Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 46(2); 2016 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effects of Self-directed Feedback Practice using Smartphone Videos on Basic Nursing Skills, Confidence in Performance and Learning Satisfaction
- Seul Gi Lee, Yun Hee Shin
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2016;46(2):283-292.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.2.283
Published online: April 29, 2016
1Department of Nursing, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Shin, Yun Hee. Department of Nursing, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, 20 Ilsan-ro, Wonju 26426, Korea. Tel: +82-33-741-0387, Fax: +82-33-743-9490, yhshin@yonsei.ac.kr
© 2016 Korean Society of Nursing Science
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NoDerivs License. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/) If the original work is properly cited and retained without any modification or reproduction, it can be used and re-distributed in any format and medium.
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was done to verify effects of a self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos on nursing students' basic nursing skills, confidence in performance and learning satisfaction.
-
Methods
- In this study an experimental study with a post-test only control group design was used. Twenty-nine students were assigned to the experimental group and 29 to the control group. Experimental treatment was exchanging feedback on deficiencies through smartphone recorded videos of nursing practice process taken by peers during self-directed practice.
-
Results
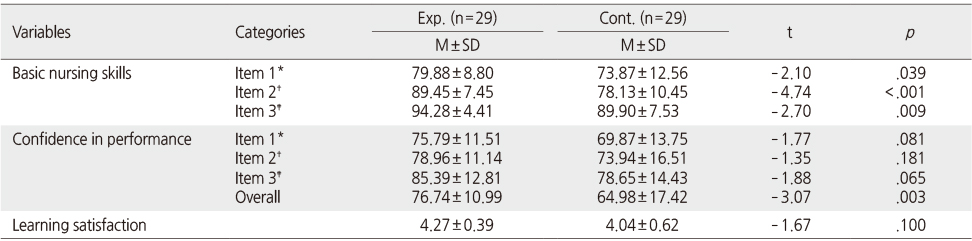
- Basic nursing skills scores were higher for all items in the experimental group compared to the control group, and differences were statistically significant ["Measuring vital signs" (t=-2.10, p=.039); "Wearing protective equipment when entering and exiting the quarantine room and the management of waste materials" (t=-4.74, p<.001) "Gavage tube feeding" (t=-2.70, p=.009)]. Confidence in performance was higher in the experimental group compared to the control group, but the differences were not statistically significant. However, after the complete practice, there was a statistically significant difference in overall performance confidence (t=-3.07. p=.003). Learning satisfaction was higher in the experimental group compared to the control group, but the difference was not statistically significant (t=-1.67, p=.100).
-
Conclusion
- Results of this study indicate that self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos can improve basic nursing skills. The significance is that it can help nursing students gain confidence in their nursing skills for the future through improvement of basic nursing skills and performance of quality care, thus providing patients with safer care.
This manuscript is a condensed form of the first author's master's thesis from Yonsei University.
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
- 1. Kitajima Y, Nakamura M, Maeda J, Kanai-Pak M, Aida K, Huang Z, et al. Robotics as a tool in fundamental nursing education. In: Duffy VG, editor. Digital human modeling Applications in health, safety, ergonomics and risk management. Cham, CH: Springer International Publishing; 2014. p. 392–402.
- 2. Suwan N, Kasatpibal N, Sawasdisingha P. Effects of student-centered teaching on knowledge, practice, and satisfaction of clean techniques among second year nursing students. Singapore Nurs J. 2013;40(4):30–37.
- 3. Choi SH, So HS, Choi JY, Yoo SH, Yun SY, Kim MH, et al. Comparison of blended practicum combined e-learning between cooperative and individual learning on learning outcomes. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2014;20(2):341–349. Article
- 4. Korean Accreditation Board of Nursing Education. The accreditation nursing education: Core basic nursing skills protocol [Internet]. Seoul, Author. 2014;cited 2015 February 16. Available from: http://www.kabone.or.kr/HyAdmin/upload/goodFile/120140117153430.pdf
- 5. Paik HJ. Educational evaluation of competency in nursing skills through open laboratory self-directed practice. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2004;11(1):13–20.
- 6. Kim HS. A study on relationship between stress of clinical practice and clinical competency in nursing students. J Korea Community Health Nurs Acad Soc. 2002;16(1):64–76.
- 7. Song S. The effect of self-evaluation method using video recording on competency in nursing skills, self-directed learning ability, problem solving ability and academic self-efficacy [master's thesis]. Seoul, Sungshin Women's University. 2013.
- 8. Shin EJ. A study related to self-efficacy, satisfaction with practice and fundamentals of nursing practicum. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2008;15(3):380–386.
- 9. Jho MY. Effects of core fundamental nursing skills education on self-efficacy, clinical competence and practice satisfaction in nursing students. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2014;21(3):292–301.Article
- 10. Cheon EY. The effects of video-aided peer feedback on enhancing nursing students' understanding of foley catheterization. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2013;19(1):43–51. Article
- 11. Cardoso AF, Moreli L, Braga FT, Vasques CI, Santos CB, Carvalho EC. Effect of a video on developing skills in undergraduate nursing students for the management of totally implantable central venous access ports. Nurse Educ Today. 2012;32(6):709–713. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Bashir GMM, Rahaman A, Galib SM, Rahaman MM. Smart phone based social networking for teaching & learning. Int J Comput Sci Mob Comput. 2014;3(4):151–155.
- 13. Park HG. A study on the smart learning service for smart phone [master's thesis]. Seoul, Konkuk University. 2011.
- 14. Kim YH. Satisfaction with evaluation method for fundamental nursing practical skill education through cell phone animation self-monitoring and feedback: Focus on foley catheterization. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2008;15(2):134–142.
- 15. Yeun EJ. Effectiveness of video-record method on fundamental nursing skill education: Focused on intramuscular injection practice. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 1999;5(1):86–96.
- 16. Ji YR, Chung HM. Effects of case-based learning on task achievement and learning satisfaction in the university class. J Learner Cent Curriculum Instr. 2014;14(9):243–265.
- 17. Park WW, Ko SK. Procedures and methods of multilevel analysis: With a focus on WABA. Seoul J Bus. 2005;39(1):59–90.
- 18. McKenny K. Using an online video to teach nursing skills. Teach Learn Nurs. 2011;6(4):172–175. Article
- 19. Farquharson AL, Cresswell AC, Beard JD, Chan P. Randomized trial of the effect of video feedback on the acquisition of surgical skills. Br J Surg. 2013;100(11):1448–1453. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 20. Yoo MS, Son YJ, Kim YS, Park JH. Video-based self-assessment: Implementation and evaluation in an undergraduate nursing course. Nurse Educ Today. 2009;29(6):585–589. ArticlePubMed
- 21. Grant JS, Moss J, Epps C, Watts P. Using video-facilitated feedback to improve student performance following high-fidelity simulation. Clin Simul Nurs. 2010;6(5):e177–e184. Article
- 22. Park IH, Shin S. The effects of video-based peer assisted learning in standardized patients simulation: Pre and post operative care. Korean J Adult Nurs. 2015;27(1):73–82. ArticlePDF
- 23. Kang KS. Effectiveness of video-record method on fundamental nursing skill education: Focused on enema. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 1996;3(2):273–283.
- 24. Hong SH, Kwon YS. Nursing student's practice scores, confidence and satisfaction in fundamentals of nursing according to teaching method for self-directed practice. Keimyung J Nurs Sci. 2010;14(1):1–10.
- 25. Kim YH. Nursing students' performance and confidence in basic nursing skills after the completion of clinical practice: Focused on basic nursing skills of low performance [master's thesis]. Daegu, Keimyung University. 2002.
- 26. Bowden T, Rowlands A, Buckwell M, Abbott S. Web-based video and feedback in the teaching of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Nurse Educ Today. 2012;32(4):443–447. ArticlePubMed
- 27. Eröz-Tu B. Reflective feedback sessions using video recordings. ELT J. 2012;67(2):175–183. Article
- 28. Ryoo EN, Park YS, Ha EH. Outcomes and satisfaction of simulationbased learning in nursing of patient with UGI bleeding. Korea Acad Ind Coop Soc. 2013;14(3):1274–1282. Article
- 29. Han KS, Park EH, Cho JY. An inquiry into subjectivity of fundamental nursing practice attitude. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2000;30(3):682–693.ArticlePDF
- 30. Shen W. Using video recording system to improve student performance in high-fidelity simulation. In: Li S, Jin Q, Jiang X, Park JJ, editors. Frontier and future development of information technology in medicine and education. Dordrecht, NL: Springer Netherlands; 2013. p. 1753–1757.
- 31. Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service. Hira-SDA & Hira-RoB [Internet]. Seoul, Author. 2011;cited 2015 June 17. Available from: http://www.hira.or.kr/dummy.do?pgmid=HIRAA030067030000&cmsurl=/cms/medi_info/08/02/03/1205728_27027.html&subject=임상연구문헌분류도구및비뚤림위험평가도구Hira-SDA&Hira-RoB)#none
REFERENCES
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; Item 1=Measuring vital sign; Item 2=Wearing protective equipment when entering and exiting the quarantine room and the management of waste materials; Item 3=Gavage tube feeding.
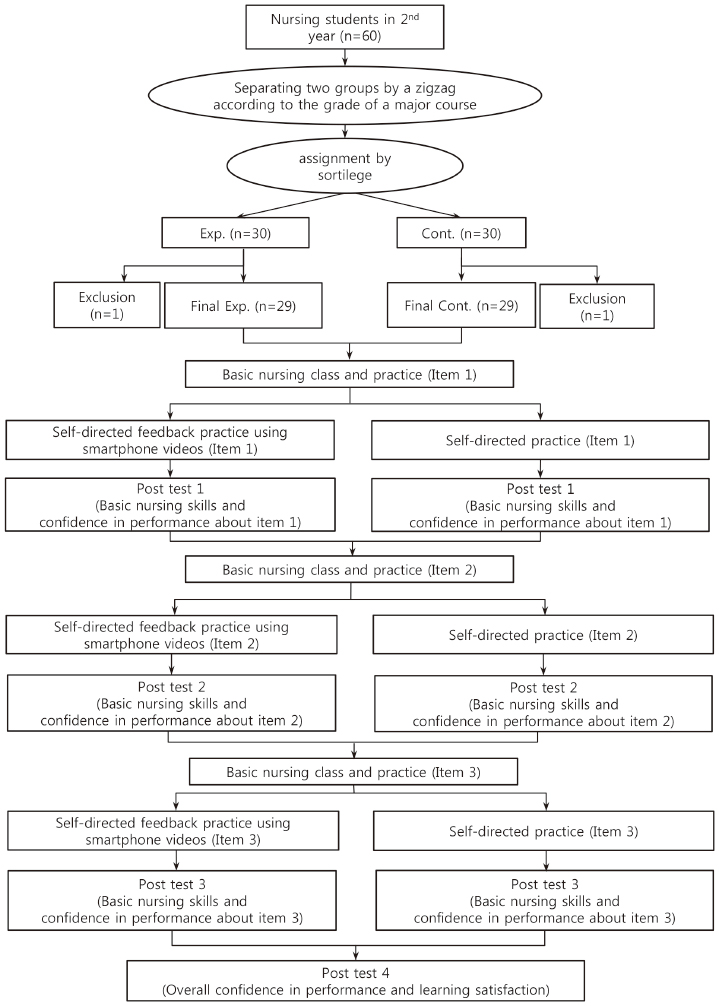
Study Design

Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; X1=Self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos; X2=Self-directed practice; E 1=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Measuring vital sign' after self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos; C1=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Measuring vital sign' after self-directed practice; E2=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Wearing protective equipment when entering and exiting the quarantine room and the management of waste materials' after self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos; C2=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Wearing protective equipment when entering and exiting the quarantine room and the management of waste materials' after self-directed practice; E3=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Gavage tube feeding' after self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos; C3=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Gavage tube feeding' after self-directed practice; E4=Overall confidence in performance and learning satisfaction after self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos; C4=Overall confidence in performance and learning satisfaction after self-directed practice
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Challenges in educating nursing students on mechanical ventilation: the case for interactive mobile learning tools – a randomized controlled trial
Alireza Samimi Sarangi, Kolsoum Deldar, Ahmad Bagheri Moghaddam, Razieh Froutan
BMC Nursing.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Expanding virtual reality simulation with reflective learning to improve mental health nursing skills of undergraduate nursing students
Sun Kyung Kim, Mihyun Lee, Youngho Lee, Younghye Go, Mi Hyeon Park
Education and Information Technologies.2025; 30(7): 8541. CrossRef - The impact of training using six thinking hats versus video training on nursing students’ insulin administration skills: a mixed-methods study
Ayşe Soylu, Ahmet Seven, Dilek Soylu
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of flipped learning and mobile learning methods on nursing students’ knowledge, skills and self-efficacy in urinary catheterization: A randomized controlled trial
Ozan Konateke, Hakime Aslan
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 89: 104593. CrossRef - Effect of a Hybrid Simulation-based Patient Safety Education Program on Patient Safety Knowledge, Attitudes, Performance Confidence and Decision-Making Abilities in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Hyun-Sook Jeong, Mi Yang Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 432. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Nursing Clinical Practice Education Using M-Learning
Sungeun Kim, Mihae Im
Healthcare.2024; 12(2): 206. CrossRef - Development and Effects of Metaverse-Based Intradermal Injection Content for Nursing Students
Min-Kweon Ahn
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2024; 25(9): 2543. CrossRef - Dental hygienists' knowledge, performance confidence and awareness of importance of assessing oral cancer risk factors
Boguen Lee, Sojung Mun
International Journal of Dental Hygiene.2024; 22(4): 998. CrossRef - The Development and Effects of Metaverse-based Core Nursing Skill Contents (CNSC) for Nursing Students: Drainage Management
Min Kweon Ahn, Min Jeong Chae
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(4): 447. CrossRef - Akıllı Telefon Bağımlılığı ve Ruh Hali Düzenlemenin Akış Deneyimi Aracılığı ile Çevrimiçi Anlık Satın Alma Davranışındaki Rolü
Özsev Berk, Remzi Altunışık, Nilgün Sarıkaya
Abant Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi.2024; 24(2): 780. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a virtual reality application‐based education programme on patient safety management for nursing students: A pre‐test–post‐test study
Jae Woo Oh, Ji Eun Kim
Nursing Open.2023; 10(12): 7622. CrossRef - Clinical Practice Experience of Nursing Students in the Context of the COVID-19 Pandemic
Hyeon-Young Kim, Eun-Hye Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(1): 45. CrossRef - The development and effects of metaverse-based core nursing skill contents of vital signs measurements and subcutaneous injections for nursing students
Min Kweon Ahn
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 378. CrossRef - Development and application of a mobile-based multimedia nursing competency evaluation system for nursing students: A mixed-method randomized controlled study
Soyoung Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh
Nurse Education in Practice.2022; 64: 103458. CrossRef - Effects of a Self-Directed Clinical Practicum on Self-Confidence and Satisfaction with Clinical Practicum among South Korean Nursing Students: A Mixed-Methods Study
Hyangjin Park, Haeryun Cho
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(9): 5231. CrossRef - Effects of mobile learning for nursing students in clinical education: A meta-analysis
Bin Chen, Yan Wang, Lei Xiao, Changxia Xu, Yuan Shen, Qin Qin, Cheng Li, Fengqin Chen, Yufei Leng, Ting Yang, Zhiling Sun
Nurse Education Today.2021; 97: 104706. CrossRef - Interactive and non-interactive e-learning in prenatal care
Mehrnaz Geranmayeh, Zinat Keshtkar Bareghany, Mitra Zolfghari, Farahnaz Azizi
British Journal of Midwifery.2021; 29(10): 564. CrossRef - The Effects of Video Instruction on Neuroscience Intensive Care Unit Nursing Skills in Case Presentations and Neurological Examinations
K. H. Vincent Lau, Emily Hamlyn, Thomas James Williams, M. Mustafa Qureshi, Kimberly Mak, Asim Mian, Anna Cervantes-Arslanian, Shuhan Zhu, Courtney Takahashi
Journal of Neuroscience Nursing.2021; 53(3): 129. CrossRef - Development, Application, and Effectiveness of a Smart Device-based Nursing Competency Evaluation Test
Soyoung Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2021; 39(11): 634. CrossRef - Effects of Education on the Use of Personal Protective Equipment for Reduction of Contamination: A Randomized Trial
Jeong Hwa Yeon, Yong Soon Shin
SAGE Open Nursing.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of video feedback system on medical students’ perception of their clinical performance assessment
Bee Sung Kam, So Jung Yune, Sang Yeoup Lee, Sun Ju Im, Sun Yong Baek
BMC Medical Education.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Nursing Students' Peer Feedback Types and Emotional Response, Quality of Feedback, and Self-efficacy for Learning from Peer Feedback in Skill Training
Young A Park, Eun Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2019; 25(2): 186. CrossRef - Effects of Smartphone-Based Mobile Learning in Nursing Education: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Ju Hee Kim, Hanjong Park
Asian Nursing Research.2019; 13(1): 20. CrossRef - Nursing students' experiences of using a smart phone application for a physical assessment course: A qualitative study
Li‐Ling Hsu, Hsiu‐Chuan Hsiang, Yi‐Hua Tseng, Siang‐Yun Huang, Suh‐Ing Hsieh
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2019; 16(2): 115. CrossRef - Effect of Learning Core Fundamental Nursing Skill with Social Network Service (SNS) for Nursing Students in South Korea
HyeSun Jeong, Hyuksoo Kwon, Jeonghwa Kum
EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of an Interactive Nursing Skills Mobile Application on Nursing Students' Knowledge, Self-efficacy, and Skills Performance: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Hyunsun Kim, Eunyoung E. Suh
Asian Nursing Research.2018; 12(1): 17. CrossRef - Trends and research issues of mobile learning studies in nursing education: A review of academic publications from 1971 to 2016
Ching-Yi Chang, Chiu-Lin Lai, Gwo-Jen Hwang
Computers & Education.2018; 116: 28. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Education Program Using Video Recording and Feedback on Skill Competency for Students of Majors in Health Care: A Meta-Analysis
Yun Hee Shin, Sun Kyung Kim, Hyunjoo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2018; 25(2): 120. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Self-directed Learning on Competency in Physical Assessment, Academic Self-confidence and Learning Satisfaction of Nursing Students
Yun Hee Shin, Jihea Choi, Margaret J. Storey, Seul Gi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2017; 24(3): 181. CrossRef - The Effect of Smartphone Video Educational Program on Educational Satisfaction of Patients in Rehabilitation Units at a University Hospital
Kyeong- Man Jung, Min-Cheol Joo, Yu-Jin Jung, Hee-Han Kim, Kyeong-Hwa Lee, Dong-Sun Lee, Jun-Wan Choi
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2017; 23(1): 43. CrossRef - A Study on Nursing Students’ Knowledge, Attitude, Confidence in Performance and Behavior of Patient Safety
Suk-Hyun SON, Jeong Sook PARK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2017; 29(4): 1043. CrossRef
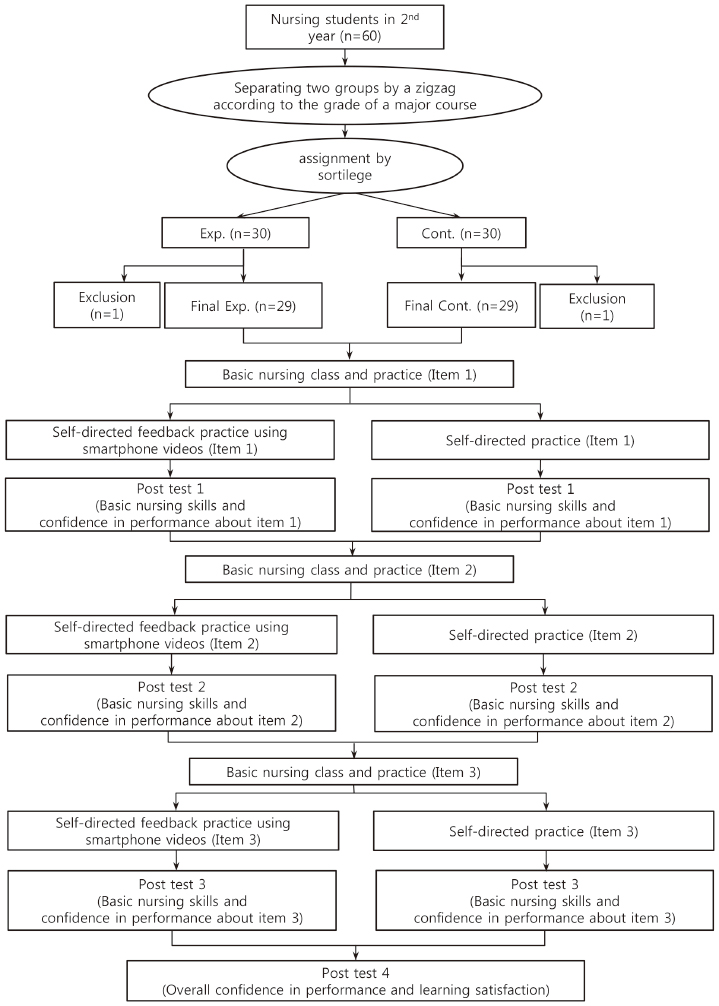
Figure 1
Study Design
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; X1=Self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos; X2=Self-directed practice; E 1=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Measuring vital sign' after self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos; C1=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Measuring vital sign' after self-directed practice; E2=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Wearing protective equipment when entering and exiting the quarantine room and the management of waste materials' after self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos; C2=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Wearing protective equipment when entering and exiting the quarantine room and the management of waste materials' after self-directed practice; E3=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Gavage tube feeding' after self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos; C3=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Gavage tube feeding' after self-directed practice; E4=Overall confidence in performance and learning satisfaction after self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos; C4=Overall confidence in performance and learning satisfaction after self-directed practice
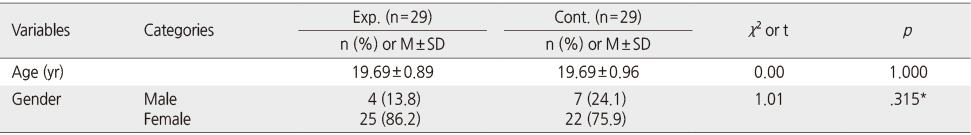
Homogeneity between the Experimental and Control Group (N=58)
*Fisher's exact test; Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
Comparisons between the Experimental and Control Group (N=58)
*Measuring vital sign; †Wearing protective equipment when entering and exiting the quarantine room and the management of waste materials; ‡Gavage tube feeding; Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; X1=Self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos; X2=Self-directed practice; E 1=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Measuring vital sign' after self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos; C1=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Measuring vital sign' after self-directed practice; E2=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Wearing protective equipment when entering and exiting the quarantine room and the management of waste materials' after self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos; C2=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Wearing protective equipment when entering and exiting the quarantine room and the management of waste materials' after self-directed practice; E3=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Gavage tube feeding' after self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos; C3=Basic nursing skills and confidence in performance of 'Gavage tube feeding' after self-directed practice; E4=Overall confidence in performance and learning satisfaction after self-directed feedback practice using smartphone videos; C4=Overall confidence in performance and learning satisfaction after self-directed practice
*Fisher's exact test; Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
*Measuring vital sign; †Wearing protective equipment when entering and exiting the quarantine room and the management of waste materials; ‡Gavage tube feeding; Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

