Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 41(3); 2011 > Article
-
Original Article
- Development and Validation of the Hospice Palliative Care Performance Scale
- So-Hi Kwon
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2011;41(3):374-381.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.3.374
Published online: June 13, 2011
Full-time Lecturer, College of Nursing, Kyungpook National University·Kyungpook National University The Research Institute of Nursing Science, Daegu, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kwon, So-Hi. College of Nursing, Kyungpook National University, 101 Dongin-dong 2-ga, Jung-gu, Deagu 700-422, Korea. Tel: +82-53-420-4924, Fax: +82-53-421-2758, sh235@knu.ac.kr
© 2011 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to develop and validate a hospice·palliative care performance measure which would cover more than just physical symptoms or quality of life.
-
Methods
- Through an intensive literature review, the author chose questions that measured aspects of physical, emotional, spiritual, social, or practical domains pertinent to hospice·palliative care for inclusion in the scale. Content validation of the questions was established by 15 hospice·palliative care professionals. A preliminary Hospice Palliative Care Performance Scale (HPCPS) of 20 questions was administered to 134 pairs of terminal cancer patients from 5 hospice palliative care units and their main family caregiver. A validation study was conducted to evaluate construct validity and internal consistency.
-
Results
- Factor analysis showed 14 significant questions in five subscales; Physical, Emotional, Spiritual, Social, and Patient' rights. There were no significant differences between the ratings by patients and family members except for three out of the 14 questions. The measure demonstrated construct validity, and Cronbach's α of the subscales ranged from .73 to .79.
-
Conclusion
- The HPCOS demonstrated acceptable validity and reliability. It can be used to assess effectiveness of hospice·palliative care for terminal cancer patients in practice and research.
- 1. Bosma H, Apland L, Kazanjian A. Cultural conceptualizations of hospice palliative care: More similarities than differences. Palliative Medicine. 2010;24:510–522. doi: 10.1177/0269216309351380.PubMed
- 2. A model to guide hospice palliative care: Based on national principles and norms of practice. Canadian Hospice Palliative Care Association. 2002;Retrieved August 23, 2010. from http://www.chpca.net/.
- 3. Ferris FD, Bruera E, Chernry N, Cummings C, Currow D, Dudgeon H, et al. Palliative cancer care a decade later: Accomplishments, the need, next steps-from the American Society of Clinical Oncology. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2009;27:3052–3058. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.1558.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. A study on the hospice payment-development of the payment system for hospice service and of the quality control system, and designing of pilot program (Issue No. K46-2008-85). 2008;Seoul, Author.
- 5. The hospice general inpatient level of care: Criteria, service guidelines, reimbursement and contracting. Hospice general inpatient level of care task force. 2008;Retrieved March 15, 2011. from http://edocket.access.cpo.gov/2008/pdf/08-1305.pdf.
- 6. Kang BS, Kim KS. SPSS 17.0: Statistical analysis of the social sciences. 2009;Seoul, Hannarae Academy.
- 7. Kang KA. Development of a tool to measure suffering in patients with cancer. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 1999;29:1365–1378.ArticlePDF
- 8. Kim KS. AMOS Analysis structural equation modeling. 2004;Seoul, Data Solution Inc.
- 9. Kim MS, Oh DG. Psychological testing. 2004;Seoul, Sigma press.
- 10. Kim SH, Choi YS, Lee J, Oh SC, Yeom CH, Lee MA, et al. Reliability and validity of the hospice quality of life scale for Korean cancer patients. Journal of pain and Symptom Management. 2009;37:156–167. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2008.02.008.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Kim SY. Development of the service model for hospice palliative care in terminal cancer care (Issue No. 0420270-1). 2005;Seoul, Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare.
- 12. Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare. Hospice palliative care norms and regulations. 2003;Seoul, Author.
- 13. Lee EH, Chun MC, Wang HJ, Lim HY, Choi JH. Multidimensional constructs of the EORTC Quality of Life Questionnaire (QLQ-C30) in Korean cancer patients with heterogeneous diagnosis. Cancer Research and Treatment. 2005;37:148–156. doi: 10.4143/crt.2005.37.3.148.PubMedPMC
- 14. Lee EH, Moon S, Cho SY, Oh YT, Chun M, Kim SH, et al. Psychometric evaluation of a need scale for cancer patients undergoing follow up care. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2010;40:551–560. doi: 10.4040/jkan.2010.40.4.551.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Lee EO, Lim NY, Park HA, Kim JI, Bai JY, Lee SM. Nursing research and statistical analysis. 2009;Seoul, Soomoonsa.
- 16. Lee KS, Joo J, Kim JH, Kim KY. Current status and challenge of hospice palliative care in Korea. Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care. 2008;11:196–205.
- 17. Mularski RA, Dy SM, Shugarman LR, Wilkinson AM, Lynn J, Shekelle PG, et al. A systematic review of measures of end-of-life care and its outcomes. Health Services Research. 2007;42:1848–1870. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2007.00721.x.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 18. Hospice palliative care. National Cancer Information Center. 2010;04 30 Retrieved September 18, 2010. from http://www.cancer.go.kr/cms/public_project/hospice/index.html.
- 19. Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J, Davis TE, Carbone PP. Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. American Journal of Clinical Oncology. 1982;5:649–655.Article
- 20. Pouchot J, Le Parc J, Queffelec L, Sichère P, Flinois A. Perceptions in 7,700 patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared to their families and physicians. Joint Bone Spine. 2007;74:622–626. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2006.11.024.Article
- 21. Toscani F, Brunelli C, Miccinesi G, Costantini M, Gallucci M, Tamburini M, et al. Predicting survival in terminal cancer patients: Clinical observation or quality-of-life evaluation? Palliative Medicine. 2005;19:220–227.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 22. Tu MS, Chiou CP. Perceptual consistency of pain and quality of life between hospice cancer patients and family caregivers: A pilot study. International Journal of Clinical Practice. 2007;61:1686–1691. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01347.x.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Waltz CW, Bausell RB. Nursing research: Design, statistics and computer analysis. 1981;Philadelphia, PA, F.A. Davis.
- 24. Hospice palliative care. World Health Organization. 1998;Retrieved September 18, 2010. from http://www.who.int/cancer/palliative/definition/en/.
- 25. Yeager KA, Miaskowski C, Dibble SL, Wallhagen M. Differences in pain knowledge and perception of the pain experience between outpatients with cancer and their family caregivers. Oncology Nursing Forum. 1995;22:1235–1241.PubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Evaluation of Outcomes of the Busan Community-based Palliative Care Project in Korea
Soon-Ock Choi, Sook-Nam Kim, Seong-Hoon Shin, Ji-Seon Ryu, Jeong-Won Baik, Jung-Rim Kim, Nae-Hyeon Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2018; 12(4): 286. CrossRef - Analysis of Knowledge About, Attitude Toward, and Educational Needs for Dementia in Certified Caregivers
Eun-Ho Ha, Jin-Young Cho
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 108. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Measurement Tool of Public Benefits in Regional Cardiocerebrovascular Center
Kunsei Lee, Eunyoung Shin, Hyoseon Jeong, Jung-Hyun Lee, Hee-Sook Kim, Young Sil Lim, Young Taek Kim
Health Policy and Management.2013; 23(4): 434. CrossRef
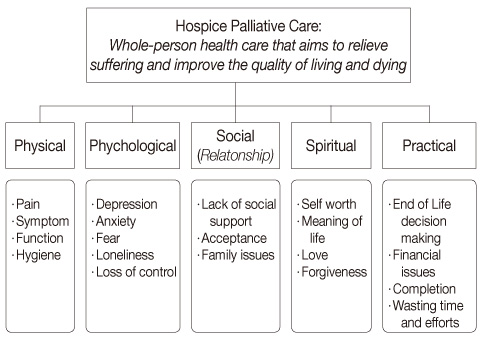
Figure 1
Content Analysis Behavioral Event Interview
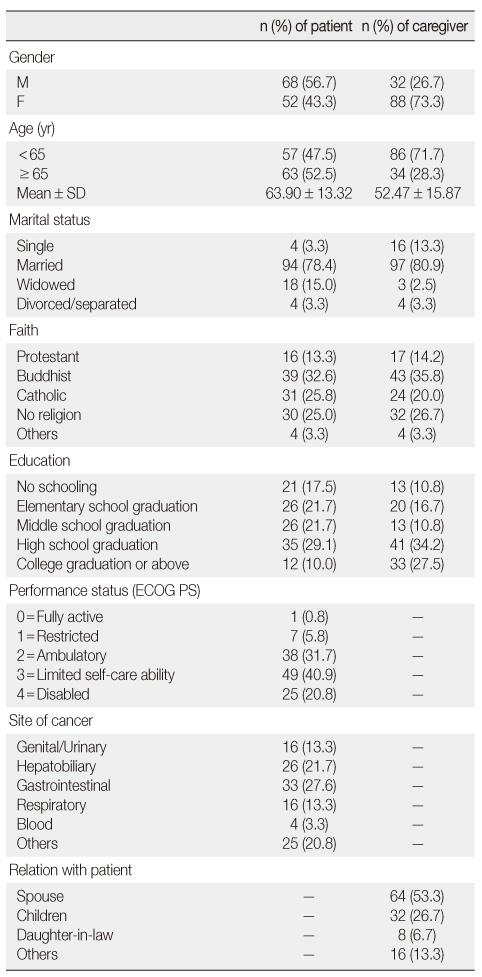
ECOG PS=Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Scale.
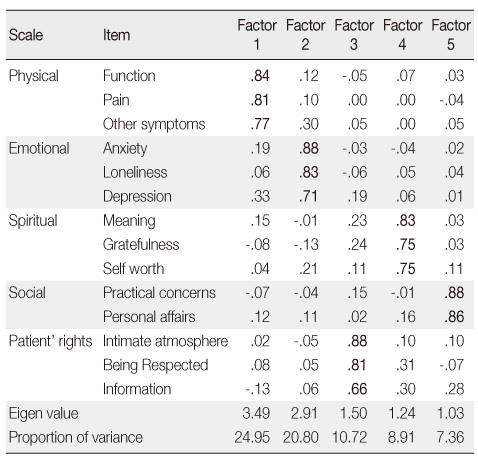
Factor Analysis of Patients' Responses to HPCPS* Items (N=120)
*Hospice Palliative Care Performance Scale. Extraction method was principal component analysis with varimax rotation. We employed a decision rule of retaining factors whose eigen value were >1.0. Bold type indicates loadings >0.60.
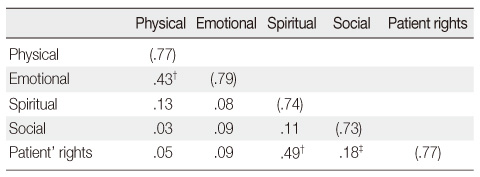
Inter-subscale Correlations and Reliability Coefficients of each Subscale of HPCPS*
*Spearman's correlation analysis; †p<.001; ‡p<.05; ( )=Cronbach's α of each subscale.
HPCPS=Hospice Palliative Care Performance Scale.
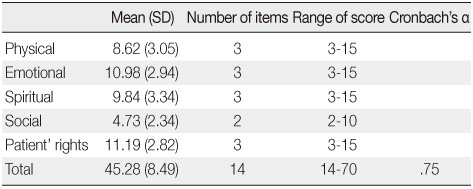
Descriptive Statistics of each Scale/Item of the HPCPS, and their Cronbach's α values. (N=120, Patients)
HPCPS=Hospice Palliative Care Performance Scale.
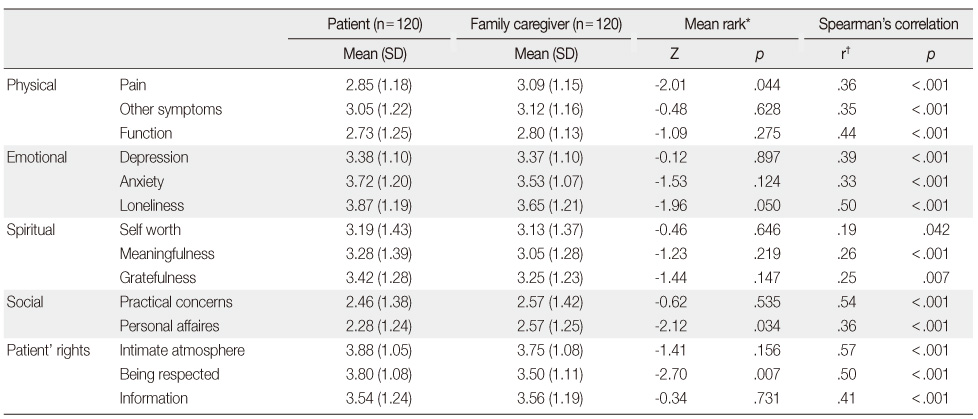
Summary of Comparison and Correlation of HPCPS* between Patients and Caregivers in Paired Group
*Wilcoxon signed ranks test; †Spearman's correlation coefficients.
HPCPS=Hospice Palliative Care Performance Scale.
ECOG PS=Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Scale.
*Hospice Palliative Care Performance Scale. Extraction method was principal component analysis with varimax rotation. We employed a decision rule of retaining factors whose eigen value were >1.0. Bold type indicates loadings >0.60.
*Spearman's correlation analysis; † HPCPS=Hospice Palliative Care Performance Scale.
HPCPS=Hospice Palliative Care Performance Scale.
*Wilcoxon signed ranks test; †Spearman's correlation coefficients. HPCPS=Hospice Palliative Care Performance Scale.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

