-
Serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression on the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety in high-risk pregnant couples of South Korea
-
Mihyeon Park, Sukhee Ahn
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):19-33. Published online February 4, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24070
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
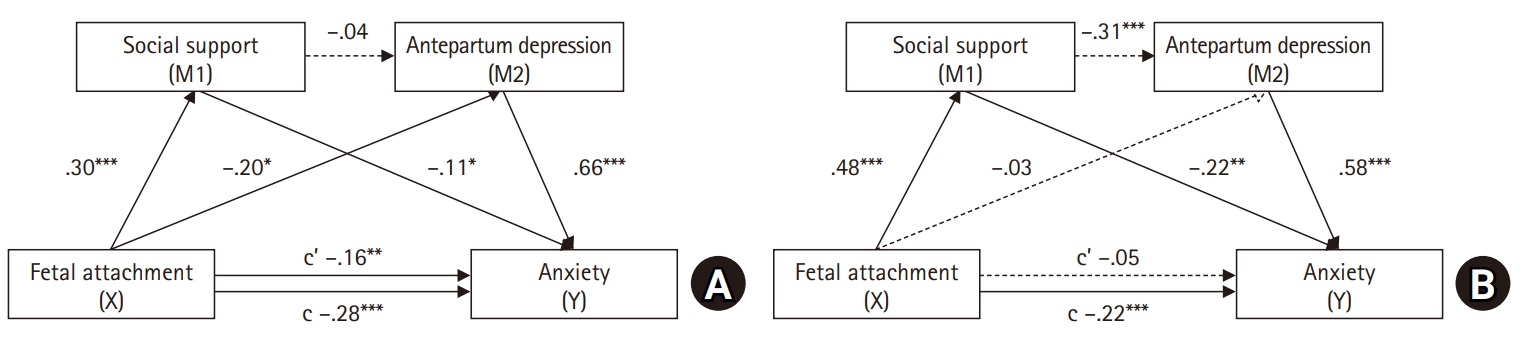
This study examined the direct effects of fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression on anxiety in pregnant women with high-risk pregnancy-related conditions and their husbands. Furthermore, it aimed to explore the serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression in the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety.
Methods
A survey-based study was conducted among pregnant women diagnosed with high-risk pregnancy conditions at 24–32 weeks and their husbands, recruited from a pregnant women’s online community between January 20, 2021 and July 20, 2022. Data were collected from 294 individuals (147 couples) using self-report questionnaires. Correlations between variables were analyzed using the IBM SPSS software ver. 26.0 (IBM Corp.), and the mediation effects were assessed using the PROCESS macro, model 6.
Results
In the maternal model, maternal-fetal attachment directly affected anxiety (p=.005), with antepartum depression partially mediating this relationship (95% confidence interval [CI], –0.26 to –0.01). In the paternal model, paternal-fetal attachment had no direct effect on anxiety (p=.458). However, social support and antepartum depression fully mediated the relationship between paternal-fetal attachment and anxiety (95% CI, –0.14 to –0.03).
Conclusion
The findings indicate that social support in the relationship between fetal attachment and depression in high-risk pregnant women and their partners can have direct or indirect effects on the negative emotions of high-risk pregnant couples. It is necessary to assess the level of anxiety in couples experiencing high-risk pregnancies and provide comprehensive nursing interventions that address fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression in order to reduce anxiety.
-
Perceptual Factors Associated with Gestational Weight Gain: A Cross-Sectional Survey
-
Sehee Kim, Sukhee Ahn
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):495-508. Published online November 1, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24052
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
Recent years have seen an increase in the number of pregnant women whose weight gain during pregnancy exceeds the recommended range. This study was intended to determine the relationships among demographic attributes, key perceptual factors, and gestational weight gain (GWG).
Methods
This cross-sectional study was conducted between April and July 2022. First-time pregnant women beyond 36 weeks of gestation who were recruited via social media completed an online survey. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA, chi-square test, and logistic regression, all performed using SPSS software.
Results
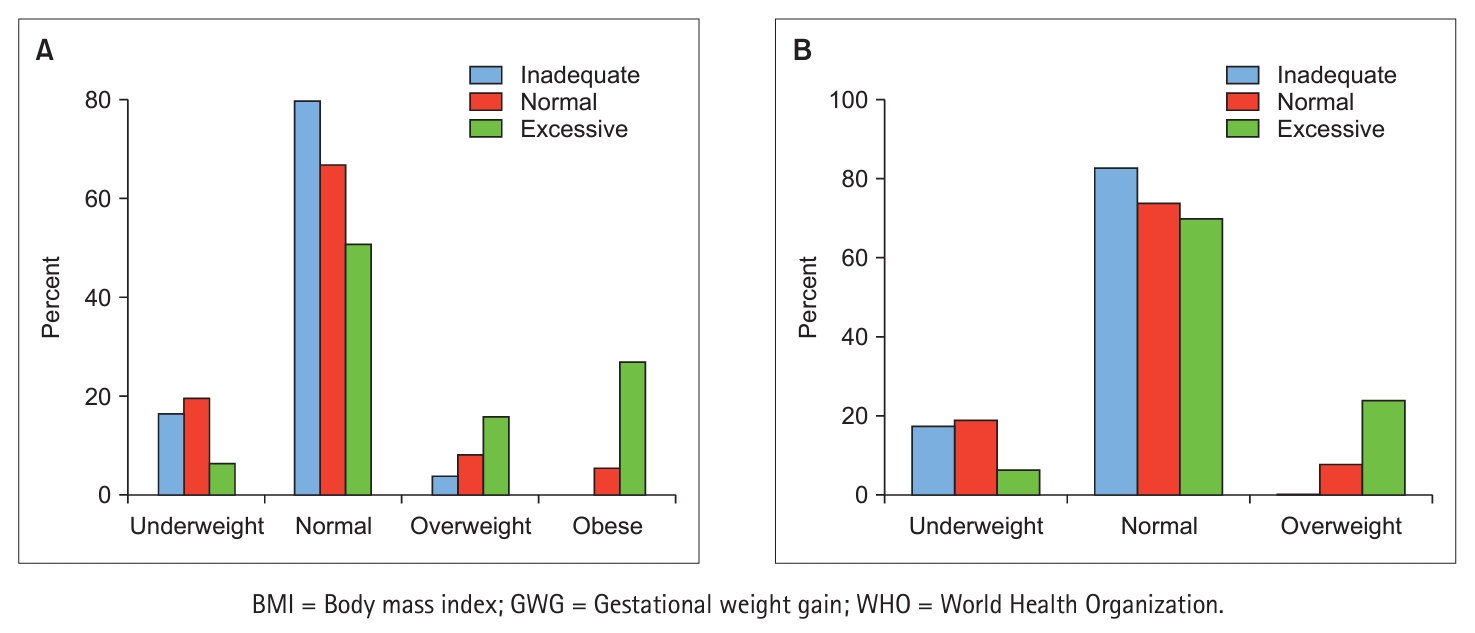
Of the 369 participants, 63 (17.1%) exceeded the recommended GWG guidelines, while 148 (40.1%) fell within the recommended range, and the remaining 158 (42.8%) had inadequate GWG. Being overweight or obese before pregnancy significantly increased the risk of excessive GWG (p < .001). This risk was also significantly greater for women with low internal weight locus of control (OR = 0.58, 95% CI 0.41~0.82), high external weight locus of control (OR = 1.75, 95% CI 1.31~2.34), and negative body image (OR = 0.62, 95% CI 0.51~0.75).
Conclusion
The growing trend of excessive GWG among pregnant women is influenced by a combination of prepregnancy body mass index (BMI) and perceptual factors, including weight locus of control and body image. These findings underscore the need to implement weight management intervention strategies before pregnancy, taking into consideration BMI, and to enhance positive body image and internal locus of control.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Factors Associated With Gestational Weight Gain Among Nurses in Korea
Sook Jung Kang, Woon Young Hwang, Hyunju Dan, Sue Kim, Kwang-Pil Ko
Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, & Neonatal Nursing.2025; 54(5): 543. CrossRef - Attitudes toward body weight and shape during pregnancy among Japanese women who were underweight before pregnancy: A qualitative study
Chisato KOROGI, Mie SHIRAISHI, Kaori MATSUDA, Natsuki HORI, Hanna HORIGUCHI
Journal of Japan Academy of Midwifery.2025; 39(3): 456. CrossRef
-
2,796
View
-
109
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
2
Crossref
-
A Predictive Model of Fall Prevention Behaviors in Postmenopausal Women
-
Hyun-Jung Jang, Sukhee Ahn
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(5):525-533. Published online October 15, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.5.525
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Abstract
Purpose
This study was done to propose and test a predictive model that would explain and predict fall prevention behaviors in postmenopausal women. The health belief model was the theoretical basis to aid development of a nursing intervention fall prevention program.
Methods
Data for 421 postmenopausal women were selected from an original data set using a survey design. The structural equation model was tested for 3 constructs: modifying factors, expectation factors, and threat factors. Expectation factors were measured as relative perceived benefit (perceived benefit minus perceived barrier), self-efficacy, and health motivation; threat factors, as perceived susceptibility (fear of falling) and perceived severity (avoiding activity for fear of falling); and modifying factors: level of education and knowledge about fall prevention. Data were analyzed using SPSS Windows and AMOS program.
Results
Mean age was 55.7 years (range 45-64), and 19.7% had experienced a fall within the past year. Fall prevention behaviors were explained by expectation and threat factors indicating significant direct effects. Mediating effect of health beliefs was significant in the relationship between modifying factors and fall prevention behaviors. The proposed model explained 33% of the variance.
Conclusion
Results indicate that fall prevention education should include knowledge, expectation, and threat factors based on health belief model.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Construction and validation of a nomogram for predicting fear of falling related activity restrictions in community-dwelling older adults
Yuxin Zhang, Rong Xue, Yuxiu Zhou, Yu Liu, Yumeng Li, Xiaoyue Zhang, Kaili Zhang
Geriatric Nursing.2024; 55: 286. CrossRef - Osteoporosis or fracture risk associated with thiazolidinedione and proton pump inhibitor co‐administration in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Miyoung Ock, Sera Lee, Hyunah Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2022; 47(7): 1028. CrossRef - Associations between sleep duration, midday napping, depression, and falls among postmenopausal women in China: a population-based nationwide study
Zonglei Zhou, Yu Yu, Ruzhen Zhou, Rongsheng Luan, Kunpeng Li
Menopause.2021; 28(5): 554. CrossRef - Exploring Fear of Falling Related Activity Avoidance among Postmenopausal Women
Sukhee Ahn, Rhayun Song
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4042. CrossRef - Effects of a health-belief-model-based osteoporosis- and fall-prevention program on women at early old age
Sukhee Ahn, Jiwon Oh
Applied Nursing Research.2021; 59: 151430. CrossRef - Identification of risk factors for falls in postmenopausal women: a systematic review and meta-analysis
J. Zhao, G. Liang, H. Huang, L. Zeng, W. Yang, J. Pan, J. Liu
Osteoporosis International.2020; 31(10): 1895. CrossRef - Structural Analysis of Variables related to Fall Prevention Behavior of Registered Nurses in Small-to-Medium Sized Hospitals
Ji Hyun Park, Jung Tae Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2018; 25(4): 269. CrossRef - Relationships among Knowledge, Self-efficacy, and Health Behavior of Osteoporosis and Fall Prevention in Old Aged Women
Sukhee Ahn, Jiwon Oh
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(2): 209. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Fall Risk Perception on the Relationship between Fracture Risk and Fall Prevention Behaviors in Women with Osteoporosis
Eun Nam Lee, Eun Jung Choi, Moon Jung Jang, Hyun Ju Hwang
Journal of muscle and joint health.2015; 22(2): 130. CrossRef - An Equation Model Development and Test based on Health Belief Model Regarding Osteoporosis Prevention Behaviors among Postmenopausal Women
Hyun-Jung Jang, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(6): 624. CrossRef - A Structural Equation Model of Fall Prevention Behavior among Community-dwelling Older Adults with Osteoarthritis
Keong Sook Jang, Rhayun Song
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(6): 684. CrossRef
-
1,117
View
-
9
Download
-
11
Crossref
-
Development and Evaluation of Breastfeeding Promotion Program for Mothers with Breast Engorgement following Cesarean Birth
-
Jeongsug Cho, Sukhee Ahn
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(2):170-178. Published online April 30, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.2.170
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
This study was to develop a breastfeeding promotion program and to test effects of the program on levels of breast discomfort, breast size, sodium in breast milk, and type of feeding in mothers with breast engorgement following cesarean birth.
Methods
A non-synchronized non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used in this study. The participants were 70 postpartum mothers who were admitted to a postpartum care center and experienced breast engorgement following cesarean birth. The planned nursing intervention was the breastfeeding promotion program consisting of breast massage and 1:1 breastfeeding education, counseling, and support focusing on individualized problem solving provided for 10 days. Fifty-three women completed the program (experimental group 26, control group, 27). Measurements were level of breast discomfort, breast size, sodium in breast milk and type of feeding at pre and posttest.
Results
Women who participated in the program experienced lower scores for breast discomfort, greater decrease in breast size, lower levels of sodium in breast milk, and practiced breastfeeding more than those in the control group.
Conclusion
Results indicate that this breastfeeding promotion program is effective in reducing breast engorgement and improving breastfeeding practices, and is therefore recommended to enhance breastfeeding promotion practice in postpartum care centers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of midwife-led continuity of care combined with individualized breast management on postpartum recovery and lactation function in women undergoing cesarean section
Hua Cai, Yan Lu, Xinyi Kang, Liping Chen
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A randomized controlled trial of pectoralis major myofascial release massage for breastfeeding mothers: breast pain, engorgement, and newborns’ breast milk intake and sleeping patterns
Won-Ryung Choi, Myung-Haeng Hur, Yeon-Suk Kim, Ju-Ri Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(1): 66. CrossRef - Effect of aloe vera gel compresses on breast engorgement among postpartum mother
Siti Raihanah, Jasmawati Jasmawati, Nursyahid Siregar
Healthcare in Low-resource Settings.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between Selected Trace Elements in Human Milk and Psychosocial Characteristics in Korean Early Postpartum Women
Sookjin Noh, Eunjoo Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(1): 350. CrossRef - The Influence of Knowledge and Health Beliefs about Gestational Diabetes on Breastfeeding Intention of Women with Gestational Diabetes
Seungmi Park, Deulle Min, Jiyeon Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(4): 427. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of Breast Care for Postpartum Mothers
Ji-Ah Song, Myung Haeng Hur
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(3): 258. CrossRef - Fibroadenoma of bilateral axillary ectopic breast tissue: A rare case report based on Orem’s Self Care theory
G Pinar, H Erbaba
Archives of Nursing Practice and Care.2019; 5(1): 008. CrossRef - Effects of Breastfeeding Interventions on Breastfeeding Rates at 1, 3 and 6 Months Postpartum: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Seol Hui Park, Seang Ryu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(6): 713. CrossRef - Effects of Boheotang-gagam on Milk Production and Factors Related Lactation in Postpartum Mice
Ah-Yeong Lee, Eun-Hee Lee, Ji-Yeong Im, Hong-Jun Kim, Chang-Hyun Lee
The Journal of Oriental Obstetrics and Gynecology.2016; 29(1): 35. CrossRef - Comparison of Lactation Problems, Knowledge, and Adaptation on Breastfeeding between Users and Non-Users of Lactation Clinic
Myoung Hee Yun, Hye Sook Shin
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2014; 20(2): 112. CrossRef
-
1,313
View
-
16
Download
-
10
Crossref
-
Depression of Married and Employed Women Based on Social-Role Theory
-
Insook Cho, Sukhee Ahn, Souk Young Kim, Young Sook Park, Hae Won Kim, Sun Ok Lee, Sook Hee Lee, Chae Weon Chung
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(4):496-507. Published online August 12, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.4.496
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Abstract
Purpose
This study was based on social-role theory, and purposes were to investigate (1) how depression and health determinants vary with married and employed women, and (2) what factors contribute to depression according to family cycle.
Methods
A stratified convenience sample of 765 married and employed women was recruited during May to August 2010. Study variables of depression, socio-demographic threatening factors, psycho-stimulating factors, and social-role related factors were measured via a structured questionnaire.
Results
Prevalence rate for depression was 18.6%, with highest rate (25.4%) from elementary laborers. Greater levels of depression were related to women’s occupation, higher life stress, and poorer health; lower social support and vulnerable personality; higher levels of social-role related stress. From multivariate analysis, women with preadolescents were the most vulnerable to depression affected by occupation, life stress, personality, and parenting stress. These factors (except for occupational class) combined with economic status, social support, and housework unfairness were significant for depression in women with adolescents.
Conclusion
Depression among married and employed women differs by psycho-stimulating and social role relevant factors in addition to occupational class and family life cycle. Female elementary laborers and women with children need to have the highest prioritization for community mental health programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Latent profile analysis of depression among dual-income couples raising young children before and after COVID-19
Jiwon Bang, Sung-Kyung Yoo
Journal of Families and Better Life.2024; 42(1): 43. CrossRef - Comparison of Quality of Life and Coping Strategies among Firefighters and Emergency Medical Services Personnel in Saveh, Iran
Bahram Armoon, Parisa Hosseini Koukamari, Mohammad Reza Rouhani, Leila Gharegozloo, Mahmood Karimy, Anthony Coetzer-Liversage
NEW SOLUTIONS: A Journal of Environmental and Occupational Health Policy.2024; 34(2): 120. CrossRef - Work–Family Conflict and Depressive Symptoms of Married Working Women in Korea: The Role of Marriage Satisfaction and Organizational Gender Discrimination Climate
Ji-Young Kim, Gye-Hyun Jung, Ji-Hye Kim
SAGE Open Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The multilevel factors related to the depression symptoms of married middle-aged working women
Jiwon Choi, Soohyun Noh, Haram Jeong, Hyekyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2023; 40(2): 67. CrossRef - Effects of Women’s Work-Family Multiple Role and Role Combination on Depressive Symptoms in Korea
Ji-won Kang, Soong-nang Jang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(4): 1249. CrossRef - The Mediating Effects of Marital Intimacy and Work Satisfaction in the Relationship between Husbands’ Domestic Labor and Depressive Mood of Married Working Women
Su-Yeon Choi, Hyoung-Ryoul Kim, Jun-Pyo Myong
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(12): 4547. CrossRef - Partners' relationship and depression
Petra Kasalová, Ján Praško, Marie Ocisková, Jakub Vaněk, Michaela Holubová, Aleš Grambal, František Hodný, Lucie Bundárová, Vlastimil Nesnídal, Daniela Zmeškalová, Antonín Kolek
Psychiatrie pro praxi.2020; 21(2): 90. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Meaning in Life on the Relationship between Social Connectedness and Depression among Middle-aged Women
Jung A Son, JinJu Kim, Myung Sun Hyun
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(4): 373. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Unmet Healthcare Needs of Working Married Immigrant Women in South Korea
Jinseon Yi, Insook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(1): 41. CrossRef - Life's Experiences of Middle-aged Divorced Women with Higher Education and Profession
Hyeong-Sook Park, Young-Sil Bae, Sung-Hwa Lee, Su-Jeong Yu, So-Young Jeon
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(1): 11. CrossRef - Effect of Job Insecurity on Job related Depression and Anxiety: Large- and Small-sized Company Employees
Yeongmi Ha, Hyunju Park
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(4): 329. CrossRef - The Influence of Health Behaviors and Health related Quality of Life on Depression among Korean Female Problem Drinker
Min Hee Park, Hae Ok Jeon
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(11): 7844. CrossRef - Relating Factors for Depression in Korean Working Women: Secondary Analysis of the Fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V)
Kyung-Jae Lee, Jeung-Im Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(3): 265. CrossRef
-
1,252
View
-
6
Download
-
13
Crossref
-
Effects of Breast Massage on Breast Pain, Breast-milk Sodium, and Newborn Suckling in Early Postpartum Mothers
-
Sukhee Ahn, Jinhee Kim, Jungsuk Cho
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(4):451-459. Published online August 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.4.451
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
In this study the effects of breast massage on breast pain, breast-milk sodium, and newborn suckling in early postpartum mothers were investigated.
Methods
The design was a non-synchronized nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design. Sixty postpartum mothers who were admitted to a postpartum care center and had problems with breastfeeding were recruited. Of these mothers, 44 were assigned to the intervention group and received two 30-minute breast massages within 10 days of postpartum period. The others were assigned control group and received only routine care. Breast pain was measured using a numeric pain scale and number of times newborns suckled was observed throughout breastfeeding. Breast milk was self-collected to evaluate breast-milk sodium.
Results
Mean age of postpartum mothers was 30 years old. Compared to the control group, women in the intervention group reported significant decreases in breast pain (p<.001), increases in number of times newborns suckled after the first and second massage (p<.001), and a decrease in breast-milk sodium after the first massage (p=.034).
Conclusion
Breast massage may have effects on relieving breast pain, decreasing breast-milk sodium, and improving newborn suckling. Breast massage can be used to solve breast problems. Further research is needed to validate our findings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Auricular Acupressure on Breast Pain Among Breastfeeding Mothers Receiving Gentle Hand Techniques: A Randomized, Single-Blind, Sham-Controlled Trial
Shinae Han, Bomi Kim, Hyojung Park
Journal of Human Lactation.2024; 40(2): 248. CrossRef - Physical therapists’ experiences and perceptions of antepartum and postpartum care
Kuan-Yin Lin, Yi-Ju Tsai, Jeng-Feng Yang, Meng-Hsing Wu
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Five-step Systematic Therapy for Treating Plugged Ducts and Mastitis in Breastfeeding Women: A Case–Control Study
Yuzhi Yao, Tianzhu Long, Yuhong Pan, Yin Li, Ling Wu, Benjie Fu, Hongmin Ma
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(3): 197. CrossRef - The Acceptability, Feasibility, and Effectiveness of Breast Massage Combined with Acupoint Stimulation to Promote the Volume of Human Milk in Mothers with Preterm Infants: A Pilot Study
Jia Sheng, Yan Ding, Jing Wang, Junping Zhang, Xingling Qi, Haiou Xia, Longfei Yang
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - The Influence of Knowledge and Health Beliefs about Gestational Diabetes on Breastfeeding Intention of Women with Gestational Diabetes
Seungmi Park, Deulle Min, Jiyeon Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(4): 427. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of Breast Care for Postpartum Mothers
Ji-Ah Song, Myung Haeng Hur
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(3): 258. CrossRef - TO STUDY THE IMPACT OF UNILATERAL BREAST MASSAGE ON MILK VOLUME AMONG POSTNATAL MOTHERS - A QUASI-EXPERIMENTAL STUDY
Santhosh Kumar Kraleti ., Swapna Lingaldinna ., Sravani Kalvala ., Sadiqua Anjum ., Himabindu Singh .
Indian Journal of Child Health.2018; 5(12): 731. CrossRef - Multiple-Case Studies of Hand-on Breast Massage Techniques used by Breastfeeding Experts
Hyunsoon Park, Insook Cho, Min-Kyeong Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2017; 23(3): 155. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Breastfeeding Promotion Program for Mothers with Breast Engorgement following Cesarean Birth
Jeongsug Cho, Sukhee Ahn
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(2): 170. CrossRef - Effects of Oketani Breast Massage on Breast Discomfort, Breast Pumping Time and Breast-milk compositions in Preterm Infants' Mothers
Hee-Young Kim, Kyeong-Uoon Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(2): 701. CrossRef - Effects of Self-breast Pumping in Primiparous Women after Cesarean Delivery
Jung Hee Yeo, Guil Nam Moon, Sun-Ok Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2012; 18(2): 98. CrossRef
-
3,084
View
-
50
Download
-
11
Crossref
-
Effects of Tai Chi Exercise on Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Quality of Life in Post-menopausal Women
-
Rhayun Song, Sukhee Ahn, Hee Young So, In Sook Park, Hyun Li Kim, Kyung Ok Joo, Jong Sung Kim
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(1):136-144. Published online February 17, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.1.136
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose:
Natural menopause resulting in the decline in endogenous estrogen concentrations is responsible for an increased risk of coronary heart disease in postmenopausal women. The purpose of the study was to examine the effects of a 6-month Tai Chi exercise program on cardiovascular risk factors and quality of life in post-menopausal women.
Methods:
A quasi-experimental design with pretest and posttest measures was used. The participants in the study, 29 women in the Tai Chi group and 31 in the control group, were enrolled for 6 months.
Results:
After 6 months of Tai Chi exercise, total cholesterol (M=213 to 185), LDL-cholesterol (M=135 to 128), and their 10 yr cardiovascular disease risk (M=2.62 to 2.27) had improved significantly for the Tai Chi participants compared to the control group. Total scores for quality of life along with the sub-dimensions of health perception and mental functioning were also significantly higher in the Tai Chi participants.
Conclusion:
Tai Chi exercise favorably affected cardiovascular health and quality of life in post-menopausal women after 6 months. Additional rigorous studies are needed to examine long term effects on the prevention of cardiovascular disease in this population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Meta-analysis of the intervention effects of tai chi on fasting blood glucose, blood pressure and triglyceride in middle-aged and elderly people
Wenzheng Zhao, Hanyu Ju, Kaituo Zhu
The Aging Male.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Study on the Joint Biomechanics of Different Skill Level Practitioners in Chen-Style Tai Chi Punching
Hongguang Hua, Dong Zhu, Yifan Wang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(10): 5915. CrossRef - Self-Rated Health Status Based on the Type of Health Insurance: A Socioeconomic Perspective
Minsung Sohn, Minsoo Jung, Mankyu Choi
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlates of health-related quality of life in patients with myocardial infarction: A literature review
Kyoungrim Kang, Leila Gholizadeh, Sally C. Inglis, Hae-Ra Han
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2017; 73: 1. CrossRef - Effects of tai chi on symptoms and quality of life in women with overactive bladder symptoms: A non-randomized clinical trial
Jeong Lim Cho, Eun Nam Lee, Myeong Soo Lee
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2017; 12: 189. CrossRef - Interventions that improve health-related quality of life in patients with myocardial infarction
Kyoungrim Kang, Leila Gholizadeh, Sally C. Inglis, Hae-Ra Han
Quality of Life Research.2016; 25(11): 2725. CrossRef - Atherogenic index of plasma and risk of cardiovascular disease among Cameroonian postmenopausal women
Jobert Richie N. Nansseu, Vicky Jocelyne Ama Moor, Murielle Elsa D. Nouaga, Bertrand Zing-Awona, Gladys Tchanana, Arthur Ketcha
Lipids in Health and Disease.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - The job analysis of Korean nurses as a strategy to improve the Korean Nursing Licensing Examination
In Sook Park, Yeon Ok Suh, Hae Sook Park, Soo Yeon Ahn, Ahn Kang, Il Sun Ko
Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions.2016; 13: 24. CrossRef - A Pilot Study of APN-led Self-management Program to Improve Cardiovascular Health Status among Korean Women with Risk Factors
Nah-Mee Shin, Ji-Won Yoon, Jiwon Choi, Younghee Park, Songi Jeon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(2): 237. CrossRef - A Pilot Study Examining the Effects of 12-week Tai chi Exercise on the Activity of Autonomic Nervous System and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
Kyoung Ran Kong, Eun Nam Lee, Hyun Ju Hwang
Journal of muscle and joint health.2016; 23(1): 1. CrossRef - Teaching Experience of Tai Chi Instructors with Nursing Background
In Sook Park, Rhayun Song
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(1): 10. CrossRef - Effects of Tai Chi Exercises on Cardiovascular Risks, Recurrence Risk, and Quality of Life in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Rha Yun Song, Moon Kyoung Park, Jin-Ok Cheong, Jae-Hyeong Park, In-Whan Seong
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(5): 515. CrossRef - Tai Chi research review
Tiffany Field
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2011; 17(3): 141. CrossRef - Women Religious and Married Women's Attitudes toward Menopause and Menopausal Symptoms
Myung-Sook Yoo
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(2): 186. CrossRef - Comparison of Cardiovascular Health Status and Health Behaviors in Korean Women based on Household Income
Young-Joo Park, Nah-Mee Shin, Ji-Won Yoon, Jiwon Choi, Sook-Ja Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(6): 831. CrossRef
-
1,239
View
-
11
Download
-
15
Crossref
-
Factors explaining Quality of Life in Individuals with Coronary Artery Disease
-
In Sook Park, Rhayun Song, Sukhee Ahn, Hee Young So, Hyun Li Kim, Kyung Ok Joo
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2008;38(6):866-873. Published online December 31, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.6.866
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The study was done to compare quality of life by gender, and to identify factors which explain quality of life in
individuals with coronary artery disease.
Methods
For the survey, 91 individuals (53 men and 38 women) agreed to participate in the study. Cardiovascular risk factors, systolic blood pressure, body mass index, total cholesterol, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein-cholesterol, and low density lipoprotein-cholesterol, health behavior as well as quality of life, were measured. Descriptive statistics, t-test, correlation and hierarchical multiple regression with SPSS WIN 12.0 were used to analyze the data.
Results
Significant gender differences were found for education, smoking status, chronic disease, perceived health status, and quality of life within sub-dimensions. Hierarchical regression analysis showed gender (men), age, perceived health status, cardiovascular risk scores, and health behaviors together explained 40.2% (adjusted R2) of variance in quality of life.
Conclusion
As the factors explaining quality of life in individuals with coronary artery disease have been identified as gender (men), age, perceived health status, and health behaviors, health promotion programs designed for this population should focus on these factors for effective behavioral modification, and consequent improvement in quality of life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Prediction Model for Health-related Quality of Life in Coronary Artery Disease Patients According to Stress Level
Minju Kim, Ju Youn Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(3): 320. CrossRef - Prevalence of coronary artery disease according to lifestyle characteristics, nutrient intake level, and comorbidities among Koreans aged 40 years and older: a cross-sectional study using data from the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition E
Areum Song, Sook-Bae Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(6): 457. CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life Based on Comorbidities Among Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease
Jieun Cha, Dallong Han
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2020; 11(4): 194. CrossRef - The Effects of Smart Program for Patients Who Underwent Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (SP-PCI) on Disease-Related Knowledge, Health Behavior, and Quality of Life: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
Jueun Lee, Haejung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(6): 756. CrossRef - Predictors of health-promoting behaviors in Taiwanese patients with coronary artery disease
Ai-Fu Chiou, Shu-Pen Hsu, Huei-Fong Hung
Applied Nursing Research.2016; 30: 1. CrossRef - Effects of position change on lumbar pain and discomfort of Korean patients after invasive percutaneous coronary intervention: a RCT study
Nam Hyun Cha, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2016; 28(10): 2742. CrossRef - Influencing Effects of Type D Personality on Symptom Experiences and Quality of Life in Patients with Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Eun Hee Jo, Sun Hee Han, Myung Ha Lee, Sung Reul Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(5): 536. CrossRef - Relationships of Depression Symptom, Self-Esteem, and Stress to Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Hypertension Registered to a Community Health Center
Mi Ni Choi, Eun-Hyun Lee
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2015; 29(2): 165. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Self Care Education Program for Elderly Patients with Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Gyeong-Jin Jo, Jin-Hyang Yang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(2): 266. CrossRef - The Health Behavioral Experience of Patients with Myocardial Infarction during the Recovery Period
Kyung Ja Kang, Moon Jeong Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(2): 203. CrossRef - Effects of Tai Chi Exercises on Cardiovascular Risks, Recurrence Risk, and Quality of Life in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Rha Yun Song, Moon Kyoung Park, Jin-Ok Cheong, Jae-Hyeong Park, In-Whan Seong
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(5): 515. CrossRef - Teaching Experience of Tai Chi Instructors with Nursing Background
In Sook Park, Rhayun Song
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(1): 10. CrossRef - Postoperative Quality of Life in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Ju-Sung Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2011; 12(3): 1260. CrossRef - Assessment of nurses' nutritional knowledge regarding therapeutic diet regimens
K.A. Park, W.I. Cho, K.J. Song, Y.S. Lee, I.S. Sung, S.M. Choi-Kwon
Nurse Education Today.2011; 31(2): 192. CrossRef - Comparison of Cardiovascular Health Status and Health Behaviors in Korean Women based on Household Income
Young-Joo Park, Nah-Mee Shin, Ji-Won Yoon, Jiwon Choi, Sook-Ja Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(6): 831. CrossRef
-
954
View
-
2
Download
-
15
Crossref
-
Construction of an Explanatory Model of Female Sexual Dysfunction
-
Jeongyee Bae, Kweonsik Min, Sukhee Ahn
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(7):1080-1090. Published online December 31, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.7.1080
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
Although concerns of female sexual dysfunction (FSD) are increasing in Korea, sexual dysfunction related factors are limited in research studies. The aim of this study was to develop an explanatory model that will further explain the continuously increasing female sexual dysfunction cases in Korea.
Methods
Survey visits were conducted to four hundred and eighty five women, over 25 years of age and presently residing in either urban or rural areas. All of them were analyzed using a structured questionnaire. A total of 8 instruments were used in this model. The analysis of data was done with both SPSS WIN for descriptive statistics and AMOS 5.0 for covariance structure analysis.
Results
As a result, variables that showed notably direct effects on FSD were: sexual concept (sexual attitude), sexual distress, and psychosocial health (depression, crisis, traumatic life events). On the other hand, variables such as age, educational level, economic status, and marital status showed indirect influences on health-promoting behaviors.
Conclusion
By comprehensively addressing the factors related to sexual dysfunction, and comparing each influence, this study can contribute to designing an appropriate sexual dysfunction prevention strategy in tune with the particular characteristics and problems of a client.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Unmet Needs and Sexual Distress of Gynecological Cancer Patients according to the Period after Initial Treatment
Yeon Hee Bae, Jeong Sook Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(4): 221. CrossRef - A Study on Sexual Function, Sexual Stress, and Quality of Life in Middle Aged Women Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Sunyoung Ahn, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2016; 23(4): 393. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Sexual Function in Postmenopausal Married Women
Hye Young Kim, Eun Ko
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(4): 287. CrossRef - Factors influencing sexual function of middle-aged married Korean women
YoungJu Jee, YoungHae Kim
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2015; 27(3): 819. CrossRef - Study of the Sexual Behaviors and Influential Factors Affecting Premenopausal Women with Breast Cancer: Application of the Method of Triangulation
Eun Ja Kim, Myung Ae Kim, Na Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2014; 20(1): 72. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Illness Intrusiveness of the Sexual Life in Women with Overactive Bladder
Jeong Lim Cho, Eun Nam Lee
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(1): 62. CrossRef - Factors Related to Female Sexual Dysfunction of North Korean Women Defectors
Young Sun Rhee, Hye Wan Ku, In Young Han
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(2): 55. CrossRef - Relationship among Sexual Knowledge, Frequency, Satisfaction, Marital Intimacy and Levels of Depression in Stroke Survivors and Their Spouses
Jung-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(3): 483. CrossRef - A Structural Equation Model on Sexual Function in Women with Gynecologic Cancer
Nami Chun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 639. CrossRef
-
851
View
-
0
Download
-
9
Crossref
-
Discriminating Power of Socio-demographic and Psychological Variables on Addictive Use of Cellular Phones Among Middle School Students
-
Haejung Lee, Myoung Soo Kim, Hyun Kyung Son, Sukhee Ahn, Jung Soon Kim, Young Hae Kim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(6):957-965. Published online March 28, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.6.957
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to examine the degrees of cellular phone usage among middle school students and to identify discriminating factors of addictive use of cellular phones among sociodemographic and psychological variables.
METHODS: From 123 middle schools in Busan, potential participants were identified through stratified random sampling and 747 middle school students participated in the study. The data was collected from December 1, 2004 to December 30, 2004. Descriptive and discriminant analyses were used.
RESULTS: Fifty seven percent of the participants were male and 89.7% used cellular phones at school. The participants were grouped into three groups depending on the levels of the cellular phone usage: addicted (n=117), dependent (n=418), non-addicted (n=212). Within the three groups, two functions were produced and only one function was significant, discriminating the addiction group from non-addiction group. Additional discriminant analysis with only two groups produced one function that classified 81.2% of the participants correctly into the two groups. Impulsiveness, anxiety, and stress were significant discriminating factors.
CONCLUSION: Based on the findings of this study, developing intervention programs focusing on impulsiveness, anxiety and stress to reduce the possible addictive use of cellular phones is suggested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Psychometric evaluation of smartphone addiction scale – short version (SAS-SV) among young adults of India
George Felix, Manoj K. Sharma, Nitin Anand, Binukumar Bhaskarapillai, Kalpana Srivastava
Industrial Psychiatry Journal.2025; 34(1): 53. CrossRef - App-based tracking of smartphone use and its association with perceived stress and sense of coherence among undergraduate medical students in Southern India
Kathiresan Jeyashree, Jane S. Sathiavadivu, AbdulkaderRizwan Suliankatchi
International Journal of Adolescent Medicine and Health .2021; 33(3): 245. CrossRef - Interaction between physical activity and problematic mobile phone use on suicidality in Chinese college students
Yang Xie, Ming Zhu, Xiaoyan Wu, Shuman Tao, Yajuan Yang, Tingting Li, Liwei Zou, Honglv Xu, Fangbiao Tao
BMC Psychiatry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Sleep Quality on the Relationship Between Problematic Mobile Phone Use and Depressive Symptoms in College Students
Liwei Zou, Xiaoyan Wu, Shuman Tao, Honglv Xu, Yang Xie, Yajuan Yang, Fangbiao Tao
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Prevention Program for Media Addiction on Television Addiction, Internet Addiction, Cellular Addiction, and Impulsiveness in Elementary School Students.
Hyun Young Koo
Child Health Nursing Research.2013; 19(4): 270. CrossRef - Development of a Cell Phone Addiction Scale for Korean Parents of Young Children.
Hyun Young Koo
Child Health Nursing Research.2013; 19(1): 29. CrossRef - Development and Validation Study of a Cell Phone Addiction Scale for Korean Children
Hyun-Young Koo, Myung-Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2012; 18(2): 76. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Prevention Program for Cell Phone Addiction in Middle School Students
Hyun-Young Koo
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2011; 17(2): 91. CrossRef - Factors related to the Overuse of Mobile Phone in Elementary School Students
Kyoung Sook Lee, Hwang Ran Ahn, Kyung Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2011; 20(3): 271. CrossRef - Effects of an Empowerment Education Program in the Prevention of Internet Games Addiction in Middle School Students
Aeran Joo, Inhyae Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(2): 255. CrossRef
-
839
View
-
3
Download
-
10
Crossref
-
Effects of Walking on Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Psychosocial Outcomes in Postmenopausal Obese Women
-
Sukhee Ahn
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(4):519-528. Published online March 28, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.4.519
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of a moderate-intensity, walking exercise program on the body composition, blood lipids and psychosocial outcomes in postmenopausal obese women.
Methods
With a quasi-experimental pre- and post-test design, a total of 36 postmenopausal obese women was recruited in 2 metropolitan areas by convenience sampling. Sixteen women participated in 1 hour of moderate-intensity walking exercise 5 days per week for 3 months and 20 women did not. Cardiovascular risk factors include body composition and blood lipids. Body composition was measured as body mass index, % body fat, and waist/hip ratio; Blood lipids were measured with total cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL and LDL; psychosocial outcomes were evaluated by self-esteem and depression.
Results
Over 3 months, the score of self-esteem increased and depression decreased in the exercise group relative to the control group. However, there were no significant differences in body composition and blood lipids.
Conclusions
This study suggests that 3 months of moderate-intensity exercise training can improve psychosocial outcomes but further studies are needed to replicate walking exercise on physiologic variables among postmenopausal obese women. These findings are of public health relevance and add a new facet to the growing literature on the health benefits of moderate exercise.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Walking Exercise on Depression
Jonghwa Lee, Youngho Kim
The Asian Journal of Kinesiology.2023; 25(4): 12. CrossRef - The Effects of Exclusive Walking on Lipids and Lipoproteins in Women with Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Anjulyn M. Ballard, Ashlee Davis, Brett Wong, Rodney Lyn, Walter R. Thompson
American Journal of Health Promotion.2022; 36(2): 328. CrossRef - A Pilot Study of APN-led Self-management Program to Improve Cardiovascular Health Status among Korean Women with Risk Factors
Nah-Mee Shin, Ji-Won Yoon, Jiwon Choi, Younghee Park, Songi Jeon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(2): 237. CrossRef - The Effects of a Regular Walking Program on Body Composition, Functional Fitness, and Anxiety and Depression in Elderly Women
Samcheol Lee
Journal of The Korean Society of Integrative Medicine.2016; 4(2): 67. CrossRef - Effects of Lifestyle Modification Program on Body Composition, Metabolic Syndrome Markers, and Depression in Obese Postmenopausal Women
Nam Hee Park
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2013; 27(2): 313. CrossRef - Women Religious and Married Women's Attitudes toward Menopause and Menopausal Symptoms
Myung-Sook Yoo
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(2): 186. CrossRef
-
685
View
-
6
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Canonical Correlation between Korean Traditional Postpartum Care Performance and Postpartum Health Status
-
Sukhee Ahn
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(1):37-46. Published online March 28, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.1.37
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this longitudinal study was to examine the relationship between postpartum care performance and postpartum health status.
Sample
The study subjects were 82 mothers who delivered full-term infants at 3 hospitals at P city. Data were collected for their health status at the postpartum unit and the sample was followed up to 6 weeks postpartum to collect postpartum care performance and health status.
Results
Mothers rated postpartum care performance as moderate to high and especially rated the maternal role attainment the highest. Mothers experienced 4 physical symptoms and moderate levels of fatigue. In addition, they experienced moderate levels of positive affect and low levels of negative affect at both times. Canonical correlation revealed that postpartum care performance was related to postpartum health status with 2 significant canonical variables. The first variate indicated that mothers who performed hospitality, physical and emotional recovery, self-caring, and role attainment well showed higher positive affects, lower negative affects, fewer physical symptoms, and lower levels of fatigue. The second variate showed that the greater the performance of caring and physical and emotional recovery, the fewer physical symptoms and lower levels of fatigue.
Conclusion
Although Korean traditional postpartum care performance was related to postpartum health status, the further study is needed to identify the causal relationship between them. Nurses need to integrate the perspective of westernized postpartum care and Korean traditional views of postpartum approach to maintain and promote women's health better.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Trajectories of maternal postpartum distress and employment profiles: implications for parenting
Jihyoung Kim, K. A. S. Wickrama
Journal of Family Studies.2022; 28(3): 879. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Trends on Postpartum-women Healthcare : A Scoping Review
Do-Eun Lee, Han-Song Park, Joon-Soo Jin, Beak-Ki Min, In-Ae Youn, Hyo-Weon Suh, Joo-Hee Seo
Journal of Korean Medicine.2020; 41(3): 32. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Health Promoting Behavior in Postpartum Women at Sanhujoriwon
Hyekyung Choi, Namok Jung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2017; 23(2): 135. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Use of Postpartum Care Services
Yun-Sun Jung, Young-Dae Kwon
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2017; 11(1): 143. CrossRef - Patterns and Factors associated with Complementary and Alternative Medicine Use among Korean Postpartum Women
Ju Hee Kim, Hye Sook Shin, So Young Kim, Hye Kyung Lee, So Hee Lim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - Experiences of Sanhujori Facility Use among the First Time Mothers by the Focus Group Interview
Ju-Eun Song, Hyun Ju Chae, Bo-Lim Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2015; 21(3): 184. CrossRef - Empirical test of an explanatory theory of postpartum fatigue in Korea
Ju‐Eun Song, Soon‐Bok Chang, So‐Mi Park, Sue Kim, Chung‐Mo Nam
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2010; 66(12): 2627. CrossRef - Influencing Factors of Postpartum Depression between 4 to 6 Weeks after Childbirth in the Postpartum Women
Ju-Eun Song
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(3): 216. CrossRef
-
828
View
-
7
Download
-
8
Crossref
|