Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Transforming nursing education to enhance integrated nursing competency: a Delphi-based methodological study on symptom-based clinical reasoning
- Jeung-Im Kim, Soyoung Yu, Jin-Hee Park, Ju-Eun Song, Eunjung Ryu, JuHee Lee, YeoJin Im
- Received November 7, 2025 Accepted December 10, 2025 Published online February 5, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25151 [Epub ahead of print]
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to address the shift toward competency-based education and the planned 2028 “Integrated Nursing” National Licensing Examination (NLE), this study aimed to establish structural alignment among NLE domains, the seven integrated nursing competencies (INCs), and curriculum goals, with a particular focus on implementing symptom-based clinical reasoning (SBCR).
Methods
This Delphi-based methodological study included seven content experts for content validity index (CVI) assessment and 24 nursing education experts who participated in a consensus workshop. The item-level CVI and the scale-level CVI/average were calculated to confirm the linkage between INCs and NLE domains. In addition, qualitative analysis of workshop materials and meeting records was conducted to derive 10 integrated learning topics and to develop an SBCR educational model for the key symptom of headache, grounded in Miller’s Clinical Competence Pyramid (levels 2–4).
Results
The analysis confirmed the validity of integrating the INCs within the overall curriculum structure. The resulting framework delineates staged learning objectives and core clinical questions designed to systematically enhance clinical reasoning, promote safe nursing practice, and support professional reflection within a unified curriculum.
Conclusion
This study provides a practical foundation for nursing curriculum redesign by facilitating a transition from fragmented, subject-based instruction to a holistic, patient-centered SBCR model. This approach aligns with the requirements of the integrated NLE and is expected to contribute to meaningful improvements in actual clinical competency.
- 34 View
- 1 Download

- Development of an end-of-life care competency scale for nurses in long-term care hospitals: a psychometric validation study
- Sookyeon Son, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):598-612. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure end-of-life care (EOLC) competency among nurses working in long-term care hospitals and to evaluate its validity and reliability.
Methods
Preliminary items were developed based on attributes and indicators identified through a conceptual analysis of EOLC competency. The initial version of the scale was refined through expert content validity assessment, item revision, and a pilot test. The main survey was conducted among 460 nurses in long-term care hospitals, and 409 valid responses were analyzed after excluding 51 incomplete or invalid cases. Data were analyzed using software-assisted item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses, and assessments of convergent, discriminant, and criterion-related validity, as well as reliability testing.
Results
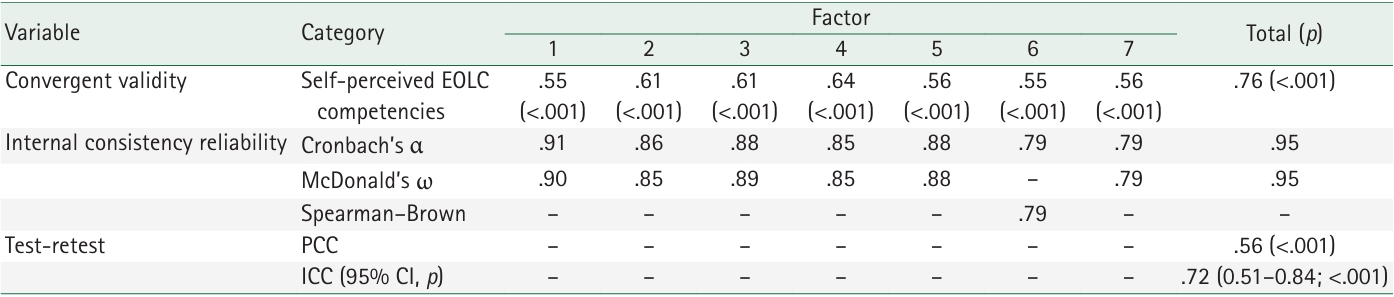
The initial 55 items were reduced to a final set of 30 items across seven dimensions. Model fit indices indicated good construct validity (χ²/degrees of freedom=1.91, standardized root mean square residual=.06, root mean square error of approximation=.07, Tucker-Lewis index=.90, comparative fit index=.91), with a total explained variance of 70.2%. The scale demonstrated strong criterion-related validity (r=.76, p<.001), high internal consistency (Cronbach’s α=.95; McDonald’s ω=.95), acceptable test–retest reliability (r=.56, p<.001), and an intraclass correlation coefficient of .72 (95% confidence interval, .51–.84; p<.001).
Conclusion
The developed scale is a valid and reliable instrument for assessing EOLC competency among nurses in long-term care hospitals. It can be effectively utilized for educational assessment, training evaluation, and the measurement of program effectiveness in end-of-life care.
- 842 View
- 95 Download

- Core domains for pre-registered nurses based on program outcomes and licensing competencies
- Soyoung Yu, Hye Young Kim, Jeung-Im Kim, JuHee Lee, Ju-Eun Song, Hyang Yuol Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):249-268. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify core domains for pre-registered nurses by comparing licensing competencies with program outcomes (POs) in undergraduate nursing education. This was accomplished in preparation for the transition of the Korean Nurse Licensing Examination (KNLE) from a tradition seven-subject format to a newly integrated, competency-based single-subject format that reflects current trends in nursing assessment.
Methods
A literature review and survey were conducted. From 828 studies retrieved via PubMed, CINAHL, and Google Scholar using keywords such as “newly graduated registered nurses” and “competency OR competence,” 18 were selected according to pre-established inclusion and exclusion criteria. Documents from national and international nursing organizations were included to extract relevant licensing competencies. We also reviewed POs from all undergraduate nursing schools in South Korea to align educational outcomes with the identified core domains.
Results
The core domains identified were clinical performance and decision-making, professional attitudes and ethics, communication and interpersonal skills, leadership and teamwork, quality improvement and safety, health promotion and prevention, and information technology and digital health. These domains showed strong alignment with POs under the fourth-cycle accreditation standards.
Conclusion
It concludes the seven core domains will be appropriate for evaluating pre-registered nurses in the integrated KNLE. Based on the seven identified core domains, expert consensus should be sought in the next phase to support the development of integrated, competency-based test items grounded in these domains.
- 3,930 View
- 152 Download

- Mediating effect of grit on the influence of nurses’ silence behavior on medication safety competence: a cross-sectional study
- Haengsuk Kim, Wanju Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):81-92. Published online February 20, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24088
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study investigated the mediating effect of grit in the relationship between silence behavior and medication safety competence among nurses.
Methods
The study included 166 nurses from four university hospitals and general hospitals in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do, South Korea. Data were collected from March 1 to 10, 2024, using self-report questionnaires. Data were analyzed using the t-test, analysis of variance, Scheffé’s test, and Pearson’s correlation coefficients with IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 23.0 (IBM Corp.). A mediation analysis was performed using Hayes’s PROCESS macro model 4 and the bootstrapping method.
Results
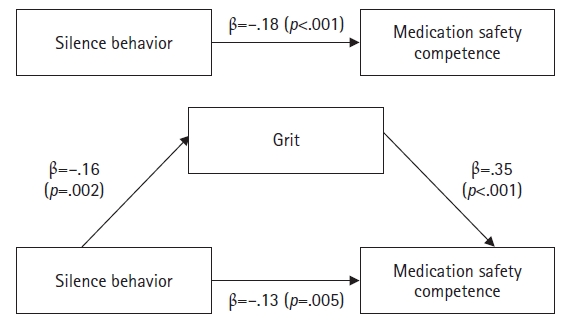
Medication safety competence showed significant correlations with silence behavior (r=–.21, p=.008) and grit (r=.43, p<.001). Furthermore, grit partially mediated the relationship between silence behavior and medication safety competence.
Conclusion
This study indicates that grit is a significant mediator in the relationship between silence behavior and medication safety competence. Therefore, an integrated approach that reduces silence behavior and promotes grit is essential for strengthening nurses’ medication safety competence. Ultimately, these strategies will help ensure patient safety by improving medication safety competence.
- 5,259 View
- 456 Download

- Development and Effectiveness of Progressive Simulation Education Program on Medication Safety for Nursing Students
- Se-Young Jung, Eun-Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):563-576. Published online October 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24054
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Purpose This study aimed to develop and verify a progressive simulation education program aimed at enhancing nursing students’ medication safety competency.
Methods A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was adopted. The participants were 40 third-year nursing students with no prior simulation education experience, comprising 20 each in the experimental and control groups. The experimental treatment utilized a hybrid simulation approach incorporating both full-body mannequins and standardized patients and was, conducted over three sessions with durations of 65, 80, and 95 minutes for the first, second, and third sessions, respectively, for a total of 240 minutes. The program was constructed based on Jeffries’ simulation model.
Results The levels of medication safety competencies, communication self-efficacy, learning self-efficacy, and problem-solving abilities of the experimental group were significantly higher than that of the control group.
Conclusion Our results confirm that the program effectively improves nursing students’ medication safety competence, communication self-efficacy, learning self-efficacy, and problem-solving ability. Therefore, this program can serve as a basis for developing educational strategies related to medication safety for nursing education institutions. Furthermore, the program is anticipated to have a positive impact on novice nurses’ education and practice in clinical settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Safety-centered simulation education using the 360-degree video room of errors: A mixed-methods study
Jiyoung Kim, Yeji Kim, Hyunji Park, Jiyeong Won, Jiwon Yun, Yuran Lee
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2026; 111: 101899. CrossRef
- Safety-centered simulation education using the 360-degree video room of errors: A mixed-methods study
- 4,678 View
- 403 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Concept Analysis of Social Intelligence of Nurses Using Hybrid Model
- Kyung Ran Lee, Na Kyoung Lee, Hee Oh, Kyoung Ae Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):459-474. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to conduct a concept analysis of social intelligence in nurses so that applying social intelligence to the nursing field.
Methods
In this study, we followed the hybrid model procedure, involving the following steps: First, in the theoretical stage, the attributes and definitions of the concept of social intelligence were determined through literature review. Second, the concepts’ reality was confirmed during fieldwork. In the final analysis stage, the results confirmed in the theoretical and fieldwork stages were compared and analyzed to confirm the properties and definition of the concept.
Results
Nurses’ social intelligence consists of three dimensions: social cognitive nursing competency, human-centered social evolution, and skills for solving complex nursing situations. Nurses’ social intelligence is a professional nursing competency that flexibly coordinates complex nursing situations, developed through accumulating experiences of continuous reflection and relationship expansion based on receptive listening and social sensitivity in clinical interpersonal relationships.
Conclusion
Nurses’ social intelligence is widely used in clinical practice and is shown to have a significant direct and indirect impact on clinical nursing. To effectively apply social intelligence in the clinical context, individual and organizational efforts are required to share and transfer knowledge and capacity-building methods through collective intelligence and education.
- 2,303 View
- 126 Download

- A Structural Model on the Nursing Competencies of Nursing Simulation Learners
- Soo Jin Park, Eun Sun Ji
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(5):588-600. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.5.588
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to test a model of nursing competencies of nursing simulation learners. The conceptual model was based on the theory of Jeffries's simulaton theory.
Methods Data collection was conducted in October 2017 for 310 students from two nursing universities in Kyungbuk area for 20 days. Data analysis methods were covariance structure analysis using SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 22.0 statistical programs.
Results The hypothetical model was a good fit for the data. The model fit indices were comparative fit index=.97, normed fit index=.94, Tucker-Lewis Index=.97, root mean square error of approximation=.44, and standardized root mean square residual=.04. Teacher factors were directly related to simulation design characteristics, and it was confirmed that the curriculum, classroom operation and teaching method of the instructors were important factors. Learner factors were found to have a direct effect on nursing competence, self-confidence, and clinical performance that belong to nursing capacity. In particular, the results of this study indicate that the simulation design characteristics have a partial mediating effect on learner factors and clinical performance, and a complete mediating effect on learner factors and clinical judgment ability.
Conclusion In order to improve the learner's clinical performance and clinical judgment ability, it is necessary to conduct practical training through nursing simulation besides preparing the learner and the educator.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Care Simulation Learning Module on Nursing Knowledge, Clinical Competence, Team Psychological Safety, and Learning Satisfaction in Nursing Students
MinHee Jo, SungJung Hong
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2025; 13(1): 95. CrossRef - The mediating role of flow in the relationship between simulation design and simulation educational satisfaction in korean nursing students: a cross-sectional study
Eun-Kyung Lee, Eun-Joo Ji
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Students’ Self-confidence in Simulation Learning Based on National League for Nursing/Jeffries Simulation Framework
Jung-Suk Kim
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2024; 12(1): 73. CrossRef - The Development and Evaluation of the Online Respiratory Infectious Disease Nursing Simulation Course for Nursing Students
Jisu Lee, Hye Won Yoon
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2023; 11(2): 91. CrossRef - Does a preterm labor-assessment algorithm improve preterm labor-related knowledge, clinical practice confidence, and educational satisfaction?: a quasi-experimental study
Hee-Young Choi, Jeung-Im Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(3): 219. CrossRef - Relationship between Simulation Design Characteristics and Clinical Reasoning Competence: Multiple Additive Moderating Effects of Teaching Effectiveness and Students' Anxiety on Nursing Students
Kyung-In Cheon, Hea Kung Hur
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(4): 322. CrossRef - Development and Effects of Leukemia Nursing Simulation Based on Clinical Reasoning
Aeri Jang, Miok Song, Suhyun Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4190. CrossRef - A Comparative Study on Learning Outcomes according to the Integration Sequences of S-PBL in Nursing Students: Randomized Crossover Design
So Young Yun, Ja Yun Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(1): 92. CrossRef
- The Effect of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Care Simulation Learning Module on Nursing Knowledge, Clinical Competence, Team Psychological Safety, and Learning Satisfaction in Nursing Students
- 1,858 View
- 76 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Development and Psychometric Testing of the Clinical Nursing Competency Scale for Clinical Preceptor Use (CNCS-CP)
- Eunmi Kwak, Heeyoung Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(4):419-431. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.4.419
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop and establish the psychometric properties of a clinical nursing competency evaluation tool to be utilized by clinical preceptors.
Methods The initial items were identified through in-depth literature review and field interviews based on a hybrid model. Content validation of the items was evaluated through three rounds of content validity testing. Participants were 34 clinical preceptors and 443 nursing students participating in clinical practice. Data were analyzed using exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, convergence and discriminant validity, internal consistency and inter-rater reliability.
Results The final scale consisted of 23 items and four factors, fundamental nursing skills performance, critical thinking skills based on the nursing process, basic nursing knowledge, and professional attitude; these factor explained 69.7% of the total variance. The analysis with multi-trait/multi-item matrix correlation coefficients yielded 100.0% and 95.7 % convergence and discriminant validity, respectively. Cronbach's alpha for the total items was .95. The four subscale model tested by confirmatory factor analysis was satisfactory. Inter-rater reliability ranged from .912 to .967.
Conclusion This scale was found to be a reliable and valid instrument that clinical preceptors can apply for evaluating the clinical nursing competency of nursing students in clinical settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on the Perception of Non-Cognitive Skills Education according to the Type of Clinical Training Institution in Optometry
Se-Hoon Jung
Journal of Korean Ophthalmic Optics Society.2025; 30(2): 109. CrossRef - Core dimensions and measurement characteristics of multidimensional nursing competency assessment instruments: A systematic review
Lianfeng Wang, Junlin Chen, Othman Talib
Journal of Professional Nursing.2025; 61: 96. CrossRef - Evaluation and Analysis of English Teaching Ability Based on Nonlinear Random Matrix Model
Jianliang Zhou, Huixin Zhou, Zaoli Yang
Mathematical Problems in Engineering.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Development of Core Competency Scale for clinical nursing student educators
Hyun Sook Park, Eun Hee Choi, Gyung Duck Kim, Young Hee Kim, Mi Yang Jeon, Hyenam Hwang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 345. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Self-Efficacy Scale for Nursing Educators’ Role in Sri Lanka
Shyamamala S. Weerasekara, Jina Oh, Haeryun Cho, Mihae Im
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(15): 7773. CrossRef - Effects of Clinical Practice Satisfaction on Major Satisfaction Based on the Survey of Satisfaction of Clinical Laboratory Science Students on Clinical Practice
Kyung A Shin, Hyo Shin Kim, Sun Kyung Lee
The Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2019; 51(2): 252. CrossRef
- A Study on the Perception of Non-Cognitive Skills Education according to the Type of Clinical Training Institution in Optometry
- 1,630 View
- 60 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Development of a Triage Competency Scale for Emergency Nurses
- Sun Hee Moon, Yeon Hwan Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(3):362-374. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.3.362
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to develop a triage competency scale (TCS) for emergency nurses, and to evaluate its validity and reliability.
Methods Preliminary items were derived based on the attributes and indicators elicited from a concept analysis study on triage competency. Ten experts assessed whether the preliminary items belonged to the construct factor and determined the appropriateness of each item. A revised questionnaire was administered to 250 nurses in 18 emergency departments to evaluate the reliability and validity of the scale. Data analysis comprised item analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, contrasted group validity, and criterion-related validity, including criterion-related validity of the problem solving method using video scenarios.
Results The item analysis and confirmatory factor analysis yielded 5 factors with 30 items; the fit index of the derived model was good (χ 2/
df =2.46, Root Mean squared Residual=.04, Root Mean Squared Error of Approximation=.08). Additionally, contrasted group validity was assessed. Participants were classified as novice, advanced beginner, competent, and proficient, and significant differences were observed in the mean score for each group (F=6.02,p =.001). With reference to criterion-related validity, there was a positive correlation between scores on the TCS and the Clinical Decision Making in Nursing Scale (r=.48,p <.001). Further, the total score on the problem solving method using video scenarios was positively correlated with the TCS score (r=.13,p =.04). The Cronbach's α of the final model was .91.Conclusion Our TCS is useful for the objective assessment of triage competency among emergency nurses and the evaluation of triage education programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Patient Satisfaction With the Level of Competence of the Triage Nurse in Hospital Emergency Departments
Meritxell López Hernández, Montserrat Puig‐Llobet, Sergio Higon Fernández, Marta Franco Freirut, Yolanda Moreno Mateos, Jordi Galimany Masclans
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2025; 34(9): 3893. CrossRef - Effects of Critical Thinking Disposition, Clinical Judgement, and Nurse–Physician Collaboration on Triage Competency Among Triage Nurses
Ji-Won Song, Hyung-Ran Park
Healthcare.2025; 13(4): 405. CrossRef - The Impact of the Nursing Professionalism and Triage Competency of Emergency Department Nurses on Disaster Nursing Competency
Hyo Jin Im, Ju Young Ha
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2025; 39(1): 19. CrossRef - Effects of Disaster Nursing Education Based on the Korean Triage and Acuity Scale (KTAS): Focus on Competency in Emergency Patient Triage, Core Competencies in Disaster Nursing, Confidence in Disaster Nursing, and Self-efficacy
Yoonhee Seok, Hye-Ryeon Park
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2025; 13(1): 83. CrossRef - Influence of work stress, clinical decision-making ability, and teamwork on triage competency among emergency room nurses in Korea: a cross-sectional study
Seon-Hyeong Kim, Ae-Ri Jung
Journal of Acute Care Surgery.2025; 15(2): 60. CrossRef - Validation of the Persian Triage Decision-Making Inventory (TDMI): a cross-cultural adaptation study
Mahdi Nabi Foodani, Amir Hossein Goudarzian, Özkan Görgülü, Kelly Jo Cone, Khosro Shakeri, Zahra Abbasi Dolatabadi
BMC Emergency Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of risk prediction models for high-risk patients with non-traumatic acute abdominal pain: a prospective observational study
Rui Li, Xiao-Hui Wei, Xiao-Qin Li, Ai-Hua Dong, Dan-Nan Ai, Li-Jin Zhou, Yan Yang
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Triage—clinical reasoning on emergency nursing competency: a multiple linear mediation effect
Won-Oak Oh, Myung-Jin Jung
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Korean Triage and Acuity Scale education using role-playing and its effects on triage competency: A quasi-experimental design
Yon Hee Seo, Sun-Og Lim, Vanessa Carels
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(10): e0311892. CrossRef - Construction of learning objectives and content for emergency triage nurses in tertiary general hospitals: A Delphi study
Linyuan Zhang, Bo Gao, Fang He, Chao Wu, Juan Du, Li Zhang, Juan Liang, Hongjuan Lang
Nurse Education in Practice.2024; 80: 104145. CrossRef - Concept analysis of psychiatric nursing competency in psychiatric nursing
Hwa-Bok Choi
Archives of Psychiatric Nursing.2024; 52: 130. CrossRef - Enhancing triage accuracy in emergency nurses: The impact of a game-based triage educational app
Sun-Hee Moon, Su Ol Kim
International Emergency Nursing.2024; 72: 101398. CrossRef - Emergency nurses’ communication experiences with patients and their families during the COVID-19 pandemic: A qualitative study
Soyoung Shin, Hye Jin Yoo
International Emergency Nursing.2023; 66: 101240. CrossRef - Influence of Emergency Department Nurses' Grit, Self-Leadership, and Communication on Their Triage Competencies: A Descriptive Survey Study
Gwiseon Jeong, Hyeongsuk Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(4): 356. CrossRef - Factors affecting triage competence among emergency room nurses: A cross‐sectional study
Seokhwa Hwang, Sujin Shin
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(13-14): 3589. CrossRef - Professional Self-Concept, Job Stress, and Triage Competency Among Emergency Nurses: Secondary Data Analysis of a Cross-Sectional Survey
You-Jin Cho, Young-Ran Han, Yeo-Won Jeong
Journal of Emergency Nursing.2022; 48(3): 288. CrossRef - The Effect of Competency-Based Triage Education Application on Emergency Nurses’ Triage Competency and Performance
Sun-Hee Moon, In-Young Cho
Healthcare.2022; 10(4): 596. CrossRef - Factors Associated with School Nurses’ Triage Competency in South Korea
Jaehee Yoon, Heesook Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(16): 8279. CrossRef - Development of emergency nursing care competency scale for school nurses
Jaehee Yoon
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with the undertriage of patients with abdominal pain in an emergency room
Boo Young Oh, Kisook Kim
International Emergency Nursing.2021; 54: 100933. CrossRef - Development and validity of the Korea psychiatric triage algorithm
Jeongmin Ha, Kyeongmin Jang, Misuk An
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Patient Satisfaction With the Level of Competence of the Triage Nurse in Hospital Emergency Departments
- 2,949 View
- 116 Download
- 21 Crossref

- The Effects of Violence Coping Program Based on Middle-Range Theory of Resilience on Emergency Room Nurses’ Resilience, Violence Coping, Nursing Competency and Burnout
- Seung Min Lee, Kyung Mi Sung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(3):332-344. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.3.332
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of a violence coping program (VCP) based on Polk's middle-range theory of resilience on nursing competency, resilience, burnout, and the ability to cope with violence in nurses working in emergency rooms.
Methods A quasi-experimental study, with a nonequivalent control group and a pretest-posttest design, was conducted. Participants were 36 nurses who worked in emergency rooms and had experienced violence; 18 nurses from D hospital and 18 nurses from C hospital were assigned to the experimental and control groups, respectively. The experimental group received the VCP twice per week for 8 weeks.
Results Levels of resilience,
F =59.41,p <.001, active coping behavior, c2=33.09,p <.001, and nursing competency,F =59.41p <.001, increased significantly and levels of passive coping behavior, c2=22.92,p <.001, and burnout,F =52.74,p <.001, decreased significantly in the experimental group.Conclusion The results suggest that the VCP could be an effective strategy for reducing burnout and improving resilience, active coping behavior, and nursing competency. Therefore, it would be a useful intervention for improving the quality of nursing care provided in emergency rooms.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations Between Workplace Violence and Work Performance Among Nurses: A Longitudinal Study Based on Affective Events Theory
Yifei Pei, Yiping Xiao, Xuan Zhang, Yan'e Lu, Meng Sun, Ran Lyu, Fenglin Cao
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2026; 35(2): 756. CrossRef - ОСОБЛИВОСТІ ПСИХОЛОГІЧНОЇ СТІЙКОСТІ МЕДСЕСТЕР РІЗНИХ ВІДДІЛЕНЬ
Н. Д. Дейнека, М. І. Марущак, О. Є. Оксенюк, В. М. Стернік, О. П. Мялюк
Медсестринство.2025; (1): 16. CrossRef - Effects of a Remote Videoconferencing-based Expressive Writing Program on Posttraumatic Stress, Resilience, and Post-traumatic Growth among Traumatized Nurses
Nam Hee Chae, Ji Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(2): 152. CrossRef - Relationship Between Illness Uncertainty and Family Resilience Among Caregivers of Stroke Patients in Chinese Nuclear Families: The Mediating Role of Perceived Stress
Qian Li, Caifeng Luo, Jianqin Ye, Zekun Bian, Weiyi Sun, Man Zhou, Mingzhu Rong
Patient Preference and Adherence.2024; Volume 18: 1095. CrossRef - Mixed‐methods study protocol for exploring the perception of nurses' resilience in the COVID‐19 pandemic: Designing, implementing and evaluation of intervention
Tooba Hoseini Azizi, Nahid Dehghan Nayeri, Alun C. Jackson, Fatemeh Bahramnezhad
Nursing Open.2023; 10(6): 4111. CrossRef - Psychological Intervention to Promote Resilience in Nurses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Suk-Jung Han, Young-Ran Yeun
Healthcare.2023; 12(1): 73. CrossRef - The Influence of Infection Control Knowledge, Emergency Nursing Competency, and Infection Prevention Environment on Burnout among Psychiatric Nurses Caring for Patients with COVID-19
Hyeran Cho, Suyon Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(4): 482. CrossRef - Interventions to reduce burnout among clinical nurses: systematic review and meta-analysis
Miran Lee, Chiyoung Cha
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Needs assessment of a home-visit safety management training program for visiting nurses
Eunjoo Kim, Hyori Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 138. CrossRef - Relationships between Violence Experience, Resilience, and the Nursing Performance of Emergency Room Nurses in South Korea
Sarang Kim, Minkyung Gu, Sohyune Sok
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(5): 2617. CrossRef - Verbal violence and turnover intention among new nurses in Korea: A time‐lagged survey
Ae Kyung Chang, Ah Young Kim
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(6): 1823. CrossRef - Clinical nurses’ experiences of workplace verbal violence: a phenomenological study
Min Soo Woo, Hyoung Suk Kim, Jeung-Im Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(2): 154. CrossRef - Recent advancements in microfluidic chip biosensor detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria: a review
Fang Mi, Cunming Hu, Ying Wang, Li Wang, Fei Peng, PengFei Geng, Ming Guan
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry.2022; 414(9): 2883. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Psychological Burnout in Nurses Caring for Terminal Cancer Patients
Na-Ri Seo, Hyun-E Yeom
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2022; 25(4): 159. CrossRef - Predictors of compassion fatigue, burnout, and compassion satisfaction among emergency nurses: A cross-sectional survey
Hairong Yu, Anhua Qiao, Li Gui
International Emergency Nursing.2021; 55: 100961. CrossRef - Effects of Hospital-Based Violence-Prevention and Coping Programs on Nurses' Violence Experience, Violence Responses, Self-Efficacy, and Organizational Commitment
Yu Jeong Yang, Jeong-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 550. CrossRef - Relationship of Workplace Violence to Turnover Intention in Hospital Nurses: Resilience as a Mediator
Hyun-Jung Kang, Jaeyong Shin, Eun-Hyun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 728. CrossRef - Impact of Traumatic Events and Resilience on the Professional Quality of Life among Clinical Nurses
Dan-Bi Yoo, Hye-Ja Park, Phill-Ja Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2019; 22(1): 27. CrossRef - Effectiveness of interventions to reduce occupational stress among emergency department staff: a systematic review protocol
Hui (Grace) Xu, Kathryn Kynoch, Anthony Tuckett, Robert Eley, Peter Newcombe
JBI Database of Systematic Reviews and Implementation Reports.2019; 17(4): 513. CrossRef - Mediating effects of workplace violence on the relationships between emotional labour and burnout among clinical nurses
Hyejin Kim, Ji‐Su Kim, Kwisoon Choe, Yeunhee Kwak, Jae‐seok Song
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2018; 74(10): 2331. CrossRef - Resilience and Coping After Hospital Mergers
Cynthia Russo, Oriana Calo, Georgia Harrison, Kathleen Mahoney, Kathleen Evanovich Zavotsky
Clinical Nurse Specialist.2018; 32(2): 97. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Empathy and Resilience on the Relationship between Terminal Care Stress and Performance for Nurses in a Tertiary Hospital
Heui Yeoung Kim, Keum Hee Nam, Su Hye Kwon
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2017; 20(4): 253. CrossRef
- Associations Between Workplace Violence and Work Performance Among Nurses: A Longitudinal Study Based on Affective Events Theory
- 1,639 View
- 63 Download
- 22 Crossref

- Development of the Developmental Support Competency Scale for Nurses Caring for Preterm Infants
- Jeong Soon Kim, Hee Sun Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(6):793-803. Published online December 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.6.793
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Developmental care has been recognized as a very important component for the development and health promotion of preterm infants. However, research on how to assess developmental nursing competency has not been studied as expected. This study was done to develop and evaluate a new scale to measure nursing competency for developmental support of preterm infants.
Methods Concept analysis was done with using the Hybrid model of Schwartz-Barcott and Kim (2000), from which a preliminary new scale (30 items) was developed. To test the validity and reliability of the new scale being developed, data were collected from 122 NICU nurses at 4 hospitals in 3 cities in the Republic of Korea, from December, 2014 to March, 2015.
Results The final version of the Developmental Support Competency Scale for Nurses (DSCS-N) caring for premature infants was a 4-point Likert type scale, consisting of 19 items, and categorized as 6 factors, explaining 62.5% of the total variance. Each of the factors were named as follows; ‘environmental support’ (4 items), ‘parental support’ (3 items), ‘interaction’ (3 items), ‘critical thinking’ (3 items), ‘professional development’ (3 items), and ‘partnership’ (3 items). The Cronbach's α coefficient for the scale was .83 and the reliability of the subscales ranged from .60~.76.
Conclusion The psychometric evaluation of the new scale demonstrated an acceptable validity and reliability. Findings indicate that the DSCS-N can be used as the tool to test the effect of educational programs for nurses and contribute to advance developmental care for preterm infants.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Developmentally Supportive Care Among Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Nurses in South Korea
Han Na Lee, Ji Hyeon Park, Haeryun Cho
Advances in Neonatal Care.2023; 23(3): E60. CrossRef - Factors influencing neonatal intensive care unit nurses' parent partnership development
Eun Kyoung Kim, In Young Cho, Ji Yeong Yun, Bobae Park
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2023; 68: e27. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Nicu nurses’ competence enhancement program for developmentally supportive care for preterm infants: A quasi-experimental study
Han Na Lee, Haeryun Cho
Heliyon.2023; 9(1): e12944. CrossRef - Development of the Individualised Developmental Care Knowledge and Attitude Scale
Kamile Akça, Fatma Kurudirek
Applied Nursing Research.2023; 72: 151697. CrossRef - Development and validation of the information security attitude questionnaire (ISA‐Q) for nurses
Jiwon Kang, GyeongAe Seomun
Nursing Open.2023; 10(2): 850. CrossRef - Analysis of research on developmentally supportive care for prematurity in neonatal intensive care unit: a scoping review
Hanna Lee, Ji Hyeon Park, Haeryun Cho
Child Health Nursing Research.2022; 28(1): 9. CrossRef - Effects of a Neonatal Supportive Positioning Training Video Program for Preterm Infants on the Knowledge and Performance of Nurses in Neonatal Intensive Care Units
Hyun Jin Moon, Kyung Sook Cho, Mi Young An, Dong Woo Son
Asian Nursing Research.2022; 16(1): 25. CrossRef - Research Trends of Follow-Up Care after Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Graduation for Children Born Preterm: A Scoping Review
So Ra Kang, Haeryun Cho
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(6): 3268. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Turkish Version of the Developmental Support Competency Scale for Nurses (DSCS-N)
Ayşe Kahraman, Sibel Serap Ceylan
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2020; 54: e47. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Developmental Care Practice Among Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Nurses
Jisun Park, Ji-Soo Kim
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2019; 47: e10. CrossRef - Limits of professional competency in nurses working in Nicu
Natalija Skorobogatova, Nida Žemaitienė, Kastytis Šmigelskas, Rasa Tamelienė, Eglė Markūnienė, Dalia Stonienė
Open Medicine.2018; 13(1): 410. CrossRef
- Developmentally Supportive Care Among Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Nurses in South Korea
- 1,495 View
- 40 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Development and Effects of Assertiveness Training applying Dongsasub Training for Nursing Students in Clinical Practice
- Myoungsuk Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(4):490-500. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.4.490
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to develop assertiveness training applying Dongsasub training for junior nursing students, and to verify effectiveness of the training on assertiveness behavior, self-esteem, clinical practice stress, and clinical competence.
Methods The study design was a non-equivalent control group non-synchronized design. Participants were 63 nursing students in clinical training (31 students in the experimental group and 32 students in the control group). The assertiveness training applying Dongsasub training consisted of four sessions. Outcome variables included assertiveness behavior, self-esteem, clinical practice stress, and clinical competence. Data were analyzed using Chi-square, Fisher's exact test and independent samples t-test with SPSS/WIN 21.0.
Results Scores of assertiveness behavior (t=-2.49,
p =.015), self-esteem (t=-4.80,p <.001) and clinical competence (t=-2.33,p =.023) were significantly higher and clinical practice stress (t=4.22,p <.001) was significantly lower in the experimental group compared to the control group.Conclusion Results indicate that the assertiveness training applying Dongsasub training can be used as a nursing intervention to lower clinical practice stress and improve the clinical competence of nursing students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of verbal violence, clinical practice stress, and coping with stress on nursing students’ major satisfaction during clinical practice
Heejung Heo, Yeoungsuk Song
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 190. CrossRef - Imagine All the People: A Guided Internet-Based Imagery Training to Increase Assertiveness among University Students—Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial
Micaela Di Consiglio, Jessica Burrai, Emanuela Mari, Anna Maria Giannini, Alessandro Couyoumdjian
Healthcare.2023; 11(13): 1874. CrossRef - A structural model of nursing students’ performing communication skills
Cho Rong Gil, Kyung Mi Sung
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 148. CrossRef - Effect of Clinical Practice Stress and Anger Expression on Assertive Behavior in Nursing Students
Eun-Ju LEE, Gyu-Li BAEK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2022; 34(1): 104. CrossRef - Effectiveness of assertiveness training, SBAR, and combined SBAR and assertiveness training for nursing students undergoing clinical training: A quasi-experimental study
Gie Ok Noh, Myongsuk Kim
Nurse Education Today.2021; 103: 104958. CrossRef - Educational Needs of Communication among Nursing Students
Min Young Jung, Jeongyee Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(1): 91. CrossRef - The Impacts of Assertiveness on Attitudes toward Nurse-Physician Collaboration in Nursing Students
Sang Min Lee, Young Ho Ryu, Ju Hyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2018; 24(4): 326. CrossRef
- The effect of verbal violence, clinical practice stress, and coping with stress on nursing students’ major satisfaction during clinical practice
- 1,405 View
- 26 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Development and Effects of Emotional Intelligence Program for Undergraduate Nursing Students: Mixed Methods Research
- Oi Sun Lee, Mee Ock Gu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(6):682-696. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.6.682
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to develop and test the effects of an emotional intelligence program for undergraduate nursing students.
Methods The study design was a mixed method research. Participants were 36 nursing students (intervention group: 17, control group: 19). The emotional intelligence program was provided for 4 weeks (8 sessions, 20 hours). Data were collected between August 6 and October 4, 2013. Quantitative data were analyzed using Chi-square, Fisher's exact test, t-test, repeated measure ANOVA, and paired t-test with SPSS/WIN 18.0. Qualitative data were analyzed using content analysis.
Results Quantitative results showed that emotional intelligence, communication skills, resilience, stress coping strategy, and clinical competence were significantly better in the experimental group compared to the control group. According to the qualitative results, the nursing students experienced improvement in emotional intelligence, interpersonal relationships, and empowerment, as well as a reduction in clinical practice stress after participation in the emotional intelligence program.
Conclusion Study findings indicate that the emotional intelligence program for undergraduate nursing students is effective and can be recommended as an intervention for improving the clinical competence of undergraduate students in a nursing curriculum.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research trends and effectiveness analysis of social and emotional learning programs for adult learners: A scoping review
Yoon-ju Lee, Insook Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(3): 299. CrossRef - Emotional Intelligence, Academic Motivation, and Achievement among Health Science Students in Saudi Arabia: A Self-Deterministic Approach
Rasha Mohammed Mahrous, Bussma Ahmed Bugis, Samiha Hamdi Sayed
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 571. CrossRef - A Literature Review of Simulation-Based Nursing Education in Korea
Sumee Oh, Jungmin Park
Nursing Reports.2023; 13(1): 506. CrossRef - The Effects of a Non-Technical Skills Training Program on Emotional Intelligence and Resilience in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Diana Jiménez-Rodríguez, María del Mar Molero Jurado, María del Carmen Pérez-Fuentes, Oscar Arrogante, Nieves Fátima Oropesa-Ruiz, José Jesús Gázquez-Linares
Healthcare.2022; 10(5): 866. CrossRef - Development and effects of a high-risk pregnancy emotive role-play program for nursing students: a quasi-experimental study
Bo Gyeong Lee, Sun-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(4): 317. CrossRef - The development and effects of an emotional competency promotion program for nursing students: A nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design
Hyewon Kang, Jeongyee Bae
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(4): 369. CrossRef - Understanding the relationships among emotional exhaustion, job satisfaction, and emotional intelligence of hotel front desk employees
Kwang-Hi Park, Dae-Kwan Kim
Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research.2021; 26(5): 504. CrossRef - The assessment of emotional intelligence in social care and healthcare student selection: a qualitative descriptive study
Anne Pienimaa, Kirsi Talman, Elina Haavisto
Educational Research.2021; 63(3): 302. CrossRef - Social–Emotional Competence and Academic Achievement of Nursing Students: A Canonical Correlation Analysis
Sun-Hee Kim, Sujin Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(4): 1752. CrossRef - The Influences of Nursing Professionalism and Emotional Intelligence on the Clinical Performance Ability in Nursing Students
Hyo-Won Kim, Myung-Sook Yoo
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2020; 14(2): 41. CrossRef - Impact of emotional development intervention program on subjective well-being of university students
Konstanze Schoeps, Usue de la Barrera, Inmaculada Montoya-Castilla
Higher Education.2020; 79(4): 711. CrossRef - The Reliability and Validity of Korean Version of Wong and Law Emotional Intelligence Scale (K-WLEIS)
Harim Jeong, Heejung Choi, Myungsook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(4): 611. CrossRef - Influence of Metacognition and Emotional Intelligence on Self-leadership in Nursing Students
Myoung Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2019; 25(2): 146. CrossRef - The Effect of an Empathy Education Program on Nursing Students' Empathy Ability, Interpersonal Ability, and Caring
Jin Ok Jeong, Sue Kim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(3): 344. CrossRef - The Effects of Emotional Labor on Job Satisfaction of Hotel Employees: Analyzing Moderating Effects of Emotional Intelligence
Kwang-Hi Park
Stress.2018; 26(3): 166. CrossRef - Effects of Communication Empowerment Program Based on Situated Learning Theory for Nursing Students
Soo Jin Kim, Boyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(6): 708. CrossRef - The level of emotional intelligence in undergraduate students of nursing
Ľudmila Majerníková, Andrea Obročníková
Pielegniarstwo XXI wieku / Nursing in the 21st Century.2017; 16(1): 25. CrossRef - Relationships between Personal Traits, Emotional Intelligence, Internal Marketing, Service Management, and Customer Orientation in Korean Outpatient Department Nurses
Bogyun Kim, Jia Lee
Asian Nursing Research.2016; 10(1): 18. CrossRef - Vocational Identity and Ego Identity Status in Korean Nursing Students
Hyun-Young Koo, Eun-Jung Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2016; 10(1): 68. CrossRef - Effects of Discipline-based Career Course on Nursing Students' Career Search Self-efficacy, Career Preparation Behavior, and Perceptions of Career Barriers
Soonjoo Park
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(3): 259. CrossRef - Influence of Emotional Intelligence and Ego Resilience on Interpersonal Relationship of Nurses
Oi Sun Lee, Mee Ock Gu, Mi Jung Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(6): 3902. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Stress on Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Burnout among Nursing College Students
Chung Mee Ko
Journal of the Korean Society of School Health.2015; 28(3): 239. CrossRef
- Research trends and effectiveness analysis of social and emotional learning programs for adult learners: A scoping review
- 1,568 View
- 41 Download
- 22 Crossref

- Critical Thinking Disposition and Clinical Competence in General Hospital Nurses
- Jin-Ah Park, Bog-Ja Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(6):840-850. Published online December 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.6.840
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to investigate the relationship between critical thinking disposition and clinical competence among nurses in general hospitals.
Methods This study was a descriptive-correlational study with a convenience sample of 560 nurses from 5 general hospitals. The data were collected by self-administered questionnaires. Critical thinking disposition was measured using the Critical Thinking Disposition Scale for Nursing Students. Clinical competence was measured using the Standardized Nurse Performance Appraisal Tool.
Results The mean score for critical thinking disposition and clinical competence was 3.37 and 4.10 respectively on a 5 point scale. A statistically significant correlation was found between critical thinking disposition and clinical competence. A regression model explained 72.8% of clinical competence. Prudence is the most significant predictor of clinical competence (R2=.728).
Conclusion Study findings suggest that nurses with a higher level of critical thinking disposition would have a higher level of clinical competence. Furthermore, prudence might be the most important predictor of clinical competence. In order to strengthen clinical competence in nurses, the development and enhancement of critical thinking should be emphasized at the college level and nurses should be encouraged to make a clinical decision with greater prudence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In teaching youths to learn critically: the role of family, formal and non-formal education – findings from a middle-income context
Le Anh Vinh, Hoang Phuong Hanh, Bui Dieu Quynh, Trinh Thi Ngoc Lan, Bui Thi Dien, Do Duc Lan, Luong Viet Thai
Asia Pacific Journal of Education.2025; 45(1): 84. CrossRef - The effect of a 10‐week field‐oriented transition programme for new graduate registered nurses in critical care
Hana Kim, Eunhye Kim, Jamin Noh, Eunkyung Bang, Sunghee H. Tak
Nursing in Critical Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Impacts of an AI Tutor for Nursing Students: Emphasizing on Clinical Practice Education
Min-Kweon Ahn, Min-Jeong Chae
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2025; 26(5): 1285. CrossRef - Nursing students’ satisfaction and clinical competence by type of pediatric nursing practicum during the COVID-19 pandemic
Hyeon Ok Ju, Jung Hwa Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2024; 30(1): 29. CrossRef - Association between Nurses’ Perceptions of Patient Safety Culture, Willingness to Report Near Misses, Critical Thinking Disposition, and Nursing Care Activities for Patient Safety
Da Eun Lee, Bo Gyeong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 283. CrossRef - THE LEVEL OF NURSES' CLINICAL COMPETENCE WITH BACHELOR'S AND MASTER'S DEGREES WORKING IN URMIA HOSPITALS IN 2024
Yusef Haghighimoghadam, Zahraalsadat Abedi, Farshad Mohammadi, Vahid Alinejad
Nursing and Midwifery Journal.2024; 22(6): 486. CrossRef - Exploring the link of personality traits and tutors’ instruction on critical thinking disposition: a cross-sectional study among Chinese medical graduate students
LingYing Wang, WenLing Chang, HaiTao Tang, WenBo He, Yan Wu
BMJ Open.2024; 14(8): e082461. CrossRef - Factors affecting the development of clinical nurses’ competency: A systematic review
Abdulaziz Mofdy Almarwani, Naif S. Alzahrani
Nurse Education in Practice.2023; 73: 103826. CrossRef - Chinese version of Yoon Critical Thinking Disposition Instrument: validation using classical test theory and Rasch analysis
Mio Leng Au, Yue Yi Li, Lai Kun Tong, Si Chen Wang, Wai I Ng
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation between moral distress and clinical competence in COVID-19 ICU nurses
Zohreh Kalani, Maasoumeh Barkhordari-Sharifabad, Niloufar Chehelmard
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects on Triage Competency Based on Nursing Task Performance and Self-Efficacy of Nurses in Regional Emergency Medical Institutions
Su Jin Kim, Su Ol Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(3): 304. CrossRef - Grafik Tasarımı Bölümü Öğrenme Çıktılarının 21. Yüzyıl Becerileri Temelinde İncelenmesi
Aytaç ÖZMUTLU, Emel BAYRAK ÖZMUTLU
Güzel Sanatlar Enstitüsü Dergisi.2021; 27(46): 138. CrossRef - Is nurses’ clinical competence associated with their compassion satisfaction, burnout and secondary traumatic stress? A cross‐sectional study
Mohammad Ali Zakeri, Gholamreza Bazmandegan, Hamid Ganjeh, Maryam Zakeri, Sekineh Mollaahmadi, Ali Anbariyan, Zahra Kamiab
Nursing Open.2021; 8(1): 354. CrossRef - Chinese medical students’ disposition for critical thinking: a mixed methods exploration
Lei Huang, Angela Pei-Chen Fan, Na Su, Jessica Thai, Russell Olive Kosik, Xudong Zhao
BMC Medical Education.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Critical Thinking Level among Medical Sciences Students in Iran
Faranak Jafari, Seyyed Mohsen Azizi, Ali Soroush, Alireza Khatony, Ahmed Rachid
Education Research International.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Influences of Critical Thinking Disposition, Nurse Managers' Transformation and Transactional Leadership Style on Nurses' Competency with Evidence Based Practice
Geum Ah Lee, Sung Hee Shin, Suk Jeong Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 305. CrossRef - FACTORS INFLUENCING COMPETENCY DEVELOPMENT OF NURSES AS PERCEIVED BY STAKEHOLDERS IN VIETNAM
Do Thi Ha, Khanitta Nuntaboot
Belitung Nursing Journal.2020; 6(4): 103. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Student-Educator Negotiated Critical Thinking Dispositions Scale (SENCTDS)
Sarah Quinn, Michael Hogan, Christopher Dwyer, Patrick Finn, Emer Fogarty
Thinking Skills and Creativity.2020; 38: 100710. CrossRef - Effect of a Situational Module Learning Course on Critical Thinking Disposition and Metacognition in Nursing Students: A Quasi-experimental Study
Kwang Ok Park, Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(2): 251. CrossRef - General Self-Efficacy Mediates the Effect of Family Socioeconomic Status on Critical Thinking in Chinese Medical Students
Lei Huang, Yun-Lin Liang, Jiao-Jiao Hou, Jessica Thai, Yu-Jia Huang, Jia-Xuan Li, Ying Zeng, Xu-Dong Zhao
Frontiers in Psychology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The influence of informal learning and learning transfer on nurses' clinical performance: A descriptive cross-sectional study
Jungmi Yun, Dong-Hee Kim, Youngchoon Park
Nurse Education Today.2019; 80: 85. CrossRef - The Association of Competence and Critical Thinking in the Nurses in Imam Khomeini Hospital, Affiliated to Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Iran
H Jafari, T Taghavi Larijani, F Ghadirian, HS Emamzadeh Ghasemi
Iran Journal of Nursing.2019; 32(121): 28. CrossRef - The Competence Screening Questionnaire for Higher Education: Adaptable to the needs of a study programme
Evelyn Bergsmann, Julia Klug, Christoph Burger, Nora Först, Christiane Spiel
Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education.2018; 43(4): 537. CrossRef - Critical Thinking, Stress of Clinical Practice and Competence of Clinical Practice of the Nursing Students
Gyoo-Yeong CHO
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2018; 30(4): 1223. CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Practice Environment and Self-esteem on Critical Thinking Disposition among Clinical Nurses
Eunju Choi, Jihyeon Hwang, Insil Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(2): 161. CrossRef - Effects of Moral Sensitivity and Critical Thinking Disposition on Perceived Ethical Confidence in Nursing Students
Mi-Hye Lim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(9): 610. CrossRef - A Study on the Critical Thinking Disposition, Self-directed Learning Readiness and Professional Nursing Competency
An-Na Park, Kyung-Hee Chung, Weon Gyeong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of SBAR Program on Communication Clarity, Clinical Competence and Self-efficacy for Nurses in Cancer Hospitals
Youn Hwa Kim, Yooun Sook Choi, Hye Young Jun, Myung Ja Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2016; 19(1): 20. CrossRef - The Experiences of Students Transferring into the Nursing Program at Local Universities
Moon-Jeong KIM, So-Hee KIM, Eun-Kyung BYUN
Journal of Fisheries and Marine Sciences Education.2016; 28(2): 366. CrossRef - The relationship among critical thinking disposition, nursing process competency and evidence-based practice competency in nurses working in hospitals
Kyoung Yun Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2016; 27(2): 451. CrossRef - A Design for and Evaluation of a Critical Thinking Class for New Community Health Practitioners
Ji Yeon Park, MinGyu Seo, Hyoung Suk Kim, Kyung Hee Yoo, Kyung Ja June
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 141. CrossRef - A Study on Interpersonal Relation Disposition, Critical Thinking Disposition, and Communication Competence in Undergraduate Students in Nursing
Narae Heo
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2015; 24(1): 22. CrossRef - Evaluation of tools used to measure critical thinking development in nursing and midwifery undergraduate students: A systematic review
Amanda G. Carter, Debra K. Creedy, Mary Sidebotham
Nurse Education Today.2015; 35(7): 864. CrossRef - Exploring the association between parental rearing styles and medical students’ critical thinking disposition in China
Lei Huang, Zhaoxin Wang, Yuhong Yao, Chang Shan, Haojie Wang, Mengyi Zhu, Yuan Lu, Pengfei Sun, Xudong Zhao
BMC Medical Education.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Professional Quality of Life and Clinical Competencies among Korean Nurses
Kyunghee Kim, Yonghee Han, Yeunhee Kwak, Ji-su Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(3): 200. CrossRef - The Knowledge, Need, and Usage of Medical Terminology in Clinical Nursing Practice
Gisoo Shin, Mi-Kyoung Cho
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2014; 16(4): 276. CrossRef - Accuracy and Satisfaction with IVIC300 (Intravenous infusion controller)
Jung Hee Park, Nam Young Yang, Moon Jun Na, Young Jin Go, Ki Suk Kim, Young Aue Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(1): 114. CrossRef - Development of Nursing Competence Scale for Graduating Nursing Students
Ga Eul Joo, Kyeong-Yae Sohng
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(3): 590. CrossRef - Clinical Competence according to Experiences on the Essential of Fundamental Nursing Skills in Nursing Students
Dongwon Choi
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(2): 184. CrossRef - Clinical Reasoning Ability of Oncology Nurses
Eun Young Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(4): 265. CrossRef - Use of the 5E Learning Cycle Model Combined With Problem-Based Learning for a Fundamentals of Nursing Course
Won Hee Jun, Eun Ju Lee, Han Jong Park, Ae Kyung Chang, Mi Ja Kim
Journal of Nursing Education.2013; 52(12): 681. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Evidence-Based Practice Readiness for Tertiary General Hospital Nurses
Jeong-Sook Kim, Mee-Ock Gu, Sun-Yon Jo
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(6): 2945. CrossRef - Effects of Self-leadership and Job Involvement on Clinical Competence in General Hospital Nurses
Yonghee Han, Youngrye Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(4): 462. CrossRef - Professional Self-Concept, Critical Thinking Disposition and Clinical Competence in Nursing Students
Kyung-Ah Shin, Bok-Hee Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(1): 46. CrossRef - Perceived Relationship among Professional Self-Concept, Head Nurse's Leadership, and Nursing Clinical Competency by Clinical Nurses
Young-Jin Kim, Hyun-Kyoung Song, Mi-Aie Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2011; 17(1): 96. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Clinical Competence for General Hospital Nurses
Kyung-Ja Kang, Eun-Man Kim, Se-Ang Ryu
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2011; 11(1): 284. CrossRef - Critical thinking disposition, stress of clinical practice and clinical competence of nursing students
In-Sook Kim, Youn-Kyoung Jang, Su-Ho Park, So-Hyeon Song
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2011; 17(3): 337. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Patient Safety-focused Inservice Education Program for Surgical Nurse
Young Mee Kim, Myung Sook You, Yaun Hee Cho, Seung Hae Park, Seung Nam Nam, Mi Ok Park, Se Young Kim, Min Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(2): 152. CrossRef
- In teaching youths to learn critically: the role of family, formal and non-formal education – findings from a middle-income context
- 2,512 View
- 40 Download
- 48 Crossref

- Validity and Reliability of a Clinical Performance Examination using Standardized Patients
- Ja Yun Choi, Keum Seong Jang, Soon Hee Choi, Mi Soon Hong
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(1):83-91. Published online February 28, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.1.83
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to test the validity of a modified clinical performance examination (CPX) for preclinical students in nursing.
Methods 70 nursing students in their second semester of the junior year at C University participated in CPX. Scenarios and checklists were developed by our research team from September to October 2005. Six stations were organized. Evaluation included physical examination of a patient with lung cancer, education on usage of a metered dosage inhaler, and lobectomy postoperative care. Students were randomly assigned to a station
Results There was a difference in the CPX scores according to stations. The agreement of scoring between trained faculty members and SPs was more than moderate (r=.647). The correlation between the CPX score and the average grade in the previous semester and between the CPX score and the average grade of a paper and pen test of the pulmonary system of adults was low (r=.276; r=.048).
Conclusion Traditional CPX is generally recommended, however, modified CPX is appropriate for preclinical students in the current Korean Nursing school setting if there are additional scoring systems to balance the testing level at each station.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The development and effects of a nursing education program for hyperglycemia patient care using standardized patients for nursing students
Jin Lee, Pok Ja Oh
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(4): 427. CrossRef - Reliable Prognostic Cardiopulmonary Function Variables in 110 Patients With Acute Ischemic Heart Disease
Jeong Jae Lee, Chan-hee Park, Joshua (Sung) Hyun You
Physical Therapy Korea.2022; 29(3): 200. CrossRef - A study on evaluator factors affecting physician-patient interaction scores in clinical performance examinations: a single medical school experience
Young Soon Park, Kyung Hee Chun, Kyeong Soo Lee, Young Hwan Lee
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2021; 38(2): 118. CrossRef - New Viewpoint of Surface Anatomy Using the Curved Sectional Planes of a Male Cadaver
Koojoo Kwon, Byeong-Seok Shin, Min Suk Chung, Beom Sun Chung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Standardized Patient and Faculty Agreement in Evaluating Nursing Students’ Assessment and Communication Skills
Young Ju Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2017; 24(3): 189. CrossRef - The Effects of Preclinical Clinical Performance Examination on Nursing Students' Confidence in Nursing Skills and Critical Thinking Competence
Jeong Sook Park, Mi Jung Choi, Soon Yang Jang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 75. CrossRef - The effect of Simulation-based learning scenario using standardized repiratory patients on learning satisfaction, clinical skill competency and self-efficacy in Health-related department students
Hye-Young Cho
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(3): 2100. CrossRef - Empowerment on Clinical Nursing Skills Core Program
Hye-Suk Kim, Hae-Ryoung Park, Eun-Hee Park
Journal of Digital Convergence.2014; 12(12): 589. CrossRef - The Effects of Simulation-Based Training, Underwent Before or After the Clinical Practice for the Nursing Students
Jung Ok Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(2): 203. CrossRef - Clinical Competence and Self-confidence of New Graduate Nurses with an Integrated Nursing Curriculum of Simulation with Problem-Based Learning
Young Sook Roh, Sunghee Kim, Sun Hee Yang, Yoon Sook Kang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(7): 3349. CrossRef - Systematic Review of Korean Studies on Simulation within Nursing Education
Jung-Hee Kim, In-Hee Park, Sujin Shin
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(3): 307. CrossRef - The Effects of Simulation Training With Hybrid Model for Nursing Students on Nursing Performance Ability and Self Confidence
Suk Jeong Lee, Young Mi Park, Sang Mi Noh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(2): 170. CrossRef - Effects of using Standardized Patients on Nursing Competence, Communication Skills, and Learning Satisfaction in Health Assessment
Sun Ju Choi, Mal Suk Kwon, Seon Hwa Kim, Hyeon Mi Kim, Yang Sook Jung, Geum Yi Jo
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(1): 97. CrossRef - Effects and Adequacy of High-Fidelity Simulation-Based Training for Obstetrical Nursing
Woo Sook Lee, Miok Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(4): 433. CrossRef - Effects of Teaching Method using Standardized Patients on Nursing Competence in Subcutaneous Injection, Self-Directed Learning Readiness, and Problem Solving Ability
Mi-Ran Eom, Hyun-Sook Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Kayeon Seong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(2): 151. CrossRef - Development of a Multimedia Learning DM Diet Education Program using Standardized Patients and Analysis of Its Effects on Clinical Competency and Learning Satisfaction for Nursing Students
Kyung Sun Hyun, Hyun Sook Kang, Won Ock Kim, Sunhee Park, Jia Lee, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(2): 249. CrossRef
- The development and effects of a nursing education program for hyperglycemia patient care using standardized patients for nursing students
- 1,181 View
- 4 Download
- 16 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


