Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 44(2); 2014 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Effects of an Asthma Management Education Program for Preschoolers
- Soyoun Yim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2014;44(2):189-197.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.2.189
Published online: April 30, 2014
Department of Nursing Science, The Baekseok University, Cheonan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Yim, Soyoun. Department of Nursing Science, The Baekseok University, 76 Munam-ro, Dongnam-gu, Cheonan 330-704, Korea. Tel: +82-41-550-0722, Fax: +82-41-550-2829, ysybest@bu.ac.kr
© 2014 Korean Society of Nursing Science
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NoDerivs License. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/) If the original work is properly cited and retained without any modification or reproduction, it can be used and re-distributed in any format and medium.
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Environmental management education using immersive virtual reality in asthmatic children
Seung Hyun Kim, Sang Hyun Park, Insoon Kang, Yuyoung Song, Jaehoon Lim, Wonsuck Yoon, Young Yoo
Allergy, Asthma & Respiratory Disease.2022; 10(1): 33. CrossRef - Environmental management education using immersive virtual reality in asthmatic children in Korea: a randomized controlled study (secondary publication)
Seung Hyun Kim, Sang Hyun Park, Insoon Kang, Yuyoung Song, Jaehoon Lim, Wonsuck Yoon, Young Yoo
Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions.2022; 19: 15. CrossRef - Knowledge and Practice in Self-Management on Asthma of School-Aged Children with Asthma
Seon Su Kim, In Soo Kwon
Child Health Nursing Research.2016; 22(2): 87. CrossRef - Educational Programs for the Management of Childhood Atopic Dermatitis: An Integrative Review
Yunmi Lee, Jina Oh
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(3): 185. CrossRef
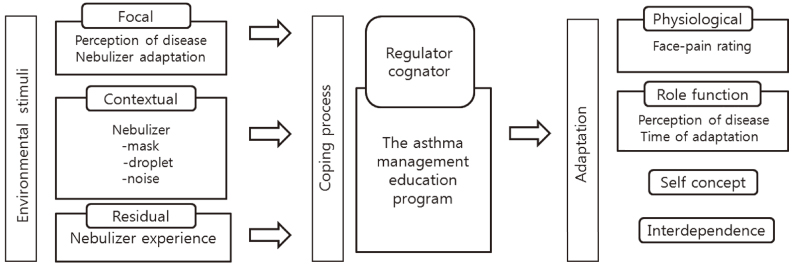
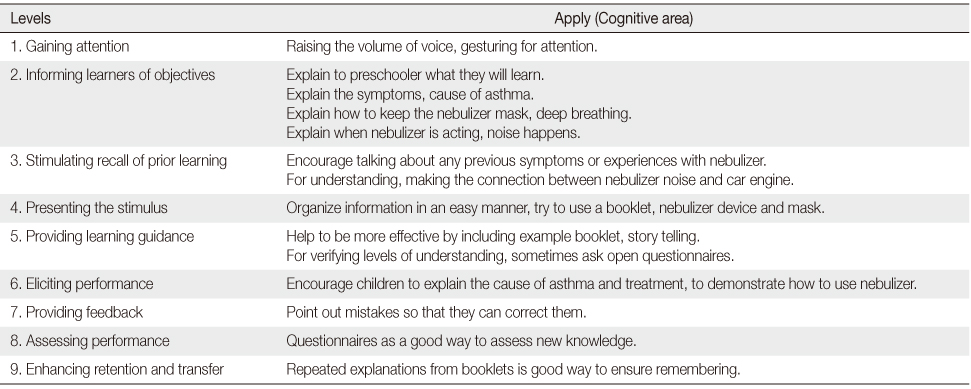
Figure 1
Gagné and Briggs's Nine Levels of Learning Steps
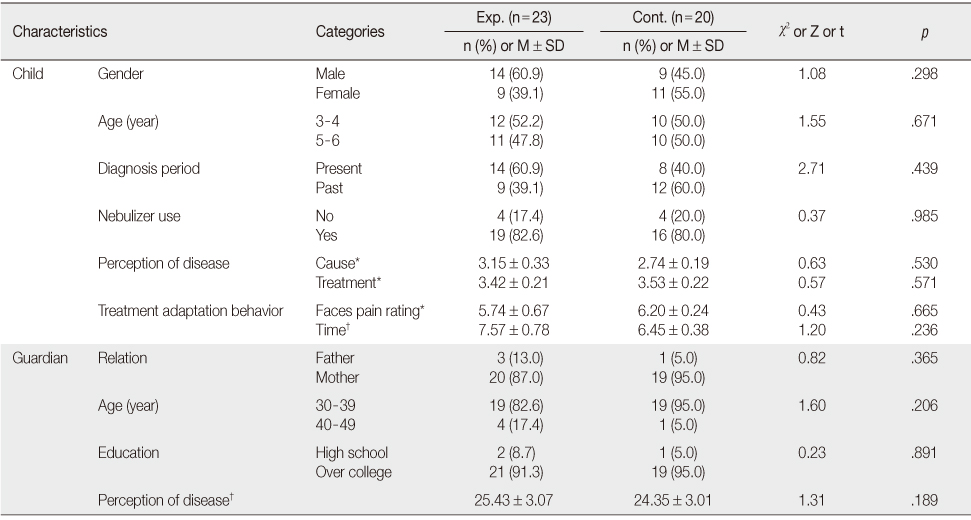
General Characteristics and Homogeneity of Experimental and Control Groups (N=43)
*Wilcoxon rank-sum test; †independent t-test; Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
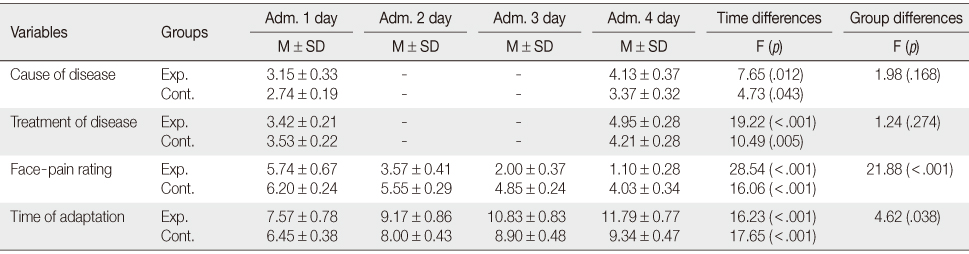
Comparison between Experimental Group and Control Group for Perception of Disease, Treatment-Adaptation Behavior (N=43)
Adm.=Admission; Exp.=Experimental group (n=23); Cont.=Control group (n=20).
*Wilcoxon rank-sum test; †independent t-test; Exp.=Experimental group; Cont.=Control group.
Adm.=Admission; Exp.=Experimental group (n=23); Cont.=Control group (n=20).
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

