Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
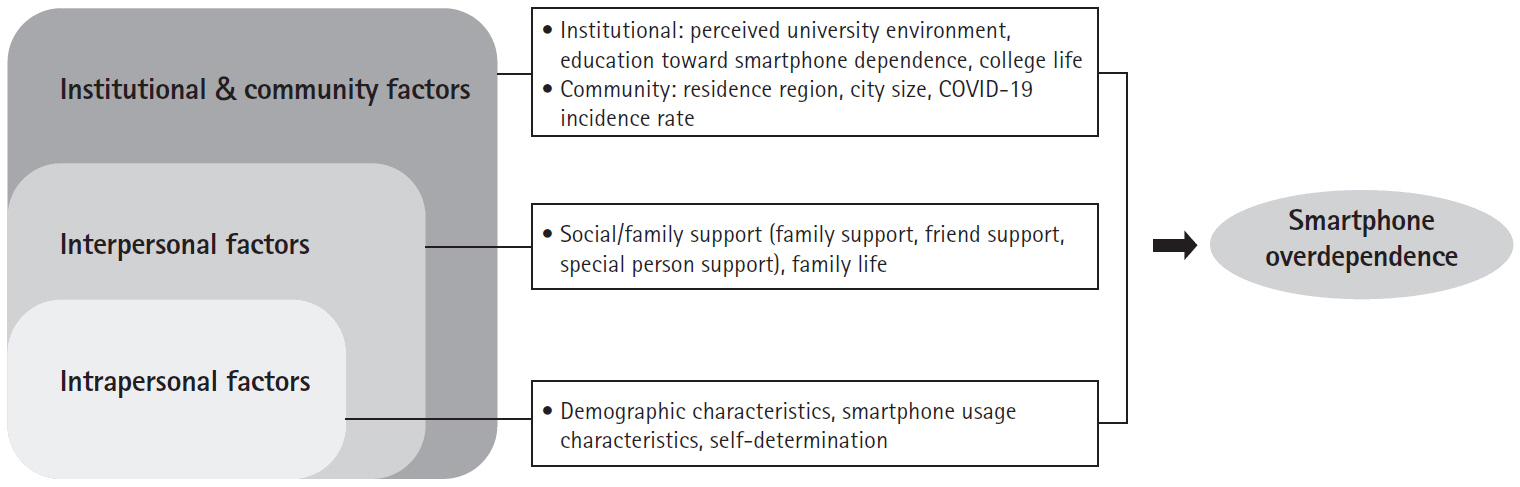
- Factors influencing smartphone overdependence in university students: an ecological model: a descriptive study
- Jeong Soon Yu, Myung Soon Kwon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):64-80. Published online February 20, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24092
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study investigated the factors influencing smartphone overdependence in university students using an ecological model and descriptive research.
Methods
Data were collected from 482 students at 13 universities in the six regions in South Korea from October 20, 2020, to March 25, 2021. Data analysis involved descriptive statistics, the chi-square test, the independent samples t-test, analysis of variance, and hierarchical multiple regression.
Results
The significant ecological factors influencing smartphone overdependence included self-awareness of smartphone overdependence (β=.33, p<.001), autonomy (β=–.25, p<.001), average daily smartphone usage time (β=.18, p<.001), gender (β=.15, p=.001), college year (β=.15, p=.020), forming relationships with others as a motivation for smartphone use (β=–.15, p=.008), friend support (β=.14, p=.006), and age (β=–.12, p=.047). The model explained 34.9% of the variance.
Conclusion
The study emphasized the role of personal and interpersonal factors, in smartphone overdependence among university students. Tailored intervention strategies are necessary to address smartphone overdependence, considering the unique characteristics of students’ environments. A significant aspect of this study is that it provides an explanation of the multidimensional factors contributing to smartphone overdependence among university students, including intrapersonal, interpersonal, and environmental influences.
- 3,715 View
- 195 Download

- The Influence of Parental Self-Esteem on Late School-Aged Children’s Media Device Addiction: The Mediating Effect of Marital Conflict and Children’s Self-Esteem
- Dayeon Heo, Suk-Sun Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(4):421-434. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22036
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the effect of parental self-esteem on late school-aged children’s media device addiction by mediating marital conflict and children’s self-esteem.
Methods
This study used data from the 11th (2018) Panel Study on Korean Children. The participants consisted of 1,082 family triads (fathers, mothers, and children). Data were collected using the Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale, Marital Conflict Scale, and K-Internet Addiction Scale. The data were analyzed using structural equation modeling with SPSS/WIN 27.0 and Mplus 8.7.
Results
The final model showed a good fit for the data. Children’s media device addiction was directly related to mothers’ self-esteem, mothers’ marital conflict, and children’s self-esteem. Fathers’ self-esteem had a significant indirect effect on children’s media device addiction by mediating both fathers’ and mothers’ marital conflict. In addition, mothers’ self-esteem had a significant indirect effect on children’s media device addiction by mediating mothers’ marital conflict.
Conclusion
The findings indicates that self-esteem and marital conflict for both fathers and mothers have a significant effect on children’s media device addiction. It suggests that more attention might be given to fathers and mothers in developing interventions to prevent children’s media device addiction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A longitudinal study of the relationship between parents’ self-esteem and children’s digital media addiction: Testing the mediating roles of children’s self-esteem and aggression
Il Bong Mun, Seyoung Lee
The Social Science Journal.2025; 62(3): 802. CrossRef
- A longitudinal study of the relationship between parents’ self-esteem and children’s digital media addiction: Testing the mediating roles of children’s self-esteem and aggression
- 1,414 View
- 36 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Parental Factors Associated with Smartphone Overuse in Preschoolers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Gumhee Lee, Sungjae Kim, Heajin Yu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):349-368. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19186
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify parental factors associated with smartphone overuse in preschoolers.
Methods
A systematic reviewwas conducted according to PRISMA guidelines. Relevant studies published in peer-reviewed journals from 2009 to June 2019 were identifiedthrough systematic search in 10 electronic databases (PubMed, CINAHL, Cochrane Central, EMBASE, Web of Science, NDSL, KISS, KMbase,KoreaMed, and RISS). Standardized effect sizes were calculated to quantify the associations of parental factors with smartphoneoveruse in preschoolers using meta-analysis.
Results
A total of 30 cross-sectional studies involving 7,943 participants met the inclusioncriteria. The following were negatively correlated with smartphone overuse in preschoolers: mother’s parenting self-efficacy (r =-.35),mother-child attachment (r =-.28), mother’s positive parenting behavior (r =-.28), mother’s positive parenting attitude (r =-.25), and father’sparenting involvement (r =-.15). Further, maternal factors such as smartphone addiction tendency (r =.41), parenting stress (r =.40), negativeparenting behavior (r =.35), negative parenting attitude (r =.14), smartphone usage time (r =.26), employment status (r =.18), and age(r =.12) were positively correlated with smartphone overuse in preschoolers.
Conclusion
Several parental factors influence smartphoneoveruse in preschoolers. These findings emphasize the need to assess and enhance the parental factors identified in this study to preventsmartphone overuse in preschoolers. Accordingly, we recommend the development of preventive interventions to strengthen parent-relatedprotective factors and mitigate risk factors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sequential Dual Mediating Effects of Smartphone Dependence and Aggression on the Relationship Between Negative Parenting Attitudes and Depressive Symptoms Among Adolescents
Jihun Na, Sungkyu Lee, Hyeyeon Sung, Jinho Jhone
Child & Family Social Work.2026; 31(1): 23. CrossRef - FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH SMARTPHONE OVERDEPENDENCE IN PRESCHOOL CHILDREN AND ITS EFFECT ON SOCIAL BEHAVIORAL PROBLEMS
Leyla Çakmak, Fikriye Aksoy Boğanak, Nurettin Menteş, Mustafa Volkan
Sağlık ve Sosyal Refah Araştırmaları Dergisi.2025; 7(1): 43. CrossRef - Empowering Parents: The Impact of a Parenting Practice-Based Care Module on Preventing Internet Gaming Disorder in Elementary School Children
Nur Hidaayah, Esti Yunitasari, Hanik Endang Nihayati
Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research.2025; 30(2): 211. CrossRef - Parent-Child Relationships and Children’s Addiction to Smartphones: A Review of International Studies
Victor P. Sheinov
RUDN Journal of Psychology and Pedagogics.2025; 22(1): 75. CrossRef - Effects of digitalization in preschool education on the creative and cognitive development of children
Yiyi Chen, Zihe Ding
Education and Information Technologies.2024; 29(16): 21567. CrossRef - Clinical Manifestations’ Spectrum of Smartphone Addiction: Moving from an Addiction toward a Clinical Syndrome
Mudar Alwazzeh, Muhdammad Harfouch, Manal Ahmed Hasan, Safi Alqatari, Abir Hamad AlSaid, Marwan Jabr Alwazzeh
Clinical Practice & Epidemiology in Mental Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The experiences of counselors caring for children and adolescents with problematic smartphone use
Jaewon Joung, Eunhee Oh, Eun Jee Lee
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of emotion coaching group programme for mothers of preschool children with smart device overdependence: a mixed methods study
Gumhee Lee, Sungjae Kim
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence, determinants and consequences of problematic smartphone use among preschoolers (3–5 years) from Dhaka, Bangladesh: A cross-sectional investigation
Faruq Abdulla, Md. Moyazzem Hossain, Mohammed Nazmul Huq, Abdul Hai, Azizur Rahman, Russell Kabir, Farhana Jahan Peya, Sinigdha Islam, Hafiz T.A. Khan
Journal of Affective Disorders.2023; 329: 413. CrossRef - Factors related to the organizational silence of Korean nurses: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Kyungja Kang, Jeong-Hee Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(3): 302. CrossRef - What Do Mothers Consider When Choosing Screen Media Programs for Their Infants?
Yoon Kyung Kim, Dongmee Lee, Ju Hee Park
Family and Environment Research.2022; 60(1): 115. CrossRef - Relationship between Mother’s emotional intelligence, negative parenting behaviour, Preschooler’s attachment instability, and smart device overdependence
Gumhee Lee, Sungjae Kim
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Related to Smartphone Overdependence in Mothers of Preschoolers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Gumhee Lee, Eunjin Yang
Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services.2022; 60(3): 40. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Online-Based Leisure Between Parenting Attitudes and Children’s Smartphone Dependency
Yoonju Cho
Korean Journal of Child Studies.2021; 42(6): 695. CrossRef - Pathway from Maternal Parenting Efficacy, Inappropriate Motives for Allowing Smart Devices, and Smart Device Dependency to Preschoolers’ Ability to Understand Minds
Yun Mi Park, Min Ju Kang
Korean Journal of Child Studies.2020; 41(6): 9. CrossRef
- Sequential Dual Mediating Effects of Smartphone Dependence and Aggression on the Relationship Between Negative Parenting Attitudes and Depressive Symptoms Among Adolescents
- 2,057 View
- 57 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- Development and Effect of a Smartphone Overdependence Prevention Program for University Students Based on Self-Determination Theory
- Myung Soon Kwon, Jeong Soon Yu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(1):116-131. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2020.50.1.116
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose: This study aimed to develop a smartphone overdependence prevention program for college students based on the self-determination theory (SDT) and evaluate its effectiveness.
Methods: A non-equivalent control group repeated measures design was used for the study. Participants were 64 university freshmen (experimental group: 29, control group: 35). The developed program consists of eight sessions conducted twice a week. The program was designed to promote autonomy, competence, and relatedness the three elements of the basic psychological needs of self-determination theory. The participants were assessed before the program, immediately after, and 1 and 3 months after the program. Data were collected from April 23 to September 14, 2018 and analyzed by performing a Chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, independent t-test, and repeated measures ANOVA using SPSS/WIN 23.0.
Results: This study showed improvement in the basic psychological needs (F=3.90,
p =.010) in the experimental group compared to the control group. Specifically, competence (F=2.93,p =.035), relatedness (F=2.89,p =.045), and self-regulatory ability (F=3.11,p =.028) improved significantly.Conclusion Study findings indicate that the smartphone overdependence prevention program based on the Self-determination theory could be an effective intervention for improving basic psychological needs and self-regulation ability. Therefore, this program could be an efficient strategy for smartphone overdependence prevention in university students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Parental Smartphone Dependency and Its Impact on Child Smartphone Use: Insights From a National Survey
Hyeon Jo, Pil‐Tae Hong, Xin‐Ran Li
Child Abuse Review.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations Between Academic Motivation, Academic Stress, and Mobile Phone Addiction: Mediating Roles of Wisdom
Abolghasem Yaghoobi, Kambiz Karimi, Maryam Asoudeh, Sahar Mohammadi
International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction.2025; 23(4): 2926. CrossRef - Factors influencing smartphone overdependence in university students: an ecological model: a descriptive study
Jeong Soon Yu, Myung Soon Kwon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(1): 64. CrossRef - The Effect of Psychological Needs Satisfaction on Protective Gaming Beliefs and Behaviors
Mu He, Rushui Shan, Jiahui Lu, Kwok Kit Tong
Journal of Media Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Examining the Roles of Problematic Internet Use and Emotional Regulation Self-Efficacy on the Relationship Between Digital Game Addiction and Motivation Among Turkish Adolescents
Öner Çelikkaleli, Rıdvan Ata, Muhammet Mustafa Alpaslan, Zafer Tangülü, Özgür Ulubey
Behavioral Sciences.2025; 15(3): 241. CrossRef - Problematic smartphone use and risk behaviors in adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic
Yeseul Lee, Hyeseon Choi, Yedong Son
BMC Pediatrics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adolescent Smartphone Overdependence in South Korea: A Place-Stratified Evaluation of Conceptually Informed AI/ML Modeling
Andrew H. Kim, Uibin Lee, Yohan Cho, Sangmi Kim, Vatsal Shah
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2025; 22(10): 1515. CrossRef - Davranışsal Bağımlılıklara Yönelik Müdahalelere İlişkin Bir Derleme
Ayşegül SAYAN KARAHAN
AYNA Klinik Psikoloji Dergisi.2023; 10(3): 356. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Self-Determination Improvement Program for Preventing Non-Suicidal Self-Injury in Adolescents: A Pilot Study
Jae Woon Lee, In Sook Kim, Ji Won Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(4): 506. CrossRef - Current prevention strategies and future directions for problem Internet use
Jing Shi, Mark van der Maas, Lu Yu, Qiaolei Jiang, Sarah Agasee, Nigel E Turner
Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences.2022; 48: 101231. CrossRef - Effects of an intervention based on self-determination theory on self-health management capabilities of middle-aged women in rural areas through the concept of leisure cafeteria
Yang Jun Park, Heui Sug Jo, Hyang Hee Hwang, Yukyung Park
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2022; 39(1): 59. CrossRef - Effects of On-Campus and Off-Campus Smartphone Overdependence Prevention Programs Among University Students
Jeong Soon Yu, Ok Kyung Ham, Myung Soon Kwon
Asian Nursing Research.2022; 16(4): 215. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Drinking Reduction Program Focused on Self-Determination Enhancement for College Students with Problematic Drinking
Jin-Kyoung Ma, Moon-Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(3): 265. CrossRef
- Parental Smartphone Dependency and Its Impact on Child Smartphone Use: Insights From a National Survey
- 2,265 View
- 57 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

- Construction of the Addiction Prevention Core Competency Model for Preventing Addictive Behavior in Adolescents
- Hyun Sook Park, Sun Young Jung
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(6):714-725. Published online December 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.6.714
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to provide fundamental data for the development of competency reinforcement programs to prevent addictive behavior in adolescents through the construction and examination of an addiction prevention core competency model.
Methods In this study core competencies for preventing addictive behavior in adolescents through competency modeling were identified, and the addiction prevention core competency model was developed. It was validated methodologically.
Results Competencies for preventing addictive behavior in adolescents as defined by the addiction prevention core competency model are as follows: positive self-worth, self-control skill, time management skill, reality perception skill, risk coping skill, and positive communication with parents and with peers or social group. After construction, concurrent cross validation of the addiction prevention core competency model showed that this model was appropriate.
Conclusion The study results indicate that the addiction prevention core competency model for the prevention of addictive behavior in adolescents through competency modeling can be used as a foundation for an integral approach to enhance adolescent is used as an adjective and prevent addictive behavior. This approach can be a school-centered, cost-efficient strategy which not only reduces addictive behavior in adolescents, but also improves the quality of their resources.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Strength Based I-Change Smoking Cessation Program for Smoking Middle School Boys
Jung Hee Kim, Yeon Hee Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2017; 47(2): 164. CrossRef - Health Behaviors and Related Demographic Factors among Korean Adolescents
YunHee Shin, Sook Jung Kang
Asian Nursing Research.2014; 8(2): 150. CrossRef - Predictors of Protective Factors for Internet Game Addiction in Middle School Students using Data Mining Decision Tree Analysis
Young-Ran Kweon, Se-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 23(1): 12. CrossRef - Development of Expert Competency Model for Preventing Adolescent Addictive Behavior and Educational Needs of Psychiatric Mental Health Nurses
Hyun Sook Park, Sun Young Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 23(4): 199. CrossRef
- Effects of a Strength Based I-Change Smoking Cessation Program for Smoking Middle School Boys
- 1,105 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Development of a Cell Phone Addiction Scale for Korean Adolescents
- Hyun Young Koo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(6):818-828. Published online December 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.6.818
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to develop a cell phone addiction scale for Korean adolescents.
Methods The process included construction of a conceptual framework, generation of initial items, verification of content validity, selection of secondary items, preliminary study, and extraction of final items. The participants were 577 adolescents in two middle schools and three high schools. Item analysis, factor analysis, criterion related validity, and internal consistency were used to analyze the data.
Results Twenty items were selected for the final scale, and categorized into 3 factors explaining 55.45% of total variance. The factors were labeled as withdrawal/tolerance (7 items), life dysfunction (6 items), and compulsion/persistence (7 items). The scores for the scale were significantly correlated with self-control, impulsiveness, and cell phone use. Cronbach's alpha coefficient for the 20 items was .92. Scale scores identified students as cell phone addicted, heavy users, or average users.
Conclusion The above findings indicate that the cell phone addiction scale has good validity and reliability when used with Korean adolescents.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations Between Academic Motivation, Academic Stress, and Mobile Phone Addiction: Mediating Roles of Wisdom
Abolghasem Yaghoobi, Kambiz Karimi, Maryam Asoudeh, Sahar Mohammadi
International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction.2025; 23(4): 2926. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation of smartphone addiction scale – short version (SAS-SV) among young adults of India
George Felix, Manoj K. Sharma, Nitin Anand, Binukumar Bhaskarapillai, Kalpana Srivastava
Industrial Psychiatry Journal.2025; 34(1): 53. CrossRef - A Study to Assess the Knowledge regarding Hazards of Mobile Addiction among adults (21-40 years) Residing at Appannapally Village, Mahabubnagar, Telangana
C. Venkata Raju, Dhanyamol C P, Lakshmi Priya
A and V Pub International Journal of Nursing and Medical Research.2025; : 130. CrossRef - Assessment Tools and Psychosocial Consequences of Smartphone Addiction in Nursing Students: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
María Dolores Lazo-Caparrós, José Luis Gómez-Urquiza, Ana González-Díaz, Inmaculada Pérez-Conde, Piedad Gómez-Torres, María José Membrive-Jiménez
Healthcare.2025; 13(20): 2639. CrossRef - Unveiling the grip of mobile phone addiction: an in-depth review
Jinyu Li, Hong Yang
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A systematic review and meta-analysis of smartphone addiction among Iranian high school and university students
Reza Ghanei Gheshlagh, Jamal Amiri, Vajiheh Baghi, Fazel Dehvan
Journal of Health Administration.2024; 27(3): 36. CrossRef - Effects of Self-Management Training on Smartphone Dependence in Low to Moderate Adolescent Males’ Users
Mostafa Motamedi Heravi, Shahla Khosravan, Aeen Mohammadi, Mohammad Reza Mansoorian
Behaviour Change.2023; 40(1): 67. CrossRef - Are South Korean College Students Benefitting from Digital Learning?
Phillip Sangwoo Lee, Chong Min Lee
International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction.2023; 39(4): 743. CrossRef - TEKNOLOJİYLE BAĞLANTILI YENİ DAVRANIŞSAL BOZUKLUKLAR / RECENT BEHAVIORAL DISORDERS DUE TO TECHNOLOGY
Kamer Kalip, Meltem Çöl
Eskişehir Türk Dünyası Uygulama ve Araştırma Merkezi Halk Sağlığı Dergisi.2020; 5(2): 318. CrossRef - Problematic Mobile Phone and Smartphone Use Scales: A Systematic Review
Bethany Harris, Timothy Regan, Jordan Schueler, Sherecce A. Fields
Frontiers in Psychology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise as an Alternative Approach for Treating Smartphone Addiction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Random Controlled Trials
Shijie Liu, Tao Xiao, Lin Yang, Paul D. Loprinzi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(20): 3912. CrossRef - Are smartphones really that bad? Improving the psychological measurement of technology-related behaviors
David A. Ellis
Computers in Human Behavior.2019; 97: 60. CrossRef - Internal Consistency and Confirmatory Factor Analysis of Smartphone Addiction Inventory (SPAI)
Saeed Imani, Jaber Alizadeh Goradel, Sadegh Mousavi, Alireza Noroozi
Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between addiction to mobile phone and sense of loneliness among students of medical sciences in Kermanshah, Iran
Hale Jafari, Abas Aghaei, Alireza khatony
BMC Research Notes.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Smart phone addiction and mindfulness: an intergenerational comparison
Kaeun Kim, George R. Milne, Shalini Bahl
International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Marketing.2018; 12(1): 25. CrossRef - Impact of Smartphone Addiction on Academic Performance of Business Students: A Case Study
Md. Shamsul Arefin, Md. Islam, Mohitul Mustafi, Sharmina Afrin, Nazrul Islam
SSRN Electronic Journal .2018;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review of Studies on the Relationship between Mobile Phone Addiction and Impulsiveness
君凤 冯
Advances in Psychology.2017; 07(01): 60. CrossRef - Cell-Phone Addiction: A Review
José De-Sola Gutiérrez, Fernando Rodríguez de Fonseca, Gabriel Rubio
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Smartphone Addiction Inventory (SPAI): Psychometric properties and confirmatory factor analysis
Laura Pavia, Paola Cavani, Maria Di Blasi, Cecilia Giordano
Computers in Human Behavior.2016; 63: 170. CrossRef - Influence of Cell Phone Addiction on Communication Skills and Interpersonal Relationship Ability of Adolescents
Mi-Young Choi, Ji-Soo Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of School Health.2016; 29(3): 149. CrossRef - Development of a Brief Multicultural Version of the Test of Mobile Phone Dependence (TMDbrief) Questionnaire
Mariano Chóliz, Lourdes Pinto, Sukanya S. Phansalkar, Emily Corr, Ayman Mujjahid, Conni Flores, Pablo E. Barrientos
Frontiers in Psychology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study of on the influence of techno-stress, flow and smartphone addiction on the Satisfaction of Smart-phones use
Jongsoon Park, Jongman Lee
Journal of the Korea Society of Digital Industry and Information Management.2015; 11(4): 189. CrossRef - General Strain Theory approach to the Use of Cellular Phone Dependence of Middle School Students
Hyun-Jin Shim, Il-Hyun Lee, Hyun-Sill Rhee
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(2): 355. CrossRef - Context-aware Framework and Applications for Improving UI and UX of Smartphones
Choonsung Shin, Byoung-Ha Park, Kwang-Mo Jung
Journal of the Korea society of IT services.2014; 13(1): 197. CrossRef - The dark side of smartphone usage: Psychological traits, compulsive behavior and technostress
Yu-Kang Lee, Chun-Tuan Chang, You Lin, Zhao-Hong Cheng
Computers in Human Behavior.2014; 31: 373. CrossRef - Development of a Cell Phone Addiction Scale for Korean Parents of Young Children.
Hyun Young Koo
Child Health Nursing Research.2013; 19(1): 29. CrossRef - Development of a Problematic Mobile Phone Use Scale for Turkish Adolescents
Cem Oktay Güzeller, Tolga Coşguner
Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking.2012; 15(4): 205. CrossRef - Development and Validation Study of a Cell Phone Addiction Scale for Korean Children
Hyun-Young Koo, Myung-Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2012; 18(2): 76. CrossRef - The Study on Predictors of Addictive Personality in Adolescents
Hyun Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2012; 21(4): 263. CrossRef - Development of the Multidimensional Scale of Addictive Behavior for Adolescents
Hyun-Sook Park, Sun-Young Jung
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(8): 3597. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Prevention Program for Cell Phone Addiction in Middle School Students
Hyun-Young Koo
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2011; 17(2): 91. CrossRef - Validation of Addictive Personality Scale for Screening Adolescents
Hyun Sook Park, Sun Young Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2011; 20(4): 395. CrossRef - Factors related to the Overuse of Mobile Phone in Elementary School Students
Kyoung Sook Lee, Hwang Ran Ahn, Kyung Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2011; 20(3): 271. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Cell Phone Addiction in Adolescents
Hyun Young Koo, Hyun Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(1): 56. CrossRef - Cell Phone Addiction in Highschool Students and Its Predictors
Hyun Young Koo
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(3): 203. CrossRef - Educational Needs for Prevention of Cell Phone Addiction in Korean Adolescents
Hyun Young Koo, Hyun Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(4): 304. CrossRef
- Associations Between Academic Motivation, Academic Stress, and Mobile Phone Addiction: Mediating Roles of Wisdom
- 2,158 View
- 33 Download
- 36 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


