Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
- Haesun Lee, Hye Jin Nam, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):454-467. Published online August 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
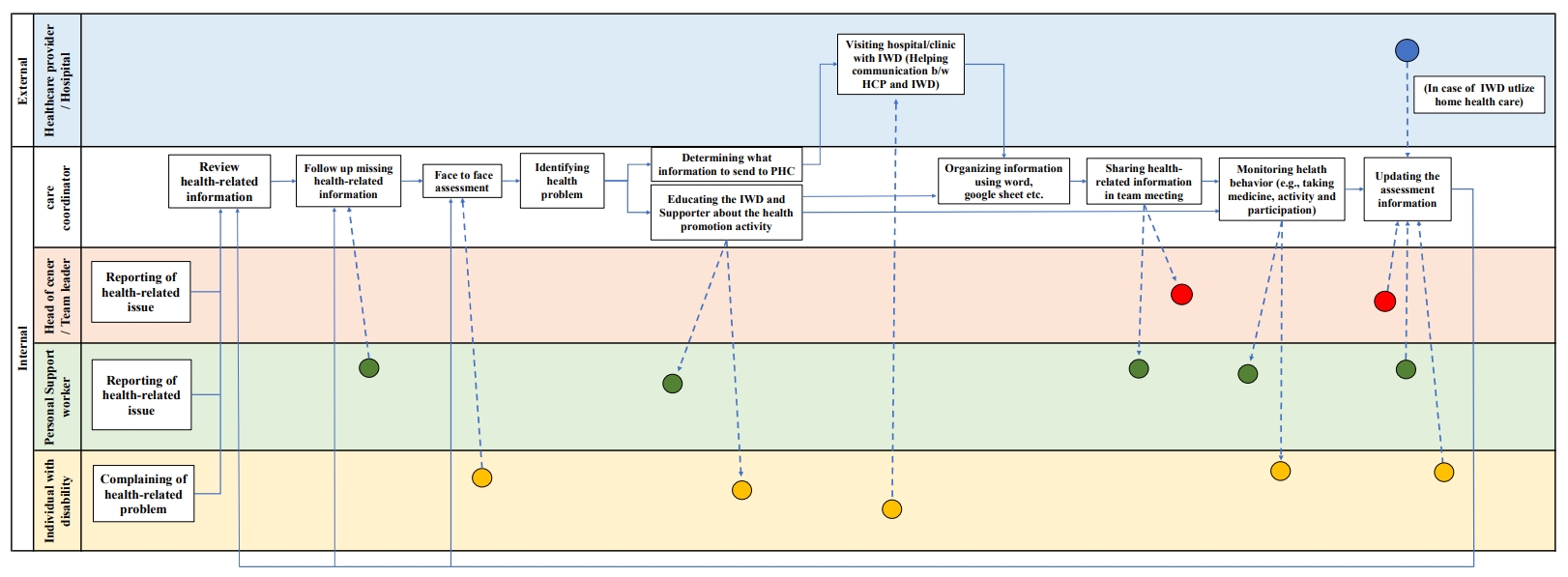
This study conducted a work-system analysis using the Systems Engineering Initiative for Patient Safety (SEIPS) framework to assess the flow of health-related information, and the current status of health management tasks for individuals with disabilities (IWD) in supportive housing.
Methods
This qualitative study utilized focus groups. Participants included a head of supportive housing, a team leader, a care coordinator and three personal support workers for IWD. Semi-structured interviews were guided by the SEIPS framework to explore the components of persons, tasks, tools and technology, organization, and environments.
Results
This study identified five key themes within the five SEIPS components: (1) disparities in role identity and health literacy among staff, (2) challenges in health care support reflecting a person-centered approach, (3) barriers in health-related information exchange and communication tools, (4) needs for organizational strategies or information communication, and (5) needs for integrating health-related information across external healthcare institutions. Additionally, 10 sub-themes were identified.
Conclusions
These findings provide a comprehensive system-wide perspective and offer insights into the systematic approaches needed to improve healthcare processes and structures within disability supportive housing. Specifically, healthcare providers and effective tools for integrating health-related information are identified as critical components.
- 1,352 View
- 80 Download

- Support Needs for Health Promotion of Community-Dwelling People with Disabilities: Perspectives of Operators Managing Disability Supportive Housing
- Hye Jin Nam, Haesun Lee, Han Nah Park, Sujin Lee, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):211-223. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Recent studies have focused on policies aimed at supporting the independence of individuals with disabilities in communities. As part of this initiative, supportive housing, integrated care, and residential spaces offer tailored services based on individual needs and autonomy. The attitudes and knowledge of the administrators supporting supportive housing residents regarding health management can influence the well-being of individuals with disabilities. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the challenges faced by supporting housing workers in enhancing the self-management skills of individuals with disabilities.
Methods
In this qualitative study, focus group interviews were conducted in August 2023 with nine administrators working to support housing in Seoul. Qualitative content analysis was used to analyze the interview data.
Results
The needs and challenges in enhancing the self-management skills of individuals with disabilities were as follows: (1) the complexity of health management challenges, (2) bidirectional strategies for strengthening health management capabilities, and (3) support for systematic health management. Additionally, eight subthemes were derived.
Conclusion
By investigating the difficulties experienced and identifying the necessary support requirements for supportive housing workers, this study seeks to uncover insights and identifies areas for improvement and strategies for health management. This study acknowledges the educational and institutional support necessary to improve the health and quality of life of individuals with disabilities residing in supportive housing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
Haesun Lee, Hye Jin Nam, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(3): 454. CrossRef - Intention to use a health information platform in supportive housing for people with disabilities: An application of the UTAUT model
Bohye Kim, Hye Jin Nam, Haesun Lee, Hannah Park, Ju Young Yoon, Nicola Diviani
PLOS One.2025; 20(10): e0332072. CrossRef - A preliminary study on the development of a chronic disease self-management curriculum for disability support workers: educational needs analysis
Han Nah PARK, Hye Jin NAM, Haesun LEE MSN, Sujin LEE, Bohye KIM, Ju Young YOON
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
- 2,191 View
- 96 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of Motivational Interviewing Pulmonary Rehabilitation Program Based on Self-Determination Theory for Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Jun Hee Jang, Hye Sook Min
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):191-207. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22093
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a motivational interviewing pulmonary rehabilitation program based on self-determination theory to maintain pulmonary rehabilitation-related health behaviors in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The program was developed by reviewing the literature on pulmonary rehabilitation guidelines, drawing on the self-determinism theory to establish its contents, recruiting experts to test its validity, and conducting a preliminary survey.
Methods
A quasi-experimental design was used to confirm the effect of the program. The participants were outpatients diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease at three general hospitals in Busan. There were 33 subjects: 15 in the experimental group and 18 in the control group. The experimental group performed a motivational interviewing pulmonary rehabilitation program which comprised 11 sessions delivered over 10 weeks. The outcomes were measured using basic psychological needs, dyspnea, 6-minute walking distance, and functional status. Intervention effects were analyzed using repeated-measures ANOVA.
Results
The analysis revealed significant differences between the experimental and control groups in competence among the subdomains of basic psychological needs, dyspnea during exercise, and functional status.
Conclusion
The developed program affects physical conditions and can be applied as an effective clinical nursing intervention to continuously improve the pulmonary rehabilitation behavior of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating Effect of Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Symptom Experience and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Enhee Jo, Ju-Young Park, Young Jun Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(3): 315. CrossRef
- Mediating Effect of Self-Efficacy on the Relationship between Symptom Experience and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- 2,472 View
- 131 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Comparison of Nursing Activities Reflected in Nursing Notes and In-depth Interviews of Nurses in an Acute Hospital
- Misoon Song, Mae Ja Kim, Young Sook Park, Eun Ok Lee, Yang Sook Hah, Kyung Ja Han, Se Ang Ryu, Hae Young Kang, Kyung Nam Kim, Moon Sook Cho
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(6):802-811. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.6.802
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare the nursing activities delineated by interview of nurses with those on nursing notes.
Method The participants of interview were 18 nurses working in medical and surgical units of a large hospital in Seoul. Each nurse was asked to choose one patient who demand most nursing care among her patients. The nurse was then interviewed to describe what her nursing activities for the patient was that day. The audio-taped interview was transcribed and the content was analyzed by researchers. Nursing notes of each nurses' patients were copied and the content analyzed by researchers. Finally, themes from the interview data and those from nursing notes were compared.
Result Activities related to emotional or psychological nursing, education for patient and families, and problem solving related to treatment or nursing procedure were most often omitted in nursing notes. Most of the documentation in nursing notes were related to physical condition of patients or physician's orders. Nurses described that they will do better recording if they were given less patient care responsibility, had better nursing knowledge, had better recording system, and received more training on nursing record.
Conclusion Nursing notes did not reflect nursing activities properly. Few independent nursing roles were documented in the nursing notes. Development of nursing education program and nursing record system is needed for improvement of nursing record.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects on Knowledge and Performance in Clinical Nursing of Education on Nursing Recording Focusing on Legal Aspects
Eun-Young Kim, Yeo-Jin Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2011; 17(3): 277. CrossRef - A Comparison of the Nursing Records of Hysterectomy Patients: Pre and Post Implementation of an ICNP Based Electronic Nursing Record System
Woan Heui Choi, Young Sook Park, InSook Cho
Journal of Korean Society of Medical Informatics.2009; 15(4): 455. CrossRef - Identifying outcomes from the nursing outcomes classification as indicators of quality of care in Korea: A modified delphi study
B. Lee
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2007; 44(6): 1021. CrossRef
- Effects on Knowledge and Performance in Clinical Nursing of Education on Nursing Recording Focusing on Legal Aspects
- 684 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of a Motivational Interviewing Program for Exercise Improvement in Persons with Physical Disabilities
- Jeong Hee Jeong, Ihn Sook Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(3):406-419. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.3.406
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The aims of this study were to develop a motivational interviewing program for exercise improvement in persons with physical disabilities and to examine the effect of this motivational interviewing intervention.
Methods The study employed a nonequivalent control group pretest and posttest design. A total of 62 persons with physical disabilities (30 in the experimental group, 32 in the control group) were recruited from 2 community rehabilitation centers. The experimental group received 8 sessions of a group motivational interviewing program, scheduled once a week, with each session lasting 60 minutes. Test measures were completed before the intervention, immediately after the end of the intervention, 2 weeks later, and 6 weeks after the end of the intervention. Measures included self-efficacy for exercise, decisional balance for exercise, stage of change for exercise, regularity of exercise, exercise maintenance, and independent living ability. Data were analyzed using the c2-test, Fisher's exact test, Independent samples t-test, and repeated measures ANOVA, conducted using IBM SPSS Statistics version 18.
Results The experimental group showed a significant increase in self-efficacy for exercise (F=50.98,
p <.001), benefit (pros) of exercise (F=24.16,p <.001), and independent living ability (F=50.94,p <.001), and a significant decrease in loss (cons) of exercise (F=26.50,p <.001). There were significant differences between the two groups in stages of change for exercise (p <.001), regularity of exercise (p <.001), and exercise maintenance (c2=26.61,p <.001).Conclusion The motivational interviewing program has the potential to improve exercise levels in persons with physical disabilities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- SOSYAL HİZMET PERSPEKTİFİNDEN MOTİVASYONEL GÖRÜŞME TEKNİĞİNE BAKIŞ
Aliye Beyza Bayyar
Tıbbi Sosyal Hizmet Dergisi.2023; 0(21): 110. CrossRef - The Effects of Nurse-Led Motivational Interviewing on Exercise and Quality of Life among Koreans with Heart Failure: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Haejung Lee, Gaeun Park, Hyekyung Jin, Kook Jin Chun, Jong Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(6): 588. CrossRef - Engaging youth with major depression in an exercise intervention with motivational interviewing
Yasmina Nasstasia, Amanda L. Baker, Terry J. Lewin, Sean A. Halpin, Leanne Hides, Brian J. Kelly, Robin Callister
Mental Health and Physical Activity.2019; 17: 100295. CrossRef
- SOSYAL HİZMET PERSPEKTİFİNDEN MOTİVASYONEL GÖRÜŞME TEKNİĞİNE BAKIŞ
- 1,305 View
- 16 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Experience of Fluid Management in Hemodialysis Patients
- Yoonsoo Kim, Miyoung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(5):773-782. Published online October 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.5.773
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the experience of fluid management in hemodialysis patients by describing how they manage fluid intake and what affects fluid management.
Methods Purposive sampling yielded 11 patients who have received hemodialysis for one year or longer in one general hospital. Data were collected through in-depth interviews and analysed using Giorgi's phenomenological method. Data collection and analysis were performed concurrently.
Results The findings regarding how hemodialysis patients manage fluid intake were classified into four constituents: 'recognizing the need for fluid control', 'observing the status of fluid accumulation', 'controlling fluid intake and output', 'getting used to fluid management'. The factors that affect fluid management of hemodialysis patients were revealed as 'willpower', 'change in the mindset', 'support system', and 'emotional state'.
Conclusion The study results show that hemodialysis patients manage fluid intake through food and exercise as well as interpersonal relationships. These findings suggest that strategies in the development of nursing interventions for hemodialysis patients should be directed at assisting them in familiarization with fluid management based on an understanding of their sociocultural contexts.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Mediating Effects of Symptom Experiences on the Relationship between Body Image and Quality of Life among Hemodialysis Patients in a Single Center
Yaki Yang
Healthcare.2024; 12(17): 1779. CrossRef - Healthy life of Korean patients with chronic kidney failure undergoing hemodialysis: A situation-specific nursing theory
Jinhyang Yang, Myung-Ok Cho, Haeok Lee
Applied Nursing Research.2022; 65: 151584. CrossRef - Socioecological Factors Affecting Fluid Restriction Adherence Among Korean Patients Receiving Hemodialysis: A Qualitative Study
Eun Ju Lee, Ae Kyung Chang, Yoon Chung Chung
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2021; 32(3): 239. CrossRef - Design Criteria for Haemodialysis Patients Based on Self-Weight-Management Behaviour
Bogyeong Kim, Chorong Kim, Ki-Young Nam
Archives of Design Research.2019; 32(1): 31. CrossRef - Family Characteristics, Family Support, Family Function and Compliance of Patient Role Behavior in Long-term Hemodialysis Patients
Sinhye Kang, Inja Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2019; 22(1): 58. CrossRef - Phenomenology on the Hemodialysis Experience of Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease
Eun Ja Lee, Hyun Sook Jo, Sang Suk Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2018; 21(1): 22. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability Test of the Korean Version of the Hemodialysis Self-Management Instrument (HDSMI-K)
Jieun Cha, Jiyoung Kang
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2017; 42(2): 153. CrossRef
- The Mediating Effects of Symptom Experiences on the Relationship between Body Image and Quality of Life among Hemodialysis Patients in a Single Center
- 1,186 View
- 19 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Development and Effects of a Motivational Interviewing Self-management Program for Elderly Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- Hye-Yeon Kang, Mee Ock Gu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(4):533-543. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.4.533
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to develop and test the effects of a motivational interviewing self-management program for use with elderly patients with diabetes mellitus.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The participants were 42 elderly diabetic patients (experimental group: 21, control group: 21). The motivational interviewing self-management program for elders with diabetes mellitus developed in this study consisted of a 12-week program in total (8 weeks for group motivational interviewing and education and 4 weeks for individual motivational interviewing on the phone). Data were collected between February 13 and May 3, 2013 and were analyzed using t-test, paired t-test, and repeated measure ANOVA with SPSS/WIN 18.0.
Results For the experimental group, significant improvement was found for self-efficacy, self-care behavior, glycemic control and quality of life (daily life satisfaction, influence of disease) as compared to the control group.
Conclusion The study findings indicate that the motivational interviewing self-management program is effective and can be recommended as a nursing intervention for elderly patients with diabetes mellitus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of An Oral Health Education Program for Elementary School Students Based on Motivational Interviews
Yi-Seul Kim, Soon-Ryun Lim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2025; 25(1): 31. CrossRef - The Association between the Low-density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol to High-density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol Ratio and the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Adults: A Secondary Data Analysis Using a Community-based Cohort Study in Korea
Bo-Kyoung Cha
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(1): 66. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Motivational Interviewing Pulmonary Rehabilitation Program Based on Self-Determination Theory for Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Jun Hee Jang, Hye Sook Min
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(2): 191. CrossRef - Trends and Effects in Evidence-Based Psycho-Social Interventions for Patients with Diabetes
Jung-won Lim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 164. CrossRef - Can chatbots help to motivate smoking cessation? A study on the effectiveness of motivational interviewing on engagement and therapeutic alliance
Linwei He, Erkan Basar, Reinout W. Wiers, Marjolijn L. Antheunis, Emiel Krahmer
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Multimodal Diabetes Empowerment for Older Adults with Diabetes
Keumok Park, Youngshin Song
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(18): 11299. CrossRef - The effects of diabetes knowledge, self-efficacy, and depression on self-management in older patients with diabetes in the community: A cross-sectional study
Hyeok Gyu Park, Myoung Jin Kwon
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2022; 24(4): 389. CrossRef - Asian Best Practices for Care of Diabetes in Elderly (ABCDE)
Sanjay Kalra, Minakshi Dhar, Faria Afsana, Pankaj Aggarwal, Than Than Aye, Ganapathy Bantwal, Manash Barua, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Ashok Kumar Das, Sambit Das, Arundhati Dasgupta, Guruprasad Dhakal, Atul Dhingra, Fatemeh Esfahanian, Sharvil Gadve, Jubbin
Review of Diabetic Studies.2022; 18(2): 100. CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Self-Efficacy for Managing Chronic Disease 6-Item Scale
Sook-Nam Kim, Hyun-Ju Lee, So-Young Kim, Nayoon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(5): 617. CrossRef - Comparing the effectiveness of motivational interviewing and self-development education on type II diabetes mellitus patients’ lifestyle
Javad Kazemi, Fatemeh Rahmati
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Physical Exercise Program on Physiological, Psychological, and Physical Function of Older Adults in Rural Areas
Sunmi Kim, Eun-Jee Lee, Hyeon-Ok Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(16): 8487. CrossRef - The role of psychological insulin resistance in diabetes self‐care management
Ancho Lim, Youngshin Song
Nursing Open.2020; 7(3): 887. CrossRef - Influence of Self-care Competency, Family Support, and Depression on Life Satisfaction in Older Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Gyo Min Lee, So Young Shin
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2020; 22(4): 326. CrossRef - MALAYSIAN DIABETES PATIENTS’ PERCEPTIONS, ATTITUDES AND PRACTICES IN RELATION TO SELF-CARE AND ENCOUNTERS WITH PRIMARY HEALTH CARE PROVIDERS
Lim Shiang Cheng, Jens Aagaard-Hansen, Feisul Idzwan Mustapha, Ulla Bjerre-Christensen
Malaysian Journal of Medical Research.2018; 2(3): 1. CrossRef - The Effects of a Health Mentoring Program in Community-dwelling Vulnerable Elderly Individuals with Diabetes
Ki wol Sung, Hye Seung Kang, Ji Ran Nam, Mi Kyung Park, Ji Hyeon Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(2): 182. CrossRef - Health-Related Quality-of-Life and Diabetes Self-Care Activity in Elderly Patients with Diabetes in Korea
Hacksun Kim, Kisook Kim
Journal of Community Health.2017; 42(5): 998. CrossRef - Effect of Diabetic Dietary Education Program on Diabetes Knowledge and Dietary Behaviors of Elderly Diabetic Patients
Ji Young Ye, Sung Hee Min, Min June Lee
Korean Journal of Food & Cookery Science.2017; 33(5): 601. CrossRef - The Effect of a Dementia Preventive Intervention based on Motivational Interviewing among the Elderly over 75 Years of Age in Nursing Homes
Hyun Mi Jo, Suk-Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2017; 28(3): 260. CrossRef - Effects of Health Literacy and Knowledge on Diabetic Self-care in the Elderly with DM Living Alone
Nan Hui Kim, Youngran Yang, Myung Ha Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 370. CrossRef - The Effects of Motivational Interviewing Training Program on Communication Skills and Self-Efficacy of Home Visiting Nurses
Sungjae Kim, Jeongwoon Yang
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(2): 274. CrossRef - The Effects of a Self-care Management Program for Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Jung Yoon Kim, Eui-Young Cheon
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2016; 18(2): 78. CrossRef - Development and Application of Motivation-enhancing Self-management Program for Rural Aged with Hypertension
Hailian Zhang, Hyunli Kim
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2016; 41(3): 152. CrossRef
- Evaluation of An Oral Health Education Program for Elementary School Students Based on Motivational Interviews
- 1,643 View
- 54 Download
- 22 Crossref

- Effectiveness of the Self-determination Theory based a Motivational Interviewing YOU-TURN Program for Smoking Cessation among Adolescents
- Young Sun Ha, Yeon Hee Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(3):347-356. Published online June 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.3.347
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose In this study, the effectiveness of a motivational interviewing smoking cessation YOU-TURN program for adolescents was examined. The program was based on the self-determination theory.
Methods The study was carried out with a nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design. Participants in the present study were 136 high school students living in D city. The students were assigned to the experimental group (n=52) who participated in the motivational interviewing smoking cessation YOU-TURN program based on self-determination theory, or to the control group (n=84) who participated in a general smoking cessation program. Data were collected from September 1, 2013 through April 30, 2014. Collected data were analyzed using SPSS PC+ 21.0 with Chi-square test, Fisher's exact test, t-test, Mann-Whitney U test, Repeated Measures ANOVA, and MANOVA-Wilk's Lambda.
Results The experimental group had a significant increase in basic psychological needs, and duration of quitting-smoking in comparison with the control group. The experimental group had a significant decrease in cigarettes smoked per day and cotinine in urine in comparison with the control group.
Conclusion The motivational interviewing YOU-TURN program, when delivered to adolescents who smoked, was effective in discouraging smoking, and can be utilized as an effective nursing intervention for adolescents who smoke.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Evaluation of Motivational Interviewing Pulmonary Rehabilitation Program Based on Self-Determination Theory for Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Jun Hee Jang, Hye Sook Min
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(2): 191. CrossRef - Reducing the Negative Environmental Impact of Consumerization of IT: An Individual-Level Approach
Ayodhya Wathuge, Darshana Sedera
Sustainability.2023; 15(16): 12160. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Self-Determination Improvement Program for Preventing Non-Suicidal Self-Injury in Adolescents: A Pilot Study
Jae Woon Lee, In Sook Kim, Ji Won Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(4): 506. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Drinking Reduction Program Focused on Self-Determination Enhancement for College Students with Problematic Drinking
Jin-Kyoung Ma, Moon-Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(3): 265. CrossRef - Comparison of the Prediction Model of Adolescents' Suicide Attempt Using Logistic Regression and Decision Tree: Secondary Data Analysis of the 2019 Youth Health Risk Behavior Web-Based Survey
Yoonju Lee, Heejin Kim, Yesul Lee, Hyesun Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(1): 40. CrossRef - The Effects of the Smoking Cessation Program of Life Skill Training Using Flipped Learning for Middle School Male Students
Eun Hee Seo, Eun Suk Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(3): 268. CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Smartphone Overdependence Prevention Program for University Students Based on Self-Determination Theory
Myung Soon Kwon, Jeong Soon Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(1): 116. CrossRef - Exploring the Basic Psychological Needs Necessary for the Internalized Motivation of University Students with Smartphone Overdependence: Applying a Self-Determination Theory
Myung Soon Kwon, Juhye Jin
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(1): 26. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a smoking cessation program on self-esteem, attitude, perception, and practice regarding control over smoking among male high school
Niyom Junnual, Chulaporn Sota, Anun Chaikoolvatana
Journal of Health Research.2019; 33(5): 366. CrossRef - Motivational interviewing for smoking cessation
Nicola Lindson, Tom P Thompson, Anne Ferrey, Jeffrey D Lambert, Paul Aveyard
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Strength Based I-Change Smoking Cessation Program for Smoking Middle School Boys
Jung Hee Kim, Yeon Hee Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(2): 164. CrossRef - Tobacco cessation interventions for young people
Thomas R Fanshawe, William Halliwell, Nicola Lindson, Paul Aveyard, Jonathan Livingstone-Banks, Jamie Hartmann-Boyce
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The Relationship between Psychological Needs and Health Promoting Behavior in Community-dwelling Older Women
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2015; 21(2): 126. CrossRef
- Development and Evaluation of Motivational Interviewing Pulmonary Rehabilitation Program Based on Self-Determination Theory for Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- 1,349 View
- 28 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effectiveness of a Motivational Interviewing Smoking Cessation Program on Cessation Change in Adolescents
- Young Sun Ha, Yeon Hee Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(1):19-27. Published online February 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.1.19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study examined the effectiveness of an Adolescent Motivational Interviewing Cessation program on smoking cessation change. The study was done with a nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design.
Methods The participants were 39 high school students from G city, who were in school from September 1 to October 30, 2009. The students were assigned to the experimental group (20) and participated in the motivational interviewing cessation program or to the control group (19) who did not participate. Data analyses involved χ2-test, independent t-test, Repeated Measures ANOVA, and utilized the SPSS program.
Results The experimental group had significantly less daily smoking, nicotine dependence and smoking temptation in comparison to the control group. The experimental group had significantly higher stage of change in comparison to the control group.
Conclusion The results of the study indicate that a motivational interviewing cessation program delivered to adolescents who smoke is an effective method of encouraging cessation, and can be utilized as an effective nursing intervention for adolescents who smoke.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An interventional study to assess the impact of behavior modification therapy on motivation level for tobacco cessation among adult tobacco users in a resettlement colony of South Delhi
Richa Gautam, Yasir Alvi, Farzana Islam, Nitesh Kumar, Rambha Pathak, Rashmi Agarwalla, Meely Panda, Ekta Gupta, Mamta Parashar, Rashmi Prakash Dayal
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a Motivational Interviewing Oral Health Education Program for Elementary School Students
Yi-Seul Kim, Soon-Ryun Lim
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2024; 24(4): 274. CrossRef - Smoking cessation and its significant role in the Indian scenario
Raj Kumar, Manoj Kumar, Sukriti Raj, Dileep Kumar Arisham, Anil Kumar Mavi, Kamal Singh
Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Prospective Study to Assess the Outcome of Motivational Interviewing Among Male Students of Haryana, India: A Strive Towards Smoking Cessation in the Youth
Virinder S Gill, Neha Chaudhary, Avneet Randhawa, Manisha Verma, Gurleen K Rai, Shradha Mishra
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of Transtheoretical Model based motivational interviewing on smokeless tobacco cessation in high school students
Filiz Taş, E. Ümit Seviğ, Zeynep Güngörmüş
Journal of Substance Use.2020; 25(6): 639. CrossRef - Motivational interviewing for smoking cessation
Nicola Lindson, Tom P Thompson, Anne Ferrey, Jeffrey D Lambert, Paul Aveyard
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Affecting Nicotine Dependence of Social Psychological Variables in Smoking middle school
Young-Mun Cho, Mi-Young Woo
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(2): 295. CrossRef - Using the WHO ASSIST to Assess Drug and Alcohol Misuse in the Acute Mental Health Setting to Guide Treatment Interventions
Karen R. Heslop, Calum Ross, John Berkin, Dianne Wynaden
International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction.2015; 13(5): 618. CrossRef - Effectiveness of the Self-determination Theory based a Motivational Interviewing YOU-TURN Program for Smoking Cessation among Adolescents
Young Sun Ha, Yeon Hee Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(3): 347. CrossRef - The effectiveness of a Autonomous Regulation Improvement Smoking Cessation Program on the Amount of Daily Smoking, Perceived Motivation, Cotinine in Saliva, and Autonomous Regulation for Girls High School Students who Smoked
Young-Sun Ha, Yeon-Hee Cho
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(9): 6169. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Secondhand Smoking Prevention Program on Adolescents
Min Ah Park, Mi Ye Kim, Young Sun Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(1): 44. CrossRef - Efficacy of Smoking Cessation and Prevention Programs by Intervention Methods: A Systematic Review of Published Studies in Korean Journals during Recent 3 Years
Hye Kyeong Kim, Ji Yeon Park, Eun Joo Kwon, Seung Hee Choi, Han-Ik Cho
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2013; 30(5): 61. CrossRef - Influencing Factors on Smoking Cessation Motivation of Adult Males
Young Mi Yoon, Eun Kyung Yang, Sung Rae Shin
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(5): 520. CrossRef
- An interventional study to assess the impact of behavior modification therapy on motivation level for tobacco cessation among adult tobacco users in a resettlement colony of South Delhi
- 1,429 View
- 19 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Healing Effects of the Forest Experience on Alcoholics
- Jingyung Cha, Sungjae Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(3):338-348. Published online June 29, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.3.338
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore and describe healing effects of the forest on alcoholics through a forest experience program.
Methods The qualitative data was gathered from one focus group discussion with 6 alcoholics and individual interviews with 8 alcoholics. They had all participated in a "healing forest" program. All interviews were recorded and transcribed according to thematic content analysis processes.
Results The four main themes on the attributes of forest were "a lively living being", "placidity and tranquility", "acceptive atmosphere", and "beautifulness as it is" which revealed the participants' perceived nature of the forest which was attributed to the healing effects. Eight other themes on participants' positive changes included "revived senses", "aspired to live", "relieved and relaxed from being tense", "gaining insight on self", "having an acceptive attitude", "becoming compliant with his/her life", "learning that life is being together" and "recognizing the value of one's existence".
Conclusion The findings of the study illustrated the participants' self-healing processes through interactions with the nature of the forest. Nursing interventions utilizing healing atmospheres such as "healing forest" programs can be considered helpful in providing a venue to alcoholics to reflect on their lives affirmatively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Healing forests as potential natural resources for visitor health therapy in the post-pandemic period
DR Kurniasari, LR Wibowo, N Seraphine, AS Kurniawan
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.2023; 1266(1): 012004. CrossRef - Forest Therapy Trails: A Conceptual Framework and Scoping Review of Research
Paul H. Gobster, Courtney L. Schultz, Linda E. Kruger, John R. Henderson
Forests.2022; 13(10): 1613. CrossRef - Effects of an Urban Forest-Based Health Promotion Program on Children Living in Group Homes
Min Kyung Song, Kyung-Sook Bang, Sungjae Kim, Gumhee Lee, Yeseul Jeong
Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services.2020; 58(6): 18. CrossRef - Environmental influence in the forested area toward human health: incorporating the ecological environment into art psychotherapy
Ju-hyoung Lee, Ji-sook Park, Sunnam Choi
Journal of Mountain Science.2020; 17(4): 992. CrossRef - The Effects of the Forest Environment on Internet Addition Treatment
Chang-Hong Oh, Sang-Gyu Park, Jung-Hwan Park, In-Ja Oh
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(4): 489. CrossRef - A Study on the Development of Forest Healing Village Based on the Survey on the Stakeholder Perception
Mi-Ae Jeong, Jeong-Weon Seo
Journal of Korean Society of Rural Planning.2016; 22(3): 11. CrossRef - Physiological and Psychological Effects of Walking Around and Viewing a Lake in a Forest Environment
Chorong Song
Journal of Korean Forest Society.2015; 104(1): 140. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Healing: Focusing on Patient Health related Literatures
Jiyoung Kim, Nayeon Shin
Asian Oncology Nursing.2015; 15(1): 51. CrossRef - Comparing the Current Health Status and Health Behaviors of Residents from Urban and Forested Areas
Insook Lee, Kowoon Lee, Sung Jae Kim, Kyung Sook Bang, Hee Seung Choi
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2015; 12(1): 14. CrossRef - An Analysis of Health Promotion Programs Utilizing Forests based on Korea's Regional Healthcare Program Plans
Insook Lee, Sungjae Kim, Kyung-Sook Bang, Heeseung Choi, Chinkang Ko, Jieun Kim, Sunyoung Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2014; 11(1): 10. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of a Forest-experience-integration Intervention for Community Dwelling Cancer Patients' Depression and Resilience
Yeon Hee Choi, Young Sun Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2014; 25(2): 109. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study of Diffusion of Health Promotion Programs using Forests
Insook Lee, Heeseung Choi, Kyung-Sook Bang, Ko-Woon Lee, Ji-Eun Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2014; 11(1): 30. CrossRef
- Healing forests as potential natural resources for visitor health therapy in the post-pandemic period
- 1,008 View
- 1 Download
- 12 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


