Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 54(4); 2024 > Article
-
Research Paper
간호대학생의 투약안전을 위한 점진적 시뮬레이션 교육프로그램 개발 및 효과 -
정세영
 , 김은영
, 김은영
- Development and Effectiveness of Progressive Simulation Education Program on Medication Safety for Nursing Students
-
Se-Young Jung
 , Eun-Young Kim
, Eun-Young Kim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2024;54(4):563-576.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24054
Published online: October 14, 2024
동아대학교 간호학부
College of Nursing, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea
- Address reprint requests to : Kim, Eun-Young College of Nursing, Dong-A University, Daesingongwon-ro 32, Seo-gu, Busan 49201, Korea Tel: +82-51-240-2785 Fax: +82-51-240-2695 E-mail: eykim@dau.ac.kr
© 2024 Korean Society of Nursing Science
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NoDerivs License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0) If the original work is properly cited and retained without any modification or reproduction, it can be used and re-distributed in any format and medium.
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study aimed to develop and verify a progressive simulation education program aimed at enhancing nursing students’ medication safety competency.
-
Methods
- A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was adopted. The participants were 40 third-year nursing students with no prior simulation education experience, comprising 20 each in the experimental and control groups. The experimental treatment utilized a hybrid simulation approach incorporating both full-body mannequins and standardized patients and was, conducted over three sessions with durations of 65, 80, and 95 minutes for the first, second, and third sessions, respectively, for a total of 240 minutes. The program was constructed based on Jeffries’ simulation model.
-
Results
- The levels of medication safety competencies, communication self-efficacy, learning self-efficacy, and problem-solving abilities of the experimental group were significantly higher than that of the control group.
-
Conclusion
- Our results confirm that the program effectively improves nursing students’ medication safety competence, communication self-efficacy, learning self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability. Therefore, this program can serve as a basis for developing educational strategies related to medication safety for nursing education institutions. Furthermore, the program is anticipated to have a positive impact on novice nurses’ education and practice in clinical settings.
서 론
연구 방법
1) 일반적 특성
2) 투약안전 역량
3) 의사소통 자기효능감
4) 학습 자기효능감
5) 문제해결능력
1) 프로그램 개발
2) 프로그램 적용
연구 결과
논 의
결 론
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
-
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
None.
-
DATA SHARING STATEMENT
Please contact the corresponding author for data availability.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization or/and Methodology: Jung S & Kim E.
Data curation or/and Analysis: Jung S.
Funding acquisition: Jung S.
Investigation: Jung S.
Project administration or/and Supervision: Jung S & Kim E.
Resources or/and Software: Jung S & Kim E.
Validation: Kim E.
Visualization: Jung S & Kim E.
Writing original draft or/and Review & Editing: Jung S & Kim E.
Article Information
| Variables | Categories |
Exp. (n = 20) |
Cont. (n = 20) |
t or χ2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) or M ± SD | |||||
| General characteristics | |||||
| Age (yr) | 21.4 ± 1.23 | 21.5 ± 1.10 | – 0.41 | .686 | |
| Gender | Woman | 18 (90.0) | 19 (95.0) | < .999† | |
| Man | 2 (10.0) | 1 (5.0) | |||
| Religion | Yes | 6 (30.0) | 4 (20.0) | 0.53 | .465 |
| No | 14 (70.0) | 16 (80.0) | |||
| Previous semester grade | ≥ 3.5 | 9 (45.0) | 12 (60.0) | 0.90 | .342 |
| < 3.5 | 11 (55.0) | 8 (40.0) | |||
| Experience of healthcare service | Have | 3 (15.0) | 3 (15.0) | < .999† | |
| Haven’t | 17 (85.0) | 17 (85.0) | |||
| Satisfaction of major | Above high | 12 (60.0) | 15 (75.0) | 1.03 | .311 |
| Middle or less | 8 (40.0) | 5 (25.0) | |||
| Satisfaction of clinical practice | Above high | 11 (55.0) | 10 (50.0) | 0.10 | .752 |
| Middle or less | 9 (45.0) | 10 (50.0) | |||
| Reasons for entering nursing college | Easy employment | 11 (55.0) | 10 (50.0) | 2.56 | .333† |
| Aptitude | 5 (25.0) | 2 (10.0) | |||
| Recommendation | 4 (20.0) | 8 (40.0) | |||
| Type of apply for a job | Hospitals | 18 (90.0) | 19 (95.0) | 0.36 | .548 |
| Other than hospitals | 2 (10.0) | 1 (5.0) | |||
| Medication safety competence | 119.70 ± 10.68 | 120.05 ± 11.79 | – 0.10 | .922 | |
| Communication self-efficacy | 86.55 ± 11.86 | 83.80 ± 11.96 | 0.73 | .470 | |
| Learning self-efficacy | 56.90 ± 5.71 | 57.10 ± 4.23 | – 0.13 | .901 | |
| Problem-solving ability | 108.75 ± 14.41 | 112.00 ± 11.13 | – 0.80 | .430 | |
- 1. Conceptual framework for the international classification for patient safety version 1.1: Final technical report January 2009 [Internet]. World Health Organization & WHO Patient Safety; c2009 [cited 2023 Jun 30]. Available from: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/70882
- 2. Nieva VF, Sorra J. Safety culture assessment: A tool for improving patient safety in healthcare organizations. Quality & Safety in Health Care. 2003;12 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):ii17-ii23. https://doi.org/10.1136/qhc.12.suppl_2.ii17ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. World Health Organization (WHO). WHO launches global effort to halve medication-related errors in 5 years [Internet]. WHO; c2017 [cited 2023 Jun 30]. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2017/medication-related-errors/en/
- 4. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). Medication errors and adverse drug events [Internet]. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, US Department of Health and Human Services; c2019 [cited 2023 Jun 30]. Available from: https://psnet.ahrq.gov/primer/medication-errors-and-adverse-drug-events
- 5. Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW). Korea Institute for Healthcare Accreditation. Korean Patient Safety Incident Report 2022. Seoul: Korea Institute for Healthcare Accreditation; 2023.
- 6. Tang FI, Sheu SJ, Yu S, Wei IL, Chen CH. Nurses relate the contributing factors involved in medication errors. Journal of Clinical Nursing. 2007;16(3):447-457. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2005.01540.xArticlePubMed
- 7. Park J, Seomun G. Development and validation of the Medication Safety Competence Scale for nurses. Western Journal of Nursing Research. 2021;43(7):686-697. https://doi.org/10.1177/0193945920969929ArticlePubMed
- 8. Noort MC, Reader TW, Gillespie A. Speaking up to prevent harm: A systematic review of the safety voice literature. Safety Science. 2019;117:375-387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2019.04.039Article
- 9. Smeulers M, Onderwater AT, van Zwieten MC, Vermeulen H. Nurses’ experiences and perspectives on medication safety practices: An explorative qualitative study. Journal of Nursing Management. 2014;22(3):276-285. https://doi.org/10.1111/jonm.12225ArticlePubMed
- 10. Ko EJ, Kim EJ. Enhancing nurses’ medication administration safety competence using simulation training focused on high-alert medication. Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing. 2021;9(1):41-55. https://doi.org/10.17333/JKSSN.2021.9.1.41Article
- 11. Park JH, Kim SH. Development of a measuring scale for nursing student’ self-test competency on medication activity. Asia-pacific Journal of Multimedia Services Convergent with Art, Humanities, and Sociology. 2019;9(9):465-474. https://doi.org/10.35873/ajmahs.2019.9.9.040Article
- 12. Kim JH, Park IH, Shin S. Systematic review of Korean studies on simulation within nursing education. The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education. 2013;19(3):307-319. https://doi.org/10.5977/jkasne.2013.19.3.307Article
- 13. Kukulu K, Korukcu O, Ozdemir Y, Bezci A, Calik C. Self-confidence, gender and academic achievement of undergraduate nursing students. Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 2013;20(4):330-335. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2850.2012.01924.xArticlePubMed
- 14. Jarvill M, Jenkins S, Akman O, Astroth KS, Pohl C, Jacobs PJ. Effect of simulation on nursing students’ medication administration competence. Clinical Simulation in Nursing. 2018;14:3-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecns.2017.08.001Article
- 15. Mariani B, Ross JG, Paparella S, Allen LR. Medication safety simulation to assess student knowledge and competence. Clinical Simulation in Nursing. 2017;13(5):210-216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecns.2017.01.003Article
- 16. Pauly-O’Neill S, Prion S. Using integrated simulation in a nursing program to improve medication administration skills in the pediatric population. Nursing Education Perspectives. 2013;34(3):148-153. https://doi.org/10.5480/1536-5026-34.3.148ArticlePubMed
- 17. Sears K, Goldsworthy S, Goodman WM. The relationship between simulation in nursing education and medication safety. Journal of Nursing Education. 2010;49(1):52-55. https://doi.org/10.3928/01484834-20090918-12ArticlePubMed
- 18. Hayes C, Power T, Davidson PM, Daly J, Jackson D. Nurse interrupted: Development of a realistic medication administration simulation for undergraduate nurses. Nurse Education Today. 2015;35(9):981-986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2015.07.002ArticlePubMed
- 19. Kuo SY, Wu JC, Chen HW, Chen CJ, Hu SH. Comparison of the effects of simulation training and problem-based scenarios on the improvement of graduating nursing students to speak up about medication errors: A quasi-experimental study. Nurse Education Today. 2020;87:104359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2020.104359ArticlePubMed
- 20. Marvanova M, Henkel PJ. Collaborating on medication errors in nursing. The Clinical Teacher. 2018;15(2):163-168. https://doi.org/10.1111/tct.12655ArticlePubMed
- 21. Kim JY. Nursing students medication error and recovery in simulation education. Journal of Learner-Centered Curriculum and Instruction. 2021;21(4):603-622. https://doi.org/10.22251/jlcci.2021.21.4.603Article
- 22. Park MJ, Choi D. The effect of simulation integrated with problem based learning on system thinking, learning flow, proactivity in problem solving and performance ability for medication in nursing students. Journal of Digital Convergence. 2018;16(8):221-231. https://doi.org/10.14400/JDC.2018.16.8.221Article
- 23. Eom MR, Kim HS, Kim EK, Seong K. Effects of teaching method using standardized patients on nursing competence in subcutaneous injection, self-directed learning readiness, and problem solving ability. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2010;40(2):151-160. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.2.151ArticlePubMed
- 24. Yu M, Kim EY, Kim JK, Lee Y. Development of a simulation program related to patient safety: Focusing on medication error. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2021;27(2):107-117. https://doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2021.27.2.107Article
- 25. Son MS, Yim M, Ji ES. Development and evaluation of a neonatal intensive care unit medication safety simulation for nursing students in South Korea: A quasi-experimental study. Child Health Nursing Research. 2022;28(4):259-268. https://doi.org/10.4094/chnr.2022.28.4.259ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Hur HK, Kim KK, Lim YM, Kim J, Park KH, Park YC. Patient safety interprofessional education program using medical error scenarios for undergraduate nursing and medical students in Korea. Journal of Interprofessional Care. 2023;37(6):944-953. https://doi.org/10.1080/13561820.2023.2183184ArticlePubMed
- 27. Garrouste-Orgeas M, Philippart F, Bruel C, Max A, Lau N, Misset B. Overview of medical errors and adverse events. Annals of Intensive Care. 2012;2(1):2. https://doi.org/10.1186/2110-5820-2-2ArticlePubMedPMC
- 28. Brown WJ, Tortorella RA. Hybrid medical simulation: A systematic literature review. Smart Learning Environments. 2020;7(1):1-16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-020-00127-6Article
- 29. Park SJ. Effect of simulation-based communication education on the problem-solving process, communication self-efficacy and communication ability of nursing college students. Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing. 2022;10(1):31-42. https://doi.org/10.17333/JKSSN.2022.10.1.31Article
- 30. Chung SK, Kim KA, Jeong EY. The effects of simulation practicum using a standardized patient on nursing students’ communication skills, problem-solving skills, critical thinking dispositions, and clinical competency. Korean Academic Society of Home Health Care Nursing. 2016;23(2):186-194. https://doi.org/10.22705/jkashcn.2016.23.2.186Article
- 31. Bak YG, Kim TK. The effect of simulation-based education using a standardized patients for schizophrenia nursing care on communication self-efficacy, learning self-efficacy and flow experience in nursing students. Asia-pacific Journal of Multimedia Services Convergent with Art, Humanities, and Sociology. 2018;8(6):437-447. https://doi.org/10.35873/ajmahs.2018.8.6.040Article
- 32. Lee HJ. Development and evaluation of a nursing student therapeutic communication learning scenario using standardized-patient [dissertation]. Seoul: Yonsei University; 2015;1-119.
- 33. Kim SH, Ham Y. A meta-analysis of the effect of simulation based education: Korean nurses and nursing students. The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education. 2015;21(3):308-319. https://doi.org/10.5977/jkasne.2015.21.3.308Article
- 34. Axboe MK, Christensen KS, Kofoed PE, Ammentorp J. Development and validation of a self-efficacy questionnaire (SE-12) measuring the clinical communication skills of health care professionals. BMC Medical Education. 2016;16(1):272. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-016-0798-7ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Gil CR, Sung KM. Validity and reliability of the Korean Version of Self-Efficacy Questionnaire (KSE-12). Journal of Digital Convergence. 2020;18(5):337-345. https://doi.org/10.14400/JDC.2020.18.5.337Article
- 36. Ayres HW. Factors related to motivation to learn and motivation to transfer learning in a nursing population [dissertation]. USA (NC): North Carolina State University; 2005;1-325.
- 37. Park SY, Kweon YR. Standardized patients in psychiatric nursing practical training for nursing college students. Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 2012;21(1):79-88. https://doi.org/10.12934/jkpmhn.2012.21.1.79Article
- 38. Lee WS, Park SH, Choi EY. Development of a Korean problem solving process inventory for adults. Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing. 2008;15(4):548-557.
- 39. Jeffries PR. The NLN Jeffries simulation theory. Philadelphia (PA): Wolters Kluwer; 2016. p. 1-72.
- 40. Benner P. From novice to expert. The American Journal of Nursing. 1982;82(3):402-407. https://doi.org/10.2307/3462928ArticlePubMed
- 41. Lasater K. Clinical judgment: The last frontier for evaluation. Nurse Education in Practice. 2011;11(2):86-92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2010.11.013ArticlePubMed
- 42. Unver V, Basak T, Ayhan H, Cinar FI, Iyigun E, Tosun N, et al. Integrating simulation based learning into nursing education programs: Hybrid simulation. Technology and Health Care. 2018;26(2):263-270. https://doi.org/10.3233/THC-170853ArticlePubMed
- 43. Lee H, Cho M, Yoo L, Choi E, Jung D. Nursing students’ experiences of virtual and hybrid simulation in gerontological nursing: A mixed-methods study. Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing. 2022;24(2):185-196. https://doi.org/10.17079/jkgn.2022.24.2.185Article
- 44. Lee SJ, Park YM, Noh SM. The effects of simulation training with hybrid model for nursing students on nursing performance ability and self confidence. Korean Journal of Adult Nursing. 2013;25(2):170-182. https://doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2013.25.2.170Article
- 45. Jin E. Development and effects of hybrid simulation education program of nursing pre/post pediatric cardiac catheterization [dissertation]. Chuncheon: Kangwon National University; 2023;1-130.
- 46. Jung SJ. Development and effects of a simulation-based patient safety management training program for new graduate nurses in the intensive care unit [dissertation]. Suwon: Ajou University; 2023;1-141.
- 47. INACSL Standards Committee. INACSL standards of best practice: SimulationSM outcomes and objectives. Clinical Simulation in Nursing. 2016;12:S13-S15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecns.2016.09.006Article
References
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Safety-centered simulation education using the 360-degree video room of errors: A mixed-methods study
Jiyoung Kim, Yeji Kim, Hyunji Park, Jiyeong Won, Jiwon Yun, Yuran Lee
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2026; 111: 101899. CrossRef
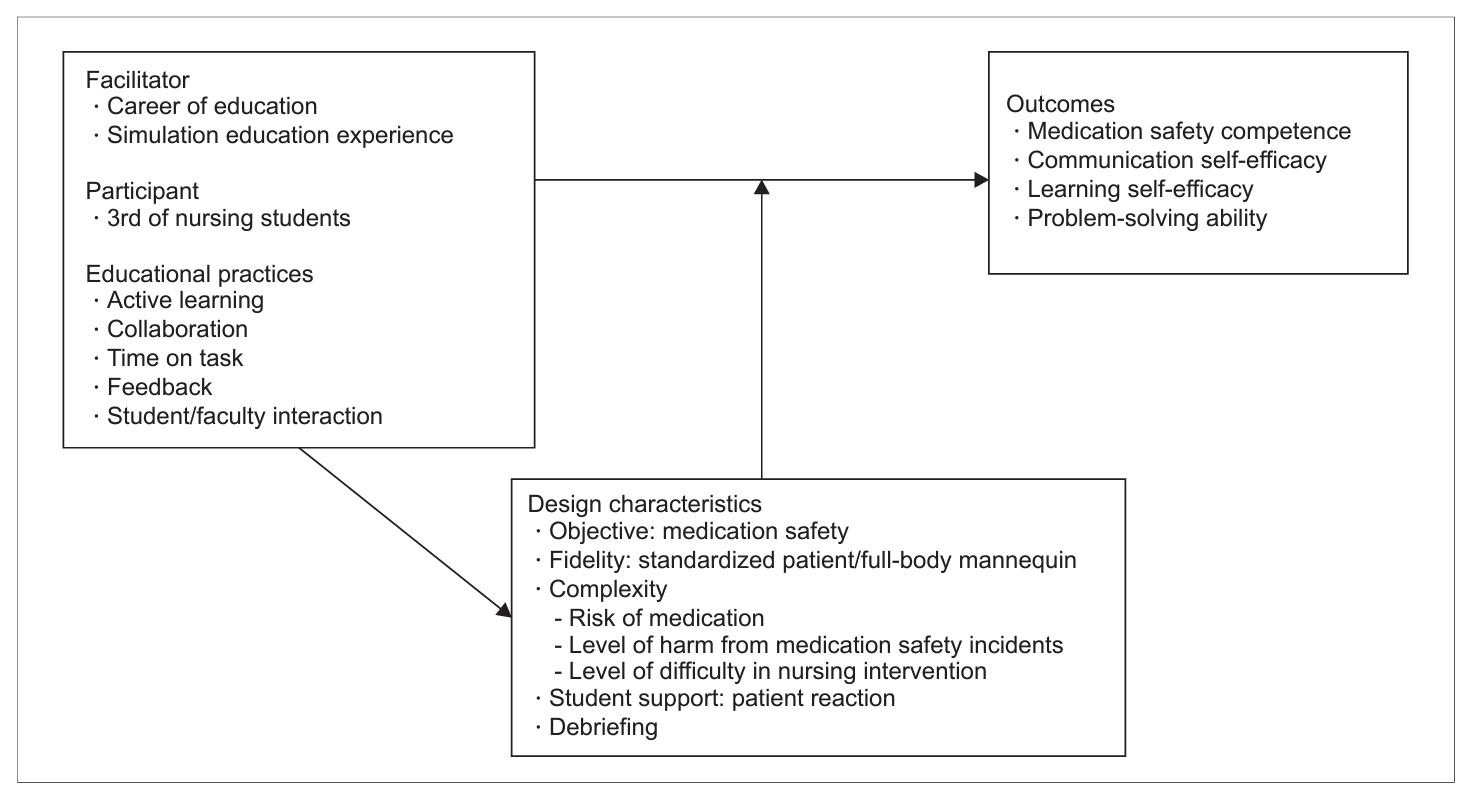
Fig. 1.
| Scenarios | Learning objectives | Situations | Role and expected learner behaviors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1 | The nurses can identify medication safety-related problem situations (near-misses). | • Hospital day 1 | • An evening-shift nurse (student) detects an error using a patient identification bracelet (ID band) and asks open-ended questions before administering the medication. |
| • A medication error may occur if an evening-shift nurse does not accurately check a patient with the same name during the medication preparation stage when administering fluid that the previous shift nurse prepared in advance for a patient with the same name. | • If a nurse cannot detect the error, the nursing manager provides a clue. | ||
| Scenario 2 | The nurses can identify and respond to problem situations related to medication safety (prescription errors/none). | • Hospital day 2 | • An evening-shift nurse (student) discovers that the patient took oral drugs whose administration was prohibited before the CT scan. |
| • A situation in which a patient’s scheduled upper abdominal CT scan was delayed because a doctor’s incorrect prescription instructions caused the previous shift nurse to incorrectly administer medication to the patient that should have been stopped prior to the CT scan. | • If a nurse cannot detect the error, the nursing manager provides a clue. | ||
| Scenario 3 | The nurses can identify and respond to crisis situations related to medication safety (adverse events/moderate). | • Hospital day 3 | • An evening-shift nurse (student) suspects that the patient is suffering from hypoglycemic shock and responds to it. |
| • A situation in which serious damage occurred because a day-shift nurse administered medication to the patient using the wrong dosage and a route that was inconsistent with a doctor’s prescription instructions. | • If the nurse cannot detect the error, the nursing manager provides a clue. |
| Sessions | Sequences | Contents | Time (min) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Cumulative | |||
| Session 1 | Pre-learning | • Medication safety–related knowledge (lecture) | 20 | 65 |
| - Basic principles of medication administration, types of patient safety accidents, activities to prevent medication errors | ||||
| Pre-briefing | • Guide to simulation practice environment and process | 15 | ||
| • Introduction to scenario case outlines | ||||
| • Introduction to Scenario 1 situation | ||||
| • Identifying nursing issues and setting priorities | ||||
| • Assigning simulation roles | ||||
| Simulation run | • Detecting and dealing with near-misses (SP, full-body mannequin) | 10 | ||
| • Nursing performance evaluation | ||||
| Debriefing | • Reflection and feedback | 20 | ||
| Session 2 | Pre-learning | • Medication safety–related knowledge (lecture) | 20 | 80 |
| - Medication process, types of medication errors, communicating patient safety accidents (SBAR) | ||||
| Pre-briefing | • Introduction to Scenario 2 situation | 15 | ||
| • Identifying nursing issues and setting priorities | ||||
| • Assigning simulation roles | ||||
| Simulation run | • Identifying and dealing with prescription errors (SP, full-body mannequin) | 15 | ||
| • Nursing performance evaluation | ||||
| Debriefing | • Reflection and feedback | 30 | ||
| Session 3 | Pre-learning | • Medication safety–related knowledge (lecture) | 20 | 95 |
| - High-alert medication management, patient safety accident reporting, patient safety accident analysis | ||||
| Pre-briefing | • Introduction to Scenario 3 situation | 15 | ||
| • Identifying nursing problems and setting priorities | ||||
| • Assigning simulation roles | ||||
| Simulation run | • Detecting and dealing with adverse events (SP, full-body mannequin) | 20 | ||
| • Nursing performance evaluation | ||||
| Debriefing | • Reflection and feedback | 40 | ||
| Variables | Categories | Exp. (n = 20) |
Cont. (n = 20) |
t or χ2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) or M ± SD | |||||
| General characteristics | |||||
| Age (yr) | 21.4 ± 1.23 | 21.5 ± 1.10 | – 0.41 | .686 | |
| Gender | Woman | 18 (90.0) | 19 (95.0) | < .999 |
|
| Man | 2 (10.0) | 1 (5.0) | |||
| Religion | Yes | 6 (30.0) | 4 (20.0) | 0.53 | .465 |
| No | 14 (70.0) | 16 (80.0) | |||
| Previous semester grade | ≥ 3.5 | 9 (45.0) | 12 (60.0) | 0.90 | .342 |
| < 3.5 | 11 (55.0) | 8 (40.0) | |||
| Experience of healthcare service | Have | 3 (15.0) | 3 (15.0) | < .999 |
|
| Haven’t | 17 (85.0) | 17 (85.0) | |||
| Satisfaction of major | Above high | 12 (60.0) | 15 (75.0) | 1.03 | .311 |
| Middle or less | 8 (40.0) | 5 (25.0) | |||
| Satisfaction of clinical practice | Above high | 11 (55.0) | 10 (50.0) | 0.10 | .752 |
| Middle or less | 9 (45.0) | 10 (50.0) | |||
| Reasons for entering nursing college | Easy employment | 11 (55.0) | 10 (50.0) | 2.56 | .333 |
| Aptitude | 5 (25.0) | 2 (10.0) | |||
| Recommendation | 4 (20.0) | 8 (40.0) | |||
| Type of apply for a job | Hospitals | 18 (90.0) | 19 (95.0) | 0.36 | .548 |
| Other than hospitals | 2 (10.0) | 1 (5.0) | |||
| Medication safety competence | 119.70 ± 10.68 | 120.05 ± 11.79 | – 0.10 | .922 | |
| Communication self-efficacy | 86.55 ± 11.86 | 83.80 ± 11.96 | 0.73 | .470 | |
| Learning self-efficacy | 56.90 ± 5.71 | 57.10 ± 4.23 | – 0.13 | .901 | |
| Problem-solving ability | 108.75 ± 14.41 | 112.00 ± 11.13 | – 0.80 | .430 | |
| Variables | Pre-test |
Post-test |
Difference |
t | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp. (n = 20) | Cont. (n = 20) | Exp. (n = 20) | Cont. (n = 20) | Exp. (n = 20) | Cont. (n = 20) | |||
| Medication safety competence | 119.70 ± 10.68 | 120.05 ± 11.79 | 144.90 ± 10.47 | 132.55 ± 10.96 | 25.20 ± 10.05 | 12.50 ± 8.56 | 4.30 | < .001 |
| Communication self-efficacy | 86.55 ± 11.86 | 83.80 ± 11.96 | 99.80 ± 10.28 | 87.35 ± 12.23 | 13.25 ± 7.44 | 3.55 ± 7.50 | 4.11 | < .001 |
| Learning self-efficacy | 56.90 ± 5.71 | 57.10 ± 4.23 | 77.40 ± 4.45 | 72.78 ± 4.97 | 20.50 ± 4.37 | 15.68 ± 4.65 | 3.01 | .005 |
| Problem-solving ability | 108.75 ± 14.41 | 112.00 ± 11.13 | 124.40 ± 12.48 | 114.00 ± 9.49 | 15.65 ± 7.60 | 2.00 ± 5.42 | 6.54 | < .001 |
CT = Computed tomography; ID = Identification.
SBAR = Situation, background, assessment, recommendation; SP = Simulated patient.
Fisher’s exact test. Cont. = Control group; Exp. = Experimental group; M = Mean; SD = Standard deviation.
Cont. = Control group; Exp. = Experimental group.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

