Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Triglyceride-glucose parameters as predictors of diabetes mellitus incidence in Korean adults: a secondary analysis of a Prospective Cohort Study
- Yu Jin Park, Miseon Shin, Hyun Seon Jeon, Eun Hee Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):205-221. Published online April 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24108
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
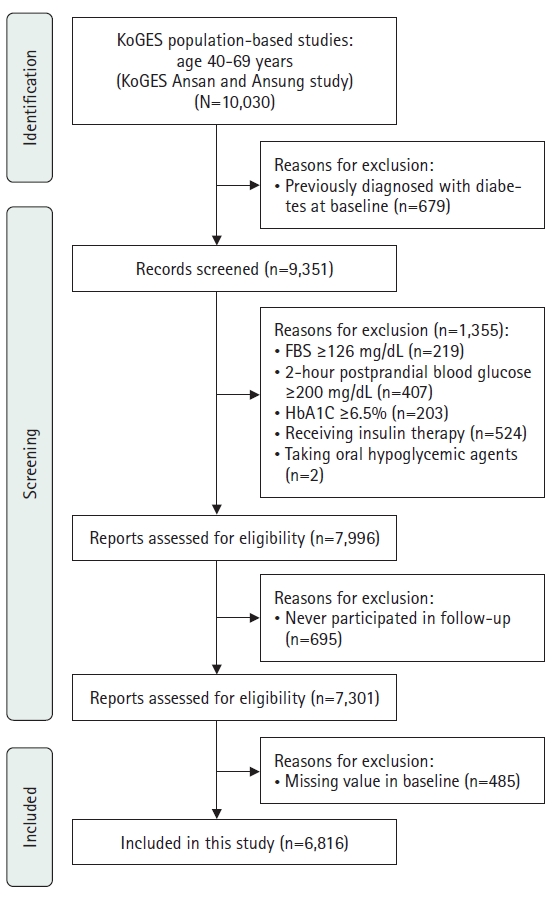
This study aimed to evaluate the association between triglyceride-glucose (TyG)–related parameters and the incidence of diabetes mellitus in Korean adults. Data were obtained from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES).
Methods
This secondary analysis examined data from 6,816 adults aged 40–69 years who participated in the KoGES from 2001 to 2020. TyG–related parameters, including the TyG index, TyG–body mass index (TyG–BMI), TyG–waist circumference (TyG–WC), and TyG–waist-to-height ratio (TyG–WHtR), were assessed. Cox proportional hazards models were employed to determine the association between these parameters and the incidence of diabetes mellitus, with adjustments made for demographic, lifestyle, and health-related characteristics.
Results
Higher levels of all TyG–related parameters were significantly associated with an increased risk of developing diabetes mellitus. Specifically, participants in the highest quartile of the TyG index, TyG–BMI, TyG–WC, and TyG–WHtR exhibited significantly higher hazard ratios for diabetes mellitus incidence compared with those in the lowest quartile (p<.001 for all). Notably, the TyG index demonstrated a stronger predictive value for diabetes mellitus than traditional measures such as the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance.
Conclusion
TyG–related parameters are robust predictors of diabetes mellitus incidence in Korean adults. These findings support the incorporation of TyG–related measures into clinical settings for the early identification and intervention of high-risk populations. Utilizing these parameters for early diagnosis and preventive strategies may significantly enhance diabetes mellitus management.
- 2,326 View
- 148 Download

- Incidence of Colon Cancer Related to Cigarette Smoking and Alcohol Consumption in Adults with Metabolic Syndrome: Prospective Cohort Study
- Ahra Jo, Heeyoung Oh
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2019;49(6):713-723. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.6.713
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the impact of cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption on the incidence of colon cancer in adults with metabolic syndrome.
Methods This study employed a longitudinal study design and utilized secondary data drawn from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES). The data of a sample of 2,327 adults with metabolic syndrome tracked every two years from 2001 to 2014 were used in this study. Statistical data analyses of the frequency, number of cases per 100,000 person-years, log-rank test, Kaplan-Meier curve, and Cox's proportional hazards regression were performed using IBM SPSS statistics version 24.
Results During the observation period, the number of colon cancer cases was 46, and the total person-years were 252,444. The incidence of colon cancer was higher in current, over 10 pack-year smokers when compared to non-smokers (hazard ratio=3.38, 95% confidence interval=1.09~8.42).
Conclusion Excessive and long-term smoking should be avoided to prevent colon cancer, especially in adults with metabolic syndrome, since it might exacerbate the risk factors of colon cancer. Particularly, health professionals need to provide individualized smoking cessation interventions to those at high risk of colon cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Genetic correlation, and causal relationships between 3 solid cancer types and human traits
Claudia Cava, Ehsan Nazemalhosseini Mojarad, Isabella Castiglioni
Network Modeling Analysis in Health Informatics and Bioinformatics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Ribosomal Protein L9 Maintains Stemness of Colorectal Cancer via an ID-1 Dependent Mechanism
Eun-Hye Jeon, So-Young Park, Keon Uk Park, Yun-Han Lee
Journal of Cancer Prevention.2024; 29(2): 25. CrossRef - Unhealthy lifestyle factors and the risk of colorectal cancer: a Mendelian randomization study
Xingyuan Li, Zewen Chang, Jiaqi Wang, Ke Ding, Shengqi Pan, Hanqing Hu, Qingchao Tang
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between WHO First-Step Analgesic Use and Risk of Breast Cancer in Women of Working Age
Hyun Sook Oh, Hwa Jeong Seo
Pharmaceuticals.2023; 16(2): 323. CrossRef - RPL27 contributes to colorectal cancer proliferation and stemness via PLK1 signaling
So-Young Park, Daekwan Seo, Eun-Hye Jeon, Jee Park, Byeong-Churl Jang, Jee Kim, Seung-Soon Im, Jae-Ho Lee, Shin Kim, Chi Cho, Yun-Han Lee
International Journal of Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Time to Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus among Korean Adults with Hyperglycemia: Using a Community-Based Cohort Study
Ihn-Sook Jeong, Chan-Mi Kang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(19): 12090. CrossRef - Effects of Nutritious Meal Combined with Online Publicity and Education on Postoperative Nutrition and Psychological State in Patients with Low Rectal Cancer After Colostomy
Lijuan Qu, Mei Zhou, Yi Yu, Kaili Li, Deepika Koundal
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Burden of Cancer Due to Cigarette Smoking and Alcohol Consumption in Korea
Yoon-Sun Jung, Seok-Jun Yoon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(6): 3493. CrossRef - Effect and Prognosis Factors of Combining Laparoscopic Radical Resection of Colon Adenocarcinoma with Docetaxel Therapy in Treating Middle and Advanced Colon Adenocarcinoma
Qi Gao, Caifeng Zhang, Zhichao Dong, Yan Guo, Li Zhang, Sudipta Roy
Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Cuproptosis-Related genes in the prognosis of colorectal cancer and their correlation with the tumor microenvironment
Weiqiang Wu, Jingqing Dong, Yang Lv, Dongmin Chang
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Motivational Factors for Smoking Behaviors in Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome
Moonkyoung Park, Baram Kang, Ahyun Ryu, YueLin Li, Rhayun Song
Patient Preference and Adherence.2021; Volume 15: 2847. CrossRef
- Genetic correlation, and causal relationships between 3 solid cancer types and human traits
- 1,443 View
- 21 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- Predictors of Postpartum Depression: Prospective Cohort Study
- Ji Hyang Youn, Ihn Sook Jeong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2013;43(2):225-235. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.2.225
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This prospective cohort study was done to investigate recall bias to antepartum variables measured at postpartum periods and predictors of postpartum depression.
Methods Participants were 215 women who answered a self-administered questionnaire which included demographics, Postpartum Depression Predictors Inventory-Revised and Korean version of Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale at antepartum 36-40 weeks and postpartum 2 weeks and 6 weeks. Data were analyzed using kappa, and hierarchical multiple logistic regression.
Results Agreement between antepartum variables at both antepartum and two postpartum periods was relatively high (κ=.55-.95). Postpartum depression rates were 36.3% and 36.7% at two follow-up points. In hierarchical multiple logistic regression analysis, prenatal depression (OR=4.32, 95% CI: 1.41-13.19; OR=5.19, 95% CI: 1.41-19.08), social support (OR=1.40, 95% CI: 1.18-1.66; OR=1.27, 95% CI: 1.06-1.53) and maternity blues (OR=4.75, 95% CI: 1.89-11.98; OR=4.22, 95% CI: 1.60-11.12) were commonly associated with postpartum depression at two follow-up points. Child care stress (OR=1.85, 95% CI: 1.01-3.37) was only associated with postpartum depression at 2 weeks postpartum and pregnancy intendedness (OR=1.57, 95% CI: 1.09-2.27) was only associated with postpartum depression at 6 weeks postpartum.
Conclusions The results indicate a need to apply nursing interventions such as prenatal education and counseling with families from antenatal period.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of the Association of Dietary Patterns With Depression in Pregnant Women using Big Data – Mediating Effect of Blood Heavy Metal Concentration
Seowoo Jung, Minji Kim, Jungsil Lee, Jieun Min, Hyesook Kim, Eun-Kyung Lee, Eunhee Ha
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2025; 50(2): 181. CrossRef - Preventive Effects of Prenatal Folic Acid on Postpartum Depression
Xueqin Feng, Chunxia Wang, Fuling Wang, Xiaoyun Zhang, Hua Shu, Hui Chen, Liting Duan, Yuxi Wei, Jishui Wang, Dongmei Man, Fanyong Zhang
Topics in Clinical Nutrition.2024; 39(1): 46. CrossRef - Is social support associated with postpartum depression, anxiety and perceived stress among Korean women within the first year postpartum?
Mi-Sun Lee, Jung Jae Lee, Soyeon Park, Seongju Kim, Hooyeon Lee
Journal of Psychosomatic Obstetrics & Gynecology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Postpartum Blues in Fathers: Prevalence, Associated Factors, and Impact on Father-to-Infant Bond
Claire Baldy, Eloi Piffault, Margaux Chabbert Chopin, Jaqueline Wendland
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(10): 5899. CrossRef - Effectiveness of the Korean Medicine-Based Postnatal Healthcare Program: A Retrospective Observational Study
Joohee Seo, Doeun Lee, Hansong Park, Inae Youn, Jungtae Leem, Minjung Park
Perspectives on Integrative Medicine.2023; 2(2): 117. CrossRef - Factors influencing prenatal and postpartum depression in Korea: a prospective cohort study
Hyeji Yoo, Sukhee Ahn, Seyeon Park, Jisoon Kim, Jiwon Oh, Minseon Koh
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(4): 326. CrossRef - Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale used in South Korea
Rora Oh, Young-Ho Khang, Yu-Mi Kim
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2021; 64(10): 699. CrossRef - Depression and stress in Korean parents: A cohort study
Hyeji Yoo, Sukhee Ahn, Jiwon Oh, Seyeon Park, Jisoon Kim, Minseon Koh
Applied Nursing Research.2021; 62: 151519. CrossRef - Association between dietary patterns during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum depression in China
Lujia Cao, Yuyan Liu, Xuan Liang, Yuzhi Zheng, Wen Li, Jing Yan, Guowei Huang
Journal of Affective Disorders.2020; 264: 370. CrossRef - Relationships of Perfectionism Dimensions with Postpartum Depression
Suyoung Choi, Mi Yeul Hyun
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(1): 1. CrossRef - Postpartum depression screening: are we doing a competent job?
Sathyanarayan Sudhanthar, Zile-e-huma Sheikh, Kripa Thakur
BMJ Open Quality.2019; 8(4): e000616. CrossRef - Pregnant Women's Antenatal Depression and Influencing Factors
Minseon Koh, Sukhee Ahn, Jisoon Kim, Seyeon Park, Jiwon Oh
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(1): 112. CrossRef - Antenatal Depressive Symptoms and Associated Risk Factors among Pregnant Women
Seung Jae Baek, Ji-ae Yun, Ji ae Nam, Eun Young Seo, Seo Young Kwon, Chang Hwa Lee, Kyeong-Sook Choi
Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association.2019; 58(4): 346. CrossRef - The Psychometric Validation of the EPDS-K Among Korean Women: Does It Only Measure Depressive Symptoms?
Young-sun Rhee, Jeong-hwan Park, Hee-Jung Cha, Kye-ha Kim
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2018; 54(2): 115. CrossRef - Trajectories of First-Time Mothers’ Depressive Symptoms During Six Years Postpartum and Behavioral Problems of Their First Child at Age 6 Years
Yeon Ha Kim
Korean Journal of Child Studies.2018; 39(6): 101. CrossRef - Association between Duration of Folic Acid Supplementation during Pregnancy and Risk of Postpartum Depression
Jing Yan, Yuyan Liu, Lujia Cao, Yuzhi Zheng, Wen Li, Guowei Huang
Nutrients.2017; 9(11): 1206. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Maternal Depression: Secondary Data Analysis
Chul-Gyu Kim, Mi-Young Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(3): 288. CrossRef - Status and Influencing factors of health behavior in pregnant women in Yanbian area
Hai-Lian Zhang, Chun-Yu Li, Hyun-Li Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(11): 7863. CrossRef - Effects of Foot-Reflexology Massage on Fatigue, Stress and Postpartum Depression in Postpartum Women
Mi Son Choi, Eun Ja Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(4): 587. CrossRef - Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Depressive Symptoms in Korean Women throughout Pregnancy and in Postpartum Period
Jeong-hwan Park, Wilfried Karmaus, Hongmei Zhang
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(3): 219. CrossRef - Effects of Self Efficacy, Body Image and Family Support on Postpartum Depression in Early Postpartum Mothers
Ji-Won Lee, Yong-Sook Eo, Eun-Hye Moon
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(6): 4011. CrossRef - The Trajectories and Predictors of Maternal Post Natal Depressive Symptoms in a High Risk Group, Based on Latent Growth Modeling
Wanjeong Lee, Gyunhee Kim
Korean Journal of Child Studies.2015; 36(3): 77. CrossRef - Factors associated with Postpartum Depression and Its Influence on Maternal Identity
Yoen Yi Jung, Hae Won Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2014; 20(1): 29. CrossRef - Predictors of Early Postpartum Depression in Mothers of Preterm Infants in Neonatal Intensive Care Units.
Jae Young Lee, Hyeon Ok Ju
Child Health Nursing Research.2014; 20(2): 87. CrossRef - Prevalence and risk factors of postpartum depression in a population-based sample of women in Tangxia Community, Guangzhou
Ai-Wen Deng, Ri-Bo Xiong, Ting-Ting Jiang, Ying-Ping Luo, Wang-Zhong Chen
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine.2014; 7(3): 244. CrossRef - Status of Antepartum Depression and Its Influencing Factors in Pregnant Women
Eun-Joo Lee, Jeong-Sook Park
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(8): 3897. CrossRef
- Analysis of the Association of Dietary Patterns With Depression in Pregnant Women using Big Data – Mediating Effect of Blood Heavy Metal Concentration
- 1,765 View
- 18 Download
- 26 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev


