Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Nurs > Volume 38(1); 2008 > Article
-
Original Article
- Prevalence Rate and Associated Factors of Urinary Incontinence among Nursing Home Residents
- Moon-Sil Kim, Seung-Hee Lee
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2008;38(1):92-100.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.1.92
Published online: February 29, 2008
1Professor, Division of Nursing Science, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
2Postdoctoral Researcher, School of Nursing, University of Texas at Austin, USA.
- Address reprint requests to: Lee, Seung-Hee. School of Nursing, University of Texas at Austin, 1700 Red river st., Austin, TX78701, USA. Tel: 1-512-299-4475, Fax: 1-512-471-5470, woaiyoung@naver.com
• Received: September 20, 2007 • Accepted: November 27, 2007
Copyright © 2008 Korean Society of Nursing Science
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The aim of this study was to estimate the prevalence of urinary incontinence among nursing home residents and to identify the factors associated with this condition.
-
Methods
- The data were collected from 618 subjects (146 males and 472 females; mean age 79.9±8.4 yr; range 65-102 yr) of 30 nursing homes in Seoul, Gyeonggi-do and Gangwon-do in this cross-sectional study. The data were analyzed by chi-square test, t-test, and multiple logistic regression by using the SPSS/PC ver 12.0 program.
-
Results
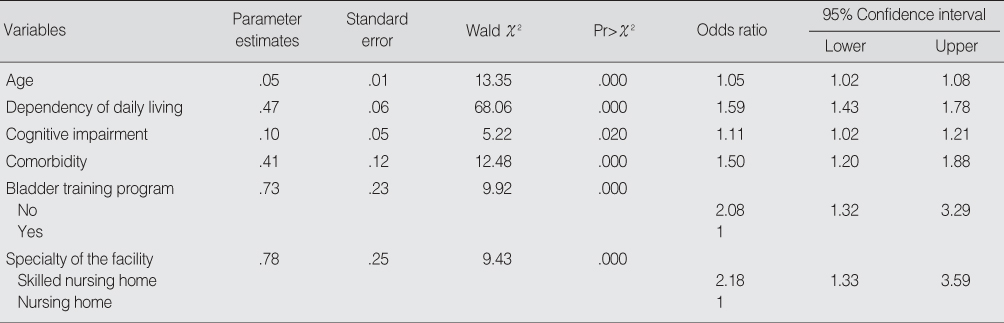
- The prevalence of UI was 64.7% (64.6% in women; 65.1% in men). After adjustment for each of the variables considered in this study, six potential factors were strongly associated with UI: activities of daily living, comorbidity, age, cognition, specialty of the facility, and a bladder training program.
-
Conclusion
- Our finding suggests that it is necessary to develop a program for promotion of activities of daily living and to provide a bladder training program to prevent urinary incontinence among nursing home residents.
- 1. Carpenter GI. Accuracy, validity and reliability in assessment and in evaluation of services for older people: the role of the inter RAI MDS assessment system. Age Ageing. 2006;35:327–329.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Coppola L, Caserta F, Grassia A, Mastrolorenzo L, Altrui L, Tondi G, et al. Urinary incontinence in the elderly: Relation to cognitive and motor function. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2002;35(1):27–34.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Durrant J, Snape J. Urinary incontinence in nursing homes for older people. Age Ageing. 2003;32(1):12–18.Article
- 4. Klein P, Haab F. Influence of the severity of stress urinary incontinence on quality of life, health care seeking, and treatment: A national cross-sectional survey. Eur Urol. 2006;50:818–825.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Hawes C, Morris JN, Phillips CD, Mor V, Fries BE, Nonemaker S. Reliability estimates for the minimum data set for nursing home resident assessment and care screening (MDS). Gerontologist. 1995;35:172–178.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Holroyd-Leduc JM, Mehta KM, Covinsky KE. Urinary incontinence and its association with death, nursing home admission, and functional decline. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52:712–718.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Holtedahl K, Hunskaar S. Prevalence, 1-year incidence and factors associated with urinary incontinence: a population based study of women 50-74 years of age in primary care. Maturitas. 1998;28:205–211.ArticlePubMed
- 8. International Continence Society. First reports on the standardization of terminology of lower urinary tract function. Br J Urol. 1976;48:39–42.PubMed
- 9. Jennifer TA, Christopher SS, Jennifer P, Larissa VR, Mark SL. True prevalence of urinary incontinence among female nursing home residents. Urology. 2006;67:281–287.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Joo YH, Kim JS. A study on urinary incontinence of elderly communities. J Korean Comm Nurs. 2000;11:441–452.
- 11. Jumadilova Z, Zyczynski T, Paul B, Narayanan S. Urinary incontinence in nursing home: resident characteristics and prevalence of drug treatment. Am J Manag Care. 2005;11(4 Suppl):S112–S120.PubMed
- 12. Kim JI. Prevalence of urinary incontinence and other urologic symptoms in a community residing elderly people. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2002;32(1):28–39.ArticlePDF
- 13. Kim JS. Prevalence of urinary incontinence among aged home residents. 1999;Pusan, Pusan national university. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 14. Kikuchi A, Niu K, Ikeda Y, Hozawa A, Nakagawa H, Guo H, et al. Association between physical activity and urinary incontinence in a community-based elderly population aged 70 years and over. Eur Urol. 2007;52:868–875.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Population movement estimation. Korea National Statistical Office. 2006;09;archived at http://www.nso.go.kr/nso2006/k01___0000/k01c__0000/k01ca_0000/k01caa0000/k01caa0000.html?method=view&board_id=4&seq=5&num=5&parent_num=0&page=1.
- 16. Landi F, Cesari M, Russo A, Onder G, Lattanzio F, Bernabei R, et al. Potentially reversible risk factors and urinary incontinence in frail older people living in community. Age Ageing. 2003;32:194–199.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Miles TP, Palmer RF, Espino DV, Mouton CP, Lichtenstein MJ, Markides KS. New-onset incontinence and makers of frailty: Data from hispanic established populations for epidemiologic studies of the elderly. J Gerontol. 2001;56A(1):19–24.
- 18. Park OH, Kwon IS, Kang YS. A study on urinary incontinence of elderly women in a community. Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2001;7:536–546.ArticlePDF
- 19. Park SC, Koh MW, Lee TH, Youn HS. The prevalence of urinary incontinence of the women in Daegu. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2004;21(1):60–66.Article
- 20. Resnick NM, Brandeis GH, Baumann MM, Morris JN. Evaluating a national assessment strategy for urinary incontinence in nursing home residents: Reliability of the minimum data set and validity of the resident assessment protocol. Neurourol Urodyn. 1996;15:583–598.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Richard LN, Sylvia EF. Risk factors for the development of fecal and urinary incontinence in Wisconsin nursing home residents. J Maturitas. 2005;52:26–31.Article
- 22. Raudenbush SW, Bryk AS. Hierarchial linear models. 2002;2nd ed.Thousands oaks, Sage Publications.
- 23. Ryu SA. Review on urinary incontinence of the cognitively impaired older adults. J Donshin Univ. 2006;16:547–561.
- 24. Saxer S, Halfens RJ, Müller M, Dassen T. Risk factors for urinary incontinence in nursing home residents. Swiss Med Wkly. 2005;135:495–502.PubMed
- 25. Schnelle JF, Alessi CA, Simmons SF, Al-Samarrai NR, Beck JC, Duslander JG. Translating clinical research into practice: a randomized controlled trial of exercise and incontinence care in nursing home residents. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50:1476–1483.PubMed
- 26. Schnelle JF, Cadogan MP, Yoshii J, Al-Samarrai NR, Osterweil D, Bates-Jensen BM, et al. The minimum data set urinary incontinence quality indicators: do they reflect difference in care processes related to incontinence? Med Care. 2003;41:909–922.PubMed
- 27. Thom DH, Haan MN, Van Den Eeden SK. Medically recognized urinary incontinence and risks of hospitalization, nursing home admission and mortality. Age Ageing. 1997;26:367–374.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Valk M, Moons KG, Cools HJ, Schrijvers AJ. Classifying the probability of urinary incontinence in psychogeriatric nursing home patients. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2002;34:79–91.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Wagner TH, Hu TW. Economic costs of urinary incontinence in 1995. Urology. 1998;51:355–361.Article
- 30. Watson N, Brink C, Zimmer J, Mayer R. Use of the agency for health care policy and research urinary incontinence guideline in nursing homes. J Am Gerictric Soc. 2003;51:1779–1786.Article
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Impact of pressure ulcer prevention knowledge and attitude on the care performance of long-term care facility care workers: a cross-sectional multicenter study
Sae-Beul Lee, Hyang-Yuol Lee
BMC Geriatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Meal-Monitoring Systems Using Weight and Temperature Sensors for Elder Residents in Long-Term Care Facilities
Yu Hu, Ji-Eun Joo, Eunju Choi, Leeho Yoo, Dukyoo Jung, Juh-Hyun Shin, Jeong-Ho Kim, Sung-Min Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(2): 808. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling on Quality of Life in Middle-Aged Women with Urinary Incontinence
Young Ran Yeom, Aekyung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(1): 43. CrossRef - Determinants of Urinary Incontinence and Subtypes Among the Elderly in Nursing Homes
Hongyan Tai, Shunying Liu, Haiqin Wang, Hongzhuan Tan
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms, Sexual Function, and the Quality of Life of Married Women with Urinary Incontinence
Seon Hwa Kim, Hye Young Kim
Journal of Comprehensive Nursing Research and Care.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Effects of a Self-management Program for Older Women With Urinary Incontinence in Rural Korea
Aeyoung So, Jennie C. De Gagne, Sunah Park
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2019; 46(1): 55. CrossRef - Effect of Pila-dance to Ease Urinary Incontinence of Middle-aged Women
Hye-Jeon Hong
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2018; 57(2): 431. CrossRef - Prevalence and management status of urologic diseases in geriatric hospitals in South Korea: A field research
Sang Heon Lee, Jungyo Suh, Hyung Suk Kim, Young Ju Lee, Sang Rim Lee, Khae Hawn Kim, Chang Wook Jeong
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2017; 58(1): 70. CrossRef - Urinary incontinence in women in relation to occupational status
Yoonjung Kim, Yeunhee Kwak
Women & Health.2017; 57(1): 1. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life and mental health in older women with urinary incontinence
YeunHee Kwak, HaeJin Kwon, YoonJung Kim
Aging & Mental Health.2016; 20(7): 719. CrossRef - The Prevalence of Urinary Tract Infections in Institutionalized vs. Noninstitutionalized Elderly Persons
Jung-Sik Huh
Urogenital Tract Infection.2016; 11(2): 56. CrossRef - The Effect of an Exercise Program for Preventing Urinary Incontinence among Community-Dwelling Elderly Females Living Alone
Mi Sook Song, Sunjoo Boo
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(2): 247. CrossRef - Effect of Muscle Strength Training on Urinary Incontinence and Physical Function: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Long-term Care Facilities
Hyekyung Kang, Gwi-Ryung Son Hong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(1): 35. CrossRef - The role of primary care of voiding dysfunction in rehabilitation and convalescent hospitals
Khae Hawn Kim
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2015; 58(6): 557. CrossRef - Knowledge, Attitudes, Beliefs, and Practices in Registered Nurses and Care Aids About Urinary Incontinence in Korean Nursing Homes
Sunah Park, Jennie C. De Gagne, Aeyoung So, Mary H. Palmer
Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing.2015; 42(2): 183. CrossRef - Nursing outcomes of inpatient on level of nursing staffing in long term care hospitals
Eun Hee Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2015; 26(3): 715. CrossRef - Activities of daily living and cognitive status: associations with urinary incontinence in Korea
Gwi‐Ryung Son Hong, Jeongok Park, Hye‐Kyung Kang, Mary H. Palmer
International Journal of Urological Nursing.2014; 8(3): 130. CrossRef - Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence, Single Voided Volume, Post Void Residual Volume, Daytime Frequency, and Nocturia in Women over 40 Years
Ok Boon Kim, Haesang Yoon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(6): 679. CrossRef - Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence, Single Voided Volume, Post Void Residual Volume, Daytime Frequency, and Nocturia in Women over 40 Years
Ok Boon Kim, Haesang Yoon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2013; 25(6): 679. CrossRef - Prevalence of urinary incontinence in older Korean women
Aeyoung So, Jennie C De Gagné, Mary H Palmer
International Journal of Urological Nursing.2012; 6(2): 51. CrossRef - Factors related to the Quality of Sleep in the Elderly Women
Young-Hee Kim, Jin-Sook Han
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2011; 12(10): 4467. CrossRef - The Relationship of Quality of Sleep, Depression, Late-Life Function and Disability (LLFDI) in Community-Dwelling Older Women with Urinary Incontinence
Kyung Rim Shin, Younhee Kang, Jiwon Oak
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(4): 573. CrossRef
Prevalence Rate and Associated Factors of Urinary Incontinence among Nursing Home Residents
Prevalence Rate and Associated Factors of Urinary Incontinence among Nursing Home Residents
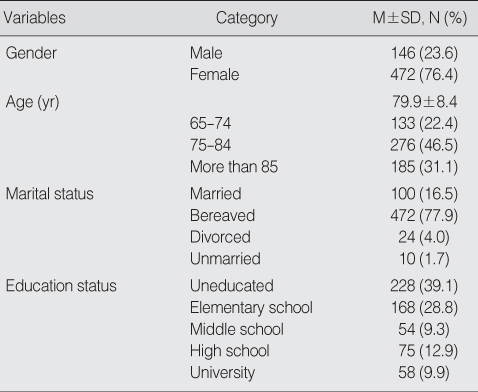
General Characteristics of Subjects (N=618)
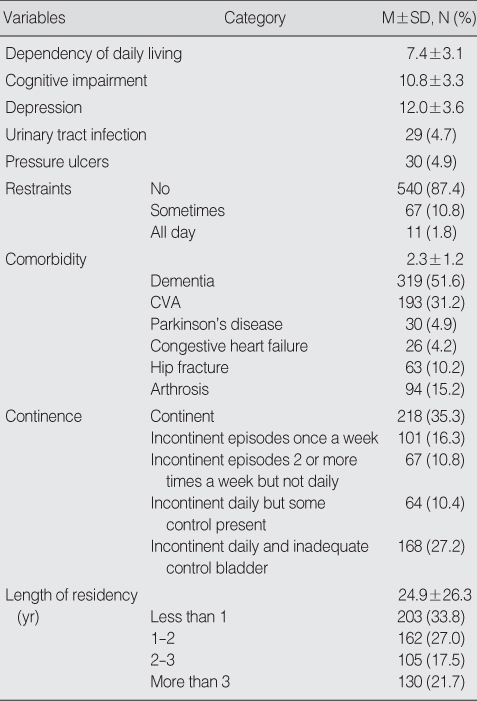
Characteristics related to Health of Subjects (N=618)
CVA=cerebral vascular accident.
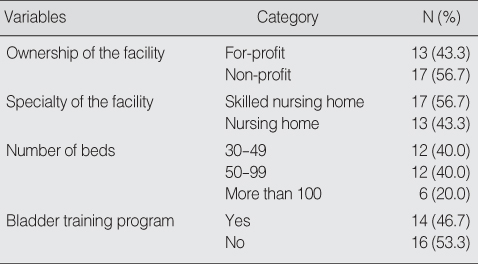
Characteristics of Nursing Home (N=30)
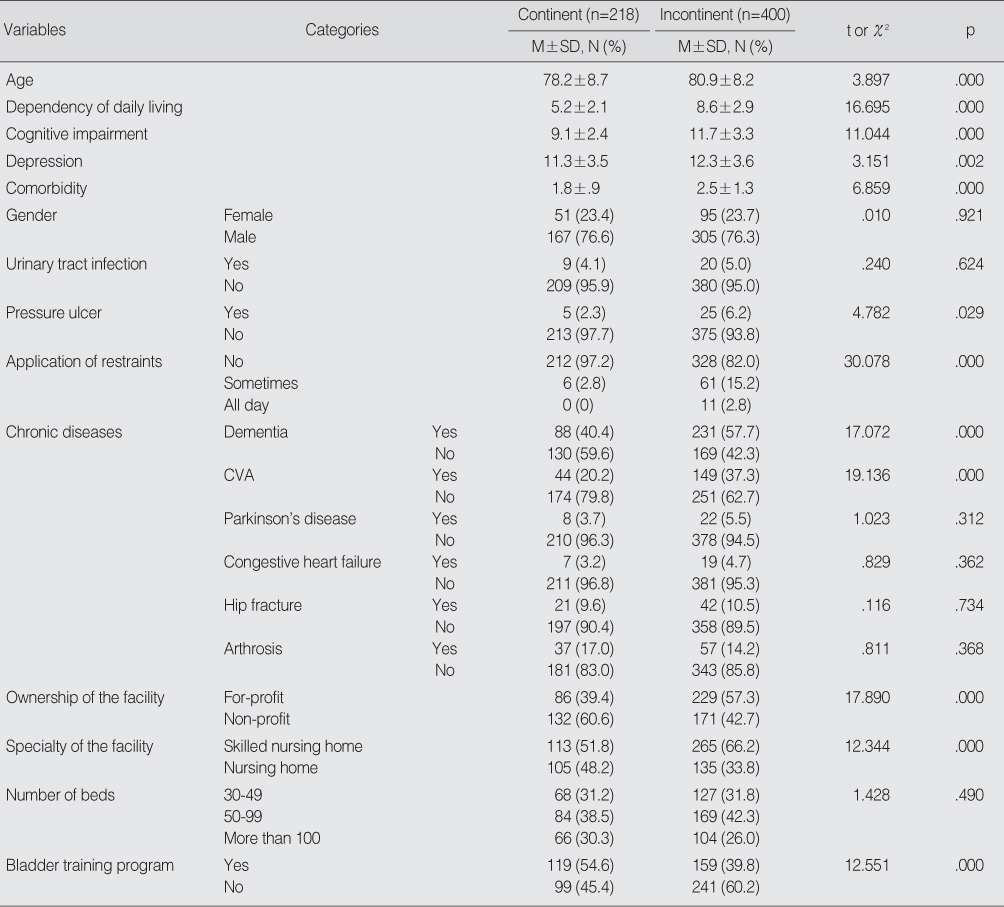
Comparison of Characteristics between Continent and Incontinent Subjects (N=618)
CVA=cerebral vascular accident.
Associated Factors of Urinary Incontinence (N=618)
Table 1
General Characteristics of Subjects (N=618)
Table 2
Characteristics related to Health of Subjects (N=618)
CVA=cerebral vascular accident.
Table 3
Characteristics of Nursing Home (N=30)
Table 4
Comparison of Characteristics between Continent and Incontinent Subjects (N=618)
CVA=cerebral vascular accident.
Table 5
Associated Factors of Urinary Incontinence (N=618)
 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 Cite
Cite

