-
Ten-year trends in research designs and keywords: a bibliometric comparison of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and leading international nursing journals
-
Jin-Hee Park, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Gaeun Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):557-567. Published online November 19, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25119
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
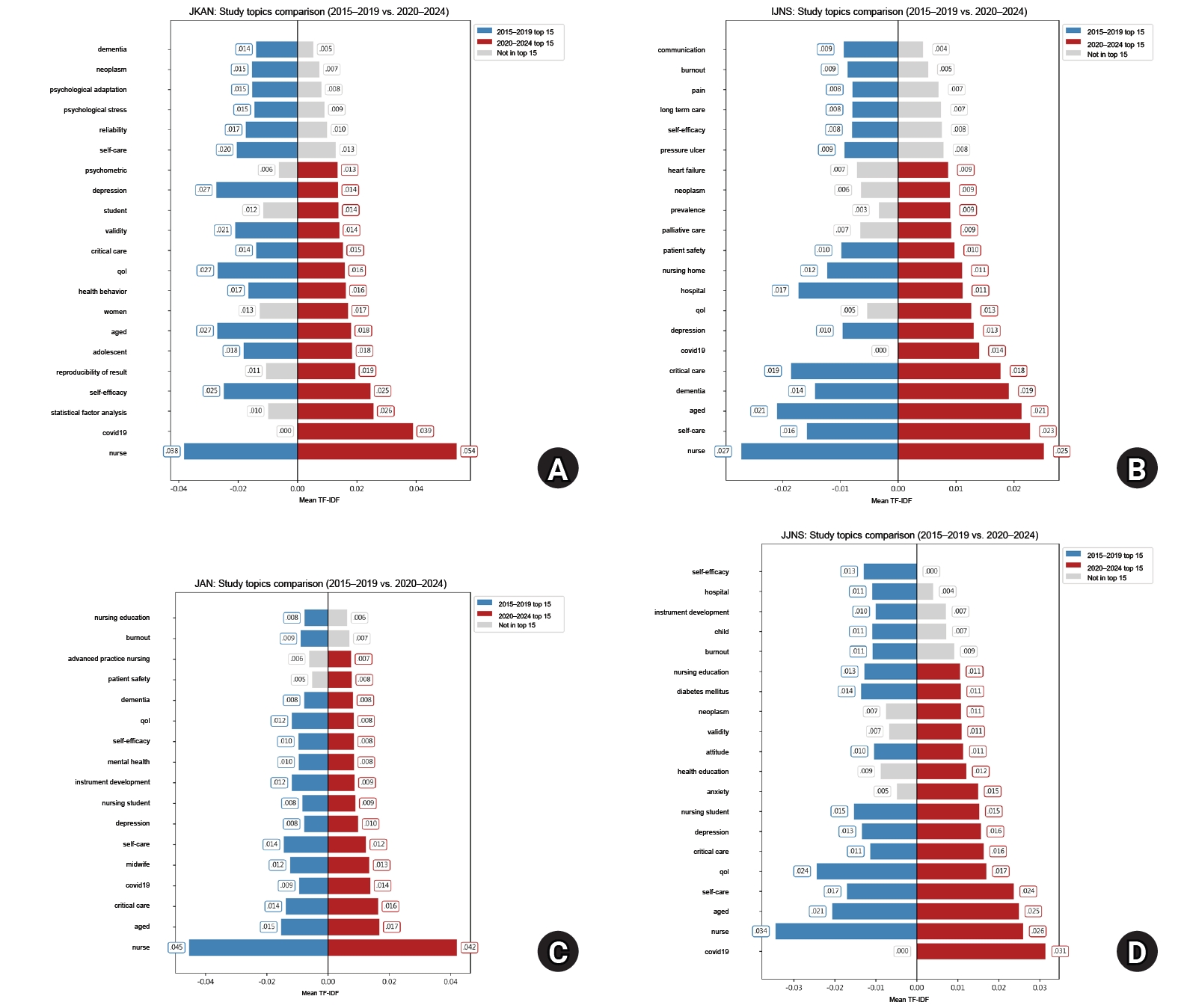
This study compared trends in research designs and keywords by analyzing the abstracts of four major nursing journals over the past decade, focusing on the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing (JKAN) in comparison with the International Journal of Nursing Studies (IJNS), Journal of Advanced Nursing (JAN), and Japan Journal of Nursing Science (JJNS).
Methods
A bibliometric analysis was conducted, encompassing 5,522 abstracts published between 2015 and 2024. Research designs were first classified as “quantitative,” “qualitative,” or “other,” and then further sub-classified based on international evidence-based frameworks. Text preprocessing was also conducted, and term frequency–inverse document frequency was applied to evaluate keyword importance. The 2015–2019 and 2020–2024 periods were compared to examine changes in both research designs and keyword importance.
Results
Compared to IJNS, JAN, and JJNS, JKAN published more instrument development and analytic studies but fewer randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews. Over time, the number of instrument development and mixed-methods studies in JKAN increased, while high-evidence designs remained scarce. Keyword analysis showed JKAN’s emphasis on psychosocial themes such as self-efficacy, quality of life, and depression, whereas the other journals more often highlighted policy- and institution-related topics. Across journals, COVID-19 and patient safety emerged as important themes after 2020.
Conclusion
JKAN demonstrates strengths in methodological diversity within quantitative research and in digital health–related analytics. However, high-evidence study designs and policy-oriented keywords are underrepresented in JKAN. Strategic expansion toward randomized controlled trials, systematic review, global and digital health, and policy-relevant research is recommended to strengthen JKAN’s international competitiveness.
-
Effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions to reduce internalized stigma in people with severe mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
Soyoung Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae, Myung-Sun Hyun
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):1-18. Published online February 25, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24072
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study systematically reviewed and analyzed the effects of non-pharmacological interventions on internalized stigma among people with severe mental illness.
Methods
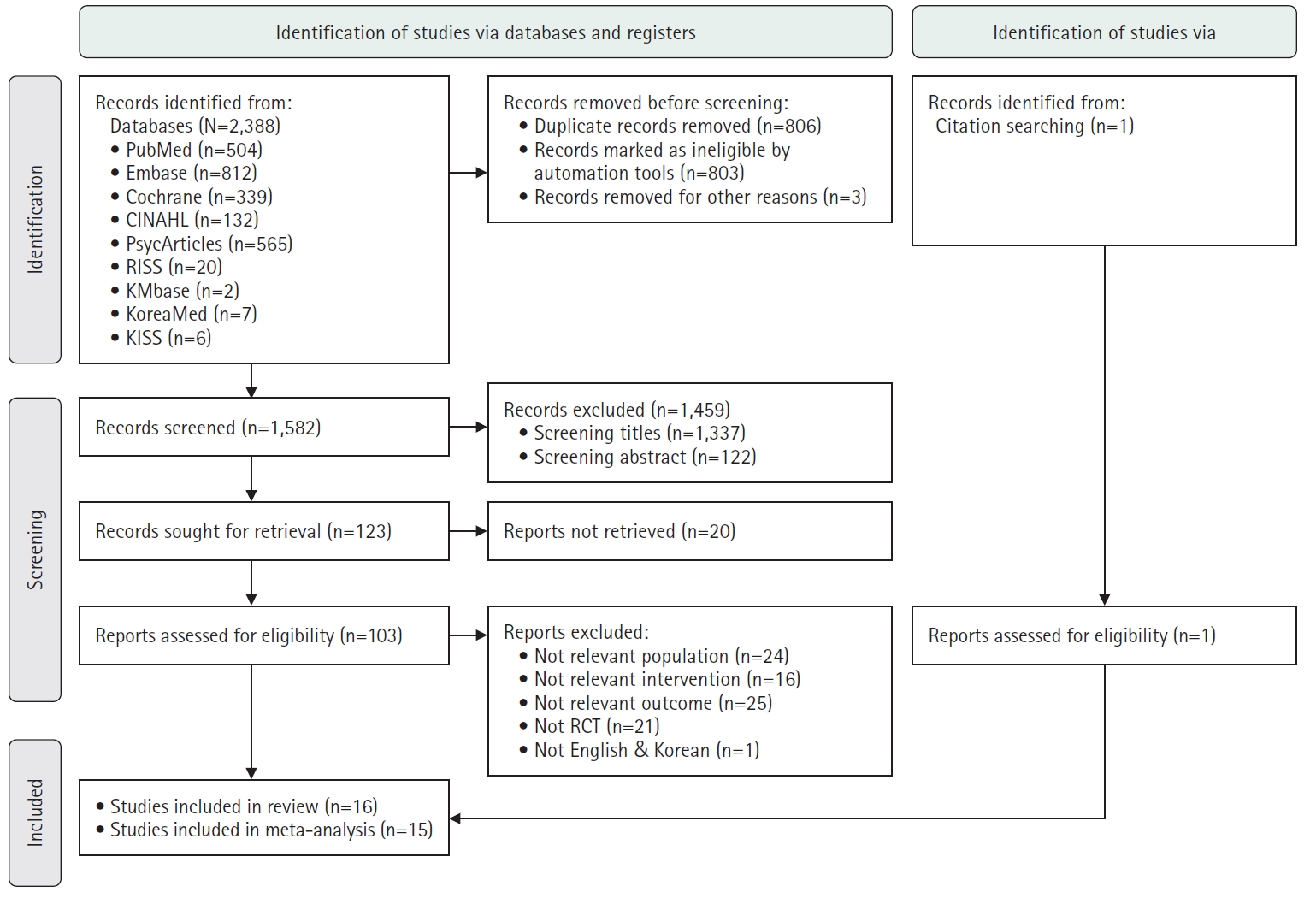
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted following the Cochrane Intervention Research Systematic Review Manual and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis guidelines. This study targeted people with severe mental illness as the population, interventions aimed at reducing internalized stigma, comparisons with control groups, and internalized stigma as the outcome. A literature search was performed across multiple databases, including PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, CINAHL, PsycArticles, RISS, KMbase, and KoreaMed. The risk of bias was evaluated using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2.0 tool. Effect sizes were computed using Hedges’s g, and subgroup analyses were conducted with Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software version 4.0.
Results
Of 2,388 papers, 15 were included in the meta-analysis. The overall effect size (Hedges’s g) of the intervention was –0.60 (95% confidence interval, –1.01 to –0.19), indicating a statistically significant reduction in internalized stigma (Z=–2.88, p=.004). Subgroup analyses revealed that the intervention type (p=.008) and session length (p=.011) were significant moderators influencing the effectiveness of the interventions.
Conclusion
Tailoring interventions by considering variables such as the intervention type and session length could enhance the effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions for reducing internalized stigma among people with severe mental illness (PROSPERO: CRD42023418561).
-
Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Menopause-Specific Quality of Life
-
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Young-Mi Jung
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):487-500. Published online June 30, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20049
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of Menopause-Specific Quality of Life (MENQOL).
Methods
The MENQOL was translated into Korean according to algorithm of linguistic validation process. A total of 308 menopausal womenwere recruited and assessed using the Korean version of MENQOL (MENQOL-K), the World Health Organization Quality of Life BriefVersion (WHOQOL-BREF), and Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale (CES-D-K). In estimating reliability, internal consistencyreliability coefficients were calculated. Validity was evaluated through criterion validity and construct validity with confirmatory factor analysesusing SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 25.0 software.
Results
In item analyses, the “increased facial hair” symptom was excluded because of thelow contribution of MENQOL-K. The confirmatory factor analysis supported good fit and reliable scores for MENQOL-K model, and thefour-factor structure was validated (x2=553.28, p <.001, NC=1.84, RMSEA=.05, AGIF=.85, AIC=765.28). The MENQOL-K consists of 28 itemsin 4 domains, including vasomotor (3 items), psychosocial (7 items), physical (15 items), and sexual subscales (3 items). There was an acceptablecriterion validity with moderately significant correlation between MENQOL-K and WHOQOL-BREF. The Cronbach’s a for the 4subsacles ranged from .80 to .93.
Conclusion
The MENQOL-K is a valid and reliable scale to measure condition-specific quality of life forperimenopausal and postmenopausal women. It can be used to assess the impact of menopausal symptoms on the quality of life of Koreanwomen in clinical trials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Longitudinal analysis of alcohol consumption pattern and menopause‐specific quality of life in middle‐aged women undergoing the menopausal transition
Ria Kwon, Yoosoo Chang, Yoonyoung Jang, Ga‐young Lim, Yoo‐Jung Kim, Seungho Ryu
Addiction.2026; 121(3): 586. CrossRef - Examining the relationship between symptoms and quality of life related to menopausal period of women with gynecologic cancer: a cross-sectional study
Ahsen Demirhan Kayacik, Gulsah Kok
Supportive Care in Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The 3-dimensionel Ovarian Volume Assessment to Evaluate Whether Menopausal Related Symptoms and Hormone Levels Correlate with the Ovarian Volume
Gizem Işık Solmaz, İsmail Güler, Esra İşçi Bostancı, Serhan Can İşcan, Nuray Bozkurt, Mehmet Anıl Onan
Gazi Medical Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Aerobic Exercise Vs Surya Namaskar on Quality of Life in Postmenopausal Women Using Menopause Specific Quality of Life (MENQOL) Questionnaire
Dr. Dhanashree P. Shinde (PT), Alphina E. Jules
International Journal of Advanced Research in Science, Communication and Technology.2025; : 51. CrossRef - Longitudinal patterns and group heterogeneity of depressive symptoms during menopausal transition in middle-aged Korean women
Yoonyoung Jang, Yoosoo Chang, Junhee Park, Sang Won Jeon, Byungtae Seo, Jae Ho Park, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Seungho Ryu
Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Early-onset vasomotor symptoms and development of depressive symptoms among premenopausal women
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Jungeun Park, Yoosun Cho, Chanmin Kim, Min-Jung Kwon, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-young Lim, Jiin Ahn, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 354: 376. CrossRef - Association between Menopausal Women’s Quality of Life and Aging Anxiety: The Role of Life Satisfaction and Depression
Seunghee Lee, Mijung Jang, Dohhee Kim, KyooSang Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(8): 1189. CrossRef - Vasomotor and other menopause symptoms and the prevalence of ideal cardiovascular health metrics among premenopausal stage women
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Yoosun Cho, Min-Jung Kwon, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Menopause.2023; 30(7): 750. CrossRef - Research trends in the Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing from 2011 to 2021: a quantitative content analysis
Ju-Hee Nho, Sookkyoung Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(2): 128. CrossRef - Low anti-Müllerian hormone levels are associated with an increased risk of incident early-onset vasomotor symptoms among premenopausal women
SunJu NamGoung, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Hoon Kim, In Young Cho, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Hye Rin Choi, Jeonggyu Kang, Kye-Hyun Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Hyun-Young Park, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Min-Jung Kwon, Seungho Ryu
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - High low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level is associated with an increased risk of incident early-onset vasomotor symptoms
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Jeonggyu Kang, Min-Jung Kwon, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Ideal Cardiovascular Health Metrics and Risk of Incident Early-Onset Vasomotor Symptoms Among Premenopausal Women
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Yoosun Cho, Jeonggyu Kang, Min-Jung Kwon, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(9): 2666. CrossRef - Alcohol Consumption Patterns and Risk of Early-Onset Vasomotor Symptoms in Premenopausal Women
Ria Kwon, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Yoosun Cho, Hye Rin Choi, Ga-Young Lim, Jeonggyu Kang, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Sanjay Rampal, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Nutrients.2022; 14(11): 2276. CrossRef - Metabolically healthy and unhealthy obesity and risk of vasomotor symptoms in premenopausal women: cross‐sectional and cohort studies
Sunju Namgoung, Yoosoo Chang, Chae‐Yeon Woo, Yejin Kim, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga‐Young Lim, Hye Rin Choi, Kye‐Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun‐Young Park, Seungho Ryu
BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology.2022; 129(11): 1926. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Risk of Early-Onset Vasomotor Symptoms in Lean and Overweight Premenopausal Women
Yoosun Cho, Yoosoo Chang, Hye Rin Choi, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Jiin Ahn, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Sanjay Rampal, Juhee Cho, Hyun-Young Park, Eliseo Guallar, Seungho Ryu
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2805. CrossRef
-
3,367
View
-
132
Download
-
14
Web of Science
-
15
Crossref
-
Psychoeducational Approach to Distress Management of Newly Diagnosed Patients with Breast Cancer
-
Jin-Hee Park, Mison Chun, Yong Sik Jung, Sun Hyoung Bae, Young-Mi Jung
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):669-678. Published online January 15, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.669
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of integrated psychoeducational program for distress management of newly diagnosed patients with breast cancer.
Methods
A quasi-experimental trial was conducted. The participants consisted of 47 female patients with breast cancer assigned to an intervention group (n=25) and control group (n=22). The intervention group participated in integrated psychoeducational program, consisting of individual face-to-face education and telephone-delivered health-coaching sessions. Data were collected at three time points: pre-intervention (T1), post-intervention (T2), and 6-month follow-up (T3). Study instruments were Distress thermometer, Supportive Care Needs Survey Short Form 34 and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast.
Results
Compared with the control group, breast cancer patients in the intervention group reported lower distress and supportive care needs than the control group. The intervention group reported higher quality of life (QOL) overall and higher emotional well-being than the control group.
Conclusion
These findings indicate that the integrated psychoeducational program is an effective intervention for reducing distress and supportive care needs and increasing QOL of newly diagnosed patients with breast cancer. Oncology nurses need to provide psychoeducational intervention to support patients with breast cancer in managing their distress and helping them adjust to their life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
Young-Hee Je, Kyoung-Ah Kang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Tailored Psychoeducational Intervention for Patients With Advanced Cancer in Indonesia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Nurul Huda, Made Satya Nugraha Gautama, Wan Nishfa Dewi, Agung Waluyo, Hsiu Ju Chang, Malissa Kay Shaw
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2025; 57(5): 848. CrossRef - Evidence on the benefits of mind-body Qigong exercise in women with breast cancer
Michel Marcos Dalmedico, Jackson Adriano Canavarro Ribeiro, Juliana Londero Silva Avila, Prisley Pereira de Oliveira, Paula Karina Hembecker, Sergio Ossamu Ioshii
Fisioterapia em Movimento.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychological Distress and Influencing Factors in Newly Diagnosed Patients with Breast Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Min Hee Hur, Yu Jin Jeong
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(4): 311. CrossRef - Effects of Psychosocial Interventions for Patients with Breast Cancer: A Meta-analysis
Kyu-Sic Hwang, Kuy-Haeng Lee, Chan-Mo Yang, Hye-Jin Lee, Sang-Yeol Lee
Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience.2023; 21(1): 118. CrossRef - The development of a lifestyle modification mobile application, “Health for You” for overweight and obese breast cancer survivors in Korea
Su-Jin Seo, Ju-Hee Nho, Youngsam Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(3): 243. CrossRef - Development and Effect of the Integrated Health Promotion Program for Cancer Survivors Living at Home
Hee Sang Yoon, Eun A Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(1): 51. CrossRef - Adjustment to life with metastatic cancer through psychodrama group therapy: A qualitative study in Turkey
Songül Kamışlı, Bahar Gökler
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2021; 57(2): 488. CrossRef - Integration of longitudinal psychoeducation programmes during the phases of diagnosis, management and survivorship of breast cancer patients: A narrative review
Athena Michaelides, Constantina Constantinou
Journal of Cancer Policy.2020; 23: 100214. CrossRef - Quality of Life in Patients Undergoing Mastectomy for Breast Cancer
Kavitha Konnakkaparambil Ramakrishnan, Sreekumar Damodaran
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2020; 7(28): 1368. CrossRef - Mediating and Moderating Factors of Adherence to Nutrition and Physical Activity Guidelines, Breastfeeding Experience, and Spousal Support on the Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors
Nam Mi Kang, Won-Ho Hahn, Suyeon Park, Jung Eun Lee, Young Bum Yoo, Chung Ja Ryoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7532. CrossRef - Uncertainty and unmet care needs before and after surgery in patients with gastric cancer: A survey study
Ji Yea Lee, Yeonsoo Jang, Sanghee Kim, Woo Jin Hyung
Nursing & Health Sciences.2020; 22(2): 427. CrossRef - Effects of Different Exercise Interventions on Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Tetiana Odynets, Yuriy Briskin, Valentina Todorova
Integrative Cancer Therapies.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,832
View
-
41
Download
-
13
Crossref
-
Effects of Psychoeducational Intervention for Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
-
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):143-163. Published online April 28, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.143
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material
-
Purpose
This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis designed to investigate effects of psychoeducational intervention for cancer survivors.
Methods
Ten databases were searched. Two reviewers independently performed the selection of the studies, data extraction and assessment. The risk of bias was assessed using Cochrane Collaboration's tool. To estimate the effect size, meta-analysis of the studies was performed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis and RevMan programs.
Results
Of 18,781 publications identified, 35 met inclusion criteria, and 25 studies were used to estimate effect size of psychoeducational intervention. Effect sizes (standardized mean difference [SMD]) were heterogeneous and random effects models were used in the analyses. Psychoeducational intervention was effective for quality of life (n=2,410, ES=0.23; 95% CI: 0.09~0.37), coping and self-efficacy (n=179, ES=0.68; 95% CI: 0.26~1.11), anxiety (n=1,786, ES=-0.26; 95% CI: -0.37~-0.15), depression (n=1,910, ES=-0.28; 95% CI: -0.37~-0.18), and psychological distress (n=2,242, ES=-0.31; 95% CI: -0.46~-0.17). Subgroup analysis showed that counseling was the most effective intervention for quality of life, and behavioral therapy was an effective intervention for all positive and negative outcomes. Publication bias was not detected except for psychological distress.
Conclusion
Psychoeducational intervention appears to be effective in improving quality of life and coping and self-efficacy, and it is effective in reducing psychological symptoms in cancer survivors. Behavioral therapy, especially, is commonly effective in improving psychosocial outcomes. However, low-quality evidence, variability in the designs of existing studies, and publication bias suggest that additional high-quality trials should be conducted in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Factors associated with post-treatment smoking among a diverse sample of cancer survivors in the US
Safa Elkefi, Corina T. Lelutiu-Weinberger, Jean-Marie Bruzzese, Alicia K. Matthews
Discover Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Group‐Based Support Interventions for Adolescents and Young Adults With Lymphoma: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Dalnim Cho, Sairah Ahmed, Stella Snyder, Juliet Kroll, Minxing Chen, Michael Roth, Kathrin Milbury
Psycho-Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Mind Health of Persons with Cancer: Psycho-Oncology and Nursing
Park Eun Young
Journal of Clinical Psychooncology.2025; 11(1): 24. CrossRef - Psychosocial interventions for people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and motor neuron disease and their caregivers: a scoping review
Juyeon Oh, Jiwon An, Kyongok Park, Youngok Park
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of telemedicine psychoeducational interventions for adults with non‐oncological chronic disease: A systematic review
Carmen Sánchez‐Gutiérrez, Eugenia Gil‐García, Adriana Rivera‐Sequeiros, José M. López‐Millán
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2022; 78(5): 1267. CrossRef - Cancer-Related Psychological Distress in Lymphoma Survivor: An Italian Cross-Sectional Study
Giulia Agostinelli, Barbara Muzzatti, Samantha Serpentini, Michele Spina, Maria Antonietta Annunziata
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the Advanced Practice Nurse-Led Psychoeducational Program for Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hye Kyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 245. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Led Intervention Programs Based on Goal Attainment Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 699. CrossRef - Effects of Psychosocial Interventions on Physical Function and Depression in Stroke Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jinhyang YANG, Changwan KANG, Hye-Won PARK, Euna PARK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(2): 396. CrossRef - Development of A Nurse-Led Educational Intervention Program in Managing the Nutrition Impact Symptom Cluster in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma following the Medical Research Council Framework
Wenli Xiao, Carmen W Chan, Jinnan Xiao, Cho L Wong, Ka M Chow
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 8(6): 653. CrossRef - Chemotherapy Education and Support: A Model for Use in the Ambulatory Care Setting
Terri Jabaley, Patricia Rizzo, Nina Grenon, Clare Sullivan, Janet Bagley, Maritza Nassif, Renee Siegel, Meghan Underhill-Blazey
Clinical Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 24(4): E43. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for Chronic Pain Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Hee-Sook Kang, Sung-Dong Hwang, Sang-Eun Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(3): 271. CrossRef
-
2,108
View
-
35
Download
-
12
Crossref
-
Prevalence and Characteristics of Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Breast Cancer
-
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Yong-Sik Jung, Young-Mi Jung
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(1):118-128. Published online February 27, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.118
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
Evidence suggests that some patients with breast cancer experience cognitive difficulties following chemotherapy. This longitudinal study was done to examine the prevalence of cognitive impairment and trajectory of cognitive function over time in women with breast cancer, who received adjuvant chemotherapy.
Methods
Participants were 137 patients with breast cancer. They completed neuropsychological tests and the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Cognitive Function before adjuvant therapy (pretest), toward the end of adjuvant therapy (posttest), and 6 months after the completion of adjuvant therapy (follow-up test). Of the patients, 91 were treated with adjuvant chemotherapy and 46 patients who did not receive chemotherapy made up the comparison group. A reliable-change index and repeated-measure ANOVA were used for statistical analyses.
Results
At the posttest point, over 30% of patients showed complex cognitive impairment and reported greater difficulty in subjective cognitive function. At the follow-up test point, 22.0% of patients exhibited complex cognitive impairment and 30.8% of patients complained of subjective cognitive impairment. Repeated-measure ANOVA showed significant decreases after receiving chemotherapy followed by small improvements 6 months after the completion of chemotherapy in cognitive domains of change for attention and concentration, memory, executive function, and subjective cognitive function.
Conclusion
These results suggest that chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer may be associated with objective and subjective cognitive impairments. Further studies are needed to explore the potential risk factors and predictor of chemotherapy-related cognitive changes. Also nursing interventions for prevention and intervention of cognitive impairments should be developed and tested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Impact of nonpharmacological interventions on cognitive impairment in women with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jin-Hee Park, Su Jin Jung, Lena J. Lee, Junghyun Rhu, Sun Hyoung Bae
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(4): 100212. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Self-reported Memory Problems of Adult Cancer Survivors Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
Sangjin Ko
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(1): 51. CrossRef - Brain network deficits in breast cancer patients after early neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A longitudinal MRI study
Jing Yang, Yongchun Deng, Daihong Liu, Yong Tan, Meng Lin, Xiaoyu Zhou, Jing Zhang, Hong Yu, Yixin Hu, Yu Tang, Shixi Jiang, Jiuquan Zhang
Journal of Neuroscience Research.2023; 101(7): 1138. CrossRef - Frailty and its associated factors among older adults with cancer undergoing chemotherapy as outpatients: A cross-sectional study
Misun Jeon, Hyoeun Jang, Arum Lim, Sanghee Kim
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 60: 102192. CrossRef - The Experience of Chemotherapy Related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Ji Hyun Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - Distinct sleep disturbance and cognitive dysfunction profiles in oncology outpatients receiving chemotherapy
Vivian Huang, Lynda Mackin, Kord M. Kober, Steven M. Paul, Bruce A. Cooper, Yvette P. Conley, Marilyn J. Hammer, Jon D. Levine, Christine Miaskowski
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(11): 9243. CrossRef - Measurement, outcomes and interventions of cognitive function after breast cancer treatment: A narrative review
Miaomiao Jia, Xiaojun Zhang, Liyuan Wei, Jinnan Gao
Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology.2021; 17(4): 321. CrossRef - Improving preoperative breast reconstruction consultations: a qualitative study on the impact of personalised audio-recordings
Josipa Petric, Bahara Sadri, Phillipa van Essen, Nicola Ruth Dean
BMC Women's Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on Neurologic and Cognitive Dysfunction in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy with Resting State fMRI
Fenshan Zheng, Peiying Cao, Jie Zhou, Chunyu Li, John Norris
World Neurosurgery.2021; 149: 388. CrossRef - Changes of Cognitive Function and Fatigue following Chemotherapy in Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer: A Prospective Controlled Study
Pok-Ja Oh, Sun Mi Moon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(3): 126. CrossRef - Computerized programs for cancer survivors with cognitive problems: a systematic review
Yoonjung Kim, Sook Jung Kang
Journal of Cancer Survivorship.2019; 13(6): 911. CrossRef - Cancer treatment effects on cognition and depression: The moderating role of physical activity
Margaret F. Bedillion, Emily B. Ansell, Gwendolyn A. Thomas
The Breast.2019; 44: 73. CrossRef - Changes of Cognitive Function and Depression following Chemotherapy in Women with Breast Cancer: A Prospective Study
Pok Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee, Hyun Ah Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(2): 66. CrossRef - Mulheres Submetidas à Quimioterapia e suas Funções Cognitivas
Camila Vasconcelos Carnaúba Lima, Raner Miguel Ferreira Póvoa
Psicologia: Ciência e Profissão.2017; 37(4): 970. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-induced prospective memory impairment in breast cancer patients with different hormone receptor expression
Wen Li, Chen Gan, Yue Lv, Shanghu Wang, Huaidong Cheng
Medicine.2017; 96(13): e6514. CrossRef - Altered network efficiency of functional brain networks in patients with breast cancer after chemotherapy
Han Xuan, Chen Gan, Wen Li, Zhonglian Huang, Longsheng Wang, Qianqian Jia, Zhendong Chen, Huaidong Cheng
Oncotarget.2017; 8(62): 105648. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in People with Colon Cancer: The Mediating Effect of Psychological Distress
Pok Ja Oh, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(1): 19. CrossRef - Effect of Cancer Symptoms and Fatigue on Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Depression in People with Gastrointestinal Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(3): 420. CrossRef - A review of traditional Korean medical treatment for cancer-related cognitive impairment
Hye-Yoon Lee, Jung-Eun Kim, Mikyung Kim, Joo-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Medicine.2016; 37(3): 74. CrossRef - Cognitive outcome after radiotherapy in brain tumor
Thomas Durand, Marie-Odile Bernier, Isabelle Léger, Hervé Taillia, Georges Noël, Dimitri Psimaras, Damien Ricard
Current Opinion in Oncology.2015; 27(6): 510. CrossRef - Changes of Symptom Distress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Adjuvant Therapy
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Young-Mi Jung
Asian Oncology Nursing.2015; 15(2): 67. CrossRef
-
1,411
View
-
12
Download
-
21
Crossref
-
A Meta-analysis of Chemotherapy related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Breast Cancer
-
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(5):644-658. Published online October 12, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.5.644
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the cognitive effects of chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer.
Methods
Using several databases, prospective studies were collected up to August 2011. Of 2,106 publications identified, 12 met the inclusion criteria, and 8 studies were used to estimate the effect size of chemotherapy on cognitive impairment.
Results
Twelve studies were done since 2005 and most of the research was performed in Europe or North America. Eight studies were used to generate effect size across the cognitive domains of attention/concentration, verbal and visual memory, executive function, visuospatial skill, language, and subjective cognitive function. Each of the cognitive domains showed small effect sizes (-0.02 ~ -0.26), indicating diminished cognitive function for the chemotherapy group compared with non-chemotherapy groups.
Conclusion
Finding suggests that breast cancer patients who undergo chemotherapy may experience mild cognitive decline. Further study is needed to generate knowledge and guideline for interventions to address chemotherapy related cognitive impairment in these patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Experience of Chemotherapy Related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Ji Hyun Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of smart-care services program for breast cancer survivors
Bok Yae Chung, Sung Jung Hong
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(2): 95. CrossRef - Changes of Cognitive Function and Fatigue following Chemotherapy in Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer: A Prospective Controlled Study
Pok-Ja Oh, Sun Mi Moon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(3): 126. CrossRef - Effects of compensatory cognitive training intervention for breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: a pilot study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ku Sang Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
Supportive Care in Cancer.2017; 25(6): 1887. CrossRef - Impact of Cognitive Function and Cancer Coping on Quality of Life among Women with Post-chemotherapy Breast Cancer
Yoon Jung Kim, Sook Jung Kang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(3): 182. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in People with Colon Cancer: The Mediating Effect of Psychological Distress
Pok Ja Oh, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(1): 19. CrossRef - QLU-C10D: a health state classification system for a multi-attribute utility measure based on the EORTC QLQ-C30
M. T. King, D. S. J. Costa, N. K. Aaronson, J. E. Brazier, D. F. Cella, P. M. Fayers, P. Grimison, M. Janda, G. Kemmler, R. Norman, A. S. Pickard, D. Rowen, G. Velikova, T. A. Young, R. Viney
Quality of Life Research.2016; 25(3): 625. CrossRef - The Impact of Cancer on Psychological and Social Outcomes
Daniel Sj Costa, Rebecca Mercieca‐bebber, Claudia Rutherford, Liam Gabb, Madeleine T King
Australian Psychologist.2016; 51(2): 89. CrossRef - Prevalence and Characteristics of Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Breast Cancer
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Yong-Sik Jung, Young-Mi Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(1): 118. CrossRef
-
1,188
View
-
5
Download
-
9
Crossref
-
A Systematic Review of Psychological Distress as a Risk Factor for Recurrent Cardiac Events in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
-
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(5):704-714. Published online October 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.5.704
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to determine whether psychological distress is an independent risk factor for recurrent cardiac events in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD).
Methods
A prospective cohort of studies that measured psychological distress and the incidence of recurrent cardiac events in the adult population were included. Three computerized databases were assessed (PubMed, CINAHL, and PSYCINFO). Meta-analysis was conducted using a random-effects model to determine summary estimates of risks of major recurrent cardiac events associated with each psychological distress. Of 506 publications identified, 33 met inclusion criteria, and 24 studies were used to estimate effect size of psychological distress on recurrent cardiac events.
Results
Mean number in the research sample was 736 and mean time of follow-up was 4.0 years. Depression, anxiety, anger, and hostility as psychological factors were studied. According to estimation of effect size using random model effect, depression (OR=1.39, 95% CI: 1.22-1.57), anxiety (OR=1.22, 95% CI: 0.96-1.56), and anger/hostility (OR=1.29, 95% CI: 1.07-1.57) CAD patients in significantly increased risk for recurrent cardiac events.
Conclusion
Finding suggests that psychological distress in forms of depression, anxiety, anger, and hostility impact unfavorably on recurrent cardiac events in CAD patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - NAMS task force report on mental stress
Rajesh Sagar, Kaushik Chatterjee, Sandeep Thareja, Anurag Timothy, A.S. Yadav, Prateek Yadav, Rajinder Dhamija, S.V. Madhu, Preethy Kathiresan, Pratibha Prasad, Swati Kedia Gupta, Kalpana Srivastava
Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences (India).2025; 61: 66. CrossRef - Impact of Type D Personality and Health Literacy on Resilience of Inpatients with Cardiovascular Diseases: A Cross-Sectional Study
Da Eun Kim, Seon Young Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(1): 23. CrossRef - The Effect of Perceived Stress, Fine Dust Risk Perception, and Resilience on Stress Response in Patients with Respiratory and Circulatory Disorders
Jin-Hee Park, Kuem-Sun Han
STRESS.2021; 29(1): 21. CrossRef - Associations of depression and anxiety with cardiovascular risk among people living with HIV/AIDS in Korea
Kyong Sil Park, Seon Young Hwang, Bo Youl Choi, June Kim, Sang Il Kim, Woo-Joo Kim, Chun Kang
Epidemiology and Health.2020; 43: e2021002. CrossRef - Impact of Type D Personality on Depression, Anxiety, and Health-related Quality of Life among Coronary Artery Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Sun Hyoung Bae, Jin-Hee Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(3): 219. CrossRef - Analysis of the relationship between community characteristics and depression using geographically weighted regression
Hyungyun Choi, Ho Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2017; 39: e2017025. CrossRef - Influencing Effects of Type D Personality on Symptom Experiences and Quality of Life in Patients with Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Eun Hee Jo, Sun Hee Han, Myung Ha Lee, Sung Reul Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(5): 536. CrossRef - Depression and Anxiety as Predictors of Recurrent Cardiac Events 12 Months After Percutaneous Coronary Interventions
Jin-Hee Park, Seung-Jea Tahk, Sun Hyoung Bae
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2015; 30(4): 351. CrossRef - Anger, anger expression, cardiovascular risk factors, and gastrointestinal symptoms by hwa-byung symptoms in Korean adult women
Young-Joo Park, Sook-Ja Lee, Nah-Mee Shin, Hyunjeong Shin, Hyun Cheol Kang, Yoon Tae Jin, Song I. Jeon, Inhae Cho
Applied Nursing Research.2015; 28(4): 398. CrossRef - Risk Factor–tailored Small Group Education for Patients with First-time Acute Coronary Syndrome
Seon Young Hwang, Jin Shil Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(4): 291. CrossRef - Influences of Knowledge, Self-efficacy, and Social Support on Sick Role Behavior in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Soonhee Kim, Sunhee Lee
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(2): 228. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Quality of Life in Low- Income Elders Living at Home: A Literature Review
Chung-Min Cho
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2013; 27(2): 372. CrossRef - Effects of a psychoeducational intervention for secondary prevention in Korean patients with coronary artery disease: A pilot study
Jin‐Hee Park, Seung‐Jae Tahk, Sun Hyoung Bae, Youn‐Jung Son
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2013; 19(3): 295. CrossRef - Stress and cardiovascular disease
Jung Jin Cho
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2013; 56(6): 462. CrossRef
-
1,320
View
-
11
Download
-
14
Crossref
-
Factors Influencing Relocation Stress Syndrome in Patients Following Transfer from Intensive Care Units
-
Jin-Hee Park, Moon-Sook Yoo, Youn-Jung Son, Sun Hyoung Bae
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(3):307-316. Published online June 30, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.3.307
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the levels of relocation stress syndrome (RSS) and influencing the stress experienced by Intensive Care Unit (ICU) patients just after transfer to general wards.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted with 257 patients who transferred from the intensive care unit. Data were collected through self-report questionnaires from May to October, 2009. Data were analyzed using the Pearson correlation coefficient, t-test, one-way ANOVA, and stepwise multiple linear regression with SPSS/WIN 12.0.
Results
The mean score for RSS was 17.80±9.16. The factors predicting relocation stress syndrome were symptom experience, differences in scope and quality of care provided by ICU and ward nursing staffs, satisfaction with transfer process, length of stay in ICU and economic status, and these factors explained 40% of relocation stress syndrome (F=31.61, p<.001).
Conclusion
By understanding the stress experienced by ICU patients, nurses are better able to provide psychological support and thus more holistic care to critically ill patients. Further research is needed to consider the impact of relocation stress syndrome on patients' health outcomes in the recovery trajectory.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A phenomenological study on the experiences of patient transfer from the intensive care unit to general wards
Eun-Young Lee, Jin-Hee Park, Alvisa Palese
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(7): e0254316. CrossRef - Development and psychometric evaluation of the Relocation Stress Syndrome Scale-Short Form for patients transferred from adult intensive care units to general wards
Mi Hwa Won, Youn-Jung Son
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2020; 58: 102800. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Transition Nursing Program for Patients and Family Caregivers at a Neurological ICU in Korea
Sun Hee Yun, Eui Geum Oh, Yang Sook Yoo, So Sun Kim, Yeon Soo Jang
Clinical Nursing Research.2017; 26(1): 27. CrossRef - The Effects of Aromatherapy on Intensive Care Unit Patients’ Stress and Sleep Quality: A Nonrandomised Controlled Trial
Eun Hee Cho, Mi-Young Lee, Myung-Haeng Hur, Nativ Dudai
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - A tailored relocation stress intervention programme for family caregivers of patients transferred from a surgical intensive care unit to a general ward
Seul Lee, HyunSoo Oh, YeonOk Suh, WhaSook Seo
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2017; 26(5-6): 784. CrossRef - Clinical validity of a relocation stress scale for the families of patients transferred from intensive care units
HyunSoo Oh, Seul Lee, JiSun Kim, EunJu Lee, HyoNam Min, OkJa Cho, WhaSook Seo
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2015; 24(13-14): 1805. CrossRef
-
1,425
View
-
12
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Factors Influencing Learning Achievement of Nursing Students in E-learning
-
Jin-Hee Park, Eunha Lee, Sun Hyoung Bae
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(2):182-190. Published online April 30, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.2.182
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
This study was done to identify self-directed learning readiness, achievement goal orientations, learning satisfaction and learning achievement, and to evaluate the factors affecting learning achievement for nursing students using a web-based Health Assessment e-Book.
Methods
The research design was a cross-sectional study with a structured questionnaire and data were collected before using the web-based Health Assessment e-Book and 1 week after finishing. The participants were 80 nursing students who were taking the Health Assessment class from March to June 2009.
Results
Mean score for subjective learning achievement was 31.26 and for objective learning achievement, 69.25. Subjective and objective learning achievement were positively correlated with self-directed learning readiness, mastery goal, attitude toward distance education, and learning satisfaction. In subjective learning achievement, learning satisfaction and mastery goal were significant predictive factors and explained 64% of the variance. Objective learning achievement was significantly predicted by learning satisfaction and self-directed learning readiness, which explained 24% of the variance.
Conclusion
Learning satisfaction, mastery goal and self-directed learning readiness were found to be very important factors associated with learning achievement for nursing students using a web-based Health Assessment e-Book. To provide high quality and effective web-based courses and to improve nursing students' learning achievement and learning satisfaction, educators should consider the learner's characteristics from the initial stages of lecture planning.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Exploring the effectiveness of different “escape room simulation teaching” methods on clinical preceptors’ knowledge and skills in judging and handling violent situations in the healthcare profession
Huang-Chin Wu, Han-Jen Hsu, Yi-Ting Chou, Chun-Ju Lin, Chun-Hong Shen, Ruey Chen
Interactive Learning Environments.2025; 33(8): 4932. CrossRef - The effectiveness of 3D cadaver simulation learning on the perceived learning achievement, satisfaction, and flow state of nursing students
Hyeongyeong Yoon
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2024; 97: 101645. CrossRef - The influence of self-directed learning ability and self-leadership on the learning satisfaction and academic achievement of nursing students who experienced blended learning
Sungjun Kim, Ji Young Lim, Hwasoon Kim, Kyoung Ja Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2024; 30(3): 232. CrossRef - A study on the factors influencing users’ willingness to continue using online learning platforms
Junren Ming, Qiuyu Zhu, Yu Cheng, Ruide Tu, Rong Chen
Procedia Computer Science.2024; 242: 492. CrossRef - Students’ learning preferences for forms and activities – suggestions for academic teachers
Hubert Wojciechowski, Łukasz Hadaś, Roman Domański
Przegląd Organizacji.2023; : 416. CrossRef - HOW ATTITUDES TOWARDS E-LEARNING AFFECTED THE ACADEMIC ACHIEVEMENT DURING THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC: AN EXAMPLE OF A NURSING SKILLS TEACHING
Oznur GURLEK KISACIK, Munevver SONMEZ, Azize OZDAS
Turkish Online Journal of Distance Education.2023; 24(1): 129. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Attitudes of Nursing Students Towards Web-Based Learning and their Readiness for Online Learning
İlkay ÇULHA
Artuklu International Journal of Health Sciences.2023; 3(3): 253. CrossRef - The effects of collaborative reasoning strategies on improving primary school students’ argumentative decision-making skills
Mohsen Bayat, Seyyed Kazem Banihashem, Omid Noroozi
The Journal of Educational Research.2022; 115(6): 349. CrossRef - Academic Success of Online Learning in Undergraduate Nursing Education Programs in the COVID-19 Pandemic Era
Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Young Ju Jeong
Journal of Professional Nursing.2022; 38: 6. CrossRef - Self-Directed Learning versus Problem-Based Learning in Korean Nurse Education: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Jaehee Jeon, Sihyun Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(12): 1763. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Academic Achievement of Nursing College Students in a Flipped Learning Simulation Practice
Minkyung Gu, Sohyune Sok
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(11): 5970. CrossRef - The Effect of Self-directed Learning Strategies on e-Learning Pre-learning of Nursing Students: Focusing on the Flow Experience
Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(1): 52. CrossRef - Effects of Flipped Learning on the Critical Thinking Disposition, Academic Achievement and Academic Self-efficacy of Nursing Students: A Mixed Methods Study
Ju Cha, Jin Kim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(1): 25. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Students’ Preferences for Online and Blended Learning:
Motivational vs. Cognitive
Sinan Keskin, Halil Yurdugül
European Journal of Open, Distance and E-Learning.2020; 22(2): 72. CrossRef - Measuring Teachers-As-Learners’ Digital Skills and Readiness to Study Online for Successful e-Learning Experience
Evija Mirķe, Sarma Cakula, Lilian Tzivian
Journal of Teacher Education for Sustainability.2019; 21(2): 5. CrossRef - Differences in Non‐Cognitive Factors Influencing the Academic Achievement of Medical and Nursing Students: Focusing on Achievement Goal Orientation and Self‐Regulated Learning
Eun A Park, Kyung Hee Chun
Korean Medical Education Review.2014; 16(1): 32. CrossRef - Academic Achievement, Self-directed Learning, and Critical Thinking Disposition According to Learning Styles of Nursing Students
Sun-Hee Yang, Eun-Ho Ha, Og-Cheol Lee, In-Ok Sim, Young-Mi Park, Hyun-A Nam, Jeong-Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(3): 334. CrossRef - Development and Effects of an e-Learning Program in Operating Room Nursing for Nursing Students
Eun Hee Park, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(1): 36. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Problem Solving Abilities of Freshmen Nursing Students
Yun Min Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(2): 190. CrossRef
-
1,796
View
-
151
Download
-
19
Crossref
|