Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 39(6); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- Development of a Cell Phone Addiction Scale for Korean Adolescents
- Hyun Young Koo
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2009;39(6):818-828.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.6.818
Published online: December 31, 2009
Associate Professor, College of Nursing, Catholic University of Daegu, Daegu, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Koo, Hyun Young. College of Nursing, Catholic University of Daegu, 3056-6 Daemyeong 4-dong, Nam-gu, Daegu 705-718, Korea. Tel: 82-53-650-4829, Fax: 82-53-650-4392, hykoo@cu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2009 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was done to develop a cell phone addiction scale for Korean adolescents.
-
Methods
- The process included construction of a conceptual framework, generation of initial items, verification of content validity, selection of secondary items, preliminary study, and extraction of final items. The participants were 577 adolescents in two middle schools and three high schools. Item analysis, factor analysis, criterion related validity, and internal consistency were used to analyze the data.
-
Results
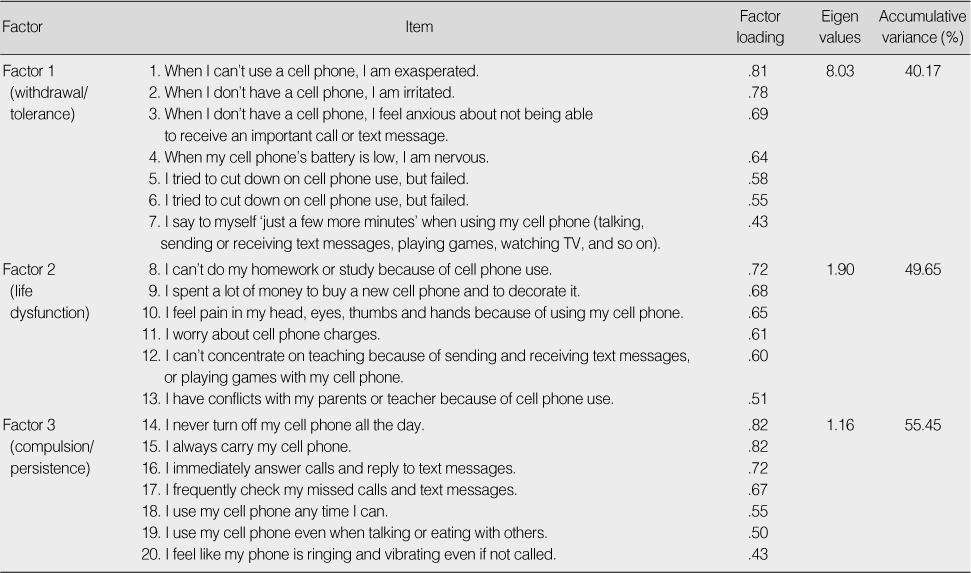
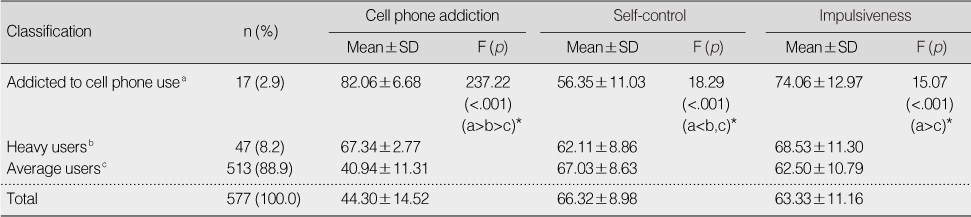
- Twenty items were selected for the final scale, and categorized into 3 factors explaining 55.45% of total variance. The factors were labeled as withdrawal/tolerance (7 items), life dysfunction (6 items), and compulsion/persistence (7 items). The scores for the scale were significantly correlated with self-control, impulsiveness, and cell phone use. Cronbach's alpha coefficient for the 20 items was .92. Scale scores identified students as cell phone addicted, heavy users, or average users.
-
Conclusion
- The above findings indicate that the cell phone addiction scale has good validity and reliability when used with Korean adolescents.
This work was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Korean government (KRF-2007-313-E00567).
- 1. Barratt ES, White R. Impulsiveness and anxiety related to medical student's performance and attitudes. Journal of Medical Education. 1969;44:604–607.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Choi ES. A study on teenagers' addictiveness on cellular phone living in local area-specialized in students in Pochon. 2005;Seoul, Kookmin University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 3. Dimonte M, Ricchiuto G. Mobile phone and young people: A survey pilot study to explore the controversial aspects of a new social phenomenon. Minerva Pediatrica. 2006;58:357–363.PubMed
- 4. Goldberg I. Internet addiction electronic message posted to research discussionist. 1996;Retrieved December 27, 2004. from http://www.rider.edu/users/suler/psycyber/supportgp.html.
- 5. Han JL, Hur GH. Construction and validation of mobile phone addiction scale. Korean Association for Broadcasting & Telecommunication Studies. 2004;48(6):138–165.
- 6. Han SS, Oh KS. A study on cellular phone addiction symptom dependent on interpersonal relationship types and using inclination: Focus on the case of undergraduates. Korean Association for Broadcasting & Telecommunication Studies. 2006;20:371–405.
- 7. Jang HJ. The psychological characteristics of adolescents addictive using cellular phone. 2002;Seoul, Sungshin Women's University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 8. Jang HJ, Chae KM. The psychological characteristics of adolescents with technological addiction: Cellular phone addiction. The Korean Journal of Health Psychology. 2006;11:839–852.
- 9. June KJ, Sohn SY, So AY, Yi GM, Park SH. A study of factors that influence internet addiction, smoking, and drinking in high school students. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2007;37:872–882.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 10. Kamibeppu K, Sugiura H. Impact of the mobile phone on junior high school students' friendships in the Tokyo metropolitan area. Cyberpsychology & Behavior. 2005;8:121–130.Article
- 11. Kim BK, Yun SO, Lee HG. The analysis for the causes of mobile phone addiction. 2006;Seoul, Korea Agency for Digital Opportunity & Promotion.
- 12. Kim HS, Bae SM, Hyun MH. Predicting mobile phone addiction in adolescents. The Korean Journal of Health Psychology. 2007;12:383–393.Article
- 13. Kim KH. The psychological perspectives of addictive behaviors. The Korean Journal of Health Psychology. 2002;7:159–179.
- 14. Lee EO, Im NY, Park HA. Nursing/medical research and statistical analysis. 1998;Seoul, Soomoonsa.
- 15. Lee HG. Exploration of the predicting variables affecting the addictive mobile phone use. Korean Journal of Social and Personality Psychology. 2008;22:133–157.
- 16. Lee HS. Impulsiveness test guide. 1992;Seoul, Hankook guidance.
- 17. Lee JY. An exploration of socio-environmental and individual-psychological variables affecting the adolescent's cellular phone addiction. 2006;Cheongwon, Korea National University of Education. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 18. Ministry of Information and Communication, & Korea Agency for Digital Opportunity and Promotion. Internet addiction self-report questionnaires (K-tool) and prevention and education program. 2003;Seoul, Korea Agency for Digital Opportunity and Promotion.
- 19. Moon JS. Nursing research. 1997;Seoul, Shinkwang.
- 20. Nam HM. The effects of psychological family environment, self-control and friends characteristics of middle school students on their problem behaviors. 1999;Seoul, Seoul National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 21. O'Reilly M. Internet addiction: A new disorder enters the medical lexicon. Canadian Medical Association Journal. 1996;154:1882–1883.PubMedPMC
- 22. Park HS, Kwon YH, Park KM. Factors on internet game addiction among adolescents. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2007;37:754–761.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Park WK. The mobile phone addiction among Korean college students. Korean Society for Journalism & Communication Studies. 2003;47:250–281.
- 24. Salama OE, Abou EI, Naga RM. Cellular phones: Are they detrimental? The Journal of the Egyptian Public Health Association. 2004;79:197–223.PubMed
- 25. Song EJ. The relationship between the using mobile phone and mental health state of high school students. Journal of KoreanAcademy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 2006;15:325–333.
- 26. Walsh SP, White KM, Young RM. Over-connected? A qualitative exploration of the relationship between Australian youth and their mobile phones. Journal of Adolescence. 2007;31:77–92.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 27. Wong DL. Whaley & Wong's nursing care of infants and children. 1999;6th ed. St. Louis, MO, Mosby.
- 28. Yang SY, Park YS. A prediction model of cellular phone tendency among adolescents. The Korean Home Economics Association. 2005;43(4):1–16.
- 29. Young KS. Caught in the net: How to recognize the signs of internet addiction and a winning strategy for recovery. 1998;New York, NY, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
REFERENCES
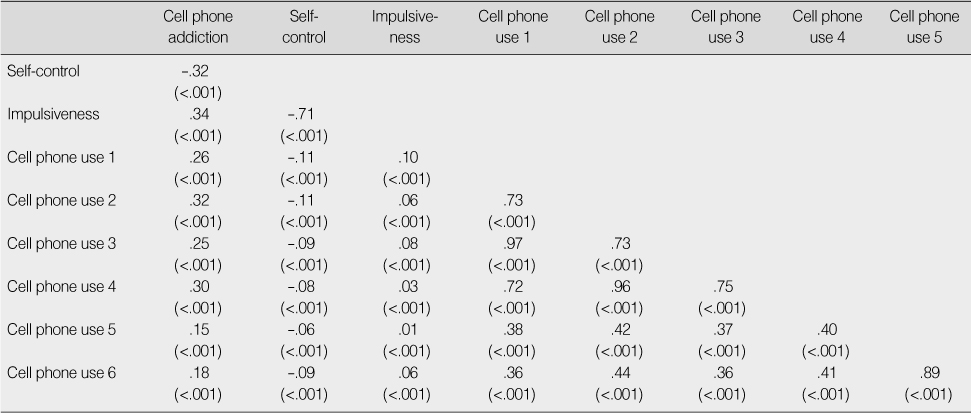
Cell phone use 1=sending text message on weekdays; Cell phone use 2=sending text message on weekends; Cell phone use 3=receiving text message on weekdays; Cell phone use 4=receiving text message on weekends; Cell phone use 5=talking by cell phone on weekdays; Cell phone use 6=talking by cell phone on weekends.
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Associations Between Academic Motivation, Academic Stress, and Mobile Phone Addiction: Mediating Roles of Wisdom
Abolghasem Yaghoobi, Kambiz Karimi, Maryam Asoudeh, Sahar Mohammadi
International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction.2025; 23(4): 2926. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of smartphone addiction scale – short version (SAS-SV) among young adults of India
George Felix, Manoj K. Sharma, Nitin Anand, Binukumar Bhaskarapillai, Kalpana Srivastava
Industrial Psychiatry Journal.2025; 34(1): 53. CrossRef - A Study to Assess the Knowledge regarding Hazards of Mobile Addiction among adults (21-40 years) Residing at Appannapally Village, Mahabubnagar, Telangana
C. Venkata Raju, Dhanyamol C P, Lakshmi Priya
A and V Pub International Journal of Nursing and Medical Research.2025; : 130. CrossRef - Assessment Tools and Psychosocial Consequences of Smartphone Addiction in Nursing Students: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
María Dolores Lazo-Caparrós, José Luis Gómez-Urquiza, Ana González-Díaz, Inmaculada Pérez-Conde, Piedad Gómez-Torres, María José Membrive-Jiménez
Healthcare.2025; 13(20): 2639. CrossRef - Unveiling the grip of mobile phone addiction: an in-depth review
Jinyu Li, Hong Yang
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A systematic review and meta-analysis of smartphone addiction among Iranian high school and university students
Reza Ghanei Gheshlagh, Jamal Amiri, Vajiheh Baghi, Fazel Dehvan
Journal of Health Administration.2024; 27(3): 36. CrossRef - Effects of Self-Management Training on Smartphone Dependence in Low to Moderate Adolescent Males’ Users
Mostafa Motamedi Heravi, Shahla Khosravan, Aeen Mohammadi, Mohammad Reza Mansoorian
Behaviour Change.2023; 40(1): 67. CrossRef - Are South Korean College Students Benefitting from Digital Learning?
Phillip Sangwoo Lee, Chong Min Lee
International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction.2023; 39(4): 743. CrossRef - TEKNOLOJİYLE BAĞLANTILI YENİ DAVRANIŞSAL BOZUKLUKLAR / RECENT BEHAVIORAL DISORDERS DUE TO TECHNOLOGY
Kamer Kalip, Meltem Çöl
Eskişehir Türk Dünyası Uygulama ve Araştırma Merkezi Halk Sağlığı Dergisi.2020; 5(2): 318. CrossRef - Problematic Mobile Phone and Smartphone Use Scales: A Systematic Review
Bethany Harris, Timothy Regan, Jordan Schueler, Sherecce A. Fields
Frontiers in Psychology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise as an Alternative Approach for Treating Smartphone Addiction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Random Controlled Trials
Shijie Liu, Tao Xiao, Lin Yang, Paul D. Loprinzi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(20): 3912. CrossRef - Are smartphones really that bad? Improving the psychological measurement of technology-related behaviors
David A. Ellis
Computers in Human Behavior.2019; 97: 60. CrossRef - Internal Consistency and Confirmatory Factor Analysis of Smartphone Addiction Inventory (SPAI)
Saeed Imani, Jaber Alizadeh Goradel, Sadegh Mousavi, Alireza Noroozi
Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between addiction to mobile phone and sense of loneliness among students of medical sciences in Kermanshah, Iran
Hale Jafari, Abas Aghaei, Alireza khatony
BMC Research Notes.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Smart phone addiction and mindfulness: an intergenerational comparison
Kaeun Kim, George R. Milne, Shalini Bahl
International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Marketing.2018; 12(1): 25. CrossRef - Impact of Smartphone Addiction on Academic Performance of Business Students: A Case Study
Md. Shamsul Arefin, Md. Islam, Mohitul Mustafi, Sharmina Afrin, Nazrul Islam
SSRN Electronic Journal .2018;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review of Studies on the Relationship between Mobile Phone Addiction and Impulsiveness
君凤 冯
Advances in Psychology.2017; 07(01): 60. CrossRef - Cell-Phone Addiction: A Review
José De-Sola Gutiérrez, Fernando Rodríguez de Fonseca, Gabriel Rubio
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Smartphone Addiction Inventory (SPAI): Psychometric properties and confirmatory factor analysis
Laura Pavia, Paola Cavani, Maria Di Blasi, Cecilia Giordano
Computers in Human Behavior.2016; 63: 170. CrossRef - Influence of Cell Phone Addiction on Communication Skills and Interpersonal Relationship Ability of Adolescents
Mi-Young Choi, Ji-Soo Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of School Health.2016; 29(3): 149. CrossRef - Development of a Brief Multicultural Version of the Test of Mobile Phone Dependence (TMDbrief) Questionnaire
Mariano Chóliz, Lourdes Pinto, Sukanya S. Phansalkar, Emily Corr, Ayman Mujjahid, Conni Flores, Pablo E. Barrientos
Frontiers in Psychology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study of on the influence of techno-stress, flow and smartphone addiction on the Satisfaction of Smart-phones use
Jongsoon Park, Jongman Lee
Journal of the Korea Society of Digital Industry and Information Management.2015; 11(4): 189. CrossRef - General Strain Theory approach to the Use of Cellular Phone Dependence of Middle School Students
Hyun-Jin Shim, Il-Hyun Lee, Hyun-Sill Rhee
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(2): 355. CrossRef - Context-aware Framework and Applications for Improving UI and UX of Smartphones
Choonsung Shin, Byoung-Ha Park, Kwang-Mo Jung
Journal of the Korea society of IT services.2014; 13(1): 197. CrossRef - The dark side of smartphone usage: Psychological traits, compulsive behavior and technostress
Yu-Kang Lee, Chun-Tuan Chang, You Lin, Zhao-Hong Cheng
Computers in Human Behavior.2014; 31: 373. CrossRef - Development of a Cell Phone Addiction Scale for Korean Parents of Young Children.
Hyun Young Koo
Child Health Nursing Research.2013; 19(1): 29. CrossRef - Development of a Problematic Mobile Phone Use Scale for Turkish Adolescents
Cem Oktay Güzeller, Tolga Coşguner
Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking.2012; 15(4): 205. CrossRef - Development and Validation Study of a Cell Phone Addiction Scale for Korean Children
Hyun-Young Koo, Myung-Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2012; 18(2): 76. CrossRef - The Study on Predictors of Addictive Personality in Adolescents
Hyun Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2012; 21(4): 263. CrossRef - Development of the Multidimensional Scale of Addictive Behavior for Adolescents
Hyun-Sook Park, Sun-Young Jung
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(8): 3597. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Prevention Program for Cell Phone Addiction in Middle School Students
Hyun-Young Koo
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2011; 17(2): 91. CrossRef - Validation of Addictive Personality Scale for Screening Adolescents
Hyun Sook Park, Sun Young Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2011; 20(4): 395. CrossRef - Factors related to the Overuse of Mobile Phone in Elementary School Students
Kyoung Sook Lee, Hwang Ran Ahn, Kyung Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2011; 20(3): 271. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Cell Phone Addiction in Adolescents
Hyun Young Koo, Hyun Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(1): 56. CrossRef - Cell Phone Addiction in Highschool Students and Its Predictors
Hyun Young Koo
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(3): 203. CrossRef - Educational Needs for Prevention of Cell Phone Addiction in Korean Adolescents
Hyun Young Koo, Hyun Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(4): 304. CrossRef
- We recommend
- Related articles
-
- Development of a communication self-efficacy scale for nurses: a psychometric validation study
- Development of a well-dying awareness scale for middle-aged adults in Korea: a mixed-methods study
- Development and Effectiveness of Progressive Simulation Education Program on Medication Safety for Nursing Students
- Development of the Hybrid Clinical Practicum Environment Scale for Nursing Students
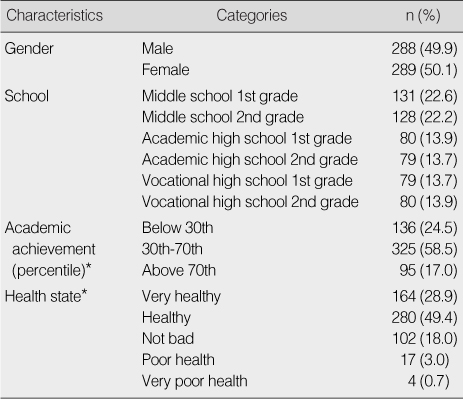
Demographic Characteristics of Participants (N=577)
*Missing data excluded.
Item Analysis (N=577)
Factor Analysis (N=577)
Correlations of Cell Phone Addiction Scale with Self-control, Impulsiveness and Cell Phone Use (N=577)
Cell phone use 1=sending text message on weekdays; Cell phone use 2=sending text message on weekends; Cell phone use 3=receiving text message on weekdays; Cell phone use 4=receiving text message on weekends; Cell phone use 5=talking by cell phone on weekdays; Cell phone use 6=talking by cell phone on weekends.
Classification of Cell Phone Addiction in Adolescents (N=577)
*Scheffe multiple comparison test.
*Missing data excluded.
Cell phone use 1=sending text message on weekdays; Cell phone use 2=sending text message on weekends; Cell phone use 3=receiving text message on weekdays; Cell phone use 4=receiving text message on weekends; Cell phone use 5=talking by cell phone on weekdays; Cell phone use 6=talking by cell phone on weekends.
*Scheffe multiple comparison test.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 Cite
Cite

