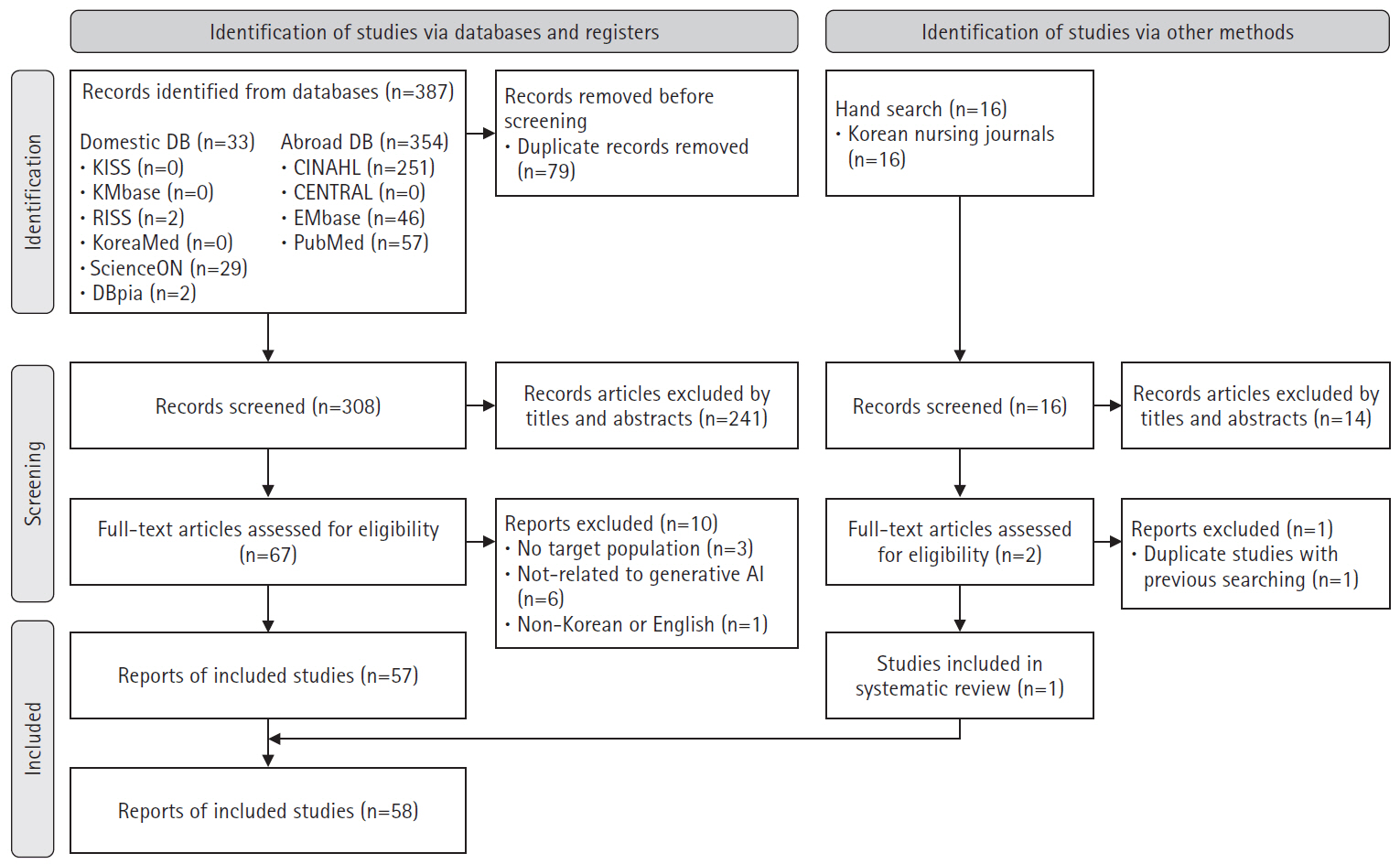
In total, 403 studies were initially identified, and 58 were included in the final analysis. In the care domain, strengths included rapid information retrieval and improved nurse-patient communication, while limitations included the irreplaceable human element and low reliability. The administration domain had no relevant studies. In the research domain, generative AI exhibited strengths such as enhanced efficiency in the paper writing process and improved dissemination speed, but its weaknesses included lack of ethical and legal accountability and a risk of inaccurate or biased information. In the education domain, generative AI was effective in saving time in educational design and implementation, as well as supporting content creation, but challenges included algorithmic bias and risks of plagiarism.
Conclusion
This study identified potential benefits and limitations of generative AI across nursing domains. For effective application, it is essential to develop comprehensive guidelines and policies, provide user education and support, and create opportunities for nurses, educators, and students to learn about strengths and risks of generative AI. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nursing Students' Perspectives on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Psychiatric Nursing Education: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
Sukyung Son, Eunyoung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(Special Is): 9. CrossRef
- Nursing Students' Perspectives on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Psychiatric Nursing Education: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
- 6,919 View
- 505 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A qualitative meta-synthesis of the essence of patient experiences of dialysis
- Soyoung Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh, Yoonhee Seok
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):119-136. Published online February 19, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24102
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to understand the experiences of dialysis and their meaning among patients with chronic kidney disease through a meta-synthesis of the existing literature. Since 2010, the prevalence of end-stage renal disease has doubled in South Korea, which has the sixth-highest incidence worldwide. Although most kidney disease patients undergo dialysis to attenuate disease-related symptoms and prolong their lives, the implications of dialysis on their lives, together with the role played by patients’ significant others, remain underexplored. Similarly, existing research has not considered both patients with hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
Methods
In this meta-synthesis, seven electronic databases (PubMed, CINAHL, EMBASE, PsycINFO, DBpia, KISS, and RISS) were searched for the terms “dialysis” and “qualitative.” Thirty qualitative studies were selected for examination.
Results
The overriding theme observed in the studies was “I do not have much time left.”–navigating the dual realities of one’s limited existence, while other key themes were: (1) the inevitable experience of the troubles of dialysis, (2) life is extended, but deteriorating in every aspect, (3) accepting dialysis with a positive outlook for life, and (4) essential support experienced in an exhausting life.
Conclusion
These findings are important for the design and delivery of practical and tailored nursing interventions to help patients overcome the various challenges related to dialysis treatment, and improve their quality of life.
- 3,405 View
- 161 Download

- Factors Related to Emotional Leadership in Nurses Manager: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Se Young Jang, Chan Mi Park, Eun Hee Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):119-138. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24026
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify research trends related to emotional leadership among nurse managers by conducting a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. This study sought to derive insights that could contribute to improving emotional leadership in nursing practice.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) and Meta-Analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines. Databases including PubMed, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, Scopus, Web of Science, Research Information Sharing Service, Koreanstudies Information Service System, Korean Medical Database, KoreaMed, ScienceON, and DBpia were searched to obtain papers published in English and Korean. Literature searches and screenings were conducted for the period December 1, 2023 to December 17, 2023. The effect size correlation (ESr) was calculated for each variable and the meta-analysis was performed using the statistical software SPSS 29.0, R 4.3.1.
Results
Twenty-five (four personal, six job, and fifteen organizational) relevant variables were identified through the systematic review. The results of the meta-analysis showed that the total overall effect size was ESr = .33. Job satisfaction (ESr = .40) and leader-member exchange (ESr = .75) had the largest effect size among the job and organizational-related factors.
Conclusion
Emotional leadership helps promote positive changes within organizations, improves organizational effectiveness, and increases member engagement and satisfaction. Therefore, it is considered an important strategic factor in improving organizational performance. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Emotional leadership in health care: A dire need illuminated by pivotal resource cuts
Jacqueline Hoare
South African Journal of Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Emotional leadership in health care: A dire need illuminated by pivotal resource cuts
- 3,720 View
- 193 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Descriptive Review of Patents in Healthcare and Nursing: Based on Network Analysis
- Misun Jeon, Nayung Youn, Sanghee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):1-17. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23064
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The significance of the healthcare industry has grown exponentially in recent years due to the impact of the fourth industrial revolution and the ongoing pandemic. Accordingly, this study aimed to examine domestic healthcare-related patents comprehensively. Big data analysis was used to present the trend and status of patents filed in nursing.
Methods
The descriptive review was conducted based on Grant and Booth’s descriptive review framework. Patents related to nursing was searched in the Korea Intellectual Property Rights Information Service between January 2016 to December 2020. Data analysis included descriptive statistics, phi-coefficient for correlations, and network analysis using the R program (version 4.2.2).
Results
Among 37,824 patents initially searched, 1,574 were selected based on the inclusion criteria. Nursing-related patents did not specify subjects, and many patents (41.4%) were related to treatment in the healthcare delivery phase. Furthermore, most patents (56.1%) were designed to increase effectiveness. The words frequently used in the titles of nursing-related patents were, in order, “artificial intelligence,” “health management,” and “medical information,” and the main terms with high connection centrality were “artificial intelligence” and “therapeutic system.” Conclusion: The industrialization of nursing is the best solution for developing the healthcare industry and national health promotion. Collaborations in education, research, and policy will help the nursing industry become a healthcare industry of the future. This will prime the enhancement of the national economy and public health.
- 2,329 View
- 83 Download

- Effects of Health Education Using Virtual Reality for Adolescents: A Systematic Review and MetaAnalysis
- SoMi Park, ChaeWeon Chung, Gaeun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):177-190. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of health interventions using virtual reality (VR) on improving knowledge, attitudes, and skills; and inducing behavioral change among adolescents.
Methods
This study is a systematic review and meta-analysis following PRISMA guidelines. We searched Cochrane, MEDLINE, Embase, CINAHL, Scopus, Web of Science, and Korean databases between database inception and April 10, 2021. Based on heterogeneity, a random- or fixed-effects model was used, as appropriate, to calculate effect sizes in terms of the standardized mean difference (SMD) and odds ratio (OR). Studies were selected if they verified the effects of health education using VR on adolescents; there was an appropriate control group; and if the effects of education were reported in terms of changes in knowledge, attitudes, skills, or behaviors.
Results
This analysis included six studies (n = 1,086). The intervention groups showed greater responses in knowledge and attitudes (SMD = 0.57, 95% confidence interval (CI) [0.12 to 1.02]), skills related to health behavior (SMD = -0.45, 95% CI [-0.71 to -0.19]), and behavioral change after 12 months (OR = 2.36, 95% CI [1.03 to 5.41]).
Conclusion
The results confirm the effectiveness of health interventions using virtual reality (VR). Although the analysis include a small number of studies, a case can be made for health interventions using VR to be utilized as educational methods and strategies to prevent risky behaviors among adolescents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Implementation of a Childcare-Based Obesity Prevention Program for Vulnerable Families During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons for School Nurses
Jiyoung Park, Gill ten Hoor, Seohyun Won, Gahui Hwang, Sein Hwang, Siew Tiang Lau
The Journal of School Nursing.2025; 41(5): 579. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Virtual Reality Intervention for Reducing Exposure to Endocrine Disruptors in Female Adolescents: A Pilot Study
SoMi Park, Yun Jeong Hwang, ChaeWeon Chung
Journal for Specialists in Pediatric Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Chinese nurses’ perspectives on child-friendly healthcare practice assessment: a qualitative study
Wei Xiao Huang, Mei Chan Chong, Li Yoong Tang, Xiao Xia Liu, Mei Fang, Yun Yun Shen, Xiao Li Guo
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing anatomy education with virtual reality: integrating three-dimensional models for improved learning efficiency and student satisfaction
Shuliang Niu, Jinlong Zhang, Jiang Lin, Binbin Wang, Jie Yan
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Implementation of a Childcare-Based Obesity Prevention Program for Vulnerable Families During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons for School Nurses
- 4,496 View
- 103 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effect of Digital Health Interventions on Psychotic Symptoms among Persons with Severe Mental Illness in Community: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Eunjin Oh, Moonhee Gang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):69-86. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of digital health interventions on the psychotic symptoms among people with severe mental illness in the community.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the Cochrane Intervention Research Systematic Review Manual and PRISMA. A literature search was conducted of published randomized controlled trials (RCTs) for digital health interventions from January 2022 to April 2022. RevMan software 5.3 was used for quality assessment and meta-analysis.
Results
A total 14 studies out of 9,864 studies were included in the review, and 13 were included in meta-analysis. The overall effect size of digital health interventions on psychotic symptoms was - 0.21 (95% CI = - 0.32 to - 0.10). Sub-analysis showed that the reduction of the psychotic symptoms was effective in the schizophrenia spectrum group (SMD = - 0.22; 95% CI = - 0.36 to - 0.09), web (SMD = - 0.41; 95% CI = - 0.82 to 0.01), virtual reality (SMD = - 0.33; 95% CI = - 0.56 to - 0.10), mobile (SMD = - 0.15; 95% CI = - 0.28 to - 0.03), intervention period of less than 3 months (SMD = - 0.23; 95% CI = - 0.35 to - 0.11), and non-treatment group (SMD = - 0.23; 95% CI = - 0.36 to - 0.11).
Conclusion
These findings suggest that digital health interventions alleviate psychotic symptoms in patients with severe mental illnesses. However, well-designed digital health studies should be conducted in the future. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Review of Mobile App-Based Psychosocial Intervention for Personal and Clinical Recovery for People With Psychosis
Dowon You, Narae Jeong
Korean Journal of Schizophrenia Research.2024; 27(1): 1. CrossRef
- A Review of Mobile App-Based Psychosocial Intervention for Personal and Clinical Recovery for People With Psychosis
- 2,732 View
- 89 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of Auriculotherapy on Musculoskeletal Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Sun Yeob Choi, Yeo Ju Kim, Bomi Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):4-23. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of auriculotherapy on musculoskeletal pain in adults.
Methods
A total of 885 studies were retrieved from nine databases (PubMed, Scopus, CINAHL, Web of Science, Ovid Medline, Cochrane Library, RISS, KMbase, and KISS). Sixteen studies were selected for meta-analysis, which satisfied the inclusion criteria and the evaluation of risk of bias. Demographic data, auriculotherapy types, intervention characteristics, auricular points, and outcomes related to pain (subjective pain scale, and amount of analgesic) were extracted from all included studies. The effect size of auriculotherapy was analyzed through comprehensive meta analysis 3.0, and the presence of publication bias was analyzed through a funnel plot and Egger’s regression.
Results
The results of the meta-analysis (n = 16) revealed that the auriculotherapy was significantly superior to the control group on present pain in adults (Hedges’ g = - 0.35, 95% Confidence Interval [CI] = - 0.55~- 0.15). According to the results of subgroup analysis, the effect size of auricular acupuncture therapy (Hedges’ g = 0.45, 95% CI = - 0.75~- 0.15) was higher than the auricular acupuncture (Hedges’ g = 0.27, 95% CI = - 0.53~0.00): the longer the intervention period, the greater the effect size.
Conclusion
In this study, auriculotherapy demonstrates a significant reduction in musculoskeletal pain in adults. Therefore, it is necessary to refine the curriculum to include auriculotherapy as a nursing intervention to relieve musculoskeletal pain in adults and encourage its use in clinical settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Nurses’ Perceived Stress, Sleep Quality, and Presenteeism
Hyunseo Sim, Younghee Park
Holistic Nursing Practice.2025; 39(1): 15. CrossRef - Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Pain and Stress in Nursing College Students With Cervical Pain: A Single-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial
Yuna Cho, Eunmi Cho, Eunseol Cho, Yeonju Chae, Eunkyung Choi, Hyeongyeong Yoon
Pain Management Nursing.2025; 26(1): e59. CrossRef - Effect of Auriculotherapy on Stress: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunyeob Choi, Bomi Kim
Journal of Holistic Nursing.2025; 43(4): 336. CrossRef - Comparative Effectiveness of Ear and Body Acupressure for Postoperative Pain in Elderly Women Following Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Trial
Fatemeh Ghanbari, Nahid Rejeh, Tahereh Bahrami, Hooman Yahyazadeh, Kiarash Saatchi
Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine.2025; 31(11): 987. CrossRef - Estratégias de adaptação dos profissionais de enfermagem com dor musculoesquelética no trabalho hospitalar: uma revisão sistemática
Jorge Gabriel Tuz-Colli, Yolanda Flores-Peña, Heloisa Ehmke Cardoso dos Santos, Fernanda Ludmilla Rossi Rocha, Maria Helena Palucci Marziale
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adaptation strategies for nurses with musculoskeletal pain in hospital work: a systematic review
Jorge Gabriel Tuz-Colli, Yolanda Flores-Peña, Heloisa Ehmke Cardoso dos Santos, Fernanda Ludmilla Rossi Rocha, Maria Helena Palucci Marziale
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Estrategias de adaptación de los profesionales de Enfermería con dolor musculoesquelético en el trabajo hospitalario: revisión sistemática
Jorge Gabriel Tuz-Colli, Yolanda Flores-Peña, Heloisa Ehmke Cardoso dos Santos, Fernanda Ludmilla Rossi Rocha, Maria Helena Palucci Marziale
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adapting and Evaluating a Theory-Driven, Non-Pharmacological Intervention to Self-Manage Pain
Jennifer Kawi, Chao Hsing Yeh, Lauren Grant, Johannes Thrul, Hulin Wu, Paul J. Christo, Lorraine S. Evangelista
Healthcare.2024; 12(10): 969. CrossRef - The State of 21st Century Acupuncture in the United States
Clasina Smith, Bill Reddy, Charis Wolf, Rosa Schnyer, Korina St John, Lisa Conboy, Jen Stone, Lixing Lao
Journal of Pain Research.2024; Volume 17: 3329. CrossRef - The effects of auricular acupressure on blood pressure, stress, and sleep in elders with essential hypertension: a randomized single-blind sham-controlled trial
Bomi Kim, Hyojung Park
European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2023; 22(6): 610. CrossRef
- Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Nurses’ Perceived Stress, Sleep Quality, and Presenteeism
- 3,063 View
- 126 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- The Effects of Programs on Body-Image Improvement in Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Hyun Jung Yun, Kyoungsan Seo, Dallong Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):597-616. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study’s objective was to investigate the effects of programs that improve adolescents’ body image, using a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
A literature search was performed in eleven electronic databases, using preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis guidelines. Population characteristics, contents of the programs, and measured outcomes were systematically reviewed from 21 selected studies. To estimate the size of the effects, meta-analysis was conducted using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software.
Results
The contents of the programs that aimed to improve body image included physical, psychological, interpersonal, and sociocultural interventions. Sixteen studies were meta-analyzed to estimate the effect size of body-image improvement programs. Results showed that the program for body-image improvement had significant effects on body satisfaction (effect size [ES] = 0.56, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.23 to 0.89), and body dissatisfaction (ES = - 0.15, 95% CI = - 0.23 to - 0.08).
Conclusion
The program for body image improvement in adolescents includes a combination of physical, psychological, interpersonal relationship, and socio-cultural dimensions. The program that seeks to improve body image appears to be effective at increasing body satisfaction, and at reducing body dissatisfaction in adolescents. Thus, it is necessary to develop and apply multidimensional programs for adolescents to have a positive body image. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 청소년의 신체상과 행복감 간의 관계: 가족 의사소통으로 조절된 자아존중감의 매개역할*
종일 여
Journal of Family Relations.2025; 30(1): 55. CrossRef
- 청소년의 신체상과 행복감 간의 관계: 가족 의사소통으로 조절된 자아존중감의 매개역할*
- 2,885 View
- 62 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Analysis of Research Topics and Trends in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing to Improve Its International Influence
- Soyoung Yu, Jeung-Im Kim, Jin-Hee Park, Sun Joo Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh, Ju-Eun Song, YeoJin Im
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(4):501-512. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20167
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to analyze articles published in the Journal of the Korean Academy of Nursing (JKAN) between 2010 and 2019, along with those published in three international nursing journals, to improve JKAN’s international reputation.
Methods
The overall characteristics of JKAN’s published papers and keywords, study participants, types of nursing interventions and dependent variables, citations, and cited journals were analyzed. Additionally, the keywords and study designs, publication-related characteristics, journal impact factors (JIF), and Eigenfactor scores of International Journal of Nursing Studies (IJNS), International Nursing Review (INR), Nursing & Health Sciences (NHS), and JKAN were analyzed and compared.
Results
Among the four journals, JKAN’s score was the lowest in both the journal impact factor and Eigenfactor score. In particular, while the JIF of INR and NHS has been continuously increasing; JKAN’s JIF has remained static for almost 10 years. The journals which had cited JKAN and those which JKAN had cited were mainly published in Korean.
Conclusion
JKAN still has a low IF and a low ranking among Social Citation Index (E) journals during the past 10 years, as compared to that of four international journals. To enhance JKAN’s status as an international journal, it is necessary to consider publishing it in English and to continuously improve the conditions of other publications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ten-year trends in research designs and keywords: a bibliometric comparison of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and leading international nursing journals
Jin-Hee Park, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Gaeun Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(4): 557. CrossRef - Commemorating the 50th Anniversary of Korean Society of Nursing Science and Contemplating Direction to Move Forward
Kyung-Sook Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 641. CrossRef
- Ten-year trends in research designs and keywords: a bibliometric comparison of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and leading international nursing journals
- 2,418 View
- 28 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Trends of Concept Development in Nursing Published in Korean Journals
- Sumi Lee, Jinhae Lee, Yugyeong Hwang, Il Sun Ko
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(2):178-190. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.2.178
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify trends of nursing concept development in Korean journal papers to improve accurate understanding of nursing concepts.
Methods
A systematic review of 216 concept development articles published from 1970 to 2018 that met the inclusion criteria was conducted using Research Information Sharing Service (RISS) databases.
Results
The most common method of concept development was Walker and Avant’s concept analysis method, identified in 139 (64.3%) of the 216 studies, followed by 48 examples of hybrid models (22.2%) and 15 examples of evolutionary methods (6.9%). Chinn and Kramer’s method, Norris’s clarification, Wilson’s method, and others were also used. The concepts of “spirituality” and “fatigue” were most frequently analyzed. Among the 139 studies that used Walker and Avant’s concept analysis method, 127 studies (91.4%) applied all the recommended steps; the others applied the recommended steps partially, omitting description of model cases/additional cases, antecedents/consequences, and empirical indicators. Among the studies using the hybrid model, among two (5.7%) did not describe attributes, three (8.5%) did not provide definitions, and 16 (45.7%) did not present empirical indicators in the final stage.
Conclusion
Among concept development studies published in Korean journals, Walker and Avant’s concept analysis method is most commonly used. In case of most studies using Walker and Avant’s method a suitable concept analysis process is applied, but in case of other studies using the other concept development method, a suitable concept analysis process is not applied. Therefore, a suitable concept analysis process must be applied for concept development in nursing research. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concept Analysis of Nurses’ Job Crafting
Sujeong Han, Eunha Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(3): 375. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Spiritual Distress in Cancer Patients Using a Hybrid Model
Jin Sook Kim, Il-Sun Ko
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(2): 169. CrossRef
- Concept Analysis of Nurses’ Job Crafting
- 2,642 View
- 65 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Factors Related to Persistent Postoperative Pain after Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Jaewon Bae, Sujin Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(2):159-177. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.2.159
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed at identifying factors related to persistent postoperative pain after cardiac surgery and estimating their effect sizes.
Methods
The literature search and selection was conducted in four different databases (CINAHL, Cochrane Library, PubMed, and PQDT) using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Statement. A total of 14 studies met the inclusion criteria and were systematically reviewed. For the meta-analysis, R was used to analyze 30 effect sizes of for both individual and operative factors as well as publication biases from a total of nine studies.
Results
The meta-analysis revealed that persistent postoperative pain after cardiac surgery was related to one individual factor (gender) and two operative factors (acute postoperative pain and use of the internal mammary artery). Operative factors (OR=5.26) had a larger effect size than individual factors (OR=1.53).
Conclusion
Female gender, acute pain after surgery, and use of the internal mammary artery are related factors to persistent postoperative pain. The development of interventions focusing on modifiable related factors, such as acute postoperative pain, may help to minimize or prevent PPP after cardiac surgery. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pain-Friendly Strategies: Nursing Intervention in Postoperative Myocardial Revascularization
Debora Milena Alvarez Yañez, Gloria Carvajal Carrascal
Revista de Investigación e Innovación en Ciencias de la Salud.2025; 8(1): 1. CrossRef - Prognostic factors for chronic post‐surgical pain after lung and pleural surgery: a systematic review with meta‐analysis, meta‐regression and trial sequential analysis
P. R. D. Clephas, S. E. Hoeks, P. M. Singh, C. S. Guay, M. Trivella, M. Klimek, M. Heesen
Anaesthesia.2023; 78(8): 1005. CrossRef - Regional anesthesia in coronary artery bypass grafting: a narrative review
Viktor A. Koriachkin, Maksim A. Dzhopua, Beka S. Ezugbaia, Vaagn A. Avetisian, Dmitriy V. Zabolotskiy, Vladimir A. Evgrafov
Regional Anesthesia and Acute Pain Management.2023; 17(3): 161. CrossRef
- Pain-Friendly Strategies: Nursing Intervention in Postoperative Myocardial Revascularization
- 1,593 View
- 28 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of Aromatherapy on Sleep Quality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Mi-Eun Kim, Ji Hee Jun, Muyng-Haeng Hur
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):655-676. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.655
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of aromatherapy on sleep quality.
Methods This is a systematic review of randomized controlled trial studies (PROSPERO registration number CRD42017064519). In this study, the PICO were adults and the elderly, aromatherapy intervention, a comparative intervention with the control and placebo oil groups, and sleep. The selected articles were in English, Korean, and Chinese.
Results The results of the meta-analysis showed that the effect sizes of the experimental group were 1.03 (n=763, SMD=1.03, 95% CI 0.66 to 1.39) (Z=5.47,
p <.001). In the aromatherapy intervention group, the effect size of sleep was statistically significant (QB=9.39, df=2,p =.009), with a difference of 0.77 for inhalation, 1.12 for oral intake and 2.05 for massage. A post-analysis showed that the effect of massage on sleep was significantly greater than the inhalation method. The regression coefficient of the intervention period, B=0.01 (Z=1.43,p =.154), also showed that the longer the intervention period, the larger the effect size; however, it was not statistically significant.Conclusion A total of 23 literature analyses showed that aromatherapy is effective in improving quality of sleep, and the massage method is more effective in improving quality of sleep than the inhalation method. A meta-ANOVA showed that the aromatherapy intervention affected the high heterogeneity of the effect size. Thus, future research with stricter control in methods and experimental procedures is necessary.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of aroma inhalation on the quality of sleep, professional quality of life, and near-misses in medication errors among emergency room nurses on night duty in Korea: a randomized controlled trial
Jungha Son, Chul-Gyu Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(1): 25. CrossRef - Effects of a Multimodal Intervention on Sleep Quality and Duration in Intensive Care Unit Patients
Jieun Nam, Sukhee Ahn
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2025; 18(1): 70. CrossRef - Efficacy of Aromatherapy Against Behavioral and Psychological Disturbances in People With Dementia: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Po-Hao Wang, Ho-Wei Lin, Truc Tran Thanh Nguyen, Chaur-Jong Hu, Li-Kai Huang, Ka-Wai Tam, Yi-Chun Kuan
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2024; 25(11): 105199. CrossRef - Meta-analysis of the Effect Size of Lavender Essential Oil and Lavender Blended Essential Oils on Psychological Factors in Adults
Mi-Na Yu, Ae-Jung Kim
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2024; 22(3): 477. CrossRef - THE EFFECT OF LAVENDER AROMA THERAPY ON THE SLEEP QUALITY OF PREGNANT WOMEN TM III
Hajar Nur Fathur Rohmah
Jurnal Midpro.2024; 16(1): 59. CrossRef - Effects of aromatherapy on sore throat, nasal symptoms and sleep quality in adults infected with COVID-19: A randomized controlled trial
Hye-Young Kang, Hye Young Ahn, Mi-Jung Kang, Myung-Haeng Hur
Integrative Medicine Research.2023; 12(4): 101001. CrossRef - Pain and sleep after open-heart surgery-inhalation peppermint essence: double-blind randomized clinical trial
Mahla Maghami, Mohammad-Sadegh Pour‑Abbasi, Safoura Yadollahi, Mahboobeh Maghami, Ismail Azizi-fini, Mohammad-Reza Afazel
BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care.2023; 13(e3): e1318. CrossRef - Effects of Aromatherapy on Cancer Patients' Sleep and Fatigue: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ju Hyun Ahn, Myoungsuk Kim
Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine.2023; 29(4): 212. CrossRef - Harnessing the power of a good night's sleep
Karen Colombo
Nursing Made Incredibly Easy!.2023; 21(1): 34. CrossRef - Effectiveness of aromatherapy on anxiety and sleep quality among adult patients admitted into intensive care units: A systematic review
Jie Xi Jassie Tan, Junyao Stefanie Cai, Jeanette Ignacio
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2023; 76: 103396. CrossRef - Fatigue relief by aromatherapy use in prenatal and postnatal women: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ji-Ah Song, Hyejin Yang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(2): 87. CrossRef - Aromatherapy with single essential oils can significantly improve the sleep quality of cancer patients: a meta-analysis
Hui Cheng, Lu Lin, Shaotong Wang, Yueyue Zhang, Tingting Liu, Yang Yuan, Qiuyun Chen, Li Tian
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of aromatherapy on fatigue, quality of sleep and quality of life in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A feasibility study
Lili You, Na Guo, Tiantian Wang, Xiang Yu, Xiaofeng Kang, Yuxia Guan, Hongpeng Liu, Jing Dong, Peili Bian, Siyao Wang, Chenxiao Bai
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2022; 49: 101648. CrossRef - The Effects of Non-pharmacological Interventions on Sleep among Older Adults in Korean Long-term Care Facilities: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Sun Ok Jung, Hyeyoung Kim, Eunju Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(3): 340. CrossRef - Visualizing Research Trends and Identifying Hotspots of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Nursing Technology for Insomnia: A 18-Years Bibliometric Analysis of Web of Science Core Collection
Junxin Wang, Yufeng Chen, Xing Zhai, Yupeng Chu, Xiangdi Liu, Xueling Ma
Frontiers in Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of aromatherapy on sleep disorders
Xin Song, Jiahua Peng, Weiyu Jiang, Minghua Ye, Lisheng Jiang
Medicine.2021; 100(17): e25727. CrossRef - Effect of aromatherapy on sleep quality of adults and elderly people: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis
Jihoo Her, Mi-Kyoung Cho
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2021; 60: 102739. CrossRef - Effect of Rosa damascena on improvement of adults’ sleep quality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Mohammad Sadegh Ghorbani Rami, Morteza Nasiri, Mohammad Sadegh Aghili Nasab, Zohre Jafari, Mahya Torkaman, Shahoo Feizi, Behnam Farahmandnia, Masoomeh Asadi
Sleep Medicine.2021; 87: 8. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Sleep Quality in the Relationship between Academic Stress and Social Network Service Addiction Tendency among Adolescents
Eun Sook Bae, Hye Seung Kang, Ha Na Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(3): 290. CrossRef
- The effects of aroma inhalation on the quality of sleep, professional quality of life, and near-misses in medication errors among emergency room nurses on night duty in Korea: a randomized controlled trial
- 6,150 View
- 166 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref

- Changes in Strauss & Corbin's Grounded Theory
- Ji Eun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(5):505-514. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.5.505
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to introduce and elucidate changes in Strauss and Corbin's grounded theory and discuss its application to the field of nursing in South Korea.
Methods The changes in grounded theory by Strauss and Corbin were examined through a literature review of grounded theory from its inception.
Results Strauss and Corbin acknowledged their philosophical backgrounds of symbolic interactionism and pragmatism; however, their methodology based on positivism overwhelmed their epistemology and ontology. This inconsistency has been represented by the coding paradigm and the premise of “emergent from the data.” In the revised version of
Basics , Strauss and Corbin modified their theory to weaken the coding paradigm and strengthen the strategies for the development of substantive theory.Conclusion Strauss and Corbin's revised grounded theory did not fully address the inconsistency of their epistemology and ontology between their acknowledgement and methodology. However, these changes constitute a meaningful step toward resolving inconsistencies and highlight the development of substantive theory. This has implications for Korean nursing researchers who have utilized methodologies in grounded theory with dogmatic approaches; grounded theory, with its evolving nature, is not a finalized method and calls for open approaches for the development of a grounded theory that fits Korean nursing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Emergency Nurses’ Comprehensive process of surrogate decision Support: Reanalysis of qualitative data Using a grounded theory
Sadami Momiyama, Hayato Katayanagi, Makoto Nakabayashi, Tomoko Fujino, Noriko Sakoda, Yoshiko Sato, Takafumi Noguchi, Hiroko Susaka, Hidekazu Hishinuma, Tomoya Tozawa, Tomomi Muraoka
International Emergency Nursing.2026; 84: 101749. CrossRef - From Perception to Practice: Identifying and Ranking Human Factors Driving Unsafe Industrial Behaviors
Azim Karimi, Esmaeil Zarei, Ehsanollah Habibi
Safety.2026; 12(1): 14. CrossRef - Exploration of Family-Centered Care in NICUs: A Grounded Theory Methodology
Young Ah Park, YeoJin Im
Qualitative Health Research.2025; 35(10-11): 1231. CrossRef - Breaking boundaries: integration of sports and medicine in the community elderly service model
Yuanli Chen, Mohd Firdaus Bin Abdullah, Nor Eeza Zainal Abidin, Fanghui Li
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Expert school nurses' experiences of reopening schools during the COVID-19 pandemic: A qualitative study
Ji Eun Kim, Hyun-Ju Seo, Jaehee Yoon
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2024; 76: 16. CrossRef - Digital textbooks for undergraduate nursing education: a scoping review protocol
Aeri Jang, Hyunyoung Park
BMJ Open.2024; 14(7): e071147. CrossRef - Qualitative Research in Healthcare: Data Analysis
Dasom Im, Jeehye Pyo, Haneul Lee, Hyeran Jung, Minsu Ock
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(2): 100. CrossRef - Efeitos da intervenção terapêutica de enfermagem em pacientes com doença cardíaca coronária
Bifei Yan, Jing Chen, Juanhua Tu, Yan Wang
Acta Paulista de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Developing and Validating Educational Strategies for Couples to Enhance Family Bonds: A Qualitative Expert Analysis
Seyed Amin Saadat, Mohammad Hosein Fallah, Saeid Vaziri Yazdi
Thrita.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Illness Experiences of Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
Ji Eun Kim, Ilaria Campesi
Journal of Diabetes Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Internet of things platform technology used in undergraduate nursing student education: a scoping review protocol
A Jang, CE Song
BMJ Open.2022; 12(4): e058556. CrossRef - The Health Management Experience of Vietnamese Married Immigrant Women Living in the City
Jiyoung Chun
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(4): 506. CrossRef
- Emergency Nurses’ Comprehensive process of surrogate decision Support: Reanalysis of qualitative data Using a grounded theory
- 3,422 View
- 79 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref

- Effect of Autogenic Training for Stress Response: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Eunju Seo, Soukyoung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):361-374. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.361
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of autogenic training on stress responses through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods A systematic search was conducted using eight core electronic databases (Embase, CENTRAL, Medline, CINAHL, PsycInfo, DBpia, KISS, and RISS). To estimate the effect size, a meta-analysis of the studies was performed using RevMan 5.3.5 program.
Results A total 21 studies out of 950 studies were included in the review, and 11 were included for meta-analysis. These studies showed that autogenic training decreased anxiety and depression, and increased the high frequency of heart rate variability. Calculations to understand the effect of autogenic training on anxiety, through a meta-analysis, observed a reduction effect of anxiety score by 1.37 points (n=85, SMD=-1.37: 95% CI -2.07 to -0.67), in the studies on short-term intervention targeting healthy adults. On the other hand, similar calculations to understand the effect of autogenic training on depression observed, a reduction effect on the depression score by 0.29 point (n=327, SMD=-0.29: 95% CI -0.50 to -0.07), in the studies on long term intervention targeting the patient group.
Conclusion Autogenic training is effective for adults’ stress management, and nurses will be able to effectively perform autogenic training programs for workers’ stress relief at the workplace.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A peer-led group intervention based on relaxation (soRELAX) to improve well-being and mental health in nursing students: A mixed method pilot study
Maria Pilar Ramirez Garcia, Jérôme Leclerc-Loiselle, Christine Genest, Etienne Paradis-Gagné, Caroline Larue, Marikim Poitras-Crête, Sylvie Corbeil, Camille Saseville
Journal of Professional Nursing.2025; 57: 8. CrossRef - Effects of Autogenic Training on Pain Modulation in Burning Mouth Syndrome: A Preliminary Study
Keita Takizawa, Kana Ozasa, Kohei Shimizu, Noboru Noma
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Strengthening psychological resilience: The effectiveness of autogenic training of community pharmacists
Dragana Jocic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2024; 81(11): 696. CrossRef - Ampliación del Informe de Sanidad: Evidencia Sobre la Seguridad y Eficacia del Entrenamiento Autógeno
Juan Manuel Guiote, Miguel Angel Vallejo Pareja, Blanca Mas
Papeles del Psicólogo - Psychologist Papers.2024; 45(3): 172. CrossRef - Autogenic Training in Mental Disorders: What Can We Expect?
Dagmar Breznoscakova, Milana Kovanicova, Eva Sedlakova, Maria Pallayova
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(5): 4344. CrossRef - The effects of online enactive education on secondary school students
Deborah R. Vivo
The Journal of Educational Research.2023; 116(4): 230. CrossRef - Self-reported symptom burden in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS): A narrative review of observational and interventional studies
Iris Knoop, Federica Picariello, Emma Jenkinson, Nicholas Gall, Claudia Chisari, Rona Moss-Morris
Autonomic Neuroscience.2023; 244: 103052. CrossRef - Efficacy of Individualized Sensory-Based mHealth Interventions to Improve Distress Coping in Healthcare Professionals: A Multi-Arm Parallel-Group Randomized Controlled Trial
Hannes Baumann, Luis Heuel, Laura Louise Bischoff, Bettina Wollesen
Sensors.2023; 23(4): 2322. CrossRef - The Effect of Autogenic Training in a Form of Audio Recording on Sleep Quality and Physiological Stress Reactions of University Athletes—Pilot Study
Kamila Litwic-Kaminska, Martyna Kotyśko, Tadeusz Pracki, Monika Wiłkość-Dębczyńska, Błażej Stankiewicz
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(23): 16043. CrossRef - Combined effect of autogenic relaxation and aerobic exercise on postmenopausal hypertension: A randomized clinical trial
Shreen R Aboelmagd, Afaf M Botla, Hossam ELdine Hussein, Sahar M. Ali, Nehad A. Abo-Zaid
International journal of health sciences.2022; 6(S10): 2314. CrossRef - Temporomandibular Myofascial Pain Syndrome—Aetiology and Biopsychosocial Modulation. A Narrative Review
Paulina Golanska, Klara Saczuk, Monika Domarecka, Joanna Kuć, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(15): 7807. CrossRef - To stress or not to stress: Brain-behavior-immune interaction may weaken or promote the immune response to SARS-CoV-2
Eva M.J. Peters, Manfred Schedlowski, Carsten Watzl, Ulrike Gimsa
Neurobiology of Stress.2021; 14: 100296. CrossRef - Non‐pharmacologic treatment of insomnia in primary care settings
Laura Hrehová, Kamal Mezian
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Single Session of Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback Produced Greater Increases in Heart Rate Variability Than Autogenic Training
I-Mei Lin, San-Yu Wang, Sheng-Yu Fan, Erik Peper, Sui-Pi Chen, Ching-Yu Huang
Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback.2020; 45(4): 343. CrossRef - A Multimodal Stress-Prevention Program Supplemented by Telephone-Coaching Sessions to Reduce Perceived Stress among German Farmers: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial
Marita Stier-Jarmer, Cornelia Oberhauser, Dieter Frisch, Götz Berberich, Thomas Loew, Carina Schels-Klemens, Birgit Braun, Angela Schuh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(24): 9227. CrossRef
- A peer-led group intervention based on relaxation (soRELAX) to improve well-being and mental health in nursing students: A mixed method pilot study
- 4,007 View
- 182 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Telemonitoring Intervention in Children and Adolescents with Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Youjin Jung, Jimin Kim, Dong Ah Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(4):389-406. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.4.389
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This review aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of telemonitoring (TM) in the management of children and adolescents with asthma.
Methods We searched Ovid-MEDLINE, Ovid-EMBASE, CENTRAL (Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials), CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature), and 5 domestic databases to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published through December 2017. Two reviewers independently selected relevant studies, assessed methodological quality and extracted data. We performed a meta-analysis of TM versus usual care and summarized the intervention characteristics of included studies.
Results Of the 3,095 articles identified, 8 RCTs (9 articles) were included in this review. The type of TM intervention of included studies was varying across studies (transmitted data, transmission frequency, data review, etc.). The pooled asthma control score was not significantly different between TM and usual care (standardized mean difference 0.04, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.20~0.28). Another pooled analysis demonstrated no statistically significant difference in asthma exacerbation between TM and usual care (odds ratio 0.95, 95% CI 0.43~2.09). Overall, the pooled results from these studies revealed that TM did not lead to clinically significant improvements in health outcomes, but some studies in our analysis suggested that TM increased patient medication adherence and intervention adherence.
Conclusion The current evidence base does not demonstrate any differences between TM intervention and usual care, but TM intervention might be considered a promising strategy for the delivery of self-management support for children and adolescents with asthma. Further well-designed studies are needed to assess the effects on clinical outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Telemedicine in chronic lung disease management: progress and prospects
Hee-Young Yoon, Jin Woo Song
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2026; 41(1): 31. CrossRef - Impact of Telemedicine on Asthma Control and Quality of Life in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Julen Garcia Gerriko, Tregony Simoneau, Jonathan M. Gaffin, Marina Ortúzar Menéndez, Alejandro Fernandez-Montero, Laura Moreno-Galarraga
Children.2025; 12(7): 849. CrossRef - Visitas virtuales en pediatría: experiencias, preferencias y expectativas de pacientes y cuidadores
Miren Ibarzabal Arregi, Tregony Simoneau, Jonathan M. Gaffin, María Gimeno Castillo, Isabel Castro Garrido, Claudia María Chaverri Reparaz, Laura Moreno-Galarraga
Anales de Pediatría.2025; 103(4): 503993. CrossRef - Pediatric virtual visits: experiences, preferences, and expectations of patients and caregivers
Miren Ibarzabal Arregi, Tregony Simoneau, Jonathan M. Gaffin, María Gimeno Castillo, Isabel Castro Garrido, Claudia María Chaverri Reparaz, Laura Moreno-Galarraga
Anales de Pediatría (English Edition).2025; 103(4): 503993. CrossRef - Effectiveness of eAsthmaCare on Symptoms, Childhood Asthma Control Test, and Lung Function among Asthmatic Children
Tzu-Ning Wen, Hsueh-Chun Lin, Kuo-Wei Yeh, Jing-Long Huang, Li-Chi Chiang
Journal of Medical Systems.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Real‐time effects of COVID‐19 pandemic lockdown on pediatric respiratory patients
Michal Cahal, Israel Amirav, Nir Diamant, Moria Be'er, Omri Besor, Moran Lavie
Pediatric Pulmonology.2021; 56(6): 1401. CrossRef - Comparison of Learning Effects of Virtual Reality Simulation on Nursing Students Caring for Children with Asthma
Kyung-Ah Kang, Shin-Jeong Kim, Myung-Nam Lee, Mikang Kim, Sunghee Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(22): 8417. CrossRef - Effects of a Virtual Reality Simulation and a Blended Simulation of Care for Pediatric Patient with Asthma
Mikang Kim, Sunghee Kim, Woo Sook Lee
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(4): 496. CrossRef
- Telemedicine in chronic lung disease management: progress and prospects
- 2,388 View
- 43 Download
- 8 Crossref

- How Does Advance Provision of Emergency Contraceptives Affect Contraceptive Use and Sexual Activity Among Adolescents? Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Kyungsoon Ryu, Misoon Lee, Younghae Kim, Seonhwa Ban, Mihyang Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):255-265. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.255
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyze the effect of emergency contraceptive pill on adolescent sexuality and contraceptive behaviors through a meta - analysis of intervention studies on advance provision of emergency contraceptives. This study aimed to provide objective data on the transition of general medicines to be discussed in relation to the reclassification of emergency contraceptive pills.
Methods Using electronic database, 1,820 studies written in Korean or English without limitation of the year were reviewed and for analysis, 5 studies were selected, in which emergency contraceptives were provided to adolescents.
Results The advance provision of emergency contraceptives has increased their use and shortened the time it takes to take contraceptive pills after unprotected sex. There was no change in the frequency of engaging in sexual intercourse and unprotected sex or in existing contraceptive behavior, pregnancy rates decreased, but there was no increase in sexually transmitted infection.
Conclusion The results of this study provide objective grounds for the reclassification of emergency contraceptive pills and propose effective interventional programs on contraceptive education, such as on efficacy and side effects of the contraceptive drug and its proper use among the youth who engage in sexual activity, to improve their reproductive health.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Affecting Condom-Use Behaviors Among Female Emerging Adults in South Korea
Jungmin Lee
Psychology Research and Behavior Management.2022; Volume 15: 1771. CrossRef
- Factors Affecting Condom-Use Behaviors Among Female Emerging Adults in South Korea
- 1,671 View
- 11 Download
- 1 Crossref

- An Integrative Review and Meta-analysis of Oncology Nursing Research: 1985-1997.2
- Sun Ock Lim, Eun Yung Hong
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(4):857-870. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.4.857
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study were to describe 12 years of patient-related oncology nursing research in Korea, identifying various nursing interventions, and assessing the effectiveness of the interventions, through analysis and synthesis of the accumulated research papers. One hundred and seventy-nine studies were selected fro this study and these were mostly descriptive in design(69.2%). Of the 179 studies, 25 met the criteria for meta-analytic treatment. Twenty-five experimental studies were found in theses and dissertations(68%), 92% used convenience sample, and the median sample size was 40. Subjects were predominantly in treatment and rehabilitation(76%). Most studies(68%) were not derived from a theory base, with only 8% reporting use of a nursing theory. Results of the meta-analysis are as follows. The effect size of the nursing intervention type was found to be significantly effective. The standardized mean difference ranged from a high positive of 2.55 to a low negative of -0.22. Direct personal nursing intervention method was more effective than indirect group method. Two nursing intervention methods were more effective than one. The greatest effect size was thyxical intervention. The greatest mean effect size was scalp hypothermia technique. Teaching was a frequent intervention after 1990, although a wide range of treatments were studied. Effect size of intervention for symptom management was largest in relieving pain Effective intervention method for relieving anxiety was exercise.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trend Analysis of Theory-based Research Published in Asian Oncology Nursing
Hye-young Lee, Min-Kyeong Kim, Won-jin Seo, Min-jin Lee, Ye-rin Heo, Sanghee Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - A Study on the Knowledge Structure of Cancer Survivors based on Social Network Analysis
Sun Young Kwon, Ka Ryeong Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(1): 50. CrossRef - The analysis of Trends and Contents of Nursing Intervention Research for Cancer Patients in Korea
Myung Sun Hong, Young Hee Yom, Geun Myun Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(4): 247. CrossRef
- Trend Analysis of Theory-based Research Published in Asian Oncology Nursing
- 756 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- An Integrative Review of Oncology Nursing Research: 1980-1998
- Sun Hae Choi, Young Hwa Nam, Eun Jung Ryu, Myung Wha Baek, Dong Hee Suh, Soon Rim Suh, Gui Yun Choi, Kyung Sook Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(3):786-800. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.3.786
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purposes of this study were to describe systematically 18 years of oncology nursing research in Korea and suggest it's direction in future. 149 nursing studies published from 1980 to 1998 were selected for the present study. There were examined the source and the design of study, type of subjects, measurement variables, the intervention outcome of experimental research, and theme of qualitative research. The results were as follows : 1. 121 of 149 studies were composed of master thesis and dissertation of graduate school. There were 55 correlations, 30 descriptions, 19 comparisons, 19 qualitative studies and 2 Q-methods as the type of research design. 2. Cancer patients without describing specified diagnose as subjects' characteristic were 44 of total studies. The others had various diagnoses such as gastric cancer, uterine cancer, breast cancer, leukemia, Iymphoma, colorectal cancer, and lung cancer. According to treatment type. patients receiving chemotherapy were the highest number distribution as 53 of all researches. 3. Most measurement instruments used for research were translated it into Korean that developed by foreigners, such as Zung's depression. Spielberg's anxiety, and Wallston's locus of control. 4. Quality of life was shown the most frequently among correlational researches. the next one was depression the third was hope, and so on. 5. There was the most frequent comparison between cancer and non-cancer patients in comparative researches. It was surveyed those variables as diet habits, risk factors, stressful life events, anxiety and depression and self-care capacity between two groups. 6. The subjects were mostly chemotherapy Patients as 15 of 24 experimental studies. Oral care and education were respectively the highest experimental interventions. 7. Qualitative researches about cancer were reported since 1991. Their themes were illness experience, adaptation process, dying experience, family experience, hope. caring, experience of health behavior, meaning of chemotherapy and experience of cancer survivor. Phenomenologic methodology was designed above 50% of qualitative researches. According to the above findings, cancer research had increased since 1990 and done mostly by descriptive design but a few experimental studies. As recommendations for the future, It is necessary to study the comparison of oncology nursing research internationally. the replication to establish the effect of nursing intervention and the family care of cancer patient.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trend Analysis of Theory-based Research Published in Asian Oncology Nursing
Hye-young Lee, Min-Kyeong Kim, Won-jin Seo, Min-jin Lee, Ye-rin Heo, Sanghee Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - A Study on the Knowledge Structure of Cancer Survivors based on Social Network Analysis
Sun Young Kwon, Ka Ryeong Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(1): 50. CrossRef - Trends in Nursing Research on Children and Adolescents with Cancer in Korea
Sang-Dol Kim, So-Eun Choi, Sun-Hee Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2015; 15(3): 123. CrossRef - Prioritization of Research Topics of Korean Oncology Nurses
Eun-Hyun Lee, Bok Yae Chung, Nami Chun, Pok Ja Oh, Soo-Yeon Cho
Asian Oncology Nursing.2013; 13(4): 295. CrossRef - The analysis of Trends and Contents of Nursing Intervention Research for Cancer Patients in Korea
Myung Sun Hong, Young Hee Yom, Geun Myun Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(4): 247. CrossRef - An Analysis of Articles Related to Smoking and Smoking Cessation of Korean Adolescents
Young Sook Kim, Bok Rae Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(1): 53. CrossRef - Trends in Research on Children with Cancer and Their Families in Korea
Hun Ha Cho, Ji-Won Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(1): 73. CrossRef - Symptom experience in Korean adults with lung cancer
Eui-Geum Oh
Journal of Pain and Symptom Management.2004; 28(2): 133. CrossRef - Research Priorities of Korean Oncology Nurses
Eun-Hyun Lee, Jin-Sun Kim, Bok Yae Chung, Mi Suuk Bok, Byung Eun Song, Sung Wha Kong, Eun-Ok Lee
Cancer Nursing.2003; 26(5): 387. CrossRef
- Trend Analysis of Theory-based Research Published in Asian Oncology Nursing
- 784 View
- 0 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Analysis of Research Papers Published in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing
- Yeon Ok Suh, Jeong Sook Park, Jin Hyang Yang, Hae Won Kim, Min Hyun Suk, Hyun Sook Shin, Hee Jung Jang, Myun Sook Jung, Myung Sill Chung
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(6):1013-1019. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.6.1013
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was to determine the current trend of nursing research as exploring both quantitative and qualitative methodologies, and to provide the explicit direction to improve the quality of published papers. METHODS: Total of 366 articles published between 2004 and 2006 was reviewed using the criteria of analysis. RESULTS: There was more number of quantitative studies than qualitative studies. More studies were conducted with subjects who had health problems, and studies that targeted women and elderly population have been significantly increased. In quantitative methodology, utilization of experimental and quasi-experimental designs has been increased, however descriptive study was dominant as yet. In qualitative methodology, studies using grounded theory and phenomenology were frequently published. It was noted that theoretical framework and rational for sample size were rarely presented in quantitative study. Philosophical position and the process of preparation for study, which guided the research, were not clearly described in qualitative study. CONCLUSION: The findings of this review suggest that published studies have been improved and diversified, however, detailed and clear evaluation tool that assesses study process and method should be developed as a way to further improve the quality of published papers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Non-Pharmacological Interventions to Improve the Sleep of Korean Elderly: A Systematic Review
Yunhee Park, Hyun Jung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(1): 67. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Topics and Trends in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing to Improve Its International Influence
Soyoung Yu, Jeung-Im Kim, Jin-Hee Park, Sun Joo Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh, Ju-Eun Song, YeoJin Im
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(4): 501. CrossRef - Analysis of Theory-applied Research in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration (2007~2016)
Hyunju Ji, Soyun Hong, Yi-Rang Jeong, Kyung Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(2): 130. CrossRef - The Analysis of Research Trends of Elderly in the Dental Hygiene Discipline
Hwa-Soo Goong, Kawoun Seo
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2018; 18(4): 201. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Articles Published in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration for 3 Years (2013~2015): The Application of Text Network Analysis
Tae Wha Lee, Kwang-Ok Park, GyeongAe Seomun, Miyoung Kim, Jee-In Hwang, Soyoung Yu, Seok Hee Jeong, Min Jung, Mikyung Moon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(1): 101. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Papers Published in the Journal of Muscle and Joint Health on Research Trends, Nursing Intervention and Quality Assessment of Intervention Studies
Mi Yang Jeon, Young Eun, Eun Nam Lee, Hye Sook Min, Won-Sook Bak, Mi-Kyung Choi, Rhayun Song, Inok Lee, Hee Kwon Choi, Gyeyoung Shin, Minju Kim, Kyung-Sook Lee, Myung Sook Lee, Kyung-Sook Cho, Ju Sung Kim, Yeo Sook Chung
Journal of muscle and joint health.2016; 23(3): 214. CrossRef - An Analysis of Research Studies Published in the Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing (JKPMHN) based on Knowledge Development Classifications of Nursing: Publication Articles from 2010 to 2014
Ji-Hye Kim, Seog-Bun Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2016; 25(1): 21. CrossRef - Comparison of Domestic and International Research (1992-2011): Intensive Care Nursing Studies
Eun Hee Choi, Eun Hee Jang, Ji Youn Choi, So Jung Lee, Hyo Kuyng Seo, Kyung Sook Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(4): 384. CrossRef - An analysis of research trends related with job stress in nursing
Eun-Yeon Lee, Kyung-Hee Shon
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2015; 6(3): 87. CrossRef - Trend Analysis of Research in the Korean Journal of Adult Nursing for 5 Years (2010~2014): Focused on Usage of Nursing Theories
Nam Kyung Han, Sanghee Kim, Myoung Shin Kim, Jong Gun Kim, Chang Hwan Kim, Seung Hye Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(5): 527. CrossRef - Trend Analysis of Articles Published in the Journal of East-West Nursing Research
Hyun Ji Kim, Hanna Lee, Hyun Su Oh, Yu Jeong Yang, Sung Hee Shin
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2014; 20(2): 167. CrossRef - Trend Analysis of Experimental Research Papers on Community Health Nursing: Based on Researches Published in the Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing, 1989~2012
Chunmi Kim, Seung Joo Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(2): 146. CrossRef - An Integrative Review of Infection Control Research in Korean Nursing Journals
Kyung Mi Kim, Jeong Sil Choi
Asian Nursing Research.2014; 8(2): 128. CrossRef - Trends in Nursing Research in Korea: Research Trends for Studies Published from the Inaugural Issue to 2010 in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and the Journals Published by Member Societies under Korean Academy of Nursing Science
Myoung-Ae Choe, Nam Cho Kim, Kyung Mi Kim, Sung Jae Kim, Kyung Sook Park, Young Soon Byeon, Sung Rae Shin, Soo Yang, Kyung Sook Lee, Eun Hyun Lee, In Sook Lee, Tae Wha Lee, Myung Ok Cho, Jin Hak Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(5): 484. CrossRef - Current Status and Challenges of Research Methology for Health Promotion Research: Focusing on Research Funded by the Korea Health Promotion Foundation, 2005-2011
Ji-Young An, Kwang Kee Kim, Jung JeKarl, Hyunjung Moon, Sun Kyung Cha, Eunha Jeong
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(5): 47. CrossRef - Domestic Research Trends in Health Education
Soo Ja Kwon
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(3): 75. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Articles Published in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration for 3 Years (2010~2012)
Keum Seong Jang, Bok Nam Kim, Yun Min Kim, Jung Sook Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(5): 679. CrossRef - Problems and Prospects of Nursing Research on Job Stress in Korea
Wonsup Cho, Myoungsoon You
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(1): 63. CrossRef - Trends in Research Studies Published in Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing: 2009-2011
Kyung-Hee Kim, Sung-Ok Chang, Hyun-Sook Kang, Keum-Soon Kim, Jong-Im Kim, Hwa-Soon Kim, Jin-Hee Park, Mi-Ran Eom, Jong-Soon Won, Mi-Sun Youn, Og-Cheol Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(3): 383. CrossRef - Analysis of Quantitative Research Published by Korean Journal of Adult Nursing (1989~2011)
Young-Kyeong Kim, Sun-Kyung Hwang, In-Ja Kim, Ju-Sung Kim, Hee-Young Oh, Jong-Kyung Lee, Eun-Sook Jung, Gui-Yun Choi, Ja-Yun Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(1): 85. CrossRef - Analysis of Trends and Contents of Nursing Doctoral Dissertations in Korea
Kwang-Ja Lee, Younhee Kang, Mee Ock Gu, Kyunghee Kim, Oksoo Kim, Yeon-Ok Suh, Eunyoung Suh, Soo Yang, Eun-Hyun Lee, Ja Hyung Lee, Myoung-Ae Choe, Yang Sook Hah
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(2): 302. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Trends in Papers Published in the Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing (2005-2009)
Jin-Sun Kim, Ji-Young Lim, In-Soo Kwon, Tae-Im Kim, Ho-Ran Park, Hae-Young Ahn, Soo-Yeon Lee, Hyang-Mi Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2011; 17(2): 100. CrossRef - A Social Network Analysis of Research Topics in Korean Nursing Science
Soo-Kyoung Lee, Senator Jeong, Hong-Gee Kim, Young-Hee Yom
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(5): 623. CrossRef - Trends of Occupational Health Nursing Research in Korea
Young-Im Kim, Bok-Im Lee
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2011; 20(2): 195. CrossRef - Analysis of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration for 3 Years (2007-2009)
Jong Kyung Kim, Myun Sook Jung, Keum Seong Jang, Jinhyun Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Haejung Lee, Young Mee Kim, Se Young Kim, Eun Jun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(4): 517. CrossRef - The Analysis on Published Research in the Journal of Muscle and Joint Health
Nan-Young Lim, Jong-Im Kim, Eun-Nam Lee, Kyung-Sook Lee, In-Ok Lee, Kyung-Sook Cho, Won-Sook Bak, Yoon-Kyoung Lee, Hyun-Sook Kang, Keum-Soon Kim, Mi-Young Chon
Journal of muscle and joint health.2010; 17(1): 79. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Papers Published in the Journal of the Korean Academy of Nursing-Focused on Research Trends, Intervention Studies, and Level of Evidence in the Research
Hyun-Sook Shin, Myung-Sun Hyun, Mi-Ok Ku, Myung-Ok Cho, Sook-Young Kim, Jea-Sim Jeong, Geum-Hee Jeong, Gyeong-Ae Seomoon, Youn-Jung Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(1): 139. CrossRef
- Effects of Non-Pharmacological Interventions to Improve the Sleep of Korean Elderly: A Systematic Review
- 1,117 View
- 1 Download
- 27 Crossref

- Conversation Analysis for Improving Nursing Communication
- Myungsun Yi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(5):772-780. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.5.772
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Nursing communication has become more important than ever before because quality of nursing services largely depends on the quality of communication in a very competitive health care environment. This article was to introduce ways to improve nursing communication using conversation analysis.
Methods This was a review study on conversation analysis, critically examining previous studies in nursing communication and interpersonal relationships.
Results This study provided theoretical backgrounds and basic assumptions of conversation analysis which was influenced by ethnomethodology, phenomenology, and sociolinguistic. In addition, the characteristics and analysis methods of conversation analysis were illustrated in detail. Lastly, how conversation analysis could help improve communication was shown, by examining researches using conversation analysis not only for ordinary conversations but also for extraordinary or difficult conversations such as conversations between patients with dementia and their professional nurses.
Conclusion Conversation analysis can help in improving nursing communication by providing various structures and patterns as well as prototypes of conversation, and by suggesting specific problems and problem-solving strategies in communication.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of nurses’ communication styles, nurse-mother partnerships, and mothers’ anxiety on coping of hospitalized children’s mothers
Yonghee Kim, Areum Choi, Insun Jang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 170. CrossRef - The Validity and Reliability of Nursing Assessment Communication-Competence Scale for Clinical Nurses
Hyojin Kim, Heeyoung Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(1): 78. CrossRef - Influence of Communication Competence and Communication Style on the Nurse-Parent Partnership in Pediatric Nurses
Hyun Jin Cho, Hyoung Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(2): 170. CrossRef - Effects of Customer Orientation, Belief of Patient Activation and Professional Self-concept on Caring Behaviors of Nurses in Comprehensive Nursing Care Units
Ji Eun Jeon, Eun Hee Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(3): 344. CrossRef - Educational Needs of Communication among Nursing Students
Min Young Jung, Jeongyee Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(1): 91. CrossRef - The Relation between Interpersonal Attitude and Communication Competence of New Visiting Nurses in Community Health Center
Seung Joo Lim, Eun A Park
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2014; 23(2): 115. CrossRef - Effect of Perceived Nurse's Communication Style on Admitted Children Mother's Stress and Coping
In Sook Park, Jaewoo Oh, Yang-Sin Kim
Journal of Digital Convergence.2014; 12(6): 365. CrossRef - Occupational Health Nurses' Role Experiences
Kyung-Ja June, Hea-Ju Joo, Young-Mi Kim
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2011; 20(3): 250. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nurses' Competency in Nurse-Patient Communication about Medications: Conversational Analysis Approach
Haeng-Mi Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of Conversation between Elderly Patients with Dementia and Nurses: Focusing on Structure and Sequential Patterns
Myungsun Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(4): 166. CrossRef
- The effects of nurses’ communication styles, nurse-mother partnerships, and mothers’ anxiety on coping of hospitalized children’s mothers
- 919 View
- 10 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Associations between Smoking and Depression in Adolescence: An Integrative Review
- Sunhee Park, Dan Romer
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(2):227-241. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.2.227
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Although research has established the existence of an association between smoking and depression among adolescents, researchers have not reached consensus on the nature of the association.
Objectives The purpose of this paper is to review the literature, to examine the nature of the relationship between smoking and depression in adolescence, and to suggest future research directions.
Method A literature search was conducted from the following six databases: (a) Ovid MEDLINE, (b) CINAHL, (c) PubMed Unrestricted, (d) PsycINFO, (e) ERIC, and (f) Sociological Abstracts. The combinations of the words, “depression,” “smoking,” “tobacco,” “adolescent,” and “teen” were used for keyword searches to find relevant articles.
Results In 47 of 57 studies, significant associations between smoking and depression were found. However, these significant relationships may either be spurious or unrelated to depression because a substantial number of studies did not adjust for confounders or did not use validated instruments to measure depression. Additionally, if the relationship is causal, its direction remains controversial. Five relationships have been suggested: (a) Depression causes smoking, (b) smoking causes depression, (c) there is a bidirectional relationship between smoking and depression, (d) smoking and depression occur due to confounders, and (e) subgroups with different relationships between the two conditions exist.
Conclusions It is necessary to further explore the relationship between smoking and depression. Future research should consider the need for: (a) longitudinal research designs, (b) more accurate measurement of depression, and (c) the control of confounders between smoking and depression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Use of Tobacco Products and Suicide Attempts Among Elementary School–Aged Children
Phil H. Lee, Brenden Tervo-Clemmens, Richard T. Liu, Maia B. Gersten, Jae-Yoon Jung, Amy C. Janes, Jodi Gilman
JAMA Network Open.2024; 7(2): e240376. CrossRef - Perceived Occupational Noise Exposure and Depression in Young Finnish Adults
Marja Heinonen-Guzejev, Alyce M. Whipp, Zhiyang Wang, Anu Ranjit, Teemu Palviainen, Irene van Kamp, Jaakko Kaprio
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(6): 4850. CrossRef - Risk Factors of Relapse After Smoking Cessation: Results in China Family Panel Studies From 2010 to 2018
Naifan Hu, Zhenfan Yu, Yurun Du, Jiangping Li
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of heated tobacco product use and secondhand smoke exposure
with suicidal ideation, suicide plans and suicide attempts
among Korean adolescents: A 2019 national survey
Soyoon Park, Kang-Sook Lee
Tobacco Induced Diseases.2021; 19(September): 1. CrossRef - Association of Environmental tobacco smoke exposure with depression among non-smoking adults
Akinkunmi Paul Okekunle, Jeffery Osahon Asowata, Jung Eun Lee, Onoja Matthew Akpa
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between the Location of Secondhand Smoke Exposure and Depressive Symptoms among South Korean Adolescents
Bich Na Jang, Wonjeong Jeong, Soo Hyun Kang, Sung-In Jang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(14): 5116. CrossRef - Predictive Association of Smoking with Depressive Symptoms: a Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Twins
Anu Ranjit, Jadwiga Buchwald, Antti Latvala, Kauko Heikkilä, Annamari Tuulio-Henriksson, Richard J. Rose, Jaakko Kaprio, Tellervo Korhonen
Prevention Science.2019; 20(7): 1021. CrossRef - How Health Behaviour Affects Depression Across Different Age and Gender Cohorts in India?
Reshmi Sengupta
SSRN Electronic Journal.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Smoking, heavy drinking, and depression among U.S. middle-aged and older adults
Ruopeng An, Xiaoling Xiang
Preventive Medicine.2015; 81: 295. CrossRef - The association between smoking and depression from adolescence to adulthood
Tore Tjora, Jørn Hetland, Leif Edvard Aarø, Bente Wold, Nora Wiium, Simon Øverland
Addiction.2014; 109(6): 1022. CrossRef - Does Smoking Initiation in Adolescence Increase Risk for Depression Across the Lifespan?
Sunhee Park, Daniel Romer, Sungwon Lim
Journal of Addictions Nursing.2013; 24(3): 142. CrossRef - Is depression associated with health risk-related behaviour clusters in adults?
P. Verger, C. Lions, B. Ventelou
The European Journal of Public Health.2009; 19(6): 618. CrossRef - The Causal Association Between Smoking and Depression Among South Korean Adolescents
Sunhee Park
Journal of Addictions Nursing.2009; 20(2): 93. CrossRef - Predictors of the Transition From Experimental to Daily Smoking Among Adolescents in the United States
Sunhee Park, Terri E. Weaver, Daniel Romer
Journal for Specialists in Pediatric Nursing.2009; 14(2): 102. CrossRef - La dépression co-morbide favorise-t-elle certains comportements à risque chez les personnes ayant des problèmes de poids?
Pierre Verger, Sophie Dizière, Aurélie Bocquier, Bruno Ventelou
Revue française des affaires sociales.2008; (1): 49. CrossRef
- Use of Tobacco Products and Suicide Attempts Among Elementary School–Aged Children
- 938 View
- 3 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Effects of Breastfeeding Interventions on Breastfeeding Rates at 1, 3 and 6 Months Postpartum: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Seol Hui Park, Seang Ryu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(6):713-730. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.6.713
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis designed to evaluate the effects of breastfeeding intervention on breastfeeding rates.
Methods Based on the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA), a systematic search was conducted using eight core electronic databases and other sources including gray literature from January 9 to 19, 2017. Two reviewers independently select the studies and assessed methodological risk of bias of studies using the Cochrane criteria. The topics of breastfeeding interventions were analyzed using descriptive analysis and the effects of intervention were meta-analyzed using the Review Manager 5.2 software.
Results A total of 16 studies were included in the review and 15 were included for meta-analysis. The most frequently used intervention topics were the importance of good latch-on and frequency of feeding and determining adequate intake followed. The pooled total effect of breastfeeding intervention was 1.08 (95% CI 1.03~1.13). In the subgroup analysis, neither pre-nor post-childbirth intervention was effective on the breastfeeding rates at 1, 3, and 6 months, and neither group nor individual interventions had an effect. Only the 1 month breastfeeding rate was found to be affected by the individual intervention with the persistent strategies 1.21 (95% CI 1.04~1.40).
Conclusion Effective breastfeeding interventions are needed to help the mother to start breastfeeding after childbirth and continue for at least six months. It should be programmed such that individuals can acquire information and specific breastfeeding skills. After returning home, there should be continuous support strategies for breastfeeding as well as managing various difficulties related to childcare.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond Intentions: The Breastfeeding Intention-Practice Gap in Tunisia- A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Initiation and Continuation among Post-Partum Women
Narjes karmous, Omar Oualha, Anouar Drira, Abdelwaheb Masmoudi, Badreddine Bouguerra, Abdennour Karmous
F1000Research.2025; 14: 881. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Breastfeeding Duration in Tunisia: A Cross-Sectional Analysis Highlighting the Role of Early Initiation
Narjes karmous, Omar Oualha, Anouar Drira, Abdelwaheb Masmoudi, Badreddine Bouguerra, Abdennour Karmous
F1000Research.2025; 14: 881. CrossRef - Postpartum Breastfeeding Practices and Attitudes in Parents: A Randomized Study to Evaluate the Effects of Individual and Group Breastfeeding Education of Mothers and Fathers
Yeşim Yeşil, Hafize Öztürk Can
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Social policies and breastfeeding duration in South Korea: A survival analysis of the national data
Jung Hee Yeo, Eun-Young Kim
Midwifery.2022; 107: 103282. CrossRef - Information Resource Network Analysis of Factors Influencing Breastfeeding Planning and Duration
Eunyoung Lee, Insook Cho, Seong Jin Cho, Eunju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(2): 232. CrossRef - A Structural Model for Breastfeeding Behavior of First-Time Mothers
Seol Hui Park, Seang Ryu
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2021; 25(3): 184. CrossRef - The Relationship of Previous Breastfeeding Experiences and Factors Affecting Breastfeeding Rates: A Follow-Up Study
Jun-Yan Li, Yi Huang, Hao-Qi Liu, Jing Xu, Lu Li, Sharon R. Redding, Yan-Qiong Ouyang
Breastfeeding Medicine.2020; 15(12): 789. CrossRef - Effects of galactagogue herbal tea containing Chrysanthemum indicum as the main component on milk production in postpartum rats
Jiyoung Choi, Yunjung Lee, Sunuk Choi, Eunju Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(5): 445. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta-analysis of interventions incorporating behaviour change techniques to promote breastfeeding among postpartum women
Angelos P. Kassianos, Emma Ward, Antonio Rojas-Garcia, Allison Kurti, Fiona C. Mitchell, Dian Nostikasari, Jamie Payton, Julian Pascal-Saadi, Claire Adams Spears, Caitlin Notley
Health Psychology Review.2019; 13(3): 344. CrossRef
- Beyond Intentions: The Breastfeeding Intention-Practice Gap in Tunisia- A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Initiation and Continuation among Post-Partum Women
- 2,458 View
- 20 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Effects of Aromatherapy on Menopausal Symptoms, Perceived Stress and Depression in Middle-aged Women: A Systematic Review
- Shinmi Kim, Ji-Ah Song, Mi-Eun Kim, Myung-Haeng Hur
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(5):619-629. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.5.619
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was a systematic review to evaluate the effects of aromatherapy on menopausal symptoms, perceived stress and depression in middle aged-women.
Methods Eight databases were searched from their inception September 8, 2015. Two reviewers independently performed the selection of the studies, data abstraction and validations. The risk of bias was assessed using Cochrane criteria. For analysis of the data, a meta-analysis of the studies was performed.
Results From the electronic databases, 73 articles were selected, and 19 removed due to duplication. After two reviewers read the abstracts of 54 studies, 34 studies were selected. Complete papers for 34 original articles were read and, 12 studies which met selection criteria were reviewed and the effects of aromatherapy on menopausal symptoms, stress and depression analyzed using meta-analysis with RevMan. In the 2 studies which included Randomized Controlled Trials testing of aromatherapy on menopausal symptoms and comparison of control and placebo groups were done. Aromatherapy massage was favorably effective in reducing the menopausal symptoms compared to the control group (n=118, MD=-6.33; 95% CI -11.51 to -1.15), and compared to the placebo group (n=117, MD=-4.14; 95% CI -7.63 to -0.64). Also aromatherapy was effective in reducing stress (n=72, SMD=-0.64; 95% CI -1.12 to -0.17) and depression (n=158, MD=-5.63; 95% CI -10.04 to -1.22).
Conclusion There is limited evidence suggesting that aromatherapy for middle-aged women may be effective in controlling menopausal symptoms, perceived stress and depression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of aromatherapy on pain in individuals with diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Mi-Kyoung Cho, Mi Young Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2024; 26(2): 71. CrossRef - Examining the Health-Related Needs of Females during Menopause: A Systematic Review Study
Masoumeh Rostami-Moez, Seyedeh Zahra Masoumi, Marzieh Otogara, Farhad Farahani, Shohreh Alimohammadi, Khodayar Oshvandi
Journal of Menopausal Medicine.2023; 29(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of Aromatherapy with Essential oil of Lavandula Angustifolia Mill- Citrus Bergamia and Mindfulness-Based Intervention on Sexual Function, Anxiety, and Depression in Postmenopausal Women
Mandana Mojtehedi, Hanieh Salehi-Pourmehr, Alireza Ostadrahimi, Solmaz Asnaashari, Khalil Esmaeilpour, Azizeh Farshbaf-Khalili
Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research.2022; 27(5): 392. CrossRef - Aromatherapy for Managing Menopausal Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials
Hye Won Lee, Lin Ang, Jiae Choi, Myeong Soo Lee
The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine.2021; 27(10): 813. CrossRef - Effects of the Healing Beats Program among University Students after Exposure to a Source of Psychological Stress: A Randomized Control Trial
Jiah Song, Wonjong Kim, Iklyul Bae
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(21): 11716. CrossRef - Nano-Aromatic Drugs Based on Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles and Bergamot Essential Oil for Anti-Depression
Xiao-Hong Yang, Huan Peng, Qiu-Lian Hao, Jian-Ze Wang, Zhi-Guo Lu, Yun-Wei Niu, Zuo-Bing Xiao, Xin Zhang
Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology.2021; 17(6): 1242. CrossRef - The Effects of Providing Lavender Inhalation Therapy on Anxiety and Alleviation of Pain before Burn Dressings
Kyung Ja Kim, Jihyun Kim, Gye Seon Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(1): 29. CrossRef - EEG Revealed That Fragrances Positively Affect Menopausal Symptoms in Mid-life Women
Sun Ae Moon, Jisub Bae, Kwangsu Kim, Si Young Cho, Gusang Kwon, Ran Lee, Seung Ho Ko, Soyeon Lim, Cheil Moon
Experimental Neurobiology.2020; 29(5): 389. CrossRef - Combination of 3-Dimensional Virtual Reality and Hands-On Aromatherapy in Improving Institutionalized Older Adults’ Psychological Health: Quasi-Experimental Study
Vivian Ya-Wen Cheng, Chiu-Mieh Huang, Jung-Yu Liao, Hsiao-Pei Hsu, Shih-Wen Wang, Su-Fei Huang, Jong-Long Guo
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2020; 22(7): e17096. CrossRef - How Strong is the Evidence for the Anxiolytic Efficacy of Lavender?: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Hyun-Ju Kang, Eun Sook Nam, Yongmi Lee, Myoungsuk Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2019; 13(5): 295. CrossRef - Effect of aromatherapy interventions on hemodialysis complications: A systematic review
Salehoddin Bouya, Sudabeh Ahmadidarehsima, Mahin Badakhsh, Abbas Balouchi, Maryam koochakzai
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2018; 32: 130. CrossRef - Effects of Aroma Inhalation on Stress, Fatigue and Depression among Nurses Working in Intensive Care Unit
Eun Young Jung, Ji-hyeun Song
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2018; 16(3): 321. CrossRef - Aromatherapy for managing menopausal symptoms
Jiae Choi, Hye Won Lee, Ju Ah Lee, Hyun-Ja Lim, Myeong Soo Lee
Medicine.2018; 97(6): e9792. CrossRef - Effect of Aromatherapy on the Treatment of Psychological Symptoms in Postmenopausal and Elderly Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Masoudeh Babakhanian, Masumeh Ghazanfarpour, Leila Kargarfard, Nasibeh Roozbeh, Leili Darvish, Talat Khadivzadeh, Fatemeh Rajab Dizavandi
Journal of Menopausal Medicine.2018; 24(2): 127. CrossRef - Behavioral Characteristics and Cardiovascular Disease Risks Associated With Insomnia and Sleep Quality Among Middle‐Aged Women in South Korea
Ok Kyung Ham, Jinyoung Kim, Bo Gyeong Lee, Eunju Choi
Research in Nursing & Health.2017; 40(3): 206. CrossRef
- The effect of aromatherapy on pain in individuals with diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- 2,230 View
- 53 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Correlates of Cognitive Impairment of Rheumatic Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- JinA Mo, JiSuk Park, HyunSoo Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(1):1-18. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to synthesis the results of research on relationships of cognitive impairment with multi-dimensional correlates of rheumatic disease through a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.
Methods For the study purpose, 23 studies were selected through a systematic process of searching the literature.
Results The study results showed that among general characteristics, age and education were the variables having a significant relationship with cognitive impairment. Among health risk factors, obesity appeared to have a significant positive relationship with cognitive impairment. For past history, diabetes and hypertension were shown to have a significant positive relationship with cognitive impairment. It was noted also that aPL, one of the physiological factor, had significant association with cognitive impairment. None of the medication related factors had a significant relationship with cognitive impairment. Results showed that among disease related factors, disease activity had the highest relationship with cognitive impairment. Depression, among psychological factors, was the only variable having a significant relationship with cognitive impairment.
Conclusion The findings indicate that the variables strongly impacting on cognitive impairment in rheumatic disease are depression and disease activity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of Cognitive Impairment among Iraqi Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
Zahraa Hussein Altemimi, Faiq I. Gorial
Medical Journal of Babylon.2024; 21(2): 324. CrossRef - Temporal Changes in Metabolic Syndrome Indices and Factors of Metabolic Syndrome Development in Patients With Rheumatic Disease
HyunSoo Oh, JiSuk Park, JiYoung Kim, SungKyung Jang, Yeona Ryu, YeoJu Jeong, SuYeon Kwon, SoHyun Suh, HaYoung Lee, DaHee Choi, HanNa Lee, GaWon Cho, WhaSook Seo
Orthopaedic Nursing.2023; 42(4): 251. CrossRef - Correlates of cognitive impairment in patients with chronic kidney failure on haemodialysis: Systematic review and meta‐analysis
HyunSoo Oh, JinA Mo, WhaSook Seo
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2019; 75(5): 962. CrossRef - Comparisons of the Incidence and Critical Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome in Patients With a Rheumatic Disease or Gout
HyunSoo Oh, JiSuk Park, YoungSub Yoon, WhaSook Seo
Orthopaedic Nursing.2019; 38(3): 201. CrossRef
- Prevalence of Cognitive Impairment among Iraqi Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- 1,169 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of Family Support Programs for Caregivers of People with Dementia - Caregiving Burden, Depression, and Stress: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Seyeon Park, Myonghwa Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(5):627-640. Published online October 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.5.627
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The objective of this systematic review was to assess the effects of family support programs on caregiving burden, depression, and stress in family caregivers of people with dementia.
Methods A literature search was conducted of electronic databases to identify randomized controlled studies with family support programs done between 2000 and 2014. Studies published in English and/or Korean were included for the analysis with search strategies adapted from the Cochrane Dementia and Cognitive Improvement Group. Studies were rated for quality assessment by two independent reviewers using the appraisal checklist developed by Cochrane Reviews and Dissemination. Of 8,334 articles identified in the literature search, full texts of 76 articles that met the inclusion criteria were reviewed and 38 were found to include relevant outcomes.
Results Results from selected studies were pooled in statistical meta-analysis using Review Manager Software and heterogeneity between combined studies was assessed using the Chi-square test. Meta-analysis showed that the effect sizes of family caregiver support programs were small to medium for categories of caregiving burden (Hedge's g= - 0.17, 95% CI= - 0.30~ - 0.04), depression (Hedge's g= - 0.30, 95% CI= - 0.40~ - 0.20), and stress (Hedge's g= - 0.39, 95% CI= - 0.52~ - 0.25).
Conclusion The review results indicate that a support programs can assist family care-givers in reducing their psycho-emotional distress.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of the presence of a family member with dementia on the prevalence of depression: a comparison based on household income level
Min Hui Moon, Suk Woong Kang, Min Hyeok Choi
International Journal for Equity in Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Reitman Centre CARERS program for supporting dementia family caregivers: a pre–post intervention study
Joel Sadavoy, Sima Sajedinejad, Mary Chiu
International Psychogeriatrics.2022; 34(9): 827. CrossRef - Caregiver Burden among Caregivers of Patients with Mental Illness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Choy Qing Cham, Norhayati Ibrahim, Ching Sin Siau, Clarisse Roswini Kalaman, Meng Chuan Ho, Amira Najiha Yahya, Uma Visvalingam, Samsilah Roslan, Fairuz Nazri Abd Rahman, Kai Wei Lee
Healthcare.2022; 10(12): 2423. CrossRef - Evaluating the Effectiveness of Community-Based Dementia Caregiver Intervention on Caregiving Burden, Depression, and Attitude Toward Dementia: A Quasi‐experimental Study
Su Jung Lee, Hyun-Ju Seo, IL Han Choo, Seong Min Kim, Jeong Min Park, Eun-Young Yang, Yu Mi Choi
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2022; Volume 17: 937. CrossRef - Loss and Grief in the Context of Dementia Caregiving
Olimpia Paun, Dimitra Loukissa, Marianne G. Chirica, Horace M. Nowell
Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services.2022; 60(10): 7. CrossRef - Korean Family Caregivers' Experiences With Managing Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia: Keeping Harmony in Daily Life
Jiyeon Kim, Jun-Ah Song, Sua Jung, Hongjin Cheon, Jiyeon Kim
Research in Gerontological Nursing.2022; 15(3): 141. CrossRef - Health Promotion Behavior among Older Korean Family Caregivers of People with Dementia
Aram Cho, Chiyoung Cha
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4123. CrossRef - A systematic review of interventions for family caregivers of the elderly with dementia in Korea
Seonghee Jeong, Jeonghae Hwang, Doonam Oh
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 306. CrossRef - An empowerment program for family caregivers of people with dementia
Heun Keung Yoon, Gwang Suk Kim
Public Health Nursing.2020; 37(2): 222. CrossRef - Horticultural Therapy Programs Enhancing Quality of Life and Reducing Depression and Burden for Caregivers of Elderly with Dementia
Yong Hyun Kim, Chul Soo Park, Hwa-Ok Bae, Eun Ji Lim, Kyung Heui Kang, Euy Sun Lee, Su Hyeon Jo, Moo Ryong Huh
Journal of People, Plants, and Environment.2020; 23(3): 305. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study of the Research on Caregiver Depression: Using Bibliometrics and LDA Topic Modeling
Soyoung Choi, JooYoung Seo
Issues in Mental Health Nursing.2020; 41(7): 592. CrossRef - The Effects of a Support Program for Family Caregivers of Elderly with Dementia on Empowerment and Attitudes toward Dementia
So Yoon Kim, Seonghee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(1): 103. CrossRef - Behavioural Changes in Dementia and their Impact on Professional Caregivers: A Grounded Theory Approach
Katie Appleton, Antonina Pereira
Dementia.2019; 18(4): 1479. CrossRef - The Effects of Group Occupational Therapy Including Education Programs on Depression, Anxiety, and Participation of Activities in People With Dementia
Min-Joo Ham, Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational Therapy.2018; 26(4): 97. CrossRef - Shifting of Centricity: Qualitative Meta Synthetic Approach on Caring Experience of Family Members of Patients with Dementia
Young Mi Ryu, Mi Yu, Seieun Oh, Haeyoung Lee, Haejin Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(5): 601. CrossRef - Effects of a Dementia Family Education Program for Dementia Recognition, Burden, and Depression in Caregivers of Elders with Dementia
Sun-A Lee, Hee-Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2017; 26(1): 14. CrossRef - Hermeneutic Phenomenological Study on Caring Experience of Spouses of Elderly People with Dementia at Home
Hye-Young Jang, Myungsun Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(3): 367. CrossRef - The voices of family caregivers of seniors with chronic conditions: a window into their experience using a qualitative design
Suzette Brémault-Phillips, Jasneet Parmar, Melissa Johnson, Arlene Huhn, Anna Mann, Victoria Tian, Lori-Ann R. Sacrey
SpringerPlus.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Conceptualization of an evidence-based smartphone innovation for caregivers and persons living with dementia
Melvyn W.B. Zhang, Sally Chan, Olivia Wynne, Sarah Jeong, Sharyn Hunter, Amada Wilson, Roger C.M. Ho
Technology and Health Care.2016; 24(5): 769. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Caregiving Satisfaction among Family Caregivers of Patients with Dementia
Yunhee Lee, Myonghwa Park
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2016; 18(3): 117. CrossRef
- Impact of the presence of a family member with dementia on the prevalence of depression: a comparison based on household income level
- 2,196 View
- 34 Download
- 20 Crossref

- A Methodological Quality Assessment of South Korean Nursing Research using Structural Equation Modeling in South Korea
- Jung-Hee Kim, Sujin Shin, Jin-Hwa Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(2):159-168. Published online April 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.2.159
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the methodological quality of nursing studies using structural equation modeling in Korea.
Methods Databases of KISS, DBPIA, and National Assembly Library up to March 2014 were searched using the MeSH terms 'nursing', 'structure', 'model'. A total of 152 studies were screened. After removal of duplicates and non-relevant titles, 61 papers were read in full.
Results Of the sixty-one articles retrieved, 14 studies were published between 1992 and 2000, 27, between 2001 and 2010, and 20, between 2011 and March 2014. The methodological quality of the review examined varied considerably.
Conclusion The findings of this study suggest that more rigorous research is necessary to address theoretical identification, two indicator rule, distribution of sample, treatment of missing values, mediator effect, discriminant validity, convergent validity, post hoc model modification, equivalent models issues, and alternative models issues should be undergone. Further research with robust consistent methodological study designs from model identification to model respecification is needed to improve the validity of the research.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations between prebriefing quality and learning satisfaction in simulation-based learning among nursing students: A structural equation model
Young Sook Roh, Young Ju Kim, Yoon Hee Na, Mi Kang Kim, Eun Jung Kim
Nurse Education Today.2026; : 107036. CrossRef - Influencing factors and learning outcomes in virtual simulation learning experiences: A structural equation modeling
Young Sook Roh, Kie In Jang, Elinda Ai Lim Lee
Nurse Education Today.2025; 150: 106681. CrossRef - A Review of Adolescents' Digital Self-Efficacy: Conceptualization, Measurement, Impacts, Influencing Factors, and Future Directions
Qing Tan, Wenzhuo Wu, Siying An
Journal of Current Social Issues Studies.2025; 2(5): 306. CrossRef - Translation and psychometric validation of the Korean version of the academic nurse self-efficacy scale for Korean bachelor-level nursing students
Eunkyung Lee, Jin-Hwa Park
Frontiers of Nursing.2024; 11(2): 209. CrossRef - Determining food tourism consumption of wild mushrooms in Yunnan Provence, China: A projection-pursuit approach
Jinping Lin, Bowen Zhang, Jiajia Feng, Zeyu Yi, Hao Zhang, Man Luo, Zhujun Zhong, Fei Zhao
Heliyon.2023; 9(3): e14638. CrossRef - A Structural Equation Model for Posttraumatic Growth among Cured Patients with COVID-19
Soo Young An, Heejung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(3): 309. CrossRef - Quality of Life Structural Equation Model for Patients With Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Juyeon Oh, Jung A. Kim
Rehabilitation Nursing Journal.2021; 46(5): 253. CrossRef - Predictive Model for Quality of Life of the Older Men Living Alone
Su Jin Kim, Gyeong-Suk Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(6): 799. CrossRef - A Validation Study of the Korean Version of the Jefferson Empathy Scale for Health Professionals for Korean Nurses
Hye-Ran Ryu, Kyung-Sook Bang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(2): 207. CrossRef - Effect of universal primer on shear bond strength between resin cement and restorative materials
Nahong Kim, June-Sung Shim, Hong-Suk Moon, Keun-Woo Lee
The Journal of Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.2012; 50(2): 112. CrossRef
- Associations between prebriefing quality and learning satisfaction in simulation-based learning among nursing students: A structural equation model
- 1,289 View
- 8 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Dysphagia Screening Measures for Use in Nursing Homes: A Systematic Review
- Yeon-Hwan Park, Hwal Lan Bang, Hae-Ra Han, Hee-Kyung Chang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(1):1-13. Published online February 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the psychometric quality and feasibility of measurements for screening dysphagia in older adults to identify the 'right tool' for nurses to use in nursing homes.
Methods A systematic review was done. Electronic databases were searched for studies related to dysphagia screening measurements. A checklist was used to evaluate the psychometric quality and applicability. Tools were evaluated for feasible incorporation into routine care by nurses.
Results 29 tools from 31 studies were identified. Dysphagia screening tools with an acceptable validity and reliability had sensitivity between 68% and 100% and specificity between 52% and 100%. The Gugging Swallowing Screen (GUSS) and the Standardized Swallowing Assessment (SSA) were the tools with high psychometric quality, especially with high sensitivity, that nurses could perform feasibly to identify the risk and to grade the severity of dysphagia and aspiration of nursing home residents.
Conclusion Results show that GUSS and SSA are reliable and sensitive tools for screening dysphagia which nurses can use in nursing homes. Further research is needed to examine feasibility of screening with identified tools, and also, to establish effective and standardized protocols for these tools so they can be effectively incorporated into routine care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- eTWST: An Extension to the Timed Water Swallow Test for Increased Dysphagia Screening Accuracy
Louise Brage, Fredrik Nylén, Patricia Hägglund, Thorbjörn Holmlund
Dysphagia.2025; 40(4): 801. CrossRef - Evaluation of the performance of screening tools for dysphagia in older adults: A diagnostic meta-analysis
Lingli Zhang, Ran Hou, Lin Liu, Yan Liu, Qinqin Yu
Geriatric Nursing.2025; 61: 629. CrossRef - Effect of artificial intelligence-based video-game system on dysphagia in patients with stroke: A randomized controlled trial
Bohan Zhang, Ka Po Wong, Mingyue Liu, Vivian Hui, Cai Guo, Zihan Liu, Yue Liu, Qian Xiao, Jing Qin
Clinical Nutrition.2025; 45: 81. CrossRef - Progress on aspiration assessment methods for patients after esophageal cancer surgery in early: A review
Yushuang Su, Yan Li, Zhongbin Chen, Hong Gao, Yaxie He, Xiaohua Li, Xiaying Zeng, Wei Lan, Qin Yang
Medicine.2025; 104(3): e41214. CrossRef - Reliability and validity of the Standardized swallowing assessment among community-dwelling older adults in China
Jing Wang, Caixia Chen, Yuzhen Qin, Jing Zeng, Chunhua Zhang, Liugen Wang, Heping Li, Xi Zeng
Annals of Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Occurrence of impaired swallowing ability and change over a year in older adults living in nursing homes
Ida Crossler, Clara Shrestha Jensen, Karin Eriksson, Lisa Tuomi
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental Factors Associated With Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Institutionalised Older Adults: A Systematic Review
Raquel Soncini de Morais, Juliana Balbinot Hilgert, Fernando Neves Hugo, Rafaela Soares Rech
Gerodontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Feasibility of Oral Function Evaluation According to Dementia Severity in Older Adults with Alzheimer’s Disease
Maki Shirobe, Ayako Edahiro, Keiko Motokawa, Shiho Morishita, Yoshiko Motohashi, Chiaki Matsubara, Masanori Iwasaki, Yutaka Watanabe, Hirohiko Hirano
Nutrients.2024; 16(7): 992. CrossRef - Research trends on dysphagia among Korean older adults in long-term care facilities: A scoping review
Seyoung Cho, Dukyoo Jung, Jisung Park
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(2): 134. CrossRef - Appropriate volumes of water for non-invasive swallowing assessments of nursing home residents: A descriptive correlational study
Meng Rung Tsai, Wann Yun Shieh, Hsiu Hsin Tsai, Yea Ing Lotus Shyu, Kuo Hsuan Chang, Fur Hsing Wen, Chia Yih Liu
Heliyon.2024; 10(17): e37340. CrossRef - Aspiration pneumonia in nursing literature—a mapping review
Dominika Lisiecka, Áine Kearns, William Evans, Dawn Farrell
Frontiers in Rehabilitation Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting dysphagia in long-term care facility residents
Jinmei Liu, Mingshu Liao, Hui Yang, Xiaofang Chen, Yang Peng, Jing Zeng
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2023; 35(6): 1293. CrossRef - Understanding how primary care practitioners can be supported to recognise, screen and initially diagnose oropharyngeal dysphagia: protocol for a behavioural science realist review
Caroline Smith, Debi Bhattacharya, Sion Scott
BMJ Open.2023; 13(2): e065121. CrossRef - Effects of chin tuck against resistance exercise on post-stroke dysphagia rehabilitation: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jing Liu, Qiuyi Wang, Jing Tian, Wanqiong Zhou, Yitian Gao, Xuemei Chen, Wei Zhang, Yajing Gao, Lanshu Zhou
Frontiers in Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of a predictive model for patients with post-extubation dysphagia
Jia-ying Tang, Xiu-qin Feng, Xiao-xia Huang, Yu-ping Zhang, Zhi-ting Guo, Lan Chen, Hao-tian Chen, Xiao-xiao Ying
World Journal of Emergency Medicine.2023; 14(1): 49. CrossRef - Evaluation of preventive care for swallowing difficulty through policy changes in Japanese long-term care insurance: analysis of a nationwide claims dataset for long-term care insurance
Hiroko Mori, Ayako Nakane, Haruka Tohara, Takeo Nakayama
BMC Health Services Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Are Oropharyngeal Dysphagia Screening Tests Effective in Preventing Pneumonia?
Ikuko Okuni, Satoru Ebihara
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(2): 370. CrossRef - Altered Brain Function Activity in Patients With Dysphagia After Cerebral Infarction: A Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study
Lei Li, Jiayu Liu, Fenxiong Liang, Haidong Chen, Rungen Zhan, Shengli Zhao, Tiao Li, Yongjun Peng
Frontiers in Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Instrumental Swallowing Assessment in Adults in Residential Aged Care Homes: A National Modified Delphi Survey Examining Beliefs and Practices
Olga Birchall, Michelle Bennett, Nadine Lawson, Susan M. Cotton, Adam P. Vogel
Dysphagia.2022; 37(3): 510. CrossRef - Predicting feeding-tube dependence in patients following endotracheal extubation: a two-item swallowing screen
Shu-Fen Siao, Wen-Hsuan Tseng, Tyng-Guey Wang, Yu-Chung Wei, Tzu-Yu Hsiao, Shih-Chi Ku, Cheryl Chia-Hui Chen
BMC Pulmonary Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - European white paper: oropharyngeal dysphagia in head and neck cancer
Laura W. J. Baijens, Margaret Walshe, Leena-Maija Aaltonen, Christoph Arens, Reinie Cordier, Patrick Cras, Lise Crevier-Buchman, Chris Curtis, Wojciech Golusinski, Roganie Govender, Jesper Grau Eriksen, Kevin Hansen, Kate Heathcote, Markus M. Hess, Sefik
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology.2021; 278(2): 577. CrossRef - Dysphagia screening in residential care settings: A scoping review
Constantino Estupiñán Artiles, Julie Regan, Claire Donnellan
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2021; 114: 103813. CrossRef - A Swallowing Screening Test Enhances a Better Recognition of Patients with a Hip Fracture at Risk for Oropharyngeal Dysphagia
Hugo Wijnen, Peter P. Schmitz, Martine Jansen, Linda Hendrix, Job L. C. van Susante, Hanna Willems
Orthopaedic Nursing.2021; 40(2): 94. CrossRef - Comparison studies of ultrasound-guided botulinum toxin injection and balloon catheter dilatation in the treatment of neurogenic cricopharyngeal muscle dysfunction
Shuo Luan, Shao-Ling Wu, Ling-Jun Xiao, Hai-Yun Yang, Mei-Xin Liao, Shao-Ling Wang, Sheng-Nuo Fan, Chao Ma
NeuroRehabilitation.2021; 49(4): 629. CrossRef - Instrumental Swallowing Assessment in Adults in Residential Aged Care Homes: A Scoping Review
Olga Birchall, Michelle Bennett, Nadine Lawson, Susan M. Cotton, Adam P. Vogel
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2021; 22(2): 372. CrossRef - Validation of the Munich Swallowing Score (MUCSS) in patients with neurogenic dysphagia: A preliminary study
G. Bartolome, U. Starrost, H. Schröter-Morasch, B. Schilling, L. Fischbacher, L. Kues, S. Graf, W. Ziegler
NeuroRehabilitation.2021; 49(3): 445. CrossRef - Dietary inflammatory index is associated with pain intensity and some components of quality of life in patients with knee osteoarthritis
Vahideh Toopchizadeh, Neda Dolatkhah, Dawood Aghamohammadi, Mahrokh Rasouli, Maryam Hashemian
BMC Research Notes.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Dysphagia and mealtime difficulties in dementia: Speech and language therapists’ practices and perspectives
Aisling Egan, Carolyn Andrews, Anja Lowit
International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders.2020; 55(5): 777. CrossRef - The Gugging Swallowing Screen in dysphagia screening for patients with stroke: A systematic review
Ki Deok Park, Tae Hee Kim, Seon Heui Lee
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2020; 107: 103588. CrossRef - Optimising Medicines Administration for Patients with Dysphagia in Hospital: Medical or Nursing Responsibility?
David J. Wright, David G. Smithard, Richard Griffith
Geriatrics.2020; 5(1): 9. CrossRef - Risk Factors of Dysphagia Among Community-Dwelling Middle-Aged Women
Young Hee Lee, Dukyoo Jung, Ok Jong Yun, Hyesoon Lee, Minkyung Lee
Gastroenterology Nursing.2020; 43(2): 164. CrossRef - Developing and Testing the Diagnostic Accuracy of a Brief Nursing Dysphagia Screen
Sarah Groppo-Lawless, Claire C. Davies, Alex Lengerich
Rehabilitation Nursing.2020; 45(6): 367. CrossRef - The Easy Dysphagia Symptom Questionnaire (EDSQ): a new dysphagia screening questionnaire for the older adults
Kyeong Eun Uhm, Minsun Kim, Yong Min Lee, Bo-Ram Kim, Yoon-Sook Kim, Jaekyung Choi, Seol-Heui Han, Hee Joung Kim, Kwang Ha Yoo, Jongmin Lee
European Geriatric Medicine.2019; 10(1): 47. CrossRef - Sarcopenia is an Independent Risk Factor for Dysphagia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults
Seungwoo Cha, Won-Seok Kim, Ki Woong Kim, Ji Won Han, Hak Chul Jang, Soo Lim, Nam-Jong Paik
Dysphagia.2019; 34(5): 692. CrossRef - The GUSS test as a good indicator to evaluate dysphagia in healthy older people: a multicenter reliability and validity study
Ebru Umay, Sibel Eyigor, Ali Yavuz Karahan, Ilknur Albayrak Gezer, Ayse Kurkcu, Dilek Keskin, Gulten Karaca, Zeliha Unlu, Canan Tıkız, Meltem Vural, Banu Aydeniz, Ebru Alemdaroglu, Emine Esra Bilir, Ayse Yalıman, Ekin Ilke Sen, Mazlum Serdar Akaltun, Ozle
European Geriatric Medicine.2019; 10(6): 879. CrossRef - Repetitive Saliva Swallowing Test: Norms, Clinical Relevance and the Impact of Saliva Secretion
Emmelie Persson, Inger Wårdh, Per Östberg
Dysphagia.2019; 34(2): 271. CrossRef - Dysphagia in Frail Older Persons: Making the Most of Current Knowledge
Nicole Rogus-Pulia, Rainer Wirth, Philip D. Sloane
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2018; 19(9): 736. CrossRef - Frailty, Swallowing and Dysphagia
David G. Smithard, Mariyam Shazra, Dharinee Hansjee, Ian Swaine
Current Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Reports.2018; 6(3): 192. CrossRef - Nursing interventions in adult patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia: a systematic review
Lorena Molina, Susana Santos-Ruiz, Pere Clavé, Luis González-de Paz, Esther Cabrera
European Geriatric Medicine.2018; 9(1): 5. CrossRef - Nursing home-acquired pneumonia, dysphagia and associated diseases in nursing home residents: A retrospective, cross-sectional study
Vanessa R.Y. Hollaar, Gert-Jan van der Putten, Claar D. van der Maarel-Wierink, Ewald M. Bronkhorst, Bert J.M. de Swart, Cees de Baat, Nico H.J. Creugers
Geriatric Nursing.2017; 38(5): 437. CrossRef - Oropharyngeal dysphagia: manifestations and diagnosis
Nathalie Rommel, Shaheen Hamdy
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2016; 13(1): 49. CrossRef - Dysphagia and Aspiration
John E. Morley
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2015; 16(8): 631. CrossRef - Expanding Instrumental Options for Dysphagia Diagnosis and Research: Ultrasound and Manometry
Maggie-Lee Huckabee, Phoebe Macrae, Kristin Lamvik
Folia Phoniatrica et Logopaedica.2015; 67(6): 269. CrossRef
- eTWST: An Extension to the Timed Water Swallow Test for Increased Dysphagia Screening Accuracy
- 3,937 View
- 60 Download
- 43 Crossref

- Effects of Foot Reflexology on Fatigue, Sleep and Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Jeongsoon Lee, Misook Han, Younghae Chung, Jinsun Kim, Jungsook Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(6):821-833. Published online December 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.6.821
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of foot reflexology on fatigue, sleep and pain.
Methods A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted. Electronic database and manual searches were conducted on all published studies reporting the effects of foot reflexology on fatigue, sleep, and pain. Forty four studies were eligible including 15 studies associated with fatigue, 18 with sleep, and 11 with pain. The effects of foot reflexology were analyzed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis Version 2.0. The homogeneity and the fail-safe N were calculated. Moreover, a funnel plot was used to assess publication bias.
Results The effects on fatigue, sleep, and pain were not homogeneous and ranged from 0.63 to 5.29, 0.01 to 3.22, and 0.43 to 2.67, respectively. The weighted averages for fatigue, sleep, and pain were 1.43, 1.19, and 1.35, respectively. No publication bias was detected as evaluated by fail-safe N. Foot reflexology had a larger effect on fatigue and sleep and a smaller effect on pain.
Conclusion This meta-analysis indicates that foot reflexology is a useful nursing intervention to relieve fatigue and to promote sleep. Further studies are needed to evaluate the effects of foot reflexology on outcome variables other than fatigue, sleep and pain.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combined effects of reflexology massage and respiratory relaxation on pain following chest tube removal in heart surgery patients
Zainab Bahramian, Majid Kazemi, Reza Vazirinejad, Hadi Hasani
Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Foot Reflexology for Managing Menopausal Symptoms in Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Mahsa Maghalian, Maryam Alikamali, Farzaneh Aslanpur, Mojgan Mirghafourvand
Current Women s Health Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Foot Reflexology on Postpartum Comfort and Breastfeeding Outcomes in Postpartum Women: A Meta-Analysis Study
Dilek Menekse, Ahsen Demirhan Kayacik, Kevser Ilcioglu
Breastfeeding Medicine.2025; 20(6): 441. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Reflexology on Fatigue, Constipation, Nausea and Vomiting During Pregnancy: A Narrative Review
Niloofar Nezhadahmad, Fereshteh Khoshkhoo, Mansour Arad, Zahra Zarei
Journal of Health Reports and Technology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review of Nursing Thesis on Complementary and Supportive Medicine Practices for Patients with Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review
Alev Yildirim Keskin, Deniz Zeynep Sönmez
Sakarya Üniversitesi Holistik Sağlık Dergisi.2025; 8(1): 44. CrossRef - Effect of foot reflexology on chronic pain in Parkinson’s disease: A randomized controlled trial
Karel Joineau, Estelle Harroch, Mathilde Boussac, Margherita Fabbri, Clémence Leung, Fabienne Ory-Magne, Vanessa Rousseau, Patrice Peran, Christine Brefel-Courbon, Emeline Descamps, Federico Giove
PLOS One.2025; 20(7): e0327865. CrossRef - The Effect of Foot Reflexology Massage on Fatigue and Sleep Quality in Hemodialysis Patients
Raheleh Rajabi, Fatemeh Akhlaghi, Neda Asadi, Fatemeh Zamani Babgohari, Fatemeh Arabpoor
SAGE Open Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Leitlinie „Insomnie bei Erwachsenen“ – Update 2025 (AWMF-Registernummer 063-003)
K. Spiegelhalder, E. Baum, M. Becker, C. Cornaro, T. Crönlein, L. Frase, V. Harth, E. Hertenstein, A. F. Johann, I. Mertel, D. Kunz, J. Langhorst, J. T. Maurer, G. Mayer, C. Nissen, R. Pietrowsky, T. Pollmächer, C. Schumacher, H. Sitter, A. Steffen, H. G.
Somnologie.2025; 29(4): 240. CrossRef - Comparing the impact of acupressure and reflexology on fatigue in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients: A randomized controlled trial with three arms
Naser Parizad, Amireh Hassanpour, Rasoul Goli, Hamidreza Khalkhali, Aysan Nozad
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2024; 70: 102573. CrossRef - A narrative review of research linking non‐sexual social touch to sleep quality
Yuxi Xie, Brooke C. Feeney
Journal of Sleep Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - COMPARISON OF THE EFFECT OF AURICULOTHERAPY AND FOOT REFLEXOLOGY ON THE SENSORY AND EMOTIONAL ASPECTS OF PAIN AND THE USE OF PAINKILLERS AFTER ELECTIVE CAESAREAN SECTION
Fatemeh Sadat Mousavi, Nahid Golmakani, Seyyedeh adeleh Rahmanian
Studies in Medical Sciences.2024; 35(1): 30. CrossRef - Reflexology evidence map
Erika Cardozo Pereira, Caio Fabio Schlechta Portella, Ricardo Ghelman, Carmen Verônica Mendes Abdala, Ana Cláudia Moraes Barros Leite-Mor, Arthur Schveitzer Ferreira, Pamela Gissi Lima, Mariana Cabral Schveitzer
Advances in Integrative Medicine.2024; 11(4): 191. CrossRef - Effect of Reflexology on Pain, Fatigue, Sleep Quality, and Lactation in Postpartum Primiparous Women After Cesarean Delivery: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Ayşegül Kiliçli ID, Simge Zeyneloglu ID
Journal of Human Lactation.2024; 40(2): 221. CrossRef - A Review of the Effect of Foot Reflexology on Pain in Patients
Kinga Vindis, Călin Tudor Hozan, Adrian Coțe, Gheorghe Szilagyi
Archives of Pharmacy Practice.2024; 15(1): 12. CrossRef - The Effect of Foot Reflexology on Fatigue, Sleep Quality, Physiological Indices, and Electrocardiogram Changes in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Nilofar Pasyar, Masoume Rambod, Zahra Najafian, Mohammad Hossein Nikoo, Amin Kordi Yoosefinejad, Mahdi Salmanpour
Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research.2024; 29(5): 608. CrossRef - Effects of foot reflexology on disease
Ming-Ying He, M Jalal Ud Din, Hai-Feng Xu, Shang-Yu Wang, Guo-Huan Ying, Hao Qian, Bing Wu, Hong-Dan Qi, Xin Wang, Gang Zhang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2024; 12(35): 6851. CrossRef - Mental Fatigue Classification Aided by Machine Learning-Driven Model Under the Influence of Foot and Auditory Binaural Beats Brain Massages via fNIRS
Nazo Haroon, Hamid Jabbar, Umar Shahbaz Khan, Taikyeong Ted. Jeong, Noman Naseer
IEEE Access.2024; 12: 187160. CrossRef - Comparing the Effects of Hand and Foot Reflexology on Chest Pain in Patients After Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Nasrin Hanifi, Sahar Asali, Ali Imani
Journal of Archives in Military Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Reflexology on the Anxiety of Pregnant Women During
Labor: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Zeinab Abbaszadeh, Jamileh Malakouti, Mahsa Maghalian, Mojgan Mirghafourvand
Current Women s Health Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Massage therapy significantly improves cancer-related fatigue in cancer patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Shengnan Shan, Lu Lin, Qian Fang, Fengmei Tian, Daoxia Guo, Yanling Zhou, Li Tian
Supportive Care in Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - El efecto de la reflexología podal sobre la fatiga en pacientes en hemodiálisis: un estudio de metaanálisis
Seda Şahan, Sevil Güler
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of foot reflexology on fatigue in hemodialysis patients: a meta-analysis study
Seda Şahan, Sevil Güler
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Peer Review of an Evidence-Based Decision-Support Tool for Non-Drug Prescribing for Healthy Ageing
Zara Quail, Mark Carter, Charles Young
Journal of Ageing and Longevity.2023; 3(2): 116. CrossRef - Comparing the influence of foot reflexology and fasting mimicking diet on quality of life and sleep quality in obesity hypoventilation syndrome
Rana Hesham Mohamed Elbanna, Sherif Osama Abdelsalam Elabd, Salma Ibrahim Abdelmohsen Alghitany
Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine.2023; 20(1): 207. CrossRef - O efeito da reflexologia podal sobre a fadiga em pacientes em hemodiálise: um estudo de metanálise
Seda Şahan, Sevil Güler
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Foot Reflexology on Nausea-Vomiting and Sleep Quality for Lung Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy in Turkey
Hilal Pekmezci, Sevilay Hintistan
Cyprus Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 7(5): 614. CrossRef - Impact of Nonpharmacologic Interventions Targeting Sleep Disturbances or Disorders in Patients With Inflammatory Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis of Randomized Trials
Kristine M. Latocha, Katrine B. Løppenthin, Safa Al‐Bazy, Tannie L. Albrechtsen, Helle E. Jensen, Mikkel Østergaard, Poul J. Jennum, Bente A. Esbensen, Robin Christensen
Arthritis Care & Research.2022; 74(12): 2108. CrossRef - Effect of Complementary and Integrative Treatments on Fatigue Symptoms in Hemodialysis Patients
Melek Yeşil Bayülgen, Meral Gün
Holistic Nursing Practice.2022; 36(1): 17. CrossRef - The impact of foot massage given to postmenopausal women on anxiety, fatigue, and sleep: a randomized-controlled trial
Nilay Gökbulut, Emine Ibici Akça, Çiğdem Karakayali Ay
Menopause.2022; 29(11): 1254. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the Turkish version of the attitudes toward massage (ATOM) scale
Gizem Göktuna, Gülşah Gürol Arslan, Dilek Özden
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2022; 55: 102178. CrossRef - The Effects of Foot Reflexology on Vital Signs: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Yunyan Jing, Shanxin Liu, Chunqi Pan, Ying Jian, Mingwei Wang, Bin Ni, Chan-Yen Kuo
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Effects of nonpharmacological intervention on sleep quality in hemodialysis patients
Hui Li, Long Zuo, Siyu Long, Baifei Li
Medicine.2021; 100(27): e26401. CrossRef - The effect of foot reflexology massage on delirium and sleep quality following cardiac surgery: A randomized clinical trial
Ahmad Fazlollah, Hosein Babatabar Darzi, Esmail Heidaranlu, Seyed Tayeb Moradian
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2021; 60: 102738. CrossRef - Comparing the Effect of Reflexology and Effleurage Massages on Fatigue and Insomnia in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
Sh. Sehat Nejad, A. Pour Samad, M. Behnam Moghadam, A. Mousavi zadeh, N. kaidani
Journal of Clinical Care and Skills.2021; 2(3): 139. CrossRef - Randomized controlled trial of the foot reflexology on pain and anxiety severity during dressing change in burn patients
Fahimeh Davodabady, Vahid Naseri-Salahshour, Mahbobeh Sajadi, Abolfazl Mohtarami, Fatemeh Rafiei
Burns.2021; 47(1): 215. CrossRef - Can foot reflexology be a complementary therapy for sleep disturbances? Evidence appraisal through a meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials
Hui‐Chuan Huang, Kee‐Hsin Chen, Shu‐Fen Kuo, I‐Hui Chen
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2021; 77(4): 1683. CrossRef - Effect of foot reflexology on chest pain and anxiety in patients with acute myocardial infarction: A double blind randomized clinical trial
Saeedeh Sayari, Monir Nobahar, Raheb Ghorbani
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2021; 42: 101296. CrossRef - How Long Can they Stand it? Examining the Effectiveness of Reflexology and a Passive Relaxation Intervention in Improving Health Outcomes in Workers Who Stand
Kathryn Kavanagh, Linda Rhoades Shanock
Occupational Health Science.2021; 5(1-2): 95. CrossRef - The effects of reflexology on anxiety, depression and quality of life in patients with gynecological cancers with reference to Watson's theory of human caring
Sinem Göral Türkcü, Sevgi Özkan
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2021; 44: 101428. CrossRef - The effect of reflexology on sleep quality and fatigue in postmenopausal women: A randomized control trial
Leyla Zengin Aydın, Gülhan Yiğitalp
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2021; 43: 101281. CrossRef - The Challenges and Perspectives of the Integration Between Virtual and Augmented Reality and Manual Therapies
Francesco Cerritelli, Marco Chiera, Marco Abbro, Valentino Megale, Jorge Esteves, Alberto Gallace, Andrea Manzotti
Frontiers in Neurology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Regards sur l’utilisation de la réflexologie palmaire lors d’entretiens cliniques auprès de personnes âgées institutionnalisées : un outil vecteur de bien-être et de qualité de vie ?
C. Moretto, A. Soubelet, C. Bonardi
NPG Neurologie - Psychiatrie - Gériatrie.2021; 21(121): 52. CrossRef - Relaxation interventions for improving sleep outcomes in perinatal women: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Xing Yee Jolyn Tan, Shanise Yi Xin Choong, Ling Jie Cheng, Ying Lau
Midwifery.2021; 103: 103151. CrossRef - Effect of Foot Reflexology and Aromatherapy on Anxiety and Pain During Brachytherapy for Cervical Cancer
Lisa Blackburn, Catherine Hill, Amy Lindsey, Loraine Sinnott, Kathrynn Thompson, Allison Quick
Oncology Nursing Forum.2021; 48(3): 265. CrossRef - Effect of Reflexology in Treating Cancer Pain: A Meta-Analysis
Zhila Najafpour, Kamran Shayanfard
International Journal of Cancer Management.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Foot Reflexology Intervention on Depression, Anxiety, and Sleep Quality in Adults: A Meta‐Analysis and Metaregression of Randomized Controlled Trials
Wei-Li Wang, Hao-Yuan Hung, Ying-Ren Chen, Kuang-Huei Chen, Szu-Nian Yang, Chi-Ming Chu, Yuan-Yu Chan, Gerhard Litscher
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of foot reflexology massage on burn-specific pain anxiety and sleep quality and quantity of patients hospitalized in the burn intensive care unit (ICU)
Reza Alinia-najjar, Masoumeh Bagheri-Nesami, Seyed Afshin Shorofi, Seyed Nouraddin Mousavinasab, Kiarash Saatchi
Burns.2020; 46(8): 1942. CrossRef - Effect of Foot Reflexology on Pain, Fatigue, and Quality of Sleep after Kidney Transplantation Surgery: A Parallel Randomized Controlled Trial
Atena Samarehfekri, Mahlagha Dehghan, Mansoor Arab, Mohammad Reza Ebadzadeh, Albert Moraska
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of reflexology on anxiety and sleep of informal cancer caregiver: Randomized controlled trial
İsmail Toygar, Öznur Usta Yeşilbalkan, Yasemin Güzel Malseven, Esra Sönmez
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2020; 39: 101143. CrossRef - Effectiveness of reflexology on anxiety of patients undergoing cardiovascular interventional procedures: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials
Ramesh Chandrababu, Eilean Lazarus Rathinasamy, C. Suresh, Jyothi Ramesh
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2019; 75(1): 43. CrossRef - Effects of reflexology on premenstrual syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Marzieh Hasanpour, Mohammad Mehdi Mohammadi, Habib Shareinia
BioPsychoSocial Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - La réflexologie plantaire
Emmanuelle Pinon Cartron
Soins Aides-Soignantes.2019; 16(89): 17. CrossRef - Réflexologie dans les troubles du sommeil
Alexandra Lemercier
Hegel.2019; N° 3(3): 246. CrossRef - The effects of sleep hygiene education and reflexology on sleep quality and fatigue in patients receiving chemotherapy
Leyla Zengin, Rukuye Aylaz
European Journal of Cancer Care.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of foot reflexology massage on breast milk volume of mothers with premature infants: A randomized controlled trial
Parisa Mirzaie, Sakineh Mohammad-Alizadeh-Charandabi, Sakineh Goljarian, Mojgan Mirghafourvand, Mohammad Bager Hoseinie
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2018; 17: 72. CrossRef - Evaluation des réflexothérapies en 2018
Nathalie Thilly
Hegel.2018; N° 1(1): 76a. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Foot Reflexology in the Severity of Restless Legs Syndrome in Female Patients Undergoing Dialysis: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Mahbobeh Ghasemi, Nahid Rejeh, Majideh Heravi-Karimooi, Seyed Davood Tadrisi, Parvaneh Samady Kia
Critical Care Nursing.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigating the Impact of Foot Reflexology on Severity of Fatigue in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Clinical Trial Study
Simin Sharifi, Ali Navidian, Mozhgan Jahantigh, Abouzar Shamsoddini Lori
Medical - Surgical Nursing Journal.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of reflexology on pain and sleep deprivation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized controlled trial
Ercan Bakir, Sevgin Samancioglu Baglama, Savas Gursoy
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2018; 31: 315. CrossRef - Réflexologie dans les troubles du sommeil
Alexandra Lemercier
Hegel.2018; N° 1(1): 95. CrossRef - The effect of acupressure stimulation of ST-36 – Zusanli, point on lower limbs explosive strength
Dariusz Mucha, Tadeusz Ambroży, Dawid Mucha
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2017; 11: 59. CrossRef - Effects of foot massage applied in two different methods on symptom control in colorectal cancer patients: Randomised control trial
Neşe Uysal, Sevinç Kutlutürkan, Işıl Uğur
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - El masaje, una técnica basada en la evidencia
T. Rulleau, C. Rivette, L. Toussaint
EMC - Kinesiterapia - Medicina Física.2017; 38(3): 1. CrossRef - A comparison the effects of reflexology and relaxation on the psychological symptoms in women with multiple sclerosis
Mozhgan Soheili, Fatemeh Nazari, Vahid Shaygannejad, Mahboobeh Valiani
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Reflexology and polysomnography: Changes in cerebral wave activity induced by reflexology promote N1 and N2 sleep stages
N. Esmel-Esmel, E. Tomás-Esmel, M. Tous-Andreu, A. Bové-Ribé, M. Jiménez-Herrera
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2017; 28: 54. CrossRef - European guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of insomnia
Dieter Riemann, Chiara Baglioni, Claudio Bassetti, Bjørn Bjorvatn, Leja Dolenc Groselj, Jason G. Ellis, Colin A. Espie, Diego Garcia‐Borreguero, Michaela Gjerstad, Marta Gonçalves, Elisabeth Hertenstein, Markus Jansson‐Fröjmark, Poul J. Jennum, Damien Leg
Journal of Sleep Research.2017; 26(6): 675. CrossRef - S3-Leitlinie Nicht erholsamer Schlaf/Schlafstörungen
D. Riemann, E. Baum, S. Cohrs, T. Crönlein, G. Hajak, E. Hertenstein, P. Klose, J. Langhorst, G. Mayer, C. Nissen, T. Pollmächer, S. Rabstein, A. Schlarb, H. Sitter, H.-G. Weeß, T. Wetter, K. Spiegelhalder
Somnologie.2017; 21(1): 2. CrossRef - Il massaggio, approccio basato sulle evidenze
T. Rulleau, C. Rivette, L. Toussaint
EMC - Medicina Riabilitativa.2017; 24(3): 1. CrossRef - Foot Reflexotherapy Induces Analgesia in Elderly Individuals with Low Back Pain: A Randomized, Double‐Blind, Controlled Pilot Study
Bruna Hoffmann de Oliveira, Anna Quialheiro de Abreu da Silva, Daniela Dero Ludtke, Fernanda Madeira, Graciela Mendonça da Silva Medeiros, Rodolfo Borges Parreira, Afonso Shiguemi Inoue Salgado, Luiz Augusto Oliveira Belmonte, Francisco José Cidral-Filho,
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of foot reflexology and back massage on hemodialysis patients' fatigue and sleep quality
Kevser Sevgi Unal, Reva Balci Akpinar
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2016; 24: 139. CrossRef - Influence of Study Design on Outcomes Following Reflexology Massage: An Integrative and Critical Review of Interventional Studies
Andrew McVicar, Christina Greenwood, Carol Ellis, Chantelle LeForis
The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine.2016; 22(9): 739. CrossRef - A comparison of the effects of reflexology and relaxation on pain in women with multiple sclerosis
Fatemeh Nazari, Mozhgan Soheili, SayedMohsen Hosseini, Vahid Shaygannejad
Journal of Complementary and Integrative Medicine.2016; 13(1): 65. CrossRef - L’impact de la réflexologie plantaire sur le stress des professionnels de santé
Mireille Guillon, Françoise Bourdarias, Nathalie Lecour
Revue internationale de soins palliatifs.2016; Vol. 30(3): 135. CrossRef - The effects of two methods of reflexology and stretching exercises on the severity of restless leg syndrome among hemodialysis patients
Nahid Shahgholian, ShahrzadKhojandi Jazi, Jahangir Karimian, Mahboubeh Valiani
Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research.2016; 21(3): 219. CrossRef - Complementary and Alternative Medicine Therapies as Symptom Management Strategies for the Late Effects of Breast Cancer Treatment
Ashley M. Henneghan, Tracie Harrison
Journal of Holistic Nursing.2015; 33(1): 84. CrossRef - Topography of spinal column and kidney receptors as illustrated by microsystem of the foot
Tadeusz Kasperczyk, Robert Walaszek
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine.2015; 35(3): 329. CrossRef - Self-Administered Foot Reflexology for the Management of Chronic Health Conditions: A Systematic Review
Hyun Jin Song, Sun Mi Choi, Hyun-Ju Seo, Heeyoung Lee, Heejeong Son, Sanghun Lee
The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine.2015; 21(2): 69. CrossRef - Effect of self-administered foot reflexology for symptom management in healthy persons: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Hyun Jin Song, Heejeong Son, Hyun-Ju Seo, Heeyoung Lee, Sun Mi Choi, Sanghun Lee
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2015; 23(1): 79. CrossRef - The effect of foot reflexology on physiologic parameters and mechanical ventilation weaning time in patients undergoing open-heart surgery: A clinical trial study
Abbas Ebadi, Parastoo Kavei, Seyyed Tayyeb Moradian, Yaser Saeid
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2015; 21(3): 188. CrossRef - Healing Art of Hand: Reflexology
H. Dilek Doğan
European Journal of Basic Medical Sciences.2014; 4(4): 89. CrossRef - The Physiological and Biochemical Outcomes Associated with a Reflexology Treatment: A Systematic Review
J. E. M. McCullough, S. D. Liddle, M. Sinclair, C. Close, C. M. Hughes, Peter Mackereth
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Meta-Analysis of Spiritual Intervention Studies on Biological, Psychological, and Spiritual Outcomes
Pok-Ja Oh, Young-Hyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(6): 833. CrossRef - RECENT LITERATURE
Focus on Alternative and Complementary Therapies.2012;[Epub] CrossRef - RECENT LITERATURE
Focus on Alternative and Complementary Therapies.2012;[Epub] CrossRef
- Combined effects of reflexology massage and respiratory relaxation on pain following chest tube removal in heart surgery patients
- 3,793 View
- 105 Download
- 84 Crossref

- Developmental Direction for Review System of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing
- Hae Won Kim, Myungsill Chung, Jeong Sook Park, Yeon Ok Suh, Min Hyun Suk, Hyunsook Shin, Jin Hyang Yang, Hee Jung Jang, Myun Sook Jung
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(3):422-430. Published online April 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.3.422
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was performed to identify current characteristics of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and to explore a way to elevate it to an international level and to critique the overall review process so as to delineate the advanced, objective paper appraisal in this journal.
Methods Data was collected using self administered questionnaires to 75 journal reviewers belonging to the Korean academy of nursing and its division academy of nursing from August 15th to September 30th, 2006.
Results The majority of reviewers pointed out a lack of discrimination between the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and other journals. Among the main answers of reviewers, Creativeness(52.3%) and excellence of nursing(38%) will be critical factors to develop in order to elevate to an the journal to an international level. In specific evaluation areas, reviewers preferred a subjective critique method(60%), and the condition of the decision making process regarding paper acceptance as a combination of checklist and subjective evaluation(84%). Subjective evaluation opinions with major categories will occur in the next revised evaluation format. 76% of reviewers agreed with the current objective evaluation form.
Conclusions The journal review process should be evaluated on a regular basis to elevate the journal level and a mutual agreement of the journal's scope, range, and purpose will be necessary. As a recommendation, an attempt at various approaches in journal reviews and reviewer training should be made.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Manuscripts Rejected by the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration [2012~2015 Jun]
Seok Hee Jeong, Taewha Lee, Soyoung Yu, Myoung Hee Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(5): 561. CrossRef
- Analysis of Manuscripts Rejected by the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration [2012~2015 Jun]
- 709 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Review Study on the Strategies for Concept Analysis
- Myungsun Yi, So Woo Lee, Kum Ja Kim, Myo Gyeong Kim, Ji Hyun Kim, Kyung Hee Lee, Inok Lee, Jung Sook Lee, Jeong Hee Hong
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(3):493-502. Published online June 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.3.493
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Concept analysis is an essential part of theory development in nursing. Thus, many strategies or methods of concept analysis have been suggested in nursing literature. However, in Korea, only limited strategies were utilized, without much consideration on a wide range of strategies in choosing a method that coincides with the characteristics of each concept to analyze. The purpose of this article was to propose various strategies for concept analysis.
Method A literature review method was used.
Result Ten methods of concept analysis were identified in the literature, and they were evaluated for advantages and limitations. In addition to the method by Walker and Avant and a hybrid model, more advanced strategies, such as triangulation method, critical analysis and the feminist approach were introduced and described in detail. The examples used in each concept analysis method were presented in table to provide the extent of utilization of each method.
Conclusion This article provides a wide range of strategies in identifying, clarifying, or elaborating a concept. It might help in choosing a method that best fits the concept to analyze, thus enhancing quality of concept analysis research.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Defining Organizational Trust in Nursing: A Concept Analysis Using Walker and Avant's Model
Reyhaneh Babanataj, Mohsen Adib Hajbaghery, Maryam Shoja
Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Family Participation in Hospitalized Patient Care: Using Hybrid Models
Maryam Ahmadi, Farahnaz Mohammadi Shahboulaghi
Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research.2025; 30(3): 332. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Presenteeism Among Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Jiyeon Jung, Jihyun Moon
Sage Open Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - An Evolutionary Concept Analysis of Pediatric Hospice and Palliative Care
Jung Hwa Lee, Soon Young Lee, Kyung Mi Cha
Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2024; 27(2): 51. CrossRef - Clarifying the Concept of Professional Curiosity in Nursing: A Concept Analysis With Walker and Avant Approach
Fatemeh Taheri, Ahmad Nasiri, Cheryl Green
Nursing Forum.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Concept Analysis of Spiritual Self-Care in Hospice Team Members by Hybrid Model
Sunhee Jang, Sungju Lee, Minyeong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(4): 501. CrossRef - Transfer anxiety in parents of children transferred from pediatric intensive care units to general wards in South Korea: a hybrid concept analysis
Jisu Park, Eun Kyoung Choi
Child Health Nursing Research.2022; 28(2): 154. CrossRef - Conceptual Analysis of Health Behavior in Tuberculosis Patients
Hye-Jin Kim, Myung Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(3): 280. CrossRef - CONCEPT ANALYSIS OF FRAGMENTED CARE WITH WALKER AND AVANT MODEL
Seyed Javad Hosseini, Mahbobeh Firooz, Abbas Heydari
Nursing and Midwifery Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Anxiety in Patients with Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm
Ji Eun Lee, Suk Jeong Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(1): 85. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Parents' Treatment Adherence for an Epileptic Child or Adolescent
Juna Lee, Ju Young Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(2): 205. CrossRef - Concept analysis of Korean spiritual health: Using a hybrid model
Gyeong Hye Choi, Joo Hyun Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(2): 117. CrossRef - Theoretical evaluation of Cox’s interaction model of client health behavior for health promotion in adult
women
Youlim Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Gi Wook Ryu
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(2): 120. CrossRef - Trends of Concept Development in Nursing Published in Korean Journals
Sumi Lee, Jinhae Lee, Yugyeong Hwang, Il Sun Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(2): 178. CrossRef Health and Psychosocial Self-Care Needs in Off-Therapy Childhood Cancer: Hybrid Model Concept Analysis
M Akbarbegloo, V Zamanzadeh, A Ghahramanian, L Valizadeh, H Matin
Patient Preference and Adherence.2020; Volume 14: 803. CrossRef- Concept Analysis of Patient Rights
Hye Suk Jun
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(1): 89. CrossRef - Concept analysis of impressionability among adolescents and young adults
Seok Hyun Gwon, Suyong Jeong
Nursing Open.2018; 5(4): 601. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Tacit Nursing Knowledge
Hyeon Ju Kim, Joo Hyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(6): 637. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Healing: Focusing on Patient Health related Literatures
Jiyoung Kim, Nayeon Shin
Asian Oncology Nursing.2015; 15(1): 51. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Motivation for Vocational Rehabilitation in Persons with Mental Disabilities
Eun-Seon An, Ji-Min Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2015; 24(4): 279. CrossRef
- Defining Organizational Trust in Nursing: A Concept Analysis Using Walker and Avant's Model
- 1,015 View
- 16 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Analysis of Review Contents of the Submitted Papers in Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing: Focus: The Submitted Papers in 2003
- Kyung Sook Cho, Myung Sun Hyun, Dong Sook Cho
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(1):197-205. Published online February 28, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.1.197
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The objective of the study is to analyze the review contents of reviewers for the submitted papers in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing in 2003.
Method The review contents of the 165 papers were selected 217 papers that were submitted in 2003. Among those 165 papers, the 21 papers belonged to the ‘Do not publish’ list and 17 papers, ‘Revise manuscript and resubmit’, list and the 94 papers, ‘Publish if revisions are made’ list. There are more than two level differences among the four levels of decision in acceptance of publication in 33 papers.
Results The analysis of the review contents for the papers were suggested according to review categories : introduction, method, results, discussion and conclusion. In addition, if papers had more than two levels of review they were rated poor accord or inconsistent.
Conclusion For the quality of the academic journal and development of the nursing science, it is important to disseminate and publish the research paper. Therefore, review of the submitted paper is also important. Implications for the profitable review were suggested in the study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of the Submitted Papers’ Evaluations for the Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing
Narae Heo, Jiyoung Kim
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2024; 12(2): 73. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Trends in Papers Published in the Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing (2005-2009)
Jin-Sun Kim, Ji-Young Lim, In-Soo Kwon, Tae-Im Kim, Ho-Ran Park, Hae-Young Ahn, Soo-Yeon Lee, Hyang-Mi Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2011; 17(2): 100. CrossRef
- Analysis of the Submitted Papers’ Evaluations for the Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing
- 738 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


