Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effects of presenteeism on turnover intention in clinical nurses through the serial mediating roles of missed nursing care and job satisfaction: a cross-sectional predictive correlational study
- Hyeonseon Cheon, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyung Kim, Hyoung Eun Chang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):584-597. Published online November 10, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25015
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
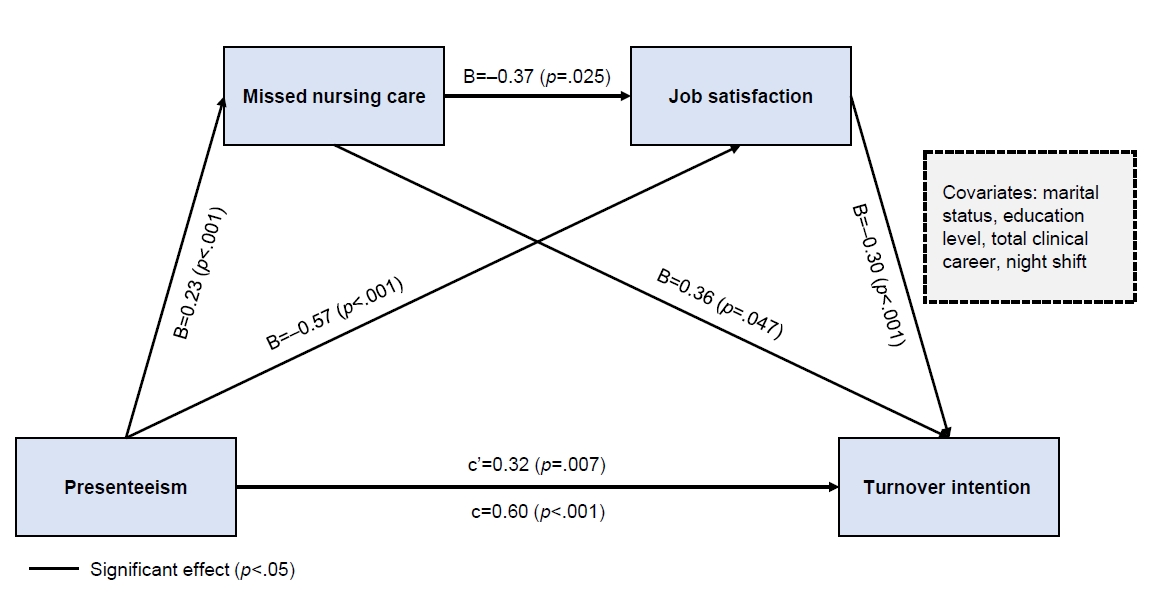
This study aimed to investigate the two-mediator serial mediation effect of missed nursing care and job satisfaction on the relationship between presenteeism and turnover intention in clinical nurses.
Methods
A cross-sectional predictive correlational study was conducted, and the participants were 208 clinical nurses working in advanced general hospitals in South Korea. Data were collected from October 6 to November 7, 2023 using self-reported questionnaires, including general characteristics, presenteeism, missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS/WIN ver. 29.0 and PROCESS macro ver. 4.2.
Results
Missed nursing care and job satisfaction exhibited a double mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. In addition, missed nursing care showed a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Job satisfaction had a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Presenteeism had a direct effect on missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Missed nursing care exerted a direct effect on job satisfaction and turnover intention among clinical nurses. Job satisfaction had a direct effect on turnover intention.
Conclusion
To reduce nurses’ turnover intention, it is essential to develop and implement programs focused on preventing presenteeism. Additionally, organizational initiatives should prioritize active support for nurses’ health management, alleviating the shortage of nursing staff, augmenting job satisfaction, and improving the overall working environment.
- 1,540 View
- 217 Download

- Effects of Leadership Styles of Nursing Managers on Turnover Intention of Hospital Nurses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Yunjeong Cho, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Young Man Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(5):479-498. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22039
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine effect sizes of leadership styles of nursing managers on turnover intention of hospital nurses.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the PRISMA and MOOSE guidelines. Participants were nurses working in hospitals. The intervention involved nursing managers’ leadership styles; the outcome assessed was nurses’ turnover intention. This was an observational study design. Eleven databases were searched to obtain articles published in Korean or English. Of the 14,428 articles reviewed, 21 were included in systematic review and meta-analysis. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis and R software programs were used.
Results
The total effect size r (ESr) was - 0.25 (95% confidence interval: - 0.29 to - 0.20). Effect sizes of each leadership style on turnover intention were as follows: ethical leadership (ESr = - 0.34), transformational leadership (ESr = - 0.28), authentic leadership (ESr = - 0.23), transactional leadership (ESr = - 0.21), and passive avoidant leadership (ESr = 0.13). Ethical leadership was the most effective style in decreasing turnover intention of hospital nurses.
Conclusion
Positive leadership styles of nurse managers effectively decrease turnover intention of hospital nurses, and negative leadership styles of nurse managers effectively increase turnover intention of hospital nurses. The ethical leadership style is the most effective in decreasing turnover intention of hospital nurses; however, it requires careful interpretation as its effects are reported by only two studies. This study contributes to addressing the high turnover rate of hospital nurses and developing positive leadership styles of nurse managers in hospital settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of organizational communication and grit on turnover intention of rehabilitation hospital nurses: A cross-sectional correlation study
Inji Ha, Heeok Park, Ji Hun Joung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(1): 35. CrossRef - Influence of Leadership Styles on Turnover Intentions in Technology Startups
Sheeza Fayyaz, Saima Majeed
Journal of Professional & Applied Psychology .2025; 6(1): 36. CrossRef - Protecting Workers From Rude Customers to Enhance Organizational Identification in Emotional Labor Environments: A Study With Call Center Agents
Hyojeong Kim, Nagesh N Murthy, Anurag Agarwal, Kwangtae Park
Production and Operations Management.2025; 34(10): 3250. CrossRef - Humanistic nursing care management strategies: from formulation to implementation
Jing Lv, Yajie Su, Hongmei Tang, Xiaolin Jiang, Xiaojuan Chen
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - When Leadership Drives Nurses Away: Empirical Research Qualitative on High Turnover Rates Reasons
Saleem Al‐Rjoub
Nursing Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between different leadership styles of nursing managers and nurses’ turnover intention in hospitals: an integrative review
Alicia Jimenez-Caceres, Anna Agusti-Boada, Conxi Caro-Benito, Olga Monistrol
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Structured Subjective Readiness in Situational Leadership: Validating the 4D Model as an Associative Predictor
Dino Giergia, Nikola Drašković, Mario Fraculj
Administrative Sciences.2025; 15(12): 488. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Leader-Member Exchange on the Ethical Leadership of Nursing Unit Managers and Turnover Intention of Clinical Nurses: A Nationwide Survey using Proportional Quota Sampling
Jihun Kim, Sunmi Kim, Nara Han, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(1): 42. CrossRef - Effects of Resilience, Nursing Managers’ Empowering Leadership on Turnover Intention among New Nurses: Mediating role of Transition Shock
Hyun Jin Jung, Hyun Kyung Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 212. CrossRef - Investigation of the relationship between nurses' perception of toxic leadership and their organizational trust levels and turnover intentions
Sultan Türkmen Keskin, Meltem Özduyan Kiliç
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2024; 80(5): 1859. CrossRef - The structural relationship of job stress, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention among youth sports education leaders in Korea
Myung Kyu Jung, Tae Gyeom Jung, Min Woo Jeon, Ji Hae Lee
Frontiers in Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Patient Safety Management System, Leadership, and Communication Types on Nurse’ Patient Safety Management Activities
Eunji Lee, Haejung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 367. CrossRef - Nursing-sensitive Indicators in East Asian Hospitals: A Scoping Review
Jae Jun Lee, Won Jin Seo, Dong Ah Park, Hwa Yeong Oh, Seung Eun Lee
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2024; 30(2): 88. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nurses Turnover in Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Review
Abdulmajeed M. Albalawi, Glezzeelyne P. Pascua, Sameer A. Alsaleh, Walaa Sabry, Sitti Nursa Ahajan, Jeseela Abdulla, Amal Abdulalim, Suad S. Salih, Sulaiman Al Sabei
Nursing Forum.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Unit Managers’ Authentic Leadership, Transformational Leadership, and Transactional Leadership on Turnover Intention in Advanced Beginner Nurses: Mediation Effects of Positive Psychological Capital
Eun Jeong Kim, Eungyung Kim, Son Ja Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 409. CrossRef - Factors related to the organizational silence of Korean nurses: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Kyungja Kang, Jeong-Hee Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(3): 302. CrossRef
- The effect of organizational communication and grit on turnover intention of rehabilitation hospital nurses: A cross-sectional correlation study
- 7,755 View
- 491 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref

- Relationships among Non-Nursing Tasks, Nursing Care Left Undone, Nurse Outcomes and Medical Errors in Integrated Nursing Care Wards in Small and Medium-Sized General Hospitals
- Ju-Young Park, Jee-In Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(1):27-39. Published online February 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the degree of non-nursing tasks and nursing care left undone in integrated nursing care wards, and examine their relationships with nurses’ burnout, job satisfaction, turnover intentions, and medical errors.
Methods
A cross-sectional questionnaire survey was conducted. Data were collected using self-report questionnaires from 346 nurses working in 20 wards of seven small and medium-sized general hospitals, and analyzed using multiple regression and multiple logistic regression analysis with the SPSS WIN 25.0 program.
Results
The mean score for non-nursing tasks was 7.32±1.71, and that for nursing care left undone was 4.42 ± 3.67. An increase in non-nursing tasks (β = .12, p = .021) and nursing care left undone (β = .18, p < .001) led to an increase in nurses’ burnout (F = 6.26, p < .001). As nursing care left undone (β = .13, p = .018) increased, their turnover intentions also (F = 3.96, p < .001) increased, and more medical errors occurred (odds ratio 1.08, 95% confidence interval 1.02~1.15).
Conclusion
Non-nursing tasks and nursing care left undone are positively associated with nurses’ burnout, turnover intentions, and the occurrence of medical errors. Therefore, it is important to reduce non-nursing tasks and nursing care left undone in order to deliver high quality nursing care and in turn increase patient safety. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- First Integration of a Service Robot and a Communication Application into a Nursing Isolation Setting – An Observational Study Evaluating Walking Distances, Stress and Radiation Doses
Angelika Warmbein, Laura Sehn, Ivanka Rathgeber, Janesca Seif, Christoph Ohneberg, Nicole Stöbich, Astrid Delker, Christian Zach, Inge Eberl, Uli Fischer
International Journal of Social Robotics.2025; 17(9): 1809. CrossRef - Effects of a mobile simulation program for nursing delegation: A randomised controlled trial
Haena Lim, Yeojin Yi
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 83: 104283. CrossRef - Study of Nurses' Malpractice Tendencies and Burnout Levels
Leman Şenturan, Gizem Kaya, Tuba Emirtaş
Research in Nursing & Health.2025; 48(3): 385. CrossRef - The relationship between job stress and the perception of patient safety culture among Palestinian hospital nurses
Loai M. Zabin, Jamal Qaddumi, Sajed Faisal Ghawadra
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Grit, Teamwork, Organizational Communication Competence, Perception of Patient Safety Culture on Patient Safety Nursing Activities in Integrated Nursing Care Units
Jeeseon Kim, Haejung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 237. CrossRef - Non-Value-Added Activities and Non-Nursing Tasks Affecting Nursing Task Efficiency: A Scoping Review
Mi Ha Chung, Yongah Kim, Na Yeong Kim, Min Ju Kim, Hyeon Jin Kim, Ju Hee Park, Ji In Park, Su Yeon Bae, Heajin Bae, Eunjeong Lee, Min Young Jeon, Suyoung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 405. CrossRef - Relationships bewteen Non-nursing Tasks, Missed Nursing Care, Patient Safety Nursing Activities, and Medical Errors in Nurses
Tae-Ryun Lee, Jee-In Hwang
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2025; 31(2): 2. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Care Left Undone by Cancer Ward Nurses
Chung Hee Woo, Yeon Joo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 594. CrossRef - A phenomenological study of the experiences of nurses working in integrated nursing care wards in Korea
Young-mi Cho, Sun-hui Kim
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationships among Nursing Skill Mix, Missed Nursing Care, and Adverse Events in Small and Medium-Sized Hospital Comprehensive Nursing Care Wards
Yoon Sook Cho, Hyoung Eun Chang, Hyunjung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(2): 163. CrossRef - Exploring the causes and consequences of non-nursing tasks among nurses in Jordan: An in-depth qualitative investigation
Ayman Abed Aldarawsheh, Ahmad Rajeh Saifan, Murad Adnan Sawalha, Enas A. Assaf, Intima Alrimawi, Rami A. Elshatarat, Zyad T. Saleh, Wesam T. Almagharbeh, Nermen A. Mohamed, Mudathir M. Eltayeb
Applied Nursing Research.2024; 77: 151791. CrossRef - Influence of Work Environment, Missed Nursing Care, and Non-Nursing Tasks of Hospital Nurses on Job Stress
Ji Yeong Park, Kyoung Ja Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 246. CrossRef - A comparative analysis of nurses' reported number of patients and perceived appropriate number of patients in integrated nursing care services
Hyunjeong Kwon, Jinhyun Kim
Nursing & Health Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a virtual reality application‐based education programme on patient safety management for nursing students: A pre‐test–post‐test study
Jae Woo Oh, Ji Eun Kim
Nursing Open.2023; 10(12): 7622. CrossRef - The Effect of Missed Nursing Care on Adverse Event Experiences, Patient Safety Management Activity, Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention in Nurses: A Nationwide Survey using Proportional Quota Sampling
Myung Jin Choi, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 490. CrossRef - Pathway Analysis on the Effects of Nursing Informatics Competency, Nursing Care Left Undone, and Nurse Reported Quality of Care on Nursing Productivity among Clinical Nurses
Mi Yu, Se Young Kim, Ji Min Ryu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(2): 236. CrossRef - Competency Survey of Caregivers in Medical Tourism Special Zone and Other Regions
Dong-Yeop Lee, Sang-Bong Lee, Yeong-Im Park, Jin-Geun Lee, Yoon Hee Park, So Young Lee, Dong-Yoon Kang
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(2): 140. CrossRef - Influence of the Team Effectiveness of Nursing Units on Nursing Care Left Undone and Nurse-Reported Quality of Care
Se Young Kim, Young Ko
Healthcare.2023; 11(10): 1380. CrossRef - The Impact of Performance of Non-Nursing Tasks on the Attitudes of Nursing Students toward Nursing Profession
Ibrahim Rawhi Ayasreh, Ferial Hayajneh, Rana Al Awamleh
Nurse Media Journal of Nursing.2022; 12(2): 151. CrossRef - Clinical Application Value of Group‐Sharing Nursing Management Based on Case Analysis
Jing Mei, Yifan Wu, Jie Hu, Min Li, Mohammad Farukh Hashmi
Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Burnout on Quality of Care Using Donabedian’s Framework
Kathleen M. White, Dorothy Dulko, Bonnie DiPietro
Nursing Clinics of North America.2022; 57(1): 115. CrossRef - Emotional Labor, Burnout, Medical Error, and Turnover Intention among South Korean Nursing Staff in a University Hospital Setting
Chan-Young Kwon, Boram Lee, O-Jin Kwon, Myo-Sung Kim, Kyo-Lin Sim, Yung-Hyun Choi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(19): 10111. CrossRef - Integrated and Person-Centered Nursing in the Era of the 4th Industrial Revolution
Hyoung Suk Kim, Sun Joo Jang, Jeung-Im Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(3): 261. CrossRef - Analysis of Nurses' Work Experience in Comprehensive Nursing Care Units of Small and Medium-sized Hospitals
Mi Ryeong Song, Su Hyang Ryu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(4): 419. CrossRef
- First Integration of a Service Robot and a Communication Application into a Nursing Isolation Setting – An Observational Study Evaluating Walking Distances, Stress and Radiation Doses
- 4,326 View
- 194 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 24 Crossref

- The Influence of Grit on Turnover Intention of University Hospital Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Job Involvement
- Ji Yeong Jeong, Youn Sook Seo, Jung Hoon Choi, Seong Hee Kim, Min Sook Lee, Sung Hwa Hong, Jung Suk Choi, Da Eun Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(2):181-190. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.2.181
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study aimed to confirm the mediating effect of job involvement in the relationship between grit and turnover intention among nurses working at university hospitals.
Methods Participants included 437 nurses from university hospitals located in C city, Gyeongnam. Data were collected from January 8 to 19, 2018, using self-report questionnaires. Data were analyzed using the t-test, analysis of variance, Scheffe's test, Pearson's correlation coefficient, and multiple regression, with the SPSS/22.0 program. A mediation analysis was performed according to the Baron and Kenny, and bootstrapping methods.
Results There were significant relationships between grit and job involvement (r=.40,
p <.001), grit and turnover intention (r=−.29,p <.001), and turnover intention and job involvement (r=−.52,p <.001). Job involvement showed partial mediating effects in the relationship between grit and turnover intention.Conclusion Grit increased job involvement and lowered turnover intention. Therefore, to reduce nurses' turnover intention, it is necessary to develop a program and strategies to increase their grit.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Workplace Spirituality and Self‐Efficacy on Quality of Life Among Cancer Survivors: Empirical Quantitative Research
Seulgi Kang, Yoonjung Kim, Hyeji Shin
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025; 81(5): 2438. CrossRef - Mediating effect of grit on the influence of nurses’ silence behavior on medication safety competence: a cross-sectional study
Haengsuk Kim, Wanju Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(1): 81. CrossRef - Success doesn’t come to you, you go to it: the role of self-perceived employability among engineering graduates
Arun Aggarwal, Amit Mittal, Ishani Sharma, Pawan Kumar Chand, Amruta Deshpande
Industrial and Commercial Training.2025; 57(4): 361. CrossRef - The associations of grit, self-leadership, and followership with competency in evidence-based practice among nurses in Korea: a descriptive correlational study
Ha-young Kim, Jin-il Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(2): 244. CrossRef - Effects of Grit and Nursing Work Environment on Work Engagement in Clinical Nurses
Young Ju Kim, Hye Young Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(3): 312. CrossRef - Exploring personal, community, and societal conditions associated with South Korean new graduate nurses’ organizational socialization: a cross-sectional survey study
Jihye Song, Jeongsuk Lee, Youmin Cho, Ahyoung Jeon, Moonhee Gang
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Free Will Belief and Nurses’ Job Performance: The Mediating Roles of Grit and Positive Affect
Wei Liu, Song Wang
International Nursing Review.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Attitude Toward Interdepartmental Transfer, Career Growth Opportunity, and Role Breadth Self-Efficacy on Job Crafting among Nurses with Transfer Experience
Yu Jin Lee, Chung Hee Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 497. CrossRef - Effects of Grit and Retention Intention on Work Performance among Operating Room Nurses
Ae-Kyung Jang, Jun-Hee Lee, Kyeong-Soo Lee, Tae-Yoon Hwang
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2025; 39(3): 381. CrossRef - Effects of grit, calling, and resilience on the retention intention of general hospital nurses
Gi Ran Lee, Imsun Lee, Mihee Chung, Jiyeon Ha
International Nursing Review.2024; 71(4): 766. CrossRef - Relationship between the sense of nursing professional pride and adversity quotient, grit levels among nurses in blood purification centers: a multicenter cross-sectional study
Wenbin Xu, Lin Li, Qian Jiang, Yiqian Fang, Qian Yang
Frontiers in Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Experiences of Newly Graduated Nurses Trained by Clinical Nurse Educators
Yeon Hee Kim, Young Sun Jung, Kyoung Hui Lee, Eun Ji Chang
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2024; 9(1): 34. CrossRef - The influence of grit on nurse job satisfaction: Mediating effects of perceived stress and moderating effects of optimism
Cui Yang, Lu Yang, Dongmei Wu
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of grit on the work engagement of nurses: The mediating effects of positive psychological capital and burnout
Mi Kyung Park, Won Hwa Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(2): 161. CrossRef - Grit among Nursing Students at Private Nursing Institute of Karachi Pakistan
Muhammad Ishaq, Afsha Bibi, Fazal Khaliq, Ashfaq Ahmad
Pakistan Journal of Health Sciences.2023; : 115. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Grit on the Relationship between Work Environment and Intention to Stay at Work among Regional Trauma Center Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study
Ji Sun Yang, Myung Jin Jang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(2): 107. CrossRef - Similarity in functional connectome architecture predicts teenage grit
Sujin Park, Daeun Park, M Justin Kim
Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Gratitude Disposition, Social Support, and Occupational Stress of Clinical Nurses on Grit
Ha-Na Lee, Hwee Wee
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(1): 56. CrossRef - Effects of Nurses' Grit on the Nursing Performance: Multiple Mediating Effects of Work Engagement and Job Crafting
Jeong-Lim Ryu, So-Hyoung Hong, Yoon Seo Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 468. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Nurse Retention Intention: With a Focus on Shift Nurses in South Korea
Eun-Young Cho, Hwee Wee
Healthcare.2023; 11(8): 1167. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Passion Continuation Program based on GRIT Theory for Nurses in COVID-19 Pandemic: A Non-Randomized Experimental Study
Do-Young Lee, Nam-Joo Je, Yoon Jung Kim, Chunseon Jang, Hyun-Ju Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2023; 30(3): 357. CrossRef - Antecedents and Consequences of Grit Among Working Adults: A Transpersonal Psychology Perspective
Devanshi Agrawal, Surekha Chukkali, Sabah Singh
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a scale to measure the psychological resources of grit in adults
Sarah E. Schimschal, Denis Visentin, Rachel Kornhaber, Tony Barnett, Michelle Cleary
Nursing & Health Sciences.2022; 24(3): 752. CrossRef - Effect of Nurses’ Grit on Nursing Job Performance and the Double Mediating Effect of Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment
Hyun-Kuk Cho, Boyoung Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(2): 396. CrossRef - An Exploratory Study on the Mediating Effect of Clinical Competence in the Relationship Between Grit and Field Adaptation in Newly Graduated Nurses
Eunhee Shin
SAGE Open Nursing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Pediatric nurses' grit and nursing intention during the COVID-19 pandemic: Mediating and moderating effects of mindset and psychological collectivism
Young Soo Chu, Won-Oak Oh, Il Tae Park, Anna Lee, Myung-Jin Jung
Child Health Nursing Research.2021; 27(4): 395. CrossRef - Grit and Meaning in Life of Chinese Nurses: The Chain Mediating Effect of Social Support and Hope
Lei Yang, Dongmei Wu
Frontiers in Psychology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Grit-S in Chinese Nurses
Changjiu He, Dongmei Wu, Lu Yang, Lei Yang, Yuchuan Yue
Frontiers in Psychology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influences of Grit, Emotional Labor and Organizational Intimacy on Nurses' Intention to Stay in Comprehensive Nursing Care Service Units
Dae Yeon Lee, Sook Young Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2020; 23(2): 149. CrossRef - Studying the effects of future-oriented factors and turnover when threatened
Sean McGinley, Nathaniel Discepoli Line, Wei Wei, Taylor Peyton
International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management.2020; 32(8): 2737. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Clinical Nurses Grit Scale (CN-GRIT)
Hyosun Park, Kyungmi Lee, Nayeon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(1): 55. CrossRef - The Relationship between Occupational Stress and Burnout among Firefighters: Mediating of Grit
Yun Ah Jung, Myung Soo Oh, Hee Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2020; 29(2): 96. CrossRef - Mediation Effects of Calling and Role Breadth Self-efficacy on the Relationship between Supportive Supervision and Job Crafting of Nurses in General Hospitals
Sujeong Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(3): 251. CrossRef - Effects of Grit and Critical Thinking Disposition on Nursing Students’
Clinical Competence
Sook-Hee Cho, Kyung-Soon Yun
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2020; 14(2): 117. CrossRef - The Impact of Grit on University Student’s Core Competency in Dental Hygiene Students
Soo-Auk Park, Young-Sik Cho
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2019; 19(3): 170. CrossRef
- The Effects of Workplace Spirituality and Self‐Efficacy on Quality of Life Among Cancer Survivors: Empirical Quantitative Research
- 2,548 View
- 73 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 35 Crossref

- The Effects of Hospitals’ Family Friendly Management on Married Female Nurses’ Retention Intention: Focused on the Mediating Effects of Work-Family Interface
- Jin Hwa Lee, Jee-In Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):386-397. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.386
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study examined the effect of hospitals’ family-friendly management on married female nurses’ retention intention. The focus was the mediating effects of the work-family interface (work-family conflict, work-family enrichment and work-family balance).
Methods This study was a cross-sectional study. The participants were 307 nurses working at five public and five private hospitals with more than 200 beds in Seoul. Data were collected using structured questionnaires from September 10 to September 17, 2018 and analyzed with SPSS 24.0. Data were analyzed using an independent t-test, a one-way ANOVA, Pearson's correlation coefficients, and multiple regression following the Baron and Kenny method and Sobel test for mediation.
Results There were significant correlations among family-friendly management, the work-family interface, and retention intention. Work-family conflict showed a partial mediating effect on the relationship between family-friendly management and retention intention. Work-family enrichment showed a partial mediating effect on the relationship between family-friendly management and retention intention. Work-family balance showed a partial mediating effect on the relationship between family-friendly management and retention intention.
Conclusion These findings indicate that both hospitals’ family-friendly management and nurses’ work-family interface are important factors associated with nurses’ retention intention. Therefore, hospitals should actively implement family-friendly management for nurses and establish strategies to enhance nurses’ work-family interface for effective human resource management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How parenting-related characteristics influence parenting stress among nurses with young children in the Seoul metropolitan area, South Korea: a cross-sectional study
Minhwa Hwang, Nagyeong Lee, Gunjeong Lee
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Retention Intention of Female Nurses Raising Young and School-Age Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Ha Neul Lee, Suyon Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 504. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of Instruments Measuring Dyadic Communication and Environment in Dementia Care: A Systematic Review
Sohyun Kim, Wen Liu, Patricia Heyn
The Gerontologist.2023; 63(1): 52. CrossRef - Disaster Preparedness and Associated Factors Among Emergency Nurses in Guangdong Province, China: A Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study
Jia Wang, Xinglan Sun, Sihui Lu, Fen Wang, Meijuan Wan, Hanxi Chen, Yibing Tan
Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Causes and Effects of Burnout Experienced by Insurance Review Nurses: Focus Group Interview
Eun Sil Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyung Kim, Myoung Hee Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(5): 545. CrossRef - Nurses’ Clinical Work Experience during Pregnancy
Hyunjung Lee, Hyoung Eun Chang, Jiyeon Ha
Healthcare.2020; 9(1): 16. CrossRef
- How parenting-related characteristics influence parenting stress among nurses with young children in the Seoul metropolitan area, South Korea: a cross-sectional study
- 1,246 View
- 33 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- The Effect of Nurse's Emotional Labor on Turnover Intention: Mediation Effect of Burnout and Moderated Mediation Effect of Authentic Leadership
- Soo Yang Na, Hanjong Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(3):286-297. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.3.286
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose To investigate the effect of nurses’ emotional labor on their turnover intention that was mediated by burnout and to examine the moderated mediation effect of authentic leadership.
Methods A total of 227 nurses working at two general hospitals in Seoul were recruited from March 21 to May 6 in 2016. Emotional labor including surface acting and deep acting; burnout factors such as emotional exhaustion and personal accomplishment; and turnover intention were assessed. The data were analyzed using SPSS 22.0 and SPSS PROCESS macro.
Results Surface acting significantly increased emotional exhaustion and reduced personal accomplishment. Deep acting significantly increased personal accomplishment. Emotional exhaustion significantly increased turnover intention. Conversely, personal accomplishment significantly reduced turnover intention. Surface acting had an indirect effect on turnover intention that was mediated by emotional exhaustion. Deep acting had an indirect effect on turnover intention that was mediated by personal accomplishment. Authentic leadership had a moderated mediation effect on the relationship between surface acting and turnover intention that was mediated by emotional exhaustion.
Conclusion The findings of this study indicate that the establishment of strong authentic leadership by head nurses would help nurses reduce their burnout and turnover intention. Conducting intervention studies would be also important to promote better work environments that would enable nurses to fortify the positive aspect of emotional labor and to reduce their burnout levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigation of professional values education's effect on pediatric nurses' perception of professional values, emotional labour behaviours and burnout levels: A randomised controlled trial
Nazmiye Yirik, Şerife Tutar
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2026; 87: 99. CrossRef - Effect of a Nursing Practice Environment, Nursing Performance on Retention Intention: Focused on the Mediating Effects of Nursing Professional Pride
Shin Hee Kim, Mi Sook Oh, Yun Bok Kwak
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(1): 64. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Burnout of Nurses in Comprehensive Nursing Care Service Wards: Focusing on Positive Psychological Capital, Role Conflict, and Authentic Leadership
Jung Wha Park, Kyoung Ja Kim, Ji Young Im, Ji Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(4): 345. CrossRef - The Relationship between School Managers' Authentic Leadership Behaviors and Teachers' Emotional Labor Behaviors
Mehmet Akif Köse, Esra Töre
İZÜ Eğitim Dergisi.2024; 6(1): 1. CrossRef - Servant leadership and nurses' deep acting: a moderated mediation model
Shu-Chen Susan Chang, Anyi Chung, Shu Yu Chen, Chu Yen Lin, I-Heng Chen
Journal of Organizational Change Management.2024; 37(3): 546. CrossRef - Association between Emotional Labor and Work Absence Due to Dental Treatment in Korean Workers
Ji-Young Son, Se-Hwan Jung, Jae-In Ryu, Dong-Hun Han
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2024; 24(4): 350. CrossRef - Turnover intention and its related factors of clinical research coordinator in Hunan, China: a cross-sectional study
Juan Li, JinHua Li, ZhengDi She, LiWen Guo, ShanZhi Gu, Wen Lu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - How surface acting affects turnover intention among family doctors in rural China: the mediating role of emotional exhaustion and the moderating role of occupational commitment
Anqi Wang, Changhai Tang, Lifang Zhou, Haiyuan Lv, Jia Song, Zhongming Chen, Wenqiang Yin
Human Resources for Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Effect of Emotional Labor on Turnover Intention and the Moderating Role of Perceived Organizational Support: Evidence from Korean Firefighters
Jaeyoung Lim, Kuk-Kyoung Moon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(5): 4379. CrossRef - Key Factors for Enhancing Home Care Workers’ Intention to Stay by Multiple-Criteria Decision Analysis
Wei Hsu, Fang-Ping Shih
Healthcare.2023; 11(5): 750. CrossRef - The relationship between job burnout and intention to change occupation in the accounting profession: the mediating role of psychological well-being
Lum Çollaku, Muhamet Aliu, Skender Ahmeti
Management Research Review.2023; 46(12): 1694. CrossRef - The effect of organizational justice on young nurses’ turnover intention: The mediating roles of organizational climate and emotional labour
Yue Su, Zhe Jiang, Ran Meng, Guangli Lu, Chaoran Chen
Nurse Education in Practice.2023; 72: 103723. CrossRef - Authentic leadership in nurses’ professional practice: an integrative review
Ellen Daiane Biavatti de Oliviera Algeri, Rosemary Silva da Silveira, Jamila Geri Tomaschewski Barlem, Maria Claudia Medeiros Dantas de Rubim Costa, Danubia Andressa da Silva Stigger, Cristiane de Sá Dan
Revista Brasileira de Enfermagem.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of burnout and its dimensions on turnover intention among nurses: A meta‐analytic review
Ahmet Hakan Özkan
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(3): 660. CrossRef - A liderança autêntica no exercício profissional do enfermeiro: uma revisão integrativa
Ellen Daiane Biavatti de Oliviera Algeri, Rosemary Silva da Silveira, Jamila Geri Tomaschewski Barlem, Maria Claudia Medeiros Dantas de Rubim Costa, Danubia Andressa da Silva Stigger, Cristiane de Sá Dan
Revista Brasileira de Enfermagem.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of burnout and its dimensions on turnover intention among nurses: a meta-analytic review
AHmet Hakan Özkan
Kybernetes.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of professional identity, job satisfaction and burnout with turnover intention among general practitioners in China: evidence from a national survey
Tao Zhang, Jing Feng, Heng Jiang, Xin Shen, Bo Pu, Yong Gan
BMC Health Services Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Collegial surface acting emotional labour, burnout and intention to leave in novice and pre‐retirement nurses in the United Kingdom: A cross‐sectional study
Catherine Theodosius, Christina Koulouglioti, Paula Kersten, Claire Rosten
Nursing Open.2021; 8(1): 463. CrossRef - The Experience of Emotional Labor and Its Related Factors among Nurses in General Hospital Settings in Republic of Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Da-Jung Ha, Jung-Hyun Park, Su-Eun Jung, Boram Lee, Myo-Sung Kim, Kyo-Lin Sim, Yung-Hyun Choi, Chan-Young Kwon
Sustainability.2021; 13(21): 11634. CrossRef
- Investigation of professional values education's effect on pediatric nurses' perception of professional values, emotional labour behaviours and burnout levels: A randomised controlled trial
- 2,551 View
- 84 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref

- Patterns and Influential Factors of Inter-Regional Migration of New and Experienced Nurses in 2011~2015
- Bohyun Park, Se Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(5):676-688. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.5.676
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyze the migration patterns of new nurses and experienced nurses and to identify the factors influencing inter-regional migration for solving regional imbalances of clinical nurses in South Korea.
Methods This study involved a secondary analysis of data from the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA). Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and multiple logistic regression analysis.
Results New nurses tended to migrate from Kyunggi to Seoul. However, experienced nurses tended to migrate from Seoul and Chungchung to Kyunggi. Significant predictors of inter-regional migration among new nurses were location and nurse staffing grade of hospitals. Significant predictors of inter-regional migration among experienced nurses were location, hospital type, nurse staffing grade, ownership of hospitals and age of nurses.
Conclusion Inter-regional migration occupied a small portion of total hospital movement among clinical nurses. The regional imbalances of nurses were not caused by the migration from non-metropolitan areas to Seoul. Nurse shortage problems in the small and medium hospitals of the non-metropolitan area can be solved only through improvement of work environment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ideation Model for Healthcare Workforce Management in the Philippine Context
Jose Abantao, Jose Marlon Refuncion, Marife Lacaba
Journal of Interdisciplinary Perspectives.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Turnover Rates and Factors Associated With Turnover: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Retention Period of Clinical Nurses in Korea Using National Data
Yunmi Kim, Hyun-Young Kim
Policy, Politics, & Nursing Practice.2024; 25(2): 83. CrossRef - A Study on the Outflow Intention of Nursing Students in Non-Metropolitan Area: Honam Region
Purum Kang, A Young Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(3): 234. CrossRef - Impact evaluation of nurse staffing policy reform in Korea: A quasi‐experimental study
Jinseon Yi, Jinhyun Kim
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 3457. CrossRef - Re-employment Hospital Types of Early Career Nurses and Changes in Work-Life Balance
Eun-Young Kim, Yun-Kyung Oh
STRESS.2022; 30(3): 163. CrossRef - Retention Rates and the Associated Risk Factors of Turnover among Newly Hired Nurses at South Korean Hospitals: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Yunmi Kim, Hyun-Young Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(19): 10013. CrossRef - Emotional Labor Strategies, Stress, and Burnout Among Hospital Nurses: A Path Analysis
Ji‐Soo Kim
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2020; 52(1): 105. CrossRef - Nursing stress factors affecting turnover intention among hospital nurses
Eun‐Kyoung Lee, Ji‐Soo Kim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Organizational Justice, Organizational Culture and Emotional Intelligence on Intention of Retention in Reemployed Nurses
Yu Ri Jung, So Young Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 501. CrossRef - Intention to leave among staff nurses in small‐ and medium‐sized hospitals
Jeong Hye Park, Min Jung Park, Hye Young Hwang
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2019; 28(9-10): 1856. CrossRef - Why newly graduated nurses in South Korea leave their first job in a short time? A survival analysis
Eunhee Lee
Human Resources for Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nursing Students' Choices of a Place of Employment
Sun Ju You, Jong Kyung Kim, Myun Sook Jung, Se Young Kim, Eun Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2018; 18(4): 184. CrossRef
- Ideation Model for Healthcare Workforce Management in the Philippine Context
- 1,637 View
- 13 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Turnover Experience of Male Nurses
- Hyunsu Kim, Jeongseop Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(1):25-38. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.1.25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The aim of this study was to identify turnover experiences of men in nursing and to derive a substantive theory on the turnover experience of men who are nurses.
Methods Data were collected through in-depth interviews with 13 men who had worked as a nurse for 1 year or more, and had a turnover experience during that period. Collected data were analyzed on the basis of Strauss and Corbin's grounded theory.
Results The core category in the turnover experiences of the respondents was ‘seeking a stable place for me’. In the analysis of the core category, types of ‘contentment’, ‘seeking’, ‘survival’ and ‘confusion’ were identified. The sequential stages of these nurses’ turnover experience were ‘confrontation’, ‘incertitude’, ‘retrying’ and ‘realization’. However, when a problem arose in the process, they returned to the stage of confusion. Thus, these stages could occur in a circular fashion.
Conclusion These findings provide a deep understanding of the turnover experience of men in nursing and offers new information about how they adapt to nursing practice. The findings should be useful as foundational data for men who hope to become nurses and also for managers responsible for nurses who are men.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Male nurses’ adaptation experiences after turnover to community institutions in Korea: A grounded theory methodology
Ja-Sook Kim, Suhyun Kim, Hyang-In Cho Chung, Sally Mohammed Farghaly
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(5): e0302819. CrossRef - Turnover Rates and Factors Associated With Turnover: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Retention Period of Clinical Nurses in Korea Using National Data
Yunmi Kim, Hyun-Young Kim
Policy, Politics, & Nursing Practice.2024; 25(2): 83. CrossRef - A survival analysis approach to determine factors associated with non-retention of newly hired health workers in Iran
Vahid Ghavami, Seyed Saeed Tabatabaee
BMC Health Services Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing work engagement among male nurses: A structural equation model
Chao Wu, Si‐zhe Cheng, Jing Wu, Yin‐juan Zhang, Ya‐wei Lin, Lu Li, Juan Du, Yu‐hai Zhang, Hong‐juan Lang
Nursing Open.2023; 10(12): 7749. CrossRef - Turnover intention and retention of newly licensed nurses in their first job: A longitudinal study
Hyoung Eun Chang, Sung‐Hyun Cho
International Nursing Review.2023; 70(3): 338. CrossRef - Clinical Work and Life of Mid-Career Male Nurses: A Qualitative Study
Soo-Yong Shin, Eun-Ju Lim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(12): 6224. CrossRef - Analysis of Male and Female Nurses’ Attitudes toward Nurse Uniforms in South Korea: The Functional, Expressive, and Aesthetic (FEA) Framework
Seon Mi Jang, Sae Eun Lee, Jeong-Ju Yoo
International Journal of Costume and Fashion.2021; 21(1): 25. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Turnover Intention among Male Nurses in Korea
Su Ol Kim, Sun-Hee Moon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(18): 9862. CrossRef - Factors associated with the nurses’ intent to stay in China, Japan, and Korea: an integrative review
Ting Xue, Wen-Bin Jiang, Meng-Di Ma, Jie Zhang, Ming-Hui Lu, Yong-Mei Jiang
Frontiers of Nursing.2020; 7(3): 269. CrossRef - Why newly graduated nurses in South Korea leave their first job in a short time? A survival analysis
Eunhee Lee
Human Resources for Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Subjectivity About Turnover Intention Among Male Nurses in South Korea: A Q-Methodological Study
Ick-Jee Kim, Hyung-Wha Shim
Asian Nursing Research.2018; 12(2): 113. CrossRef - Win-Win Partnership in the Clinical Setting: Female Nurses' Adaptive Experience to Male Nurses
Hyunsu Kim, Eun Jin Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(5): 423. CrossRef
- Male nurses’ adaptation experiences after turnover to community institutions in Korea: A grounded theory methodology
- 2,252 View
- 23 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Association between Emotional Labor, Emotional Dissonance, Burnout and Turnover Intention in Clinical Nurses: A Multiple-Group Path Analysis across Job Satisfaction
- Chi-Yun Back, Dae-Sung Hyun, Sei-Jin Chang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(6):770-780. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.6.770
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study was conducted to investigate the influence of emotional labor, emotional dissonance, and burnout on nurse's turnover intention and examine the effect of job satisfaction on the relationships among emotional labor, emotional dissonance, burnout, and turnover intention.
Methods The sample consisted of 350 nurses recruited from 6 general hospitals in 2 cities in Korea. A multiple-group analysis was utilized. Data were analyzed using SPSS statistics 23 and AMOS 20.
Results In the path analysis, turnover intention was directly related to burnout in clinical nurses who had a high job satisfaction (b=.24,
p =.003), while it was indirectly related to emotional dissonance (b=.13,p =.002). In the multiple-group path analysis, turnover intention was directly related to emotional dissonance (b=.18,p =.033) and burnout (b=.26,p =.002) for nurses with low job satisfaction.Conclusion These results indicate that manuals and guidelines to alleviate the negative effects of emotional labor, emotional dissonance, and burnout, and to increase job satisfaction are strongly required to reduce turnover intention in nurses at the organizational level as well as at the individual level.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of work–family conflict on teachers’ turnover intention: the mediating role of emotional labor
Yang yang Zhou, Man Jiang
Cogent Education.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Resilience on the Relationship Between Job Stress and the Professional Quality of Life of Hospice and Palliative Care Nurses: A Multicenter Cross-sectional Study
Eunhee Jo, Soon-Jung Hwang, Hyang-Suk Kwon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(3): 241. CrossRef - Emotional dissonance and burnout among child welfare workers: The moderating role of social support from colleagues, supervisors, and organization
Morten Birkeland Nielsen, Håkon A. Johannessen, Jan Olav Christensen, Live Bakke Finne
Journal of Social Work.2023; 23(4): 615. CrossRef - Emotional labor and job satisfaction among nurses: The mediating effect of nurse–patient relationship
Yi-wei Xu, Ling Fan
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Professional Quality of Life, Work-Related Stress, and Job Satisfaction among Nurses in Saudi Arabia: A Structural Equation Modelling Approach
Emad Shdaifat, Noha Al-Shdayfat, Najla Al-Ansari, Jonathan Haughton
Journal of Environmental and Public Health.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - A structural equation model of organizational commitment by hospital nurses: The moderating effect of each generation through multi-group analysis
Jeong Hye Chae, Young Suk Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(3): 305. CrossRef - Emotional Labor, Burnout, Medical Error, and Turnover Intention among South Korean Nursing Staff in a University Hospital Setting
Chan-Young Kwon, Boram Lee, O-Jin Kwon, Myo-Sung Kim, Kyo-Lin Sim, Yung-Hyun Choi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(19): 10111. CrossRef - The Experience of Emotional Labor and Its Related Factors among Nurses in General Hospital Settings in Republic of Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Da-Jung Ha, Jung-Hyun Park, Su-Eun Jung, Boram Lee, Myo-Sung Kim, Kyo-Lin Sim, Yung-Hyun Choi, Chan-Young Kwon
Sustainability.2021; 13(21): 11634. CrossRef - Health-Related Symptoms and Working Conditions on Vulnerability to Presenteeism Among Nurses in South Korea
Jee-Seon Yi, Eungyung Kim, Hyeoneui Kim
Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health.2021; 33(8): 880. CrossRef - Effects of Hospital Characteristics on Employment Rate, Working Period and Retirement of Ward Nurses in Korea: A Retrospective Cohort Study Based on HIRAS Data
Hee-Jung Seo, Gi Yon Kim, Sei-Jin Chang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(6): 837. CrossRef - The Influence of Mistreatment by Patients on Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention among Chinese Nurses: A Three-Wave Survey
Lei Qi, Xin Wei, Yuhan Li, Bing Liu, Zikun Xu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(4): 1256. CrossRef - Emotional Labor Strategies, Stress, and Burnout Among Hospital Nurses: A Path Analysis
Ji‐Soo Kim
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2020; 52(1): 105. CrossRef - Nursing stress factors affecting turnover intention among hospital nurses
Eun‐Kyoung Lee, Ji‐Soo Kim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of the Tromsø Social Intelligence Scale
Sook Kyoung Park, Ya Ki Yang, Eunju Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(2): 165. CrossRef - Nurses' organizational communication satisfaction, emotional labor, and prosocial service behavior: A cross‐sectional study
Youngsoo Kim, Sun Joo Jang
Nursing & Health Sciences.2019; 21(2): 223. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Mindfulness in the Relationship between Self-Esteem and Burnout among Clinical Nurses
Hanju Bea, Heekyung Chang, Young Eun
Stress.2018; 26(3): 243. CrossRef
- The impact of work–family conflict on teachers’ turnover intention: the mediating role of emotional labor
- 1,490 View
- 35 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Influences of Hospital Nurses' perceived reciprocity and Emotional Labor on Quality of Nursing Service and Intent to Leave
- Mi-Aie Lee, Eunjeong Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(3):364-374. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.364
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was performed to investigate the relationship among reciprocity, emotional labor, nursing service quality and intent to leave, and to identify factors influencing nursing service quality and intent to leave.
Methods This study was a cross-sectional survey. Participants were 300 nurses working at five general hospitals in two provincial cities in Gyeongsang Province, Korea. From May 1 to June 30, 2014, data were collected using structured questionnaires and analyzed with SPSS/PC ver 20.0 programs.
Results There were relationships between reciprocity and nursing service quality, and intent to leave, and between emotional labor and intent to leave. Participants' general characteristics, reciprocity and emotional labor explained 48.4% of variance in nursing service quality and participants' general characteristics and these two independent variables explained 31.9% of intent to leave.
Conclusion These findings indicate that from the perception of hospital nurses, reciprocity and emotional labor are both very important factors to improve the quality of nursing service and decrease the intent to leave. So nursing managers should try to develop various personnel management programs focused on human emotions, and create a mutual respectable organizational culture and work environment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and Moderating Factors of Turnover Rate and Turnover Intention Among Nurses Worldwide: A Meta-Analysis
Dluha Mafula, Hidayat Arifin, Ruey Chen, Chien-Mei Sung, Chiu-Kuei Lee, Kai-Jo Chiang, Kondwani Joseph Banda, Kuei-Ru Chou
Journal of Nursing Regulation.2025; 15(4): 20. CrossRef - Impact of Structural Empowerment, Thriving at Work, and Caregiver Reciprocity on the Psychological Empowerment of Home Care Workers in South Korea
Heekyung Chang, Youngjoo Do, Jinyeong Ahn, Yumi Kim
Healthcare.2025; 13(15): 1809. CrossRef - Does emotional labor affect nurses suffering from workplace violence? A moderated mediation model
Hakan Erkutlu, Jamel Chafra, Hatice Ucak, Rahsan Kolutek
Journal of Aggression, Conflict and Peace Research.2024; 16(1): 28. CrossRef - Effect of Nursing Practice Environment on Intent to Leave in Hospital Nurses: Focused on the Mediating Effect of Reciprocity
So Young Lee, Mi-Aie Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 201. CrossRef - Negative emotional status and influencing factors among young employees in center of disease control and prevention
Lu Han, Qiyu Li, Yu Zhang, Tuo Liu, Ran Niu, Qi Wang, Lina Zhao
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Experience of Emotional Labor and Its Related Factors among Nurses in General Hospital Settings in Republic of Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Da-Jung Ha, Jung-Hyun Park, Su-Eun Jung, Boram Lee, Myo-Sung Kim, Kyo-Lin Sim, Yung-Hyun Choi, Chan-Young Kwon
Sustainability.2021; 13(21): 11634. CrossRef - Nurses' organizational communication satisfaction, emotional labor, and prosocial service behavior: A cross‐sectional study
Youngsoo Kim, Sun Joo Jang
Nursing & Health Sciences.2019; 21(2): 223. CrossRef - The Effect of Nurse's Emotional Labor on Turnover Intention: Mediation Effect of Burnout and Moderated Mediation Effect of Authentic Leadership
Soo Yang Na, Hanjong Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2019; 49(3): 286. CrossRef - Influences of Interpersonal Problems and Character of Nurses on Quality of Nursing Service
Eun-Yi Yeom, Kawoun Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2018; 24(5): 445. CrossRef
- Prevalence and Moderating Factors of Turnover Rate and Turnover Intention Among Nurses Worldwide: A Meta-Analysis
- 1,282 View
- 13 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Structural Equation Modeling on Nursing Productivity of Nurses in Korea
- Se Young Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Heon Man Lim, Mi Young Lee, Kwang-Ok Park, Kyoung A Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(1):20-29. Published online February 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.1.20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to propose and test a predictive model that could explain and predict nursing productivity.
Methods A survey using a structured questionnaire was conducted with 360 nurses in Korea. The data were analyzed using SPSS Windows 18.0 and AMOS 19.0 program.
Results Based on the constructed model, burnout and organizational commitment were found to have direct effects on nurses' turnover intention and nursing productivity. While nursing work environment was found to have indirect effects on nurses' turnover intention and nursing productivity.
Conclusion This structural equational model is a comprehensive theoretical model that explains the related factors and their relationship with nursing productivity. Comprehensive organizational interventions to improve nursing productivity should focus on improving the nursing work environment. Findings from this study can be used to design appropriate strategies to decrease nurse turnover in Korea. Further studies are needed to prospectively verify these causal relationships with larger samples.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of Self-Efficacy for HIV Disease Management Skills
Gwang Suk Kim, Layoung Kim, Mi-So Shim, Seoyoung Baek, Namhee Kim, Min Kyung Park, Youngjin Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(3): 295. CrossRef - Effect of Job Embeddedness on Turnover Intention of Nurses in Long Term Care Hospitals: The Mediating Effect of Nursing Work Environment
Sun Mi Ha, Yeong Ju Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2020; 26(5): 439. CrossRef - A Meta-Analytic Path Analysis on the Outcome Variables of Nursing Unit Managers' Transformational Leadership: Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(6): 757. CrossRef - Clinical nurses’ beliefs, knowledge, organizational readiness and level of implementation of evidence-based practice: The first step to creating an evidence-based practice culture
Jae Yong Yoo, Jin Hee Kim, Jin Sun Kim, Hyun Lye Kim, Jung Suk Ki, Tim Schultz
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(12): e0226742. CrossRef - Relationship among Nursing Professionalism, Nursing Work Environment, and Patient Safety Nursing Activities in General Hospital Nurses
Mi-Aie Lee, Sunjoo Kang, Hye Sun Hyun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2019; 25(4): 317. CrossRef - Influence of Emotional Intelligence, Communication, and Organizational Commitment on Nursing Productivity among Korean Nurses
Hyo Geun Geun, Eunok Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2019; 30(2): 226. CrossRef - Impact of Burnout on Organizational Outcomes, the Influence of Legal Demands: The Case of Ecuadorian Physicians
Paola Ochoa
Frontiers in Psychology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Nurses' Social Capital and Job Engagement on Nursing Performance: Focused on the Mediating effects of Organizational Citizenship Behavior
Mi Soon Ko, Hyunsook Zin Lee, Myung Suk Koh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(1): 42. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Social capital between Transformational leadership and Organizational Commitment of Nurses in Hospitals
Soon-gu Kim, Young-sook Seo
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(2): 282. CrossRef - Relationship of between Task Performance, Job Satisfaction, and Organizational Contribution of Dental Hygienists
Jun-Yeong Kwon, Su-Young Lee
Journal of dental hygiene science.2016; 16(4): 302. CrossRef - A Path Analysis of Variables Influencing customer orientation of Hospital Nurses
Eun-Su Do, Young-Sook Seo
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(1): 275. CrossRef - Nurses' Perception of Organizational Commitment, Nursing Work Environment, and Social Support in a General Hospital
Sook Bin Im, Mi Young Lee, Se Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2015; 21(1): 1. CrossRef - Literature Review of Structural Equation Models for Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention in Korea
Eunhye Kim, Jinhyun Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2014; 11(2): 109. CrossRef - Clinical Nurses' Experience of Positive Organizational Culture
Young-Hee Yom, Sang Mi Noh, Kyung Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(5): 469. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Intensive Care Units Nursing Workload
Mohammad Karim Bahadori, Ramin Ravangard, Mehdi Raadabadi, Seyed Masod Mosavi, Mohammad Gholami Fesharaki, Fardin Mehrabian
Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Hospital Nurses' Recognition of the Team System and Effects on the Nursing Organizational Team System
Kwang-ok Park, Sung Hee Park, Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(4): 414. CrossRef
- Psychometric Properties of the Korean Version of Self-Efficacy for HIV Disease Management Skills
- 1,533 View
- 10 Download
- 16 Crossref

- A Model on Turnover Intention of Chief Nurse Officers
- Kwang-Ok Park, Jong Kyung Kim, Se Young Kim, Sunju Chang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(1):9-18. Published online February 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.1.9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to test the turnover intention model for chief nurse officers in general hospitals. The variables for the study included job stress, social support, job satisfaction, and organization commitment.
Methods A predictive, non-experimental design was used with a sample of 144 chief nurse officers from 144 general hospitals. Data were collected using self-administered questionnaires and analyzed using SPSS, AMOS program.
Results The overall fitness of the hypothetical model to the data was good (χ2=16.80,
p =.052, GFI=.96, AGFI=.90, NFI=.97, CFI=.99). Job stress, social support, job satisfaction, and organization commitment explained 59.0% of the variance in turnover intention by chief nurse officers. Both organization commitment and social support directly influenced turnover intention for chief nurse officers, and job stress and job satisfaction indirectly influenced turnover intention.Conclusion The results imply that chief nurse officers in hospitals need social support and management of job stress to increase job satisfaction and organization commitment, and lower turnover intention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nurse Staffing, Work Hours, Mandatory Overtime, and Turnover in Acute Care Hospitals Affect Nurse Job Satisfaction, Intent to Leave, and Burnout: A Cross-Sectional Study
Sung-Heui Bae
International Journal of Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mediating effects of workgroup processes on the relationship between nurse turnover and nurse outcomes in hospitals
Sung-Heui Bae, Suin Kim, Hwasook Myung
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationships among Non-Nursing Tasks, Nursing Care Left Undone, Nurse Outcomes and Medical Errors in Integrated Nursing Care Wards in Small and Medium-Sized General Hospitals
Ju-Young Park, Jee-In Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(1): 27. CrossRef - Assessing the Presence of Post-Traumatic Stress and Turnover Intention Among Nurses Post–Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Outbreak: The Importance of Supervisor Support
Heeja Jung, Sun Young Jung, Mi Hyang Lee, Mi Sun Kim
Workplace Health & Safety.2020; 68(7): 337. CrossRef - The Convergence Study of Interpersonal Caring Behaviors on Anger, Job Stress and Social Support in Nurses
Jin-Ah Han, Mi-Jin Kim
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(3): 87. CrossRef - Influences of Customer Orientation, Emotional Labor, Unit Manager-nurse Exchange and Relational Bonds on Nurses' Turnover Intension
Young-Soon Kim, Kyung-Yeon Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2016; 22(4): 396. CrossRef - Literature Review of Structural Equation Models for Hospital Nurses' Turnover Intention in Korea
Eunhye Kim, Jinhyun Kim
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2014; 11(2): 109. CrossRef - Effects of Nurses' Social Capital on Turnover Intention: Focused on the Mediating Effects Organizational Commitment and Organizational Cynicism
Jeongwon Han, Heeyoung Woo, Eunsil Ju, Sohee Lim, Sangsook Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(4): 517. CrossRef - The Effects of DISC Behavior Styles of Office Workers on Job Satisfaction, Organizational Commitment and Job Performance
Yun-Young Kim, Young-Hwa Baek, Ki-Hyun Park, Jong-Hyang Yoo, Eun-Su Jang
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2012; 21(2): 98. CrossRef
- Nurse Staffing, Work Hours, Mandatory Overtime, and Turnover in Acute Care Hospitals Affect Nurse Job Satisfaction, Intent to Leave, and Burnout: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 1,201 View
- 8 Download
- 9 Crossref

- The Effect of Assertiveness Training on Communication Related Factors and Personnel Turnover Rate among Hospital Nurses
- Myung Ja Kang, Haejung Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(5):681-690. Published online August 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.5.681
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of assertiveness training on nurses' assertive behaviors, interpersonal relations, communication conflicts, conflict management style and personnel turnover rate.
Method A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used in this study. Nurses were assigned into the experimental or control groups, each consisting of 39 nurses. Data was collected between January to March 2004. An ‘Assertiveness Training Program’ for Nurses developed by Park was used for the study. To emphasize assertiveness practice, 5 practice sessions utilizing ABCDE principles were added to Park's program. To examine the effects of the program, differences between the two groups in assertive behaviors, interpersonal relations, communication conflicts, conflict management style and personnel turnover rate were analyzed using ANCOVA.
Results The assertiveness training was effective in improving the nurses' assertiveness behaviors, but was not effective in improving interpersonal relations, reducing the subjects' communication conflicts, changing the conflict management style or reducing their personnel turnover rate.
Conclusion There have been many studies about factors affecting nurses' personnel turnover rates, but few have been done about methods of intervention to reduce the personnel turnover rate. Thus, this study provides a significant contribution in attempting such an intervention from nursing management perspectives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of speak-up training programs for clinical nurses: A scoping review
Eunhee Lee, Jennie C. De Gagne, Paige S. Randall, Hyokyung Kim, Branti Tuttle
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2022; 136: 104375. CrossRef - The Experience of Emotional Labor and Its Related Factors among Nurses in General Hospital Settings in Republic of Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Da-Jung Ha, Jung-Hyun Park, Su-Eun Jung, Boram Lee, Myo-Sung Kim, Kyo-Lin Sim, Yung-Hyun Choi, Chan-Young Kwon
Sustainability.2021; 13(21): 11634. CrossRef - Assess the Level of Assertiveness among BSc Nursing Final Year Students in a Selected Nursing College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
C Sumathi, J Van Vagula Devi, V Prathiba Sivakumar
Pondicherry Journal of Nursing.2020; 13(2): 33. CrossRef - The Effect of Assertiveness Program on Clinical Competence of Intensive Care Units Nurses; A Randomized Clinical Trial
Samira Abbasi, Reza Masoudi, Leili Rabiei, Koroush Shahbazi
Avicenna Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Care.2019; 27(5): 293. CrossRef - Effects of SBAR Program on Communication Clarity, Clinical Competence and Self-efficacy for Nurses in Cancer Hospitals
Youn Hwa Kim, Yooun Sook Choi, Hye Young Jun, Myung Ja Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2016; 19(1): 20. CrossRef - Content Analysis of Communication between Nurses during Preceptorship
Yeon Ok Jeoung, Song Chol Park, Jeong Kun Jin, Joo Young Kim, Ji Uhn Lee, Soon Young Park, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2014; 23(2): 82. CrossRef - Moral Distress, Moral Sensitivity and Ethical Climate of Nurses Working in Psychiatric Wards
Dabok Noh, Sunah Kim, Sanghee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2013; 22(4): 307. CrossRef - Turnover intention of graduate nurses in South Korea
Haejung LEE, Yeonjung LIM, Hee Young JUNG, Youn‐Wha SHIN
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2012; 9(1): 63. CrossRef - Work Stress, Turnover Intention and Burnout among Nurses in Neonatal Intensive Care Units
Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2011; 17(1): 115. CrossRef - Comparison of Anger Expression, Assertive Behavior, and Self-esteem between a Nursing Student Group and an Educational Student Group
Ki-Wol Sung, Oh-Gye Kwag, Won-Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(1): 1. CrossRef - A Phenomenological Study on the Experience of Hurt and Forgiveness of Clinical Nurses in Korea after Loss of Employment
Kae-Hwa Jo, Ki-Wol Sung, Yeong-Kyeong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(4): 561. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of speak-up training programs for clinical nurses: A scoping review
- 1,275 View
- 9 Download
- 11 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


