Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 40(2); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effects of Teaching Method using Standardized Patients on Nursing Competence in Subcutaneous Injection, Self-Directed Learning Readiness, and Problem Solving Ability
- Mi-Ran Eom, Hyun-Sook Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Kayeon Seong
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2010;40(2):151-160.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.2.151
Published online: April 30, 2010
1Associate Professor, Department of Nursing, Mokpo National University, Mokpo, Korea.
2Associate Professor, College of Nursing, Eulji University, Seongnam, Korea.
3Assistant Professor, Department of Nursing, Mokpo National University, Mokpo, Korea.
4Part-time Lecturer, College of Nursing, Eulji University, Deajeon, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kim, Eun-Kyung. Department of Nursing, Mokpo National University, 61 Dorim-ri, Cheonggye-myeon, Muan 534-729, Korea. Tel: 82-61-450-2672, Fax: 82-61-450-2679, eunkyung@mokpo.ac.kr
Copyright © 2010 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of teaching method using Standardized Patients (SPs) on nursing competence, self-directed learning readiness, and problem solving ability-focusing on subcutaneous insulin injection.
-
Methods
- This research was a nonequivalent control group non-synchronized post-test design. The subjects consisted of 62 junior nursing students at E University. Scenarios to train SPs and checklists to evaluate the students' competence were developed by our research team. The experimental group (n=31) participated in the teaching class using SPs. The control group (n=31) received traditional practice education. The collected data were analyzed with descriptive analysis, χ2/Fisher's exact test, t-test, Pearson's correlation coefficient, and Cronbach's α using SPSS WIN 14.0 Program.
-
Results
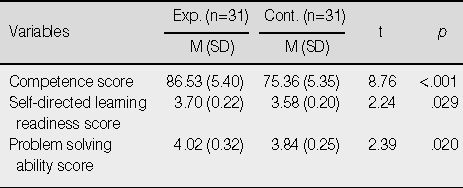
- The mean scores of competence, self-directed learning readiness, and problem solving were significantly higher in the experimental group than the control group.
-
Conclusion
- As confirmed by this research findings, the teaching method using SPs was more effective than the traditional method to improve junior nursing students' competence, self-directed learning readiness, and problem solving. Therefore, It is necessary to develop a various of scenarios and to testify their effectiveness.
- 1. Alexander M, Runciman P. ICN Framework of Competencies for the Generalist Nurse. 2003;Geneva, International Council of Nurses.
- 2. Bond WF, Deitrick LM, Arnold DC, Kostenbader M, Barr GC, Kimmel SR, et al. Using simulation to instruct emergency medicine residents in cognition forcing strategies. Academic Medicine. 2004;79:438–446.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Bowles K. The relationship of critical-thinking skills and clinical judgement skills of baccalaureate nursing students. Journal of Nursing Education. 2000;39:373–376.PubMed
- 4. Choi JY, Jang KS, Choi SH, Hong MS. Validity and reliability of a clinical performance examination usng standardized patients. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008;38:83–91.PubMed
- 5. Cohen J. Statistical power for the behavioral sciences. 1988;2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc.
- 6. Dunn SV, Hansford B. Undergraduate nursing students' perceptions of their clinical learning environment. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 1997;25:1299–1306.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Fehring RJ. Methods to validate nursing diagnosis. Heart & Lung. 1987;16:625–629.
- 8. Frejlach G, Corcoran S. Measuring clinical performance. Nursing Outlook. 1971;19:270–271.PubMed
- 9. Guglielmino LM. Development of the self-directed learning readiness scale. 1977;Athens, University of Georgia. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 10. Heppner PP, Peterson CH. The development and implications of a personal problem-solving inventory. Journal of Counselling Psychology. 1982;29:66–75.Article
- 11. Hong YP. The self-directed learning readiness of specialized high school students and its related variables. 2002;Seoul, Seoul National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 12. Jeon SG. A study on the effectiveness of social skills training program for rehabilitation of the schizophrenic patients. 1995;Seoul, Soongsil University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 13. Jung KH, Choi EH, Bae JD, Na DY, Son IK, Ko CW, et al. Comparison of professional standardized and amteur standardized patients in OSCE. Korean Journal of Medical Education. 2005;17:97–105.
- 14. Kneebone R. Simulation in surgical training: Educational issues and practical implications. Medical Education. 2003;37:267–275.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Ko J, Yoon TY, Park J. Inter-rater reliability in a clinical performance examination using multiple standardized patients for the same case. Korean Journal of Medical Education. 2008;20:61–72.Article
- 16. Ko JE. A study is the relationship between nursing students' self-efficacy and self-directed learning readiness. Dongnam Health Junior College Journal. 2003;21:97–106.
- 17. Kwon IS. An analysis of research on clinical nursing education. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2002;32:706–715.ArticlePDF
- 18. Lee BG. Recent world trend in performance-based assessments and application of the standardized patient program in Korean medical education. Korean Journal of Medical Education. 2000;12:377–392.Article
- 19. Oh WO. Factors influencing self-directedness in learning of nursing studnets. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2002;32:684–693.
- 20. Packer JL. Education for clinical practice: An alternative approach. Journal of Nursing Education. 1994;33:411–416.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Patterson C, Grooks D, Lunyk-Child D. A new perspective on competencies for self-directed learning. Journal of Nursing Education. 2002;4:25–31.
- 22. Randolph HS, Wendy CC, Yue MH, Rima M, Baxter RL. Simulation-based training is superior to problem-based learning for the acquisition of clinical assessment and management skill. Critical Care Medicine. 2006;34:151–157.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Sung YH, Kwon IG, Hwang JW, Kim JY. Development of an e-learning program about medication for new nurses. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2005;35:1113–1124.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 24. Theroux R, Pearce C. Graduate students' experiences with standardized patients as adjuncts for teaching pelvic examinations. Journal of American Academic Nurse Practice. 2006;18:429–435.Article
- 25. Wallace P. Coaching standardized patients: For use in the assessment of clinical competence. 2007;New York, NY, Springer Publishing.
- 26. Yi YJ, Lim NY, Lee EH, Han HJ, Kim JH, Son HM, et al. Evaluation on the practicum using standardized patients for nursing assessment to articular disease. Journal of Muscle and Joint Health. 2007;14:137–148.
- 27. Yoo MS. The effectiveness of standardized patient managed instruction for a fundamental nursing corse. Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education. 2001;7:94–109.
- 28. Yoo MS, Yoo IY. Effects of OSCE method on performance of clinical skills of students in fundamentals of nursing course. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2003;33:228–235.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 29. Yoo MS, Yoo IY, Park YO, Son YJ. Comparison of student's clinical competency in different instructional methods for fundamentals of nursing practicum. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2002;32:327–335.ArticlePDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Effects of Diabetes Home-Visiting Healthcare Simulation Education on Nursing Students Using Virtual Reality
Young-Sun Ha, Yong-Kyung Park, Hye-Sun Byun, Kyeng-Jin Kim, Moon-Ji Choi
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2025; 26(9): 2501. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Pharmacist-Led Nurse Education on Enoxaparin Injection Technique in Baghdad Teaching Hospital, Iraq
Ehab Mudher Mikhael, Kawthar Faris Nassir, Ahmed Lateef Alkhaqani, Zahraa Riyqdh Jabbar
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2024; 6(1): 202. CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness of Progressive Simulation Education Program on Medication Safety for Nursing Students
Se-Young Jung, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(4): 563. CrossRef - Comparing the effects of patient safety education using design thinking and case based learning on nursing students’ competence and professional socialization: A quasi-experimental design
Seongmi Moon, Soo Jung Chang
Heliyon.2024; 10(9): e29942. CrossRef - The development and effects of a nursing education program for hyperglycemia patient care using standardized patients for nursing students
Jin Lee, Pok Ja Oh
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(4): 427. CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Simulation Using Mixed Reality: A Scoping Review
Kyeng-Jin Kim, Moon-Ji Choi, Kyu-Jin Kim
Healthcare.2021; 9(8): 947. CrossRef - Effects of integrative simulation practice on nursing knowledge, critical thinking, problem-solving ability, and immersion in problem-based learning among nursing students
Young A Song
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(1): 61. CrossRef - The Educational Effects of the Experience of Nursing Students' Patients Role in the Simulation Practice Education for the Women's Health Nursing
Bo Gyeong Lee, Sun Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(4): 436. CrossRef - Simulation scenarios in Korea according to the learning objectives of adult health nursing: A literature review
Ae Ri Jang, In Kyoung Lee, Hang Nan Cho, Piotr Mikiewicz
Cogent Education.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Policy issues in simulation-based nursing education and technology development
Hyunbong Park, Soyoung Yu
Health Policy and Technology.2018; 7(3): 318. CrossRef - Experience of nursing students with standardized patients in simulation-based learning: Q-methodology study
Eun-Ho Ha
Nurse Education Today.2018; 66: 123. CrossRef - Japanese Nursing Students' Learning Experience, Self-directed Learning Ability, and Self-efficacy in Nursing Practice Utilizing Portfolios
Hye Young Lee, Rie Shimotakahara, Hye Weon Kim, Shige Mitsu Ogata
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2017; 23(3): 279. CrossRef - Effects of Simulation with Problem-based Learning on Care for Patients with Autonomic Dysreflexia
Ji Eun Park
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2017; 20(2): 140. CrossRef - Learning Outcomes and Teaching Methods in Fundamentals of Nursing*
Jongsoon Won, HyoungSook Park, YunHee Shin, Hyojung Park, Se Hyun Lim, Mee-Kyung Shin, Jung-Hee Kim, Young-Ju Kim, Sung Ok Chang, Seung Kyo Chaung, Young-Ok Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2016; 23(3): 292. CrossRef - Selection of nursing teaching strategies in mainland China: A questionnaire survey
HouXiu Zhou, MengJie Liu, Jing Zeng, JingCi Zhu
Nurse Education Today.2016; 39: 147. CrossRef - The Effects of Clinical Education Program for Nurses in Regional Public Hospital
Yoonhee Shin, Kwanjun Park, Eunkyung Byun, Dongwon Lee, Woong Ju
Health Policy and Management.2016; 26(4): 373. CrossRef - The Effects of Self-efficacy and Self-directed Learning Readiness to Self-leadership of Nursing Student
Sun-Young Lee, Yun-Young Kim
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(3): 309. CrossRef - Effects of Maternity Nursing Simulation using High-fidelity Patient Simulator for Undergraduate Nursing Students
Ahrin Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(3): 177. CrossRef - Development and Application of Integrated-Simulation Practice Program using Standardized Patients : Caring for Alcoholism with Diabetes Mellitus in the Community
Gwang-Soon Kang, Younkyoung Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(8): 662. CrossRef - The Effects of Clinical Convergence Self-directedness Practice Learning Program on Self-directedness and Competency in Fundamental Nursing Skills in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Jihyun Park
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(4): 51. CrossRef - Effects of a Simulation-based education on Cardiopulmonary Emergency Care Knowledge, Critical Thinking and Problem solving ability in Nursing Students
Gyoo-Yeong CHO
Journal of Fisheries and Marine Sciences Education.2016; 28(2): 439. CrossRef - Relationships among Information Resources Use, Problem Solving Ability, Nursing Information Literacy Competency in General Hospital Nurses
Yeong-Mi Ha, Jeong-Eui Cho, Seung-Kyoung Yang
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(7): 289. CrossRef - Effects of a Simulation-based Stroke Care Education on Nursing Performance Ability and Satisfaction in Nursing Students
Kie In Jang, Young Sook Roh
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(1): 408. CrossRef - The effect of Simulation-based learning scenario using standardized repiratory patients on learning satisfaction, clinical skill competency and self-efficacy in Health-related department students
Hye-Young Cho
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(3): 2100. CrossRef - Comparison of the Problem Solving Abilities as Simulation Learning Stage -Focused on Care for Patients with Asthma in Emergency Units
Young-Hee Kim, Kyung-Ah Kang, Myung-Nam Lee, Yun-Kyung Kim, Ye-Jean Kim, Jung-Jae Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Jeong
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2015; 15(1): 495. CrossRef - Effects of a Standardized Patient Simulation Program for Nursing Students on Nursing Competence, Communication Skill, Self-efficacy and Critical Thinking Ability for Blood Transfusion*
Ga Eul Joo, Kyeong-Yae Sohng, Hee-Ju Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2015; 22(1): 49. CrossRef - Effects on Problem Solving Ability and Learning Satisfaction of Nursing Students of Receiving a Teaching Method Using Standardized Patients - Blood Transfusion
Su Mi Kim, Min Jung Park, Ya Ki Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2015; 22(4): 406. CrossRef - The effects of simulation-based learning using standardized patients in nursing students: A meta-analysis
Pok-Ja Oh, Kyeong Deok Jeon, Myung Suk Koh
Nurse Education Today.2015; 35(5): e6. CrossRef - Effects of Psychiatric Nursing Practicum using Simulated Patients on Self-Directed Learning Readiness, Learning Self-Efficacy, Satisfaction of Learning
Soon-Ok Kim, Hyun-Sook Kim
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(2): 396. CrossRef - A Study on Learning Experiences and Self-Confidence of Core Nursing Skills in Nursing Practicum among Final Year Nursing Students
Aekyung Han, Dong Sook Cho, Jongsoon Won
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2014; 21(2): 162. CrossRef - Effects of Basic Clinical Practice Program in Academic Motivation, Critical Thinking and Clinical Nursing Competence of Nursing Students
In-Soon Seo, Su-Min Oh, Dongwon Choi, Hee-Ok Park, Rye-Won Ma
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(4): 2276. CrossRef - Qualitative content analysis experiences with objective structured clinical examination among Korean nursing students
Kae‐Hwa JO, Gyeong‐Ju AN
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2014; 11(2): 79. CrossRef - Systematic Review of Korean Studies on Simulation within Nursing Education
Jung-Hee Kim, In-Hee Park, Sujin Shin
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(3): 307. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Scenario for Simulation Learning of Care for Children with Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Neonatal Intensive Care Units.
Myung Nam Lee, Hee Soon Kim, Hyun Chul Jung, Young Hee Kim, Kyung Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2013; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - Clinical Competence and Self-confidence of New Graduate Nurses with an Integrated Nursing Curriculum of Simulation with Problem-Based Learning
Young Sook Roh, Sunghee Kim, Sun Hee Yang, Yoon Sook Kang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(7): 3349. CrossRef - The Effects of Simulation Training With Hybrid Model for Nursing Students on Nursing Performance Ability and Self Confidence
Suk Jeong Lee, Young Mi Park, Sang Mi Noh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(2): 170. CrossRef - Effects of using Standardized Patients on Nursing Competence, Communication Skills, and Learning Satisfaction in Health Assessment
Sun Ju Choi, Mal Suk Kwon, Seon Hwa Kim, Hyeon Mi Kim, Yang Sook Jung, Geum Yi Jo
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(1): 97. CrossRef - Development and Application of Simulation Learning Scenario using Standardized Patients: Caring for Neurological Patients in Particular
Ye-Eun Kim, Hee-Young Kang
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2013; 13(11): 236. CrossRef - The Development and Evaluation of a New Educational Program, Introduction to Clinical Nursing, for Third Year Nursing Students
Kyung-Ae Song, Hyun-Jung Park, Hye-A Yeom, Jong-Eun Lee, Ga-Eul Joo, Hee-Ju Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(3): 322. CrossRef - Effectiveness of web based learning program on self efficacy, knowledge, and competence in measurement of blood pressure
Sook-Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(1): 66. CrossRef - The Effect of Using Standardized Patients in Psychiatric Nursing Practical Training for Nursing College Students
Shin Young Park, Young Ran Kweon
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2012; 21(1): 79. CrossRef - Effects and Adequacy of High-Fidelity Simulation-Based Training for Obstetrical Nursing
Woo Sook Lee, Miok Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(4): 433. CrossRef
Research Design
X1=Traditional teaching method; X2=Teaching method using Standardized Patients; Yc2, Ye2=Data collection (competence, self-directed learning readiness, and problem solving ability).
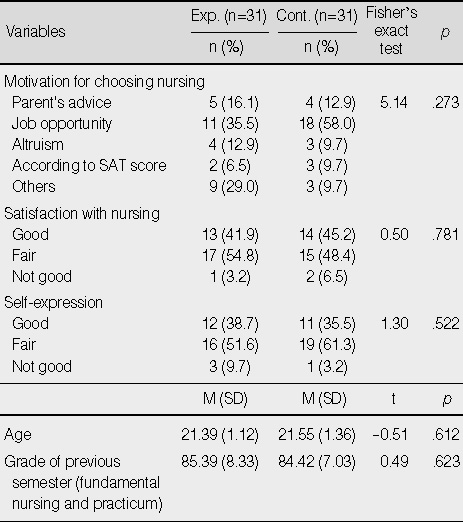
Homogeneity for Characteristics between Experimental and Control Groups
Exp.=experimental group; Cont.=control group.
Comparisons of Competence, Self-Directed Learning Readiness, and Problem Solving Ability Scores between Experimental and Control Groups after Treatment
Exp.=experimental group; Cont.=control group.
X1=Traditional teaching method; X2=Teaching method using Standardized Patients; Yc2, Ye2=Data collection (competence, self-directed learning readiness, and problem solving ability).
Exp.=experimental group; Cont.=control group.
Exp.=experimental group; Cont.=control group.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 Cite
Cite

