Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
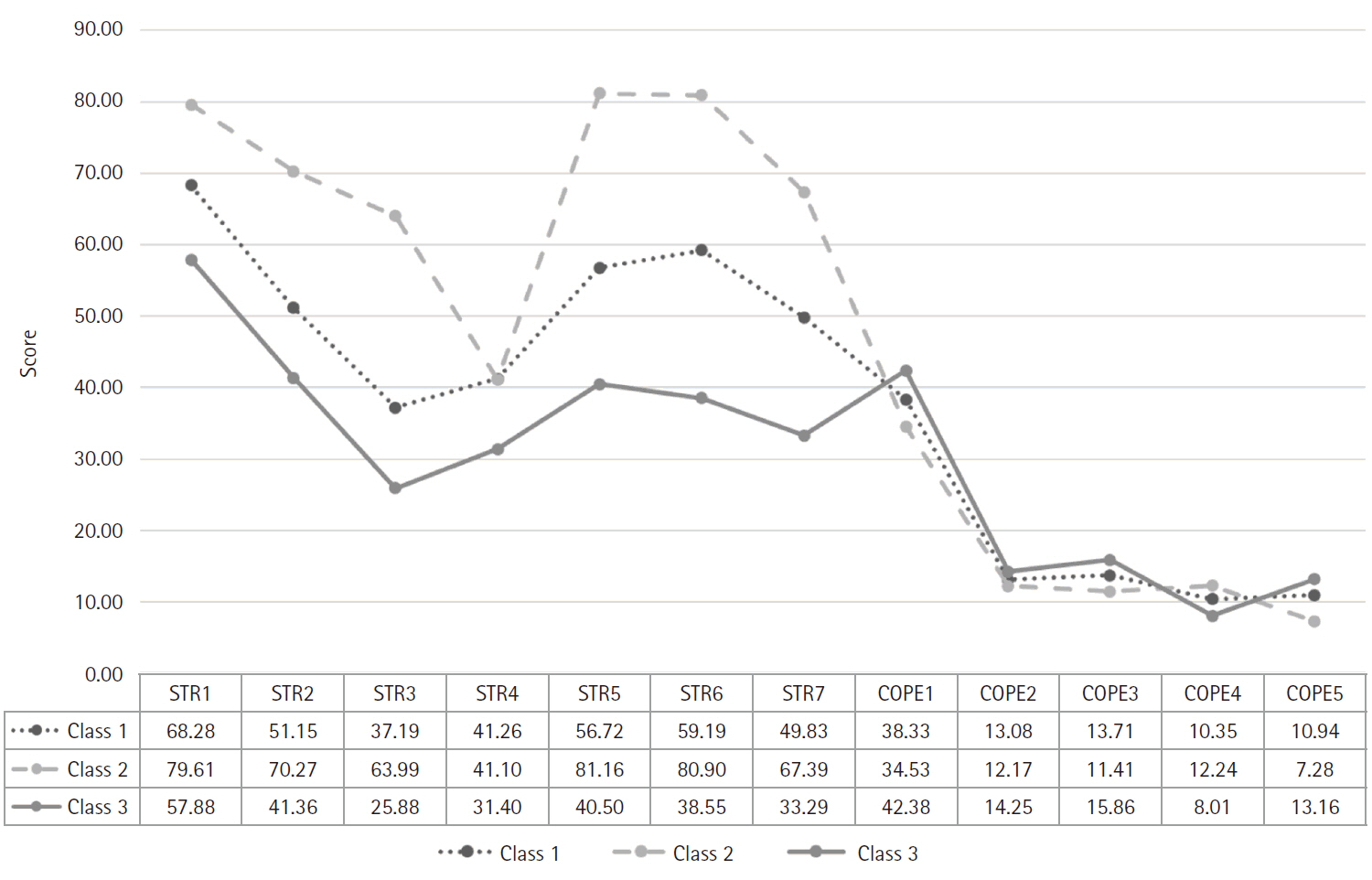
- Job stress levels and coping among hospital nurses: a latent profile analysis
- Myungji Kim, Hyunkyung Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):377-387. Published online August 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25061
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to identify job stress levels and coping profiles among hospital nurses, explore the factors influencing profile classification, and determine whether levels of job embeddedness and happiness varied among the profiles.
Methods
Data were collected through an online survey of 325 hospital nurses, and latent profiles were identified via latent profile analysis. The R3STEP (three-step auxiliary variable approach) method was used to examine the factors influencing the latent profiles, and one-way analysis of variance was conducted to analyze differences in levels of job embeddedness and happiness.
Results
Three job stress and coping profiles were identified: (1) the “moderate stress-balanced coping group”, characterized by moderate levels of job stress and moderate use of all coping strategies; (2) the “high stress-emotional coping group”, with high job stress and primary use of emotional display strategies; and (3) the “low stress-adaptive coping group, with low job stress and the utilization of a variety of coping strategies. Workplace location and monthly income influenced the classification of latent profiles. Nurses working in metropolitan areas and those with lower monthly incomes were more likely to be classified into the high stress-emotional coping group than other groups. The levels of job embeddedness and happiness were highest in the low stress-adaptive coping group and lowest in the high stress-emotional coping group.
Conclusion
The results of this study indicate the need to develop strategies that offer diverse stress-coping programs and support nurses in effectively utilizing coping methods that best suit their individual needs.
- 2,044 View
- 227 Download

- The Effect of a Social Skills Program on Violent Behaviors in Children Aged 60~72 Months
- Tülay Kuzlu Ayyildiz, Güler Cimete
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):771-782. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.771
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose To determine the effects of a child and parent program on developing social skills for preventing violent behaviors in children aged 60~72 months through a specially developed pre and posttest, control group, quasi-experimental study.
Methods A social skills development program based on Gardner's Multiple Intelligence Theory was used. The data were collected using the Social Skills Assessment Scale (SSAS), a Chart to Monitor Verbal and Behavioral Violence in Children, the Parental Attitude Scale and the Parent Interview Form. This quasi-experimental study that included a pretest, posttest, and control group had a sample comprising 67 children and parents, with 36 in the experimental group, and 31 in the control group.
Results Over a six-month period, while the social skill scores of the children in the experimental and control groups increased, their violent behaviors decreased (
p <.050). Increase in social skill scores and decrease in violent behaviors were higher in the experimental than in the control group children (p <.050). The parents in the experimental group stated that they had started to empathize with their children, using “I” language, and applied rules more consistently after the program.Conclusion This program was successful in preventing violent behaviors in children through the development of social skills. Hence, it can be effectively implemented through a teacher/nurse collaboration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cultural diversity in parental physical discipline and children's early social skill development: cross-lagged models in Japan and China
Zhu Zhu, Xiang Li, Tokie Anme
Child Abuse & Neglect.2025; 167: 107607. CrossRef - Effects of School-Based Interventions Implemented by Nurses for Children Aged 3-6 Years: A Systematic Review of Experimental Evidence
Gökçe Algül, Ebru Kılıçarslan
SDÜ Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Cultural diversity in parental physical discipline and children's early social skill development: cross-lagged models in Japan and China
- 2,048 View
- 23 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- The Effect of the Intergenerational Exchange Program for Older Adults and Young Children in the Community Using the Traditional Play
- Min-Jung Choi, Kyeong-Yae Sohng
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):743-753. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.743
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to explore the effects of a community-based first and third Intergenerational Exchange Program (IGEP) on older adults’ health-related quality of life (HRQoL), loneliness, depression, and walking speed, and on 4~5-year-old preschool children's learning-related social skills.
Methods This study employed a non-equivalent control group pre-post-test design. The experimental group included 42 older adults and 42 children who participated in the IGEP for 8 weeks, and the control group included 39 older adults. The experimental group participated in the IGEP once a week for 8 weeks. It comprised a traditional play program based on the intergroup contact theory.
Results Compared to the control group, there was a significant increase in scores on the HRQoL-Visual analogue scale (VAS) and a decrease in loneliness and depression in older adults in the experimental group (
p <.05). Children who participated in the IGEP showed an improvement in their learning-related social skills (p <.001).Conclusion These results confirm that the IGEP is an effective intervention to improve HRQoL-VAS, loneliness, and depression among older adults and learning-related social skills among preschool children in the community.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Intergenerational Interaction on Older Adults Depends on Children’s Developmental Stages; Observational Evaluation in Facilities for Geriatric Health Service
Rie Fukuoka, Shinji Kimura, Toru Nabika
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(1): 836. CrossRef - Intergenerational Taekwondo Program: A Narrative Review and Practical Intervention Proposal
Yongseop Kim, Junhyoung Kim, Jung-Min Lee, Dong-Chul Seo, Hyun Chul Jung
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(9): 5247. CrossRef - A Qualitative Study Exploring Negative Affect in Older Adults Residing in Long-Term Care Facilities
Zhen Chen, Hongxia Zhang, Jinhua Zhang, Suqing Li, Yanmei Zhao
Research and Theory for Nursing Practice.2022; 36(3): 301. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Intergenerational Interaction on Older Adults Depends on Children’s Developmental Stages; Observational Evaluation in Facilities for Geriatric Health Service
- 1,597 View
- 47 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Symptom Distress and Coping in Young Korean Breast Cancer Survivors: The Mediating Effects of Social Support and Resilience
- Ji Hyun Lee, Hye Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):241-253. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to test the mediating effect of social support and resilience on the relationship between symptom distress and coping in young Korean breast cancer survivors.
Methods A purposive sample of 209 young breast-cancer survivors (mean age 39.9) was recruited for a cross-sectional survey, and the data were collected between June and October 2015. The instruments used in this study were the Memorial Symptom Assessment Scale-Short Form, the Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support, 10-item Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale, and Cancer Coping Questionnaire. The collected data were then analyzed using the SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 23.0 programs.
Results Symptom distress was found to have a significant indirect effect on coping (beta=-.32,
p =.002), but not a significant direct effect (beta=.06,p =.577). Additionally, based on the values obtained for the squared multiple correlation, symptom distress, social support, and resilience were found to explain 46.4% of the total variance of coping.Conclusion Based on the results of this study, it can be suggested that in order to enhance young breast cancer survivors’ ability to cope with the distress they commonly feel, intervention methods that strengthen resilience and provide social support should be developed and made available to them.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sexual well-being in cancer care services: the role of body image and coping strategies
Judith Partouche-Sebban, Saeedeh Rezaee Vessal, Youssef Souak, Aymen Ammari, Alain Toledano
Journal of Services Marketing.2026; : 1. CrossRef - How Online Patient-Provider Communication Alleviates Psychological Distress Among Patients with Chronic Diseases: The Role of Perceived Patient-Centered Communication and Adaptive Coping Strategies
Bingqing Ling, Yu Zheng
Health Communication.2025; 40(8): 1559. CrossRef - Factors Associated With Not Returning to Work Among Breast Cancer Survivors
Leni Merdawati, Hui-Chen Lin, Chieh-Hsin Pan, Hui-Chuan Huang
Workplace Health & Safety.2025; 73(5): 216. CrossRef - Factors affecting resilience among young breast cancer survivors: A cross-sectional study
Hye Young Min, Yoonjung Kim, Hae Jeong An
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 75: 102837. CrossRef - Latent classes of health‐promoting lifestyle in breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in China: A cross‐sectional survey
Meixuan Song, Qiuyao He, Juan Yang, Jinyu Zhang
Nursing Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Postmastectomy Pain Syndrome: A Narrative Review
Sajad Ahmad Salati, Lamees Alsulaim, Mariyyah H Alharbi, Norah H Alharbi, Thana M Alsenaid, Shoug A Alaodah, Abdulsalam S Alsuhaibani, Khalid A Albaqami
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the CALM intervention on resilience in Chinese patients with early breast cancer: a randomized trial
Shaochun Liu, Runze Huang, Anlong Li, Sheng Yu, Senbang Yao, Jian Xu, Lingxue Tang, Wen Li, Chen Gan, Huaidong Cheng
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2023; 149(20): 18005. CrossRef - Perceived social support and depressive symptoms in Chinese patients with ovarian cancer and the mediating role of resilience:a cross-sectional study
Xiaoyan Pang, Fangmei Li, Lei Dou, Yichang Tian, Yi Zhang
Current Psychology.2023; 42(24): 20485. CrossRef - Resilience-related Breast Cancer: A Concept Analysis
Fitria Endah Janitra, Nur Aini, Anggi Lukman Wicaksana
Nurse Media Journal of Nursing.2023; 13(1): 31. CrossRef - Factors influencing the coping strategies of liver cancer patients undergoing transarterial chemoembolization
Su‐Chih Chen, Shu‐Fang Wu, Tsae‐Jyy Wang, John Rosenberg, Yu‐Ying Lu, Shu‐Yuan Liang
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Perceived social support and coping style as mediators between resilience and health-related quality of life in women newly diagnosed with breast cancer: a cross-sectional study
Kaina Zhou, Fan Ning, Xiao Wang, Wen Wang, Dongfang Han, Xiaomei Li
BMC Women's Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Determinants of quality of life in women immediately following the completion of primary treatment of breast cancer: A cross-sectional study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ji Young Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae, Ka Ming Chow
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(10): e0258447. CrossRef - A Mobile Healing Program Using Virtual Reality for Sexual Violence Survivors: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study
Mi‐ran Lee, Chiyoung Cha
Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing.2021; 18(1): 50. CrossRef - Factors related to the resilience and mental health of adult cancer patients: a systematic review
Saori Tamura, Kumi Suzuki, Yuri Ito, Akiko Fukawa
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(7): 3471. CrossRef - Resilience in women with breast cancer: A systematic review
Ibane Aizpurua-Perez, Joana Perez-Tejada
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 49: 101854. CrossRef - Individual resilience in adult cancer care: A concept analysis
Dan Luo, Manuela Eicher, Kate White
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2020; 102: 103467. CrossRef - Relationship between cancer stigma, social support, coping strategies and psychosocial adjustment among breast cancer survivors
No Eul Kang, Hye Young Kim, Ji Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2020; 29(21-22): 4368. CrossRef - Effects of cyclic adjustment training delivered via a mobile device on psychological resilience, depression, and anxiety in Chinese post-surgical breast cancer patients
Kaina Zhou, Jin Li, Xiaomei Li
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2019; 178(1): 95. CrossRef
- Sexual well-being in cancer care services: the role of body image and coping strategies
- 1,974 View
- 22 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Effects of Self-directed Feedback Practice using Smartphone Videos on Basic Nursing Skills, Confidence in Performance and Learning Satisfaction
- Seul Gi Lee, Yun Hee Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(2):283-292. Published online April 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.2.283
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to verify effects of a self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos on nursing students' basic nursing skills, confidence in performance and learning satisfaction.
Methods In this study an experimental study with a post-test only control group design was used. Twenty-nine students were assigned to the experimental group and 29 to the control group. Experimental treatment was exchanging feedback on deficiencies through smartphone recorded videos of nursing practice process taken by peers during self-directed practice.
Results Basic nursing skills scores were higher for all items in the experimental group compared to the control group, and differences were statistically significant ["Measuring vital signs" (t=-2.10,
p =.039); "Wearing protective equipment when entering and exiting the quarantine room and the management of waste materials" (t=-4.74,p <.001) "Gavage tube feeding" (t=-2.70,p =.009)]. Confidence in performance was higher in the experimental group compared to the control group, but the differences were not statistically significant. However, after the complete practice, there was a statistically significant difference in overall performance confidence (t=-3.07.p =.003). Learning satisfaction was higher in the experimental group compared to the control group, but the difference was not statistically significant (t=-1.67,p =.100).Conclusion Results of this study indicate that self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos can improve basic nursing skills. The significance is that it can help nursing students gain confidence in their nursing skills for the future through improvement of basic nursing skills and performance of quality care, thus providing patients with safer care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Challenges in educating nursing students on mechanical ventilation: the case for interactive mobile learning tools – a randomized controlled trial
Alireza Samimi Sarangi, Kolsoum Deldar, Ahmad Bagheri Moghaddam, Razieh Froutan
BMC Nursing.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Expanding virtual reality simulation with reflective learning to improve mental health nursing skills of undergraduate nursing students
Sun Kyung Kim, Mihyun Lee, Youngho Lee, Younghye Go, Mi Hyeon Park
Education and Information Technologies.2025; 30(7): 8541. CrossRef - The impact of training using six thinking hats versus video training on nursing students’ insulin administration skills: a mixed-methods study
Ayşe Soylu, Ahmet Seven, Dilek Soylu
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of flipped learning and mobile learning methods on nursing students’ knowledge, skills and self-efficacy in urinary catheterization: A randomized controlled trial
Ozan Konateke, Hakime Aslan
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 89: 104593. CrossRef - Effect of a Hybrid Simulation-based Patient Safety Education Program on Patient Safety Knowledge, Attitudes, Performance Confidence and Decision-Making Abilities in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Hyun-Sook Jeong, Mi Yang Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 432. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Nursing Clinical Practice Education Using M-Learning
Sungeun Kim, Mihae Im
Healthcare.2024; 12(2): 206. CrossRef - Development and Effects of Metaverse-Based Intradermal Injection Content for Nursing Students
Min-Kweon Ahn
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2024; 25(9): 2543. CrossRef - Dental hygienists' knowledge, performance confidence and awareness of importance of assessing oral cancer risk factors
Boguen Lee, Sojung Mun
International Journal of Dental Hygiene.2024; 22(4): 998. CrossRef - The Development and Effects of Metaverse-based Core Nursing Skill Contents (CNSC) for Nursing Students: Drainage Management
Min Kweon Ahn, Min Jeong Chae
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(4): 447. CrossRef - Akıllı Telefon Bağımlılığı ve Ruh Hali Düzenlemenin Akış Deneyimi Aracılığı ile Çevrimiçi Anlık Satın Alma Davranışındaki Rolü
Özsev Berk, Remzi Altunışık, Nilgün Sarıkaya
Abant Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi.2024; 24(2): 780. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a virtual reality application‐based education programme on patient safety management for nursing students: A pre‐test–post‐test study
Jae Woo Oh, Ji Eun Kim
Nursing Open.2023; 10(12): 7622. CrossRef - Clinical Practice Experience of Nursing Students in the Context of the COVID-19 Pandemic
Hyeon-Young Kim, Eun-Hye Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(1): 45. CrossRef - The development and effects of metaverse-based core nursing skill contents of vital signs measurements and subcutaneous injections for nursing students
Min Kweon Ahn
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 378. CrossRef - Development and application of a mobile-based multimedia nursing competency evaluation system for nursing students: A mixed-method randomized controlled study
Soyoung Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh
Nurse Education in Practice.2022; 64: 103458. CrossRef - Effects of a Self-Directed Clinical Practicum on Self-Confidence and Satisfaction with Clinical Practicum among South Korean Nursing Students: A Mixed-Methods Study
Hyangjin Park, Haeryun Cho
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(9): 5231. CrossRef - Effects of mobile learning for nursing students in clinical education: A meta-analysis
Bin Chen, Yan Wang, Lei Xiao, Changxia Xu, Yuan Shen, Qin Qin, Cheng Li, Fengqin Chen, Yufei Leng, Ting Yang, Zhiling Sun
Nurse Education Today.2021; 97: 104706. CrossRef - Interactive and non-interactive e-learning in prenatal care
Mehrnaz Geranmayeh, Zinat Keshtkar Bareghany, Mitra Zolfghari, Farahnaz Azizi
British Journal of Midwifery.2021; 29(10): 564. CrossRef - The Effects of Video Instruction on Neuroscience Intensive Care Unit Nursing Skills in Case Presentations and Neurological Examinations
K. H. Vincent Lau, Emily Hamlyn, Thomas James Williams, M. Mustafa Qureshi, Kimberly Mak, Asim Mian, Anna Cervantes-Arslanian, Shuhan Zhu, Courtney Takahashi
Journal of Neuroscience Nursing.2021; 53(3): 129. CrossRef - Development, Application, and Effectiveness of a Smart Device-based Nursing Competency Evaluation Test
Soyoung Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2021; 39(11): 634. CrossRef - Effects of Education on the Use of Personal Protective Equipment for Reduction of Contamination: A Randomized Trial
Jeong Hwa Yeon, Yong Soon Shin
SAGE Open Nursing.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of video feedback system on medical students’ perception of their clinical performance assessment
Bee Sung Kam, So Jung Yune, Sang Yeoup Lee, Sun Ju Im, Sun Yong Baek
BMC Medical Education.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Nursing Students' Peer Feedback Types and Emotional Response, Quality of Feedback, and Self-efficacy for Learning from Peer Feedback in Skill Training
Young A Park, Eun Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(2): 186. CrossRef - Effects of Smartphone-Based Mobile Learning in Nursing Education: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Ju Hee Kim, Hanjong Park
Asian Nursing Research.2019; 13(1): 20. CrossRef - Nursing students' experiences of using a smart phone application for a physical assessment course: A qualitative study
Li‐Ling Hsu, Hsiu‐Chuan Hsiang, Yi‐Hua Tseng, Siang‐Yun Huang, Suh‐Ing Hsieh
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2019; 16(2): 115. CrossRef - Effect of Learning Core Fundamental Nursing Skill with Social Network Service (SNS) for Nursing Students in South Korea
HyeSun Jeong, Hyuksoo Kwon, Jeonghwa Kum
EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of an Interactive Nursing Skills Mobile Application on Nursing Students' Knowledge, Self-efficacy, and Skills Performance: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Hyunsun Kim, Eunyoung E. Suh
Asian Nursing Research.2018; 12(1): 17. CrossRef - Trends and research issues of mobile learning studies in nursing education: A review of academic publications from 1971 to 2016
Ching-Yi Chang, Chiu-Lin Lai, Gwo-Jen Hwang
Computers & Education.2018; 116: 28. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Education Program Using Video Recording and Feedback on Skill Competency for Students of Majors in Health Care: A Meta-Analysis
Yun Hee Shin, Sun Kyung Kim, Hyunjoo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2018; 25(2): 120. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Self-directed Learning on Competency in Physical Assessment, Academic Self-confidence and Learning Satisfaction of Nursing Students
Yun Hee Shin, Jihea Choi, Margaret J. Storey, Seul Gi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2017; 24(3): 181. CrossRef - The Effect of Smartphone Video Educational Program on Educational Satisfaction of Patients in Rehabilitation Units at a University Hospital
Kyeong- Man Jung, Min-Cheol Joo, Yu-Jin Jung, Hee-Han Kim, Kyeong-Hwa Lee, Dong-Sun Lee, Jun-Wan Choi
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2017; 23(1): 43. CrossRef - A Study on Nursing Students’ Knowledge, Attitude, Confidence in Performance and Behavior of Patient Safety
Suk-Hyun SON, Jeong Sook PARK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2017; 29(4): 1043. CrossRef
- Challenges in educating nursing students on mechanical ventilation: the case for interactive mobile learning tools – a randomized controlled trial
- 1,608 View
- 28 Download
- 31 Crossref

- Development and Effects of Emotional Intelligence Program for Undergraduate Nursing Students: Mixed Methods Research
- Oi Sun Lee, Mee Ock Gu
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(6):682-696. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.6.682
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to develop and test the effects of an emotional intelligence program for undergraduate nursing students.
Methods The study design was a mixed method research. Participants were 36 nursing students (intervention group: 17, control group: 19). The emotional intelligence program was provided for 4 weeks (8 sessions, 20 hours). Data were collected between August 6 and October 4, 2013. Quantitative data were analyzed using Chi-square, Fisher's exact test, t-test, repeated measure ANOVA, and paired t-test with SPSS/WIN 18.0. Qualitative data were analyzed using content analysis.
Results Quantitative results showed that emotional intelligence, communication skills, resilience, stress coping strategy, and clinical competence were significantly better in the experimental group compared to the control group. According to the qualitative results, the nursing students experienced improvement in emotional intelligence, interpersonal relationships, and empowerment, as well as a reduction in clinical practice stress after participation in the emotional intelligence program.
Conclusion Study findings indicate that the emotional intelligence program for undergraduate nursing students is effective and can be recommended as an intervention for improving the clinical competence of undergraduate students in a nursing curriculum.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research trends and effectiveness analysis of social and emotional learning programs for adult learners: A scoping review
Yoon-ju Lee, Insook Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2025; 31(3): 299. CrossRef - Emotional Intelligence, Academic Motivation, and Achievement among Health Science Students in Saudi Arabia: A Self-Deterministic Approach
Rasha Mohammed Mahrous, Bussma Ahmed Bugis, Samiha Hamdi Sayed
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 571. CrossRef - A Literature Review of Simulation-Based Nursing Education in Korea
Sumee Oh, Jungmin Park
Nursing Reports.2023; 13(1): 506. CrossRef - The Effects of a Non-Technical Skills Training Program on Emotional Intelligence and Resilience in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Diana Jiménez-Rodríguez, María del Mar Molero Jurado, María del Carmen Pérez-Fuentes, Oscar Arrogante, Nieves Fátima Oropesa-Ruiz, José Jesús Gázquez-Linares
Healthcare.2022; 10(5): 866. CrossRef - Development and effects of a high-risk pregnancy emotive role-play program for nursing students: a quasi-experimental study
Bo Gyeong Lee, Sun-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(4): 317. CrossRef - The development and effects of an emotional competency promotion program for nursing students: A nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design
Hyewon Kang, Jeongyee Bae
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(4): 369. CrossRef - Understanding the relationships among emotional exhaustion, job satisfaction, and emotional intelligence of hotel front desk employees
Kwang-Hi Park, Dae-Kwan Kim
Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research.2021; 26(5): 504. CrossRef - The assessment of emotional intelligence in social care and healthcare student selection: a qualitative descriptive study
Anne Pienimaa, Kirsi Talman, Elina Haavisto
Educational Research.2021; 63(3): 302. CrossRef - Social–Emotional Competence and Academic Achievement of Nursing Students: A Canonical Correlation Analysis
Sun-Hee Kim, Sujin Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(4): 1752. CrossRef - The Influences of Nursing Professionalism and Emotional Intelligence on the Clinical Performance Ability in Nursing Students
Hyo-Won Kim, Myung-Sook Yoo
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2020; 14(2): 41. CrossRef - Impact of emotional development intervention program on subjective well-being of university students
Konstanze Schoeps, Usue de la Barrera, Inmaculada Montoya-Castilla
Higher Education.2020; 79(4): 711. CrossRef - The Reliability and Validity of Korean Version of Wong and Law Emotional Intelligence Scale (K-WLEIS)
Harim Jeong, Heejung Choi, Myungsook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(4): 611. CrossRef - Influence of Metacognition and Emotional Intelligence on Self-leadership in Nursing Students
Myoung Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2019; 25(2): 146. CrossRef - The Effect of an Empathy Education Program on Nursing Students' Empathy Ability, Interpersonal Ability, and Caring
Jin Ok Jeong, Sue Kim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(3): 344. CrossRef - The Effects of Emotional Labor on Job Satisfaction of Hotel Employees: Analyzing Moderating Effects of Emotional Intelligence
Kwang-Hi Park
Stress.2018; 26(3): 166. CrossRef - Effects of Communication Empowerment Program Based on Situated Learning Theory for Nursing Students
Soo Jin Kim, Boyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(6): 708. CrossRef - The level of emotional intelligence in undergraduate students of nursing
Ľudmila Majerníková, Andrea Obročníková
Pielegniarstwo XXI wieku / Nursing in the 21st Century.2017; 16(1): 25. CrossRef - Relationships between Personal Traits, Emotional Intelligence, Internal Marketing, Service Management, and Customer Orientation in Korean Outpatient Department Nurses
Bogyun Kim, Jia Lee
Asian Nursing Research.2016; 10(1): 18. CrossRef - Vocational Identity and Ego Identity Status in Korean Nursing Students
Hyun-Young Koo, Eun-Jung Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2016; 10(1): 68. CrossRef - Effects of Discipline-based Career Course on Nursing Students' Career Search Self-efficacy, Career Preparation Behavior, and Perceptions of Career Barriers
Soonjoo Park
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(3): 259. CrossRef - Influence of Emotional Intelligence and Ego Resilience on Interpersonal Relationship of Nurses
Oi Sun Lee, Mee Ock Gu, Mi Jung Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(6): 3902. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Stress on Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Burnout among Nursing College Students
Chung Mee Ko
Journal of the Korean Society of School Health.2015; 28(3): 239. CrossRef
- Research trends and effectiveness analysis of social and emotional learning programs for adult learners: A scoping review
- 1,641 View
- 43 Download
- 22 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


