Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 45(2); 2015 > Article
-
Original Article
- Effects of an Integrated Internet Addiction Prevention Program on Elementary Students' Self-regulation and Internet Addiction
- So Youn Mun, Byoung Sook Lee
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2015;45(2):251-261.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.2.251
Published online: April 30, 2015
1Acheon Elementary School, Gimcheon, Korea.
2College of Nursing, Keimyung University, Daegu, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Lee, Byoung Sook. College of Nursing, Keimyung University, 1095 Dalgubul-daero, Dalseo-gu, Daegu 704-701, Korea. Tel: +82-53-580-3900, Fax: +82-53-580-3916, lbs@gw.kmu.ac.kr
© 2015 Korean Society of Nursing Science
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NoDerivs License. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/) If the original work is properly cited and retained without any modification or reproduction, it can be used and re-distributed in any format and medium.
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- An Integrative Review of Interventions for Preventing Internet and Smartphone Addiction in Elementary School Students: Based on the IMB Model
Hyemin Park, Bohye Kim, Jaehee Jeong, Hwa Jeong Kim, Yebin Kim
STRESS.2024; 32(3): 133. CrossRef - Treatment effects of therapeutic interventions for gaming disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Paul A. Danielsen, Rune A. Mentzoni, Torstein Låg
Addictive Behaviors.2024; 149: 107887. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a web-based group intervention for internet addiction in university students
Andreas Brouzos, Aikaterini Papadopoulou, Vasiliki C. Baourda
Psychiatry Research.2024; 336: 115883. CrossRef - The effect of gamification-based training on the knowledge, attitudes, and academic achievement of male adolescents in preventing substance and internet addiction
Esmaeel Taghipour, Fatemeh Vizeshfar, Nahid Zarifsanaiey
BMC Medical Education.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Teknoloji bağımlılığını önlemeye yönelik psikoeğitim programının 8. sınıf öğrencileri üzerindeki etkisi
Yunus Emre Karadağ, Cemal Onur Noyan
Bağımlılık Dergisi.2023; 24(1): 43. CrossRef - The effects of mobile phone use on students’ emotional-behavioural functioning, and academic and social competencies
Hossein Eskandari, Mohammad Reza Vahdani Asadi, Rouhollah Khodabandelou
Educational Psychology in Practice.2023; 39(1): 38. CrossRef - Health-policy approaches for problematic Internet use: lessons from substance use disorders
Dan J Stein, Anna Hartford
Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences.2022; 46: 101151. CrossRef - Effects of Life Skill Training on the School Violence Attitudes and Behavior Among Elementary School Children
Jae Yeon Lee, Ok Kyung Ham, Hyun Soo Oh, Eun Jin Lee, Young Ko, Bongjeong Kim
The Journal of School Nursing.2022; 38(4): 336. CrossRef - Prevention Strategies to Address Problematic Gaming: An Evaluation of Strategy Support Among Habitual and Problem Gamers
Matthew W. R. Stevens, Paul H. Delfabbro, Daniel L. King
The Journal of Primary Prevention.2021; 42(2): 183. CrossRef - Prevention approaches to problem gaming: A large-scale qualitative investigation
Matthew W.R. Stevens, Paul H. Delfabbro, Daniel L. King
Computers in Human Behavior.2021; 115: 106611. CrossRef - The Effect of Mind Subtraction Meditation Intervention on Smartphone Addiction and the Psychological Wellbeing among Adolescents
Eun-Hi Choi, Min Young Chun, Insoo Lee, Yang-Gyeong Yoo, Min-Jae Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(9): 3263. CrossRef - Development and Effect of a Smartphone Overdependence Prevention Program for University Students Based on Self-Determination Theory
Myung Soon Kwon, Jeong Soon Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(1): 116. CrossRef - Digital Nativity and Information Technology Addiction: Age cohort versus individual difference approaches
Hsin-Yi Wang, Leif Sigerson, Cecilia Cheng
Computers in Human Behavior.2019; 90: 1. CrossRef - LA PRÉVENTION DE L’UTILISATION PROBLÉMATIQUE D’INTERNET : EXPLORATION DU POINT DE VUE DES JEUNES
Gabrielle St-Arnaud, Magali Dufour1, Andrée-Anne Légaré, Joël Tremblay, Karine Bertrand, Yasser Khazaal, Natacha Brunelle, Mathieu Goyette
Revue québécoise de psychologie.2019; 40(2): 115. CrossRef - School-based Prevention for Adolescent Internet Addiction: Prevention is the Key. A Systematic Literature Review
Melina A. Throuvala, Mark D. Griffiths, Mike Rennoldson, Daria J. Kuss
Current Neuropharmacology.2019; 17(6): 507. CrossRef - Effects of a prevention intervention concerning screens, and video games in middle-school students: Influences on beliefs and use
Céline Bonnaire, Zéphyr Serehen, Olivier Phan
Journal of Behavioral Addictions.2019; 8(3): 537. CrossRef - Effects of a prevention program for internet addiction among middle school students in South Korea
Sun‐Yi Yang, Hee‐Soon Kim
Public Health Nursing.2018; 35(3): 246. CrossRef - Policy and Prevention Approaches for Disordered and Hazardous Gaming and Internet Use: an International Perspective
Daniel L. King, Paul H. Delfabbro, Young Yim Doh, Anise M. S. Wu, Daria J. Kuss, Ståle Pallesen, Rune Mentzoni, Natacha Carragher, Hiroshi Sakuma
Prevention Science.2018; 19(2): 233. CrossRef - Internet addiction detection rate among college students in the People’s Republic of China: a meta-analysis
Yao-jun Shao, Tong Zheng, Yan-qiu Wang, Ling Liu, Yan Chen, Ying-shui Yao
Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Treatment and risk factors of Internet use disorders
Hideki Nakayama, Satoko Mihara, Susumu Higuchi
Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences.2017; 71(7): 492. CrossRef - Prevention and Policy Related to Internet Gaming Disorder
Daniel L. King, Paul H. Delfabbro
Current Addiction Reports.2017; 4(3): 284. CrossRef - Mediation Effects of Self regulation and Hopelessness between Self efficacy and Internet game addiction in Middle School Students
Bo Young Kim
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2015; 29(3): 441. CrossRef
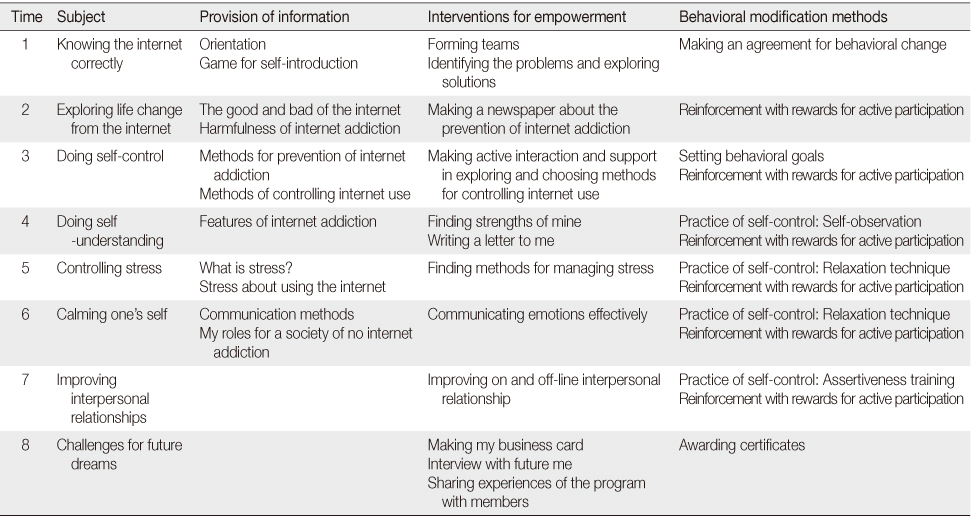
The Contents of the Integrated Internet Addiction Prevention Program
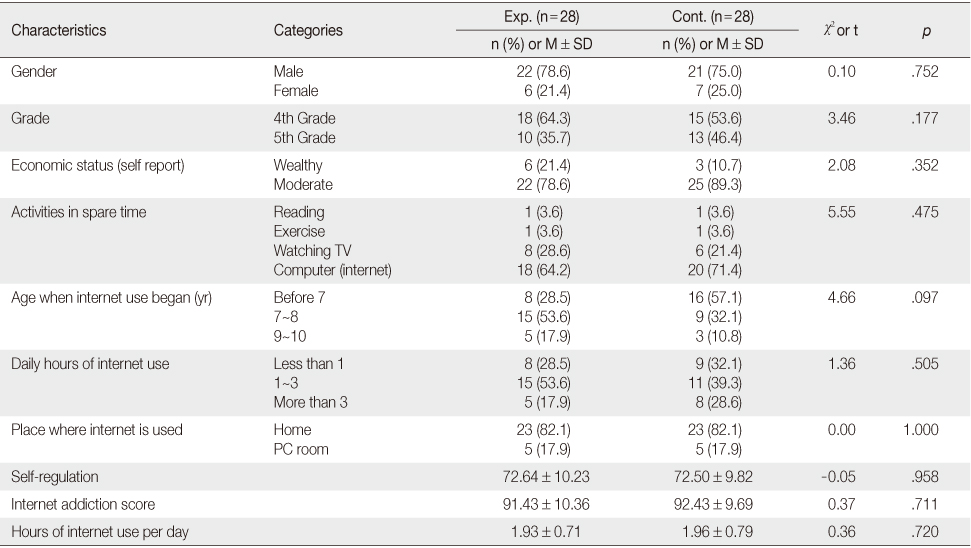
Homogeneity of the Participants
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
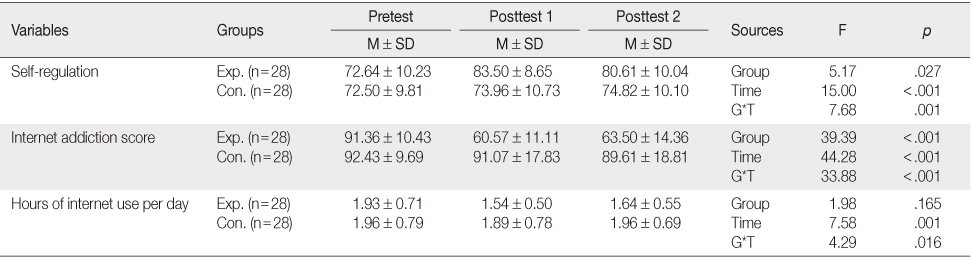
Effect of the Internet-Addiction Prevention Program
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; G*T=Interaction between group and time.
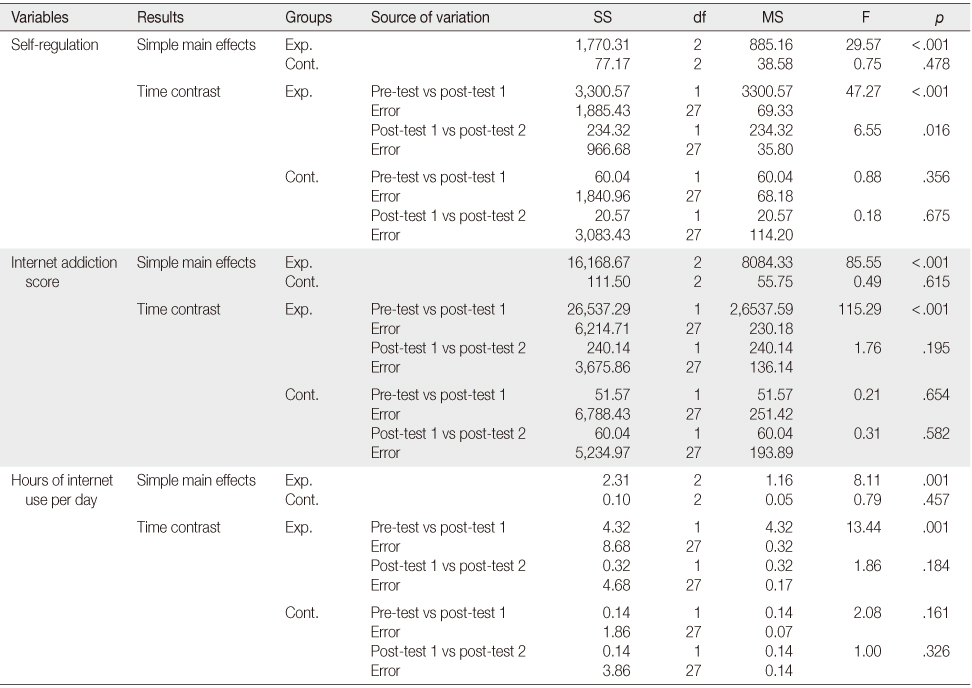
Simple Main Effects and Time Contrast in Dependent Variables by Measurement Time
Exp.=Experimental group (n=28); Cont.=Control group (n=28); SS=Sum of square; MS=Mean square.
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group; G*T=Interaction between group and time.
Exp.=Experimental group (n=28); Cont.=Control group (n=28); SS=Sum of square; MS=Mean square.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

