Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 39(4); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- Factors influencing Nurses' Organizational Citizenship Behavior
- Junhee Park, Eunkyung Yun, Sangsook Han
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2009;39(4):499-507.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.4.499
Published online: August 31, 2009
1Doctoral Student, College of Nursing Science, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
2Instructor, College of Nursing Science, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
3Professor, College of Nursing Science East-West Nursing Research Institute, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Han, Sang Sook. College of Nursing Science East-West Nursing Research Institute, Kyung Hee University, 1 Hoegi-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul 130-701, Korea. Tel: 82-2-961-9427, Fax: 82-2-961-9398, sshan12@khu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2009 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was conducted to identify the factors that influence nurses' organizational citizenship behavior.
-
Methods
- A cross-sectional design was used, with a convenience sample of 547 nurses from four university hospitals in Seoul and Gyeonggi province. The data were collected through a questionnaire survey done from September 22 to October 10, 2008. The tools used for this study were scales on organizational citizenship behavior (14 items), self-leadership (14 items), empowerment (10 items), organizational commitment (7 items), job satisfaction (8 items) and transformational·transactional leadership (14 items). Cronbach's alpha and factor analysis were examined to test reliability and construct validity of the scale. The data collected were processed using SPSS Window 15.0 Program for actual numbers and percentages, differences in the dependent variable according to general characteristics, and means, standard deviations, correlation coefficients and multiple regression analysis.
-
Results
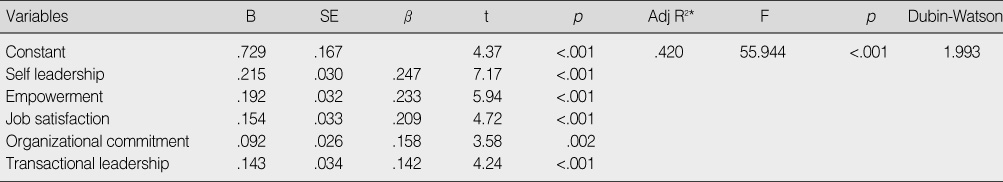
- The factors influencing nurses' organizational citizenship behavior were identified as self-leadership (β=.247), empowerment (β=.233), job satisfaction (β=.209), organizational commitment (β=.158), and transactional leadership (β=.142). Five factors explained 42.0% of nurses' organizational citizenship behavior.
-
Conclusion
- The results of this study can be used to develop further management strategies for enhancement of nurses' organizational citizenship behavior.
- 1. Bass BM. Bass and Stogdill's Handbook of Leadership: Theory, Research & Managerial Applications. 1990;New York, NY, The Free Press.
- 2. Choi J, Ha NS. The relationship between organizational citizenship behavior and customer orientation on organizational justice in clinical nurses. Journal of Korean Clinical Nursing Research. 2007;13:173–184.
- 3. Choi JY. Empirical study on the effect of transformational leadership on the organizational citizenship behavior. 2005;Busan, Pusan National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 4. Ha SB. A study on the antecedents and outcomes of subordinate's self-leadership. 2007;Seoul, Seoul National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 5. Han JH. A study on the impact of job insecurity of employment adjustment and its antecedents on empowerment and organizational citizenship behavior. Daehan Journal of Business. 2006;19:1219–1244.
- 6. Houghton JD, Neck CP. The revised self-leadership questionnaire: Testing a hierarchical factor structure for self-leadership. Journal of Managerial Psychology. 2002;17:672–691.
- 7. Jun HS. Influence of leader-member exchange and organizational commitment on organizational citizenship behavior in nursing organization. 2003;Seoul, Ewha Womans University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 8. Kim DS. The effects of transformational and transactional leadership on the organizational citizenship behavior. 2002;Seoul, Yonsei University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 9. Kim IC. The effects of servant leadership on individual empowerment and group's empowerment. 2003;Seoul, Korea University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 10. Kim IW. A structural equation model on head nurse's leadership. 2005;Seoul, Kyung Hee University. Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 11. Kim KK, Suh CH, Joo HS. The Impact of hotel employee job characteristic on organization commitment, job satisfaction, and citizenship behavior. Daehan Journal of Business. 2006;19:469–488.
- 12. Kim KS, Won YS. Effects of transactional and transformational leaderships on hotel employee job satisfaction and organizational citizenship behavior. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Studies. 2004;6:29–49.
- 13. Kim YG, Kim HS, Kim HC. The effects of communication, group cohesiveness and job satisfaction on organizational citizenship behavior in hotel industry. Korean Journal of Hotel Administration. 2000;9:231–246.
- 14. Ko YK. Identification of factors related to hospital nurses' organizational citizenship behavior using a multilevel analysis. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008;38:287–297.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Lee KM. Influence of self-leadership of nurse on organizational citizenship behavior and job satisfaction. 2007;Jeonju, Chonbuk National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 16. Lee SM, Lee EO. Nursing Research. 2005;Seoul, Korea National Open University Press.
- 17. Locke EA. Dunnette MD. The nature and causes of job satisfaction. In: Handbook of industrial and organizational psychology. 1976;Chicago, IL, Rand McNally. 1297–1349.
- 18. Manz CC, Sims HP. Business without bosses: How self managing teams are building high-performing companies. 1995;New York, NY, John Wiley & Sons.
- 19. Mowday RT, Steers RM, Porter LW. The management of organizational commitment. Journal of Vocational Behavior. 1979;14:224–247.Article
- 20. Oh SY, Chung HC. The impact of organizational commitment and emotions on organizational citizenship behavior: Focused on hospital management. Korean Governance Review. 2006;12(2):49–75.
- 21. Organ DW. Organizational citizenship behavior: The good soldier syndrome. 1988;Lexington, MA, Lexington Books.
- 22. Park HT. Transformational and transactional leadership styles of the nurse administrators and job satisfaction, organizational commitment in nursing service. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 1997;27:228–241.ArticlePDF
- 23. Park IJ. A validation study of the Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire (MSQ). 2005;Seoul, Seoul National University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 24. Park WY. The influence of organization citizenship behavior in the relation of justice and organizational effectiveness perceived by nurses. 2004;Gimhae, Inje University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 25. Podsakoff PM, Mackenzie SB, Moorman RH, Fetter R. Transformational leader behavior and their effects on followers' trust in leader, satisfaction, and organizational citizenship behavior. Leadership Quarterly. 1990;1:107–142.
- 26. Seo SJ. Relationship between organizational culture and organizational citizenship behavior among employees at a university hospital. 2003;Gimhae, Inje University. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 27. Shim JE, Chung BK. A study on the relationship among leadership, empowerment and organizational citizenship behavior in research organizations. CNU Journal of Management & Economics. 2007;29(2):49–71.
- 28. Song US, Kim JH. The influence of job autonomy on the relationship between personal characteristics and organizational citizenship behavior among lower ranking public officials. International Review of Public Administration. 2002;36:117–137.
- 29. Spreitzer GM. Psychological empowerment in the workplace: Dimensions, measurement and validation. Academy of Management Journal. 1995;38:1442–1465.Article
- 30. Weiss DJ, Dawis RV, England GW, Lofguist LH. Manual for the Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire. 1967;Minneapolis, MN, University of Minnesota, Industrial Relations Center.
REFERENCES
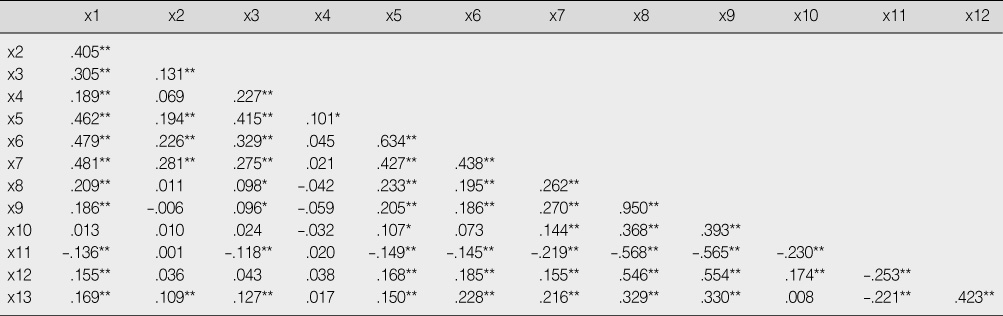
*p<.05; **p<.01.
x1=organizational citizenship behavior; x2=self leadership; x3=transformational leadership; x4=transactional leadership; x5=organization commitment; x6=job satisfaction; x7=empowerment; x8=age; x9=total period of clinical career; x10=total period on current ward; x11=marital status; x12=current position; x13=shift-work.
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Organisational Citizenship Behaviour (OCB) Model in Hospital Nurses in Indonesia
Dodi Wijaya, Stefanus Supriyanto, Ah. Yusuf Ah. Yusuf
Malaysian Journal of Medicine and Health Sciences.2023; 19(1): 165. CrossRef - The Effect of Organizational Justice on Organizational Citizenship Behavior: Double Mediating Effects of Psychological Contract and Subjective Career Success
Hee Jung Kim, Mi Yu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(1): 65. CrossRef - Decisional balance, self-leadership, self-efficacy, planning, and stages of change in adopting exercise behaviors in patients with stomach cancer: A cross-sectional study
Myung Kyung Lee
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 56: 102086. CrossRef - Links connecting nurses’ planned behavior, burnout, job satisfaction, and organizational citizenship behavior
N. Gökhan Torlak, Cemil Kuzey, Muhammet Sait Dinç, Taylan Budur
Journal of Workplace Behavioral Health.2021; 36(1): 77. CrossRef - Influence of Internal Marketing Perception on Customer Orientation and Organizational Citizenship Behavior of Nurses
Eun Sim Kim, Se Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2021; 27(1): 64. CrossRef - Moderating Effects of Career Commitment in the Relationship between Work Engagement and Organizational Citizenship Behaviors of the Clinical Nurses
Eun Jeong Song, Mi Jeong Kim, Myung Suk Koh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2019; 25(3): 167. CrossRef - Person-Organization Value Congruence between Authentic Leadership of Head Nurses and Organizational Citizenship Behavior in Clinical Nurses
Joung Ok Kim, Se Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2017; 23(5): 515. CrossRef - Path analysis of the Influence of Hospital Ethical Climate Perceived by Nurses on Supervisor Trust and Organizational Effectiveness
Yoon Goo Noh, Myun Sook Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(6): 824. CrossRef - Nursing Performance and Innovative Behavior as Factors Affecting the Self-leadership of Geriatric Hospital Nurses
Jeong-Ok Kwon
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2016; 10(1): 53. CrossRef - Nurses’ voluntary extra work in the hospital: The role of managers’ decision-making style
Mohammad Amin Bahrami, Marzieh Salehi, Omid Barati, Mohammad Ranjbar Ezzatabadi, Razieh Montazer-alfaraj, Arefeh Dehghani Tafti
International Journal of Healthcare Management.2016; 9(3): 155. CrossRef - Organisational support, organisational identification and organisational citizenship behaviour among male nurses
SHENG-HWANG CHEN, HSING-YI YU, HSIU-YUEH HSU, FANG-CHEN LIN, JIUNN-HORNG LOU
Journal of Nursing Management.2013; 21(8): 1072. CrossRef - The Effect of Organizational Culture Types of Hospital and Nursing experience on Organizational Citizenship Behaviors of Nurses
Kyoungnam Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(11): 5707. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse's Organizational Conflict on Organizational Commitment and Labor Union Commitment in University Hospitals
Soon Min, Hye Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2012; 18(4): 374. CrossRef - Mediation Effect of Organizational Citizenship Behavior between Job Embeddedness and Turnover Intention in Hospital Nurses
Eun Hee Kim, Eunjoo Lee, Hyo Jin Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2012; 18(4): 394. CrossRef - Organizational Personality Type and Citizenship Behaviors Perceived by Public Health Center Workers in Chonnam Province, Korea
Yoo-Hyang Cho
Journal of agricultural medicine and community health.2011; 36(1): 47. CrossRef
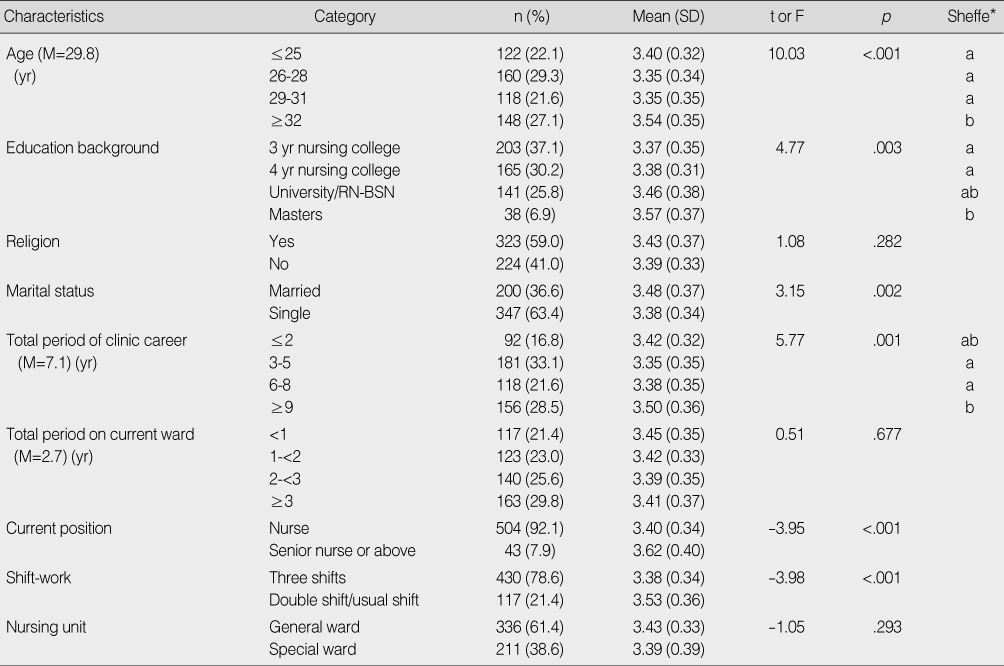
Organizational Citizenship Behavior by Demographic Variables
*Different letters means significantly different (p<.05).
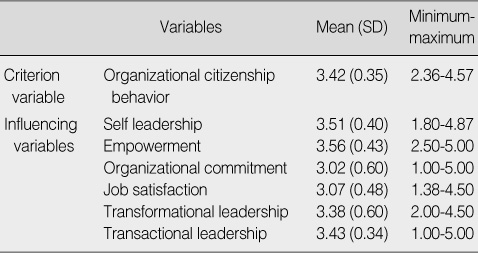
Mean and Standard Deviation of Variables
Correlation among Variables
*p<.05; **p<.01.
x1=organizational citizenship behavior; x2=self leadership; x3=transformational leadership; x4=transactional leadership; x5=organization commitment; x6=job satisfaction; x7=empowerment; x8=age; x9=total period of clinical career; x10=total period on current ward; x11=marital status; x12=current position; x13=shift-work.
Factors affecting Organizational Citizenship Behavior
*Adj R2=Adjusted R Square.
*Different letters means significantly different (
* x1=organizational citizenship behavior; x2=self leadership; x3=transformational leadership; x4=transactional leadership; x5=organization commitment; x6=job satisfaction; x7=empowerment; x8=age; x9=total period of clinical career; x10=total period on current ward; x11=marital status; x12=current position; x13=shift-work.
*Adj R2=Adjusted R Square.
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

