Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Usefulness of Charlson comorbidity index-adjusted mortality prediction tools and factors influencing mortality in intensive care unit patients: a retrospective medical record review–based study
- Jai Jung Lee, Dong Yeon Kim, Min Ji Lee, Ji Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):27-38. Published online February 11, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25094
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to estimate the mortality rate in adult intensive care units (ICUs) using the Charlson comorbidity index (CCI)-adjusted Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II and Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS) III models, and to identify factors influencing mortality.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study included adult patients admitted to the ICU at a tertiary hospital between June 1 and August 31, 2022. Among the 1,098 screened patients, those younger than 18 years, those discharged within 48 hours, and those with missing medical records were excluded. In total, 482 patients were analyzed using the chi-square test, independent t-test, and multivariate logistic regression. Model performance was evaluated using the c-statistic and the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test.
Results
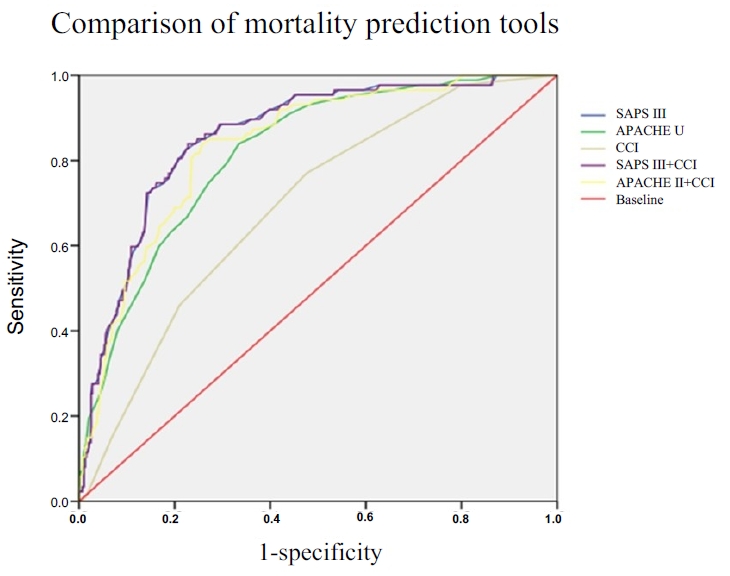
The predictive accuracy of the mortality models was shown by c-statistic values of 0.817 for APACHE II, 0.857 for SAPS III, 0.697 for CCI, and 0.834 for CCI-adjusted APACHE II (0.834). Mechanical ventilation, cardiopulmonary cerebral resuscitation, continuous renal replacement therapy, and the presence of leukemia or lymphoma were significant predictors of mortality in adult ICU patients. Among the evaluated models, SAPS III and CCI-adjusted APACHE II demonstrated the highest predictive power.
Conclusion
The findings indicate that incorporating comorbidity indices such as the CCI with acute physiological parameters improves the accuracy of mortality prediction in ICU patients. Understanding mortality prediction models is essential for nurses to provide individualized, evidence-based, and high-quality care in adult ICUs.
- 318 View
- 11 Download

- Effectiveness of the Eye Care Protocol in the Intensive Care Unit Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Kyu Won Lim, Shin Young Ha, In Soon Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):432-445. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study investigated the effects of an eye care protocol (ECP) on patients in the intensive care unit (ICU).
Methods
This study utilized a randomized controlled design. Participants were patients who met the inclusion criteria and were admitted to the ICU (36 in the experimental group and 38 in the control group). The experimental group received an ECP, while the control group received standard eye care, starting the day after admission, for a duration of 10 days. The ECP classifies the degree of eyelid obstruction into three stages based on the degree of exposure to the lower eyelid conjunctiva and cornea. The protocol included cleansing with normal saline gauze, administering eye drops, applying silicone and polyurethane films, and recommending consultation with an ophthalmologist if necessary. The effectiveness of ECP was assessed by analyzing tear volume, hyperemia, chemosis, and eye discharge. Data analysis was conducted using SPSS 27.0, employing the Mann-Whitney U-test and generalized estimating equations.
Results
On day 5, the experimental group demonstrated a significant increase in tear volume in both eyes compared with the control group. However, no statistically significant differences were observed in the incidence of hyperemia, chemosis, and eye discharge on days 5 and 10 of the intervention.
Conclusion
The application of the ECP in this study increased tear volume in ICU patients, thereby reducing discomfort caused by dry eyes. It has the potential to prevent complications such as damage to the surface of the eyeball resulting from decreased tear volume. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Da-Jung Kim
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2025; 21(5): 234. CrossRef
- A systematic review of pulmonary rehabilitation nursing interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- 1,408 View
- 199 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Delirium Experience of the Intensive Care Unit Patients
- Jaeyeon Jung, Sujin Jang, Seonmi Jo, Sunhee Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):134-143. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21240
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The study aimed to understand the delirium experience of intensive care unit (ICU) patients.
Methods
We performed a qualitative study using Colaizzi’s phenomenological method. Eleven patients, who experienced delirium according to the Confusion Assessment Method for ICU, participated after transferring to general wards from the ICU. Individual in-depth semi-structured interviews ranging from 30 minutes to 2 hours in length were conducted between November 2018 and August 2019.
Results
Nine themes and four theme clusters emerged. The four theme clusters were: 1) “Overwhelmed by fear,” which describes the experience of a patient close to death and the feeling of difficulty in understanding disorganized thinking; 2) “Anxious about not understanding the situation,” which means that patients’ sense of time and space were disordered in the ICU; 3) “Being deserted,” which indicates the feeling of being separated from others and yourself; and 4) “Resistance to protect my dignity,” which indicates that the dignity and autonomy of an individual in the patient’s position at the ICU, are ignored.
Conclusion
Nursing interventions are needed that would enable patients to maintain orientation and self-esteem in the ICU. In addition, healthcare providers need to provide information about the unfamiliar environment in the ICU in advance. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Patients' and family members' dyadic experience of post‐operative delirium in the intensive care unit: A qualitative study
Jing Dong, Weijing Sui, Yiyu Zhuang
Nursing in Critical Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Person-centered Care, Intensive Care Experience, and Post-intensive Care Syndrome in Critical Care Survivors: A Multi-center Prospective Cohort Study
Jiyeon Kang, Seonyoung Yun
Asian Nursing Research.2025; 19(3): 274. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Intensive Care Unit Nurses’ Competency in Delirium Care in A Tertiary General Hospital
Mi Ran Lim, Gyoo Yeong Cho
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(3): 37. CrossRef - Exploring patients’ and families’ preferences for auditory stimulation in ICU delirium prevention: A qualitative study
Yajun Ma, Nianqi Cui, Zhiting Guo, Yuping Zhang, Jingfen Jin
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2024; 82: 103629. CrossRef - The Influence of Ethical Nursing Competence and Positive Nursing Organizational Culture on Person-Centered Care in Intensive Care Unit Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Jae Eun Lee, Hye-Young Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(3): 304. CrossRef - A Study on Nurses' Communication Experiences with Intubation Patients
Ye Rim Kim, Hye Ree Park, Mee Kyung Shin
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2023; 26(1): 28. CrossRef - Intensive Care Experience of Critical Care Patients and Its Related Factors : A Secondary Analysis Study
Jiyeon Kang, Hyojeong Woo
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2023; 16(3): 11. CrossRef - Item analysis of the Korean version of the Intensive Care Experience Questionnaire: Using the Rasch Model based on Item Response Theory
Jiyeon Kang, Minhui Kim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2022; 15(3): 37. CrossRef
- Patients' and family members' dyadic experience of post‐operative delirium in the intensive care unit: A qualitative study
- 2,789 View
- 175 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Untact Visit Service Development Based on an Application Reflecting the Circumstances during COVID-19: Focusing on Utilization in the Pediatric Intensive Care Units
- Dahae Woo, Hanui Yu, Hyo Jin Kim, Minyoung Choi, Dong Hee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(5):573-584. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop an untact visit service based on an application that can be utilized in the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) during COVID-19.
Methods
This study adopted the double diamond process of service design comprising the discovery, defining, and development stages.
Results
We developed an untact visit service based on an application that considered the child’s status, schedule, photo, and video messages, and so on. Moreover, we derived a service flow regarding the required roles and the type of flow shown between each stakeholder.
Conclusion
Considering the ongoing pandemic, the untact visit service is designed to increase rapport and participation of parents, share the child’s information in real-time, and provide one-stop service without increasing healthcare providers’ work. It will be a useful visit service that can be applied and evaluated in various hospital settings and the PICU. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors affecting pediatric nurses’ development of partnerships with parents of hospitalized children: An evaluation based on the stress-coping adaptation model
In Young Cho, So Hyoung Hong, Ji Yeong Yun
Journal of Child Health Care.2025; 29(1): 53. CrossRef - Correlation between oral health knowledge, demand for remote education tools, and self-efficacy among parents of children and adolescents
Min-Ji Park, Herry Novrinda, Jae-Young Lee
Journal of Korean Society of Dental Hygiene.2025; 25(1): 69. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Family-centered Care Application for Intensive Care Unit Families Based on the Facilitated Sensemaking Model : Focusing on Family Satisfaction, Family Stress, and Self-Efficacy
Yun Ha Oak, Eun Ha Kim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2025; 18(2): 1. CrossRef - Experiences of Family Members With Visitation Prohibition for Critically Ill Patients
Sunjung Kim, Sunghee H. Tak
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2024; 46(11): 854. CrossRef - Factors influencing neonatal intensive care unit nurses' parent partnership development
Eun Kyoung Kim, In Young Cho, Ji Yeong Yun, Bobae Park
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2023; 68: e27. CrossRef - National Petition Analysis Related to Nursing: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
HyunJung Ko, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee, Hee Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 635. CrossRef - Relationship between parental stress and post‐traumatic stress disorder: The moderating effect of visitation restrictions in paediatric intensive care units during COVID‐19
Young Il Cho, Hyo Jin Kim, Dong Hee Kim
Nursing in Critical Care.2023; 28(5): 808. CrossRef - Need for Information and Communication Technology during COVID-19: An Exploratory Study Using Nurses’ Activity Diaries
Hyeongsuk Lee, Dongmin Lee, Seungmin Lee
Healthcare Informatics Research.2023; 29(3): 256. CrossRef - Effects of a Noncontact Visit Program in the NICU for the Prevention of COVID-19
Hye Young Ahn, Hee Jee Jo, Hyun Jeong Ko
Healthcare.2023; 11(15): 2152. CrossRef - The Development of Automated Personalized Self-Care (APSC) Program for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Gaeun Park, Haejung Lee, Ah Reum Khang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(5): 535. CrossRef
- Factors affecting pediatric nurses’ development of partnerships with parents of hospitalized children: An evaluation based on the stress-coping adaptation model
- 1,629 View
- 28 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Effect of Direct Breastfeeding Program for Premature Infants in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Ji Hyun Kang, Hyunmi Son, Shin Yun Byun, Gyumin Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):119-132. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20240
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the effects of a direct breastfeeding program for premature infants in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs).
Methods
This quasi-experimental study was conducted during August 2016 to April 2017. Sixty mothers of premature infants were assigned to the experimental (n = 31) or control groups (n = 29). The program was comprised of breastfeeding education and direct breastfeeding support. The experimental and control groups were provided with education and counseling on breastfeeding at the time of admission and discharge. In the experimental group, the mothers initiated oral feeding with direct breastfeeding and engaged in breastfeeding at least seven times during the NICU stay. The collected data were analyzed by the χ2 -test and repeated measures ANOVA using an SPSS program.
Results
The experimental group showed a higher direct breastfeeding practice rate (χ2 = 19.29, p < .001), breastfeeding continuation rate (χ2 = 3.76, p < .001), and self-efficacy (F = 25.37, p < .001) than the control group except for maternal attachment.
Conclusion
The direct breastfeeding program in the NICU has significant effects on the practice and continuation rate of breastfeeding and breastfeeding self-efficacy. Therefore, this program can be applied in the NICU settings where direct breastfeeding is limited. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploration of Family-Centered Care in NICUs: A Grounded Theory Methodology
Young Ah Park, YeoJin Im
Qualitative Health Research.2025; 35(10-11): 1231. CrossRef - Fresh Parent’s Own Milk for Preterm Infants: Barriers and Future Opportunities
Carrie-Ellen Briere, Jessica Gomez
Nutrients.2024; 16(3): 362. CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness Evaluation of Comprehensive Mobile-Based, Breastfeeding Promotion Program for Mothers with Gestational Diabetes
Eunju Kwak, Seungmi Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(2): 224. CrossRef
- Exploration of Family-Centered Care in NICUs: A Grounded Theory Methodology
- 3,167 View
- 168 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Path Analysis for Delirium on Patient Prognosis in Intensive Care Units
- Sunhee Lee, Sun-Mi Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):724-735. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.724
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to investigate relationship between delirium, risk factors on delirium, and patient prognosis based on Donabedian's structure-process-outcome model.
Methods This study utilized a path analysis design. We extracted data from the electronic medical records containing delirium screening data. Each five hundred data in a delirium and a non-delirium group were randomly selected from electronic medical records of medical and surgical intensive care patients. Data were analyzed using SPSS 20 and AMOS 24.
Results In the final model, admission via emergency department (B=.06,
p =.019), age over 65 years (B=.11,p =.001), unconsciousness (B=.18,p =.001), dependent activities (B=.12,p =.001), abnormal vital signs (B=.12,p =.001), pressure ulcer risk (B=.12,p =.001), enteral nutrition (B=.12,p =.001), and use of restraint (B=.30,p =.001) directly affecting delirium accounted for 56.0% of delirium cases. Delirium had a direct effect on hospital mortality (B=.06,p =.038), hospital length of stay (B=5.06,p =.010), and discharge to another facility (not home) (B=.12,p =.001), also risk factors on delirium indirectly affected patient prognosis through delirium.Conclusion The use of interventions to reduce delirium may improve patient prognosis. To improve the dependency activities and risk of pressure ulcers that directly affect delirium, early ambulation is encouraged, and treatment and nursing interventions to remove the ventilator and drainage tube quickly must be provided to minimize the application of restraint. Further, delirium can be prevented and patient prognosis improved through continuous intervention to stimulate cognitive awareness and monitoring of the onset of delirium. This study also discussed the effects of delirium intervention on the prognosis of patients with delirium and future research in this area.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Does ICU admission dysphagia independently contribute to delirium risk in ischemic stroke patients? Results from a cohort study
Hongtao Cheng, Simeng Song, Yonglan Tang, Shiqi Yuan, Xiaxuan Huang, Yitong Ling, Zichen Wang, Xiaoying Tian, Jun Lyu
BMC Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Preoperative Anxiety and Its Postoperative Associated Factors in Patients Receiving Post Anesthetic Recovery Care at Surgical Intensive Care Unit
Yul Ha Lee, Hye-Ja Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(3): 267. CrossRef - Delirium Experience of the Intensive Care Unit Patients
Jaeyeon Jung, Sujin Jang, Seonmi Jo, Sunhee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(2): 134. CrossRef - The training needs of Korean intensive care unit nurses regarding delirium
Young Sook Roh
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2021; 62: 102954. CrossRef - Effect on Quality of Care of a Delirium Prevention Campaign for Surgical Intensive Care Nurses
Heejeong Kim, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of Nursing Care Quality.2021; 36(4): 361. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis on the Effect of Delirium Prevention Intervention in Korean Intensive Care Units
Jiyeon Kang, Min Jeong Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2021; 14(3): 141. CrossRef
- Does ICU admission dysphagia independently contribute to delirium risk in ischemic stroke patients? Results from a cohort study
- 2,512 View
- 53 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Person-Centered Relational Care Experienced by Critical Care Nurses: An Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis Study
- Myoung Sun Jang, Sungjae Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):423-436. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.423
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The aim of the study was to explore nurses’ experience of person-centered relational care in the context of critical care.
Methods Key interview questions were developed based on the human-to-human relationship model suggested by Travelbee. Data were collected through in-depth interviews with a purposive sample of 11 nurses having more than 2 years of working experience in intensive care units. An interpretative phenomenological analysis was conducted to analyze the data.
Results Four super-ordinate and nine sub-ordinate themes were identified. Emerged super-ordinate themes were as follows: (1) encountering a live person via patient monitoring systems; (2) deep empathic connection; (3) humanistic and compassionate care, and (4) accompanying the journey to the end. Study findings revealed that nurses in intensive care units experienced ‘balancing emotions’ and ‘authenticity’ in caring when entering human-to-human relationships with dying patients. The phenomenon of person-centered relational care in intensive care units was found to subsume intrinsic attributes of empathy, compassion, and trust, similar to the central concepts of Travelbee's theory.
Conclusion The interpretative findings in this study provide deeper understanding of Travelbee's human-to-human relationship model. The technological environment in intensive care units did not hinder experienced nurses from forming human-to-human relationships. These themes need to be emphasized in critical care nursing education as well as in nursing management. The results of this study will contribute to understanding nurse-patient caring relationships in depth, and help improve the quality of nursing care in intensive care units.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Professional Identity Formation in Nursing: The Role of Travelbee's Human-to-Human Relationship Model
İnci İnceleme, Satı Demir
Journal of Gazi University Health Sciences Institute.2025; 7(1): 28. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Warmth in Nursing
Jee-Won Kim, Mina Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(2): 197. CrossRef - Workload, Teamwork, Compassion Competence, and Person-centered Critical Care Nursing among Critical Care Nurses
Hyun A Lee, Myung Sun Hyun, Jin-Hee Park, Eun Ji Seo
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2025; 18(2): 14. CrossRef - Listening to the voices of healthcare providers involved in the design of a new birthing room: an interpretative phenomenological analysis
Anwar Nader AlKhunaizi, Areej Ghalib Al-Otaibi
BMC Health Services Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Framework of humanistic care for patients in theICU: A preliminary study
Yuchen Zhang, Li Zhao, Meng Zhang, Xiaojing Guo, Chen Xin, Yubiao Gai
Nursing in Critical Care.2024; 29(1): 125. CrossRef - Exploring Healthcare Providers’ and Women’s Perspectives of Labor Companionship during Childbirth: An Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis Study
Anwar Nader AlKhunaizi, Areej Ghalib Al-Otaibi, Manal F. Alharbi, Ghareeb Bahari
Healthcare.2024; 12(9): 869. CrossRef - Experience of Clinical Adaptation among Nurses in Intensive Care Unit
Jin Young Hong, Sue Kyung Sohn
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(1): 1. CrossRef - Self-reflection of a General Ward Nurses on the Experience of End-of-Life Care for a Patient who Decided to Suspend Life-sustaining Treatment: van Manen's Hermeneutic Phenomenological Approach
Hee Jung Hong
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(3): 273. CrossRef - The impact of family care visitation programme on patients and caregivers in the intensive care unit: A mixed methods study
Hye Jin Yoo, JaeLan Shim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(13-14): 3797. CrossRef - Effective Teaching Behaviors of Clinical Nursing Teachers: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
Jian Zhang, Fenhua Zhou, Jinxia Jiang, Xia Duan, Xin Yang
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurse Spiritual Care Therapeutics Scale
Kyung-Ah Kang, Elizabeth Johnston Taylor, Jiyoung Chun
Journal of Hospice & Palliative Nursing.2022; 24(6): E250. CrossRef - Person-centred care among intensive care unit nurses: A cross-sectional study
Hyuna Youn, Miyoung Lee, Sun Joo Jang
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2022; 73: 103293. CrossRef - The Effect of a Multifaceted Family Participation Program in an Adult Cardiovascular Surgery ICU*
Hye Jin Yoo, JaeLan Shim
Critical Care Medicine.2021; 49(1): 38. CrossRef - Conceptualization of Person-Centered Care in Korean Nursing Literature: A Scoping Review
Ji Yea Lee, Sewon Lee, Eui Geum Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(4): 354. CrossRef - Critical care nurses’ communication experiences with patients and families in an intensive care unit: A qualitative study
Hye Jin Yoo, Oak Bun Lim, Jae Lan Shim, Liza Heslop
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(7): e0235694. CrossRef
- Professional Identity Formation in Nursing: The Role of Travelbee's Human-to-Human Relationship Model
- 2,848 View
- 91 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- Risk Factors of Medical Device-Related Pressure Ulcer in Intensive Care Units
- MiJee Koo, YoungA Sim, InSoon Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):36-45. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.36
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the characteristics of and risk factors for medical-device-related pressure ulcer (MDRPU) development in intensive care units.
Methods A prospective cohort study design was used, and the participants were 253 adult patients who had stayed in medical and surgical intensive care units. Data were collected regarding the application of medical devices and MDRPU-related characteristics over a period of six months from June to November, 2017. Data were analyzed using independent t-test, χ 2-test, Fisher's exact test, and binary logistic regression analysis with the SPSS 21.0 program.
Results Among the 253 participants, MDRPUs occurred in 51 (19.8%) participants. The results of the logistic regression analysis showed that the risk factors for MDRPUs were the use of endotracheal tubes (OR=5.79, 95% CI: 1.66~20.20), having had surgery (OR=2.95, 95% CI: 1.11~7.77), being in a semi-coma/coma (OR=5.79, 95% CI: 1.04~32.05), and sedation (OR=5.54, 95% CI: 1.39~22.19).
Conclusion On the basis of the study results, it is effectively facilitated by nurses when they care for patients with MDRPUs in intensive care units and the results are expected to be of help in preventive education for MDRPU development as well as preparing the base data for intervention studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characteristics of and Risk Factors for Medical Device-Related Pressure Injuries in Trauma Patients in Intensive Care Units: A Retrospective Case–Control Study
Jong Eun Hyun, Seul Ki Park
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2026; 48(2): 131. CrossRef - Patient Safety and Quality Improvement in Nursing Practice: Associations Among Workload, Occupational Coping Self-Efficacy and Medical Device-Related Pressure Injury Prevention
Hyun Suk Gwag, Jin Ah Kim
Healthcare.2026; 14(2): 270. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Pressure Injury in ICU Patients
Yang Chaonan, Chaohui Ji, Pan Huibin, Li Shen, Luo Xiaohong
Nursing Open.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Recommendations and Best Practices for the Risk Assessment of Pressure Injuries in Adults Admitted to Intensive Care Units: A Scoping Review
Ricardo Picoito, Tânia Manuel, Sofia Vieira, Rita Azevedo, Elisabete Nunes, Paulo Alves
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(4): 128. CrossRef - Association between nutrition risk and oral mucosal membrane pressure injury in critically ill adults requiring endotracheal tube placement: A prospective cohort study
Xiaohua Ai, Yuchun Deng, Bolan Wang, Hua Deng, Dongmei Tang, Linying Zeng, Yuping Jin, Yurong Liu, Lingli Jia
Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition.2025; 49(8): 983. CrossRef - Risk factors related to pressure injury after spinal surgery in the prone position in patients with diabetes mellitus: A prospective cohort study
Eren Hakki Isci, Ahmet Besir, Ersagun Tugcugil, Ali Riza Guvercin
Medicine.2025; 104(41): e45191. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Pressure Injury in Mechanically Ventilated Patients in Emergency Intensive Care Units: A Prospective Observational Study
Sun Woo Son, Mi Yu
Nursing in Critical Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fatores de risco para lesão por pressão relacionada a dispositivos médicos: revisão sistemática
Daniela Soldera, Nádia Chiodelli Salum, Mônica Stein, Juliana Balbinot Reis Girondi, Alacoque Lorenzini Erdmann, Maritza Regina Stuart
Revista Caribeña de Ciencias Sociales.2025; 14(11): e4911. CrossRef - Yoğun Bakım Hastalarında Tıbbi Cihazla İlişkili Basınç Yaralanması Gelişimi ve Etkileyen Faktörler: Nokta Prevalans Çalışması
Sevil Pamuk Cebeci, Asuman Çobanoğlu, Hatice Oğuzhan
Sağlık Bilimleri Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Dergisi.2024; 6(1): 57. CrossRef - Tıbbi Cihaza Bağlı Basınç Yarası Gelişme Riski
Handan Aydın Kahraman, Gülay İpekçoban
Gümüşhane Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2024; 13(1): 486. CrossRef - Intensive care nurses' knowledge and practices regarding medical device‐related pressure injuries: A descriptive cross‐sectional study
Aslı Kurtgöz, Selin Keskin Kızıltepe, Hülya Keskin, Münevver Sönmez, İsmail Aşatır
International Wound Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with facial pressure injury in patients receiving non‐invasive positive pressure ventilation mask: A retrospective case–control study
Pei‐Ling Wu, Yi‐Jou Li, Hsiang‐Chu Pai, Chien‐Chi Liu
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2024; 33(1): 149. CrossRef - Determination of Incidence and Risk Factors of Medical Device-Related Pressure Injury in the ICU: A Descriptive Study
Ezgi Dirgar, Neslihan Yağmur Gider, Betül Tosun
Advances in Skin & Wound Care.2024; 37(3): 1. CrossRef - Incidence, severity and characteristics of medical device-related pressure injuries in adult intensive care patients: A single-centre, cross-sectional study
Zeynep Temiz, Aylin Aydın Sayılan, Samet Sayılan, Esra Azum
Journal of Tissue Viability.2024; 33(2): 220. CrossRef - NGHIÊN CỨU TÌNH HÌNH CHẤN THƯƠNG ÁP LỰC DO THIẾT BỊ Y TẾ TẠI KHOA HỒI SỨC NGOẠI THẦN KINH BỆNH VIỆN CHỢ RẪY
Trang Nhung Nguyễn, Mai Anh Lợi Mai Anh Lợi, Nguyễn Thị Kim Bằng Nguyễn Thị Kim Bằng
Tạp Chí Khoa Học Trường Đại Học Quốc Tế Hồng Bàng.2024; : 134. CrossRef - Development and validation of a nomogram for oral mucosal membrane pressure injuries in ICU patients: A prospective cohort study
Lingli Jia, Yuchun Deng, Yu Xu, Xiaoli Wu, Dan Liu, Muying Li, Shijun Huang, Yaodan Zhang, Aiping Du, Huan Liu, Yongming Tian
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2024; 33(10): 4112. CrossRef - Factors affecting the occurrence of pressure injuries among patients receiving targeted temperature management after cardiac arrest
Shinhye Ahn, Minjeong An, Sung-Hee Yoo, Hyunyoung Park
Australian Critical Care.2023; 36(3): 313. CrossRef - Incidência de lesões por pressão relacionadas a dispositivos médicos em unidade de terapia intensiva adulto
Nara Reisdorfer, Eliane Regina Pereira do Nascimento, Daniele Delacanal Lazzari, Maria Elena Echevarría-Guanilo, Sabrina Guterres da Silva Galetto , Luciana Bihain Hagemann de Malfussi
Revista de Enfermagem da UFSM.2023; 13: e32. CrossRef - Characteristics and Risk Factors for Pressure Ulcers in Severe Trauma Patients Admitted to the Trauma Intensive Care Unit
Seung-yeon Lim, Young-min Jeong, So-young Jeong
Journal of Acute Care Surgery.2023; 13(2): 47. CrossRef - The Characteristics and Risk Factors of Medical Device Related Pressure Injury in Intensive Care Unit Patients
Mi Hyeon Jo, Hye-Ran Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2023; 16(2): 28. CrossRef - Incidence, prevalence and risk factors of device‐related pressure injuries in adult intensive care unit: A meta‐analysis of 10,084 patients from 11 countries
Yi‐Jie Jia, Fei‐Hong Hu, Wan‐Qing Zhang, Wen Tang, Meng‐Wei Ge, Wang‐Qin Shen, Hong‐Lin Chen
Wound Repair and Regeneration.2023; 31(5): 713. CrossRef - Risk factors for device-related pressure injuries in general ward inpatients of a tertiary general hospital: A case-control study
Minkyung Kim, Yong Soon Shin
Journal of Tissue Viability.2023; 32(4): 601. CrossRef - Determining the incidence and risk factors of medical device-related pressure injury in intensive care patients
Kevser Karacabay, Ayşegül Savci, Mehmet Dalkılıç, Filiz Kabu Hergül
Journal of Tissue Viability.2023; 32(4): 596. CrossRef - Risk factors for medical device-related pressure injury in ICU patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Ling Gou, Zhiqin Zhang, Yongde A., Benjamin M. Liu
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(6): e0287326. CrossRef - Determining Optimal Cut-off Score for the Braden Scale on Assessment of Pressure Injury for Tertiary Hospital Inpatients
Sook Hyun Park, hyeyeon Choi, Youn-Jung Son
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2023; 16(3): 24. CrossRef - Risk factors of medical device‐related pressure injury in intensive care units
Wen Dang, Yuan Liu, Qing Zhou, Yuyu Duan, Huaxiu Gan, Lin Wang, Qiongli Zhu, Chunyan Xie, Ailing Hu
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2022; 31(9-10): 1174. CrossRef - Incidence, characteristics and risk factors of medical device-related pressure injuries: An observational cohort study
Öznur Erbay Dallı, İlkay Ceylan, Nermin Kelebek Girgin
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2022; 69: 103180. CrossRef - Incidence of and risk factors for self‐load‐related and medical device‐related pressure injuries in critically ill patients: A prospective observational cohort study
Tomoko Shimura, Gojiro Nakagami, Rei Ogawa, Shimpei Ono, Toshiaki Takahashi, Misako Nagata, Kosuke Kashiwabara, Junko Sugama, Hiromi Sanada, Makoto Oe
Wound Repair and Regeneration.2022; 30(4): 453. CrossRef - Device-related pressure ulcers: SECURE prevention. Second edition
Amit Gefen, Paulo Alves, Guido Ciprandi, Fiona Coyer, Catherine T Milne, Karen Ousey, Norihiko Ohura, Nicola Waters, Peter Worsley, Joyce Black, Michelle Barakat-Johnson, Dimitri Beeckman, Jacqui Fletcher, Holly Kirkland-Kyhn, Nils A. Lahmann, Zena Moore,
Journal of Wound Care.2022; 31(Sup3a): S1. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Pressure Injury Among Critically Ill Patients in a Coronary Care Unit
Eunji Ko, Seunghye Choi
Advances in Skin & Wound Care.2022; 35(10): 1. CrossRef - Incidence and risk factors of medical device-related pressure injuries among patients undergoing prone position spine surgery in the operating room
Mi Ae Choi, Myoung Soo Kim, Cheol Kim
Journal of Tissue Viability.2021; 30(3): 331. CrossRef - Incidence and Risk Factors Associated with Medical Device-Related Pressure Injuries in Neurosurgery Surgery Patients
Tae Yeong Yang, Joon Bum Kim, Hye Sung Kim, Jung Eun Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 226. CrossRef - Relationships Between Oral-Mucosal Pressure Ulcers, Mechanical Conditions, and Individual Susceptibility in Intubated Patients Under Intensive Care: A PCR-Based Observational Study
Soo Hyun Kim, Hee Sam Nah, Jin Bom Kim, Chul Hoon Kim, Myoung Soo Kim
Biological Research For Nursing.2021; 23(4): 557. CrossRef - Economic Evaluation of Hospital-based Home Care Services for the Breast Cancer Surgery Patients
Jeong Yeon Ko, Ju Young Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(3): 356. CrossRef - Differences in Associated Factors according to the Time of Occurrence of Pressure Ulcers in Intensive Care Unit Patients
Mijung Lee, Eunjeoung Seo, Miok Kim, Jeongok Park, Seonmi Lee, Hyunkyung Shin, Ilsim Yun, Mina Cho, Youngcha Cho, Bomi Kang, Hyunmi Seo, Misoon Lee, Sira Lee, Hyejoo Jang, Hyunsuk Jung, Jeong-Ah Ahn
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2021; 14(3): 26. CrossRef - Development and Testing of an Algorithm to Prevent Medical Device–Related Pressure Injuries
Yeong-Mi Seong, Hyejin Lee, Ji Min Seo
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Communication Competence, Nursing Professionalism and Job Performance among Home Healthcare Nurses
Eunha Jeong, Sujeong Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 409. CrossRef - Incidence and risk factors for medical device‐related pressure ulcers: The first report in this regard in Iran
Farnoosh Rashvand, Lida Shamekhi, Hossein Rafiei, Mohammad Nosrataghaei
International Wound Journal.2020; 17(2): 436. CrossRef - Risk prediction models for the development of oral-mucosal pressure injuries in intubated patients in intensive care units: A prospective observational study
Byung Kwan Choi, Myoung Soo Kim, Soo Hyun Kim
Journal of Tissue Viability.2020; 29(4): 252. CrossRef
- Characteristics of and Risk Factors for Medical Device-Related Pressure Injuries in Trauma Patients in Intensive Care Units: A Retrospective Case–Control Study
- 3,099 View
- 93 Download
- 28 Web of Science
- 39 Crossref

- The Experiences of Patients in Intensive Care Units(ICU)
- Young Hae Kim, Mi Jee Koo, So Hee Kim, Young Mi Kim, Nae Young Lee, Koung Oh Chang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(6):924-931. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.6.924
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to describe the essence of the experiences of patients in an ICU, and to understand them from the patients' point of view. METHODS: Participants in this study were six patients in P hospital. Data collection consisted of in-depth interviews and an observation method done from January to April in 2005. The method was analysis using the phenomenological method proposed by Colaizzi(1978). RESULTS: The themes were classified into eight theme clusters. The eight theme clusters were finally grouped into four categories, 'shock', 'pain', 'gratefulness' and 'pleasure of revival'. CONCLUSION: The ICU patients had negative experiences in physical.mental critical situations, but also positive experiences in consolation and nurses and families' encouragement. Therefore, ICU nurses must support patients and their families to minimize the negative experiences and maximize the positive experiences.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on Nurses' Communication Experiences with Intubation Patients
Ye Rim Kim, Hye Ree Park, Mee Kyung Shin
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2023; 26(1): 28. CrossRef - Item analysis of the Korean version of the Intensive Care Experience Questionnaire: Using the Rasch Model based on Item Response Theory
Jiyeon Kang, Minhui Kim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2022; 15(3): 37. CrossRef - Delirium Experience of the Intensive Care Unit Patients
Jaeyeon Jung, Sujin Jang, Seonmi Jo, Sunhee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(2): 134. CrossRef - Validation of a Korean Translated Version of the Critical Care Pain Observation Tool (CPOT) for ICU Patients
Eun-Mi Kwak, Heeyoung Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(1): 76. CrossRef - Factors Predicting Patient Discomfort after Coronary Angiography
Ae Ran Park, Ja Yun Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(6): 860. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Relocation Stress - Focusing on Patients Transferred from Intensive Care Unit to General Ward -
Youn-Jung Son, Sung-Kyung Hong, Eun Young Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(3): 353. CrossRef
- A Study on Nurses' Communication Experiences with Intubation Patients
- 996 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Patients' Anxiety in Intensive Care Units and Its Related Factors
- Chin Kang Koh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(4):586-593. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.4.586
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to describe patients' anxiety in the ICU and to investigate related factors on the anxiety level.
Methods An exploratory cross-sectional survey design was used. Forty-eight patients participated in the study. Questionnaires were asked to patients who had been cared in the ICUs.
Results Related to the anxiety level, the mean of the total anxiety score was 5.47, and 60% of the patients had moderate or severe level of anxiety. Patients from the coronary care unit had a significantly higher level of anxiety than those from surgical intensive care unit or pulmonary surgery care unit. Moreover, significantly different levels of anxiety were found among patients who had been stayed for 2, 3, or 4 days.
Conclusion Patients who were from the coronary care unit or had been stayed longer (up to 4 days) in the ICU were significantly associated with higher anxiety level.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Anxiety Focused Nursing Interventions on Anxiety, Cognitive Function and Delirium in Neurocritical Patients: A Non‐Randomized Controlled Design
Seo‐young Jang, Myung Kyung Lee
Nursing in Critical Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of audiovisual media-based nursing information on environmental stress, anxiety, and uncertainty in patients undergoing open-heart surgery
Jeong-Yeong Jeon, Dong-Hee Kim, Kyoungrim Kang
Medicine.2023; 102(8): e33001. CrossRef - Effects of Prior Information About Intensive Care Unit Environment on Anxiety and Environmental Stress in Patients Undergoing Open Heart Surgery
Kyong Mi Shin, Hye Ran Choi
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 28. CrossRef - The Effect of Back Pain Prevention Intervention Program on Back Pain Relief in Patients Following Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Hyea Kyung Lee, Yeon Suk Park
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2013; 16(2): 100. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Relocation Stress Syndrome in Patients Following Transfer from Intensive Care Units
Jin-Hee Park, Moon-Sook Yoo, Youn-Jung Son, Sun Hyoung Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(3): 307. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Relocation Stress - Focusing on Patients Transferred from Intensive Care Unit to General Ward -
Youn-Jung Son, Sung-Kyung Hong, Eun Young Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(3): 353. CrossRef
- Effects of Anxiety Focused Nursing Interventions on Anxiety, Cognitive Function and Delirium in Neurocritical Patients: A Non‐Randomized Controlled Design
- 937 View
- 14 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Pain Assessment using CRIES, FLACC and PIPP in High-Risk Infants
- Youngmee Ahn, Heeok Kang, Eunjin Shin
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(7):1401-1409. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.7.1401
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Infants at neonatal intensive care units (NICU) are invariably exposed to various procedural and environmental stimuli. The study was performed to compare the pain responses in three NICU stimulants and to examine the clinical feasibility for NICU infants using CRIES, FLACC and PIPP.
Method In a correlational study, a total of 94 NICU stimulants including angio-catheter insertions, trunk-rubbings and loud noises, was observed for pain responses among 64 infants using CRIES, FLACC and PIPP.
Results A significant difference was identified among the mean scores in CRIES(F(2, 91)=47.847, p=.000), FLACC(F(2, 91)=41.249, p=.000) and PIPP(F(2, 91)=16.272, p=.000) to three stimulants. In a Post-hoc Scheff test, an angio-catheter insertion showed the highest scores in CRIES, FLACC and PIPP compared to the other two stimulations. A strong correlation was identified between CRIES and FLACC in all three stimulations(.817 < r < .945) while inconsistent findings were identified between PIPP and CRIES or FLACC.
Conclusions The results of the study support that CRIES and FLACC are reliable and clinically suitable pain measurements for NICU infants. Further studies are needed in data collection time-point as well as clinical feasibility on PIPP administration to assess pain response in infants, including premature infants.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Pain in the Pediatric Patient Admitted to Sub-Intensive Care: What Is the Evidence? A Scoping Review
Antonio Bonacaro, Carlotta Granata, Chiara Canini, Lucrezia Anderle, Federica Ambrosi, Maria Chiara Bassi, Giacomo Biasucci, Andrea Contini, Giovanna Artioli, Elisa La Malfa, Massimo Guasconi
Epidemiologia.2025; 6(1): 9. CrossRef - Clinical rating scales for assessing pain in newborn infants
Kenneth Färnqvist, Emma Olsson, Andrew Garratt, Themistoklis Paraskevas, Roger F Soll, Matteo Bruschettini, Emma Persad
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Using AI to Detect Pain through Facial Expressions: A Review
Gioacchino D. De Sario, Clifton R. Haider, Karla C. Maita, Ricardo A. Torres-Guzman, Omar S. Emam, Francisco R. Avila, John P. Garcia, Sahar Borna, Christopher J. McLeod, Charles J. Bruce, Rickey E. Carter, Antonio J. Forte
Bioengineering.2023; 10(5): 548. CrossRef - Analgesic Efficacy of Quadratus Lumborum Block in Infants Undergoing Pyeloplasty
Paul F. Chisolm, Nikhi P. Singh, Ian Cummins, Robert A. Oster, Damon Cox, Pankaj P. Dangle
Surgeries.2021; 2(3): 278. CrossRef - Defining and distinguishing infant behavioral states using acoustic cry analysis: is colic painful?
Joanna J. Parga, Sharon Lewin, Juanita Lewis, Diana Montoya-Williams, Abeer Alwan, Brianna Shaul, Carol Han, Susan Y. Bookheimer, Sherry Eyer, Mirella Dapretto, Lonnie Zeltzer, Lauren Dunlap, Usha Nookala, Daniel Sun, Bianca H. Dang, Ariana E. Anderson
Pediatric Research.2020; 87(3): 576. CrossRef - Prevention and treatment of pain in the neonatal intensive care unit
Hanna Popowicz, Wioletta Mędrzycka-Dąbrowska, Katarzyna Kwiecień-Jaguś
BÓL.2018; 19(2): 21. CrossRef - Effect of vapocoolant spray and EMLA cream upon DPT vaccination pain in infants
Gunja Jang, Eunyoung Jeon, Eunsil Lee
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2014; 25(4): 705. CrossRef - Evaluation of Mental Status in High-Risk Neonates using Infants Coma Scale
Young-Mee Ahn, Min Sohn, Sang-Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(4): 561. CrossRef - Pain Response to Procedural Pain in Premature Infants
Jung Sook Kim, Eun Jung Lee, Eun Ha Ham, Ji Hyun Kim, Young Hee Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(4): 352. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Pain in the Pediatric Patient Admitted to Sub-Intensive Care: What Is the Evidence? A Scoping Review
- 1,072 View
- 19 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Evaluating the Validity of the Pediatric Index of Mortality II in the Intensive Care Units
- Jung Soon Kim, Sun Joo Boo
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(1):47-55. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.1.47
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to evaluate the validity of the Pediatric Index of Mortality II(PIM II).
Method The first values on PIM II variables following ICU admission were collected from the patient's charts of 548 admissions retrospectively in three ICUs(medical, surgical, and neurosurgical) at P University Hospital and a cardiac ICU at D University Hospital in Busan from January 1, 2002 to December 31, 2003. Data was analyzed with the SPSSWIN 10.0 program for the descriptive statistics, correlation coefficient, standardized mortality ratio(SMR), validity index(sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value), and AUC of ROC curve.
Result The mortality rate was 10.9%(60 cases) and the predicted death rate was 9.5%. The correlation coefficient(r) between observed and expected death rates was .929(p<.01) and SMR was 1.15. Se, Sp, pPv, nPv, and the correct classification rate were .80, .96, .70, .98, and 94.0% respectively. In addition, areas under the curve(AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic(ROC) was 0.954(95% CI=0.919~0.989). According to demographic characteristics, mortality was underestimated in the medical group and overestimated in the surgical group. In addition, the AUCs of ROC curve were generally high in all subgroups.
Conclusion The PIM II showed a good, so it can be utilized for the subject hospital.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Values of the Pediatric Logistic Organ Dysfunction (PELOD) Score and the Pediatric Index of Mortality (PIM) 2 Score in Emergency Department and Intensive Care Unit
Si Kyoung Jeong, Woon Jeong Lee, Yun Joo Moon, Seon Hee Woo, Yeon Young Kyong, Se Min Choi, Won Jung Jeong, Kyu Nam Park
The Korean Journal of Critical Care Medicine.2010; 25(3): 144. CrossRef - Outcome and risk factors of pediatric hemato-oncology patients admitted in pediatric intensive care unit
Bo Eun Kim, Eun Ju Ha, Keun Wook Bae, Seonguk Kim, Ho Joon Im, Jong Jin Seo, Seong Jong Park
Korean Journal of Pediatrics.2009; 52(10): 1153. CrossRef - Performance effectiveness of pediatric index of mortality 2 (PIM2) and pediatricrisk of mortality III (PRISM III) in pediatric patients with intensive care in single institution: Retrospective study
Hui Seung Hwang, Na Young Lee, Seung Beom Han, Ga Young Kwak, Soo Young Lee, Seung Yun Chung, Jin Han Kang, Dae Chul Jeong
Korean Journal of Pediatrics.2008; 51(11): 1158. CrossRef
- The Values of the Pediatric Logistic Organ Dysfunction (PELOD) Score and the Pediatric Index of Mortality (PIM) 2 Score in Emergency Department and Intensive Care Unit
- 683 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Factors Predicting the Interface Pressure Related to Pressure Injury in Intensive Care Unit Patients
- Ji Seon Shine, Soo Jin Kim, Ji Hyun Lee, Mi Yu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(6):794-805. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.6.794
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose Interface pressure is a factor that contributes to the occurrence of pressure injuries. This study aimed to investigate interface pressure at common sites of pressure injury (occipital, gluteal and peritrochanteric areas), to explore the relationships among risk factors, skin condition and interface pressure, and to identify risk factors influencing interface pressure.
Methods A total of 100 patients admitted to the intensive care unit were enrolled at a tertiary teaching hospital in Korea. Interface pressure was recorded by a scanning aid device (PalmQ). Patient data regarding age, pulmonary disease, Braden Scale score, body mass index, serum albumin, hemoglobin, mean blood pressure, body temperature, and oxygen saturation were included as risk factors. Data collected from July to September 2016 were analyzed using binary logistic regression.
Results The mean interface pressure of the occipital, gluteal, and right and left peritrochanteric areas were 37.96 (±14.90), 41.15 (±16.04), 53.44 (±24.67), and 54.33 (±22.80) mmHg, respectively. Predictive factors for pressure injuries in the occipital area were age ≥70 years (OR 3.45, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.19~9.98), serum albumin deficit (OR 2.88, 95% CI: 1.00~8.26) and body temperature ≥36.5oC (OR 3.12, 95% CI: 1.17~8.17); age ≥70 years (OR 2.81, 95% CI: 1.10~7.15) in the right peritrochanteric area; and body temperature ≥36.5oC (OR 2.86, 95% CI: 1.17~6.98) in the left peritrochanteric area.
Conclusion Our findings suggest that old age, hypoalbuminemia, and high body temperature may be contributory factors to increasing interface pressure; therefore, careful assessment and nursing care of these patients are needed to prevent pressure injury. Further studies are needed to establish cutoff values of interface pressure for patients with pressure ulcers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Postoperative Mobility and its Relationship with Surgery-Related Pressure Injuries: Incidence and Risk Factors in Bariatric Surgery Patients
Yasemin Uslu, Rabia Tülübaş, Yakup Akyüz, Mustafa Atabey
Obesity Surgery.2026; 36(1): 128. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Pressure Injury in Mechanically Ventilated Patients in Emergency Intensive Care Units: A Prospective Observational Study
Sun Woo Son, Mi Yu
Nursing in Critical Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Innovative air mattress for the prevention of pressure ulcers in neonates
Tino Adrian Jucker, Simon Annaheim, Elodie Morlec, Martin Camenzind, Anna-Barbara Schlüer, Barbara Brotschi, René Michel Rossi
Journal of Wound Care.2024; 33(9): 652. CrossRef - A Prospective, Randomized, Non-inferiority Trial to Compare the Efficacy of 3% Povidone-Iodine Foam Dressing and Silver Foam Dressing in the Treatment of Pressure Injuries
Kyung Hee Park, Kyuwon Baek, Minkyung Kim, Myoung Jean Ju, Won Hee Jung, Yong Soon Yoon
Journal of Wound Management and Research.2023; 19(1): 13. CrossRef - Characteristics and risk factors of nasal mucosal pressure injury in intensive care units
Ruiling Nan, Yujie Su, Juhong Pei, Haixia Chen, Li He, Xinman Dou, Shuling Nan
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(1-2): 346. CrossRef - Risk Factors of Endotracheal Intubation-Related Pressure Injury among Patients Admitted to the ICU
Lili Qin, Wenjuan Yun, Cheng Hang
Advances in Skin & Wound Care.2021; 34(3): 144. CrossRef - Impact of Pressure Injuries on Patient Outcomes in a Korean Hospital
Yina Han, Yinji Jin, Taixian Jin, Sun-Mi Lee, Ju-Young Lee
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2019; 46(3): 194. CrossRef - The relationship of subepidermal moisture and early stage pressure injury by visual skin assessment
Chul-Gyu Kim, Seungmi Park, Ji Woon Ko, Sungho Jo
Journal of Tissue Viability.2018; 27(3): 130. CrossRef
- Postoperative Mobility and its Relationship with Surgery-Related Pressure Injuries: Incidence and Risk Factors in Bariatric Surgery Patients
- 1,661 View
- 30 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Model for Unplanned Self Extubation of ICU Patients Using System Dynamics Approach
- Yu Gil Song, Eun Kyoung Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(2):280-292. Published online April 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.2.280
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose In this study a system dynamics methodology was used to identify correlation and nonlinear feedback structure among factors affecting unplanned extubation (UE) of ICU patients and to construct and verify a simulation model.
Methods Factors affecting UE were identified through a theoretical background established by reviewing literature and preceding studies and referencing various statistical data. Related variables were decided through verification of content validity by an expert group. A causal loop diagram (CLD) was made based on the variables. Stock & Flow modeling using Vensim PLE Plus Version 6.0b was performed to establish a model for UE.
Results Based on the literature review and expert verification, 18 variables associated with UE were identified and CLD was prepared. From the prepared CLD, a model was developed by converting to the Stock & Flow Diagram. Results of the simulation showed that patient stress, patient in an agitated state, restraint application, patient movability, and individual intensive nursing were variables giving the greatest effect to UE probability. To verify agreement of the UE model with real situations, simulation with 5 cases was performed. Equation check and sensitivity analysis on TIME STEP were executed to validate model integrity.
Conclusion Results show that identification of a proper model enables prediction of UE probability. This prediction allows for adjustment of related factors, and provides basic data do develop nursing interventions to decrease UE.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prediction model for unplanned extubation of thoracoabdominal drainage tube in postoperative inpatients: a retrospective study
Yushu Sun, Xiuping Li, Jia Xu, Xiaojie Zhang, Fanglei Gu, Hongying Pan
European Journal of Medical Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical application and evaluation of a new type of tracheal catheter fixation belt
Fang Niu, Qinghua Liu, Xiaohui Li, Xiang Li
Nursing Open.2023; 10(4): 2593. CrossRef - Incidence of Unplanned Extubation and Related Factors of Reintubation in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Hee Moon Lim, Hyejung Lee, Mi Jung Park, Jeong Eun Shin
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2022; 26(2): 72. CrossRef - Design of assessment tool for unplanned endotracheal extubation of artificial airway patients
Ping Zhang, Li‐Ping Liu
Nursing Open.2021; 8(4): 1696. CrossRef - Critical care nurses’ communication experiences with patients and families in an intensive care unit: A qualitative study
Hye Jin Yoo, Oak Bun Lim, Jae Lan Shim, Liza Heslop
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(7): e0235694. CrossRef
- Prediction model for unplanned extubation of thoracoabdominal drainage tube in postoperative inpatients: a retrospective study
- 1,293 View
- 16 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Risk Factors for Deliberate Self-extubation
- Young Shin Cho, Jung Hee Yeo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(5):573-580. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.5.573
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to analyze intubation survival rates according to characteristics and to identify the risk factors affecting deliberate self-extubation.
Methods Data were collected from patients' electronic medical reports from one hospital in B city. Participants were 450 patients with endotracheal intubation being treated in intensive care units. The collected data were analyzed using Kaplan-Meier estimation, Log rank test, and Cox's proportional hazards model.
Results Over 15 months thirty-two (7.1%) of the 450 intubation patients intentionally extubated themselves. The patients who had experienced high level of consciousness, agitation. use of sedative, application of restraints, and day and night shift had significantly lower intubation survival rates. Risk factors for deliberate self-extubation were age (60 years and over), unit (neurological intensive care), level of consciousness (higher), agitation, application of restraints, shift (night), and nurse-to-patient ratio (one nurse caring for two or more patients).
Conclusion Appropriate use of sedative drugs, effective treatment to reduce agitation, sufficient nurse-to-patient ratio, and no restraints for patients should be the focus to diminish the number of deliberate self-extubations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ICU Nurses’ Attitudes, Practices, and Perceived Ethical Dilemmas
Regarding the Application of Physical Restraint Algorithms
Ah-Young Cho, Min-Ji Lee, Hyo-Jung Ban, Eun-Jeong Jun, Min-Jung Choi
Korean Journal of Medical Ethics.2025; 28(3): 229. CrossRef - Results of Applying a Ventilator Weaning Protocol Led by an Advanced Practice Nurse for Cardiac Surgery Patients
YoungJu Eim, Su Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(2): 42. CrossRef - Risk Factors associated with Unplanned Removal of Nasogastric Tubes in Neurocritical Patients
Jaejin Kang, Yang-Sook Yoo
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(2): 158. CrossRef - Incidence of Unplanned Extubation and Related Factors of Reintubation in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Hee Moon Lim, Hyejung Lee, Mi Jung Park, Jeong Eun Shin
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2022; 26(2): 72. CrossRef - Unplanned Extubation as a Prognostic Factor in Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Takeshi Unoki, Hideaki Sakuramoto, Shunsuke Taito, Yuki Kataoka
Annals of Clinical Epidemiology.2021; 3(3): 78. CrossRef - Nurses’ Experiences of Patients’ Safety Accidents
Yujin Hur, Miha Chung, Jinyoung Lee
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2021; 24(2): 131. CrossRef - Self-extubation in patients with traumatic head injury: Determinants, complications, and outcomes
SaeedA Mahmood, OmaimaS Mahmood, AymanA El-Menyar, MohammadM Asim, AhmedAbdel-Aziz Abdelbari, TalatSaeed Chughtai, HassanA Al-Thani
Anesthesia: Essays and Researches.2019; 13(3): 589. CrossRef - Unplanned Extubation in Patients with Mechanical Ventilation: Experience in the Medical Intensive Care Unit of a Single Tertiary Hospital
Tae Won Lee, Jeong Woo Hong, Jung-Wan Yoo, Sunmi Ju, Seung Hun Lee, Seung Jun Lee, Yu Ji Cho, Yi Yeong Jeong, Jong Deog Lee, Ho Cheol Kim
Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases.2015; 78(4): 336. CrossRef
- ICU Nurses’ Attitudes, Practices, and Perceived Ethical Dilemmas
Regarding the Application of Physical Restraint Algorithms
- 1,535 View
- 10 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Pain Perception of Nurses and Pain Expression of Patients in Critical Care Units
- Kyung Hee Bae, Ihn Sook Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(4):437-445. Published online August 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.4.437
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to identify pain perception (P-PER) by nurses and pain expression (P-EXP) by patients in critical care units (ICUs) and degree of agreement between nurses' P-PER and patients' P-EXP.
Methods Nurses' P-PER was measured with a self-administered questionnaire completed by 99 nurses working in ICUs during May, 2013. Patients' P-EXP was measured with the Critical Care Non-Verbal Pain Scale through observations of 31 ICU patients during nine nursing procedures (NPs) performed between May and July, 2013.
Results Nurses' P-PER was from 4.49 points for nasogastric tube (NGT) insertion to 0.83 for blood pressure (BP) measurement based on a 9-point scale, Patients' P-EXP was 4.48 points for NGT to 0.18 for BP measurement based on a 10-point scale. Eight NPs except oral care showed higher scores for nurses' P-PER than for patients' P-EXP. Position change (
p =.019), subcutaneous injection (p <.001), blood sugar test (p <.001), and BP measurement (p <.001) showed significant differences between nurses' P-PER and patients' P-EXP.Conclusion Nasogastric tube (NGT) insertion was scored highest by both nurses and patients. Eight NPs except 'oral care' showed nurses' P-PER was higher or similar to patients' P-EXP, which indicates that nurses may overestimate procedural pain experienced by patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding oral care in the intensive care unit: A qualitative study of nurse experiences and practices with mechanically ventilated patients
Li SuWen, Huang YuYang, Bu Wei
Nursing in Critical Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Systematic Review on Pain Assessment Tools for Intensive Care Unit Patients
Eun-Jeong Kim, Jiwon Hong, Jiyeon Kang, Na geong Kim, NaRi Kim, Su-Youn Maeng, Hye-Ryeon Park, Min Kyung Ban, Gun Young Yang, Kyung Suk Lee, Eun Hye Jang
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2020; 13(1): 44. CrossRef - Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Pain, Agitation/Sedation, Delirium, Immobility, and Sleep Disruption in Adult Patients in the ICU
John W. Devlin, Yoanna Skrobik, Céline Gélinas, Dale M. Needham, Arjen J. C. Slooter, Pratik P. Pandharipande, Paula L. Watson, Gerald L. Weinhouse, Mark E. Nunnally, Bram Rochwerg, Michele C. Balas, Mark van den Boogaard, Karen J. Bosma, Nathaniel E. Bru
Critical Care Medicine.2018; 46(9): e825. CrossRef
- Understanding oral care in the intensive care unit: A qualitative study of nurse experiences and practices with mechanically ventilated patients
- 1,114 View
- 9 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes for Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus Colonization on Intensive Care Unit Admission
- Sook-Jin Byun, Jiyeon Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(2):287-295. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.2.287
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify vancomycin-resistant enterococcus (VRE) colonization rate in patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU), associated risk factors and clinical outcomes for VRE colonization.
Methods Of the 7,703 patients admitted to the ICUs between January, 2008 and December, 2010, medical records of 554 VRE colonized and 503 uncolonized patients were reviewed retrospectively. To analyzed the impact of colonization on patients' clinical outcomes, 199 VRE colonized patients were matched with 199 uncolonized patients using a propensity score matching method.
Results During the study period, 567 (7.2%) of the 7,703 patients were colonized with VRE. Multivariate analysis identified the following independent risk factors for VRE colonization: use of antibiotics (odds ratio [OR]=3.33), having bedsores (OR=2.92), having invasive devices (OR=2.29), methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus co-colonization (OR=1.84), and previous hospitalization (OR=1.74). VRE colonized patients were more likely to have infectious diseases than uncolonized patients. VRE colonization was associated with prolonged hospitalization and higher mortality.
Conclusion Strict infection control program including preemptive isolation for high-risk group may be helpful. Further research needs to be done to investigate the effects of active surveillance program on the incidence of colonization or infection with VRE in the ICU.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci Prevalence, Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns and Colonization Risk Factors Among HIV-Positive Patients in Health-Care Facilities in Debre Berhan Town, Ethiopia
Mikiyas Zike, Abdurahaman Ahmed, Awraris Hailu, Bedru Hussien
Infection and Drug Resistance.2024; Volume 17: 17. CrossRef - Previous antibiotic therapy as independent risk factor for the presence of vancomycin-resistant enterococci in surgical inpatients. Results from a matched case-control study
Philip MacKenzie, Jacqueline Färber, Marius Post, Torben Esser, Lukas Bechmann, Siegfried Kropf, Roland Croner, Gernot Geginat
BMC Infectious Diseases.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Steady Inflow of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci from Outside a Hospital
Hye-sun An, Sang-Won Park, Su-hui Ko, Ji Hwan Bang
Korean Journal of Healthcare-Associated Infection Control and Prevention.2017; 22(2): 63. CrossRef - Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus colonization in the intensive care unit: Clinical outcomes and attributable costs of hospitalization
Euihan Jung, Sookjin Byun, Hojin Lee, Sang Yi Moon, Hyuck Lee
American Journal of Infection Control.2014; 42(10): 1062. CrossRef
- Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci Prevalence, Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns and Colonization Risk Factors Among HIV-Positive Patients in Health-Care Facilities in Debre Berhan Town, Ethiopia
- 1,158 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Relocation Stress Syndrome in Patients Following Transfer from Intensive Care Units
- Jin-Hee Park, Moon-Sook Yoo, Youn-Jung Son, Sun Hyoung Bae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(3):307-316. Published online June 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.3.307
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the levels of relocation stress syndrome (RSS) and influencing the stress experienced by Intensive Care Unit (ICU) patients just after transfer to general wards.
Methods A cross-sectional study was conducted with 257 patients who transferred from the intensive care unit. Data were collected through self-report questionnaires from May to October, 2009. Data were analyzed using the Pearson correlation coefficient, t-test, one-way ANOVA, and stepwise multiple linear regression with SPSS/WIN 12.0.
Results The mean score for RSS was 17.80±9.16. The factors predicting relocation stress syndrome were symptom experience, differences in scope and quality of care provided by ICU and ward nursing staffs, satisfaction with transfer process, length of stay in ICU and economic status, and these factors explained 40% of relocation stress syndrome (F=31.61,
p <.001).Conclusion By understanding the stress experienced by ICU patients, nurses are better able to provide psychological support and thus more holistic care to critically ill patients. Further research is needed to consider the impact of relocation stress syndrome on patients' health outcomes in the recovery trajectory.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A phenomenological study on the experiences of patient transfer from the intensive care unit to general wards
Eun-Young Lee, Jin-Hee Park, Alvisa Palese
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(7): e0254316. CrossRef - Development and psychometric evaluation of the Relocation Stress Syndrome Scale-Short Form for patients transferred from adult intensive care units to general wards
Mi Hwa Won, Youn-Jung Son
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2020; 58: 102800. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Transition Nursing Program for Patients and Family Caregivers at a Neurological ICU in Korea
Sun Hee Yun, Eui Geum Oh, Yang Sook Yoo, So Sun Kim, Yeon Soo Jang
Clinical Nursing Research.2017; 26(1): 27. CrossRef - The Effects of Aromatherapy on Intensive Care Unit Patients’ Stress and Sleep Quality: A Nonrandomised Controlled Trial
Eun Hee Cho, Mi-Young Lee, Myung-Haeng Hur, Nativ Dudai
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - A tailored relocation stress intervention programme for family caregivers of patients transferred from a surgical intensive care unit to a general ward
Seul Lee, HyunSoo Oh, YeonOk Suh, WhaSook Seo
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2017; 26(5-6): 784. CrossRef - Clinical validity of a relocation stress scale for the families of patients transferred from intensive care units
HyunSoo Oh, Seul Lee, JiSun Kim, EunJu Lee, HyoNam Min, OkJa Cho, WhaSook Seo
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2015; 24(13-14): 1805. CrossRef
- A phenomenological study on the experiences of patient transfer from the intensive care unit to general wards
- 1,425 View
- 12 Download
- 6 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


