Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
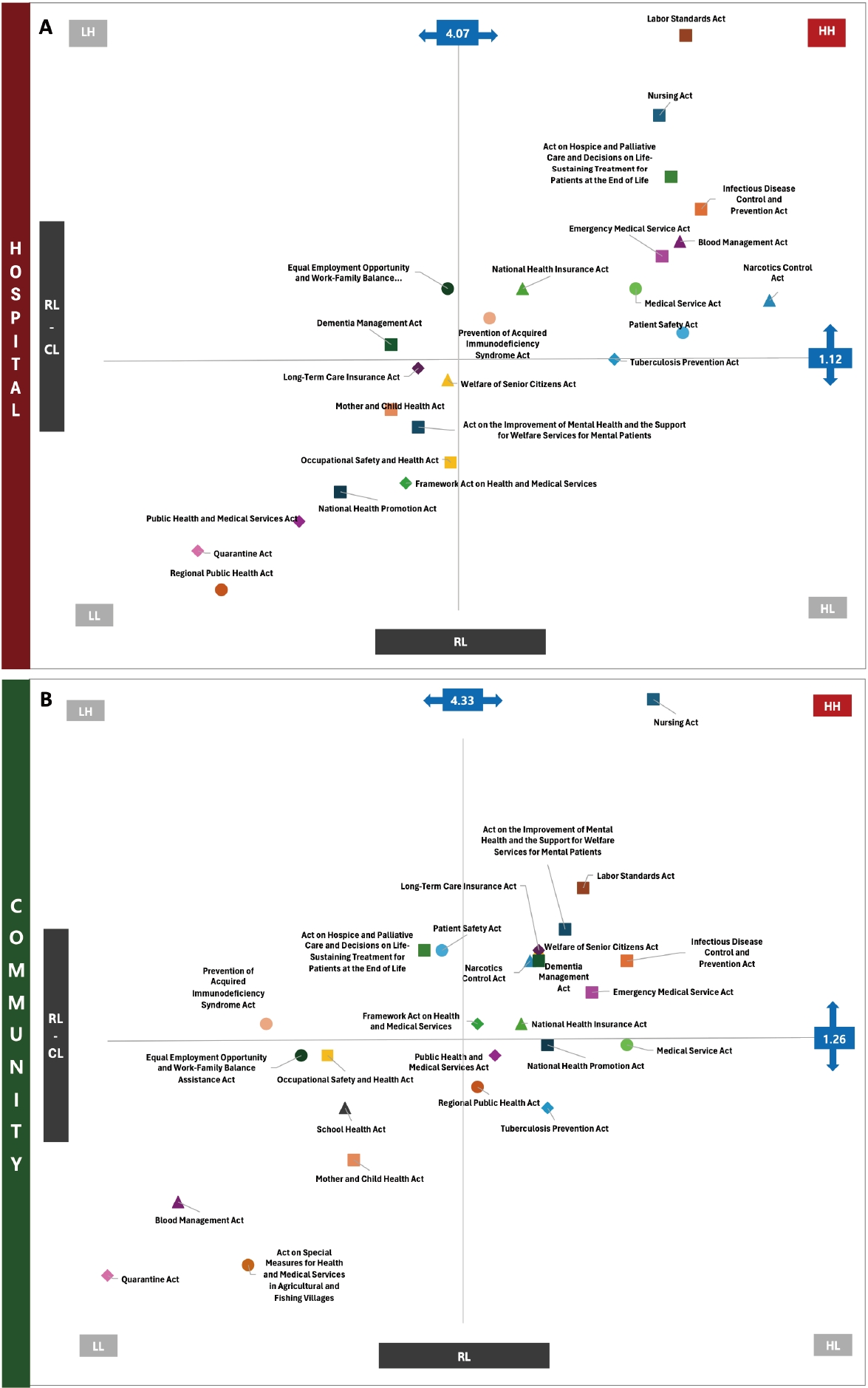
- Comparison of educational needs and priorities for work-related laws between hospital and community-based nurses
- Jeonghyun Kim, Min Kyoung Han, Minjae Lee, Sujin Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):400-412. Published online August 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25049
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the practical utilization of work-related laws in nursing practice and to prioritize educational needs to provide foundational data for improving nurses’ legal competencies.
Methods
A descriptive survey was employed using an online self-reported questionnaire. Participants included 275 nurses with over 3 years of clinical experience, categorized into hospital and community-based. Convenience sampling was used, and data were collected between January 9 and February 3, 2025. Descriptive statistics and the paired t-test were conducted using IBM SPSS 26.0. Educational needs were analyzed using the Borich Needs Assessment and the Locus for Focus model.
Results
Among participants, 75.6% had received education on work-related laws, and 79.3% of those participants received related education during their undergraduate studies. However, 32.4% of nurses reported experiencing practice related difficulties due to insufficient legal knowledge, particularly related to unclear legal responsibilities and ambiguity in the scope of practice. High educational needs were identified for the Nursing Act and the Labor Standards Act across all workplaces. Hospital nurses emphasized the Hospice and Palliative Care Act and Emergency Medical Services Act, while community-based nurses prioritized the Mental Health Welfare Act, Elderly Welfare Act, and Dementia Management Act.
Conclusion
Nurses’ legal education needs are related to practical applications and their capability to respond appropriately to legal requirements, and these needs vary depending on their work environment and social changes. These findings underscore the necessity of restructuring legal education curricula to improve practical relevance and support nurses’ rights, providing a basis for developing workplace-specific legal education programs.
- 1,933 View
- 141 Download

- Willingness to Use and Appropriate Payable Cost for Visiting Nurse Service for the Elderly in the Community
- Soyoung Seo, Soong-nang Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):105-119. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21193
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to measure willingness to use (WTU) and appropriate payable cost of visiting nurse service for the elderly and explore their impact factors.
Methods
The study included 752 participants selected from data that were completed in 2017 for the elderly aged over 60 nationwide. Logit and Tobit regression analysis were performed to confirm the influencing factors.
Results
The study found that 39.1% of the elderly in the community were WTU the visiting nurse service, and they reported that the cost per visit was 12,650 Korean Won. The factors influencing WTU were having less than moderate subjective health status (OR = 1.63, p = .011), being part of a social participating groups (OR = 1.50, p = .046), or participation in senior health promotion programs (SHPPs) (OR = 1.96, p = .003). The cost was also influenced by less than moderate subjective health status (β = 4.37, p = .021), being part of a social participating groups (β = 4.41, p = .028), or participation in SHPPs (β = 4.87, p = .023). Additionally, elderly people living alone who were used as covariates were highly WTU (OR = 2.20, p = .029).
Conclusion
This study provides evidence to predict demand for visiting nurse service and reflects consumer value in setting the service cost. This is the first study to derive cost from consumers' perspective regarding the service for the elderly. As it is the result of an open-ended survey, follow-up studies are needed to estimate more reliable and reasonable results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Health and Environmental Monitoring Services for Smart Healthy Cities : Current Practices and Challenges in Local Government Plans
Dong-ah Choi, Yun-jeong Song, Andy Hong
Journal of Korea Planning Association.2024; 59(5): 147. CrossRef
- Health and Environmental Monitoring Services for Smart Healthy Cities : Current Practices and Challenges in Local Government Plans
- 2,796 View
- 52 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Development and Validation of the Nurse Needs Satisfaction Scale Based on Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory
- Hwa Jin Kim, Sun Hwa Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(6):848-862. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20195
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop an instrument to evaluate the needs satisfaction of nurses and examine its validity and reliability.
Methods
The initial items for the instrument were developed through a literature review and interviews, using the conceptual framework of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory. The initial items were evaluated for content validity by 14 experts. Four hundred and eighty-six clinical nurses participated in this study through offline and online surveys to test the reliability and validity of the instrument. The first evaluation (n = 256) was used for item analysis and exploratory factor analysis, and the second evaluation (n = 230) was used to conduct a confirmatory factor analysis and to assess the criterion-related validity and internal consistency of the instrument. Test-retest reliability was analyzed using data from 30 nurses.
Results
The final instrument consisted of 30 items with two sub-factors for five needs that were identified through the confirmatory factor analysis. The criterion-related validity was established using the five need satisfaction measures (r = .56). Cronbach’s a for total items was .90, and test-retest reliability was .89.
Conclusion
The findings from this study indicate that this instrument has sufficient validity and reliability. This instrument can be used for the development of nursing interventions to improve the needs satisfaction of clinical nurses. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Latent profile analysis of missed nursing care and their predictors among neuro-oncology nurses: a multicenter cross-sectional study
Li Ying, Duan Yuyu, Zou Daili, Su Yangmei, Xiang Qing, Zhou Zhihuan
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of COVID-19–Induced Anxiety on Job Turnover Intention among Emergency Room Nurses during the COVID-19 Pandemic, the Mediating Effect of Needs Satisfaction: A Cross-Sectional Study
YuJin Seo, Myung Kyung Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(2): 104. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of disease‐specific health‐related quality of life instruments for food allergy: A COnsensus‐based Standards for the selection of health Measurement INstruments‐based systematic review
Ke Liu, Shuyi Wang, Zeen Li, Yuting Xia, Qirong Chen
Pediatric Allergy and Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Work Environment, Need Satisfaction, and Depression on Turnover Intention in Korea
Sun-Hwa Shin, On-Jeon Baek, Eun-Hye Lee
Healthcare.2023; 11(12): 1698. CrossRef - Analysis of influencing factors of job demands of healthcare workers working in mobile cabin hospitals in China
Hongmei Yi, Sha Wei, Jingyan Song, Mingzhao Xiao, Huanhuan Huang, Di Luo, Qinghua Zhao
Nursing Open.2023; 10(11): 7368. CrossRef - Consumption Structure Optimization Strategy for Scenic Spots Using the Deep Learning Model under Digital Economy
Yi Wang, Na Li, Xiaoe Qu, Vijay Kumar
Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Self-Care in Nurses
Susan G. Williams, Sharon Fruh, Jennifer L. Barinas, Rebecca J. Graves
Journal of Radiology Nursing.2022; 41(1): 22. CrossRef - Clinical Application Value of Group‐Sharing Nursing Management Based on Case Analysis
Jing Mei, Yifan Wu, Jie Hu, Min Li, Mohammad Farukh Hashmi
Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of nursing intervention based on Maslow's hierarchy of needs in patients with coronary heart disease interventional surgery
Ji-Xue Xu, Lin-Xue Wu, Wei Jiang, Gui-Hong Fan
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(33): 10189. CrossRef
- Latent profile analysis of missed nursing care and their predictors among neuro-oncology nurses: a multicenter cross-sectional study
- 2,471 View
- 87 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Analysis of Subgroups with Lower Level of Patient Safety Perceptions Using Decision-Tree Analysis
- Sun Hwa Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(5):686-698. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20044
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study was aimed to investigate experiences, perceptions, and educational needs related to patient safety and the factors affecting these perceptions.
Methods
Study design was a descriptive survey conducted in November 2019. A sample of 1,187 Koreans aged 20-80 years participated in the online survey. Based on previous research, the questionnaire used patient safety-related and educational requirement items, and the Patient Safety Perception Scale. Descriptive statistics and a decision tree analysis were performed using SPSS 25.0.
Results
The average patient safety perception was 71.71 (± 9.21). Approximately 95.9% of the participants reported a need for patient safety education, and 88.0% answered that they would participate in such education. The most influential factors in the group with low patient safety perceptions were the recognition of patient safety activities, age, preference of accredited hospitals, experience of patient safety problems, and willingness to participate in patient safety education.
Conclusion
It was confirmed that the vulnerable group for patient safety perception is not aware of patient safety activities and did not prefer an accredited hospital. To prevent patient safety accidents and establish a culture of patient safety, appropriate educational strategies must be provided to the general public. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Structural Topic Modeling Analysis of Patient Safety Interest among Health Consumers in Social Media
Nari Kim, Nam-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(2): 266. CrossRef - Analysis of Factors Related to Domestic Patient Safety Incidents Using Decision Tree Technique
Jieun Shin, Ji-Hoon Lee, Nam-Yi Kim
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2023; Volume 16: 1467. CrossRef - Smoking Awareness and Intention to Quit Smoking in Smoking Female Workers: Secondary Data Analysis
Eun-Hye Lee, Sun-Hwa Shin, Goo-Churl Jeong
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(5): 2841. CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness of a Patient Safety Education Program for Inpatients
Sun Hwa Shin, Mi Jung Kim, Ho Jin Moon, Eun Hye Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(6): 3262. CrossRef
- Structural Topic Modeling Analysis of Patient Safety Interest among Health Consumers in Social Media
- 1,213 View
- 14 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- HOME NURSING CARE NEEDS IN PUPAL KOREA
- Sung Sill Kim
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1988;18(1):44-69. Published online March 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1988.18.1.44
- 390 View
- 1 Download

- The Educational Needs Of Mothers of Nephrotic Syndrome Patients and the Degree of Nurse's Educational Performances Perceived by Mothers
- Mi Hae Sung, Seung Nam Paik
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(2):303-314. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.2.303
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This is descriptive study conducted to identify educational needs of mothers of nephrotic syndrome patients and the degree of nurses' educational performances perceived by mothers who look after mainly nephrotic syndrome patients. The study subjects were composed of 74 mothers of nephrotic syndrome patients whose children were hospitalized in 2 Pediatric wards of University Hospital in Seoul and 1 in Pusan from Jure in 1996 to January in 1997. A questionnaire for this study was item Kikert type 5 point scale, developed on the basis of previous literature and researcher's clinical experience and the reliability of the used instruments was q=.97. The data analysis was done by SAS. t-test, and ANOVA were done to determine the effect of general characteristics of subjects on their educational needs. Pearson correlation was done to measure relations between general characteristics of subjects and their educational needs and Stepwise Multiple Regression was done to test a variable affecting educational needs. The results were as follows. 1. Mean score of educational needs of subjects was 137.06(Maximum 176). The score of the educational needs of home care was the highest, but the question numbers(of that category) are smaller than others. So, the educational need of the diagnosis and treatment was regarded as the highest in contents. 2. The mean score of nurses' educational performances was very low, 74.91(Maximum 176). Nurse's educational performances score in the diagnosis and treatment of the disease ranked as the highest Burt that score in the care during hoapitalization was the highest in contents as the educational needs was. 3. The number of children excepting the patient(r2=.215289, P=.006)and the age of patient(r2=.23770, P=.001) were emerged as important variables affecting the degree of mother's educational need.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Educational Needs for Prevention of Cell Phone Addiction in Korean Adolescents
Hyun Young Koo, Hyun Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(4): 304. CrossRef
- Educational Needs for Prevention of Cell Phone Addiction in Korean Adolescents
- 695 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Educational Needs of a Mother when Nurturing Children
- Kyung Hee Yoo
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(4):905-916. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.4.905
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to investigate the educational needs of a mother when nurturing children from neonates to the schoolage. A total of 657 subjects responded to the survey about the level of educational needs when nurturing children. The subjects of the study constituted of 401 mothers who visited the health center for immunization and 256 mothers who visited the pediatric outpatient department or whose children were hospitalized in pediatrics. This instrument had 64 items about nurturing children from neonates to the schoolage and one item had a score range of one to four. In data analysis, SPSSWIN 9.0 program was utilized for descriptive statistics. The results were as follows. 1) Mothers who had the neonates represented the highest educational needs about parental-neonates attachments with 3.47 of mean score compared to neonatal convulsion(3.44), management of common colds(3.44), nutrition(3.44), fever control (3.42). 2) Mothers who had infancy represented the highest educational needs about management of common colds with 3.34 of mean score compared to psychosocial developments (3.23), management of foreign bodies (3.22), feeding the food(3.19), playing with the infant(3.16). 3) Mothers who had toddlers represented the highest educational needs about psychosocial developments with 3.35 of mean score compared to discipline for children(3.34), management of teeth (3.29), management of common colds (3.21), management of accidents(3.20). 4) Mothers who had the a child in preschool represented the highest educational needs about psychosocial developments with 3.53 of mean score compared to management of accidents(3.23), discipline for children (3.00). 5) Mothers who had the child in secondary school represented the highest educational needs about psychosocial developments with 3.42 of mean score compared to management of teeth(3.13), management of accidents (3.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quality Evaluation of Online Health Information Related to Young Child
Hyun-Mi Son, Minji Je, Young-Sil Sohn
Child Health Nursing Research.2018; 24(1): 91. CrossRef - Effects of an Early Nursing Intervention Program for Infants' Development and Mother's Child Rearing in Poverty
Kyung-Sook Bang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(6): 796. CrossRef
- Quality Evaluation of Online Health Information Related to Young Child
- 603 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Correlation Between Knowledge and Educational Needs Related to Recurrent in Coronary Artery bypass graft patients
- Hee Seung Kim, Min Jeong Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):549-559. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.549
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to investigate the correlation between the knowledge and educational needs related to recurrent in coronary artery bypass graft patients as a basis to provide an individual nursing education for the population. The subjects consisted of 110 patients who had coronary artery bypass graft(CABG) at Asan Medical Center in Seoul and Sechong hospital in Buchon. Data was obtained from a knowledge questionnaire and a learning needs questionnaire between November 1998 and February 1999. Data were analyzed using SAS program for Wilcoxon rank sum test and Spearman correlation coefficient. The results were as follows : 1. With regard to the 18 items to measure knowledge, the mean (median) of items 'don't know' was 4.9(4) items. The mean (median) of items answered wrong was 3.2(3) items. The number of items answered 'don't know' tend to show higher in those who had less education, blue color jobs and myocardiac infarction history than in their counter parts. 2. With regard to the level of knowledge by questionnaire about CABG, The most "I dont know" (59.1%) highly response was 'He has to be treated with anticoagulant drug to prevent revasculized vessel from obstructing.' The seond highest response (56.4%) was 'If you were hypotensive, the coronary attack would collapse. 'During the hospitalized day, the patient has complete bedrest.' The highest error probability was cholesterol has not to intake.', 'After surgery, the sexual life is need controlled for 1 year. 3. The mean of educational needs was 3.38. With regard to the level of learning needs by sentence about CABG, 'Food that benefit heart disease', 'Recurrence possibility of heart disease', 'Management
method
of operation site', 'Risk symptom that visit hospital or report immediately' were higher than other sentenses. With regard to the level of learning needs by factor 'food(5 items)', 'disease(9 items)' and 'exercise(3 items)' showed the highest than other factors. The educational needs by patients characteristics tend to show higher in males, under the age of 49, middle or high school degree, previous experience of admission with coronary artery disease, history of myocardial infarction, expierience of PTCA, history of cerebro-vascular accident, previous expierience of smoking than in their counter parts. 4. The number of items answered 'don't know', wrong and correct weren't correlated with the level educational needs. As the results, the number of items answered 'don't know' tend to show higher in those who had less educated, blue color jobs and myocardiac infarction history than in their counter parts. There were higher frequency of items answered 'don't know' in those who had no hypertension . There were higher frequency of items answered 'don't know' on anti-thrombolitic theraphy, hypotension and pain relief. Also there were higher frequency of items answered wrong on bed rest period, cholesterol intake, and sexual life. Educational needs were higher in young age group, had previous experience of procesure and history of other disease. And when we educate CABG patients, education for diet, recurrence possibility of disease, management methods of operation site and risk symptom should be emphasized. There were higher frequency of items answered 'don't know' in those who had no hypertension.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Development and Effects of an Integrated Symptom Management Program for Prevention of Recurrent Cardiac Events after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Youn-Jung Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(2): 217. CrossRef
- The Development and Effects of an Integrated Symptom Management Program for Prevention of Recurrent Cardiac Events after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- 635 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Learning Needs in Patients undergoing Bone Marrow Transplantation
- So Eun Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):514-525. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.514
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The active treatment phase in preparation for bone marrow transplantation(BMT) of che- motherapy regimen and total body irradiation (TBI) containing regimen requires considerable teaching. There have been researches that are related to treatment onto BMT patients and to psychological change during BMT process. However, it was hard to find researches focused on learning needs of patients undergoing BMT. The purpose of this study was to provide the basic data for effective educational program about BMT by investigating the learning needs in patients undergoing BMT. The subjects consisted of 90 BMT patients who have been admitted to the department of BMT at three university hospitals. Data were obtained from October 1998 to March 1999 and analyzed by SAS program for unpaired t-test, ANOVA, Duncan test. The results were as follows : 1. Learning needs related to demographic characteristics was identified as below. That of male was higher than that of female. That of under age 29, unmarried, religious and university graduated group was higher than that of opposite group but it didn't show significant difference. Learning needs of group of patients who were employed was significantly higher then that of unemployed patients. 2. According to types of diagnosis, learning needs of myelodysplastic syndrome(MDS) patients was the higher than that of others, but admission frequency was the least. Learning needs of unrelated matched BMT(UBMT) patients was higher than that of autologous BMT patients. However, it didn't show significant difference. With regard to learning needs according to process of BMT, learning needs of Pre- BMT period or Post-BMT period was significantly higher than that of BMT day. 3. Learning needs related to BMT was relatively high (total mean: 3.11 of 4.0). The order of the mean score of leaning needs was shown as follows : Restricted activities after discharge, Relapse symptom, Complications of BMT, Kinds of available drugs at home. Therefore the learning needs that is related to life after discharge and to relapse and complications after BMT was high. 4. Learning needs related to radiation therapy was high (total mean: 3.35 of 4.0). The highest learning needs in radiation therapy items was the Skin care of radiation therapy and Purpose of radiation therapy. 5. Learning needs related to graft versus host disease(GVHD) therapy was high (total mean: 3.55 of 4.0). The highest learning needs in GVHD therapy items was the Preventive method GVHD. As the result above, individualized educational program is required for MDS patients who have less admission frequency and UBMT patients. It is necessary that education for BMT patients should be focused on life after discharge and on relapse and complications after BMT. Especially education for allogeneic BMT patients should be emphasized on GVHD. For all of these, it is necessary to develop systematic and concrete educational program.
- 410 View
- 0 Download

- A Study on the Forecast of Bed Demand for Institutional Long-term Care in Taegu, Korea
- Myung Hi Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):437-451. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.437
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to estimate the forecast of bed demand for institutional long-term care for the elderly persons in Taegu Metropolitan City. The study subject was the total 1,877 elderly persons over age 65 living in Taegu. Among them 1,441 elderly persons were sampled from community and 436 were from the elderly admitted 5 general hospitals. Data collection was carried out by interview from 25 August to 25 December 1997. The measuring instrument of this study was the modified tool of CARE, MAI, PCTC, and ADL which were examined for validity and reliability. In order to forecast bed demand of Nursing Home, this study revised prediction techniques suggested by Robin. The results were as follows : 1. OLDi of Taegu City were 122,202 by the year 1998 and number of Low-Income Elderly Persons were 3,210. 2. The Level I : Senior Citizen Home AQi * ASTAYi ADEMi = --------------- 365 * AOCUi . AQi = OLDi * LADLi * NASi * ALONi * LIADLi * AUTILi Predicted number of bed demand for Home Based Elderly Persons were 4,210 and Low-Income Elderly Persons were 1,081 and Total Elderly Persons were 5,291 by the year 1998, 6,343 by the year 2000 and 8,351 by the 2005. 3. The Level II : Nursing Home (BQ1i+BQ2i) * BSTAYi BDEMi = ----------------------- 365 * BOCUi . BQ1i = OLDi * HADLi * ALONi * HIADLi BQ2i = OLDi * HADLi * FAMi * OBEDi Predicted number of demand for Total Elderly Persons were 668 by the year 1998, 802 by the year 2000 and 1,055 by the 2005. 4. The Level III : Nursing Home COLDi * HDISi * CUTILi * CSTAYi CDEMi = ------------------------------------ + CQi/10 365 * COCUi Predicted number of demand for Total Elderly Persons were 1,899 by the year 1998, 2,311 by the year 2000 and 3,003 by the 2005. 5. Predicted number of bed demand of long-term care facilities in the year 1998 according to Levels were 4.3% among elderly persons in Taegu by Level I, 0.5% by Level II and 1.5% by Level III. Number of elderly persons in current long-term care facilities were 458 in LevelI I,284 in Level II. 6. Deficit number of bed demand of long-term care facilities were 4,833 in Level I, 384 in Level II , 1,899 in Level III for the elderly persons in Taegu Metropolitan City.
- 389 View
- 0 Download

- A Study on the Educational Needs of Patients with Kidney Transplants and their Family Members after Discharge from Hospital
- Jae Hyun Ahn, Nam Cho Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(6):1324-1335. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.6.1324
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to explore the educational needs of patients with, kidney transplants and their family members to develop a rehabilitational and educational program. Data were collected from January 29, 1999 to April 20, 1999 with interviews using a structured questionnaire. There were 184 subjects in this study. of them, 107 were patients who had kidney transplants and had visited at the out-patient department of three general hospitals located in Seoul and 77 were family members. The questionnaire used for this study was developed by the investigator through a literature review and from data collected from 11 professional personnel and three kidney transplant patients and their families. The data were analyzed using the SAS program with t-test, ANOVA, Scheff test, Pearson correlation coefficient. 1) In the patient group, total mean score for educational needs was 154.61 and the item mean score was 3.96. For the family group, total mean score for educational needs was 168.84 and the item mean score was 4.15. So in the family group, educational needs were scored higher than by the patient group. With regard to domains, both patient and family groups had as the highest educational needs, the domain of physical health and the top ten items in the educational needs were also in the domain of physical health. 2) In the patient group, women and the divorce/ bereavement group had higher educational needs in the domain of nutritional management, those who had been admitted longer than four weeks from their kidney transplant had higher educational needs in the domain of physical health and those who were less than 4 years from their transplant had higher educational needs in the domain of follow-up care. In the family group, those who were Catholics and had high school education had higher educational needs in the domain of nutritional management. 3) In the patient group, academic background was positively correlated(r=.208, p=.031) to educational needs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Convergence for adherence: Subjectivity of immunosuppressive medication adherence after kidney transplantation patient
Min-Young Kim, Eun-Ju Lee, Euna Park
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(6): 235. CrossRef
- Convergence for adherence: Subjectivity of immunosuppressive medication adherence after kidney transplantation patient
- 649 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Health Care Needs of Solitude Elderly
- Myung Suk Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(6):812-819. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.6.812
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to identify factors that influence the health care needs of that over 65 years of age in Mokpo, Korea.
Method The data was collected from June 2002 to September 2002. The subjects were 120 homebound solitude elderly(age=76.8). Subjects were interviewed with structured questionnaire in order to identify the health care needs, health variables (perceived health status, risk of malnutrition, K-IADL), psychological variables(self-esteem, depression) and demographic variables. physiological health variables (height, weight, blood pressure, pulse, blood sugar)were assessed after the interview.
Result In general perceived health status was poor, risk of malnutrition was high, number of disease was 3 disease, self-esteem was low but depression was high and health care needs were relatively high. Among the elderly education & counseling needs topped the list. In regression analysis, health care needs were significantly influenced by IADL(23%), duration of solitudes(4%), sex(3%), and education(1%). These variables explained 31% of the variances in health care needs.
Conclusion The result identified that health care needs should be a considered in IADL, female, duration of solitudes and education for the solitude elderly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional Risk, Perceived Health Status, and Depression of the Young-Old and the Old-Old in Low-Income Elderly Women
Myung-Suk Lee
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2012; 37(1): 12. CrossRef - The Life of Elderly Women Living Alone
Chunmi Kim, Moon Hee Ko, Moon Jeong Kim, Joohyun Kim, Hee Ja Kim, Jin Ha Moon, Kyoung Seon Baek, Haeng-Mi Son, SangEun Oh, YoungAe Lee, Jung-Sook Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 739. CrossRef
- Nutritional Risk, Perceived Health Status, and Depression of the Young-Old and the Old-Old in Low-Income Elderly Women
- 611 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- A Prediction Model for Unmet Needs of Elders with Dementia and Caregiving Experiences of Family Caregivers
- Sora Choi, Myonghwa Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(5):663-674. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.5.663
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purposes of this study were to develop and test a prediction model for caregiving experiences including caregiving satisfaction and burden in dementia family caregivers.
Methods The stress process model and a two factor model were used as the conceptual frameworks. Secondary data analysis was done with 320 family caregivers who were selected from the Seoul Dementia Management Survey (2014) data set. In the hypothesis model, the exogenous variable was patient symptomatology which included cognitive impairment, behavioral problems, dependency in activity of daily living and in instrumental activity of daily living. Endogenous variables were caregiver's perception of dementia patient's unmet needs, caregiving satisfaction and caregiving burden. Data were analysed using SPSS/WINdows and AMOS program.
Results Caregiving burden was explained by patient symptomatology and caregiving satisfaction indicating significant direct effects and significant indirect effect from unmet needs. The proposed model explained 37.8% of the variance. Caregiving satisfaction was explained by patient symptomatology and unmet needs. Mediating effect of unmet needs was significant in the relationship between patient symptomatology and caregiving satisfaction.
Conclusion Results indicate that interventions focusing on relieving caregiving burden and enhancing caregiver satisfaction should be provided to caregivers with high levels of dementia patients' unmet needs and low level of caregiving satisfaction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Experiences of Family Caregivers Utilizing Care Support of Dementia Center
Chun-Gill Kim, Myung Soon Kwon, Young Hee Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(3): 314. CrossRef
- Experiences of Family Caregivers Utilizing Care Support of Dementia Center
- 956 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Transcultural Self-efficacy and Educational Needs for Cultural Competence in Nursing of Korean Nurses
- Sun-Hee Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(1):102-113. Published online February 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.1.102
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to investigate the level of transcultural self-efficacy (TSE) and related factors and educational needs for cultural competence in nursing (CCN) of Korean hospital nurses.
Methods A self-assessment instrument was used to measure TSE and educational needs for CCN. Questionnaires were completed by 285 nurses working in four Korean hospitals. Descriptive statistics, t-test, ANOVA, Pearson correlation coefficients, and multiple regression were used to analyze the data.
Results Mean TSE score for all items was 4.54 and score for mean CCN educational needs, 5.77. Nurses with master's degrees or higher had significantly higher levels of TSE than nurses with bachelor's degrees. TSE positively correlated with English language proficiency, degrees of interest in multi-culture, degree of experience in caring for multi-cultural clients, and educational needs for CCN. The regression model explained 28% of TSE. Factors affecting TSE were degree of interest in multi-culture, degree of experience in caring for multi-cultural clients, and educational needs for CCN.
Conclusion The results of the study indicate a need for nurse educators to support nurses to strengthen TSE and provide educational program for TSE to provide nurses with strategies for raising interests in cultural diversity and successful experiences of cultural congruent care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing nursing students’ cross-cultural competence: The impact of a design thinking-based multicultural education program
Do Young Lee, Im Sun Seo
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(3): 280. CrossRef - An educational program for enhancing cultural competence and cultural self-efficacy in healthcare providers: a quasi-experimental single-group study in Southern Iran
Motahareh Faramarzpour, Nasibeh Salari, Neda Dastyar, Foozieh Rafati, Jamileh Farokhzadian, Ali Asghar Kheirkhah Vakilabad, Maryam Sadat Mousavi
BMC Medical Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The moderating effect of cultural competence educational needs on the relationship between transcultural self-efficacy and cultural competence in Korean public health nurses
Young-Ran Han, Yeo-Won Jeong
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Educational Needs of European Intensive Care Nurses with Respect to Multicultural Care: A Mix-Method Study
Aleksandra Gutysz-Wojnicka, Dorota Ozga, Eva Barkestad, Julie Benbenishty, Bronagh Blackwood, Kristijan Breznik, Bojana Filej, Darja Jarošová, Boris Miha Kaučič, Ivana Nytra, Barbara Smrke, Renáta Zeleníková, Beata Dobrowolska
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(2): 724. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Transcultural Self-Efficacy Among Nurses With Foreign Patient Care Experience
HyunJung Ham, Sunghee H. Tak
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2022; 33(1): 87. CrossRef - Nursing students’ experiences of a global outreach program: A mixed-method study
Sook Ja Yang, Chiyoung Cha, Hyerim Lee, Sookyung Jeong
Nurse Education in Practice.2021; 50: 102927. CrossRef - Determinants of transcultural self‐efficacy among nurses in China: A cross‐sectional study
Ling Tong, Tong Tong, Jingping Wang, Yao Li, Ariko Noji
Nursing & Health Sciences.2021; 23(4): 880. CrossRef - Perceived cultural differences in healthcare for foreign patients visiting South Korea: tool development and measurement
Sumi Sung, Hyeoun-Ae Park
BMC Health Services Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - CULTURAL COMPETENCE LEVEL, ITS IMPORTANCE, AND EDUCATIONAL NEEDS FOR CULTURAL COMPETENCE AMONG NURSES CARING FOR FOREIGNERS IN KOREA
Nageong KIM, M. N., Dong-Hee KIM, Jungha PARK
Humanities & Social Sciences Reviews.2019; 7(5): 286. CrossRef - Level of Cultural Self-Efficacy of Colombian Nursing Professionals and Related Factors
Raquel Herrero-Hahn, Juan Guillermo Rojas, Rafael Montoya-Juárez, María Paz García-Caro, César Hueso-Montoro
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2019; 30(2): 137. CrossRef - Effects of a cultural nursing course to enhance the cultural competence of nursing students in Korea
Hae Sook Park, Hee Jung Jang, Geum Hee Jeong
Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions.2019; 16: 39. CrossRef - Living in Harmony: Clinical Nurses’ Perceptions of Multicultural Society
Hwa-Sook CHO, Euna PARK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2019; 31(1): 196. CrossRef - A Literature Review of the Studies on Cultural Competency of Nurses and Nursing Students in Korea
Min-A Kim, So-Eun Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(4): 450. CrossRef - Development and Cross-Validation of the Short Form of the Cultural Competence Scale for Nurses
Duckhee Chae, Yunhee Park
Asian Nursing Research.2018; 12(1): 69. CrossRef - Evidence-Based Updates and Universal Utility of Jeffreys’ Cultural Competence and Confidence Framework for Nursing Education (and Beyond) Through TIME
Marianne R. Jeffreys
Annual Review of Nursing Research.2018; 37(1): 43. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling of Cultural Competence of Nurses Caring for Foreign Patients
Jung-Won Ahn
Asian Nursing Research.2017; 11(1): 65. CrossRef - Cultural Competence and Influencing Factors of Dental Hygiene Students
Ji-Hyoung Han, Ki-Eun Kim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2017; 17(3): 242. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Transcultural Self-efficacy among Nursing Students
Kyu Eun Lee, Nam Sun Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2017; 42(1): 1. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of a Cultural Competence Training Program for Public Health Nurses using Intervention Mapping
Yune Kyong Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 410. CrossRef - Perceived Transcultural Self-Efficacy of Nurses in General Hospitals in Guangzhou, China
Juan Li, Zhuang He, Yong Luo, Rong Zhang
Nursing Research.2016; 65(5): 371. CrossRef - Level of Cultural Competence (CC) and Educational Needs for Cultural Competence in Nursing (CCN) in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Nae Young Lee, Yong Sook Eo, Ji Won Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 16. CrossRef - Effects of a Multicultural Course on the Multicultural Acceptability and Competency of Nursing Students
Myeong Jeong Chae, Jin-il Kim, Jin Hee Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(3): 373. CrossRef - Subjective View of and Attitude toward Multiculturalism in First-year Undergraduate Nursing Students after Completing a Multicultural Subject
Eun-Ho Ha, Jin-Young Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(3): 248. CrossRef - The Study on Relationship between Characteristics of Cultural Exchanges, Self-efficacy, and Cultural Competency of Nursing Students
Sun-Yi Yang
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(7): 334. CrossRef - Development and Psychometric Evaluation of the Korean Version of the Cultural Competence Scale for Clinical Nurses
Duck-Hee Chae, Chung-Yul Lee
Asian Nursing Research.2014; 8(4): 305. CrossRef - Experiences of Nurses Who Provide Childbirth Care for Women with Multi-cultural Background
Sun Hee Kim, Kyung Won Kim, Kyung Eui Bae
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(1): 87. CrossRef - Development of Educational Program for Cultural Competence in Nursing for Nursing Students and its Effects
Sun-Hee Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(4): 580. CrossRef - Cultural Competence and Factors Influencing Cultural Competence in Nursing Students
Duck Hee Kim, Seong Eun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2013; 22(3): 159. CrossRef
- Enhancing nursing students’ cross-cultural competence: The impact of a design thinking-based multicultural education program
- 1,352 View
- 12 Download
- 28 Crossref

- Validation of a Needs Assessment Tool for Case Management in Korean Medical Aid Beneficiaries
- Yang Heui Ahn, Eui Sook Kim, Ok Kyung Ham, Soo Hyun Kim, Soon Ok Kim, Myung Kyung Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(4):549-558. Published online August 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.4.549
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to validate the Needs Assessment Tool for Case Management (NATCM) for use with Korean medical aid beneficiaries.
Methods Psychometric testing was performed with a sample of 645 Korean medical aid beneficiaries, which included 41 beneficiaries who were selected using proportional sampling method, to examine intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC). Data were evaluated using item analyses, exploratory factor analysis (EFA), confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), Cronbach's alpha, and ICC.
Results Through psychometric testing the final version of NATCM was found to consist of two subscales: 1) Appropriateness of Health Care Utilization (5 items) and 2) Self Care Ability (6 items). The two subscale model was validated by CFA (RMSEA=.08, GFI=.97, and CFI=.93). Internal consistency measured by Cronbach's alpha was .82, and subscale reliability ranged from .79 to .84. The ICC of the NATCM between case managers was .73 and between case managers and health care professionals. .82.
Conclusion This study suggests that the final version of NATCM is a brief, reliable, and valid instrument to measure needs of Korean medical aid beneficiaries. Therefore, the NATCM can be effectively utilized as an important needs assessment as well as outcome evaluation tool for case management programs in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trends of Research on the Case Management of Medicaid Beneficiaries in Korea
Soon Ock Kim, Jeonghyun Cho
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2015; 29(3): 412. CrossRef - Comparing the Needs of Case Management between Medical Aid Beneficiaries with Simple and Multiple Chronic Diseases
Yang Heui Ahn, Yeonok Suh, Ok Kyung Ham, Hee Kyung Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2015; 18(2): 98. CrossRef
- Trends of Research on the Case Management of Medicaid Beneficiaries in Korea
- 877 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Educational Needs Assessment on Research Ethics among Nursing Researchers
- Ihn Sook Jeong, Mee Ock Gu, Keum Soon Kim, Kwang Ja Lee, Soo Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(4):515-523. Published online August 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.4.515
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to investigate the educational needs of research ethics among nursing researchers.
Methods Convenience sample of 161 nursing professors and 262 master or doctoral nursing students participated in the study. Data was collected with self-reported questionnaire from June to August 2009, and analyzed with descriptive statistics using SPSS WIN (version 14.0).
Results Among 161 nursing professors, about 31.7% has educated nursing ethics in the postgraduate course. The most common course was nursing research or methodology (62.7%), and median education time was 2 hr. Areas that showed difficulty in understanding was the conflict of interest and plagiarism for professors and falsification and fabrication for graduate students. Average knowledge on the research ethics was 75.4 points for professors and 61.6 points for students based on the 100 points.
Conclusion Educational needs of research ethics among nursing professors and students in the postgraduate course was high. We recommend both basic and advanced research ethics educational programs for the nursing researchers. The basic course should be at least 6 hr and include various cases and something to discuss.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nurses’ Experience and Satisfaction as Research Participants in Nursing Research - A View of Protecting Vulnerable Populations: A Cross-sectional Descriptive Study
Go-Eun Lee, Sanghee Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(6): 565. CrossRef - Nursing Faculties’ Knowledge of and Attitudes Toward Research Ethics According to Demographic Characteristics and Institutional Environment in Korea
Sukhee Ahn, Geum Hee Jeong, Hye Sook Shin, Jeung-Im Kim, Yunmi Kim, Ju-Eun Song, Sun-Hee Kim, Ju Hee Kim, Yun Jung Lee, Young A. Song, Eun Hee Lee, Myoung-Hee Kim
Sage Open.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge and Attitudes of Social Behavioral Researchers on Institutional Review Board (IRB) Reviews*
Go-Eun LEE, Sanghee KIM, Min-Shik KIM, Eui Geum OH
Korean Journal of Medical Ethics.2017; 20(3): 287. CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Research Support Program on the Attitudes and the Barriers of the Nurse
Young-Ok Yang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(12): 8556. CrossRef - Operational effectiveness of blended e-learning program for nursing research ethics
Kap-Chul Cho, Gisoo Shin
Nursing Ethics.2014; 21(4): 484. CrossRef - A Study on the Research Ethics of Occupational Therapy Researchers
So-Yeon Park, Jin-Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational Therapy.2014; 22(1): 97. CrossRef - Level of Awareness, Self-efficacy and Knowledge of Research Ethics among Nursing Graduate Students*
Eui Geum OH, Sang Hee KIM, Jae Yong YOO
Korean Journal of Medical Ethics.2012; 15(2): 244. CrossRef - The Development and Evaluation of a Research Ethics Course for a Graduate-level Educational Program in Nursing
Euigeum OH, Sanghee KIM, Jae Yong YOO, Sosun KIM, Sunah KIM, Eunhee CHO
Korean Journal of Medical Ethics.2011; 14(4): 482. CrossRef
- Nurses’ Experience and Satisfaction as Research Participants in Nursing Research - A View of Protecting Vulnerable Populations: A Cross-sectional Descriptive Study
- 862 View
- 4 Download
- 8 Crossref

- A Comparison of Perceived Nursing Needs among Oncology Nurses, Patients with Non-terminal Cancer and Patients with Terminal Cancer
- Ja Yun Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(6):1135-1143. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.6.1135
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare the perceived importance and the perceived caring of nursing needs among oncology nurses, patients with non-terminal cancer and patients with terminal cancer.
Method A total of 83 oncology nurses, 56 patients with non-terminal cancer and 39 patients with terminal cancer served as subjects. Data was collected based on the 4-point Likert scale using a self-administered questionnaire from Mar. to Sept. 2004. Finally, data was analyzed using mean, SD, paired-test, and ANOVA.
Results The score of the perceived importance of nursing needs was higher than that of the perceived performance of nursing needs in all three groups. There was also a difference in the degree of perceived performance of nursing needs among the three groups. In contrast, there was no difference in the total score of the perceived importance of nursing needs among the three groups, unlike the importance of informational and physical needs as a subgroup of perceived importance, where a difference was noted.
Conclusions Strategies should be developed to narrow down these gaps between nurses and patients. In particular, informational and educational programs should be designed for patients with terminal cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Nursing Hospital Workers’ Hospice·Palliative Care Knowledge and Awareness, End-of-Life Care Attitude and Death Awareness on Their End-of-Life Care Performance
Meera Park, Nam Joo Je
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2018; 21(4): 124. CrossRef - A Study on the Factors Affecting the Service Failure ZOT and severity Perception
Jung Won Ock, Dae Hoong Yun, Seong Won Eum, Sun Joo Yim
Journal of Service Research and Studies.2016; 6(2): 215. CrossRef - Clinical Nurses' Perceived or Experienced Obstacles and Supportive Behaviors in Providing Care for Terminally Ill Cancer Patients
Kyung Suk Heo, Eun-Jun Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2016; 16(3): 147. CrossRef - Death Anxiety and Terminal Care Stress among Nurses and the Relationship to Terminal Care Performance
Young Wha Woo, Kyung Hee Kim, Ki Sook Kim
Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2013; 16(1): 33. CrossRef - Death Anxiety and Terminal Care Stress among Nurses and the Relationship to Terminal Care Performance
Young Wha Woo, Kyung Hee Kim, Ki Sook Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2013; 16(1): 33. CrossRef
- The Impact of Nursing Hospital Workers’ Hospice·Palliative Care Knowledge and Awareness, End-of-Life Care Attitude and Death Awareness on Their End-of-Life Care Performance
- 658 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


