Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 38(2); 2008 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Influence of Functional Literacy on Perceived Health Status in Korean Older Adults
- Su Hyun Kim, Eunjoo Lee
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(2):195-203.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.2.195
Published online: April 30, 2008
1Assistant Professor, College of Nursing, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
2Associate Professor, College of Nursing, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kim, Su Hyun. College of Nursing, Kyungpook National University, 101 Dongin-dong 2ga, Jung-gu, Daegu 700-422, Korea. Tel: 82-53-420-4928, Fax: 82-53-421-2758, suhyun_kim@knu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2008 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to understand the level of functional health literacy and its influence on perceived health status in Korean older adults.
-
Methods
- A cross-sectional survey was conducted in Daegu, Kyungpook and Busan province. A total of 103 older adults aged 65 yr or older were interviewed in person between July 1 to August 30, 2007.
-
Results
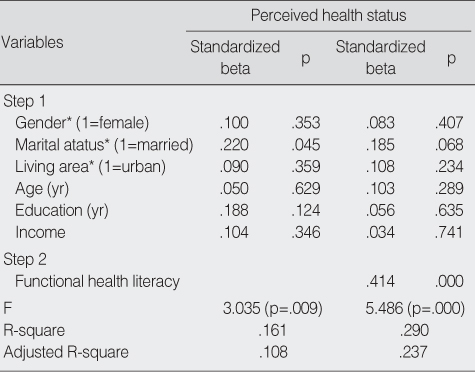
- A high proportion of older adults were unable to read and understand written basic medical instructions. Only 40-50% were able to comprehend directions for taking medication four times a day or on an empty stomach. Only 11-38% were able to understand information regarding treatment procedure, informed consent, or educational material for elderly fall prevention. Individuals who were older, single, and had less education and income were more likely to have lower functional health literacy. After adjusting for sociodemographic variables, individuals with lower health literacy had poorly perceived health status.
-
Conclusion
- Many Korean older adults have a very low level of fuctional literacy. Low health literacy was independently associated with poorly perceived health status.
- 1. Ad Hoc Committee on Health Literacy for the Council on Scientific Affairs, American Medical Association. Health literacy: Report of the council on scientific affairs. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 1999;281:552–557.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Amella EJ. Presentation of illness in older adults. The American Journal of Nursing. 2004;104(10):40–52.Article
- 3. Andrus MR, Roth MT. Health literacy: A review. Pharmacotherapy. 2002;22:282–302.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Baker DW, Williams MV, Parker RM, Gazmararian JA, Nurss J. Development of a brief test to measure functional health literacy. Patient Education and Counseling. 1999;38:33–42.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Billek-Sawhney B, Reicherter EA. Literacy and the older adult: Educational considerations for health professionals. Topics in Geriatric Rehabilitation. 2005;21:275–281.Article
- 6. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 1988;2nd ed. New Jersey, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- 7. Cutilli CC. Do your patients understand? Determining your patients' health literacy skills. Orthopedic Nursing. 2005;24:372–377.PubMed
- 8. Dewalt DA, Pignone MP. The role of literacy in health and health care. American Family Physician. 2005;5:783–790.
- 9. Dewalt DA, Berkman ND, Sheridan S, Lohr KN, Pignone MP. Literacy and health outcomes: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 2004;19:1228–1239.PubMedPMC
- 10. Faul F. G*Power version 3.0.5. 2006;Germany, Universitat Kiel.
- 11. Ferrini AF, Ferrini PL. Health in the later years. 2000;3rd ed. Boston, McGraw-Hill Higher Education.
- 12. Gazmaraian JA, Baker DW, Williams MV, Parker RM, Scott TL, Green DC, et al. Health literacy among medicare enrollees in a managed care organization. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 1999;281:545–551.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Population projections for Korea. Korea National Statistical Office. 2007;;Retrieved September 1, 2007. from http://www.nso.go.kr.
- 14. Health Industry Development Institute. Educational material for tailored home visiting service.. 2007.
- 15. The study on the status of health and living in Korean older adults. Ministry of Health and Welfare. 2004;Retrieved April 2, 2006. from http://www.mohw.go.kr/index.jsp.
- 16. Nurss JR, Parker RM, Baker DW. Test of functional health literacy in adults. 2001;NC, Peppercorn Books & Press Inc.
- 17. Parker RM, Baker DW, Williams MV, Nurss JR. The test of functional health literacy in adults: A new instrument for measuring patients' literacy skills . Journal of General Internal Medicine. 1995;10:537–541.PubMed
- 18. Schloman BF. Health literacy: A key ingredient for managing personal health. Online Journal of Issues on Nursing. 2004;9(2):14–21.
- 19. The health literacy of America's adults: Results from the 2003 national assessment of adult literacy. U.S. Department of Education. 2006;Retrieved April 4, 2006. from http://www.edpubs.org.
- 20. Weiss BD, Hart G, McGee DL, D'Estelle S. Health status of illiterate adults: Relation between literacy and health status among persons with low literacy skills. The Journal of the American Board of Family Practice. 1992;5:257–264.PubMed
- 21. Williams MV, Parker RM, Baker DW, Parikh NS, Pitkin K, Coates WC, et al. Inadequate functional health literacy among patients at two public hospitals. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 1995;274:1677–1682.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Wolf MS, Gazmararian JA, Baker DW. Health literacy and functional health status among older adults. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2005;165:1946–1952.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
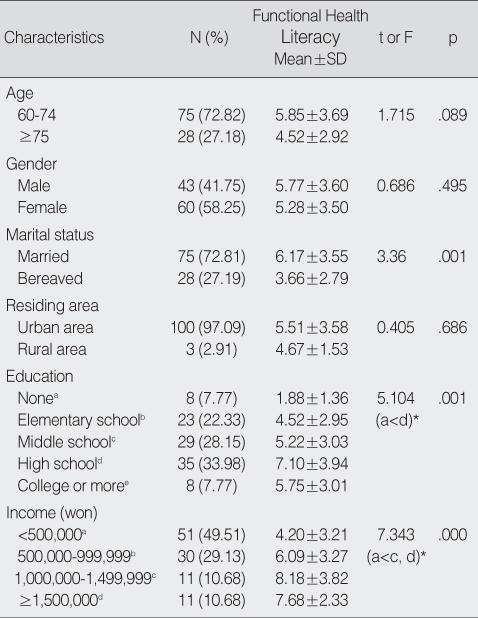
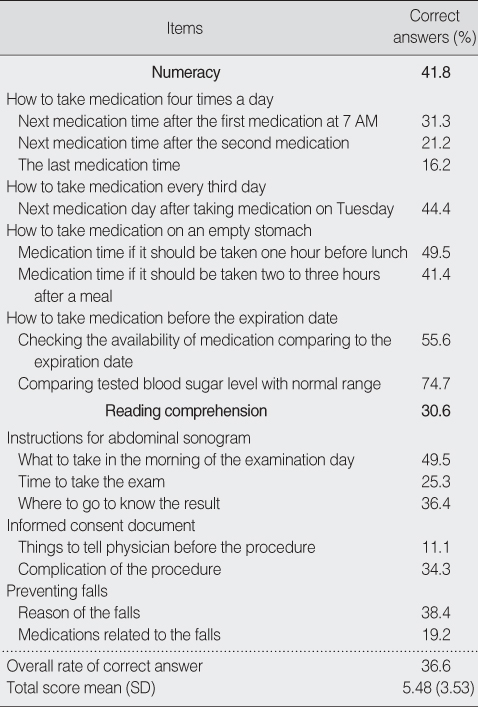
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- The Effect of Sexuality Education During Pregnancy on Female Sexual Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study
Güleser Ada, Yasemin Hamlacı Başkaya, Kevser İlçioğlu
International Journal of Sexual Health.2025; 37(1): 116. CrossRef - Hospitalization experience of elderly surgical patients: A phenomenological study
Yujeong Shin, Dukyoo Jung, Hyunjoo Oh
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(1): 84. CrossRef - Patterns of health literacy and influencing factors differ by age: a cross-sectional study
Da Hae Kwon, Young Dae Kwon
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of self-management behaviors among patients undergoing hemodialysis
Yusun Park, Sunyoung Jung
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - eHealth Literacy and Its Outcomes Among Postsecondary Students: Systematic Review
Qin Li, Fang Fang, Yan Zhang, Jiayuan Tu, Pingting Zhu, Lijuan Xi
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2025; 27: e64489. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Self‐Management Education for Deaf Individuals With Hypertension: A Quasi‐Experimental Study
Gi Won Choi, Hee Jung Kim, Yujin Park, Ha Na Jeong, Sun Ju Chang
Research in Nursing & Health.2025; 48(6): 724. CrossRef - Examining the relationships between e-health literacy, cyberchondria, health anxiety, and health perception among foreign university students
Harun Aslan, Gülsüm Şeyma Koca
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of 8-item Health Literacy Assessment Tool (K-HLAT-8)
Mirae Jo, Eun-mi Kwak
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2024; 35: 351. CrossRef - Current Status of Informed Consent Form for Acupotomy in Korean Medicine Hospitals and Development of a Standard Informed Consent Form Using Delphi Method
Jihun Kim, Bonhyuk Goo, Hyongjun Kim, Kyoungsuk Seo, Myungjin Oh, Myungseok Ryu, Sang-Hoon Yoon, Kwang Ho Lee, Hyun-Jong Lee, Jungtae Leem, Hyungsun Jun, Ihn Sook Jeong, Sung Woon Choi, Tae Wook Lee, Yeonhak Kim, Yoona Oh, Kunhyung Kim, Gi Young Yang, Eun
Journal of Korean Medicine.2024; 45(1): 180. CrossRef - Mental Health Literacy Levels and General Health Perceptions of Faculty of Health Sciences Students
Meryem TURGUT, Münevver ERYALÇIN, Gamze KUTLU
Psikiyatride Güncel Yaklaşımlar.2023; 15(Supplement): 203. CrossRef - Hospital Pharmacists’ Patient-Centered Communication, Trust, and Satisfaction: Patients’ Perceptions and Opinions
Hye Kyung Jin, Sung Yun Suh, Sung Hwan Kim, A Jeong Kim, Hyun Jeong Kim, Nigh Choi, Jeong Yun Choi, Hayeon Lee, Jiseung Hong, Oksang Lee, Hyeri Oh, Ah Young Jeon, Gahyun Kim, Jihyeon Do, Yumi Lee, Yoon Sook Cho
Journal of Korean Society of Health-System Pharmacists.2023; 40(4): 387. CrossRef - Understanding health literacy of deaf persons with hypertension in South Korea: A cross-sectional study
Gi Won Choi, Sun Ju Chang, Hee Jung Kim, Ha Na Jeong, Pracheth Raghuveer
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(11): e0294765. CrossRef - Usefulness Analysis of Public PHR Information Service
Minji Kim, Minji Kim, Minhyuk Kim, Minhyuk Kim, Byungkeun Oh, Byungkeun Oh
Archives of Design Research.2023; 36(2): 303. CrossRef - Usability of a new digital walking program for older adults: a pilot study
Jisan Lee, Hyeongju Ryu
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Health Literacy and Health Promoting Behavior (Eating Habits, Physical Activity, and Stress) of University Students
Yoon-Sun Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(2): 94. CrossRef - Relationship between Health Literacy and Knowledge, Compliance with Bowel Preparation, and Bowel Cleanliness in Older Patients Undergoing Colonoscopy
Minju Gwag, Jaeyong Yoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(5): 2676. CrossRef - The Effects of Digital Literacy and Health Empowerment on Elders' Communication with Doctors: Focusing on Moderating Effect of Health Beliefs
Soontae An, Yujin Lim, Soondool Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(1): 53. CrossRef - A Study on the Reliability and Validity of the Korean Health Literacy Instrument for Late School-Aged Children
Sook-Kyoung Park, Eun-Gyeong Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(19): 10304. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of Assessment of Health Literacy in Breast and Cervical Cancer Screening
Hye Sook Shin, Eunlim Chi, Hae-Ra Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(6): 769. CrossRef - Influence of Health Literacy and Insight on Medication Adherence in Mental Illness
Moonhee Gang, Seonhee Kim, Mi-Ae Ahn
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2021; 30(1): 9. CrossRef - Health literacy, health perception and related factors among different ethnic groups: a cross-sectional study in southeastern Turkey
Gülhan Yiğitalp, Vasfiye Bayram Değer, Sema Çifçi
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between Health Literacy and Self-care Behavior in Patients with Stomach Cancer after Gastrectomy: Mediating Effects of Subjective Health Status and Specific Self-efficacy
Min Jung Kim, Yong Soon Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 259. CrossRef - Health Literacy and Related Factors Depending on Socioeconomic Status
Yoon Jin Oh, Ki Hyun Park
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2021; 11(4): 280. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Korean version of Short-Form Health Literacy Scale for Adults
Young Joo Seo, Eun-Mi Kwak, Mirae Jo, A-Ra Ko, Soon Hwan Kim, Heeyoung Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(4): 416. CrossRef - Development and validation of a nutrition literacy assessment tool for young adults
Seokyoung Ahn, Bogyeong Kim, Mihyang Um, Yookyung Park, Seunghee Kye
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(2): 175. CrossRef - How to Improve Patient Safety Literacy?
Yoon-Sook Kim, Hyun Ah Kim, Moon-Sook Kim, Hyuo Sun Kim, Mi Jeong Kwak, Jahae Chun, Jee-In Hwang, Hyeran Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(19): 7308. CrossRef - Health Literacy, Knowledge and Self-care Behaviors in Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis Living in Community
Seo Hui Yang, Eun Young Jung, Yang Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparing two health literacy measurements used for assessing older adults’ medication adherence
Min‐Sun Song, Soohyun Park
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2020; 29(21-22): 4313. CrossRef - Food Literacy in South Korea: Operational Definition and Measurement Issues
Dahyun Park, Min-Jeong Shin, Sunmi Song
Clinical Nutrition Research.2019; 8(2): 79. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Health Literacy for Patients with Cardiovascular Disease using Hybrid Model
Jeong Eun Sim, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(4): 494. CrossRef - Medication Adherence and Its Association with Health Literacy and Performance in Activities of Daily Livings among Elderly Hypertensive Patients in Islamabad, Pakistan
Muhammad Saqlain, Asad Riaz, Muhammad Naeem Malik, Salman Khan, Ali Ahmed, Sohail Kamran, Hussain Ali
Medicina.2019; 55(5): 163. CrossRef - Effects of Diabetic Foot Care Education for the Aged with Low Health Literacy
Hyemin Kim, Ji Min Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(4): 560. CrossRef - Impact of Health Literacy on Hypertension Control of Elderly Women Patients Receiving Home Visiting Health Care Services
Hwa Bae, Nam-Soo Hong, Eun-Kyoung Shin
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2019; 44(3): 237. CrossRef - Predictors of Smartphone Uses for Health Information Seeking in the Korean Elderly
Young Sam Oh, Eun Young Choi, Young Sun Kim
Social Work in Public Health.2018; 33(1): 43. CrossRef - The effects of medication adherence and health literacy on health‐related quality of life in older people with hypertension
Nam Hee Park, Mi Sook Song, So Young Shin, Ji‐hye Jeong, Hyo Young Lee
International Journal of Older People Nursing.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Justificatory Information Forefending in Digital Age: Self-Sealing Informational Conviction of Risky Health Behavior
Jeong-Nam Kim, Yu Won Oh, Arunima Krishna
Health Communication.2018; 33(1): 85. CrossRef - Age Differences in Health Literacy: Do Younger Korean Adults Have a Higher Level of Health Literacy than Older Korean Adults?
Eun Jin Lee, Hee Yun Lee, Soondool Chung
Health & Social Work.2017; 42(3): 133. CrossRef - Validation of the short version of Korean functional Health Literacy Test
Su Hyun Kim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of a Health Literacy–Considered Diabetes Self-Management Program for Older Adults in South Korea
Soo Jin Lee, Misoon Song, Eun-Ok Im
Research in Gerontological Nursing.2017; 10(5): 215. CrossRef - Developing and Evaluating a Drug Information Leaflet of Antidiabetics for Senior Citizens; Employing Performance-based User-testing
Jin Kim, Haeri Shim, Iyn-Hyang Lee
Korean Journal of Clinical Pharmacy.2017; 27(3): 171. CrossRef - Differences between Nurses and Patients' Perception of Nurses' Communication Skills
Soonjoo Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(2): 166. CrossRef - Health Literacy and Its Related Factors in North Korean Refugees
Youn Jung Son, Hyun Joon Kim, Hye Jin Jeong, In Young Hwang, Moo Young Kim, Soo Hyoung Lee, Ki Hyun Park, Kee Ho Park, Chae Bong Kim, Hyang Im, Ji Young Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2017; 17(2): 71. CrossRef - Health Empowerment of Older Adults with High-risk of Cardio-cerebrovascular Diseases
HyoJin Son, Gwang Suk Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2017; 28(4): 410. CrossRef - Health Literacy and Health Promoting Behaviors in adolescents
Ji Young Kim, Min Hyun Suk
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(3): 570. CrossRef - Different Use of Hypertension-related Vocabulary in Patients with Hypertension and Public Health Nurses
Myo-Sung Kim, Ihn-Sook Jeong
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2016; 22(1): 41. CrossRef - Development of test for Korean functional health literacy in dentistry
Hyun-Kyung Kim, Hie-Jin Noh, Im-Hee Jung, Won-Gyun Chung, Yun Lee, So-Jung Mun, Hyun-Sun Jeon, Sun-Young Han, Eun-Hee Choi, Jun-Sung Ki, Min-Ji Koo, Ju-Hui Jeong
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2016; 16(3): 355. CrossRef - Health literacy and barriers to health information seeking: A nationwide survey in South Korea
Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyung Kim
Patient Education and Counseling.2016; 99(11): 1880. CrossRef - Effects of Health Literacy and Knowledge on Diabetic Self-care in the Elderly with DM Living Alone
Nan Hui Kim, Youngran Yang, Myung Ha Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 370. CrossRef - Health Literacy and Health Behavior Compliance in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Eun-Young Jung, Sun-Kyung Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(3): 251. CrossRef - Development of a Health Literacy Assessment Scale for Asian Immigrant Women in South Korea
Jisook An, Sook Ja Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(4): 330. CrossRef - Evidence-based health literacy improvements: trends on health literacy studies in Korea
Soo Jin Kang, Mi Sook Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2015; 32(4): 93. CrossRef - Simplification improves understanding of informed consent information in clinical trials regardless of health literacy level
Eun Jin Kim, Su Hyun Kim
Clinical Trials.2015; 12(3): 232. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Health Literacy Among Korean Adults
Hee Yun Lee, Jiwoo Lee, Nam Keol Kim
American Journal of Men's Health.2015; 9(5): 370. CrossRef - Efficacy of Chronic Disease Self-management Program in Older Korean Adults with Low and High Health Literacy
Su Hyun Kim, Chang Ho Youn
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(1): 42. CrossRef - The influence of functional health literacy on health promotion behavior
Ji Eun Lee, Seo Young Lee, Hyun Kyung Noh, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2015; 26(6): 1427. CrossRef - Association among ageing‐related stereotypic beliefs, self‐efficacy and health‐promoting behaviors in elderly Korean adults
Hyun‐E Yeom
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2014; 23(9-10): 1365. CrossRef - Extraction of Hypertension-related Consumer Vocabulary and Mediator Vocabulary and Selection of Recommended Vocabulary
Myo Sung Kim, Ihn Sook Jeong
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(5): 13. CrossRef - Risk Factors of Colorectal Polyps in Jeju Island
Yeoun Ja Na, Mira Um, Mi Hee Kong, Hyeon Ju Kim
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2014; 14(4): 141. CrossRef - A Study on Structural Relationship Among Perceived Interactivity and User Related Variables in Health Information Websites
Jaewoo Nam, Taeyoun Park
Journal of the Korean Society for information Management.2014; 31(4): 103. CrossRef - The Influence of Health Literacy and Diabetes Knowledge on Diabetes Self-care Activities in Korean Low-income Elders with Diabetes
Jihye Jeong, Namhee Park, So Young Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(3): 217. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Oral Health Literacy related Factors among Elderly People
Kyu Eun Lee, Young-Hee Yom, Sang Suk Kim, Jung Hee Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(1): 54. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of the Korean Health Literacy Instrument
Soo Jin Kang, Tae Wha Lee, Michael K. Paasche-Orlow, Gwang Suk Kim, Hee Kwan Won
Journal of Health Communication.2014; 19(sup2): 254. CrossRef - Health Literacy, Health Risk Perception and Health Behavior of Elders
Jeong Hee Jeong, Jung Soon Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(1): 65. CrossRef - Health Literacy of Elementary School Students.
Eun Jung Ahn, In Soo Kwon
Child Health Nursing Research.2014; 20(4): 322. CrossRef - Factors Related to Perceived Health Status in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Ang Li Won, Seung Hyun Yoo, Myoung Soon You
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(3): 1. CrossRef - Health Literacy: An Evolutionary Concept Analysis
Sungeun Kim, Jina Oh, Yunmi Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(4): 558. CrossRef - Evaluation on validity of health literacy measurement scale
Kyounh-Ho Choi, Jeong-Ok Lee
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2013; 24(2): 257. CrossRef - A cross-sectional study on oral health literacy and its influencing factors among adults: II. Functional oral health literacy
Hyun-Jeong Ju, Hyo-Won Oh, Heung-Soo Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2013; 37(2): 81. CrossRef - Impact of Health Literacy on Disease-related Knowledge and Adherence to Self-care in Patients with Hypertension
Youn-Jung Son, Eun-Kyeung Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(1): 6. CrossRef - Health Literacy of Inpatients at General Hospital
In Hwa Hong, Young Eun
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(5): 477. CrossRef - Influencing Factors on Functional Health Literacy among the Rural Elderly
Ji Yeon Park, Kyung Ja June
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2011; 22(1): 75. CrossRef - Concern in and Utilization of the Mass Media Health Information in Community-dwelling Elderly
Hye-Jung Kim, Hee-Kyung Joh, Hyeok-Kyu Kwon, Hyun-Jin Do, Seung-Won Oh, Youl-Lee Lym, Jae-Kyung Choi, Hyuk-Jung Kweon, Dong-Yung Cho
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2009; 30(6): 426. CrossRef - Health literacy and functional health status in Korean older adults
Su Hyun Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2009; 18(16): 2337. CrossRef - Testing health literacy skills in older Korean adults
Tae Wha Lee, Soo Jin Kang, Han Joo Lee, Soo In Hyun
Patient Education and Counseling.2009; 75(3): 302. CrossRef
General Characteristics of the Subjects and Functional Health Literacy Levels according to Selected Respondent Characteristics (N=103)
*Scheffe test.
Health Literacy Levels, Proportion of Patients Correctly Answering Numeracy Items and Reading Comprehension Passages (N=103)
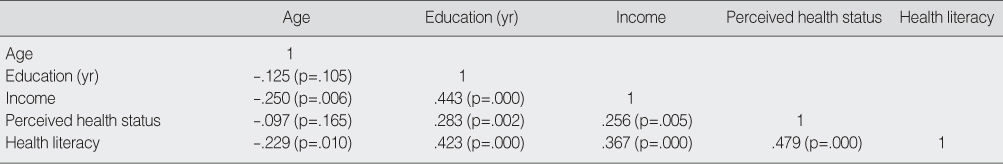
Zero-Order Correlation Coefficients among the Study Variables*
*All variables entered in the analysis were continuous variables.
The Influence of Health Literacy on Perceived Health Status in Older Adults (N=103)
*Dummy coded.
*Scheffe test.
*All variables entered in the analysis were continuous variables.
*Dummy coded.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

