Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effectiveness of a mobile application for tracking symptoms and enhancing symptom management among breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy in Bangkok, Thailand: a non-randomized controlled trial
- Duangrat Kaveenuntachai, Supawan Jaiboon, Bualuang Sumdaengrit, Chureeporn Silaguntsuti, Arveewan Vittayatigonnasak, Pornchan Sailamai
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):178-190. Published online May 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25011
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study evaluated the effectiveness of a mobile application in tracking symptoms and improving symptom management and quality of life (QoL) among breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in Thailand.
Methods
A non-randomized controlled trial was used, with 25 participants in the intervention group and 25 in the control group. Research instruments included a demographic data form, the NCI-PRO-CTCAE Items-Thai-Thailand version 1.0, and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Core Questionnaire and Breast Cancer-Specific Module.
Results
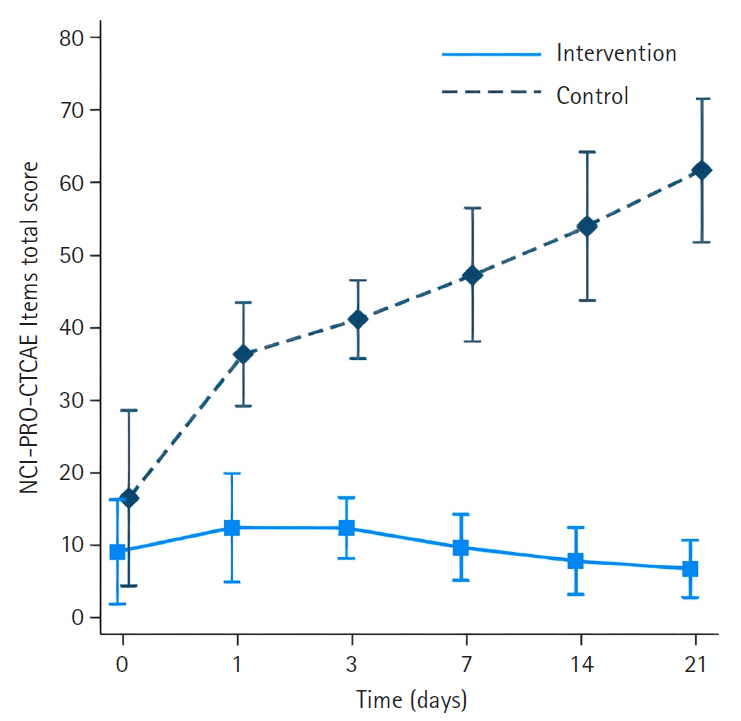
The intervention group had significantly less severe side effects than the control group, with mean differences of –23.33 (95% confidence interval [CI], –27.82 to –18.83) on day 1, –28.18 (95% CI, –33.22 to –23.14) on day 3, –34.63 (95% CI, –40.18 to –29.08) on day 7, –42.56 (95% CI, –48.72 to –36.40) on day 14, and –51.31 (95% CI, –58.13 to –44.48) on day 21 (p<.001 for all). On day 21, participants in the intervention group reported significantly higher scores in the Global Health QoL and Functional Scales compared to the control group (p<.001). Additionally, intervention group participants reported lower scores on the Symptom Scales and higher scores on the Functional Scales than those in the control group (p<.001).
Conclusion
The ChemoPro application helped manage chemotherapy-related symptoms and was associated with improved symptom monitoring and QoL. Nonetheless, the study was limited by a small sample size and restriction to Android users. Future research with larger and more diverse populations is recommended before broader implementation in clinical practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of a digital health intervention on the supportive care needs and quality of life in Mexican patients with breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial
Saúl Eduardo Contreras-Sánchez, Svetlana V. Doubova, Rocío Grajales-Álvarez, Ricardo Villalobos-Valencia, Abdel Karim Dip-Borunda, José Gustavo Nuñez-Cerrillo, Alma Diana Huerta-López, Álvaro José Montiel-Jarquín, Arturo García-Galicia, Enrique Isay Talam
BMC Cancer.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effectiveness of a digital health intervention on the supportive care needs and quality of life in Mexican patients with breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial
- 4,369 View
- 219 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Moderating Effect of Organizational Justice on the Relationship between Self-Efficacy and Nursing Performance in Clinical Nurses
- Ju-Ra Kim, Yukyung Ko, Youngjin Lee, Chun-Ja Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(5):511-521. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22076
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the moderating effect of organizational justice on the relationship between self-efficacy and nursing performance among clinical nurses.
Methods
In January 2021, a cross-sectional survey was conducted with 224 clinical nurses recruited from a university-affiliated hospital in Suwon, South Korea. Participants completed online-based, self-report structured questionnaires. Collected data were analyzed using multiple regression and a simple model of PROCESS macro with a 95% bias-corrected bootstrap confidence interval.
Results
Self-efficacy and organizational justice were found to be significant predictors of nursing performance. These two predictors explained the additional 34.8% variance of nursing performance in the hierarchical regression model, after adjusting the other covariates. In addition, organizational justice moderated the relationship between self-efficacy and nursing performance among the clinical nurses. In particular, at low self-efficacy level, participants with high organizational justice had higher nursing performance compared to those with low organizational justice.
Conclusion
Enhancing organizational justice can be used as an organizational strategy for improving the organizational culture in terms of distribution, procedure, and interaction. Ultimately, these efforts will contribute to the improvement of nursing performance through a synergistic effect on organizational justice beyond nurses’ individual competency and self-efficacy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Balancing efficiency and fairness in an output-based agency relationship: an empirical investigation of the cognitive factors favouring a win–win situation
Filippo Ferrari
Evidence-based HRM: a Global Forum for Empirical Scholarship.2025; 13(5): 866. CrossRef - Work-family balance mediates self-efficacy and subjective well-being among nurses in Chinese intensive care units: A cross-sectional study
Lating Zhang, Xianzhen Jin, Na Cheng, Ruhua Wang, Xinhui Liang, Haiyan Fan, Xue Jiang
Applied Nursing Research.2025; 82: 151932. CrossRef - Relationship between resilience and self-efficacy among Iranian nurses: a cross-sectional study during the post-Corona era
Saeed Ghasempour, Ali Abbasi, Mohammad Hasan Basirinezhad, Ali Dadgari, Hossein Ebrahimi
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Nurse Collaboration and Nurse-Physician Collaboration on Nursing Performance in Nurses: The Mediating Effect of Patient Safety Management Activities
JaHyun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Sunmi Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 343. CrossRef - The Impact of Self-Efficacy on Nurses’ Well-Being: Does Digital Competence Matter?
Yali Li, Qi Jing, Taiwen Feng, Xiaoling Yang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(4): 385. CrossRef
- Balancing efficiency and fairness in an output-based agency relationship: an empirical investigation of the cognitive factors favouring a win–win situation
- 2,356 View
- 117 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref

- The Second Study on the Effectiveness of Nursing Organization
- Young Joo Park, Sook Ja Lee, Sung Ok Chang
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(2):253-263. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.2.253
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This second study on the effectiveness of nursing organization was designed to test the relationships between effectiveness of nursing organizations and structural variables that had been significant variables in the first study, the group design variable and the personal characteristic variables that had not been analysed in the first study based on personal resource productivity model. The data were collected through self-reported questionnaires completed by 605 nurses working in hospitals in seoul and 782 patients being hospitalized in 5 tertiary hospitals in Seoul. The results showed that according to the canonical correlation analysis, the managing job design, nursing delivery system. nurse's age career, and formalization were revealed as predicting variables of a nurses' job satisfaction and patients satisfaction among the five hospitals. Hospitals in which the team nursing method was used showed a higher score in nurses' job satisfaction and patient satisfaction than in hospitals which used the functional nursing model.
- 516 View
- 6 Download

- The Effectiveness of Nursing Organization(I)
- Young Joo Park, Sook Ja Lee, Jin Kyu Lee, Sung Ok Jang
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(1):189-200. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.1.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was designed to test relationship between effectiveness of nursing organizations and structural and managerial variables of nursing organizations that are described in the Robbins Organizational theory model. The data were collected through self reported questionnaires from 605 nurses working in, and 782 patients hospitalized in, five tertiary hospitals in seoul. Results showed that according to MANOVA there was a significant difference in nurses job satisfaction and patient satisfaction among the five hospitals. According to cluster analysis of the structural and managerial variables of nursing organizations, the five hospitals were divided into two clusters and there was no significant difference in nurses job satisfaction or patient satisfaction between the two clusters. According to canonical correlation analysis the formalization and centralization of structural variables were shown to be predicting variables for nurses job satisfaction, and the managing job design and managing change of managerial variables were shown to be predicting variables for nurses job satisfaction.
- 436 View
- 1 Download

- A Study of Teaching Effectiveness on Clinical Nursing Education
- Mi Ae Kim
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1996;26(4):946-962. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1996.26.4.946
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study was to contribute to the development of clinical instruction by students' ratings of teaching effectiveness in clinical nursing education. The subjects were comprised of graduating class 618 students from 24 nursing colleges in the nation. The instruments used in this study were "general characteristics and status of clinical nursing education" developed by the researcher and "Instrument to Measure Effectiveness of Clinical Instructors " by Reeve (1994). The 50 questions used in the questionaire were categorized into 13 components subject to factor analysis. The 13 components were interpersonal relationships, communication skills, role model, resource for students, favorable to students, encouraging to think for selves, teaching methods, evaluation, finding assignments for objectives, organization of subject matter, professional competence, knowledge of subject matter and working with agency personnel. The results of this study are as follows 1. Status of clinical nursing educaion: 1) Clinical nursing education were led by nursing professors(44.9%), a team of both nuring professor and head nurse(6.8%), instructors from specific hospital(15.1%), instuctos for a specific subject(14.6%), and head nurse (6.8%). For 3-year program students, 34.6% of the clinical nursing education were led by instructors from specific hospital and 51.4% of the education by nursing professors for Bachelor's program. 2) The contents for clinical education comprised of Conference being the most frequent of 34.5%; a combination of Nursing skills, Orientation, Conference etc. 22.0%; Nursing process 21.7%; Orientation 13.5%; Inspection (making rounds) 6.4%, and Nursing skills of 2% being the least frequent. 3) Students' preference of clinical teachers from the highest to the lowest were instructors for a specific subject being the most desired(44.9%) followed by nursing professor, head nurse, a team of both nursing professor and head nurse, and instructors from specific hospital being the least desired. 4) Students felt that the qualification for clinical teachers should be at least a master's degree holder and 5 or more years of clinical experience. The reason they felt was because knowledge and experience are imperative for professional education. 2. Clinical teaching effectiveness: The total points for teaching effectiveness was 147.97(mean of 2.95 +/- 0.98) where the total score is considered to be an average rating. 3. Teaching effectiveness as status of clinical nursing education: 1) The score ratings for the clinical instructors from the highest to the lowest were as follows; instructors for a specific subject, instructors from specific hospitals, a team of both nursing professors and head nurses, nursing professors, head nurses, which resulted in significunt differ-ence(F=4.53, P<0.001). 2) The rating scores based on the teaching program from the highest to the lowest were as follws; nursing skills, nursing process, a combination of nursing skills, orientation, conference etc., conferences, orientation, inspection, which resulted in significunt difference(F-10.97, P<0.001). 4. Based on 13 categorized components from the questionaires, questions related to communication skills scored the highest points of 3.20 where inquiries regarding resource for students scored the lowest points of 2.38. 5. Among the 13 categorial components from the questionaire, Interpersonal relationship, Communication skills, Resource for students, Encouraging to think for selves, Evaluation, Teaching method, Finding assignment for objectives, Organization of subject matter, Professional competence, and Working with agency personnel, instructors for a specific subject scored the highest points and head nurse scored the lowest, which resulted in significant diference. Favorable for students, instructors for a specific subject scored highest points and nursing professor scored the lowest, which resulted in significant deference (F=5.39, P<0.001). Role model and Professional competence, instructors for a specific subject scored the highest points and head nurse scored the lowest, with minimum variation(F-1.29, p>0.05:F=1.64,P>0.05). 6. Based on 13 categorial components as a whole, the highest points scored among the 5 groups of clinical teachers was instructors for a specific subject and the lowest, by head nurse(F=1.94, P<0. 001). A team of both nursing professor and head nurse attained higher score in clinical education than their independent education.
- 496 View
- 5 Download

- Methodological Issues in Nursing Research on Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
- Taewha Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(7):1202-1209. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.7.1202
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Cost effectiveness is a recent and newly emerging approach in nursing evaluation studies. Nursing is in a unique position among health care providers to respond to these efforts and is ready to provide evidence of its cost-effectiveness because nurses has long advocated a holistic view of patient care, that means, nurses are unique position to identify the full range of costs and effects. The cumulative evidence showed that nurses provided cost-effective care that substituted for physician services in many situations and new and important services in long-term care and nursing homes. The purpose of this article is to review, critique, and synthesize research on the cost-effectiveness of nursing care from the research methodology perspective. Two major problems are apparent from this review. First, there is no uniform approach to identifying and valuing resources used in producing nursing intervention options. Second, although it is not difficult to find reports of cost savings, the cost to effect ratio was not used to evaluate the relationship between the cost and effects of alternative options. Based on my analysis, the nursing CEA literature seemed to have huge variation in methods, so that it is not easy to compare the CEA methods among studies. There are still such methodological problems as we found in the literature review. Many of the studies reviewed here would have profited from improved designs. Therefore, future cost-effectiveness analyses should include methodological progress in the context of nursing area application such as the definition and quantification of multi-attribute effectiveness measures, employment of sensitivity analysis, a concept of discount. Nurse and nurse researchers should consider cost-effectiveness questions when addressing other research questions. Because these efforts are forcing policy makers to consider the economics of nursing, nurses should demonstrate and document the value of nursing as compared to other uses of society's health care resources.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Economic Evaluation of Enhancing Nurse Educational Level on In-Hospital Mortality: Cost per Prevented Death Analysis
Rasmus Emil Sørensen, Mads Christian Holst
Journal of Medical Sciences and Interdisciplinary Research.2025; 5(1): 108. CrossRef - Cost-effectiveness Analysis of Home Care Services for Patients with Diabetic Foot
Chong Rye Song, Yong Soon Kim, Jin Hyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2013; 19(4): 437. CrossRef
- Economic Evaluation of Enhancing Nurse Educational Level on In-Hospital Mortality: Cost per Prevented Death Analysis
- 777 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Effect of Education for Prevention of Osteoporosis Patients with Bone Fracture
- Hyang Yeon Lee, Sook Young Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2001;31(2):194-205. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2001.31.2.194
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of the study was to identify the effect of structured patients education had on prevention of osteoporosis, with fracture and the resulting of life style changes in patients. In this study, a non equivalent control group pre and a post test design was employed. Data were collected through an interview process using questionnaires from April to December of 1999. The subjects, consisting of 59 patients with fractures and over 40 years of age, were diagnosed in K University Hospital. This study tested the patients knowledge at three times. The times were before the program 2 weeks into the program, and 6 months after education program. Life style change related to prevention of osteoporosis was shown twice (before and 6 months after the education program) in the experimental group, and control group went without it. The instruments used for this study were developed by literature review according to a reliability test. Data was analyzed using X2 test and t test to determine similarities between the experimental and control groups. The hypothesis was tested using repeated measures of ANOVA, t-test and Pearson correlation coefficients. The results of the study were summarized as follows: 1. The first hypothesis was accepted: a higher level of knowledge about osteoporosis was found in experimental groups who received education than to the control group during the period (F=19.82, p=.0001). 2. The second hypothesis was accepted: a higher level of life style changes about osteoporosis on experimental group were recorded than as compared to control group (t=3.55, p=.001). 3. The third hypothesis was accepted: the higher the knowledge about osteoporosis the higher the level of performance of life style changes about prevention of osteoporosis (r=.600, p=.0001). In conclusion, structured patient education in patient with fractures improved the level of knowledge about osteoporosis and more likely undergo of life style changes 6 months after the education program. Also reeducation would be needed 6 months after program ends. That is structured patient education in pamphlet form would be very effective in nursing intervention that may to result in life style changes. Therefore further research is needed to reinforce the education material and to generalize the education effect.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of a Group Educational Intervention on the Prevention of Osteoporosis in Breast Cancer Patients
Bong Hae Ma, Chai-Soon Park, Hee Chong Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2015; 26(4): 398. CrossRef - Gender Difference in Osteoporosis Prevalence, Awareness and Treatment: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008~2011
Yunmi Kim, Jung Hwan Kim, Dong Sook Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(2): 293. CrossRef - Study of the Level of Osteoporosis Awareness among Women Dwelling in Urban Area
Miyoung Chung, Kyunghye Hwang, Euysoon Choi
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2009; 15(4): 362. CrossRef - Decreased Bone Mineral Density and Fractures in Low-Income Korean Women
Kyunghee Yang, Beverly J. McElmurry, Chang G. Park
Health Care for Women International.2006; 27(3): 254. CrossRef
- The Effects of a Group Educational Intervention on the Prevention of Osteoporosis in Breast Cancer Patients
- 846 View
- 6 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Major Effect Models of Social Support and Its Statistical Methods in Korean Nursing Research
- Eun Hyun Lee, Jin Sun Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(6):1503-1520. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.6.1503
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of the present study is 1) to explain major effect models (main, moderating, and mediating) of social support and statistical methods for testing the effect models and 2) to analyze and evaluate the consistency in the use of the effect models and its statistical methods in Korean nursing studies. A total of 57 studies were selected from Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing, Journal of Korean Academic Society of Adult Nursing, Journal of Korean Women's Health Nursing Academic Society, Journal of Fundamentals of Nursing, Journal of Korean Community Nursing, Journal of Korean Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing Academic Society, and Journal of Korean Pediatric Nursing Academic Society published in the year of 1990-1999. In results, most studies on social support performed in Korea Nursing Society were about a main effect model. There are few studies on moderating or mediating model of social support. Thus, it was difficult to find research findings how, why, under what conditions social support impacted on health outcomes. Most studies on the moderating or mediating effect model of social support used statistical methods for testing main effect model rather than for testing moderating or mediating effect model. That is, there are inconsistency between effect models of social support and its statistical methods in Korean nursing researches. Therefore, it is recommended to perform studies on moderating or mediating effect model and use appropriate statistical methods.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Social support for nursing students: A concept analysis study
Mi-Young Choi, Sunghee Park, Gie Ok Noh
Nurse Education Today.2024; 132: 106038. CrossRef - Measurement Properties of Self-report Questionnaires Published in Korean Nursing Journals
Eun-Hyun Lee, Chun-Ja Kim, Eun Jung Kim, Hyun-Ju Chae, Soo-Yeon Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(1): 50. CrossRef - A Structural Model of Caring Behavior of Mothers of Disabled Children
Ae-Ran Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 673. CrossRef
- Social support for nursing students: A concept analysis study
- 736 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Mediation Effect of Hope between Fatigue and Psychosoical Adjustment in Women with Breast Cancer
- Eun Hyun Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(4):857-868. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.4.857
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of the present study is to identify the mediation effect of hope between fatigue and psychosocial adjustment in women with breast cancer. The framework for this study was guided by concepts and propositions derived from the theoretical and empirical literature on fatigue, hope and adjustment. The design of this study is a descriptive correlation study using a cross-sectional design. One hundred and twenty two outpatients with early breast cancer, receiving post-surgical radiation therapy or chemotherapy, were selected from three major medical centers in Seoul, Korea. A packet including PABCF (Psychosoical Adjustment to Breast Cancer Factor), revised RPFS (Revised Piper Fatigue Scale), HHI (Herth Hope Index), and self-addressed return envelope was given to the participants at seven to eight weeks post surgery. The questionnaires were to be completed at home and returned to the researcher by mail. The obtained data were analyzed using three regression equations guided by Baron and Kenny (1986); first, hope was regressed on fatigue; second, psychosocial adjustment was regressed on fatigue; and third, psychosocial adjustment was regressed on fatigue and hope, simultaneously. In the first equation, fatigue explained 4% of the variance in hope. In the second equation, fatigue explained 47% of the variance in psychosocial adjustment. In the last equation, hope and fatigue significantly explained the variance in psychosocial adjustment. Therefore, all conditions for the test of mediation effect of hope were satisfied. For the test of the mediation effect, the beta coefficients of fatigue on psychosocial adjustment on the second and third regression equations were compared. The beta coefficients were decreased from .69 (p < .001) on the second regression equation to .63 (p < .001) on the third regression equation. Thus, the hypothesis of this study was supported. As a result of this study, the negative Influence of fatigue on psychosocial adjustment is dampened through the mediator effect of hope in women with breast cancer. Therefore, when planning care for the adverse effect of fatigue on psychosocial adjustment, oncology nurses should consider hope as a mediator between fatigue and psychosocial adjustment to breast cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship of Spiritual Well-being, Hope on Fatigue in Cancer Patients on Chemotherapy
So Yeun Jun, Il Sun Ko
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(6): 557. CrossRef
- Relationship of Spiritual Well-being, Hope on Fatigue in Cancer Patients on Chemotherapy
- 665 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effects of a Rehabilitation Program on Physical Health, Physiological Indicator and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Mastectomy Patients
- Hyoung Sook Park, Gyoo Yeong Cho, Kyung Yeon Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(2):310-320. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.2.310
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of a rehabilitation program on physical health, physiological indicators and quality of life in breast cancer mastectomy patients.
Methods The subjects included thirty-one patients with breast cancer (17 in the experimental group and 14 in the control group). The subjects in the experimental group participated in a rehabilitation program for 10 weeks, which was composed of an exercise program, teaching, counseling and support for 2 sessions per week.
Results There was a significant increase in flexion, internal rotation and external rotation but no significant increase in extension in the experimental group compared to the control group. The total cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL, LDL, and CD56 in the experimental group compared to the control group was not significantly decreased after the rehabilitation program. Compared to the control group, quality of life in the experimental group was significantly improved and fatigue in that group was significantly decreased after the rehabilitation program.
Conclusion The 10-week rehabilitation program showed a large affirmative effect on physical health, physiological indicators and quality of life in breast cancer mastectomy patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding the Influence of Window Views, Plantscapes, and Green Décor in Virtual Reality Hospital Rooms on Simulated Acute-Care Patients’ Stress Recovery and Relaxation Responses
Courtney Suess, Jay Maddock
HERD: Health Environments Research & Design Journal.2025; 18(3): 165. CrossRef - The Role of Rehabilitation Nurses in Empowering Mastectomised Women for Self-Care: A Scoping Review
Madalena Rodrigues, Inês Deus, Pedro Bengalinha, Raquel Duro, David Carpinteiro, Rogério Ferreira, Celso Silva, César Fonseca
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2025; 22(6): 957. CrossRef - Relationships Among Self-Efficacy, Social Support, and Community Participation in Breast Cancer Survivors
Hye-Mi Kim, Gyeong-A Park, Jin-Ju Park, Myung-Hwa Oh
Journal of Korean Society of Occupational Therapy.2019; 27(4): 69. CrossRef - The effectiveness of a rehabilitation programme for Chinese cancer survivors: A pilot study
Hui Zhang, Yuqiu Zhou, Yuxia Cui, Jinwei Yang
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2016; 22(1): 79. CrossRef - The Effect of home education convergence program on arm functions, occupational performance, quality of life, and depression in mastectomy patients with arm function impairment
Ko-Un Kim, Hye-Won Oh
Journal of Digital Convergence.2016; 14(9): 515. CrossRef - The Effects of Sensory Motor Training Using Ball Exercise on Shoulder Functions and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Women After Mastectomy
Ji-Yoon Seo, Jong-Duk Choi
Journal of the Korean Society of Physical Medicine.2016; 11(4): 147. CrossRef - An Analysis of Cancer Survival Narratives Using Computerized Text Analysis Program
Dal Sook Kim, Ah Hyun Park, Nam Jun Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(3): 328. CrossRef - An exploratory study on clothing benefits sought by breast cancer survivors
YoungJu Rhee, EunOk Lee
The Research Journal of the Costume Culture.2014; 22(5): 823. CrossRef - Effects of a Home-based Exercise Program for Patients with Stomach Cancer Receiving Oral Chemotherapy after Surgery
Jin Yi Choi, Hyun Sook Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(1): 95. CrossRef - Effects of Laughter Therapy on Depression, Quality of Life, Resilience and Immune Responses in Breast Cancer Survivors
Eun A Cho, Hyun Ei Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(3): 285. CrossRef - Effects of a Nurse-Led Cognitive-Behavior Therapy on Fatigue and Quality of Life of Patients With Breast Cancer Undergoing Radiotherapy
Haejung Lee, Yeonjung Lim, Myung-Sook Yoo, Yongsuk Kim
Cancer Nursing.2011; 34(6): E22. CrossRef
- Understanding the Influence of Window Views, Plantscapes, and Green Décor in Virtual Reality Hospital Rooms on Simulated Acute-Care Patients’ Stress Recovery and Relaxation Responses
- 851 View
- 5 Download
- 11 Crossref

- The Effect of Web-based Multimedia Contents for a Course of Physical Examination and Health Assessment
- Pok Ja Oh, Il Ok Kim, Sung Rae Shin, Hoe Kyung Jung
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2005;35(5):810-816. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2005.35.5.810
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to test the effectiveness of Web-based multimedia contents for Physical Examination and Health Assessment on learning achievement.
Method Multimedia contents based on Jung's teaching and learning structure model were used to enhance learning achievement. Learning achievement was measured by the knowledge of Physical Examination and Health Assessment. The participants of this study were students in a BSN and RN-BSN program in a university located in Seoul. 59 students in the experimental group received lectures using web-based multimedia contents and 75 students in the control group received regular lectures.
Results The mean score of the degree of educational achievement in the experimental group(mean=31.09) was significantly higher than in the control group(mean=25.55)(t=-3.883, p=.000).
Conclusion These web-based multimedia contents were found to maximizethe effectiveness of the teaching process when used as a teaching aid, and yet kept the strength of a face to face teaching learning method. This program is recommended as part of a main text, vital teaching aid or cyber lecture materials in nursing schools and in health care educational institutions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of the Flipped Learning on Self-efficacy, Critical Thinking Disposition, and Communication Competence of Nursing Students
Young-Sil Lee, Young Eun
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2016; 22(4): 567. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Web-based Education Program for Nursing Students on Control of Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus Infection
Ju Gong, Ji-Yeon Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(1): 122. CrossRef - Effect of a Web-enhanced Clinical Practicum on Learning Outcome of Adult Nursing Practicum in Nursing Students
Seon-Young Hwang, Hee-Young Kang, Ja-Yun Choi, Hyang-Sook So
International Journal of Contents.2012; 8(2): 36. CrossRef - Effectiveness of web based learning program on self efficacy, knowledge, and competence in measurement of blood pressure
Sook-Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(1): 66. CrossRef - Development of a Web-based Senescence Preparation Education Program for Successful Aging for Middle-aged Adults
Young-Mi Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(6): 831. CrossRef
- The Effect of the Flipped Learning on Self-efficacy, Critical Thinking Disposition, and Communication Competence of Nursing Students
- 733 View
- 0 Download
- 5 Crossref

- A Meta-analysis of the Effects of Smoking Prevention Programs in Korea
- Eun Ok Park
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(6):1004-1013. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.6.1004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this paper was to describe the characteristics of smoking prevention programs in Korea, to estimate overall effect size of Korean smoking prevention programs, and to investigate effect size variations by program modality and instruction method.
Method Meta-analysis was performed on21 programs in 20 studies.
Result The estimation of overall effect size for knowledge and attitude was not possible because effect sizes were not homogeneous in this meta-analysis. However, effect sizes of studies that were socially influential programs or active/interactive methods were larger than information-oriented programs or passive/non-interactive methods in the pictures. The effects for behavioral outcomes were generally not as positive and not statistically significant. Q statistics showed that variations among effect sizes within program modality and instruction method classifications were heterogeneous.
Conclusion The results from this meta-analysis support the continued use of socially influential programs and active/interactive methods for smoking prevention programs. Because behavioral effect might be the fundamental objective of smoking prevention programs, the present results indicate that smoking prevention programs should consider adopting more effective programs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of a Staged Smoking Prevention Program for Primary School Children
Jae-Hee Kim, Yu-Jeong Lee, Seong-Mi Kang, Yu-Mi Oh
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(8): 5131. CrossRef - Influence of Depression, Anxiety and Stress-Coping Aspect upon Smoking Desire of Undergraduates, according to Their Lifestyles
Sung-Sik Ahn, Chun-Sook Kim, Sung-Hwan Choi
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2012; 6(1): 205. CrossRef - A Meta-Analysis on the Effectiveness of Computer-Based Education in Nursing
Kook Hee Roh, Hyeoun-Ae Park
Healthcare Informatics Research.2010; 16(3): 149. CrossRef - Meta-Analysis of Effects on Adolescent Smoking Cessation Programs in Korea
Younkyoung Kim, Inhyae Park, Jeong-Soo Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2008; 38(2): 204. CrossRef
- The Effects of a Staged Smoking Prevention Program for Primary School Children
- 736 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Crossref

- The Relationships of Treatment Side Effects, Family Support, and Quality of Life in Patient with Cancer
- Hea Kung Hur, Dae Ran Kim, Dae Hwa Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(1):71-78. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.1.71
-
 Abstract
Abstract
Purpose The study was done to identify the relationship of treatment side effects, family support, and quality of life in patients with cancer, and factors influencing quality of life.
Method A convenience sample of 106 patients who were receiving cancer treatment at W hospital were interviewed using the Side Effects scale by Hur, Family Support scale by Kang, and QOL scale by Ro.
Result Results indicate that women experienced more severe side effects than men. There was a negative relationship between side effects and quality of life, and a positive relationship between family support and quality of life. The most bothersome side effects were changes in taste and appetite, followed by general weakness and fatigue. Side effects such as loss of hair, nausea, dizziness, numbness, pins and needles in fingers and toes, and dry mouth were also experienced. General weakness and family support were analysed as to whether they were factors influencing quality of life.
Conclusion The results revealed that relieving general weakness should be given high priority in nursing interventions for patients undergoing cancer treatment. In addition, nursing programs should be developed that can reinforce family support.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prediction Model for Health-related Quality of Life in Coronary Artery Disease Patients According to Stress Level
Minju Kim, Ju Youn Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(3): 320. CrossRef - The Effects of Chemotherapy Education Reflecting Educational Needs on Self-Care Knowledge and Performance in Female Cancer Patients: A Non-Equivalent Control Group Pretest-Posttest Design
Jin Hee Jun, Se-Na Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(3): 103. CrossRef - Identification of Korean cancer survivors’ unmet needs and desired psychosocial assistance: A focus group study
Joo Young Kim, Mison Chun, Sang-Won Kim, Joonsup Song, Rosemary Frey
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(1): e0228054. CrossRef - Factors affecting the Fatigue of Hospitalized Women Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy
Kyunghee Kim, MyoSuk Lee, Yeunhee Kwak, Ji-Su Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(3): 182. CrossRef - Stories of Suffering with Leprosy and Cancer in Korea
Steven L. Baumann, Ok Ja Lee, Sook-Bin Im
Nursing Science Quarterly.2013; 26(3): 274. CrossRef - Psychosocial Adjustment of Low-Income Koreans with Cancer
Myungsun Yi, Eun Young Park, Dal Sook Kim, Young Sook Tae, Bok Yae Chung, Hyang Sook So
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(2): 225. CrossRef - The Influencing Factors on Quality of Life among Breast Cancer Survivors
Yoon Sun Kim, Young Sook Tae
Journal of Korean Oncology Nursing.2011; 11(3): 221. CrossRef - A Study on the Relationship among Family Support, Stress and Quality of Life on according to the Phases of Illness in Breast Cancer Patients
Sang Sun Cheon, So Young Choi
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(1): 10. CrossRef - Fatigue and Quality of Life of Korean Cancer Inpatients
Hye Sun Byun, Gyung Duck Kim, Bok Yae Chung, Kyung Hye Kim
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2010; 13(2): 98. CrossRef - Relationships between Side Effects, Depression and Quality of Sleep in Gynecological Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Young-Hwa Kim, Ji-Hyun Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2010; 16(3): 276. CrossRef
- Prediction Model for Health-related Quality of Life in Coronary Artery Disease Patients According to Stress Level
- 868 View
- 0 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Effects of Breastfeeding Empowerment Program on Breastfeeding Self-efficacy, Adaptation and Continuation in Primiparous Women
- Seon Mi Song, Mi Kyung Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(3):409-419. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.409
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a breastfeeding empowerment program and to investigate the effects of the breastfeeding empowerment program on self-efficacy, adaptation and continuation of breastfeeding for primiparous women.
Methods The 5 session breastfeeding empowerment program was developed and a non-equivalent control group non-synchronized quasi-experiment design was used. Fifty-five participants were assigned to either the experimental group (n=27) or the control group (n=28). Effects were tested using repeated measures ANOVA and χ2-test.
Results Scores for self-efficacy, adaptation and continuation of breastfeeding of in the experimental group after program were significantly higher than 1week, 4weeks, 8weeks scores in control group.
Conclusion The effects of the breastfeeding empowerment program for elevating self-efficacy, adaptation and continuation of breastfeeding in primiparous women were validated. Therefore, this program can be recommended for vigorous use in clinical practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of the effectiveness of video and breastfeeding simulator support to mothers who could not breastfeed their babies in the neonatal intensive care unit: a randomized controlled study
Hatice Tetik Metin, Feride Yiğit
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness Evaluation of Comprehensive Mobile-Based, Breastfeeding Promotion Program for Mothers with Gestational Diabetes
Eunju Kwak, Seungmi Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(2): 224. CrossRef - The effectiveness of prenatal breastfeeding education on breastfeeding uptake postpartum: A systematic review
Jennifer Kehinde, Claire O'Donnell, Annmarie Grealish
Midwifery.2023; 118: 103579. CrossRef - Effectiveness of distance education program on mothers’ empowerment in exclusive breastfeeding
Zeynab Taheri, Fatemeh Bakouei, Mouloud Agajani Delavar, Mahbobeh Faramarzi, Afsaneh Bakhtiari, Fatemeh Nasiri Amiri
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2022; 11(1): 420. CrossRef - Social policies and breastfeeding duration in South Korea: A survival analysis of the national data
Jung Hee Yeo, Eun-Young Kim
Midwifery.2022; 107: 103282. CrossRef - A Structural Model for Breastfeeding Behavior of First-Time Mothers
Seol Hui Park, Seang Ryu
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2021; 25(3): 184. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of the Parenting Support Group Program for Mothers with Infants
Sun Hwa Park, Kyung Ja June
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(1): 40. CrossRef - Breastfeeding Adaptation Scale-Short Form for mothers at 2 weeks postpartum: construct validity, reliability, and measurement invariance
Sun-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(4): 326. CrossRef - Knowledge of and Attitude toward Breastfeeding among Medical Staff Working in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit and Obstetric Unit
Eun Sook Kim, Young Hee Cho, Hyejung Lee
Journal of The Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health.2020; 24(2): 102. CrossRef - Knowledge and health beliefs about gestational diabetes and healthy pregnancy's breastfeeding intention
Seungmi Park, Jung Lim Lee, Jang In Sun, Youngji Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2018; 27(21-22): 4058. CrossRef
- Comparison of the effectiveness of video and breastfeeding simulator support to mothers who could not breastfeed their babies in the neonatal intensive care unit: a randomized controlled study
- 1,374 View
- 19 Download
- 10 Crossref

- A Review on the Use of Effect Size in Nursing Research
- Hyuncheol Kang, Kyupil Yeon, Sang-Tae Han
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(5):641-649. Published online October 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.5.641
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to introduce the main concepts of statistical testing and effect size and to provide researchers in nursing science with guidance on how to calculate the effect size for the statistical analysis methods mainly used in nursing.
Methods For t-test, analysis of variance, correlation analysis, regression analysis which are used frequently in nursing research, the generally accepted definitions of the effect size were explained.
Results Some formulae for calculating the effect size are described with several examples in nursing research. Furthermore, the authors present the required minimum sample size for each example utilizing G*Power 3 software that is the most widely used program for calculating sample size.
Conclusion It is noted that statistical significance testing and effect size measurement serve different purposes, and the reliance on only one side may be misleading. Some practical guidelines are recommended for combining statistical significance testing and effect size measure in order to make more balanced decisions in quantitative analyses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Challenging Assumptions
Teale Ryan, Kesa Herlihy, Ericka Sanner-Stiehr, Mihaela Sardiu, Karen Weis, Becky Christian
Nurse Educator.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Video-based Handover Training on Nursing Students’ Teamwork Attitude
Seung Hee Lee, Hye Jin Yoo
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of a blended (distance and in-person) simulation education program on advanced cardiac life support for nursing students using the PARTNER model
Miyoung Kang, Eunju Lee
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Client Violence and Supervision On Burnout of Community Mental Health Professionals
Eunmi Hwang, Yujin Han
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(1): 104. CrossRef - Comparative Outcomes of Amblyopia Treatment in High Astigmatism: Stability and Sustained Improvements
Chia-Chen Hsu, Lung-Chi Lee, Hsu-Chieh Chang, Chun-Hao Huang, Ke-Hung Chien
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(10): 3577. CrossRef - Status of Early Childhood Health Promotion Education and Educational Needs Perceived by Primary Caregivers
Young-Ran Lee, Eunjeong Nam, Sun-Nam Park, Mi-Ran Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(3): 376. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of an Online Oncology Nursing Septic Shock Simulation Module for Nursing Students: A Mixed Methods Experimental Design
Jiyoung Kang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(3): 169. CrossRef - Comparison of educational needs and priorities for work-related laws between hospital and community-based nurses
Jeonghyun Kim, Min Kyoung Han, Minjae Lee, Sujin Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(3): 400. CrossRef - Exploring the relative importance of the factors associated with menopausal symptoms using a random forest model: a cross-sectional study
Meejung Chin, Sowon Hahn, Yeon Soo Kim, Young Hye Kwon, Yeon-Hwan Park, Younghwan Choi, Gahye Kim, Youjin Kim, Inju Lee, Hyun Jeong Yoon, Hanjin Bae
Women's Health Nursing.2025; 31(3): 227. CrossRef - The Key Role of Nurse–Patient Mutuality in Shaping Professional Quality of Life Among Nurses: A Bayesian Path Analysis
Silvia Cilluffo, Rosario Caruso, Barbara Bassola, Ercole Vellone, Gianluca Pucciarelli, Stefano Terzoni, Camilla Ripari, Maura Lusignani
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Academic performance, emotional intelligence, and academic burnout: A cross-sectional study of a mediational effect in nursing students
César Merino-Soto, Marisol Angulo-Ramos, Victoria Llaja-Rojas, Guillermo M. Chans
Nurse Education Today.2024; 139: 106221. CrossRef - First-line Nurse Managerial Competence and Its Influencing Factors in Public Jordanian Hospitals
Abdulkareem S. Iblasi, Samer Makahleh, Yupin Aungsuroch, Joko Gunawan, I Gede Juanamasta
Nurse Media Journal of Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Pre-basic Nursing Science Program for First-year Nursing Students
Eun Hee Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2024; 49(4): 374. CrossRef - Relationship between the Perceptions of ICU Nurses on the Disclosure of Patient Safety Incidents and Communication Barriers
In Sun Cho, Su Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(1): 44. CrossRef - Factors associated with self-management behaviors among Chinese adults with ischemic stroke: A cross-sectional study
Xiaoxiao Chen, Niphawan Samartkit, Khemaradee Masingboon
Belitung Nursing Journal.2024; 10(3): 285. CrossRef - Comparison of halitosis according to herbal mouthwash containing Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract and saline mouthwash: A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study
Yu‐Rin Kim, Seoul‐Hee Nam
International Journal of Dental Hygiene.2024; 22(3): 614. CrossRef - Development and application of the mobile-based virtual nursing simulation training content: A mixed methods study
Hyun-Sun Kim, Jiyoung Kang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2024; 30(3): 290. CrossRef - Benefit-finding profiles and comparison of caregiving ability among informal caregivers of patients with lung cancer: A latent profile analysis
Xiaoyuan Lin, Ziqing Chen, Qi Zhao, Xiaozhou Zhou
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2024; 11(5): 100480. CrossRef - Changes in the Health Status of Children and Adolescents Before, During, and After the COVID-19 Pandemic: Focus on the Results of Health Examination
Eun-Joo Choi, Chung-Sook Kim, Jeong-Mo Park, Sang-Soon Gwon
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2024; 38(2): 132. CrossRef - Therapeutic Communication Using Mirroring Interventions in Nursing Education: A Mixed Methods Study
Seung Hee Lee, Hye Jin Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(5): 435. CrossRef - Digital Health Literacy and Associated Factors Among Older Adults Living Alone in South Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study
Minhwa Hwang, Gahye Kim, Seonghyeon Lee, Yeon-Hwan Park
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2024; 35: 389. CrossRef - The Development and Effects of Metaverse-based Core Nursing Skill Contents (CNSC) for Nursing Students: Drainage Management
Min Kweon Ahn, Min Jeong Chae
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(4): 447. CrossRef - Analysis of the Submitted Papers’ Evaluations for the Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing
Narae Heo, Jiyoung Kim
Journal of Korea Society for Simulation in Nursing.2024; 12(2): 73. CrossRef - Global Health Competencies and Educational Needs for Nursing Students in South Korea
Sujin Lee, Eunjoo Kim, Ju Young Yoon
Journal of Nursing Education.2023; 62(2): 75. CrossRef - Comparison of perceived parental empathy between adolescents with leukemia and healthy adolescents: A comparative descriptive study
Youngji Moon, Sunhee Lee
Heliyon.2023; 9(11): e22528. CrossRef - Dietary behavior and its influencing factors among experienced shiftwork nurses: a secondary analysis
Soyeon Kim, Jison Ki, Ji Yun Choi, Woan Heui Choi, Smi Choi-Kwon
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(1): 32. CrossRef - Factors influencing neonatal intensive care unit nurses' parent partnership development
Eun Kyoung Kim, In Young Cho, Ji Yeong Yun, Bobae Park
Journal of Pediatric Nursing.2023; 68: e27. CrossRef - Predictors of Quality of Life in Patients With Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy Receiving Nonsurgical Management Due to Chronic Pain
Yeong Gi Lee, Sung Reul Kim
Pain Management Nursing.2023; 24(4): e26. CrossRef - The Effects of Emotional Labor and Workplace Violence on the Somatic Symptoms of Customer Service Employees in Department Stores
Bongsoon Ryu, Bo Hyun Park
Research in Community and Public Health Nursing.2023; 34: 61. CrossRef - Effects of Post Traumatic Growth on Successful Aging in Breast Cancer Survivors in South Korea: The Mediating Effect of Resilience and Intolerance of Uncertainty
Su Jeong Yi, Ku Sang Kim, Seunghee Lee, Hyunjung Lee
Healthcare.2023; 11(21): 2843. CrossRef - Genetic Testing on Patients with Developmental Delay: A Preliminary Study from the Perspective of Physicians
Gwanwook Bang, Sook Joung Lee, Bomyee Lee, Minji Park, So-Youn Park
Healthcare.2022; 10(7): 1236. CrossRef - The development and effects of metaverse-based core nursing skill contents of vital signs measurements and subcutaneous injections for nursing students
Min Kweon Ahn
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 378. CrossRef - Effects of a mouthwash containing Lespedeza cuneata extract on risk of dental caries: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial
Yu-Rin Kim, Seoul-Hee Nam
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Do lifestyle factors influence risk of breast cancer recurrence in Korean women?: a cross-sectional survey
So-Jung Park, Hye-Ah Yeom
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(2): 145. CrossRef - Relationship between type D personality, symptoms, cancer stigma, and quality of life among patients with lung cancer
Yu Mi Park, Hye Young Kim, Ji Young Kim, Sung Reul Kim, Yeong Hun Choe
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 57: 102098. CrossRef - Validation of the Risk Prediction Tool for Wound Infection in Abdominal Surgery Patients
Hyun Kyoung Jung, Eun Nam Lee
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2022; 15(3): 75. CrossRef - Effect of the Strategic Thinking, Problem Solving Skills, and Grit on the Disaster Triage Ability of Emergency Room Nurses
Jina Yang, Kon Hee Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(2): 987. CrossRef - Effects of a Sociodrama-based Communication Enhancement Program on Mothers of Children with Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Pilot Study
Sun Joo Jang, Jong-Sook Han, Myoung Hee Bang, Jung-Won Ahn
Asian Nursing Research.2022; 16(2): 114. CrossRef - Changes in Dietary Behavior of Shift Work Nurses: A Longitudinal Study
Soyeon Kim, Smi Choi-Kwon, Jison Ki, Jae Geum Ryu, Jihyun Baek, Kyeongsug Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2022; 28(5): 596. CrossRef - Compassion Satisfaction, Secondary Traumatic Stress, and Burnout among Nurses Working in Trauma Centers: A Cross-Sectional Study
Hyoung Ju Lee, Miyoung Lee, Sun Joo Jang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(14): 7228. CrossRef - Intentions of frontline nurses regarding COVID‐19 patient care: A cross‐sectional study in Korea
Yu‐Mi Heo, Miyoung Lee, Sun Joo Jang
Journal of Nursing Management.2021; 29(6): 1880. CrossRef - Developing and Evaluating a Mobile-based Parental Education Program for Preventing Unintentional Injuries in Early Childhood: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Younglee Choi, Hye Young Ahn
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(5): 329. CrossRef - The Effect of Perceived Stress, Fine Dust Risk Perception, and Resilience on Stress Response in Patients with Respiratory and Circulatory Disorders
Jin-Hee Park, Kuem-Sun Han
STRESS.2021; 29(1): 21. CrossRef - Critical Thinking Disposition, Job Competency, and Educational Needs of Home Visiting Nurses in the Long-term Care Insurance
Keunyoung Shin, Sujin Shin
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2021; 23(1): 54. CrossRef - Interaction and main effects of physical and depressive symptoms on quality of life in Korean women seeking care for rectal prolapse: a cross-sectional observational study
Hee Moon, Youngrye Park, Mili Kim, Seonah Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(4): 297. CrossRef - Effects of Gymnastics-based Nursing Intervention on Stress, Obesity, and Mental Health Confidence in Patients with Chronic Mental Illness
Hee Jeong Kim, Sookbin Im
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2021; 30(1): 53. CrossRef - Development and Effects of Head-Mounted Display-Based Home-Visits Virtual Reality Simulation Program for Nursing Students
Min Kweon Ahn, Chong Mi Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(4): 465. CrossRef - Effectiveness of self-re-learning using video recordings of advanced life support on nursing students’ knowledge, self-efficacy, and skills performance
Kyeongmin Jang, Sung Hwan Kim, Ja Young Oh, Ji Yeon Mun
BMC Nursing.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The effectiveness of a career efficacy enhancement program for KOREAN nursing students: A quasi-experimental study
Young-Mi Jung, In-Young Yoo
Nurse Education Today.2020; 89: 104423. CrossRef - A Comparison of Nursing Work Environment, Role Conflict, and Job Embeddedness of Nurses Working in Comprehensive Nursing Care Service Wards and General Wards in a Tertiary Hospital
Hye-Eun So, Jee-In Hwang
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2020; 26(1): 11. CrossRef - Relation between Mother’s Taekyo, Prenatal and Postpartum Depression, and Infant’s Temperament and Colic: A Longitudinal Prospective Approach
Kyung-Sook Bang, Insook Lee, Sungjae Kim, Yunjeong Yi, Iksoo Huh, Sang-Youn Jang, Dasom Kim, Sujin Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7691. CrossRef - Nursing students’ career identity, satisfaction with major, and career stress by career decision type
Young‐Mi Jung
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Subjective Happiness according to Temperament and Character Type of Nursing Students
EunJoo Kim, Geunmyun Kim
Stress.2020; 28(2): 76. CrossRef - Effect of an emotion management programme for patients with schizophrenia: A quasi‐experimental design
Minju Cho, Sun Joo Jang
International Journal of Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(2): 592. CrossRef - Influence of Partnerships with Nurses and Social Support on Readiness for Discharge among Mothers of Premature Infants
Soyeon Yoon, Jeongok Park, Hyejung Lee, Ari Min
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(4): 417. CrossRef - The Effects of the 5-step Method for Infant Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Training on Nursing Students' Knowledge, Attitude, and Performance Ability
Jin Young Kim, Hye Young Ahn
Child Health Nursing Research.2019; 25(1): 17. CrossRef - The Influence of Stress and Role Conflict on Quality of Life among Graduate Students in Nursing
Yu-Jin Jeong, Eun Kyung Kim
STRESS.2019; 27(4): 365. CrossRef - Family Characteristics, Family Support, Family Function and Compliance of Patient Role Behavior in Long-term Hemodialysis Patients
Sinhye Kang, Inja Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2019; 22(1): 58. CrossRef - Utilizing Video vs Simulation Practice for Handoff Education of Nursing Students in Pediatric Nursing
Sun-Nam Park, Young Soon Im
Child Health Nursing Research.2018; 24(1): 27. CrossRef - Educational Needs Analysis for Developing an Occupational Education Program for Nursing Students: Focusing on Nursing Students and Nursing Professionals
Young-Mi Jung
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(2): 136. CrossRef - Comparison of analgesic efficacy of oxycodone and fentanyl after total hip replacement surgery
Mi Kyeong Kim, Sang Eun Ahn, Eunsil Shin, Sung Wook Park, Jeong-Hyun Choi, Hee Yong Kang
Medicine.2018; 97(49): e13385. CrossRef - The Effect of a Teaching Model for Improving Undergraduate Nursing Students' Cultural Competency
Kyung Sook Choi, Woo Sook Lee, Yeon Suk Park, Myunghee Jun, So Young Lee, Yeonwoo Park, Soo Young Park, Zabler Bev
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2018; 24(1): 100. CrossRef - An Integrative Review of Korean Nursing Studies on Pediatric Tonsillectomy
Kyoung Eun Yu, Jin Sun Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2017; 23(4): 416. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Self-leadership in the Relationship between Career Decision Level and Career Preparation Behavior of Nursing Students
Mikyung Moon, Soyeon Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2017; 42(2): 162. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Rehabilitation among Cancer Survivors
Jooyeon Park, Nahyun Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(5): 463. CrossRef - Health Promotion Behavior in Colorectal Cancer Patients and General Adults
Sunhee Hwang, Nami Chun
Asian Oncology Nursing.2016; 16(2): 94. CrossRef - The Effect of A Salivation Stimulation Method on Xerostomia in Colon Cancer Patients after Surgery
Anna Kim, Jeong Sook Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2016; 16(2): 75. CrossRef - The relationship between sense of humor, stress and depression in the nursing students
Hae Jin Lee, Ye Jung Ko, Seung Woo Han
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2016; 27(4): 1035. CrossRef - Maternal Role Development in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Graduate Mothers of Premature Infant
Ah Rim Kim, Young Ran Tak
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2015; 21(4): 308. CrossRef
- Challenging Assumptions
- 2,710 View
- 100 Download
- 69 Crossref

- Development of a Prediction Model for Postpartum Depression: Based on the Mediation Effect of Antepartum Depression
- Eun Joo Lee, Jeong Sook Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(2):211-220. Published online April 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.2.211
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to develop a prediction model for postpartum depression by verifying the mediation effect of antepartum depression. A hypothesized model was developed based on literature reviews and predictors of postpartum depression by Beck.
Methods Data were collected from 186 pregnant women who had a gestation period of more than 32 weeks and were patients at a maternity hospital, two obstetrics and gynecology specialized hospitals, or the outpatient clinic of K medical center. Data were analysed with descriptive statistics, correlation and exploratory factor analysis using the SPSS/WIN 18.0 and AMOS 18.0 programs.
Results The final modified model had good fit indices. Parenting stress, antepartum depression and postpartum family support had statistically significant effects on postpartum depression, and defined 74.7% of total explained variance of postpartum depression. Antepartum depression had significant mediation effects on postpartum depression from stress in pregnancy and self-esteem.
Conclusion The results of this study suggest that it is important to develop nursing interventions including strategies to reduce parenting stress and improve postpartum family support in order to prevent postpartum depression. Especially, it is necessary to detect and treat antepartum depression early to prevent postpartum depression as antepartum depression can affect postpartum depression by mediating antepartum factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Latent profiles of depression and post-traumatic growth and their associations with social support and religious participation in mothers of children with developmental disabilities in South Korea
Soo Kyung Park, Haenim Lee
Research in Developmental Disabilities.2026; 169: 105235. CrossRef - Domestic Violence Experience, Past Depressive Disorder, Unplanned Pregnancy, and Suicide Risk in the First Year Postpartum: Mediating Effect of Postpartum Depression
Mi-Sun Lee, Jung Jae Lee, Hooyeon Lee
Psychiatry Investigation.2024; 21(10): 1129. CrossRef - High-risk Pregnancy Nursing: Analyzing the Impact of Prenatal Stress, Maternal-Fetal Attachment, and Social Support on Prenatal Depression
Jae Hui Choe, Sun Jeong Yun, Hye Young Kim
The Open Nursing Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Are the effects of stress on antenatal depression mediated by self-esteem and moderated by social support?: a cross-sectional study
Eunjoo Lee
Women's Health Nursing.2024; 30(4): 299. CrossRef - Postpartum Depression and Health: Role of Perceived Social Support among Pakistani Women
Samrah Jamshaid, Najma Iqbal Malik, Irfan Ullah, Sundas Saboor, Fauzia Arain, Domenico De Berardis
Diseases.2023; 11(2): 53. CrossRef - Do taegyo practices, self-esteem, and social support affect maternal-fetal attachment in high-risk pregnant women? A cross-sectional survey
Da-In Kang, Euna Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2022; 28(4): 338. CrossRef - Body Appreciation, Depressive Symptoms, and Self-Esteem in Pregnant and Postpartum Brazilian Women
Juliana Fernandes Filgueiras Meireles, Clara Mockdece Neves, Ana Carolina Soares Amaral, Fabiane Frota da Rocha Morgado, Maria Elisa Caputo Ferreira
Frontiers in Global Women's Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Depression and stress in Korean parents: A cohort study
Hyeji Yoo, Sukhee Ahn, Jiwon Oh, Seyeon Park, Jisoon Kim, Minseon Koh
Applied Nursing Research.2021; 62: 151519. CrossRef - Factors influencing prenatal and postpartum depression in Korea: a prospective cohort study
Hyeji Yoo, Sukhee Ahn, Seyeon Park, Jisoon Kim, Jiwon Oh, Minseon Koh
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(4): 326. CrossRef - Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale used in South Korea
Rora Oh, Young-Ho Khang, Yu-Mi Kim
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2021; 64(10): 699. CrossRef - Relation between Mother’s Taekyo, Prenatal and Postpartum Depression, and Infant’s Temperament and Colic: A Longitudinal Prospective Approach
Kyung-Sook Bang, Insook Lee, Sungjae Kim, Yunjeong Yi, Iksoo Huh, Sang-Youn Jang, Dasom Kim, Sujin Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7691. CrossRef - Longitudinal Relationship Study of Depression and Self-Esteem in Postnatal Korean Women Using Autoregressive Cross-Lagged Modeling
Jeong-Won Han, Da-Jung Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(10): 3743. CrossRef - The Effects of Neuroticism on Postpartum Depression: A Dual Mediating Effect of Gratitude and Parenting Stress
Yuji Lee, Myoung-Ho Hyun
Stress.2019; 27(2): 191. CrossRef - Adverse Childhood Experiences and Postpartum Depression in Home Visiting Programs: Prevalence, Association, and Mediating Mechanisms
Joshua P. Mersky, Colleen E. Janczewski
Maternal and Child Health Journal.2018; 22(7): 1051. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Postpartum Care Mobile Application for First-time Mothers
Ju Yeon Lee, Hye Young Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2017; 23(3): 210. CrossRef
- Latent profiles of depression and post-traumatic growth and their associations with social support and religious participation in mothers of children with developmental disabilities in South Korea
- 1,522 View
- 19 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Late Effects, Social Adjustment, and Quality of Life in Adolescent Survivors of Childhood Leukemia
- Sung Sil Hong, Ho Ran Park, Kwang Sung Kim, Sun Hee Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(1):55-63. Published online February 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.1.55
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to examine the late effects, social adjustment, and quality of life in adolescents who had been completely treated for childhood leukemia and their parents.
Methods Participants consisted of 41 pairs of adolescent survivors (13-18 years) and their parents. Parents checked for their child's physical late effects. The Korean Version of Post-Traumatic Symptoms for psychological late effects, social functioning questionnaire for social adjustment and the PedsQL 4.0 Generic Core Scales for quality of life were completed by adolescents and parents. Data were analyzed using SPSS.
Results Twenty out of 41 adolescents had one or more physical late effects. Adolescents showed more serious psychological late effect than parents. Five children and seven parents had above cut-off scores and they were considered the high risk group for posttraumatic symptoms. Parent-reported scores were significantly higher than child-reported scores in terms of social adjustment and emotional functioning of quality of life. Low school functioning in adolescents was associated with physical late effects.
Conclusion The results indicate that long-term and systematic management for childhood leukemia survivors affect positive social adjustment and can further improve quality of life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Integrated Review of Health Care in Child and Adolescent Cancer Survivors Based on Roy’s Adaptation Model
Hye Jin Kim, Eunjoo Lee
Asian Oncology Nursing.2024; 24(2): 82. CrossRef - Technology-based psychosocial support for adolescent survivors of leukemia
Tuba ARPACI, Naime ALTAY
Journal of Integrative Nursing.2022; 4(3): 157. CrossRef - Self-efficacy, post-traumatic growth, and quality of life of pediatric cancer survivors: A cross-sectional study
Yeunhee Kwak, Yoonjung Kim, Eun Seok Choi, Ho Joon Im
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 54: 102019. CrossRef - Difficulty in returning to school among adolescent leukemia survivors: A qualitative descriptive study
Hyeran An, Sunhee Lee
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2019; 38: 70. CrossRef - Sleep Pattern and Factors Causing Sleep Disturbance in Adolescents with Cancer before and after Hospital Admission
Jin Jung, Eun-Hye Lee, You-Jin Yang, Bo-Yoon Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2017; 17(3): 143. CrossRef - Qualitative Evaluation of Effectiveness of ‘Family Hope Partner Project’ for Pediatric Cancer Patients and their Families
김선희
Korean Journal of Family Social Work.2017; null(55): 59. CrossRef - The Experiences of Korean Young Adult Survivors of Childhood Cancer
Jaehee Yi, Min Ah Kim, Sangmin An
Qualitative Health Research.2016; 26(8): 1044. CrossRef - The Effect of Perceived Social Stigma on Self-Esteem of Childhood Cancer Survivors
김민아, 남석인, 장은혜, Lee Daji
Health and Social Welfare Review.2016; 36(1): 497. CrossRef - Health-related Needs and Quality of Life in Childhood Cancer Survivors
Su-Jin Lim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2015; 15(4): 246. CrossRef
- An Integrated Review of Health Care in Child and Adolescent Cancer Survivors Based on Roy’s Adaptation Model
- 1,143 View
- 5 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Development and Effectiveness of a Drug Dosage Calculation Training Program using Cognitive Loading Theory based on Smartphone Application
- Myoung Soo Kim, Jung Ha Park, Kyung-Yeon Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(5):689-698. Published online October 12, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.5.689
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to develop and evaluate a drug dosage calculation training program using cognitive loading theory based on a smartphone application. Calculation ability, dosage calculation related self-efficacy and anxiety were measured.
Methods A nonequivalent control group design was used. Smartphone application and a handout for self-study were developed and administered to the experimental group and only a handout was provided for control group. Intervention period was 4 weeks. Data were analyzed using descriptive analysis,
χ 2-test, t-test, and ANCOVA with the SPSS 18.0.Results The experimental group showed more ‘self-efficacy for drug dosage calculation’ than the control group (t= 3.82,
p < .001). Experimental group students had higher ability to perform drug dosage calculations than control group students (t= 3.98,p < .001), with regard to ‘metric conversion’ (t= 2.25,p = .027), ‘table dosage calculation’ (t= 2.20,p = .031) and ‘drop rate calculation’ (t= 4.60,p < .001). There was no difference in improvement in ‘anxiety for drug dosage calculation’. Mean satisfaction score for the program was 86.1.Conclusion These results indicate that this drug dosage calculation training program using smart-phone application is effective in improving dosage calculation related self-efficacy and calculation ability. Further study should be done to develop additional interventions for reducing anxiety.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Challenges in educating nursing students on mechanical ventilation: the case for interactive mobile learning tools – a randomized controlled trial
Alireza Samimi Sarangi, Kolsoum Deldar, Ahmad Bagheri Moghaddam, Razieh Froutan
BMC Nursing.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and effectiveness of online teaching on practical skills among nursing students: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Afang Li, Norhasmah Mohd Zain, Azlina Yusuf, Haiyan Deng, Qi He
Nurse Education in Practice.2024; 78: 103988. CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness of a Clinical Decision Support System for Pressure Ulcer Prevention Care Using Machine Learning
Myoung Soo Kim, Jung Mi Ryu, Byung Kwan Choi
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2023; 41(4): 236. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a virtual reality application‐based education programme on patient safety management for nursing students: A pre‐test–post‐test study
Jae Woo Oh, Ji Eun Kim
Nursing Open.2023; 10(12): 7622. CrossRef - The Effect of Game-Based Clinical Nursing Skills Mobile Application on Nursing Students
Donghee Suh, Hyekyung Kim, Eunyoung E. Suh, Hyunsun Kim
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2022; 40(11): 769. CrossRef - The effect of case-based learning based on flipped learning for nursing students
Min Hee Lee, Myung Sook Park
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(2): 107. CrossRef - Smartphone distraction during nursing care: Systematic literature review
Massimo Fiorinelli, Sofia Di Mario, Antonella Surace, Micol Mattei, Carla Russo, Giulia Villa, Sara Dionisi, Emanuele Di Simone, Noemi Giannetta, Marco Di Muzio
Applied Nursing Research.2021; 58: 151405. CrossRef - A systematic review into the assessment of medical apps: motivations, challenges, recommendations and methodological aspect
A. H. Alamoodi, Salem Garfan, B. B. Zaidan, A. A. Zaidan, Moceheb Lazam Shuwandy, Mussab Alaa, M. A. Alsalem, Ali Mohammed, A. M. Aleesa, O. S. Albahri, Ward Ahmed Al-Hussein, O. R. Alobaidi
Health and Technology.2020; 10(5): 1045. CrossRef - Development and Utilization of a Clinical Decision Support System Contents for Pressure Ulcer Prevention Care
Myoung Soo Kim, Jung Mi Ryu
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2020; 45(4): 365. CrossRef - The Effect of Cell Phones on Attention and Learning in Nursing Students
Lorena Gutiérrez-Puertas, Verónica V. Márquez-Hernández, Vanesa Gutiérrez-Puertas, Genoveva Granados-Gámez, Gabriel Aguilera-Manrique
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2020; 38(8): 408. CrossRef - Using Video Feedback Through Smartphone Instant Messaging in Fundamental Nursing Skills Teaching: Observational Study
Xiaoxian Yang, Ri-Hua Xie, Si Chen, Wei Yu, Yan Liao, Daniel Krewski, Shi Wu Wen
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2019; 7(9): e15386. CrossRef - Effects of Smartphone-Based Mobile Learning in Nursing Education: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Ju Hee Kim, Hanjong Park
Asian Nursing Research.2019; 13(1): 20. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of “Chronic Illness Care Smartphone Apps” on Nursing Students’ Knowledge, Self-efficacy, and Learning Experience
Jiyoung Kang, Eunyoung E. Suh
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2018; 36(11): 550. CrossRef - Mobile Technology in Undergraduate Nursing Education: A Systematic Review
Hyejung Lee, Haeyoung Min, Su-mi Oh, Kaka Shim
Healthcare Informatics Research.2018; 24(2): 97. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Acceptance Intention Toward a Smartphone Healthcare Application and Health-Promoting Behaviors Among Nursing Students
Eun-Jin Choi, Se-Won Kang
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2018; 36(10): 494. CrossRef - The Effects of an Interactive Nursing Skills Mobile Application on Nursing Students' Knowledge, Self-efficacy, and Skills Performance: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Hyunsun Kim, Eunyoung E. Suh
Asian Nursing Research.2018; 12(1): 17. CrossRef - Outcomes of a Drug Dosage Calculation Training Smartphone App on Learning Achievement, Metacognition, and Flow State According to Prior Knowledge
Kyung Yeon Park, Myoung Soo Kim
EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Cross-cultural Validation of the Korean Version of SMArtphone’s uSability Heuristics (SMASH)
Yeo Won Jeong, Jung A Kim
Healthcare Informatics Research.2017; 23(4): 328. CrossRef - The Effects of Smartphone Application to Educate Patient on Patient Safety in Hospitalized Surgical Patients
Hyo Jin Choi, Eunjoo Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2017; 29(2): 154. CrossRef - Use of mobile devices and medication errors in acute care
Nicole Harder, Jannell Plouffe, Diane Cepanec, Kari Mann, Mê-Linh Lê, Patricia Gregory, Patrick Griffith, Kathy Doerksen
JBI Database of Systematic Reviews and Implementation Reports.2016; 14(9): 47. CrossRef - Development of a Smartphone Application for Clinical Decision Making of Medication Administration
Myoung-Soo Kim, Jung-Ha Park, Sungmin Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(3): 1650. CrossRef - Predictors of Drug Dosage Calculation Error Risk in Newly Graduated Nurses
Myoung Soo Kim, Jung Soon Kim, Won Choon Ha
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2014; 16(2): 113. CrossRef - Development and Effectiveness of Smartphone Application for the Medication Confirmation of High-alert Medications
Myoung Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(3): 253. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Drug Calculation Confidence in the Relationship between Interest in Medication and Drug Calculation Competency
Hyoung Sook Park, Gyoo Yeong Cho, Dong-Hee Kim, Sang Hee Kim, Myoung Soo Kim
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2013; 15(4): 155. CrossRef
- Challenges in educating nursing students on mechanical ventilation: the case for interactive mobile learning tools – a randomized controlled trial
- 1,543 View
- 13 Download
- 24 Crossref

- Effectiveness of PLISSIT Model Sexual Program on Female Sexual Function for Women with Gynecologic Cancer
- Nami Chun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(4):471-480. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.4.471
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of the Permission, Limited Information, Specific Suggestions, Intensive Therapy (PLISSIT) model sexual program on female sexual function for women with gynecologic cancer.
Methods The integrative 6-hr (two hours per session) program reflecting physical and psychosocial aspects of women's sexuality was developed based on Annon's PLISSIT model. Participants were 61 women with cervical, ovarian, or endometrial cancer. Of them, 29 were assigned to the experimental group and 32 to the control group. The women completed the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) including sexual desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, satisfaction, and pain. Independent t-test and repeated measured ANOVA were used to test the effectiveness of the program.
Results Significant group differences were found on FSFI sub-domain scores including sexual desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, and satisfaction but not pain. Significant time differences were found on all domains except for pain in the experimental group repeated measured ANOVA.
Conclusion The results indicate that the three-week PLISSIT model sexual program is effective in increasing sexual function for women with gynecologic cancer. Nurses may contribute to improving women's sexual function by utilizing the program. Strategies to relieve sexual pain need to be considered for greater effectiveness of the program.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- “Maybe if this was addressed sooner, maybe things might be different in our relationship. I don’t know. But who knows?” Sexuality after TBI and its place in healthcare: A qualitative exploration of survivors’ experiences
Jill H. A. Hwang, Marina Downing, Jennie L. Ponsford
Neuropsychological Rehabilitation.2025; 35(5): 960. CrossRef - The Effect of Sexual Education Program on Sexual Function and Genital Self-image, Sexual Quality of Life among Primiparous Women
Athar Rasekh Jahromi, Hanie Jafari, Parvin Adedi, Mojgan Javadnoori, Solmaz Mohammadi, Vahid Rahmanian, Safieh Jamali
Current Womens Health Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a sexual health enhancement program for women with breast cancer: A quasi-experimental study
Hye Sook Kim, Chaewon Yun
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2025; 76: 102852. CrossRef - Effect of PLISSIT model counseling on the sexual quality of life of infertile women: a randomized controlled trial
Reyhane Amini, Mahboube Taebi, Hatav Ghasemi Tehrani
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Feasibility and effectiveness of communication tools for addressing intimacy and sexuality in patients with cancer: a systematic review
Susanne A. M. Arends, Carlijn E. van Rossum, Corien M. Eeltink, Jantien E. Robertus, Linda J. Schoonmade, Anneke L. Francke, Irene P. Jongerden
Supportive Care in Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Educational programs and counseling models for improving postpartum sexual health: a narrative review
Tayebeh Darooneh, Giti Ozgoli, Zohreh Keshavarz, Malihe Nasiri
Sexual and Relationship Therapy.2024; 39(3): 1044. CrossRef - The Effect of Post-Operative Sexual Counseling Carried out with PLISSIT Model on Sexual Function and Sexual Satisfaction in Gynecologic Cancers
Çiğdem BİLGE, Ergül ASLAN
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2023; 13(3): 623. CrossRef - The effect of a psycho-educational intervention on sexuality of women with acute coronary syndromes: a randomized controlled trial
Fatemeh Soleimaninejad, Razieh Lotfi, Mehdi Mousavi, Majid Taghizadeh, Kourosh Kabir
Sexual and Relationship Therapy.2023; 38(2): 277. CrossRef - The Effect of BETTER-Based Sex Counseling on Sexual Quality of Life in Infertile Women: a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Farzaneh Dastaran, Raziyeh Maasoumi, Fatemeh Foroozanfard, Shima Haghani
Sexuality and Disability.2022; 40(4): 785. CrossRef - Relationships among sexual function, marital intimacy, type D personality and quality of life in patients with ovarian cancer, with spouses
Ju‐Hee Nho, Sung Reul Kim, Won Ku Choi
European Journal of Cancer Care.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Sexual health and function in women with diabetes
Kirsty Winkley, Camilla Kristensen, Jackie Fosbury
Diabetic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Sexual Health Improvement Program for Women with Gynecologic Cancer
Soon Yang Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(3): 163. CrossRef - The effect of PLISSIT based counseling model on sexual function, quality of life, and sexual distress in women surviving breast cancer: a single-group pretest–posttest trial
Zohreh Keshavarz, Elham Karimi, Samira Golezar, Giti Ozgoli, Maliheh Nasiri
BMC Women's Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - ´Tratamientos psicológicos para mejorar la vida sexual en mujeres supervivientes de cáncer ginecológico: revisión sistemática.
Karla Maricela Figueroa Espinoza
Psicooncología.2020; 17(2): 293. CrossRef - Sexual Health After Acute Myocardial Infarction: The Lived Experience of Women During the First-Year Post Discharge
Silvio Simeone, Assunta Guillari, Gianluca Pucciarelli, Filomena Stile, Gianpaolo Gargiulo, Mauro Esposito, Rosaria Alvaro, Teresa Rea
Sexuality and Disability.2020; 38(3): 547. CrossRef - Effects of Education About Rheumatoid Arthritis and Sexuality on the Sexual Problems of Women With Rheumatoid Arthritis
Tülay Kars Fertelli
Clinical Nursing Research.2020; 29(3): 189. CrossRef - Effectiveness of sexual counseling using PLISSIT model on sexual function of women with type 2 diabetes mellitus: results from a randomized controlled trial
Maryam Mehrabi, Razieh Lotfi, Mitra Rahimzadeh, Effat Merghati Khoei
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2019; 39(4): 626. CrossRef - The Effect of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy on Sexual Function in Infertile Women: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Maryam Sahraeian, Razieh Lotfi, Mostafa Qorbani, Mahbobeh Faramarzi, Fatemeh Dinpajooh, Fahimeh Ramezani Tehrani
Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy.2019; 45(7): 574. CrossRef - PLISSIT Interventions and Sexual Functioning: Useful Tools for Social Work in Palliative Care?
Michael R. Bennett
Journal of Social Work in End-of-Life & Palliative Care.2019; 15(4): 157. CrossRef - Influence of Urinary Dysfunction on Quality of Life in Women with Cervical Cancer after Radical Hysterectomy
Nami Chun, Gie-Ok Noh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(3): 150. CrossRef - The Influence of Ex-PLISSIT (Extended Permission, Limited Information, Specific Suggestions, Intensive Therapy) Model on Intimacy and Sexuality of Married Women with Multiple Sclerosis
Fatemeh Daneshfar, Zahra Behboodi-Moghadam, Zohreh Khakbazan, Seyed Massood Nabavi, Nahid Dehghan Nayeri, Sogand Ghasemzadeh, Ali Montazeri
Sexuality and Disability.2017; 35(4): 399. CrossRef - Comments on female sexual dysfunction with cervical cancer in Republic of Korea
Gyeong-Eun Heo, Tae-Hee Kim, Hae-Hyeog Lee, Jun-Mo Kim
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics.2016; 294(1): 209. CrossRef - Reply to letter to the editor by J.-M. Kim et al. on "Sexual function and quality of life in women with cervical cancer before radiotherapy: a pilot study" by Grion et al.
R. C. Grion, Luiz Francisco Baccaro, A. F. Vaz, L. Costa-Paiva, D. M. Conde, A. M. Pinto-Neto
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics.2016; 294(1): 211. CrossRef - The effectiveness of the Permission, Limited Information, Specific suggestions, Intensive Therapy (PLISSIT) model based sexual counseling on the sexual function of women with Multiple Sclerosis who are sexually active
Zohreh Khakbazan, Fatemeh. Daneshfar, Zahra Behboodi-Moghadam, Seyed Massood Nabavi, Sogand Ghasemzadeh, Abbas Mehran
Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders.2016; 8: 113. CrossRef - Sexual Health Care Attitudes and Practices of Nurses Caring for Patients with Cancer
Young Hee Chae, Young Ok Song, Soon Tae Oh, Won Hee Lee, Young Mi Min, Hyang Mi Kim, Seung A Lee, Young Sin Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2015; 15(1): 28. CrossRef - The Effect of Face-to-Face With Telephone-Based Counseling on Sexual Satisfaction Among Reproductive Aged Women in Iran
Shirin Zargar Shoushtari, Poorandokht Afshari, Parvin Abedi, Hamed Tabesh
Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy.2015; 41(4): 361. CrossRef - Compare the Effectiveness of PLISSIT and Sexual Health Models on Women's Sexual Problems in Tehran, Iran: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Farnaz Farnam, Mohsen Janghorbani, Firoozeh Raisi, Effat Merghati-Khoei
The Journal of Sexual Medicine.2014; 11(11): 2679. CrossRef - Discussing Sexuality with Cancer Patients: Oncology Nurses Attitudes and Views
Umran Oskay, Gulbeyaz Can, Sukran Basgol
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2014; 15(17): 7321. CrossRef - Effect of PLISSIT Model Sexual Health Enhancement Program for Women with Gynecologic Cancer and Their Husbands
Ju-Hee Nho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2013; 43(5): 681. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of the Psychosocial Distress Nursing Intervention for Patients with Gynecological Cancer
Jeong-Sook Park, Yun-Jung Oh
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(3): 219. CrossRef
- “Maybe if this was addressed sooner, maybe things might be different in our relationship. I don’t know. But who knows?” Sexuality after TBI and its place in healthcare: A qualitative exploration of survivors’ experiences
- 2,257 View
- 26 Download
- 30 Crossref

- Economic Evaluation of Gemcitabine-cisplatin Chemotherapy for Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patient in an Outpatient Setting
- Su Hyun Min, Su-kyoung Ko, Ji Young Lim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2008;38(3):363-371. Published online June 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.3.363
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This analysis was conducted to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of gemcitabine-cisplatin chemotherapy for non small-cell lung cancer patients in an outpatient setting compared with the traditional inpatient setting.
Methods A cost-effective analysis was conducted from a societal perspective. The effects of treatment, which was measured as an adverse event rate, were abstracted from a published literature search and empirical data from one university hospital. The costs included both direct and indirect costs. Direct costs included hospitalizations, outpatient visits, and lab tests. Pharmaceutical costs were excluded in analysis because they were same for both options. Indirect costs included productivity loss of patients as well as care-givers. In order to determine the robustness of the results, sensitivity analysis on treatment protocol was conducted.
Results Literature search showed no difference in adverse effect rates between inpatient treatment protocol and outpatient treatment protocol. Therefore, this analysis is a cost-minimization analysis. Cost-savings in the outpatient setting was 555,936 won for one treatment cycle. Our sensitivity analysis indicated that the outpatient chemotherapy still showed cost-savings, regardless of changes in treatment protocol.
Conclusion The outpatient gemcitabine-cisplatin chemotherapy for non small-cell lung cancer resulted in cost savings compared to inpatient chemotherapy. More importantly, outpatient chemotherapy could improve the utilization of health service resources in terms of available beds.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Evaluation of Effects on Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus Management of a Community-Based Nursing Care Center Using Cost-Benefit Analysis
Ji Young Lim, Jung Nam Im, In A Kim, Su Kyoung Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(3): 295. CrossRef
- An Evaluation of Effects on Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus Management of a Community-Based Nursing Care Center Using Cost-Benefit Analysis
- 870 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


