Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Media discourse on physician assistant nurses in South Korea: a text network and topic modeling approach
- Young Gyu Kwon, Daun Jeong, Song Hee Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Chan Woong Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):388-399. Published online July 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25038
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study quantitatively examined the portrayal of physician assistant (PA) nurses in Korean media by integrating text network analysis with latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) topic modeling.
Methods
A total of 3,564 news articles published by nine major Korean media outlets between 2020 and 2024 were analyzed. Content analysis was conducted using term frequency-inverse document frequency calculations, network centrality analysis, and LDA topic modeling to extract key terms, map discourse structures, and identify latent topics.
Results
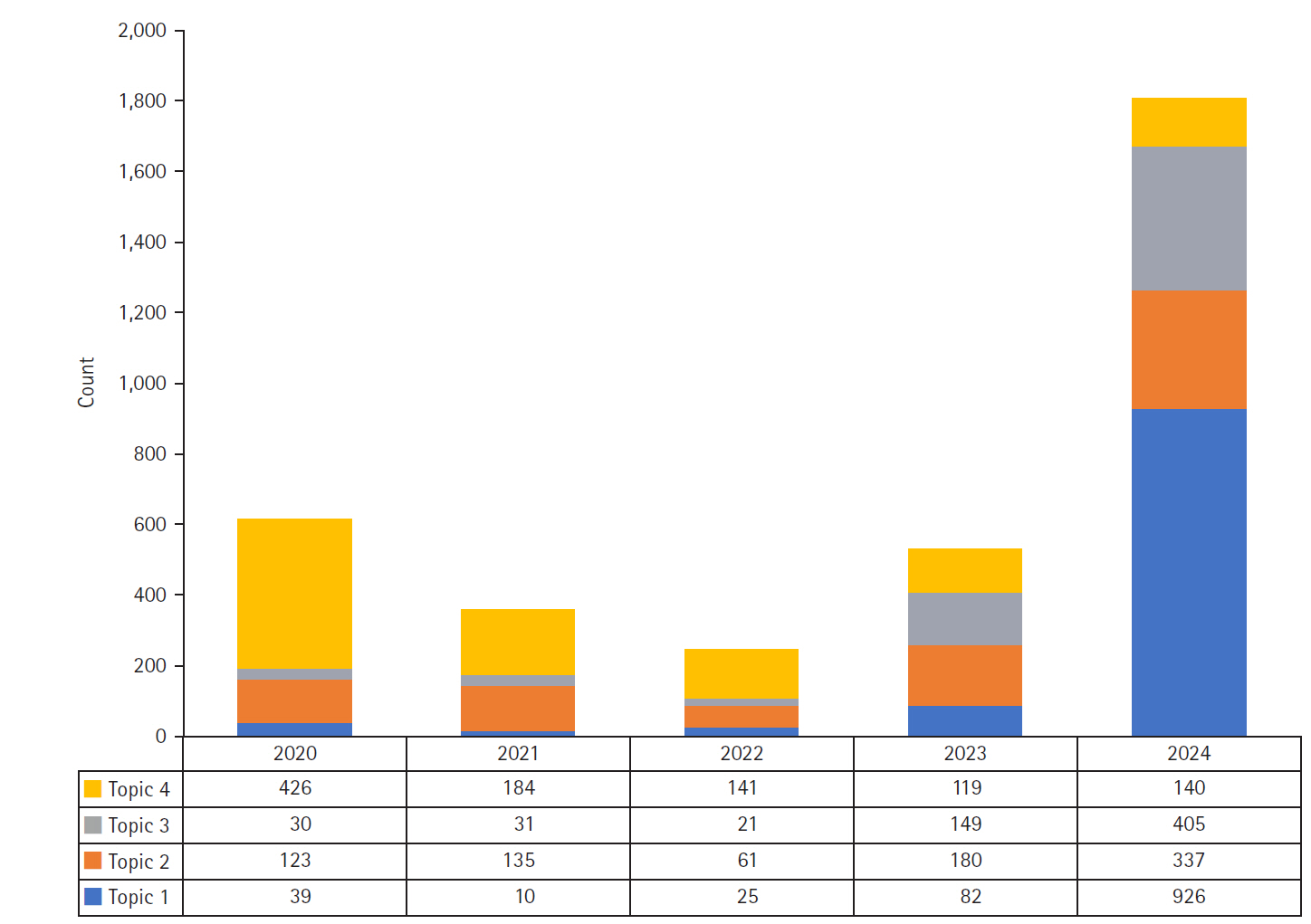
The analysis identified four primary topics in Korean media discourse: “healthcare workforce expansion policies” (30.4%), “hospital clinical practice and operational management” (23.5%), “institutionalization of the PA nursing role” (17.8%), and “COVID-19 response and public health crisis management” (28.3%). High-centrality keywords included “hospital,” “medical,” “patient,” “physician,” “government,” and “nurse,” indicating that the discourse primarily focused on clinical settings. Topic modeling revealed a major shift from pandemic-centered coverage in 2020 to a focus on healthcare workforce policy and PA nurse institutionalization in 2024, coinciding with the passage of the Nursing Act.
Conclusion
This study provides empirical evidence suggesting that the portrayal of PA nurses in Korean media discourse evolved from a peripheral regulatory issue to a central healthcare delivery solution, particularly in the contexts of workforce management, clinical practice, and crisis response. Our findings suggest that PA nurse institutionalization received broader attention when positioned as part of systemic healthcare improvements addressing concrete clinical needs. These results offer valuable insights for policymakers and administrators in framing and implementing workforce policy reforms.
- 3,403 View
- 114 Download

- A review of domestic and international contexts for establishing a communication platform for early-career nurse scientists
- Jeung-Im Kim, Jin-Hee Park, Hye Young Kim, Mi Yu, Sun Joo Jang, Yeonsoo Jang, Sangeun Jun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):317-325. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25041
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
As nursing continues to advance through digital health, clinical specialization, and interdisciplinary research, early-career nurse scientists are central to advancing innovation. However, Korea lacks a structured platform to support their research, collaboration, and career development. This review aimed to identify the needs of early-career nurse scientists and examine international best practices to guide the creation of an effective communication platform.
Methods
This study involved a secondary analysis of the final report from the project “Establishment of a communication platform for young nursing scientists,” carried out by the Korean Society of Nursing Science. The report comprises data from focus group interviews with domestic graduate students and early-career researchers, a literature review of international communication and support systems, and a global policy analysis related to young nursing scientists. Based on this report, the present review synthesizes key findings and draws implications for the development of a communication platform in Korea.
Results
International examples, such as grant writing programs, mentoring initiatives, and digital collaboration hubs, showed positive outcomes in strengthening research capacity and promoting the professional growth of nurse scientists. Based on these findings, key considerations for platform development include: (1) establishing clear leadership and a participatory governance model; (2) providing demand-driven content such as research guides, mentoring, and mental health resources; (3) implementing mechanisms to ensure sustainability, content quality, and user data protection; and (4) designing an integrated platform that fosters synergy across research, policy development, education, and global networking.
Conclusion
A digital platform for early-career nurse scientists should function not merely as an information portal, but also as dynamic infrastructure for collaboration, mentorship, and growth. It is recommended that the Korean Society of Nursing Science spearhead this initiative, with governmental support, to enhance the research capacity and expand the global engagement of Korean nursing scientists.
- 2,322 View
- 78 Download

- Analysis of the relative importance of key factors in nursing workforce management for pandemic response in general hospitals and long-term care hospitals
- Jeong Eun Cha, Eun Kyoung Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):236-248. Published online May 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the key factors in nursing workforce management for pandemic response in general hospitals and long-term care hospitals and to analyze the relative importance of these factors.
Methods
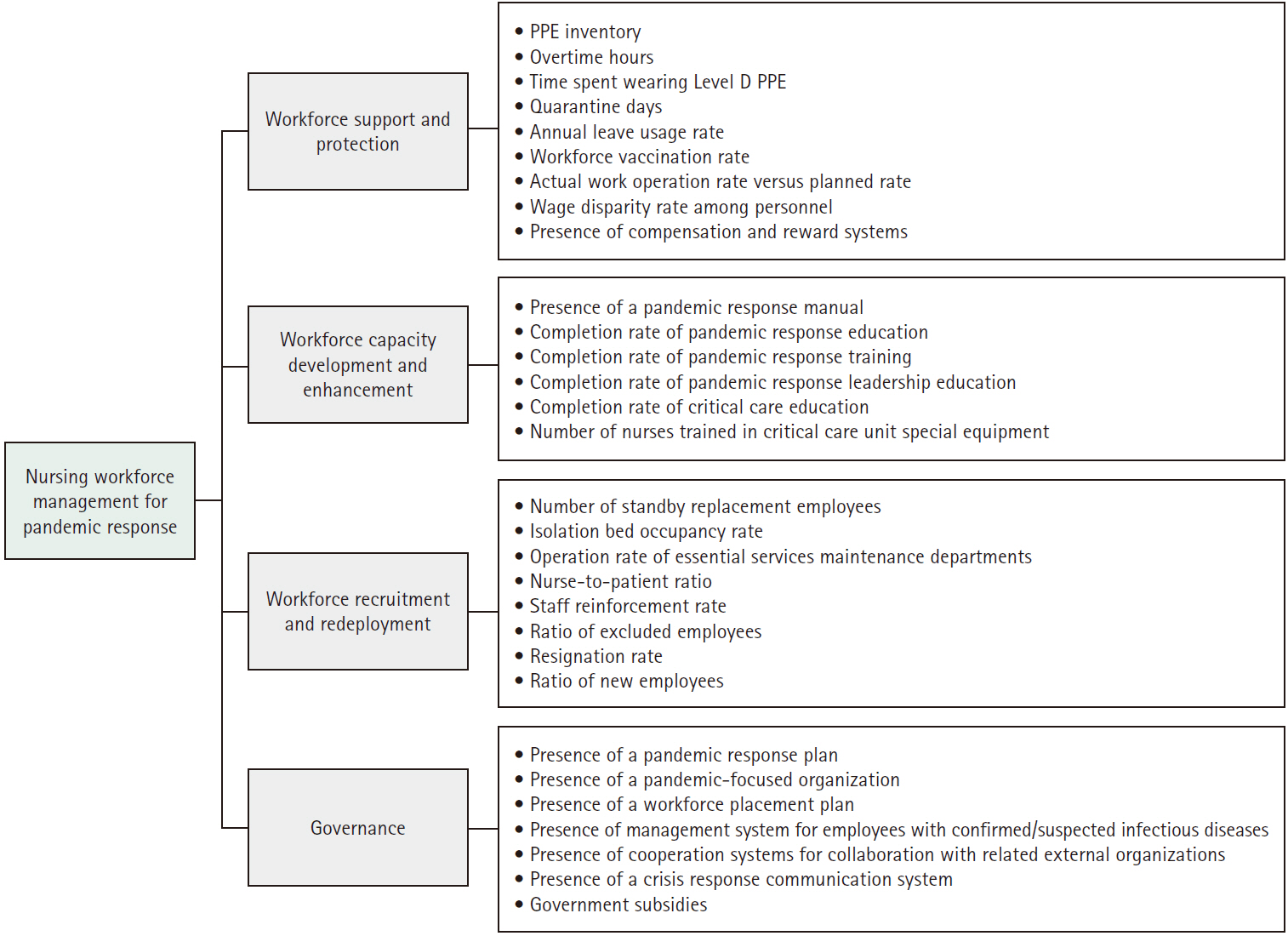
A validity test was conducted with experts to select four categories and 30 key factors related to nursing workforce management for pandemic response. Surveys were collected from 25 nursing managers in general hospitals and 21 nursing managers in long-term care hospitals, and the relative importance of the key factors was analyzed using the analytic hierarchy process method.
Results
Differences were found between the two groups in the relative importance of nursing workforce management for pandemic response. Specifically, the highest-ranking category was “workforce recruitment and redeployment” for general hospitals, but “workforce support and protection” for long-term care hospitals. The most important factor regarding nursing workforce management was the “nurse-to-patient ratio” for both general and long-term care hospitals.
Conclusion
General and long-term care hospitals need to establish nursing workforce management strategies to effectively respond to pandemics with appropriate consideration of the relative importance and prioritization of key factors based on hospital characteristics.
- 1,890 View
- 74 Download

- Analysis of the Adequacy of Nurse Staffing Level through the Estimation of Nursing Activity Hours and Implementation of Focus Group Interviews in a Tertiary Hospital: Using a Mixed-Method Design
- Hyun-Joo Kim, Sun-Hee Lee, Jai-Jung Lee, Sun-Suk Seong, Hee Yang, Hyang-Yuol Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):237-249. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22142
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the adequacy of current nurse staffing levels by identifying nursing activities and workload.
Methods
The study used a mixed-method design. A nursing activity survey was conducted using the work sampling method over 2 working days with 119 general ward nurses. A focus group interview was conducted with 12 nurses. Quantitative and qualitative data were analyzed using SPSS 20.0 and content analysis, respectively.
Results
The most amount of time was spent on medication (in direct nursing) and electronic medical record documentation (in indirect nursing). The appropriate nurse-to-patient ratio is 1:7.7 for the day shift, 1:9.0 for the evening shift, and 1:11.9 for the night shift. However, the current nurse-to-patient ratio is 1:9.4, 1:11.0, and 1:13.8 for the day, evening, and night shifts, respectively. Therefore, the current nurse staffing level is insufficient for the workload. In the focus group interview, the main reasons cited for being unable to complete tasks within working hours were communication and coordination, and the nursing electronic medical record. The essential nursing activities of basic nursing and emotional support were overlooked owing to a heavy workload. Therefore, an adequate nurse staffing level should be higher than the measured quantitative workload.
Conclusion
These results suggest the general wards of tertiary hospitals should evaluate the adequacy of their current nurse staffing and allocate sufficient nurses to improve patient safety and nursing care quality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nurses' Experience Working with Substitute Nurses
Hye Mi Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 208. CrossRef
- Nurses' Experience Working with Substitute Nurses
- 2,992 View
- 255 Download
- 1 Crossref

- National Petition Analysis Related to Nursing: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
- HyunJung Ko, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee, Hee Sun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):635-651. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23052
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the main keyword, network structure, and main topics of the national petition related to “nursing” in South Korea.
Methods
Data were gathered from petitions related to the national petition in Korea Blue House related to the topic “nursing” or “nurse” from August 17, 2017, to May 9, 2022. A total of 5,154 petitions were searched, and 995 were selected for the final analysis. Text network analysis and topic modeling were analyzed using the Netminer 4.5.0 program.
Results
Regarding network characteristics, a density of 0.03, an average degree of 144.483, and an average distance of 1.943 were found. Compared to results of degree centrality and betweenness centrality, keywords such as “work environment,” “nursing university,” “license,” and “education” appeared typically in the eigenvector centrality analysis. Topic modeling derived four topics: (1) “Improving the working environment and dealing with nursing professionals,” (2) “requesting investigation and punishment related to medical accidents,” (3) “requiring clear role regulation and legislation of medical and nonmedical professions,” and (4) “demanding improvement of healthcare-related systems and services.” Conclusion: This is the first study to analyze Korea's national petitions in the field of nursing. This study's results confirmed both the internal needs and external demands for nurses in South Korea. Policies and laws that reflect these results should be developed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Voice of Customer Analysis of Nursing Care in a Tertiary Hospital: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Hyunjung Ko, Nara Han, Seulki Jeong, Jeong A Jeong, Hye Ryoung Yun, Eun Sil Kim, Young Jun Jang, Eun Ju Choi, Chun Hoe Lim, Min Hee Jung, Jung Hee Kim, Dong Hyu Cho, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 529. CrossRef - A Study on Internet News for Patient Safety Campaigns: Focusing on Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Sun-Hwa Shin, On-Jeon Baek
Healthcare.2024; 12(19): 1914. CrossRef
- Voice of Customer Analysis of Nursing Care in a Tertiary Hospital: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
- 2,733 View
- 43 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of Nursing Work Environment on Intention to Stay of Hospital Nurses: A Two-Mediator Serial Mediation Effect of Career Motivation and Job-Esteem
- Yu Na Lee, Eungyung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):622-634. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23038
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the mediating effects of career motivation and job-esteem and the effect of the nursing work environment on intention to stay among hospital nurses.
Methods
Data were collected from 289 nurses working at an advanced general hospital. The research model design was based on the PROCESS macro proposed by Hayes and analyzed using SPSS 24.0 program.
Results
The results showed a positive correlation between intention to stay and nursing work environment (r = .19, p = .001), career motivation (r = .34, p < .001), and job-esteem (r = .37, p < .001). Nursing work environment (B = 0.34 [.09~.59]) and job-esteem (B = 0.27 [.04~.49]) had a direct effect on intention to stay. There was a two-mediator sereal mediation effect of career motivation and job-esteem. The nursing work environment showed a significant effect on the intention to stay among hospital nurses through career motivation and job-esteem.
Conclusion
In order to increase the retention rate of hospital nurses, it is suggested that government and medical institutions provide multifaceted support that can increase nurses’ motivation for career development and recognition of the nursing profession through improvement of the nursing work environment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Weight analysis of Chinese nurses' behaviors to maintain patient dignity and its relationship with job-esteem: a cross-sectional study controlling for agreeableness
Cong Guo, Chunlin Zhang, Cuizhu Zhou, Mengqi Zhu, Lingling Chen, Youran Liu, Yequn Zhang, Jie Wang, Tengfei Liang
Frontiers in Psychology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Grit and Nursing Work Environment on Work Engagement in Clinical Nurses
Young Ju Kim, Hye Young Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 312. CrossRef - The Effects of Emotional Intelligence and the Practice Environment on the Job-Esteem of Physician Assistant Nurses in University Hospitals
Yoonjung Cho, Yeoungsuk Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 488. CrossRef - The Korean Version of Health Work Environment Assessment Tool for Clinical Nurses: A Validation and Reliability Study
Im Sun Seo, Mihyun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 483. CrossRef
- Weight analysis of Chinese nurses' behaviors to maintain patient dignity and its relationship with job-esteem: a cross-sectional study controlling for agreeableness
- 2,456 View
- 178 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of Clinical Nurses’ Job Crafting on Organizational Effectiveness Based on Job DemandsResource Model
- Eun Young Lee, Eungyung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):129-143. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22138
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the mediating effects of clinical nurses’ job crafting on organizational effectiveness based on the job demands-resources model proposed by Bakker and Demerouti (2017).
Methods
The participants consisted of 393 nurses working in nursing units of a tertiary general hospital located in Cheongju region. The data, collected using questionnaire from August 9 to August 20, 2021, were analyzed using SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 27.0.
Results
The goodness-of-fit (GoF) test results on the modified model (χ 2 = 2.7, GFI = .94, SRMR = .03, RMSEA = .06, NFI = .92, CFI = .94, TLI = .92, AGFI = .90), indicated that the GoF index satisfied the recommended level. Regarding the effects of each variable on organizational effectiveness, job crafting showed statistically significant direct (β = .48, p < .001), indirect (β = .23, p < .001), and total effects (β = .71, p < .001). Burnout showed statistically significant direct effect (β = - .17, p < .001). Work engagement showed statistically significant direct (β = .41, p < .001) and total effects (β = .41, p < .001). The factors explaining organizational effectiveness were job crafting, burnout, and work engagement, which had an explanatory power of 76.7%.
Conclusion
Nurses’ job crafting is an important mediating factor for enhancing the organizational effectiveness of nursing organizations. Hospitals should develop job-crafting success cases and related education and training programs as a strategy for enhancing the job crafting of nurses and, consequently organizational effectiveness. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hospital Nurses’ Professional Quality of Life Model: A Cross‐Sectional Study Based on the Expanded Job Demands‐Resources Model
Younghee Kim, Mi Yu, Jacopo Fiorini
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of grit and job crafting on organizational commitment and job satisfaction among hospital nurses in Korea
Mi-Suk Hyun
Medicine.2025; 104(45): e45890. CrossRef - Effects of Attitude Toward Interdepartmental Transfer, Career Growth Opportunity, and Role Breadth Self-Efficacy on Job Crafting among Nurses with Transfer Experience
Yu Jin Lee, Chung Hee Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 497. CrossRef - Job Crafting as the Missing Link: Understanding Its Role in Nurses’ Work Engagement
Kyungjin Lee, Ja Kyung Seo, Seung Eun Lee, Yunhong Liu
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Commitment to Organizational Change in Clinical Nurses: A Structural Model Applying Lewin's Change Theory
Mihwa Hong, Sujeong Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 38. CrossRef
- Hospital Nurses’ Professional Quality of Life Model: A Cross‐Sectional Study Based on the Expanded Job Demands‐Resources Model
- 3,855 View
- 165 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Keyword Network Analysis and Topic Modeling of News Articles Related to Artificial Intelligence and Nursing
- Ju-Young Ha, Hyo-Jin Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):55-68. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22117
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the main keywords, network properties, and main topics of news articles related to artificial intelligence technology in the field of nursing.
Methods
After collecting artificial intelligence-and nursing-related news articles published between January 1, 1991, and July 24, 2022, keywords were extracted via preprocessing. A total of 3,267 articles were searched, and 2,996 were used for the final analysis. Text network analysis and topic modeling were performed using NetMiner 4.4.
Results
As a result of analyzing the frequency of appearance, the keywords used most frequently were education, medical robot, telecom, dementia, and the older adults living alone. Keyword network analysis revealed the following results: a density of 0.002, an average degree of 8.79, and an average distance of 2.43; the central keywords identified were ’education,’ ‘medical robot,’ and ‘fourth industry.’ Five topics were derived from news articles related to artificial intelligence and nursing: ‘Artificial intelligence nursing research and development in the health and medical field,’ ‘Education using artificial intelligence for children and youth care,’ ‘Nursing robot for older adults care,’ ‘Community care policy and artificial intelligence,’ and ‘Smart care technology in an aging society.’ Conclusion: The use of artificial intelligence may be helpful among the local community, older adult, children, and adolescents. In particular, health management using artificial intelligence is indispensable now that we are facing a super-aging society. In the future, studies on nursing intervention and development of nursing programs using artificial intelligence should be conducted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mapping the Landscape of AI-Driven Human Resource Management: A Social Network Analysis of Research Collaboration
Mehrdad Maghsoudi, Motahareh Kamrani Shahri, Mehrdad Agha Mohammad Ali Kermani, Rahim Khanizad
IEEE Access.2025; 13: 3090. CrossRef - Characteristics of Online Articles Related to Youth Drug Use: An Analysis Using Keyword Network Analysis
Ji-Min Kim
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2025; 26(11): 3087. CrossRef - The Impact of Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Learning on Nursing Students' Ethical Decision-making and Clinical Reasoning in Pediatric Care
Hyewon Shin, Jennie C. De Gagne, Sang Suk Kim, Minjoo Hong
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2024; 42(10): 704. CrossRef - Research trends over 10 years (2010-2021) in infant and toddler rearing behavior by family caregivers in South Korea: text network and topic modeling
In-Hye Song, Kyung-Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(3): 182. CrossRef
- Mapping the Landscape of AI-Driven Human Resource Management: A Social Network Analysis of Research Collaboration
- 6,684 View
- 173 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- The Moderating Effect of Organizational Justice on the Relationship between Self-Efficacy and Nursing Performance in Clinical Nurses
- Ju-Ra Kim, Yukyung Ko, Youngjin Lee, Chun-Ja Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(5):511-521. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22076
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the moderating effect of organizational justice on the relationship between self-efficacy and nursing performance among clinical nurses.
Methods
In January 2021, a cross-sectional survey was conducted with 224 clinical nurses recruited from a university-affiliated hospital in Suwon, South Korea. Participants completed online-based, self-report structured questionnaires. Collected data were analyzed using multiple regression and a simple model of PROCESS macro with a 95% bias-corrected bootstrap confidence interval.
Results
Self-efficacy and organizational justice were found to be significant predictors of nursing performance. These two predictors explained the additional 34.8% variance of nursing performance in the hierarchical regression model, after adjusting the other covariates. In addition, organizational justice moderated the relationship between self-efficacy and nursing performance among the clinical nurses. In particular, at low self-efficacy level, participants with high organizational justice had higher nursing performance compared to those with low organizational justice.
Conclusion
Enhancing organizational justice can be used as an organizational strategy for improving the organizational culture in terms of distribution, procedure, and interaction. Ultimately, these efforts will contribute to the improvement of nursing performance through a synergistic effect on organizational justice beyond nurses’ individual competency and self-efficacy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Balancing efficiency and fairness in an output-based agency relationship: an empirical investigation of the cognitive factors favouring a win–win situation
Filippo Ferrari
Evidence-based HRM: a Global Forum for Empirical Scholarship.2025; 13(5): 866. CrossRef - Work-family balance mediates self-efficacy and subjective well-being among nurses in Chinese intensive care units: A cross-sectional study
Lating Zhang, Xianzhen Jin, Na Cheng, Ruhua Wang, Xinhui Liang, Haiyan Fan, Xue Jiang
Applied Nursing Research.2025; 82: 151932. CrossRef - Relationship between resilience and self-efficacy among Iranian nurses: a cross-sectional study during the post-Corona era
Saeed Ghasempour, Ali Abbasi, Mohammad Hasan Basirinezhad, Ali Dadgari, Hossein Ebrahimi
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Nurse Collaboration and Nurse-Physician Collaboration on Nursing Performance in Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Patient Safety Management Activities
JaHyun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Sunmi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 343. CrossRef - The Impact of Self-Efficacy on Nurses’ Well-Being: Does Digital Competence Matter?
Yali Li, Qi Jing, Taiwen Feng, Xiaoling Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(4): 385. CrossRef
- Balancing efficiency and fairness in an output-based agency relationship: an empirical investigation of the cognitive factors favouring a win–win situation
- 2,251 View
- 115 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Images of Nurses Appeared in Media Reports Before and After Outbreak of COVID-19: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
- Min Young Park, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Eun Jee Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):291-307. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aims of study were to identify the main keywords, the network structure, and the main topics of press articles related to nurses that have appeared in media reports.
Methods
Data were media articles related to the topic “nurse” reported in 16 central media within a one-year period spanning July 1, 2019 to June 30, 2020. Data were collected from the Big Kinds database. A total of 7,800 articles were searched, and 1,038 were used for the final analysis. Text network analysis and topic modeling were performed using NetMiner 4.4.
Results
The number of media reports related to nurses increased by 3.86 times after the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak compared to prior. Pre- and post-COVID-19 network characteristics were density 0.002, 0.001; average degree 4.63, 4.92; and average distance 4.25, 4.01, respectively. Four topics were derived before and after the COVID-19 outbreak, respectively. Pre-COVID-19 example topics are “a nurse who committed suicide because she could not withstand the Taewoom at work” andf “a nurse as a perpetrator of a newborn abuse case,” while post-COVID-19 examples are “a nurse as a victim of COVID-19,” “a nurse working with the support of the people,” and “a nurse as a top contributor and a warrior to protect from COVID-19.” Conclusion: Topic modeling shows that topics become more positive after the COVID-19 outbreak. Individual nurses and nursing organizations should continuously monitor and conduct further research on nurses’ image. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Honoring donors: medical students’ reflections on cadaveric dissection
Young Gyu Kwon, Myeong Namgung, Song Hee Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Chan Woong Kim, Hyo Hyun Yoo
BMC Medical Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the relative importance of key factors in nursing workforce management for pandemic response in general hospitals and long-term care hospitals
Jeong Eun Cha, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(2): 236. CrossRef - Shifting social perceptions of dietitians in Korea after the legislation of nutrition teachers: a keyword network analysis of unstructured data
Yunkyoung Oh, Eunsil Her
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 214. CrossRef - Media Portrayals of Nurse Retention: A Decade of News With Topic Modeling and Network Analysis
Taewha Lee, JooHyun Lee
International Nursing Review.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Text Network Analysis of Research on the Bereaved After Sudden Death Since 2000
Kyung-Ah Kang, Suk-Jung Han, Jiyoung Chun
Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2025; 28(4): 160. CrossRef - Voice of Customer Analysis of Nursing Care in a Tertiary Hospital: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Hyunjung Ko, Nara Han, Seulki Jeong, Jeong A Jeong, Hye Ryoung Yun, Eun Sil Kim, Young Jun Jang, Eun Ju Choi, Chun Hoe Lim, Min Hee Jung, Jung Hee Kim, Dong Hyu Cho, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 529. CrossRef - Impact of a game-based interprofessional education program on medical students’ perceptions: a text network analysis using essays
Young Gyu Kwon, Myeong Namgung, Song Hee Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Sun Jung Myung, Eun Kyung Eo, Chan Woong Kim
BMC Medical Education.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of issues related to nursing law: Examination of news articles using topic modeling
JooHyun Lee, Hyoung Eun Chang, Jaehyuk Cho, Seohyun Yoo, Joonseo Hyeon, Andrea Cioffi
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(8): e0308065. CrossRef - Medical students’ perceptions of improving physician satisfaction and patient care: a text network analysis approach
Young Gyu Kwon, Myeong Namgung, Song Hee Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Hyo Hyun Yoo, Chan Woong Kim
BMC Medical Education.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Socialisation of children to nurse and nursing images: A Goffman‐inspired thematic analysis of children's picture books in a Swedish context
Stinne Glasdam, Hongxuan Xu, Sigrid Stjernswärd
Nursing Inquiry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Agendas on Nursing in South Korea Media: Natural Language Processing and Network Analysis of News From 2005 to 2022
Daemin Park, Dasom Kim, Ah-hyun Park
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2024; 26: e50518. CrossRef - Research trends over 10 years (2010-2021) in infant and toddler rearing behavior by family caregivers in South Korea: text network and topic modeling
In-Hye Song, Kyung-Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(3): 182. CrossRef - The Analysis of Research Trends and Public Awareness of Smart Farms using Text Mining
Sung-Ho Kil, Hye-Mi Park, Eunseok Lee, Jin-Young Kim, Ji-Woo Kim
Journal of People, Plants, and Environment.2023; 26(1): 9. CrossRef - National Petition Analysis Related to Nursing: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
HyunJung Ko, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee, Hee Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 635. CrossRef - An analysis of Research Published in the Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing from 2013 to 2022 using Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Eun Jo Kim, Kuem-Sun Han
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(2): 188. CrossRef - Chronological Changes in the Portrayal of Korean Nurses in TV Documentaries
Eunjin Kim, Gumhee Baek, Aram Cho, Mijin Byun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 341. CrossRef - A topic modeling analysis for Korean online newspapers: Focusing on the social perceptions of nurses during the COVID-19 epidemic period
Soo Jung Chang, Sunah Park, Yedong Son
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 444. CrossRef
- Honoring donors: medical students’ reflections on cadaveric dissection
- 3,410 View
- 51 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref

- Interorganizational Networks for Smoking Prevention and Cessation: A Blockmodeling Approach
- Eun-Jun Park, Hyeongsu Kim, Kun Sei Lee, Junghee Cho, Jin Hyeong Kim, Ho Jin Jeong, Ji An Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(2):202-213. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined characteristics and patterns of interorganizational networks for smoking prevention and cessation in Korea.
Methods
We surveyed two community health centers, ninety-five hospitals or clinics, ninety- two pharmacies, and sixty-five health welfare organizations in two districts of Seoul in 2020. Data on the organizations’ characteristics of smoking cessation and interorganizational activities for information sharing, client referral, and program collaboration were collected and analyzed using network statistics and blockmodeling.
Results
Network size was in the order of information sharing, client referral, and program collaboration networks. Network patterns for interorganizational activities on information sharing, client referral, and program collaboration among four organizations were similar between the two districts. Community health centers provided information and received clients from a majority of the organizations. Their interactions were not unidirectional but mutual with other organizations. Pharmacies were involved in information sharing with health welfare organizations and client referrals to hospitals or clinics. Health welfare organizations were primarily connected with the community health centers for client referrals and program collaboration.
Conclusion
A community health center is the lead agency in interorganizational activities for smoking prevention and cessation. However, hospitals or clinics, pharmacies, and health welfare organizations also participate in interorganizational networks for smoking prevention and cessation with diverse roles. This study would be evidence for developing future interorganizational networks for smoking prevention and cessation.
- 756 View
- 19 Download

- Topic Modeling and Keyword Network Analysis of News Articles Related to Nurses before and after “the Thanks to You Challenge” during the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Eun Kyoung Yun, Jung Ok Kim, Hye Min Byun, Guk Geun Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(4):442-453. Published online August 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20287
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study was conducted to assess public awareness and policy challenges faced by practicing nurses.
Methods
After collecting nurse-related news articles published before and after ‘the Thanks to You Challenge’ campaign (between December 31, 2019, and July 15, 2020), keywords were extracted via preprocessing. A three-step method keyword analysis, latent Dirichlet allocation topic modeling, and keyword network analysis was used to examine the text and the structure of the selected news articles.
Results
Top 30 keywords with similar occurrences were collected before and after the campaign. The five dominant topics before the campaign were: pandemic, infection of medical staff, local transmission, medical resources, and return of overseas Koreans. After the campaign, the topics ‘infection of medical staff’ and ‘return of overseas Koreans’ disappeared, but ‘the Thanks to You Challenge’ emerged as a dominant topic. A keyword network analysis revealed that the word of nurse was linked with keywords like thanks and campaign, through the word of sacrifice. These words formed interrelated domains of ‘the Thanks to You Challenge’ topic.
Conclusion
The findings of this study can provide useful information for understanding various issues and social perspectives on COVID-19 nursing. The major themes of news reports lagged behind the real problems faced by nurses in COVID-19 crisis. While the press tends to focus on heroism and whole society, issues and policies mutually beneficial to public and nursing need to be further explored and enhanced by nurses. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Nursing Professionalism on Turnover Intention among Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Job Embeddedness
Ja In Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyoung Eun Chang, Sunmi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 446. CrossRef - Patent Technology Trends of Oral Health: Application of Text Mining
Hee-Kyeong Bak, Yong-Hwan Kim, Han-Na Kim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2024; 24(1): 9. CrossRef - Agendas on Nursing in South Korea Media: Natural Language Processing and Network Analysis of News From 2005 to 2022
Daemin Park, Dasom Kim, Ah-hyun Park
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2024; 26: e50518. CrossRef - Analysis of issues related to nursing law: Examination of news articles using topic modeling
JooHyun Lee, Hyoung Eun Chang, Jaehyuk Cho, Seohyun Yoo, Joonseo Hyeon, Andrea Cioffi
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(8): e0308065. CrossRef - Research Trends on Cancer-Related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Non-Central Nervous System Cancer: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Hee-Jun Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae, Jin-Hee Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(3): 313. CrossRef - Perspectives of Frontline Nurses Working in South Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Combined Method of Text Network Analysis and Summative Content Analysis
SangA Lee, Tae Wha Lee, Seung Eun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 584. CrossRef - Nurses’ Experience in COVID-19 Patient Care
Soojin Chung, Mihyeon Seong, Ju-young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(2): 142. CrossRef - A topic modeling analysis for Korean online newspapers: Focusing on the social perceptions of nurses during the COVID-19 epidemic period
Soo Jung Chang, Sunah Park, Yedong Son
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 444. CrossRef - Images of Nurses Appeared in Media Reports Before and After Outbreak of COVID-19: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Min Young Park, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Eun Jee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 291. CrossRef - Experience of Nurses in Charge of COVID-19 Screening at General Hospitals in Korea
Boo Young Ha, Yun-Sook Bae, Han Sol Ryu, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 66. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on Current Nursing Issues in the COVID-19 era through Newspaper Articles: The Application of Text Network Analysis
Young Joo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(3): 307. CrossRef - Analysis of Headline News about Nurses Before and After the COVID-19 Pandemic
Su-Mi Baek, Myonghwa Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(4): 319. CrossRef - Warmth and competence perceptions of key protagonists are associated with containment measures during the COVID-19 pandemic: Evidence from 35 countries
Maria-Therese Friehs, Patrick F. Kotzur, Christine Kraus, Moritz Schemmerling, Jessica A. Herzig, Adrian Stanciu, Sebastian Dilly, Lisa Hellert, Doreen Hübner, Anja Rückwardt, Veruschka Ulizcay, Oliver Christ, Marco Brambilla, Jonas De keersmaecker, Feder
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of Nursing Professionalism on Turnover Intention among Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Job Embeddedness
- 2,051 View
- 25 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

- Information Resource Network Analysis of Factors Influencing Breastfeeding Planning and Duration
- Eunyoung Lee, Insook Cho, Seong Jin Cho, Eunju Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(2):232-244. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20280
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the modifiable factors affecting breastfeeding planning and duration among healthy mothers and their use of breastfeeding information resources.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey was conducted in a community setting. Four hundreds participants were recruited at five pediatric clinics and three community health centers located in Paju-si and Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, between January and May 2019. Based on the breastfeeding decision-making model, driven by Martens and Young’s work, the survey items consisted of demographics, childbirth and breastfeeding characteristics, and breastfeeding information resources. In the analysis, 389 responses were used in the t-test, ANOVA, and logistic regression. Information resource networks were compared before and after childbirth including a subgroup analysis depending on the breastfeeding duration.
Results
The modifiable factors affecting breastfeeding planning and duration were antenatal and postpartum breastfeeding education and the provision of information in the hospital. The frequency of Internet use and websites visited were notable and potentially modifiable factors, which were also observed in the networks showing different relationship patterns according to participant subgroups and times. The childbirth event increased the centralization of the network in the planned group, while the network of the non-planned group was more diffused after childbirth. The network of the short-term breastfeeding group was characterized by a more centralized pattern and the resources of high betweenness centrality than the long-term group.
Conclusion
Breastfeeding education is a consistent factor that affects breastfeeding behavior. A well-designed internet-based approach would be an effective nursing intervention to meet the needs of women seeking breastfeeding information and changing their behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Survey on the Status of Breastfeeding in Korean Medical Institution Workers
Tae Hyeong Kim, Sung-Hoon Chung, Jun Hwan Kim, Youngmin Ahn, Son Moon Shin, Woo Ryoung Lee, Eui Kyung Choi, Juyoung Lee, Hye-Jung Shin, Euiseok Jung, Ju Sun Heo, Jin A Lee, Soon Min Lee, Seong Phil Bae, Jeonglyn Song, Chae-Young Kim, Dae Yong Yi
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Multi-Center Educational Research Regarding Breastfeeding for Pediatrics Residents in Korea
Yong-Sung Choi, Sung-Hoon Chung, Eun Sun Kim, Eun Hee Lee, Euiseok Jung, So Yeon Lee, Wooryoung Lee, Hye Sun Yoon, Yong Joo Kim, Ji Kyoung Park, Son Moon Shin, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim
Neonatal Medicine.2022; 29(1): 28. CrossRef - Breastfeeding Success Experience of Primiparas
Sun Ok Lee, Sung Soon Na, Hee Sook Kim, Kyung Eui Bae, Mi Sun Youn, Eun Ju Oh
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2022; 26(4): 254. CrossRef - Breastfeeding experiences of women with gestational diabetes
Seungmi Park, Soo-Young Yu
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 274. CrossRef
- Survey on the Status of Breastfeeding in Korean Medical Institution Workers
- 1,469 View
- 22 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Secondary Data Analysis on the Quality of Sleep and Related Factors of Novice and Experienced Shift Work Nurses
- Minjeong Yu, Choi-Kwon Smi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(5):646-657. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19238
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the quality of sleep in novice and experienced shift work nurses and compare the factors associated with their quality of sleep.
Methods
We analyzed the data of 192 and 256 novice and experienced nurses, respectively. The quality of sleep, sleep hygiene, job stress, and fatigue were measured using Insomnia Severity Index, Sleep Hygiene Practice Scale, the Korean Occupational Stress Scale, and Fatigue Severity Scale. Data were analyzed using SPSS 25.0 to calculate descriptive statistics and logistic regression.
Results
Sleep quality was lower in experienced nurses (12.55 ± 5.71) than in novice nurses (11.18 ± 5.78). Fatigue was more severe in experienced nurses (4.47 ± 1.13) than in novice nurses (4.23 ± 1.12). In the logistic regression, factors related to sleep quality in novice nurses were sleep hygiene (odds ratio; OR = 1.06, p < .001) and fatigue (OR = 2.49, p < .001). Factors related to sleep quality in the experienced nurses were also sleep hygiene (OR = 1.04, p = .001) and fatigue (OR = 1.53, p = .012).
Conclusion
Sleep quality of experienced nurses is lower than those of novice nurses. Factors associated with sleep quality in novice and experienced nurses are equally identified as sleep hygiene and fatigue. Therefore, personal efforts to improve sleep hygiene, such as providing comfortable sleep environment, are needed. Furthermore, organized efforts to decrease fatigue, such as constructing a working environment with a bright light at night and providing a fatigue-decreasing program that includes meditation, are required. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Navigating night shifts: a qualitative study of exploring sleep experiences and coping strategies among nurses
Hyeonbin Lim, Su Hyun Kim
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Improving sleep health in paramedics through an app-based intervention: a randomised waitlist control pilot trial
Alexandra E. Shriane, Grace E. Vincent, Sally A. Ferguson, Amanda Rebar, Tracy Kolbe-Alexander, Gabrielle Rigney
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Sleep Disturbance of Novice Nurses: Focusing on Sleep Hygiene and Physical Activity - Longitudinal Study of Secondary Data
Minjeong Yu, Smi Choi-Kwon, Jison Ki, Kyeongsug Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(3): 278. CrossRef - Dietary behavior and its influencing factors among experienced shiftwork nurses: a secondary analysis
Soyeon Kim, Jison Ki, Ji Yun Choi, Woan Heui Choi, Smi Choi-Kwon
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(1): 32. CrossRef - Mediating effects of fatigue on the relationship between sleep quality and the quality of life of shift-working nurses
Jeongwon Yeom, Insun Yeom
Chronobiology International.2023; 40(4): 450. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Gastrointestinal Symptoms among Rotating Shift Nurses in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
Sun-Kyung Hwang, Yun-Ji Lee, Min-Eun Cho, Bo-Kyoung Kim, Yea-In Yoon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(16): 9795. CrossRef - Health-Related Factors Influencing Nurse Turnover by Clinical Career: A Secondary Data Analysis of Clinical Nurses in South Korea
Jiwon Kang, Youngjin Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(22): 15222. CrossRef - Low Back Pain and Its Influencing Factors among Intensive Care Unit Nurses: A Cross-sectional Study
Hyun Ju Uhm, Hye-Ja Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(2): 95. CrossRef - Sleep quality and its predictors among hospital-based nurses: a cross-sectional study
Khader A. Almhdawi, Hassan Alrabbaie, Donia S. Obeidat, Saddam F. Kanaan, Moh’d Rami Alahmar, Zaid Modhi Mansour, Alaa O. Oteir
Sleep and Breathing.2021; 25(4): 2269. CrossRef - Nurses' Voices: Autumn 2020
Jeung-Im Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 644. CrossRef
- Navigating night shifts: a qualitative study of exploring sleep experiences and coping strategies among nurses
- 2,823 View
- 91 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Secondary Data Analysis on the Factors Influencing Premenstrual Symptoms of Shift Work Nurses: Focused on the Sleep and Occupational Stress
- Jihyun Baek, Smi Choi-Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(4):631-640. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19230
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine premenstrual symptoms (PMS) of shift nurses and identify the association between PMS, sleep, and occupational stress.
Methods
This study was conducted with a secondary data analysis that used data from the Shift Work Nurse’s Health and Turnover study. The participants were 258 nurses who were working in shifts including night shifts. PMS, sleep patterns (sleep time and sleep time variability), sleep quality, and the occupational stress of each participant were measured using the Moos Menstrual Distress Questionnaire, a sleep diary, an actigraph, the Insomnia Severity Index, and the Korean Occupational Stress Scale, respectively. Data were analyzed using SPSS 23 and STATA 15.1 to obtain descriptive statistics, Pearson’s correlation coefficients, multiple linear regression with generalized estimating equations (GEE) and Baron and Kenny’s mediating analysis.
Results
The average PMS score, average sleep time, average sleep time variability, average sleep quality score, and average occupational stress score of the participants was 53.95 ± 40.45, 7.52 ± 0.89 hours, 32.84 ± 8.43%, 12.34 ± 5.95, and 49.89 ± 8.98, respectively. A multiple linear regression analysis with GEE indicated that sleep time variability (B = 0.86, p = .001), and sleep quality (B = 2.36, p < .001) had negative effects on nurses’ PMS. We also found that sleep quality had a complete mediating effect in the relationship between occupational stress and PMS.
Conclusion
These findings indicate that both sleep time variability and sleep quality are important factors associated with PMS among shift work nurses. To improve shift nurses’ PMS status, strategies are urgently needed to decrease sleep time variability and increase sleep quality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hospital Nurses’ Professional Quality of Life Model: A Cross‐Sectional Study Based on the Expanded Job Demands‐Resources Model
Younghee Kim, Mi Yu, Jacopo Fiorini
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Premenstrual Symptoms Risk Factors Among Newly Graduated Nurses in Shift Work: A Prospective Longitudinal Study
Iksoo Huh, Smi Choi-Kwon, Jison Ki, Soyeon Kim, Jihyun Baek
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(5): 501. CrossRef - Premenstrual Syndrome’s Impact on Work-Related Quality of Life Among Jordanian Nurses
Yamamah Al-Hmaid, Othman Beni Yonis, Mais Alkhalili, Khalid Kheirallah
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigating influencing factors on premenstrual syndrome (PMS) among female college students
Su Jeong Yi, Miok Kim, Ina Park
BMC Women's Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of risk prediction model for premenstrual syndrome in nurses: results from the nurses-based the TARGET cohort study
Li Li, Xiaoyan Lv, Yuxin Li, Xinyue Zhang, Mengli Li, Yingjuan Cao
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Shift nurses’ social jetlag, anxiety, and premenstrual symptoms: A cross-sectional study
Taeyeon Kim, Sun Joo Jang
Collegian.2022; 29(4): 477. CrossRef - Depressive symptoms and menstrual distress according to the menstrual phase in nurses: the Korea Nurses’ Health Study
Oksoo Kim, Sue Kim, Hae Ok Jeon, Ahrin Kim, Chiyoung Cha, Bohye Kim
Journal of Psychosomatic Obstetrics & Gynecology.2022; 43(4): 541. CrossRef - Secondary Data Analysis on the Quality of Sleep and Related Factors of Novice and Experienced Shift Work Nurses
Minjeong Yu, Smi Choi-Kwon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 646. CrossRef
- Hospital Nurses’ Professional Quality of Life Model: A Cross‐Sectional Study Based on the Expanded Job Demands‐Resources Model
- 1,883 View
- 80 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Factors Relating to the Quality of Care for Nursing Home Residents in Korea: Using the Delphi Method
- Juh Hyun Shin, Eun Mee Kim, Ji Yeon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):783-794. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.783
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study identified factors related to the quality of care in nursing homes, and elicited consensus opinions from experts on nursing homes.
Methods A Delphi questionnaire was developed based on a review of the literature using the keywords “nursing homes,” “workforce,” and “quality of care.” A total of two Delphi surveys were conducted with 14 experts. The important and urgent factors related to the quality of care for nursing home residents emerged.
Results A consensus was achieved on the important and urgent factors relating to the quality of care. The related factors were grouped into four sections: Organizational Characteristics, Staffing Characteristics, the Long-Term Care Market and Legal and Policy Issues, and Nursing Processes. In total, 23 items were important factors and 26 items were urgent factors relating to the quality of care. In addition, the unanimous advocacy by the experts for increased hours per resident day for registered nurses (RNs, 41 minutes 59 seconds) was much higher than the current hours per resident day of RNs in Korea.
Conclusion To provide optimal care for residents in nursing homes in Korea, the mandatory and essential placement of RNs with professional knowledge and skills is paramount.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of special nursing units in nursing homes on healthcare utilization and cost: A case-control study using propensity score matching
Eunhee Cho, Eun-Young Kim, Kyung Hee Lee, Hye-Ryoung Kim, Seonhwa Choi, Yea Seul Yoon, EunKyo Kim, Seok-Jae Heo, Se Young Jung, Jiyoon Jang
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2023; 147: 104587. CrossRef - Effects of registered nurse staffing levels, work environment, and education levels on adverse events in nursing homes
Seonhwa Choi, Eunhee Cho, Eunkyo Kim, Kyongeun Lee, Soo Jung Chang
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cost of Care and Pattern of Medical Care Use in the Last Year of Life among Long-Term Care Insurance Beneficiaries in South Korea: Using National Claims Data
Sunjoo Boo, Jungah Lee, Hyunjin Oh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(23): 9078. CrossRef - Impact of Nurse Staffing, Skill Mix and Stability on Resident Health Outcomes in Korean Nursing Homes
Juh Hyun Shin, Gui Yun Choi, Jiyeon Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2020; 22(4): 291. CrossRef - The Effects of Long-term Care Hospitals' Nurse Staffing Level on Patient Outcomes: Differences according to Region
Kyung Jin Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 354. CrossRef
- The effects of special nursing units in nursing homes on healthcare utilization and cost: A case-control study using propensity score matching
- 1,930 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- A Topic Modeling Analysis for Online News Article Comments on Nurses' Workplace Bullying
- Jiyeon Kang, Soogyeong Kim, Seungkook Roh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):736-747. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.736
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to explore public opinion on workplace bullying in the nursing field, by analyzing the keywords and topics of online news comments.
Methods This was a text-mining study that collected, processed, and analyzed text data. A total of 89,951 comments on 650 online news articles, reported between January 1, 2013 and July 31, 2018, were collected via web crawling. The collected unstructured text data were preprocessed and keyword analysis and topic modeling were performed using R programming.
Results The 10 most important keywords were “work” (37121.7), “hospital” (25286.0), “patients” (24600.8), “woman” (24015.6), “physician” (20840.6), “trouble” (18539.4), “time” (17896.3), “money” (16379.9), “new nurses” (14056.8), and “salary” (13084.1). The 22,572 preprocessed key words were categorized into four topics: “poor working environment”, “culture among women”, “unfair oppression”, and “society-level solutions”.
Conclusion Public interest in workplace bullying among nurses has continued to increase. The public agreed that negative work environment and nursing shortage could cause workplace bullying. They also considered nurse bullying as a problem that should be resolved at a societal level. It is necessary to conduct further research through gender discrimination perspectives on nurse workplace bullying and the social value of nursing work.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Topic Modeling of Nursing Issues in the Media During 4 Emerging Infectious Disease Epidemics in South Korea: Descriptive Analysis
Jungok Kim, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2025; 27: e60446. CrossRef - Exploring research themes in the Journal of Librarianship and Information Science: Insights from topic modelings
Alper Aslan, Özcan Özyurt
Journal of Librarianship and Information Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Forty Years of International Journal of Information Management: A Topic Modeling Approach
Ahmet Ayaz
Bilgi Yönetimi.2025; 8(2): 284. CrossRef - 30-year trends in research on enriching education and training with virtual reality: An innovative study based on machine learning approach
Ozcan Ozyurt, Hacer Ozyurt
Education and Information Technologies.2024; 29(7): 8221. CrossRef - Effectiveness of cognitive rehearsal programs for the prevention of workplace bullying among hospital nurses: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yulliana Jeong, Hye Sun Jung, Eun Mi Baek
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating the latest trends of Industry 4.0 based on LDA topic model
Ozcan Ozyurt, Hakan Özköse, Ahmet Ayaz
The Journal of Supercomputing.2024; 80(13): 19003. CrossRef - A Study on Internet News for Patient Safety Campaigns: Focusing on Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Sun-Hwa Shin, On-Jeon Baek
Healthcare.2024; 12(19): 1914. CrossRef - Exploring the Evolution of Educational Serious Games Research: A Topic Modeling Perspective
Hacer Ozyurt, Ozcan Ozyurt, Deepti Mishra
IEEE Access.2024; 12: 81827. CrossRef - Post-traumatic responses to workplace violence among nursing professionals: a collaborative and comparative study in South Korea and Hong Kong
Soyun Hong, Sujin Nam, Janet Yuen Ha Wong, Heejung Kim
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Topic Modeling Analysis of Diabetes-Related Health Information during the Coronavirus Disease Pandemic
Soyoon Min, Jeongwon Han
Healthcare.2023; 11(13): 1871. CrossRef - A large-scale study based on topic modeling to determine the research interests and trends on computational thinking
Ozcan Ozyurt, Hacer Ozyurt
Education and Information Technologies.2023; 28(3): 3557. CrossRef - Exploring Gamification Research Trends Using Topic Modeling
Ahmet Ayaz, Ozcan Ozyurt, Waleed Mugahed Al-Rahmi, Said A. Salloum, Anna Shutaleva, Fahad Alblehai, Mohammed Habes
IEEE Access.2023; 11: 119676. CrossRef - Research Topic Trends on Turnover Intention among Korean Registered Nurses: An Analysis Using Topic Modeling
Jung Lim Lee, Youngji Kim
Healthcare.2023; 11(8): 1139. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on Social Issues Related to ChatGPT: Focusing on News Big Data-based Topic Modeling Analysis
Taejong Kim, Songlee Han
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2023; 24(6): 1209. CrossRef - Exploring the Online News Trends of the Metaverse in South Korea: A Data-Mining-Driven Semantic Network Analysis
Eun Joung Kim, Jung Yoon Kim
Sustainability.2023; 15(23): 16279. CrossRef - Uncovering the Educational Data Mining Landscape and Future Perspective: A Comprehensive Analysis
Ozcan Ozyurt, Hacer Ozyurt, Deepti Mishra
IEEE Access.2023; 11: 120192. CrossRef - Topic Modeling: Perspectives From a Literature Review
Andres M. Grisales A., Sebastian Robledo, Martha Zuluaga
IEEE Access.2023; 11: 4066. CrossRef - Empirical research of emerging trends and patterns across the flipped classroom studies using topic modeling
Ozcan Ozyurt
Education and Information Technologies.2023; 28(4): 4335. CrossRef - Analysis of News Articles on Urban Agriculture using Text Mining from 2012 to 2021
Yumin Park, Yong-Wook Shin
Journal of People, Plants, and Environment.2023; 26(2): 105. CrossRef - Management Information Systems Research: A Topic Modeling Based Bibliometric Analysis
Hakan Özköse, Ozcan Ozyurt, Ahmet Ayaz
Journal of Computer Information Systems.2023; 63(5): 1166. CrossRef - National Petition Analysis Related to Nursing: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
HyunJung Ko, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee, Hee Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 635. CrossRef - Analysis of Telephone Counseling of Patients in Chemotherapy Using Text Mining Technique
Seoyeon Kim, Jihyun Jung, Heiyoung Kang, Jeehye Bae, Kayoung Sim, Miyoung Yoo, Eunyoung, E. Suh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 46. CrossRef - COVID-19 pandemic & cyber security issues: Sentiment analysis and topic modeling approach
Sonal Khandelwal, Aanyaa Chaudhary
Journal of Discrete Mathematical Sciences and Cryptography.2022; 25(4): 987. CrossRef - Images of Nurses Appeared in Media Reports Before and After Outbreak of COVID-19: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Min Young Park, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Eun Jee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 291. CrossRef - Comparison of the Erectile Dysfunction Drugs Sildenafil and Tadalafil Using Patient Medication Reviews: Topic Modeling Study
Maryanne Kim, Youran Noh, Akihiko Yamada, Song Hee Hong
JMIR Medical Informatics.2022; 10(2): e32689. CrossRef - Twenty-five years of education and information technologies: Insights from a topic modeling based bibliometric analysis
Ozcan Ozyurt, Ahmet Ayaz
Education and Information Technologies.2022; 27(8): 11025. CrossRef - Analysis of Headline News about Nurses Before and After the COVID-19 Pandemic
Su-Mi Baek, Myonghwa Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(4): 319. CrossRef - Comparing workplace violence among nurses and other professionals using online articles: A social network analysis
Soyun Hong, Heejung Kim, Myeongseop Cha
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(6): 1750. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on Current Nursing Issues in the COVID-19 era through Newspaper Articles: The Application of Text Network Analysis
Young Joo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(3): 307. CrossRef - Exploring Nurses' Experience and Grievance: Network Analysis and Topic Modeling using a Social Networking Service
Hyunju Ji, Arum Lim, Seung Eun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(3): 169. CrossRef - The Experience of Clinical Nurses after Korea’s Enactment of Workplace Anti-Bullying Legislation: A Phenomenological Study
Hee-Sun Kim, In-Ok Sim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(11): 5711. CrossRef - Topic Modeling and Keyword Network Analysis of News Articles Related to Nurses before and after “the Thanks to You Challenge” during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Eun Kyoung Yun, Jung Ok Kim, Hye Min Byun, Guk Geun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(4): 442. CrossRef - A Network Analysis of Research Topics and Trends in End-of-Life Care and Nursing
Kisook Kim, Seung Gyeong Jang, Ki-Seong Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(1): 313. CrossRef - Silent Counterattack: The Impact of Workplace Bullying on Employee Silence
Xiwei Liu, Shenggang Yang, Zhu Yao
Frontiers in Psychology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Bullying Measurement in Korean Nurses' Workplace
Hyo-Suk Song, So-Hee Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 478. CrossRef - Relationship of Workplace Violence to Turnover Intention in Hospital Nurses: Resilience as a Mediator
Hyun-Jung Kang, Jaeyong Shin, Eun-Hyun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 728. CrossRef
- Topic Modeling of Nursing Issues in the Media During 4 Emerging Infectious Disease Epidemics in South Korea: Descriptive Analysis
- 2,674 View
- 27 Download
- 30 Web of Science
- 36 Crossref

- Response Patterns of Nursing Unit Managers regarding Workplace Bullying: A Q Methodology Approach
- Jin Kyu Choi, Byoungsook Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(5):562-574. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.5.562
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the response patterns of nursing unit managers regarding workplace bullying.
Methods Q methodology was used to identify the response patterns. Thirty-six Q samples were selected from the Q population of 210 that included literature reviews and in-depth interviews with clinical nurses and nursing managers. Participants were 30 nursing unit managers who had experience managing workplace bullying and they classified the Q samples into a normal distribution frame measured on a nine-point scale. The data were analyzed using the PC-QUANL program.
Results Five types of response patterns were identified: (1) sympathetic-understanding acceleration, (2) harmonious-team approach, (3) preventive-organizational management, (4) passive observation, and (5) leading-active intervention. The preventive-organizational management type was most frequently used by the nursing unit managers.
Conclusion The results of this study indicated that nursing unit managers attempted to prevent and solve workplace bullying in various ways. Therefore, it is necessary to develop and conduct leadership training and intervention programs that appropriately address the response patterns of nursing unit managers, such as those identified in this study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The COVID-19 Pandemic Experience of A Cohort of Quarantined University Hospital Nurse Managers
Soon-Youl Lee, Suk Jung Han, Hee Jung Hong
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2024; 38(2): 205. CrossRef - Prevalence of workplace violence against registered nurses and their perceptions of relevant management systems in acute care hospitals
Seungmi Park, Eunju Kwak, Ye-Won Lee, Eun-Jun Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(3): 319. CrossRef - Workplace bullying among Korean registered nurses: A meta-aggregation of qualitative studies
Eun-Jun Park, Hyunwook Kang, Ji Woon Ko
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(4): 450. CrossRef - Q Methodology as an Innovative Addition to Bullying Researchers’ Methodological Repertoire
Adrian Lundberg, Lisa Hellström
International Journal of Bullying Prevention.2022; 4(3): 209. CrossRef
- The COVID-19 Pandemic Experience of A Cohort of Quarantined University Hospital Nurse Managers
- 1,282 View
- 21 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Structural Equation Model for Sleep Quality of Female Shift Work Nurses
- Ji Yeong Jeong, Mee Ock Gu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(5):622-635. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.622
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to develop and test a structural model for sleep quality in female shift work nurses. The hypothetical model was constructed on the basis of Spielman's 3P model of insomnia and previous research related to the sleep quality of shift nurses.
Methods This cross-sectional study used structural equation modeling and recruited 285 female shift work nurses from four general and university hospitals with over 300 beds located in C and J cities in Gyeongsangnamdo. Data were collected from September 27 to October 20, 2016, and then analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson's correlation, and structural equation modeling. The study used SPSS/Win 18.0 and AMOS 18.0 in processing the data.
Results The final model showed good fit to the empirical data: χ2/df=2.19, SRMR=.07, RMSEA=.07, AGFI=.85, TLI=.91, GFI=.93, GFI=.89, NFI=.87. The factors that influenced sleep quality were sleep hygiene (β=.32), perceived shift work status (β=−.16), stress response (β=.16), shift work experience (β=.15), perceived health status (β=−.14), and circadian rhythm (β=−.13) explaining 36.0% of the variance.
Conclusion The model of sleep quality of the shift work nurses constructed in this study is recommended as a model to understand and predict the sleep quality of shift work nurses. The results suggest that strategies for improving the sleep quality of shift work nurses should focus on sleep hygiene, perceived health status, stress response, circadian rhythm, perceived shift work status, and shift work experience.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring Pathways Linking Work and Nonwork Factors to Sleep, Fatigue, and Health in Night Shift Nurses: A Structural Equation Modeling Analysis
Bo Min Jeon, Su Hyun Kim, Juan Gómez-Salgado
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The influence of COVID-19-related resilience on depression, job stress, sleep quality, and burnout among intensive care unit nurses
Sojin Hwang, Jungmin Lee
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Holistic sleep improvement strategies for frontline nurses served during a public health emergency (COVID‐19) in Wuhan, China: A quasi‐experimental study
Yanli Zhang, Manli Tang, Yanrong Zhou
Nursing Open.2023; 10(3): 1471. CrossRef - Associations between the Timing and Nutritional Characteristics of Bedtime Meals and Sleep Quality for Nurses after a Rotating Night Shift: A Cross-Sectional Analysis
Jung Hoon Park, Hyuntae Park, Seongryu Bae, Jiyeon Kang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(2): 1489. CrossRef - Predictors of dropout in university students participating in an 8-week e-mail-based cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia intervention
Hyojin Nam, Jinyoung Chang, Mickey Trockel, Isa Okajima, Chien-Ming Yang, Ngan Yin Chan, Shirley Li, Sooyeon Suh
Sleep and Breathing.2023; 27(1): 345. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Gastrointestinal Symptoms among Rotating Shift Nurses in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
Sun-Kyung Hwang, Yun-Ji Lee, Min-Eun Cho, Bo-Kyoung Kim, Yea-In Yoon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(16): 9795. CrossRef - Psychosocial factors affecting sleep quality of pre-employed firefighters: a cross-sectional study
MyeongSeob Lim, Solam Lee, Kwanghyun Seo, Hyun-Jeong Oh, Ji-Su Shin, Sung-Kyung Kim, Hee-Tae Kang, Kyeong-Sook Jeong, Sung-Soo Oh, Sang-Baek Koh, Yeon-Soon Ahn
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Secondary Data Analysis on the Quality of Sleep and Related Factors of Novice and Experienced Shift Work Nurses
Minjeong Yu, Smi Choi-Kwon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 646. CrossRef - Sleep quality among shift-work nurses: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jiwon Kang, Wonjung Noh, Youngjin Lee
Applied Nursing Research.2020; 52: 151227. CrossRef - Work-related Characteristics and Sleep Quality of Nurses in Comprehensive Nursing Care Units of Small-medium Sized Hospitals
Sujin Shin, Inyoung Lee, Jeonghyun Kim, Sung-Heui Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2019; 26(4): 260. CrossRef
- Exploring Pathways Linking Work and Nonwork Factors to Sleep, Fatigue, and Health in Night Shift Nurses: A Structural Equation Modeling Analysis
- 2,282 View
- 45 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Effect of Breathing Exercise Using Panflutes on the Postoperative Compliance, Pulmonary Infections and Life Satisfaction in Elderly Patients Undergoing Spinal Surgery
- Hyun Mi Jo, Hyunsook Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):279-288. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.279
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of breathing exercises performed using panflutes in elderly patients undergoing spinal surgery.
Methods The study design was a nonequivalent control group non-synchronized pre-post test. The study included 24 patients in both the experimental group and the control group. The experimental group completed a daily breathing exercise regimen using panflutes for 30minutes after meals, whereas the control group was provided standard preoperative education, including breathing exercises using incentive spirometers. After the exercise regimen, breathing exercise compliance, pulmonary infections, and life satisfaction were measured in both groups, and the data were analyzed using the SPSS/WIN program.
Results The compliance rate of breathing exercises was significantly higher in the experimental group. The experimental group presented no pulmonary infections in the later period, whereas the control group presented higher pulmonary infection rates in the same period. In addition, the life satisfaction score in the experimental group significantly increased.
Conclusion The breathing exercise program using panflutes for elderly patients undergoing spinal surgery enhanced their breathing exercise compliance and their daily life satisfaction in addition to reducing their pulmonary infection rates.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pranayama and Breathing Exercises - Types and Its Role in Disease Prevention & Rehabilitation
Naresh Kumar Satyanarayan Dhaniwala, Venkatesh Dasari, Mukunda Naresh Dhaniwala
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2020; 9(44): 3325. CrossRef
- Pranayama and Breathing Exercises - Types and Its Role in Disease Prevention & Rehabilitation
- 944 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of the Education on AIDS for Korean Healthe Care Workers
- Soon Bok Chang, C W Lee
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(1):201-211. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.1.201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was an evaluation study of AIDS education program. The purpose of this study was to clarify the education effects on AIDS for health care workers to develop abetter next education program. This study was done by self reporting with a 67 items of structured questionnaire by 431 health care workers included doctors, nurses, laboratory technicians, and health educators. Data were collected at the time of completion of each AIDS education with the help of education program manager. Both the AIDS related knowledge score and the acceptance attitudes score were significantly higher in the male group, in the medical institution employer group, in the group who have met the HIV infected person, who has known the HIV positive person, and the group of laboratory technician, but the AIDS prevention intention score was statistically higher in the group of female and laboratory technician group. The post education scores of AIDS related knowledge, acceptance attitudes, and preventive intention were statistically higher than those of the preeducation. The most increased item among AIDS prevention intention list was 'I will provide the meeting between the HIV infected persons and the public(+21.9%)'. But even the decreased item among AIDS prevention intention list was 'I will advice to female not to have extra marital sexual contact to avoid AIDS(-3.1%)'. It could be concluded that the health care workers were ignorant of vertical transmission of AIDS, they were afraid of disclosing the infection status, and have less AIDS prevention intention. Therefore is needed to take an assessment process before each new education strategy to increase AIDS related the effect of the education on AIDS.
- 349 View
- 0 Download

- Factors Discriminating Nurses' Depression among Personal and Environmental Characteristics
- Hae Jung Lee, Yong Sook Eo, Nam Hee Park, Gil Za Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(6):867-877. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.6.867
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to examine the levels of depression experienced by Korean hospital nurses (N=198) and to identify discriminating factors of their depression experience among personal and environmental characteristics. METHOD: A cross-sectional survey design was used to answer the research questions. A sample consisted of 198 hospital nurses in Korea. The data were collected from May 1999 to March 2000. Descriptive and discriminant analyses were utilized. RESULT: Korean nurses experienced low levels of depression. Twenty nine percent of nurses in the study experienced depression based on the cut-point suggested by Radloff. Role ambiguity, working in the tertiary hospital, work satisfaction in autonomy, professional status and interaction within nurses were significant discriminating factors for nurses' depression. These factors correctly discriminated 71% of the sample (Hit ratio= .71). CONCLUSION: Based on the findings of this study, developing managemental intervention programs and examining the effects of the program for nurses to reduce their depression experience are suggested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a mobile simulation program for nursing delegation: A randomised controlled trial
Haena Lim, Yeojin Yi
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 83: 104283. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Depression among Workers by Socio-economic Factors, Health Behaviors, and Characteristics of Work Environment
Hyunkyung Lee, Minsung Sohn, Mankyu Choi
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(5): 125. CrossRef - A Study on the Uncertainty and Depression in Mothers of Hospitalized Children
Kyung Hee Yoo
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(2): 265. CrossRef - The Relationships between Emotional Labour and Depressive Symptoms Among Nurses in University Hospitals
Kyung-Ok Kim, Young-Chae Cho
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(8): 3794. CrossRef
- Effects of a mobile simulation program for nursing delegation: A randomised controlled trial
- 649 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Workload Measurement of Home Health Care Nurses' Services using Relative Value Units
- Tae Wha Lee, Jung Sook Park, In Sook Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(6):1543-1555. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.6.1543
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Home health care is moving into a set of new realities. An era of competition and cost containment has arrived. Before nurses are able to contain costs or describe the relationship between nursing activities, cost must be accurately measured based on the nurse's workload. Nurses in home health care usually desire to measure expenses for one of three reasons : reimbursement, management, or research. The purpose of the study was to investigate the work input by Registered Nurse in each of the home health care activities by relative value units and identify the factors affecting the nurses' total work input in health care services. To measure the work input by nurses, work was defined by four dimensions: time, physical effort, mental effort, and stress. This study used a descriptive-correlational design. Data collection consisted of two phases. In phase I, data on home health activities performed by nurses were collected. In phase II, data on nurses' time, physical effort, mental effort, and stress in each of home health care activities discovered phase I were collected. In this method, the respondent was asked to rate a service in relation to a reference service using a ratio scale. The sample included 39 home health care nurses. The results of the study indicated that home health care activities performed by the nurses were in 10 categories and 69 items. Measuring the relative work inputs in each of home health care activities, and foley catheterization was selected as the reference to service. In terms of time and physical effort dimensions, full bath service was rated as the most strenuous among 69 activities by the respondents, and intramuscular injection was rated as least. It was found that emergency treatment required the highest mental effort and the highest stress, while blood sugar tests required the lowest mental effort. Approximately 91.3% of the variance in total work input was accounted for by the linear combination of time, physical effort, mental effort judgement, and stress. Examining the regression coefficients of those variables, physical effort, time, and stress were found as the predictors which were significantly associated with the total work of nurses in home health care. Professional nursing's next step in the conundrum of economic volatility is to develop a tool to reflect the interaction of functional deficiency and direct professional nursing care. And this will be a more accurate predictor of nursing resource use and ultimately a great forcaeter cost.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of the Introduction of NIMS on Pharmacy Workflow and Proposal of Reimbursement Adjustment
Im Soon Choi, Tae Hyub Kwon, Kyung Hee Jin, Eun Ju Kim, Eu Jin Chung, Iyn-Hyang Lee
Journal of Korean Society of Health-System Pharmacists.2023; 40(3): 306. CrossRef - Korean and United States: Comparison of Costs of Nursing Interventions
Sung-Jung Hong, Eun-Joo Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(4): 358. CrossRef - Comparison of Nursing Activity Costs of Chronic Otitis Media Surgery Patients among Time, RBRVS, and CP
Mi Sun Kim, Ji Young Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(4): 399. CrossRef - Measuring Workload of Home Visit Care Activities Using Relative Values
Seong-Ok Han, Eun-Cheol Park, Dae-Ryong Kang, Im-Ok Kang
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2008; 41(5): 331. CrossRef
- Effects of the Introduction of NIMS on Pharmacy Workflow and Proposal of Reimbursement Adjustment
- 764 View
- 8 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Concept Analysis about Workers Health
- Chung Min Cho, Boon Han Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):272-281. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.272
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study is to clarify the phenomenon worker's health as a basis for the future study. Concepts help us to identify how experiences are similar or equivqlent by categorizing all the things that are similar. The concept of health in workers was investigated using the Chinn and Krammer's method. The process of analysis involves choosing the concept, clarifying the purpose, using evidence of data, exploration of context, and value and category formalization. Dimensions of health in workers were identified as follows: (1) clinical dimension (2) role execution (3) coping with dimensia (4) mental well being (5) possibility (6) concrete activity (7) symbolization (8) hardiness Characteristics of anality of health in workers are activity, dimension of symbolization and of hardiness. Through this study it is identified that health in workers is with the beyond physical well-being, focused functional ability, and harmony environment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Spirituality and Stress Responses in Small Industry Employees
Sook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2010; 19(2): 220. CrossRef
- Spirituality and Stress Responses in Small Industry Employees
- 613 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Confirmatory Analysis of Perception and Preference Scales for Work Characteristics among Korean Nurses
- Yeon Ok Suh, Rha Yun Song, Daily Barbara
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(2):215-224. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.2.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The study was conducted to confirm the construct of individual perception and preference for work characteristics as personal factors influencing Korean nurses' job satisfaction. The subjects of the study were 231 nurses who are currently working in intensive care units and have been for a minimum of 6 months. The study used the Staff Perception and Preference Scale(Song et al., 1997) to measure the individual's perception and preference on the technical, practice, and management components of the ideal work environment. The Korean version of the Staff Perception and Preference Scale consists of 16 items on perception and 13 on preference with each item related on a scale from 1 (not at all) to 4 (a great deal). Psychometric testing revealed that the preference and perception scale is internally consistent with Chronbach's alphas of .83 for perception scale and .80 for preference scale. The subscales of the perception and preference scale also showed acceptable reliability for the early stage of the development of the instruments with Chronbach alphas of .62-.76 and .69-.83 respectively. Criterion0related validity of the scale was tested by examining correlations with individual growth need that is conceptually close to individual preference, but not to individual perception. Individual growth need was significantly related to individual preference(r=.63, p<.05), but the correlation with the perception scale was not significant. A separate factor analysis for the each of perception and preference scales was performed with a three-factor loading solution based on a previous study. The results on the staff perception scale confirmed with varimax rotation that the items were cleanly and strongly loaded on technique, practice and management components, which together explained 50.7% of the variance. The factor analysis on the staff preference scale also yielded a three factor solution that explained 56.7% of the variance, but items on technique and management components were loaded together. This phenomena may due to the current nursing delivery system in Korea where nurses never experience either shared governance nor case management, and as a results they may not be able to consider management roles as their potential extended roles. Therefore, more efforts should be given to enhance nurses' autonomy and decision making in the technique, practice and management components of their work environment. Meanwhile, there is a need for continuously confirming and developing tools for individual perception and preferences to effectively enhance job satisfaction among Korea nurses through innovative work environments.
- 423 View
- 0 Download

- Effect of Rapid Rotating Shift Work on the Urinary Na+, K+, and Cl-
- Soon Min, Dae Soo Moon, Wook Bin Im
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(4):869-880. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.4.869
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In order to investigate of the effects of rapid rotating shift work on physiological stress, the activities of urinary Na+, K+, Cl- were measured in 14 rotational shift nurses, during day shifts(8AM-4PM, n=4), evening shifts(4PM-12MN, n=5), and night shifts(12MN-8AM, n=5) in hospital twenty students attending nursing college a used as control group. Urine specimens were collected in 30 minutes before and after work on the second day of shift work. In day shift nurses, Na+ activity was 137mM at 8AM and increased to 206mM at 4PM, whereas K+ activity was 42mM at 8AM and no significant change at 4PM. Cl- activity was changed from 234mM to 344mM at 4PM at 8AM. In the evening shift, Na+ activity was 117mM at 4PM and 140mM at 12MN, K+ activity was 22mM and 32mM, respectively. Cl- activity was 169mM and changed to 270mM. During the night shift, Na+ activity was 128mM at 12MN and changed to 161mM at 8AM, K+ activity was 42mM at 12MN and 8AM, and Cl- activity was from 303mM and changed to 355mM. In general, the urinary ion activities seemed to increase after work, however there were no significant changes in ion activities except the Na+ increase in day shift. The mean of the activities of K+ and Cl- before and after work during the day and night shift were significantly higher than those in control group(P<0.05). K+ activities were also higher than that of evening shift(P<0.05). However, there was no difference in Na+ activity among the control group and three shifts. There was a significant relationship among urinary Na+, Cl- and K+ in the control group and rotating shift nurses except between Na+ and K+ in shift. The relationship between Na+ and Cl- was low in shift work and there was no significant relationship between Na+ and K+ in shift, suggesting that the active regulation K+ and/or Na+ in response to stress upon the shift work disrupted the ratio of urinary Na+ to K+ and also lowered the relationship between K+ and Cl-. These results suggest that nurses working the day shift were overloaded and under stress, and the night shift interfered with the physiological rhythm of the nurses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sleep Patterns and Circadian Types of Nursing Students during Shift Schedules
Hyun Sook Kim, Mi-Ran Eom, Eun-Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(1): 43. CrossRef
- Sleep Patterns and Circadian Types of Nursing Students during Shift Schedules
- 633 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Job Satisfaction among ICU nurses according to the Preference and Perception of Work Characteristics
- Rha Yun Song, Yeon Ok Suh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(2):431-440. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.2.431
-
 Abstract
Abstract
The purposes of this study were to determine the factors that influence job satisfaction for ICU nurses and to analyze group differences in job satisfaction based on the nurses' preference and perception of the work environment with an enhanced professional role. A total of 231 nurses who had been working in Intensive Care Units at least for 6 months at selected university hospitals participated in the study while head nurses or those with administrative positions were excluded. The study participants had an average of 33 months of clinical experience with an age range of 23 to 40 years. The data were analyzed by utilizing SPSSWIN and the results are as follows. 1) Hierarchical multiple regression analysis showed that work characteristics defined by Job characteristics theory and nurses' preference/ perception of ideal work environment together explained 33% of variance in job satisfaction. Skill variety, task identity and autonomy as well as individual perception of work environment were significant variables for explaining job satisfaction. Job satisfaction was not significantly related to age, marital status, education, and clinical experience. 2) The groups classified by nurses' preference and perception of work environment were significantly different in their job satisfaction. Nurses with high preference and high perception showed significantly higher general and specific job satisfaction than other nurses. The nurses who showed high preference but perceived their work environment as not reflecting ideal job characteristics reported the lowest job satisfaction among the groups. In conclusion, the role of individual preference and perception of the work environment in explaining the relationship between the redesign of work environment and job satisfaction was supported by the study. The preferences of nurses to the innovative work characteristics should be considered in the process of enhancing job characteristics to lead job satisfaction and low turn over and ultimately to improve quality of care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- KoreanWorkEnvironmentScales forClinicalNurses
Jong‐Kyung Kim, Se‐Young Kim, Mi Yu, Myung Ja Kim, Kyoung‐A Lee
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2015; 12(1): 54. CrossRef - Predictors of life satisfaction of Korean nurses
Haejung Lee, Sunkyung Hwang, Jeongsoon Kim, Barbara Daly
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2004; 48(6): 632. CrossRef
- KoreanWorkEnvironmentScales forClinicalNurses
- 631 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Work Analysis for the Role of the Emergency Department Nurses
- Eun Jung Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(1):93-103. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.1.93
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Nursing works in emergency department were analyzed and the importance of nursing works that the emergency department nurses perceived at university hospitals in Seoul. 12 nursing domains including 76 nursing activities were identified. The most frequently performed nursing domain was records and the most frequently performed activity in the emergency department was checking the vital sign of patients. The most important nursing activity that emergency department nurses perceived was physical crisis intervention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is it possible to reduce intra-hospital transport time for computed tomography evaluation in critically ill cases using the Easy Tube Arrange Device?
Kyung Hyeok Song, Sung Uk Cho, Jin Woong Lee, Yong Chul Cho, Won Joon Jeong, Yeon Ho You, Seung Ryu, Seung Whan Kim, In Sool Yoo, Ki Hyuk Joo
Clinical and Experimental Emergency Medicine.2018; 5(1): 14. CrossRef - Development of an Instrument to Measure Triage Nursing Work in Emergency Room
Kyoung-Hee Yu, Keum-Seong Jang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(4): 477. CrossRef - A Comparison of the Rates of Hemolysis and Repeated Blood Sampling using Syringe needles versus Vacuum tube needles in the Emergency Department
Young Hee Sung, Moon Sook Hwang, Jee Hyang Lee, Hyung Doo Park, Kwang Hyun Ryu, Myung Sook Cho, Young Hee Yi, S Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(3): 443. CrossRef - Analysis of the Characteristics and the Nursing Interventions for Children in Regional Emergency Departments -Using the Nursing Intervention Classification-
Young Hae Kim, Nae-Young Lee, Jae Hyun Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(4): 277. CrossRef
- Is it possible to reduce intra-hospital transport time for computed tomography evaluation in critically ill cases using the Easy Tube Arrange Device?
- 827 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Educational Issues and Strategies to Improve APN Education
- Kasil Oh, Kang Mi Ja Kim, Keum Soon Kim, Jee Won Park, Myung Sook Sung, Eui Geum Oh, Myung Ha Lee, Chae Weon Chung, Dong Sook Cho, Young Ran Tak, Jee In Yoo
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(5):801-809. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.5.801
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was aimed at exploring the current status of graduate programs for an advanced practice nurse(APN) to recommend future directions of APN education.
Methods A total of 142 students enrolled in seven APN specialty programs, 67 professors who were involved in APN education, and nine nurse administrators participated in the study. Data was collected by questionnaires and focus group interviews.
Results The current definition of APN was found not to be specific enough to represent expected roles of APN in regards to knowledge, attitudes, roles, and skills. Standard curricula employed regardless of the area of APN specialty, lack of qualified clinical practice settings, as well as prepared instructors were found to be problematic.
Conclusion The following needs to be addressed: 1. redefining of APN roles, 2. tailoring specialty areas of APN, 3. consolidating educational programs, and 4. ensuring APN role models and faculty. Suggesting a CNS role in Korean APN, areas of APN should be rearranged toclarify their roles and educational programs need to be further developed to meet the expectations and quality of APNs. It is necessary to ensure APN's employment in the health care system by laws and policies to perform advanced nursing roles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nurses’ perceptions of gerontological nurse practitioner programme curricula: A qualitative descriptive study
Jongsun Park, Hyejin Kim
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(3): 237. CrossRef - A Comparison of Empowerment, Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment between Advanced Practice Nurses and Registered Nurses of Hospitals
Im-Jin Jung, Yun-Mi Kim
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2016; 16(3): 354. CrossRef - Korean hospice nursing interventions using the Nursing Interventions Classification system: A comparison with the USA
Sung‐Jung Hong, Eunjoo Lee
Nursing & Health Sciences.2014; 16(4): 434. CrossRef - Job Performance by Advanced Practice Nurses in Korea
Mijung Kim, Yeong Kyeong Kim, Sujin Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(6): 630. CrossRef - Job Competencies and Educational Needs Perceived by New Community Health Practitioners
Hyun Kyung Kim, Young Eun, Kyung Ja June, Ae Young So, Hee Gerl Kim, Mi Ran Eom, Yeon Yi Song, Eun Suk Choi, Ji Yeon Park, Hyoung Suk Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(2): 85. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Self-directed Learning of Students at Clinical Practice Course for Advanced Practice Nurse
Miyoung Kim, Seong-Yeon Park
Asian Nursing Research.2011; 5(1): 48. CrossRef - Use of Physical Assessment Skills and Education Needs of Advanced Practice Nurses and Nurse Specialists
Hyunsook Shin, Bog-Ja Kim, Hee Sun Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 709. CrossRef - Economic Evaluation of Gemcitabine-cisplatin Chemotherapy for Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patient in an Outpatient Setting
Su Hyun Min, Su-kyoung Ko, Ji Young Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(3): 363. CrossRef
- Nurses’ perceptions of gerontological nurse practitioner programme curricula: A qualitative descriptive study
- 856 View
- 3 Download
- 8 Crossref

- A Meta-Analysis of Effects of Job Stress Management Interventions(SMIs)
- Jeong Hee Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(4):529-539. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.4.529
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This quantitative meta analysis sought to determine the effectiveness of SMIs.
Method Forty-six experimental studies with a randomized or nonequivalent control group pre-post test design were included in the analysis. The selected studies were classified according to the sample characteristics, the types and methods of the interventions, and the types of outcome variables. Six intervention types were distinguished: cognitive-behavioral intervention(CBT), relaxation techniques(RT), exercise(EX), multimodal programs 1 and 2(MT1, 2), and organizationfocused interventions(OTs). Effect sizes were calculated for the 4 outcome categories across intervention types: psycho-social outcome, behavioral-personal resources, physiologic, and organizational outcome.
Results Individual worker-focused interventions(ITs) were more effective than OTs. A small but significant overall effect was found. A moderate effect was found for RT, and small effects were found for other ITs. The effect size for OTs was the smallest. The interventions involving CBT and RT appeared to be the preferred means of reducing worker's psycho-social and organizational outcomes. With regard to physiologic outcomes, RT appeared to be most effective. CBT appeared to be most effective in reducing psycho-social outcomes. The effects of OT were non-significant, except for the psycho-social outcomes.
Conclusions SMIs are effective. Interventions involving RT and CBT are more effective than other types.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reshaping occupational psychological health of railway construction project management practitioners: team reflexivity and family supportive supervisor behaviors interventions
Xiaodong Li, Qianhui Lou, Nipeng Zhang, Fan Yang
Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing Sleep and Reducing Occupational Stress Through Forest Therapy: A Comparative Study Across Job Groups
Juhye Kweon, Yunsoo Kim, Heeyong Choi, Wooyoung Im, Hyeyun Kim
Psychiatry Investigation.2024; 21(10): 1120. CrossRef - Examining Academics’ Strategies for Coping With Stress and Emotions: A Review of Research
Raheleh Salimzadeh, Nathan C. Hall, Alenoush Saroyan
Frontiers in Education.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Importance of Non-pharmacological Approaches for Treating Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Mechanisms and Clinical Relevance
Albert Orock, Tian Yuan, Beverley Greenwood-Van Meerveld
Frontiers in Pain Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Aggression Management Training on Perceived Stress Levels of Nurses Working in Mental Health Care Settings in Jordan
Rami Masa'Deh, Omayma Masadeh, Samiha Jarrah, Manar AlAzzam, Fadwa Alhalaiqa
Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services.2020; 58(10): 32. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Workplace Yoga Interventions to Reduce Perceived Stress in Employees: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Elisabetta Della Valle, Stefano Palermi, Irene Aloe, Roberto Marcantonio, Rocco Spera, Stefania Montagnani, Felice Sirico
Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology.2020; 5(2): 33. CrossRef - The Effect of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy on Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Levels in Iranian Males With Addiction
Ghorban Hemati Alamdarloo, Soheila Moradzadeh Khorasani, Mahmoud Najafi, Fatemeh Soosan Jabbari, Setareh Shojaee
Sage Open.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Group Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy on the Nurses' Job Stress, Burnout, Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment and Turnover Intention
Hye-Lyun Kim, Sook-Hee Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(4): 432. CrossRef - Mediating Role of Psychological Capital in Relationship between Occupational Stress and Turnover Intention among Nurses at Veterans Administration Hospitals in Korea
Hee-Yun Yim, Hyun-Ju Seo, Yoonhyung Cho, JinHee Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2017; 11(1): 6. CrossRef - Ecological Correlates of Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Korean Blue-collar Workers: A Multi-level Study
Won Ju Hwang, Yunhee Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(6): 857. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Comprehensive Stress Management Program to Reduce Work-Related Stress in a Medium-Sized Enterprise
Shin-Ae Kim, Chunhui Suh, Mi-Hee Park, Kunhyung Kim, Chae-Kwan Lee, Byung-Chul Son, Jeong-Ho Kim, Jong-Tae Lee, Kuck-Hyun Woo, Kabsoon Kang, Hyunjin Jung
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Stress Management Program Providing Cognitive Behavior Therapy on Problem-focused Coping, Job Stress, and Depression in Firefighters
Chun Youn Nam, Hee Sook Kim, So Hee Kwon
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2013; 22(1): 12. CrossRef
- Reshaping occupational psychological health of railway construction project management practitioners: team reflexivity and family supportive supervisor behaviors interventions
- 1,008 View
- 15 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Comparison of Cardiovascular Risk Profile Clusters Among Industrial Workers
- Seon Young Hwang, Ji Hyun Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(8):1500-1507. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.8.1500
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify subgroups of the physical and behavioral risk profiles for cardiovascular disease among industrial workers, and to examine predicting factors for the subgroups.
Sample and Methods Health records of 2,616 male and female workers aged 19-56 years who were employed in an airplane manufacturing industry were analyzed. Data were analyzed using the Latent class cluster analysis.
Results Four different clusters (two high-risk groups, one low-risk group, and one normal group) were found and these clusters were significantly different by age, gender, and work type (p<.05). The two high-risk groups had higher chances of drinking alcohol, elevated BMI, FBS, total cholesterol, having hypertension, and were significantly older, and had relatively high chances of being day workers rather than other groups. The low-risk group had higher chances of drinking alcohol, higher BMI and total cholesterols compared to normal group, and highest portions of current smokers and shift workers in the four clusters and their mean BP was within prehypertension criteria.
Conclusion Industrial nurses should guide the lifestyle behaviors and risk factors of the high risk groups for CVD and need to intervene early for behavioral change for the low-risk group who are young and shift workers. Age, and work environment should be considered in planning for targeted preventive interventions for industrial workers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated with Blue-collar Workers' Risk Perception of Cardiovascular Disease
Won Ju Hwang, OiSaeng Hong, Mi Ja Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(7): 1095. CrossRef
- Factors Associated with Blue-collar Workers' Risk Perception of Cardiovascular Disease
- 722 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Estimating the Cost of Visiting Nursing Service by Visiting Nursing Model for Urban Public Health Center in Korea
- Ho Sihn Ryu
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(6):983-993. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.6.983
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study focused on analysing costs per visiting nursing care based on nursing activities in a public health center.
Method The Easley-Storfjell Instrument(1997) was used for a prospective descriptive analysis of self-records for workload data from 10 visiting nurses during 4 weeks on all nursing activities. In addition, analysis of the 478 visiting nursing records and cost data from 5 home visiting departments in public health centers during one year of 2003 was done.
Result The workload of visiting nurses by the type of model was identified as follows: Type I showed that caseloads made up 32.9 % of all nurse activities, and type II showed that the caseloads made up 45.8 %. Second, The cost per visit in type I was 33,088 won and 31,323 won in type II. Third, the estimated budgets were 1,902,436 won to 12,057,696 won for the type I model. and 4,151,316 won to 17,432,712 won for the type II model for one year.
Conclusion This study's results will contribute to baseline data used to establish on infrastructure for visiting nursing program and visiting nursing agencies based on the budget of visiting nursing services.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estimating need for Home Visiting Nurse from Public Health Centers
Hyun-Ji Bae, Jinhyun Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2015; 12(1): 23. CrossRef - Estimation of Nursing Costs Based on Nurse Visit Time for Long-Term Care Services
Eun-Kyung Kim, Yun Mi Kim, Myung Ae Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(3): 349. CrossRef
- Estimating need for Home Visiting Nurse from Public Health Centers
- 707 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Study on Influencing Factors in Health Promoting Behaviors of Women Workers at Small-scale Industries
- Soo Min Bae, Ihn Sook Jeong, Jeong Soon Kim, Seong Sook Jeon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(6):964-973. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.6.964
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was aimed to identify the major factors affecting performance in health promoting behaviors in women workers at small-scale industries.
Method This study was based on the Pender's Health Promotion Model. The subjects for this study were 251 women workers at 23 small-scale industries in Busan city. The data for this study was collected from July 15th to August 15th 2003 by structured questionaries, and were analyzed with ANOVA, t-test, Pearson' correlation coefficient, and multiple Regression in the SPSS/WIN 10.0.
Result The mean performance of the health promoting behavior was 2.56. The factors related to the performance of the health promoting behaviors were social support, marital status, status of owning a house, perceived barriers to action, working time, and self-efficacy, and they explained 58.4% of the variance of the health promoting behaviors.
Conclusion The mean performance of the health promoting behavior seemed to be low, and the most important variable related to health promoting behaviorsof women working at a small-scale industry was social support. Therefore, intervention programs to increase the social support for women worker need to be developed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing health-promoting behaviors in Korean breast cancer survivors
Myungsun Yi, Jeongeun Kim
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2013; 17(2): 138. CrossRef - Effect Factors on Health Promotion Lifestyle of Shift Work Nurses
Young-Im Kim
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2011; 20(3): 356. CrossRef - Spirituality and Stress Responses in Small Industry Employees
Sook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2010; 19(2): 220. CrossRef
- Factors influencing health-promoting behaviors in Korean breast cancer survivors
- 747 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Developing a Home Care Nursing Information System by utilizing Wire-Wireless Network and Mobile Computing System
- Jung Ho Park, Sung Ae Park, Soon Nyoung Yoon, Sung Rye Kang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(2):290-296. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.2.290
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a home care nursing network system for operating home care effectively and efficiently by utilizing a wire-wireless network and mobile computing in order to record and send patients' data in real time, and by combining the headquarter office and the local offices with home care nurses over the Internet. It complements the preceding research from1999 by adding home care nursing standard guidelines and upgrading the PDA program.
Method Method/1 and Prototyping were adopted to develop the main network system.
Result The detailed research process is as follows : 1)home care nursing standard guidelines for Diabetes, cancer and peritoneal-dialysis were added in 12 domains of nursing problem fields with nursing assessment/intervention algorithms. 2) complementing the PDA program was done by omitting and integrating the home care nursing algorhythm path which is unnecessary and duplicated. Also, upgrading the PDA system was done by utilizing the machinery and tools where the PDA and the data transmission modem are integrated, CDMX-1X base construction, in order to reduce a transmission error or transmission failure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Application of a Web-based Expert System using Artificial Intelligence for Management of Mental Health by Korean Emigrants
Jeongyee Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(2): 203. CrossRef - Developing an Electronic Nursing Record System for Clinical Care and Nursing Effectiveness Research in a Korean Home Healthcare Setting
EUN JOO LEE, MIKYOUNG LEE, SUE MOORHEAD
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2009; 27(4): 234. CrossRef
- Development and Application of a Web-based Expert System using Artificial Intelligence for Management of Mental Health by Korean Emigrants
- 660 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Workload Analysis of a Visiting Nursing Service based on a Health Center in Seoul
- Ho Sihn Ryu, Eun Sook Park, Young Joo Park, Kuem Sun Han, Ji Young Lim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(7):1018-1027. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.7.1018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study focused on analysing the workload of visiting nurses based on a health center.
Method A Prospective descriptive analysis of self-records for workload data from 115 visiting nurses during 4 weeks was done. In addition, a cross-sectional analysis of linked data to grasp the priority of visiting nursing services from 155 visiting nurses at the 25 health centers in Seoul.
Result Time allocation that was performed on all nursing workload of visiting nurses was identified as follows: First, the inside workload of the health center took up 60% of all visiting nurse activities. Second, providing direct nursing care(caseload) took up 25%. Third, outside nursing activities excluding the caseload provided in the health center took up 15% of all working time. Fourth, the core works to have a high priority among visiting nursing activities were family health assessment, planning and evaluation of a visiting nursing program, personal health assessment, and so forth.
Conclusion The workload of a visiting nurse suggests that the caseload of visiting nurses in a health center needs to be increased. Also, our results will contribute to baseline data used to establish a proper visiting nurses infrastructure based on the demand of visiting nursing services.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estimating need for Home Visiting Nurse from Public Health Centers
Hyun-Ji Bae, Jinhyun Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2015; 12(1): 23. CrossRef - Job Performance and Self Confidence by Visiting Nurses who are engaged in the Consolidated Health Promotion Program in Gangwon-Province
Myung Soon Kwon, Soon Ok Yang, Sun Ok Eom
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2015; 29(2): 190. CrossRef - The Effects of a Mobile Computerized System for Individual Tailored Home Care Services in a City
Nam Hee Park, Rang Jang, Jung Young Kim, Myoung Soo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(1): 71. CrossRef - Statistical Methods to Control Response Bias in Nursing Activity Surveys
Ji Young Lim, Chang Gi Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(1): 48. CrossRef - Task Analysis of Managers in the Customized Visiting Health Services
Young Ran Han, Young Rye Park, Young Hee Kim, Hee Chung Choi, Mi Ja Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(2): 165. CrossRef - Relations among the Decision Making Style, Self Leadership and Communication Competence of Visiting Nurses
Eun-Joo Kim, Ji-Young Lim, Kyung-Won Choi
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2011; 11(10): 324. CrossRef - Elders' Health Status, Quality of Life, and Satisfaction with Customized Home Visiting Health Service Depending on Connection to Volunteerism
Ji Eun Park, Chungnam Kim, Yunhee Kwon
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(4): 448. CrossRef
- Estimating need for Home Visiting Nurse from Public Health Centers
- 726 View
- 1 Download
- 7 Crossref

- A Study on Link of Health and Welfare Service and Barrier's Factors of Visiting Nurses and Social Welfare workers
- In Young Yoo
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(1):113-121. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.1.113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the link between health and welfare service and barrier's factors by reviewing the connection between the public health center's visiting nurse and social welfare center's social workers
Method A survey by mail or a face-to-face interview of 151 visiting nurses in 25 public health centers and 48 social welfare workers in general social welfare centers in Seoul, was preformed from Feb. 12, 2001 to Mar. 15, 2001. The data were analyzed with frequency, percentage, mean value, paired t-test and independent t-test using SPSS/WIN 7.5 program.
Result 1. ‘ The necessity and degree of cooperation with social welfare workers of visiting nurse’ scored average 4.49 and 3.19, and ‘ The necessity and degree of cooperation with visiting nurse and social welfare workers’ scored average 4.81 and 3.15 on the five-point scale ; there was a significant difference between the two variable in visiting nurse and social welfare workers. 2. In barrier's factors which health and welfare service offer to, visiting nurses showed statistically significant higher score than social welfare staff ; ‘ job factor’, ‘ resource factor’, ‘ clients factor’, ‘ individual ability factor’
Conclusion In order to provide link system that hold clients in common in public health center and social welfare center, it is recommended a case management team should be constructed and educate visiting nurses for case manager.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Correlation between Nursing Professional Values and Job Satisfaction Depending on the Types of Visiting Nurses' Personality
Hae In Park, Kyung Min Park, Kyung Hee Lee
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2012; 21(2): 77. CrossRef
- The Correlation between Nursing Professional Values and Job Satisfaction Depending on the Types of Visiting Nurses' Personality
- 704 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of a Cognitive Rehearsal Program on Interpersonal Relationships, Workplace Bullying, Symptom Experience, and Turnover Intention among Nurses: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Jiyeon Kang, Jeung-Im Kim, Seonyoung Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(5):689-699. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.5.689
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This research aimed to investigate the effects of a cognitive rehearsal program (CRP) on workplace bullying among nurses.
Methods A randomized controlled trial was performed. Participants were 40 nurses working in different university hospitals in B city, South Korea. The experimental group was provided with a 20-hour CRP comprising scenarios on bullying situations, standard communication, and role-playing. To evaluate effects of the CRP, we measured interpersonal relationships, workplace bullying, symptom experience, and turnover intention at pre-and post-intervention. Follow-up effect was measured in the experimental group only at 4 weeks after the intervention.
Results After the intervention, there were significant differences in interpersonal relationships (F=6.21,
p =.022) and turnover intention (F=5.55,p =.024) between experimental and wait-list groups. However, there was no significant difference in workplace bullying or symptom experience between the 2 groups. The beneficial effects on interpersonal relationships and turnover intention lasted at least up to 4 weeks after CRP.Conclusion The CRP for workplace bullying improves interpersonal relationships and decreases turnover intention. So it can be utilized as one of the personal coping strategies to reduce the the turnover among nurses. Further studies on the effects of unit- or hospital-based CRP and on the long-term effects of CRP are necessary.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Success factors for effective workplace bullying interventions: a scoping review
Kate Blackwood, Azadeh Shafaei, Tim Bentley, Maryam Omari, Dayna Fawkes
Personnel Review.2026; : 1. CrossRef - The effect of the ROOTS Program on empathy and bullying behavior in high school students in Bandung
Iyus Yosep, Shelly Iskandar, Ai Mardhiyah, Muhammad Rasyid Ramdhani, Rohman Hikmat
International Journal of Africa Nursing Sciences.2026; 24: 100995. CrossRef - Instruments to measure nurses' intention-to-stay in the profession: A systematic literature review
Myrthe van der Zanden, Saba Hinrichs-Krapels, Christa Niehot, Anna Teeuw, Swasti Madan, Naomi van der Linden
International Journal of Nursing Studies Advances.2026; 10: 100496. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Interventions to Increase Employment in Education and Healthcare: A Systematic Literature Review
Lara Fleck, Melline Somers, Tom Stolp, Wim Groot, Frits van Merode, Ralph de Vries
De Economist.2025; 173(1): 1. CrossRef - Interventions against bullying at work: a meta-analysis
Alfredo Rodríguez-Muñoz, Alejandro Díaz-Guerra, Mirko Antino, William Fernando Duran, Iván Sánchez
Work & Stress.2025; 39(1): 1. CrossRef - EFFECTIVE INTERVENTIONS FOR REDUCING VIOLENCE AGAINST EMERGENCY NURSES: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Hadi Yousefi, Fariba Asadinoghabi, Saeed Salari
Nursing and Midwifery Journal.2025; 22(10): 811. CrossRef - Workplace violence experiences of intensive care unit healthcare providers: a qualitative systematic review and meta-synthesis
Jingyi Wang, Mao Liu, Hongling Zheng, Mingfang Xiang
BMC Health Services Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - What are the steps to resolution taken by key stakeholders following a case of workplace bullying: A scoping review
Kassandra Gagnon, François Courcy, Frédéric Mallette, Marc Corbière
WORK: A Journal of Prevention, Assessment & Rehabilitation.2025; 82(4): 957. CrossRef - Systematically analyzing behavior change techniques used in 44 interventions to reduce unprofessional behavior between healthcare staff
Justin Aunger, Bianca Ungureanu, Jill Maben, Ruth Abrams, Alice M Turner, Johanna I Westbrook, Erin K Tagai
Translational Behavioral Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Improving the Psychosocial Work Environment to Prevent Sickness Absence and Turnover in Nurses: A Systematic Review
Laurent Corthésy-Blondin, Alessia Negrini, Samantha Vila Masse, Christine Genest, Lesley Barr
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Why do acute healthcare staff behave unprofessionally towards each other and how can these behaviours be reduced? A realist review
Justin A Aunger, Ruth Abrams, Johanna I Westbrook, Judy M Wright, Mark Pearson, Aled Jones, Russell Mannion, Jill Maben
Health and Social Care Delivery Research.2024; : 1. CrossRef - How can interventions more directly address drivers of unprofessional behaviour between healthcare staff?
Justin A Aunger, Ruth Abrams, Russell Mannion, Johanna I Westbrook, Aled Jones, Judy M Wright, Mark Pearson, Jill Maben
BMJ Open Quality.2024; 13(3): e002830. CrossRef - Interventions for Preventing and Resolving Bullying in Nursing: A Scoping Review
Corina Elena Luca, Alessia Sartorio, Loris Bonetti, Monica Bianchi
Healthcare.2024; 12(2): 280. CrossRef - Effectiveness of cognitive rehearsal programs for the prevention of workplace bullying among hospital nurses: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yulliana Jeong, Hye Sun Jung, Eun Mi Baek
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Consensus on relevant psychosocial interventions applied in health institutions to prevent psychological violence at work: Delphi method
Luis Fidel Abregú-Tueros, Cinthia Jannete Bravo-Esquivel, Sheyla Karol Abregú-Arroyo, Roger Dos Santos-Rosa, José Luis Galve-Manzano
BMC Research Notes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Cognitive Rehearsal in Addressing Nursing Incivility: An Integrative Review
Janet L. Givler, Lynn Varagona
The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing.2024; 55(11): 523. CrossRef - Interventions for Reducing Negative Impacts of Workplace Violence Among Health Workers: A Scoping Review
Iyus Yosep, Ai Mardhiyah, Hendrawati Hendrawati, Sri Hendrawati
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2023; Volume 16: 1409. CrossRef - LATERAL VIOLENCE IN THE NURSING PROFESSION
Denise Goddard, Heather M. Mason
Gastroenterology Nursing.2023; 46(3): 259. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Workplace Bullying Cognitive Rehearsal-Based Nursing Simulation Education Program: A Mixed-Methods Study
Mijeong Park, Jeong Sil Choi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(6): 4974. CrossRef - Pilot Study Using Cognitive Rehearsal, Simulation, and Biomarker Data to Address Workplace Incivility
Cynthia M. Clark, Suzan Kardong-Edgren, Janet Willhaus
The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing.2023; 54(2): 79. CrossRef - Interventions to address unprofessional behaviours between staff in acute care: what works for whom and why? A realist review
Jill Maben, Justin Avery Aunger, Ruth Abrams, Judy M. Wright, Mark Pearson, Johanna I. Westbrook, Aled Jones, Russell Mannion
BMC Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Workplace bullying among Korean registered nurses: A meta-aggregation of qualitative studies
Eun-Jun Park, Hyunwook Kang, Ji Woon Ko
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(4): 450. CrossRef - Retaining Healthcare Workers: A Systematic Review of Strategies for Sustaining Power in the Workplace
Neeltje De Vries, Olivia Lavreysen, Anke Boone, José Bouman, Szymon Szemik, Kamil Baranski, Lode Godderis, Peter De Winter
Healthcare.2023; 11(13): 1887. CrossRef - School-Based Nursing Interventions for Preventing Bullying and Reducing Its Incidence on Students: A Scoping Review
Iyus Yosep, Rohman Hikmat, Ai Mardhiyah
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(2): 1577. CrossRef - A Pilot Study to Examine the Effects of a Workplace Cyberbullying Cognitive Rehearsal Mobile Learning Program for Head Nurses: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Mijeong Park, Ok Yeon Cho, Jeong Sil Choi
Healthcare.2023; 11(14): 2041. CrossRef - Promoting Civility in the Workplace
Sandy Phan, Michelle DeCoux Hampton
Journal for Nurses in Professional Development.2023; 39(5): 244. CrossRef - Nursing Students and Cognitive Rehearsal Training as an Antibullying Strategy: A Canadian National Study
Florriann Carissa Fehr, Michelle Seibel
Journal of Nursing Education.2022; 61(2): 80. CrossRef - Types of Nursing Intervention to Reduce Impact of Bullying and Aggression on Nurses in the Workplace
Iyus Yosep, Rohman Hikmat, Ai Mardhiyah
Healthcare.2022; 10(8): 1463. CrossRef - Impact of Cognitive Rehearsal Training Over Time for New Registered Nurses
Lana Michelle Seibel, Florriann Carissa Fehr, Shalina Sarwal, Haley Josephine Panchuk
The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing.2022; 53(5): 203. CrossRef - The effects of the type of delivery of cognitive‐behavioral therapy for healthcare workers: A systematic review
In Gyu Yoo
Journal of Clinical Psychology.2022; 78(2): 149. CrossRef - Interventions for workplace violence against health-care professionals: A systematic review
Archana Kumari, Siddharth Sarkar, Piyush Ranjan, Sakshi Chopra, Tanveer Kaur, Upendra Baitha, Avinash Chakrawarty, Kamal Bandhu Klanidhi
Work.2022; 73(2): 415. CrossRef - Effectiveness of educational intervention and cognitive rehearsal on perceived incivility among emergency nurses: a randomized controlled trial
Shohreh Kousha, Ali Shahrami, Mohammad Mehdi Forouzanfar, Neda Sanaie, Foroozan Atashzadeh-Shoorideh, Victoria Skerrett
BMC Nursing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intervention types and their effects on workplace bullying among nurses: A systematic review
Sun Joo Jang, Youn‐Jung Son, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(6): 1788. CrossRef - Conflict or connection? A feasibility study on the implementation of a training based on connecting communication in a nursing curriculum
Ellen J.M. Bakker, Connie M. Dekker-van Doorn, Jos H.A.M. Kox, Harald S. Miedema, Anneke L. Francke, Pepijn D.D.M. Roelofs
Nurse Education Today.2022; 111: 105302. CrossRef - A Systematic Review: Effectiveness of Interventions to De-escalate Workplace Violence against Nurses in Healthcare Settings
Rozina Somani, Carles Muntaner, Edith Hillan, Alisa J. Velonis, Peter Smith
Safety and Health at Work.2021; 12(3): 289. CrossRef - Could social media help in newcomers' socialization? The moderating effect of newcomers’ utilitarian motivation
Di Cai, Jia Liu, Haichuan Zhao, Mingyu Li
Computers in Human Behavior.2020; 107: 106273. CrossRef - Factors associated with the nurses’ intent to stay in China, Japan, and Korea: an integrative review
Ting Xue, Wen-Bin Jiang, Meng-Di Ma, Jie Zhang, Ming-Hui Lu, Yong-Mei Jiang
Frontiers of Nursing.2020; 7(3): 269. CrossRef - Education and training for preventing and minimizing workplace aggression directed toward healthcare workers
Steve Geoffrion, Danny J Hills, Heather M Ross, Jacqueline Pich, April T Hill, Therese K Dalsbø, Sanaz Riahi, Begoña Martínez-Jarreta, Stéphane Guay
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - A Mixed-Methods Systematic Review of Interventions to Address Incivility in Nursing
Jeanette M. Olsen, Ann Aschenbrenner, Rachel Merkel, Shelley-Rae Pehler, Linda Sargent, Rita Sperstad
Journal of Nursing Education.2020; 59(6): 319. CrossRef - Effects of a smartphone application for cognitive rehearsal intervention on workplace bullying and turnover intention among nurses
Jiyeon Kang, Yeon Jin Jeong
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Bullying in the nursing work environment: integrative review
Roberta Nazario Aoki, Edinêis de Brito Guirardello
Revista Gaúcha de Enfermagem.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Evidence-Based Practice Guideline: Nurse Retention for Nurse Managers
Jane H-C. Tang, Pamela Hudson, Marianne Smith, Ryleigh Maas
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2019; 45(11): 11. CrossRef - Interventions against bullying of prelicensure students and nursing professionals: An integrative review
Dawna Elicia Rutherford, Gordon Lee Gillespie, Carolyn R. Smith
Nursing Forum.2019; 54(1): 84. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Interventions for Workplace Bullying among Nurses: A Systematic Review
Sun-young Park, Hana Shin, Yeuok Cho, Sue Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(4): 339. CrossRef
- Success factors for effective workplace bullying interventions: a scoping review
- 3,732 View
- 218 Download
- 44 Crossref

- Inhalation Effects of Aroma Essential Oil on Quality of Sleep for Shift Nurses after Night Work
- WonJong Kim, Myung-Haeng Hur
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(6):769-779. Published online December 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.6.769
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was an experimental study to compare the inhalation effects of aroma essential oil on the quality of sleep (QOS) for shift nurses after working nights.
Methods The participants were 60 healthy adults who didn't have any disease. As an experimental treatment, the participants in the experimental group were asked to inhale essential oil for 3 minutes at a distance of approximately 10 cm fromt heir nose and then they were asked to sleep with the aroma stone beside their head (within a 30 cm distance). QOS were measured four times on Pretest, Day 1, Day 2, and Day 3 after they slept. To measure QOS, Perceived QOS (Numeric Rating Scale), the Verran & Synder-Halpern (VSH) Sleep Scale were used, and number of awakenings (NoA) was measured by Actigraph.
Results There were no significant differences in the homogeneity tests for general characteristics and dependent variables prior to the experiments, except for VSH of subjective sleep quality. Also, there was no significant interaction between group and time. The VSH of the experimental group was higher than the control group (F=6.39,
p =.002). The NoA between the experimental group and the control group was significantly different after experimental treatment 3rd day (F=13.35,p =.001).Conclusion The findings show that the inhalation of aroma essential oil had effects to increase the quality of sleep. Therefore, the inhalation of aroma essential oil could be applied to general nursing interventions to improve the quality of sleep.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Aromatherapy Experiences of Intensive Care Nurses Regarding Sleep and Fatigue: A Phenomenological Study
Fatma Gönül Burkev, Sultan Taşci
Nursing in Critical Care.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of aroma inhalation on the quality of sleep, professional quality of life, and near-misses in medication errors among emergency room nurses on night duty in Korea: a randomized controlled trial
Jungha Son, Chul-Gyu Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(1): 25. CrossRef - Effective Interventions for Reducing the Negative Effects of Night Shifts on Doctors’ and Nurses’ Health and Well-Being: A Systematic Review
Michael Shakhloul, Ahmed Amer, Mina Zekry, Mohamed Elgewely, Abanoub Saleeb, Shenoda Ghobrial, Mario Zaghar A Shehata, Ibrahim Abouelkhir, Muhammad O Kamal, Bishoy Manqaryos, Mahmoud Abdulfattah, Ahmed Syed, David Shakhloul, Mina Kamel
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of Aromatherapy with Pelargonium graveolens (P. graveolens) on the fatigue and sleep quality of critical care nurses during the Covid-19 pandemic: A randomized controlled trial
Nasrin Karimi, Shirin Hasanvand, Afsaneh Beiranvand, Mohammad Gholami, Mehdi Birjandi
EXPLORE.2024; 20(1): 82. CrossRef - Meta-analysis of the Effect Size of Lavender Essential Oil and Lavender Blended Essential Oils on Psychological Factors in Adults
Mi-Na Yu, Ae-Jung Kim
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2024; 22(3): 477. CrossRef - Effectiveness of sleep interventions for rotating night shift workers: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Bo Min Jeon, Su Hyun Kim, Seung Hwa Shin
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Polymeric nanoparticles for enhanced delivery and improved bioactivity of essential oils
Sherif Babatunde Adeyemi, Aishat Mojisola Akere, Joshua Iseoluwa Orege, Onome Ejeromeghene, Odunola Blessing Orege, Jubril Olayinka Akolade
Heliyon.2023; 9(6): e16543. CrossRef - The Effects of Aroma Essential Oil Inhalation on Stress, Pain, and Sleep Quality in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
JiA Lee, Myung-Haeng Hur
Asian Nursing Research.2022; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - Effectiveness of aromatherapy inhalation on anxiety and haemodynamic variables for patients with cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Selma Turan Kavradim, Şefika Tuğba Yangöz, Zeynep Ozer
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of aromatherapy with essential oil massage on the sleep quality of critical care nurses: A randomized controlled trial
Hsiu-Chin Hsu, Mei-Hsiang Lin, Hsiu-Fang Lee, Chiu-Yen Wu, Chih-Ting Chou, Shu-Fen Lin
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2021; 43: 101358. CrossRef - The effect of rosemary essential oil inhalation on sleepiness and alertness of shift-working nurses: A randomized, controlled field trial
Ahmad Nasiri, Masoomeh Mo'tamed Boroomand
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2021; 43: 101326. CrossRef - Sleep quality among shift-work nurses: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jiwon Kang, Wonjung Noh, Youngjin Lee
Applied Nursing Research.2020; 52: 151227. CrossRef - Effects of Aromatherapy on Sleep Quality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Mi-Eun Kim, Ji Hee Jun, Muyng-Haeng Hur
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(6): 655. CrossRef - Effect of aromatherapy on cancer complications: A systematic review
Mansoureh Ashghali Farahani, Roghaiyeh Afsargharehbagh, Fatemeh Marandi, Mojgan Moradi, Seyed-Mehdi Hashemi, Mahdieh Poodineh Moghadam, Abbas Balouchi
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2019; 47: 102169. CrossRef - The Effects of Aromatherapy Massage on Sleep Quality of Nurses on Monthly Rotating Night Shifts
Ying-Ying Chang, Chao-Ling Lin, Li-Yin Chang, Vincenzo De Feo
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Essential Oils and Their Constituents: An Alternative Source for Novel Antidepressants
Damião De Sousa, Rayanne Silva, Epifanio Silva, Elaine Gavioli
Molecules.2017; 22(8): 1290. CrossRef
- Aromatherapy Experiences of Intensive Care Nurses Regarding Sleep and Fatigue: A Phenomenological Study
- 2,043 View
- 60 Download
- 16 Crossref

- A Grounded Theory Approach on Nurses’ Experience with Workplace Bullying
- Jiyeon Kang, Seonyoung Yun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(2):226-237. Published online April 17, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.2.226
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose: The purpose of this qualitative study was to explore the workplace bullying experience of Korean nurses.
Methods: Participants were twenty current or former hospital nurses who had experienced workplace bullying. Data were collected through focus group and individual in-depth interviews from February to May, 2015. Theoretical sampling method was applied to the point of theoretical saturation. Transcribed interview contents were analyzed using Corbin and Strauss’s grounded theory method.
Results: A total of 110 concepts, 48 sub-categories, and 17 categories were identified through the open coding process. As a result of axial coding based on the paradigm model, the central phenomenon of nurses’ workplace bullying experience was revealed as ‘teaching that has become bullying’, and the core category was extracted as ‘surviving in love-hate teaching’ consisting of a four-step process: confronting reality, trial and error, relationship formation, and settlement. The relationship formation was considered to be the key phase to proceed to the positive settlement phase, and the participants utilized various strategies such as having an open mind, developing human relationships, understanding each other in this phase.
Conclusion: The in-depth understanding of the workplace bullying experience has highlighted the importance of effective communication for cultivating desirable human relationships between nurses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Organizational Silence and Related Factors Among Shift Work Nurses in Korea: A Cross‐Sectional Study
Sung Eon Sim, Hye-Young Jang, De-Chih Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Social status mediates the propagation of unfairness
Hyeran Kang, JuYoung Kim, Daeeun Kim, Hackjin Kim
Frontiers in Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of cognitive rehearsal programs for the prevention of workplace bullying among hospital nurses: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yulliana Jeong, Hye Sun Jung, Eun Mi Baek
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Moderating Role of Perceived Social Support in the Relation between Type D Personality and PTSD Symptoms among ICU and ER Nurses
Sohyeon Kim, Myung-Ho Hyun
STRESS.2023; 31(4): 197. CrossRef - Intervention types and their effects on workplace bullying among nurses: A systematic review
Sun Joo Jang, Youn‐Jung Son, Haeyoung Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(6): 1788. CrossRef - ICU nurses’ experiences of feeling hurt by medical personnel
Jung-Hoon Lee, Yeoungsuk Song
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(4): 347. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Bullying Measurement in Korean Nurses' Workplace
Hyo-Suk Song, So-Hee Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 478. CrossRef - Traumatic Events and Factors Affecting Post-traumatic Growth of Nurses in General Hospitals
Haesook Kim, Eunsook Kim, Younghee Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(3): 218. CrossRef - Nurses’ Workplace Bullying Experiences, Responses, and Ways of Coping
Sun Yee Yoo, Hye Young Ahn
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(19): 7052. CrossRef - A Grounded Theory Approach on Experiences of Citizen Participation in Urban Regeneration
Jaeun Lee
Journal of Korea Planning Association.2019; 54(7): 24. CrossRef - The Effects of Nursing Organizational Culture, Work Performance and Workplace Bullying Type on Workplace Bullying Consequence of Nurses
Ga Yeon Jeong, Hyun Jung Jang
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(4): 424. CrossRef - A Topic Modeling Analysis for Online News Article Comments on Nurses' Workplace Bullying
Jiyeon Kang, Soogyeong Kim, Seungkook Roh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(6): 736. CrossRef - Response Patterns of Nursing Unit Managers regarding Workplace Bullying: A Q Methodology Approach
Jin Kyu Choi, Byoungsook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 562. CrossRef - The Influence of Lateral Violence on Burnout and Empathy with Patients among Nurses: The Moderating Effect of Communication
Soohyun Nam, Boyoung Hwang
Stress.2019; 27(3): 224. CrossRef - Threats to Identity: A Grounded Theory Approach on Student Nurses' Experience of Incivility during Clinical Placement
Jiyeon Kang, Yeon Jin Jeong, Kyoung Ran Kong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(1): 85. CrossRef - Effects of a Cognitive Rehearsal Program on Interpersonal Relationships, Workplace Bullying, Symptom Experience, and Turnover Intention among Nurses: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Jiyeon Kang, Jeung-Im Kim, Seonyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(5): 689. CrossRef - The Related Factors to Workplace Bullying in Nursing: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jiyeon Kang, Minju Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(4): 399. CrossRef - Qualitative Research on Nurses Experiencing Taeoom
SunHwa Choeng, InSook Lee
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(3): 238. CrossRef
- Organizational Silence and Related Factors Among Shift Work Nurses in Korea: A Cross‐Sectional Study
- 1,441 View
- 28 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Development of a Wellness Index for Workers
- Moon-Jong Choi, Chang-Sik Son, Jinsu Kim, Yeongmi Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(1):69-78. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.1.69
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a wellness index for workers (WIW) and examine the validity and reliability of the WIW for assessing workers' wellness.
Methods The developmental process for the instrument included construction of a conceptual framework based on a wellness model, generation of initial items, verification of content validity, preliminary study, extraction of final items, and psychometric testing. Content validity was verified by 4 experts from occupational health nursing and wellness disciplines. The construct validity, convergent validity and discriminant validity were examined with confirmatory factor analysis. The reliability was examined with Cronbach's alpha. The participants were 494 workers from two workplaces.
Results Eighteen items were selected for the final scale, and the results of the confirmatory factor analysis supported a five-factor model of wellness with acceptable model fit, and factors named as physical · emotional · social · intellectual · occupational wellness. The convergent and discriminant validity were also supported. The Cronbach's alpha coefficient was .91.
Conclusion The results indicate that the WIW is a valid and reliable instrument to comprehensively assess workers' wellness, and to provide basic directions for developing workplace wellness program.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Mediating Effect of Self-Transcendence on the Relationship between Job Stress and Wellness among Nurses
Sung Mi Kim, Da Eun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 394. CrossRef - Tourists' perceived value and behavioral intentions based on the choice attributes of wellness tourism
Miseong Kim, Hyunji Moon, Yeonwoo Joo, Yooshik Yoon
International Journal of Tourism Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Wellness on Job Satisfaction among Police Officers: Focused on the Mediating Effect of the Meaning in Work
Soolgi Han, Kyonghwa Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(1): 18. CrossRef - Effectiveness of End-of-Life Care Debriefing for Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Sook Hyun Park, Jung Eun Lee, Yu-Jin Jung, Ha Neul Yoo, Yeon Su Kim, Young Hee Yi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(3): 87. CrossRef - Development and effectiveness of a cognitive enhancement program based on a mobile application for preventing dementia: a study focusing on older adults who use senior citizen centers
Mi-Ra Jung, Eun Jeong, Chang-Gyeong Lee
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(2): 113. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Mobile Wellness Program for Nurses with Rotating Shifts during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Pilot Cluster-Randomized Trial
Yeongmi Ha, Sang-Ho Lee, Dong-Ha Lee, Young-Hun Kang, Woonjoo Choi, Jinung An
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(2): 1014. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Wellness of Call Center Employees
Yeonju Kim, Gwang Suk Kim, Youlim Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(1): 128. CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness of a Community Capacity Building Program for the Wellness of Traditional Marketplace Merchants: A Pilot Study
Yeojoo Chae, Yeongmi Ha
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(22): 12238. CrossRef - Impact of Mental Health on Wellness in Adult Workers
Won Ju Hwang, Hyun Hee Jo
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Moderating Effect of Nursing Practice Environment on the Relationship between Clinical Nurses’ Sleep Quality and Wellness
Kyung Jin Hong, Youngjin Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(19): 7068. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Workplace Walking Program Using a Fitness Tracker Including Individual Counseling and Tailored Text Messaging
Mira Jung, Yeongmi Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(3): 257. CrossRef - The Effects of a Mobile Wellness Intervention with Fitbit Use and Goal Setting for Workers
Sang-Ho Lee, Yeongmi Ha, Mira Jung, Seungkyoung Yang, Won-Seok Kang
Telemedicine and e-Health.2019; 25(11): 1115. CrossRef - Wellness and sleep quality in Korean nursing students: A cross-sectional study
Sunghee Park, Youngjin Lee, Moonsook Yoo, Sunyoung Jung
Applied Nursing Research.2019; 48: 13. CrossRef - The Relationship between Quality of Sleep, Job Commitment and Wellness of Night Shift Nurses in Medium and Small-sized Hospitals
Yeojoo Chae, Youngshim Go, Jia Kim, Chaecyeung Jeong, Minhui Lee, Yeongmi Ha
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2017; 42(4): 330. CrossRef
- The Mediating Effect of Self-Transcendence on the Relationship between Job Stress and Wellness among Nurses
- 1,110 View
- 21 Download
- 14 Crossref

- A Study on the Knowledge Structure of Cancer Survivors based on Social Network Analysis
- Sun Young Kwon, Ka Ryeong Bae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(1):50-58. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.1.50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the knowledge structure of cancer survivors.
Methods For data, 1099 articles were collected, with 365 keywords as a Noun phrase extracted from the articles and standardized for analyzing. Co-occurrence matrix were generated via a cosine similarity measure, and then the network analysis and visualization using PFNet and NodeXL were applied to visualize intellectual interchanges among keywords.
Results According to the result of the content analysis and the cluster analysis of author keywords from cancer survivors articles, keywords such as 'quality of life', 'breast neoplasms', 'cancer survivors', 'neoplasms', 'exercise' had a high degree centrality. The 9 most important research topics concerning cancer survivors were 'cancer-related symptoms and nursing', 'cancer treatment-related issues', 'late effects', 'psychosocial issues', 'healthy living managements', 'social supports', 'palliative cares', 'research methodology', and 'research participants'.
Conclusion Through this study, the knowledge structure of cancer survivors was identified. The 9 topics identified in this study can provide useful research direction for the development of nursing in cancer survivor research areas. The Network analysis used in this study will be useful for identifying the knowledge structure and identifying general views and current cancer survivor research trends.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Self-Assessment, TAilored Information, and Lifestyle Management for Cancer Patients’ Returning to Work (START): A Multi-center, Randomized Controlled Trial
Danbee Kang, Ka Ryeong Bae, Yeojin Ahn, Nayeon Kim, Seok Jin Nam, Jeong Eon Lee, Se Kyung Lee, Young Mog Shim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Seung Yeop Oh, Mison Chun, Jaesung Heo, Juhee Cho
Cancer Research and Treatment.2023; 55(2): 419. CrossRef - Web-Based Research Trends on Child and Adolescent Cancer Survivors Over the Last 5 Years: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling Study
Hyun-Yong Kim, Kyung-Ah Kang, Suk-Jung Han, Jiyoung Chun
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2022; 24(2): e32309. CrossRef - Network analysis based on big data in social media of Korean adolescents’ diet behaviors
JongHwi Song, SooYeun Yoo, JunRyul Yang, SangKyun Yun, YunHee Shin, Girish C. Melkani
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(8): e0273570. CrossRef - An Overview of Cognitive Reserve in Aging Based on Keyword Network Analysis
Jihyun Kim, Mi So Kim
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of research on metabolic syndrome in cancer survivors using topic modeling and social network analysis
Ji-Su Kim, Hyejin Kim, Eunkyung Lee, Yeji Seo
Science Progress.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - An Identification of the Knowledge Structure on the Resilience of Caregivers of People with Dementia using a Text Network Analysis
Eun Young Kim, Sung Ok Chang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(1): 66. CrossRef - Research Topics and Trends in Interprofessional Education in Nursing
Kisook Kim, Ki-Seong Lee
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2021; 39(10): 554. CrossRef - Social Determinants of Health of Multicultural Adolescents in South Korea: An Integrated Literature Review (2018~2020)
Youlim Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Hyeyeon Lee, Mikyung Lee, Sookyung Kim, Kennedy Diema Konlan
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(4): 430. CrossRef - A Network Analysis of Research Topics and Trends in End-of-Life Care and Nursing
Kisook Kim, Seung Gyeong Jang, Ki-Seong Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(1): 313. CrossRef - Research Trends on Factors Influencing the Quality of Life of Cancer Survivors: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling Approach
Jin-Hee Park, Mison Chun, Sun Hyoung Bae, Hee-Jun Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(4): 231. CrossRef - Knowledge Structure of Nursing Studies on Heart Failure Patients in South Korea through Text Network Analysis
Seang Ryu, Hyunyoung Park, Yun-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(4): 409. CrossRef - Semantic Network Analysis of Iussues Related to Mental Illness in Korea Media: Focusing on the Five Major Media from 2016 to 2018
Sun Joo Park, Na Ri Shin, Seung Hye Kim, Su Bin Park, Chul Eung Kim
Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association.2020; 59(1): 72. CrossRef - Identification of the Knowledge Structure of Cancer Survivors’ Return to Work and Quality of Life: A Text Network Analysis
Kisook Kim, Ki-Seong Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(24): 9368. CrossRef - Using Text Network Analysis for Analyzing Academic Papers in Nursing
Chan Sook Park
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2019; 16(1): 12. CrossRef - Identification of Knowledge Structure of Pain Management Nursing Research Applying Text Network Analysis
Chan Sook Park, Eun-Jun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 538. CrossRef - Exploring the Knowledge Structure of Nursing Care for Older Patients With Delirium
Jung Eun Choi, Mi So Kim
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2018; 36(5): 216. CrossRef - A Comparison of Hospice Care Research Topics between Korea and Other Countries Using Text Network Analysis
Eun-Jun Park, Youngji Kim, Chan Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(5): 600. CrossRef - The Network Analysis of Nursing Diagnoses for Children Admitted in Pediatric Units Determined by Nursing Students
Mikyung Moon
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2017; 42(3): 223. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Articles Published in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration for 3 Years (2013~2015): The Application of Text Network Analysis
Tae Wha Lee, Kwang-Ok Park, GyeongAe Seomun, Miyoung Kim, Jee-In Hwang, Soyoung Yu, Seok Hee Jeong, Min Jung, Mikyung Moon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(1): 101. CrossRef - Social Network Analysis on Mapping the Knowledge Structure of Dementia Research
Jung-Hee Han, Young-Hee Yom
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2017; 19(2): 69. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Self-Assessment, TAilored Information, and Lifestyle Management for Cancer Patients’ Returning to Work (START): A Multi-center, Randomized Controlled Trial
- 1,143 View
- 4 Download
- 20 Crossref

- A Structural Equation Model on Family Strength of Married Working Women
- Yeong Seon Hong, Kuem Sun Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(6):900-909. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.6.900
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the effect of predictive factors related to family strength and develop a structural equation model that explains family strength among married working women.
Methods A hypothesized model was developed based on literature reviews and predictors of family strength by Yoo. This constructed model was built of an eight pathway form. Two exogenous variables included in this model were ego-resilience and family support. Three endogenous variables included in this model were functional couple communication, family stress and family strength. Data were collected using a self-report questionnaire from 319 married working women who were 30~40 of age and lived in cities of Chungnam province in Korea. Data were analyzed with PASW/WIN 18.0 and AMOS 18.0 programs.
Results Family support had a positive direct, indirect and total effect on family strength. Family stress had a negative direct, indirect and total effect on family strength. Functional couple communication had a positive direct and total effect on family strength. These predictive variables of family strength explained 61.8% of model.
Conclusion The results of the study show a structural equation model for family strength of married working women and that predicting factors for family strength are family support, family stress, and functional couple communication. To improve family strength of married working women, the results of this study suggest nursing access and mediative programs to improve family support and functional couple communication, and reduce family stress.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of family beliefs and family strength on individual resilience and quality of life among young breast cancer survivors: A cross‐sectional study
Lin Tao, Xiaoxia Hu, Lan Fu, Xiaoxia Zhang, Hong Chen
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(11-12): 2616. CrossRef - Factors influencing quality of life in caregivers of adolescents with developmental disabilities
Joung Woo Joung
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2022; 13(4): 298. CrossRef - Developing a Prediction Model for Family Health in Families of Patients with Schizophrenia
Kuem Sun Han, Yeong Seon Hong, Hyuncheol Kang, Youn Hee Roh, Myung Sook Choi, Hee Jin Moon
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(4): 309. CrossRef
- Effects of family beliefs and family strength on individual resilience and quality of life among young breast cancer survivors: A cross‐sectional study
- 1,117 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling of Quality of Work Life in Clinical Nurses based on the Culture-Work-Health Model
- Miji Kim, Eunjung Ryu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(6):879-889. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.6.879
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to construct and test a structural equation model of quality of work life for clinical nurses based on Peterson and Wilson's Culture-Work-Health model (CWHM).
Methods A structured questionnaire was completed by 523 clinical nurses to analyze the relationships between concepts of CWHM-organizational culture, social support, employee health, organizational health, and quality of work life. Among these conceptual variables of CWHM, employee health was measured by perceived health status, and organizational health was measured by presenteeism. SPSS21.0 and AMOS 21.0 programs were used to analyze the efficiency of the hypothesized model and calculate the direct and indirect effects of factors affecting quality of work life among clinical nurses.
Results The goodness-of-fit statistics of the final modified hypothetical model are as follows: χ2=586.03, χ2/df=4.19, GFI=.89, AGFI=.85, CFI=.91, TLI=.90, NFI=.89, and RMSEA=.08. The results revealed that organizational culture, social support, organizational health, and employee health accounted for 69% of clinical nurses' quality of work life.
Conclusion The major findings of this study indicate that it is essential to create a positive organizational culture and provide adequate organizational support to maintain a balance between the health of clinical nurses and the organization. Further repeated and expanded studies are needed to explore the multidimensional aspects of clinical nurses' quality of work life in Korea, including various factors, such as work environment, work stress, and burnout.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concept Analysis of Presenteeism Among Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Jiyeon Jung, Jihyun Moon
Sage Open Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Self-Transcendence on the Relationship between Job Stress and Wellness among Nurses
Sung Mi Kim, Da Eun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 394. CrossRef - Influences of Organizational Culture, Nursing Workplace Spirituality, and Nurses’ Perceived Health Status on Quality of Nursing Work Life according to Nursing Clinical Ladder
Hyun Sook Lee, Ju Hyun Jin, Ju Ri Lee, Hye Jin Kim, Yeon Jae Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(1): 31. CrossRef - The Effects of Disaster Nursing Core Competence and Coping Flexibility on the Quality of Work Life of Emergency Room Nurses during Long COVID-19
Yu Jin Lee, Chung Hee Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 259. CrossRef - Impact of patient‐safety incidents on Korean nurses' quality of work‐related life: A descriptive correlational study
Sun Aee Kim, Taewha Lee
Nursing Open.2023; 10(6): 3862. CrossRef - Employees’ attitudes toward cancer, cancer survivors, and cancer survivors’ return to work
Si Eun Lee, Eun Young Park
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(3): 100197. CrossRef - The relationships among overcommitment, effort-reward imbalance, safety climate, emotional labour and quality of working life for hospital nurses: a structural equation modeling
Hui Yu Liang, Tzu Yi Tseng, Hung Da Dai, Jin Yun Chuang, Shu Yu
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Latent profile analysis and influence factors study of presenteeism among ICU nurses in China
Yuxin Li, Jijun Wu, Xiaoli Liu, Jiquan Zhang, Xiaoli Zhong, Lin He
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of nurses' mental well-being and professional quality of life (ProQOL) to their resiliency during the COVID-19 pandemic crisis
Bader A. Alrasheadi
International Journal of ADVANCED AND APPLIED SCIENCES.2023; 10(2): 182. CrossRef - Factors associated with the quality of work life among working breast cancer survivors
Juhyun Jin
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 9(2): 97. CrossRef - Relationship between a University Hospital Nurses’ Structural Empowerment and Quality of Nursing Work Life: Mediating Effect of Psychological Empowerment
Eun Bee Baek, Sun Hyoung Bae
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(2): 159. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Quality of Work Life of Nurses at Tertiary General Hospitals in the Context of the COVID-19 Pandemic
Eunhee Hwang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(8): 4718. CrossRef - Relationships between self‐efficacy, coping style and quality of work‐life among nursing managers in China: A cross‐sectional study
Cuicui Zhang, Xiyan Gong, Yue Xiao, Ying Zhong, Yali Zhong, Lin Chen, Yao Wang, Lili Zhu, Wanhong Xiong, Changju Liao
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 3236. CrossRef - Structural Equation Model of the Quality of Working Life among Cancer Survivors Returning to Work
Ju Hyun Jin, Eun Ju Lee
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(1): 37. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Quality of Life of Working Cancer Survivors: Based on the 6th and 7th (2014, 2016, 2018) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES)
Jahyun Choi, Sanghee Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2020; 20(4): 171. CrossRef - Nurses’ Fatigue, Job Stress, Organizational Culture, and Turnover Intention: A Culture–Work–Health Model
Eunsook Lee, Insil Jang
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2020; 42(2): 108. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Quality of Work Life in a Sample of Cancer Survivor Female Nurses
Ju Hyun Jin, Eun Ju Lee
Medicina.2020; 56(12): 721. CrossRef - Structural Relationship between Nurses' Occupational Motivation and Effectiveness based on the Job Crafting Model
Mi Suk Hyun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(3): 192. CrossRef - Effect of Workplace Spirituality on Quality of Work Life of Nurse Cancer Survivors in South Korea
Juhyun Jin, Eunju Lee
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 7(4): 346. CrossRef - Analysis of Factors Affecting the Quality of Work Life of Dental Hygienists Based on the Culture-Work-Health Model
Ji-Hyeon Park, Young-Sik Cho, Soon-Ryun Lim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2018; 18(1): 32. CrossRef - Clinical Nurses' Resilience Skills for Surviving in a Hospital Setting: A Q-methodology Study
Hye Sook Shin, Ju Hee Kim, Eun Sun Ji
Asian Nursing Research.2018; 12(3): 175. CrossRef - Seafarers’ Quality of Life: Organizational Culture, Self-Efficacy, and Perceived Fatigue
Jae-hee Kim, Soong-nang Jang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2018; 15(10): 2150. CrossRef - Quality of Nursing Work Life Scale-Korean: Validity and Reliability
Insook Kim, Hyoungshim Choi, Yeongyi Yim, Seonae Won, Jungwoo Kim, Sanga Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(6): 646. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling of Quality of Work Life in Clinical Nurses based on the Culture-Work-Health Model
Miji Kim, Eunjung Ryu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(6): 879. CrossRef
- Concept Analysis of Presenteeism Among Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- 1,371 View
- 33 Download
- 24 Crossref

- Ecological Correlates of Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Korean Blue-collar Workers: A Multi-level Study
- Won Ju Hwang, Yunhee Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(6):857-867. Published online December 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.6.857
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate individual and organizational level of cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors associated with CVD risk in Korean blue-collar workers working in small sized companies.
Methods Self-report questionnaires and blood sampling for lipid and glucose were collected from 492 workers in 31 small sized companies in Korea. Multilevel modeling was conducted to estimate effects of related factors at the individual and organizational level.
Results Multilevel regression analysis showed that workers in the workplace having a cafeteria had 1.81 times higher CVD risk after adjusting for factors at the individual level (
p =.022). The explanatory power of variables related to organizational level variances in CVD risk was 17.1%.Conclusion The results of this study indicate that differences in the CVD risk were related to organizational factors. It is necessary to consider not only individual factors but also organizational factors when planning a CVD risk reduction program. The factors caused by having cafeteria in the workplace can be reduced by improvement in the CVD-related risk environment, therefore an organizational-level intervention approach should be available to reduce CVD risk of workers in small sized companies in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multilevel Analysis of Factors Affecting Health-Related Quality of Life of the Elderly
Hyunjung Moon, Sunkyung Cha
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2022; 31(3): 391. CrossRef - Socioeconomic Disparities in Cardiovascular Health in South Korea
Chi-Young Lee, Eun-Ok Im
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2021; 36(1): 8. CrossRef - Health promotion program for office workers with SEM based on the WHO’s healthy workplace framework
Hosihn Ryu, Jiyeon Jung, Jihyun Moon
Health Promotion International.2020; 35(6): 1369. CrossRef - Effects of a Yoga Program in Reducing Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Workers of Small Workplaces: A Pilot Test
Won Ju Hwang, Jin Ah Kim, Ji Sun Ha
Sustainability.2020; 12(23): 10038. CrossRef - An Exploration of Contextual Aspects that Influence Cardiovascular Disease Risks Perceived by Workers in a Small–Medium-Sized Workplace
Jin Ah Kim, Won Ju Hwang, Juhye Jin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(14): 5155. CrossRef - Measurement of Socioeconomic Position in Research on Cardiovascular Health Disparities in Korea: A Systematic Review
Chi-Young Lee, Yong-Hwan Lee
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2019; 52(5): 281. CrossRef - Developing a Health-Promotion Program Based on the Action Research Paradigm to Reduce Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors among Blue Collar Workers
Won Ju Hwang, Jin Ah Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(24): 4958. CrossRef - Regional Factors on the Self-rated Health of Wage Workers
Minjung Kwon, Eunsuk Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(1): 21. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of Interventions for Workers with Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: Using an Ecological Model
Won Ju Hwang, Yunhee Park, Jin Ah Kim
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(1): 41. CrossRef - CVD-related Knowledge, Perception, Belief and Prevention Behaviors of Korean Blue-collar Workers: Needs Assessment for Developing the Intervention Program through Qualitative Approach
Won Ju Hwang, Yunhee Park
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(4): 362. CrossRef
- Multilevel Analysis of Factors Affecting Health-Related Quality of Life of the Elderly
- 1,117 View
- 6 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Identifying Usability Level and Factors Affecting Electronic Nursing Record Systems: A Multi-institutional Time-motion Approach
- Insook Cho, Won-Ja Choi, WoanHeui Choi, Misuk Hyun, Yeonok Park, Yoona Lee, Euiyoung Cho, Okhee Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(4):523-532. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.4.523
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The usability, user satisfaction, and impact of electronic nursing record (ENR) systems were investigated.
Methods This mixed-method research was performed as a time-motion (TM) study and a survey which were carried out at six hospitals between August and November 2013. The TM study involved 108 nurses from medical, surgical, and intensive care units at each hospital, plus an additional 48 nurses who served as nonparticipating observers. In the survey, 1879 volunteer nurses completed the Impact of ENR Systems Scale, the System Usability Scale, and a global satisfaction scale. Qualitative and quantitative analyses were performed.
Results The mean scores for the ENR impact, system usability, and satisfaction were 4.28 (out of 6), 58.62 (out of 100), and 74.31 (out of 100), respectively, and they differed significantly between hospitals (F=43.43,
p <.001, F=53.08 andp <.001, and F=29.13 andp <.001, respectively). A workflow fragmentation assessment revealed different patterns of ENR system use among the included hospitals. Three user characteristics-educational background, practice period, and experience of using paper records-significantly affected the system usability and satisfaction scores.Conclusion The system quality varied widely among the ENR systems. The generally low-to-moderate levels of system usability and user satisfaction suggest many opportunities for improvement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Usability and understandability of a web-based medical communication aid for patients with ankylosing spondylitis in South Korea: A mixed-methods study
Sang-Hoon Lee, YoungJu Park, Chan-Bum Choi, Yong-Gil Kim, Jung-Ae Kim, Hoon-Suk Cha
Medicine.2023; 102(14): e33430. CrossRef - Mobile health platform based on user-centered design to promote exercise for patients with peripheral artery disease
Mihui Kim, Yesol Kim, Mona Choi
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing usability testing outcomes and functions of six electronic nursing record systems
Insook Cho, Eunman Kim, Woan Heui Choi, Nancy Staggers
International Journal of Medical Informatics.2016; 88: 78. CrossRef
- Usability and understandability of a web-based medical communication aid for patients with ankylosing spondylitis in South Korea: A mixed-methods study
- 1,209 View
- 27 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Return to Work Experience among Military Officers with Cancer
- Mira Son, Jeong Seop Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(1):147-156. Published online February 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.147
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to describe the return to work experience of military officers with cancer.
Methods Individual in-depth interviews with 15 participants were conducted between September 2013 and April 2014. Participants were interviewed 1~4 times; interviews continued until the data became saturated. Data were analyzed using Strauss and Corbin's grounded theory.
Results The core category emerged as "living a new life after enduring difficulties". The return to work process consisted of four sequential phases: chaos, positive thought formation, behavior practices, and reformation. Action/interaction strategies used by military officers with cancer to resolve enduring difficulties were controlling emotions, accepting reality, prioritizing health, making efforts to improve relationships, and looking for future jobs.
Conclusion These results will promote understanding of military officers' return to work experience following cancer survival, and will be helpful in developing more effective nursing interventions through enhanced perspectives and insights of practitioners.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Facilitators and barriers associated with returning to work for cancer survivors: A systematic review
Jiayi Liu, Jinnan Xiao, Suqi Ou, Jiarui Chen, Siyuan Tang
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100734. CrossRef - Changes after cancer diagnosis and return to work: experience of Korean cancer patients
Ka Ryeong Bae, Juhee Cho
BMC Cancer.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Taking an obscure path, a common concern during returning to work after cancer
Vahid Zamanzadeh, Leila Valizadeh, Mohammad Zirak, Azad Rahmani
Journal of Vocational Rehabilitation.2019; 51(3): 369. CrossRef
- Facilitators and barriers associated with returning to work for cancer survivors: A systematic review
- 1,109 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Development and Validity of Workplace Bullying in Nursing-Type Inventory (WPBN-TI)
- Younju Lee, Mihyoung Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(2):209-218. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.2.209
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop an instrument to assess bullying of nurses, and test the validity and reliability of the instrument.
Methods The initial thirty items of WPBN-TI were identified through a review of the literature on types bullying related to nursing and in-depth interviews with 14 nurses who experienced bullying at work. Sixteen items were developed through 2 content validity tests by 9 experts and 10 nurses. The final WPBN-TI instrument was evaluated by 458 nurses from five general hospitals in the Incheon metropolitan area. SPSS 18.0 program was used to assess the instrument based on internal consistency reliability, construct validity, and criterion validity.
Results WPBN-TI consisted of 16 items with three distinct factors (verbal and nonverbal bullying, work-related bullying, and external threats), which explained 60.3% of the total variance. The convergent validity and determinant validity for WPBN-TI were 100.0%, 89.7%, respectively. Known-groups validity of WPBN-TI was proven through the mean difference between subjective perception of bullying. The satisfied criterion validity for WPBN-TI was more than .70. The reliability of WPBN-TI was Cronbach's α of .91.
Conclusions WPBN-TI with high validity and reliability is suitable to determine types of bullying in nursing workplace.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychological capital and organizational culture as mediators between workplace bullying type and its consequences for male nurses
Byung-Kul Lee, Young Sook Roh
Applied Nursing Research.2026; 87: 152048. CrossRef - The impact of workplace bullying on depression among clinical nurses in China: A comparative analysis
Jiao-Zhi Zhou, Xin Liu, Gong-Jie Ye
Medicine.2025; 104(2): e41246. CrossRef - Resilience as mediator and moderator in witnessing workplace bullying and professional identity
Yeoungsuk Song, Yoonmi Lee, Junghoon Lee
Advances in Health Sciences Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Examining the role of self-conscious emotions and perfectionistic self-presentation in workplace bullying among Korean nurses: a cross-sectional study
Sun Joo Jang, Haeyoung Lee, Sophia J. Chung
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Organizational Silence and Related Factors Among Shift Work Nurses in Korea: A Cross‐Sectional Study
Sung Eon Sim, Hye-Young Jang, De-Chih Lee
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of workplace violence on depression among workers: A focus on gender differences
Jiseon Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2024; 41(3): 61. CrossRef - Workplace Bullying, Hardiness, and Occupational Identity Among Nursing Students: Mediation of Academic Burnout
KyungJa Kang, Mi Yu
Journal of Nursing Education.2024; 63(9): 604. CrossRef - When Does the Reproduction of Violence Begin? The Effects of Indirect Violence during Clinical Training on Career Identity
Eun-Hi Choi, Ji-yeon Kim, Sookbin Im, Susanna Kim, Seoyeon Park, Haein Song, Daeun Lee, Seunghyun Lee, Jieun Lee, Yebin Cho
Sage Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Bullying against Healthcare Professionals and Coping Strategies: A Scoping Review
Ana Rita Valente Ribeiro, Ana Isabel Sani
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2024; 21(4): 459. CrossRef - Effects of Organizational Silence and Organizational Justice on Bullying among Hospital Nurses at Work
Mi-Aei Lee, Bi-Joo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(1): 1. CrossRef - The Influence of Nurses’ Workplace Bullying, Social Interaction Anxiety and Positive Psychological Capital on Nursing Performance
Hyang Mi Kim, Sun Hee Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(3): 331. CrossRef - Relationship between Ethical Climate, Workplace Bullying, and Turnover Intention of Hospital Nurses in Korea
Mi-Aie Lee, Hyun Ju Park, Bonghwa Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 457. CrossRef - Workplace bullying and different levels of post‐traumatic stress symptoms of nurses: A quantile regression approach for effective coping strategies
Soyun Hong, Heejung Kim, Eun Kyoung Choi, Chang Gi Park
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(6): 1445. CrossRef - Impact of workplace bullying and resilience on new nurses' turnover intention in tertiary hospitals
Gyu Li Baek, EunJu Lee
Nursing & Health Sciences.2022; 24(4): 801. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling on Workplace Incivility of Nurses: Evolution to Bullying
Seo In Kim, Soukyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(4): 406. CrossRef - Structural Model of Retention Intention of Nurses in Small- and Medium-Sized Hospitals: Based on Herzberg’s Motivation-Hygiene Theory
Joo Yeon Lee, Mi Hyang Lee
Healthcare.2022; 10(3): 502. CrossRef - Effects of Clinical Nurses’ Workplace Bullying, Empathic Ability, and Resilience on Job Satisfaction
Mi Young Lee, Youngrye Park
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2021; 14(2): 57. CrossRef - Effects of Workplace Bullying and Empowerment on Nurses' Turnover Intention
Yesul Lee, Yoonju Lee, Ju-Young Ha, Minjeong Jo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - The Association between Korean Clinical Nurses’ Workplace Bullying, Positive Psychological Capital, and Social Support on Burnout
Seong-Ryeol Bae, Hyon-Joo Hong, Jin-Joo Chang, Sung-Hee Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(21): 11583. CrossRef - Influences of Workplace Bullying and Job Satisfaction on Happiness among Perioperative Nurses
Song I Park, Key Ha Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(1): 54. CrossRef - Measuring workplace violence for clinical dental hygienists
Seung‐Eun Won, Ma‐I Choi, Hiejin Noh, Sun‐Young Han, So‐Jung Mun
International Journal of Dental Hygiene.2021; 19(3): 340. CrossRef - Moderating Effects of Structural Empowerment and Resilience in the Relationship between Nurses’ Workplace Bullying and Work Outcomes: A Cross-Sectional Correlational Study
Heiyoung Kang, Kihye Han
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(4): 1431. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Bullying Measurement in Korean Nurses' Workplace
Hyo-Suk Song, So-Hee Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 478. CrossRef - Nurses’ Workplace Bullying Experiences, Responses, and Ways of Coping
Sun Yee Yoo, Hye Young Ahn
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(19): 7052. CrossRef - Effect of Job Stress, Working Bullying, Self-Efficacy on the Professional Self-Concept of Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Sang Min Oh, Sang Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2020; 13(2): 60. CrossRef - Comparative psychometric review of the Negative Acts Questionnaire-Revised in a unionized U.S. public sector workforce
Mazen El Ghaziri, Carla L. Storr, Shellie R. Simons, Alison M. Trinkoff, Kathleen M. McPhaul, Matthew London, Jeffrey V. Johnson, Jane Lipscomb
Work.2019; 62(1): 161. CrossRef - The Influence of Lateral Violence on Burnout and Empathy with Patients among Nurses: The Moderating Effect of Communication
Soohyun Nam, Boyoung Hwang
Stress.2019; 27(3): 224. CrossRef - Response Patterns of Nursing Unit Managers regarding Workplace Bullying: A Q Methodology Approach
Jin Kyu Choi, Byoungsook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 562. CrossRef - Effects of nursing organisational culture on face‐to‐face bullying and cyberbullying in the workplace
JeongSil Choi, Mijeong Park
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2019; 28(13-14): 2577. CrossRef - Moderating effects of Professional Self-concept in Relationship between Workplace Bullying and Nursing Service Quality among Hospital Nurses
Eun Mi Lee, Duck Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(5): 375. CrossRef - Relationships among Self-esteem, Social Support, Nursing Organizational Culture, Experience of Workplace Bullying, and Consequence of Workplace Bullying in Hospital Nurses
Eun-Hye Han, Yeongmi Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(3): 303. CrossRef - Reliability and validity of the workplace harassment questionnaire for Korean finance and service workers
Myeongjun Lee, Hyunjung Kim, Donghee Shin, Sangyun Lee
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Qualitative Research on Nurses Experiencing Taeoom
SunHwa Choeng, InSook Lee
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(3): 238. CrossRef - Awareness and Attitudes Towards Violence and Abuse among Emergency Nurses
Ok-Hee Cho, Kyeong-Sook Cha, Yang-Sook Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(3): 213. CrossRef - Construct Validity of the Life Transition Scale for Parents of Children with Autism
Ae Ran Lee, Sun Woo Hong, Se Jin Ju
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(5): 563. CrossRef
- Psychological capital and organizational culture as mediators between workplace bullying type and its consequences for male nurses
- 1,895 View
- 33 Download
- 35 Crossref

- Economic Evaluation of a Workplace Occupational Health Nursing Service: Based on Comparison with Atmospheric Environment Managing Engineer
- Hye-Sun Jung, Bokim Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(4):507-516. Published online August 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.4.507
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to use cost-benefit analysis of activity to clarify the economic effect of prepared nurses versus atmospheric environment managing engineers as healthcare managers.
Methods For the study 111 workplaces were surveyed, workplaces in which nurses or atmospheric environment managing engineers were employed as healthcare managers. The survey content included annual gross salaries, participation in external job training, costs in joining association covered by the company, location and year of construction of the healthcare office, various kinds of healthcare expenditures, costs in operating healthcare office, health education, and activity performance in the work of environment management.
Results In the case of the healthcare manager being a nurse, benefit was larger than input costs at a ratio of 2.31. On the other hand, in the case of healthcare manager being an atmospheric environment managing engineer, input costs were larger than benefits (benefit-cost ratio 0.88).
Conclusion Results indicate that nurses are an effective healthcare human resource and can offer good quality healthcare service. Therefore companies should hire nurses and actively promote the economic efficiency of nurses in workplace.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the Relationship between the Economic Growth and Air Environment Quality in Harbin
怡璟 程
Sustainable Development.2024; 14(03): 661. CrossRef - An Empirical Analysis of Costs related to Nursing Practice
Yu Kyung Ko, Bo-Hyun Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(2): 139. CrossRef - Analysis of Cost Benefit Related to Appointing a Health Care Manager in the Construction Industry
Hye-Sun Jung, Jee-Seon Yi, In-Jae Shin, Eun-Hi Choi
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(2): 130. CrossRef
- Study on the Relationship between the Economic Growth and Air Environment Quality in Harbin
- 980 View
- 7 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Factors Associated with Blue-collar Workers' Risk Perception of Cardiovascular Disease
- Won Ju Hwang, OiSaeng Hong, Mi Ja Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(7):1095-1104. Published online December 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.7.1095
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the contribution of actual cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, as well as, individual, psychosocial, and work-related factors as predictors of CVD risk perception among Korean blue-collar workers.
Methods The participants were 238 Korean blue-collar workers who worked in small companies. Data were collected through a survey; anthropometric and blood pressure measures; and blood sampling for lipid levels.
Results Blue-collar workers had high actual CVD risk and low CVD risk perception. The significant predictors of risk perception included perceived health status, alcohol consumption, knowledge of CVD risk, actual CVD risk, decision latitude, and shift work. The model explained 26% of the variance in CVD risk perception.
Conclusion The result suggests when occupational health nurses are giving routine health examination in small companies, they can enhance CVD risk perception in blue-collar workers by providing essential information about CVD risk factors and personal counseling on the individual worker's CVD risk status.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of perception bias for cardiovascular disease risk on physical activity and dietary habits
Zhiting Guo, Yujia Fu, Xuyang Wang, Aline Aparecida Monroe, Yuping Zhang, Jingfen Jin, Meifen Chen
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2024; 11(5): 505. CrossRef - Work-Life Conflict, Burnout, and Associated Factors Among Hydroelectric Power Plant Employees: A Cross-Sectional Study in Turkey
İrem Medeni, Volkan Medeni, Osman Burak Demirbaş, Mustafa Necmi İlhan
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular disease in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases: The relationship between self-perceived risk and actual risk
Cristiana Sieiro Santos, Maria Miguel Oliveira, Paulo Ney Solari, Pedro Mateus, Maria José Santos, Hector Corominas, Carolina Álvarez Castro, Elvira Díez Álvarez
Reumatología Clínica.2024; 20(5): 229. CrossRef - Cardiovascular disease in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases: The relationship between self-perceived risk and actual risk
Cristiana Sieiro Santos, Maria Miguel Oliveira, Paulo Ney Solari, Pedro Mateus, Maria José Santos, Hector Corominas, Carolina Álvarez Castro, Elvira Díez Álvarez
Reumatología Clínica (English Edition).2024; 20(5): 229. CrossRef - Cardiovascular disease risk perception among community adults in South China: a latent profile analysis
Zhiting Guo, Yong Yuan, Yujia Fu, Nianqi Cui, Qunfei Yu, Erling Guo, Chuanqi Ding, Yuping Zhang, Jingfen Jin
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk perception of non-communicable diseases: A systematic review on its assessment and associated factors
Miaw Yn Jane Ling, Norfazilah Ahmad, Azimatun Noor Aizuddin, Ghobad Moradi
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(6): e0286518. CrossRef - Good general health and lack of family history influence the underestimation of cardiovascular risk: a cross-sectional study
Åsa Grauman, Jorien Veldwijk, Stefan James, Mats Hansson, Liisa Byberg
European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2021; 20(7): 676. CrossRef - Eating control and eating behavior modification to reduce abdominal obesity: a 12-month randomized controlled trial
Soo Kyoung Kim, Norma Patricia Rodriguez Rocha, Hyekyeong Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(1): 38. CrossRef - An Exploration of Contextual Aspects that Influence Cardiovascular Disease Risks Perceived by Workers in a Small–Medium-Sized Workplace
Jin Ah Kim, Won Ju Hwang, Juhye Jin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(14): 5155. CrossRef - Perceptions of the impact of non-standard work schedules on health in Australian graduates: an exploratory study
Meagan E. CROWTHER, Amy C. REYNOLDS, Sally A. FERGUSON, Robert ADAMS
Industrial Health.2020; 58(1): 54. CrossRef - Risk Perception & Risk-Reduction Behavior Model for Blue-Collar Workers: Adapted From the Health Promotion Model
Won Ju Hwang, Mi Jeong Kim
Frontiers in Psychology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Alcohol consumption in Spanish mental health patients vs. working population
Miguel Ruiz-Flores Bistuer, Maria Teofila Vicente-Herrero, Silvia Lladosa-Marco, Ángel Arturo López-González, Luisa Mercedes Capdevila-García
Revista de la Facultad de Medicina.2018; 66(2): 171. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Risk Across Occupational Groups and Industry in a Statewide Study of an Australian Working Population
Helen Louise Kelsall, Palamandadige Harsha Suranga Fernando, Stella May Gwini, Malcolm Ross Sim
Journal of Occupational & Environmental Medicine.2018; 60(3): 286. CrossRef - Psychometric Testing of the Effort-Reward Imbalance–Short Form Among Blue-Collar Workers Employed in Small Industrial Settings in Korea
Won Ju Hwang, Oi Saeng Hong, Dae Ryong Kang
Workplace Health & Safety.2018; 66(12): 597. CrossRef - Evaluating the prevalence, awareness, and control of hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia in Korea using the NHIS-NSC database
Sunjoo Boo, Young Joo Yoon, Hyunjin Oh
Medicine.2018; 97(51): e13713. CrossRef - CVD-related Knowledge, Perception, Belief and Prevention Behaviors of Korean Blue-collar Workers: Needs Assessment for Developing the Intervention Program through Qualitative Approach
Won Ju Hwang, Yunhee Park
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(4): 362. CrossRef - Occupational differences for nutrient intake and physical-activity levels in young and middle-aged men
Eric C. Conchola, Abbie E. Smith-Ryan, Brennan J. Thompson, Eric J. Sobolewski, Eric D. Ryan
Work.2016; 55(1): 187. CrossRef - Association of Work-related Characteristics and Hypertension among White Collar Workers
Chae-Bong Kim, KyooSang Kim
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene.2015; 25(3): 418. CrossRef - Ecological Correlates of Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Korean Blue-collar Workers: A Multi-level Study
Won Ju Hwang, Yunhee Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(6): 857. CrossRef - 10-Year Risk for Cardiovascular Disease Among Male Workers in Small-Sized Industries
Kyongok Park, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2015; 30(3): 267. CrossRef - Casual Dock Work: Profile of Diseases and Injuries and Perception of Influence on Health
Marta Cezar-Vaz, Marlise De Almeida, Clarice Bonow, Laurelize Rocha, Anelise Borges, Diéssica Piexak
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2014; 11(2): 2077. CrossRef - Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Predicting Factors among Small-sized Company Workers
Soo Kyoung Choi, Jeong A Jo, Seon Young Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(2): 244. CrossRef - Actual Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Related Factors
Jong Uk Won, Oi Saeng Hong, Won Ju Hwang
Workplace Health & Safety.2013; 61(4): 163. CrossRef - Grape Polyphenols Increase the Activity of HDL Enzymes in Old and Obese Rats
Andriy L. Zagayko, Ganna B. Kravchenko, Oksana A. Krasilnikova, Yuri O. Ogai
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef - Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of the Metabolic Syndrome in the Korean Workforce
Dae Ryong KANG, Yeongmi HA, Won Ju HWANG
Industrial Health.2013; 51(3): 256. CrossRef - Actual Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Related Factors: A Cross-sectional Study of Korean Blue Collar Workers Employed by Small Businesses
Jong Uk Won, Oi Saeng Hong, Won Ju Hwang
Workplace Health & Safety.2013; 61(4): 163. CrossRef
- The impact of perception bias for cardiovascular disease risk on physical activity and dietary habits
- 1,447 View
- 3 Download
- 26 Crossref

- Effects of a Volunteer-Run Peer Support Program on Health and Satisfaction with Social Support of Older Adults Living Alone
- Su Hyun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(4):525-536. Published online August 12, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.4.525
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of the study was to evaluate effectiveness of a peer support program conducted by older community volunteers for older adults living alone.
Methods Thirty volunteers trained as peer supporters were matched with low-income, older adults living alone in the community on gender. Visits occurred on a weekly basis over the 12 month study period, and the volunteers provided peer support for health management to solitary older adults. Data were collected, before the start of the program and again 6 and 12 months after its initialization, from intervention and control groups regarding physical health, general health, mental health, depression, social functioning, and satisfaction with social support. Repeated measures ANOVA was used to analyze data.
Results By the end of the program, socially isolated older adults in the intervention group had significantly higher scores in physical health and general health than elders in the control group. Significant interaction effects between time and group were found for depression, social functioning, and satisfaction with social support.
Conclusion The peer support program undertaken by older community volunteers was effective in improving physical health, general health, depression, social functioning, and satisfaction with social support in socially isolated, low-income, older adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of an informal home care support intervention program to reduce loneliness and improve quality of life among lonely community-dwelling older adults: a feasibility study
Ahmad Kousha, Elham Lotfalinezhad, Haidar Nadrian, Karen Andersen-Ranberg, Shannon Freeman, Fatemeh Barati, Hasan Mosazadeh, Mina Hashemiparast, Mohammed Asghari Jafarabadi, Ahmad Sohrabi, Mohammad Reza Honarvar
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2025; 46(3): 185. CrossRef - Comparing the effectiveness of peer‐led healthy aging interventions on depression and quality of life in community‐dwelling older adults: A systematic review and network meta‐analysis
Jieun Kim, Sarang Kim, Urim Kim, Eunshil Yim, Insook Lee, Hyejung Hong, Dongok Lee, Kyounga Lee
Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Pilot and Feasibility Study of the Aging Together Anti-Ageism Peer Support Program
Andrew T. Steward, Connor T. Keane, Yura Lee, Young Cho
Journal of Applied Gerontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of the “Aging Together” Anti-Ageism Peer Support Intervention for Older Adults
Andrew Steward, Yura Lee, Connor Thomas Francisco Keane, Young Ik Cho
Clinical Social Work Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Friendly visiting by a volunteer for reducing loneliness or social isolation in older adults: A systematic review
Jorien Laermans, Hans Scheers, Philippe Vandekerckhove, Emmy De Buck
Campbell Systematic Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes in Routine Evaluation Measures for Patients Discharged from Acute Psychiatric Care: Four-Arm Peer and Text Messaging Support Controlled Observational Study
Reham Shalaby, Pamela Spurvey, Michelle Knox, Rebecca Rathwell, Wesley Vuong, Shireen Surood, Liana Urichuk, Mark Snaterse, Andrew J. Greenshaw, Xin-Min Li, Vincent I. O. Agyapong
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(7): 3798. CrossRef - Development of a Community-Based Integrated Service Model of Health and Social Care for Older Adults Living Alone
Yu Mi Yi, Yeon-Hwan Park, BeLong Cho, Kyung-Choon Lim, Soong-Nang Jang, Sun Ju Chang, Hana Ko, Eun-Young Noh, So Im Ryu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(2): 825. CrossRef - Peer-to-Peer Support and Changes in Health and Well-being in Older Adults Over Time
Rebecca J. Schwei, Scott Hetzel, KyungMann Kim, Jane Mahoney, Kali DeYoung, Jenni Frumer, Ross P. Lanzafame, Jenny Madlof, Alis Simpson, Erika Zambrano-Morales, Elizabeth A. Jacobs
JAMA Network Open.2021; 4(6): e2112441. CrossRef - Peer Support in Mental Health: Literature Review
Reham A Hameed Shalaby, Vincent I O Agyapong
JMIR Mental Health.2020; 7(6): e15572. CrossRef - Older adults’ perspectives regarding peer-to-peer support programs and maintaining independence
Rebecca J. Schwei, Amy W. Amesoudji, Kali DeYoung, Jenny Madlof, Erika Zambrano-Morales, Jane Mahoney, Elizabeth A. Jacobs
Home Health Care Services Quarterly.2020; 39(4): 197. CrossRef - Understanding and Measuring the Value of Peer-to-Peer Community Support Programs for Older Adults
Gabrielle Kelly, Leon Neville Geffen
JAMA Network Open.2020; 3(12): e2030674. CrossRef - Evaluation of Peer-to-Peer Support and Health Care Utilization Among Community-Dwelling Older Adults
Elizabeth A. Jacobs, Rebecca Schwei, Scott Hetzel, Jane Mahoney, Katherine Sebastian, Kali DeYoung, Jenni Frumer, Jenny Madlof, Alis Simpson, Erika Zambrano-Morales, KyungMann Kim
JAMA Network Open.2020; 3(12): e2030090. CrossRef - Peer-to-peer support model to improve quality of life among highly vulnerable, low-income older adults in Cape Town, South Africa
Leon N. Geffen, Gabrielle Kelly, John N. Morris, Elizabeth P. Howard
BMC Geriatrics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Utilizing Smartphone Application Peer Support on Health Behavior and Body Mass Index among Breast Cancer Survivors
Gaeun Park, Haejung Lee, Hyun Yul Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(5): 550. CrossRef - Effects of a Health Promotion Empowerment Program Using a Resident Volunteer as a Lay Health Leader on Frail Elders' Health and Empowerment
Jeong Sook Park, Yun Jung Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(3): 335. CrossRef - The Effects of a Health Mentoring Program in Community-dwelling Vulnerable Elderly Individuals with Diabetes
Ki wol Sung, Hye Seung Kang, Ji Ran Nam, Mi Kyung Park, Ji Hyeon Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(2): 182. CrossRef - Apoio social e o cuidado integral à saúde do idoso
Marcelo Barbosa Otoni Gonçalves Guedes, Kenio Costa Lima, Célia Pereira Caldas, Renato Peixoto Veras
Physis: Revista de Saúde Coletiva.2017; 27(4): 1185. CrossRef - Effects of Social Support and Psychological Well-being on Intention to Exercise Maintenance of Elderly Pilates Participants
Seok-Il Kim, Hyun-Ok Oh
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2017; 56(1): 167. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Intention to Participate in Healthcare Programs among Elders Living Alone
Mi Sook Song, Sunjoo Boo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 319. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Highly Educated Elders' Diabetic Health Leader Attitude
Kiwol Sung, Jiran Nam, Mijin Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(2): 119. CrossRef - The Relationships between Social Determinants of Health and Health-related Quality of Life among the Community-dwelling Elderly
Junghee Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Chung Yul Lee, Eunhee Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(4): 237. CrossRef - The Effects of an Exercise Program using a Resident Volunteer as a Lay Health Leader for Elders' Physical Fitness, Cognitive Function, Depression, and Quality of Life
Yeon-Hee Choi, Na-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(3): 346. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of an informal home care support intervention program to reduce loneliness and improve quality of life among lonely community-dwelling older adults: a feasibility study
- 1,840 View
- 23 Download
- 22 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


