Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effectiveness of a mobile application for tracking symptoms and enhancing symptom management among breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy in Bangkok, Thailand: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Duangrat Kaveenuntachai, Supawan Jaiboon, Bualuang Sumdaengrit, Chureeporn Silaguntsuti, Arveewan Vittayatigonnasak, Pornchan Sailamai
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):178-190. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25011
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study evaluated the effectiveness of a mobile application in tracking symptoms and improving symptom management and quality of life (QoL) among breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in Thailand.
Methods
A non-randomized controlled trial was used, with 25 participants in the intervention group and 25 in the control group. Research instruments included a demographic data form, the NCI-PRO-CTCAE Items-Thai-Thailand version 1.0, and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Core Questionnaire and Breast Cancer-Specific Module.
Results
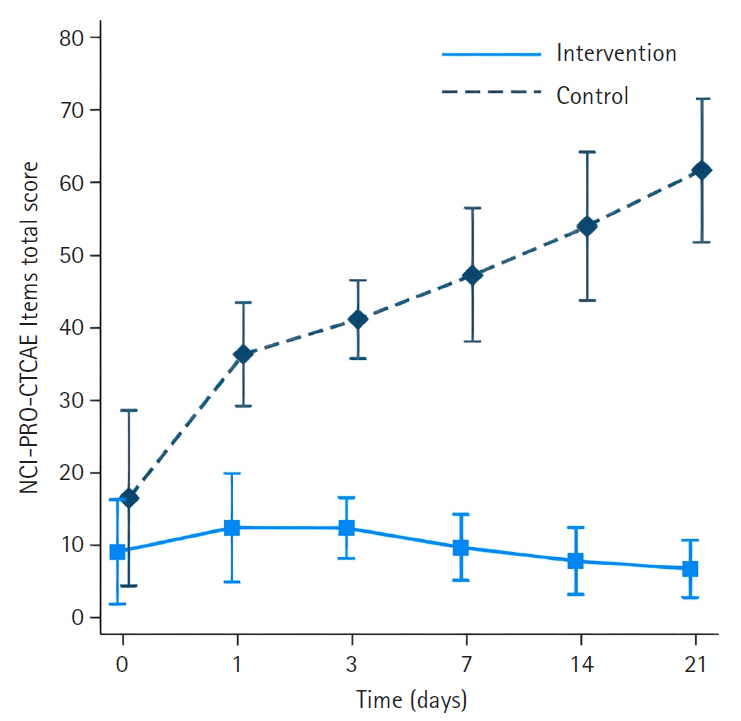
The intervention group had significantly less severe side effects than the control group, with mean differences of –23.33 (95% confidence interval [CI], –27.82 to –18.83) on day 1, –28.18 (95% CI, –33.22 to –23.14) on day 3, –34.63 (95% CI, –40.18 to –29.08) on day 7, –42.56 (95% CI, –48.72 to –36.40) on day 14, and –51.31 (95% CI, –58.13 to –44.48) on day 21 (p<.001 for all). On day 21, participants in the intervention group reported significantly higher scores in the Global Health QoL and Functional Scales compared to the control group (p<.001). Additionally, intervention group participants reported lower scores on the Symptom Scales and higher scores on the Functional Scales than those in the control group (p<.001).
Conclusion
The ChemoPro application helped manage chemotherapy-related symptoms and was associated with improved symptom monitoring and QoL. Nonetheless, the study was limited by a small sample size and restriction to Android users. Future research with larger and more diverse populations is recommended before broader implementation in clinical practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of a digital health intervention on the supportive care needs and quality of life in Mexican patients with breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial
Saúl Eduardo Contreras-Sánchez, Svetlana V. Doubova, Rocío Grajales-Álvarez, Ricardo Villalobos-Valencia, Abdel Karim Dip-Borunda, José Gustavo Nuñez-Cerrillo, Alma Diana Huerta-López, Álvaro José Montiel-Jarquín, Arturo García-Galicia, Enrique Isay Talam
BMC Cancer.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effectiveness of a digital health intervention on the supportive care needs and quality of life in Mexican patients with breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial
- 4,258 View
- 215 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Exploring Symptom Cluster Patterns in Adult Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review
- Pan Yang, Hui-juan Mei, Hao-yu Zhao, Rong-rong Wu, Yong-qin Ge, Yin Lu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):478-494. Published online November 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24041
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material ePub
ePub Purpose This systematic review aimed to scrutinize the progression of symptom cluster research in adult cancer patients who received primary or adjuvant chemotherapy between 2001 and 2023, providing a comprehensive understanding of clinical practice and future research.
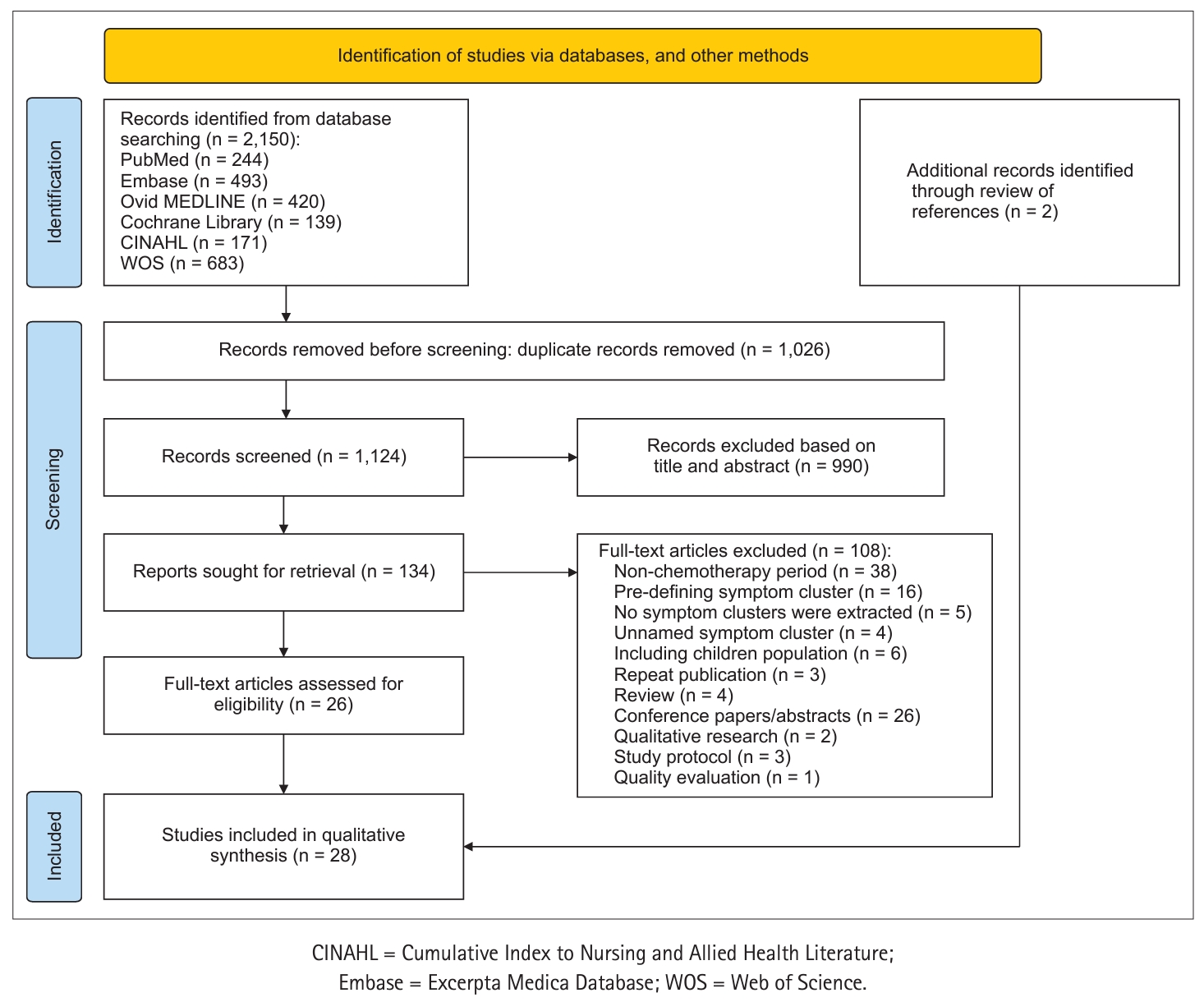
Methods PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, Excerpta Medica Database, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases were searched for theme words and free words related to symptom clusters, cancer, and chemotherapy. Eligible studies were published between January 1, 2001, and May 30, 2023; adults who were diagnosed with cancer and received primary or adjuvant chemotherapy were evaluated.
Results Twenty-eight studies were included in this review. The Memorial Symptom Assessment Scale emerged as the predominant instrument and exploratory factor analysis was the most frequently employed statistical method to identify symptom clusters. Psychological, gastrointestinal, and physical image symptom clusters were the most commonly delineated. Furthermore, the temporal stability of the symptom clusters showed varying dynamics, with psychological symptom clusters displaying relative consistency over time.
Conclusion Interventions are needed for the most common and stable symptoms in patients with cancer undergoing chemotherapy. Future endeavors may necessitate more longitudinal studies to delve deeper into the temporal stability and dynamic variations of symptom clusters. Such investigations hold promise for advancing symptom cluster research, elucidating the underlying mechanisms, and fostering the development of targeted interventions, thereby enriching the symptom management paradigm in oncological care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Network analysis used to investigate the symptoms of cancer patients during chemotherapy: a scoping review
Xiaodan Shao, Na Wang, Ke Tang, Kunning Wang, Zhangyan Tan, Jiangxiu Xie, Zhiwei Shen, Yuting Jiang, Yan Zhang
Discover Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Symptom cluster in patients with resected pancreatic cancer during adjuvant chemotherapy: A cross-sectional study
Yun Wang, Ningning Xia, Yuan Song, Neng Shi, Kuei-Ching Pan
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100810. CrossRef
- Network analysis used to investigate the symptoms of cancer patients during chemotherapy: a scoping review
- 2,725 View
- 151 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effect of Auriculotherapy on Musculoskeletal Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Sun Yeob Choi, Yeo Ju Kim, Bomi Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):4-23. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of auriculotherapy on musculoskeletal pain in adults.
Methods
A total of 885 studies were retrieved from nine databases (PubMed, Scopus, CINAHL, Web of Science, Ovid Medline, Cochrane Library, RISS, KMbase, and KISS). Sixteen studies were selected for meta-analysis, which satisfied the inclusion criteria and the evaluation of risk of bias. Demographic data, auriculotherapy types, intervention characteristics, auricular points, and outcomes related to pain (subjective pain scale, and amount of analgesic) were extracted from all included studies. The effect size of auriculotherapy was analyzed through comprehensive meta analysis 3.0, and the presence of publication bias was analyzed through a funnel plot and Egger’s regression.
Results
The results of the meta-analysis (n = 16) revealed that the auriculotherapy was significantly superior to the control group on present pain in adults (Hedges’ g = - 0.35, 95% Confidence Interval [CI] = - 0.55~- 0.15). According to the results of subgroup analysis, the effect size of auricular acupuncture therapy (Hedges’ g = 0.45, 95% CI = - 0.75~- 0.15) was higher than the auricular acupuncture (Hedges’ g = 0.27, 95% CI = - 0.53~0.00): the longer the intervention period, the greater the effect size.
Conclusion
In this study, auriculotherapy demonstrates a significant reduction in musculoskeletal pain in adults. Therefore, it is necessary to refine the curriculum to include auriculotherapy as a nursing intervention to relieve musculoskeletal pain in adults and encourage its use in clinical settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Nurses’ Perceived Stress, Sleep Quality, and Presenteeism
Hyunseo Sim, Younghee Park
Holistic Nursing Practice.2025; 39(1): 15. CrossRef - Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Pain and Stress in Nursing College Students With Cervical Pain: A Single-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial
Yuna Cho, Eunmi Cho, Eunseol Cho, Yeonju Chae, Eunkyung Choi, Hyeongyeong Yoon
Pain Management Nursing.2025; 26(1): e59. CrossRef - Effect of Auriculotherapy on Stress: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunyeob Choi, Bomi Kim
Journal of Holistic Nursing.2025; 43(4): 336. CrossRef - Comparative Effectiveness of Ear and Body Acupressure for Postoperative Pain in Elderly Women Following Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Trial
Fatemeh Ghanbari, Nahid Rejeh, Tahereh Bahrami, Hooman Yahyazadeh, Kiarash Saatchi
Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine.2025; 31(11): 987. CrossRef - Estratégias de adaptação dos profissionais de enfermagem com dor musculoesquelética no trabalho hospitalar: uma revisão sistemática
Jorge Gabriel Tuz-Colli, Yolanda Flores-Peña, Heloisa Ehmke Cardoso dos Santos, Fernanda Ludmilla Rossi Rocha, Maria Helena Palucci Marziale
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adaptation strategies for nurses with musculoskeletal pain in hospital work: a systematic review
Jorge Gabriel Tuz-Colli, Yolanda Flores-Peña, Heloisa Ehmke Cardoso dos Santos, Fernanda Ludmilla Rossi Rocha, Maria Helena Palucci Marziale
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Estrategias de adaptación de los profesionales de Enfermería con dolor musculoesquelético en el trabajo hospitalario: revisión sistemática
Jorge Gabriel Tuz-Colli, Yolanda Flores-Peña, Heloisa Ehmke Cardoso dos Santos, Fernanda Ludmilla Rossi Rocha, Maria Helena Palucci Marziale
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adapting and Evaluating a Theory-Driven, Non-Pharmacological Intervention to Self-Manage Pain
Jennifer Kawi, Chao Hsing Yeh, Lauren Grant, Johannes Thrul, Hulin Wu, Paul J. Christo, Lorraine S. Evangelista
Healthcare.2024; 12(10): 969. CrossRef - The State of 21st Century Acupuncture in the United States
Clasina Smith, Bill Reddy, Charis Wolf, Rosa Schnyer, Korina St John, Lisa Conboy, Jen Stone, Lixing Lao
Journal of Pain Research.2024; Volume 17: 3329. CrossRef - The effects of auricular acupressure on blood pressure, stress, and sleep in elders with essential hypertension: a randomized single-blind sham-controlled trial
Bomi Kim, Hyojung Park
European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2023; 22(6): 610. CrossRef
- Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Nurses’ Perceived Stress, Sleep Quality, and Presenteeism
- 3,064 View
- 126 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- Effects of a Cognitive Behavior Therapy Program for Patients with Fibromyalgia Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Kyoung Ran Kong, Eun Nam Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(3):347-362. Published online June 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21025
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study developed a cognitive behavioral therapy program aimed at altering the physical condition, emotions, and behaviors of fibromyalgia patients, and confirmed the program’s clinical applicability. The program was developed by analyzing previous studies conducting in-depth interviews with fibromyalgia patients, drawing on cognitive behavior theory to establish the program contents, recruiting experts to test its validity, and conducting a preliminary survey.
Methods
To confirm the program’s effect, this study used a randomized controlled trial design. The participants were outpatients diagnosed with fibromyalgia in Dong-A University Hospital, Busan. The 30 patients in the experimental group took part in the program, which comprised 8 sessions (90 to 120 minutes) based on cognitive behavior theory, delivered over 8 weeks. Hypothesis testing was carried out using the repeated measures ANOVA.
Results
The analysis revealed significant differences between the experimental and control groups in positive automatic thoughts, pain, fatigue, depression, and interpersonal relationships. However, there was no significant difference between the groups in terms of sleep disorders and negative automatic thoughts.
Conclusion
This program is a positive effect on physical condition, emotions, and behaviors. It is thus expected to be used to help fibromyalgia patients improve their disease conditions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How do people with fibromyalgia interpret ambiguous cues in empathy-related healthcare scenarios?
Maria Planes Alias, David J Moore, Nicholas Fallon, Katie Herron, Charlotte Krahé
The Journal of Pain.2026; 40: 106181. CrossRef - Changes in Dental Caries Risk among Middle School Students Using an ICT-Based Caries Management Program
An-Na Yeo, Yu-Min Kang, Su-Young Lee
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2025; 25(1): 42. CrossRef - Effects of pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions for the management of sleep problems in people with fibromyalgia: a multi-methods evidence synthesis
Mari Imamura, Clare Robertson, Jemma Hudson, Daniel Whibley, Lorna Aucott, Katie Gillies, Marcus Beasley, Martin J Stevens, Paul Manson, Debra Dulake, Abhishek Abhishek, Nicole KY Tang, Gary J Macfarlane, Miriam Brazzelli
Health Technology Assessment.2025; : 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Positive Psychotherapy on Pain Perception, Daily Functioning, and Mental Health in Patients With Fibromyalgia
Hamide Erol, Aysel Karaca
Pain Management Nursing.2025; 26(6): e550. CrossRef - Effects of a Internet-Based Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Program for Adolescents with Diabulimia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Hye-Ryeon Park, Hyeon Ok Ju
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(4): 320. CrossRef - Proposal for a Cognitive Reconstruction Program for Female College Students Experiencing Body Dissatisfaction
Hyun Ju Lee, Helen Ha, Yuan Mei Cui, Jee Hyun Lee, Min Ju Kang
Human Ecology Research.2024; 62(2): 369. CrossRef
- How do people with fibromyalgia interpret ambiguous cues in empathy-related healthcare scenarios?
- 1,680 View
- 79 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Effects of Oral Gargling with Aroma Solution in Psychiatric Inpatients: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
- Yun Ah Jung, Hee Sook Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(2):200-209. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.2.200
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of oral gargling with an aromatic solution on xerostomia, objective oral status, and oral health-related quality of life in psychiatric inpatients.
Methods
A nonequivalent control group with a non-synchronized design was used in this study. The experimental group (n=34) received oral gargling with an aroma solution, while the control group (n=33) gargled with 0.9% normal saline. Dependent variables were measured at pre-, post-, and follow-up test. Data were analyzed using an c2-test, Fisher’s exact probability test, t-tests, and repeated measures ANOVA using SPSS/WIN v.21.0.
Results
After the intervention, significant differences were revealed in xerostomia (F=15.30, p <.001), objective oral status (F=38.44, p <.001), and oral health-related quality of life (F=62.70, p <.001) with an interaction effect between group and time.
Conclusion
These findings indicate that gargling with an aroma solution is more effective than 0.9% normal saline for the oral health of psychiatric inpatients. Therefore gargling with an aroma can be safely recommended as a brief, economical, and positive intervention in clinical settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of sugar-free cola solution based on the ICOCFAS score in oral care of non-artificial airway patients with severe neurological conditions
Qingmei Wang, Yuanyuan Fan, Mei Chen, Ping Chen
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of aromatherapy-based oral care on oral conditions, salivary pH, and halitosis in older adults with dementia: Pilot study
Ae Kyung Chang, Bo kyoung Kim, Ah Young Kim
Geriatric Nursing.2023; 53: 109. CrossRef
- Application of sugar-free cola solution based on the ICOCFAS score in oral care of non-artificial airway patients with severe neurological conditions
- 1,265 View
- 17 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of Aromatherapy on Sleep Quality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Mi-Eun Kim, Ji Hee Jun, Muyng-Haeng Hur
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):655-676. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.655
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of aromatherapy on sleep quality.
Methods This is a systematic review of randomized controlled trial studies (PROSPERO registration number CRD42017064519). In this study, the PICO were adults and the elderly, aromatherapy intervention, a comparative intervention with the control and placebo oil groups, and sleep. The selected articles were in English, Korean, and Chinese.
Results The results of the meta-analysis showed that the effect sizes of the experimental group were 1.03 (n=763, SMD=1.03, 95% CI 0.66 to 1.39) (Z=5.47,
p <.001). In the aromatherapy intervention group, the effect size of sleep was statistically significant (QB=9.39, df=2,p =.009), with a difference of 0.77 for inhalation, 1.12 for oral intake and 2.05 for massage. A post-analysis showed that the effect of massage on sleep was significantly greater than the inhalation method. The regression coefficient of the intervention period, B=0.01 (Z=1.43,p =.154), also showed that the longer the intervention period, the larger the effect size; however, it was not statistically significant.Conclusion A total of 23 literature analyses showed that aromatherapy is effective in improving quality of sleep, and the massage method is more effective in improving quality of sleep than the inhalation method. A meta-ANOVA showed that the aromatherapy intervention affected the high heterogeneity of the effect size. Thus, future research with stricter control in methods and experimental procedures is necessary.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of aroma inhalation on the quality of sleep, professional quality of life, and near-misses in medication errors among emergency room nurses on night duty in Korea: a randomized controlled trial
Jungha Son, Chul-Gyu Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(1): 25. CrossRef - Effects of a Multimodal Intervention on Sleep Quality and Duration in Intensive Care Unit Patients
Jieun Nam, Sukhee Ahn
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2025; 18(1): 70. CrossRef - Efficacy of Aromatherapy Against Behavioral and Psychological Disturbances in People With Dementia: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Po-Hao Wang, Ho-Wei Lin, Truc Tran Thanh Nguyen, Chaur-Jong Hu, Li-Kai Huang, Ka-Wai Tam, Yi-Chun Kuan
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2024; 25(11): 105199. CrossRef - Meta-analysis of the Effect Size of Lavender Essential Oil and Lavender Blended Essential Oils on Psychological Factors in Adults
Mi-Na Yu, Ae-Jung Kim
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2024; 22(3): 477. CrossRef - THE EFFECT OF LAVENDER AROMA THERAPY ON THE SLEEP QUALITY OF PREGNANT WOMEN TM III
Hajar Nur Fathur Rohmah
Jurnal Midpro.2024; 16(1): 59. CrossRef - Effects of aromatherapy on sore throat, nasal symptoms and sleep quality in adults infected with COVID-19: A randomized controlled trial
Hye-Young Kang, Hye Young Ahn, Mi-Jung Kang, Myung-Haeng Hur
Integrative Medicine Research.2023; 12(4): 101001. CrossRef - Pain and sleep after open-heart surgery-inhalation peppermint essence: double-blind randomized clinical trial
Mahla Maghami, Mohammad-Sadegh Pour‑Abbasi, Safoura Yadollahi, Mahboobeh Maghami, Ismail Azizi-fini, Mohammad-Reza Afazel
BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care.2023; 13(e3): e1318. CrossRef - Effects of Aromatherapy on Cancer Patients' Sleep and Fatigue: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ju Hyun Ahn, Myoungsuk Kim
Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine.2023; 29(4): 212. CrossRef - Harnessing the power of a good night's sleep
Karen Colombo
Nursing Made Incredibly Easy!.2023; 21(1): 34. CrossRef - Effectiveness of aromatherapy on anxiety and sleep quality among adult patients admitted into intensive care units: A systematic review
Jie Xi Jassie Tan, Junyao Stefanie Cai, Jeanette Ignacio
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2023; 76: 103396. CrossRef - Fatigue relief by aromatherapy use in prenatal and postnatal women: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ji-Ah Song, Hyejin Yang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(2): 87. CrossRef - Aromatherapy with single essential oils can significantly improve the sleep quality of cancer patients: a meta-analysis
Hui Cheng, Lu Lin, Shaotong Wang, Yueyue Zhang, Tingting Liu, Yang Yuan, Qiuyun Chen, Li Tian
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of aromatherapy on fatigue, quality of sleep and quality of life in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A feasibility study
Lili You, Na Guo, Tiantian Wang, Xiang Yu, Xiaofeng Kang, Yuxia Guan, Hongpeng Liu, Jing Dong, Peili Bian, Siyao Wang, Chenxiao Bai
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2022; 49: 101648. CrossRef - The Effects of Non-pharmacological Interventions on Sleep among Older Adults in Korean Long-term Care Facilities: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Sun Ok Jung, Hyeyoung Kim, Eunju Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(3): 340. CrossRef - Visualizing Research Trends and Identifying Hotspots of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Nursing Technology for Insomnia: A 18-Years Bibliometric Analysis of Web of Science Core Collection
Junxin Wang, Yufeng Chen, Xing Zhai, Yupeng Chu, Xiangdi Liu, Xueling Ma
Frontiers in Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of aromatherapy on sleep disorders
Xin Song, Jiahua Peng, Weiyu Jiang, Minghua Ye, Lisheng Jiang
Medicine.2021; 100(17): e25727. CrossRef - Effect of aromatherapy on sleep quality of adults and elderly people: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis
Jihoo Her, Mi-Kyoung Cho
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2021; 60: 102739. CrossRef - Effect of Rosa damascena on improvement of adults’ sleep quality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Mohammad Sadegh Ghorbani Rami, Morteza Nasiri, Mohammad Sadegh Aghili Nasab, Zohre Jafari, Mahya Torkaman, Shahoo Feizi, Behnam Farahmandnia, Masoomeh Asadi
Sleep Medicine.2021; 87: 8. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Sleep Quality in the Relationship between Academic Stress and Social Network Service Addiction Tendency among Adolescents
Eun Sook Bae, Hye Seung Kang, Ha Na Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(3): 290. CrossRef
- The effects of aroma inhalation on the quality of sleep, professional quality of life, and near-misses in medication errors among emergency room nurses on night duty in Korea: a randomized controlled trial
- 6,151 View
- 166 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref

- The Effects of Oral Cryotherapy on Oral Mucositis, Reactive Oxygen Series, Inflammatory Cytokines, and Oral Comfort in Gynecologic Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Nayeon Shin, Younhee Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):149-160. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.149
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of oral cryotherapy on oral mucositis, reactive oxygen series, inflammatory cytokines, and oral comfort in patients undergoing chemotherapy for gynecologic cancers.
Methods Participants were randomly assigned to the experimental group (n=25, receiving oral cryotherapy during chemotherapy) and the control group (n=25, receiving the usual care consisting of 0.9% normal saline gargles three times before meals). Oral mucositis was assessed using the oral assessment guide, while oral comfort was assessed using the oral perception guide. Reactive oxygen series was measured as total oxidant stress, and the level of two inflammatory markers, interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), were examined. The data were analyzed using t-test, chi-square test, Fisher's exact test, Mann-Whitney U-test, and repeated measures analysis of variance.
Results There was a significant difference in the oral mucositis score, reactive oxygen series score, TNF-α level, and oral comfort score between the two groups, and there were significant changes over time and in the group-by-time interactions. There was a significant difference in the IL-6 score between the two groups, but there were no significant changes over time or in the group-by-time interactions.
Conclusion The study results revealed that oral cryotherapy was more effective than the usual care regime of normal saline gargles for reducing oral mucositis, reactive oxygen series, and inflammatory cytokines and for improving oral comfort in gynecologic cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of an Oral Care Program with Honey on Chemotherapy-related Mucositis among Cancer Patients
Bo Ram Song, Hye-Ja Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2024; 49(1): 9. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Photobiomodulation and Oral Cryotherapy on Oral Mucositis Among Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy Conditioning Prior to Hematological Stem Cell Transplantation
Xin Chan, Lyn Tay, Shi Jed Yap, Vivien Xi Wu, Piyanee Klainin-Yobas
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2023; 39(3): 151405. CrossRef - CLINICAL EXPERIENCE OF LOCAL HYPOTHERMIA USAGE IN THE COMPREHENSIVE TREATMENT OF ORAL LICHEN PLANUS
Irina Firsova, Valerij Mikhalchenko, Yulia Fedotova, Sergej Krajnov, Alexandra Popova, Aleksandra Khvan
Actual problems in dentistry.2022; 18(2): 109. CrossRef - The Effects of Oral Cryotherapy on Nausea, Vomiting, Oral Mucositis, and Oral Pain in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
So-Yeong Kim, Haeng-Mi Son
Asian Oncology Nursing.2020; 20(3): 132. CrossRef
- Effect of an Oral Care Program with Honey on Chemotherapy-related Mucositis among Cancer Patients
- 2,023 View
- 57 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- The Development and Evaluation of a Health Literacy-Adapted Self-Management Intervention for Elderly Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
- Yoon Sun Kim, Young Sook Tae, Kwuy-Im Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):472-485. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.472
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to develop and evaluate the effectiveness of an adapted health literacy self-management intervention for elderly cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
Methods The intervention in this study was systematically developed through the six stages of Intervention Mapping Protocol and was based on Fransen et al's causal pathway model. A quasi-experimental trial was conducted on a total of 52 elderly patients (26 in an experimental group and 26 in a control group) undergoing chemotherapy in Korea. The intervention consisted of seven sessions over 5 weeks. The experimental tool for this study was an adapted health literacy self-management intervention, which was designed to promote a reduction in the symptom experience and distress of elderly cancer patients through the promotion of self-management behavior. To develop efficient educational materials, the participants’ health literacy was measured. To educate participants, clear communication and the teach-back method were used. In addition, for the improvement of self-efficacy, four sources were utilized. For the promotion of self-management behavior, five self-management skills were strengthened. Data were collected before and after the intervention from June 4 to September 14, 2018. The data were analyzed with SPSS/WIN 21.0.
Results Following the intervention, self-management knowledge and behavior and, self-efficacy significantly improved in experimental group. Symptom experience and distress decreased in the experimental group compared to the control group.
Conclusion The self-management intervention presented in this study was found to be effective in increasing self-management knowledge and behavior and, self-efficacy, and ultimately in reducing symptom experience and distress for elderly patients undergoing chemotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Self‐Management Education for Deaf Individuals With Hypertension: A Quasi‐Experimental Study
Gi Won Choi, Hee Jung Kim, Yujin Park, Ha Na Jeong, Sun Ju Chang
Research in Nursing & Health.2025; 48(6): 724. CrossRef - The Effect of Group Education Reflecting Unmet Needs on Knowledge of Chemotherapy for Patients and Their Families Undergoing Chemotherapy: A One Group Pre-Post Design
Seyoung Lee, Hoyoung Kim, Nayeon Kim, Misun Yi, Ayoung Lee, Seonmi Cho, Minsun Nam, Juhee Cho
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(1): 42. CrossRef - Health Information Seeking Pathways and Factors Influencing Health Literacy Among Cancer Patients: Based on Data from the 2nd Korean Health Panel 2021
Yun-La Hur, Eun-Jeong Hong
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(3): 155. CrossRef - The Effects of Chemotherapy Education Reflecting Educational Needs on Self-Care Knowledge and Performance in Female Cancer Patients: A Non-Equivalent Control Group Pretest-Posttest Design
Jin Hee Jun, Se-Na Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(3): 103. CrossRef - Effectiveness of teach‐back for chronic kidney disease patient education: A systematic review
Hemamali M. H. Jagodage, Amanda McGuire, Charrlotte Seib, Ann Bonner
Journal of Renal Care.2024; 50(2): 92. CrossRef - Effects of Telephone-based Self-care Intervention for Gynecologic Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Boyeon Lee, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(2): 216. CrossRef - Analysis of Telephone Counseling of Patients in Chemotherapy Using Text Mining Technique
Seoyeon Kim, Jihyun Jung, Heiyoung Kang, Jeehye Bae, Kayoung Sim, Miyoung Yoo, Eunyoung, E. Suh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 46. CrossRef - Evaluating a theory-based intervention for improving eHealth literacy in older adults: a single group, pretest–posttest design
Sun Ju Chang, Kyoung-eun Lee, Eunjin Yang, Hyunju Ryu
BMC Geriatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the teach-back method among cancer patients: a systematic review of the literature
Seonhwa Choi, Jahyun Choi
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(12): 7259. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Self‐Management Education for Deaf Individuals With Hypertension: A Quasi‐Experimental Study
- 2,939 View
- 90 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- A Structural Model for Chemotherapy Related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients
- Jung Ran Lee, Pok Ja Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):375-385. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.375
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to develop and test a structural model for chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment of breast cancer patients based on a literature review and Hess and Insel's chemotherapy-related cognitive change model.
Methods The Participants consisted of 250 patients who were ≥19 years of age. The assessment tools included the Menopause Rating Scale, Symptom Experience Scale, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, Everyday Cognition, and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast Cancer. Data were analyzed using the SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0 programs.
Results The modified model was a good fit for the data. The model fit indices were χ 2=423.18 (
p <.001), χ 2/df=3.38, CFI=.91, NFI=.91, TLI=.89, SRMR=.05, RMSEA=.09, and AIC=515.18. Chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment was directly influenced by menopausal symptoms (β=.38,p =.002), depression and anxiety (β=.25,p =.002), and symptom experiences (β=.19,p =.012). These predictors explained 47.7% of the variance in chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment. Depression and anxiety mediated the relations among menopausal symptoms, symptom experiences, and with chemotherapy related cognitive impairment. Depression and anxiety (β=-.51,p =.001), symptom experiences (β=-.27,p =.001), menopausal symptoms (β=-.22,p =.008), and chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment (β=-.15,p =.024) had direct effects on the quality of life and these variables explained 91.3%.Conclusion These results suggest that chemotherapy-related toxicity is highly associated with cognitive decline and quality of life in women with breast cancer. Depression and anxiety increased vulnerability to cognitive impairment after chemotherapy. Nursing intervention is needed to relieve chemotherapy-related toxicity and psychological factor as well as cognitive decline for quality of life in patients undergoing chemotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
Young-Hee Je, Kyoung-Ah Kang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - Impact of social support on cognitive function in patients with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy: The chain-mediating role of fatigue and depression
Yuanqi Ding, Qingmei Huang, Fulei Wu, Yang Yang, Ling Wang, Xuqian Zong, Xiaoyan Yu, Changrong Yuan
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100743. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Oncofertility in Gynecological Cancer Patients: Application of Mixed Methods Study
Minji Kim, Juyoung Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 418. CrossRef - Relationships Between Chemotherapy-Related Cognitive Impairment, Self-Care Ability, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study
Nan Wu, Ze Luan, Zijun Zhou, He Wang, Shiyuan Du, Yulu Chen, Xinxin Wang, Jiong Li, Xin Peng
Seminars in Oncology Nursing.2024; 40(5): 151690. CrossRef - Effects of different exercise interventions on chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment in patients with breast cancer: a study protocol for systematic review and network meta-analysis
Yu Dong, Hao Huang, Aiping Wang
BMJ Open.2024; 14(4): e078934. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Self-reported Memory Problems of Adult Cancer Survivors Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
Sangjin Ko
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(1): 51. CrossRef - Impact of nonpharmacological interventions on cognitive impairment in women with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jin-Hee Park, Su Jin Jung, Lena J. Lee, Junghyun Rhu, Sun Hyoung Bae
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(4): 100212. CrossRef - Impact of discriminant factors on the comfort-care of nurses caring for trans-arterial chemoembolisation patients
Myoung Soo Kim, Ju-Yeon Uhm
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(9): 7773. CrossRef - Brain morphological alterations and their correlation to tumor differentiation and duration in patients with lung cancer after platinum chemotherapy
Pin Lv, Guolin Ma, Wenqian Chen, Renyuan Liu, Xiaoyan Xin, Jiaming Lu, Shu Su, Ming Li, ShangWen Yang, Yiming Ma, Ping Rong, Ningyu Dong, Qian Chen, Xin Zhang, Xiaowei Han, Bing Zhang
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Rehabilitation on Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Clinical Study
Teresa Paolucci, Aristide Saggino, Francesco Agostini, Marco Paoloni, Andrea Bernetti, Massimiliano Mangone, Valter Santilli, Raoul Saggini, Marco Tommasi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(16): 8585. CrossRef
- Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
- 1,795 View
- 23 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref

- The Effects of an Acceptance-Commitment Therapy Based Stress Management Program on Hospitalization Stress, Self-Efficacy and Psychological Well-Being of Inpatients with Schizophrenia
- Jae Woon Lee, Jae Hyun Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(4):443-453. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.4.443
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to construct an acceptance-commitment therapy (ACT)-based stress management program for inpatients with schizophrenia and to examine its effects on hospitalization stress, self-efficacy, and psychological well-being.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. Participants were 44 inpatients with a diagnosis of schizophrenia. The experimental group (n=22) received the ACT-based stress management program twice a week for a total of four weeks. The control group (n=22) received the usual care from their primary health care providers. The study was carried out from August 7 to September 1, 2017, and data were analyzed using IBM SPSS/WIN 22.0 with a Chi-square test, Fisher's exact test, and an independent t-test.
Results The experimental group showed a significant decrease in hospitalization stress (t=5.09,
p <.001) and an increase in self-efficacy (t=2.44,p =.019). However, there was no significant difference in psychological well-being between the two groups (t=0.13,p =.894).Conclusion The results of this study suggest that the ACT-based stress management program can be used as an effective mental health nursing intervention for hospitalization stress and self-efficacy for inpatients with schizophrenia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors that influence hospitalization stress in patients with chronic schizophrenia: A cross‐sectional study in psychiatric hospitals
Sumin Chai, Goun Kim
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 32(1): 102. CrossRef - Positive mental health interventions for people with schizophrenia: A scoping review
Catarina Nogueira, Emanuel Dias Pereira, Joana Catarina Ferreira Coelho, Antonio Rafael Moreno-Poyato, Carlos Alberto Cruz Sequeira
Schizophrenia Research.2025; 276: 40. CrossRef - Effects of entrapment, anger, psychological flexibility, and self-compassion on the ward climate and reactive aggression in forensic psychiatric hospital patients
Sul Hwan Kim, ChongNak Son
International Journal of Law and Psychiatry.2024; 94: 101986. CrossRef - The effect of Treatment based on Acceptance and Commitment on Pathological Worry and Death Anxiety in Nurses with the Experience of Complicated Grief Caused by COVID-19
V Aghaei, R Kazemi, S Taklovi, V Nazari
Journal of Health and Care.2024; 26(1): 52. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy on Pain
Coping Strategies and Pain Self-efficacy in Chronic Neuropathic Pain
Patients
farzaneh Dehestani, Bahram mirzaian, ramazan hassanzadeh, payam saadat
Scientific Journal of Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences.2023; 27(6): 97. CrossRef - Effects of Structured Group Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for Psychological Acceptance and Recovery Among Inpatients With Psychotic Disorder: A Pilot Study
Narae Jeong, Hyesu Jeon, Dowon You, Yu Sang Lee
Korean Journal of Schizophrenia Research.2022; 25(2): 32. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) on Sexual Self-Efficacy and Sexual Quality of Life in Reproductive-Age Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Behnaz Enjezab, Marzieh Rejaezadeh, Mahshid Bokaie, Hajar Salimi
Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy.2021; 47(8): 764. CrossRef - Training coping skills and coping with stress self-efficacy for successful daily functioning and improved clinical status in patients with psychosis: A randomized controlled pilot study
Débora Godoy Izquierdo, María Luisa Vázquez Pérez, Raquel Lara Moreno, Juan F Godoy García
Science Progress.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Smartphone Overdependence Prevention Program for University Students Based on Self-Determination Theory
Myung Soon Kwon, Jeong Soon Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(1): 116. CrossRef - Effects of Acceptance Commitment Therapy Based Recovery Enhancement Program on Psychological Flexibility, Recovery Attitude, and Quality of Life for Inpatients with Mental Illness
In Sook Kim, Jae Woon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(1): 79. CrossRef - Development and Effects of an Acceptance Commitment-based Cognitive Behavioral Program for Patients with Schizophrenia
Jae Woon Lee, Hyun Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2018; 27(4): 342. CrossRef
- Factors that influence hospitalization stress in patients with chronic schizophrenia: A cross‐sectional study in psychiatric hospitals
- 1,652 View
- 33 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Effects of Group Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy on the Nurses’ Job Stress, Burnout, Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment and Turnover Intention
- Hye-Lyun Kim, Sook-Hee Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(4):432-442. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.4.432
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to develop a Group REBT program with group counseling for nurses and test the effect of group counseling on their job stress, burnout, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention.
Methods A quasi-experimental study with nonequivalent control group design was employed to identify the effect of the Group REBT program on nurses’ job stress, burnout, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention. Data were collected from 47 participants from two hospitals. The data from the experimental (n=23) and control (n=24) groups were analyzed from January 5 to April 3, 2015. The Group REBT program was conducted eight tmes in all, once a week, with each session lasting 180 minutes. The effect of experimental intervention was measured for each group using a series of structured questionnaires at each of the phases: Pre-intervention, post-intervention (immediately after intervention), and post-intervention (four weeks after intervention). Following this, the significance of the changes in the scores was tested.
Results The scores of the experimental group, which received the Group REBT program, were compared with those of the control group; the hypotheses were supported in terms of job stress (F=8.85,
p <.001), burnout (F=5.62,p =.022), job satisfaction (F=2.70,p =.042), organizational commitment (F=2.97,p =.048), and turnover intention (F=4.60,p =.012).Conclusion The Group REBT program was shown to be an effective intervention that could reduce nurses’ job stress and burnout and increase job satisfaction and organizational commitment. Therefore, the Group REBT program can be adopted by nursing organizations to strategically decrease nurses’ turnover intention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Influencing Organizational Socialization in New Nurses: A Focus on Job Stress, Resilience, and Nursing Performance
Kyungok Park, Yeoungsuk Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(1): 118. CrossRef - Finding the paths between job demand–resources and turnover intention of community mental health nurses in Korea
Eunmi Hwang, Yeojin Yi
International Nursing Review.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the potential dimensions and influencing factors of nurses’ sense of professional achievement in “Internet + Nursing Services”
Jing Wu, Zhixia Zhang, Juanjuan Li, Heng Li, Niannian Zhang, Lili Gao, Congcong He, Xuan Wang
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Mental health interventions affecting university faculty: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Dalal Hammoudi Halat, Waqas Sami, Abderrezzaq Soltani, Ahmed Malki
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The moderating effects of positive thinking on the relationship between job stress and turnover intention
Khahan Na-Nan
Evidence-based HRM: a Global Forum for Empirical Scholarship.2024; 12(3): 531. CrossRef - Interventions to reduce burnout among clinical nurses: systematic review and meta-analysis
Miran Lee, Chiyoung Cha
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A systematic mapping review on the use of Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) with athletes
Anna Jordana, Martin J. Turner, Yago Ramis, Miquel Torregrossa
International Review of Sport and Exercise Psychology.2023; 16(1): 231. CrossRef - Psychological capital, work stress and burnout among Chinese clinical nurses
Ganjun Song, Lida C Landicho
International Journal of Research Studies in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychological Resilience and Career Success of Female Nurses in Central China: The Mediating Role of Craftsmanship
Huiyuan Xue, Xiaona Si, He Wang, Xiaoren Song, Keke Zhu, Xiaoli Liu, Fen Zhang
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of the second victim's experience and support on the career success of psychiatric nurses: The mediating effect of psychological resilience
Hua Xu, Xiang Cao, Quan‐Xiang Jin, Rui‐Shi Wang, Yan‐Hong Zhang, Zhao‐Hong Chen
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(6): 1559. CrossRef - The effect of a psychoeducation program based on the rational emotional behavioral approach in individuals with multiple sclerosis diagnosis: A randomized controlled trial
Emel Şahin, Serap Güleç Keskin, Murat Terzi
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2022; 58(4): 1449. CrossRef - The Effect of Nurse Support Programs on Job Satisfaction and Organizational Behaviors among Hospital Nurses: A Meta-Analysis
Se Young Kim, Mi-Kyoung Cho
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(24): 17061. CrossRef - Effects of the Anger Management Program for Nurses
Kyoungsun Yun, Yang-Sook Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(4): 247. CrossRef - Nursing management challenges: Effect of quality of work life on depersonalization
P. Yukthamarani Permarupan, Abdullah Al Mamun, Naeem Hayat, Roselina Ahmad Saufi, Naresh Kumar Samy
International Journal of Healthcare Management.2021; 14(4): 1040. CrossRef - Clinical benefits of rational-emotive stress management therapy for job burnout and dysfunctional distress of special education teachers
Liziana N Onuigbo, Charity N Onyishi, Chiedu Eseadi
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2020; 8(12): 2438. CrossRef - Predicting Nurses Burnout through Quality of Work Life and Psychological Empowerment: A Study Towards Sustainable Healthcare Services in Malaysia
P Yukthamarani Permarupan, Abdullah Al Mamun, Naresh Kumar Samy, Roselina Ahmad Saufi, Naeem Hayat
Sustainability.2020; 12(1): 388. CrossRef - Cognitive behavioral therapy for occupational stress among the intensive care unit nurses
MohammadHosein Fadaei, Mahya Torkaman, Naval Heydari, Maryam Kamali, Fariba Ghodsbin
Indian Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2020; 24(3): 178. CrossRef - Effects of Hospital-Based Violence-Prevention and Coping Programs on Nurses' Violence Experience, Violence Responses, Self-Efficacy, and Organizational Commitment
Yu Jeong Yang, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 550. CrossRef - Intervention for burnout among postgraduate chemistry education students
Florence Obiageli Ezeudu, Florence Oboochi Attah, Anthonia Ebere Onah, Tochukwu Longinus Nwangwu, Ekwutosi Monica Nnadi
Journal of International Medical Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of WeChat‐based 'three good things' on turnover intention and coping style in burnout nurses
Yu‐Fang Guo, Virginia Plummer, Wendy Cross, Louisa Lam, Jing‐Ping Zhang
Journal of Nursing Management.2020; 28(7): 1570. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Organizational Commitment in the Relationship between Professional Identity and Job Satisfaction
Seonghyun Yoo, Myoung Soo Kim, Hyoung Sook Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2019; 44(4): 339. CrossRef - Burnout Precursors in Oncology Nurses: A Preliminary Cross-Sectional Study with a Systemic Organizational Analysis
Loris Bonetti, Angela Tolotti, Dario Valcarenghi, Carla Pedrazzani, Serena Barello, Greta Ghizzardi, Guendalina Graffigna, Davide Sari, Monica Bianchi
Sustainability.2019; 11(5): 1246. CrossRef
- Factors Influencing Organizational Socialization in New Nurses: A Focus on Job Stress, Resilience, and Nursing Performance
- 2,546 View
- 68 Download
- 22 Crossref

- The Effects of Laughter Therapy Program on Perceived Stress, and Psycho-Neuro-Endocrino-Immuno Responses in Obese Women
- Do Young Lee, Myung Sun Hyun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):298-310. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.298
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of the laughter therapy program on perceived stress and psycho-neuro-endocrine-immune responses in obese women.
Methods A nonequivalent control group with a pretest-posttest design was used. The participants (n=60), whose age ranged from 30 to 50 years (pre-menopausal and body mass index of over 25 kg/m2), were assigned to the experimental group (n=24) or control group (n=26). The experimental group was provided with the laughter therapy program (12 sessions) for 6 weeks.
Results There were significant differences in perceived stress, psychological stress response, fasting blood sugar, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor alpha between the two groups after the program. However, there were no significant differences in normalized low frequency (norm LF), normalized high frequency (norm HF), LF/HF ratio, and cortisol between the two groups after the program.
Conclusion It was found that the laughter therapy program had positive effects on some variables in terms of perceived stress and psycho-neuro-endocrine-immuno responses. It is suggested that the laughter therapy in this study can provide the direction for developing a program for obese women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Laughter Yoga on Happiness and Stress in Nursing Students Going into Clinical Practice for the First Time
Betul Bal, Canan Demirci, Gamze Gulsum Kilicli
Journal of Holistic Nursing.2025; 43(2): 159. CrossRef - The Effect of Laughter Yoga on Vasomotor Symptoms and Sleep Quality in Menopausal Women
Ahu Aksoy-Can, Tuba Güner-Emül, Filiz Değirmenci, Aysu Buldum, Aslıhan Aksu, Duygu Vefikuluçay-Yılmaz
Holistic Nursing Practice.2025; 39(4): 192. CrossRef - The effects of acupressure, laughter yoga, and a mindfulness-based stress reduction program applied to postmenopausal women for menopause symptoms and quality of life
Hacer U. Koca, Didem S. Kucukkelepce, Gulcin Nacar, Nurdilan S. Çetin, Sermin T. Taşhan
Menopause.2024; 31(10): 879. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Laughter Therapy Program for Middle-aged Women Hospitalized in Psychiatric Wards
Do Young Lee, Ju Hyun Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(3): 273. CrossRef - Effects of Short-term Urban Forest Experiences by Season on Stress and Affective Response of University Students
Eunjin Kim, Hwayong Lee
Journal of People, Plants, and Environment.2023; 26(4): 433. CrossRef - Laughter as medicine: A systematic review and meta-analysis of interventional studies evaluating the impact of spontaneous laughter on cortisol levels
Caroline Kaercher Kramer, Cristiane Bauermann Leitao, Fares Alahdab
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(5): e0286260. CrossRef - Seasonal Forest Changes of Color and Temperature: Effects on the Mood and Physiological State of University Students
Eunjin Kim, Hwayong Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(14): 6338. CrossRef - Effects of a laughter programme with entrainment music on stress, depression, and health-related quality of life among gynaecological cancer patients
Yong Jin Lee, Myung Ah Kim, Hye-Ja Park
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2020; 39: 101118. CrossRef - Effects of aromatherapy on stress, fructosamine, fatigue, and sleep quality in prediabetic middle-aged women: A randomised controlled trial
Myung-Haeng Hur, Jun Hwa Hong, SeongHee Yeo
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2019; 31: 100978. CrossRef
- The Effects of Laughter Yoga on Happiness and Stress in Nursing Students Going into Clinical Practice for the First Time
- 2,168 View
- 35 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Effectiveness of Non-Pharmacologic Interventions in Chemotherapy Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Pok-Ja Oh, You Lim Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):123-142. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of non-pharmacologic interventions in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN).
Methods PubMed, Cochrane Library CENTRAL, EMBASE, CINAHL, and several Korean databases (Until August 2017) were searched. The main search strategy combined terms for peripheral neuropathy and presence of neoplasms. The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane's Risk of Bias tool for randomized studies and the Risk of Bias Assessment tool for non-randomized studies. To estimate the effect size, a meta-analysis of the studies was performed using the Rev Man 5.3 program of the Cochrane Library random-effects models were used in the analyses.
Results Twenty-two studies with a total of 954 participants met the inclusion criteria. Of the 22 studies, 12 were used to estimate the effect size of the non-pharmacologic interventions. The non-pharmacologic interventions used in patients with CIPN were exercise, acupuncture, massage, and foot bath. The acupuncture significantly reduced CIPN symptoms and signs (d=-0.71) and CIPN pain (d=-0.73) (
p <.001). Massage and foot bath were also effective in reducing CIPN symptoms (d=-0.68; 95% CI=-1.05, -0.30;p <.001; I2=19%).Exercis-es were effective in improving muscle strength and endurance(d=-0.55) and quality of life (d=-2.96), but they were not significantly effective in improving CIPN.Conclusion Although these results provide little evidence of the effectiveness of acupuncture, massage, and foot bath in the treatment of CIPN, they suggest that these interventions can reduce CIPN symptoms in patients with cancer. However, the findings of this study should be interpreted with caution as there is a relative lack of data in this field, and additional well-designed studies are needed. PROSPERO registration: CRD42017076278.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effectiveness and Safety of Nurse-Led Auricular Acupressure on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Among Patients With Breast Cancer
Mi Sook Jung, Mijung Kim, Eun Hee Sohn, Jin Sun Lee
Cancer Nursing.2025; 48(2): E64. CrossRef - Effects of acupuncture-related intervention on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and quality of life: An umbrella review
Mei-Ling Yeh, Chin-Che Hsu, Matthew Lin, Chuan-Ju Lin, Jaung-Geng Lin
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2025; 89: 103131. CrossRef - Effects of Swanson theory-based auricular acupressure on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, and broader health-related outcomes in patients with breast cancer: A randomized controlled trial
Yuanyuan Mi, Ying Chen, Jing Li, Xinxin Liu, Zhengrong Li, Quanlian Ye, Jinli Guo, Yuanfei Liu
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 12: 100729. CrossRef - Traditional herbal medicine for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis with association rule analysis
Eun Hye Kim, Hayun Jin, Su Hyeon Lee, Seong Woo Yoon
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Acupuncture-related interventions improve chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Mei-Ling Yeh, Ru-Wen Liao, Pin-Hsuan Yeh, Chuan-Ju Lin, Yu-Jen Wang
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Exercise Intervention on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Symptoms in Cancer Patients: A Meta-analysis
Nan Wu, Hongshi Cao, Shiyuan Du, Yulu Chen, Xinxin Wang, Jiong Li, Xin Peng
Cancer Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effectiveness and safety of acupuncture/electroacupuncture for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Li-Xia Pei, Yue Yi, Jing Guo, Lu Chen, Jin-Yong Zhou, Xiao-Liang Wu, Jian-Hua Sun, Hao Chen
Acupuncture in Medicine.2023; 41(2): 73. CrossRef - Effects of Footbath on Postoperative Pain and Sleep Quality in Patients With Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease: A Randomized Controlled Study
Seher Ünver, Ülkü Çolakoğlu, Ahmet Tolgay Akıncı
Journal of Neuroscience Nursing.2023; 55(4): 125. CrossRef - Non-pharmacological therapy for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Xia Zhang, Ao Wang, Miaowei Wang, Guo Li, Quan Wei
BMC Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Manual Therapy on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Eunsang Lee, Hyunjoong Kim
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - The impact of peripheral neuropathy symptoms, self-care ability, and disturbances to daily life on quality of life among gynecological cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: a cross-sectional survey
Sohee Mun, Hyojung Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(4): 296. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Mobile Application-based Self-Management Program for Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Colorectal Cancer Patients
Pok-Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(3): 258. CrossRef - Treatment and diagnosis of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: An update
Allison D. Desforges, Chance M. Hebert, Allyson L. Spence, Bailey Reid, Hemangini A. Dhaibar, Diana Cruz-Topete, Elyse M. Cornett, Alan David Kaye, Ivan Urits, Omar Viswanath
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 147: 112671. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in children and adolescent cancer patients
Nicolette Tay, E-Liisa Laakso, Daniel Schweitzer, Raelene Endersby, Irina Vetter, Hana Starobova
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Case Report of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Treated with Modified
Guibi-tang
Su Bin Park, Jee-Hyun Yoon, Eun Hye Kim, Seong Woo Yoon
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2022; 43(3): 451. CrossRef - Kanser Tedavisi Alan Çocuklarda Kemoterapiyle İlişkili Periferik Nöropatinin Değerlendirilmesinde Hemşirenin Rolü
Bilge ÖZDEMİR, Gülçin ÖZALP GERÇEKER
Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Fakültesi Elektronik Dergisi.2022; 15(3): 369. CrossRef - Non-Pharmacological Self-Management Strategies for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in People with Advanced Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Megan Crichton, Patsy M. Yates, Oluwaseyifunmi Andi Agbejule, Amy Spooner, Raymond J. Chan, Nicolas H. Hart
Nutrients.2022; 14(12): 2403. CrossRef - The Effects of Foot Reflexology on the Physical Symptoms of Cancer Patients
Young-Ran Yeun, Yi-Sub Kwak, Hye-Young Kim
Exercise Science.2021; 30(1): 8. CrossRef - A Case Report of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Treated with Warm Needling
Jee-Hyun Yoon, Su Bin Park, Jee Young Lee, Eun Hye Kim, Seong Woo Yoon
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2021; 42(2): 114. CrossRef - The Effect of Self-Acupressure on Peripheral Neuropathy, Disturbance in Daily Activity, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients undergoing Chemotherapy
Su Young Kim, Jeong Sook Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(3): 129. CrossRef - Effects of Exercise on Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yu Hyeon Choe, Da Hye Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(5): 458. CrossRef - Effects of pain neuroscience education on kinesiophobia in patients with chronic pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Hyunjoong Kim, Seungwon Lee
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2020; 9(4): 309. CrossRef - Prescribing for persistent cancer pain: focus on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy
Martin Galligan
Journal of Prescribing Practice.2020; 2(4): 176. CrossRef - Effects of Nonpharmacological Interventions in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: An Overview of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Jie Hao, Xiaoshu Zhu, Alan Bensoussan
Integrative Cancer Therapies.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical study on concurrent use of electro-acupuncture or Chuna manual therapy with pregabalin for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: safety and effectiveness (open-labeled, parallel, randomized controlled trial, assessor-blinded)
Jin-Hyun Lee, Tae jin Cho, Min Geun Park, Ji-Hoon Kim, Sung Kyu Song, Shin-Young Park, Yun-Young Sunwoo, Ilkyun Lee, Tae-Yong Park
Medicine.2020; 99(3): e18830. CrossRef - The Experience of Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy in People with Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Eun Sook Choi, Jin Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(2): 81. CrossRef - Acupuncture therapy improves health-related quality of life in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Po-Chun Hsieh, Mei-Chen Yang, Yao-Kuang Wu, Hsin-Yi Chen, I-Shiang Tzeng, Pei-Shan Hsu, Chang-Ti Lee, Chien-Lin Chen, Chou-Chin Lan
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2019; 35: 208. CrossRef - Acupuncture for the Relief of Chronic Pain: A Synthesis of Systematic Reviews
Carole A. Paley, Mark I. Johnson
Medicina.2019; 56(1): 6. CrossRef - Evidence, safety and recommendations for when to use acupuncture for treating cancer related symptoms: a narrative review
Stephen Birch, Myeong Soo Lee, Terje Alraek, Tae-Hun Kim
Integrative Medicine Research.2019; 8(3): 160. CrossRef - Physiotherapy management of chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy in a gynecological condition through clinical reasoning process: A case study
K. M. Amran Hossain, Mohammad Anwar Hossain, Feroz Ahmed Mamin, Ehsanur Rahman, Nasrin Afroz, Nusrat Jahan Sonia, Shati Aziz Khan
Edorium Journal of Disability and Rehabilitation.2018; 4(2): 1. CrossRef - Research Trend about Complementary and Alternative Therapy in Korea using Text Network Analysis
Hae Ree Sung, Jung Lim Lee, Youngji Kim, Jeong Sig Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2018; 21(2): 61. CrossRef - Síntesis de la evidencia científica en acupuntura
Juan Muñoz-Ortego, Jorge Vas, Betina Nishishinya Aquino, Beltrán Carrillo, Alberto Pérez Samartín, Cristina Verástegui, Rafael Cobos
Revista Internacional de Acupuntura.2018; 12(4): 97. CrossRef
- The Effectiveness and Safety of Nurse-Led Auricular Acupressure on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Among Patients With Breast Cancer
- 3,362 View
- 81 Download
- 32 Crossref

- Effects of Aromatherapy on Stress Responses, Autonomic Nervous System Activity and Blood Pressure in the Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
- Eun Jeong Song, Mi Young Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(1):1-11. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of aromatherapy on stress responses, autonomic nervous system (ANS) activity, and blood pressure in patients hospitalized to receive coronary angiography (CAG).
Methods A non-equivalent control group with a pretest-posttest design was used. The subjects were patients admitted to the day angiography room to receive CAG at E University Hospital (34 in the experimental group and 30 in the control group). The experimental group treatment was inhalation of the aroma oil blended with lavender, ylang-ylang, and neroli at a ratio of 4:2:1 twice before and after CAG. The measurements of stress index, ANS activity, and blood pressure were performed 5 times as follows: at admission, at pre-CAG after treatment I, at post-CAG, 2 hours after treatment II, and 4 hours after treatment II. The data were analyzed using the Mann-Whitney
U Test and repeated-measures analysis of variance.Results Significant interactions in the high frequency of ANS (F=5.58,
p =.005) were observed between group and time. Stress index (z =2.14,p =.016), systolic blood pressure (z =4.14,p <.005), and diastolic blood pressure (z =3.28,p =.001) were significantly different between the experimental and control groups after 4 hours of treatment II.Conclusion The findings showed that aromatherapy was not effective before CAG, but was effective after CAG. Therefore, aromatherapy can be used as a nursing intervention for patients receiving CAG.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative effects of music therapy and aromatherapy on stress, quality of life, and happiness among shift nurses in Korea: a randomized controlled trial
So-heun Lee, Won-jong Kim, Eun-Hi Choi, Myung-Haeng Hur
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2024; 26(4): 337. CrossRef - Effect of neroli-flavored chewing gum on anxiety
Mozhgan Esmaeelian, Elahe Esmaeelian
EXPLORE.2024; 20(6): 103028. CrossRef - The Effects of Aroma Essential Oil Inhalation on Stress, Pain, and Sleep Quality in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
JiA Lee, Myung-Haeng Hur
Asian Nursing Research.2022; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - Role of Aromatherapy as a Natural Complementary and Alternative Therapy in Cardiovascular Disease: A Comprehensive Systematic Review
Hamdan I AlMohammed, Nada A Alanazi, Esraa Fahad Maghrabi, Manar A Alotaibi, Muhammad Zia-Ul-Haq
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Natural essential oils: A promising strategy for treating cardio-cerebrovascular diseases
Yu Long, Dan Li, Shuang Yu, Yu-lu Zhang, Song-yu Liu, Jin-yan Wan, Ai Shi, Jie Deng, Jing Wen, Xiao-qiu Li, Ying Ma, Nan Li, Ming Yang
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2022; 297: 115421. CrossRef - In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Some Plant Essential Oils against Four Different Microbial Strains
Daniela Gheorghita, Alina Robu, Aurora Antoniac, Iulian Antoniac, Lia Mara Ditu, Anca-Daniela Raiciu, Justinian Tomescu, Elena Grosu, Adriana Saceleanu
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(19): 9482. CrossRef - The Comparative Effects of Aroma Essential Oil Inhalation and Music Listening on Stress Response, Vital Signs, and Bispectral Index of Healthy Adults
Jae-Kyeum Lee, Myung-Haeng Hur
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(1): 62. CrossRef - Therapeutic Effect and Mechanisms of Essential Oils in Mood Disorders: Interaction between the Nervous and Respiratory Systems
Timothy K. H. Fung, Benson W. M. Lau, Shirley P. C. Ngai, Hector W. H. Tsang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(9): 4844. CrossRef - Effects of Gymnastics-based Nursing Intervention on Stress, Obesity, and Mental Health Confidence in Patients with Chronic Mental Illness
Hee Jeong Kim, Sookbin Im
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2021; 30(1): 53. CrossRef - Changes in Psychological Anxiety and Physiological Stress Hormones in Korea National Shooters
Sang-Hyuk Park, In-Hye Park, Seung-Taek Lim, Eunjae Lee
Brain Sciences.2020; 10(12): 926. CrossRef
- Comparative effects of music therapy and aromatherapy on stress, quality of life, and happiness among shift nurses in Korea: a randomized controlled trial
- 1,370 View
- 24 Download
- 10 Crossref

- The Effects of Mobile Social Networking Service-Based Cognitive Behavior Therapy on Insomnia in Nurses
- Ji Eun Kim, Suk-Sun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(4):476-487. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.4.476
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to examine the effects of cognitive behavior therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) based on the mobile social networking service (SNS) on dysfunctional beliefs and attitudes about sleep, sleep quality, daytime sleepiness, depression, and quality of life among rotating-shift nurses in a hospital in Korea.
Methods A nonequivalent control group pre-post test design was used. The participants included 55 nurses with rotating three-shift work (25 in the experimental group and 30 in the control group). For the experimental group, CBT-I using mobile SNS was provided once a week for 60 minutes over six weeks. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, χ2-test, independent samples t-test, and Mann-whitney U test with the SPSS 21.0 program.
Results In the homogeneity test of the general characteristics and study variables, there were no significant differences between the two groups. Nurses in the experimental group had significantly lower scores on dysfunctional beliefs and attitudes regarding sleep and sleepiness than nurses in the control group. Nurses in the experimental group had significantly higher scores on sleep quality and quality of life than nurses in the control group.
Conclusion These findings indicate that using the mobile SNS-based CBT-I is feasible and has significant and positive treatment-related effects on rotating-shift nurses' irrational thoughts and beliefs in association with sleep, sleep quality, daytime sleepiness, and quality of life. These contribute to expanding our knowledge of rotating-shift nurses' sleep issues and their preferences for intervention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia in Patients with Alcohol Use Disorder: An Experimental Study
Sook Kyoung Park, Eun Ju Song, Keun Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(2): 211. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Quality of Life of Clinical Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Seul-Ki Park, Kyoung-Sook Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(3): 1752. CrossRef - Effectiveness of sleep interventions for rotating night shift workers: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Bo Min Jeon, Su Hyun Kim, Seung Hwa Shin
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of the type of delivery of cognitive‐behavioral therapy for healthcare workers: A systematic review
In Gyu Yoo
Journal of Clinical Psychology.2022; 78(2): 149. CrossRef - Effects of cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) on quality of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Zainab Alimoradi, Elahe Jafari, Anders Broström, Maurice M. Ohayon, Chung-Ying Lin, Mark D. Griffiths, Kerstin Blom, Susanna Jernelöv, Viktor Kaldo, Amir H. Pakpour
Sleep Medicine Reviews.2022; 64: 101646. CrossRef - Rotating between day and night shifts: Factors influencing sleep patterns of hospital nurses
Seunghwa Shin, SuHyun Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2021; 30(21-22): 3182. CrossRef - Sleep quality among shift-work nurses: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jiwon Kang, Wonjung Noh, Youngjin Lee
Applied Nursing Research.2020; 52: 151227. CrossRef
- Effects of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia in Patients with Alcohol Use Disorder: An Experimental Study
- 2,050 View
- 53 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of Psychoeducational Intervention for Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):143-163. Published online April 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material Purpose This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis designed to investigate effects of psychoeducational intervention for cancer survivors.
Methods Ten databases were searched. Two reviewers independently performed the selection of the studies, data extraction and assessment. The risk of bias was assessed using Cochrane Collaboration's tool. To estimate the effect size, meta-analysis of the studies was performed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis and RevMan programs.
Results Of 18,781 publications identified, 35 met inclusion criteria, and 25 studies were used to estimate effect size of psychoeducational intervention. Effect sizes (standardized mean difference [SMD]) were heterogeneous and random effects models were used in the analyses. Psychoeducational intervention was effective for quality of life (n=2,410, ES=0.23; 95% CI: 0.09~0.37), coping and self-efficacy (n=179, ES=0.68; 95% CI: 0.26~1.11), anxiety (n=1,786, ES=-0.26; 95% CI: -0.37~-0.15), depression (n=1,910, ES=-0.28; 95% CI: -0.37~-0.18), and psychological distress (n=2,242, ES=-0.31; 95% CI: -0.46~-0.17). Subgroup analysis showed that counseling was the most effective intervention for quality of life, and behavioral therapy was an effective intervention for all positive and negative outcomes. Publication bias was not detected except for psychological distress.
Conclusion Psychoeducational intervention appears to be effective in improving quality of life and coping and self-efficacy, and it is effective in reducing psychological symptoms in cancer survivors. Behavioral therapy, especially, is commonly effective in improving psychosocial outcomes. However, low-quality evidence, variability in the designs of existing studies, and publication bias suggest that additional high-quality trials should be conducted in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with post-treatment smoking among a diverse sample of cancer survivors in the US
Safa Elkefi, Corina T. Lelutiu-Weinberger, Jean-Marie Bruzzese, Alicia K. Matthews
Discover Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Group‐Based Support Interventions for Adolescents and Young Adults With Lymphoma: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Dalnim Cho, Sairah Ahmed, Stella Snyder, Juliet Kroll, Minxing Chen, Michael Roth, Kathrin Milbury
Psycho-Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Mind Health of Persons with Cancer: Psycho-Oncology and Nursing
Park Eun Young
Journal of Clinical Psychooncology.2025; 11(1): 24. CrossRef - Psychosocial interventions for people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and motor neuron disease and their caregivers: a scoping review
Juyeon Oh, Jiwon An, Kyongok Park, Youngok Park
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of telemedicine psychoeducational interventions for adults with non‐oncological chronic disease: A systematic review
Carmen Sánchez‐Gutiérrez, Eugenia Gil‐García, Adriana Rivera‐Sequeiros, José M. López‐Millán
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2022; 78(5): 1267. CrossRef - Cancer-Related Psychological Distress in Lymphoma Survivor: An Italian Cross-Sectional Study
Giulia Agostinelli, Barbara Muzzatti, Samantha Serpentini, Michele Spina, Maria Antonietta Annunziata
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the Advanced Practice Nurse-Led Psychoeducational Program for Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hye Kyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 245. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Led Intervention Programs Based on Goal Attainment Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 699. CrossRef - Effects of Psychosocial Interventions on Physical Function and Depression in Stroke Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jinhyang YANG, Changwan KANG, Hye-Won PARK, Euna PARK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(2): 396. CrossRef - Development of A Nurse-Led Educational Intervention Program in Managing the Nutrition Impact Symptom Cluster in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma following the Medical Research Council Framework
Wenli Xiao, Carmen W Chan, Jinnan Xiao, Cho L Wong, Ka M Chow
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 8(6): 653. CrossRef - Chemotherapy Education and Support: A Model for Use in the Ambulatory Care Setting
Terri Jabaley, Patricia Rizzo, Nina Grenon, Clare Sullivan, Janet Bagley, Maritza Nassif, Renee Siegel, Meghan Underhill-Blazey
Clinical Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 24(4): E43. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for Chronic Pain Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Hee-Sook Kang, Sung-Dong Hwang, Sang-Eun Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(3): 271. CrossRef
- Factors associated with post-treatment smoking among a diverse sample of cancer survivors in the US
- 2,108 View
- 35 Download
- 12 Crossref

- The Effects of prompted Voiding Therapy on Urinary Incontinence Control of Elderly Patients
- Kyung Ja Lee, Mi Kyung Kim, Hee Young Song
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(4):943-952. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.4.943
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was done to analyze the effects of prompted voiding therapy on urinary incontinence in elderly patients in an elderly care hospital. Specifically, this study looks to evaluate the effects of prompted voiding as an intervention for improving independent voiding and also identified the relationship of urinary continence to cognitive, emotional, and physical factors. The study was based on a pre-experimental design used to evaluate the effects of prompted voiding therapy on an experimental group without a control group. An experimental group of 143 patients was selected through convenience sampling from patients in an elderly care hospital. The data was collected from November 4 to December 14, 1996. Prompted voiding therapy is a behavioral therapy for managing incontinence and it is applied to patients who are cognitively impaired and dependent. In this study, the patients were asked at each designated time whether or not they had to urinate. If they answered yes, they were either given a bedpan or were assisted to the bathroom, and if the patient answered no, their diaper was checked to determine whether or not it was wet. The results were then recorded on the patients urinary voiding record. The urinary voiding score based on the model presented by Burton(1984), Burke and Walsh(1992), Chenitz, Stone and Salisbury(1991 was modified and used as a tool in this study. After forty six out of the total of 143 patients were selected for interviews through random sampling the levels of cognitive functions, mental depression and ADL(activities of daily life) within the given time frame were measured. In this study, the cognitive function was measured using the scale developed by Kabhn, Goldfarb, Pollack and Peck(1960), elderly mental depression, using the tool developed by Sheikh and Yesavage(1986), and the ADL(activities of daily living, through the Barthel Index. The data was analyzed through SPSS windows for descriptive statistics, repeated measured ANOVA and Pearson's correlation. According to the results of the study, the application of the prompted voiding therapy can improve the voiding pattern of patients. It was shown especially that incontinence could be controlled by the intervention developed according to the individual voiding pattern. In terms of the relationship between cognitive function, mental depression and ADL and the voiding function score, a close correlation was not found. It was shown that urinary incontinence can be improved through therapy even though patients have problems with their cognitive, mental and physical functions.
- 520 View
- 0 Download

- An Effect of Nursing-Logotherapy on Purpose in Life and Finding Meaning, and Hope of the patients of Mental Illness
- Jong Ji Lee
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(4):727-739. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.4.727
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to present an effective nursing intervention for helping the patients of mental illness by determining the effect of nursing-logotherapy on purpose in life and finding meaning, and hope of the patients of mental illness by developing and applicating program of nursing-logotherapy. The data was collected from March to September in 1995, and its subjects were the patients of mental illness who was appropriate to the standard of this study among the patients of mental illness who hospitalized into Neuro-Psychiatric ward of M. and B. hospital located in Pusan area. They were all 60 subjects, thirty of them for an experimental group and the rest for a control group. The research design was an equivalent control group pre-test and post-test design as an quasiexpe-rimental research and the conceptual framework was an interpersonal model. The data analysis was computerized by using SP-SS/PC+ and hypothesis testing was done with 2-way ANCOVA and simple correlation. Results were summarized as follows : 1. There were significant changes of purpose in life and finding meaning in an experimental group before and after treatment and a control group before and after. 2. There were significant changes of hope in an experimental group before and after treatment and a control group before and after. 3. The positive correlation between purpose in life and finding meaning and hope of the patients of mental illness were observed. Consequently, nursing-logotherapy could significantly increase the purpose in life and finding meaning, and of hope, so it could be said an effective nursing intervention for helping the healing of the patients of mental illness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Meaning in Life and Social Support on Posttraumatic Growth in Pancreatic Cancer Survivors
Youjin Kim, Boyoung Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2021; 30(4): 330. CrossRef
- Effects of Meaning in Life and Social Support on Posttraumatic Growth in Pancreatic Cancer Survivors
- 698 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- An Effect of Self: Care Education and Level of Resourcefulness on Active Coping in Patients with Chemotherapy
- Soon Rim Suh
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(3):639-647. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.3.639
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identify how internal and external coping resources influenced active coping in the process of stress-coping. The model was established theoretically by comparing and integrating the following theories : Stress-Coping, Self-Care, and Resourcefulness. The subjects consisted of sixty eight patients undergoing chemotherapy(experimental group 34, control group 34) at two general hospitals from January to July, 1995, The results were as follows : After self-care education, the active coping score of the experimental group was significantly higher than that of the control group. The active coping score of the high resourcefulness group was significantly higher than that of the low resourcefulness group. The interaction effect between self-care education and resourcfulness was not significant statistically. Specifically as to such scores of seeking social support, problem-oriented strategy and self care behavior, there were significantly higher in the experimental group and high resourcefulness group than in each of the other groups. Considering them both, self-care education and resourcefulness are effective nursing strategies to promote active coping including self-care. Consequently, the synthesis and testing of theories of stress-coping, self-care, and resoucefulness in this study are mostly proven to enhance the explanation and prediction of the change of active coping including self-care. Therefore the result of this study will contribute in the development of practice theory of nursing. A further study is necessary to reevaluate the interaction effect between self-care education and resourcefulness and to identify the difference between resourcefulness and self-efficacy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Self-Efficacy Promotion Program on Self-Efficacy, Self-Care Behavior, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy
Hea-Kyoung Ko, Geum Ja Park
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2011; 11(2): 136. CrossRef
- Effects of Self-Efficacy Promotion Program on Self-Efficacy, Self-Care Behavior, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy
- 562 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Changes in Fatigue and the Quality of Life of Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy
- Eun Sook Lee, Jucia Jo
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(3):489-502. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.3.489
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Quality of life(QOL) and fatigue in cancer patients receiving the radiotherapy was assessed. The subjects were 46 cancer patients who daily attended the radiotherapy department. Assessment was done on four occasions ; the first assessment was done on the treatment simulation visit, the second one was four week after treatment started, the third one at the completion of treatment and the last assessment was done between six and eight week following treatment. The results are as follows : The fatigue scores of the patients at each stage of assessment ranged from 5.49 points to 7.67 points and highest score was recorded at the third assessment hat is, at the completion of treatment. The fatigue points showed an increase from the 1st. to 3rd. stage. However, at the 4th. stage, fatigue points decreased to the level at the first stage, fatigue points decreased to the level at the first stage of assessment. QOL were assessed in three areas namely, physical, emotional and social/functional. The QOL scores in the physical area showed the highest score, followed by social/functional and emotional areas. The QOL scores decreased gradually to the third. stage of assessment thereafter recovered to the level of the first. stage. Correlation between QOL and fatigue scores during the treatment indicated that the level of QOL decreased as the level of fatigue increased. In particular, fatigue persisted after completion of the treatment and showed a significantly negative correlation with QOL. The present study strongly suggests that a strategy to restore the emotional well being level of the patient should be devised in order to improve QOL and reduce fatigue of patients receiving radiotherapy.
- 419 View
- 1 Download

- The Effect of Music Therapy on Anxiety in Neurotic Patients
- So YaJa Kim, Keum Sun Han
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(4):889-902. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.4.889
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identify the effects of music therapy on anxiety in neurotic patients. The subjects of the study were 41 patients that had been diagnosed as having anxiety disorder, neurotic depression, or somatization disorder and were admitted to one general hospital in Seoul. The 41 research subjects were assigned to an experimental (22 clients) and a control (19clients) group. Data were gathered from September. 25, 1995 to December. 15, 1995 using a questionnaire and physiological measurement tool. Data were analyzed with the SAS package using frequency, t-test, paired t-test and Pearson correlation coefficients. The results of this study are as follows; 1. There were significant differences between two groups on systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and pulse rate after treatment. In the experimental group, Systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and pulse rate decreased significantly after Music Therapy. 2. There were no significant differences between the two groups on the pre and post psychological anxiety score. But, after music therapy, experimental group had a lower psychological anxiety score than the control group. From these results, it is concluded that the music therapy can be effective in decreasing anxiety in neurotic patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Antagonistic muscular co-contraction for skilled, healthy piano technique: a scoping review
Cobi Ashkenazi, George Waddell, Aaron Williamon
Frontiers in Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Music Therapy as Intervention on Peripheral Neuropathic Pain and Anxiety of Gynecologic Cancer Patients Undergoing Paclitaxel Chemotherapy
Gie Ok Noh, Moon Sook Hwang, Keum Sook Cho, Joung Ah Lim, Mi Kyung Kang, Hyo Jin Kim, Ji Youn Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2011; 17(3): 215. CrossRef
- Antagonistic muscular co-contraction for skilled, healthy piano technique: a scoping review
- 939 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Experimental Study for Construction of Mouth Care in Chemotherpy Patients
- Young Soon Byun, Ae Kyung Kim
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(2):428-442. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.2.428
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Stomatitis is a common toxicity associated with the administration of certain cancer chemoth-erapeutic agents used in the treatment of malignant tumors. It represents one of the most distressing side effects of cancer chemotherapy and can interfere with the patient's ability to eat, be the cause of much pain and discomfort, and require the use of potent analgesics. The situation also creates favorable conditions for local infection which may lead to septicemia. Several authors have identified the need to estabilish protocols for the control and treatment of the oral discomfort associated with oral mucositis as a result of chemotherapy. Thus this study attempted to development of oral care protocol for chemotherapy patients. The effects of the mouth care using sterile normal saline, nystatine solution on oral stomatitis were investigated in 30 patients on chemotherapy. The subject were devided into three groups; control group: not gargling experimental group A: normal saline gargling (4 times a day) experimental group B: nystatine solution gar-gling(4 times a day) The Oral Assessment Guide (OAG) was used to assess oral status three times (once in the prechemotherapy period, on 5th, 10th day of post chemotherapy) Oral culture was used to assess oral infection on 5th day of postchemotherapy. Data was analyzed on SAS program which used repeated ANOVA, t-test, X2 test. The results are as follows; 1. The incidence of stomatitis was higher in the control group and experimental group A than in experimental group B. (X2=0.002 P=0.001) 2. The grade of stomatitis (mean of total score) for patients in the experimental group B were significantly lower than in the experimental group A (F=1.96 P=0.0024). 3. In incidence of tougue change, control group, experimental group B were significantly higher than experimental group B(F=6.84 P=0.0039). 4. In control group and experimental group A, oral infection due to pathogenic bacteria were identified. In conclusion, mouth care with nystatine solution four times a day could reduce the incidence of stomatitis and secondary oral infection due to stomatitis. Thus active mouth care protocol which used to nystatine solution gargling need to prevention of stomatitis in chemotherapy patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Frozen Gauze with Normal Saline on Thirst and Oral Health of the Patients with Nasal Surgery
Jin Ock Park, Young Soon Jung, Geum Ja Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2016; 22(1): 25. CrossRef - The Effect of Education and Communication for Self-Oral Care in Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Joung Hee Cheon,, Hye-Ran Lee
Health Communication, the Official Journal of Korean Academy on Communication in Healthcare.2013; 8(2): 87. CrossRef - Randomized Controlled Trial for Preventing Stomatitis and Discomfort among Acute Leukemic Patients
Chi Eun Song, Hyang Sook So, Deok Ju, Eun Jeong Kim
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2011; 11(1): 33. CrossRef - Effects of Frozen Gauze with Normal Saline and Ice on Thirst and Oral Condition of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Patients: Pilot Study
Eun A Cho, Kye Ha Kim, Jun Yeong Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(5): 714. CrossRef
- Effects of Frozen Gauze with Normal Saline on Thirst and Oral Health of the Patients with Nasal Surgery
- 733 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- The Effect of Auricular Acupressure Therapy on Anxiety of Cancer Pateint
- Kwuy Bun Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(6):888-896. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.6.888
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study wsa to necessitate auricular acupressure therapy as an independent nursing intervention on cancer paitents by confirming its effectiveness. METHOD: The experimental study was unequivalently controlled pre-post measure study. The subjects were 40 cancer patients who were hospitalized in K medical center in Seoul. The experimental group (20) and the control group (20) were randomly assigned. As measured tools, Spielberger's State-trait Anxiety (1976) measured tool by Kim's transplation (1978). The auricular acupressure therapy was applied to experimental group, and the pre-post measure was performed to both group. The data was analyzed by using SPSS computer program that included descriptive statistics, x2-test, and t-test. RESULT: 1) The experimental group with the auricular acupressure therapy showed lower trait anxiety scores in comparison with the control group (t= 8.036, p=.000). 2) The experimental group which applied the auricular acupressure therapy showed lower state anxiety scores in comparison with the control group (t= 19.616, p=.000). This result showed that cancer patients with the auricular acupressure therapy applied cancer patients decreased state anxiety and trait anxiety. Therefore , effectiveness of the auricular acupressure therapy was confirmed through this study. CONCLUSION: According to the result, anxiety of cancer pateint should be decreased and controlled by the auricular acupressure therapy as independent nursung intervension. In addition, the auricular acupressure therapy will provide effective independent nursing intervention that will decrease anxiety on patient with other disease and will improve quality of their lives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Auricular Acupressure Therapy on Primary Dysmenorrhea for Female High School Students in South Korea
Nam Hyun Cha, Sohyune R. Sok
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2016; 48(5): 508. CrossRef - Effects of Auricular Acupressure Therapy on Nocturia and Insomnia in the Elderly
Ji Yeon Kim, Hye Sook Ryu, Seok Hoon Nam, Kyung Sook Park
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2014; 17(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Menstrual Pain, Dysmenorrhea, and Academic Stress in Women College Students
Seung-Ok Ro, Hea-Young Lee, Jaeon Lee, Miyoung Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(3): 356. CrossRef - The Effect of Ear Reflexotherapy on Back Pain of Working Women in Middle Age
Kyung-Sook Park, Eun-Ho Ha, Yu-Na Kim, Soo-Jin Kwon, Lee-Jung Ru, Ju-Hyun Song, Yong-Wha Woo, Jae-Yeon Lee, In-Hee Chun, Hyun-Kyung Kang, Hee-Jung Park, Eun-Joo Lee, Jae-On Lee
Journal of muscle and joint health.2010; 17(1): 14. CrossRef - Effects of a Cognitive-Behavioral Nursing Intervention on Anxiety and Depression in Women with Breast Cancer undergoing Radiotherapy
Myung-Sook Yoo, Haejung Lee, Jung-A Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(2): 157. CrossRef
- Effects of Auricular Acupressure Therapy on Primary Dysmenorrhea for Female High School Students in South Korea
- 847 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- The Effects of Exercise Therapy and Exercise-Behavior Modification Therapy on Obesity, Blood Lipids, and Self-esteem of the Obese Middle-aged Women
- In Hong Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(6):844-854. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.6.844
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: To examine the effect of the exercise therapy, and exercise-behavior modifi- cation therapy on obesity, blood lipids and self-esteem of the obese middle-aged women. METHOD: A total of 35 middle-aged women (BMI: over 30) were selected for this research. Walking at a 50% intensity was administered 4 days a week for 12 weeks, while the behavior modification therapy performed for 60~90 minutes per week for 12 weeks. RESULT: Body weight and BMI has significantly reduced in the case of EG and E.BG. The result of comparing body weight between groups showed significant difference between EG and CG, and E.BG and CG whereas BMI showed significant difference between EG and CG only. TC, TG, LDL-C, %TC/HDL-C have shown significant decrease in EG and E-BG, while HDL-C displayed significant increase in EG and E.BG. And HDL-C showed significant decrease in CG. As for comparison between groups, significant difference was noted in EG and CG, and E.BG and CG at TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, and in EG and CG at %TC/HDL-C. Self-esteem displayed significant increase in EG and E.BG; however, there was no significant different in CG. As for comparison between groups, there was significant difference noted in E.BG and CG only. CONCLUSION: The results showed that the exercise therapy and the exercise-behavior modification therapy were effective in changing obesity, blood lipids and self-esteem of the obese middle-aged women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Minireview: A Need for an Adequate Diet Program for Postmenopausal Women with Obesity in the Republic of Korea
So Hee Park, Bo Dam Kim, Jae Hong Sang, Hae-Hyeog Lee, Tae-Hee Kim
Journal of Menopausal Medicine.2023; 29(2): 45. CrossRef - Brisk walking and lipid profile in obese subjects
B. J. Sushma, Chandra Sekhar Thiruveedhula
International journal of health sciences.2022; : 2555. CrossRef - Health Status Assessment Tool Development based on Dietary Patterns in Middle-Aged Women
Hye-Jin Lee, Kyung-Hea Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2016; 21(1): 37. CrossRef - Development and Efficacy Testing of a Social Network-Based Competitive Application for Weight Loss
Jisan Lee, Jeongeun Kim
Telemedicine and e-Health.2016; 22(5): 410. CrossRef - The Effect of Treadmill Exercise on Ischemic Neuronal Injury in the Stroke Animal Model: Potentiation of Cerebral Vascular Integrity
Kyoung Ah Kang, Hohyun Seong, Han-Byeol Jin, Jongmin Park, Jongmin Lee, Jae-Yong Jeon, Youn Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(2): 197. CrossRef
- Minireview: A Need for an Adequate Diet Program for Postmenopausal Women with Obesity in the Republic of Korea
- 729 View
- 1 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Effects of Group Art Therapy Program on Body Image and Self-esteem in College Women
- Kil Soo Chung, Seoung Eun Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(5):743-755. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.5.743
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of the study was to determine the effects of the 8-week, 16-session group art therapy program on body image and self-esteem in college women. METHOD: Data collected by self-reported questionnaires from 58 college women in Inchon who were selected by criteria of this study, from the 6 of March to 10 of May, 2002. The 11 experimental group participated in a 8-week group art therapy program. Descriptive statistics, homogeneity test, hypothesis, and reliability test were performed statistically by utilizing SPSS PC+ 8.0 program. RESULT: 1. 'The experimental group showed significantly higher scores in body image than the comparison group. 2. No significant differences were found between two groups in self-esteem. CONCLUSION: The findings showed the possibility of applying group art therapy as an effective intervention for clients with negative body image to improve their body image.
- 482 View
- 3 Download

- The Trajectory of Fatigue and Quality of Life in Stomach Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy
- Young Hee Yang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(4):482-491. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.4.482
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study aimed to identify the change patterns of fatigue and quality of life during consecutive chemotherapies and to determine the relationship of these two variables. METHOD: Stomach cancer patients receiving chemotherapy were recruited from a university hospital in Seoul. Each chemotherapy, subjects were asked to respond to the questionnaires regarding their fatigue and quality of life. The number of subjects who completed 4 cycles and over was 11. Fatigue was measured with Lee's tool(1999). Quality of life was measured with a tool revised by the author based on Padilla et al(1983). RESULT: Most patients were in 1st stage(5 patients) or 3rd stage(5 patients). Fatigue was revealed at its highest level in the 3rd or 4th chemotherapy and at its lowest level in the 1st or 6th chemotherapy. A quality of life appeared at its highest level in the 5th or 6th chemotherapy and the lowest level in 3rd or 4th chemotherapy. CONCLUSION: Among 6 cycles of chemotherapy, in 3-4th chemotherapy the fatigue was the highest and the quality of life were the lowest. Many patients decided to stop treatment at the same period. Therefore we can recognize cancer patients receiving chemo- therapy are in the highest risk at the time of the 3-4 th chemotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The “Ick” Factor: An Unrecognized Affective Predictor of Physical Symptoms During Chemotherapy
Vinayak Dev, Nathan S Consedine, Lisa M Reynolds
Annals of Behavioral Medicine.2021; 55(4): 345. CrossRef - Are coping styles better predictors of quality of life amongst patients undergoing chemotherapy than psychological distress?
Vinayak Dev, Nathan S. Consedine, Lisa M. Reynolds
Psycho-Oncology.2019; 28(4): 934. CrossRef - A Longitudinal Path Analysis of Symptom, Fatigue and Quality of life in Patients with Colorectal Cancer during Chemotherapy
Eun Hee Kim, Soon Rim Suh
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2018; 43(3): 200. CrossRef - The Effects of Integrated Intervention Program for Community Dwelling Cancer Patients' Quality of Life, Depression and Self Care Agency
Young Sil Kang, In Soo Kwon, Eunyoung Hong
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(3): 445. CrossRef - Factors affecting the Fatigue of Hospitalized Women Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy
Kyunghee Kim, MyoSuk Lee, Yeunhee Kwak, Ji-Su Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(3): 182. CrossRef - Causal relationships among factors associated with cancer-related fatigue
YoungMin Seo, HyunSoo Oh, WhaSook Seo
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2010; 14(5): 380. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life in Patients with Gastrointestinal Neoplasms
Eun Ok Lee, Aeyong Eom, Rhayun Song, Young Ran Chae, Paul Lam
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 649. CrossRef
- The “Ick” Factor: An Unrecognized Affective Predictor of Physical Symptoms During Chemotherapy
- 749 View
- 2 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of Aromatherapy on the Stress Response of College Women with Dysmenorrhea during Menstruation
- Sun Hee Han, Myung Haeng Hur, Ji Yeon Kang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(3):317-326. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.3.317
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to verify the effect of aromatherapy on the stress response in menstrual period. METHODS: A randomized, single-blind, pretest- posttest design was used. The study subjects were 60 college women with dysmenorrhea and they were randomized into 3 groups, experimental, 1st control(placebo) and 2nd control group. The researchers massaged treatment oil(3% dilution essential oil of Lavender, Clary sage and Rose) into the abdomen of experimental group. The placebo group used almond oil(carrier oil) instead, and the 2nd control group did not give any treatment. Baseline data including pre- treatment stress response score were obtained on the first day of usual period. Aromatherapy provided for about 7 days until the next cycle began. Post-treatment stress responses were measured by 94 item SOS(symptom of stress) scale on the first day of the cycle. RESULTS: As a results, the stress response score of experimental group was significantly lower than two control groups. And there was no significant difference in stress responses of two control groups. CONCLUSION: The results show aromatherapy using selected essential oils to be an effective intervention for stress response during menstruation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Plant Essential Oils on Physiological Changes
Cho Sin Won
Journal of Environmental Science International.2024; 33(5): 333. CrossRef - Evaluating the effectiveness of applying aroma seals to masks in reducing stress caused by wearing masks: A randomized controlled trial
Nobuyuki Wakui, Kotoha Ichikawa, Aika Okami, Hinako Kagi, Shoko Kawakubo, Chikako Togawa, Raini Matsuoka, Mai Watanabe, Miho Yamamura, Shunsuke Shirozu, Yuika Tsubota, Yukiko Yoshizawa, Yoshiaki Machida, Kamal Sharma
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(11): e0294357. CrossRef - Evaluation of aromatherapy with lavender oil on academic stress: A randomized placebo controlled clinical trial
Rizwan Ahmad, Atta Abbas Naqvi, Hamdan Moayed Al-Bukhaytan, Ahmed Habib Al-Nasser, Ali Hassan Baqer Al-Ebrahim
Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications.2019; 14: 100346. CrossRef - Impact of Menstrual Attitudes, Premenstrual Syndrome, and Stress Response on Quality of Life among Nursing Students
Hee Jin Jang, Mi-Hae Sung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(4): 346. CrossRef - Dysmenorrhea, Back Pain, and Muscular Endurance, Angle of the Trunk in High School Girl Students and Women University Students
Young Taek Doo, Yeon Woo Jeong
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2017; 42(3): 269. CrossRef - Biosignals Analysis for Kidney Function Effect Analysis of Fennel Aromatherapy
Bong-Hyun Kim, Dong-Uk Cho, Ssang-Hee Seo
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - The Ear Acupressure Therapy on Premenstrual Syndrome and Dysmenorrhea on Female college Students
Hye-Myoung Choung, Ju-Seung Song
Journal of the Korea Society of Computer and Information.2013; 18(5): 87. CrossRef - The Effect of Aroma Therapy on Well-being in Hospice Patients
Heeok Park, Youngmi Chun, Suyoung Kwak
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2013; 19(1): 7. CrossRef - Effects of Aroma Inhalation Method on Test Anxiety, Stress Response and Serum Cortisol in Nursing Students
Ye-Jung Ko, Myoung-Soon Jung, Kyung-Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2013; 20(4): 410. CrossRef - Effects of Aromatherapy on Depression, Anxiety and the Autonomic Nervous System in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Adjuvant Radiotherapy
Sun Hee Yun, Jung Hee Cha, Yang Sook Yoo, Yeong In Kim, Su Mi Chung, Hea Lim Jeong
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2012; 15(2): 68. CrossRef
- Effects of Plant Essential Oils on Physiological Changes
- 913 View
- 2 Download
- 10 Crossref

- The Nutritional Status of the Patients with Cancer during the Chemotherapies
- Young Hee Yang, Sung Joon Kwon, Chang Imc Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(6):978-987. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.6.978
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to determine the changing patterns of nausea, vomiting, anorexia and calorie intake. To examine the influence of those variables on the nutritional status of the cancer patients receiving chemotherapy.
METHOD
To assess nutritional status, anthropometry and blood test were performed on 94 stomach cancer patients receiving postoperational chemotherapy on the daily basis. NVA and calorie intake were measured during chemotherapy.
RESULT
93% of subjects had low level of hemoglobin and 45.7% was below the lymphocyte count. 57% of subjects lost 10% of usual weight. The value of anthropometry was reduced but the difference between pre- and post-chemotherapy did not reach any statistical significance. 27% of subjects was grouped into the malnutritional state. During chemotherapy, the higher the degree of NVA, the less calorie intake. The significant predictors for nutritional status were nausea and calorie intake.
CONCLUSION
The chemotherapy affected the food intake of cancer patients through NVA. Though the influence of chemotherapy on anthropopmetry was not significant in this research, nausea and food intake were the most affecting factors for nutrition of cancer patients. Therefore we need to assess nutritional status and support for cancer patients receiving chemotherapy and to develop an intervention for improvement of symptoms and food intake.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Knowledge of and Compliance with Neutropenic Diet in Patients with Hematologic Malignancy undergoing Chemotherapy
Ok Kyung Jeon, Yeon Hee Lee, Myung Hee Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(2): 75. CrossRef - Trends in Nursing Research on Cancer Patients Nutrition in Korea
Su-Ol Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2016; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of Loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.) Ethanol Extracts of Different Aerial Parts on Antioxidant Activity and Antiproliferation of Human Cancer Cells
Hwan Lee, Yeon-Kyoung Kim, Hyun-Joo Lee, Jae-Joon Lee
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2016; 27(2): 211. CrossRef - Hindlimb Muscle Atrophy Occurs From Short-Term Undernutrition in Rats
Jee Yoon Kim
Biological Research For Nursing.2013; 15(4): 459. CrossRef - Pre- and Post-Transplant Nutritional Assessment in Patients Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Mi Young Park, Jeong Yun Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(1): 110. CrossRef - Nutritional Intake and Nutritional Status by the Type of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Eun Jin So, Ji Sun Lee, Jee Yeon Kim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2012; 1(1): 3. CrossRef - The Effect of Continuous Nutritional Education and Oral Mucositis Management on Nutritional Status of Patients Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Kyoung Soon Park, Byung Hwa Lee, Ho Ran Park
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2010; 10(2): 119. CrossRef - Analysis of the Factors Relating Nutritional Status in Discharging of Leukemia Patients Receiving Chemotherapy
Eunjin So, Jeeyeon Kim, Sujin Jung, Sook Park
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2010; 43(1): 26. CrossRef - Adequacy of Nutritional Support and Reasons for Underfeeding in Neurosurgical Intensive Care Unit Patients
Hwasoon Kim, Jeong Ae Shin, Jae Youn Shin, Ok Min Cho
Asian Nursing Research.2010; 4(2): 102. CrossRef
- Knowledge of and Compliance with Neutropenic Diet in Patients with Hematologic Malignancy undergoing Chemotherapy
- 770 View
- 2 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Typological Study on Attitudes of Alternative Therapy Among Cancer Patients
- Jin Kyung Kim, Boon Han Kim, Mi Hyang Lee, Hwa Jeong Kang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(7):1718-1728. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.7.1718
-
 Abstract
Abstract
The purpose of this study is to identify and classify the different types of cancer patients who use alternative therapies, to understand their subjective frameworks in using such alternative therapies. The results of this study provided the subjective information on five types of attitudes towards alternative therapies and described characteristics of five types from 30 cancer patients. The "Dependent to Others" (the first type) decided to use alternative therapy because they were influenced by the experiences of others and invocations of the family (especially spouse) or close relatives. In general, they did not believe that it will cure the diseases but generally thought it was not harmful and it may be better than doing nothing. There were a group of patients who chose to use alternative therapy with vague hope and belief. These patients decided to try alternative methods with their own convictions and confidences because they have personally seen or heard about some people who had been cured miraculously. This group of patients was grouped as "Belief in Effects (second type)." Although, there is a very little chance for miracles, "Expecting for Effects (third type)" believed alternative therapy will strengthen immune systems, help with feces and urine, change physical constitutions, slow down the progression of cancerous cell, have no side-effects, and expects to have practical effects and uses. The fourth group of patients thought foods in alternative therapies were same as general foods, therefore, it was easy to take, did not expect miracles to happen but considered the alternative therapy as supplementary treatments. This "Supplementary for Effects (fourth type)" patients thought it was their duty to do everything possible. The last type was "Expecting for Miraculous Effects (fifth type)." The patients in this group were devastated and thought of alternative treatments as the last hope for miracles. They thought it would relieve their physical pains, reduce the chance of side effects from chemical treatments, help them for comfortable and painless death, and considered it as the last possible option with expecting for miracles. The result of this study has implications to provide practical and concrete guidelines for caring and nursing cancer patients using alternative therapies. It will be used as a tool to work on independent for nursing intervention. Furthermore, the result of study will provide practical guidelines to help develop better tools and nursing intervention strategies to nurse cancer patients.
- 454 View
- 0 Download

- Effect of Aromatherapy Massage on the Mood, the Milk ejection Reflex, and the Immunoglobulin A of the Breast Milk of Mothers with a Cesarean Section Delivery
- Sung Hee Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(5):1357-1367. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.5.1357
-
 Abstract
Abstract
The purpose of this quasi-experimental study was to explore the effect of aromatherapy massage on the mood, the milk ejection reflex, and the immunoglobulin A of the breast milk of mothers who gave birth through a Cesarean section delivery. Twenty mothers who had Cesarean section were selected as an experimental group, and twenty-two were in the control group. Lavander and Rosemary oil mixed with Jojova carrier oil was used to massage the back, both axillar and breasts. Aromatherapy massage was done once a day for 20 minutes by the researcher. Each session consisted of 4 minutes for warm-up, 14 minutes for massage and 2 minutes for closure. The levels of IgA within the breast milk was analyzed by an immunoturbidimeter assay (Cobas INTEGRA, Roche, Swiss) before and after aromatherapy massage. Mood and milk ejection reflex were measured by self-reports at the same time. The data were analyzed using SPSS 7.5 and the hypotheses were tested by ANCOVA and the Pearson coefficient correlation. The results were as follows: 1) Score of mood increased significantly after the use of aromatherapy massage. 2) Score of milk ejection reflex increased significantly after the use of aromatherapy massage. 3) Level of IgA of breast milk did not change significantly after the use of aromatherapy massage. 4) After the use of aromatherapy massage, there wasn't any correlation among mood, milk ejection reflex, and level of IgA of breast milk. In conclusion, the results suggest that aromatherapy massage is an effective nursing intervention to enhance the mood and the milk ejection reflex and to increase the rate of breastfeeding in the breastfeeding mothers under stresses like a Cesarean section.
- 511 View
- 0 Download

- The Effects of Chu-ma Therapy on Decreasing Blood Pressure in Essential Hypertension
- Nam Sun Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(4):967-981. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.4.967
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effects of Chu-ma therapy and to suggest that the therapy is an effective nursing intervention tool to reduce blood pressure. The research design employed was the non-synchronized research method with non- equivalent control group. A total of 30 people with essential hypertension, who were from forty to sixty five years old, participated in the study. The Chu-ma therapy was administered by every day for ten or fifteen minutes for eight weeks from 19, April to 13, June in 1999. In order to evaluate the effects of Chu-ma therapy, blood pressure of the two groups were measured once a week, and physiological parameters (epinephrine, norepinephrine, total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, triglycerides) were measured before and after the treatment. Collected data was analyzed by SAS package. The results of this study can be summarized as follows: 1) There were significant decrease in systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure in the experimental group. 2) There were no significant changes in epinephrine, norepinephrine of the two groups. 3) There were significant decrease in total cholesterol and triglycerides, and HDL- cholesterol increased significantly in the experimental group. 4) The effect of Chu-ma therapy on the measured time on the blood pressure in experimental group was as follows: Both of systolic and diastolic blood pressures were significantly decreased after 5weeks. The result proved that Chu-ma therapy is an effective nursing intervention tool for clients with essential hypertenion. However further research is still necessary to compare the effect with the different periods and number of times for Chu-ma therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Qi Massage Program on the Physio-psychological State of Industrial Employees with Hypertension
Yoon Ju Han, Kyung Sook Kang
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2014; 20(2): 73. CrossRef - Effects of Aroma inhalation on Blood Pressure, Pulse Rate, Sleep, Stress, and Anxiety in Patients with Essential Hypertension
Eun-Mi Choi, Kyung-Sook Lee
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2012; 14(1): 41. CrossRef - The Effects of Hypertension Self-help Program on Hypertension-related Knowledge, Self-efficacy, Self-management Compliance and Physiological Parameters in Workers
Mi-Young Gi, Young-Hae Park
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2012; 21(1): 1. CrossRef
- Effects of a Qi Massage Program on the Physio-psychological State of Industrial Employees with Hypertension
- 683 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Effects of Group Imago Psychotherapy on Comfort and Depression of Patients with Hemodialysis
- Gui Yun Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):791-798. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.791
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The hemodialysis patients with chronic renal disease have experienced negative emotions, especially depression among with physical, social, and psychological changes. Based upon a stress-coping theory, group imago psychotherapy which can induce effective coping through self awareness and positive emotional responses is implemented to the hemodialysis patients. The effects of the imago psychotherapy in regards to comfort and depression are studied here. Group imago psychotherapy was performed on forty-three subjects(twenty subjects in the experimental group and twenty-three subjects in the control group). The results of the study were as follows. After being given group imago psychotherapy, the comfort scores of the experimental group were significantly higher than those of the control group (F=15.33, p= .003). Moreover, after being given treatment, the depression scores of the experimental group were significantly lower than those of the control group (F=9.14. p=.0044). Specifically, the scores on comfort in the experimental group under emotion-focused coping style were significantly higher than those of the control group (F=18.59, p= .0002). The mean difference on comfort scores in the experimental group under problem - focused coping style was higher than that of the control group. But their scores were not significant (F=0.19, p= .6729). The scores on depression in the experimental group under emotion-focused coping style were significantly lower than those of the control group (F=14.62, p= .0006). The mean difference on depression scores in the experimental group under problem - focused coping style was much lower than that of the control group. But their scores were not significant (F=0.31, p=.5947). There was a significant positive correlation between comfort and depression variables. After group imago psychotherapy the hemodialysis patients recognized positive changes in emotional reponses, self awareness, self control, ease of mind, and felt overall more relaxed. Imago psychotherapy is a nursing intervention which as this study has shown can improve to comfort. The
results
of this study can be applied to general nursing practices. In the view of holistic nursing, the development of the nursing practice combined with imago psychotherapy will contribute to the enlargement of the nursing field with conventional nursing practices.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigation of the comfort level of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease within the scope of Kolcaba's comfort theory
Aylin Bilgin, Goncagul Aldan, Leyla Ozdemir, Sibel Gunay
Applied Nursing Research.2025; 83: 151964. CrossRef
- Investigation of the comfort level of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease within the scope of Kolcaba's comfort theory
- 602 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Relationship of Anorexia, Nausea, Vomiting, Oral Intake and Nutritional Status in Patients Receiving Chemotherapy
- Young Hee Yang, Dong Sun Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):720-730. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.720
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Malnutrition is a common problem in cancer patients. In addition anticancer drugs used in chemotherapy as a major therapeutic mode are famous as the side effect like nausea, vomiting, which lead the patients to malnourished state. This study was to determine the relationship of anorexia, nausea, vomiting and oral intake and identify the influence these side effects on the nutritional status in patients receiving chemotherapy. To assess the nutritional status, anthropometry such as weight, height, body mass index(BMI), body fat proportion, and triceps skinfold thickness, and biochemistry test such as hemoglobin and lymphocyte were measured at the pre- and post- chemotherapy and the readmission time, all three times. During chemotherapy, anorexia, nausea, and vomiting using a VAS or 5-point scale and 24 hour oral intake using a food record were measured daily. Forty-nine patients knowing their diagnosis and receiving chemotherapy were recruited from an oncological ward in a general hospital for 5 months and they were reduced 31 at readmission time for a next chemotherapy. The results were as follows. Most subjects (93.6%) were in the 4th stage of cancer and 57.1% of subjects were in the first or the second chemotherapy. In most subjects(82.6%), their weight was decreased 10.7% than as usual. The degree of anorexia, nausea, and vomiting was significantly higher and the amount of oral intake was significantly less during the chemotherapy than at the pre-chemotherapy. Weight, BMI, triceps skinfold were reduced more at the post- chemotherapy than the pre-chemotherapy and were recovered the nearly same but less level at the readmission time. Body fat proportion was increased at the post chemotherapy and then decreased at the readmission phase. Hemoglobin and the number of lymphocyte were below normal at the pre-chemotherapy and more reduced at the readmission time. Anorexia, nausea, and vomiting were related positively and oral intake was negatively related with nausea and vomiting. The nutritional status at the post- chemotherapy and the readmission time was explained 20% over by the side effect like anorexia, nausea, vomiting and oral intake during the chemotherapy. The significant nutrition predictors at the post- chemotherapy were vomiting and the significant predictors at the readmission time were anorexia, vomiting, and oral intake. These results indicated the patients receiving chemotherapy were continued to deteriorate the nutritional status. Therefore nurse should have knowledge how much the nutritional status can be affected and assess the nutritional status periodically and try to find out the intervention for side effects from the series of chemotherapies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oral nutrition supplement improves nutrition and inflammation of cancer patients by regulating iron metabolism
Xuelong Li, Changxing Cui, Wenjing Gong, Guangrun Li, Fubo Song, Peng Huang
International Journal of Food Properties.2023; 26(1): 1304. CrossRef - Nutritional Intervention Improves Nutrition Outcomes in Stomach and Colon Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy: Finding from a Quasi-Experiment in Vietnam
Le Thi Huong, Duong Thi Phuong, Dang Kim Anh, Phung Lam Toi, Nguyen Le Tuan Anh, Trinh Le Huy, Nguyen Thuy Linh
Healthcare.2021; 9(7): 843. CrossRef - The Effect of Nutrition Intervention with Oral Nutritional Supplements on Pancreatic and Bile Duct Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Seong Hyeon Kim, Song Mi Lee, Hei Cheul Jeung, Ik Jae Lee, Joon Seong Park, Mina Song, Dong Ki Lee, Seung-Min Lee
Nutrients.2019; 11(5): 1145. CrossRef - Nutritional treatment with an immune-modulating enteral formula alleviates 5-fluorouracil-induced adverse effects in rats
Kentaro Nakamura, Hidekazu Tonouchi, Akina Sasayama, Taketo Yamaji, Kinya Ashida, Juan J. Loor
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(11): e0225389. CrossRef - Nutritional Intervention Using Nutrition Care Process in a Malnourished Patient with Chemotherapy Side Effects
Hye-Ok Lee, Jung-Joo Lee
Clinical Nutrition Research.2015; 4(1): 63. CrossRef - Hindlimb Muscle Atrophy Occurs From Short-Term Undernutrition in Rats
Jee Yoon Kim
Biological Research For Nursing.2013; 15(4): 459. CrossRef - Energy Intake and Fatigue in Patients Receiving Chemotherapy
Mi Suk Byun, Na Hyun Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2012; 14(4): 258. CrossRef - Effects of Individualized Nutritional Education Programs on the Level of Nutrient Intake and Nutritional Status of Colorectal Cancer Patients Undergoing Palliative Chemotherapy
Kwi Ock Park, Smi Choi-Kwon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(6): 799. CrossRef - Nutritional Intake and Nutritional Status by the Type of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Eun Jin So, Ji Sun Lee, Jee Yeon Kim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2012; 1(1): 3. CrossRef - Nursing interventions to promote dignified dying in South Korea
Kae-Hwa Jo, Ki-Wol Sung, Ardith Z Doorenbos, Elizabeth Hong, Tessa Rue, Amy Coenen
International Journal of Palliative Nursing.2011; 17(8): 392. CrossRef - The Effect of Continuous Nutritional Education and Oral Mucositis Management on Nutritional Status of Patients Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Kyoung Soon Park, Byung Hwa Lee, Ho Ran Park
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2010; 10(2): 119. CrossRef - Analysis of the Factors Relating Nutritional Status in Discharging of Leukemia Patients Receiving Chemotherapy
Eunjin So, Jeeyeon Kim, Sujin Jung, Sook Park
The Korean Journal of Nutrition.2010; 43(1): 26. CrossRef - A Survey of Cancer Patients Who Visited Emergency Room
Sun-Ae Yang, Ok-Hee Cho, Yang-Sook Yoo
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2009; 12(4): 228. CrossRef
- Oral nutrition supplement improves nutrition and inflammation of cancer patients by regulating iron metabolism
- 1,292 View
- 4 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Deducing Coronary Artery Disease Anxiety through Musical Therapy and Providing Information
- Mi Suk Kang, Kyung Min Park, Chung Ja Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):380-390. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.380
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was performed to evaluate the effectiveness of music therapy as one of the psychiatric nursing intervention tools, with addtional information in relieving anxiety during the procedure. Data were collected through nonequivalent pre-and post tests from July 1, 1998 to September 30 1998 in 90 patients (test group A: 28 patients, test group B: 27 patients, control group: 33 patients) who were hospitalized in DongSan Medical Center in order to have cardiac catheterization. The Subjects were informed by educational videos, which were modified according to the sensory information of the 10 study patients. They were based on the informative booklet by Kim keum-soon (1989). The procedural information was also modified according to the hospital`s customs. Provided the music for patients suitable to their tastes, and measured their blood pressure, heart rate, the degree of anxiety using the Spielberger`s measurement device of anxiety, and behavioral response of Finesilver`s. The statistical significance was analyzed using chi-square test and ANOVA. The results of this study were as follows : Hypothesis 1 : There are significant differences in the degree of anxiety among test group A, Test group A was provided only information, Test group B was provided information and the control group was provided neither. Hypothesis 2 : There are significant differences in systolic blood pressure among test group A, test group B, and control group.: non-significant. Hypothesis 3 : There are significant differences in diastolic blood pressure among test group A, test group B, and control group.: significant(F=1.31, p=.27, interaction; F=3.80, p=.00). Hypothesis 4 : There are significant differences in heart rate among test group A, test group B, and control group.: non-significant. Hypothesis 5 : There are significant differences in behavioral responses among test group A, test group B, and control group.: significant(F=10.05, p=.00). Further validation study is required with other subjects and other settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Patient-Selected Music Listening on the Pain and Anxiety of Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Randomized Controlled Trial
SukKyong Kim, HyeonCheol Jeong
Healthcare.2021; 9(11): 1437. CrossRef - Effects of Aromatherapy on Stress Responses, Autonomic Nervous System Activity and Blood Pressure in the Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun Jeong Song, Mi Young Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of Music Listening on Pain, Anxiety, and Vital Signs of Burn Patients
Jungtae Son, 김선화, LeeEunJoo
Korean Journal of Music Therapy.2009; 11(1): 124. CrossRef
- Effects of Patient-Selected Music Listening on the Pain and Anxiety of Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 713 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Analysis of Exercise Therapy in Nursing Research
- Jum Yi Jun
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):319-330. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.319
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study is aimed at analyzing the trend of research on the use of exercise in nursing research, through suggesting directions for future research and implementation of the various exercise therapies. Research studies were taken from dissertations and theses selected from the Academic Society Journals of nursing science, Journals from universities, medical and nursing schools, research institutes in various universities, the Central Journal of Medicine, and the New Medical Journal. The research published between 1970 and 1997 in Korea were analyzed, 51 research were selected. The research are analyzed according to: published time, source of the research, research design, subjects, sample size, dependant variables, exercise therapy, and effect of exercise therapy. The results were as follows: 1. Research on exercise therapy increased rapidly in the 1990's. At this time, 88.2% of research was published. 2. Research areas included: 54.9% non- degree research, 27.5% Doctoral theses, and 17.6% Master's theses. 3. The experimental design included: 66.7% non- equivalent control group pre-test/ post-test design and 29.4% one group pre-test/post- test design. 4. Out of the Subjects: 52.9% were patients with various health problems, and 47.1% were healthy individuals. 5. Sample size included: 52.9% with above 31 subjects, 11.8% with 11~15 and 26~30. 6. Exercise therapy was analyzed by type, intensity, frequency, duration, and period. 1) The Types: Aerobic exercise at 60.8% was the most common, active exercise for muscle strengthening and building made up 21.6%. 2) Exercise with 40~65% intensity comprised 25.5%, 70~85% with 7.8%, and no description of the intensity was 66.7%. 3) Frequency of 3~5 per week was the most common at 78.4%. 4) Duration: 15~60 minutes was the most common length of time at 76.5%. 5) Periods: More than 5 weeks at 82.3% were the most common in their categories. 7. Dependant variables: Psychological response was measured as a dependant variable in 92.2%, Cardio-pulmonary function 88.2%, Body Composition was 86.3%, Physical Response was 60.8%, Lipid Metabolism was 58.8%, Physical Strength was 49.0%, Glucose Metabolism was 25.5%, Activities of Daily Living was 17.6% and others added to be 3.9%. 8. The effect of Exercise Therapy was categorized into 'positive', 'partially positive', and 'no effect' according to dependant variables: Having a positive effect - Glucose Metabolism (93.3%), Physical Response (85.0%), Activities of Daily Living (81.8%), Psychological Response (71.6%), Lipid Metabolism (67.6%), Cardio- pulmonary Function (63.6%), Physical Strength (68.1%), and Body Composition (56.4%). The following suggestions can be made on the above findings: 1. Research findings on Exercise Therapy as a Nursing Intervention need to be described by their elements of type, intensity, frequency, duration and period. 2. Toproperly study the positive effects of Exercise Therapy, there needs to be (1) appropriate research design, (2) selection criteria for the subjects (3) contents of exercise prescription to individuals or groups (4) measurement criterion for the dependent variables. 3. Meta-analysis on exercise therapy also needs to be done to analyze and integrate the various results.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of a stage-matched intervention to promote exercise behavior in participants with type 2 diabetes
Chun-Ja Kim, Ae-Ran Hwang, Ji-Soo Yoo
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2004; 41(8): 833. CrossRef
- The impact of a stage-matched intervention to promote exercise behavior in participants with type 2 diabetes
- 562 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Meta-Analysis of Effects of Relaxation Therapy on Anxiety and Blood Pressure
- Hee Seung Kim, Hae Hiang Song, So Eun Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):282-292. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.282
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A meta-analysis of 14 quasi-experimental studies was conducted to compare the effect of size on various relaxation therapies applied to patients and health volunteer students. These studies were selected from theses, dissertations and papers that have been done between 1982 to 1993. Also They have a randomized or nonequivalent control group in a pre test-post test design. The studies were evaluated in different ways; 1) types of relaxation therapy, 2) total amount of time of relaxation therapy, and 3) types of outcome variables. For a group of homogenious studies, the weighted mean effect size and standard error were estimated. Some findings are summarized as follows : 1. Jacobson relaxation therapy had a larger effect on systolic and diastolic blood pressures than on state anxiety. 2. For the total time of relaxation therapy, (longer than 60 minutes) had a much larger effect in decreasing systolic and diastolic blood pressures than in the case of a time period shorter than 60 minutes. 3. Relaxation therapy applied to surgery patients also had a larger effect in decreasing state anxiety than when applied to other patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Abdominal Breathing on Anxiety, Blood Pressure, Peripheral Skin Temperature and Saturation Oxygen of Pregnant Women in Preterm Labor
Soon-Bok Chang, Hee-Sook Kim, Yun-Hee Ko, Choon-Hee Bae, Sung-Eun An
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(1): 32. CrossRef
- Effects of Abdominal Breathing on Anxiety, Blood Pressure, Peripheral Skin Temperature and Saturation Oxygen of Pregnant Women in Preterm Labor
- 726 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of Group Art Therapy Program on Self-Esteem and Mental Health Status in Chronic Schizophrenic Inpatients
- Kil Soo Chung
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(6):1314-1323. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.6.1314
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of the study was to determine the effects of the 8-week, 15-session group art therapy program on self-esteem and mental health status in chronic schizophrenic inpatients. The sample consisted of two groups of chronic schizophrenic inpatients: 10 patients with an average of total disease duration of 8.90 years who participated in a 8-week group art therapy program, and 8 comparison subjects with an average of total disease duration of 8.25 years who did not participate in the program. A pretest-posttest quasiexperimental design was used to assess self-esteem and mental health status at the beginning and at the end of the 8-week, 15-session group art therapy program. The time points for obtaining data were matched for both groups. The effectiveness of the 8-week group art therapy program was assessed by Rosenberg's Self-esteem Scale(Rosenberg, 1965) and SCL-90- R(Derogatis et al., 1973). SPSSWIN 8.0 was utilized for data entry and analysis employing Mann-Whitney U test. The findings of the study indicated the followings: (a) No significant differences were found between two groups in self-esteem and (b) The experimental group showed significantly lower scores in obsessive-compulsive symptom dimension and interpersonal sensitivity symptom dimension on the SCL-90-R than the comparison group after participating in the group art therapy program. In conclusion, the findings showed the possibility of applying group art therapy as an effective nursing intervention for patients with lack of verbal communication skills and social interaction to improve their interpersonal relationship.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of an Integrated Health Care Program on the Physical, Psychosocial, and Spiritual Health of People with Mental Disorder in Community
Gwang Ha Jung, Young Ran Chin
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(2): 69. CrossRef
- The Effects of an Integrated Health Care Program on the Physical, Psychosocial, and Spiritual Health of People with Mental Disorder in Community
- 832 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Theoretical Bases and Technical Application of Breathing Therapy in Stress Management
- Pyoung Sook Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(6):1304-1313. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.6.1304
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Breathing is essential for life and at the same time takes a role as a antidote for stress. In the Orient, it was recognized early that respiration, mind, and body have a relation that is inseparable and therefore proper breathing is so important. However, since the mechanism of therapeutic effect by breathing have not been verified, the treatment has been continued till recent years. From that which originated in the Orient, several techniques in the west have been developed to regulate breathing, and have been applying to the clinical situation and to studies, however scientific studies are still lacking. Recently, relaxed breathing has been used as an efficient strategy for breathing therapy as it has an effect on reducing physiological tension and arousal, and, therefore can be used as a basic technique to control or manage stress. In this study, in order to provide basic information and guidelines for clinical application, which will aid in the application of the theoretical basics of breathing therapy and its technique, a review of the literative was conducted. The findings are as follows: 1. Since proper breathing not only has, physically, the important function in supplying oxygen to the body but also gives a good emotional, or pleasant state of mind, it is the first step in controlling physical and mental health. 2. The basic types of breathing can be classified into two types; 'diaphragmatic breathing(relaxed breathing)' and 'chest breathing(stress breathing)'. In yoga type breathing, there are four kinds of breathing, 'upper breathing', 'mid breathing', 'down breathing', and 'complete breathing'. 3. The theoretical explanation of the positive thera peutic effect of breathing therapy techniques exemplifies good brain function, sufficient air flow through the nasal passages, diaphragmatic movement, light vagal stimulation, CO2 changes and cognitive diversion but in most studies, the hypothesis of CO2 is supported. 4. The technique of breathing is designated with many names according to the muscles and techniques used for breathing, and for control of stress, diaphragmatic breathing(relaxed breathing) is explained as a basic technique best used to manage of stress. 5. The relaxed-breathing includes slow diaphragmatic breathing, breath meditation, nasal breathing, yogic abdominal breathing, Benson's relaxed response, and quiet response.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improvement of Thoracic Spine-Originated Dyspnea and Chest Tightness Through Acupotomy and Breathing Therapy: A Case Report
Jiwon Park, Jungtae Leem, Gawon Choe, Hanbit Jin
Korean Journal of Acupuncture.2025; 42(1): 32. CrossRef - Immersive Innovations: Exploring the Diverse Applications of Virtual Reality (VR) in Healthcare
Chaitanya Kumar Javvaji, Harshitha Reddy, Jayant D Vagha, Amar Taksande, Anirudh Kommareddy, Naramreddy sudheesh Reddy
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Comparison of Changes in Pulmonary Function and Respiratory Muscle Strength in Young Adults According to the Abdominal Breathing Exercise Methods
Min-Su Kim, Sam-Ho Park, Myung-Mo Lee
Annals of Applied Sport Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Virtual Reality for Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Comprehensive Review
Melpo Pittara, Maria Matsangidou, Constantinos S Pattichis
JMIR Rehabilitation and Assistive Technologies.2023; 10: e47114. CrossRef - Association of Nose Size and Shapes with Self-rated Health and Mibyeong
Ilkoo Ahn, Kwang-Ho Bae, Hee-Jeong Jin, Siwoo Lee
Journal of Physiology & Pathology in Korean Medicine.2021; 35(6): 267. CrossRef - A Study on the Assistant Device for the Treatment of Hypertension by Breathing Exercise
Baek-Ki Kim
JOURNAL OF ADVANCED INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND CONVERGENCE.2019; 9(1): 47. CrossRef - A Study on Breathing Method of Healing as a Health-Oriented Leisure Activity
Ji-Sun Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(8): 140. CrossRef - The effects of relaxation breathing on procedural pain and anxiety during burn care
Eunok Park, Hyunjin Oh, Taeim Kim
Burns.2013; 39(6): 1101. CrossRef - Effects of Abdominal Breathing on Anxiety, Blood Pressure, Peripheral Skin Temperature and Saturation Oxygen of Pregnant Women in Preterm Labor
Soon-Bok Chang, Hee-Sook Kim, Yun-Hee Ko, Choon-Hee Bae, Sung-Eun An
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(1): 32. CrossRef
- Improvement of Thoracic Spine-Originated Dyspnea and Chest Tightness Through Acupotomy and Breathing Therapy: A Case Report
- 936 View
- 7 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Effect of Aromatherapy on Skin Xerosis and Pruritus in Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis
- Hyae Chung Ha
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(6):1284-1293. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.6.1284
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was designed to investigate the effect of aromatherapy on skin xerosis and pruritus in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. Twenty one subjects of this study were selected from St. Paul's Hosipital in Seoul. All the subjects were received the mineral oil massage at the arm without fistular three timesper week for 4 weeks. After 2 weeks period of wash-out, the subjects were received the aromatherapy of lavender and tea tree essence oil in the same way. This study was carried out from March 20 to June 13, 1998. Pruritus score, skin pH and stratum corneum hydration were measured before and after each treatment. But, biochemical parameters were measured before the treatment of the mineral oil massage, after the treatment of the mineral oil massage and the aromatherapy. Data of this study were analyzed by paired t-test, repeated measures ANOVA, Bonferroni multiple comparisons and Pearson correlation coefficient. The results were as follows: 1. Pruritus score was significantly decreased after the aromatherapy, while no significant change after the treatment of the mineral oil massage. Therefore, there was a significant difference in the priritus score between the two treatments. 2. Stratum corneum hydration was significantly increased after the aromatherapy, while no significant change after the treatment of the mineral oil massage. Therefore, there was a significant difference in the stratum corneum hydration between the two treatments. 3. Skin pH was significantly increased after the treatment of the mineral oil massage, while no significant change after the aromatherapy. Therefore, there was no significant difference in the skin pH between the two treatments. 4. After the aromatherapy, the serum calcium was significantly increased. Whereas the serum parathyroid hormone intact was significantly decreased compared with the treatment of the mineral oil massage. But the level of the serum Ca and PTH-intact were within the normal range. 5. Stratum corneum hydration was decreased corresponding to the duration of hemodialysis, while pruritus score and skin pH showed no change corresponding to the duration of hemodialysis and the age of the subjects. The correlation of pruritus score on skin pH, stratum corneum hydration and biochemical parameters was not significant. In conclusion, this findings indicate that aromatherapy may be effective in decreasing skin xerosis and pruritus score in uremic pruritus patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Pruritus, Skin Dryness, and Depression in Hemodialysis Patients
Eunyoung Choi, Kyungsook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 69. CrossRef - Interventions for chronic pruritus of unknown origin
Andrea Andrade, Chii Yang Kuah, Juliana Esther Martin-Lopez, Shunjie Chua, Volha Shpadaruk, Gloria Sanclemente, Juan VA Franco
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Interventions for pruritus of unknown cause
Andrea Andrade Miranda, Juan VA Franco, Gloria Sanclemente, Chii Yang Kuah, Ashley M Yu, Volha Shpadaruk, Marta Roqué i Figuls, Juliana Esther Martin-Lopez, Sean Chua
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Pruritus, Skin Dryness, and Depression in Hemodialysis Patients
- 665 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Effect of Dance Therapy on Pulmonary and Cognitive Function in the Elderly
- Young Ran Lee, Sook Ja Yu
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(6):1273-1283. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.6.1273
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was done to explore the effects of dance therapy on pulmonary and cognitive functions in the elderly. The design of this study was a non-equivalent pre-post test experiment. The subjects consisted of elderly persons living in a facility located in Kyoungi-Do. Fifty eight subjects had normal cognition, sensory function and resting blood pressure. They underwent tests of pulmonary and cognitive function as baseline data before dance therapy, and at 6th week and at the end of 12nd week after following dance therapy. Twenty seven elderly persons were assigned to the experimental group and participated with the dance therapy. This therapy was based on the Marian Chace's dance therapy and Korean traditional dance with music. The dance therapy consisted of 50 minutes session, 3 times a week for 12 weeks. One session consisted of warming-up, expression, catharsis, sharing and closing stage. the intensity of the dance therapy was at the 40% of age-adjusted maximum heart rates. Data were analyzed with mean, standard deviation, Chi-square test, unpaired t-test, repeated measures ANOVA, and Bonferroni multiple regression using SAS program. The results were as follows: 1. Pulmonary function(forced expiratory volumn at one second and forced vital capacity) of the experimental subjects significantly increased over time more than that of the control subjects. 2. The experimental group had significantly higher score for pulmonary function than the control group at the 12nd week after dance therapy. 3. Cognitive function of the experimental subjects significantly increased over time more than that of the control subjects. 4. The experimental group had significantly higher score for cognitive function than the control group at the 6th week and 12nd week after dance therapy. The findings showed the dance therapy could be effective in improving the pulmonary and cognitive function of the elderly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of High-Intensity Aerobic Exercise on the Pulmonary Function among Inactive Male Individuals
Arwa Rawashdeh, Nedal Alnawaiseh
Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal.2018; 11(2): 735. CrossRef - Effects of high intensity aerobic exercise on treadmill on maximum-expiratory lung capacity of elderly women
Joonsung Park, Dongwook Han
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2017; 29(8): 1454. CrossRef
- The Effect of High-Intensity Aerobic Exercise on the Pulmonary Function among Inactive Male Individuals
- 662 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Assessment of Appetite and Nutritional Status in Cancer Patients Undergoing Radiation Therapy: A Prospective Study
- Hyang Sook So
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(6):1179-1191. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.6.1179
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was conducted to identify appetite and nutritional status of 48 cancer patients who have been irradiated over 150 cm2 on chest or pelvic area over the three-month period. The data were gathered 3 phases, Each from initiation to completion of radiotherapy through the questionnaires of anorexia, the anthropometric and biochemical measures were used such as weight, TSF, MAC, MAMC, serum albumin and hemoglobin, TLC. Using SAS program, data were analyzed by percentage, Mean+/-SD, and two-way repeated measures ANOVA. The results were summarized as follows: 1. Eighty five percent(85%) of the subjects were aged from fifties to sixties. Cancers in the chest area occurred in 100% of men, 56% of the all subjects. The other 44% were pelvic cancer and 71% of the pelvic cancer occurred in women. 2. There were no significant differences in the appetite scores by all groups(characteristics). Changes of the appetite score over time were statistically significant by age, sex, cancer areas staging, treatment modality, and radiation dosage (F=4.0, p=.022; t=6.09, p=.003; t=4.90, p=.009; F=3.28, p=.042; t=5.04, p=.0084; t=4.76, p=.011). The appetite score on the 2nd phase (4 weeks after initiating radiotherapy) decreased from the 1st phase (initiating irradiation), and then increased on the 3rd phase (completing irradiation). 3. There were no significant differences in the body weight and MAMC by all characteristics, and no changes in the body weight and MAMC over time. However there were significant differences of TSF, MAC, level of hemoglobin, level of albumin, and TLC by all characteristics during the three phases. TSF of the men and the chest cancer were lower than those of the women and the pelvic cancer (t=73.20, p=.0001; t=22.91, p=.0001). And there was significant difference by cancer staging(F=3.19, p=.050). But there was no change in TSF over time. MAC of the men and the chest cancer were lower than those of the women and the pelvic cancer each(t=9.23, p=.004; t=17.85, p=.0001). But no change in MAC over time. Levels of hemoglobin had significant differences by age, sex and cancer areas; levels of hemoglobin of older than the fifties, men, and chest area were higher than those on the others(F=3.82, p=.029; t=21.75, p=.0001; t=8.71, p=.005). Levels of albumin were significant differences by sex and cancer areas; levels of albumin on women, and pelvic area were higher than those on the others(t=6.34, p=.015; t=15.23, p=.0003). While the levels of hemoglobin were changed over time, levels of albumin were not changed and within normal limit. TLC of the men was higher than women(t=5.05, p=.029). Changes in the level of hemoglobin over time were statistically significant according to sex, cancer areas, and radiation dosage(t=3.49, p=.035; t=3.36, p=.039; t=4.04, p=.021).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pre- and Post-Transplant Nutritional Assessment in Patients Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Mi Young Park, Jeong Yun Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(1): 110. CrossRef - The Effect of Continuous Nutritional Education and Oral Mucositis Management on Nutritional Status of Patients Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Kyoung Soon Park, Byung Hwa Lee, Ho Ran Park
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2010; 10(2): 119. CrossRef
- Pre- and Post-Transplant Nutritional Assessment in Patients Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- 707 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Effect of Dance Therapy on Physical and Psychological Characteristics in The Elderly
- Young Ran Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(2):429-444. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.2.429
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was performed to explore the effects of a dance therapy on physical and psychological characteristics in the elderly. The design of this study was a non-equivalent pre-post test experiment. The subjects consisted of elderly persons living in a facility located in Suweon and Bucheon. Fifty eight subjects, aged between 65 and 93 years who had normal cognition, sensory function, balance, and resting blood pressure. They underwent tests of balance, flexibility, muscle strength, depression, and anxiety as baseline data before dance therapy, and at 6 th week and at the end of the 12nd week after following dance therapy. Twenty seven elderly persons were assigned to the experimental group and participated with the dance therapy between April and July, 1998. The dance therapy was developed by the author with the help of a dance therapist and a physiatrist. This therapy was based on the Marian Chace's dance therapy and Korean traditional dance with music. The dance therapy was developed by the author with the help of a dance therapist and a physiatrist. This therapy was based on the Marian Chace's dance therapy and Korean traditional dance with music. The dance therapy consists of 50 minutes session, 3 times a week for 12 weeks. One session was consisted of warming-up, expression, catharsis, sharing, and closing stage. The intensity of the dance therapy was at the 40% of age-adjusted maximum heart rates. Data were analyzed with mean, standard deviation, Chi-square test, unpaired t-test, repeated measures ANOVA, and Bonferroni multiple regression using SAS program. 1. The results related to the physical characteristics were as follows : 1) The balance (standing on one leg, walking on the balancing bar), flexibility and muscle strength (knee extensor, knee flexor, ankle plantarflexor and dorsiflexor) of the experimental subjects significantly increased over time more than that of the control subjects. 2) The experimental group had significantly higher score for balance, flexibility, muscle strength of knee extensor, and knee flexor than the control group at the 12nd week after dance therapy. 3) The experimental group had significantly higher score for muscle strength of ankle dorsiflexor and plantarflexor than the control group at the 6th week and the 12nd week after dance therapy. 2. The results related to psychological characteristics were as follows : 1) Scores of Geriatric Depression Scale, Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, and Zung's Self-rating Anxiety Scale of the experimental group were significantly decreased over time more than that of the control group. 2) The experimental group had significantly lower score for depression than the control group at the 12nd week after dance therapy. 3) The experimental group had significantly lower score for anxiety than the control group at eh 6th week and the 12nd week after dance therapy. The findings showed that the dance therapy could be effective in improving the balances, flexibility, and muscle strength of lower limb, and effective in decreasing the depression and anxiety of the elderly. Additional merits of the dance therapy would be inexpensiveness, easy accessibility, and increasing interpersonal relationship. It can be suggested that the dance therapy is effective in the health promotion of the elderly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of a Health Management Program on Health-promoting Lifestyle and Depression in Older Adults Living at Home
Young Rye Park, Yang Gyeong Yoo
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2013; 16(1): 71. CrossRef
- The Effects of a Health Management Program on Health-promoting Lifestyle and Depression in Older Adults Living at Home
- 572 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Study on the Patterns of Alternative Therapy Experienced by the Aged
- Kang Yi Lee, Soon Yi Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(2):336-345. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.2.336
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study looks at the various alternative therapy methods used in day to day life by elderly, over 60 years of age. The elderly have come to know and practice these methods for the following reasons : it is good for the health ; it is the method used in the olden days when there wesn't modern medicine ; it has been passed down from generations ; it can be done at home without having the need to go to the hospital ; acupuncture or poulticing can be used ; it can be done at home, which was an important factor in rural areas where hospitals are few and far between ; and [herbal] medicine could be prepared at home at no cast ; it derives from experience ; it is impossible to ignore tradition passed down through the generations. Diet control and plants(herbs) are methods most often used, as they are easy to find and can be readily used in critical situations. Other methods include oriental medicine practices of moxibustion with moxa cone, negative therapy, hand and finger acupunture, finger press method, ordinary acupunture, finger press method, ordinary acupunture, manual healing methods of massage, diaphoretic therapy and meditation to reach a state of calm, and qigong dirigation. The reasons for its use are as follows : it has been used before ; it is effective ; there is some improvement after the treatment ; it is not harmful to the body ; medicine cannot be obtained and it is the only thing available ; it is not good for an old person to go to the hospital everyday, the symptoms are not serious enough to go to a hospital ; and acupuncture is for these things. The means that the elderly have come to practice these methods are ; it has been used since the past ; it has been told by the elders ; they have been told by friends ; it was part of their knowledge ; and they have come to know by watching their mother. Further, to regain vitality lost through old age, the elderly have relied on hot soup, a hearty meal, brewed honey water, pumpkin, or ginseng. Humans, by instinct, would rub or massage the areas that caused pain. These actions, combined with a breathing technique have been recognized in Tong-Eui-Bo-Gam(the essential of eastern medicine), the complete work of early modern medicine, are a useful means to revive chi. This knowledge is thought to have greatly affected our healthy lifestyle. Furthermore, though the demand for medical services would increase with age, the elderly have not always been able to tend to their needs at the hospital for reasons economic or other. Hence, these alternative therapy methods seem to have been practiced as a temporary means of relief. The excellence of our traditional therapeutic custom has not received full recognition due to the argument relating to its scientific merits. As a result, it has become vital to prove their effectiveness through scientific and other experimental means. The potency of moxibustion with moxa cone and hand and finger acupunture have been proven scientifically, but diet and herbal methods appear to be practiced as a result of customs passed down from generations. In addition, it is submitted that the effectiveness of the traditional methods of disease control and our heathy lifestyle that are easily found in the nursing field must be verified.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Characterization of Wearable Film-heaters Used in Thermotherapy for Senior Citizens
Kyungwhan Yang, Kyoungah Cho, June-Seek Choi, Kiju Im, Sangsig Kim
Journal of IKEEE.2016; 20(4): 412. CrossRef
- Development and Characterization of Wearable Film-heaters Used in Thermotherapy for Senior Citizens
- 646 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effects of Exercise Therapy on Joint Mobility, Daily Activity, pain and Depression in patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Hyun Ja Lim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(2):328-335. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.2.328
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was designed to investigate the effects of exercise therapy on joint mobility, daily activity, pain and depression of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. 25 persons with the experimental group and 25 persons with the control group were conveniently sampled among out-patients diagnosed with ankylosing spondylitis at the rheumatism center of H University Medical Center. The control patients were matched to the experimental group and they were selected considering sex and age. The exercise therapy was developed by the author with the assistance of exercise specialists. The program includes muscle relaxation, flexibility, muscle strengths, breathing strengths and straight posture exercises. The 20-minute exercise therapy was carried out to the experimental group once a day for eight weeks from October, 1997 to February, 1998. Before and after the experiments, joint mobility, daily activity, pain and depression were measured respectively. Data were analyzed by x2-test, t-test, paired t-test and unpaired t-test. The results were as follows : Joint mobility(cervical flexion, extension, shoulder flexion, abduction, hip abduction, knee flexion and fingertip to floor distance) and daily activity in the experimental group after the exercise were significantly increased than that in the control group. The pain and depression score in the experimental group after the exercise were significantly decreased than that in the control group. These findings may indicate that the exercise therapy is effective in increasing the joint mobility and daily activity, and also effective in decreasing pain and depression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Accordingly, the exercise therapy can be adopted as an effective nursing intervention for ankylosing spondylitis.
- 460 View
- 0 Download

- The Effect of Exercise Therapy on Serum Lipid Level and Antioxidants of Obese College Female Students
- Eun Sook Jung
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(4):832-845. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.4.832
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study is to analyze the effects of exercise therapy on serum lipid levels and antioxidants of obese and normal college female students. The subject group composed of ten normal-weight students(below 30% body fat ratio) and ten obese students(above 30% body fat ratio). After a pilot test, the subjects were given an eight-weeks exercise program. Before and after the exercise program, the subjects were given test for serum lipid and antioxidants were analyzed. The SAS program was used in the data analysis. The statistical measurements employed here were T-test, Wilcoxon signed rank test, and Wilcoxon rank sum test. The results of this research are as follows. 1) The effects of exercise therapy on serum lipid levels; Before the exercise therapy, the levels of Total-cholesterol, Triglyceride and LDL-cholesterol of the obese group were higher than those of the normal-weight group. However, the HDL-cholesterol levels were higher in the normal-weight group than in the obese group, but these differences were not significant. With the exercise therapy, the levels of Total-cholesterol increased gradually. The HDL-cholesterol increased gradually, the LDL-cholesterol level decreased in both groups, However, the Triglyceride level decreased in the obese group and increased in normal group, but the difference was not significant. 2) The effects of the exercise therapy on serum antioxidants; Before exercise therapy, the serum FR and GSSG levels of the obese group were significantly higher than those if the normal-weight group(p=0.00, p=0.04). The serum GSH level of the normal-weight group was higher than that of the obese group, and the serum MDA level of the obese group was higher than that of the normal-weight group. Again these differences were not significant. With exercise therapy, serum FR level was reduced and serum GSSG level significantly increased in both group(obese group p=0.01, normal-weight group p=0.01), The serum GSH level of the obese group significantly increased(p=0.01), and serum MDA level significantly increase in the obese group(p=0.01), but the difference in the normal-weight group was not significant. These results show that regular exercise therapy reduces serum FR levels and activation of antioxidant systems, and suppress oxidative stress. These effects were slightly higher in the obese group than in the normal-weight group. The regular exercise therapy decrease the serum Triglyceride levels more in the obese group than in the normal-weight group. However the improvement of the serum lipid profile may require a longer exercise period than eight weeks. The results show that the exercise therapy was overall more effective in the obese group than the normal-weight group.
- 430 View
- 0 Download

- The Effects of Exercise Therapy Applied in an Efficacy Expectation Promoting Program on Self-Efficacy and Metabolism: in NIDDM(Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus) Patients
- Chun Ja Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(1):132-142. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.1.132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was conducted to investigate whether exercise therapy applied in an efficacy expectation promoting program based on the self-efficacy theory of Bandura(1977) would increase self-efficacy and metabolism in NIDDM patients. The study design was a nonequivalent control group pre-test post-test quasi-experimental design. The exercise therapy applied in the efficacy expectation promoting program was composed of a staged exercise program, a small booklet relating personal experience with diabetes mellitus and a telephone coaching program on performance accomplishment, vicarious experience and verbal persuasion, which are all induction modes of efficacy expectation. The subjects of the study were twenty eight NIDDM patients who received follow-up care regularly through the out-patient department of endocrine medicine in one general hospital which had a diabetic clinic. Fourteen were assigned to the experimental group and fourteen to the control group. The experimental group participated in the exercise therapy applied in the efficacy expectation promoting program from three to five times per week for four weeks and the control group did not have the program. The collected data were analyzed using the x2-test, t-test, paired t-test, and Cronbach's Alpha using SPSS/PC+. The results are summarized as follows : 1. Experimental group had higher efficacy score than control group(t=5.98, p=.00). And, There was a significant different in the efficacy score before exercise therapy applied in the efficacy expectation promoting program and after in experimental group(t=-6.42, p=.00). 2. Experimental group did not have lower level of glucose metabolism than control group(FBS : t=.32, p=.75, HbA1C : t=.60, p=.55, pc 2hrs. glucose : t=-.29, p=.78). But, There was a significant different in the amount of glucose metabolism before exercise therapy applied in the efficacy expectation promoting program and after in experimental group(FBS : t=3.63, p=.003, HbA1C : t=4.20, p=.00 2hrs . glucose : t=1.93, p=.001). 3. Levels of lipid metabolism were partly a significant different between Experimental group and control group(triglyceride : t=-1.87, p=.07, HDL cholesterol : t=-.29, p=.77, body weight : t=1.78, p=.09, Total cholesterol : t=-2.17, p=.04). And, There was partly a significant different in the amount of lipid metabolism before exercise therapy applied in the efficacy expectation promoting program and after in experimental group(triglyceride : t=2.50, p=.03, HDL cholesterol : t=-.43, p=.67, body weight : t=5.34, p=.00, Total cholesterol : t=2.26, p=.04). In conclusion, it was found that exercise therapy applied in an efficacy expectation promoting program was an effective nursing intervention for increasing self-efficacy and metabolism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a community‐based intervention on cardio‐metabolic risk and self‐care behaviour in older adults with metabolic syndrome
Chun‐Ja Kim, Jee‐Won Park, Hyung‐Ran Park
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2014; 20(2): 212. CrossRef - Utility of a Web-based Intervention for Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
CHUN-JA KIM, DUCK-HEE KANG
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2006; 24(6): 337. CrossRef - The impact of a stage-matched intervention to promote exercise behavior in participants with type 2 diabetes
Chun-Ja Kim, Ae-Ran Hwang, Ji-Soo Yoo
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2004; 41(8): 833. CrossRef
- Effects of a community‐based intervention on cardio‐metabolic risk and self‐care behaviour in older adults with metabolic syndrome
- 659 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Effects of Hand Acupuncture Therapy on Sleep Quality in Sleep Disrupted Adults: Verification by Polysomnography and Cerebral Blood Flow Test
- Eun Hee Hwang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(7):1108-1118. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.7.1108
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to identify the effects of hand acupuncture therapy on sleep quality by means of a sleep questionnaire, polysomnography and a cerebral blood flow test in 30~59 year old adults. METHODS: The study was a sham controlled design. Twenty-two adults were assigned to the pellet stimulating group (11) or sham group (11). The pellet stimulating group received hand acupuncture therapy using New Seoam Press Pellets number 1 for 4 weeks. On the other hand, the sham group used the same Adhesive tape in terms of shape, size and quality as New Seoam Press Pellets number 1 for 4 weeks. A Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography and Carotid Duplex Ultrasonography examination were used for evaluating cerebral blood flow. Data was analyzed using the SPSS 12.0 version program with Chi2-test, Fisher's exact test and Mann Whitney U-test. RESULTS: In the pellet stimulating group, subjective sleep quality significantly improved more than that of the sham group. Among the sleep indices of the polysomnography, total sleep time and sleep latency of the sham group significantly improved. The cerebral blood flow test didn't show any differences. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that hand acupuncture therapy is effective for subjective sleep improvement only, not polysomnographical sleep indices and cerebral blood flow.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Acupuncture for insomnia
Daniel KL Cheuk, Wing-Fai Yeung, KF Chung, Virginia Wong
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2012;[Epub] CrossRef - High-tech acupuncture made in Austria — cerebral circulation
G Litscher
Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine.2012; 10(4): 362. CrossRef - Power Analysis in Experimental Designs with t test Analysis
Jeong-Hee Kang, Kyung-Sook Bang, Sung-Hee Ko
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2009; 15(1): 120. CrossRef - Effects of Eye Protective Device and Ear Protective Device Application on Sleep Disorder with Coronary Disease Patients in CCU
Yoon Jung Koo, Hyo Jung Koh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(4): 582. CrossRef
- Acupuncture for insomnia
- 861 View
- 4 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of Telephone Intervention as Supportive Nursing on Self-Care Practices and Qualify of Life for Gynecological Cancer Patients under Chemotherapy
- Ae Sook Kim, Eun Sook Lee, Sung Hyo Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(5):744-753. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.5.744
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The effects of telephone intervention on self-care practices and quality of life for gynecological cancer patients under chemotherapy was investigated.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pre-test post-test quasi-experimental design was used. The subjects were women cancer patients who had received less than two chemotherapy sessions at C university hospital of Chonnam province(26 in the experimental group: 25 in the control group). The patient's self-care practices(Na & Lee, 1999; Jang, 2004) and quality of life(Lee & Jo, 1997) were measured three times. using a questionnaire. The data was analyzed by Repeated Measures ANOVA, the Friedman test, and the Mann-Whitney test using the SPSS window version 12.0 program.
Results This study showed that the score of self-care practices and quality of life for the experimental group under telephone counseling were higher than those of the control group.
Conclusion This study revealed that a telephone intervention as supportive nursing care for women cancer patients under going chemotherapy was effective for self-care practices and qualify of life during the recovery period. Futhermore, this study also suggests that telephone counseling can serve as a continuing nursing supportive intervention for women cancer patients for the upcoming stages of further chemotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Chemotherapy Education Reflecting Educational Needs on Self-Care Knowledge and Performance in Female Cancer Patients: A Non-Equivalent Control Group Pretest-Posttest Design
Jin Hee Jun, Se-Na Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(3): 103. CrossRef - Effects of Continuous Nutrition Care on Nutritional Status and Dietary Habits of Patients With Colorectal Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Chemotherapy After Surgery
Jina Son, Ha I Kang, Eun young Jung, Hae won Ryu, Kyung-Ha Lee
Clinical Nutrition Research.2023; 12(2): 99. CrossRef - Effects of Telephone-based Self-care Intervention for Gynecologic Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Boyeon Lee, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(2): 216. CrossRef - Effect of Self-Care Education using a QR-Code on Self-Efficacy, Self-Care Performance, and Education Satisfaction among Discharged Pneumothorax Patients
Dae Hwan Moon, Kye-Ha Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(5): 512. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Quality of Life of Cancer Patients Hospitalized in Long-term Care Hospitals
A Young Jang, Jeong Sook Park
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2018; 20(1): 35. CrossRef - The study on developing the self care tool for the elderly cancer patient undergoing hemotherapy : Focusing on the effect of Health Monitoring Diary
Yeon Ok Lim, Yojin Kim, Hyunsook Yoon, Dae Young Zang, Dae Ro Choi, Kyoungwon Choi
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2018; 35(2): 73. CrossRef - Effects of Individualized Nutritional Education Programs on the Level of Nutrient Intake and Nutritional Status of Colorectal Cancer Patients Undergoing Palliative Chemotherapy
Kwi Ock Park, Smi Choi-Kwon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(6): 799. CrossRef - Effects of a Nurse-Led Cognitive-Behavior Therapy on Fatigue and Quality of Life of Patients With Breast Cancer Undergoing Radiotherapy
Haejung Lee, Yeonjung Lim, Myung-Sook Yoo, Yongsuk Kim
Cancer Nursing.2011; 34(6): E22. CrossRef - Pilot Study on Development of Telecommunication Guideline for Symptom Management of Lung Cancer Patients
Ji Hyun Sung, Min Young Kim, Ok Hee Hwang, Han Jin Yoo, Eun Ja Lee
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2010; 10(2): 218. CrossRef
- The Effects of Chemotherapy Education Reflecting Educational Needs on Self-Care Knowledge and Performance in Female Cancer Patients: A Non-Equivalent Control Group Pretest-Posttest Design
- 834 View
- 5 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Comparing the Effects of Drug Therapy, Physical Therapy, and Exercise on Pain, Disability, and Depression in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain
- Ja Kyung Ko
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(5):645-654. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.5.645
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This research was conducted to compare the effects of drug therapy, physical therapy, and exercise on pain, disability, and depression in patients with chronic low back pain.
Methods The research design of this study was a nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design. The subjects of this study were 28 patients for the drug therapy & physical therapy, 24 patients for the drug therapy & exercise, and 22 patients for the physical therapy & exercise. Data was collected by MVAS, Oswestry disability questionnaires, and questionnaires of depression. It was analyzed by paired t-test for effectiveness, ANOVA, and Scheffe for comparison of the effects of the 3 experimental treatments, using SPSS/WIN 12.0.
Results There were no effects of drug therapy & physical therapy on pain, disability, and depression. However, there were effects of drug therapy & exercise and the physical therapy & exercise on pain, disability, and depression. The effects of physical therapy & exercise on pain, disability, and depression were the greatest, but there was no statistically significant differences between the drug therapy & exercise and the physical therapy & exercise.
Conclusions Exercise is regarded as a more effective and easily accessible nursing intervention to apply alone than drug therapy or physical therapy simultaneously in reducing pain, disability and depression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Stretching on Lumbar Muscle Flexibility, Isokinetic Parameters and Lower Extremity Function
Ye-Won Lee, Jun-Ho Yoo, Dong Yeop Lee, Jae Ho Yu, Jin Seop Kim, Seung Gil Kim, Yeon-Gyo Nam, Jihoen Hong
The Journal of Korean Physical Therapy.2024; 36(4): 145. CrossRef - Analysis of Recent Research Trends in Thread Embedding Acupuncture for Low Back Pain
Yae Gi Min, Hyang Gi Lim, Hyun Jong Lee, Jung Hee Lee, Sung Chul Lim, Yun Kyu Lee, Jae Soo Kim
Journal of Acupuncture Research.2024; 41(2): 96. CrossRef - Effects of Breathing Exercise of Pilates on Dysfunction and Lumbar Flexibility in Patients with Chronic Non-Specific Low Back Pain
Sooyong Lee, Yusik Choi
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2023; 12(3): 268. CrossRef - Effect of Exercise Stage-Matched Intervention for Elderly Women with Chronic Back Pain in the Contemplation and Preparation Stage
Hyun-Ju Oh, Soon-Rim Suh, Mihan Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(4): 414. CrossRef - The effect of abdominal drawing-in exercise and myofascial release on pain, flexibility, and balance of elderly females
Seong Hun Yu, Yong Hyeon Sim, Myung Hoon Kim, Ju Hee Bang, Kyung Hyun Son, Jae Woong Kim, Hyun Jin Kim
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2016; 28(10): 2812. CrossRef - Effect of Spinal Stabilization Exercise and Manual Therapy on Visual Analogue Scale and Oswestry Disability Index in Acute or Subacute Patients with Low Back Pain
Eun-Young Park, Won-Ho Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(4): 1792. CrossRef - Effects of the Hand Acupressure and Lumbar Strengthening Exercise on Women with Lower Back Pain
Eun Young Jeon
journal of east-west nursing research.2013; 19(2): 63. CrossRef - Adaptation Experience to Work of Nurses with Low Back Pain
Jin-Hyang Yang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(6): 597. CrossRef - Adaptation Experience to Work of Nurses with Low Back Pain
Jin Hyang Yang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(6): 597. CrossRef - A Study of Pain, Depression, and Adjustment to Military Life of Soldiers with Low Back Pain
Ji-Hyun Lee, Jong-Im Kim
Journal of muscle and joint health.2010; 17(2): 173. CrossRef - Effects of a Strengthening Program for Lower Back in Older Women with Chronic Low Back Pain
Hee-Kyoung Hyoung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(6): 902. CrossRef
- The Effect of Stretching on Lumbar Muscle Flexibility, Isokinetic Parameters and Lower Extremity Function
- 961 View
- 9 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Effect of Aromatherapy Massage on Abdominal Fat and Body Image in Post-menopausal Women
- Hee Ja Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(4):603-612. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.4.603
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to verify the effect of aromatherapy massage on abdominal fat and body image in post-menopausal women.
Method A Non-equivalent control group pre-post test Quasi-experimental design of random assignment was applied. All subjects received one hour of whole body massage as treatment by the same researcher every week for 6 weeks. Participants also massaged their own abdomen two times everyday for 5 days each week for 6 weeks. The two groups used different kinds of oil. The experimental group used 3% grapefruit oil, cypress and three other kinds of oil. The control group used grapeseed oil. Data was collected before and after the treatment using Siemens Somatom Sensation 4, a tape measure and MBSRQ. Data was analyzed by ANCOVA using the SPSS/PC+Win 12 Version.
Result Abdominal subcutaneous fat and waist circumference in the experimental group significantly decreased after aromathetapy massage compared to the control group. Body image in the experimental group was significantly better after aromathetapy massage than in the control group.
Conclusion These results suggest that Aromatheapy massage could be utilized as an effective intervention to reduce abdominal subcutaneous fat, waist circumference, and to improve body image in post-menopausal women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Production, Function, and Applications of the Sesquiterpenes Valencene and Nootkatone: a Comprehensive Review
Lu-Lu Zhang, Yan Chen, Zhi-Jian Li, Gang Fan, Xiao Li
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.2023; 71(1): 121. CrossRef - Outgoing and potential trends of composition, health benefits, juice production and waste management of the multi-faceted Grapefruit Citrus Χ paradisi: A comprehensive review for maximizing its value
Mohammed N. A. Khalil, Hebatullah H. Farghal, Mohamed A. Farag
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2022; 62(4): 935. CrossRef - The Effect of Aromatherapy on Sleep and Quality of Life in Menopausal Women with Sleeping Problems: A Non-Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Meryem Gürler, Aynur Kızılırmak, Mürüvvet Baser
Complementary Medicine Research.2020; 27(6): 421. CrossRef - The beneficial effects of therapeutic craniofacial massage on quality of life, mental health and menopausal symptoms and body image: A randomized controlled clinical trial
Gemma V. Espí-López, Lucas Monzani, Elena Gabaldón-García, Rosario Zurriaga
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2020; 51: 102415. CrossRef - Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Obesity in Women with Abdominal Obesity
Hyun Su Cha, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(2): 249. CrossRef - Body Image and Physical suffering during Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients Following Breast Conserving Operations
Mi Ok Han, Jeong Yun Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(3): 155. CrossRef
- Production, Function, and Applications of the Sesquiterpenes Valencene and Nootkatone: a Comprehensive Review
- 1,658 View
- 80 Download
- 6 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


