Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Mediating effect of grit on the influence of nurses’ silence behavior on medication safety competence: a cross-sectional study
- Haengsuk Kim, Wanju Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):81-92. Published online February 20, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24088
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
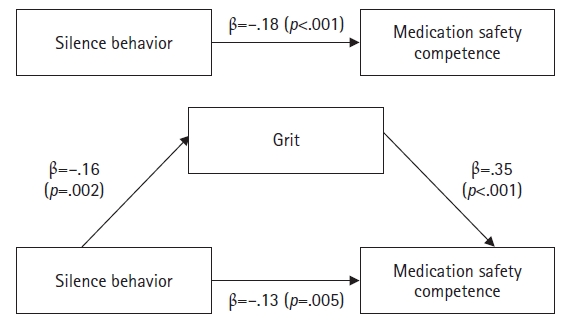
This study investigated the mediating effect of grit in the relationship between silence behavior and medication safety competence among nurses.
Methods
The study included 166 nurses from four university hospitals and general hospitals in Seoul and Gyeonggi-do, South Korea. Data were collected from March 1 to 10, 2024, using self-report questionnaires. Data were analyzed using the t-test, analysis of variance, Scheffé’s test, and Pearson’s correlation coefficients with IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 23.0 (IBM Corp.). A mediation analysis was performed using Hayes’s PROCESS macro model 4 and the bootstrapping method.
Results
Medication safety competence showed significant correlations with silence behavior (r=–.21, p=.008) and grit (r=.43, p<.001). Furthermore, grit partially mediated the relationship between silence behavior and medication safety competence.
Conclusion
This study indicates that grit is a significant mediator in the relationship between silence behavior and medication safety competence. Therefore, an integrated approach that reduces silence behavior and promotes grit is essential for strengthening nurses’ medication safety competence. Ultimately, these strategies will help ensure patient safety by improving medication safety competence.
- 5,404 View
- 468 Download

- Development of the Hospital Nurses’ Silence Behavior Scale
- Soojin Chung, Jee-In Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):279-295. Published online May 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23138
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure hospital nurses’ silence behavior and examine its validity and reliability.
Methods
A total of 52 preliminary items on hospital nurses’ silence behavior were selected using a content validity test by seven experts on 53 candidate items derived from a literature review and in-depth interviews with 14 nurses. A total of 405 hospital nurses participated in a psychometric testing. Data analysis comprised item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses, and convergent and discriminant validity tests. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used for assessing concurrent validity, and Cronbach’s alpha was used for the reliability test.
Results
The final scale consisted of nine factors with 31 items, exhibiting acceptable model fit indices, convergent validity, and discriminant validity. The score of the entire scale was positively correlated with the ‘Organizational Silence Scale (OSS)-the issues on which nurses remain silent’ (r = .60, p < .001) and ‘OSS-the reasons why nurses remain silent’ (r = .68, p < .001). Cronbach’s α of the scale was .92, and α of each subscale ranged from .71 to .90.
Conclusion
The Hospital Nurses’ Silence Behavior Scale is a useful tool for assessing multifaceted silence behavior among nurses. It can provide basic data for developing better communication strategies among nurses and other hospital staff. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mediating Effect of Emotional Labour on the Role Pressure and Silence Behaviour of Nurses
Lianci He, Jianhua Liu, Rong Sun, Yuan Deng, Ling Tang, Shaochuan Chen
Evaluation & the Health Professions.2026; 49(1): 3. CrossRef - Mediating effect of grit on the influence of nurses’ silence behavior on medication safety competence: a cross-sectional study
Haengsuk Kim, Wanju Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(1): 81. CrossRef - Influence of Clinical Nurses’ Organizational Silence on Organizational Citizenship Behavior: Mediating Effect of Organizational Commitment Moderated by Organizational Justice
Shin Ae Hwang, Haeyoung Min
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 416. CrossRef - Psychometric evaluation and translation of the Persian version of the Organizational Silence Behavior Scale (OSBS-P) for clinical nurses
Alireza Mirzaei, Mobina Jamshidinia, Mehrzad Aghabarari, Pouya Dolat Abadi, Reza Nemati-Vakilabad, Ehsan Namaziandost
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(12): e0314155. CrossRef
- Mediating Effect of Emotional Labour on the Role Pressure and Silence Behaviour of Nurses
- 4,741 View
- 280 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Effects of Assertive Training on Interpersonal Relations, Social Behavior, and Psychiatric Symptoms in Patients with a Mental Disorder
- Kuem Sun Han, Hee Su Im, Bo Kyum Yang, Hae Kyung Chung, Yong Jin Suh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(5):896-903. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.5.896
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was designed to examine the effects of an assertive training program on interpersonal relations, and psychiatric symptoms in patients with a mental disorder.
Method The study employed a quasi experimental design. The subjects included44 patients with a mental disorder, 20 in the experimental group, and 24 in the control group. Data was collected using structured questionnaires over a 3 month period.
Results There were greater significant increases in scores of interpersonal relations and content of communication in the experimental group than the control group. Also, there was a greater significant decrease in the score of psychiatric symptoms in the experimental group than the control group.
Conclusion Assertive training has an effect on increasing content of communication and decreasing psychiatric symptoms.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Psychosocial Rehabilitation Programs on the Levels of Self-Efficacy for Mentally Disabled Persons
Hyun Sook Park, Sung-Woo Bae, Yi Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(5): 704. CrossRef
- The Effects of Psychosocial Rehabilitation Programs on the Levels of Self-Efficacy for Mentally Disabled Persons
- 818 View
- 12 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of a Robot Pet-assisted Program for Elderly People with Dementia
- Jung Hee Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(4):562-573. Published online August 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.4.562
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the effects on the cognitive function, Activities of Daily Living (ADL), mood, social behaviors, and problematic behaviors of robot pet-assisted program for elderly people with dementia.
Methods This study was a nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design. The participants were 32 elders with dementia. Seventeen were assigned to the experimental group and 15 to the control group. The intervention was conducted twice a week for 6 weeks.
Results 1) After the program, cognitive function, ADL, and social behaviors did not show significant differences. 2) After the program, mood of experimental group was significantly better than that of the control group. 3) After the program, problematic behaviors of the experimental group were significantly more diminished than those of control group. 4) As a result of analyzing the response, robot pet-assisted program was effective such as inducing a positive emotional state and increasing communication and interaction.
Conclusion The robot pet-assisted program was effective in changing the mood and diminishing problematic behaviors and had positive effects such as increasing communication and interaction for elders with dementia. Therefore, this program should be considered as a positive program for physical and emotional support for elders with dementia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Digital interventions to reduce social isolation and loneliness in older adults: An evidence and gap map
Vivian Welch, Elizabeth T. Ghogomu, Victoria I. Barbeau, Sierra Dowling, Rebecca Doyle, Ella Beveridge, Elisabeth Boulton, Payaam Desai, Jimmy Huang, Nour Elmestekawy, Tarannum Hussain, Arpana Wadhwani, Sabrina Boutin, Niobe Haitas, Dylan Kneale, Douglas
Campbell Systematic Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital healthcare for dementia and cognitive impairment: A scoping review
Minsung Sohn, JungYeon Yang, Junyoung Sohn, Jun-Hyup Lee
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2023; 140: 104413. CrossRef - Systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomization controlled and nonrandomized controlled studies on nurse‐led nonpharmacological interventions to improve cognition in people with dementia
Yujin Suh, Sumi Lee, Go‐Eun Kim, JuHee Lee
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(13-14): 3155. CrossRef - The use of technology for social interaction by people with dementia: A scoping review
Merryn Anderson, Rachel Menon, Katy Oak, Louise Allan, Matthew Chua Chin Heng
PLOS Digital Health.2022; 1(6): e0000053. CrossRef - Socially assistive robots for people with dementia: Systematic review and meta-analysis of feasibility, acceptability and the effect on cognition, neuropsychiatric symptoms and quality of life
Clare Yu, Andrew Sommerlad, Lena Sakure, Gill Livingston
Ageing Research Reviews.2022; 78: 101633. CrossRef - Can Use of Digital Technologies by People with Dementia Improve Self-Management and Social Participation? A Systematic Review of Effect Studies
David Neal, Floor van den Berg, Caroline Planting, Teake Ettema, Karin Dijkstra, Evelyn Finnema, Rose-Marie Dröes
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(4): 604. CrossRef - Pet-Assisted Therapy for Delirium and Agitation in Hospitalized Patients with Neurocognitive Impairment: A Review of Literature
Abu Baker Sheikh, Nismat Javed, Katarina Leyba, Ali Hamza Khair, Zainab Ijaz, Aimen Asim Dar, Hamza Hanif, Asif Farooq, Rahul Shekhar
Geriatrics.2021; 6(4): 96. CrossRef - Factors related to the effectiveness in the use of an ICT-based toy robot for the in-home care of community dwelling elderly
Heui Sug Jo, Ji Hee Kim, Saerom Kim
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2019; 36(5): 43. CrossRef - Effects of Intervention Using PARO on the Cognition, Emotion, Problem Behavior, and Social Interaction of Elderly People with Dementia
In Soon Koh, Hee Sun Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(3): 300. CrossRef - Prospects of Geriatric Nursing Application Based on Robot Technology
Jin Hwan Oh
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2018; 20(Suppl 1): 127. CrossRef - Interaction of robot with humans by communicating simulated emotional states through expressive movements
Sara Baber Sial, Muhammad Baber Sial, Yasar Ayaz, Syed Irtiza Ali Shah, Aleksandar Zivanovic
Intelligent Service Robotics.2016; 9(3): 231. CrossRef - Effects of Silver-Care-Robot Program on Cognitive Function, Depression, and Activities of Daily Living for Institutionalized Elderly People
Jin-Hwan Oh, Yeo-Jin Yi, Chul-Jin Shin, Cheonshu Park, Sangseung Kang, Jaehong Kim, In-Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(3): 388. CrossRef - Care robots for the supermarket shelf: a product gap in assistive technologies
TIM BLACKMAN
Ageing and Society.2013; 33(5): 763. CrossRef - Effects of Multisensory Stimulation Using Familiarity: Persons with Dementia in Long-term Care Facility in Korea
Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(4): 528. CrossRef
- Digital interventions to reduce social isolation and loneliness in older adults: An evidence and gap map
- 1,590 View
- 39 Download
- 14 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


