Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Impact of an integrated disease-specific nursing care model on parental anxiety and depression in severe hypospadias patients in China: a randomized controlled trial
- Ruijuan Wu, Lucai Jia, Biyu Ding, Ying Li, Yaqing Cao, Zhaojun Shi, Yanfang Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):327-341. Published online August 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24147
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to explore the effects of an integrated disease-specific nursing care model on alleviating perioperative and post-surgical anxiety and depression in parents of children with severe hypospadias.
Methods
Parents of children with severe hypospadias were recruited and randomly allocated into a control group (n=87), which received standard nursing care, and an intervention group (n=93), which was given an integrated disease-specific nursing intervention in addition to standard care. Parental anxiety and depression were measured using the Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS) and Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS) at admission, discharge, and 6-month follow-up post-surgery.
Results
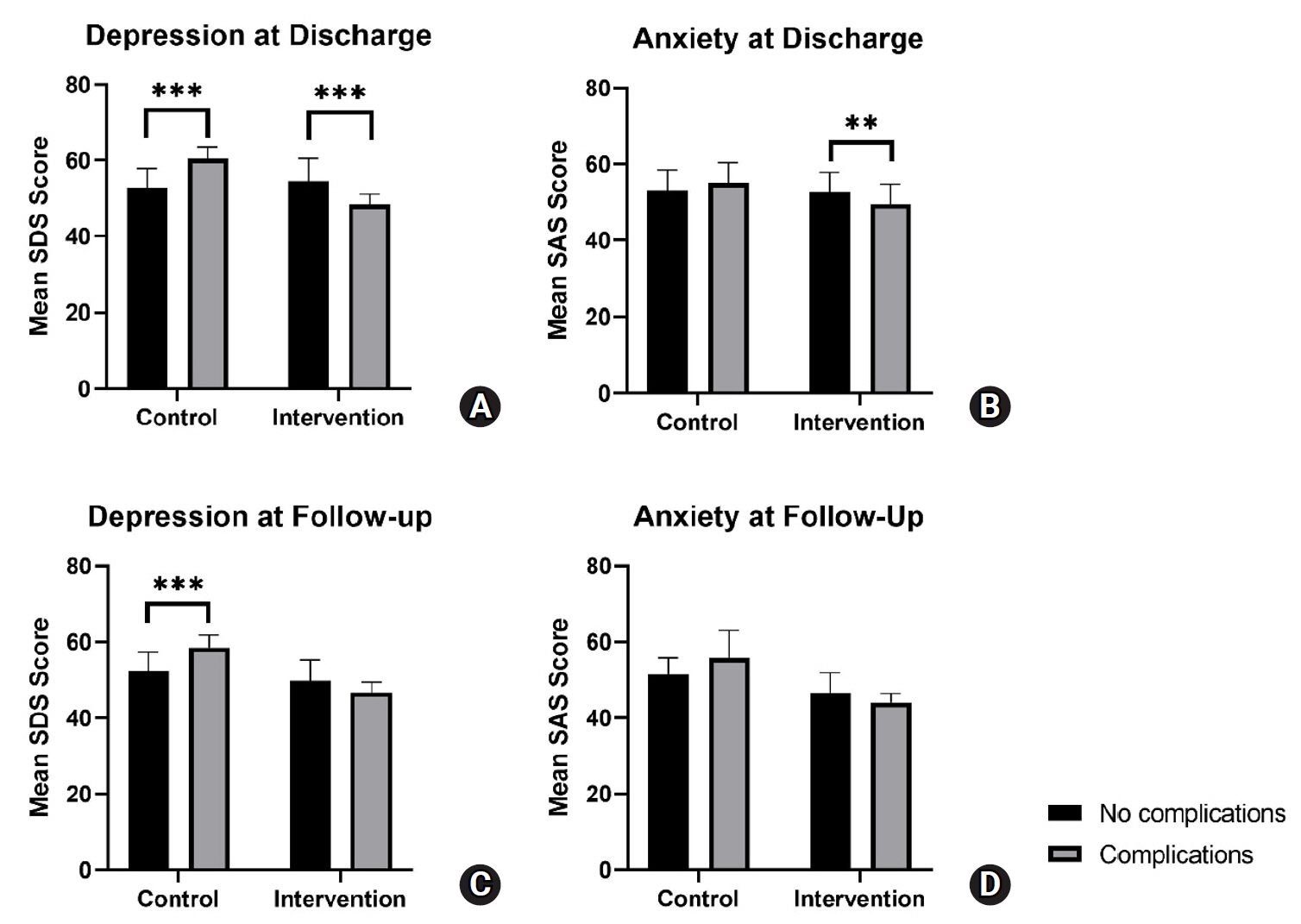
A linear mixed-effects model showed that SAS and SDS scores in the intervention group decreased to a significantly greater extent over time, from admission to follow-up, compared to the control group. Post-hoc analysis showed a trend for increased parental anxiety and depression among patients with complications at discharge and follow-up for the control group. Meanwhile, the intervention group exhibited a trend for decreased parental anxiety and depression among patients with complications at discharge and follow-up.
Conclusion
The integrated disease-specific nursing model significantly alleviated parental anxiety and depression over time compared to standard care, highlighting its effectiveness in supporting families of children with severe hypospadias. Notably, the intervention appeared to mitigate the negative emotional impact of postoperative and follow-up complications, suggesting its potential as a targeted approach to improve both emotional well-being and overall care outcomes.
- 2,328 View
- 158 Download

- Serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression on the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety in high-risk pregnant couples of South Korea
- Mihyeon Park, Sukhee Ahn
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):19-33. Published online February 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24070
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
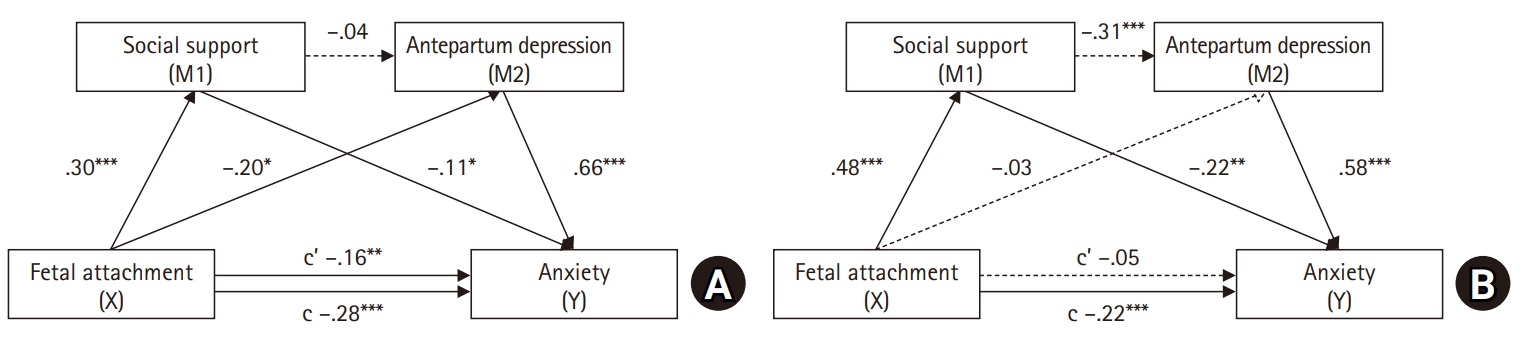
This study examined the direct effects of fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression on anxiety in pregnant women with high-risk pregnancy-related conditions and their husbands. Furthermore, it aimed to explore the serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression in the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety.
Methods
A survey-based study was conducted among pregnant women diagnosed with high-risk pregnancy conditions at 24–32 weeks and their husbands, recruited from a pregnant women’s online community between January 20, 2021 and July 20, 2022. Data were collected from 294 individuals (147 couples) using self-report questionnaires. Correlations between variables were analyzed using the IBM SPSS software ver. 26.0 (IBM Corp.), and the mediation effects were assessed using the PROCESS macro, model 6.
Results
In the maternal model, maternal-fetal attachment directly affected anxiety (p=.005), with antepartum depression partially mediating this relationship (95% confidence interval [CI], –0.26 to –0.01). In the paternal model, paternal-fetal attachment had no direct effect on anxiety (p=.458). However, social support and antepartum depression fully mediated the relationship between paternal-fetal attachment and anxiety (95% CI, –0.14 to –0.03).
Conclusion
The findings indicate that social support in the relationship between fetal attachment and depression in high-risk pregnant women and their partners can have direct or indirect effects on the negative emotions of high-risk pregnant couples. It is necessary to assess the level of anxiety in couples experiencing high-risk pregnancies and provide comprehensive nursing interventions that address fetal attachment, social support, and antepartum depression in order to reduce anxiety.
- 2,535 View
- 244 Download

- Effects of a Pre-Conception Care Program in Women with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Mixed-Methods Study Including a Randomized Controlled Trial
- Young Jin Lee, Hae Won Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Suk-Kyun Yang, Ji-Yeon Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(3):386-402. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to conduct a pre-conception care program for women of childbearing age with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in Korea and verify its effects on self-efficacy for IBD management, IBD-related pregnancy knowledge, and IBD-related pregnancy anxiety. It also aimed to explore the changes in participants through the program.
Methods
A convergent mixed-methods study design was adopted. In the quantitative phase, 35 women (17 and 18 in the intervention and control group, respectively) participated. The intervention group attended a program that included small-group sessions and individual tele-coaching. To confirm the effects, data were collected before and one and four weeks after the intervention. In the qualitative stage, focus group interviews and tele-coaching were conducted with the intervention group.
Results
After the program ended, significant differences were observed over time between the intervention and control groups for self-efficacy for IBD management (Wald χ2 = 4.41, p = .036), IBD-related pregnancy knowledge (Wald χ2 = 13.80, p < .001) and IBD-related pregnancy anxiety (Wald χ2 = 8.61, p = .003). Qualitative data analysis revealed the following themes: (1) improving confidence in IBD management and awareness for planned pregnancy; (2) improving IBD awareness related to pregnancy and childbirth; and (3) relieving anxiety about and actively facing pregnancy.
Conclusion
This study is meaningful in that, to the best of our knowledge, it is the first to develop a pre-conception care program for women diagnosed with IBD and confirm its effectiveness. Furthermore, this program is expected to be suitable for patient counseling and education in clinical practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The experiences of fertility concerns in women with inflammatory bowel disease of childbearing age: a descriptive qualitative study
Lewei Tu, Qiaoyu Wu, Mengxiao Jiang, Meihao Wei, Ying Wang, Ying Xiao
BMC Gastroenterology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Health Literacy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review of Health Outcomes, Predictors and Barriers
Caterina Mercuri, Rita Nocerino, Vincenzo Bosco, Teresa Rea, Vincenza Giordano, Michele Virgolesi, Patrizia Doldo, Silvio Simeone
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(23): 8577. CrossRef
- The experiences of fertility concerns in women with inflammatory bowel disease of childbearing age: a descriptive qualitative study
- 2,295 View
- 91 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Effect of an Intervention Using Voice Recording of a Family Member on Patients Undergoing Mechanical Ventilator Weaning Process
- Ah Young Choi, Min Young Kim, Eun Kyeung Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(1):32-43. Published online February 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23082
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to determine the impact of an intervention using voice recording of family members on pain, anxiety, and agitation in patients undergoing weaning from mechanical ventilation.
Methods
A randomized control pre-post experimental design was implemented to 53 participants, with 27 and 26 participants in the experimental and control groups, respectively. A 70-second voice recording of a family member, repeated three times at 10-minute intervals was used as an intervention for the experimental group. Meanwhile, participants in the control group used headset for 30 minutes. Structured instruments were utilized to measure pain, anxiety, agitation, and the weaning process. Wilcoxon Signed Ranks test and the Mann-Whitney U test, or χ2 test, were used for data analysis.
Results
The experimental group exhibited significant decrease in pain (Z = - 3.53, p < .001), anxiety (t = 5.45, p < .001), and agitation (Z = - 2.99, p = .003) scores compared with those of the control group. However, there was no significant difference between groups in the weaning process’ simplification (χ2 = 0.63, p = .727).
Conclusion
Intervention using family members’ voice recording effectively reduces pain, anxiety, and agitation in patients undergoing weaning from mechanical ventilation. This can be actively utilized to provide a more comfortable process for patients.
- 2,398 View
- 152 Download

- Factors Affecting the Quality of Life in Low-Income Older Adults with Sarcopenia: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Ju-Hee Nho, Eun Jin Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(1):1-11. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22126
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to identify the factors influencing quality of life (QoL) of low-income older adults (LOAs) with sarcopenia.
Methods
A convenience sample of 125 older adults was recruited from Jeonbuk Province, South Korea. Data were collected using a self-report questionnaire that included nutritional status, the Depression Anxiety Stress Scale-21, and the World Health Organization Quality of Life Instrument-Older Adults Module. Additionally, grip strength and appendicular skeletal muscle mass, were evaluated, along with the short physical performance battery.
Results
Sarcopenia and severe sarcopenia were observed in 43.2% and 56.8% of participants, respectively. Using multiple regression analysis, depression (β = - .40, p < .001), nutritional status (β = .24, p = .003), and anxiety (β = - .15, p = .042) were identified as factors affecting the QoL of the older adults in low-income groups with sarcopenia, the explanatory power of these variables was 44%.
Conclusion
The results of this study can be used to develop a nursing intervention program and establish policies to improve depression, anxiety, and nutritional status to enhance QoL of LOAs with sarcopenia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors influencing health-related quality of life in older adult women with sarcopenia: analysis of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
Sol Hyun Lee, Ju-Hee Nho, Hye Young Kim, Eun Jee Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(4): 328. CrossRef
- Factors influencing health-related quality of life in older adult women with sarcopenia: analysis of the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
- 2,208 View
- 50 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Effects of the Advanced Practice Nurse-Led Psychoeducational Program for Colorectal Cancer Survivors
- Hye Kyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):245-260. Published online June 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21207
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to investigate the effects of an advanced practice nurse-led psychoeducational program on distress, anxiety, depression, coping with cancer (CWC), health promotion behavior (HPB), and quality of life (QOL) among colorectal cancer survivors.
Methods
This study was designed as a quasi-experimental study with a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest. The participants were survivors of colorectal cancer who underwent follow-up care. There were 39 survivors: 19 in the experimental group and 20 in the control group. The experimental group performed a psychoeducational program for 120 minutes per session, once a week for a total of six weeks, while the control group received routine education and counseling. Distress, anxiety, depression, CWC, HPB, and QOL were investigated before, immediately after, and 4 weeks after the intervention. The data were analyzed with SPSS/WIN ver. 24.0, using repeated measures ANOVA.
Results
There were significant interactions between time and group for distress and anxiety. In addition, CWC interacted with the total of CWC and interpersonal coping, and QOL interacted with the total of QOL and functional status. However, there were no significant differences in the depression or HPB scores.
Conclusion
Based on the results of this study, we expect that this program can be used as an effective intervention for colorectal cancer survivors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of a mobile-based return to work program for decent return to work, fatigue, stress, and quality of working life among cancer survivors
Kisook Kim, Hyohyeon Yoon
Journal of Cancer Survivorship.2025; 19(2): 713. CrossRef - Elevating Elderly Cancer Care: A Systematic Review of Advanced Practice Nursing’s Role in Senior Oncology Patients’ Quality of Life
Cristian-David Useche-Guerrero, María-de-los-Ángeles Merino-Godoy, Eva-María Barroso-Márquez, Emilia Isabel Martins Teixeira da Costa, Rafaela Camacho Bejarano, Francisco-Javier Gago-Valiente, Rizal Angelo Grande
Journal of Nursing Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Psycho-education Interventions on Colorectal Cancer Patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
XiaoYing Zhang, HuangQin Liu, LiYing Lin, Huimin Xiao
Journal of Cancer Education.2023; 38(5): 1413. CrossRef - How should the healthcare system support cancer survivors? Survivors’ and health professionals’ expectations and perception on comprehensive cancer survivorship care in Korea: a qualitative study
Su Jung Lee, Dal-Lae Jin, Young Ae Kim, Hyun-Ju Seo, Seok-Jun Yoon
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer Survivorship Care and Roles of Oncology Nurses
Eun Young Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(3): 121. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of a mobile-based return to work program for decent return to work, fatigue, stress, and quality of working life among cancer survivors
- 1,874 View
- 90 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- Effects of Electroencephalogram Biofeedback on Emotion Regulation and Brain Homeostasis of Late Adolescents in the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Wanju Park, Mina Cho, Shinjeong Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):36-51. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21155
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of electroencephalogram (EEG) biofeedback training for emotion regulation and brain homeostasis on anxiety about COVID-19 infection, impulsivity, anger rumination, meta-mood, and self-regulation ability of late adolescents in the prolonged COVID-19 pandemic situation.
Methods
A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The participants included 55 late adolescents in the experimental and control groups. The variables were evaluated using quantitative EEG at pre-post time points in the experimental group. The experimental groups received 10 sessions using the three-band protocol for five weeks. The collected data were analyzed using the Shapiro-Wilk test, Wilcoxon rank sum test, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, t-test and paired t-test using the SAS 9.3 program. The collected EEG data used a frequency series power spectrum analysis method through fast Fourier transform.
Results
Significant differences in emotion regulation between the two groups were observed in the anxiety about COVID-19 infection (W = 585.50, p = .002), mood repair of meta-mood (W = 889.50, p = .024), self-regulation ability (t = - 5.02, p < .001), self-regulation mode (t = - 4.74, p < .001), and volitional inhibition mode (t = - 2.61, p = .012). Neurofeedback training for brain homeostasis was effected on enhanced sensory-motor rhythm (S = 177.00, p < .001) and inhibited theta (S = - 166.00, p < .001).
Conclusion
The results demonstrate the potential of EEG biofeedback training as an independent nursing intervention that can markedly improve anxiety, mood-repair, and self-regulation ability for emotional distress during the COVID-19 pandemic. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- From Neural Networks to Emotional Networks: A Systematic Review of EEG-Based Emotion Recognition in Cognitive Neuroscience and Real-World Applications
Evgenia Gkintoni, Anthimos Aroutzidis, Hera Antonopoulou, Constantinos Halkiopoulos
Brain Sciences.2025; 15(3): 220. CrossRef - Neuroimaging Insights into the Public Health Burden of Neuropsychiatric Disorders: A Systematic Review of Electroencephalography-Based Cognitive Biomarkers
Evgenia Gkintoni, Apostolos Vantarakis, Philippos Gourzis
Medicina.2025; 61(6): 1003. CrossRef - The interaction between emotion dynamics and opinion changes in the era of generative AI
Shangqian Li, Shaoyang Fan, Gianluca Demartini
Computers in Human Behavior Reports.2025; 19: 100722. CrossRef - Augmenting self-guided virtual-reality exposure therapy for social anxiety with biofeedback: a randomised controlled trial
Preethi Premkumar, Nadja Heym, James A. C. Myers, Phoebe Formby, Steven Battersby, Alexander Luke Sumich, David Joseph Brown
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Infection Anxiety and Coping Strategies Among Individuals With Schizophrenia During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Mediating Effects of Protection Motivation
Jeawon Joung, Dug Ja Choi
Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services.2023; 61(11): 43. CrossRef - The Effects of Integrated Neurofeedback and Salutogenesis Nursing Intervention to Relieve Post-COVID-19 Symptoms in Late Adolescents
Youngkyung Cho, Wanju Park
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(4): 402. CrossRef - Effects of Brain Attention Biofeedback Self-regulation Training Nursing Intervention on Attention, Multidimensional Impulsivity, Emotional Response Intensity, and Self-regulated Learning Ability of School-aged Children in the COVID-19 Pandemic Situation
Youngkyung Cho, Wanju Park
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2022; 31(2): 111. CrossRef - Comparison of QEEG Findings before and after Onset of Post-COVID-19 Brain Fog Symptoms
Marta Kopańska, Danuta Ochojska, Renata Muchacka, Agnieszka Dejnowicz-Velitchkov, Agnieszka Banaś-Ząbczyk, Jacek Szczygielski
Sensors.2022; 22(17): 6606. CrossRef
- From Neural Networks to Emotional Networks: A Systematic Review of EEG-Based Emotion Recognition in Cognitive Neuroscience and Real-World Applications
- 2,026 View
- 31 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Disease Prevention Knowledge, Anxiety, and Professional Identity during COVID-19 Pandemic in Nursing Students in Zhengzhou, China
- Yuyan Sun, Dongyang Wang, Ziting Han, Jie Gao, Shanshan Zhu, Huimin Zhang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(4):533-540. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate nursing students’ understanding of the prevention of COVID-19, as well as their anxiety towards the disease and their perception of their professional identity in the wake of the pandemic, in Zhengzhou, China.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was designed to investigate 474 nursing students by cluster sampling using a stratified questionnaire from February 15 to March 31, 2020. Multiple linear regression was used to identify the factors affecting professional identity. Binary and multiple logistic regression were used to identify the factors affecting anxiety.
Results
Responders with a high level of understanding of COVID-19 and frequent use of behavioral strategies for its prevention comprised 93.2% and 30.0% of the cohort, respectively. Professional identity was significantly associated with gender and anxiety (p < .050). The prevalence of anxiety among nursing students was 12.4%. Male (odds ratio [OR] = 2.39; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.26~4.52), sophomores (OR = 5.30; 95% CI = 1.61~7.45), and infrequent use of prevention measures (OR = 3.49; 95% CI = 1.16~5.19) had a significant effect on anxiety.
Conclusion
Anxiety during the COVID-19 epidemic gives an adverse effect on the professional identity of nursing in students. Nursing education institutions need to provide psychological counseling services for nursing students, in addition to improving their teaching of COVID-19 prevention strategies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Global prevalence of different levels of anxiety and stress symptoms in healthcare students: A meta-analysis and meta-regression
Ying Xuan Loh, Ying Lau, Wen Wei Ang, Shean Ern Shannen Lee, Siew Tiang Lau
Annals of General Psychiatry.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Anatomical dissection influences emotions of podiatry students
Alicia Mohedano‐Moriano, Carmen Romo‐Barrientos, Alicia Flores‐Cuadrado, Isabel Ubeda‐Bañon, Jaime Gonzalez‐Gonzalez, Maria Teresa Gil Ruiz, Daniel Saiz‐Sanchez, Veronica Astillero‐Lopez, Felix Marcos‐Tejedor, Alino Martinez‐Marcos, Antonio Viñuela, Juan
Journal of Foot and Ankle Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Hand Hygiene Practices and Educational Interventions Among Indonesian Nursing Students: An Analysis Using ATP Wipe Tests and Hand Hygiene Checkers
Mayumi Sato, Syahrul, Tantut Susanto, Fithria, Naoki Hokama, Ruka Saito, Andi Muhammad Fiqri Muslih Djaya, Hiroshi Sugimoto
Journal of Rural Community Nursing Practice.2025; 3(1): 60. CrossRef - The transformation of ambivalent professional identity of nursing students following clinical placement in China: A qualitative study from the perspectives of the “post-00s” generation
Jingyi Chen, Xiao Zhang, Yidan Yang, Rong Hu
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 86: 104387. CrossRef - Resilience, perceived control, and intention to receive additional vaccines for COVID‐19 among healthcare university students: Mediating role of knowledge of vaccine and infection‐preventive behaviors
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Erika Ota, Tomomi Oki, Kazuko Naruse
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The influences of nursing students’ prevention and control practice behaviours on emerging and re-emerging respiratory viral illnesses: An integrative review and narrative synthesis
Gift A. Mutsonziwa, Paul Glew, Rona Pillay
Nurse Education in Practice.2025; 88: 104564. CrossRef - Ser enfermeiro na perspectiva de estudantes de enfermagem do nordeste brasileiro no contexto pandemico
Thais Araujo da Silva, Ruth Silva dos Santos, Nayhara Rayanna Gomes da Silva, Ryanne Carolynne Marques Gomes Mendes
Journal of Nursing and Health.2025; 15(2): e1528145. CrossRef - Kayseri İlinde Öğrenim Gören Paramedik Öğrencilerinin Mesleki Kaygı Düzeyinin Belirlenmesi
Emre Bulbul, Etem Hızaler, Mehmet Doğan
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2025; 6(1): 8. CrossRef - Nursing Students’ Perceptions of Factors Influencing Nursing Intentions toward COVID-19 Patients
Nari Lee, Hae Ran Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 285. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of the training on “Home care of COVID-19 positive/suspicious patients” given to nursing students: A quasi-experimental study
Hande Sabandüzen, Öznur Kavaklı
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of alexithymia, anxiety, social pressure, and academic burnout on depression in Chinese university students: an analysis based on SEM
Mingyang Sun, Ming Piao, Zhaona Jia
BMC Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between anxiety and academic identity and the motivation to study nursing and midwifery in the covid-19 pandemic: A structural model
Ashraf Khoramirad, Sarallah Shojaei, Heydar Ghaderi, Zahra Abedini
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Holistic Approach to Nursing Students’ Changing Life and Anxiety in the Pandemic: A Descriptive Cross Sectional Study Utilizing Positive Psychotherapy
Ayşe Kuzu Durmaz, Ferhan Açıkgöz, Çiğdem Şen Tepe
Journal of Higher Education and Science.2024; 14(2): 349. CrossRef - The Mediating Role of Psychological Resilience in Chinese Nursing Students’ Professional Identity and Learning Burnout
Liu Zhang, Qin Zhang, ShuWen Li, YuHong Li, GuoCui Wu, Ying Chen, YunNa Zhou
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(4): 509. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Nurses’ Perceptions of Spirituality and Spiritual Care and Their Attitudes Towards the Nursing Profession
İbrahim Nas, Gülay İpekçoban
Gümüşhane Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2024; 13(2): 542. CrossRef - Anxiety in Nursing Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Aroa García-Rivas, María Begoña Martos-Cabrera, María José Membrive Jiménez, Raimundo Aguayo-Estremera, Nora Suleiman Martos, Luis Albendín-García, José L. Gómez-Urquiza
Healthcare.2024; 12(16): 1575. CrossRef - Work environment as perceived by nursing interns and its relation to their professional identity
Habiba A.A. Gadallah, Sahar H.A. El Banan, Faten S.A. Ahmed
Egyptian Nursing Journal.2024; 21(2): 129. CrossRef - Assesment of Occupational Anxiety of Emergency Aid and Disaster Management Students
Cüneyt Çalışkan, Kerem Kınık
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2024; 5(1): 51. CrossRef - COVID-19 Perceptions, Avoidance and Vaccine Attitudes of Nursing Students: Case of Türkiye
Gülşen ULAŞ KARAAHMETOĞLU, Zeynep ARABACI
Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Fakültesi Elektronik Dergisi.2024; : 111. CrossRef - COVID-19 Pandemi Süreci Uzaktan Eğitim Döneminde Hemşirelik Öğrencilerinde Anksiyete ve Klinik Performans Öz-Yeterlilik Algısı İlişkisi
Yeliz AKKUŞ, Nihal BOSTANCI DAŞTAN
Sağlık Bilimlerinde Değer.2024; 14(1): 106. CrossRef - Comparing factors related to perceived control and preventive behaviors from COVID‐19 between Japanese and American nursing students: A cross‐sectional study
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Kosuke Niitsu, Kazuko Naruse, Tomomi Oki, Erika Ota, Mabel C. Ezeonwu
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sağlık Hizmetleri Meslek Yüksekokulu Öğrencilerinin Mesleğe Yönelik Kaygı Düzeylerinin Belirlenmesi
Dilan AKTEPE COŞAR, Nuray BİNGÖL, Hatice DEMİRAĞ
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2023; 4(2): 66. CrossRef - Satisfied with teaching? Psychometric properties of the Teaching Satisfaction Scale
Tyrone B. Pretorius, Anita Padmanabhanunni, Kyle M. Jackson, Brendon D. Faroa
African Journal of Psychological Assessment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Risk Factors for Anxiety Symptoms among Student Nurses in Gauteng Province of South Africa
Maleke Manana, Sam Thembelihle Ntuli, Kebogile Mokwena, Kgomotso Maaga
Behavioral Sciences.2023; 13(8): 630. CrossRef - Factors related to mental health effect among nursing students in Japan and the United States during the coronavirus pandemic: A cross‐sectional study
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Kosuke Niitsu, Kazuko Naruse, Tomomi Oki, Erika Ota, Mabel C. Ezeonwu
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(1): 186. CrossRef - Effects of a Nursing Simulation Learning Module on Clinical Reasoning Competence, Clinical Competence, Performance Confidence, and Anxiety in COVID-19 Patient-Care for Nursing Students
Ye-Eun Kim, Hee-Young Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(1): 87. CrossRef - Research Progress of Chinese Nursing Students’ Professional Identity during COVID-19
毓 徐
Nursing Science.2023; 12(01): 7. CrossRef - Prevalence and levels of burnout in nursing students: A systematic review with meta-analysis
José L. Gómez-Urquiza, Almudena Velando-Soriano, María José Membrive-Jiménez, Lucia Ramírez-Baena, Raimundo Aguayo-Estremera, Elena Ortega-Campos, Guillermo A. Cañadas-De la Fuente
Nurse Education in Practice.2023; 72: 103753. CrossRef - Psychological impacts of transition to distance learning due to COVID‐19 on nursing students
Ahmad Rayan
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(3): 767. CrossRef - COMPARISON OF TWO DIFFERENT TECHNIQUES FOR TEACHING LEARNING SKILLS: EVALUATION IN THE PERIOD OF PANDEMIC
Sevim ÇELİK, Elif KARAHAN, Sibel ALTINTAŞ, Özge UÇAR
International Journal of Health Services Research and Policy.2023; 8(2): 114. CrossRef - How has the COVID-19 pandemic influenced nursing students' academic experience and career choices? A qualitative descriptive analysis
Masamitsu Kobayashi, Yuji Koga, Jun Kako, Takahiro Kakeda, Hana Kiyohara, Yasutaka Kimura, Michiko Ishida, Michihiro Tsubaki, Yoko Nishida, Kimie Harada, Yuki Wakiguchi, Yoji Endo, Yoshiyasu Ito, Shinsuke Sasaki, Kohei Kajiwara, Seiji Hamanishi, Makoto Ya
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2023; 18(1): 30. CrossRef - Perceived social support and professional identity in nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic era: the mediating effects of self-efficacy and the moderating role of anxiety
Zhi-Hui Zhao, Jin-Yi Guo, Jie Zhou, Jia Qiao, Shu-Wen Yue, Yan-Qiong Ouyang, Sharon R. Redding, Rong Wang, Zhong-Xiang Cai
BMC Medical Education.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Anxiety, depression, and stress prevalence among college students during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Chunyi Wang, Wen Wen, Haifu Zhang, Jie Ni, Jingjie Jiang, Yongran Cheng, Mengyun Zhou, Lan Ye, Zhanhui Feng, Zhongjun Ge, Hong Luo, Mingwei Wang, Xingwei Zhang, Wenmin Liu
Journal of American College Health.2023; 71(7): 2123. CrossRef - Factors associated with mental health among undergraduate nursing students early in the COVID-19 pandemic: an integrative review
Keiko Sugimoto, Rieko K. Fukuzawa, Ganchimeg Togoobaatar, Chang G. Park, Susan C. Vonderheid
International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - PANDEMİ SÜRECİNDE KLİNİK UYGULAMA YAPAMAYAN İLK VE ACİL YARDIM ÖĞRENCİLERİNİN MESLEKİ YAŞAM İLE İLGİLİ KAYGI DÜZEYLERİNİN VE İLİŞKİLİ FAKTÖRLERİN BELİRLENMESİ
Elif KILIÇ GÜNER, Özge AKBABA, Elanur YILMAZ KARABULUTLU, Havva ÖZTÜRK
Hastane Öncesi Dergisi.2023; 7(3): 331. CrossRef - Hemşirelik Öğrencilerinin Mesleğe Yönelik Tutumu ile COVID-19 Enfeksiyonu Korkusu Arasındaki İlişki
Süreyya Bulut, Nihal Taşkıran
Hacettepe Üniversitesi Hemşirelik Fakültesi Dergisi.2023; 10(3): 207. CrossRef - Investigation of the Stress Level and Coping Behaviors of Nursing Students, and Their Thoughts on Professional Life in COVİD-19 Pandemic
Belkız KIZILTAN, Nurgül KAPLAN, Seda UZUNALİ
Paramedik ve Acil Sağlık Hizmetleri Dergisi.2023; 4(1): 26. CrossRef - The development and effects of a COVID-19 nursing education program for nursing students
Hyewon Choi, Hyunju Kang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 368. CrossRef - Hemşirelik Son Sınıf Öğrencilerinin Mezuniyet Sonrası Covid-19 Kliniklerinde Çalışmaya İlişkin Görüşleri: Nitel Bir Çalışma
Ilknur TURA, Sevilay ERDEN
Hemşirelik Bilimi Dergisi.2022; 5(3): 149. CrossRef - The multidimensionality of anxiety among nursing students during COVID‐19 pandemic: A cross‐sectional study
Rizal Angelo N. Grande, Daniel Joseph E. Berdida, Rolan Rodolfo Jr C. Paulino, Eric A. Anies, Reinhard Roland T. Ebol, Roger R. Molina
Nursing Forum.2022; 57(2): 267. CrossRef - Identity Matters: Validation of the Professional Identification Scale in a Sample of Teachers in South Africa During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Tyrone B. Pretorius, Anita Padmanabhanunni, Serena Ann Isaacs
Trends in Psychology.2022; 32(4): 1426. CrossRef - The study of psychological traits among Chinese college students during the COVID-19 campus lockdown
Haibo Xu, Zhen Wang, Lixin Peng, Yanyan Mi, Ping Zeng, Xin Liu
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Perceived professional identity and related factors in Iranian nursing students: a cross-sectional study
Tahereh Gilvari, Hassan Babamohamadi, Fatemeh Paknazar
BMC Nursing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Nursing students’ experiences of mental wellness during the COVID-19 pandemic: A phenomenological study
Dana Laczko, Alex Hodson, Melissa Dykhuizen, Kelsey Knipple, Kassandra Norman, Paula Hand-Cortes
Teaching and Learning in Nursing.2022; 17(4): 392. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Infection Control Performance of School Health Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic in South Korea
Mi-Ra Yim, Boyoung Kim
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2022; Volume 15: 805. CrossRef - The Beneficial Effects of Professional Identity: The Mediating Role of Teaching Identification in the Relationship between Role Stress and Psychological Distress during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Tyrone Brian Pretorius, Anita Padmanabhanunni
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(18): 11339. CrossRef - Being a Nursing Student In a Pandemic: Fear of COVID-19 and Clinical Practice
Pınar TUNÇ TUNA, Halil İbrahim TUNA, Birsel MOLU, Alev YILDIRIM KESKİN
Genel Tıp Dergisi.2022; 32(5): 506. CrossRef - Mental Health Among Medical Students During COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Qingwen Jia, Yi Qu, Huiyuan Sun, Huisheng Huo, Hongxia Yin, Dianping You
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge and attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccination among student nurses from Saudi Arabia
Romeo Mostoles Jr, Richard Maestrado, Joyce Buta, Salman Alsaqri, Evalynn Rondilla, Hamdan Mohammad Albaqawi
Jurnal Ners.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of anxiety symptoms among Chinese university students amid the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Xiaohang Wang, Quzhi Liu
Heliyon.2022; 8(8): e10117. CrossRef - Has the COVID-19 pandemic affected nursing students’ career self-efficacy and professional calling? The mediating impact of professional identity
Li Yang, Mengfan Xu, Jinke Kuang, Kexin Zhou, Xuemei Zhu, Lingna Kong, Li QI, Heng Liu
BMC Medical Education.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research on Health Education Strategies for Improving Student Knowledge on Infectious Disease Prevention
Shailly Gupta , Manashree Mane , Debashree Priyadarshini , Ajab Singh Choudhary
Health Leadership and Quality of Life.2022; 1: 126. CrossRef - Relationship between nursing students’ attitudes toward nursing profession and online learning satisfaction during COVID-19 lockdown
Maša Černelič-Bizjak, Petra Dolenc, Ali B. Mahmoud
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(11): e0277198. CrossRef - Anxiety and fear of COVID‐19 among nursing students during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A descriptive correlation study
Nilgun Kuru Alici, Ebru Ozturk Copur
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2022; 58(1): 141. CrossRef - Professional Identity of 0.24 Million Medical Students in China Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Three Waves of National Cross-Sectional Studies
Chen Yu, Qiao Liu, Weimin Wang, Ana Xie, Jue Liu
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Attitudes of Nursing Students towards Vaccination and Other Preventive Measures for Limitation of COVID-19 Pandemic: Cross-Sectional Study in Three European Countries
Nevenka Kregar Velikonja, Beata Dobrowolska, Sanja Stanisavljević, Karmen Erjavec, Vislava Globevnik Velikonja, Ivan Verdenik
Healthcare.2021; 9(7): 781. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Preventive Practice of International Students in South Korea against COVID-19 during the Pandemic
Gun Ja Jang, Ginam Jang, Sangjin Ko
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(5): 2259. CrossRef - Perceived Control, Preventative Health Behaviors, and the Mental Health of Nursing Students During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study
Akiko Kondo, Renaguli Abuliezi, Kazuko Naruse, Tomomi Oki, Kosuke Niitsu, Mabel C. Ezeonwu
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Individual and Joint Effects of Cumulative Confirmed Cases and Attention Level of COVID-19 on Medical Students' Professional Identity: A National Cross-Sectional Study in China
Qiao Liu, Chen Yu, Ana Xie, Weimin Wang, Jue Liu
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of mental health problems and sleep disturbances in nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mulyadi Mulyadi, Santo Imanuel Tonapa, Suwandi Luneto, Wei-Ting Lin, Bih-O Lee
Nurse Education in Practice.2021; 57: 103228. CrossRef - Transition in learning during COVID‐19: Student nurse anxiety, stress, and resource support
Anita Fitzgerald, Sharon Konrad
Nursing Forum.2021; 56(2): 298. CrossRef - Nursing Students in Crisis Mode
Bella Savitsky, Yifat Findling, Anat Ereli, Tova Hendel
Nurse Educator.2021; 46(3): E33. CrossRef - Impact of Anxiety on Readiness for COVID-19 Vaccination among Polish Nursing Undergraduate Students: Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study
Joanna Gotlib, Mariusz Jaworski, Dominik Wawrzuta, Tomasz Sobierajski, Mariusz Panczyk
Vaccines.2021; 9(12): 1385. CrossRef
- Global prevalence of different levels of anxiety and stress symptoms in healthcare students: A meta-analysis and meta-regression
- 2,383 View
- 18 Download
- 47 Web of Science
- 63 Crossref

- Effects of First Assisted Reproductive Technologies on Anxiety and Depression among InfertileWomen: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Ju-Young Ha, Seon-Hwa Ban, Hae-Jung Lee, Misoon Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):369-384. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.19187
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study was to analyze anxiety and depression among infertile women at different time points during the firstIn Vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) treatment through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
Seven out of 3,011 studies were included for meta-analysis. To estimate the effect size, a meta-analysis of the studies was performedusing the RevMan 5.3 program. We compared the measurement outcomes at three time points: before the start of treatment (T0), cancellationof treatment after pregnancy detection (T2), one to six months after treatment (T3). The effect size used was the standardizedmean difference (SMD).
Results
In comparing the different time points of the pregnant women from their cycle, significantly lower levelsof depression were found at T2 than at T0. In non-pregnant women, anxiety at T2 and depression at T2 and T3 were significantly higherthan those at T0. At T2 and T3, the non-pregnant women reported higher levels of anxiety and depression compared with the pregnantwomen.
Conclusion
Anxiety and depression in infertile women undergoing the first IVF or ICSI are associated with the time points andpregnancy status after treatment. These findings suggest that attention should be paid to helping infertile women prepare for and copewith treatment and treatment failure. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Stress on Each of the Stages of the IVF Procedure: A Systematic Review
Anastasia Tsambika Zanettoullis, George Mastorakos, Panagiotis Vakas, Nikolaos Vlahos, Georgios Valsamakis
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 726. CrossRef - An Integrative Review of Psychosocial Intervention Programs for Infertile Females
Youjin Shin, Soo-Hyun Nam
STRESS.2023; 31(4): 158. CrossRef - The dynamics of mental health measures of pre- and postpartum women undergoing assisted reproductive technology
Maria E. Blokh, Varvara O. Anikina, Svetlana S. Savenysheva, Maria I. Levintsova
Journal of obstetrics and women's diseases.2023; 72(1): 17. CrossRef
- Effect of Stress on Each of the Stages of the IVF Procedure: A Systematic Review
- 1,313 View
- 34 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Reliability and Validity of Korean Version of Nursing Students’ Anxiety and Self-Confidence with Clinical Decision Making Scale
- Mi Yu, Young Eun, KA White, KyungJa Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(4):411-422. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.411
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to adapt, modify, and validate the Nursing Anxiety and Self-Confidence with Clinical Decision-Making Scale (NASC-CDM©) for Korean nursing students.
Methods Participants were 183 nursing students with clinical practice experience in two nursing colleges. The construct validity and reliability of the final Korean version of the NASC-CDM© were examined using exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses and testing of internal consistency reliability. For adaptation and modification, the instrument was translated from English to Korean. Expert review and a cross-sectional survey were used to test the instrument's validity.
Results The Korean version of the NASC-CDM© (KNASC-CDM) was composed of 23 items divided into four dimensions: (i) Listening fully and using resources to gather information; (ii) Using information to see the big picture; (iii) Knowing and acting; and (iv) Seeking information from clinical instructors. The instrument explained 60.1% of the total variance for self-confidence and 63.1% of the variance for anxiety; Cronbach's α was .93 for self-confidence and .95 for anxiety.
Conclusion The KNASC-CDM can be used to identify anxiety and self-confidence in nursing students’ clinical decision-making in Korea. However, further research should be done to test this instrument, as it is classified differently from the original NASC-CDM© version.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Evaluation of a “Speak-Up” Program for Patient Safety: A Virtual Reality-Based Intervention for Nursing Students
Jeong Hee Jeong, Mi Jin Kim
Healthcare.2025; 13(22): 2860. CrossRef - The relationship between clinical decision-making levels and self-efficacy levels of operating room nurses
Sedat Kaya, Gizem Kubat Bakir
Perioperative Care and Operating Room Management.2024; 37: 100416. CrossRef - Clinical decision making: validation of the nursing anxiety and self-confidence with clinical decision making scale (NASC-CDM ©) into Spanish and comparative cross-sectional study in nursing students
Daniel Medel, Tania Cemeli, Krista White, Williams Contreras-Higuera, Maria Jimenez Herrera, Alba Torné-Ruiz, Aïda Bonet, Judith Roca
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Implementation of a Mobile-Integrated Simulation for COVID-19 Nursing Practice: A Randomized Controlled Pretest–Posttest Experimental Design
Sun-Hwa Lee, Jeong-Sil Choi
Healthcare.2024; 12(4): 419. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of a collaborative reflection-based debriefing strategy for simulation-based education using virtual simulations in practical nursing: A randomized controlled trial
Ji-Ah Yun, In-Soon Kang
Nurse Education in Practice.2024; 81: 104170. CrossRef - Constructing a Mixed Simulation With 360° Virtual Reality and a High-Fidelity Simulator
Sun Kyung Kim, Youngho Lee, Younghye Go
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2023; 41(8): 569. CrossRef - Path model on decision‐making ability of clinical nurses
Minsook Park, Minkyung Gu, Sohyune Sok
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2023; 32(7-8): 1343. CrossRef - Achieving nursing students' clinical practice hours during the COVID‐19 pandemic: Effects of alternative and nonstandard practicum methods
Min Kyung Song, Ji‐Soo Kim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Related to the Problem-solving Ability of Nursing Students Who Experienced Simulation Training
Ji-Won Han
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2023; 11(2): 17. CrossRef - A Concept Analysis of Nurses’ Clinical Decision Making: Implications for Korea
Sunyoung Oh, Minkyung Gu, Sohyune Sok
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(6): 3596. CrossRef - The Korean version of the Virtual Patient Learning System Evaluation Tool: Assessment of reliability and validity
Hae Jeong An, Jung Suk Choi, Min Roh, Hyun Mi Cho, Eun Ju Choi
Nurse Education Today.2021; 106: 105093. CrossRef
- Development and Evaluation of a “Speak-Up” Program for Patient Safety: A Virtual Reality-Based Intervention for Nursing Students
- 2,896 View
- 85 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- Development of an Aging Anxiety Scale for Middle-Aged Women
- Haejin Lee, Mi-Ae You
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(1):14-25. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.1.14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This was a methodological study that aimed to develop a measurement scale for aging anxiety among middle-aged women.
Methods In this study, construct factors were extracted, and a conceptual framework was established through an extensive literature review and in-depth interviews with middle-aged women. Under the conceptual framework, 44 preliminary items were constructed, and a preliminary scale of 25 items was completed after two rounds of expert validation and item review. For this study, data were collected from 201 women aged 40∼59 years, and the construct validity and reliability of the preliminary scale were verified.
Results To verify the construct validity, exploratory factor analysis was conducted. Four factors containing 19 items were extracted. Concurrent validity of the developed scale was verified with Pearson's correlation analysis. The final scale comprised 4 factors (“Social valueless”, “Physical weakness”, “Concern about changes in appearance”, and “Expectations of old age”) and 19 items. The Cronbach's α value was .91.
Conclusion The scale for measuring aging anxiety in middle-aged women developed in this study validly reflected the peculiarities of aging anxiety in middle-aged women, who experience many physical, emotional, and social changes. The scale can be said to reflect the cultural background, as it reflected real experiences gained through in-depth interviews with middle-aged women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gerascophobia or Excessive Fear of Aging Scale (GEFAS): Development, validation, and exploration of psychometric properties of a brief instrument using classical testing theory and item response theory
Waqar Husain, Farrukh Ijaz, Muhammad Ahmad Husain, Ammar Achraf, Hasan M. Isa, Khaled Trabelsi, Seithikurippu R. Pandi-Perumal, Amir H. Pakpour, Haitham Jahrami
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2025; 128: 105599. CrossRef - Family support, social security, commercial insurance, and aging anxiety among Chinese residents: a study based on the 2021 CGSS data
He Gu, Qingli Tan, Yongxing Guo, Han He, Yu Zhang
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Determination of the association between aging anxiety and menopausal symptoms in middle-aged women
Seda Hazar, Gülçin Nacar, Furkan Doğan, Sermin Timur Taşhan
Menopause.2025; 32(6): 539. CrossRef - Effects of Physical Activity on Ageism and Aging Anxiety Among Chinese and Korean Adults Aged 55 to 64 Years
Jing Li, Seung-Yong Kim, Cho-Young Yook, Xiao-Long Chen, Woo-Jin An, Ju-Young Oh, Chae-Hee Park
Healthcare.2025; 13(11): 1218. CrossRef - Prevalence of depressive symptoms during the menopausal transition in Türkiye: impact of symptom severity, aging anxiety and health-related quality of life
Banu Aslan, Özgür Önal
Climacteric.2025; 28(5): 607. CrossRef - Orta Yaşlı Kadınlarda Yaşlanma Anksiyetesi, Cinsel Yaşam Kalitesi ve Öznel Mutluluk Arasındaki İlişkinin İncelenmesi Üzerine Kesitsel Bir Çalışma
Ejdane Coşkun, Burcu Çakı Döner
Turkish Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2025; 19(4): 323. CrossRef - Development of a scale to measure selection, optimization, compensation (SOC) strategy in late middle-aged women: a methodological study
Do-Young Lee, Gie Ok Noh
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(3): 216. CrossRef - Association between Menopausal Women’s Quality of Life and Aging Anxiety: The Role of Life Satisfaction and Depression
Seunghee Lee, Mijung Jang, Dohhee Kim, KyooSang Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(8): 1189. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Laughter Therapy Program for Middle-aged Women Hospitalized in Psychiatric Wards
Do Young Lee, Ju Hyun Woo
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2024; 33(3): 273. CrossRef - Determination of aging anxiety in middle-aged women
Nese Kiskac, Mahruk Rashidi, Muharrem Kiskac
Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Informal caregivers’ negative affect: The interplay of caregivers’ resilience, aging anxiety and burden
Yaira Hamama-Raz, Rachel Nissanholtz Gannot, Michal Michaelis, Yichayaou Beloosesky, Adaya Nissanholtz
Aging & Mental Health.2023; 27(7): 1300. CrossRef - Aging anxiety and beliefs about exercise in middle-aged women
Nedim TEKİN, Adeviye AYDIN
Turkish Journal of Kinesiology.2023; 9(3): 214. CrossRef - Experiences Pertaining to Successful Aging in Middle-Aged Women in South Korea
Do-young Lee, Hyun-ju Kim, A-young Jo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(19): 6882. CrossRef - Validity and reliability study of the Turkish version of the Aging Anxiety Scale for Middle‐Aged Women
Zeynep Daşıkan, Selin Paker, Ruken Yağız Altıntaş, Figen Kazankaya, Sümeyye Bakır
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2022; 58(4): 2918. CrossRef - Turkish Adaptation of the Aging Anxiety Scale for Middle-Age Women: Validity and Reliability Study
Adeviye AYDIN, Esma KABASAKAL
Journal of Basic and Clinical Health Sciences.2022; 6(1): 173. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Life Satisfaction in Middle-Aged Women
Hee Kyung Kim, Hae Kyung Chang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2022; 29(3): 326. CrossRef - The health status, aging anxiety, social networking, generativity, and happiness of late middle-aged adults
Hae Kyung Chang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(4): 392. CrossRef - The Effects of Climacteric Symptom Cognition, Self-efficacy on Aging Anxiety in Middle-Aged Couples: Actor and Partner Interdependence Mediation Model
Yeon-Suk Kim, Myung-Haeng Hur
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 247. CrossRef - Verification of the Mediating Effect of Social Support on Physical Activity and Aging Anxiety of Korean Pre-Older Adults
Ahra Oh, Jiyoun Kim, Eunsurk Yi, Jongseob Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(21): 8069. CrossRef
- Gerascophobia or Excessive Fear of Aging Scale (GEFAS): Development, validation, and exploration of psychometric properties of a brief instrument using classical testing theory and item response theory
- 2,070 View
- 49 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref

- Impact of Uncertainty on the Anxiety of Hospitalized Pregnant Women Diagnosed with Preterm Labor: Focusing on Mediating Effect of Uncertainty Appraisal and Coping Style
- Eun Mi Kim, Sehoon Hong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(4):485-496. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.4.485
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose This study aimed to test the mediating effect of uncertainty appraisal and coping style in the relation between uncertainty and anxiety in hospitalized pregnant women diagnosed with preterm labor.
Methods The participants were 105 pregnant women diagnosed with preterm labor in hospitals in Korea. Data were collected from July to October 2017. The measurements included the Uncertainty in Illness Scale, Uncertainty Appraisal Scale, Coping Style Scale, and State Anxiety Inventory. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, an independent t-test, correlation, and multiple regression following the Baron and Kenny method and Sobel test for mediation.
Results The mean score for anxiety was 2.29 out of 4.00 points and for uncertainty it was 2.46 out of 5.00 points. There were significant correlations among uncertainty, uncertainty danger appraisal, uncertainty opportunity appraisal, problem-focused coping, emotion-focused coping, and anxiety. Uncertainty danger appraisal (β=.64,
p <.001) had a complete mediating effect in the relation between uncertainty and anxiety (Z=4.54,p <.001). Uncertainty opportunity appraisal (β=-.45,p <.001) had a complete mediating effect in the relation between uncertainty and anxiety (Z=3.28,p <.001). Emotion-focused coping (β=-.23,p =.021) had a partial mediating effect in the relation between uncertainty and anxiety (Z=2.02,p =.044).Conclusion Nursing intervention programs focusing on managing uncertainty appraisal and improving emotion-focused coping are highly recommended to decrease anxiety in hospitalized pregnant women diagnosed with preterm labor.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression on the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety in high-risk pregnant couples of South Korea
Mihyeon Park, Sukhee Ahn
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(1): 19. CrossRef - Development and Effect of Prenatal Education Programs Using Virtual Reality for Pregnant Women Hospitalized With Preterm Labor: Experimental Study
SeoA Park, Hyeyoung Kim
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2025; 27: e75585. CrossRef - High-risk Pregnancy Nursing: Analyzing the Impact of Prenatal Stress, Maternal-Fetal Attachment, and Social Support on Prenatal Depression
Jae Hui Choe, Sun Jeong Yun, Hye Young Kim
The Open Nursing Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Path analysis of illness uncertainty and psychosocial adaptation of patients with Marfan syndrome
Sujin Kim, Yeonsoo Jang, JiYeon Choi, Kijun Song, Jae-kwan Song, Mona Choi
European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2024; 23(2): 197. CrossRef - An explanatory model of quality of life in high-risk pregnant women in Korea: a structural equation model
Mihyeon Park, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(4): 302. CrossRef - The effects of music therapy on labor pain, childbirth experience, and self-esteem during epidural labor analgesia in primiparas: a non-randomized experimental study
Seong Yeon An, Eun Ji Park, Yu Ri Moon, Bo Young Lee, Eunbyul Lee, Dong Yeon Kim, Seong Hee Jeong, Jin Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(2): 137. CrossRef - Anxiety, depression, and uncertainty appraisal and factors affecting uncertainty risk and opportunity appraisal of health care workers in Korea during the COVID-19 outbreak
Soo Young An, Jong Sun Ok, Hyeongsu Kim
Health Psychology and Behavioral Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and effects of a high-risk pregnancy emotive role-play program for nursing students: a quasi-experimental study
Bo Gyeong Lee, Sun-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(4): 317. CrossRef - Psychological Responses According to Gender during the Early Stage of COVID-19 in Spain
Lucía del Río-Casanova, Milagrosa Sánchez-Martín, Ana García-Dantas, Anabel González-Vázquez, Ania Justo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(7): 3731. CrossRef - Experiences of hospitalization among pregnant women with preterm labor in Korea: a phenomenological study
Joon-Young Lee, Yeoungsuk Song
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(3): 209. CrossRef - Effects of a supportive program on uncertainty, anxiety, and maternal-fetal attachment in women with high-risk pregnancy
Hyun Jin Kim, Nami Chun
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(2): 180. CrossRef - Qualitative Study on the Experience of Patients with Meniere Disease
Woo Joung Joung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 699. CrossRef
- Serial mediation effects of social support and antepartum depression on the relationship between fetal attachment and anxiety in high-risk pregnant couples of South Korea
- 1,703 View
- 23 Download
- 12 Crossref

- The Effect of Preparatory Information on the State Anxiety Depending on Coping Styles of Patients Undergoing Cardiac Catheterization
- Cho Ja Kim, Gi Yon Kim
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(3):648-659. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.3.648
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The Purpose of this study was to study what effect providing the patient with preparatory concrete information had on the state anxiety depending on coping styles of patients undergoing cardiac catheterization. State Anxiety scores for 32 patients who had cardiac catheterization were examined after information was provided about the test using and audio tape. The state anxiety of patients who had a high trait anxiety level was compared to that of those who had a low trait anxiety level. The state anxiety of those who had a monitor type were compared to those of patients who had blunter type. The Trait and State Anxiety Scale of Spielberger Miller's Behavioral Style Scale, and Krantz's Health Opinion Survey and Visual Analog Scale(I, II) were used. Findings were as follows : 1. Among the demographic characteristics, gender difference of the patients was significantly different for the trait anxiety level. Female patients had higher trait anxiety level than male patients. 2. Analysis of state anxiety scores indicated that the mean score of the state anxiety prior to the test was higher than mean score of the state anxiety examined after the test. The difference was statistically significant. 3. Among the patients, 14 patients (43.7%) used monitor type, while 18 patients(56.3%) used blunter type. The means of preference for information measured on the Krantz' subscale was 2. 45. 4. The study results indicate that the state anxiety level of those who a low trait anxiety level was lower than that of those who had a high trait anxiety level. 5. State anxiety levels depending upon the kind of coping style which patients used during the test were not significantly different. This study did not identify the influence of preparatory concrete information on the state anxiety depending on coping styles, and there fore a quasi-experimental study using a large sample according to different types of information, and the amount of information, coping styles is recommended.
- 396 View
- 0 Download

- Predictors of health Promoting Lifestyle for the Korean Immigrants in the U.S.A
- Myung Ja Kim, Hyo Jeong Song
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(2):341-352. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.2.341
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The study was to examine the relationships among health promoting lifestyle, level of anxiety, and perceived health status and to reveal those variables affecting health promoting lifestyle in Korean immigrants in the United States. The subjects were 425 adults chosen from Korean religious and social organizations located in New York from April 25th through July 5th, 1996. Data analyses were conducted by using pearson correlation coefficients, t-test, ANOVA, and stepwise multiple regression. The results were as follows : Health promoting lifestyle was significantly different according to age, religion, occupation, and the length of residence in the US. Those insured and those with no chronic conditions revealed a significantly higher score in health promoting lifestyle. Significant differences in the level of anxiety were found according to education, marital status, occupation, family income, and the length of residence. Those with no chronic conditions experienced a significantly lower level of anxiety. In the subscales of the health promoting lifestyle profile, self-actualization and interpersonal relationship revealed higher scores, whereas the scores of stress management, health responsibility, and exercise were lower. Those subjects whose perceived health status was very good, showed the lowest level of anxiety and the highest score on the health promoting lifestyle profile. Negative correlations were observed between the health promoting lifestyle profile and the level of anxiety, and between the perceived health status and the level of anxiety. Health promoting lifestyle was significantly predicted by the level of anxiety(22.0%), age(2.0%), health insurance(1.1%), respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of yoga exercise on maximum oxygen uptake, cortisol level, and creatine kinase myocardial bond activity in female patients with skeletal muscle pain syndrome
Min-Sung Ha, Yeong-Ho Baek, Jong-Won Kim, Do-Yeon Kim
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2015; 27(5): 1451. CrossRef
- Effects of yoga exercise on maximum oxygen uptake, cortisol level, and creatine kinase myocardial bond activity in female patients with skeletal muscle pain syndrome
- 577 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effect of Music Therapy on Anxiety in Neurotic Patients
- So YaJa Kim, Keum Sun Han
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(4):889-902. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.4.889
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to identify the effects of music therapy on anxiety in neurotic patients. The subjects of the study were 41 patients that had been diagnosed as having anxiety disorder, neurotic depression, or somatization disorder and were admitted to one general hospital in Seoul. The 41 research subjects were assigned to an experimental (22 clients) and a control (19clients) group. Data were gathered from September. 25, 1995 to December. 15, 1995 using a questionnaire and physiological measurement tool. Data were analyzed with the SAS package using frequency, t-test, paired t-test and Pearson correlation coefficients. The results of this study are as follows; 1. There were significant differences between two groups on systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and pulse rate after treatment. In the experimental group, Systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and pulse rate decreased significantly after Music Therapy. 2. There were no significant differences between the two groups on the pre and post psychological anxiety score. But, after music therapy, experimental group had a lower psychological anxiety score than the control group. From these results, it is concluded that the music therapy can be effective in decreasing anxiety in neurotic patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Antagonistic muscular co-contraction for skilled, healthy piano technique: a scoping review
Cobi Ashkenazi, George Waddell, Aaron Williamon
Frontiers in Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Music Therapy as Intervention on Peripheral Neuropathic Pain and Anxiety of Gynecologic Cancer Patients Undergoing Paclitaxel Chemotherapy
Gie Ok Noh, Moon Sook Hwang, Keum Sook Cho, Joung Ah Lim, Mi Kyung Kang, Hyo Jin Kim, Ji Youn Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2011; 17(3): 215. CrossRef
- Antagonistic muscular co-contraction for skilled, healthy piano technique: a scoping review
- 862 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Anxiety after Acute Myocardial Infarction and In-Hospital Complications
- Kyungeh An
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(7):999-1008. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.7.999
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE OF THE STUDY: A retrospective and descriptive survey was conducted to investigate the level of anxiety that patients experience in early stage of AMI and to examine whether anxiety independently predict inhospital complications. SIGNIFICANCE OF THE STUDY: AMI is a major cause of death and disability. Anxiety may contribute to developing complications and mortality. However, the association between anxiety and complications has not been examined.
RESULTS
Data were analyzed for 424 AMI patients enrolled for MICA (Myocardial Infarotion Complication and Anxiety) project. The mean score of the state anxiety inventory (SAI) measured within 72 hours after admission for the whole sample was 39.14 (+/-12.77) and ranged from 18 to 80. Overall, 161 patients (38.0%) experienced at least one episode of in-hospital complication (i.e. VT, VF, reinfarction, recurrent ischemia or cardiac death). Incidence of in-hospital complications was higher in the high anxiety group than in the low anxiety group (45.4% vs. 31.2%). There were significant differences in the incidence of recurrent ischemia between groups with low level of anxiety and high level of anxiety (27.5% vs. 18.9%). According to the Ward criterion from the logistic regression, anxiety reliably predicted the occurrence of in-hospital complications. Anxiety (odds ratio = 1.75, 95% CI 1.01-3.01, p= 0.04) significantly contributed to the model. Patients who were in the high anxiety group were 1.8 times more likely to have in-hospital complications than those who were in the low anxiety group.
CONCLUSION
AND SUGGESTION: This finding confirms that patients experience significant level of anxiety early after AMI, and this anxiety, after controlling other risk factors for the complications, is a reliable predictor of in-hospital complications.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reliability and Validity of the Mental Health Questionnaire for Adult
Jin Woong Yoon, Chung Yeub Chung, Dong Woo Lee, Jae Hyun Shin, Jang Won Cho, Chong Ki Kim, Seul Ki Choi, Jae Ock Kim
Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association.2019; 58(1): 64. CrossRef
- Reliability and Validity of the Mental Health Questionnaire for Adult
- 588 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effect of Auricular Acupressure Therapy on Anxiety of Cancer Pateint
- Kwuy Bun Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(6):888-896. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.6.888
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study wsa to necessitate auricular acupressure therapy as an independent nursing intervention on cancer paitents by confirming its effectiveness. METHOD: The experimental study was unequivalently controlled pre-post measure study. The subjects were 40 cancer patients who were hospitalized in K medical center in Seoul. The experimental group (20) and the control group (20) were randomly assigned. As measured tools, Spielberger's State-trait Anxiety (1976) measured tool by Kim's transplation (1978). The auricular acupressure therapy was applied to experimental group, and the pre-post measure was performed to both group. The data was analyzed by using SPSS computer program that included descriptive statistics, x2-test, and t-test. RESULT: 1) The experimental group with the auricular acupressure therapy showed lower trait anxiety scores in comparison with the control group (t= 8.036, p=.000). 2) The experimental group which applied the auricular acupressure therapy showed lower state anxiety scores in comparison with the control group (t= 19.616, p=.000). This result showed that cancer patients with the auricular acupressure therapy applied cancer patients decreased state anxiety and trait anxiety. Therefore , effectiveness of the auricular acupressure therapy was confirmed through this study. CONCLUSION: According to the result, anxiety of cancer pateint should be decreased and controlled by the auricular acupressure therapy as independent nursung intervension. In addition, the auricular acupressure therapy will provide effective independent nursing intervention that will decrease anxiety on patient with other disease and will improve quality of their lives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Auricular Acupressure Therapy on Primary Dysmenorrhea for Female High School Students in South Korea
Nam Hyun Cha, Sohyune R. Sok
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2016; 48(5): 508. CrossRef - Effects of Auricular Acupressure Therapy on Nocturia and Insomnia in the Elderly
Ji Yeon Kim, Hye Sook Ryu, Seok Hoon Nam, Kyung Sook Park
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2014; 17(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of Auricular Acupressure on Menstrual Pain, Dysmenorrhea, and Academic Stress in Women College Students
Seung-Ok Ro, Hea-Young Lee, Jaeon Lee, Miyoung Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(3): 356. CrossRef - The Effect of Ear Reflexotherapy on Back Pain of Working Women in Middle Age
Kyung-Sook Park, Eun-Ho Ha, Yu-Na Kim, Soo-Jin Kwon, Lee-Jung Ru, Ju-Hyun Song, Yong-Wha Woo, Jae-Yeon Lee, In-Hee Chun, Hyun-Kyung Kang, Hee-Jung Park, Eun-Joo Lee, Jae-On Lee
Journal of muscle and joint health.2010; 17(1): 14. CrossRef - Effects of a Cognitive-Behavioral Nursing Intervention on Anxiety and Depression in Women with Breast Cancer undergoing Radiotherapy
Myung-Sook Yoo, Haejung Lee, Jung-A Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(2): 157. CrossRef
- Effects of Auricular Acupressure Therapy on Primary Dysmenorrhea for Female High School Students in South Korea
- 788 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- The Effects of Guided Imagery on Nursing Students Performing Intramuscular Injections
- Min Hyun Suk, Suk Yong Kil, Hye Ja Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2002;32(6):784-791. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2002.32.6.784
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The anxiety and stress of nursing students on performance intramuscular injection diminished nursing skill performance. The purpose of this study was to identify the effects of the guided imagery program on anxiety, stress and nursing skill performance of nursing students. METHOD: The study design was time series with a nonequivalent control group pretest- posttest study. The Data were collected from the 30th of Oct. to the 6th of Nov. 2001. The objects of this study were 36 sophomores of university(18 for the experimental group, 18 for the control group). The Instruments used in this study were State Trait Anxiety Inventory developed by Spielberger (1972), Visual Analogue Scale for Stress and Nursing skill performance developed by the researcher. The guided imagery was provided through audiotapes to the subjects for 8 minutes. The pretest was given before the therapy to measure variables for both groups and the posttests were performed after intervention. The data were analyzed by the SAS program using t-test and paired t-test. RESULT: The results of this study are as follows. The level of anxiety of students who received the guided imagery were significantly lower than that of control group. the level of stress had a deeling tendency and the nursing skill performance level was significantly higher than that of control group. CONCLUSION: The guided imagery suggested as an effective nursing intervention did reduce the anxiety and promoted nursing skill performance of nursing students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differential effects of guided imagery and progressive muscle relaxation on physical and emotional symptoms in nursing students taking initial clinical training: A randomized clinical trial
Hossam Alhawatmeh, Raya Albataineh, Sawsan Abuhammad
Heliyon.2022; 8(10): e11147. CrossRef - The Effects of Guided Imagery on Stress, State Anxiety, Test Anxiety and Core Basic Nursing Skill Performance Score of Undergraduate Nursing Students
Eunyoung Hong, Bo Kim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(1): 16. CrossRef - Effects of Guided imagery on Stress and Anxiety of Women Receiving in Vitro Fertilization
Choon Hee Bae, Soon Bok Chang, Sue Kim, Inn Soo Kang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2011; 17(2): 178. CrossRef
- Differential effects of guided imagery and progressive muscle relaxation on physical and emotional symptoms in nursing students taking initial clinical training: A randomized clinical trial
- 798 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Uncertainty, Anxiety and Coping with Mastectomy for Breast Cancer
- Ok Hee Cho
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(4):1006-1017. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.4.1006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to provide basic information for developing a nursing intervention that helps patients learn how to acquire coping to reduce post operation uncertainty and anxiety by investigating the level of uncertainty and anxiety experienced by mastectomy patients. The subjects were 134 patients selected from St. Mary's Kangnam and St. Mary's hospital, and the data collection period was from October to December of 1998. Uncertainty was measured by using Mishel Uncertainty in Illness Scale (MUIS), anxiety measured by using State-Trait Anxiety Inventory(STAI), and coping by using a questionnaire developed by Kim & Yoo (1996). Data were analyzed with SAS program by t-test, ANOVA, Duncan's multiple range test, Pearson correlation coefficients, and stepwise multiple regression. The results were as follows: 1. The mean uncertainty score was 57.6. The results of the correlation between the compliance of medical regimen and demographic characteristics were as follows ; Those who monthly income over 2,010,000 won had lower than above 1,000,000 won, and those with the experience of chemotherapy had higher than those without, and the patient who has 7~12 months(1 yr.) post operation period had higher than the one below 6months, 25~36 months(3 yrs.), 37~60 months(5 yrs.), and over 61 months. 2. The mean anxiety score was 45.9. Anxiety tended to be increased slightly in subjects with low educational background, poor monthly income, experience of chemotherapy, and 7~12 months(1 yr.) post operation period, but there was no significant difference by general characteristics. 3. The mean value of the coping score was 100.7. The study revealed higher score in problem-focused coping than emotion-focused coping. In regard to coping by demographic characteristics were as follows ; those who had monthly income over 2,010,000 won had higher level of coping than those whose monthly income was between 1,010,000 and 2,000,000 won. In terms of problem- focused coping, those who had 25~36 months of post operation period showed significantly lower level of coping than those below 6 months or 37~60 months(5 yrs.) or over 61 months of post operation period. Regarding the emotion-focused coping, those with the christianity had significantly lower level of coping than those without it. Also, those whose monthly income over 2,010,000 won had significantly higher coping level than those with income of between 1,010,000 and 2,000,000 won. 4. A positive relationship was found between uncertainty and anxiety. Patients who experienced more uncertainty also showed more anxiety. Problem-focused coping was inversely related to uncertainty and anxiety. 5. The major variable that affected uncertainty was anxiety, explaining 63.3% of the uncertainty. In addition to this, it would explain 66.4% in total when experience of chemotherapy was added.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding mental health in breast cancer from screening to Survivorship: an integrative phasic Model and tool
Justine Fortin, Émilie Rudd, Claudia Trudel-Fitzgerald, Matthew J. Cordova, Marie-France Marin, Alain Brunet
Psychology, Health & Medicine.2025; 30(3): 437. CrossRef - Effect of audiovisual media-based nursing information on environmental stress, anxiety, and uncertainty in patients undergoing open-heart surgery
Jeong-Yeong Jeon, Dong-Hee Kim, Kyoungrim Kang
Medicine.2023; 102(8): e33001. CrossRef - The Effects of Repeated Information using Visual and Video-Audio Media on Uncertainty and Anxiety in Patients undergoing Thyroidectomy
Hyeon-Ok Lee, Ji-Yeong Seo
Asian Oncology Nursing.2020; 20(2): 92. CrossRef - The Effect of Nursing Information on Anxiety and Uncertainty in Patients for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection before the procedure of the patients
Eun-Jung Shin, Young-Sook Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(2): 66. CrossRef - The Effects of Visual Information on Anxiety and Uncertainty in Elderly Patients after the Total Knee Arthroplasty
Kyung Ryu, Sook-Hee Cho
Journal of muscle and joint health.2015; 22(1): 48. CrossRef - Uncertainty in Elderly Women with Osteoarthritis: Relationship to Pain, Self-care Agency and Health Conservation
Jiran Nam, Kiwol Sung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2014; 16(3): 201. CrossRef - Adaptation Experience to Work of Nurses with Low Back Pain
Jin-Hyang Yang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(6): 597. CrossRef - Anxiety, Depression and Uncertainty in Cancer Patients Participating in Clinical Trial of Anticancer Drugs
Haejin Kim, Myungsun Yi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(1): 53. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Uncertainty in Dialysis Patient by Duration of Dialysis
Su Jung Yun, Young Hee Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(6): 597. CrossRef - A Structural Model for Psychosocial Adjustment in Patients with Early Breast Cancer
Hye Young Kim, Hyang Sook So
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(1): 105. CrossRef
- Understanding mental health in breast cancer from screening to Survivorship: an integrative phasic Model and tool
- 709 View
- 6 Download
- 10 Crossref

- An Application Effect of Rhythmic Movement Program for the Health Promotion in the Elderly
- Sook Ja Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(3):776-790. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.3.776
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Every year the number of the elderly increases in Korea thanks to the improvement of social and economical levels and the development of medicine. However, many problems such as insufficent care and the isolation of the elderly have been commonplace. This trend exists not only because of increased lifespan but also the changing social structure of the nuclear family. Accordingly, inspite of the development of medicine, geriatric diseases including circulatory diseases are increasing in proportion of elderly population, as well as the severity. Therefore, it is important to emphasize that health care programs provide the best possible health care and functional capacities in terms of healthy elderly lifestyles. Especially, the phenomena of aging and geriatric diseases taking place with the elderly naturally are affected by lifestyle and the drastic changes in exercise patterns. This study aims to improve geriatric health by introducing a rhythmic movement program for the elderly to estabilish a health-promoting self-care system and by developing quality of life, perceived health status, their physical and physiological functions and emotional state. The theoretical framework used in this dissertation is derived from the Health-Promoting Self-Care System Model (Simmons, 1990), which integrates the Self-Care Deficit Nursing Theory (Orem, 1985), the interaction model of Client Health Behavior (Cox, 1982) and the Health Promotion Model (Pender, 1987). As a quasi-experimental design, the nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design is utilized for this study. The subjects of this study consist of 64 people, over 65 years old who live in 2 nursing homes for the aged located in S city , Kyong-gi province and volunteered for this study from July, 12, 1999 to September, 17, 1999. They are divided into two groups: 33 in the experimental group and 31 in the control group. The experimental group particpated in the Rhythmic Movement Program at the nursing home, which was comprised of 45 minutes a session, 5 sessions a week during 9 weeks. In order to measure the results of the Rhythmic Movement Program, aspects of perceived health status, balance, flexibility, grip strength, leg strength, heart rate, blood pressure, depression, anxiety and the quality of life were measured before and after participating in the Rhythimic Movement Program for the experimental group after 9 weeks, as well as the control group. The collected data were processed by SPSS PC+ and analyzed by the X2 test, t-test, ANCOVA and the Pearson Correlation Coefficient. The results of this study are as follows: 1. The perceived health status conditions in the experimental group show statistically significant improvement when compared to the control group (F=17.51, p=.000). 2. The physical and physiological functions, that is, balance (F=17.51, p=.000), flexibility (F=8.01, p=.006), grip strength (F=3.21, p=.018) and leg strength (F=25.78, p=.000) in the experimental group are higher than the control group. The vital signs, that is, the number of heart rate (F=.022, p=.884), systolic pressure (F=1.73 p=.193), and diastolic pressure (F=2.74, p=.103) in the experimental group compared to the control group decreased, but doesn't show statistically significant differences. Immune responses (F=5.13, p=.003) showed statistically significant increases in the experimental group when compared to the control group. 3. The emotional state are improved, that is, degree of depression (F=11.56, p=.001) and degree of anxiety (F=9.14, p=.004) in the experimental group showed statistically significant decreases. 4. The quality of life in the experimental group (F=3.03, p=.037) showed statistically significant differences compared to the control group. 5. The observations of the relationships among the perceived health status, emotional state , the quality of life, the relationships between the perceived health status, the degree of depression (r=-.653, p=.000) and the degree of anxiety (r=-.786, p=.000) were in contrary propotions, while the relationships between the perceived health status and the quality of life (r=.234, p=.008) were in direct propotion. In conclusion, the Rhythmic Movement Program used in this study for geriatric nursing care is simple and safe for application to the elderly and shows significant effects by implementing 5 sessions a week for 9 weeks. The Rhythmic Movement Program improves the quality of life, maintains as well as improves the physical and physiological fuctions and emotional state, therefore this program is strongly recommended for positive applications for independant geriatric nursing health care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Dance Sports Program on Physical Function, Cognition, Depression and Quality of Life in Rural Elderly Women
Yun-Hee An, Nam-Soo Hong, Hee-Jung Yoon
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2020; 45(4): 385. CrossRef - The Effects of Self-Care Intervention Programs for Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairment
Myung-Suk Kim, Moonhee Gang, Jihye Lee, Eunyoung Park
Issues in Mental Health Nursing.2019; 40(11): 973. CrossRef - The Effects of Qi-gong Exercise on the Health of the Elderly - With Respect to the Physical Health Status, the Fear of Falling, Balance Efficacy, and Hwa-Byung -
Kum-Sook Park, Heon-Young Jeong, Young-Hee Kim
Journal of Oriental Neuropsychiatry.2016; 27(4): 207. CrossRef - Impact Factors for Health of Family Caregivers of Hospice Patients
Bok Yae Chung, Hyeon Sook Park
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2014; 17(2): 75. CrossRef - The Effects of a Health Management Program on Health-promoting Lifestyle and Depression in Older Adults Living at Home
Young Rye Park, Yang Gyeong Yoo
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2013; 16(1): 71. CrossRef - The Effects of an Aerobic Exercise Program on Mobility, Fall Efficacy, Balance, and Stress in the Elderly at Senior Centers
Su Kyung Chu, Chung Yul Lee, Jang Hak Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2012; 23(1): 22. CrossRef - The Effects of Aerobic Exercise Therapy on Physical Functions in the Elderly
Sook Hee Jung, Kyung Hee Chung
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(2): 252. CrossRef - Relations among Depression, Life Satisfaction and Health Promoting Behavior in the Elderly
Ji-Hye Seo, Hyun-Sook Ryu
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2010; 21(2): 169. CrossRef - Effects of Music Therapy and Rhythmic Exercise on Quality of Life, Blood Pressure and Upper Extremity Muscle Strength in Institution-Dwelling Elderly Women
Eun Young Jeon, Sook Young Kim, Hyun Suk Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(6): 829. CrossRef - Effects of Aroma Hand Massage On Sleep, Depression and Quality of Life in the Institutionalized Elderly Women
Soon Yi Seo, So Young Chang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(4): 372. CrossRef - The effect of modified jazz dance on balance, cognition, and mood in older adults
Patricia T Alpert, Sally K Miller, Harvey Wallmann, Richard Havey, Chad Cross, Theresa Chevalia, Carrie B Gillis, Keshavan Kodandapari
Journal of the American Academy of Nurse Practitioners.2009; 21(2): 108. CrossRef - Effects of a Strengthening Program for Lower Back in Older Women with Chronic Low Back Pain
Hee-Kyoung Hyoung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(6): 902. CrossRef - Comparisons of Motivation, Health Behaviors, and Functional Status Among Elders in Residential Homes in Korea
Rhayun Song, Kyung Ja June, Chun Gill Kim, Mi Yang Jeon
Public Health Nursing.2004; 21(4): 361. CrossRef
- The Effect of Dance Sports Program on Physical Function, Cognition, Depression and Quality of Life in Rural Elderly Women
- 688 View
- 5 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Effects of Postpartum Massage Program on Stress response in the Cesarean section Mothers
- Sung Hee Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):488-497. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.488
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to explore the effect of a postpartum massage program on stress response in the Cesarean section mothers. The study focused on evaluating the effect of postpartum massage program on mood, anxiety, skin temperature and concentration of saliva and breast milk immunoglobulin A in the Cesarean section mothers. This study was designed as a nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest quasi-experimental study. Twenty-eight Cesarean section mothers were selected as experimental group, whereas twenty- seven were control group. The postpartum massage program consisted of 20 minutes of warm-up, massage and ending phases and used once a day. During each program, there were 4 minutes of warm-up, 14 minutes of massage on back, axillary and breasts, and 2 minutes of ending. Massage were used for the experimental group by the same investigator 20 times per minute. The massage technique used were efflurage, petrissage, accupressure, kneading and vibration. Skin temperature was monitored with YSI Tele-thermometer(Simpson electric Co., USA) before and after massage program. The concentration of immunoglobulin A in saliva and breast milk was analyzed by immunoturbididimeter assay(Cobas INTEGRA, Roche, Swiss) before and after massage program. Also at this time mood and anxiety were measured by self-report. The data were analyzed using SPSS version 7.5 and hypothesis was tested with ANCOVA analysis and Pearson coefficient correlation. The results were as follows : 1) Score of mood increased significantly after use of postpartum massage program. 2) Level of anxiety decreased significantly after use of postpartum massage program. 3) Skin temperature increased significantly after use of postpartum massage program. 4) Concentration of saliva immunoglobulin A increased significantly after use of postpartum massage program. 5) Concentration of breast milk immunoglobulin A did not change significantly after use of postpartum massage program. 6) After use of postpartum massage program, there was significant correlation between psychological stress response and physiological stress response. The results suggest that postpartum massage program can be effective nursing intervention to reduce stress response in the postpartum mothers under stress.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Meridian Acupressure Massage on Body Composition, Edema, Stress, and Fatigue in Postpartum Women
Geum-Sook Jung, In-Ryoung Choi, Hee-Young Kang, Eun-Young Choi
The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine.2017; 23(10): 787. CrossRef - Effects of Laughter Therapy on Immune Responses in Postpartum Women
Kyung Hee Ryu, Hye Sook Shin, Eun Young Yang
The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine.2015; 21(12): 781. CrossRef
- Effects of Meridian Acupressure Massage on Body Composition, Edema, Stress, and Fatigue in Postpartum Women
- 730 View
- 10 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Effect of Hand Massage on the Anxiety of the Hysterectomy Patients in Immediately prior to Surgery
- Jeong Mee Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):476-487. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.476
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of hand massage as a nursing intervention on the anxiety of the hysterectomy patients in immediately prior to surgery. The method of this study was Nonequivalent Control Group Non-Synchronized Design. The data were selected from at K university hospital in Pusan, and they consisted of Experimental group-25 patients, Control group -24 patients. The data were collected from Jan. 4 to Jan. 30 in 1999. The subjects' self-reports of anxiety (measured by the Spielberger Trait-State anxiety Inventory and Visual Analogue Scale developed by Cline et al.) were recorded before and immediately after the intervention. The objective physiologic measures of blood pressure and pulse rate. The collected data were analysed by means of frequency, percentage, standard deviation, chi- square test, t-test, ANCOVA with SPSS program. The results of this study were as following; 1. Hypothesis 1: The 1st hypothesis that "There will be significant difference of the state anxiety level just before surgery in the experimental group and control group" was supported(P= .000). 2. Hypothesis 2: The 2nd hypothesis that "There will be significant difference of the visual analogue scale score just before surgery in the experimental group and control group"was supported(P= .000). 3. Hypothesis 3: The 3rd hypothesis that "There will be significant difference of the systolic and diastolic blood pressure level just before surgery in the experimental group and control group"was supported (P= .003, P= .041). 4. Hypothesis 4: The 4th hypothesis that "There will be significant difference of the pulse rate just before surgery in the experimental group and control group"was supported(P= .004). In conclusion, hand massage is a benefical nursing intervention that alleviates the psychological, physiological anxiety of the hysterectomy patients in immediately prior to surgery. therefore it is recomended to use the hand massage as a nursing intervention for patients undergoing anxiety. The results of this study appear promising, additional research is recomended to further the appropriate uses of hand massage in nursing practice for this and other patient population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Hand Massage in Patients Who Underwent Transradial Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Eun Sil Shin, Myung-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(4): 465. CrossRef - Effects of Hand Massage on Depression, Self-esteem and Vitality of the Elderly Patients in Convalescent Hospital
Hye-Jeong Kim, Kang-Yi Lee
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2016; 22(2): 202. CrossRef - The Effect of Hand Holding and Nei-Guan Acupressure on Anxiety and Pain under Local Anesthetic Patients during Surgery
Sun Hee Park, Hee Jung Jang
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(11): 378. CrossRef - Analysis of Studies on Hand Massage Published in Korea: On the Effects of Sleep, Pain, Anxiety and Depression
In-Ja Kim, Yu-Na Cho
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2012; 15(1): 47. CrossRef - Effects of Head and Neck Massage on Anxiety, Pain, and Discomfort in Hysterectomy Patients
Eun-Young Kim, Euy-Soon Choi
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(1): 60. CrossRef - Effects of a Cognitive-Behavioral Nursing Intervention on Anxiety and Depression in Women with Breast Cancer undergoing Radiotherapy
Myung-Sook Yoo, Haejung Lee, Jung-A Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(2): 157. CrossRef
- The Effects of Hand Massage in Patients Who Underwent Transradial Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- 646 View
- 1 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Deducing Coronary Artery Disease Anxiety through Musical Therapy and Providing Information
- Mi Suk Kang, Kyung Min Park, Chung Ja Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):380-390. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.380
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was performed to evaluate the effectiveness of music therapy as one of the psychiatric nursing intervention tools, with addtional information in relieving anxiety during the procedure. Data were collected through nonequivalent pre-and post tests from July 1, 1998 to September 30 1998 in 90 patients (test group A: 28 patients, test group B: 27 patients, control group: 33 patients) who were hospitalized in DongSan Medical Center in order to have cardiac catheterization. The Subjects were informed by educational videos, which were modified according to the sensory information of the 10 study patients. They were based on the informative booklet by Kim keum-soon (1989). The procedural information was also modified according to the hospital`s customs. Provided the music for patients suitable to their tastes, and measured their blood pressure, heart rate, the degree of anxiety using the Spielberger`s measurement device of anxiety, and behavioral response of Finesilver`s. The statistical significance was analyzed using chi-square test and ANOVA. The results of this study were as follows : Hypothesis 1 : There are significant differences in the degree of anxiety among test group A, Test group A was provided only information, Test group B was provided information and the control group was provided neither. Hypothesis 2 : There are significant differences in systolic blood pressure among test group A, test group B, and control group.: non-significant. Hypothesis 3 : There are significant differences in diastolic blood pressure among test group A, test group B, and control group.: significant(F=1.31, p=.27, interaction; F=3.80, p=.00). Hypothesis 4 : There are significant differences in heart rate among test group A, test group B, and control group.: non-significant. Hypothesis 5 : There are significant differences in behavioral responses among test group A, test group B, and control group.: significant(F=10.05, p=.00). Further validation study is required with other subjects and other settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Patient-Selected Music Listening on the Pain and Anxiety of Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Randomized Controlled Trial
SukKyong Kim, HyeonCheol Jeong
Healthcare.2021; 9(11): 1437. CrossRef - Effects of Aromatherapy on Stress Responses, Autonomic Nervous System Activity and Blood Pressure in the Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun Jeong Song, Mi Young Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of Music Listening on Pain, Anxiety, and Vital Signs of Burn Patients
Jungtae Son, 김선화, LeeEunJoo
Korean Journal of Music Therapy.2009; 11(1): 124. CrossRef
- Effects of Patient-Selected Music Listening on the Pain and Anxiety of Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 665 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Crossref

- A Meta-Analysis of Effects of Relaxation Therapy on Anxiety and Blood Pressure
- Hee Seung Kim, Hae Hiang Song, So Eun Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(2):282-292. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.2.282
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A meta-analysis of 14 quasi-experimental studies was conducted to compare the effect of size on various relaxation therapies applied to patients and health volunteer students. These studies were selected from theses, dissertations and papers that have been done between 1982 to 1993. Also They have a randomized or nonequivalent control group in a pre test-post test design. The studies were evaluated in different ways; 1) types of relaxation therapy, 2) total amount of time of relaxation therapy, and 3) types of outcome variables. For a group of homogenious studies, the weighted mean effect size and standard error were estimated. Some findings are summarized as follows : 1. Jacobson relaxation therapy had a larger effect on systolic and diastolic blood pressures than on state anxiety. 2. For the total time of relaxation therapy, (longer than 60 minutes) had a much larger effect in decreasing systolic and diastolic blood pressures than in the case of a time period shorter than 60 minutes. 3. Relaxation therapy applied to surgery patients also had a larger effect in decreasing state anxiety than when applied to other patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Abdominal Breathing on Anxiety, Blood Pressure, Peripheral Skin Temperature and Saturation Oxygen of Pregnant Women in Preterm Labor
Soon-Bok Chang, Hee-Sook Kim, Yun-Hee Ko, Choon-Hee Bae, Sung-Eun An
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(1): 32. CrossRef
- Effects of Abdominal Breathing on Anxiety, Blood Pressure, Peripheral Skin Temperature and Saturation Oxygen of Pregnant Women in Preterm Labor
- 663 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effect of Dance Therapy on Physical and Psychological Characteristics in The Elderly
- Young Ran Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(2):429-444. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.2.429
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was performed to explore the effects of a dance therapy on physical and psychological characteristics in the elderly. The design of this study was a non-equivalent pre-post test experiment. The subjects consisted of elderly persons living in a facility located in Suweon and Bucheon. Fifty eight subjects, aged between 65 and 93 years who had normal cognition, sensory function, balance, and resting blood pressure. They underwent tests of balance, flexibility, muscle strength, depression, and anxiety as baseline data before dance therapy, and at 6 th week and at the end of the 12nd week after following dance therapy. Twenty seven elderly persons were assigned to the experimental group and participated with the dance therapy between April and July, 1998. The dance therapy was developed by the author with the help of a dance therapist and a physiatrist. This therapy was based on the Marian Chace's dance therapy and Korean traditional dance with music. The dance therapy was developed by the author with the help of a dance therapist and a physiatrist. This therapy was based on the Marian Chace's dance therapy and Korean traditional dance with music. The dance therapy consists of 50 minutes session, 3 times a week for 12 weeks. One session was consisted of warming-up, expression, catharsis, sharing, and closing stage. The intensity of the dance therapy was at the 40% of age-adjusted maximum heart rates. Data were analyzed with mean, standard deviation, Chi-square test, unpaired t-test, repeated measures ANOVA, and Bonferroni multiple regression using SAS program. 1. The results related to the physical characteristics were as follows : 1) The balance (standing on one leg, walking on the balancing bar), flexibility and muscle strength (knee extensor, knee flexor, ankle plantarflexor and dorsiflexor) of the experimental subjects significantly increased over time more than that of the control subjects. 2) The experimental group had significantly higher score for balance, flexibility, muscle strength of knee extensor, and knee flexor than the control group at the 12nd week after dance therapy. 3) The experimental group had significantly higher score for muscle strength of ankle dorsiflexor and plantarflexor than the control group at the 6th week and the 12nd week after dance therapy. 2. The results related to psychological characteristics were as follows : 1) Scores of Geriatric Depression Scale, Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, and Zung's Self-rating Anxiety Scale of the experimental group were significantly decreased over time more than that of the control group. 2) The experimental group had significantly lower score for depression than the control group at the 12nd week after dance therapy. 3) The experimental group had significantly lower score for anxiety than the control group at eh 6th week and the 12nd week after dance therapy. The findings showed that the dance therapy could be effective in improving the balances, flexibility, and muscle strength of lower limb, and effective in decreasing the depression and anxiety of the elderly. Additional merits of the dance therapy would be inexpensiveness, easy accessibility, and increasing interpersonal relationship. It can be suggested that the dance therapy is effective in the health promotion of the elderly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of a Health Management Program on Health-promoting Lifestyle and Depression in Older Adults Living at Home
Young Rye Park, Yang Gyeong Yoo
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2013; 16(1): 71. CrossRef
- The Effects of a Health Management Program on Health-promoting Lifestyle and Depression in Older Adults Living at Home
- 524 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effect of a Hand Massage Program on Anxiety and Immune Function in Clients with Cataract Surgery under Local Anesthesia
- Kyung Sook Cho
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1999;29(1):97-106. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1999.29.1.97
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was designed to investigate the effect of a hand massage program on anxiety and immune function in patients during cataract surgery. The hand massage program, in this study, consisted of hand massage and hand-holding. The subjects were sixty-three patients, thirty for the experimental and thirty-three for the control group, who were admitted at Kang Nam St. Mary's Hospital for cataract surgery. This study was carried out from December 10, 1997 to February 26, 1998. The level of anxiety as measured by the Visual Analogue Scale, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and pulse rate were measured before, after hand massage, and after hand-holding. Epinephrine, norepinephrine, cortisol, blood sugar levels, neutrophil, lymphocyte, and natural killer cell percentages also were measured before hand massage and five minutes before the end of the operation. Data were analyzed by t-test, ANCOVA, repeated measure ANOVA, and Bonferroni multiple comparisons. The results were as follows : 1) After hand massage, psychological anxiety levels decreased significantly compare with before hand massage in the experimental group, not in the control group. After hand holding, there were significant decrease in both groups. 2) There were no significant differences on systolic blood pressure, diastorlc blood pressure, and pulse rates in both groups. 3) The hand massage program decreased epinephrine, norepinephrine, and cortisol significantly in the experimental group and increased epinephrine, norepinephrine, and cortisol in the control group. 4) There were no differences in blood sugar levels, neutrophil and lymphocyte percentages in white blood cells after the hand massage program. However, natural killer cells in lymphocytes were significantly increased in the experimental group. These findings indicate that a hand massage program could be a effective nursing intervention in decreasing the psychological and physiological anxiety levels and improving immune function in clients having cataract surgery under local anesthesia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An intervention study of a combined intervention of positioning and hand massage in patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation
Yun Kyeong Lee, Mihae Im, Haeryun Cho
Nursing Open.2023; 10(3): 1404. CrossRef - Effects of Extremity Massage on Preoperative Anxiety: A Three-Arm Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial on Phacoemulsification Candidates
Moloud Farmahini Farahani, Masoomeh Noruzi Zamenjani, Morteza Nasiri, Soheila Shamsikhani, Zahra Purfarzad, Mehdi Harorani
Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing.2020; 35(3): 277. CrossRef - The Effects of Hand Massage in Patients Who Underwent Transradial Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Eun Sil Shin, Myung-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(4): 465. CrossRef - Effects of the Provision of Information on Anxiety in Patients during Outpatient Surgery: A Systematic Review
Ae-Ri Jung, In-Sook Lee
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2016; 13(1): 48. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Hand Massage Combined with Analgesics on Pain Control in Patients with Terminal Cancer
Yunmi Lee, Hosoon Yoon, Sungwoon Lee, Young Mi Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2016; 19(4): 296. CrossRef - Effect of Music Therapy on Vital Signs, Anxiety, Cortisol and Pain of Cataract Surgery Patients in Elderly
Jung-Hae Park, Kwang-Hi Park
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(8): 549. CrossRef - The Effect of Hand Holding and Nei-Guan Acupressure on Anxiety and Pain under Local Anesthetic Patients during Surgery
Sun Hee Park, Hee Jung Jang
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(11): 378. CrossRef - Effect of Aroma Hand Massage on Anxiety and Immune Function in Patients with Gynecology Surgery under Local Anesthesia
Yun Ah Kim, Mi Hae Sung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2014; 20(2): 126. CrossRef - Relational and Health Correlates of Affection Deprivation
Kory Floyd
Western Journal of Communication.2014; 78(4): 383. CrossRef - Analysis of Studies on Hand Massage Published in Korea: On the Effects of Sleep, Pain, Anxiety and Depression
In-Ja Kim, Yu-Na Cho
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2012; 15(1): 47. CrossRef - Effects of Foot Reflexology on Fatigue, Sleep and Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jeongsoon Lee, Misook Han, Younghae Chung, Jinsun Kim, Jungsook Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(6): 821. CrossRef - Effects of Hand Holding on Self-esteem and Assertiveness in Women Patients with Depression
Mi-Hae Sung, Mi Young Choi, Ok Bong Eum
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2010; 19(2): 154. CrossRef - Effects of Self-Foot Reflexology on Stress, Fatigue and Blood Circulation in Premenopausal Middle-Aged Women
Soo Hyun Jang, Kye Ha Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 662. CrossRef - The effects of handholding on anxiety in cataract surgery patients under local anaesthesia
Jung‐Soon Moon, Kyung‐Sook Cho
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2001; 35(3): 407. CrossRef
- An intervention study of a combined intervention of positioning and hand massage in patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation
- 793 View
- 6 Download
- 14 Crossref

- The Effect of Slow Stroke Back Massage on Anxiety and Immune Response in the Patients undergoing Open Heart Surgery
- Hae Soon Kim, Hyang Yeon Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(4):980-991. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.4.980
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of slow stroke back massage(SSBM) on anxiety and immune response in patients undergoing open heart surgery and to compare the effect of 5-minutes with 10-minutes SSBM. Among the sixty-four patient subjects, twenty-one were one experimental group receiving massage for 10-minutes, twenty for the other experimental group receiving massage for 5-minutes and twenty-three for the control group. Subjects were admitted at Hospitals in Inchon and Puchon for open heart surgery. This study was carried out from October 10, 1997 to May 10, 1998. The levels of anxiety were measured by the Visual Analogue Scale(VAS), Trait anxiety scale, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, pulse rate, blood cortisol and the levels of immune response were measured by the blood T-lymphocyte and Natural killer cell. Study measurements were taken before and after SSBM on the 1st pst operative day. Data were analyzed using x2test, oneway ANOVA, paired t-test, t-test and Pearson product moment correlation. The results were summarized as follows: 1. After SSBM, VAS anxiety level, systolic and diastolic blood pressure and pulse rate of the experimental group were decreased significantly than those measurements before the SSBM. After SSBM, significant difference in the VAS anxiety level, systolic blood pressure and pulse rate between the experimental and control groups were found. 2. After SSBM, the blood cortisol of the experimental and control groups were increased significantly compared with before SSBM. But the significant difference in blood cortisol between the two groups was not found. 3. After SSBM, the blood T-lymphocyte percentages of the experimental and control groups were decease significantly and blood Natural killer cell percentages of the two groups were increased compared with before SSBM. But significant difference in blood T-lymphocyte and Natural killer cell percentages between the two groups was not found. 4. Significant difference in VAS anxiety level, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, pulse rate, blood cortisol, blood T-lymphocyte and Natural killer cell percentages between SSBM for 5 minutes and SSBM for 10 minutes were not found. Based upon the results, this study concludes that the slow stroke back massage for 5 minutes is a useful intervention that decreases anxiety and produces relaxation in patients undergoing open heart surgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Back Massage on Degree of Pain, State Anxiety and Quality of Sleep of Postoperative Patients with Gastrectomy
Mi Suk Han, Kang-Yi Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(1): 69. CrossRef
- The Effect of Back Massage on Degree of Pain, State Anxiety and Quality of Sleep of Postoperative Patients with Gastrectomy
- 738 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Correlation Study of Maternal Stress, Anxiety, and Perception of the Newborn in the Early Postpartum Stage
- Hyun Young Koo, Young Im Moon
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(3):616-624. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.3.616
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to contribute to maternal nursing in early postpartum stage and to neonatal nursing. Data were collected through self-report questionnaires which were constructed to include parental role stress scale, state- trait anxiety scale, and perception of the newborn scale. The subjects consisted of 100 mothers in the early postpartum stage at three hospitals in the Kyoung-In area, from November 8 to December 26, 1997. The data were analyzed by an SPSS program. The results are follows: 1. The mean of parental role stress of mothers in the early postpartum stage was 10.70+/-2.63. The means of stage anxiety and trait anxiety of mothers were 36.29+/-8.45 and 38.53+/-8.36. The mean of perception of the newborn was 2.65+/-5.05, and 59% of mothers rated their newborn as better than the average newborn. 2. The level of parental role stress correlated to the level of state anxiety and trait anxiety. The level of state anxiety and trait anxiety were also related. The level of perception of the newborn was related to the level of state anxiety and trait anxiety. 3. Mothers who did not want the pregnancy, whose newborn were girls, and who already had one child had higher state anxiety than those who did not. Mothers who already had one child, and whose newborn had no specific signs had higher trait anxiety than those who did not. Mothers who professed a religions had a higher perception of the newborn than those who did not. The above findings indicate that the levels of parental role stress, state anxiety, trait anxiety and perception of the newborn of mothers in early postpartum stage were correlated. Therefore nursing intervention for reducing stress and anxiety, and improving perception of the newborn should be provided for mothers in early postpartum stage.
- 414 View
- 0 Download

- The Effect of Information by using Cartoon on Preoperative Anxiety of children following Tonsillectomy
- Sun Nam Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(2):490-497. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.2.490
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was designed to investigate the effects of information by using cartoon on preoperative anxiety of children following tonsillectomy. The subjects were 30 children aged between 7 and 12 who were hospitalized at C university hospital for undergoing tonsillectomy from December 20, 1996 to August 14, 1997. Sixteen of them were assigned to the experimental group, while fourteen subjects to the control group. The data were collected through preoperative state anxiety, pulse rate, pain before and after giving information by using cartoon. The results were as follows : 1. Preoperative state anxiety increased in both groups(P=0.0348). No significant difference found between experimental and control group. But preoperative anxiety in experimental group was apt to increase less than that in the control group. 2. Pulse rate didn't make significant difference within and between groups. 3. Pain increased in both groups(P=0.0001). No significant difference found between experimental and control group. 4. Experimental group between the aged 7 and 9 decreased preoperative state anxiety, but experimental group between the aged 10 and 12 increased preoperative state anxiety after treatment(P=0.0298). These findings may indicate that the information by using cartoon is effective in children between the aged 7 and 12.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychometric Assessment of the Emotional Reactions Instrument-Korean (ERI-K) to Measure Korean Children’s Emotional Reaction to Hospitalization
Jin-Sun Kim, Jeong-Hwan Park, Roxie L. Foster, Sufen Cheng
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2011; 22(1): 31. CrossRef
- Psychometric Assessment of the Emotional Reactions Instrument-Korean (ERI-K) to Measure Korean Children’s Emotional Reaction to Hospitalization
- 671 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Discriminating Power of Socio-demographic and Psychological Variables on Addictive Use of Cellular Phones Among Middle School Students
- Haejung Lee, Myoung Soo Kim, Hyun Kyung Son, Sukhee Ahn, Jung Soon Kim, Young Hae Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(6):957-965. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.6.957
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to examine the degrees of cellular phone usage among middle school students and to identify discriminating factors of addictive use of cellular phones among sociodemographic and psychological variables. METHODS: From 123 middle schools in Busan, potential participants were identified through stratified random sampling and 747 middle school students participated in the study. The data was collected from December 1, 2004 to December 30, 2004. Descriptive and discriminant analyses were used. RESULTS: Fifty seven percent of the participants were male and 89.7% used cellular phones at school. The participants were grouped into three groups depending on the levels of the cellular phone usage: addicted (n=117), dependent (n=418), non-addicted (n=212). Within the three groups, two functions were produced and only one function was significant, discriminating the addiction group from non-addiction group. Additional discriminant analysis with only two groups produced one function that classified 81.2% of the participants correctly into the two groups. Impulsiveness, anxiety, and stress were significant discriminating factors. CONCLUSION: Based on the findings of this study, developing intervention programs focusing on impulsiveness, anxiety and stress to reduce the possible addictive use of cellular phones is suggested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychometric evaluation of smartphone addiction scale – short version (SAS-SV) among young adults of India
George Felix, Manoj K. Sharma, Nitin Anand, Binukumar Bhaskarapillai, Kalpana Srivastava
Industrial Psychiatry Journal.2025; 34(1): 53. CrossRef - App-based tracking of smartphone use and its association with perceived stress and sense of coherence among undergraduate medical students in Southern India
Kathiresan Jeyashree, Jane S. Sathiavadivu, AbdulkaderRizwan Suliankatchi
International Journal of Adolescent Medicine and Health .2021; 33(3): 245. CrossRef - Interaction between physical activity and problematic mobile phone use on suicidality in Chinese college students
Yang Xie, Ming Zhu, Xiaoyan Wu, Shuman Tao, Yajuan Yang, Tingting Li, Liwei Zou, Honglv Xu, Fangbiao Tao
BMC Psychiatry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Sleep Quality on the Relationship Between Problematic Mobile Phone Use and Depressive Symptoms in College Students
Liwei Zou, Xiaoyan Wu, Shuman Tao, Honglv Xu, Yang Xie, Yajuan Yang, Fangbiao Tao
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Prevention Program for Media Addiction on Television Addiction, Internet Addiction, Cellular Addiction, and Impulsiveness in Elementary School Students.
Hyun Young Koo
Child Health Nursing Research.2013; 19(4): 270. CrossRef - Development of a Cell Phone Addiction Scale for Korean Parents of Young Children.
Hyun Young Koo
Child Health Nursing Research.2013; 19(1): 29. CrossRef - Development and Validation Study of a Cell Phone Addiction Scale for Korean Children
Hyun-Young Koo, Myung-Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2012; 18(2): 76. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Prevention Program for Cell Phone Addiction in Middle School Students
Hyun-Young Koo
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2011; 17(2): 91. CrossRef - Factors related to the Overuse of Mobile Phone in Elementary School Students
Kyoung Sook Lee, Hwang Ran Ahn, Kyung Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2011; 20(3): 271. CrossRef - Effects of an Empowerment Education Program in the Prevention of Internet Games Addiction in Middle School Students
Aeran Joo, Inhyae Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(2): 255. CrossRef
- Psychometric evaluation of smartphone addiction scale – short version (SAS-SV) among young adults of India
- 775 View
- 3 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Effects of Kangaroo Care on Anxiety, Maternal Role Confidence, and Maternal Infant Attachment of Mothers who Delivered Preterm Infants
- Sang Bok Lee, Hye Sook Shin
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(6):949-956. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.6.949
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of Kangaroo Care(KC) on anxiety, maternal role confidence, and maternal infant attachment of mothers who delivered preterm infants. METHODS: The research design was a nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest. Data was collected from September 1. 2006 to June 20. 2007. The participants were 22 mothers in the experimental group and 21 in the control group. KC was applied three times per day, for a total of ten times in 4 days to the experimental group. RESULTS: The degree of anxiety was statistically significantly different between the two groups but maternal role confidence and maternal infant attachment was statistically insignificant. CONCLUSION: This data suggests that KC was effective for mothers anxiety relief but it was not effective for maternal role confidence and maternal infant attachment of mothers. The implications for nursing practice and directions for future research need to be discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Parental perception, knowledge, barriers and practice of kangaroo care for preterm infants in Indonesia
Susri Utami, Mei-Chih Huang, Shan Tair Wang
Journal of Neonatal Nursing.2023; 29(3): 529. CrossRef - Effects for kangaroo care: systematic review & meta analysis
Junghee Lim, Gaeun Kim, Yeonghee Shin
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(3): 599. CrossRef - Effects of Kangaroo Care on Physical Development and Adaptation of External Environment of Prematurity, and Maternal Role Confidence who Delivered Premature Infants
Ji-Won Lee, Yong-Sook Eo, Jung Hwa Han
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(12): 128. CrossRef - Integrative Review of Nursing Intervention Studies on Mother-Infant Interactions.
Sun Jung Park, Shin Jeong Kim, Kyung Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2014; 20(2): 75. CrossRef - Mothers' Parenting Experience of Premature Infants: Q Methodological Approach
Mi-Young Chon, Eun Sun Ji, Shin-Hwa Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(6): 704. CrossRef - Perception of Nurses and Physicians in Neonatal Intensive Care Units on Kangaroo Care
Kyung-Sook Bang
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2011; 17(4): 230. CrossRef - Effects of a Home-based Discharge Program for Mothers of Premature Infants on Oxygen Therapy at Home
Ji Min Lee, Soon Ja Oh, Kyung A Kim, Eun Jung Lee, Ji Yoon Lee, Moon Sook Hwang, Jung Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(2): 144. CrossRef - Effects of Kangaroo Care on Growth in Premature Infants and on Maternal Attachment
Meyoung Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2009; 15(4): 335. CrossRef
- Parental perception, knowledge, barriers and practice of kangaroo care for preterm infants in Indonesia
- 706 View
- 11 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Patients' Anxiety in Intensive Care Units and Its Related Factors
- Chin Kang Koh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2007;37(4):586-593. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2007.37.4.586
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to describe patients' anxiety in the ICU and to investigate related factors on the anxiety level.
Methods An exploratory cross-sectional survey design was used. Forty-eight patients participated in the study. Questionnaires were asked to patients who had been cared in the ICUs.
Results Related to the anxiety level, the mean of the total anxiety score was 5.47, and 60% of the patients had moderate or severe level of anxiety. Patients from the coronary care unit had a significantly higher level of anxiety than those from surgical intensive care unit or pulmonary surgery care unit. Moreover, significantly different levels of anxiety were found among patients who had been stayed for 2, 3, or 4 days.
Conclusion Patients who were from the coronary care unit or had been stayed longer (up to 4 days) in the ICU were significantly associated with higher anxiety level.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Anxiety Focused Nursing Interventions on Anxiety, Cognitive Function and Delirium in Neurocritical Patients: A Non‐Randomized Controlled Design
Seo‐young Jang, Myung Kyung Lee
Nursing in Critical Care.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of audiovisual media-based nursing information on environmental stress, anxiety, and uncertainty in patients undergoing open-heart surgery
Jeong-Yeong Jeon, Dong-Hee Kim, Kyoungrim Kang
Medicine.2023; 102(8): e33001. CrossRef - Effects of Prior Information About Intensive Care Unit Environment on Anxiety and Environmental Stress in Patients Undergoing Open Heart Surgery
Kyong Mi Shin, Hye Ran Choi
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2015; 21(1): 28. CrossRef - The Effect of Back Pain Prevention Intervention Program on Back Pain Relief in Patients Following Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Hyea Kyung Lee, Yeon Suk Park
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2013; 16(2): 100. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Relocation Stress Syndrome in Patients Following Transfer from Intensive Care Units
Jin-Hee Park, Moon-Sook Yoo, Youn-Jung Son, Sun Hyoung Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(3): 307. CrossRef - Concept Analysis of Relocation Stress - Focusing on Patients Transferred from Intensive Care Unit to General Ward -
Youn-Jung Son, Sung-Kyung Hong, Eun Young Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(3): 353. CrossRef
- Effects of Anxiety Focused Nursing Interventions on Anxiety, Cognitive Function and Delirium in Neurocritical Patients: A Non‐Randomized Controlled Design
- 871 View
- 13 Download
- 6 Crossref

- The Effect of Music Therapy on Anxiety and Depression in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis
- Kwuy Bun Kim, Mi Hunn Lee, Sohyune R Sok
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(2):321-329. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.2.321
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of music therpy on anxiety and depression in patients undergoing hemodialysis.
Method The study was designed using a nonequivalent control group pretest-posttest design. The subjects consisted of 36 patients (Experimental group: 18, Control group: 18) who received hemodialysis in three hospitals located in Seoul. The measures were a Music Preference Questionnaire (MPQ), anxiety measurement, and depression measurement. Data was collected from December 26, 2004 to April 2, 2005 through questionnaires. The collected data was analyzed by the SPSS 10.0 program.
Result The first hypothesis that patients undergoing hemodialysis who received music therapy would have less anxiety than patients undergoing hemodialysis who did not receive music therapy was supported (F=8.05, p=.008). The second hypothesis that patient undergoing hemodialysis who received music therapy would have less depression than patients undergoing hemodialysis who did not receive music therapy was supported(F=11.86, p=.002).
Conclusion The results of this study suggest that music therapy may be applied as a method of nursing intervention contributing to the improvement of quality life by reducing their anxiety and depression of patients undergoing hemodialysis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of the healing beats application on anxiety, stress, and well-being in hemodialysis patients in Korea: a randomized controlled trial
Se-Na Yu, Myung-Haeng Hur
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(1): 12. CrossRef - The effect of the holy Quran recitation and listening on anxiety, stress, and depression: A scoping review on outcomes
Khadijeh Moulaei, Ali‐Akbar Haghdoost, Kambiz Bahaadinbeigy, Fatemeh Dinari
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of music therapy for alleviating pain during haemodialysis access cannulation for patients undergoing haemodialysis: a multi-facility, single-blind, randomised controlled trial
Masatsugu Kishida, Yosuke Yamada, Emi Inayama, Mineaki Kitamura, Tomoya Nishino, Keiko Ota, Ayumi Shintani, Tatsuyoshi Ikenoue
Trials.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Reviewing the Effectiveness of Music Interventions in Treating Depression
Daniel Leubner, Thilo Hinterberger
Frontiers in Psychology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Music Therapy on Anxiety, Blood Pressure, Heart Rate and Glucose Levels of Patients Undergoing Surgery during Spinal Anesthesia
Gye Seon Jeong, Mi Hyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2015; 22(1): 25. CrossRef - The Effects of Music Therapy on Postpartum Blues and Maternal Attachment of Puerperal Women
Sun Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2010; 40(1): 60. CrossRef - Effect of Jang-Gu Program and Self-help Management Program on Depression, Stress, Pain and Body Discomfort in Women with Osteoarthritis
Yeong-Hee Jeong, Jong-Im Kim, Sun-Ae Kim, Keum-Ok Lim
Journal of muscle and joint health.2010; 17(2): 212. CrossRef - Kinésithérapie et dépression
Gilles Guetemme
Kinésithérapie, la Revue.2009; 9(85-86): 7. CrossRef
- Effects of the healing beats application on anxiety, stress, and well-being in hemodialysis patients in Korea: a randomized controlled trial
- 1,169 View
- 55 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Effects of Hand Massage and Hand Holding on the Anxiety in Patients with Local Infiltration Anesthesia
- Hyun Jung Oh, Jeong Sook Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(6):924-933. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.6.924
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to examine the effects of hand massage and hand holding as nursing interventions on the anxiety in patients with local infiltration anesthesia.
Method The design of this study was a nonequivalent, control group, non- synchronized design. The subjects of this study consisted of 15 patients for the hand group, 15 patients for the hand holding group and 17 patients for the control group awaiting surgery in the operation room of a general hospitalin Daegu. As an experimental treatment, hand massage was carried out by the Hand Massage Protocol developed by Snyder(1995) and interpreted by Cho(1998) and hand holding developed by Cho(1998). The data were analyzed by SPSS/WIN, T-test, ANOVA, Cronbach's α, and the Scheffe test.
Results The hand massage group and hand holding group were more effective than the control group in reducing anxiety, VAS score, systolic blood pressure and pulse rate.
Conclusion Hand massage and hand holding are effective nursing interventions that alleviates the psychological and physiological anxiety of patients with local infiltration anesthesia. In particular, the simple contact of hand holding is regarded as an effective and easily accessible nursing intervention in the operating room.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a Video-based Education Program for Cerebral Angiography on Patients’ Outcomes: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Sung-Hyun Tark, Jee-In Hwang
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2024; 30(1): 76. CrossRef - The Effects of Hand Massage in Patients Who Underwent Transradial Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Eun Sil Shin, Myung-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(4): 465. CrossRef - Effects of the Provision of Information on Anxiety in Patients during Outpatient Surgery: A Systematic Review
Ae-Ri Jung, In-Sook Lee
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2016; 13(1): 48. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Hand Massage Combined with Analgesics on Pain Control in Patients with Terminal Cancer
Yunmi Lee, Hosoon Yoon, Sungwoon Lee, Young Mi Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2016; 19(4): 296. CrossRef - Intraoperative Caring Behavior and Anxiety as Perceived by Patients Undergoing Spinal Surgery under Local Anesthesia
Jung Suck Ha, Eun Nam Lee
Journal of muscle and joint health.2015; 22(2): 96. CrossRef - Effects of handholding and providing information on anxiety in patients undergoing percutaneous vertebroplasty
Bong‐Hee Kim, Hee‐Young Kang, Eun‐Young Choi
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2015; 24(23-24): 3459. CrossRef - Effect of Aroma Hand Massage on Anxiety and Immune Function in Patients with Gynecology Surgery under Local Anesthesia
Yun Ah Kim, Mi Hae Sung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2014; 20(2): 126. CrossRef - The Effect of Hand Holding and Nei-Guan Acupressure on Anxiety and Pain under Local Anesthetic Patients during Surgery
Sun Hee Park, Hee Jung Jang
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(11): 378. CrossRef - Analysis of Studies on Hand Massage Published in Korea: On the Effects of Sleep, Pain, Anxiety and Depression
In-Ja Kim, Yu-Na Cho
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2012; 15(1): 47. CrossRef - Effects of Hand Holding on Self-esteem and Assertiveness in Women Patients with Depression
Mi-Hae Sung, Mi Young Choi, Ok Bong Eum
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2010; 19(2): 154. CrossRef
- Effects of a Video-based Education Program for Cerebral Angiography on Patients’ Outcomes: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 827 View
- 15 Download
- 10 Crossref

- The Effects of a Physical Activity Reinforcement Program on Exercise Compliance, Depression, and Anxiety in Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Patients
- Suk Jeong Lee, Ji Soo Yoo
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(3):440-448. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.3.440
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to evaluate the effects of a physical activity reinforcement program on exercise compliance, depression, and anxiety in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis(CAPD) patients.
Method A nonequivalent control group with a pre-post test was designed. Data collection was done from December, 2002 to June, 2003 at a hoapital. The degree of depression and anxiety of the patients was assessed by the score of SCL-90-R, and exercise compliance was measured by exercise period, frequency, time and intensity. The experimental group was composed of 19 participants who were educated based on an exercise education protocol and carried out walking exercises two to four times a week after hearing verbal persuasion biweekly through the telephone or a face-to-face interview for 12 weeks, while 17 participants in control group received no intervention.
Result 1. The experimental group showed significant improvement in self-efficacy of exercise compliance (U=79.00, p=.01), exercise period (χ2=20.84, p=.00), exercise frequency (χ2=9.03, p=.01), exercise time (χ2=9.03, p=.01) and exercise intensity (χ2=11.09, p=.00) compared to those of the control group. 2. The experimental group showed a lower depression score (U=84.50, p=.01) than the results of the control group. 3. However, there were no changes in anxiety level compared to the control group.
Conclusion The physical activity reinforcement program was found to have an effect on exercise compliance and the depression score of CAPD patients. The results provided evidence for the importance of physical activity and verbal persuasion in CAPD patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Peritoneal Dialysis and the Role of Exercise Training Interventions
Osasuyi Iyasere, Hannah M. L. Young, James O. Burton
Kidney and Dialysis.2022; 2(1): 57. CrossRef - Effects of Exercise Intervention on Physical Fitness and Health-relalted Quality of Life in Hemodialysis Patients
Eun-Joung Jang, Hee-Seung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(4): 584. CrossRef
- Peritoneal Dialysis and the Role of Exercise Training Interventions
- 724 View
- 8 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Testing the Mediating Effect of Appraisal in the Model of Uncertainty in Illness study
- Younhee Kang
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(8):1127-1134. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.8.1127
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Although there have been a great number of research studies based on the model of uncertainty in illness, few studies have considered the appraisal portion of model.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to test the mediating effect of appraisal in the model of uncertainty in illness. Additionally, this study aimed to examine the relationships among uncertainty, symptom severity, appraisal, and anxiety in patients newly diagnosed with atrial fibrillation.
Methods This study employed a descriptive correlational and cross-sectional survey design using a face-to-face interview method. Patients diagnosed with atrial fibrillation within the previous 6 months prior to data collection were interviewed by Mishel Uncertainty in Illness Scale-Community Form, appraisal scale, Symptom Checklist-Severity V.3, and State Anxiety Inventory.
Results A total of 81 patients with atrial fibrillation were recruited from two large urban medical centers in Cleveland, Ohio, U.S.A.. Symptom severity was the significant variable in explaining uncertainty (β=0.34). Individuals with greater symptom severity perceived more uncertainty. Uncertainty was appraised as a danger rather than opportunity, and those with greater uncertainty appraised a greater danger (p<.01). While the appraisal of opportunity had the negative relationship with anxiety (r=-0.25), the appraisal of danger was positively associated with anxiety (r=0.78). The measure of goodness of fit (Q) of the model was .7863, and the significant test (X2) for the Q was statistically significant (df =3, p<.001). Accordingly, the overall mediating model of uncertainty in illness was proven not to be fit to the empirical data of patients with atrial fibrillation. Consequently, the mediating effect of appraisal was not supported by the empirical data of this study.
Conclusion The findings of this study were discussed in terms of their relevance compared with those of previous studies or theoretical framework and the plausible explanations on study findings. Lastly, in order to expand the present body of knowledge on uncertainty in illness model, recommendations for the future nursing studies were included.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Conservative Media Use and Childhood COVID-19 Vaccine Information: A Test of the Contradictory Health Information Processing Model
Thais M. Zimbres, Jeanette B. Ruiz, Robert A. Bell
Journal of Health Communication.2022; 27(4): 250. CrossRef - Impact of Uncertainty on the Anxiety of Hospitalized Pregnant Women Diagnosed with Preterm Labor: Focusing on Mediating Effect of Uncertainty Appraisal and Coping Style
Eun Mi Kim, Sehoon Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(4): 485. CrossRef - Evaluating the reasons underlying treatment nonadherence in VLU patients: Mishel's theory of uncertainty. Part 2 of 2
A. Brown
Journal of Wound Care.2014; 23(2): 73. CrossRef - The Influence of Uncertainty and Social Support on General Well-being among Hemodialysis Patients
Youn-Jin Kim, Hee-Jung Choi
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2012; 15(1): 20. CrossRef - The effect of preoperative uncertainty and anxiety on short‐term recovery after elective arthroplasty
Ilya Kagan, Yoram Bar‐Tal
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2008; 17(5): 576. CrossRef
- Conservative Media Use and Childhood COVID-19 Vaccine Information: A Test of the Contradictory Health Information Processing Model
- 728 View
- 3 Download
- 5 Crossref

- Effects of a Sleep Improvement Program Combined with Aroma-Necklace on Sleep, Depression, Anxiety and Blood Pressure in Elderly Women
- Nami Chun, Myoungsuk Kim, Gie ok Noh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(5):651-662. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.5.651
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of a sleep improvement program combined with an aroma-necklace on sleep, depression, anxiety, and blood pressure in elderly women living at home.
Methods A program consisting of a four-week (one hour per week) sleep improvement intervention plus use of an aroma-necklace, was developed based on Cox's Interaction Model of Client Health Behavior. 70 elderly women were assigned to the experimental (n=35) or control group with no intervention (n=35). Data from 62 participants (32 in the experimental and 30 in the control) were analyzed using the SPSS 21.0 program. Women in the experimental group were instructed to constantly wear the aroma necklace filled with marjoram and orange oil until the program was completed. Sleep quality, sleep duration, sleep satisfaction, depression, anxiety, and blood pressure were measured to identify the effectiveness of the program.
Results Significant group differences were found in sleep quality (t=-5.10,
p <.001), sleep duration (z=-3.10,p =.002), sleep satisfaction (z=-4.13,p =<.001), depression (t=2.53,p =.015), and anxiety (z=-2.47,p =.014). No differences were found in the systolic or diastolic blood pressure.Conclusion The results indicate that a sleep improvement program combined with an aroma-necklace was effective in improving sleep disturbances in elderly women living at home. Nurses may contribute to improving sleep among elderly women by applying this program to aged women living in various environments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of an intervention based on Cox's interaction model of client health behavior for reducing symptom burden among post-stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial
Sumin Ma, Qiaomin Tang, Songlin Li, Cui Zhou, Linyun Hu, Zhiying Wang, Xianyan Liao, Weiya Ma, Lili Hu
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of exercise interventions on sleep quality in patients with emotion-related insomnia (ERI):A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Baoyi Ouyang, Jianan Gao, Xiaojie Zhou, Liang Gao, Hui He
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2025; 95: 103298. CrossRef - Effects of a Good Sleep Program on Sleep Quality, Stress, and Functional Health in Old-Old Women with Insomnia: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Yujin Suh, Eun-Kyoung Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(4): 515. CrossRef - Effects of Orange Oil Aromatherapy on Pain and Anxiety During Invasive Interventions in Patients With Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplants
Seckin Erdal, Merve Harman Özdoğan, Dilek Yildirim, Ayşem Kuni, Sevinc Selçuk, Azize Güneri, Elif Naz Arslan
Journal of Infusion Nursing.2024; 47(1): 54. CrossRef - Effects of the dual-task training program for Korean older adults with mild cognitive impairment in community
Eunyoung Shin, Hyun Jin Roh, Sohyune Sok
Geriatric Nursing.2024; 60: 5. CrossRef - Effects of aromatherapy on sleep quality in older adults: A meta-analysis
Kun Xu, Shouyan Wang, Quanyue Ji, Yan Ni, Tianyun Liu
Medicine.2024; 103(49): e40688. CrossRef - Effects of Aromatherapy on Mental Health: A Meta-analysis
Xinchen Zheng, Myung-Sun Lee
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2023; 21(3): 347. CrossRef - Effects of Non-Pharmacological Sleep Interventions in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Hye-Ja Gu, Oi-Sun Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(4): 3101. CrossRef - Effect of a Hospital-To-Home Transitional Intervention Based on an Interaction Model of Client Health Behavior for Adult Patients with Stroke
Su-Jin Cho, Sung Reul Kim, Kyung-Hee Cho, Nah-Mee Shin, Won-Oak Oh
Journal of Community Health Nursing.2023; 40(4): 273. CrossRef - The Effects of Aroma Essential Oil Inhalation on Stress, Pain, and Sleep Quality in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
JiA Lee, Myung-Haeng Hur
Asian Nursing Research.2022; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - Secondary prevention of coronary heart disease: The effect of a nursing intervention using Cox's interaction model of client health behaviour
Qianqian Shen, Pingping He, Min Wen, Juping Yu, Yeshi Chen, Junyi Li, Xinping Ouyang
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2021; 77(10): 4104. CrossRef - Theoretical evaluation of Cox’s interaction model of client health behavior for health promotion in adult
women
Youlim Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Gi Wook Ryu
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(2): 120. CrossRef - The Effect of Pain Catastrophizing on Depression among Older Korean Adults with Chronic Pain: The Mediating Role of Chronic Pain Interference and Sleep Quality
Kyoung-eun Lee, Hyunju Ryu, Sun Ju Chang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(23): 8716. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of an intervention based on Cox's interaction model of client health behavior for reducing symptom burden among post-stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial
- 1,489 View
- 26 Download
- 13 Crossref

- The Relationships among Perceived Parental Bonding, Illness Perception, and Anxiety in Adult Patients with Congenital Heart Diseases
- Nayeon Shin, Youha Jang, Younhee Kang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):178-187. Published online January 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.178
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Abstract Purpose The purposes of this study were to identify the relationships among perceived parental bonding, illness perception, and anxiety and to determine the influences of perceived parental bonding and illness perception on anxiety in adult patients with congenital heart diseases.
Methods In this study a descriptive correlational design with survey method was utilized. The participants were 143 adult patients with congenital heart disease being cared for in the cardiology out-patient clinic of A medical center. Data were collected using the Parental Bonding Instrument, Illness Perception Questionnaire Revised Scale, and Cardiac Anxiety Questionnaire Scale. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, independent t-test, one-way ANOVA, Pearson correlation analysis, and hierarchial regression analyses.
Results There showed significant positive relationships of anxiety with maternal overprotection, consequences, and personal control respectively. Among predictors, maternal overprotection (b=.45), consequence (b=.26), and personal control (b=-.03) had statistically significant influence on anxiety.
Conclusion Nursing interventions to decrease maternal overprotection and negative consequence, and to enhance personal control are essential to decrease the anxiety of adult patients with congenital heart diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Relationship Between Perceived Parenting Practices and Anxiety in Adults With Congenital Heart Disease
Cylia Houchi, Marie-Joëlle Marcil, Kishani Nadarajah, Geneviève A. Mageau, Paul Khairy, Marie-France Marin, Mariève Cossette, Marie-Pierre Dubé, Marie-A. Chaix, François-Pierre Mongeon, Annie Dore, Blandine Mondésert, Reda Ibrahim, Judith Brouillette
Canadian Journal of Cardiology.2024; 40(11): 2233. CrossRef
- The Relationship Between Perceived Parenting Practices and Anxiety in Adults With Congenital Heart Disease
- 1,323 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of Music Intervention on Maternal Anxiety and Fetal Heart Rate Pattern During Non-Stress Test
- Myung Ok Oh, Young Jeoum Kim, Cho Hee Baek, Ju Hee Kim, No Mi Park, Mi Jeong Yu, Han Sol Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(3):315-326. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.315
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this cross-over experimental study was to examine effects of music intervention on maternal anxiety, fetal heart rate pattern and testing time during non-stress tests (NST) for antenatal fetal assessment.
Methods Sixty pregnant women within 28 to 40 gestational weeks were randomly assigned to either the experimental group (n=30) or control group (n=30). Music intervention was provided to pregnant women in the experimental group during NST. Degree of maternal anxiety and fetal heart rate pattern were our primary outcomes. State-trait anxiety inventory, blood pressure, pulse rate, and changes in peripheral skin temperature were assessed to determine the degree of maternal anxiety. Baseline fetal heart rate, frequency of acceleration in fetal heart rate, fetal movement test and testing time for reactive NST were assessed to measure the fetal heart rate pattern.
Results The experimental group showed significantly lower scores in state anxiety than the control group. There were no significant differences in systolic blood pressure and pulse rate between the two groups. Baseline fetal heart rate was significantly lower in the experimental group than in the control group. Frequency of acceleration in fetal heart rate was significantly increased in the experimental group compared to the control group. There were no significant differences in fetal movement and testing time for reactive NST between the two groups.
Conclusion Present results suggest that music intervention could be an effective nursing intervention for alel viating anxiety during non-stress test.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of spousal support during the non-stress test on the anxiety levels of pregnant women and fetal well-being: a randomized controlled study
Yeter Şener, Mürüvvet Başer
Advances in Mental Health.2025; 23(3): 335. CrossRef - The effect of virtual reality on pregnant women and fetuses: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Xiaopu Shi, Chunguang Liang, Haitao Ren, Chunxia Liao, Na Yue
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics.2025; 312(2): 337. CrossRef - The effects of the pregnant woman’s mental visualization of her baby during the non-stress test on maternal anxiety and fetal parameters: A randomized controlled clinical trial
Fatma Keskin Töre, Cansu Ağralı, Gülçin Nacar, Özlem Özel Özcan
Advances in Integrative Medicine.2025; 12(4): 100508. CrossRef - The effect of virtual reality on fetal movement, fetal heart rate, maternal satisfaction, fatigue, and anxiety levels and vital signs of pregnant women during non-stress test: A randomized controlled trial
Eylem Toker, Mine Gökduman Keleş
Health Care for Women International.2024; 45(7): 765. CrossRef - The effects of listening to lullabies and self-selected music at home on prenatal stress and anxiety in nulliparous pregnant women: A randomized-controlled study
Nazlı Baltacı, Özlem Doğan Yüksekol, Emine Koç, Mihriban Ulucan
Health Care for Women International.2024; 45(5): 562. CrossRef - Fetuses can Listen, Learn, and Remember: We Need to be Cautious about What and How We Say It!
Akhil Maheshwari, Thierry AGM Huisman, Srijan Singh, Gayatri Athalye-Jape, Adrianna Frydrysiak-Brzozowska, Kedar Jape, Kinga Piórkowska
Newborn.2024; 3(4): 281. CrossRef - The effect of virtual reality and music on anxiety, non-stress test parameters, and satisfaction of high-risk pregnant women undergoing non-stress tests: Randomized controlled trial
Neslihan Yılmaz Sezer, Menekşe Nazlı Aker, Aykan Yücel, Dilan Çalışıcı
European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology.2024; 296: 52. CrossRef - Effect of Virtual Reality and Music Therapy on the Physiologic Parameters of Pregnant Women and Fetuses and on Anxiety Levels: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Fatima Estrella‐Juarez, Mar Requena‐Mullor, Jessica Garcia‐Gonzalez, Antonia Lopez‐Villen, Raquel Alarcon‐Rodriguez
Journal of Midwifery & Women's Health.2023; 68(1): 35. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Music on Perinatal Anxiety Among Pregnant Women and Newborn Behaviors: A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis
Meena Konsam, Sonia R. B. D’Souza, Samir Kumar Praharaj, Baby S. Nayak, Jyothi Shetty, Shashikala Bhat, Judith A. Noronha, Sunita Panda
Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine.2023; 45(6): 565. CrossRef - Effects of music therapy on the fetal outcomes of non-stress test and maternal anxiety
L. Fathi, A. Shakarami, K. Amraei, F. Yari, A. Behzadvand
Neuropsychiatrie de l'Enfance et de l'Adolescence.2023; 71(6): 316. CrossRef - Environmental factors influencing women’s childbirth experiences in labor–delivery–recovery–postpartum unit: a qualitative cross-sectional study
Ashraf Kazemi, Marjan Beigi, Hajar Enteshary Najafabadi
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of music on fetal well-being and anxiety levels and vital signs of pregnant women during non-stress test: Turkey sample
Nurseli Soylu, Tülay Bülbül, İptisam İpek Müderris
Health Care for Women International.2022; 43(5): 499. CrossRef - Renkli Abdominal Örtü ve Kemer Kullanımının Non-Stress Test Parametreleri ve Maternal Kaygıya Etkisi: Randomize Kontrollü Bir Çalışma
Esra GÜNEY, Zeynep BAL, Esra KARATAŞ OKYAY, Tuba UÇAR
Samsun Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2022; 7(2): 393. CrossRef - The Effect of a Breathing Relaxation Therapy for Pregnant Women with Preterm Labor Pain: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Seo-A Park
Keimyung Medical Journal.2021; 40(1): 39. CrossRef - Interventions among Pregnant Women in the Field of Music Therapy: A Systematic Review
Bruna Mayumi Omori Shimada, Magda da Silva Oliveira Menezes dos Santos, Mayara Alvares Cabral, Vanessa Oliveira Silva, Gislaine Cristina Vagetti
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia / RBGO Gynecology and Obstetrics.2021; 43(05): 403. CrossRef - The effectiveness of music on the result of non-stress test
Tuan Vo, Anh Huynh, Thao Nguyen Thi Thu, Lora Claywell
MedPharmRes.2020; 4(3): 12. CrossRef - The Effect of Music on Fetus Movement During Non-Stress Test
Batoul Khodakarami, Marzieh Janesari Ladani, Farideh Kazemi, Soudabeh Aghababaei
Avicenna Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Care.2020; 28(4): 1. CrossRef - The effect of music on the non-stress test and maternal anxiety
Hatice Erkun Dolker, Fatma Basar
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2019; 35: 259. CrossRef - Müziğin non-stres test üzerine etkilerinin incelenmesi
Ramazan DENİZLİ, Nayif ÇİÇEKLİ, Gökhan GÜLYAŞAR, Yasmin ABOALHASAN, Taylan AYGÜN, Nihat FARİSOĞULLARI, Önder SAKİN
SDÜ Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi.2019; 26(4): 464. CrossRef - The effect of music on the results of a non-stress test: A non-randomized controlled clinical trial
Didem Şimşek Küçükkelepçe, Sermin Timur Taşhan
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2018; 18: 8. CrossRef - The effect of traditional Persian music on the cardiac functioning of young Iranian women
Behzad Abedi, Ataollah Abbasi, Atefeh Goshvarpour, Hamid Tayebi Khosroshai, Elnaz Javanshir
Indian Heart Journal.2017; 69(4): 491. CrossRef
- The effect of spousal support during the non-stress test on the anxiety levels of pregnant women and fetal well-being: a randomized controlled study
- 2,047 View
- 62 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Effect of Adolescents' Abuse Experience on Suicidal Ideation: Focused on Moderated Mediation Effect of Self-esteem on Depression and Anxiety
- Ji Young Kim, Kyunghee Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(5):752-760. Published online October 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.5.752
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the moderating mediation effect of self-esteem on the relations among adolescents' abuse experiences, depression and anxiety, and suicidal ideation.
Methods The participants were selected using secondary data from a population in the 2012 Korea Welfare Panel Survey (KOWEPS). Data were analyzed using SPSS 15.0 and SPSS Macro, and bootstrapping and hierarchical regression analysis were performed to analyze multilevel models.
Results First, analysis of the mediating effect of the adolescents' abuse showed that there was significant mediating influence between suicidal ideation and depression and anxiety. Second, hierarchical regression analysis showed that self-esteem had significant mediation effect on depression and anxiety in adolescents' suicidal ideation. Third, SPSS Macro showed that self-esteem also significantly moderated the mediating effect of adolescents' abuse experiences on suicidal ideation through depression and anxiety.
Conclusion The study results suggest that in future research on adolescent's abuse experience, the risk of suicide in depression and anxiety scores should be selected through evaluation of each individual's self-esteem scale. Coping strategies with immediate early intervention should be suggested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictors of Adolescents’ Subjective Happiness Based on Roy’s Adaptation Model: A Longitudinal Study
Jeong-Eun Yang, SeolHwa Moon
The Open Public Health Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of school and domestic violence on suicidal ideation in adolescents by levels of self-esteem
Soojin Lee, Kyungwon Paek
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2024; 41(1): 1. CrossRef - The correlation of childhood maltreatment and aggression among incarcerated adolescents: testing the mediating effects of self-esteem and self-control
Jiaxi Peng, Jiaxi Zhang, Weizhuo Yuan, Xuan Zhou, Pang Fang
Current Psychology.2023; 42(29): 25648. CrossRef - The Effect of Perceived Size of a Plus-Size Model on Body Satisfaction : A Moderated Mediation Effect of Perceived Similarity and Implicit Belief about the Malleability of Body Sizes
Sunwoo Kim, Su jin Yang
Journal of the Korean Society of Costume.2023; 73(2): 117. CrossRef - Mental Health Profiles in a Sample of Moroccan High School Students: Comparison Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abdennour El Mzadi, Btissame Zouini, Nóra Kerekes, Meftaha Senhaji
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship of explicit/implicit self‐esteem discrepancies, suicide ideation, and suicide risk in patients with major depressive disorder
Xunbao Yin, Jianfei Shen, Nengzhi Jiang, Jing Sun, Yanyu Wang, Hongwei Sun
PsyCh Journal.2022; 11(6): 936. CrossRef - Self-esteem as a Moderator of the Effects of Happiness, Depression, and Hostility on Suicidality Among Early Adolescents in Korea
Yeun-Soon Choi, Hee Kyoung Shin, Dae-Yong Hong, Jang-Rak Kim, Yune-Sik Kang, Baekgeun Jeong, Ki Soo Park, Key Hyo Lee
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2019; 52(1): 30. CrossRef - Mental health profile and its relation with parental alcohol use problems and/or the experience of abuse in a sample of Moroccan high school students: an explorative study
Btissame Zouini, Anis Sfendla, Britt Hedman Ahlström, Meftaha Senhaji, Nóra Kerekes
Annals of General Psychiatry.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between suicidal ideation and experience with drug in South Korean adolescents using data from the 12th 2016 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-Based Survey
Hye Ja Gu
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2018; 35(2): 13. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Trajectories of Child Maltreatment and Adolescent Suicidal Ideation
Se Won Kim, Deok-Seong Kim
Korean Journal of Child Studies.2017; 38(2): 81. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Stress Coping Type and Self-esteem between Life Stress and Suicidal Ideation in Nursing College Students
Pil-Nam Park
Journal of the Korean Society of School Health.2016; 29(1): 1. CrossRef
- Predictors of Adolescents’ Subjective Happiness Based on Roy’s Adaptation Model: A Longitudinal Study
- 1,215 View
- 18 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Impact of Bowel Function, Anxiety and Depression on Quality of Life in Patients with Sphincter-preserving Resection for Rectal Cancer
- Hyun Jun Kwoun, Yun Hee Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(5):733-741. Published online October 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.5.733
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was a descriptive survey research to identify the impact of bowel function, anxiety and depression on quality of life in patients with rectal cancer who had a sphincter-preserving resection.
Methods articipants were 100 patients who had rectal cancer surgery at W hospital in Korea. Bowel function, anxiety & depression, and quality of life were measured using the BFI (Bowel Function Instrument), HADS (Hospital Anxiety-Depression Scale) and the FACT-C (Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Colorectal).
Results The mean scores were 39.81±5.16 for bowel function, 6.15±3.25 for anxiety, 7.24±3.13 for depression, and 72.50±13.27 for quality of life. There were significant negative correlations between quality of life and anxiety (r= -.59,
p <.001) and between quality of life and depression (r= -.53,p <.001). But the correlation between quality of life and bowel function was significantly positive (r=.22,p =.025). The influence of the independent variables on the total quality of life was examined using multiple regression analysis. Anxiety (β= -.38,p =.002), bowel function (β= -.25,p =.028) and occupation (β=.16,p =.048) were identified as factors affecting quality of life. The explanation power of this regression model was 44% and it was statistically significant (F=16.53,p <.001).Conclusion The results of this study indicate that in order to improve the bowel function of patients after sphincter-preserving resection for rectal cancer, effective nursing interventions should be developed. As psychological problem such as anxiety and depression can relate to quality of life for these patients, nurses should work on improving the situation by providing continuous emotional nursing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lack of Regular Access to Primary Care Physician Associated With Increased Emergency Department Visits Related to Survivorship Needs Among Rectal Cancer Survivors
Jeongyoon Moon, Ebram M. Salama, Anna Y. Wang, Mylène Arsenault, Nathalie Leon, Carmen G. Loiselle, Fateme Rajabiyazdi, Marylise Boutros
Diseases of the Colon & Rectum.2024; 67(12): 1536. CrossRef - Major Low Anterior Resection Syndrome (LARS) and Quality of Life in Patients With Low Rectal Cancer: A Preoperative Survey Using LARS Score and European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer’s 30-Item Core Quality of Life Questionnaire
Ly Huu Phu, Ho Tat Bang, Nguyen Viet Binh, Hoang Danh Tan, Ung Van Viet, Nguyen Trung Tin
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Low Anterior Resection Syndrome in a Reference North American Sample: Prevalence and Associated Factors
Jeongyoon Moon, Alexa Ehlebracht, Michelle Cwintal, Julio Faria, Gabriela Ghitulescu, Nancy Morin, Allison Pang, Carol-Ann Vasilevsky, Marylise Boutros
Journal of the American College of Surgeons.2023; 237(5): 679. CrossRef - The Relationships among Social Support, Bowel Function Symptoms and Uncertainty in Rectal Cancer Patients
Kyungmi Lee, Semi Lim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(4): 421. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Supportive Care Needs of Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hyekyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(1): 60. CrossRef - Effectiveness and safety of acupuncture and moxibustion for defecation dysfunction after sphincter-preserving surgery for rectal cancer: protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis
Guixing Xu, Qiwei Xiao, Hanzhou Lei, Yanan Fu, Jing Kong, Qianhua Zheng, Ling Zhao, Fanrong Liang
BMJ Open.2020; 10(5): e034152. CrossRef - Psychosocial behaviour reactions, psychosocial needs, anxiety and depression among patients with rectal cancer before and after colostomy surgery: A longitudinal study
Ying Jin, Jing Zhang, Mei‐Chun Zheng, Xiu‐Qing Bu, Jun‐E Zhang
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2019; 28(19-20): 3547. CrossRef - Predictors of Quality of Life and Social Support as a Mediator between Defecation Function and Quality of Life among Rectal Cancer Patients
Jung Rang Kim, Seon Young Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(5): 487. CrossRef
- Lack of Regular Access to Primary Care Physician Associated With Increased Emergency Department Visits Related to Survivorship Needs Among Rectal Cancer Survivors
- 1,000 View
- 7 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Factors Influencing Quality of Life during Chemotherapy for Colorectal Cancer Patients in South Korea
- Yongae Baek, Myungsun Yi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(4):604-612. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.4.604
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the levels of physical symptoms, anxiety, depression, and quality of life (QOL) during chemotherapy for colorectal cancer patients in South Korea and to identify factors influencing their QOL.
Methods Data were collected from 144 colorectal cancer patients receiving chemotherapy during 2012 at one general hospital located in Seoul. Physical symptoms were measured by the M. D. Anderson Symptom Inventory-Gastrointestinal Cancer Module, and anxiety and depression were measured by the Hospital Anxiety Depression Scale. QOL was measured by the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Colorectal. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-test, one-way ANOVA, Scheffé post hoc test, Pearson correlation and stepwise multiple regression.
Results Mean age of the participants was 56.6 and most of them were not employed. In terms of cancer stage, 38.2% were in stage 3, followed by stage 4 (34.7%). The most frequent symptom was lack of appetite, followed by sleep disturbance and fatigue. The mean score for anxiety was 5.40 with a prevalence of 23% and that of depression 8.85 with a prevalence of 64.6%. The mean score for quality of life was 81.93 out of 136 and 75.3% of the variance in QOL was explained by depression, symptoms, anxiety, treatment place, and occupational status. Depression was the strongest predictive factor.
Conclusion Oncology professionals need to pay special attention to relieving depression as well as physical symptoms to improve QOL during chemotherapy for colorectal cancer patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influences of Patient Activation on Quality of Life in Colorectal Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy through a Chemoport
Hyun Seung Lee, Jeong Hye Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(4): 206. CrossRef - Disease Perception, Stigma, Distress, Physical Symptom Experience and Quality of Life in Colorectal Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: A Cross-Sectional Study
Eun-Hee Lee, Dongwon Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(4): 494. CrossRef - Effects of Family Support and Health Promotion Behaviors on Quality of Life of Cancer Patients after Gastrectomy
Eun Hee Yang, Jeong Hee Kang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(4): 196. CrossRef - Anxiety and depression prevalence in digestive cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammad Zamani, Shaghayegh Alizadeh-Tabari
BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care.2023; 13(e2): e235. CrossRef - The Experience of Chemotherapy Related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Ji Hyun Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of Ambulatory Chemotherapy (Portable Infusion Pump Use) Video Education on Knowledge, Self-efficacy and Anxiety of Colorectal Cancer Patients
Eun Hee Choi, Eun Young Park, Young A Park, You Hee Son, Myung Jin Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(3): 193. CrossRef - A Structural Model of Quality of Life in Patients after Colorectal Cancer Surgery
Jeong Won Yeom, Yeon Ok Suh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(5): 2564. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Supportive Care Needs of Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hyekyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(1): 60. CrossRef - Effect of PRM1201 Combined With Adjuvant Chemotherapy on Preventing Recurrence and Metastasis of Stage III Colon Cancer: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
Ru Jia, Ningning Liu, Guoxiang Cai, Yun Zhang, Haijuan Xiao, Lihong Zhou, Qing Ji, Ling Zhao, Puhua Zeng, Huaimin Liu, Jiege Huo, Xiaoqiang Yue, Yi Zhang, Chaojun Wu, Xiaoting Sun, Yuanyuan Feng, Hongjie Liu, Hui Liu, Zhifen Han, Youying Lai, Yanbo Zhang,
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing the effect of acupressure and ginger on chemotherapy gastrointestinal side-effects in children with leukemia
Magda A. Essawy, Rasha M. Abohadida, Wafaa M. Abd-Elkader, Hoda M. Fathy, Hoda M. Hassab
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2021; 60: 102730. CrossRef - Experience and Satisfaction of Cancer Patients With a Central Venous Catheter at a Tertiary Hospital in South Korea
Jeong Yun Park, Da In Lee
Journal of Infusion Nursing.2020; 43(2): 97. CrossRef - Changes in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, disturbance in activities of daily living, and depression following chemotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer: A prospective study
Pok-Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee, Sook-Kyoung Kim, Jeong-Hye Kim
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 44: 101676. CrossRef - The prognoses and postoperative outcomes of patients with both colorectal cancer and liver cirrhosis based on a nationwide cohort in Korea
Nari Shin, Eon Chul Han, Sungho Won, Seung-Bum Ryoo, Eun Kyung Choe, Byung Kwan Park, Kyu Joo Park
Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research.2020; 99(2): 82. CrossRef - Oxaliplatin-induced Peripheral Neuropathy, Symptoms, Distress and Quality of Life among Korean Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer
Hye Jeong Jung, Soo jung Ahn, Yoo Ri Yang, Kyoung A Kim, Sang Joon Shin, Min Kyu Jung, Sang Hui Chu
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(4): 204. CrossRef - The Effect of Self-efficacy and Depression on Sense of Family Coherence in Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy and Primary Caregivers in Day Care Wards: Using the Method Actor-partner Interdependence Model
Eun-Hee Do, Eun Joung Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(4): 214. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Enhanced Recovery After Surgery Program for Patients with Colorectal Cancer Surgery
Eun Ja Kim, Jeong Sook Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(6): 677. CrossRef - Postoperative Weight Changes, Nutritional Status and Clinical Significance of Colorectal Cancer Patients
Sun Young Kim, Ji Sun Kim, Eon Chul Han
Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition.2019; 10(2): 46. CrossRef - The Effect of Symptom Experience, Nutritional Status, and Self Care on Quality of Life in Elderly Patients with Colorectal Cancer
Jeong Won Yeom, Yeon Ok Suh
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2019; 22(1): 48. CrossRef - Factors influencing quality of life in patients with multiple myeloma
Hee-Young Kang, Eun-Young Choi
Contemporary Nurse.2019; 55(2-3): 109. CrossRef - Distress and Quality of Life in Patients with Esophageal Cancer
Yeon Hwa Ju, Yeon Hee Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(1): 40. CrossRef - Psychosocial Adjustment in Korean Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hyejin Sun, Jia Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(5): 545. CrossRef - Effect of Auricular Acupressure on Nausea, Vomiting, and Retching in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy
Nayeon Shin, Jummi Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(3): 227. CrossRef - Discomfort related to Peripherally Inserted Central Catheters in Cancer Patient
Misun Yi, Im-Ryung Kim, Eun-Kyung Choi, Seyoung Lee, Mikyong Kwak, Juhee Cho, Jin Seok Ahn, In Gak Kwon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2017; 17(4): 229. CrossRef - Effect of Cancer Symptoms and Fatigue on Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Depression in People with Gastrointestinal Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(3): 420. CrossRef
- Influences of Patient Activation on Quality of Life in Colorectal Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy through a Chemoport
- 1,248 View
- 21 Download
- 24 Crossref

- Effects of Death Anxiety and Meaning of Life on Somatization of Grandparent Raising Grandchildren
- Se-Young Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(2):262-270. Published online April 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.2.262
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted in order to examine the effects of death anxiety and meaning of life on somatization of grandparents raising grandchildren.
Methods A convenience sample of 92 elderly grandparents raising grandchildren was recruited. The study instrument for death anxiety was the 5-point 15 items scale designed by Templer and translated by Ko, Choi, & Lee and for meaning of life, the 7-point 10-items scale by Steger, Frazier, Oishi & Kaler and translated by Won, Kim & Kwon. For somatization, the 5-point 12 items scale designed by Derogatis and translated by Kim, Kim & Won was used. Collected data were analyzed with descriptive statistics, independent t-test, one-way ANOVA, Pearson Correlation and regression using the SPSS 21.0 program.
Results Average scores were 3.55 for death anxiety, 3.43 for meaning of life, and 2.74 for somatization. Death anxiety had the highest positive correlation with somatization. Meaning of life was negatively correlated with death anxiety and somatization. Death anxiety and health status were shown to influence somatization but meaning of life was not shown to influence somatization.
Conclusion The research results indicate that death anxiety and health status influence somatization in grandparents raising grandchildren. These results also provide basic information on the importance of nursing interventions in which the variables influencing somatization in grandparents raising grandchildren are considered.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Korean Grandparents Raising Grandchildren: The Influence of Cultural Factors
Youjung Lee, Sok An, Nancy Mendoza
Journal of Intergenerational Relationships.2026; 24(1): 97. CrossRef - Understanding Grandparent Caregiving in Korean and U.S. Culture: An Analysis Using Role Theory
Youjung Lee, Nancy Mendoza, Sok An
The International Journal of Aging and Human Development.2025; 101(4): 399. CrossRef - “Who is going to take care of these grandkids if I go?”: End-of-life planning by caregivers in grandparent-headed households
Jessica D. Freeman, Jessica Elton, Andrea Lambert South
Death Studies.2023; 47(3): 268. CrossRef - “What If You Die?”: Skipped‐Generation Caregivers' Reported Conversations With Their Grandchildren About Death
Jessica D. Freeman, Jessica Elton
Family Relations.2021; 70(2): 374. CrossRef - The Effect of Physical Health Variables on the Depression of the Korean Rural Elderly : with a Focus on a Comparison of Young-old and Old-old
Junggook Go, Jeonghwa Lee, Young eun Oh
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2019; 30(1): 83. CrossRef - Death Anxiety Among New Zealanders: The Predictive Roles of Religion, Spirituality, and Family Connection
Rod MacLeod, Donna M. Wilson, Jackie Crandall, Phil Austin
OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.2019; 80(1): 3. CrossRef - Correlates of perceived death competence: What role does meaning-in-life and quality-of-life play?
Lauren Miller-Lewis, Jennifer Tieman, Deb Rawlings, Christine Sanderson, Deborah Parker
Palliative and Supportive Care.2019; 17(5): 550. CrossRef - Factors associated with Meaning in Life among Elderly Female Community Dwellers Living Alone
Si Eun Lee, Boon Han Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(3): 221. CrossRef
- Korean Grandparents Raising Grandchildren: The Influence of Cultural Factors
- 1,147 View
- 4 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Comparison of the Factors Influencing Young Adolescents' Aggression according to Family Structure
- Eun Kyoung Yun, Sung Hee Shin
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(3):321-330. Published online June 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.3.321
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This cross-sectional study was done to compare factors influencing young adolescents' aggression according to family structure.
Methods Participants were 680 young adolescents aged 11 to 15 years (113 in single father families, 136 in single mother families, 49 in grandparent families, and 382 in both-parent families). All measures were self-administered. Data were analyzed using SPSS 18.0 program and factors affecting young adolescents' aggression were analyzed by stepwise multiple regression.
Results Levels of young adolescents' aggression and all variables were significantly different among the four family structure groups. Factors influencing young adolescents' aggression were also different according to these 4 groups. For single father families, depression-anxiety and family hardiness significantly predicted the level of young adolescents' aggression (adjusted R square=.37,
p <.001). For single mother families, depression-anxiety, gender, and friends' support significantly predicted the level of young adolescents' aggression (adjusted R square=.58,p <.001). For grandparent families, depression-anxiety and family support significantly predicted the level of young adolescents' aggression (adjusted R square=.58,p <.001). For both-parent families, depression-anxiety, family hardiness, and friends' support significantly predicted the level of young adolescents' aggression (adjusted R square=.48,p <.001).Conclusion Nurses working with young adolescents should consider family structure-specific factors influencing aggression in this population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How do grandparents influence child health and development? A systematic review
Aalyia F.A. Sadruddin, Liliana A. Ponguta, Anna L. Zonderman, Kyle S. Wiley, Alyssa Grimshaw, Catherine Panter-Brick
Social Science & Medicine.2019; 239: 112476. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Adolescents’ Self-control According to Family Structure
In Young Cho, Ja Sook Kim, Ja Ok Kim
Journal of Child and Family Studies.2018; 27(11): 3520. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Cognitive Emotion Regulation on Influences of Self-differentiation and Family Function in High School Students' Problem Behavior
Jin Joo Chang, Sung Hee Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2017; 26(3): 248. CrossRef - Survey on Foodservice Satisfaction and Dietary Education needs for Improvement of School Foodservice in Middle School Students in Seoul
Kyung-Hee Shin, Youngmee Lee, Wookyoun Cho
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(2): 127. CrossRef - Comparison of Boys' and Girls' Families for Actor and Partner Effect of Stress, Depression and Parent-Adolescent Communication on Middle School Students' Suicidal Ideation: Triadic Data Analysis
Sung Hee Shin, Suk Jeong Ko, Yu Jeong Yang, Hyun Su Oh, Mi Young Jang, Joong Myung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(3): 317. CrossRef - A Study on the Relationship among Family Functioning, Empathy, and Aggression by High School Students
Hee Jung Choi, Eun Sun Lim, Jang Hak Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2013; 24(4): 480. CrossRef
- How do grandparents influence child health and development? A systematic review
- 1,174 View
- 9 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Effect of Family Cohesion, Subjective Happiness and other Factors on Death Anxiety in Korean Elders
- Kae Hwa Jo, Byung Sook Song
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(5):680-688. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.5.680
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purposes of this study were to explore the effects of family cohesion and subjective happiness on death anxiety of Korean elders and to identify other factors contributing to death anxiety.
Methods The participants were 280 elders who lived in P metropolitan city. Data were collected between November 5, 2011 and January 12, 2012 using the Short Portable Mental Status Questionnaire (SPMSQ), Family Cohesion Evaluation Scale, Subjective Happiness Scale, and Fear of Death Scale (FODS). Data were analyzed using the SPSS/WIN 19.0 program.
Results Family cohesion, marital status, religious activity, perceived health status, and subjective happiness were included in the factors affecting death anxiety of Korean elders. These variables explained 50.1% of death anxiety.
Conclusion The results of the study indicate that these variables should be considered in developing nursing intervention programs to decrease death anxiety and increase family cohesion and subjective happiness for life integration in Korean elders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with attitudes toward death and dying in the second half of life: A scoping review
Alana Officer, Matthew Prina, Andreea Badache, Barbara Broers, Sam Gnanapragasam, Sophie Pautex
Death Studies.2026; 50(1): 53. CrossRef - Relationship of Depression, Hopelessness and Life Satisfaction With Death Anxiety in Individuals Who Have Had COVID-19
Neslihan Lok, Zekiye Aydın, Gülten Uzun, Büşra Kayaaslan, Alime Selçuk Tosun
OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.2025; 92(1): 5. CrossRef - Translation and Validation Study of the Korean Self-Compassion Scale
Si Woo Chae, Jeong Eun Cheon, Janet D. Latner, Young-Hoon Kim
Mindfulness.2024; 15(10): 2697. CrossRef - Impact of Death Anxiety on Psychological Well-Being and Successful Aging of Older Adults With Chronic Illness
Akanksha Bharti, Das Ambika Bharti
OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Societal impact of death anxiety and mental health among nurses in India
Monika Srivastava, Anindita Ghosh
Societal Impacts.2024; 4: 100095. CrossRef - Stress-related to COVID-19, anxiety, and protective factors among middle-aged and older adults in the largest outbreak areas in South Korea
Sukyung Yoon, Soochan Choi
Aging & Mental Health.2022; 26(10): 2090. CrossRef - The effect of group logotherapy on spirituality and preoperative anxiety in patients seeking open heart surgery referring to Tehran Heart Center in 2020
Fatemehsadat Alavi, Seyed Hossein Ahmadi Tafti, Farshid Alaeddini, Zainab Ebrahimyan, Atieh Ebrahimyan, Morteza Mansourian
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2022; 11(1): 233. CrossRef - Factors associated with family cohesion and adaptability among Chinese registered nurses
Lei Huang, Ya Wang, Hao Huang
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2021; 30(1-2): 113. CrossRef - The mediating effect of resilience on happiness of advanced lung cancer patients
Sunwha Cho, Eunjung Ryu
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(11): 6217. CrossRef - Patterns of Religiosity, Death Anxiety, and Hope in a Population of Community-Dwelling Palliative Care Patients in New Zealand—What Gives Hope If Religion Can’t?
Catherine M. Byrne, Deidre D. Morgan
American Journal of Hospice and Palliative Medicine®.2020; 37(5): 377. CrossRef - Effects of Social Support, Family Support and Repulsion Related Nursing Home Use on the Well-Dying of Elderly
Young Ju Oh, Kyeong In Cha, Young Hee Jeon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(3): 235. CrossRef - The Effect of Spiritual Care Program on Death Anxiety of Cardiac Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Jalil Azimian, Mohammad ali Soleimany, Saeed Pahlevan Sharif, Hedyeh Banihashemi
Avicenna Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Care.2019; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - Death Anxiety Among New Zealanders: The Predictive Roles of Religion, Spirituality, and Family Connection
Rod MacLeod, Donna M. Wilson, Jackie Crandall, Phil Austin
OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.2019; 80(1): 3. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Death Anxiety among Rural Elderly
Hyenam Hwang
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2019; 44(2): 111. CrossRef - Posttraumatic Growth and Related Factors in Firefighters
Minyeong Kwak, Jeongyee Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2017; 26(2): 124. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Death Anxiety in Elderly Patients in Long-term Care Hospitals
Mi Suk Lee, Hee Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2016; 18(3): 138. CrossRef - Service improving the subjective happiness in Cancer Patient receiving Radiation Therapy
Mi Soon Song, Hyun Li Kim
Journal of Service Research and Studies.2016; 6(2): 51. CrossRef - A Meta Analysis on Variables related to Death Anxiety of Elderly in Korea
Sinhyang Kim, Kyung Sook Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(2): 156. CrossRef - Study of Death Attitudes by General Characteristics and Death Perceptions of the Severely Diseased Persons in Hospice Facilities -Focus in O City, Gyeonggi-do
Moon-Dol Kim, Sung-Je Cho
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(12): 7148. CrossRef
- Factors associated with attitudes toward death and dying in the second half of life: A scoping review
- 1,170 View
- 6 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Development and Effectiveness of a Drug Dosage Calculation Training Program using Cognitive Loading Theory based on Smartphone Application
- Myoung Soo Kim, Jung Ha Park, Kyung-Yeon Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(5):689-698. Published online October 12, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.5.689
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to develop and evaluate a drug dosage calculation training program using cognitive loading theory based on a smartphone application. Calculation ability, dosage calculation related self-efficacy and anxiety were measured.
Methods A nonequivalent control group design was used. Smartphone application and a handout for self-study were developed and administered to the experimental group and only a handout was provided for control group. Intervention period was 4 weeks. Data were analyzed using descriptive analysis,
χ 2-test, t-test, and ANCOVA with the SPSS 18.0.Results The experimental group showed more ‘self-efficacy for drug dosage calculation’ than the control group (t= 3.82,
p < .001). Experimental group students had higher ability to perform drug dosage calculations than control group students (t= 3.98,p < .001), with regard to ‘metric conversion’ (t= 2.25,p = .027), ‘table dosage calculation’ (t= 2.20,p = .031) and ‘drop rate calculation’ (t= 4.60,p < .001). There was no difference in improvement in ‘anxiety for drug dosage calculation’. Mean satisfaction score for the program was 86.1.Conclusion These results indicate that this drug dosage calculation training program using smart-phone application is effective in improving dosage calculation related self-efficacy and calculation ability. Further study should be done to develop additional interventions for reducing anxiety.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and effectiveness of online teaching on practical skills among nursing students: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Afang Li, Norhasmah Mohd Zain, Azlina Yusuf, Haiyan Deng, Qi He
Nurse Education in Practice.2024; 78: 103988. CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness of a Clinical Decision Support System for Pressure Ulcer Prevention Care Using Machine Learning
Myoung Soo Kim, Jung Mi Ryu, Byung Kwan Choi
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2023; 41(4): 236. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a virtual reality application‐based education programme on patient safety management for nursing students: A pre‐test–post‐test study
Jae Woo Oh, Ji Eun Kim
Nursing Open.2023; 10(12): 7622. CrossRef - The Effect of Game-Based Clinical Nursing Skills Mobile Application on Nursing Students
Donghee Suh, Hyekyung Kim, Eunyoung E. Suh, Hyunsun Kim
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2022; 40(11): 769. CrossRef - The effect of case-based learning based on flipped learning for nursing students
Min Hee Lee, Myung Sook Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(2): 107. CrossRef - Smartphone distraction during nursing care: Systematic literature review
Massimo Fiorinelli, Sofia Di Mario, Antonella Surace, Micol Mattei, Carla Russo, Giulia Villa, Sara Dionisi, Emanuele Di Simone, Noemi Giannetta, Marco Di Muzio
Applied Nursing Research.2021; 58: 151405. CrossRef - A systematic review into the assessment of medical apps: motivations, challenges, recommendations and methodological aspect
A. H. Alamoodi, Salem Garfan, B. B. Zaidan, A. A. Zaidan, Moceheb Lazam Shuwandy, Mussab Alaa, M. A. Alsalem, Ali Mohammed, A. M. Aleesa, O. S. Albahri, Ward Ahmed Al-Hussein, O. R. Alobaidi
Health and Technology.2020; 10(5): 1045. CrossRef - Development and Utilization of a Clinical Decision Support System Contents for Pressure Ulcer Prevention Care
Myoung Soo Kim, Jung Mi Ryu
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2020; 45(4): 365. CrossRef - The Effect of Cell Phones on Attention and Learning in Nursing Students
Lorena Gutiérrez-Puertas, Verónica V. Márquez-Hernández, Vanesa Gutiérrez-Puertas, Genoveva Granados-Gámez, Gabriel Aguilera-Manrique
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2020; 38(8): 408. CrossRef - Using Video Feedback Through Smartphone Instant Messaging in Fundamental Nursing Skills Teaching: Observational Study
Xiaoxian Yang, Ri-Hua Xie, Si Chen, Wei Yu, Yan Liao, Daniel Krewski, Shi Wu Wen
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2019; 7(9): e15386. CrossRef - Effects of Smartphone-Based Mobile Learning in Nursing Education: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Ju Hee Kim, Hanjong Park
Asian Nursing Research.2019; 13(1): 20. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of “Chronic Illness Care Smartphone Apps” on Nursing Students’ Knowledge, Self-efficacy, and Learning Experience
Jiyoung Kang, Eunyoung E. Suh
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2018; 36(11): 550. CrossRef - Mobile Technology in Undergraduate Nursing Education: A Systematic Review
Hyejung Lee, Haeyoung Min, Su-mi Oh, Kaka Shim
Healthcare Informatics Research.2018; 24(2): 97. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Acceptance Intention Toward a Smartphone Healthcare Application and Health-Promoting Behaviors Among Nursing Students
Eun-Jin Choi, Se-Won Kang
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2018; 36(10): 494. CrossRef - The Effects of an Interactive Nursing Skills Mobile Application on Nursing Students' Knowledge, Self-efficacy, and Skills Performance: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Hyunsun Kim, Eunyoung E. Suh
Asian Nursing Research.2018; 12(1): 17. CrossRef - Outcomes of a Drug Dosage Calculation Training Smartphone App on Learning Achievement, Metacognition, and Flow State According to Prior Knowledge
Kyung Yeon Park, Myoung Soo Kim
EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Cross-cultural Validation of the Korean Version of SMArtphone’s uSability Heuristics (SMASH)
Yeo Won Jeong, Jung A Kim
Healthcare Informatics Research.2017; 23(4): 328. CrossRef - The Effects of Smartphone Application to Educate Patient on Patient Safety in Hospitalized Surgical Patients
Hyo Jin Choi, Eunjoo Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(2): 154. CrossRef - Use of mobile devices and medication errors in acute care
Nicole Harder, Jannell Plouffe, Diane Cepanec, Kari Mann, Mê-Linh Lê, Patricia Gregory, Patrick Griffith, Kathy Doerksen
JBI Database of Systematic Reviews and Implementation Reports.2016; 14(9): 47. CrossRef - Development of a Smartphone Application for Clinical Decision Making of Medication Administration
Myoung-Soo Kim, Jung-Ha Park, Sungmin Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(3): 1650. CrossRef - Predictors of Drug Dosage Calculation Error Risk in Newly Graduated Nurses
Myoung Soo Kim, Jung Soon Kim, Won Choon Ha
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2014; 16(2): 113. CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness of Smartphone Application for the Medication Confirmation of High-alert Medications
Myoung Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(3): 253. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Drug Calculation Confidence in the Relationship between Interest in Medication and Drug Calculation Competency
Hyoung Sook Park, Gyoo Yeong Cho, Dong-Hee Kim, Sang Hee Kim, Myoung Soo Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2013; 15(4): 155. CrossRef
- Development and effectiveness of online teaching on practical skills among nursing students: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- 1,434 View
- 13 Download
- 23 Crossref

- Effects of a Yoga-focused Prenatal Program on Stress, Anxiety, Self Confidence and Labor Pain in Pregnant Women with In Vitro Fertilization Treatment
- Chung Sin Shim, Young-Sook Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(3):369-376. Published online June 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.3.369
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the effects of a Yoga-focused prenatal program on the stress, anxiety, self confidence and labor pain of pregnant women who had in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment.
Methods A quasi experimental study with a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The data collection period and meditation program were between January 9 and August 31, 2009. Forty-six women who were pregnant following IVF, and were between 12-20 weeks gestation, participated in the study (23 experimental group, 23 control group). Data were analyzed using Chi-square test, Mann-Whitney U Test, ANCOVA, and Cronbach's alpha coefficients with the SPSS 12.0 for Windows Program.
Results Although the sample size was limited, women who participated in the program showed statistically significant improvements in stress, anxiety, labor pain, and labor confidence for women pregnant after IVF.
Conclusion The result indicate that this 12-week Yoga-focused educational program can be utilized for women pregnant following IVF to reduce their stress, anxiety, and labor pain, and to increase delivery confidence. It is suggested that the Yoga-focused educational program be offered to every pregnant woman.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A spiritual intervention to reduce stress, anxiety and depression in pregnant women: Randomized controlled trial
Hormoz Sanaeinasab, Mohsen Saffari, Zarrindokht Sheykh-Oliya, Kazem Khalaji, Afsaneh Laluie, Faten Al Zaben, Harold G. Koenig
Health Care for Women International.2021; 42(12): 1340. CrossRef - Effect of Lifestyle Intervention Program for Overweight and Obesity Pregnant Women
Hye Kyung Choi, Hyeon Ok Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(3): 459. CrossRef - A comprehensive review on scientific evidence-based effects (including adverse effects) of yoga for normal and high-risk pregnancy-related health problems
A. Mooventhan
Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies.2019; 23(4): 721. CrossRef - Effects of a Web-Based Self-Management Program on the Behavior and Blood Glucose Levels of Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Yun-Su Kim, Hee-Seung Kim, Yoo-Lee Kim
Telemedicine and e-Health.2019; 25(5): 407. CrossRef - Effects of an Experience-focused Prenatal Program on Stress, Anxiety, Childbirth Confidence, and Maternal-Fetal Attachment on Women in Their First Pregnancy
Mira Park, Sunok Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(2): 126. CrossRef - Relaxation techniques for pain management in labour
Caroline A Smith, Kate M Levett, Carmel T Collins, Mike Armour, Hannah G Dahlen, Machiko Suganuma
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Anxiety, Pain and Maternal-fetal Attachment between Women who became Pregnant after Infertility Treatment and became Pregnant Naturally
Hee Ja Yoon, Seung Shin Lee, Song Hee Ye, Ah Reum Han, So Ri Lim, Hyun Jung Chung, Jum Mi Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(2): 71. CrossRef - The Review Study on Yoga, Qigong, and Taichi Interventions for Anxiety: Based on Korean Journal Articles from 2009 to 2015
Young-Joon Ahn, Sang-Ho Jo, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jung-Hwa Lim
Journal of Oriental Neuropsychiatry.2016; 27(1): 23. CrossRef - Stress, Coping Style and Nursing Needs for Hospitalized Pregnant Women due to Preterm Labor
Su Hyun Kim, Hyang-In Cho Chung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2015; 21(2): 83. CrossRef - Yoga for prenatal depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Hong Gong, Chenxu Ni, Xiaoliang Shen, Tengyun Wu, Chunlei Jiang
BMC Psychiatry.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Stress in pregnant women and the effect of cesarean delivery on anxiety and subjective anxiety statuses
Chung-Sin Shim, Ji-Yon Chong, Sang-Yeol Bae
The Korean Journal of Emergency Medical Services.2014; 18(3): 77. CrossRef
- A spiritual intervention to reduce stress, anxiety and depression in pregnant women: Randomized controlled trial
- 1,285 View
- 35 Download
- 11 Crossref

- The Effects of Pre-operative Visual Information and Parental Presence Intervention on Anxiety, Delirium, and Pain of Post-Operative Pediatric Patients in PACU
- Je-Bog Yoo, Min-Jung Kim, Soo-Hyun Cho, Yoo-Jung Shin, Nam-Cho Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(3):333-341. Published online June 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.3.333
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to test whether pre-operative visual information and parental presence had positive effects on anxiety, delirium, and pain in pediatric patients who awoke from general anesthesia in a post-surgical stage.
Methods This study used a non equivalent control-group post test design (n=76). Independent variables were provision of pre-operative visual information and parental presence for post-surgical pediatric patients in PACU (post anesthesia care unit). Dependent variables were anxiety, delirium, and pain in the pediatric patients measured three times at 10 minute intervals after extubation in the PACU. Measurements included Numerical Rating Scale for assessing state anxiety, Pediatric Anesthesia Emergence Delirium Scale by Sikich & Lerman (
2004 ) for delirium, and Objective Pain Scale by Broadman, Rice & Hannallah (1988 ) for pain.Results Experimental group showed significantly decreased state anxiety at time points-10, 20, and 30 minutes after extubation. Delirium was significantly lower at 10 minutes and 30 minutes after extubation in the experimental group. Pain was significantly lower at 10 minutes after extubation in the experimental group.
Conclusion The results of this study suggest that this intervention can be a safe pre-operative nursing intervention for post-surgical pediatric patients at PACU.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Virtual Reality Simulation to Improve Postoperative Cardiothoracic Surgical Patient Outcomes
Robert J. Anderson, Philippe R. Bauer, Arman Arghami, Rory M. Haney, Emily M. Reisdorf, Kiersten Baalson
American Journal of Critical Care.2025; 34(2): 111. CrossRef - Nursing experiences and knowledge of paediatric delirium: Analysing knowledge‐practice gaps
Soonyoung Shon, Minkyung Kang
Nursing in Critical Care.2024; 29(5): 923. CrossRef - ASSISTÊNCIA DE ENFERMAGEM PERIOPERATÓRIA AO ADOLESCENTE: SCOPING REVIEW
Layane Cristina Araújo, Danielle Mendonça Oliveira, Taysa de Fátima Garcia, Vanessa de Brito Poveda, Liliane de Lourdes Teixeira Silva
Texto & Contexto - Enfermagem.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - PERIOPERATIVE NURSING CARE FOR ADOLESCENTS: A SCOPING REVIEW
Layane Cristina Araújo, Danielle Mendonça Oliveira, Taysa de Fátima Garcia, Vanessa de Brito Poveda, Liliane de Lourdes Teixeira Silva
Texto & Contexto - Enfermagem.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Parental Presence on Emergence Delirium in Pediatric Patients After General Anesthesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jihyun Baek, Young Man Kim
Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing.2024; 39(3): 475. CrossRef - Sucking lollipop after awakening from sevoflurane anesthesia reduces the degree of emergence agitation in children undergoing ambulatory surgery: A prospective randomized controlled trial
Xiaofei Mo, Jiequn Zeng, Xiaoying Wu, Fa Huang, Kunling Zhang
Medicine.2023; 102(44): e35651. CrossRef - Investigating Non-Pharmacological Stress Reduction Interventions in Pediatric Patients Confirmed with Salivary Cortisol Levels: A Systematic Review
Maria Grigoropoulou, Emmanouil I. Kapetanakis, Achilleas Attilakos, Anestis Charalampopoulos, Anastasia Dimopoulou, Efstratios Vamvakas, Eleftheria Mavrigiannaki, Nikolaos Zavras
Pediatric Reports.2023; 15(2): 349. CrossRef - Intervention to Reduce Anxiety Pre- and Post-Eye Surgery in Pediatric Patients in South Korea: A Preliminary Quasi-Experimental Study
Hyeran Yi, Hanna Lee
Children.2022; 9(1): 65. CrossRef - Effectiveness of preoperative tour to a simulated anaesthesia induction at operating theatre in reducing preoperative anxiety in children and their parents: a pragmatic, single-blinded, randomised controlled trial/ King Fahad Medical City
Hussein Battah, Usamah AlZoraigi, Firas Shubbak
BMJ Simulation and Technology Enhanced Learning.2021; : bmjstel-2020-000707. CrossRef - The Effect of a Parental Visitation Program on Emergence Delirium Among Postoperative Children in the PACU
WooYoung In, Young Man Kim, Hee Soon Kim, SeoHee Hong, YuRi Suh, Yerin Cha, Naeun Kim, JongWon Kim, HyunJi Kang, HyoEun Kwon, YangSoo Kim, Wyunkon Park
Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing.2019; 34(1): 108. CrossRef - Factors associated with Pediatric Delirium in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit
Hyo Jin Kim, Dong Hee Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(2): 103. CrossRef - Stress, Pain, and Nursing Needs of Surgical Patients under General Anesthesia in the Recovery Room
Jihyun Jo, Minkyung Gu, Sohyune Sok
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(3): 249. CrossRef - Reduction of Postanesthetic Pediatric Distress: A Coordinated Approach
Simon Hayhoe, Scott Pallett, Juliet Zani, Joanne Trott
Journal of PeriAnesthesia Nursing.2018; 33(3): 312. CrossRef - The effects of maternal presence during anesthesia induction on salivary cortisol levels in children undergoing tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy
Hatice K. Ozdogan, Sibel Cetinalp, Gokhan Kuran, Onder Tugal, Murat Tahiroglu, Ummuhan E. Herdem, Suheyl Haytoglu
Journal of Clinical Anesthesia.2017; 39: 64. CrossRef - Effects of Family Presence Intervention on Anxiety, Delirium, Pain and Length of Time in Recovery Room of Post-operative Elderly Patients in Post-anesthesia Care Units
Kyunghee Kim, Sookhee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2015; 22(2): 149. CrossRef - Preoperative Anxiety Management, Emergence Delirium, and Postoperative Behavior
Richard J. Banchs, Jerrold Lerman
Anesthesiology Clinics.2014; 32(1): 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Hand Holding and Nei-Guan Acupressure on Anxiety and Pain under Local Anesthetic Patients during Surgery
Sun Hee Park, Hee Jung Jang
The Journal of the Korea Contents Association.2014; 14(11): 378. CrossRef - Emergence agitation after sevoflurane anaesthesia in children
A.K. Narayanasamy, A Ghori
British Journal of Anaesthesia.2013; 111(1): 121. CrossRef
- Virtual Reality Simulation to Improve Postoperative Cardiothoracic Surgical Patient Outcomes
- 1,462 View
- 27 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Effects of a Short-term Life Review on Spiritual Well-being, Depression, and Anxiety in Terminally Ill Cancer Patients
- Sung Hee Ahn, Young Lan An, Yang Sook Yoo, Michiyo Ando, Soo Jin Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(1):28-35. Published online February 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.1.28
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to evaluate the effects of a short-term life review on spiritual well-being, depression, and anxiety in patients with terminal cancer.
Methods The study used a pre posttest quasi experimental design with a nonequivalent control group. Measurement instruments included the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Spiritual scale (FACIT-Sp12) and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). Participants were 32 patients with terminal cancer who were receiving chemotherapy or palliative care at hospitals or at home. Eighteen patients were assigned to the experimental group and 14 to the control group. A sixty minute short-term life review session was held twice a week as the intervention with the experimental group.
Results There was a statistically significant increase in spiritual well-being in the experimental group compared to the control group. There were also significant decreases in depression and anxiety in the experimental group compared to the control group.
Conclusion The results indicate that a short-term life review can be used as a nursing intervention for enhancing the spiritual well-being of patients with terminal cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Progress on Lung Cancer Patients' Sense of Meaning of Life
Xinrui Lin, Shanshan Qu, Yue Yang, Xiaoge Ding, Yinji Jin
Nursing and Health Research.2025; 4(3): 28. CrossRef - The effectiveness of reminiscence therapy on anxiety, depression, and quality of life in adult cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Canan Bozkurt, Öznur Erbay-Dalli, Yasemin Yildirim
Supportive Care in Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Efficacy of Reminiscence Therapy in Cancer-Related Symptom Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jie Sun, Jieting Jiang, Yiyan Wang, Mingyue Zhang, Lu Dong, Kunpeng Li, Caiqin Wu
Integrative Cancer Therapies.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Studying the Effect of Life Review Therapy on Psychological Well-being and Anxiety of Teenage Girls in Divorced Families
Fatemeh Bay, Alireza Ghorbani
Iranian Evolutionary and Educational Psychology.2023; 5(2): 145. CrossRef - Effects of a Mind Map–Based Life Review Program on Anxiety and Depressive Symptoms on Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Ying Chen, Jianwei Zheng, Huimin Xiao, Xiaoyan Lin, Xiaoling Zhang
Cancer Nursing.2022; 45(1): E116. CrossRef - Dignity therapy for effective palliative care: a literature review
Se-Ryun Park, Yu-Jung Cha
Kosin Medical Journal.2022; 37(3): 192. CrossRef - The Effect of Hospice Patients' Pain, Anxiety, Depression, Perception of Dignity, and Spiritual Well-Being on their Attitudes toward Dignified Death
Yun Sil Ahn, Pok Ja Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2021; 33(3): 212. CrossRef - Development of a One-item Screening Question to Assess Spiritual Well-Being for Advanced Cancer Inpatients in Korea
Youngmin Park, Sang-Yeon Suh, Sun-Hyun Kim, Jeanno Park, Seok Joon Yoon, Yu Jung Kim, Beodeul Kang, Jung Hye Kwon, Kwonoh Park, David Hui, Hyeon Jeong Kim, Sanghee Lee, Hong-Yup Ahn
Journal of Pain and Symptom Management.2021; 62(5): 910. CrossRef - Verbal responses, depressive symptoms, reminiscence functions and cognitive emotion regulation in older women receiving individual reminiscence therapy
Dongmei Wu, Taolin Chen, Hao Yang, Qiyong Gong, Xiuying Hu
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2018; 27(13-14): 2609. CrossRef - Developing a mind map–based life review program to improve psychological well‐being of cancer patients: a feasibility study
Ying Chen, Huimin Xiao, Xiaoyan Lin
Psycho-Oncology.2018; 27(1): 339. CrossRef - Spiritual Well-being Among Palliative Care Patients With Different Religious Affiliations: A Multicenter Korean Study
Seok Joon Yoon, Sang-Yeon Suh, Sun Hyun Kim, Jeanno Park, Yu Jung Kim, Beodeul Kang, Youngmin Park, Jung Hye Kwon, Kwonoh Park, Dong Wook Shin, Hyeon Jeong Kim, Hong-Yup Ahn, David Hui
Journal of Pain and Symptom Management.2018; 56(6): 893. CrossRef - Anxiety and Spiritual Well-Being in Nursing Students: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jéssika Leão Fabbris, Ana Cláudia Mesquita, Sílvia Caldeira, Ana Maria Pimenta Carvalho, Emilia Campos de Carvalho
Journal of Holistic Nursing.2017; 35(3): 261. CrossRef - The effects of life review interventions on spiritual well-being, psychological distress, and quality of life in patients with terminal or advanced cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Chong-Wen Wang, Amy YM Chow, Cecilia LW Chan
Palliative Medicine.2017; 31(10): 883. CrossRef - Effects of Dignity Interventions on Psychosocial and Existential Distress in Terminally ill Patients: A Meta-analysis
Pok Ja Oh, Sung-Rae Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(5): 471. CrossRef
- Research Progress on Lung Cancer Patients' Sense of Meaning of Life
- 1,321 View
- 38 Download
- 14 Crossref

- The Influence of Workplace Violence on Work-related Anxiety and Depression Experience among Korean Employees
- Eun Sook Choi, Hye-Sun Jung, Su-Hyun Kim, Hyunju Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(5):650-661. Published online October 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.5.650
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose Work-related anxiety and depression are frequent work-related mental health problems. In this study the relationship between workplace violence and work-related anxiety and/or depression among Korean employees was evaluated.
Methods Data were obtained from the Korean Working Condition Survey of 2006. Participants were 9,094 Korean workers aged 15-64 yr. Multiple logistic regression using SAS version 9.1 was used.
Results The incidence of work-related anxiety, work-related depression and workplace violence were 4.5%, 3.5%, and 1.8% respectively. When personal and occupational risk factors were adjusted, workplace violence was significantly associated with work-related anxiety and depression (OR for anxiety: 4.07, CI: 2.62-6.34; OR for depression: 4.60, CI: 2.92-7.25). Work-related anxiety was significantly related to type of employment, working period at present workplace, work time, shift work, job demand, and social support from superiors. Factors influencing work-related depression were gender, education, alcohol consumption, company size, type of employment, working period at present workplace, work time, shift work, and job demand.
Conclusion To promote psychological health in workers there is a need to develop work-related anxiety and depression prevention programs and to decrease in workplace violence. In developing these programs, consideration should be given to personal factors, working conditions, and psychosocial working environments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Interrelationships of Anxiety, Burnout, Depression, and Insomnia Among Chinese Healthcare Workers Exposed to Workplace Violence: A Network Analysis
Huixue Xu, Zejun Li, Xin Wang, Min Wu, Tieqiao Liu, Qiuxia Wu, Raffaella Bosurgi
Depression and Anxiety.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on Experiences of Workplace Violence and Workplace Gender Discrimination among Korean Women Employees: A Cross-Sectional Study
Joohee Kim
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2025; 36: 268. CrossRef - Differences in the Effects of Work Environment on Health Problems and Satisfaction of Working Condition by Gender: The 6th Korean Working Conditions Survey
Chae Hyeseon, Park Sooin, Kim Insoo, Ko Myungsun
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(19): 6824. CrossRef - Performance-Based Pay System and Job Stress Related to Depression/Anxiety in Korea: Analysis of Korea Working Condition Survey
Myeong-Hun Lim, Jin-Ha Yoon, Won-Tae Lee, Min-Seok Kim, Seong-Uk Baek, Jong-Uk Won
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(5): 4065. CrossRef - Relationships Between Depressive Symptoms, Interpersonal Sensitivity and Social Support of Employees Before and During the COVID-19 Epidemic: A Cross-lag Study
Songli Mei, Cuicui Meng, Yueyang Hu, Xinmeng Guo, Jianping Lv, Zeying Qin, Leilei Liang, Chuanen Li, Junsong Fei, Ruilin Cao, Yuanchao Hu
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Workplace Violence and Depressive Symptoms among Primary Healthcare Professionals in Shandong, China: Meaning in Life as a Moderator
Meiqi Wang, Haipeng Wang, Zhen Wei, Yifan Wang, Long Sun
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(22): 15184. CrossRef - Mediating Effects of Psychological States on Work Performance of Visiting Nurses According to COVID-19 Workplace Quarantine Measures: A Multi-Group Path Analysis Study
Jee-Hyun Hwang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 19(1): 444. CrossRef - Depressive Symptoms Following Work-Related Violence and Threats and the Modifying Effect of Organizational Justice, Social Support, and Safety Perceptions
Lars Peter Sønderbo Andersen, Annie Hogh, Johan Hviid Andersen, Karin Biering
Journal of Interpersonal Violence.2021; 36(15-16): 7110. CrossRef - Does the Type of Exposure to Workplace Violence Matter to Nurses’ Mental Health?
Farinaz Havaei
Healthcare.2021; 9(1): 41. CrossRef - What Are the Experiences of Emotional Labor and Workplace Violence that Are More Harmful to Health in Korean Workforce?
Won Ju Hwang, Hye Kyung Yang, Ji Hye Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(21): 8019. CrossRef - Psychological depletion in physicians and nurses exposed to workplace violence: A cross-sectional study using propensity score analysis
Lei Shi, Guoqiang Li, Jiatong Hao, Weidong Wang, Wei Chen, Shihui Liu, Zhixin Yu, Yu Shi, Yuanshuo Ma, Lihua Fan, Leijing Zhang, Xuanye Han
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2020; 103: 103493. CrossRef - The Relationship between Workplace Violence and Innovative Work Behavior: The Mediating Roles of Employee Wellbeing
Xiang Zhou, Samma Faiz Rasool, Dawei Ma
Healthcare.2020; 8(3): 332. CrossRef - Suppressing emotion and engaging with complaining customers at work related to experience of depression and anxiety symptoms: a nationwide cross-sectional study
Jin-Ha YOON, Mo-Yeol KANG, Dayee JEUNG, Sei-Jin CHANG
INDUSTRIAL HEALTH.2017; 55(3): 265. CrossRef - Influences of Working Conditions and Health Status on Absence due to Sickness in Health and Medical related Workers
Yoonjeong Lee, Hyun-Li Kim
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(3): 216. CrossRef - Relationship of workplace violence and perpetrators on sleep disturbance-data from the 4th Korean working conditions survey
Taejun Yoo, Byeongjin Ye, Jung-Il Kim, Siwoo Park
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Job Insecurity on Job related Depression and Anxiety: Large- and Small-sized Company Employees
Yeongmi Ha, Hyunju Park
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2016; 25(4): 329. CrossRef - Relating Factors for Depression in Korean Working Women: Secondary Analysis of the Fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V)
Kyung-Jae Lee, Jeung-Im Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(3): 265. CrossRef - Associations of neighborhood‐level workplace violence with workers’ mental distress problems: a multilevel analysis of Taiwanese employees
Li‐Chung Pien, Duan‐Rung Chen, Chiou‐Jong Chen, Kuei‐Min Liang, Yawen Cheng
Journal of Occupational Health.2015; 57(6): 555. CrossRef - Work‐related Risk Factors for Workplace Violence among Korean Employees
Hye‐Eun Lee, Hyoung‐Ryoul Kim, Jung Sun Park
Journal of Occupational Health.2014; 56(1): 12. CrossRef - The Influence of Workplace Violence on Anger and Post Traumatic Stress Disorder among Nurses
Hyeryeon Yi, Hyun-Sook Moon, Mee-Kyung Shin
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2013; 22(3): 240. CrossRef - Health Status and Affecting Factors related to Job among Korean Women Employees
Eun-Young Hong, Sang-Dol Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(9): 4107. CrossRef
- Interrelationships of Anxiety, Burnout, Depression, and Insomnia Among Chinese Healthcare Workers Exposed to Workplace Violence: A Network Analysis
- 1,235 View
- 7 Download
- 21 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


