Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 40(2); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- Factors Influencing Health-related Quality of Life in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Jeong Sun Kim, Vit Na Moon
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2010;40(2):287-297.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.2.287
Published online: April 30, 2010
1Assistant Professor, College of Nursing, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
2Nurse, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kim, Jeong Sun. College of Nursing, Chonnam National University, 5 Hak-dong, Dong-gu, Gwangju 501-746, Korea. Tel: 82-62-220-4055, Fax: 82-62-220-3307, kjs0114@jnu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2010 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was done to examine the relationship of low urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), depression, sexual function, and health-related quality of life (HRQoL), and to identify factors influencing HRQoL in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) living in the community.
-
Methods
- A total of 218 patients with BPH were recruited into the study. The data were collected by personal interviews using questionnaires and were analyzed with SPSS (version 17.0) computer program, and included descriptive statistics, one-way ANOVA, Pearson's correlation coefficient, and stepwise multiple regression analysis.
-
Results
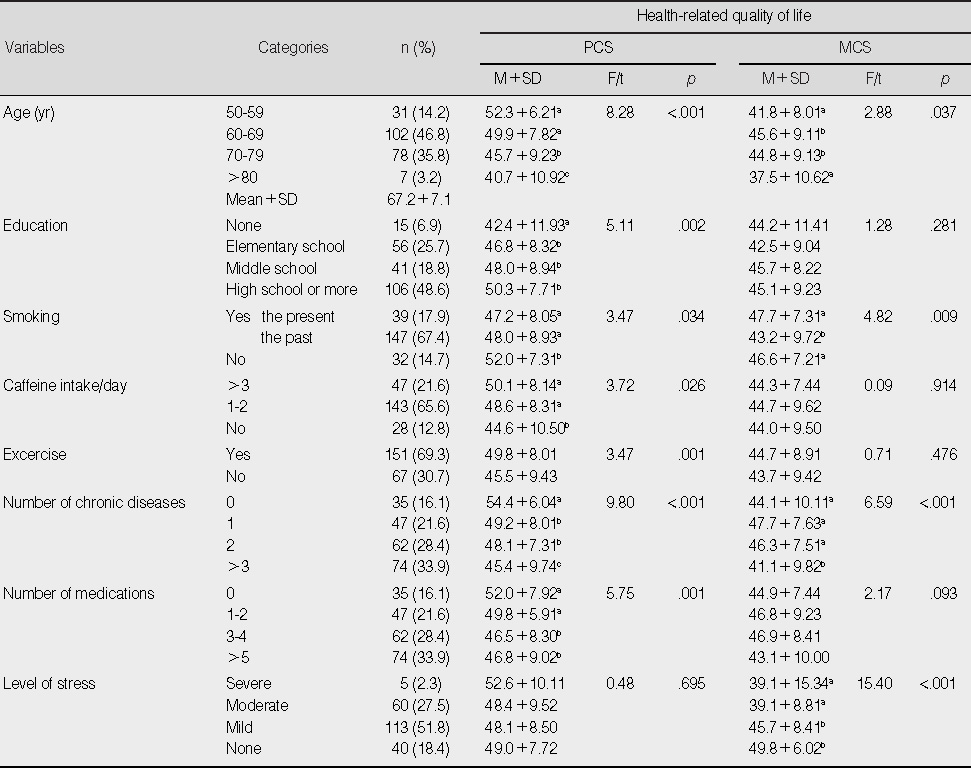
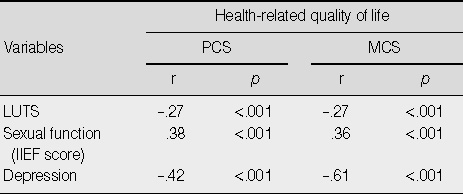
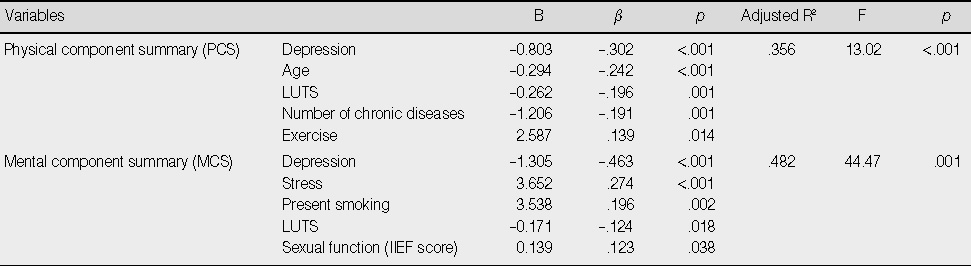
- The relationship between HRQoL and LUTS with depression had a significant negative correlation, whereas the relationship between HRQoL and sexual function had a significant positive correlation. Depression, age, LUTS, number of chronic disease, and excercise were found to be significant predictors (35.6%) of the Physical Component Summary of HRQoL. Depression, stress, smoking, LUTS, and sexual function were found to be significant predictors (48.2%) of the Mental Component Summary of HRQoL.
-
Conclusion
- To improve HRQoL of patients with BPH, nurses should focus on the factors identified in this study when doing nursing assessments, and should develop nursing intervention programs for BPH prevention and symptoms management in primary care settings.
- 1. Ahn TY, Lee DS, Kang W, Hong JH, Kim YS. Validation of an abridged korean version of the international index of erectile function (IIEF-5) as a diagnostic tool for erectile dysfunction. Korean Journal of Urology. 2001;42:535–540.
- 2. Calvert MJ, Freemantle N. Use of health-related quality of life in prescribing research. part 1: Why evaluate health-related quality of life? Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics. 2003;28:513–521.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Cha JS, Park JK. Association between lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction. Korean Journal of Urology. 2005;46:1023–1027.
- 4. Chang SJ. A study on factors affecting health-related quality of life of the BPH patients. 2006;Busan, Dong-A University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 5. Cheng Jackie YW, Emil ML, John SN. Depressive symptomatology and male sexual function in late life. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2007;104:225–229.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Choi HR, Chung WS, Shim BS, Kwon SW, Hong SJ, Chung BH, et al. Translation validity and reliability of I-PSS Korean version. Korean Journal of Urology. 1996;37:659–665.
- 7. Coyne KS, Wein AI, Tubaro A, Sexton CC, Thompson CL, Kopp ZC, et al. The burden of lower urinary tract symptoms: Evaluating the effect of LUTS on health-related quality of life. Anxiety and depression: EpiLUTS. British Journal of Urology International. 2009;103:suppl. 3. 4–11.Article
- 8. Finas D, Bals-Pratsch M, Sandmann J, Eichenauer R, Jocham D, Diedrich K, et al. Quality of life in elderly men with androgen deficiency. Andrologia. 2006;38(2):48–53.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Girman GJ, Jacobsen SJ, Tsukamoto T, Richard F, Garryway WA, Sagnier PP, et al. Health-related quality of life associated with lower urinary tract symptoms in four countries. Urology. 1998;51:428–436.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Han CW, Lee EJ, Iwaya T, Kataoka H. Development of the Korean version of short-form 36-item health survey: Health related QOL of healthy elderly people and elderly patients in Korea. Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2004;203:189–194.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Han DH, Lee HS, Kim JH, Lee SW. Korean males attitudes and behaviors on men's health and erectile dysfunction. Korean Journal of Andrology. 2005;23(2):61–70.
- 12. Hong SJ. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: Multiple factors for prostate tissue change with aging. Korean Journal of Urology. 2005;46:547–554.
- 13. Hunter DJ, Mekee M, Black N, Sanderson CF. Health status and quality of life of British men with lower urinary tract symptoms: Results from the SF-36. Urology. 1995;45:962–971.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Joo JM. Mood states and health related quality of life in older adults. 2008;Seoul, Hanyang University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 15. Kee BS. A preliminary study for the standardization of geriatric depression scale short form-Korea Version. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 1996;35:298–307.
- 16. Kim EJ. An analysis of dietary life and lifestyle factors to affect benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). 2006;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 17. Kim JH. A study on difference of depression pattern according to gender in elderly. 2003;Seoul, Seoul National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 18. Kim MS. Affecting factors to the quality of life in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. 2008;Seoul, Yonsei University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 19. Ko DS, Jeong JY, Jang SN, Choi YJ, Kim DH, Kim JB, et al. Association between lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction in aging men. Korean Journal of Urology. 2008;49:633–640.
- 20. Lee EH, Chun KH, Lee YH. Benign prostatic hyperplasia in community-dwelling elderly in Korea. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2005;35:1508–1518.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 21. Lee SR, Choi SJ, Na YH. Literature review about health related quality of life. Korean Journal of Gastrointestinal Motility. 2001;7:6–7.
- 22. Liu CC, Huang SP, Li WM, Wang CJ, Wu WJ, Chou YH, et al. Are lower urinary tract symptoms associated with erectile dysfunction in aging males of Taiwan? Urologia Internationalis. 2006;77:251–254.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 23. Masumori N, Homma D, Tsukamoto T. Web-based research of lower urinary tract symptoms that affect quality of life in elderly Japanese men: Analysis using a structural equation model. International British Journal of Urology. 2005;95:1013–1022.Article
- 24. McVary KT. Erectile dysfunction and low urinary tract symptoms secondary to BPH. European Urology. 2005;47:838–845.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs (MIHWAF). The epidemiology study on the benign prostatic hyperplasia in community adult male. 2004;Seoul, Author.
- 26. Quek KF. Factors affecting health-related quality of life among patients with lower urinary tract symptoms. International Journal of Urology. 2005;12:1032–1036.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Salinas Sanchez AS, Hernandez Millan I, Lorenzo Romero JG, Segura Martin M, Fernandez Olano C, Virseda Rodriguez JA. Quality of life of patients on the waiting list for benign prostatic hyperplasia surgery. Quality of Life Research. 2001;10:543–553.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 28. Salinas Sanchez AS, Hernandez Millan I, Segura Martin M, Lorenzo Romero JG, Virseda Rodriguez JA. he impact of benign prostatic hyperplasia surgery on patients' quality of life. Urologia Internationalis. 2002;68:32–37.PubMed
- 29. Shin KR, Byeon YS, Kang Y, Oak J. A study on physical symptom, activity of daily living, and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in the community-dwelling older adults. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008;38:437–444.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Wares JE, Sherbourne C. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). Medical care. 1992;30:473–483.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Wein AJ, Coyne KS, Tubaro A, Sexton CC, Kopp ZS, Aiyer LP. The impact of lower urinary tract symptoms on male sexual health: EpiLUTS. British Journal of Urology International. 2009;103:suppl. 3. 33–41.Article
- 32. Welch G, Weinger K, Berry MJ. Quality of life impact of lower urinary tract symptom severity: Results from the health professionals follow-up study. Urology. 2002;59:245–250.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Wong Smuel YS, Hong A, Leung J, Kwok T, Leung PC, Woo J. Lower urinary tract symptoms and depressive symptoms in the elderly men. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2006;96:83–88.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- The effect of transurethral resection of the prostate on sexual life quality in patient spouses
Aylin Aydin Sayilan, Nursen Kulakac
International Journal of Urological Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality of Life in Middle-aged Men with Prostatic hyperplasia: A Structural Equation Model
Hee Nam Moon, Seung Hee Yang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(4): 327. CrossRef - Effectiveness and safety of electroacupuncture and its cotreatment with electronic moxibustion in the treatment of patients with moderate benign prostatic hyperplasia using alpha blocker: An assessor-blinded, randomized, controlled pilot study
Hyo Bin Kim, Chang-Hyun Han, Ju Hyun Jeon, Eunseok Kim, Ojin Kwon, Young Eun Choi, Changsop Yang, Yang Chun Park, Young Il Kim
Medicine.2022; 101(36): e30386. CrossRef - Depression risk associated with the use of 5α-reductase inhibitors versus α-blockers: A retrospective cohort study in South Korea
Bora Yeon, Ah Young Suh, Eunmi Choi, Bonggi Kim, Eunsun Noh, Soo Youn Chung, Soon Young Han, Peter F.W.M. Rosier
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(3): e0265169. CrossRef - Amelioration of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Costunolide and Dehydrocostus Lactone in Wistar Rats
Dohyun Choi, Jiyeon Kim, Jinho An, Seonhwa Hong, Youngcheon Song, Hyunseok Kong
The World Journal of Men's Health.2021; 39(2): 315. CrossRef - Metabolic Factors Associated with Incidence of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Korea: Using National Health Insurance Service Data
Tae-Hwa Go, Hye Sim Kim, Dae Ryong Kang, Jae Hung Jung, Sung Won Kwon, Sae Chul Kim, Jae Mann Song, Hyun Chul Chung, Sang Baek Koh
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2020; 45(4): 418. CrossRef - Association of Exercise with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
Yoo-Hyun Lee, Dong-Hee Kim, Jin-Hwan Yoon, Jeong-Sun Ju
Exercise Science.2019; 28(1): 3. CrossRef - The Prevalence of Benign Prostate Hyperplasia in Korea: Using National Health Insurance Service Data
Hye Sim Kim, Tae Hwa Go, Dae Ryong Kang, Jae Hung Jung, Sung Won Kwon, Sae Chul Kim, Jae Mann Song, Hyun Chul Chung, Sang Baek Koh
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2018; 43(3): 208. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Health-related Quality of Life in Middle-aged Male Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Dohyung Kim, Soo-Kyoung Lee
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2017; 17(3): 199. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Quality of Life of Prostate Cancer Patients
Jeonghye Chae, Youngsuk Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2017; 17(4): 237. CrossRef - A Study on Physiological Index, Anxiety and Depression by the Severity of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Jung Kyoun Kim, Jin Bum Kim, Min Sun Song
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2016; 18(3): 127. CrossRef - Effects of Aroma Foot Bath on Urination Status and Stress related to Urination in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Kye Ha Kim, Eun Ha
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(3): 213. CrossRef - Postoperative Quality of Life in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Ju-Sung Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2011; 12(3): 1260. CrossRef
Health-related quality of life by General and Health-related characteristics (N=218)
PCS=physical component summary; MCS=mental component summary.
Correlations between Health-related quality of life and LUTS, Sexual function, or Depression (N=218)
PCS=physical component summary; MCS=mental component summary; LUTS=low urinary tract symptom; IIEF=international index of erectile function.
Factors Influencing Health-related quality of life of Patients with BPH (N=218)
BPH=benign prostatic hyperplasia; LUTS=low urinary tract symptom; IIEF=international index of erectile function.
PCS=physical component summary; MCS=mental component summary.
PCS=physical component summary; MCS=mental component summary; LUTS=low urinary tract symptom; IIEF=international index of erectile function.
BPH=benign prostatic hyperplasia; LUTS=low urinary tract symptom; IIEF=international index of erectile function.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

