Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Variables influencing digital health literacy in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Jin Hwa Park, Eun Ju Mun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):651-667. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
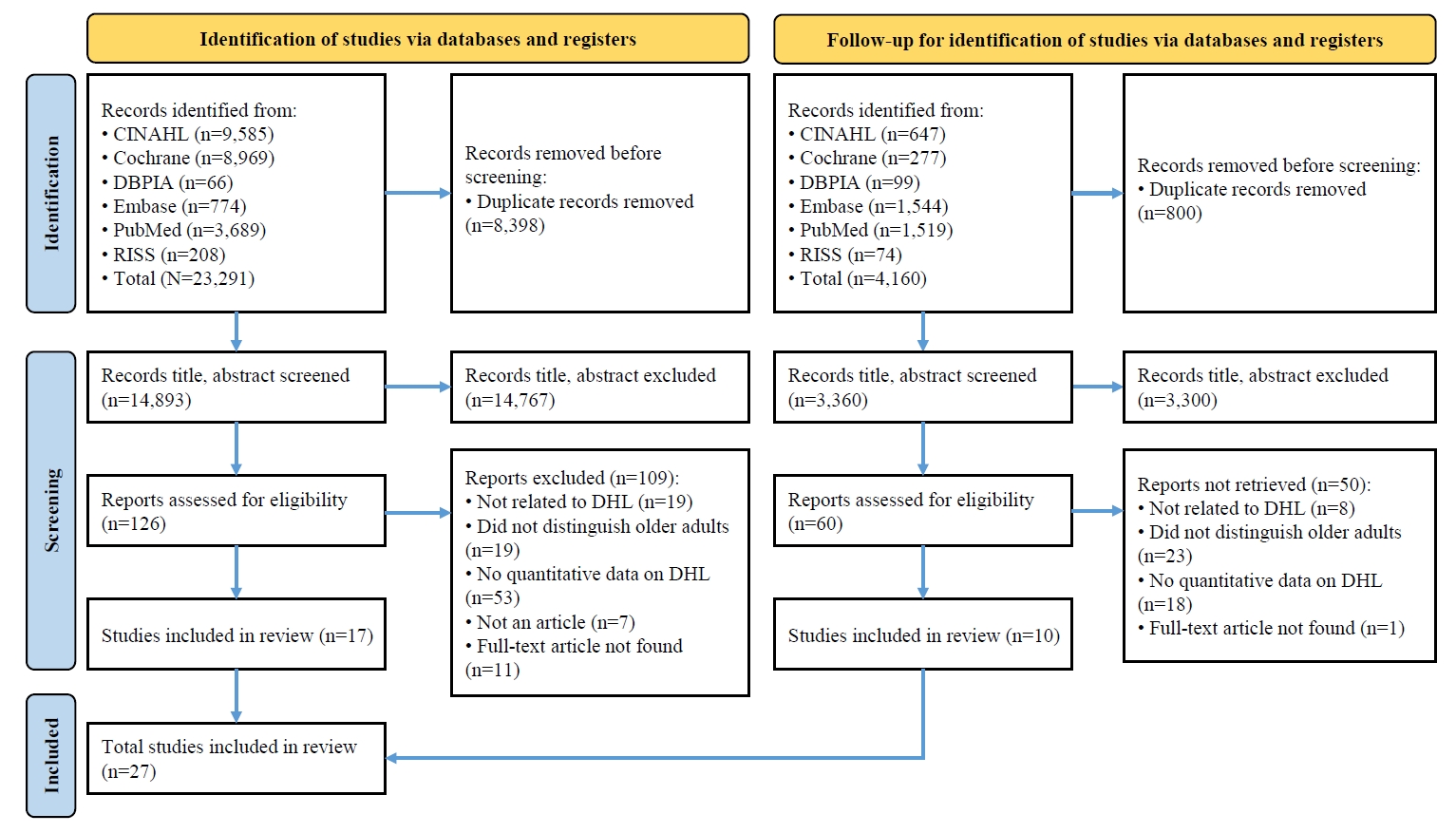
This study aimed to synthesize existing evidence on digital health literacy (DHL) among older adults and to estimate the associations between related influencing factors through a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines. Literature searches were performed across PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, RISS, and DBPIA. The search and screening process was conducted from December 24, 2023, to March 31, 2025. Effect sizes (ESr) using correlation coefficient for each variable were calculated, and meta-analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel and R version 4.3.1.
Results
Forty-seven variables were identified, including two demographic, six physical, six behavioral, 23 psychosocial, and 10 cognitive factors. Meta-analysis results showed that physical, behavioral, psychosocial, and cognitive factors had significant effects on DHL. Among these, digital information level (ESr=.62; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55 to 0.69) within the cognitive domain and technophobia (ESr=−.55; 95% CI, −0.47 to −0.40) within the psychosocial domain demonstrated the largest ESr.
Conclusion
Among factors influencing DHL, digital information level and technophobia showed the strongest associations. These findings suggest that improving DHL in older adults requires a dual approach targeting both cognitive and psychosocial dimensions—enhancing digital information skills while reducing technophobia—to effectively support digital engagement and health empowerment in this population (PROSPERO registration number: CRD42023487486).
- 1,264 View
- 131 Download

- A non-face-to-face diabetes self-management program based on self-efficacy theory and health literacy: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Jung Hee Lee, Soo Jin Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):165-177. Published online May 23, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
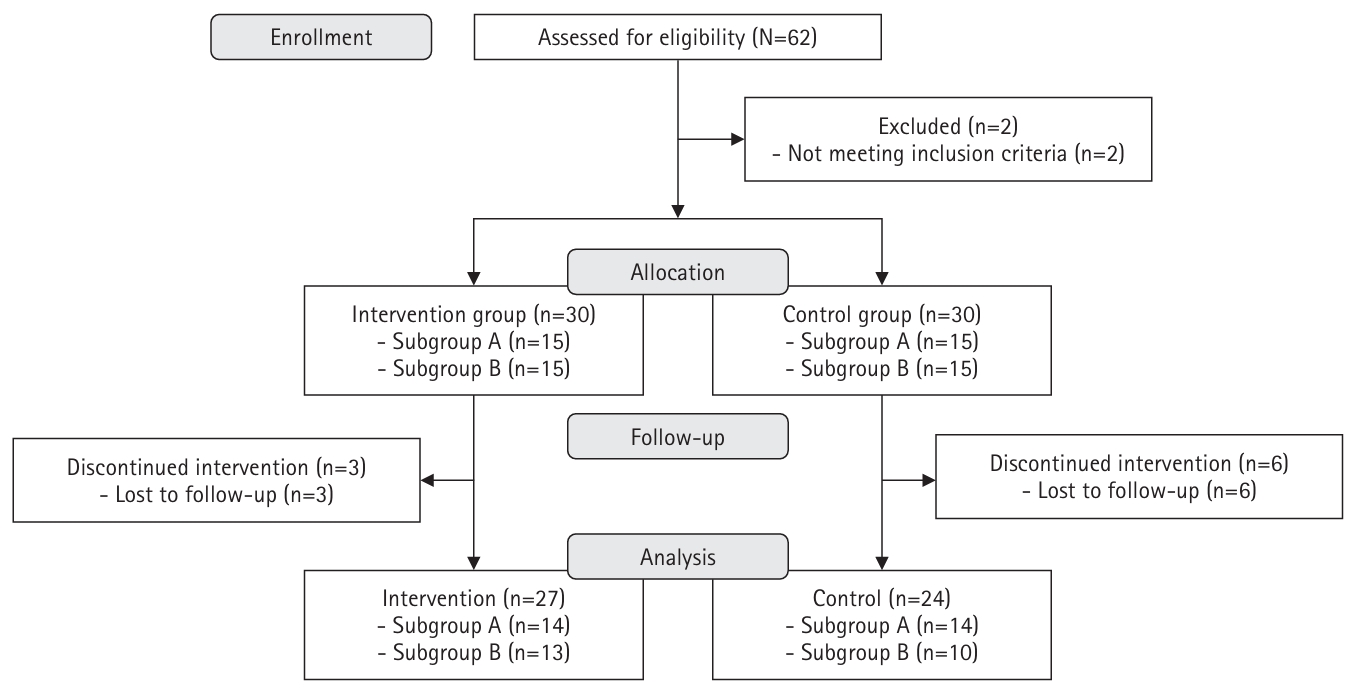
This study aimed to assess the impact of a non-face-to-face diabetes self-management program based on self-efficacy theory and focusing on health literacy.
Methods
A quasi-experimental, nonequivalent control group pre–post design was used. Participants from a community health promotion center were included if they (1) were 30–70 years of age, (2) had type 2 diabetes with glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥6.5%, and (3) had internet access via computers or mobile devices. The 8-week program was developed based on self-efficacy theory, and it included virtual education using an online platform, telephone counseling, videos, and social networking site activities considering health literacy. Fasting blood glucose levels, HbA1c levels, diabetes self-efficacy, social support, depression, and self-management behaviors were assessed. Data were analyzed using the independent t-test, paired t-test, and others.
Results
Post-test results showed that the intervention group had significantly lower fasting blood glucose levels and improved diabetes self-efficacy, social support, and self-management behaviors compared with the control group. An analysis of the pre-to-post changes in scores indicated that the intervention group had significantly greater improvements in fasting blood glucose levels, diabetes self-efficacy, and overall diabetes self-management behaviors than those observed in the control group.
Conclusion
Non-face-to-face programs based on self-efficacy theory that consider health literacy can provide effective diabetes management support to patients when in-person diabetes management at community health centers is challenging.
- 3,202 View
- 235 Download

- Structural Equation Modeling of Health Promotion Behavior on Migrant Workers: A Multi-Group Analysis Based on the Period of Residence
- Hanna Jeong, Youngsuk Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):73-92. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study developed and tested a hypothetical model of health promotion behavior on migrant workers based on the Health Promotion Model and the Health Literacy Skills Framework.
Methods
Data were collected from 298 migrant workers in 9 regions across the country from December 2020 to March 2021. The exogenous variables were e-health literacy, occupational stress, acculturation, and social support. The endogenous variables were perceived benefits of action, self-efficacy, and health promotion behavior. Data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 25.0, AMOS 20.0, and R-4.0.3 program.
Results
The model fit was appropriate. Social support had the most significant direct impact on the health promotion behavior of migrant workers. Perceived benefits of action and self-efficacy played a mediating role in the relationship among e-health literacy, social support, and health promotion behavior. Based on multi-group analysis, the migrant worker group with less than 5 years of residency had a more statistically significant effect on the relationship between perceived benefits of action and health promotion behavior than those with over 5 years.
Conclusion
Providing social support as a critical administrative strategy to enhance the health promotion behavior of migrant workers is necessary. Furthermore, when developing an intervention program utilizing the internal mechanism between social support and health promotion behavior, a self-efficacy-enhancing strategy is considered to be more effective. Additionally, educating migrant workers with short-term residence of less than 5 years about the benefits of health behaviors is essential. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing cardiovascular health behaviors among Korean-Chinese migrant workers with metabolic syndrome using mixed methods
Yu Zhu Zhang, Seon Young Hwang
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated With Physical Activity in Home‐Based Rehabilitation Patients With Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Prospective Longitudinal Study
Heng‐Ying Fang, Ying‐Hua Pan, Yi‐Heng Zhang, Yu‐Hua Deng, Xiao‐Wen Li, Lei Huang, Hui‐Ting Gu, Yue Ding, Xin‐Xin Hu, Mu Liu, Rui‐Chong Wang, MeiFen Zhang
Musculoskeletal Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Factors influencing cardiovascular health behaviors among Korean-Chinese migrant workers with metabolic syndrome using mixed methods
- 2,674 View
- 101 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Influence of Learning Presence of Non-Face-to-Face Class Experience in Nursing Students on Academic Achievement: Mediating Effect of Learning Flow and Moderated Mediation of Digital Literacy
- Eui Jeong Ryu, Keum Seong Jang, Eun A Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):278-290. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the mediating effect of learning flow and the moderated mediation effect of digital literacy on the effect of the learning presence of non-face-to-face class experience in nursing students on academic achievement.
Methods
Participants were 272 nursing students from six universities in two different cities. A self-report questionnaire was used to measure learning presence, learning flow, digital literacy, and academic achievement. Analysis was performed using SPSS 26.0 and SPSS PROCESS Macro (4.0).
Results
The mediating effect of learning flow on the effect of learning presence on academic achievement was 0.42, and the moderated mediation index of digital literacy was 0.17. Learning flow showed a mediating effect on the relationship between learning presence and academic achievement. Digital literacy had a moderated mediation effect on the relationship between learning presence and academic achievement that was mediated by learning flow.
Conclusion
The intensity of the mediating effect of nursing students’ learning presence on academic achievement through learning flow increases as the level of digital literacy increases. These results suggest that educational programs considering the level of learning presence, learning flow, and digital literacy are required to promote the academic achievement of nursing college students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Information Literacy Competencies and Associated Variables among Korean Nursing Students
Shin Hyang Kim, Jong Mi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 358. CrossRef - The influence of nursing students’ digital literacy on academic achievement in a blended learning environment: Parallel multiple mediation effects of learning presence
Ja Hyeon Ha, Eun Ju Choi
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(4): 452. CrossRef - Study on the Attitudes toward Artificial Intelligence and Digital Literacy of Dental Hygiene Students
Seon-Ju Sim, Ji-Hye Kim, Min-Hee Hong, Su-Min Hong, Myung-Jin Lee
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2024; 24(3): 171. CrossRef - The influence of e-learning digital literacy on cognitive flexibility and learning flow in nursing students
Jeongim Lee, Su Ol Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2023; 25(2): 87. CrossRef - The Impact of Self-Efficacy on Nurses’ Well-Being: Does Digital Competence Matter?
Yali Li, Qi Jing, Taiwen Feng, Xiaoling Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(4): 385. CrossRef - Relationship between learning flow and academic performance among students: a systematic evaluation and meta-analysis
Zhang Jinmin, Fang Qi
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Information Literacy Competencies and Associated Variables among Korean Nursing Students
- 2,604 View
- 184 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Assessment of Health Literacy in Breast and Cervical Cancer Screening
- Hye Sook Shin, Eunlim Chi, Hae-Ra Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):769-781. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21108
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Health literacy is a significant determinant of health and health behaviors such as cancer screening. Despite its significance, there are limited instruments available to assess health literacy targeting Koreans. The purpose of this study was to test the psychometric properties of Korean translation of a validated health literacy instrument in cancer screening—Korean version of assessment of health literacy in breast and cervical cancer screening (K-AHL-C).
Methods
A total of 555 women aged 20~65 participated in the online survey study. Of 52 items addressing five domains included in the original version, we focused on 36 items addressing three key domains closely associated with cancer screening: familiarity, health navigation, and comprehension.
Results
During content validation, two items from the health navigation domain were removed, yielding 34 items. Using Rasch analysis and confirmatory factor analysis, we found the evidence of construct validity of K-AHL-C. The Korean version was also significantly correlated with measures of Functional Health Literacy scale, cancer prevention behaviors, and subjective health status, suggesting convergent validities respectively. Finally, K-AHL-C had acceptable reliability coefficients (α) ranging from 0.71 to 0.92 for each domain and the total scale.
Conclusion
These psychometric properties support the K-AHL-C is a valid and reliable instrument for measuring Koreans’ health literacy in cancer screening. Also it is expected to use the instrument to detect breast and cervical cancer early and improve the screening rate, and ultimately to contribute to the promotion of women's health and women's health nursing practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Web-Based Delivery of an Effective Church-Based Intervention Program to Promote Cancer Screening (Community-based Health litEracy-focused intervention for breast and cervical Cancer Control) Among Korean Immigrant Women in the United States: Randomized Co
Hae-Ra Han, Yoon-Jae Lee, Deborah Min, Joyline Chepkorir, DaSol Amy Hwang, Steve Chae
JMIR Human Factors.2025; 12: e66092. CrossRef - Associations and gender differences between OHI-seeking behaviors and eHealth literacy among Chinese university students
Jie Chen, Hua Tian
Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Health Information Seeking Pathways and Factors Influencing Health Literacy Among Cancer Patients: Based on Data from the 2nd Korean Health Panel 2021
Yun-La Hur, Eun-Jeong Hong
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(3): 155. CrossRef - A Psychometric Validation of the Korean Version of Disaster Response Self-Efficacy Scale for Nursing Students
Sung Hae Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(4): 2804. CrossRef - Health literacy measures in South Korea: A scoping review
Heeran Chun, Su Hyun Kim, Eunja Park
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(4): 39. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Climate, Health, and Nursing Tool
Da Woon Jeong, Gwang Suk Kim, Min Kyung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(2): 173. CrossRef
- Web-Based Delivery of an Effective Church-Based Intervention Program to Promote Cancer Screening (Community-based Health litEracy-focused intervention for breast and cervical Cancer Control) Among Korean Immigrant Women in the United States: Randomized Co
- 2,569 View
- 49 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- The Development and Evaluation of a Health Literacy-Adapted Self-Management Intervention for Elderly Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
- Yoon Sun Kim, Young Sook Tae, Kwuy-Im Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):472-485. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.472
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to develop and evaluate the effectiveness of an adapted health literacy self-management intervention for elderly cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
Methods The intervention in this study was systematically developed through the six stages of Intervention Mapping Protocol and was based on Fransen et al's causal pathway model. A quasi-experimental trial was conducted on a total of 52 elderly patients (26 in an experimental group and 26 in a control group) undergoing chemotherapy in Korea. The intervention consisted of seven sessions over 5 weeks. The experimental tool for this study was an adapted health literacy self-management intervention, which was designed to promote a reduction in the symptom experience and distress of elderly cancer patients through the promotion of self-management behavior. To develop efficient educational materials, the participants’ health literacy was measured. To educate participants, clear communication and the teach-back method were used. In addition, for the improvement of self-efficacy, four sources were utilized. For the promotion of self-management behavior, five self-management skills were strengthened. Data were collected before and after the intervention from June 4 to September 14, 2018. The data were analyzed with SPSS/WIN 21.0.
Results Following the intervention, self-management knowledge and behavior and, self-efficacy significantly improved in experimental group. Symptom experience and distress decreased in the experimental group compared to the control group.
Conclusion The self-management intervention presented in this study was found to be effective in increasing self-management knowledge and behavior and, self-efficacy, and ultimately in reducing symptom experience and distress for elderly patients undergoing chemotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Self‐Management Education for Deaf Individuals With Hypertension: A Quasi‐Experimental Study
Gi Won Choi, Hee Jung Kim, Yujin Park, Ha Na Jeong, Sun Ju Chang
Research in Nursing & Health.2025; 48(6): 724. CrossRef - The Effect of Group Education Reflecting Unmet Needs on Knowledge of Chemotherapy for Patients and Their Families Undergoing Chemotherapy: A One Group Pre-Post Design
Seyoung Lee, Hoyoung Kim, Nayeon Kim, Misun Yi, Ayoung Lee, Seonmi Cho, Minsun Nam, Juhee Cho
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(1): 42. CrossRef - Health Information Seeking Pathways and Factors Influencing Health Literacy Among Cancer Patients: Based on Data from the 2nd Korean Health Panel 2021
Yun-La Hur, Eun-Jeong Hong
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(3): 155. CrossRef - The Effects of Chemotherapy Education Reflecting Educational Needs on Self-Care Knowledge and Performance in Female Cancer Patients: A Non-Equivalent Control Group Pretest-Posttest Design
Jin Hee Jun, Se-Na Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(3): 103. CrossRef - Effectiveness of teach‐back for chronic kidney disease patient education: A systematic review
Hemamali M. H. Jagodage, Amanda McGuire, Charrlotte Seib, Ann Bonner
Journal of Renal Care.2024; 50(2): 92. CrossRef - Effects of Telephone-based Self-care Intervention for Gynecologic Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Boyeon Lee, Hyojung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(2): 216. CrossRef - Analysis of Telephone Counseling of Patients in Chemotherapy Using Text Mining Technique
Seoyeon Kim, Jihyun Jung, Heiyoung Kang, Jeehye Bae, Kayoung Sim, Miyoung Yoo, Eunyoung, E. Suh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 46. CrossRef - Evaluating a theory-based intervention for improving eHealth literacy in older adults: a single group, pretest–posttest design
Sun Ju Chang, Kyoung-eun Lee, Eunjin Yang, Hyunju Ryu
BMC Geriatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the teach-back method among cancer patients: a systematic review of the literature
Seonhwa Choi, Jahyun Choi
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(12): 7259. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Self‐Management Education for Deaf Individuals With Hypertension: A Quasi‐Experimental Study
- 2,897 View
- 90 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref

- Association between Awareness of Nutrition Labels and Menstrual Cycle Irregularity in Korean Women: The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2010~2012)
- Hae Young Yoo, Eunjung Ryu, Ji-Su Kim, Kyung-do Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(1):133-141. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.1.133
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The aim of this study was to identify the relationship between awareness of nutrition labeling and menstrual cycle irregularity in women from a nationally representative sample of the Korean population.
Methods A cross-sectional analysis was performed using hierarchical multivariable logistic regression analysis models. A total of 4,324 women aged 19~54 years from the 2010~2012 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey participated in the study. The participants were classified into three groups based on self-report responses to a questionnaire about their awareness of nutrition labels: Reading, Not-Reading, and Not-Knowing Groups.
Results The Reading, Not-Reading, and Not-Knowing Groups comprised 46.4%, 44.9%, and 8.7% of the participants, respectively, and 53.6% of the participants had never used nutrition labels. In the Not-Knowing Group, irregular menstrual cycles for more than 3 months were significantly more common than women with irregular menstrual cycles for up to 3 months and women with regular menstrual cycles. Women in the Not-Knowing Group were more likely to exhibit menstrual cycle irregularity (adjusted odds ratio: 1.63, 95% confidence interval: 1.10~2.41) compared to women in the Reading Group after adjusting for age, body mass index, smoking status, alcohol intake, exercise regularity, stress, depression, suicidal ideation, metabolic syndrome, age at menarche, parity, and use of oral contraceptives.
Conclusion No awareness of nutrition labeling appears to be associated with a higher prevalence of menstrual cycle irregularity in a nationally representative group of Korean women.
- 1,149 View
- 12 Download

- Psychometric Properties of the Alzheimer's Disease Knowledge Scale-Korean Version
- Eun Joo Kim, Ji-young Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(1):107-117. Published online February 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.107
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the psychometric properties of the Korean version of the Alzheimer's Disease Knowledge Scale (ADKS-K) to determine its applicability to Korean adults.
Methods Cross-cultural validity was performed according to Consensus-based Standards for the Selection of Health Measurement Instruments (COSMIN). The Kuder-Richardson Formula 20 for internal consistency and Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) for test-retest reliability were conducted. Content validity, criterion related validity and construct validity were evaluated. The Classical Test Theory (CTT) model and the Item Response Theory (IRT) model were applied in performing the item analysis.
Results The KR 20 was .71, and the ICC was .90, indicating that the ADKS-K has internal consistency and stability reliability. Thirty items of the ADKS-K had significant Content Validity Ratio (CVR) values, i.e., mean of 0.82 and range of 0.60~1.00. Mean item difficulty and discrimination indices calculated by TestAn program were 0.63 and 0.23, respectively. Mean item difficulty and discrimination indices calculated by BayesiAn program were -0.60 and 0.77, respectively. These tests indicate that ADKS-K has an acceptable level of difficulty and discriminating efficiency.
Conclusion Results suggest that ADKS-K has the potential to be a proper instrument for assessing AD knowledge in Korean adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expanding the health belief model on dementia knowledge, fear, and preventive behaviors among older adults in Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive study
Jeong Eui Yun, Suyoung Choi
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(1): 60. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of the Alzheimer's Disease Knowledge Scale in Ecuadorian university students
José Alejandro Valdevila Figueira, Andrés Ramírez, María Alejandra Espinosa de los Monteros, Rocío Valdevila Santiesteban, Indira Dayana Carvajal Parra, Lilia Romero-Sacoto, María José Pico Cucalón
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Mediating Role of Attitudes Towards Dementia on the Relationship Between Dementia Knowledge and Behaviors Towards Persons with Dementia: A Cross-Sectional Study
Yang-Tzu Li, Jing-Xuan Bai, Jia-Ming He, Shao-Wei Yang, Hsiu-Li Huang
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2023; Volume 16: 4213. CrossRef - Alzheimer’s disease (AD) knowledge in Korean Americans: identifying knowledge gaps and misconceptions and examining predictors of AD knowledge
Sang E. Lee, Michin Hong, Banghwa L. Casado
Ethnicity & Health.2023; 28(3): 431. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Assessment of Health Literacy in Breast and Cervical Cancer Screening
Hye Sook Shin, Eunlim Chi, Hae-Ra Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(6): 769. CrossRef - Quantifying Knowledge of Alzheimer’s Disease: An Analysis of the Psychometric Properties of the Alzheimer’s Disease Knowledge Scale
Guillermo Garcia-Ribas, Elena García-Arcelay, Alonso Montoya, Jorge Maurino, Javier Ballesteros
Neurology and Therapy.2021; 10(1): 213. CrossRef - The Impact of Dementia Knowledge and Attitude on Caregiving Appraisal among Caregivers of Older Adults with Dementia Using Dementia Care Centers
Ji Yeon Hong, Dukyoo Jung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2020; 22(4): 348. CrossRef - Development of Knowledge and Attitudes Survey on Pain Management for Korean Long-term Care Professionals
So-Hi Kwon, Hyunsim Kim, Seurk Park, Wooseok Jeon
Asian Nursing Research.2020; 14(2): 105. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Korean version of the Pain in Older Adults Knowledge Survey (K-POAKS) among Nurses Who Have Worked in Long-term Care Hospitals
Young Seun Ryu, Jeong Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(2): 130. CrossRef - Validation of the Spanish Version of the Dementia Knowledge Assessment Tool 2
Laura Parra-Anguita, Sara Moreno-Cámara, María Dolores López-Franco, Pedro L. Pancorbo-Hidalgo, Alden Gross
Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.2018; 65(4): 1175. CrossRef - Knowledge and Attitudes in Alzheimer’s Disease in a Cohort of Older African Americans and Caucasians
J. Christina Howell, Oretunlewa Soyinka, Monica Parker, Thomas L. Jarrett, David L. Roberts, Cornelya D. Dorbin, William T. Hu
American Journal of Alzheimer's Disease & Other Dementias®.2016; 31(4): 361. CrossRef - Knowledge about dementia in South Korean nursing students: a cross-sectional survey
Jung Ha Shin, Hyun-Ju Seo, Kye Ha Kim, Kyoung-Hoon Kim, Youngjin Lee
BMC Nursing.2015;[Epub] CrossRef
- Expanding the health belief model on dementia knowledge, fear, and preventive behaviors among older adults in Korea: a cross-sectional descriptive study
- 1,316 View
- 22 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Health Literacy and Health Status of Korean-Chinese Elderly People Living in Yanbian, China
- Chun Yu Li, Ogcheol Lee, Gi Soo Shin, Xian Wen Li
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(3):386-392. Published online June 29, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.3.386
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This descriptive study was done to identify the relationship between health literacy and health status and to provide basic data for developing nursing interventions for Korean-Chinese elders living in Yanbian, China.
Methods For data collection, intentional sampling of 300 elders was used. The questionnaire was composed of 5 items based on "Ministry of Health, the People's Republic of China (2008)" to measure health literacy, 33 health status items from the "Korean Health Status Measure for Elderly People" developed by Shin (2002), revised for use in China, and 9 general characteristics. Data were analyzed using SPSS Win 13.0 program.
Results Total level of health literacy was relatively high (68.7%). Elders had high scores for taking medicines according to doctor's instruction, but lower ones for full comprehension through communication with doctors. Health status was high for emotional, physical, and social function in that order. There were significant differences between general characteristics and health status for gender, age, marital status, education, family, smoking, and alcohol consumption in that order. Results of multiple regression analysis for factors influencing health status showed that self-report health level was the most influential, followed by health literacy, age, gender.
Conclusion Health literacy is the main factor affecting health promotion among minority elders indicating a need to develop health promotion programs for elders who have low health literacy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Parents' Oral Health Literacy on Their Own and Their Children's Oral Health in Chinese Population
Yu Wang, Marita R. Inglehart, Chao Yuan
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with health literacy among older adults: Results of the HLS-EU-Q16 measure
Heeran Chun, Ju Yul Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2020; 37(1): 1. CrossRef - Food Literacy in South Korea: Operational Definition and Measurement Issues
Dahyun Park, Min-Jeong Shin, Sunmi Song
Clinical Nutrition Research.2019; 8(2): 79. CrossRef - Survey of health literacy level and related influencing factors in military college students in Chongqing, China: A cross-sectional analysis
Honghui Rong, Xin Cheng, Jose M. Garcia, Ling Zhang, Lu Lu, Jian Fang, Mingshan Le, Peng Hu, Xinlu Dong, Junli Yang, Ya Wang, Ting Luo, Jun Liu, Ji-an Chen, Noora Hirvonen
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(5): e0177776. CrossRef - Barriers, Attitudes, and Dietary Behaviors Regarding Sodium Reduction in the Elderly Korean-Chinese Population in Yanbian, China
Jounghee Lee, Wenying Cui, Meixiang Jin
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2017; 8(3): 185. CrossRef - Letramento funcional em saúde na perspectiva da Enfermagem Gerontológica: revisão integrativa da literatura
Maria Izabel Penha de Oliveira Santos, Marilene Rodrigues Portella, Helenice de Moura Scortegagna, Paulo Cassiano Simor dos Santos
Revista Brasileira de Geriatria e Gerontologia.2015; 18(3): 651. CrossRef - Health literacy in Mainland China: Validation of a functional health literacy test in simplified Chinese
S. Mantwill, P. J. Schulz
Health Promotion International.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study on Relationships between Health Literacy, Disease-related Knowledge and Compliance to Medical Recommendations in Patients with Hypertension
Myung Soon Kwon, Ghee-Young Noh, Ji Hye Jang
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2013; 27(1): 190. CrossRef - A cross-sectional study on oral health literacy and its influencing factors among adults: II. Functional oral health literacy
Hyun-Jeong Ju, Hyo-Won Oh, Heung-Soo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2013; 37(2): 81. CrossRef - Health Literacy: An Evolutionary Concept Analysis
Sungeun Kim, Jina Oh, Yunmi Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(4): 558. CrossRef - Health Literacy and Multicultural Populations
Mercedes Benitez McCrary, Eva Jackson Hester
Perspectives on Communication Disorders and Sciences in Culturally and Linguistically Diverse (CLD) Populations.2011; 18(3): 79. CrossRef - Exercise Performance and Exercise-related Factors of Korean and Korean-Chinese Nursing Students: A comparative Study
Young-Ran Lee, Sun-Nam Park, Sook-Ja Yu, Jung-Soon Moon
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2011; 22(3): 234. CrossRef - Commentary: Response regarding the commentary of van der Ploeg W. Assessment and measurement of health literacy: An integrative review of the literature. Nursing & Health Sciences 2010; 12: 145-146
Josephine M. Mancuso
Nursing & Health Sciences.2010; 12(3): 304. CrossRef
- Impact of Parents' Oral Health Literacy on Their Own and Their Children's Oral Health in Chinese Population
- 1,166 View
- 5 Download
- 13 Crossref

- The Influence of Functional Literacy on Perceived Health Status in Korean Older Adults
- Su Hyun Kim, Eunjoo Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(2):195-203. Published online April 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.2.195
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to understand the level of functional health literacy and its influence on perceived health status in Korean older adults.
Methods A cross-sectional survey was conducted in Daegu, Kyungpook and Busan province. A total of 103 older adults aged 65 yr or older were interviewed in person between July 1 to August 30, 2007.
Results A high proportion of older adults were unable to read and understand written basic medical instructions. Only 40-50% were able to comprehend directions for taking medication four times a day or on an empty stomach. Only 11-38% were able to understand information regarding treatment procedure, informed consent, or educational material for elderly fall prevention. Individuals who were older, single, and had less education and income were more likely to have lower functional health literacy. After adjusting for sociodemographic variables, individuals with lower health literacy had poorly perceived health status.
Conclusion Many Korean older adults have a very low level of fuctional literacy. Low health literacy was independently associated with poorly perceived health status.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Sexuality Education During Pregnancy on Female Sexual Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study
Güleser Ada, Yasemin Hamlacı Başkaya, Kevser İlçioğlu
International Journal of Sexual Health.2025; 37(1): 116. CrossRef - Hospitalization experience of elderly surgical patients: A phenomenological study
Yujeong Shin, Dukyoo Jung, Hyunjoo Oh
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(1): 84. CrossRef - Patterns of health literacy and influencing factors differ by age: a cross-sectional study
Da Hae Kwon, Young Dae Kwon
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of self-management behaviors among patients undergoing hemodialysis
Yusun Park, Sunyoung Jung
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - eHealth Literacy and Its Outcomes Among Postsecondary Students: Systematic Review
Qin Li, Fang Fang, Yan Zhang, Jiayuan Tu, Pingting Zhu, Lijuan Xi
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2025; 27: e64489. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Self‐Management Education for Deaf Individuals With Hypertension: A Quasi‐Experimental Study
Gi Won Choi, Hee Jung Kim, Yujin Park, Ha Na Jeong, Sun Ju Chang
Research in Nursing & Health.2025; 48(6): 724. CrossRef - Examining the relationships between e-health literacy, cyberchondria, health anxiety, and health perception among foreign university students
Harun Aslan, Gülsüm Şeyma Koca
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of 8-item Health Literacy Assessment Tool (K-HLAT-8)
Mirae Jo, Eun-mi Kwak
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2024; 35: 351. CrossRef - Current Status of Informed Consent Form for Acupotomy in Korean Medicine Hospitals and Development of a Standard Informed Consent Form Using Delphi Method
Jihun Kim, Bonhyuk Goo, Hyongjun Kim, Kyoungsuk Seo, Myungjin Oh, Myungseok Ryu, Sang-Hoon Yoon, Kwang Ho Lee, Hyun-Jong Lee, Jungtae Leem, Hyungsun Jun, Ihn Sook Jeong, Sung Woon Choi, Tae Wook Lee, Yeonhak Kim, Yoona Oh, Kunhyung Kim, Gi Young Yang, Eun
Journal of Korean Medicine.2024; 45(1): 180. CrossRef - Mental Health Literacy Levels and General Health Perceptions of Faculty of Health Sciences Students
Meryem TURGUT, Münevver ERYALÇIN, Gamze KUTLU
Psikiyatride Güncel Yaklaşımlar.2023; 15(Supplement): 203. CrossRef - Hospital Pharmacists’ Patient-Centered Communication, Trust, and Satisfaction: Patients’ Perceptions and Opinions
Hye Kyung Jin, Sung Yun Suh, Sung Hwan Kim, A Jeong Kim, Hyun Jeong Kim, Nigh Choi, Jeong Yun Choi, Hayeon Lee, Jiseung Hong, Oksang Lee, Hyeri Oh, Ah Young Jeon, Gahyun Kim, Jihyeon Do, Yumi Lee, Yoon Sook Cho
Journal of Korean Society of Health-System Pharmacists.2023; 40(4): 387. CrossRef - Understanding health literacy of deaf persons with hypertension in South Korea: A cross-sectional study
Gi Won Choi, Sun Ju Chang, Hee Jung Kim, Ha Na Jeong, Pracheth Raghuveer
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(11): e0294765. CrossRef - Usefulness Analysis of Public PHR Information Service
Minji Kim, Minji Kim, Minhyuk Kim, Minhyuk Kim, Byungkeun Oh, Byungkeun Oh
Archives of Design Research.2023; 36(2): 303. CrossRef - Usability of a new digital walking program for older adults: a pilot study
Jisan Lee, Hyeongju Ryu
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Health Literacy and Health Promoting Behavior (Eating Habits, Physical Activity, and Stress) of University Students
Yoon-Sun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(2): 94. CrossRef - Relationship between Health Literacy and Knowledge, Compliance with Bowel Preparation, and Bowel Cleanliness in Older Patients Undergoing Colonoscopy
Minju Gwag, Jaeyong Yoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(5): 2676. CrossRef - The Effects of Digital Literacy and Health Empowerment on Elders' Communication with Doctors: Focusing on Moderating Effect of Health Beliefs
Soontae An, Yujin Lim, Soondool Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(1): 53. CrossRef - A Study on the Reliability and Validity of the Korean Health Literacy Instrument for Late School-Aged Children
Sook-Kyoung Park, Eun-Gyeong Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(19): 10304. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Assessment of Health Literacy in Breast and Cervical Cancer Screening
Hye Sook Shin, Eunlim Chi, Hae-Ra Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(6): 769. CrossRef - Influence of Health Literacy and Insight on Medication Adherence in Mental Illness
Moonhee Gang, Seonhee Kim, Mi-Ae Ahn
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2021; 30(1): 9. CrossRef - Health literacy, health perception and related factors among different ethnic groups: a cross-sectional study in southeastern Turkey
Gülhan Yiğitalp, Vasfiye Bayram Değer, Sema Çifçi
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between Health Literacy and Self-care Behavior in Patients with Stomach Cancer after Gastrectomy: Mediating Effects of Subjective Health Status and Specific Self-efficacy
Min Jung Kim, Yong Soon Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 259. CrossRef - Health Literacy and Related Factors Depending on Socioeconomic Status
Yoon Jin Oh, Ki Hyun Park
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2021; 11(4): 280. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Korean version of Short-Form Health Literacy Scale for Adults
Young Joo Seo, Eun-Mi Kwak, Mirae Jo, A-Ra Ko, Soon Hwan Kim, Heeyoung Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(4): 416. CrossRef - Development and validation of a nutrition literacy assessment tool for young adults
Seokyoung Ahn, Bogyeong Kim, Mihyang Um, Yookyung Park, Seunghee Kye
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(2): 175. CrossRef - How to Improve Patient Safety Literacy?
Yoon-Sook Kim, Hyun Ah Kim, Moon-Sook Kim, Hyuo Sun Kim, Mi Jeong Kwak, Jahae Chun, Jee-In Hwang, Hyeran Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(19): 7308. CrossRef - Health Literacy, Knowledge and Self-care Behaviors in Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis Living in Community
Seo Hui Yang, Eun Young Jung, Yang Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparing two health literacy measurements used for assessing older adults’ medication adherence
Min‐Sun Song, Soohyun Park
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2020; 29(21-22): 4313. CrossRef - Food Literacy in South Korea: Operational Definition and Measurement Issues
Dahyun Park, Min-Jeong Shin, Sunmi Song
Clinical Nutrition Research.2019; 8(2): 79. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Health Literacy for Patients with Cardiovascular Disease using Hybrid Model
Jeong Eun Sim, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(4): 494. CrossRef - Medication Adherence and Its Association with Health Literacy and Performance in Activities of Daily Livings among Elderly Hypertensive Patients in Islamabad, Pakistan
Muhammad Saqlain, Asad Riaz, Muhammad Naeem Malik, Salman Khan, Ali Ahmed, Sohail Kamran, Hussain Ali
Medicina.2019; 55(5): 163. CrossRef - Effects of Diabetic Foot Care Education for the Aged with Low Health Literacy
Hyemin Kim, Ji Min Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(4): 560. CrossRef - Impact of Health Literacy on Hypertension Control of Elderly Women Patients Receiving Home Visiting Health Care Services
Hwa Bae, Nam-Soo Hong, Eun-Kyoung Shin
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2019; 44(3): 237. CrossRef - Predictors of Smartphone Uses for Health Information Seeking in the Korean Elderly
Young Sam Oh, Eun Young Choi, Young Sun Kim
Social Work in Public Health.2018; 33(1): 43. CrossRef - The effects of medication adherence and health literacy on health‐related quality of life in older people with hypertension
Nam Hee Park, Mi Sook Song, So Young Shin, Ji‐hye Jeong, Hyo Young Lee
International Journal of Older People Nursing.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Justificatory Information Forefending in Digital Age: Self-Sealing Informational Conviction of Risky Health Behavior
Jeong-Nam Kim, Yu Won Oh, Arunima Krishna
Health Communication.2018; 33(1): 85. CrossRef - Age Differences in Health Literacy: Do Younger Korean Adults Have a Higher Level of Health Literacy than Older Korean Adults?
Eun Jin Lee, Hee Yun Lee, Soondool Chung
Health & Social Work.2017; 42(3): 133. CrossRef - Validation of the short version of Korean functional Health Literacy Test
Su Hyun Kim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of a Health Literacy–Considered Diabetes Self-Management Program for Older Adults in South Korea
Soo Jin Lee, Misoon Song, Eun-Ok Im
Research in Gerontological Nursing.2017; 10(5): 215. CrossRef - Developing and Evaluating a Drug Information Leaflet of Antidiabetics for Senior Citizens; Employing Performance-based User-testing
Jin Kim, Haeri Shim, Iyn-Hyang Lee
Korean Journal of Clinical Pharmacy.2017; 27(3): 171. CrossRef - Differences between Nurses and Patients' Perception of Nurses' Communication Skills
Soonjoo Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(2): 166. CrossRef - Health Literacy and Its Related Factors in North Korean Refugees
Youn Jung Son, Hyun Joon Kim, Hye Jin Jeong, In Young Hwang, Moo Young Kim, Soo Hyoung Lee, Ki Hyun Park, Kee Ho Park, Chae Bong Kim, Hyang Im, Ji Young Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2017; 17(2): 71. CrossRef - Health Empowerment of Older Adults with High-risk of Cardio-cerebrovascular Diseases
HyoJin Son, Gwang Suk Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2017; 28(4): 410. CrossRef - Health Literacy and Health Promoting Behaviors in adolescents
Ji Young Kim, Min Hyun Suk
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(3): 570. CrossRef - Different Use of Hypertension-related Vocabulary in Patients with Hypertension and Public Health Nurses
Myo-Sung Kim, Ihn-Sook Jeong
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2016; 22(1): 41. CrossRef - Development of test for Korean functional health literacy in dentistry
Hyun-Kyung Kim, Hie-Jin Noh, Im-Hee Jung, Won-Gyun Chung, Yun Lee, So-Jung Mun, Hyun-Sun Jeon, Sun-Young Han, Eun-Hee Choi, Jun-Sung Ki, Min-Ji Koo, Ju-Hui Jeong
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2016; 16(3): 355. CrossRef - Health literacy and barriers to health information seeking: A nationwide survey in South Korea
Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyung Kim
Patient Education and Counseling.2016; 99(11): 1880. CrossRef - Effects of Health Literacy and Knowledge on Diabetic Self-care in the Elderly with DM Living Alone
Nan Hui Kim, Youngran Yang, Myung Ha Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 370. CrossRef - Health Literacy and Health Behavior Compliance in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Eun-Young Jung, Sun-Kyung Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(3): 251. CrossRef - Development of a Health Literacy Assessment Scale for Asian Immigrant Women in South Korea
Jisook An, Sook Ja Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(4): 330. CrossRef - Evidence-based health literacy improvements: trends on health literacy studies in Korea
Soo Jin Kang, Mi Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2015; 32(4): 93. CrossRef - Simplification improves understanding of informed consent information in clinical trials regardless of health literacy level
Eun Jin Kim, Su Hyun Kim
Clinical Trials.2015; 12(3): 232. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Health Literacy Among Korean Adults
Hee Yun Lee, Jiwoo Lee, Nam Keol Kim
American Journal of Men's Health.2015; 9(5): 370. CrossRef - Efficacy of Chronic Disease Self-management Program in Older Korean Adults with Low and High Health Literacy
Su Hyun Kim, Chang Ho Youn
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(1): 42. CrossRef - The influence of functional health literacy on health promotion behavior
Ji Eun Lee, Seo Young Lee, Hyun Kyung Noh, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2015; 26(6): 1427. CrossRef - Association among ageing‐related stereotypic beliefs, self‐efficacy and health‐promoting behaviors in elderly Korean adults
Hyun‐E Yeom
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2014; 23(9-10): 1365. CrossRef - Extraction of Hypertension-related Consumer Vocabulary and Mediator Vocabulary and Selection of Recommended Vocabulary
Myo Sung Kim, Ihn Sook Jeong
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(5): 13. CrossRef - Risk Factors of Colorectal Polyps in Jeju Island
Yeoun Ja Na, Mira Um, Mi Hee Kong, Hyeon Ju Kim
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2014; 14(4): 141. CrossRef - A Study on Structural Relationship Among Perceived Interactivity and User Related Variables in Health Information Websites
Jaewoo Nam, Taeyoun Park
Journal of the Korean Society for information Management.2014; 31(4): 103. CrossRef - The Influence of Health Literacy and Diabetes Knowledge on Diabetes Self-care Activities in Korean Low-income Elders with Diabetes
Jihye Jeong, Namhee Park, So Young Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(3): 217. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Oral Health Literacy related Factors among Elderly People
Kyu Eun Lee, Young-Hee Yom, Sang Suk Kim, Jung Hee Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(1): 54. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of the Korean Health Literacy Instrument
Soo Jin Kang, Tae Wha Lee, Michael K. Paasche-Orlow, Gwang Suk Kim, Hee Kwan Won
Journal of Health Communication.2014; 19(sup2): 254. CrossRef - Health Literacy, Health Risk Perception and Health Behavior of Elders
Jeong Hee Jeong, Jung Soon Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(1): 65. CrossRef - Health Literacy of Elementary School Students.
Eun Jung Ahn, In Soo Kwon
Child Health Nursing Research.2014; 20(4): 322. CrossRef - Factors Related to Perceived Health Status in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Ang Li Won, Seung Hyun Yoo, Myoung Soon You
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(3): 1. CrossRef - Health Literacy: An Evolutionary Concept Analysis
Sungeun Kim, Jina Oh, Yunmi Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(4): 558. CrossRef - Evaluation on validity of health literacy measurement scale
Kyounh-Ho Choi, Jeong-Ok Lee
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2013; 24(2): 257. CrossRef - A cross-sectional study on oral health literacy and its influencing factors among adults: II. Functional oral health literacy
Hyun-Jeong Ju, Hyo-Won Oh, Heung-Soo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2013; 37(2): 81. CrossRef - Impact of Health Literacy on Disease-related Knowledge and Adherence to Self-care in Patients with Hypertension
Youn-Jung Son, Eun-Kyeung Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(1): 6. CrossRef - Health Literacy of Inpatients at General Hospital
In Hwa Hong, Young Eun
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(5): 477. CrossRef - Influencing Factors on Functional Health Literacy among the Rural Elderly
Ji Yeon Park, Kyung Ja June
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2011; 22(1): 75. CrossRef - Concern in and Utilization of the Mass Media Health Information in Community-dwelling Elderly
Hye-Jung Kim, Hee-Kyung Joh, Hyeok-Kyu Kwon, Hyun-Jin Do, Seung-Won Oh, Youl-Lee Lym, Jae-Kyung Choi, Hyuk-Jung Kweon, Dong-Yung Cho
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2009; 30(6): 426. CrossRef - Health literacy and functional health status in Korean older adults
Su Hyun Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2009; 18(16): 2337. CrossRef - Testing health literacy skills in older Korean adults
Tae Wha Lee, Soo Jin Kang, Han Joo Lee, Soo In Hyun
Patient Education and Counseling.2009; 75(3): 302. CrossRef
- The Effect of Sexuality Education During Pregnancy on Female Sexual Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study
- 1,635 View
- 45 Download
- 74 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


