Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Successful aging among the elderly with mild cognitive impairment facing the crisis of old age: a grounded theory study
- Haeyun Shin, Suhye Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):301-316. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to understand experiences of successful aging experience in older adults with mild cognitive impairment.
Methods
The participants were 15 older adults with mild cognitive impairment who had experienced successful aging. Data were collected from January to October 2021 through individual deep, unstructured interviews. Data analysis was performed using Charmaz’s grounded theory method. In addition, the consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research checklist was used to ensure the quality of the study.
Results
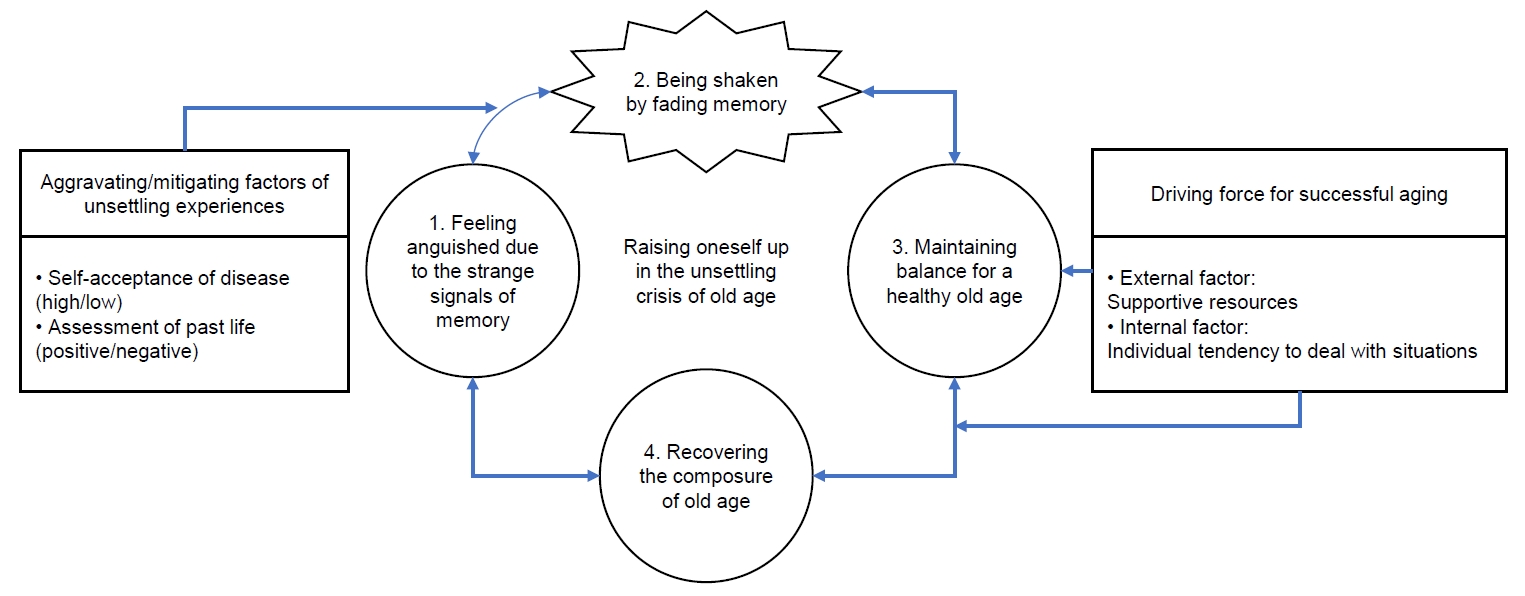
The key category representing experiences of successful aging experience in older adults with mild cognitive impairment was “raising oneself up in the unsettling crisis of old age.” Four stages were derived: “feeling anguished due to the strange signals of memory,” “being shaken by fading memory,” “maintaining balance for a healthy old age,” and “recovering the composure of old age.”
Conclusion
Participants tried to successfully achieve aging while implementing their own plans and strategies in the midst of the challenges of old age, when the mind and body were unsettled by mild cognitive impairment. The results of this study provide a deep understanding of experiences of successful aging in older adults with mild cognitive impairment, potentially contributing to the development and implement of nursing intervention programs to promote the successful pursuit of aging in this population.
- 2,426 View
- 118 Download

- Assessment of Risk Factors for Postoperative Delirium in Older Adults Who Underwent Spinal Surgery and Identifying Associated Biomarkers Using Exosomal Protein
- Wonhee Baek, JuHee Lee, Yeonsoo Jang, Jeongmin Kim, Dong Ah Shin, Hyunki Park, Bon-Nyeo Koo, Hyangkyu Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):371-384. Published online August 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22146
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
With an increase in the aging population, the number of patients with degenerative spinal diseases undergoing surgery has risen, as has the incidence of postoperative delirium. This study aimed to investigate the risk factors affecting postoperative delirium in older adults who had undergone spine surgery and to identify the associated biomarkers.
Methods
This study is a prospective study. Data of 100 patients aged ≥ 70 years who underwent spinal surgery were analyzed. Demographic data, medical history, clinical characteristics, cognitive function, depression symptoms, functional status, frailty, and nutritional status were investigated to identify the risk factors for delirium. The Confusion Assessment Method, Delirium Rating Scale-R-98, and Nursing Delirium Scale were also used for diagnosing deliri-um. To discover the biomarkers, urine extracellular vesicles (EVs) were analyzed for tau, ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1), neurofilament light, and glial fibrillary acidic protein using digital immunoassay technology.
Results
Nine patients were excluded, and data obtained from the remaining 91 were analyzed. Among them, 18 (19.8%) developed delirium. Differences were observed between partici-pants with and without delirium in the contexts of a history of mental disorder and use of benzodiazepines (p = .005 and p = .026, respectively). Tau and UCH-L1—concentrations of urine EVs—were comparatively higher in participants with severe delirium than that in partici-pants without delirium (p = .002 and p = .001, respectively).
Conclusion
These findings can assist clinicians in accurately identifying the risk factors before surgery, classifying high-risk patients, and predicting and detecting delirium in older patients. Moreover, urine EV analysis revealed that postoperative delirium following spinal surgery is most likely associated with brain damage. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychological factors associated with postoperative cognitive outcomes in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Anahita Amirpour, Lina Bergman, Jeanette Eckerblad, Gabriela Markovic, Ulrica Nilsson, Anna Falk
British Journal of Anaesthesia.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Emerging biomarkers of postoperative delirium at the intersection of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration
Kun Leng, Mervyn Maze, Odmara L. Barreto Chang
Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Psychological factors associated with postoperative cognitive outcomes in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- 2,047 View
- 69 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Development of an Aging Anxiety Scale for Middle-Aged Women
- Haejin Lee, Mi-Ae You
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):14-25. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This was a methodological study that aimed to develop a measurement scale for aging anxiety among middle-aged women.
Methods In this study, construct factors were extracted, and a conceptual framework was established through an extensive literature review and in-depth interviews with middle-aged women. Under the conceptual framework, 44 preliminary items were constructed, and a preliminary scale of 25 items was completed after two rounds of expert validation and item review. For this study, data were collected from 201 women aged 40∼59 years, and the construct validity and reliability of the preliminary scale were verified.
Results To verify the construct validity, exploratory factor analysis was conducted. Four factors containing 19 items were extracted. Concurrent validity of the developed scale was verified with Pearson's correlation analysis. The final scale comprised 4 factors (“Social valueless”, “Physical weakness”, “Concern about changes in appearance”, and “Expectations of old age”) and 19 items. The Cronbach's α value was .91.
Conclusion The scale for measuring aging anxiety in middle-aged women developed in this study validly reflected the peculiarities of aging anxiety in middle-aged women, who experience many physical, emotional, and social changes. The scale can be said to reflect the cultural background, as it reflected real experiences gained through in-depth interviews with middle-aged women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Self-Determination Theory–Based Cardiovascular Disease Prevention Program for Community-Dwelling Middle-Aged Women
Yein Lee, Yunhee Kim
Journal of Community Health Nursing.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Gerascophobia or Excessive Fear of Aging Scale (GEFAS): Development, validation, and exploration of psychometric properties of a brief instrument using classical testing theory and item response theory
Waqar Husain, Farrukh Ijaz, Muhammad Ahmad Husain, Ammar Achraf, Hasan M. Isa, Khaled Trabelsi, Seithikurippu R. Pandi-Perumal, Amir H. Pakpour, Haitham Jahrami
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2025; 128: 105599. CrossRef - Family support, social security, commercial insurance, and aging anxiety among Chinese residents: a study based on the 2021 CGSS data
He Gu, Qingli Tan, Yongxing Guo, Han He, Yu Zhang
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Determination of the association between aging anxiety and menopausal symptoms in middle-aged women
Seda Hazar, Gülçin Nacar, Furkan Doğan, Sermin Timur Taşhan
Menopause.2025; 32(6): 539. CrossRef - Effects of Physical Activity on Ageism and Aging Anxiety Among Chinese and Korean Adults Aged 55 to 64 Years
Jing Li, Seung-Yong Kim, Cho-Young Yook, Xiao-Long Chen, Woo-Jin An, Ju-Young Oh, Chae-Hee Park
Healthcare.2025; 13(11): 1218. CrossRef - Prevalence of depressive symptoms during the menopausal transition in Türkiye: impact of symptom severity, aging anxiety and health-related quality of life
Banu Aslan, Özgür Önal
Climacteric.2025; 28(5): 607. CrossRef - Orta Yaşlı Kadınlarda Yaşlanma Anksiyetesi, Cinsel Yaşam Kalitesi ve Öznel Mutluluk Arasındaki İlişkinin İncelenmesi Üzerine Kesitsel Bir Çalışma
Ejdane Coşkun, Burcu Çakı Döner
Turkish Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2025; 19(4): 323. CrossRef - Development of a scale to measure selection, optimization, compensation (SOC) strategy in late middle-aged women: a methodological study
Do-Young Lee, Gie Ok Noh
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(3): 216. CrossRef - Association between Menopausal Women’s Quality of Life and Aging Anxiety: The Role of Life Satisfaction and Depression
Seunghee Lee, Mijung Jang, Dohhee Kim, KyooSang Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(8): 1189. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Laughter Therapy Program for Middle-aged Women Hospitalized in Psychiatric Wards
Do Young Lee, Ju Hyun Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(3): 273. CrossRef - Determination of aging anxiety in middle-aged women
Nese Kiskac, Mahruk Rashidi, Muharrem Kiskac
Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Informal caregivers’ negative affect: The interplay of caregivers’ resilience, aging anxiety and burden
Yaira Hamama-Raz, Rachel Nissanholtz Gannot, Michal Michaelis, Yichayaou Beloosesky, Adaya Nissanholtz
Aging & Mental Health.2023; 27(7): 1300. CrossRef - Aging anxiety and beliefs about exercise in middle-aged women
Nedim TEKİN, Adeviye AYDIN
Turkish Journal of Kinesiology.2023; 9(3): 214. CrossRef - Experiences Pertaining to Successful Aging in Middle-Aged Women in South Korea
Do-young Lee, Hyun-ju Kim, A-young Jo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(19): 6882. CrossRef - Validity and reliability study of the Turkish version of the Aging Anxiety Scale for Middle‐Aged Women
Zeynep Daşıkan, Selin Paker, Ruken Yağız Altıntaş, Figen Kazankaya, Sümeyye Bakır
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2022; 58(4): 2918. CrossRef - Turkish Adaptation of the Aging Anxiety Scale for Middle-Age Women: Validity and Reliability Study
Adeviye AYDIN, Esma KABASAKAL
Journal of Basic and Clinical Health Sciences.2022; 6(1): 173. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Life Satisfaction in Middle-Aged Women
Hee Kyung Kim, Hae Kyung Chang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(3): 326. CrossRef - The health status, aging anxiety, social networking, generativity, and happiness of late middle-aged adults
Hae Kyung Chang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(4): 392. CrossRef - The Effects of Climacteric Symptom Cognition, Self-efficacy on Aging Anxiety in Middle-Aged Couples: Actor and Partner Interdependence Mediation Model
Yeon-Suk Kim, Myung-Haeng Hur
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 247. CrossRef - Verification of the Mediating Effect of Social Support on Physical Activity and Aging Anxiety of Korean Pre-Older Adults
Ahra Oh, Jiyoun Kim, Eunsurk Yi, Jongseob Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(21): 8069. CrossRef
- A Self-Determination Theory–Based Cardiovascular Disease Prevention Program for Community-Dwelling Middle-Aged Women
- 2,262 View
- 56 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling on Successful Aging in Elders with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on Selection-Optimization-Compensation Strategy
- Young Mi Jang, Rhayun Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(4):488-498. Published online August 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.4.488
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The focus of the study was on the selection-optimization-compensation (SOC) strategy to predict successful aging mediated by dyspnea symptoms in older adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The model was constructed based on the hypotheses that coping strategy and social support of the elders predict successful aging through the SOC strategies.
Methods Participants were 218 outpatients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease recruited for the study. Data collection was done from March 25 to September 11, 2015, and analyzed using SPSSWIN 22.0 and AMOS 21.0.
Results The hypothetical model appeared to be fit to the data. Seven of eight hypotheses selected for hypothetical model were statistically significant. The SOC strategy has only significant indirect effects through dyspnea symptoms on successful aging. Coping strategy, social support, SOC strategies and dyspnea symptoms explained 62% of variance in successful aging.
Conclusion The SOC strategies with social support and dyspnea symptoms significantly explained successful aging among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nursing strategies should be focused on social support and coping strategies to optimize SOC strategies so that older adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are able to manage dyspnea symptoms and eventually achieve successful aging.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A structural equation modeling analysis of successful aging in older adults with osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional descriptive study
Jeong Hwa Kum
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(2): 131. CrossRef - Development of a scale to measure selection, optimization, compensation (SOC) strategy in late middle-aged women: a methodological study
Do-Young Lee, Gie Ok Noh
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(3): 216. CrossRef - Factors contributing to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients' functional performance: Structural equation modelling based on theory of unpleasant symptoms
Hye Suk Jun, Younhee Kang
Nursing Open.2023; 10(5): 3132. CrossRef - Experiences on Self Management of Aged Men with Mild Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Jeong-Soo KIM
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(3): 758. CrossRef - The Relationships among Social Support, Bowel Function Symptoms and Uncertainty in Rectal Cancer Patients
Kyungmi Lee, Semi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 421. CrossRef - Life experience of older women with chronic conditions: Flow and Balance as a coping resource
Sanghee Lee, Jinmoo Heo
Educational Gerontology.2019; 45(4): 259. CrossRef
- A structural equation modeling analysis of successful aging in older adults with osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional descriptive study
- 1,150 View
- 13 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Lived Experience with Aging in Middle-Aged Woman
- K R Shin, E S Kong, G B Kim, N C Kim, C H Kim, C K Kim, H K Kim, Y J Ro, M S Song, S Y Ahn, K J Lee, Y W Lee, S O Chang, S J Chon, N O Cho, M O Cho, K S Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(6):878-887. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.6.878
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was to explore lived experience of middle-aged women with aging. The ultimate purpose of this inquiry was to discover the essence of middle-aged women's experience of aging and to promote understanding. METHOD: This inquiry was performed by using Van Manen's hermeneutical phenomenological approach to make more plausible interpretation of experience. First-handed experiences were explored through multi-stage in-depth interview with 6 women aged between 40 and 64. Second- handed experiences were explored with text such as essay, novel, and photographs. RESULT: As the process of reflecting and analysing the data of experience were performed, essential themes were emerged: striking onset of event, discomfort and tired body and mind, everything in ones mind, age of harvest gaining much more than loss. CONCLUSION: This inquiry would be a cornerstone for humanistic nursing care for the mid-aged women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concept Analysis of Middle-aged Women's Seogeulpeum
Hye-Ja Gu, Young Eun
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(4): 381. CrossRef - Korean Older Adults' Perceptions of the Aging Process
Yeon-Gang Chung, Kyung-Hee Kim, Kyung-Sook Choi, Hye-Jin Kwon, Kyung-Sook Park, Mi-Hye Choi, Young-Hee Yom
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2008; 34(5): 36. CrossRef
- Concept Analysis of Middle-aged Women's Seogeulpeum
- 719 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Association Between Expectations Regarding Aging and Health-Promoting Behaviors Among Korean Older Adults
- Su Hyun Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(6):932-940. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.6.932
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: This study was performed to measure expectations regarding aging among community-residing older adults, identify sociodemographic characteristics associated with the level of expectations regarding aging, and examine whether expectations regarding aging were associated with health-promoting behaviors. METHODS: Data was collected by using questionnaires of a short version of the Expectations Regarding Aging Survey (ERA-18) and Health Promoting Lifestyle Profile II (HPLP II) from 99 older adults who resided in the community of Kyunggi, Daegu, and Kyungpook province. RESULTS: More than 75% of the participants reported that it was an expected part of aging to have more aches and pains, to become depressed, and to become more forgetful. The mean score of expectations regarding aging was 23.15+/-17.80 (possible range 0-100). The old-old, women, those with less education, less monthly allowance and poor health status had lower expectations regarding aging than other elderly. After controlling for sociodemographic characteristics and perceived health, expectations regarding aging were independently associated with health-promoting behaviors in older adults. CONCLUSION: The findings demonstrate that older Korean adults have low expectations regarding aging, and expectations regarding aging influence health-promoting behaviors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between expectations regarding aging and productive engagement among community-dwelling older adults: a cross-sectional study
Shuangshuang Dai, Yijia Zhuo, Siyuan Feng, Xinyue Zhao, Beibei Qiao, Jingjing Wang, Mingli Zhao
Frontiers in Public Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Recreation Specialization, Leisure Constraints, and Continuous Participation Intention of Middle-Aged Leisure Sports Participants on the Expected Health Benefits on Old Age
Young-Mi Kim, Kyoung-Shil Park, Sae-Sook Oh
Korean Journal of Lesure, Recreation & Park.2025; 49(4): 1. CrossRef - Effects of Subjective Health Perception on Health Behavior and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Patients with Prediabetes and Diabetes
Sungjung Kwak, Yoonmi Lee, Seunghui Baek, Jieun Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 7900. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Health Promotion Program Using Action Planning Strategy for Young Adults
Su Hyun Kim, Min Ji Kim, Sang Hee Kim, So Yeon Kim, Chae Yeon Park, Jee Yun Bang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(4): 461. CrossRef - The association of locomotive and non-locomotive physical activity measured by an accelerometer with functional fitness in healthy elderly men: a pilot study
Hyejoon Park, Wonil Park, Moran Lee, Nayoung Ko, Eunkyung Kim, Kazuko Ishikawa-takata, Jonghoon Park
Journal of Exercise Nutrition & Biochemistry.2018; 22(1): 41. CrossRef - Frequency, Intensity and Daily Life Distress of Urinary Dysfunction in Women with Cervical Cancer after Radical Hysterectomy
Nami Chun, Gie Ok Noh, Hyun Ju Song, Sang Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(3): 400. CrossRef - Relationship between Expectations Regarding Aging and Physical Activity among Middle Aged Adults in Urban Areas: Based on the Pender's Health Promotion Model
Sung-Hye Cho, MoonKi Choi, JuHee Lee, Hyewon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(1): 14. CrossRef - The effects of age identity and attitude toward aging on the use of health promotion in late life
Jina Han
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2015; 32(5): 33. CrossRef - The Effects of Age and Walkway Type on Lower Extremities Kinematics in Elderly Women
Byung-Hoon Woo, Yang-Sun Park
Korean Journal of Sport Biomechanics.2015; 25(3): 249. CrossRef - The influence of expectations regarding aging on health-promoting behaviors
Hyeyoung Bae, Aranbyeol Kim, Soojin Nam, Jia Youn, Haeju Youn, Gayoung Kim, Daehyae Jang, Su Hyun Kim
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2014; 25(1): 77. CrossRef - Association among ageing‐related stereotypic beliefs, self‐efficacy and health‐promoting behaviors in elderly Korean adults
Hyun‐E Yeom
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2014; 23(9-10): 1365. CrossRef - Cultural Adaptation and the Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of the Symptom Management Beliefs Questionnaire
Hyun-E Yeom
Asian Nursing Research.2013; 7(3): 104. CrossRef - Effects of Perceived Health Status, Self-esteem and Family Function on Expectations Regarding Aging among Middle-aged Women
Yoo Rim Kweon, Hae Ok Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(2): 176. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Expectation Regarding Aging and Functional Health Status Among Older Adults in China
Xianwen Li, Qiyuan Lv, Chunyu Li, Hailian Zhang, Caifu Li, Jinzhen Jin
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2013; 45(4): 328. CrossRef - Barriers to Health Behaviors in Male and Female Elderly People in Korea
Young Eun, Mee Soon Song, Mee Ock Gu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(2): 332. CrossRef
- Relationship between expectations regarding aging and productive engagement among community-dwelling older adults: a cross-sectional study
- 998 View
- 14 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Types of Nurse's Attitudes Toward the Aging Process: A Q-Methodological Approach
- Kae Hwa Jo, Gyeong Ju An
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(6):823-834. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.6.823
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to analyze types of nurse's attitudes toward the aging process. METHODS: A Q-methodology which provides a method of analyzing the subjectivity of each item was used. Thirty-four selected Q-statements from each of 38 subjects were classified into a shape of normal distribution using a 9 point scale. The collected data was analyzed using a QUANL PC program. RESULTS: Five types of attitudes towards the aging process from research subjects in Korean nurses were identified. Type I is a positive acceptance type, Type II is a negative acceptance type, Type III is a passive coping type, Type IV is an active coping type, and Type V is an ambiguous acceptance type. CONCLUSION: The results of the study indicate that different approaches of educational programs for elderly care are recommended based on the five types of nurse's attitude toward the aging process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Types of literary therapy's subjective perceptions utilized by Q-methodology
Jeong Hye Park, Kyoungho Choi
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2015; 26(6): 1465. CrossRef
- Types of literary therapy's subjective perceptions utilized by Q-methodology
- 741 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Development and Evaluation of Online Aging and Health Management Education for Undergraduate Students
- Myonghwa Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(4):540-548. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.4.540
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop online aging and health management education for undergraduate students and to evaluate its effects analyzing the differences in knowledge and attitude toward aging and the elderly.
Method An Online aging and health management education program was established through analysis, planning, content framing and production, program application, and evaluation stages. The study sample consisted of 98 undergraduate students in one university in D city. The instruments used were FAQ I for knowledge of aging and a 20 item semantic differential scale for attitude toward aging and the elderly.
Results The results of this study were as follows. First, undergraduate students' knowledge level was low and attitudes were negative at the baseline. Second, after the class, knowledge scores improved significantly from 14.44 to 20.12. In addition, the attitudes toward elderly and aging changed from negative to a more positive way showing a 23.57 point difference.
Conclusion This study shows that the online aging and health management education program was an effective educational method to improve knowledge and attitude of aging for the young generation such as college students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Evaluation of a Web-based Education Program for Nursing Students on Control of Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus Infection
Ju Gong, Ji-Yeon Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(1): 122. CrossRef
- Development and Evaluation of a Web-based Education Program for Nursing Students on Control of Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus Infection
- 713 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Experience of Frailty in Korean Elderly: A Phenomenological Study Utilizing the Colaizzi Method
- Jin Kyoung Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(4):562-574. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.4.562
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study attempts to explore the subjective experience of frailty among elderly individuals in Korea.
Methods From June to August in 2014, 11 elderly persons who had experienced frailty in a community were interviewed. For data analysis, the method suggested by Colaizzi was applied as a phenomenological method.
Results According to the analysis, the study participants’ frailty process was structured in seven categories: ⒜ ‘natural phenomenon with ageing,’ ⒝ ‘life force comes to an end,’ ⒞ ‘the light in my heart turns off,’ ⒟ ‘unavoidable situation,’ ⒠ ‘continuous and connected vicious cycle,’ ⒡ ‘the limit of recovery energy already passes,’ and ⒢ ‘life is supported by someone's help.’
Conclusion The frailty experience in the participants is a natural process of aging, which cause vicious cycle acting with each other among physical, psychological, and social health. It is said that the cycle of frailty was started from weight loss and insufficient sleep, and boostered by pain. The participants from repetition of the vicious cycle become exhausted and pass the threshold of their recovery energy at some points. If they meet with sudden accidents such as falling, traffic accident and so on, they become to live a dependent life supported by someone's help in a moment. To prevent frailty and worsening conditions in Korean elderly individuals, it is recommended to provide a interventional programs using this study's results.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hospitalization experience of elderly surgical patients: A phenomenological study
Yujeong Shin, Dukyoo Jung, Hyunjoo Oh
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(1): 84. CrossRef - Constructing hope in the Katingan River: A phenomenological analysis
Rendi Indiwara
Priviet Social Sciences Journal.2025; 5(11): 175. CrossRef - Experiences of community-dwelling frail older adults with diabetes: Using phenomenological methods
Junhee Ahn, Youngran Yang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(3): 267. CrossRef - A phenomenological study on the meaning of presence of elderly participants in an exercise-music program
Kyungsun Kim, Hyeoncheol Jeong
Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science.2020; 9(4): 295. CrossRef - Effects of a Health Promotion Empowerment Program Using a Resident Volunteer as a Lay Health Leader on Frail Elders' Health and Empowerment
Jeong Sook Park, Yun Jung Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(3): 335. CrossRef
- Hospitalization experience of elderly surgical patients: A phenomenological study
- 2,014 View
- 22 Download
- 5 Crossref

- The Influence of Subjective Health Status, Post-Traumatic Growth, and Social Support on Successful Aging in Middle-Aged Women
- Seung Hee Lee, Hyung Suk Jang, Young Hee Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(5):744-752. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.5.744
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to investigate factors influencing successful aging in middle-aged women.
Methods A convenience sample of 103 middle-aged women was selected from the community. Data were collected using a structured questionnaire and analyzed using descriptive statistics, two-sample t-test, one-way ANOVA, Kruskal Wallis test, Pearson correlations, Spearman correlations and multiple regression analysis with the SPSS/WIN 22.0 program.
Results Results of regression analysis showed that significant factors influencing successful aging were post-traumatic growth and social support. This regression model explained 48% of the variance in successful aging.
Conclusion Findings show that the concept 'post-traumatic growth' is an important factor influencing successful aging in middle-aged women. In addition, social support from friends/co-workers had greater influence on successful aging than social support from family. Thus, we need to consider the positive impact of post-traumatic growth and increase the chances of social participation in a successful aging program for middle-aged women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Studies on chemical profiling and pharmacokinetics of traditional Chinese medicine Formula Kang Shuai Lao Pian
Chengjuan Liu, Qibao Jiang, Zhirong Zhou, Peng Lei, Peng Zhang, Xin Chai, Guixiang Pan, Yuefei Wang, Miaomiao Jiang
Arabian Journal of Chemistry.2024; 17(1): 105398. CrossRef - Effects of Physical Health Status, Social Support, and Depression on Quality of Life in the Korean Community-Dwelling Elderly
Koung-Oh Chang, Dazhou Li
Advances in Public Health.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effects of a Self-Growing Program Based on the Ecological System Theory for Parenting Stress and Posttraumatic Growth of Middle-aged Women with Adolescent Children
Seung Min Lee, Kyung Mi Sung
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2022; 31(2): 264. CrossRef - Posttraumatic Growth and Health Promotion Behavior in Patients with Cancer: The Mediating Effect of Spiritual Well-Being
Shunji Piao, Pok Ja Oh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(1): 33. CrossRef - Pattern of Smartphone Usage and Psychosocial Factors Affecting Smartphone Overdependence in Middle-Aged Women
Yeo Won Jeong, Juyeon Oh
Journal of Addictions Nursing.2020; 31(1): 39. CrossRef - Influence of Midlife Health Condition and Awareness of Successful Aging on Preparation for Old Age
Eun Ho Ha, Young Mi Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(5): 472. CrossRef - A Concept Analysis of Posttraumatic Growth in Family Caregivers of Cancer Patients
Kyoung Hee Kim, Yong Soon Shin
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(1): 9. CrossRef - The Influence of Health Status and Type of Health Management on Depression in Middle-Aged Women
Myung Sill Chung, Yeon Ha Kim, Kyung Choon Lim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2018; 24(3): 250. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Successful Aging of Late Middle-Aged Adults
YonJi Kim, JuHee Lee, Young Joo Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2018; 18(2): 90. CrossRef
- Studies on chemical profiling and pharmacokinetics of traditional Chinese medicine Formula Kang Shuai Lao Pian
- 1,162 View
- 8 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Successful Aging of Korean Older Adults based on Rowe and Kahn's Model: A Comparative Study According to the Use of Community Senior Facilities
- Soo Jin Lee, Misoon Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(2):231-239. Published online April 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.2.231
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to examine the prevalence of successful aging and factors influencing successful aging.
Methods This was a secondary analysis study. Data were analyzed from 10,462 elderly people who participated in the 2011 National Elderly Survey. According to the use of community senior facilities, participants were divided into 4 groups: those who used senior centers (group A, n=580), village senior clubs (group B, n=3,240), both of the 2 facilities (group C, n=339), and neither of the 2 facilities (group D, n=6,303). Cross-tabulation and logistic regression were performed.
Results The prevalence of successful aging was highest in group C (20.94%) and lowest in group D (10.41%). The physical & mental function and active engagement domains were highest in group C, while they were lowest in group D. The disease & risk factors domain were highest in group A, while lowest in group B. An educational level of middleschool or higher and income level in the third or higher quintile were significant factors for predicting successful aging in all groups.
Conclusion These results provide a basis for designing prevention and management programs as interventions to increase the prevalence of successful aging in Korean older adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Determining the affecting predictors on successful aging among older adults in Iran
Mohsen Shafiee, Raoof Nopour, Esmat Mirbagheri, Homa Hajizadegan, Hadi Kazemi-Arpanahi
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Residential Environmental Factors Affecting Healthy Aging Among Older Adults: A Comparison Between Urban and Rural Areas in South Korea
Bongjeong Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2025; 39(3): 340. CrossRef - Changes in successful aging and its related indicators among community-dwelling older adults: The Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study (KFACS)
Hohyun Seong, Sohee Kim, Hyunsook Shin, Chang Won Won, Youn-Jung Kim
Geriatric Nursing.2024; 59: 392. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of successful aging in young-old and old-old adults based on Rowe and Kahn’s model: A secondary data analysis
Ji Eun Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(2): 203. CrossRef - Using an adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system for prediction of successful aging: a comparison with common machine learning algorithms
Azita Yazdani, Mostafa Shanbehzadeh, Hadi Kazemi-Arpanahi
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction of successful aging using ensemble machine learning algorithms
Zahra Asghari Varzaneh, Mostafa Shanbehzadeh, Hadi Kazemi-Arpanahi
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of the related factors of depression, social support and social participation in kyungro‐dang among older adults in South Korea: A structural equation modelling analysis
Hocheol Lee, Seokjun Moon, Geurum Song, Eun Woo Nam
Nursing Open.2021; 8(2): 562. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Successful Aging among Community-Dwelling Older Adults Based on Ecological System Model
Hye-Young Jang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(9): 3220. CrossRef - The Effect of Basic Psychological Needs and Wisdom on Successful Aging in the Elderly
Min-Jeong Nam, Young-Mun Cho
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(1): 70. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Successful Aging of Late Middle-Aged Adults
YonJi Kim, JuHee Lee, Young Joo Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2018; 18(2): 90. CrossRef - Correlates of Successful Aging in South Korean Older Adults: A Meta-Analytic Review
Sin-Hyang Kim, Sihyun Park, Kyung-Sook Park
Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health.2017; 29(7): 544. CrossRef - Successful Aging and the Influencing Factors in the Korean Elderly: Focused on Family Support
SongYi Han, Soon-Nyung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(4): 372. CrossRef
- Determining the affecting predictors on successful aging among older adults in Iran
- 1,906 View
- 19 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Relationship between Expectations Regarding Aging and Physical Activity among Middle Aged Adults in Urban Areas: Based on the Pender's Health Promotion Model
- Sung-Hye Cho, MoonKi Choi, JuHee Lee, Hyewon Cho
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(1):14-24. Published online February 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to measure the level of expectations regarding aging (ERA) and identify relationship between ERA and physical activity of middle aged adults.
Methods Participants were middle aged adults who resided in the community in three cities in Korea. Data were collected using questionnaires that contained items on individual characteristic, International Physical Activity Questionnaires (IPAQ), and behavior-specific cognitive factors including ERA-12. Hierarchical multiple regression was conducted to examine whether ERA would predict physical activity by controlling other factors.
Results The mean age of the participants was 51.1±6.9 years. The mean score for ERA (possible range=0 to 100) was 40.04±14.31. More than half of the participants (62.6%) were not engaged in health promoting physical activity. Gender, employment status and exercise confidence were associated with level of physical activity (F=7.14,
p <.001, R2=.36). After controlling for individual factors and behavior-specific cognitive factors, ERA was independently related to physical activity (F=7.19,p <.001, R2=.38).Conclusion The results demonstrate that individuals' belief about aging has effects on physical activity in Korean middle aged adults. Thus, nursing interventions which focused on ERA could help enhance physical activity in middle aged adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Relationship Among Stress, Sense of Coherence and Sleep Quality in Middle-aged Women
So Hyeon Kim, So Young Choi
Journal of Korean Maternal and Child Health.2025; 29(3): 137. CrossRef - Family care and health-promoting behaviors among community elders: The chain mediating effect of self-efficacy and aging expectations
Yian Chen, Lin Zhang, Jiashuang Xu, Miaojing Song, Pengjuan Ji, Qiqi Ji, Leilei Guo
Geriatric Nursing.2025; 66: 103606. CrossRef - The Effects of Health Status and Social Support on Happiness in MiddleAged Women
Bok Hui Baek, So Young Choi
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2024; 38(1): 16. CrossRef - Impact of WhatsApp-Based Self-Care Education on Self-Care Behaviors and Lifestyle in Overweight and Obese Pregnant Women with Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Fatemeh Salarkarimi, Majid Karandish, Mehrnoosh Zakerkish, Zahra Abbaspoor
Jundishapur Journal of Chronic Disease Care.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Level of Expectations Regarding Aging Among Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Lunwei Lin, Shunqi Liao, Zhangrong Yan, Chaofan Liu, Qi Wang, Fang Wang
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2024; 25(3): 410. CrossRef - The Effect of a Training Intervention Based on Pender’s Health Promotion Model on the Lifestyle of Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis
Hossein Hassannezhad, Hasan Robabi, Fatihe Kerman Saravi
Medical-Surgical Nursing Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Validity and Reliability of Persian Version of the 12-Item Expectations Regarding Aging Survey
Hamid Sharif Nia, Long She, Sotheeswari Somasundram, Fatemeh Khoshnavay Fomani, Omolhoda Kaveh, Lida Hosseini
The International Journal of Aging and Human Development.2023; 96(2): 248. CrossRef - Health-Related Expectations Regarding Aging among Middle-Aged and Older Japanese: Psychometric Performance and Novel Findings from the ERA-12-J
Michael Annear, Yasuo Shimizu, Tetsuhiro Kidokoro
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(20): 13509. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Physical Activity of Foreign Workers: Based on a Health Promotion Model
Jeong Eui Cho, Yeongmi Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(3): 344. CrossRef - Lower serum levels of alpha tocopherol and lycopene are associated with higher pain and physical disability in subjects with primary knee osteoarthritis: A case-control study
Bina Eftekharsadat, Dawood Aghamohammadi, Neda Dolatkhah, Maryam Hashemian, Halale Salami
International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research.2021; 91(3-4): 304. CrossRef - Effects of a Daily Life-Based Physical Activity Enhancement Program for Middle-Aged Women at Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
Kyung Ae Kim, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(2): 113. CrossRef - Applying the theory of planned behavior to determine factors associated with physical activity by women with hypertension in rural areas of Iran
Effat Hatefnia, Kobra Alizadeh, Mostafa Ghorbani
Asian Biomedicine.2019; 12(2): 83. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Successful Aging of Late Middle-Aged Adults
YonJi Kim, JuHee Lee, Young Joo Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2018; 18(2): 90. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Exercise Behavior of the Male Manual Worker and Office Worker based on Health Promotion Model
SeungKyoung Yang, Yeongmi Ha, Mi-Ra Jung
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2015; 24(3): 235. CrossRef
- The Relationship Among Stress, Sense of Coherence and Sleep Quality in Middle-aged Women
- 1,322 View
- 19 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Accessing Factor Structure and Construct Validity of the Successful Aging Inventory
- Eun Joo Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(4):568-578. Published online August 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.4.568
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Successful Aging Inventory (SAI-K) to determine its suitability for use with older Korean adults.
Methods Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses were utilized to assess the factor structure and the construct validity of the SAI-K. First- and second-order Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) were conducted to identify the most adequate model. Cronbach's alpha was used to test the reliability.
Results Using a second-order CFA, a four-factor structure was validated (χ2=122.82,
p <.001, GFI=.92, AGFI=.88, SRMR=.06 RMSEA=.07, 90% CI=.05-.09, CFI=.93). The four-factor SAI-K showed reliable internal consistency with a Cronbach's alpha for the total scale of .86.Conclusion The four-factor, 13-item SAI-K showed satisfactory reliability and validity and, thus, has the potential to be an appropriate instrument for measuring successful aging in older Korean adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary habits and successful aging in Chinese older adults: a cross-sectional analysis of the CLHLS
Yecheng Wang, Keying Song, Zijian Zhao
Archives of Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Uloga bolesti i samoprocjene zdravlja pri subjektivnom uspješnom starenju
Neala Ambrosi-Randić, Ivana Tucak Junaković, Marina Nekić, Marina Martinčević
Socijalna Psihijatrija.2025; 53(3): 293. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Perceived Community Food Accessibility Measurement Questionnaire for Korean Older Adults
Jisoo Hong, Narae Yang, Kirang Kim
Nutrients.2023; 15(19): 4301. CrossRef - Effects of Health Status, Depression, Gerotranscendence, Self-Efficacy, and Social Support on Healthy Aging in the Older Adults with Chronic Diseases
Hee-Kyung Kim, Jeong-Hyo Seo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 7930. CrossRef - Item response analysis to explore psychometric properties of the Persian version of Troutman successful aging inventory: Rasch partial credit model
Mozhgan Seif, Abdolrahim Asadollahi, Mahsa Yarelahi, Elham Rezaian
Journal of Health Psychology.2021; 26(14): 2711. CrossRef - Successful aging and environmental factors in older individuals in urban and rural areas: A cross-sectional study
Wenxiu Ding, Yanqi Zhang, Liyao Zhang, Zhaoxiu Wang, Jie Yu, Hong Ji
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2020; 91: 104229. CrossRef - Contributions of Psychosocial Factors and Physical Activity to Successful Aging
Melchor Gutiérrez, José Manuel Tomás, Pablo Calatayud
The Spanish Journal of Psychology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of patient education on patient safety: can we change patient perceptions and attitudes?: Lessons from the Armed Forces Capital Hospital in Korea
JinOk An, Seung Ju Kim, Sohee Park, Ki Tae Moon, Eun-Cheol Park
International Journal for Quality in Health Care.2017; 29(3): 392. CrossRef - Disjoint factor analysis with cross-loadings
Maurizio Vichi
Advances in Data Analysis and Classification.2017; 11(3): 563. CrossRef - Successful Aging and the Influencing Factors in the Korean Elderly: Focused on Family Support
SongYi Han, Soon-Nyung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(4): 372. CrossRef - Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire to Assess Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy
Hye Young Kim, Jeong Hee Kang, Hyun Jo Youn, Hyang Sook So, Chi Eun Song, Seo Young Chae, Sung Hoo Jung, Sung Reul Kim, Ji Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(6): 735. CrossRef - Testing the Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Expectations Regarding Aging (ERA-12) Instrument among Middle-aged and Elderly Women
Min Hee Park, Yoorim Kweon
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(3): 460. CrossRef - Construct Validity of the Life Transition Scale for Parents of Children with Autism
Ae Ran Lee, Sun Woo Hong, Se Jin Ju
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(5): 563. CrossRef
- Dietary habits and successful aging in Chinese older adults: a cross-sectional analysis of the CLHLS
- 1,161 View
- 12 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effects of a Smoking Cessation Program including Telephone Counseling and Text Messaging using Stages of Change for Outpatients after a Myocardial Infarction
- Jung-Hyeon Kong, Yeongmi Ha
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(4):557-567. Published online August 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.4.557
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to identify effects of a smoking cessation program including telephone counseling and text messaging using stages of change for outpatients who have had a myocardial infarction (MI).
Methods This research was a quasi-experimental design with a nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest. The participants were 48 outpatients (experimental group=24, control group=24) recruited from one university hospital. They were randomly assigned to one of two groups: (a) an experimental group with telephone counseling (once a week) and text messaging (five times a week) using stages of change, and (b) a control group with traditional telephone counseling (once a month). Efficacy of the intervention was measured by comparing the two groups on smoking-related variables at 3 weeks and 12 weeks.
Results At the 3-week and 12-week measurements, there were significant differences between the experimental and control groups on smoking cessation self-efficacy (
p <.001), nicotine dependence (p <.001), CO levels (p <.001), and smoking cessation rates (p <.001).Conclusion The results indicate that the smoking cessation program including telephone counseling and text messaging using stages of change is effective for outpatients after a MI. Further attention should be paid to the intensity of the smoking cessation program and periods for long-term follow-up.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of emotional distress on attentional bias toward cigarette warnings according to smokers' anxiety levels
Younji Jung, Jang-Sun Hwang, Jang-Han Lee
Frontiers in Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Related to Smoking Relapse Within Six-Months of Smoking Cessation Among Inpatients
Ji Eun Bae, Chul-Woung Kim, Seung Eun Lee, Myungwha Jang
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2023; 34: 307. CrossRef - The effectiveness of a motivational text-messaging program for smoking cessation after coronary angioplasty: a quasi-experimental study
Mohammad Sadegh Mobaraki, Zahra Khademian, Fatemeh Shirazi
BMC Research Notes.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Improving smoking cessation after myocardial infarction by systematically implementing evidence-based treatment methods
Margret Leosdottir, Sanne Wärjerstam, Halldora Ögmundsdottir Michelsen, Mona Schlyter, Emma Hag, John Wallert, Matz Larsson
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Improving the quality of bowel preparation by smartphone education platform prior to colonoscopy: a randomized trail
Kai Zhao, Ruonan Dong, Suhong Xia, Lina Feng, Wangdong Zhou, Mingyu Zhang, Yu Zhang, Dean Tian, Mei Liu, Jiazhi Liao
Annals of Medicine.2022; 54(1): 2776. CrossRef - Personalized Reminders for Immunization Using Short Messaging Systems to Improve Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Series Completion: Parallel-Group Randomized Trial
Chelsea S Wynn, Marina Catallozzi, Chelsea A Kolff, Stephen Holleran, Dodi Meyer, Rajasekhar Ramakrishnan, Melissa S Stockwell
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2021; 9(12): e26356. CrossRef - The effect of theory - Based educational intervention on consumption of smokeless tobacco products by merchants’ guilds
Mohammad Saeed Jadgal, Somayeh Alizadeh, Hadi Alizadeh -Siuki, Saeedeh Sadeghi, Tahmineh Salehian, Moradali Zareipour
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of WeChat and short message service on bowel preparation: an endoscopist-blinded, randomized controlled trial
Shu-Ling Wang, Qian Wang, Jun Yao, Sheng-Bing Zhao, Li-Sheng Wang, Zhao-Shen Li, Yu Bai
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2019; 31(2): 170. CrossRef - The Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Smoking Cessation for Male College Students
Shinae Lee, Hyojung Park
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2017; 39(3): 374. CrossRef - Enhanced education for bowel preparation before colonoscopy: A state‐of‐the‐art review
Zhu Liu, Ming Ming Zhang, Yue Yue Li, Li Xiang Li, Yan Qing Li
Journal of Digestive Diseases.2017; 18(2): 84. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Smoking Cessation Success during 4-week Smoking Cessation Program for University Students
Sang Mee Koo, Jeong Hee Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2017; 28(2): 165. CrossRef - The Effects of Smoking Cessation Coaching Program based on Motivation Stage to Stop Smoking of Patients at a Public Hospital
Mi-Young Kwak, Eun Jeong Hwang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(4): 188. CrossRef - Continuous Abstinence Rates from Smoking Over 12 Months according to the Frequency of Participation in a Hospital-based Smoking Cessation Program among Patients Discharged after Acute Myocardial Infarction
Young-Hoon Lee, Mi-Hee Han, Mi Rim Lee, Jin-Won Jeong, Nam-Ho Kim, Seok Kyu Oh, Kyeong Ho Yun, Sang Jae Rhee, Jum Suk Ko, Gyung-Jae Oh
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2016; 16(1): 48. CrossRef - The effectiveness of mobile-health behaviour change interventions for cardiovascular disease self-management: A systematic review
Leila Pfaeffli Dale, Rosie Dobson, Robyn Whittaker, Ralph Maddison
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2016; 23(8): 801. CrossRef - Effect of Auricular Acupressure Therapy on Decreasing Smoking rates, Desire for Smoking, and Exhaled Carbon Monoxide in Male College Students
Oh Yun Kwon, Jung Hee Song, Kyung Sook Park
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2015; 18(2): 88. CrossRef - The Effects of Job Characteristics on Smoking and Mediating Effects of Job Stress among Older Workers
Sungeun Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2014; 31(3): 51. CrossRef - Effects of a Smoking Cession Program Using Telephone Counselling and Text Messaging for Patients after Ischemic Heart Disease
Eun-Shim Kim, Hye-Ok Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(12): 7248. CrossRef
- The effects of emotional distress on attentional bias toward cigarette warnings according to smokers' anxiety levels
- 1,354 View
- 11 Download
- 17 Crossref

- Effects of Perceived Health Status, Self-esteem and Family Function on Expectations Regarding Aging among Middle-aged Women
- Yoo Rim Kweon, Hae Ok Jeon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(2):176-184. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.2.176
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate expectations regarding aging by middle-aged women in the community, and identify factors contributing to their expectations about aging.
Methods Participants in the survey for this study were 303 middle-aged women from community health centers and religious facilities in Seoul, Gyeonggi Province, and Chungcheongbuk Province. Data were collected from March 2 to April 17, 2012 using self-report structured questionnaires. The instruments were the Health Perceptions, Rosenberg Self-esteem Scale (RSES), Family APGAR, Expectations Regarding Aging (ERA-12). The data were analyzed using t-test, one-way ANOVA, Scheffe test, Pearson correlation coefficients and hierarchical multiple regression with IBM SPSS/WIN 20.0 program.
Results Perceived health status (β=0.16,
p =.009) and self-esteem (β=0.20,p =.001) of middle-aged women were identified as significant predictors of expectations regarding aging, after adjusting for age, education, occupation, monthly income and menstrual status.Conclusion These results suggest that nurses should make an effort to improve expectations about aging among middle-aged women. Ultimately, community health programs for middle aged women need to be developed to achieve successful aging.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nonpharmacological Intervention Effects on Middle-Aged Women with Menopausal Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ji-Hyun Kim, Hea-Jin Yu
Healthcare.2025; 13(24): 3206. CrossRef - The Level of Expectations Regarding Aging Among Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Lunwei Lin, Shunqi Liao, Zhangrong Yan, Chaofan Liu, Qi Wang, Fang Wang
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2024; 25(3): 410. CrossRef - Digital Health Literacy and Associated Factors Among Older Adults Living Alone in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
Minhwa Hwang, Gahye Kim, Seonghyeon Lee, Yeon-Hwan Park
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2024; 35: 389. CrossRef - Just as expected? Older adults’ aging expectations are associated with subjective cognition
Nikki L. Hill, Sakshi Bhargava, Justin Do, Emily Bratlee-Whitaker, Monique J. Brown, Renata Komalasari, Rachel Wu, Jacqueline Mogle
Aging & Mental Health.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Relationship between Fatigue, Sleep, Subjective Health Status, and Job Involvement in Shift-working Production Workers
Yeojoo Chae, Sein Ryu
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(4): 391. CrossRef - Factors influencing the health-related quality of life in Korean menopausal women: a cross-sectional study based on the theory of unpleasant symptoms
Ji-Hyun Kang, Moon-Jeong Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(2): 100. CrossRef - Factors influencing quality of life in caregivers of adolescents with developmental disabilities
Joung Woo Joung
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2022; 13(4): 298. CrossRef - Face Mask Usage, Knowledge and Behavior of Face Mask Usage in Older Adults Living Alone in the COVID-19 Era
A-Reum Han, Yeon-Hwan Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(2): 203. CrossRef - Physical Activity Level and Self-Esteem in Middle-Aged Women
Magdalena Dąbrowska-Galas, Jolanta Dąbrowska
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(14): 7293. CrossRef - Study on health anxiety issues, health-promoting behavior, and quality of life of middle-aged women in Jeonbuk area
Sun Young Jeon, Sung Suk Chung, Jeong Ok Rho
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2020; 53(6): 613. CrossRef - Design and psychometric analysis of a climacteric adjustment questionnaire for middle-aged women
Mitra Reyhani, Ashraf Kazemi, Ziba Farajzadegan, Mahrokh Keshvari
Menopause.2020; 27(3): 333. CrossRef - The Concept of Successful Aging: A Review Article
Fatemeh Estebsari, Maryam Dastoorpoor, Zahra Rahimi Khalifehkandi, Azadeh Nouri, Davoud Mostafaei, Meimanat Hosseini, Roghayeh Esmaeili, Hamidreza Aghababaeian
Current Aging Science.2020; 13(1): 4. CrossRef - Influence of the Perception of Aging Symptoms as a Mediator and Moderator on the Relationship between Family Function and Stress in Middle-Aged Adults
Hyun-E Yeom, Kyoung Ok Ju
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(2): 175. CrossRef - The Effect of Family Adaptation and Cohesion on the Well-being of Married Women: A Multiple Mediation Effect
Shuman Wu, Xue Zheng
The Journal of General Psychology.2020; 147(1): 90. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Metabolic Syndrome Among Middle-Aged Women in Their 50s: Based on National Health Screening Data
HyungSeon Kim, YeonHee Cho
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(9): 3008. CrossRef - Health Promotion Behavior, Self-efficacy, Marital Intimacy, and Successful Aging in Middle-aged
Kyung-In Cheon, Yun Hee Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(3): 259. CrossRef - Experiences on Psycho-social Health Support of Middle-aged Women
Jeong-Soo KIM, Euna PARK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2019; 31(5): 1432. CrossRef - Structural Equation Model for Sleep Quality of Female Shift Work Nurses
Ji Yeong Jeong, Mee Ock Gu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(5): 622. CrossRef - Self-Care Compliance among Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: Focusing on Symptom Experiences, Perceived Health Status and Disease Status
Mi-Jeong Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2018; 25(3): 165. CrossRef - Rise and fall: two sides of a coin of middle aged women’s perceptions of reproductive: a qualitative study
Mitra Reyhani, Ashraf Kazemi, Mahrokh Keshvari
Archives of Women's Mental Health.2018; 21(4): 421. CrossRef - Health-Related Effects of the Elderly Care Program
Young-Eun Kim, Seok-Won Hong
BioMed Research International.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Relationships between social skills and self-esteem in nurses: a questionnaire study
Marta Elena Losa-Iglesias, Daniel López López, Rocío Rodriguez Vazquez, Ricardo Becerro de Bengoa-Vallejo
Contemporary Nurse.2017; 53(6): 681. CrossRef - The Effect of Work-Family Conflict, Fatigue and Perceived Health on the Health Promoting Behavior of Married Working Women a Rural Population
HyeaKyung Lee, EunHee Shin
Korean Journal of Stress Research.2016; 24(3): 167. CrossRef - Effects of Self-esteem, Aggression and Violence Recognition on the Academic Achievement of Adolescents
Chang Seek Lee, Hi Ran Son, Ha Young Jang
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(7): 29. CrossRef - Effects of Exercise Program for Women of Old-Old Age in Senior Citizen Halls based on Pender's Health Promotion Model
Kyoung Im Lee, Young Eun
Journal of muscle and joint health.2016; 23(2): 71. CrossRef - Influence on Health Promotion Behavior among Government-funded Research Institute's Employee according to Perceptive Health Status and Social Support
Ji Hyun Kim, Sook Kyoung Park
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2015; 24(4): 270. CrossRef - Relationship between Expectations Regarding Aging and Physical Activity among Middle Aged Adults in Urban Areas: Based on the Pender's Health Promotion Model
Sung-Hye Cho, MoonKi Choi, JuHee Lee, Hyewon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(1): 14. CrossRef - Experience of Late–Middle-Aged Women who Reside in Small and Medium-Sized Cities in Becoming Psychologically Mature Women
Euna Park, Haeok Kim
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2015; 6(3): 159. CrossRef - Testing the Validity and Reliability of Korean Version of the Expectations Regarding Aging (ERA-12) Instrument among Middle-aged and Elderly Women
Min Hee Park, Yoorim Kweon
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(3): 460. CrossRef - The influence of expectations regarding aging on health-promoting behaviors
Hyeyoung Bae, Aranbyeol Kim, Soojin Nam, Jia Youn, Haeju Youn, Gayoung Kim, Daehyae Jang, Su Hyun Kim
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2014; 25(1): 77. CrossRef
- Nonpharmacological Intervention Effects on Middle-Aged Women with Menopausal Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1,538 View
- 18 Download
- 30 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling on Successful Aging in Elders - Focused on Selection · Optimization · Compensation Strategy -
- Doo Nam Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(3):311-321. Published online June 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.3.311
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was designed to construct and test a structural equation modeling on specific domain health status and the Selection · Optimization · Compensation (SOC) strategy affecting successful aging in elderly people.
Methods The model construction was based on the SOC model by Baltes and Baltes. Interviews were done with 201 elderly people aged 65 or older. Interview contents included demographics, functional health status, emotional health status, social health status, SOC strategies, and successful aging. Data were analyzed using SPSS 15.0 and AMOS 7.0.
Results Model fit indices for the modified model were GFI=.93, CFI=.94, and RMSEA=.07. Three out of 7 paths were found to have a significant effect on successful aging in this final model. Functional health status had a direct and positive effect on successful aging. Emotional health status influenced successful aging through SOC strategies.
Conclusion This study suggests that interventions for improving functional health status and for strengthening SOC strategies are critical for successful aging. Continuous development of a variety of successful aging programs using SOC strategy is suggested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Theoretical Approaches to Communicative Practices in the Study of Intergenerational Communication and Aging
Howard Giles
The International Journal of Aging and Human Development.2025; 101(1): 3. CrossRef - A structural equation modeling analysis of successful aging in older adults with osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional descriptive study
Jeong Hwa Kum
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(2): 131. CrossRef - Development of a scale to measure selection, optimization, compensation (SOC) strategy in late middle-aged women: a methodological study
Do-Young Lee, Gie Ok Noh
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(3): 216. CrossRef - Understanding the influencing factors and mechanism of social compensation for Chinese older adults using social media in the context of smart home: a qualitative analysis
Ke Ma, Meng Gao, Francesco Ermanno Guida, Renke He
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Health Status, Depression, Gerotranscendence, Self-Efficacy, and Social Support on Healthy Aging in the Older Adults with Chronic Diseases
Hee-Kyung Kim, Jeong-Hyo Seo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 7930. CrossRef - A structural equation model of successful aging in Korean older women: using selection-optimization-compensation (SOC) strategies
Song Yi Han, Young Ko
Journal of Women & Aging.2021; 33(1): 84. CrossRef - The Concept of Successful Aging: A Review Article
Fatemeh Estebsari, Maryam Dastoorpoor, Zahra Rahimi Khalifehkandi, Azadeh Nouri, Davoud Mostafaei, Meimanat Hosseini, Roghayeh Esmaeili, Hamidreza Aghababaeian
Current Aging Science.2020; 13(1): 4. CrossRef - The Level of Successful Aging and Influencing Factors of the Community Elderly
Kyeong-Sook Cha, Hung Sa Lee, Chunmi Kim, Eun Man Kim
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2019; 19(1): 39. CrossRef - Expanding the aging self: Investigating successful aging among Korean older adults using grounded theory
Hyung-Ran Park
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2015; 29(3): 426. CrossRef - Operational definitions of successful aging: a systematic review
Theodore D. Cosco, A. Matthew Prina, Jaime Perales, Blossom C.M. Stephan, Carol Brayne
International Psychogeriatrics.2014; 26(3): 373. CrossRef
- Theoretical Approaches to Communicative Practices in the Study of Intergenerational Communication and Aging
- 1,537 View
- 15 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Development of a Web-based Senescence Preparation Education Program for Successful Aging for Middle-aged Adults
- Young-Mi Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2008;38(6):831-842. Published online December 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.6.831
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a web-based senescence preparation education program to promote successful aging.
Methods This program was developed based on Network-Based Instructional System Design (NBISD) model, using the following 5 processes: analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation. The program was operated for 10 weeks from March 17 to May 25, 2008.
Results There were 4 menu bars, introduction, related data, lecture room, and communication on the main page. In the operation of this program, HTML, ASP, JAVA Script, Namo web editor, Edit Plus, Front Page and multimedia technology were applied. The program content consisted of understanding elderly people, physical health, activity & exercise, nutrition, medication use, psychological health, intellectual health, understanding death, welfare system and leisure activity.
Conclusion This program could be a useful means to provide senescence preparation information to middle-aged adults. Also, it is expected to offer individualized learning opportunities to many learners in various settings. Nurses should further develop and facilitate various learning strategies including web- based programs for elder care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Concept of Successful Aging: A Review Article
Fatemeh Estebsari, Maryam Dastoorpoor, Zahra Rahimi Khalifehkandi, Azadeh Nouri, Davoud Mostafaei, Meimanat Hosseini, Roghayeh Esmaeili, Hamidreza Aghababaeian
Current Aging Science.2020; 13(1): 4. CrossRef - Associations between Breast Density on Mammography and Lifestyle Related Disease
Dae Yeon Hwang, Yu Lee Kim, Bong Woon Hwang, Kwang Hyun Kim, Ji Young Lym
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2017; 17(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of a Health Promotion Program on Healthy Aging Preparation for Late Middle Aged Women
Hee-Jung Choi, Soon-Rim Suh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2015; 27(5): 594. CrossRef - The effect of a web‐based education programme (WBEP) on disease severity, quality of life and mothers' self‐efficacy in children with atopic dermatitis
Hae Kyoung Son, Jiyoung Lim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2014; 70(10): 2326. CrossRef - Development of a Web-based Education Program for Nurses working in Nursing Homes on Human Rights of Older Adults
Ki-Kyong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(4): 463. CrossRef - Application and Evaluation of a Web-based Education Program on Blood-borne Infection Control for Nurses
Jeong Sil Choi, Keum Soon Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(2): 298. CrossRef
- The Concept of Successful Aging: A Review Article
- 1,160 View
- 2 Download
- 6 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


